I need to write some data from my program to an Excel spreadsheet. I’ve searched online and there seem to be many packages available (xlwt, XlsXcessive, openpyxl). Others suggest writing to a .csv file (never used CSV and don’t really understand what it is).
The program is very simple. I have two lists (float) and three variables (strings). I don’t know the lengths of the two lists and they probably won’t be the same length.
I want the layout to be as in the picture below:
The pink column will have the values of the first list and the green column will have the values of the second list.
So what’s the best way to do this?
I am running Windows 7 but I won’t necessarily have Office installed on the computers running this program.
import xlwt
x=1
y=2
z=3
list1=[2.34,4.346,4.234]
book = xlwt.Workbook(encoding="utf-8")
sheet1 = book.add_sheet("Sheet 1")
sheet1.write(0, 0, "Display")
sheet1.write(1, 0, "Dominance")
sheet1.write(2, 0, "Test")
sheet1.write(0, 1, x)
sheet1.write(1, 1, y)
sheet1.write(2, 1, z)
sheet1.write(4, 0, "Stimulus Time")
sheet1.write(4, 1, "Reaction Time")
i=4
for n in list1:
i = i+1
sheet1.write(i, 0, n)
book.save("trial.xls")
I wrote this using all your suggestions. It gets the job done but it can be slightly improved.
How do I format the cells created in the for loop (list1 values) as scientific or number?
I do not want to truncate the values. The actual values used in the program would have around 10 digits after the decimal.
- Export Data to Excel With the
DataFrame.to_excel()Function in Python - Export Data to Excel With the
xlwtLibrary in Python - Export Data to Excel With the
openpyxlLibrary in Python - Export Data to Excel With the
XlsWriterLibrary in Python

This tutorial will demonstrate different methods to write tabular data to an excel file in Python.
Export Data to Excel With the DataFrame.to_excel() Function in Python
If we want to write tabular data to an Excel sheet in Python, we can use the to_excel() function in Pandas DataFrame.
A pandas DataFrame is a data structure that stores tabular data. The to_excel() function takes two input parameters: the file’s name and the sheet’s name. We must store our data inside a pandas DataFrame and then call the to_excel() function to export that data into an Excel file.
We need to have the pandas library already installed on our system for this method to work. The command to install the pandas library is given below.
A working demonstration of this approach is given below.
import pandas as pd
list1 = [10,20,30,40]
list2 = [40,30,20,10]
col1 = "X"
col2 = "Y"
data = pd.DataFrame({col1:list1,col2:list2})
data.to_excel('sample_data.xlsx', sheet_name='sheet1', index=False)
sample_data.xlsx file:
In the above code, we exported the data inside list1 and list2 as columns into the sample_data.xlsx Excel file with Python’s to_excel() function.
We first stored the data inside both lists into a pandas DataFrame. After that, we called the to_excel() function and passed the names of our output file and the sheet.
Keep in mind that this method will only work as long as the length of both lists is equal. If the lengths aren’t equal, we can compensate for the missing values by filling the shorter list with the None value.
This is the easiest method to write data to an Excel-compatible file in Python.
Export Data to Excel With the xlwt Library in Python
The xlwt library is used to write data into old spreadsheets compatible with Excel versions from 95 to 2003 in Python. It is the standard way for writing data to Excel files in Python.
It is also fairly simple and gives us more control over the Excel file than the previous method. We can create an object of the xlwt.Workbook class and call the .add_sheet() function to create a new sheet in our workbook.
We can then use the write() method to write our data. This write() function takes the row index (starting from 0), the column index (also starting from 0), and the data to be written as input parameters.
We need to install the xlwt library on our machine for this method to work. The command to install the library is given below.
A brief working example of this method is given below.
import xlwt
from xlwt import Workbook
wb = Workbook()
sheet1 = wb.add_sheet('Sheet 1')
#sheet1.write(row,col, data, style)
sheet1.write(1, 0, '1st Data')
sheet1.write(2, 0, '2nd Data')
sheet1.write(3, 0, '3rd Data')
sheet1.write(4, 0, '4th Data')
wb.save('sample_data2.xls')
sample_data2.xls file:
In Python, we wrote data to the sample_data2.xls file with the xlwt library.
We first created an object of the Workbook class. Using this object, we created a sheet with the add_sheet() method of the Workbook class.
We then wrote our data into the newly created sheet with the write() function. Lastly, when all the data has been properly written to its specified index, we saved the workbook into an Excel file with the save() function of the Workbook class.
This is a pretty straightforward approach, but the only drawback is that we have to remember the row and column index for each cell in our file. We can’t just use A1 and A2 indices. Another disadvantage of this approach is that we can only write files with the .xls extension.
Export Data to Excel With the openpyxl Library in Python
Another method that can be used to write data to an Excel-compatible file is the openpyxl library in Python.
This approach addresses all the drawbacks of the previous methods. We don’t need to remember the exact row and column indices for each data point. Simply specify our cells like A1 or A2 in the write() function.
Another cool advantage of this approach is that it can be used to write files with the new .xlsx file extensions, which wasn’t the case in the previous approach. This method works just like the previous one.
The only difference here is that we have to initialize each cell in addition to a sheet with the cell(row,col) method in the openpyxl library.
The openpyxl is also an external library. We need to install this library for this method to work properly. The command to install the openpyxl library on our machine is below.
A simple working demonstration of this approach is given below.
import openpyxl
my_wb = openpyxl.Workbook()
my_sheet = my_wb.active
c1 = my_sheet.cell(row = 1, column = 1)
c1.value = "Maisam"
c2 = my_sheet.cell(row= 1 , column = 2)
c2.value = "Abbas"
c3 = my_sheet['A2']
c3.value = "Excel"
# for B2: column = 2 & row = 2.
c4 = my_sheet['B2']
c4.value = "file"
my_wb.save("sample_data3.xlsx")
sample_data3.xlsx file:
In the above code, we wrote data to the sample_data3.xlsx Excel file with the openpyxl library in Python.
We first created an object of the Workbook class. We created a sheet with the Workbook.active using this object. We also created a cell object with my_sheet.cell(row = 1, column = 1).
Instead of writing the exact row and column number, we can also specify the cell name like A1. We can then assign our newly created cell value with c1.value = "Maisam".
Lastly, when all the data has been properly written to its specified index, we saved the workbook into an Excel file with the save() function of the Workbook class.
Export Data to Excel With the XlsWriter Library in Python
Another great and simple way to write data to an Excel-compatible file is the XlsWriter library in Python.
This library gives us much more control over our output file than any previous methods mentioned above. This library also supports the latest Excel compatible file extensions like xlsx.
To write data to an Excel file, we first have to create an object of the Workbook class by providing the constructor’s file name as an input parameter. We then have to create a sheet with the add_worksheet() function in the Workbook class.
After adding a sheet, we can write data with the sheet.write(cell, data) function. This sheet.write() function takes two parameters: the cell’s name and the data to be written.
After writing all the data to the sheet, we need to close our workbook with the close() method inside the Workbook class.
The XlsWriter is an external library and does not come pre-installed with Python. We first have to install the XlsWriter library on our machine for this method to work. The command to install the XlsWriter library is given below.
A working demonstration of this approach is shown below.
import xlsxwriter
workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook('sample_data4.xlsx')
sheet = workbook.add_worksheet()
sheet.write('A1', 'Maisam')
sheet.write('A2', 'Abbas')
workbook.close()
sample_data4.xlsx file:
We wrote data to the sample_data4.xlsx Excel file with Python’s xlswriter library in the above code.
Improve Article
Save Article
Like Article
Improve Article
Save Article
Like Article
XlsxWriter is a Python module for writing files in the XLSX file format. It can be used to write text, numbers, and formulas to multiple worksheets. Also, it supports features such as formatting, images, charts, page setup, auto filters, conditional formatting and many others.
Use this command to install xlsxwriter module:
pip install xlsxwriter
Note: Throughout XlsxWriter, rows and columns are zero indexed. The first cell in a worksheet, A1 is (0, 0), B1 is (0, 1), A2 is (1, 0), B2 is (1, 1) ..similarly for all.
Let’s see how to create and write to an excel-sheet using Python.
Code #1 : Using A1 notation(cell name) for writing data in the specific cells.
Python3
import xlsxwriter
workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook('hello.xlsx')
worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet()
worksheet.write('A1', 'Hello..')
worksheet.write('B1', 'Geeks')
worksheet.write('C1', 'For')
worksheet.write('D1', 'Geeks')
workbook.close()
Output:
Code #2 : Using the row-column notation(indexing value) for writing data in the specific cells.
Python3
import xlsxwriter
workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook('Example2.xlsx')
worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet()
row = 0
column = 0
content = ["ankit", "rahul", "priya", "harshita",
"sumit", "neeraj", "shivam"]
for item in content :
worksheet.write(row, column, item)
row += 1
workbook.close()
Output:
Code #3 : Creating a new sheet with the specific name
Python3
import xlsxwriter
workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook('Example3.xlsx')
worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet("My sheet")
scores = (
['ankit', 1000],
['rahul', 100],
['priya', 300],
['harshita', 50],
)
row = 0
col = 0
for name, score in (scores):
worksheet.write(row, col, name)
worksheet.write(row, col + 1, score)
row += 1
workbook.close()
Output:
XlsxWriter has some advantages and disadvantages over the alternative Python modules for writing Excel files.
Advantages:
- It supports more Excel features than any of the alternative modules.
- It has a high degree of fidelity with files produced by Excel. In most cases the files produced are 100% equivalent to files produced by Excel.
- It has extensive documentation, example files and tests.
- It is fast and can be configured to use very little memory even for very large output files.
Disadvantages:
- It cannot read or modify existing Excel XLSX files.
Like Article
Save Article
Watch Now This tutorial has a related video course created by the Real Python team. Watch it together with the written tutorial to deepen your understanding: Editing Excel Spreadsheets in Python With openpyxl
Excel spreadsheets are one of those things you might have to deal with at some point. Either it’s because your boss loves them or because marketing needs them, you might have to learn how to work with spreadsheets, and that’s when knowing openpyxl comes in handy!
Spreadsheets are a very intuitive and user-friendly way to manipulate large datasets without any prior technical background. That’s why they’re still so commonly used today.
In this article, you’ll learn how to use openpyxl to:
- Manipulate Excel spreadsheets with confidence
- Extract information from spreadsheets
- Create simple or more complex spreadsheets, including adding styles, charts, and so on
This article is written for intermediate developers who have a pretty good knowledge of Python data structures, such as dicts and lists, but also feel comfortable around OOP and more intermediate level topics.
Before You Begin
If you ever get asked to extract some data from a database or log file into an Excel spreadsheet, or if you often have to convert an Excel spreadsheet into some more usable programmatic form, then this tutorial is perfect for you. Let’s jump into the openpyxl caravan!
Practical Use Cases
First things first, when would you need to use a package like openpyxl in a real-world scenario? You’ll see a few examples below, but really, there are hundreds of possible scenarios where this knowledge could come in handy.
Importing New Products Into a Database
You are responsible for tech in an online store company, and your boss doesn’t want to pay for a cool and expensive CMS system.
Every time they want to add new products to the online store, they come to you with an Excel spreadsheet with a few hundred rows and, for each of them, you have the product name, description, price, and so forth.
Now, to import the data, you’ll have to iterate over each spreadsheet row and add each product to the online store.
Exporting Database Data Into a Spreadsheet
Say you have a Database table where you record all your users’ information, including name, phone number, email address, and so forth.
Now, the Marketing team wants to contact all users to give them some discounted offer or promotion. However, they don’t have access to the Database, or they don’t know how to use SQL to extract that information easily.
What can you do to help? Well, you can make a quick script using openpyxl that iterates over every single User record and puts all the essential information into an Excel spreadsheet.
That’s gonna earn you an extra slice of cake at your company’s next birthday party!
Appending Information to an Existing Spreadsheet
You may also have to open a spreadsheet, read the information in it and, according to some business logic, append more data to it.
For example, using the online store scenario again, say you get an Excel spreadsheet with a list of users and you need to append to each row the total amount they’ve spent in your store.
This data is in the Database and, in order to do this, you have to read the spreadsheet, iterate through each row, fetch the total amount spent from the Database and then write back to the spreadsheet.
Not a problem for openpyxl!
Learning Some Basic Excel Terminology
Here’s a quick list of basic terms you’ll see when you’re working with Excel spreadsheets:
| Term | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Spreadsheet or Workbook | A Spreadsheet is the main file you are creating or working with. |
| Worksheet or Sheet | A Sheet is used to split different kinds of content within the same spreadsheet. A Spreadsheet can have one or more Sheets. |
| Column | A Column is a vertical line, and it’s represented by an uppercase letter: A. |
| Row | A Row is a horizontal line, and it’s represented by a number: 1. |
| Cell | A Cell is a combination of Column and Row, represented by both an uppercase letter and a number: A1. |
Getting Started With openpyxl
Now that you’re aware of the benefits of a tool like openpyxl, let’s get down to it and start by installing the package. For this tutorial, you should use Python 3.7 and openpyxl 2.6.2. To install the package, you can do the following:
After you install the package, you should be able to create a super simple spreadsheet with the following code:
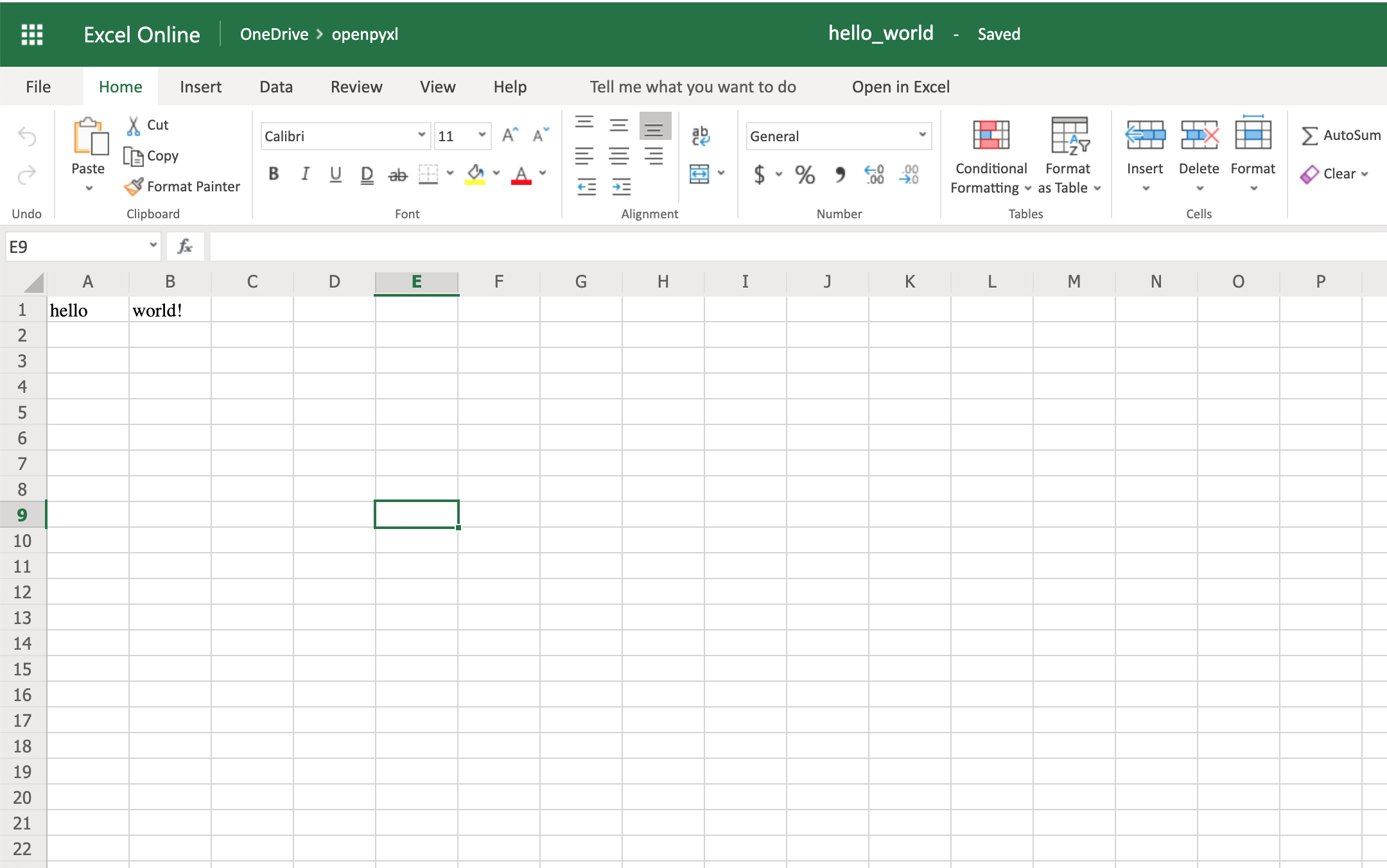
from openpyxl import Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
sheet = workbook.active
sheet["A1"] = "hello"
sheet["B1"] = "world!"
workbook.save(filename="hello_world.xlsx")
The code above should create a file called hello_world.xlsx in the folder you are using to run the code. If you open that file with Excel you should see something like this:
Woohoo, your first spreadsheet created!
Reading Excel Spreadsheets With openpyxl
Let’s start with the most essential thing one can do with a spreadsheet: read it.
You’ll go from a straightforward approach to reading a spreadsheet to more complex examples where you read the data and convert it into more useful Python structures.
Dataset for This Tutorial
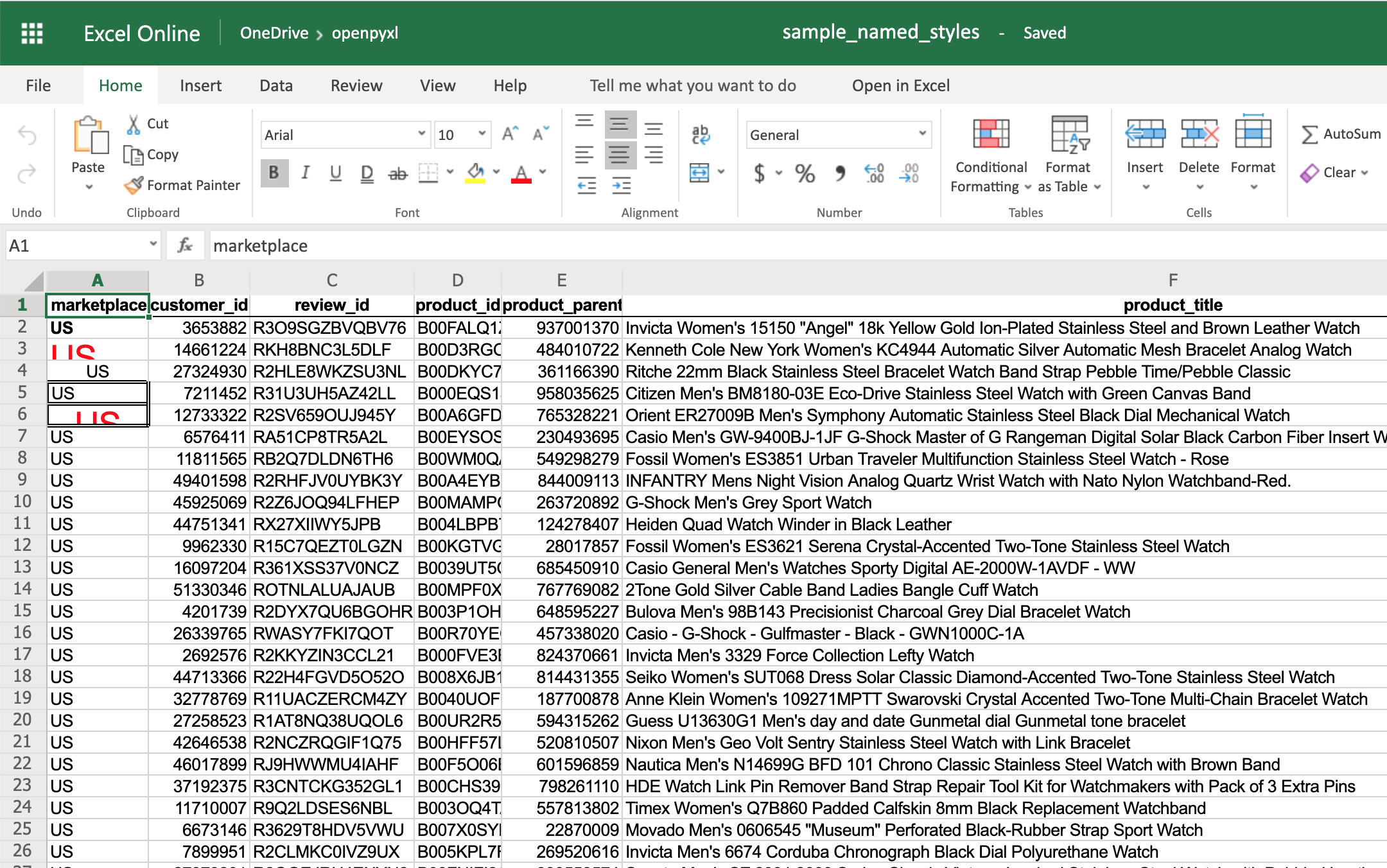
Before you dive deep into some code examples, you should download this sample dataset and store it somewhere as sample.xlsx:
This is one of the datasets you’ll be using throughout this tutorial, and it’s a spreadsheet with a sample of real data from Amazon’s online product reviews. This dataset is only a tiny fraction of what Amazon provides, but for testing purposes, it’s more than enough.
A Simple Approach to Reading an Excel Spreadsheet
Finally, let’s start reading some spreadsheets! To begin with, open our sample spreadsheet:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl import load_workbook
>>> workbook = load_workbook(filename="sample.xlsx")
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Sheet 1']
>>> sheet = workbook.active
>>> sheet
<Worksheet "Sheet 1">
>>> sheet.title
'Sheet 1'
In the code above, you first open the spreadsheet sample.xlsx using load_workbook(), and then you can use workbook.sheetnames to see all the sheets you have available to work with. After that, workbook.active selects the first available sheet and, in this case, you can see that it selects Sheet 1 automatically. Using these methods is the default way of opening a spreadsheet, and you’ll see it many times during this tutorial.
Now, after opening a spreadsheet, you can easily retrieve data from it like this:
>>>
>>> sheet["A1"]
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A1>
>>> sheet["A1"].value
'marketplace'
>>> sheet["F10"].value
"G-Shock Men's Grey Sport Watch"
To return the actual value of a cell, you need to do .value. Otherwise, you’ll get the main Cell object. You can also use the method .cell() to retrieve a cell using index notation. Remember to add .value to get the actual value and not a Cell object:
>>>
>>> sheet.cell(row=10, column=6)
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.F10>
>>> sheet.cell(row=10, column=6).value
"G-Shock Men's Grey Sport Watch"
You can see that the results returned are the same, no matter which way you decide to go with. However, in this tutorial, you’ll be mostly using the first approach: ["A1"].
The above shows you the quickest way to open a spreadsheet. However, you can pass additional parameters to change the way a spreadsheet is loaded.
Additional Reading Options
There are a few arguments you can pass to load_workbook() that change the way a spreadsheet is loaded. The most important ones are the following two Booleans:
- read_only loads a spreadsheet in read-only mode allowing you to open very large Excel files.
- data_only ignores loading formulas and instead loads only the resulting values.
Importing Data From a Spreadsheet
Now that you’ve learned the basics about loading a spreadsheet, it’s about time you get to the fun part: the iteration and actual usage of the values within the spreadsheet.
This section is where you’ll learn all the different ways you can iterate through the data, but also how to convert that data into something usable and, more importantly, how to do it in a Pythonic way.
Iterating Through the Data
There are a few different ways you can iterate through the data depending on your needs.
You can slice the data with a combination of columns and rows:
>>>
>>> sheet["A1:C2"]
((<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.B1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.C1>),
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A2>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.B2>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.C2>))
You can get ranges of rows or columns:
>>>
>>> # Get all cells from column A
>>> sheet["A"]
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A1>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A2>,
...
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A99>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A100>)
>>> # Get all cells for a range of columns
>>> sheet["A:B"]
((<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A1>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A2>,
...
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A99>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A100>),
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B1>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B2>,
...
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B99>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B100>))
>>> # Get all cells from row 5
>>> sheet[5]
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A5>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B5>,
...
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.N5>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.O5>)
>>> # Get all cells for a range of rows
>>> sheet[5:6]
((<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A5>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B5>,
...
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.N5>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.O5>),
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A6>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B6>,
...
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.N6>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.O6>))
You’ll notice that all of the above examples return a tuple. If you want to refresh your memory on how to handle tuples in Python, check out the article on Lists and Tuples in Python.
There are also multiple ways of using normal Python generators to go through the data. The main methods you can use to achieve this are:
.iter_rows().iter_cols()
Both methods can receive the following arguments:
min_rowmax_rowmin_colmax_col
These arguments are used to set boundaries for the iteration:
>>>
>>> for row in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=1,
... max_row=2,
... min_col=1,
... max_col=3):
... print(row)
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.B1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.C1>)
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A2>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.B2>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.C2>)
>>> for column in sheet.iter_cols(min_row=1,
... max_row=2,
... min_col=1,
... max_col=3):
... print(column)
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.A2>)
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.B2>)
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.C1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.C2>)
You’ll notice that in the first example, when iterating through the rows using .iter_rows(), you get one tuple element per row selected. While when using .iter_cols() and iterating through columns, you’ll get one tuple per column instead.
One additional argument you can pass to both methods is the Boolean values_only. When it’s set to True, the values of the cell are returned, instead of the Cell object:
>>>
>>> for value in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=1,
... max_row=2,
... min_col=1,
... max_col=3,
... values_only=True):
... print(value)
('marketplace', 'customer_id', 'review_id')
('US', 3653882, 'R3O9SGZBVQBV76')
If you want to iterate through the whole dataset, then you can also use the attributes .rows or .columns directly, which are shortcuts to using .iter_rows() and .iter_cols() without any arguments:
>>>
>>> for row in sheet.rows:
... print(row)
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.B1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.C1>
...
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.M100>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.N100>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.O100>)
These shortcuts are very useful when you’re iterating through the whole dataset.
Manipulate Data Using Python’s Default Data Structures
Now that you know the basics of iterating through the data in a workbook, let’s look at smart ways of converting that data into Python structures.
As you saw earlier, the result from all iterations comes in the form of tuples. However, since a tuple is nothing more than an immutable list, you can easily access its data and transform it into other structures.
For example, say you want to extract product information from the sample.xlsx spreadsheet and into a dictionary where each key is a product ID.
A straightforward way to do this is to iterate over all the rows, pick the columns you know are related to product information, and then store that in a dictionary. Let’s code this out!
First of all, have a look at the headers and see what information you care most about:
>>>
>>> for value in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=1,
... max_row=1,
... values_only=True):
... print(value)
('marketplace', 'customer_id', 'review_id', 'product_id', ...)
This code returns a list of all the column names you have in the spreadsheet. To start, grab the columns with names:
product_idproduct_parentproduct_titleproduct_category
Lucky for you, the columns you need are all next to each other so you can use the min_column and max_column to easily get the data you want:
>>>
>>> for value in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=2,
... min_col=4,
... max_col=7,
... values_only=True):
... print(value)
('B00FALQ1ZC', 937001370, 'Invicta Women's 15150 "Angel" 18k Yellow...)
('B00D3RGO20', 484010722, "Kenneth Cole New York Women's KC4944...)
...
Nice! Now that you know how to get all the important product information you need, let’s put that data into a dictionary:
import json
from openpyxl import load_workbook
workbook = load_workbook(filename="sample.xlsx")
sheet = workbook.active
products = {}
# Using the values_only because you want to return the cells' values
for row in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=2,
min_col=4,
max_col=7,
values_only=True):
product_id = row[0]
product = {
"parent": row[1],
"title": row[2],
"category": row[3]
}
products[product_id] = product
# Using json here to be able to format the output for displaying later
print(json.dumps(products))
The code above returns a JSON similar to this:
{
"B00FALQ1ZC": {
"parent": 937001370,
"title": "Invicta Women's 15150 ...",
"category": "Watches"
},
"B00D3RGO20": {
"parent": 484010722,
"title": "Kenneth Cole New York ...",
"category": "Watches"
}
}
Here you can see that the output is trimmed to 2 products only, but if you run the script as it is, then you should get 98 products.
Convert Data Into Python Classes
To finalize the reading section of this tutorial, let’s dive into Python classes and see how you could improve on the example above and better structure the data.
For this, you’ll be using the new Python Data Classes that are available from Python 3.7. If you’re using an older version of Python, then you can use the default Classes instead.
So, first things first, let’s look at the data you have and decide what you want to store and how you want to store it.
As you saw right at the start, this data comes from Amazon, and it’s a list of product reviews. You can check the list of all the columns and their meaning on Amazon.
There are two significant elements you can extract from the data available:
- Products
- Reviews
A Product has:
- ID
- Title
- Parent
- Category
The Review has a few more fields:
- ID
- Customer ID
- Stars
- Headline
- Body
- Date
You can ignore a few of the review fields to make things a bit simpler.
So, a straightforward implementation of these two classes could be written in a separate file classes.py:
import datetime
from dataclasses import dataclass
@dataclass
class Product:
id: str
parent: str
title: str
category: str
@dataclass
class Review:
id: str
customer_id: str
stars: int
headline: str
body: str
date: datetime.datetime
After defining your data classes, you need to convert the data from the spreadsheet into these new structures.
Before doing the conversion, it’s worth looking at our header again and creating a mapping between columns and the fields you need:
>>>
>>> for value in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=1,
... max_row=1,
... values_only=True):
... print(value)
('marketplace', 'customer_id', 'review_id', 'product_id', ...)
>>> # Or an alternative
>>> for cell in sheet[1]:
... print(cell.value)
marketplace
customer_id
review_id
product_id
product_parent
...
Let’s create a file mapping.py where you have a list of all the field names and their column location (zero-indexed) on the spreadsheet:
# Product fields
PRODUCT_ID = 3
PRODUCT_PARENT = 4
PRODUCT_TITLE = 5
PRODUCT_CATEGORY = 6
# Review fields
REVIEW_ID = 2
REVIEW_CUSTOMER = 1
REVIEW_STARS = 7
REVIEW_HEADLINE = 12
REVIEW_BODY = 13
REVIEW_DATE = 14
You don’t necessarily have to do the mapping above. It’s more for readability when parsing the row data, so you don’t end up with a lot of magic numbers lying around.
Finally, let’s look at the code needed to parse the spreadsheet data into a list of product and review objects:
from datetime import datetime
from openpyxl import load_workbook
from classes import Product, Review
from mapping import PRODUCT_ID, PRODUCT_PARENT, PRODUCT_TITLE,
PRODUCT_CATEGORY, REVIEW_DATE, REVIEW_ID, REVIEW_CUSTOMER,
REVIEW_STARS, REVIEW_HEADLINE, REVIEW_BODY
# Using the read_only method since you're not gonna be editing the spreadsheet
workbook = load_workbook(filename="sample.xlsx", read_only=True)
sheet = workbook.active
products = []
reviews = []
# Using the values_only because you just want to return the cell value
for row in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=2, values_only=True):
product = Product(id=row[PRODUCT_ID],
parent=row[PRODUCT_PARENT],
title=row[PRODUCT_TITLE],
category=row[PRODUCT_CATEGORY])
products.append(product)
# You need to parse the date from the spreadsheet into a datetime format
spread_date = row[REVIEW_DATE]
parsed_date = datetime.strptime(spread_date, "%Y-%m-%d")
review = Review(id=row[REVIEW_ID],
customer_id=row[REVIEW_CUSTOMER],
stars=row[REVIEW_STARS],
headline=row[REVIEW_HEADLINE],
body=row[REVIEW_BODY],
date=parsed_date)
reviews.append(review)
print(products[0])
print(reviews[0])
After you run the code above, you should get some output like this:
Product(id='B00FALQ1ZC', parent=937001370, ...)
Review(id='R3O9SGZBVQBV76', customer_id=3653882, ...)
That’s it! Now you should have the data in a very simple and digestible class format, and you can start thinking of storing this in a Database or any other type of data storage you like.
Using this kind of OOP strategy to parse spreadsheets makes handling the data much simpler later on.
Appending New Data
Before you start creating very complex spreadsheets, have a quick look at an example of how to append data to an existing spreadsheet.
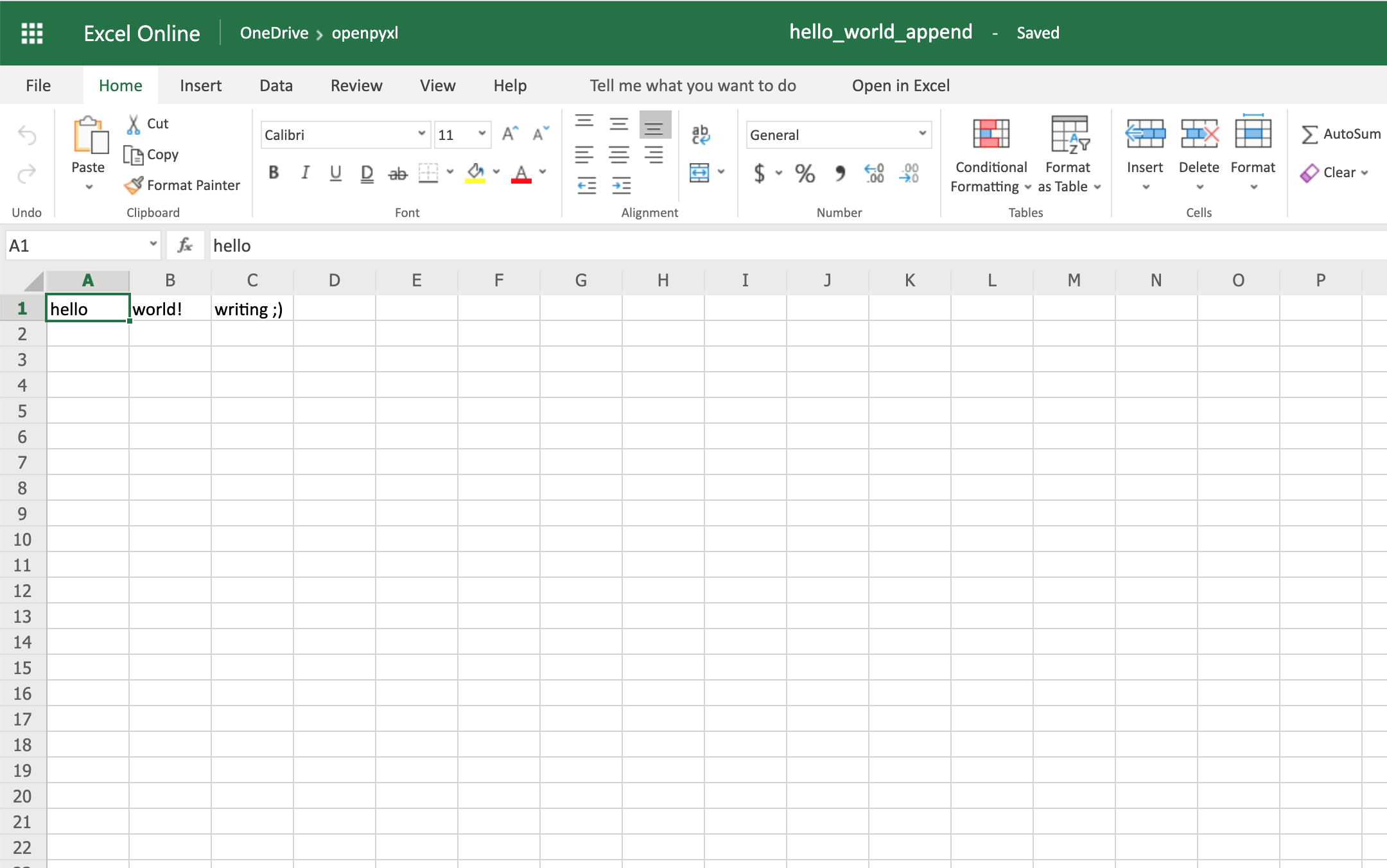
Go back to the first example spreadsheet you created (hello_world.xlsx) and try opening it and appending some data to it, like this:
from openpyxl import load_workbook
# Start by opening the spreadsheet and selecting the main sheet
workbook = load_workbook(filename="hello_world.xlsx")
sheet = workbook.active
# Write what you want into a specific cell
sheet["C1"] = "writing ;)"
# Save the spreadsheet
workbook.save(filename="hello_world_append.xlsx")
Et voilà, if you open the new hello_world_append.xlsx spreadsheet, you’ll see the following change:
Notice the additional writing 
C1.
Writing Excel Spreadsheets With openpyxl
There are a lot of different things you can write to a spreadsheet, from simple text or number values to complex formulas, charts, or even images.
Let’s start creating some spreadsheets!
Creating a Simple Spreadsheet
Previously, you saw a very quick example of how to write “Hello world!” into a spreadsheet, so you can start with that:
1from openpyxl import Workbook
2
3filename = "hello_world.xlsx"
4
5workbook = Workbook()
6sheet = workbook.active
7
8sheet["A1"] = "hello"
9sheet["B1"] = "world!"
10
11workbook.save(filename=filename)
The highlighted lines in the code above are the most important ones for writing. In the code, you can see that:
- Line 5 shows you how to create a new empty workbook.
- Lines 8 and 9 show you how to add data to specific cells.
- Line 11 shows you how to save the spreadsheet when you’re done.
Even though these lines above can be straightforward, it’s still good to know them well for when things get a bit more complicated.
One thing you can do to help with coming code examples is add the following method to your Python file or console:
>>>
>>> def print_rows():
... for row in sheet.iter_rows(values_only=True):
... print(row)
It makes it easier to print all of your spreadsheet values by just calling print_rows().
Basic Spreadsheet Operations
Before you get into the more advanced topics, it’s good for you to know how to manage the most simple elements of a spreadsheet.
Adding and Updating Cell Values
You already learned how to add values to a spreadsheet like this:
>>>
>>> sheet["A1"] = "value"
There’s another way you can do this, by first selecting a cell and then changing its value:
>>>
>>> cell = sheet["A1"]
>>> cell
<Cell 'Sheet'.A1>
>>> cell.value
'hello'
>>> cell.value = "hey"
>>> cell.value
'hey'
The new value is only stored into the spreadsheet once you call workbook.save().
The openpyxl creates a cell when adding a value, if that cell didn’t exist before:
>>>
>>> # Before, our spreadsheet has only 1 row
>>> print_rows()
('hello', 'world!')
>>> # Try adding a value to row 10
>>> sheet["B10"] = "test"
>>> print_rows()
('hello', 'world!')
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, 'test')
As you can see, when trying to add a value to cell B10, you end up with a tuple with 10 rows, just so you can have that test value.
Managing Rows and Columns
One of the most common things you have to do when manipulating spreadsheets is adding or removing rows and columns. The openpyxl package allows you to do that in a very straightforward way by using the methods:
.insert_rows().delete_rows().insert_cols().delete_cols()
Every single one of those methods can receive two arguments:
idxamount
Using our basic hello_world.xlsx example again, let’s see how these methods work:
>>>
>>> print_rows()
('hello', 'world!')
>>> # Insert a column before the existing column 1 ("A")
>>> sheet.insert_cols(idx=1)
>>> print_rows()
(None, 'hello', 'world!')
>>> # Insert 5 columns between column 2 ("B") and 3 ("C")
>>> sheet.insert_cols(idx=3, amount=5)
>>> print_rows()
(None, 'hello', None, None, None, None, None, 'world!')
>>> # Delete the created columns
>>> sheet.delete_cols(idx=3, amount=5)
>>> sheet.delete_cols(idx=1)
>>> print_rows()
('hello', 'world!')
>>> # Insert a new row in the beginning
>>> sheet.insert_rows(idx=1)
>>> print_rows()
(None, None)
('hello', 'world!')
>>> # Insert 3 new rows in the beginning
>>> sheet.insert_rows(idx=1, amount=3)
>>> print_rows()
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
('hello', 'world!')
>>> # Delete the first 4 rows
>>> sheet.delete_rows(idx=1, amount=4)
>>> print_rows()
('hello', 'world!')
The only thing you need to remember is that when inserting new data (rows or columns), the insertion happens before the idx parameter.
So, if you do insert_rows(1), it inserts a new row before the existing first row.
It’s the same for columns: when you call insert_cols(2), it inserts a new column right before the already existing second column (B).
However, when deleting rows or columns, .delete_... deletes data starting from the index passed as an argument.
For example, when doing delete_rows(2) it deletes row 2, and when doing delete_cols(3) it deletes the third column (C).
Managing Sheets
Sheet management is also one of those things you might need to know, even though it might be something that you don’t use that often.
If you look back at the code examples from this tutorial, you’ll notice the following recurring piece of code:
This is the way to select the default sheet from a spreadsheet. However, if you’re opening a spreadsheet with multiple sheets, then you can always select a specific one like this:
>>>
>>> # Let's say you have two sheets: "Products" and "Company Sales"
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Products', 'Company Sales']
>>> # You can select a sheet using its title
>>> products_sheet = workbook["Products"]
>>> sales_sheet = workbook["Company Sales"]
You can also change a sheet title very easily:
>>>
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Products', 'Company Sales']
>>> products_sheet = workbook["Products"]
>>> products_sheet.title = "New Products"
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['New Products', 'Company Sales']
If you want to create or delete sheets, then you can also do that with .create_sheet() and .remove():
>>>
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Products', 'Company Sales']
>>> operations_sheet = workbook.create_sheet("Operations")
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Products', 'Company Sales', 'Operations']
>>> # You can also define the position to create the sheet at
>>> hr_sheet = workbook.create_sheet("HR", 0)
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['HR', 'Products', 'Company Sales', 'Operations']
>>> # To remove them, just pass the sheet as an argument to the .remove()
>>> workbook.remove(operations_sheet)
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['HR', 'Products', 'Company Sales']
>>> workbook.remove(hr_sheet)
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Products', 'Company Sales']
One other thing you can do is make duplicates of a sheet using copy_worksheet():
>>>
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Products', 'Company Sales']
>>> products_sheet = workbook["Products"]
>>> workbook.copy_worksheet(products_sheet)
<Worksheet "Products Copy">
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Products', 'Company Sales', 'Products Copy']
If you open your spreadsheet after saving the above code, you’ll notice that the sheet Products Copy is a duplicate of the sheet Products.
Freezing Rows and Columns
Something that you might want to do when working with big spreadsheets is to freeze a few rows or columns, so they remain visible when you scroll right or down.
Freezing data allows you to keep an eye on important rows or columns, regardless of where you scroll in the spreadsheet.
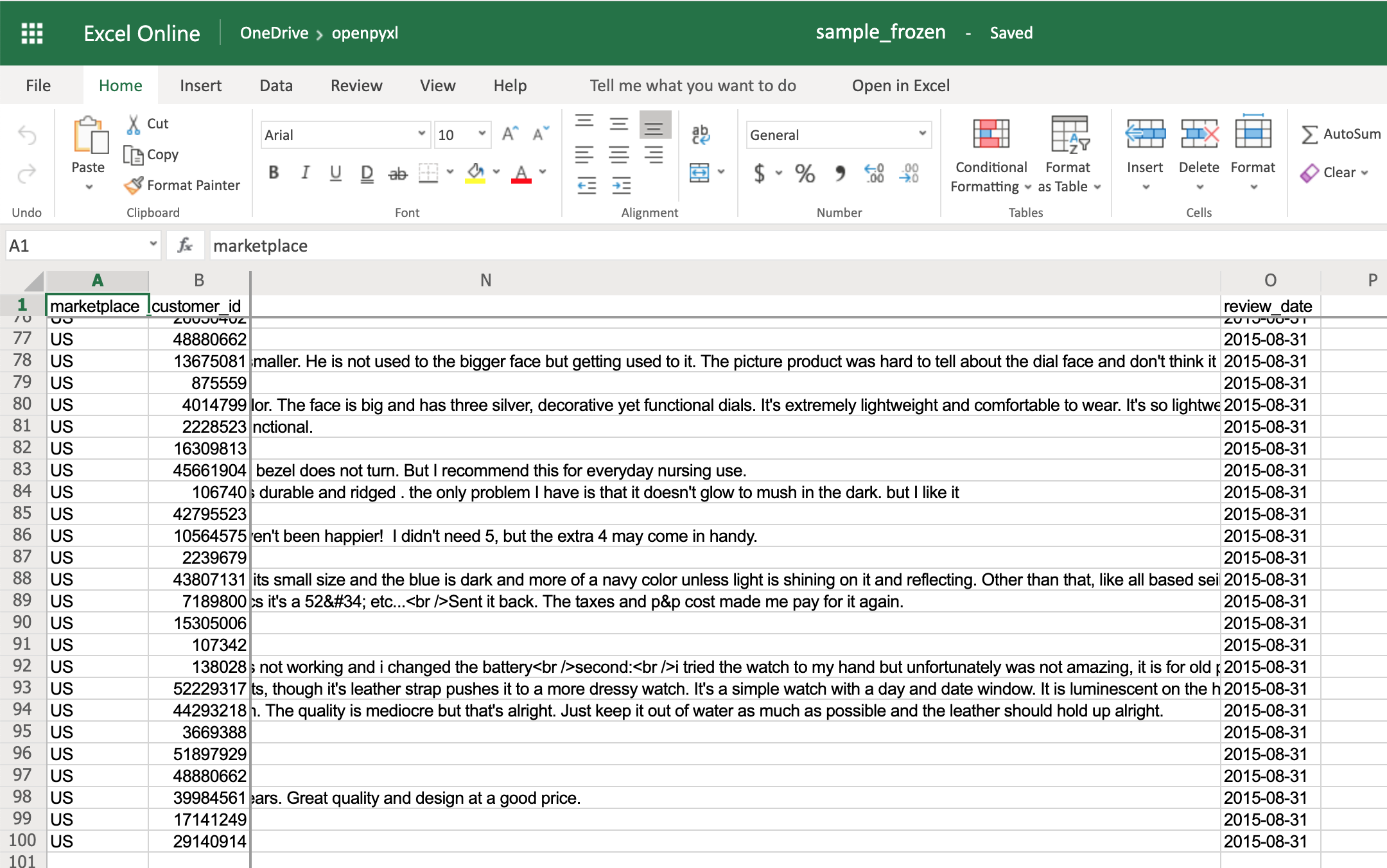
Again, openpyxl also has a way to accomplish this by using the worksheet freeze_panes attribute. For this example, go back to our sample.xlsx spreadsheet and try doing the following:
>>>
>>> workbook = load_workbook(filename="sample.xlsx")
>>> sheet = workbook.active
>>> sheet.freeze_panes = "C2"
>>> workbook.save("sample_frozen.xlsx")
If you open the sample_frozen.xlsx spreadsheet in your favorite spreadsheet editor, you’ll notice that row 1 and columns A and B are frozen and are always visible no matter where you navigate within the spreadsheet.
This feature is handy, for example, to keep headers within sight, so you always know what each column represents.
Here’s how it looks in the editor:
Notice how you’re at the end of the spreadsheet, and yet, you can see both row 1 and columns A and B.
Adding Filters
You can use openpyxl to add filters and sorts to your spreadsheet. However, when you open the spreadsheet, the data won’t be rearranged according to these sorts and filters.
At first, this might seem like a pretty useless feature, but when you’re programmatically creating a spreadsheet that is going to be sent and used by somebody else, it’s still nice to at least create the filters and allow people to use it afterward.
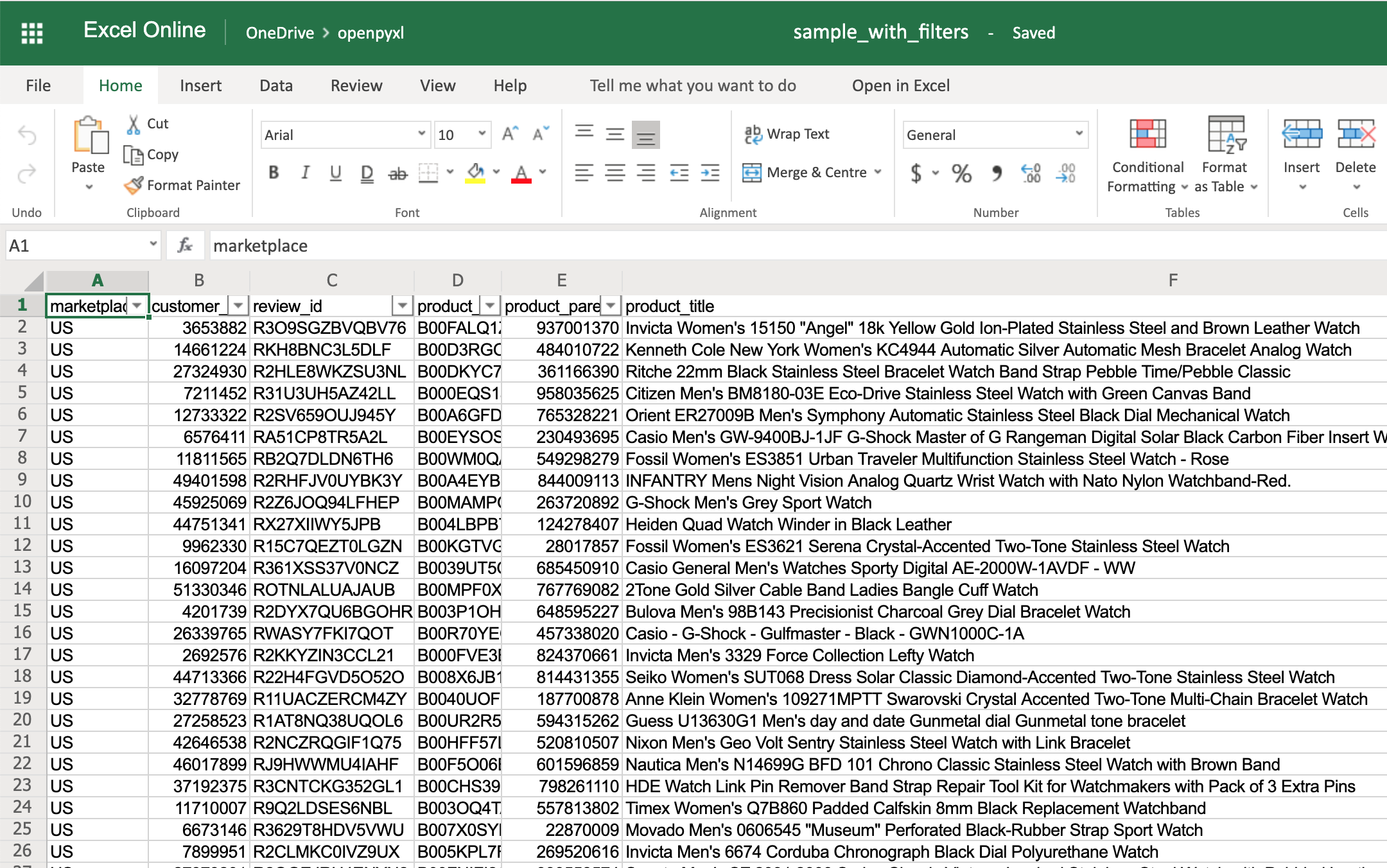
The code below is an example of how you would add some filters to our existing sample.xlsx spreadsheet:
>>>
>>> # Check the used spreadsheet space using the attribute "dimensions"
>>> sheet.dimensions
'A1:O100'
>>> sheet.auto_filter.ref = "A1:O100"
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_with_filters.xlsx")
You should now see the filters created when opening the spreadsheet in your editor:
You don’t have to use sheet.dimensions if you know precisely which part of the spreadsheet you want to apply filters to.
Adding Formulas
Formulas (or formulae) are one of the most powerful features of spreadsheets.
They gives you the power to apply specific mathematical equations to a range of cells. Using formulas with openpyxl is as simple as editing the value of a cell.
You can see the list of formulas supported by openpyxl:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl.utils import FORMULAE
>>> FORMULAE
frozenset({'ABS',
'ACCRINT',
'ACCRINTM',
'ACOS',
'ACOSH',
'AMORDEGRC',
'AMORLINC',
'AND',
...
'YEARFRAC',
'YIELD',
'YIELDDISC',
'YIELDMAT',
'ZTEST'})
Let’s add some formulas to our sample.xlsx spreadsheet.
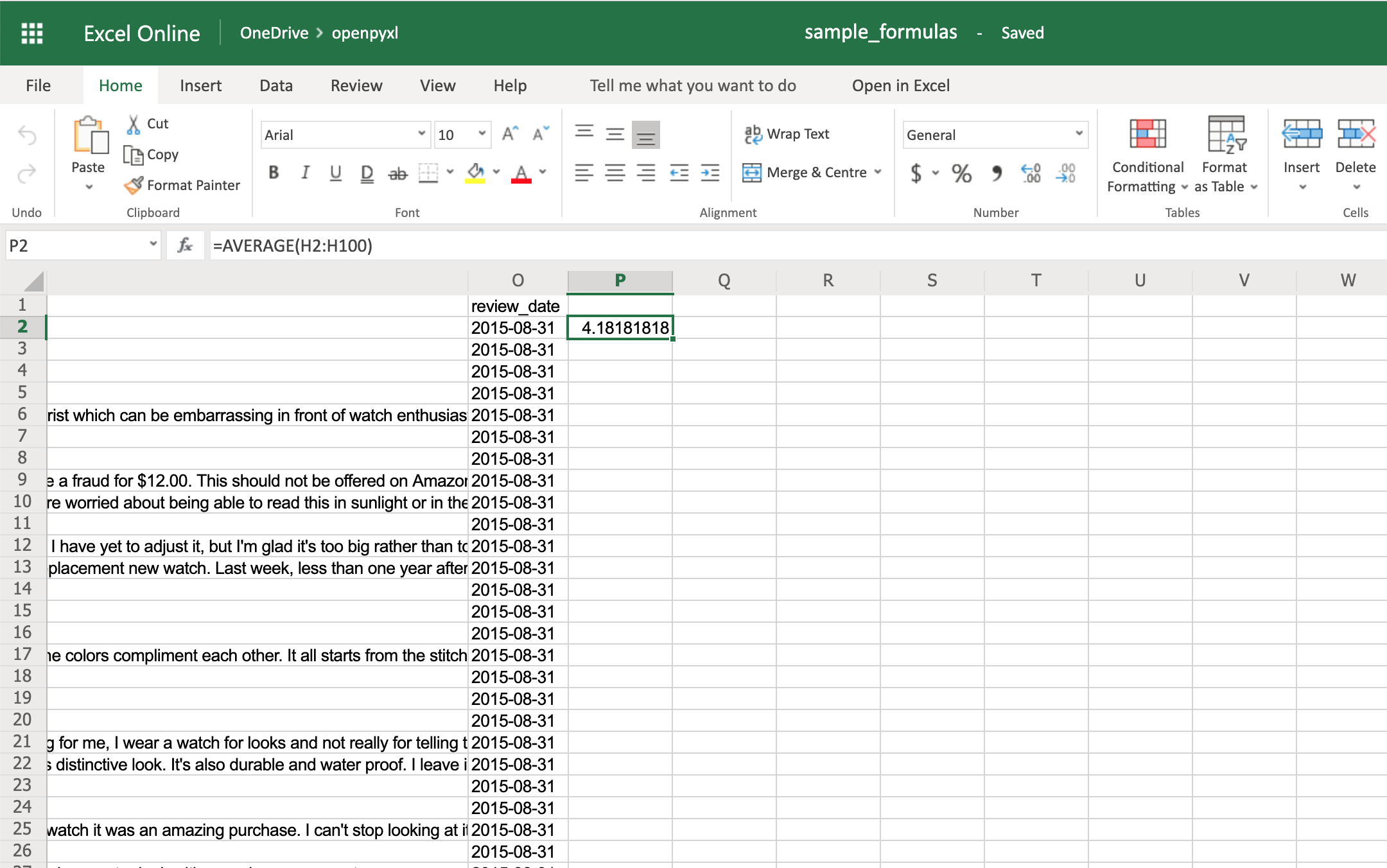
Starting with something easy, let’s check the average star rating for the 99 reviews within the spreadsheet:
>>>
>>> # Star rating is column "H"
>>> sheet["P2"] = "=AVERAGE(H2:H100)"
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_formulas.xlsx")
If you open the spreadsheet now and go to cell P2, you should see that its value is: 4.18181818181818. Have a look in the editor:
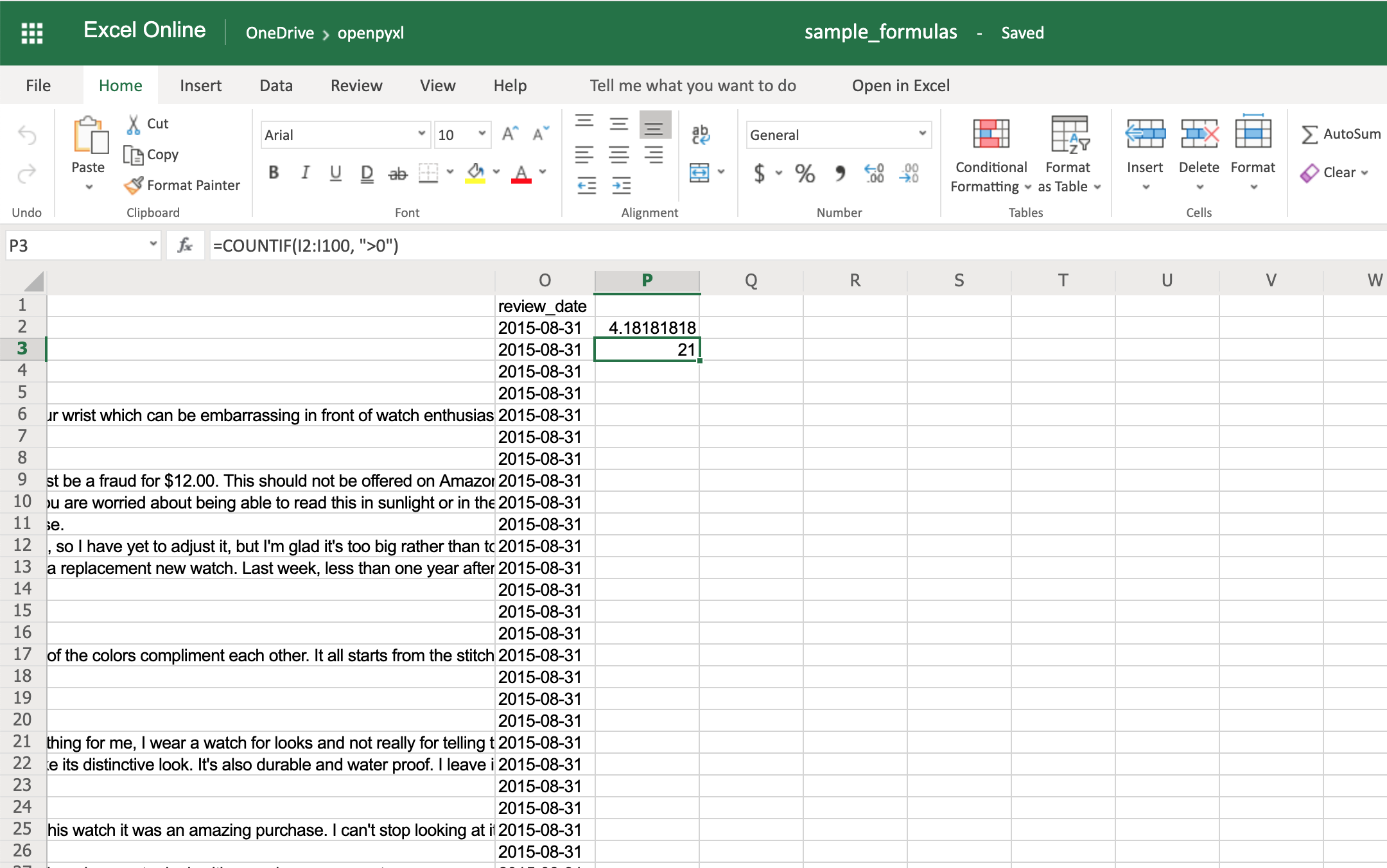
You can use the same methodology to add any formulas to your spreadsheet. For example, let’s count the number of reviews that had helpful votes:
>>>
>>> # The helpful votes are counted on column "I"
>>> sheet["P3"] = '=COUNTIF(I2:I100, ">0")'
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_formulas.xlsx")
You should get the number 21 on your P3 spreadsheet cell like so:
You’ll have to make sure that the strings within a formula are always in double quotes, so you either have to use single quotes around the formula like in the example above or you’ll have to escape the double quotes inside the formula: "=COUNTIF(I2:I100, ">0")".
There are a ton of other formulas you can add to your spreadsheet using the same procedure you tried above. Give it a go yourself!
Adding Styles
Even though styling a spreadsheet might not be something you would do every day, it’s still good to know how to do it.
Using openpyxl, you can apply multiple styling options to your spreadsheet, including fonts, borders, colors, and so on. Have a look at the openpyxl documentation to learn more.
You can also choose to either apply a style directly to a cell or create a template and reuse it to apply styles to multiple cells.
Let’s start by having a look at simple cell styling, using our sample.xlsx again as the base spreadsheet:
>>>
>>> # Import necessary style classes
>>> from openpyxl.styles import Font, Color, Alignment, Border, Side
>>> # Create a few styles
>>> bold_font = Font(bold=True)
>>> big_red_text = Font(color="00FF0000", size=20)
>>> center_aligned_text = Alignment(horizontal="center")
>>> double_border_side = Side(border_style="double")
>>> square_border = Border(top=double_border_side,
... right=double_border_side,
... bottom=double_border_side,
... left=double_border_side)
>>> # Style some cells!
>>> sheet["A2"].font = bold_font
>>> sheet["A3"].font = big_red_text
>>> sheet["A4"].alignment = center_aligned_text
>>> sheet["A5"].border = square_border
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_styles.xlsx")
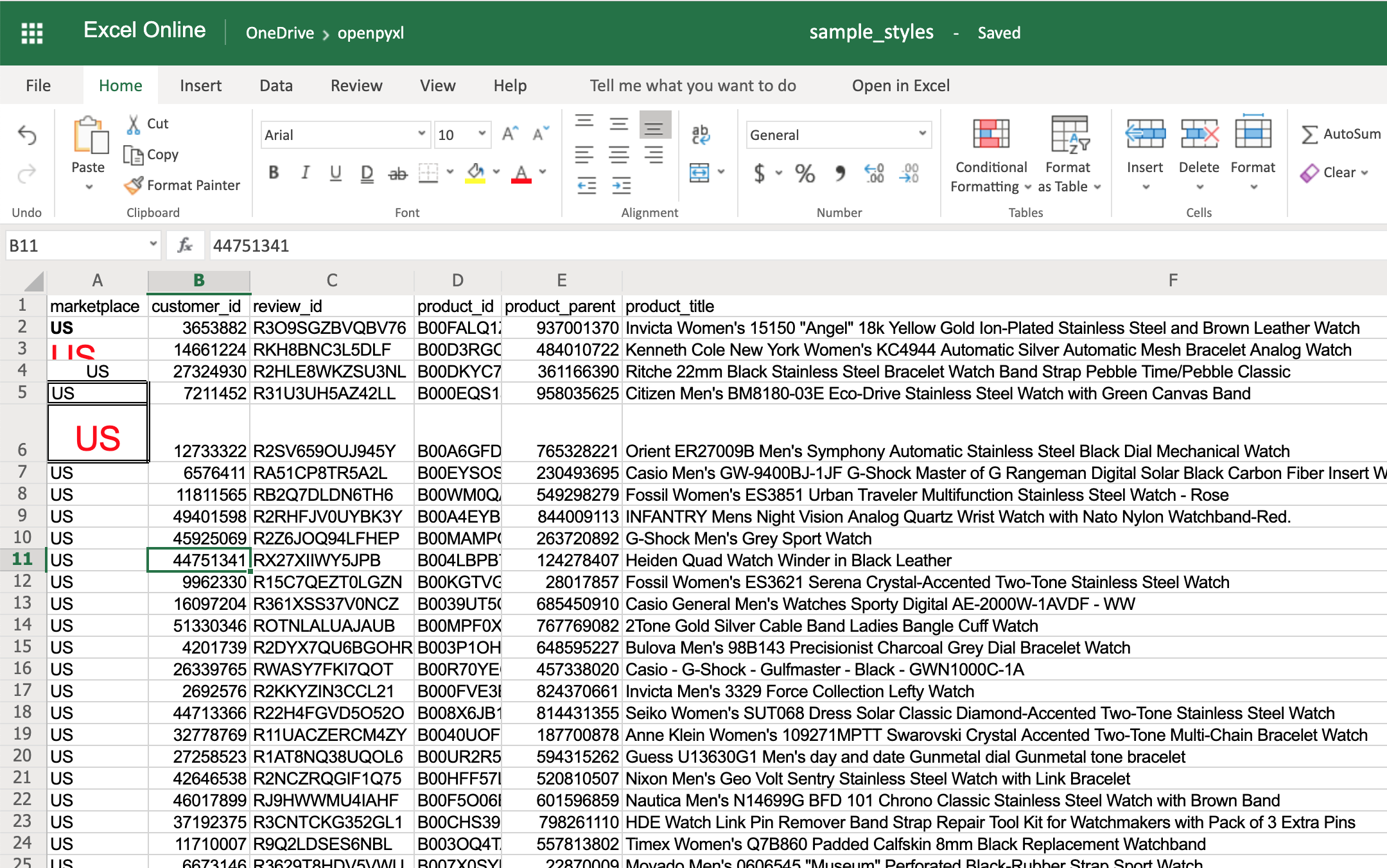
If you open your spreadsheet now, you should see quite a few different styles on the first 5 cells of column A:
There you go. You got:
- A2 with the text in bold
- A3 with the text in red and bigger font size
- A4 with the text centered
- A5 with a square border around the text
You can also combine styles by simply adding them to the cell at the same time:
>>>
>>> # Reusing the same styles from the example above
>>> sheet["A6"].alignment = center_aligned_text
>>> sheet["A6"].font = big_red_text
>>> sheet["A6"].border = square_border
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_styles.xlsx")
Have a look at cell A6 here:
When you want to apply multiple styles to one or several cells, you can use a NamedStyle class instead, which is like a style template that you can use over and over again. Have a look at the example below:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl.styles import NamedStyle
>>> # Let's create a style template for the header row
>>> header = NamedStyle(name="header")
>>> header.font = Font(bold=True)
>>> header.border = Border(bottom=Side(border_style="thin"))
>>> header.alignment = Alignment(horizontal="center", vertical="center")
>>> # Now let's apply this to all first row (header) cells
>>> header_row = sheet[1]
>>> for cell in header_row:
... cell.style = header
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_styles.xlsx")
If you open the spreadsheet now, you should see that its first row is bold, the text is aligned to the center, and there’s a small bottom border! Have a look below:
As you saw above, there are many options when it comes to styling, and it depends on the use case, so feel free to check openpyxl documentation and see what other things you can do.
Conditional Formatting
This feature is one of my personal favorites when it comes to adding styles to a spreadsheet.
It’s a much more powerful approach to styling because it dynamically applies styles according to how the data in the spreadsheet changes.
In a nutshell, conditional formatting allows you to specify a list of styles to apply to a cell (or cell range) according to specific conditions.
For example, a widespread use case is to have a balance sheet where all the negative totals are in red, and the positive ones are in green. This formatting makes it much more efficient to spot good vs bad periods.
Without further ado, let’s pick our favorite spreadsheet—sample.xlsx—and add some conditional formatting.
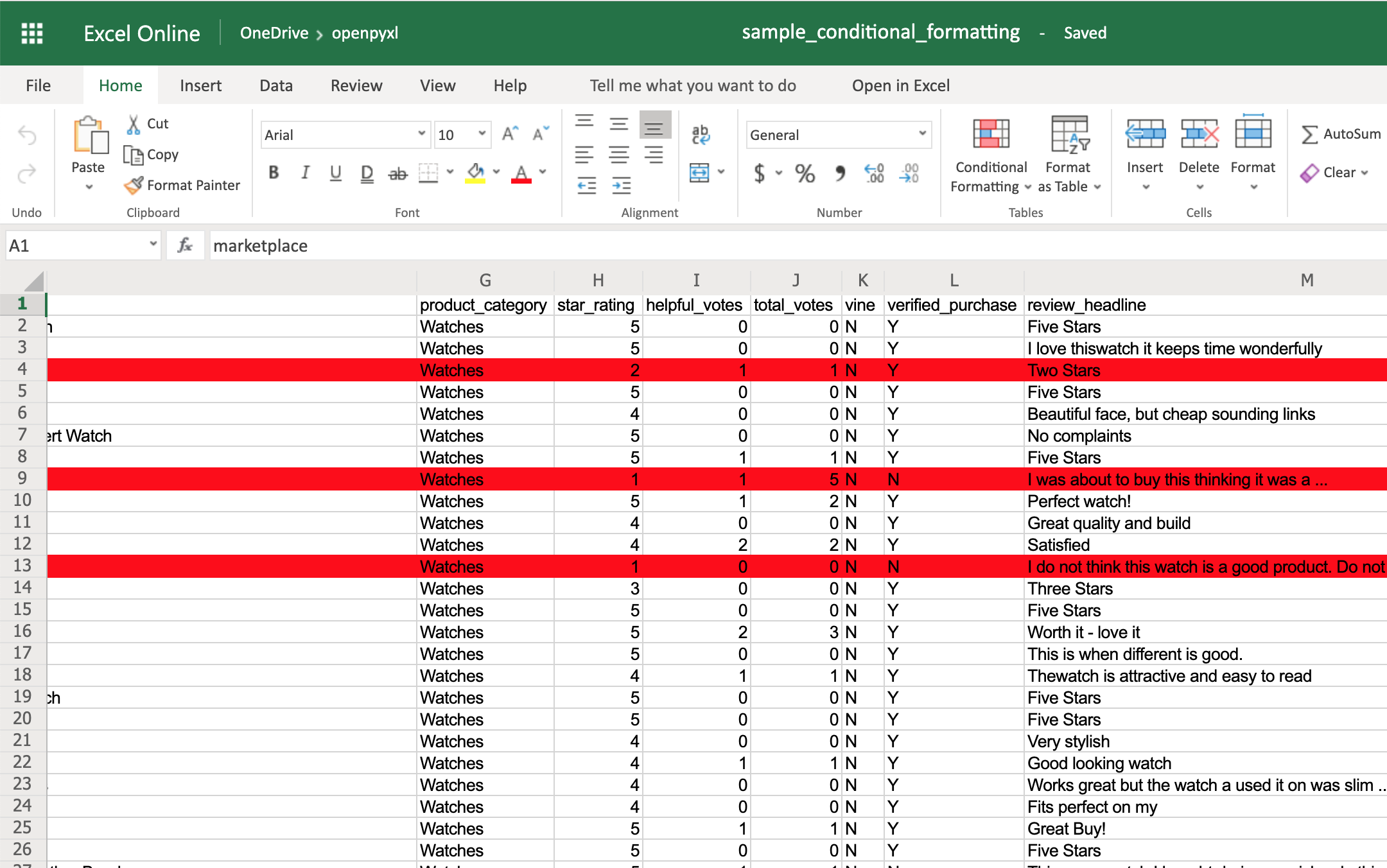
You can start by adding a simple one that adds a red background to all reviews with less than 3 stars:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl.styles import PatternFill
>>> from openpyxl.styles.differential import DifferentialStyle
>>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import Rule
>>> red_background = PatternFill(fgColor="00FF0000")
>>> diff_style = DifferentialStyle(fill=red_background)
>>> rule = Rule(type="expression", dxf=diff_style)
>>> rule.formula = ["$H1<3"]
>>> sheet.conditional_formatting.add("A1:O100", rule)
>>> workbook.save("sample_conditional_formatting.xlsx")
Now you’ll see all the reviews with a star rating below 3 marked with a red background:
Code-wise, the only things that are new here are the objects DifferentialStyle and Rule:
DifferentialStyleis quite similar toNamedStyle, which you already saw above, and it’s used to aggregate multiple styles such as fonts, borders, alignment, and so forth.Ruleis responsible for selecting the cells and applying the styles if the cells match the rule’s logic.
Using a Rule object, you can create numerous conditional formatting scenarios.
However, for simplicity sake, the openpyxl package offers 3 built-in formats that make it easier to create a few common conditional formatting patterns. These built-ins are:
ColorScaleIconSetDataBar
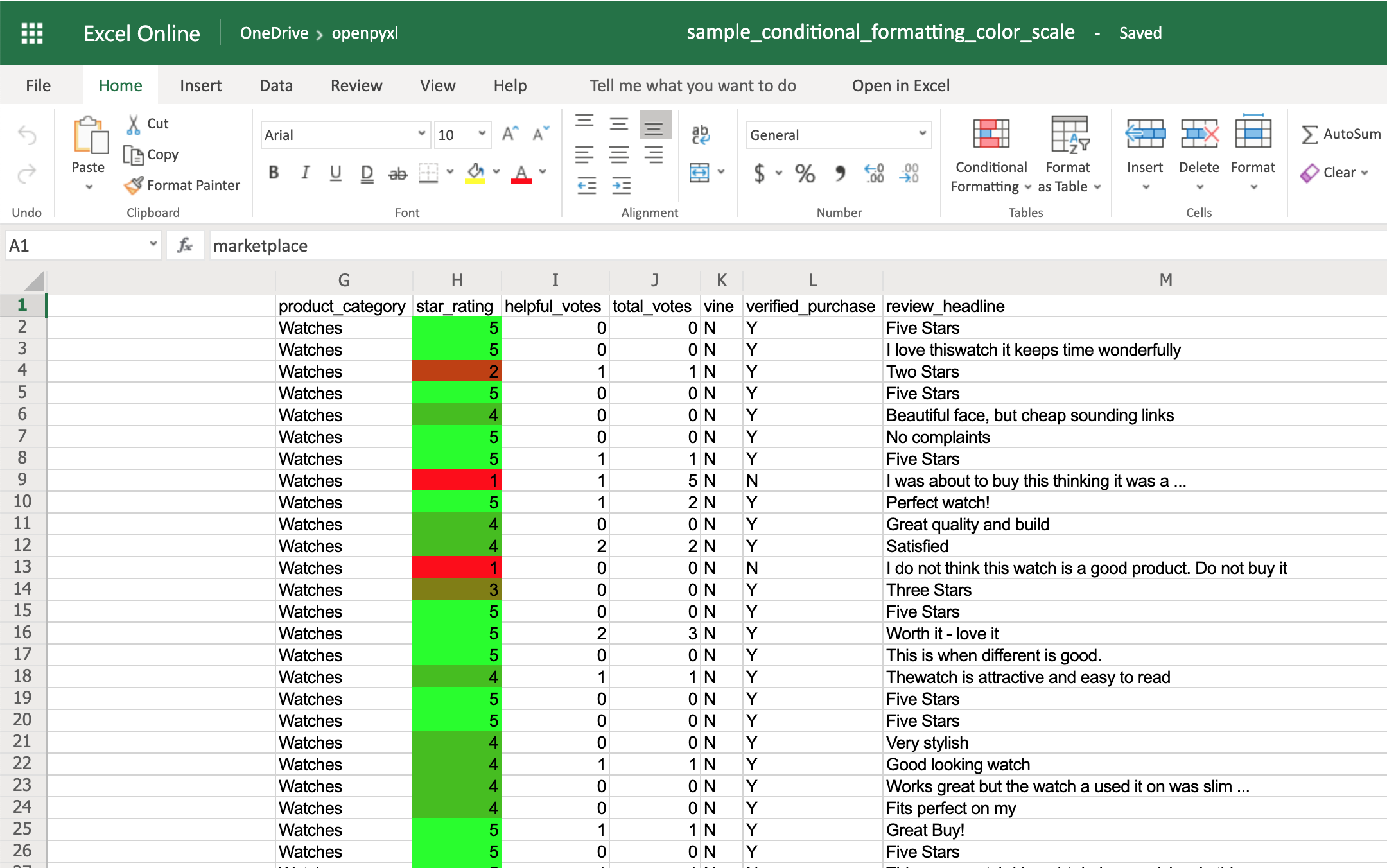
The ColorScale gives you the ability to create color gradients:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import ColorScaleRule
>>> color_scale_rule = ColorScaleRule(start_type="min",
... start_color="00FF0000", # Red
... end_type="max",
... end_color="0000FF00") # Green
>>> # Again, let's add this gradient to the star ratings, column "H"
>>> sheet.conditional_formatting.add("H2:H100", color_scale_rule)
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_conditional_formatting_color_scale.xlsx")
Now you should see a color gradient on column H, from red to green, according to the star rating:
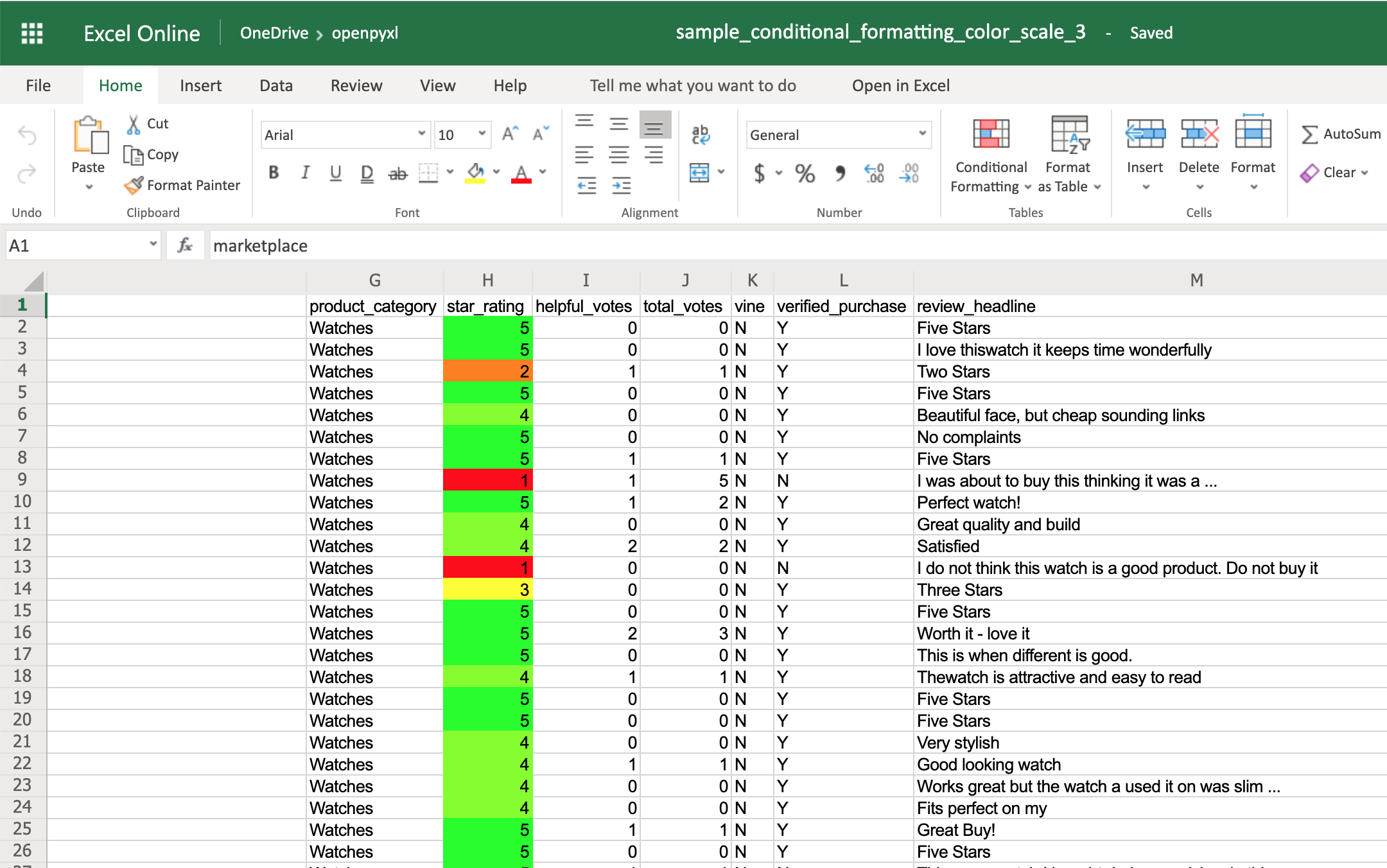
You can also add a third color and make two gradients instead:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import ColorScaleRule
>>> color_scale_rule = ColorScaleRule(start_type="num",
... start_value=1,
... start_color="00FF0000", # Red
... mid_type="num",
... mid_value=3,
... mid_color="00FFFF00", # Yellow
... end_type="num",
... end_value=5,
... end_color="0000FF00") # Green
>>> # Again, let's add this gradient to the star ratings, column "H"
>>> sheet.conditional_formatting.add("H2:H100", color_scale_rule)
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_conditional_formatting_color_scale_3.xlsx")
This time, you’ll notice that star ratings between 1 and 3 have a gradient from red to yellow, and star ratings between 3 and 5 have a gradient from yellow to green:
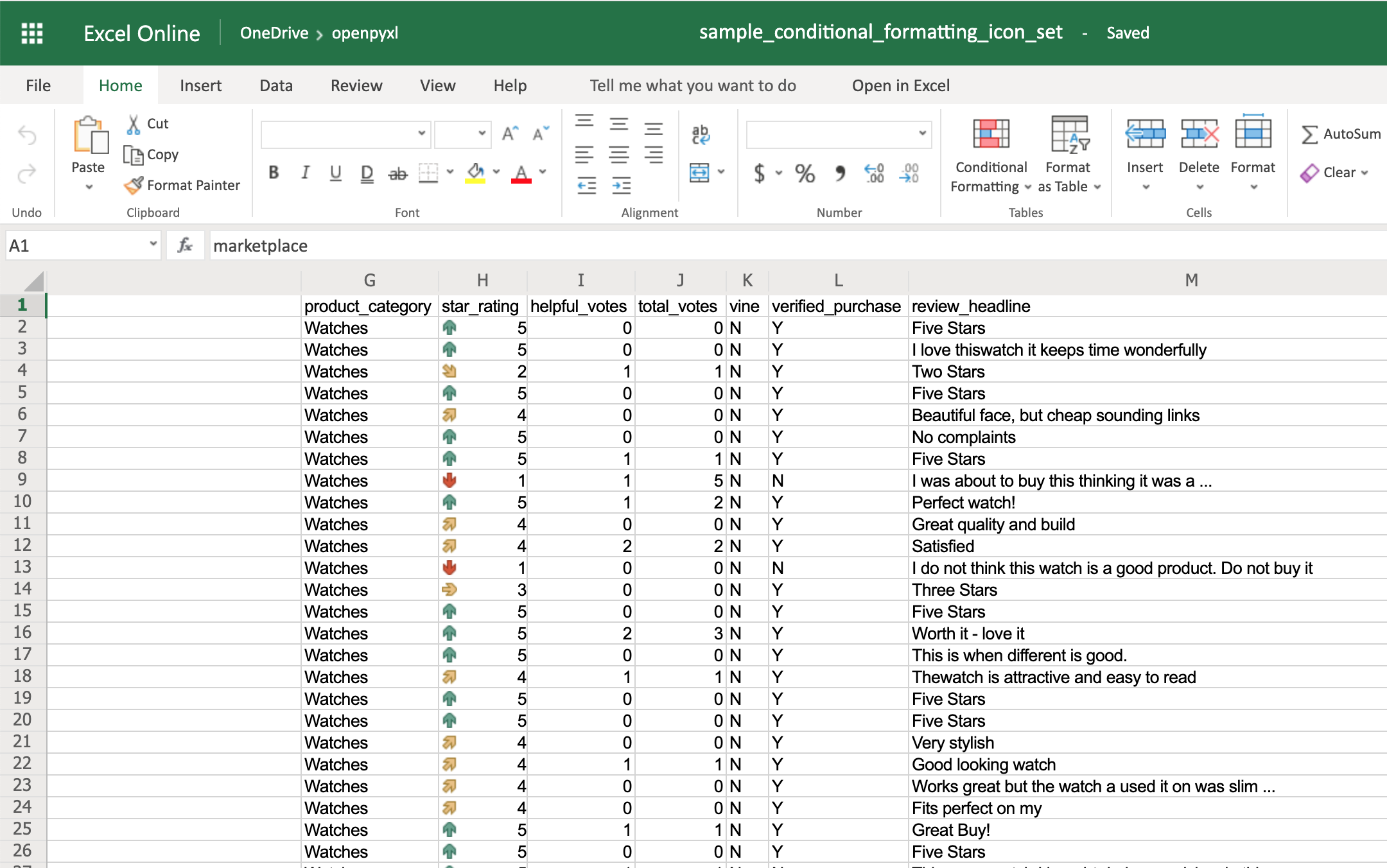
The IconSet allows you to add an icon to the cell according to its value:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import IconSetRule
>>> icon_set_rule = IconSetRule("5Arrows", "num", [1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
>>> sheet.conditional_formatting.add("H2:H100", icon_set_rule)
>>> workbook.save("sample_conditional_formatting_icon_set.xlsx")
You’ll see a colored arrow next to the star rating. This arrow is red and points down when the value of the cell is 1 and, as the rating gets better, the arrow starts pointing up and becomes green:
The openpyxl package has a full list of other icons you can use, besides the arrow.
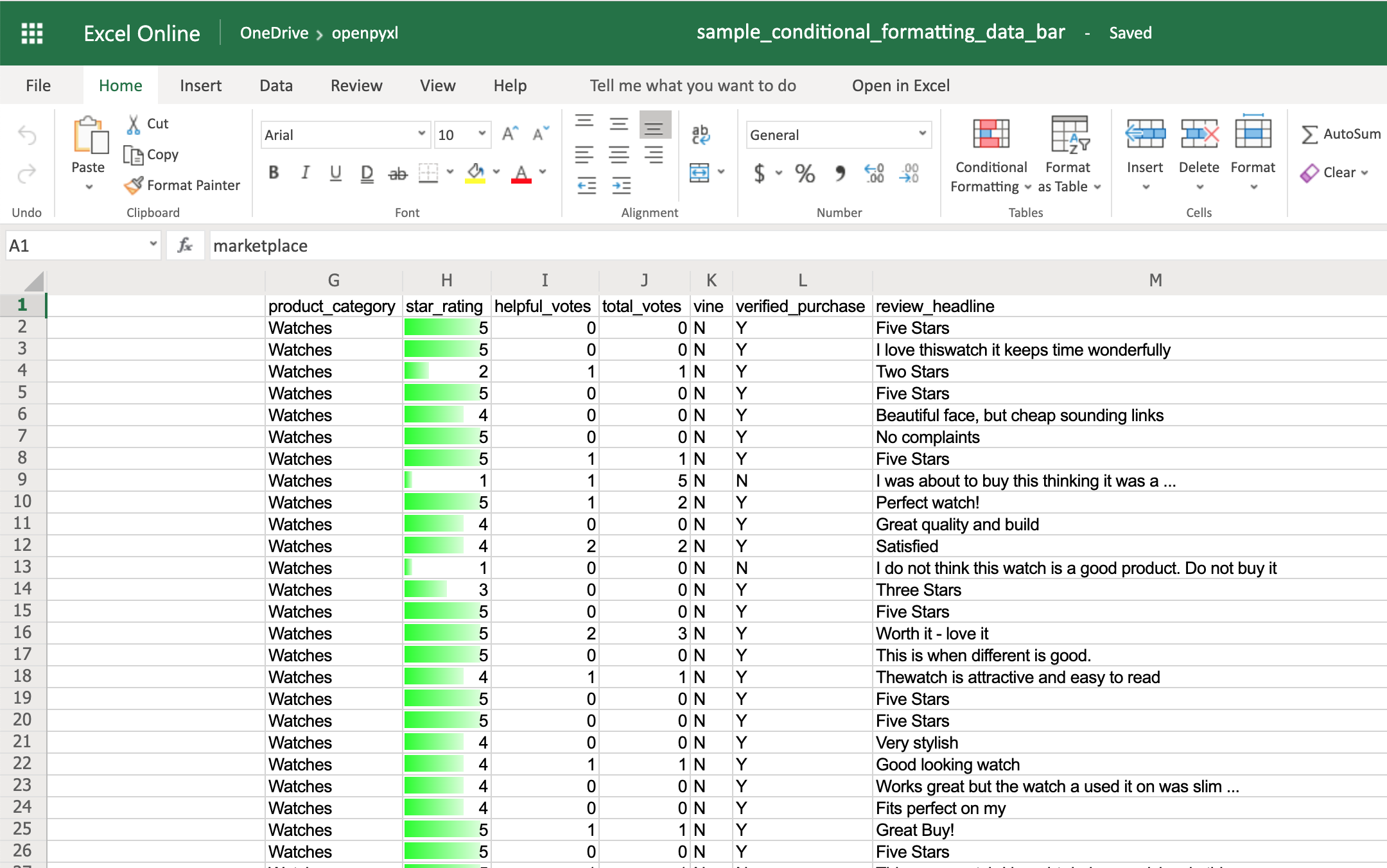
Finally, the DataBar allows you to create progress bars:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import DataBarRule
>>> data_bar_rule = DataBarRule(start_type="num",
... start_value=1,
... end_type="num",
... end_value="5",
... color="0000FF00") # Green
>>> sheet.conditional_formatting.add("H2:H100", data_bar_rule)
>>> workbook.save("sample_conditional_formatting_data_bar.xlsx")
You’ll now see a green progress bar that gets fuller the closer the star rating is to the number 5:
As you can see, there are a lot of cool things you can do with conditional formatting.
Here, you saw only a few examples of what you can achieve with it, but check the openpyxl documentation to see a bunch of other options.
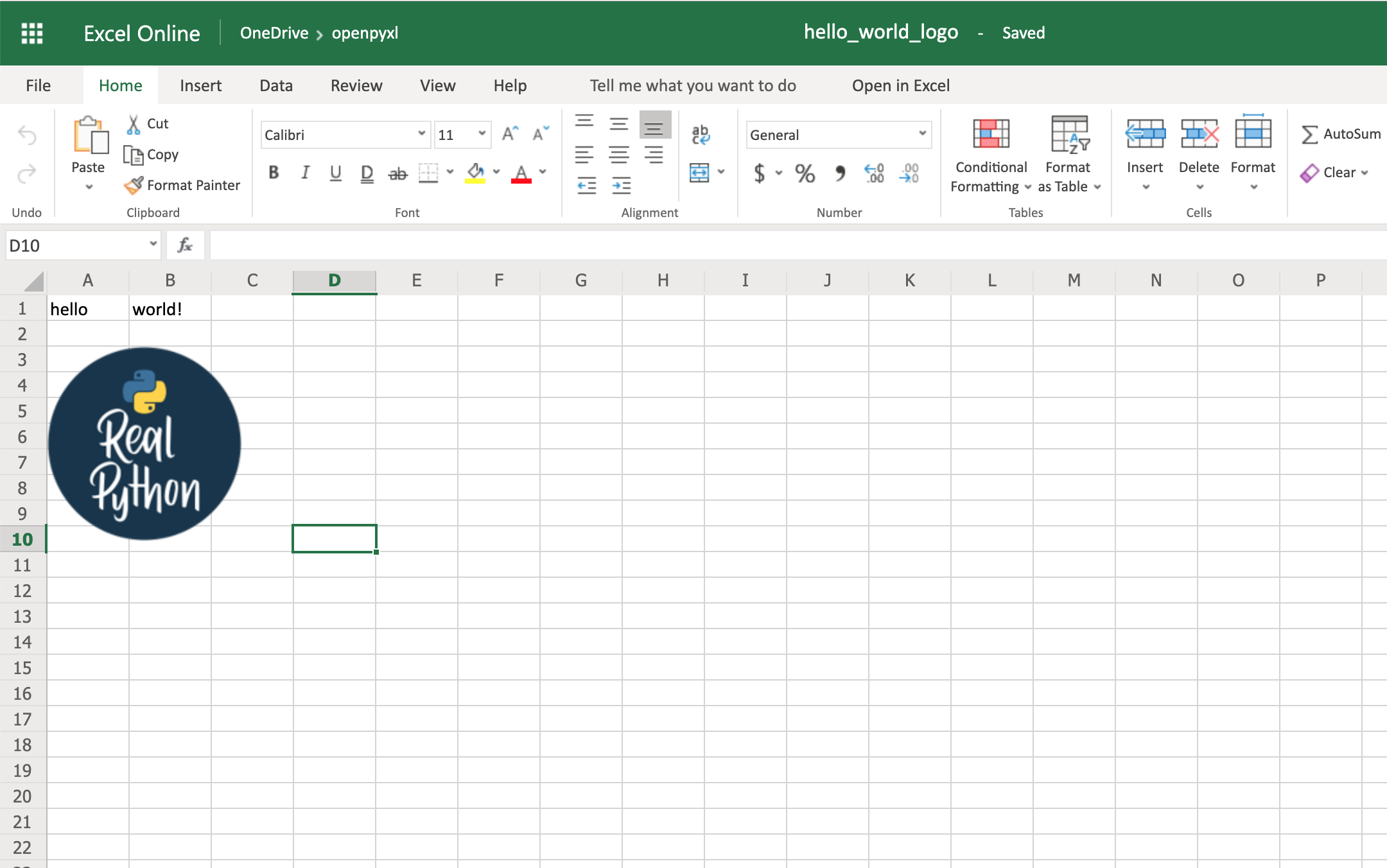
Adding Images
Even though images are not something that you’ll often see in a spreadsheet, it’s quite cool to be able to add them. Maybe you can use it for branding purposes or to make spreadsheets more personal.
To be able to load images to a spreadsheet using openpyxl, you’ll have to install Pillow:
Apart from that, you’ll also need an image. For this example, you can grab the Real Python logo below and convert it from .webp to .png using an online converter such as cloudconvert.com, save the final file as logo.png, and copy it to the root folder where you’re running your examples:
Afterward, this is the code you need to import that image into the hello_word.xlsx spreadsheet:
from openpyxl import load_workbook
from openpyxl.drawing.image import Image
# Let's use the hello_world spreadsheet since it has less data
workbook = load_workbook(filename="hello_world.xlsx")
sheet = workbook.active
logo = Image("logo.png")
# A bit of resizing to not fill the whole spreadsheet with the logo
logo.height = 150
logo.width = 150
sheet.add_image(logo, "A3")
workbook.save(filename="hello_world_logo.xlsx")
You have an image on your spreadsheet! Here it is:
The image’s left top corner is on the cell you chose, in this case, A3.
Adding Pretty Charts
Another powerful thing you can do with spreadsheets is create an incredible variety of charts.
Charts are a great way to visualize and understand loads of data quickly. There are a lot of different chart types: bar chart, pie chart, line chart, and so on. openpyxl has support for a lot of them.
Here, you’ll see only a couple of examples of charts because the theory behind it is the same for every single chart type:
For any chart you want to build, you’ll need to define the chart type: BarChart, LineChart, and so forth, plus the data to be used for the chart, which is called Reference.
Before you can build your chart, you need to define what data you want to see represented in it. Sometimes, you can use the dataset as is, but other times you need to massage the data a bit to get additional information.
Let’s start by building a new workbook with some sample data:
1from openpyxl import Workbook
2from openpyxl.chart import BarChart, Reference
3
4workbook = Workbook()
5sheet = workbook.active
6
7# Let's create some sample sales data
8rows = [
9 ["Product", "Online", "Store"],
10 [1, 30, 45],
11 [2, 40, 30],
12 [3, 40, 25],
13 [4, 50, 30],
14 [5, 30, 25],
15 [6, 25, 35],
16 [7, 20, 40],
17]
18
19for row in rows:
20 sheet.append(row)
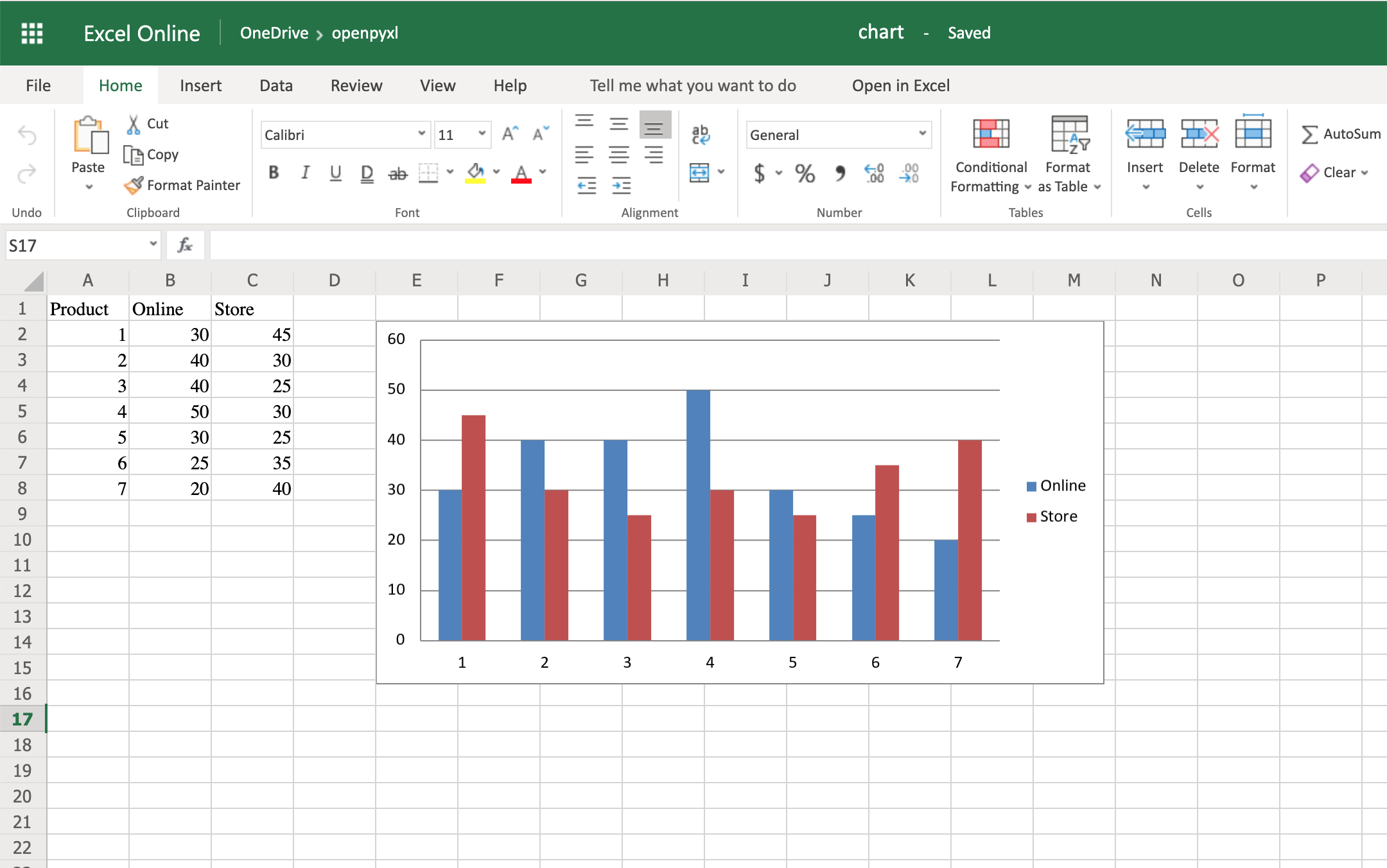
Now you’re going to start by creating a bar chart that displays the total number of sales per product:
22chart = BarChart()
23data = Reference(worksheet=sheet,
24 min_row=1,
25 max_row=8,
26 min_col=2,
27 max_col=3)
28
29chart.add_data(data, titles_from_data=True)
30sheet.add_chart(chart, "E2")
31
32workbook.save("chart.xlsx")
There you have it. Below, you can see a very straightforward bar chart showing the difference between online product sales online and in-store product sales:
Like with images, the top left corner of the chart is on the cell you added the chart to. In your case, it was on cell E2.
Try creating a line chart instead, changing the data a bit:
1import random
2from openpyxl import Workbook
3from openpyxl.chart import LineChart, Reference
4
5workbook = Workbook()
6sheet = workbook.active
7
8# Let's create some sample sales data
9rows = [
10 ["", "January", "February", "March", "April",
11 "May", "June", "July", "August", "September",
12 "October", "November", "December"],
13 [1, ],
14 [2, ],
15 [3, ],
16]
17
18for row in rows:
19 sheet.append(row)
20
21for row in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=2,
22 max_row=4,
23 min_col=2,
24 max_col=13):
25 for cell in row:
26 cell.value = random.randrange(5, 100)
With the above code, you’ll be able to generate some random data regarding the sales of 3 different products across a whole year.
Once that’s done, you can very easily create a line chart with the following code:
28chart = LineChart()
29data = Reference(worksheet=sheet,
30 min_row=2,
31 max_row=4,
32 min_col=1,
33 max_col=13)
34
35chart.add_data(data, from_rows=True, titles_from_data=True)
36sheet.add_chart(chart, "C6")
37
38workbook.save("line_chart.xlsx")
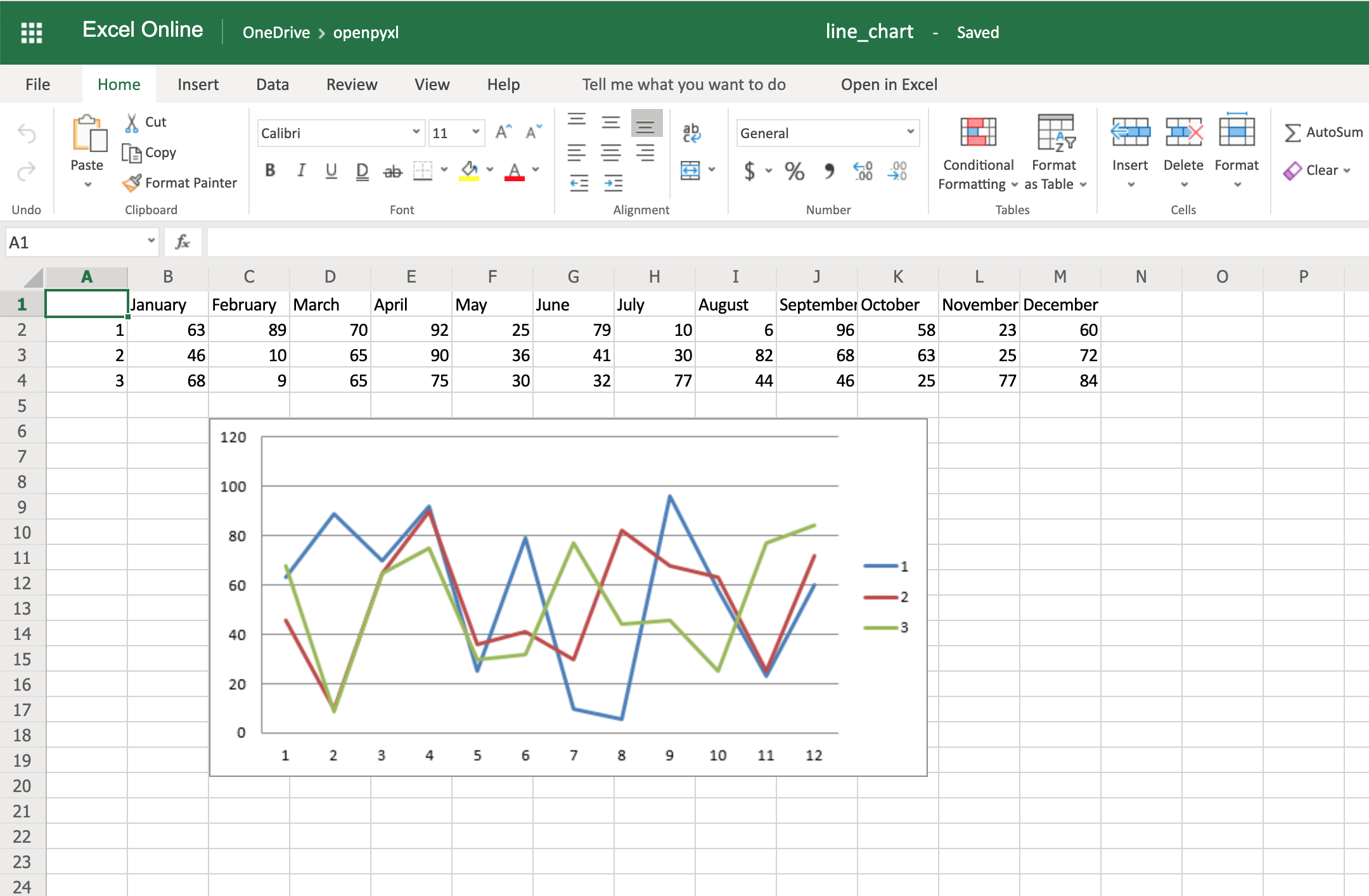
Here’s the outcome of the above piece of code:
One thing to keep in mind here is the fact that you’re using from_rows=True when adding the data. This argument makes the chart plot row by row instead of column by column.
In your sample data, you see that each product has a row with 12 values (1 column per month). That’s why you use from_rows. If you don’t pass that argument, by default, the chart tries to plot by column, and you’ll get a month-by-month comparison of sales.
Another difference that has to do with the above argument change is the fact that our Reference now starts from the first column, min_col=1, instead of the second one. This change is needed because the chart now expects the first column to have the titles.
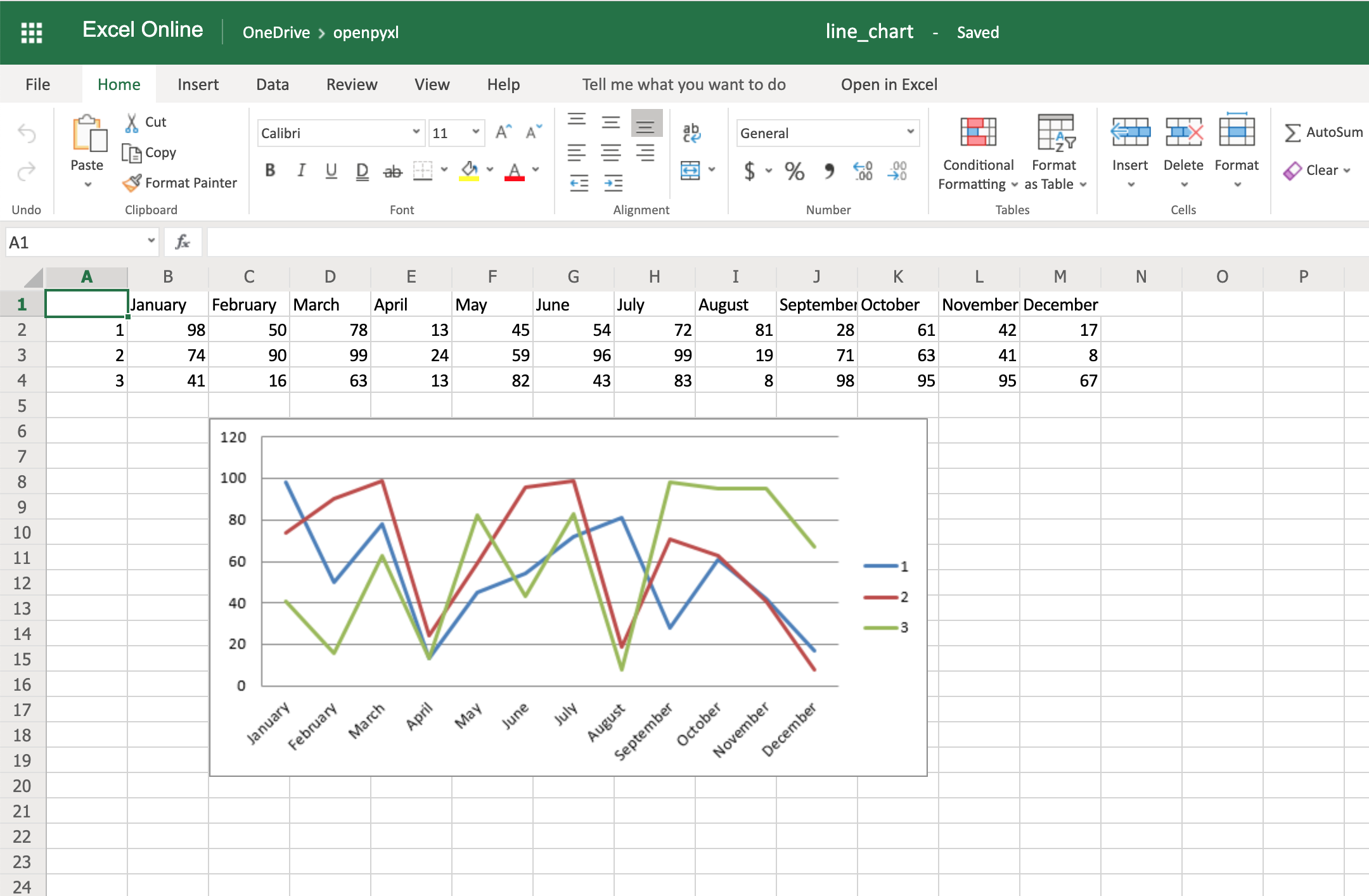
There are a couple of other things you can also change regarding the style of the chart. For example, you can add specific categories to the chart:
cats = Reference(worksheet=sheet,
min_row=1,
max_row=1,
min_col=2,
max_col=13)
chart.set_categories(cats)
Add this piece of code before saving the workbook, and you should see the month names appearing instead of numbers:
Code-wise, this is a minimal change. But in terms of the readability of the spreadsheet, this makes it much easier for someone to open the spreadsheet and understand the chart straight away.
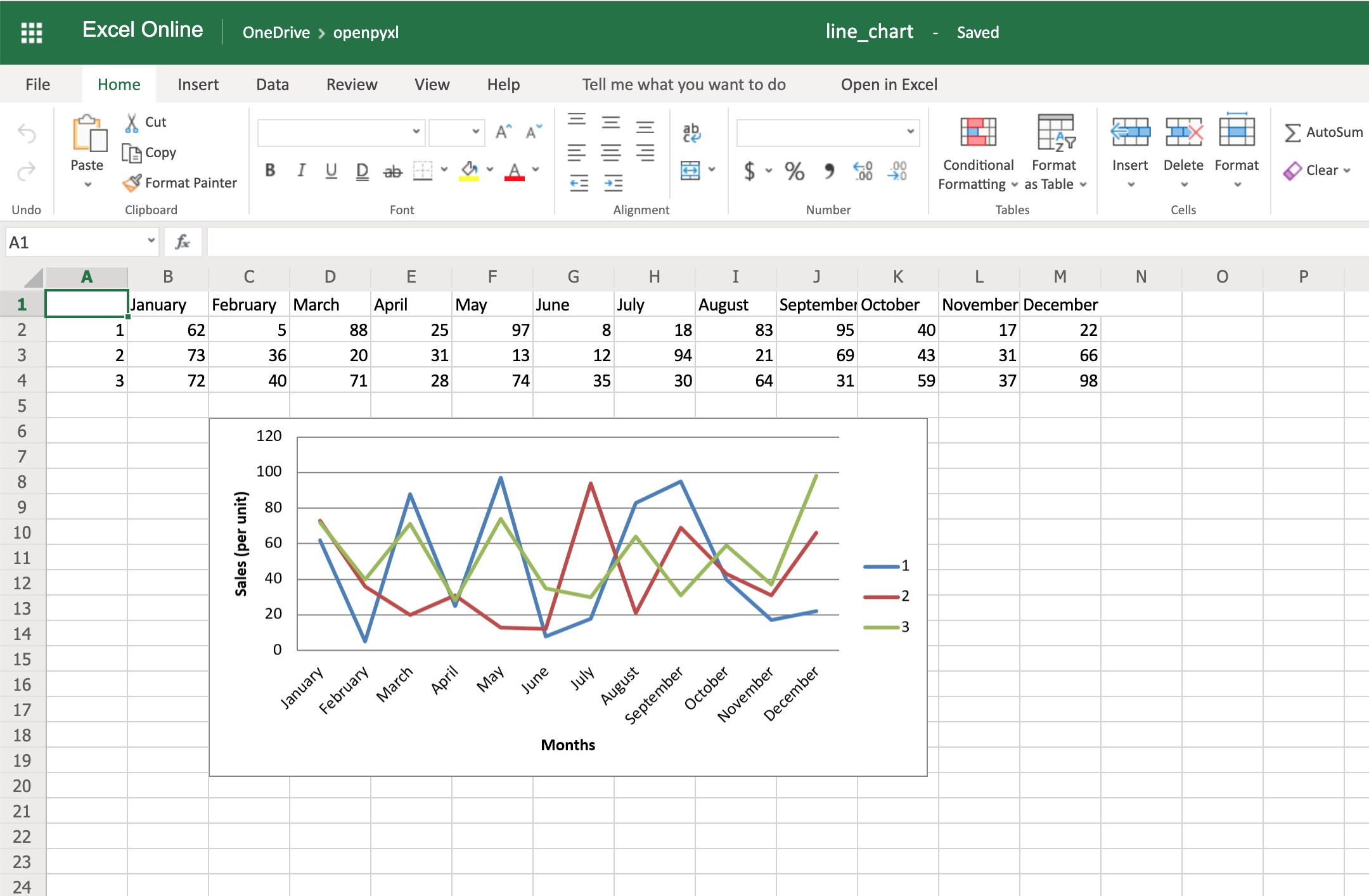
Another thing you can do to improve the chart readability is to add an axis. You can do it using the attributes x_axis and y_axis:
chart.x_axis.title = "Months"
chart.y_axis.title = "Sales (per unit)"
This will generate a spreadsheet like the below one:
As you can see, small changes like the above make reading your chart a much easier and quicker task.
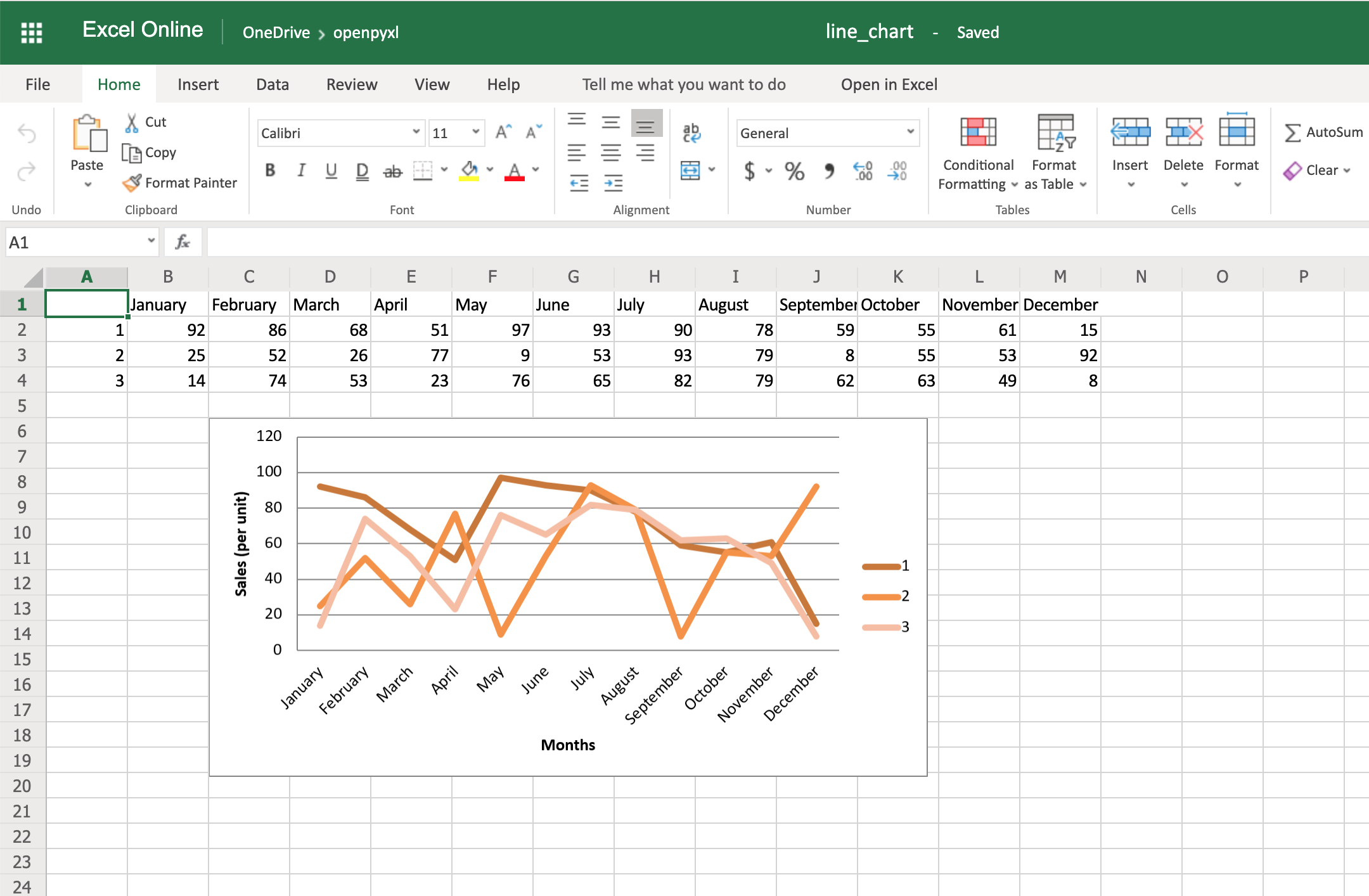
There is also a way to style your chart by using Excel’s default ChartStyle property. In this case, you have to choose a number between 1 and 48. Depending on your choice, the colors of your chart change as well:
# You can play with this by choosing any number between 1 and 48
chart.style = 24
With the style selected above, all lines have some shade of orange:
There is no clear documentation on what each style number looks like, but this spreadsheet has a few examples of the styles available.
Here’s the full code used to generate the line chart with categories, axis titles, and style:
import random
from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.chart import LineChart, Reference
workbook = Workbook()
sheet = workbook.active
# Let's create some sample sales data
rows = [
["", "January", "February", "March", "April",
"May", "June", "July", "August", "September",
"October", "November", "December"],
[1, ],
[2, ],
[3, ],
]
for row in rows:
sheet.append(row)
for row in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=2,
max_row=4,
min_col=2,
max_col=13):
for cell in row:
cell.value = random.randrange(5, 100)
# Create a LineChart and add the main data
chart = LineChart()
data = Reference(worksheet=sheet,
min_row=2,
max_row=4,
min_col=1,
max_col=13)
chart.add_data(data, titles_from_data=True, from_rows=True)
# Add categories to the chart
cats = Reference(worksheet=sheet,
min_row=1,
max_row=1,
min_col=2,
max_col=13)
chart.set_categories(cats)
# Rename the X and Y Axis
chart.x_axis.title = "Months"
chart.y_axis.title = "Sales (per unit)"
# Apply a specific Style
chart.style = 24
# Save!
sheet.add_chart(chart, "C6")
workbook.save("line_chart.xlsx")
There are a lot more chart types and customization you can apply, so be sure to check out the package documentation on this if you need some specific formatting.
Convert Python Classes to Excel Spreadsheet
You already saw how to convert an Excel spreadsheet’s data into Python classes, but now let’s do the opposite.
Let’s imagine you have a database and are using some Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) to map DB objects into Python classes. Now, you want to export those same objects into a spreadsheet.
Let’s assume the following data classes to represent the data coming from your database regarding product sales:
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import List
@dataclass
class Sale:
quantity: int
@dataclass
class Product:
id: str
name: str
sales: List[Sale]
Now, let’s generate some random data, assuming the above classes are stored in a db_classes.py file:
1import random
2
3# Ignore these for now. You'll use them in a sec ;)
4from openpyxl import Workbook
5from openpyxl.chart import LineChart, Reference
6
7from db_classes import Product, Sale
8
9products = []
10
11# Let's create 5 products
12for idx in range(1, 6):
13 sales = []
14
15 # Create 5 months of sales
16 for _ in range(5):
17 sale = Sale(quantity=random.randrange(5, 100))
18 sales.append(sale)
19
20 product = Product(id=str(idx),
21 name="Product %s" % idx,
22 sales=sales)
23 products.append(product)
By running this piece of code, you should get 5 products with 5 months of sales with a random quantity of sales for each month.
Now, to convert this into a spreadsheet, you need to iterate over the data and append it to the spreadsheet:
25workbook = Workbook()
26sheet = workbook.active
27
28# Append column names first
29sheet.append(["Product ID", "Product Name", "Month 1",
30 "Month 2", "Month 3", "Month 4", "Month 5"])
31
32# Append the data
33for product in products:
34 data = [product.id, product.name]
35 for sale in product.sales:
36 data.append(sale.quantity)
37 sheet.append(data)
That’s it. That should allow you to create a spreadsheet with some data coming from your database.
However, why not use some of that cool knowledge you gained recently to add a chart as well to display that data more visually?
All right, then you could probably do something like this:
38chart = LineChart()
39data = Reference(worksheet=sheet,
40 min_row=2,
41 max_row=6,
42 min_col=2,
43 max_col=7)
44
45chart.add_data(data, titles_from_data=True, from_rows=True)
46sheet.add_chart(chart, "B8")
47
48cats = Reference(worksheet=sheet,
49 min_row=1,
50 max_row=1,
51 min_col=3,
52 max_col=7)
53chart.set_categories(cats)
54
55chart.x_axis.title = "Months"
56chart.y_axis.title = "Sales (per unit)"
57
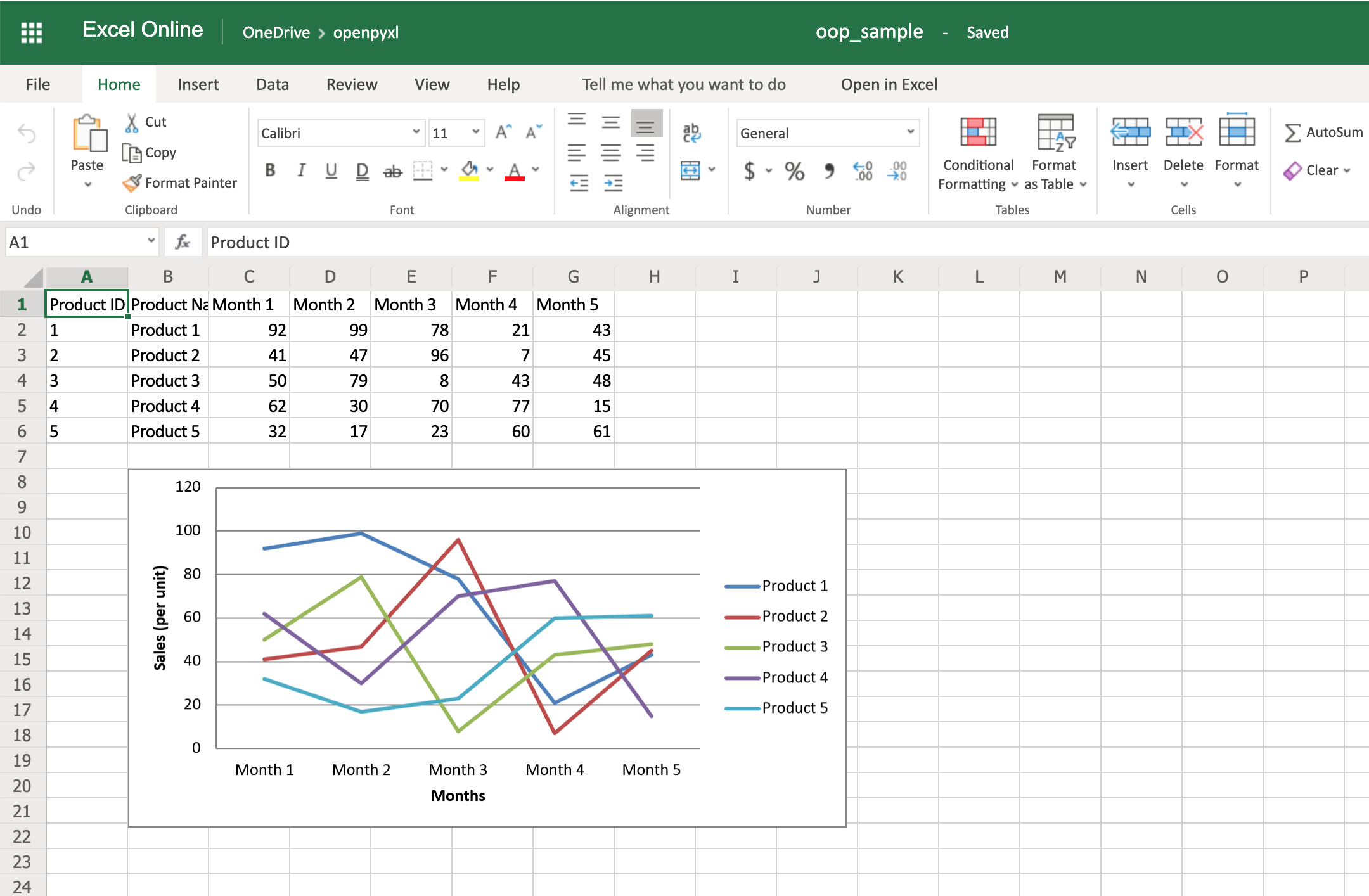
58workbook.save(filename="oop_sample.xlsx")
Now we’re talking! Here’s a spreadsheet generated from database objects and with a chart and everything:
That’s a great way for you to wrap up your new knowledge of charts!
Bonus: Working With Pandas
Even though you can use Pandas to handle Excel files, there are few things that you either can’t accomplish with Pandas or that you’d be better off just using openpyxl directly.
For example, some of the advantages of using openpyxl are the ability to easily customize your spreadsheet with styles, conditional formatting, and such.
But guess what, you don’t have to worry about picking. In fact, openpyxl has support for both converting data from a Pandas DataFrame into a workbook or the opposite, converting an openpyxl workbook into a Pandas DataFrame.
First things first, remember to install the pandas package:
Then, let’s create a sample DataFrame:
1import pandas as pd
2
3data = {
4 "Product Name": ["Product 1", "Product 2"],
5 "Sales Month 1": [10, 20],
6 "Sales Month 2": [5, 35],
7}
8df = pd.DataFrame(data)
Now that you have some data, you can use .dataframe_to_rows() to convert it from a DataFrame into a worksheet:
10from openpyxl import Workbook
11from openpyxl.utils.dataframe import dataframe_to_rows
12
13workbook = Workbook()
14sheet = workbook.active
15
16for row in dataframe_to_rows(df, index=False, header=True):
17 sheet.append(row)
18
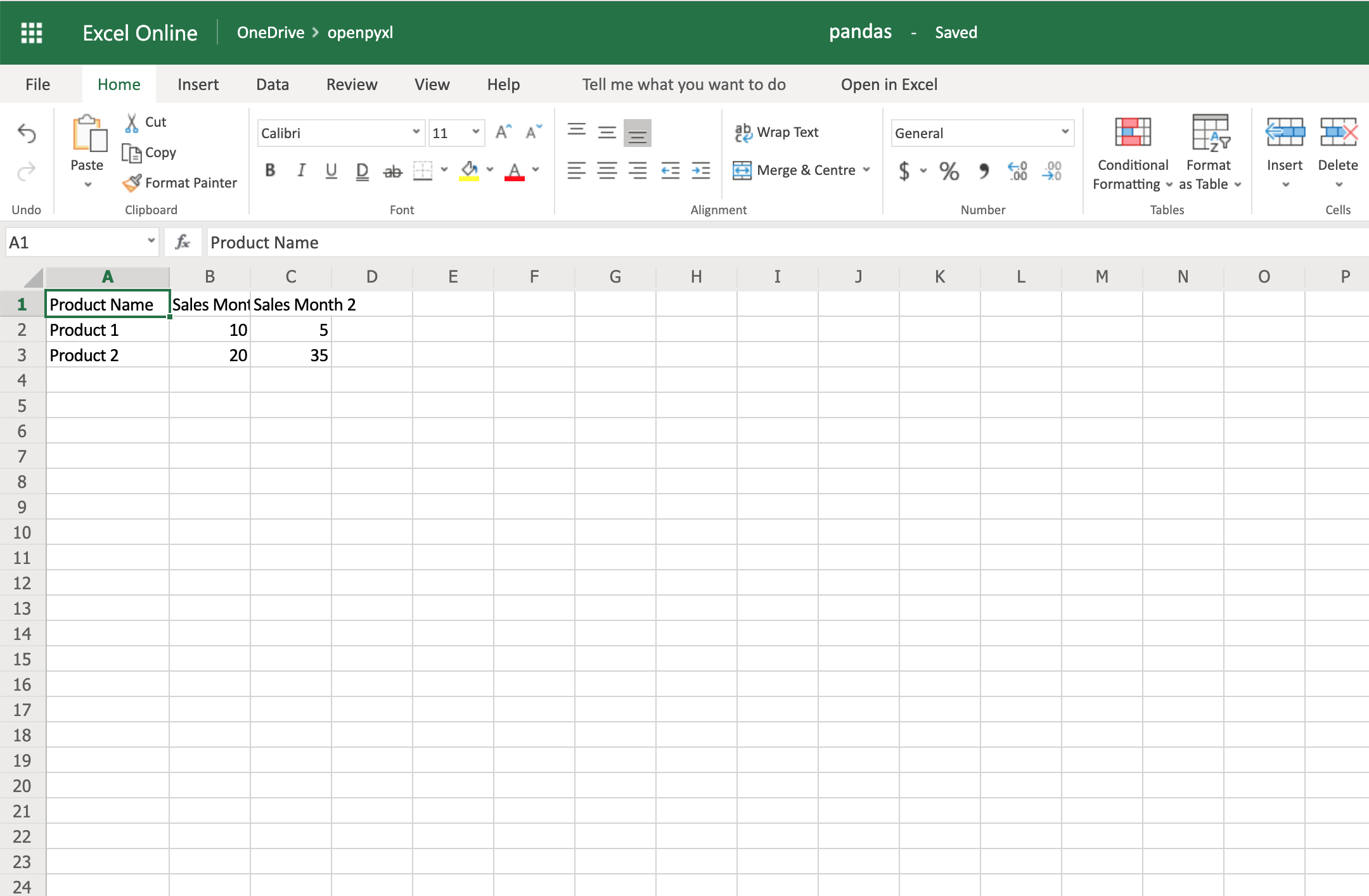
19workbook.save("pandas.xlsx")
You should see a spreadsheet that looks like this:
If you want to add the DataFrame’s index, you can change index=True, and it adds each row’s index into your spreadsheet.
On the other hand, if you want to convert a spreadsheet into a DataFrame, you can also do it in a very straightforward way like so:
import pandas as pd
from openpyxl import load_workbook
workbook = load_workbook(filename="sample.xlsx")
sheet = workbook.active
values = sheet.values
df = pd.DataFrame(values)
Alternatively, if you want to add the correct headers and use the review ID as the index, for example, then you can also do it like this instead:
import pandas as pd
from openpyxl import load_workbook
from mapping import REVIEW_ID
workbook = load_workbook(filename="sample.xlsx")
sheet = workbook.active
data = sheet.values
# Set the first row as the columns for the DataFrame
cols = next(data)
data = list(data)
# Set the field "review_id" as the indexes for each row
idx = [row[REVIEW_ID] for row in data]
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=idx, columns=cols)
Using indexes and columns allows you to access data from your DataFrame easily:
>>>
>>> df.columns
Index(['marketplace', 'customer_id', 'review_id', 'product_id',
'product_parent', 'product_title', 'product_category', 'star_rating',
'helpful_votes', 'total_votes', 'vine', 'verified_purchase',
'review_headline', 'review_body', 'review_date'],
dtype='object')
>>> # Get first 10 reviews' star rating
>>> df["star_rating"][:10]
R3O9SGZBVQBV76 5
RKH8BNC3L5DLF 5
R2HLE8WKZSU3NL 2
R31U3UH5AZ42LL 5
R2SV659OUJ945Y 4
RA51CP8TR5A2L 5
RB2Q7DLDN6TH6 5
R2RHFJV0UYBK3Y 1
R2Z6JOQ94LFHEP 5
RX27XIIWY5JPB 4
Name: star_rating, dtype: int64
>>> # Grab review with id "R2EQL1V1L6E0C9", using the index
>>> df.loc["R2EQL1V1L6E0C9"]
marketplace US
customer_id 15305006
review_id R2EQL1V1L6E0C9
product_id B004LURNO6
product_parent 892860326
review_headline Five Stars
review_body Love it
review_date 2015-08-31
Name: R2EQL1V1L6E0C9, dtype: object
There you go, whether you want to use openpyxl to prettify your Pandas dataset or use Pandas to do some hardcore algebra, you now know how to switch between both packages.
Conclusion
Phew, after that long read, you now know how to work with spreadsheets in Python! You can rely on openpyxl, your trustworthy companion, to:
- Extract valuable information from spreadsheets in a Pythonic manner
- Create your own spreadsheets, no matter the complexity level
- Add cool features such as conditional formatting or charts to your spreadsheets
There are a few other things you can do with openpyxl that might not have been covered in this tutorial, but you can always check the package’s official documentation website to learn more about it. You can even venture into checking its source code and improving the package further.
Feel free to leave any comments below if you have any questions, or if there’s any section you’d love to hear more about.
Watch Now This tutorial has a related video course created by the Real Python team. Watch it together with the written tutorial to deepen your understanding: Editing Excel Spreadsheets in Python With openpyxl
The following sections explain how to write various types of data to an Excel
worksheet using XlsxWriter.
Writing data to a worksheet cell
The worksheet write() method is the most common means of writing
Python data to cells based on its type:
import xlsxwriter workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook('write_data.xlsx') worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet() worksheet.write(0, 0, 1234) # Writes an int worksheet.write(1, 0, 1234.56) # Writes a float worksheet.write(2, 0, 'Hello') # Writes a string worksheet.write(3, 0, None) # Writes None worksheet.write(4, 0, True) # Writes a bool workbook.close()
The write() method uses the type() of the data to determine which
specific method to use for writing the data. These methods then map some basic
Python types to corresponding Excel types. The mapping is as follows:
| Python type | Excel type | Worksheet methods |
|---|---|---|
int |
Number | write(), write_number() |
long |
||
float |
||
Decimal |
||
Fraction |
||
basestring |
String | write(), write_string() |
str |
||
unicode |
||
None |
String (blank) | write(), write_blank() |
datetime.date |
Number | write(), write_datetime() |
datetime.datetime |
||
datetime.time |
||
datetime.timedelta |
||
bool |
Boolean | write(), write_boolean() |
The write() method also handles a few other Excel types that are
encoded as Python strings in XlsxWriter:
| Pseudo-type | Excel type | Worksheet methods |
|---|---|---|
| formula string | Formula | write(), write_formula() |
| url string | URL | write(), write_url() |
It should be noted that Excel has a very limited set of types to map to. The
Python types that the write() method can handle can be extended as
explained in the Writing user defined types section below.
Writing lists of data
Writing compound data types such as lists with XlsxWriter is done the same way
it would be in any other Python program: with a loop. The Python
enumerate() function is also very useful in this context:
import xlsxwriter workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook('write_list.xlsx') worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet() my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] for row_num, data in enumerate(my_list): worksheet.write(row_num, 0, data) workbook.close()
Or if you wanted to write this horizontally as a row:
import xlsxwriter workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook('write_list.xlsx') worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet() my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] for col_num, data in enumerate(my_list): worksheet.write(0, col_num, data) workbook.close()
For a list of lists structure you would use two loop levels:
import xlsxwriter workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook('write_list.xlsx') worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet() my_list = [[1, 1, 1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2, 2, 1], [3, 3, 3, 3, 1], [4, 4, 4, 4, 1], [5, 5, 5, 5, 1]] for row_num, row_data in enumerate(my_list): for col_num, col_data in enumerate(row_data): worksheet.write(row_num, col_num, col_data) workbook.close()
The worksheet class has two utility functions called
write_row() and write_column() which are basically a loop around
the write() method:
import xlsxwriter workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook('write_list.xlsx') worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet() my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] worksheet.write_row(0, 1, my_list) worksheet.write_column(1, 0, my_list) workbook.close()

Writing dicts of data
Unlike lists there is no single simple way to write a Python dictionary to an
Excel worksheet using Xlsxwriter. The method will depend of the structure of
the data in the dictionary. Here is a simple example for a simple data
structure:
import xlsxwriter workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook('write_dict.xlsx') worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet() my_dict = {'Bob': [10, 11, 12], 'Ann': [20, 21, 22], 'May': [30, 31, 32]} col_num = 0 for key, value in my_dict.items(): worksheet.write(0, col_num, key) worksheet.write_column(1, col_num, value) col_num += 1 workbook.close()

Writing dataframes
The best way to deal with dataframes or complex data structure is to use
Python Pandas. Pandas is a Python data analysis
library. It can read, filter and re-arrange small and large data sets and
output them in a range of formats including Excel.
To use XlsxWriter with Pandas you specify it as the Excel writer engine:
import pandas as pd # Create a Pandas dataframe from the data. df = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [10, 20, 30, 20, 15, 30, 45]}) # Create a Pandas Excel writer using XlsxWriter as the engine. writer = pd.ExcelWriter('pandas_simple.xlsx', engine='xlsxwriter') # Convert the dataframe to an XlsxWriter Excel object. df.to_excel(writer, sheet_name='Sheet1') # Close the Pandas Excel writer and output the Excel file. writer.close()
The output from this would look like the following:
For more information on using Pandas with XlsxWriter see Working with Pandas and XlsxWriter.
Writing user defined types
As shown in the first section above, the worksheet write() method
maps the main Python data types to Excel’s data types. If you want to write an
unsupported type then you can either avoid write() and map the user type
in your code to one of the more specific write methods or you can extend it
using the add_write_handler() method. This can be, occasionally, more
convenient then adding a lot of if/else logic to your code.
As an example, say you wanted to modify write() to automatically write
uuid types as strings. You would start by creating a function that
takes the uuid, converts it to a string and then writes it using
write_string():
def write_uuid(worksheet, row, col, uuid, format=None): return worksheet.write_string(row, col, str(uuid), format)
You could then add a handler that matches the uuid type and calls your
user defined function:
# match, action() worksheet.add_write_handler(uuid.UUID, write_uuid)
Then you can use write() without further modification:
my_uuid = uuid.uuid3(uuid.NAMESPACE_DNS, 'python.org') # Write the UUID. This would raise a TypeError without the handler. worksheet.write('A1', my_uuid)
Multiple callback functions can be added using add_write_handler() but
only one callback action is allowed per type. However, it is valid to use the
same callback function for different types:
worksheet.add_write_handler(int, test_number_range) worksheet.add_write_handler(float, test_number_range)
How the write handler feature works
The write() method is mainly a large if() statement that checks the
type() of the input value and calls the appropriate worksheet method to
write the data. The add_write_handler() method works by injecting
additional type checks and associated actions into this if() statement.
Here is a simplified version of the write() method:
def write(self, row, col, *args): # The first arg should be the token for all write calls. token = args[0] # Get the token type. token_type = type(token) # Check for any user defined type handlers with callback functions. if token_type in self.write_handlers: write_handler = self.write_handlers[token_type] function_return = write_handler(self, row, col, *args) # If the return value is None then the callback has returned # control to this function and we should continue as # normal. Otherwise we return the value to the caller and exit. if function_return is None: pass else: return function_return # Check for standard Python types, if we haven't returned already. if token_type is bool: return self.write_boolean(row, col, *args) # Etc. ...
The syntax of write handler functions
Functions used in the add_write_handler() method should have the
following method signature/parameters:
def my_function(worksheet, row, col, token, format=None): return worksheet.write_string(row, col, token, format)
The function will be passed a worksheet instance, an
integer row and col value, a token that matches the type added to
add_write_handler() and some additional parameters. Usually the
additional parameter(s) will only be a cell format
instance. However, if you need to handle other additional parameters, such as
those passed to write_url() then you can have more generic handling
like this:
def my_function(worksheet, row, col, token, *args): return worksheet.write_string(row, col, token, *args)
Note, you don’t have to explicitly handle A1 style cell ranges. These will
be converted to row and column values prior to your function being called.
You can also make use of the row and col parameters to control the
logic of the function. Say for example you wanted to hide/replace user
passwords with ‘****’ when writing string data. If your data was
structured so that the password data was in the second column, apart from the
header row, you could write a handler function like this:
def hide_password(worksheet, row, col, string, format=None): if col == 1 and row > 0: return worksheet.write_string(row, col, '****', format) else: return worksheet.write_string(row, col, string, format)

The return value of write handler functions
Functions used in the add_write_handler() method should return one of
the following values:
None: to indicate that control is return to the parentwrite()
method to continue as normal. This is used if your handler function logic
decides that you don’t need to handle the matched token.- The return value of the called
write_xxx()function. This is generally 0
for no error and a negative number for errors. This causes an immediate
return from the callingwrite()method with the return value that was
passed back.
For example, say you wanted to ignore NaN values in your data since Excel
doesn’t support them. You could create a handler function like the following
that matched against floats and which wrote a blank cell if it was a NaN
or else just returned to write() to continue as normal:
def ignore_nan(worksheet, row, col, number, format=None): if math.isnan(number): return worksheet.write_blank(row, col, None, format) else: # Return control to the calling write() method. return None
If you wanted to just drop the NaN values completely and not add any
formatting to the cell you could just return 0, for no error:
def ignore_nan(worksheet, row, col, number, format=None): if math.isnan(number): return 0 else: # Return control to the calling write() method. return None
Write Excel with Python Pandas. You can write any data (lists, strings, numbers etc) to Excel, by first converting it into a Pandas DataFrame and then writing the DataFrame to Excel.
To export a Pandas DataFrame as an Excel file (extension: .xlsx, .xls), use the to_excel() method.
Related course: Data Analysis with Python Pandas
installxlwt, openpyxl
to_excel() uses a library called xlwt and openpyxl internally.
- xlwt is used to write .xls files (formats up to Excel2003)
- openpyxl is used to write .xlsx (Excel2007 or later formats).
Both can be installed with pip. (pip3 depending on the environment)
1 |
$ pip install xlwt |
Write Excel
Write DataFrame to Excel file
Importing openpyxl is required if you want to append it to an existing Excel file described at the end.
A dataframe is defined below:
1 |
import pandas as pd |
You can specify a path as the first argument of the to_excel() method.
Note: that the data in the original file is deleted when overwriting.
The argument new_sheet_name is the name of the sheet. If omitted, it will be named Sheet1.
1 |
df.to_excel('pandas_to_excel.xlsx', sheet_name='new_sheet_name') |
Related course: Data Analysis with Python Pandas
If you do not need to write index (row name), columns (column name), the argument index, columns is False.
1 |
df.to_excel('pandas_to_excel_no_index_header.xlsx', index=False, header=False) |
Write multiple DataFrames to Excel files
The ExcelWriter object allows you to use multiple pandas. DataFrame objects can be exported to separate sheets.
As an example, pandas. Prepare another DataFrame object.
1 |
df2 = df[['a', 'c']] |
Then use the ExcelWriter() function like this:
1 |
with pd.ExcelWriter('pandas_to_excel.xlsx') as writer: |
You don’t need to call writer.save(), writer.close() within the blocks.
Append to an existing Excel file
You can append a DataFrame to an existing Excel file. The code below opens an existing file, then adds two sheets with the data of the dataframes.
Note: Because it is processed using openpyxl, only .xlsx files are included.
1 |
path = 'pandas_to_excel.xlsx' |
Related course: Data Analysis with Python Pandas
Время чтения 4 мин.
Python Pandas — это библиотека для анализа данных. Она может читать, фильтровать и переупорядочивать небольшие и большие наборы данных и выводить их в различных форматах, включая Excel. ExcelWriter() определен в библиотеке Pandas.
Содержание
- Что такое функция Pandas.ExcelWriter() в Python?
- Синтаксис
- Параметры
- Возвращаемое значение
- Пример программы с Pandas ExcelWriter()
- Что такое функция Pandas DataFrame to_excel()?
- Запись нескольких DataFrames на несколько листов
- Заключение
Метод Pandas.ExcelWriter() — это класс для записи объектов DataFrame в файлы Excel в Python. ExcelWriter() можно использовать для записи текста, чисел, строк, формул. Он также может работать на нескольких листах.Для данного примера необходимо, чтоб вы установили на свой компьютер библиотеки Numpy и Pandas.
Синтаксис
|
pandas.ExcelWriter(path, engine= None, date_format=None, datetime_format=None, mode=’w’,**engine_krawgs) |
Параметры
Все параметры установлены на значения по умолчанию.
Функция Pandas.ExcelWriter() имеет пять параметров.
- path: имеет строковый тип, указывающий путь к файлу xls или xlsx.
- engine: он также имеет строковый тип и является необязательным. Это движок для написания.
- date_format: также имеет строковый тип и имеет значение по умолчанию None. Он форматирует строку для дат, записанных в файлы Excel.
- datetime_format: также имеет строковый тип и имеет значение по умолчанию None. Он форматирует строку для объектов даты и времени, записанных в файлы Excel.
- Mode: это режим файла для записи или добавления. Его значение по умолчанию — запись, то есть ‘w’.
Возвращаемое значение
Он экспортирует данные в файл Excel.
Пример программы с Pandas ExcelWriter()
Вам необходимо установить и импортировать модуль xlsxwriter. Если вы используете блокнот Jupyter, он вам не понадобится; в противном случае вы должны установить его.
Напишем программу, показывающую работу ExcelWriter() в Python.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import xlsxwriter # Creating dataset using dictionary data_set = { ‘Name’: [‘Rohit’, ‘Arun’, ‘Sohit’, ‘Arun’, ‘Shubh’], ‘Roll no’: [’01’, ’02’, ’03’, ’04’, np.nan], ‘maths’: [’93’, ’63’, np.nan, ’94’, ’83’], ‘science’: [’88’, np.nan, ’66’, ’94’, np.nan], ‘english’: [’93’, ’74’, ’84’, ’92’, ’87’]} # Converting into dataframe df = pd.DataFrame(data_set) # Writing the data into the excel sheet writer_obj = pd.ExcelWriter(‘Write.xlsx’, engine=‘xlsxwriter’) df.to_excel(writer_obj, sheet_name=‘Sheet’) writer_obj.save() print(‘Please check out the Write.xlsx file.’) |
Выход:
|
Please check out the Write.xlsx file. |
Содержимое файла Excel следующее.
В приведенном выше коде мы создали DataFrame, в котором хранятся данные студентов. Затем мы создали объект для записи данных DataFrame на лист Excel, и после записи данных мы сохранили лист. Некоторые значения в приведенном выше листе Excel пусты, потому что в DataFrame эти значения — np.nan. Чтобы проверить данные DataFrame, проверьте лист Excel.
Что такое функция Pandas DataFrame to_excel()?
Функция Pandas DataFrame to_excel() записывает объект на лист Excel. Мы использовали функцию to_excel() в приведенном выше примере, потому что метод ExcelWriter() возвращает объект записи, а затем мы используем метод DataFrame.to_excel() для его экспорта в файл Excel.
Чтобы записать один объект в файл Excel .xlsx, необходимо только указать имя целевого файла. Для записи на несколько листов необходимо создать объект ExcelWriter с именем целевого файла и указать лист в файле для записи.
На несколько листов можно записать, указав уникальное имя листа. При записи всех данных в файл необходимо сохранить изменения. Обратите внимание, что создание объекта ExcelWriter с уже существующим именем файла приведет к удалению содержимого существующего файла.
Мы также можем написать приведенный выше пример, используя Python с оператором.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import xlsxwriter # Creating dataset using dictionary data_set = { ‘Name’: [‘Rohit’, ‘Arun’, ‘Sohit’, ‘Arun’, ‘Shubh’], ‘Roll no’: [’01’, ’02’, ’03’, ’04’, np.nan], ‘maths’: [’93’, ’63’, np.nan, ’94’, ’83’], ‘science’: [’88’, np.nan, ’66’, ’94’, np.nan], ‘english’: [’93’, ’74’, ’84’, ’92’, ’87’]} # Converting into dataframe df = pd.DataFrame(data_set) with pd.ExcelWriter(‘WriteWith.xlsx’, engine=‘xlsxwriter’) as writer: df.to_excel(writer, sheet_name=‘Sheet’) print(‘Please check out the WriteWith.xlsx file.’) |
Выход:
|
Please check out the WriteWith.xlsx file. |
Вы можете проверить файл WriteWith.xlsx и просмотреть его содержимое. Это будет то же самое, что и файл Write.xlsx.
Запись нескольких DataFrames на несколько листов
В приведенном выше примере мы видели только один лист для одного фрейма данных. Мы можем написать несколько фреймов с несколькими листами, используя Pandas.ExcelWriter.
Давайте напишем пример, в котором мы создадим три DataFrames и сохраним эти DataFrames в файле multiplesheet.xlsx с тремя разными листами.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 |
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import xlsxwriter # Creating dataset using dictionary data_set = { ‘Name’: [‘Rohit’, ‘Arun’, ‘Sohit’, ‘Arun’, ‘Shubh’], ‘Roll no’: [’01’, ’02’, ’03’, ’04’, np.nan], ‘maths’: [’93’, ’63’, np.nan, ’94’, ’83’], ‘science’: [’88’, np.nan, ’66’, ’94’, np.nan], ‘english’: [’93’, ’74’, ’84’, ’92’, ’87’]} data_set2 = { ‘Name’: [‘Ankit’, ‘Krunal’, ‘Rushabh’, ‘Dhaval’, ‘Nehal’], ‘Roll no’: [’01’, ’02’, ’03’, ’04’, np.nan], ‘maths’: [’93’, ’63’, np.nan, ’94’, ’83’], ‘science’: [’88’, np.nan, ’66’, ’94’, np.nan], ‘english’: [’93’, ’74’, ’84’, ’92’, ’87’]} data_set3 = { ‘Name’: [‘Millie’, ‘Jane’, ‘Michael’, ‘Bobby’, ‘Brown’], ‘Roll no’: [’01’, ’02’, ’03’, ’04’, np.nan], ‘maths’: [’93’, ’63’, np.nan, ’94’, ’83’], ‘science’: [’88’, np.nan, ’66’, ’94’, np.nan], ‘english’: [’93’, ’74’, ’84’, ’92’, ’87’]} # Converting into dataframe df = pd.DataFrame(data_set) df2 = pd.DataFrame(data_set2) df3 = pd.DataFrame(data_set3) with pd.ExcelWriter(‘multiplesheet.xlsx’, engine=‘xlsxwriter’) as writer: df.to_excel(writer, sheet_name=‘Sheet’) df2.to_excel(writer, sheet_name=‘Sheet2’) df3.to_excel(writer, sheet_name=‘Sheet3’) print(‘Please check out the multiplesheet.xlsx file.’) |
Выход:
Вы можете видеть, что есть три листа, и каждый лист имеет разные столбцы имени.
Функция to_excel() принимает имя листа в качестве параметра, и здесь мы можем передать три разных имени листа, и этот DataFrame сохраняется на соответствующих листах.
Заключение
Если вы хотите экспортировать Pandas DataFrame в файлы Excel, вам нужен только класс ExcelWriter(). Класс ExcelWrite() предоставляет объект записи, а затем мы можем использовать функцию to_excel() для экспорта DataFrame в файл Excel.
Last Updated on March 12, 2022 by
We can write both raw data and formulas into an Excel file using Python. The openpyxl library gives us lots of flexibility for creating Excel files.
Navigate Excel File using Python
We discussed how to access Sheets and Cells in this guide.
Let’s first create an Excel workbook using openpyxl. Note a Workbook is always created with at least one Worksheet, wb.active returns the first Worksheet inside the Workbook:
from openpyxl import Workbook
wb = Workbook()
ws = wb.activeIn Excel, two common ways to reference a cell location is by 1) the column-row notation and 2) the (row, col) notation. For example, the below refer to the same cell at B3:
ws['C2']
<Cell 'Sheet'.C2>
ws.cell(2,3)
<Cell 'Sheet'.C2>Although it’s easy for humans to read the column-row notation like “C2”, when we interact with cells programmatically, it’s easier to use the (row, col) notation because they are just index/numbers. The only thing to pay attention to is that the row and col index starts from 1 as opposed to 0.
Cell Coordinate Utility Methods
openpyxl provides several handy utility methods for coordinate conversion. From column-row to (row, col) and vice versa:
from openpyxl.utils.cell import (cols_from_range,
rows_from_range,
column_index_from_string,
get_column_letter,
coordinate_to_tuple)
column_index_from_string("A")
1
get_column_letter(26)
'Z'
coordinate_to_tuple('B2')
(2, 2)
c = (2,3)
get_column_letter(c[1]) + str(c[0])
'C2'We can also get all cells addresses individually from a range. Note the difference below:
- cols_from_range() produces one column at a time
- rows_from_range() produces one row at a time
for c in cols_from_range("A1:F6"):
print(c)
('A1', 'A2', 'A3', 'A4', 'A5', 'A6')
('B1', 'B2', 'B3', 'B4', 'B5', 'B6')
('C1', 'C2', 'C3', 'C4', 'C5', 'C6')
('D1', 'D2', 'D3', 'D4', 'D5', 'D6')
('E1', 'E2', 'E3', 'E4', 'E5', 'E6')
('F1', 'F2', 'F3', 'F4', 'F5', 'F6')
for c in rows_from_range("A1:F6"):
print(c)
('A1', 'B1', 'C1', 'D1', 'E1', 'F1')
('A2', 'B2', 'C2', 'D2', 'E2', 'F2')
('A3', 'B3', 'C3', 'D3', 'E3', 'F3')
('A4', 'B4', 'C4', 'D4', 'E4', 'F4')
('A5', 'B5', 'C5', 'D5', 'E5', 'F5')
('A6', 'B6', 'C6', 'D6', 'E6', 'F6')There are two ways to write values into a cell. One is by setting the cell.value attribute, the other is by calling the cell(row, col, value) method. Note below the subtle difference between lines #2 and #3.
ws['C2'].value = 'Pi'
ws.cell(2,4,value = 'Radius') #cell D2
ws.cell(2,5).value = 'Area' #cell E2The (row, col) notation makes looping through cells easy:
for i in range(1, 6):
# starts from cell D3, ends at cell D7
ws.cell(2+i, 4).value = i We can also use the cell.offset(row, col) method to return a cell location relative to an active cell.
curr_cell = ws['D8']
for i in range(0,5):
curr_cell.offset(row=i, column = 0).value = i+6Write Formulas to Excel using Python
Writing formulas is as easy as writing values into Excel. All we need is to treat the Excel formulas as String values and assign them to the .value attribute. Inside the Python String value, we want to start with the equal sign = since that’s how we start an Excel formula.
ws['C3'].value = '=pi()'Want to use absolute reference by “fixing” a cell coordinate in your formula? No problem! We can get the coordinate from a Cell object from its .coordinate attribute which returns a String value representing the cell address. Of course, in this example, we already know it’s “C3” since that’s what we entered into the code. This is to show how to get the coordinate of a cell programmatically.
ws['C3'].coordinate
'C3'To make an absolute reference, we can use the absolute_coordinate() method in the utility module. It basically just adds the $ signs to fix a cell.
from openpyxl.utils.cell import absolute_coordinate
absolute_coordinate(ws['C3'].coordinate)
'$C$3'Let’s calculate the Area column by writing Excel formulas to the cells, then save the Excel file to disk.
pi_cell = absolute_coordinate('C3')
for i in range(1,11):
ws.cell(i+2,5).value = f'={pi_cell} * {ws.cell(i+2,4).coordinate} ^ 2'
wb.save('pi_eg.xlsx')Additional Resources
How to Use Python to Read Excel Formula
How to Work with Excel Named Range in Python
Work with Excel Named Range in Python