In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to save your Pandas DataFrame or DataFrames to Excel files. Being able to save data to this ubiquitous data format is an important skill in many organizations. In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to save a simple DataFrame to Excel, but also how to customize your options to create the report you want!
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have learned:
- How to save a Pandas DataFrame to Excel
- How to customize the sheet name of your DataFrame in Excel
- How to customize the index and column names when writing to Excel
- How to write multiple DataFrames to Excel in Pandas
- Whether to merge cells or freeze panes when writing to Excel in Pandas
- How to format missing values and infinity values when writing Pandas to Excel
Let’s get started!
The Quick Answer: Use Pandas to_excel
To write a Pandas DataFrame to an Excel file, you can apply the .to_excel() method to the DataFrame, as shown below:
# Saving a Pandas DataFrame to an Excel File
# Without a Sheet Name
df.to_excel(file_name)
# With a Sheet Name
df.to_excel(file_name, sheet_name='My Sheet')
# Without an Index
df.to_excel(file_name, index=False)Understanding the Pandas to_excel Function
Before diving into any specifics, let’s take a look at the different parameters that the method offers. The method provides a ton of different options, allowing you to customize the output of your DataFrame in many different ways. Let’s take a look:
# The many parameters of the .to_excel() function
df.to_excel(excel_writer, sheet_name='Sheet1', na_rep='', float_format=None, columns=None, header=True, index=True, index_label=None, startrow=0, startcol=0, engine=None, merge_cells=True, encoding=None, inf_rep='inf', verbose=True, freeze_panes=None, storage_options=None)Let’s break down what each of these parameters does:
| Parameter | Description | Available Options |
|---|---|---|
excel_writer= |
The path of the ExcelWriter to use | path-like, file-like, or ExcelWriter object |
sheet_name= |
The name of the sheet to use | String representing name, default ‘Sheet1’ |
na_rep= |
How to represent missing data | String, default '' |
float_format= |
Allows you to pass in a format string to format floating point values | String |
columns= |
The columns to use when writing to the file | List of strings. If blank, all will be written |
header= |
Accepts either a boolean or a list of values. If a boolean, will either include the header or not. If a list of values is provided, aliases will be used for the column names. | Boolean or list of values |
index= |
Whether to include an index column or not. | Boolean |
index_label= |
Column labels to use for the index. | String or list of strings. |
startrow= |
The upper left cell to start the DataFrame on. | Integer, default 0 |
startcol= |
The upper left column to start the DataFrame on | Integer, default 0 |
engine= |
The engine to use to write. | openpyxl or xlsxwriter |
merge_cells= |
Whether to write multi-index cells or hierarchical rows as merged cells | Boolean, default True |
encoding= |
The encoding of the resulting file. | String |
inf_rep= |
How to represent infinity values (as Excel doesn’t have a representation) | String, default 'inf' |
verbose= |
Whether to display more information in the error logs. | Boolean, default True |
freeze_panes= |
Allows you to pass in a tuple of the row, column to start freezing panes on | Tuple of integers with length 2 |
storage_options= |
Extra options that allow you to save to a particular storage connection | Dictionary |
.to_excel() methodHow to Save a Pandas DataFrame to Excel
The easiest way to save a Pandas DataFrame to an Excel file is by passing a path to the .to_excel() method. This will save the DataFrame to an Excel file at that path, overwriting an Excel file if it exists already.
Let’s take a look at how this works:
# Saving a Pandas DataFrame to an Excel File
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(
{'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6], 'C': [7, 8, 9]}
)
df.to_excel('filename.xlsx')Running the code as shown above will save the file with all other default parameters. This returns the following image:
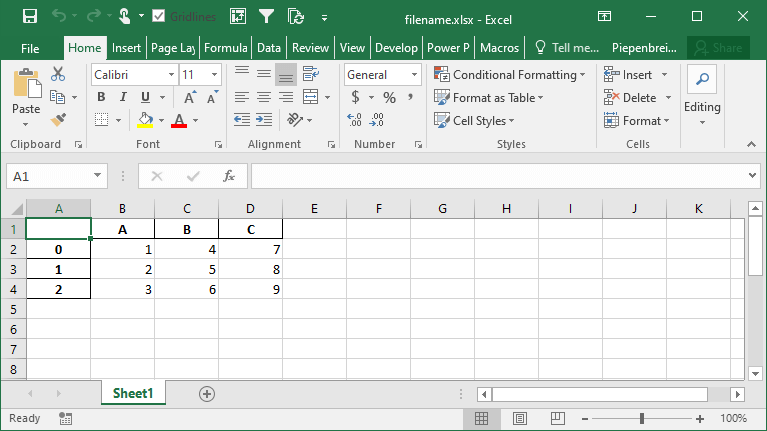
You can specify a sheetname by using the sheet_name= parameter. By default, Pandas will use 'sheet1'.
# Specifying a Sheet Name When Saving to Excel
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(
{'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6], 'C': [7, 8, 9]}
)
df.to_excel('filename.xlsx', sheet_name='Your Sheet')This returns the following workbook:
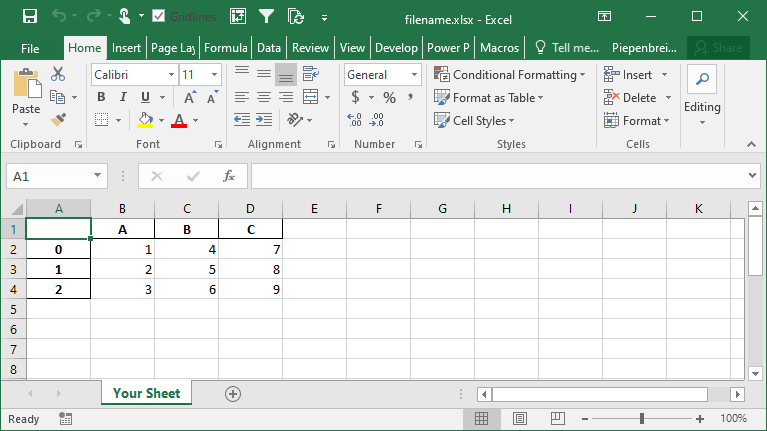
In the following section, you’ll learn how to customize whether to include an index column or not.
How to Include an Index when Saving a Pandas DataFrame to Excel
By default, Pandas will include the index when saving a Pandas Dataframe to an Excel file. This can be helpful when the index is a meaningful index (such as a date and time). However, in many cases, the index will simply represent the values from 0 through to the end of the records.
If you don’t want to include the index in your Excel file, you can use the index= parameter, as shown below:
# How to exclude the index when saving a DataFrame to Excel
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(
{'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6], 'C': [7, 8, 9]}
)
df.to_excel('filename.xlsx', index=False)This returns the following Excel file:
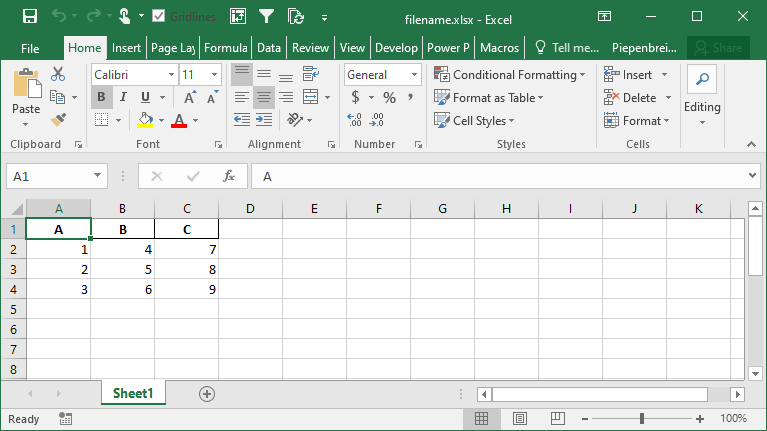
In the following section, you’ll learn how to rename an index when saving a Pandas DataFrame to an Excel file.
How to Rename an Index when Saving a Pandas DataFrame to Excel
By default, Pandas will not named the index of your DataFrame. This, however, can be confusing and can lead to poorer results when trying to manipulate the data in Excel, either by filtering or by pivoting the data. Because of this, it can be helpful to provide a name or names for your indices.
Pandas makes this easy by using the index_label= parameter. This parameter accepts either a single string (for a single index) or a list of strings (for a multi-index). Check out below how you can use this parameter:
# Providing a name for your Pandas index
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(
{'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6], 'C': [7, 8, 9]}
)
df.to_excel('filename.xlsx', index_label='Your Index')This returns the following sheet:
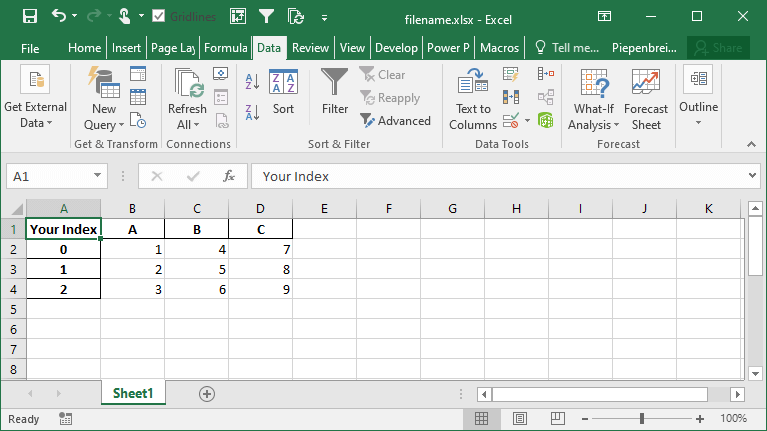
How to Save Multiple DataFrames to Different Sheets in Excel
One of the tasks you may encounter quite frequently is the need to save multi Pandas DataFrames to the same Excel file, but in different sheets. This is where Pandas makes it a less intuitive. If you were to simply write the following code, the second command would overwrite the first command:
# The wrong way to save multiple DataFrames to the same workbook
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(
{'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6], 'C': [7, 8, 9]}
)
df.to_excel('filename.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet1')
df.to_excel('filename.xlsx', sheet_name='Sheet2')Instead, we need to use a Pandas Excel Writer to manage opening and saving our workbook. This can be done easily by using a context manager, as shown below:
# The Correct Way to Save Multiple DataFrames to the Same Workbook
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(
{'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6], 'C': [7, 8, 9]}
)
with pd.ExcelWriter('filename.xlsx') as writer:
df.to_excel(writer, sheet_name='Sheet1')
df.to_excel(writer, sheet_name='Sheet2')This will create multiple sheets in the same workbook. The sheets will be created in the same order as you specify them in the command above.
This returns the following workbook:
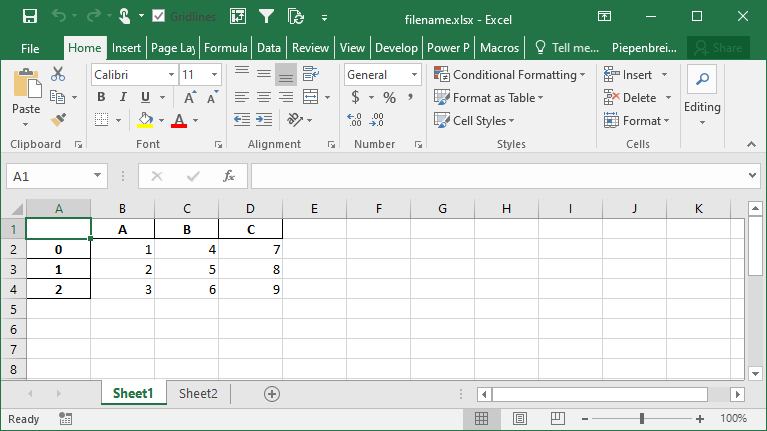
How to Save Only Some Columns when Exporting Pandas DataFrames to Excel
When saving a Pandas DataFrame to an Excel file, you may not always want to save every single column. In many cases, the Excel file will be used for reporting and it may be redundant to save every column. Because of this, you can use the columns= parameter to accomplish this.
Let’s see how we can save only a number of columns from our dataset:
# Saving Only a Subset of Columns to Excel
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(
{'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6], 'C': [7, 8, 9]}
)
df.to_excel('filename.xlsx', columns=['A', 'B'])This returns the following Excel file:
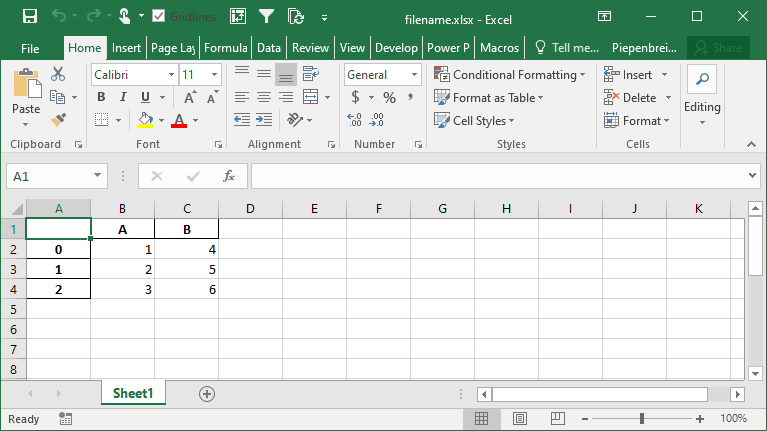
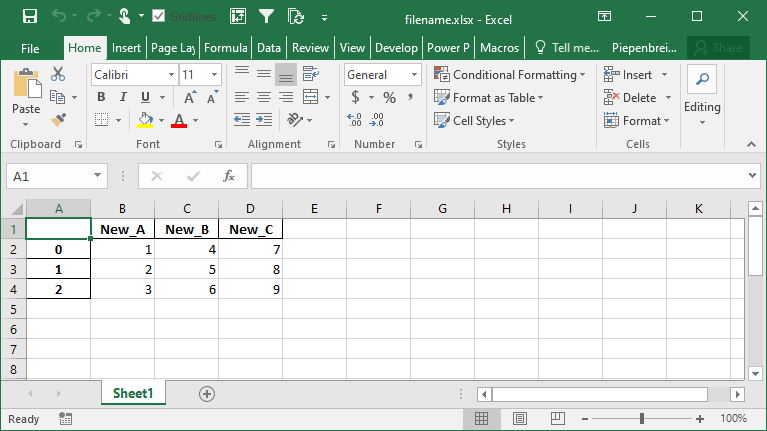
How to Rename Columns when Exporting Pandas DataFrames to Excel
Continuing our discussion about how to handle Pandas DataFrame columns when exporting to Excel, we can also rename our columns in the saved Excel file. The benefit of this is that we can work with aliases in Pandas, which may be easier to write, but then output presentation-ready column names when saving to Excel.
We can accomplish this using the header= parameter. The parameter accepts either a boolean value of a list of values. If a boolean value is passed, you can decide whether to include or a header or not. When a list of strings is provided, then you can modify the column names in the resulting Excel file, as shown below:
# Modifying Column Names when Exporting a Pandas DataFrame to Excel
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(
{'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6], 'C': [7, 8, 9]}
)
df.to_excel('filename.xlsx', header=['New_A', 'New_B', 'New_C'])This returns the following Excel sheet:
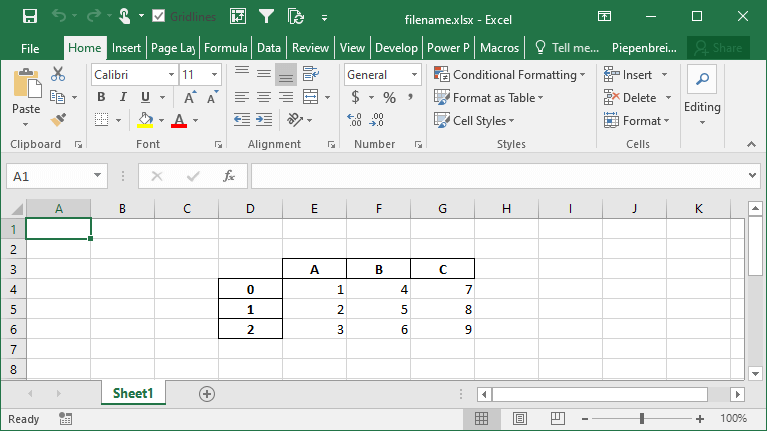
How to Specify Starting Positions when Exporting a Pandas DataFrame to Excel
One of the interesting features that Pandas provides is the ability to modify the starting position of where your DataFrame will be saved on the Excel sheet. This can be helpful if you know you’ll be including different rows above your data or a logo of your company.
Let’s see how we can use the startrow= and startcol= parameters to modify this:
# Changing the Start Row and Column When Saving a DataFrame to an Excel File
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(
{'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6], 'C': [7, 8, 9]}
)
df.to_excel('filename.xlsx', startcol=3, startrow=2)This returns the following worksheet:
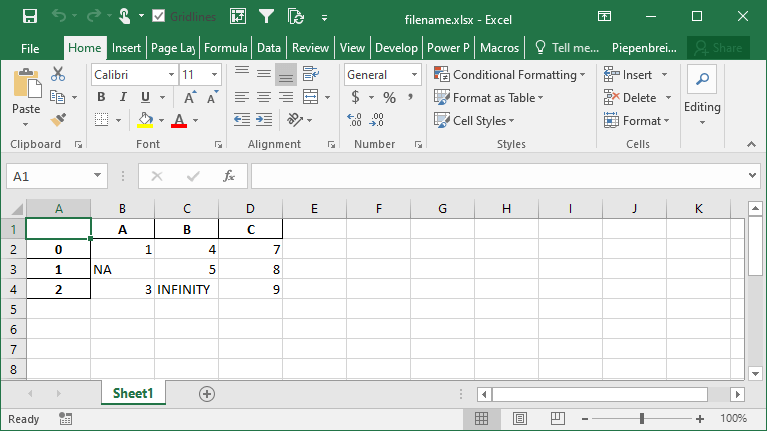
How to Represent Missing and Infinity Values When Saving Pandas DataFrame to Excel
In this section, you’ll learn how to represent missing data and infinity values when saving a Pandas DataFrame to Excel. Because Excel doesn’t have a way to represent infinity, Pandas will default to the string 'inf' to represent any values of infinity.
In order to modify these behaviors, we can use the na_rep= and inf_rep= parameters to modify the missing and infinity values respectively. Let’s see how we can do this by adding some of these values to our DataFrame:
# Customizing Output of Missing and Infinity Values When Saving to Excel
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(
{'A': [1, np.NaN, 3], 'B': [4, 5, np.inf], 'C': [7, 8, 9]}
)
df.to_excel('filename.xlsx', na_rep='NA', inf_rep='INFINITY')This returns the following worksheet:
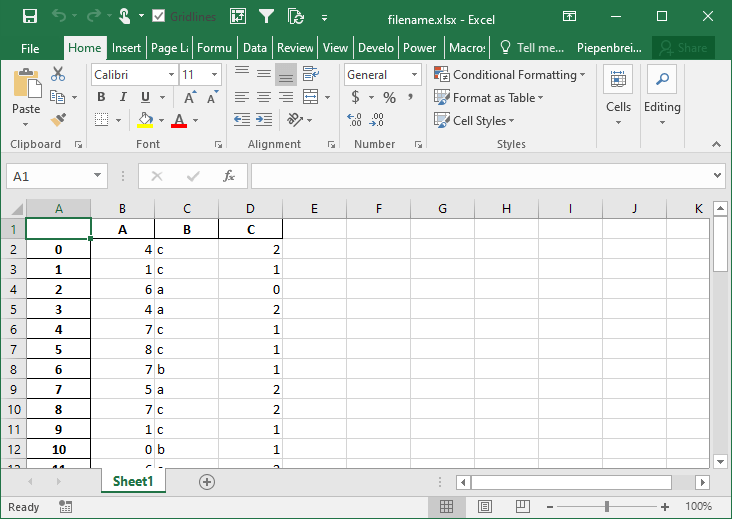
How to Merge Cells when Writing Multi-Index DataFrames to Excel
In this section, you’ll learn how to modify the behavior of multi-index DataFrames when saved to Excel. By default Pandas will set the merge_cells= parameter to True, meaning that the cells will be merged. Let’s see what happens when we set this behavior to False, indicating that the cells should not be merged:
# Modifying Merge Cell Behavior for Multi-Index DataFrames
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from random import choice
df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict({
'A': np.random.randint(0, 10, size=50),
'B': [choice(['a', 'b', 'c']) for i in range(50)],
'C': np.random.randint(0, 3, size=50)})
pivot = df.pivot_table(index=['B', 'C'], values='A')
pivot.to_excel('filename.xlsx', merge_cells=False)This returns the Excel worksheet below:
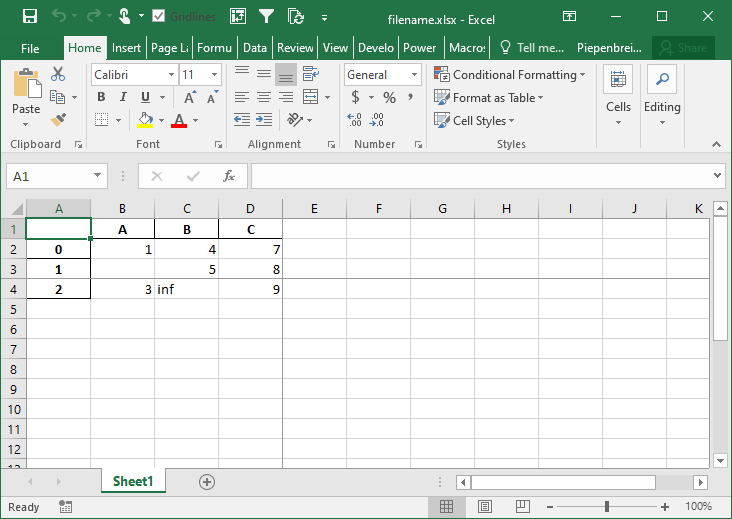
How to Freeze Panes when Saving a Pandas DataFrame to Excel
In this final section, you’ll learn how to freeze panes in your resulting Excel worksheet. This allows you to specify the row and column at which you want Excel to freeze the panes. This can be done using the freeze_panes= parameter. The parameter accepts a tuple of integers (of length 2). The tuple represents the bottommost row and the rightmost column that is to be frozen.
Let’s see how we can use the freeze_panes= parameter to freeze our panes in Excel:
# Freezing Panes in an Excel Workbook Using Pandas
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(
{'A': [1, np.NaN, 3], 'B': [4, 5, np.inf], 'C': [7, 8, 9]}
)
df.to_excel('filename.xlsx', freeze_panes=(3,4))This returns the following workbook:
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned how to save a Pandas DataFrame to an Excel file using the to_excel method. You first explored all of the different parameters that the function had to offer at a high level. Following that, you learned how to use these parameters to gain control over how the resulting Excel file should be saved. For example, you learned how to specify sheet names, index names, and whether to include the index or not. Then you learned how to include only some columns in the resulting file and how to rename the columns of your DataFrame. You also learned how to modify the starting position of the data and how to freeze panes.
Additional Resources
To learn more about related topics, check out the tutorials below:
- How to Use Pandas to Read Excel Files in Python
- Pandas Dataframe to CSV File – Export Using .to_csv()
- Introduction to Pandas for Data Science
- Official Documentation: Pandas to_excel
Write Excel with Python Pandas. You can write any data (lists, strings, numbers etc) to Excel, by first converting it into a Pandas DataFrame and then writing the DataFrame to Excel.
To export a Pandas DataFrame as an Excel file (extension: .xlsx, .xls), use the to_excel() method.
Related course: Data Analysis with Python Pandas
installxlwt, openpyxl
to_excel() uses a library called xlwt and openpyxl internally.
- xlwt is used to write .xls files (formats up to Excel2003)
- openpyxl is used to write .xlsx (Excel2007 or later formats).
Both can be installed with pip. (pip3 depending on the environment)
1 |
$ pip install xlwt |
Write Excel
Write DataFrame to Excel file
Importing openpyxl is required if you want to append it to an existing Excel file described at the end.
A dataframe is defined below:
1 |
import pandas as pd |
You can specify a path as the first argument of the to_excel() method.
Note: that the data in the original file is deleted when overwriting.
The argument new_sheet_name is the name of the sheet. If omitted, it will be named Sheet1.
1 |
df.to_excel('pandas_to_excel.xlsx', sheet_name='new_sheet_name') |
Related course: Data Analysis with Python Pandas
If you do not need to write index (row name), columns (column name), the argument index, columns is False.
1 |
df.to_excel('pandas_to_excel_no_index_header.xlsx', index=False, header=False) |
Write multiple DataFrames to Excel files
The ExcelWriter object allows you to use multiple pandas. DataFrame objects can be exported to separate sheets.
As an example, pandas. Prepare another DataFrame object.
1 |
df2 = df[['a', 'c']] |
Then use the ExcelWriter() function like this:
1 |
with pd.ExcelWriter('pandas_to_excel.xlsx') as writer: |
You don’t need to call writer.save(), writer.close() within the blocks.
Append to an existing Excel file
You can append a DataFrame to an existing Excel file. The code below opens an existing file, then adds two sheets with the data of the dataframes.
Note: Because it is processed using openpyxl, only .xlsx files are included.
1 |
path = 'pandas_to_excel.xlsx' |
Related course: Data Analysis with Python Pandas
Improve Article
Save Article
Like Article
Improve Article
Save Article
Like Article
The to_excel() method is used to export the DataFrame to the excel file. To write a single object to the excel file, we have to specify the target file name. If we want to write to multiple sheets, we need to create an ExcelWriter object with target filename and also need to specify the sheet in the file in which we have to write. The multiple sheets can also be written by specifying the unique sheet_name. It is necessary to save the changes for all the data written to the file.
Syntax:
data.to_excel( excel_writer, sheet_name='Sheet1', **kwargs )
Parameters:
| Arguments | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| excel_writer | str or ExcelWriter object | File path or existing ExcelWriter |
| sheet_name | str, default ‘Sheet1’ | Name of sheet which will contain DataFrame |
| columns | sequence or list of str, optional | Columns to write |
| index | bool, default True | Write row names (index) |
| index_label | str or sequence, optional | Column label for index column(s) if desired. If not specified, and `header` and `index` are True, then the index names are used. A sequence should be given if the DataFrame uses MultiIndex. |
- One can provide the excel file name or the Excelwrite object.
- By default the sheet number is 1, one can change it by input the value of argument “sheet_name”.
- One can provide the name of the columns to store the data by input the value of the argument “columns”.
- By default the index is labeled with numbers as 0,1,2 … and so on, one can change it by passing a sequence of the list for the value of the argument “index”.
Below is the implementation of the above method :
Python3
import pandas as pd
dct = {'ID': {0: 23, 1: 43, 2: 12,
3: 13, 4: 67, 5: 89,
6: 90, 7: 56, 8: 34},
'Name': {0: 'Ram', 1: 'Deep',
2: 'Yash', 3: 'Aman',
4: 'Arjun', 5: 'Aditya',
6: 'Divya', 7: 'Chalsea',
8: 'Akash' },
'Marks': {0: 89, 1: 97, 2: 45, 3: 78,
4: 56, 5: 76, 6: 100, 7: 87,
8: 81},
'Grade': {0: 'B', 1: 'A', 2: 'F', 3: 'C',
4: 'E', 5: 'C', 6: 'A', 7: 'B',
8: 'B'}
}
data = pd.DataFrame(dct)
data.to_excel("output.xlsx")
Output :
In the above example,
- By default index is labeled as 0,1,…. and so on.
- As our DataFrame has columns names so columns are labeled.
- By default, it is saved in “Sheet1”.
Like Article
Save Article
Время чтения 4 мин.
Python Pandas — это библиотека для анализа данных. Она может читать, фильтровать и переупорядочивать небольшие и большие наборы данных и выводить их в различных форматах, включая Excel. ExcelWriter() определен в библиотеке Pandas.
Содержание
- Что такое функция Pandas.ExcelWriter() в Python?
- Синтаксис
- Параметры
- Возвращаемое значение
- Пример программы с Pandas ExcelWriter()
- Что такое функция Pandas DataFrame to_excel()?
- Запись нескольких DataFrames на несколько листов
- Заключение
Метод Pandas.ExcelWriter() — это класс для записи объектов DataFrame в файлы Excel в Python. ExcelWriter() можно использовать для записи текста, чисел, строк, формул. Он также может работать на нескольких листах.Для данного примера необходимо, чтоб вы установили на свой компьютер библиотеки Numpy и Pandas.
Синтаксис
|
pandas.ExcelWriter(path, engine= None, date_format=None, datetime_format=None, mode=’w’,**engine_krawgs) |
Параметры
Все параметры установлены на значения по умолчанию.
Функция Pandas.ExcelWriter() имеет пять параметров.
- path: имеет строковый тип, указывающий путь к файлу xls или xlsx.
- engine: он также имеет строковый тип и является необязательным. Это движок для написания.
- date_format: также имеет строковый тип и имеет значение по умолчанию None. Он форматирует строку для дат, записанных в файлы Excel.
- datetime_format: также имеет строковый тип и имеет значение по умолчанию None. Он форматирует строку для объектов даты и времени, записанных в файлы Excel.
- Mode: это режим файла для записи или добавления. Его значение по умолчанию — запись, то есть ‘w’.
Возвращаемое значение
Он экспортирует данные в файл Excel.
Пример программы с Pandas ExcelWriter()
Вам необходимо установить и импортировать модуль xlsxwriter. Если вы используете блокнот Jupyter, он вам не понадобится; в противном случае вы должны установить его.
Напишем программу, показывающую работу ExcelWriter() в Python.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import xlsxwriter # Creating dataset using dictionary data_set = { ‘Name’: [‘Rohit’, ‘Arun’, ‘Sohit’, ‘Arun’, ‘Shubh’], ‘Roll no’: [’01’, ’02’, ’03’, ’04’, np.nan], ‘maths’: [’93’, ’63’, np.nan, ’94’, ’83’], ‘science’: [’88’, np.nan, ’66’, ’94’, np.nan], ‘english’: [’93’, ’74’, ’84’, ’92’, ’87’]} # Converting into dataframe df = pd.DataFrame(data_set) # Writing the data into the excel sheet writer_obj = pd.ExcelWriter(‘Write.xlsx’, engine=‘xlsxwriter’) df.to_excel(writer_obj, sheet_name=‘Sheet’) writer_obj.save() print(‘Please check out the Write.xlsx file.’) |
Выход:
|
Please check out the Write.xlsx file. |
Содержимое файла Excel следующее.
В приведенном выше коде мы создали DataFrame, в котором хранятся данные студентов. Затем мы создали объект для записи данных DataFrame на лист Excel, и после записи данных мы сохранили лист. Некоторые значения в приведенном выше листе Excel пусты, потому что в DataFrame эти значения — np.nan. Чтобы проверить данные DataFrame, проверьте лист Excel.
Что такое функция Pandas DataFrame to_excel()?
Функция Pandas DataFrame to_excel() записывает объект на лист Excel. Мы использовали функцию to_excel() в приведенном выше примере, потому что метод ExcelWriter() возвращает объект записи, а затем мы используем метод DataFrame.to_excel() для его экспорта в файл Excel.
Чтобы записать один объект в файл Excel .xlsx, необходимо только указать имя целевого файла. Для записи на несколько листов необходимо создать объект ExcelWriter с именем целевого файла и указать лист в файле для записи.
На несколько листов можно записать, указав уникальное имя листа. При записи всех данных в файл необходимо сохранить изменения. Обратите внимание, что создание объекта ExcelWriter с уже существующим именем файла приведет к удалению содержимого существующего файла.
Мы также можем написать приведенный выше пример, используя Python с оператором.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import xlsxwriter # Creating dataset using dictionary data_set = { ‘Name’: [‘Rohit’, ‘Arun’, ‘Sohit’, ‘Arun’, ‘Shubh’], ‘Roll no’: [’01’, ’02’, ’03’, ’04’, np.nan], ‘maths’: [’93’, ’63’, np.nan, ’94’, ’83’], ‘science’: [’88’, np.nan, ’66’, ’94’, np.nan], ‘english’: [’93’, ’74’, ’84’, ’92’, ’87’]} # Converting into dataframe df = pd.DataFrame(data_set) with pd.ExcelWriter(‘WriteWith.xlsx’, engine=‘xlsxwriter’) as writer: df.to_excel(writer, sheet_name=‘Sheet’) print(‘Please check out the WriteWith.xlsx file.’) |
Выход:
|
Please check out the WriteWith.xlsx file. |
Вы можете проверить файл WriteWith.xlsx и просмотреть его содержимое. Это будет то же самое, что и файл Write.xlsx.
Запись нескольких DataFrames на несколько листов
В приведенном выше примере мы видели только один лист для одного фрейма данных. Мы можем написать несколько фреймов с несколькими листами, используя Pandas.ExcelWriter.
Давайте напишем пример, в котором мы создадим три DataFrames и сохраним эти DataFrames в файле multiplesheet.xlsx с тремя разными листами.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 |
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import xlsxwriter # Creating dataset using dictionary data_set = { ‘Name’: [‘Rohit’, ‘Arun’, ‘Sohit’, ‘Arun’, ‘Shubh’], ‘Roll no’: [’01’, ’02’, ’03’, ’04’, np.nan], ‘maths’: [’93’, ’63’, np.nan, ’94’, ’83’], ‘science’: [’88’, np.nan, ’66’, ’94’, np.nan], ‘english’: [’93’, ’74’, ’84’, ’92’, ’87’]} data_set2 = { ‘Name’: [‘Ankit’, ‘Krunal’, ‘Rushabh’, ‘Dhaval’, ‘Nehal’], ‘Roll no’: [’01’, ’02’, ’03’, ’04’, np.nan], ‘maths’: [’93’, ’63’, np.nan, ’94’, ’83’], ‘science’: [’88’, np.nan, ’66’, ’94’, np.nan], ‘english’: [’93’, ’74’, ’84’, ’92’, ’87’]} data_set3 = { ‘Name’: [‘Millie’, ‘Jane’, ‘Michael’, ‘Bobby’, ‘Brown’], ‘Roll no’: [’01’, ’02’, ’03’, ’04’, np.nan], ‘maths’: [’93’, ’63’, np.nan, ’94’, ’83’], ‘science’: [’88’, np.nan, ’66’, ’94’, np.nan], ‘english’: [’93’, ’74’, ’84’, ’92’, ’87’]} # Converting into dataframe df = pd.DataFrame(data_set) df2 = pd.DataFrame(data_set2) df3 = pd.DataFrame(data_set3) with pd.ExcelWriter(‘multiplesheet.xlsx’, engine=‘xlsxwriter’) as writer: df.to_excel(writer, sheet_name=‘Sheet’) df2.to_excel(writer, sheet_name=‘Sheet2’) df3.to_excel(writer, sheet_name=‘Sheet3’) print(‘Please check out the multiplesheet.xlsx file.’) |
Выход:
Вы можете видеть, что есть три листа, и каждый лист имеет разные столбцы имени.
Функция to_excel() принимает имя листа в качестве параметра, и здесь мы можем передать три разных имени листа, и этот DataFrame сохраняется на соответствующих листах.
Заключение
Если вы хотите экспортировать Pandas DataFrame в файлы Excel, вам нужен только класс ExcelWriter(). Класс ExcelWrite() предоставляет объект записи, а затем мы можем использовать функцию to_excel() для экспорта DataFrame в файл Excel.
Excel files can be a great way of saving your tabular data particularly when you want to display it (and even perform some formatting to it) in a nice GUI like Microsoft Excel. In this tutorial, we’ll look at how to save a pandas dataframe to an excel .xlsx file.
Note: The terms “excel file” and “excel workbook” are used interchangeably in this tutorial.
The to_excel() function
The pandas DataFrame to_excel() function is used to save a pandas dataframe to an excel file. It’s like the to_csv() function but instead of a CSV, it writes the dataframe to a .xlsx file. The following is its syntax:
df.to_excel("pathfile_name.xlsx")
Here, df is a pandas dataframe and is written to the excel file file_name.xlsx present at the location path. By default, the dataframe is written to Sheet1 but you can also give custom sheet names. You can also write to multiple sheets in the same excel workbook as well (See the examples below).
Note that once the excel workbook is saved, you cannot write further data without rewriting the whole workbook.
Examples
First, we’ll create a sample dataframe that we’ll be using throughout this tutorial.
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['Microsoft Corporation', 'Google, LLC', 'Tesla, Inc.',
'Apple Inc.', 'Netflix, Inc.'],
'Symbol': ['MSFT', 'GOOG', 'TSLA', 'AAPL', 'NFLX'],
'Shares': [100, 50, 150, 200, 80]
}
# create dataframe from data
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# display the dataframe
df
Now, let’s look at examples of some of the different use-cases where the to_excel() function might be useful.
1. Save dataframe to an excel file with default parameters
df.to_excel("portfolio.xlsx")
If you just pass the file name to the to_excel() function and use the default values for all the other parameters, the resulting Excel file gets saved in your current working directory with the given file name. Here’s a snapshot of the file when opened in Excel.
You can see that by default, the dataframe is saved to the sheet Sheet1. Also, note that the index of the dataframe is saved as a separate column. Pass index=False if you don’t want the index as a separate column in the excel file.
# to not include index as a column
df.to_excel("portfolio.xlsx", index=False)
Here’s how the saved excel file looks now.
2. Save dataframe to an excel file with custom sheet name
You can specify the name of the worksheet using the sheet_name parameter.
# with custom sheet name
df.to_excel("portfolio.xlsx", sheet_name="stocks")
You can see in the above snapshot that the resulting excel file has stocks as its sheet name.
3. Save to multiple sheets in the same workbook
You can also save dataframes to multiple worksheets within the same workbook using the to_excel() function. For this, you need to specify an ExcelWriter object which is a pandas object used to write to excel files. See the example below:
# write to multiple sheets
df2 = df.copy()
with pd.ExcelWriter("portfolio.xlsx") as writer:
df.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="stocks1")
df2.to_excel(writer, sheet_name="stocks2")
Here’s how the saved excel file looks.
In the above example, an ExcelWriter object is used to write the dataframes df and df2 to the worksheets stocks1 and stocks2 respectively.
Note that creating an ExcelWriter object with a file name that already exists will result in the contents of the existing file being erased.
For more on the pandas dataframe to_excel() function, refer to its official documentation.
You might also be interested in –
- Write a Pandas DataFrame to a JSON File
- Copy Pandas DataFrame to the Clipboard
- Save Pandas DataFrame to a CSV file
With this, we come to the end of this tutorial. The code examples and results presented in this tutorial have been implemented in a Jupyter Notebook with a python (version 3.8.3) kernel having pandas version 1.0.5
Subscribe to our newsletter for more informative guides and tutorials.
We do not spam and you can opt out any time.
-
Piyush is a data professional passionate about using data to understand things better and make informed decisions. He has experience working as a Data Scientist in the consulting domain and holds an engineering degree from IIT Roorkee. His hobbies include watching cricket, reading, and working on side projects.
View all posts










