Continue Learning about English Language Arts
What part of speech the word next is in what next?
the type of part of speech next is a preposition if you dont
believe me go ask your teacher. Then if your teacher says it’s not,
then she/he is wrong.
What part of speech is the word my-?
The part of speech that the word my is used as is an
adjective.
What part of the speech is the word warily?
what part of speech is the word warily
Does a dictionary determine the part of speech of a word?
A dictionary can show a word’s part of speech, but it does not
determine it. How a word is used in a sentence determines its part
of speech.
What part of speech is the word specifically?
The part of speech for the word specifically is an adverb.
On the line next to the number, write the fi rst letter of the word indicated by the part of speech in the parentheses. Underline the indicated word within the sentence. If your consecutive letters are correct, you will spell out the names of four trees in items 1 through 12 and four fi rst names in items 13 to 25. Write these six names on the lines below the last numbered item. Each correct answer is worth 4 points. Name Date Period Score % Name Date Period Score % All nouns are either common or proper nouns: A common noun names any person, place, or thing. Examples are basketball, video, wizard, coin, woman, and coach. A proper noun names a particular person, place, or thing and begins with a capital letter. Examples are Winston Churchill, Babe Ruth, Mr. Richard Turner, and Chicago. Know the difference between a common and a proper noun: Common Nouns Proper Nouns hospital Mercy General Hospital woman Martha Washington school Sayville Middle School newspaper The New York Times
Parts of Speech
Every word is a part of speech, each playing a specific role in a sentence. There are 8 different parts of speech including noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, and interjection. Each word in a sentence plays a vital role in conveying the meaning and intent of the sentence.
What is Part of Speech?
The English language has thousands of words and every word has some function to perform. Some words are there to show action, some to join, and some to name something. And together, all the functions performed by words in the English language fall under Parts of speech.
Parts of Speech Definition
The parts of speech are the “traditional grammatical categories to which words are assigned in accordance with their syntactic functions, such as noun, verb, adjective, adverb, and so on.” In other words, they refer to the different roles that words can play in a sentence and how they relate to one another based on grammar and syntax.
Parts of Speech Table
| Types | Function | Examples | Sentences |
| Noun | Refers Things or person | Pen, Chair, Ram, Honesty |
Cars are expensive. This chair is of wood. Ram is a topper. Honesty is the best policy. |
| Pronoun | Replaces a noun | I, you, he, she, it, they |
They are expensive. It is of wood. He is a topper. It is the best policy |
| Adjective | Describes a noun |
Super, Red, Our, Big, Great class |
Super cars are expensive Red chair is for kids Ram is a class topper. Great things take time. |
| Verb | Describes action or state | Play, be, work, love, like |
I play football I will be a doctor I like to work I love writing poem. |
| Adverb | Describes a verb, adjective or adverb | Silently, too, very |
I love reading silently. It is too tough to handle. He can speak very fast. |
| Preposition | Links a noun to another word | at, in, of, after, under, |
The ball is under the table. I am at a restaurant. she is in trouble. I am going after her. It is so nice of him |
| Conjunction | Joins clauses and sentences | and, but, though, after |
First, I will go to college and then I may go to fest. I don’t have a car but I know how to drive. She failed the exam though she worked hard. He will come after he finish his match. |
| Interjection | Shows exclamation | oh!, wow!, alas! Hurray! |
Oh! I got fail again. Wow! I got the job. Alas! She is no more. Hurray! we are going to party. |
Parts of Speech Examples with Sentences
Noun
Examples: Luggage, Cattle.
Sentence: Never leave your luggage unattended.
In some places, cattle are fed barely.
Pronoun
Examples: who, either, themselves
Sentence: I know a man who plays the guitar very well.
Either of the two cars is for sale.
They enjoyed themselves at the party.
Adjective
Examples: kind, moving, wounder.
Sentence:
She is a kind person.
Boarding a moving bus can be dangerous.
Never poke a wounded animal.
Verb
Examples: Praise, Hate, Punish
Sentence: She always praises her friends.
I don’t hate anybody.
The boy has been punished by his teacher
Adverb
Examples: Always, enough, immediately
Sentence: we should always help each other.
We should be wise enough to understand what is good for us.
We should leave bad habits immediately.
Preposition
Examples: Off, Below, From. to
Sentence:
He plunged off the cliff
I live below the 9th floor.
I travel daily from Delhi to Noida.
Conjunction
Examples: whereas, as well as, so,
Sentence: The new software is fairly simple whereas the old one was a bit complicated.
The finance company is not performing well as well as some of its competitors.
He was ready so he may come.
Interjection
Examples: oops! whoa! phew!
Sentence: Oops! I forgot to mention her name.
Whoa! you drive fast.
Phew! That was close call, we had a narrow escape.
Parts of Speech Quiz
Choose the correct Parts of Speech of the BOLD word from the following questions.
1. Let us play, Shall We?
a. Conjunction
b. Pronoun
c. Verb
2. It is a good practice to arrange books on shelves.
a. Verb
b. Noun
c. Adjective
3. Whose books are these?
a. Pronoun
b. Preposition
c. verb
4. Father, please get me that toy.
a. Pronoun
b. Adverb
c. Adjective
5. His mentality is rather obnoxious.
a. Adverb
b. Adjective
c. Noun
6. He is the guy whose money got stolen.
a. Pronoun
b. Conjunction
c. Adjective
7. I will have finished my semester by the end of this year.
a. Interjection
b. Conjunction
c. Preposition
8. Bingo! That’s the one I have been looking for
a. Interjection
b. Conjunction
c. Preposition
Quiz Answers
1. c, 2. b, 3. a, 4. c, 5. a, 6. b, 7. c, 8. a
FAQs on Parts of Speech
Q1. What are Parts of Speech?
Ans. A word is assigned to a category as per its function, and those categories are together known as Parts of Speech.
Q2. What are the 8 Parts of Speech?
Ans. Noun, Pronoun, Adjective, Verb, Adverb, Preposition, Conjunction, Interjection.
Q3. How many Parts of Speech are there?
Ans. There are a total of 8 parts of Speech.
Q4. What Part of Speech is “our”?
Ans. Adjective. Eg. Our car.
Q5. What Part of Speech is “Quickly”?
Ans. Adverb. let us understand it with this example – Milk sours quickly in warm weather.
It is a fact that almost every word of English has got the capacity to be employed as a different part of speech. At one place, a particular word may be used as a noun, at another as a verb, and yet at another place as an adjective.
These words enable the learners of the English language to understand the behavior of a particular word in various positions.
Importance of Parts of Speech in Communication
As you know, English sentences are used to communicate a complete thought. The importance of parts of speech lies in their proper utilization, which can help your understanding and confidence grow immensely.
Proper usage of parts of speech means that you can impart clear messages and understand them because you know the rules of the language.
Each word in a sentence belongs to one of the eight parts of speech according to the work it is doing in that sentence. There are 8 parts of speech.
- Noun
- Verb
- Adjective
- Adverb
- Pronoun
- Prepositions
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
1 – Noun (Naming words)
The nouns stand for the names of people, places, animals, and things. The word noun means name. Look at these sentences.
“John lives in Chicago. He has two bikes. He is fond of riding bikes.”
In the above example, John is the name. We cannot use the same name again and again in different sentences. Here, we used “he” in the next two sentences instead of “John”. “He” is called the pronoun.
Types of nouns are
1.1 – Common Noun
It describes a person, place, and thing.
Examples: City, country, town, boy.
1.2 – Proper Noun
It includes a particular person, place, thing, or idea and begins with a capital letter.
Examples: Austria, Manchester, United Kingdom, etc.
1.3 – Abstract Noun
An abstract noun describes names, ideas, feelings, emotions or qualities, the subject of any paragraph comes under this category. It does not take “the”.
Examples: grief, loss, happiness, greatness.
1.4 – Concrete Noun
It describes material things, persons or places. The existence of that thing can be physically observed.
Examples: Book, table, car, etc.
1.5 – Countable and Uncountable Noun
Countable nouns can be singular or plural. It can be counted.
Examples: Ships, cars, buses, books, etc.
The uncountable noun is neither singular nor plural. It cannot be counted.
Examples: Water, milk, juice, butter, music, etc.
1.6 – Collective Noun
It includes the group and collection
people, things or ideas. It is in unit form and is considered as singular.
Examples: Staff of office, group of visitors.
However, people and police can be
considered both singular and plural.
1.7 – Possessive Noun
It shows ownership or relationship.
Examples: Jimmy’s pen.
Further Reading: 11 Types of Nouns with Examples
2 – Verb (Saying words)
These are used for saying something
about persons or things. The verb is concerned with doing or being.
Examples
- A hare runs (action) very fast.
- Aslam is a good student.
Types of verbs
2.1 – Actions verbs
(run, move, write etc)
2.2 – Linking verbs
(to be (is, am, are, was, were), seem, feel, look, understand)
2.3 – Auxiliary (helping) verbs
(have, do, be)
2.4 – Modal Verbs
(can, could, may, might, will/shall)
2.5 – Transitive verbs
It takes an object.
Example – He is reading a newspaper.
2.6 – Intransitive verbs
It does not take the object.
Example – He awakes.
Further Reading: What are the verbs in English?
3 – Adjectives (describing words)
These are joining to nouns to describe
them.
Examples
- A hungry wolf.
- A brown wolf.
- A lazy boy.
- A tall man.
It is used before a noun and after a linking verb.
Before noun example
A new brand has been launched.
After linking verb example
Imran is rich.
It is used to clarify nouns.
Example: smart boy, blind man
Types of adjectives
3.1 – Simple degree
He is intelligent.
3.2 – Comparative
Ali is intelligent than Imran.
3.3 – Superlative
Comparison of one person with class,
country or world. In this type “the” is used.
Example: Ali is the wisest boy.
3.4 – Demonstrative adjective
It points out a noun. These are four
in number.
This That These Those
3.5 – Indefinite adjectives
It points out nouns. They often tell
“how many” or “how much” of something.
Interrogative adjectives: it is used to ask questions
Examples
- Which book?
- What time?
- Whose car?
Further Reading: More About Adjectives
4 – Adverbs
Describing words that are added to verbs. Just as adjectives are added to describe them, adverbs are added to verbs to modify their meaning. The word “modify” means to enlarge the meaning of the adverbs.
Examples
- Emma sings beautifully. (used with verb)
- Cameron is extremely clever. (used with adjective)
- This motor car goes incredibly fast. (used with another adverb)
Types of adverb
4.1 – Adverb of manner
This type of adverb deals with the
action something
Example
- I walk quickly.
- He wrote slowly.
4.2 – Adverb of place
Happening of something or the place where it happens.
Examples:
There was somebody sitting nearby.
Here, these, upstairs, nowhere everywhere, outside, in, out, are called adverb of place.
4.3 – Adverb of time
It determines the time of the happening of something.
Examples
- She went there last night.
- Have you seen him before?
- He wrote a letter yesterday.
Tomorrow, today, now, then,
yesterday, already, ago.
4.4 – Linking adverbs (then, however)
It creates a connection between two clauses or sentences.
Example
There will be clouds in Lahore. However, the sun is expected in Multan.
Note: Besides modifying the meaning of a verb, adverbs also modify adjectives and other adverbs.
Examples
- It is a very large house.
- He is too weak to walk.
- He ran too fast.
Further Reading: 11 Types of Adverbs with Examples
5 – Pronouns
Words that are used instead of nouns to avoid tiresome repetition. Instead of using the word man in a composition, we often write he, him, himself. In place of the word “woman”, we write she, her, or herself. For both the nouns ‘men’ and ‘women’ we use, they, them, themselves.
Some of the most common pronouns are
Singular: I, he, she, it, me, him,
her
Plural: We, they, out, us, them.
Examples
Imran was hurt. He didn’t panic.
He checked the mobile. It still
worked.
Types of Pronouns
It stands instead of persons. They have different forms according to the person who is supposed to be speaking.
First person: I, we, me, us, mine, our, ourselves.
Second person: thou, you, there.
Third person: He, she, it, his, him
5.1 – Possessive pronouns
Such as mine, ours, yours, hers and theirs.
- This book is mine.
- My horse and yours are tired.
5.2 – Relative pronoun
Who, whom, which and they are called relative pronouns. They are called relative because they relate to some word in the main clause. The word to which pronoun relates is called the antecedent.
Example
I saw a boy who was going.
In this sentence, who is the relative pronoun and boy is its antecedent.
This is the girl who won the prize.
“which” is used for animals and things.
The dog which barks.
That is used instead of who or which in this case.
This is the best picture that I ever saw.
5.3 – Interrogative pronouns
It is used to introduce or create an asking position in a sentence. Who, whom, which, and whose are interrogative pronouns.
Examples
Who wrote this book? (for persons
only)
What is your name? (for things)
Which boy here is your friend?
5.4 – Demonstrative pronoun
It points out a person, thing, place
or idea. This, that, these and those are called demonstrative pronouns.
That is a circuit-breaker.
These are cups of a team.
5.5 – Reflexive pronoun
The type of pronoun that ends in self or selves is called a reflexive pronoun.
Examples: myself, ourselves, yourself, herself, himself, itself, themselves.
Use in sentence: They worked hard to
get out themselves from the debt.
Indefinite pronoun: An indefinite
pronoun does not refer to a specific person, place thing or idea.
Examples
Nothing lasts forever.
No one can make this design.
Further Reading: Different Types of Pronouns with 60+ Examples
6 – Prepositions
Words placed before a noun or pronoun
to show how the person or thing denoted stands in relation to some other person
or thing.
Examples: A house on a hill. Here, the word “on” is a preposition.
The noun and pronoun that follow the preposition are called its object. We can identify prepositions in the following examples.
In 2006, in March, in the garden,
On 14th August, on Friday, on the table
At 8:30 pm, at 9 o’clock, at the door, at noon, at night, at midnight
However, we use “in” for morning and evening.
Further Reading: Preposition Usage and Examples
7 – Conjunctions (joining words)
They join words or sentences.
Examples: Jimmy and Tom are good players.
In the above sentence, “and” is a conjunction.
Types of conjunctions
These are the types of conjunctions.
- Nor (used in later part of the negative sentence)
- But (when two different ideas are described in a sentence)
- Yet (when two contrast things are being described in a sentence)
- So (To explain the reason)
- For (it connects a reason to a result)
- Or (to adopt two equal choices)
- And (to join two things or work)
Further Reading: Conjunction Rules with Examples
8 – Interjections
Interjection words are not connected with other parts of a sentence. They are through into a sentence to express some feeling of a mind.
Examples: Hurrah! We won the match.
Alas, hurrah, wow, uh, oh-no, gush, shh are some words used to express the feeling.
It is important to note that placing a word in this or that part of speech is not fixed. It depends upon the work the words are doing in a particular sentence. Thus the same word may appear in three or four parts of speech.
Further Reading: More about Interjections
You can read a detailed article about parts of speech here.
Parts of Speech Exercise with Answers

Read also: 71 Idioms with Meaning and Sentences
- Join our Team
- Online Platform Tutorial
- TEFL Courses
- Contact Us / FAQ
- Grammar
- Adverbial Clauses
- Adverbial Phrases
- Be Going To Statements
- Be Going To Wh Questions
- Be Going To Yes/No Questions
- Be Going To & Present Continuous
- Comparatives
- Superlatives
- Comparatives & Superlatives
- Zero Conditional
- First Conditional
- Second Conditional
- Third Conditional
- Mixed Conditionals
- Future Continuous
- Future Continuous vs. Future Perfect
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect Simple
- Future Simple
- Future Time Clauses
- Mixed Future Tenses
- Gerunds & Infinitives
- Have Got & Has Got
- I wish & If only
- Imperatives
- Irregular Verbs
- Narrative Tenses
- Noun Clauses
- Noun Phrases
- Passive Voice
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect
- Past Perfect Continuous
- Past Perfect Simple & Continuous
- Past Simple Affirmative & Negative
- Past Simple Passive
- Past Simple Regular Verbs
- Past Simple vs. Past Continuous
- Past Simple Was and Were
- Past Simple Wh Questions
- Past Simple Yes/No Questions
- Past Tense Review
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
- Present Perfect — Ever and Never
- Present Perfect — For and Since
- Present Perfect — Just, Yet & Already
- Present Perfect vs. Past Simple
- Present Simple Affirmative & Negative
- Present Simple Passive
- Present Simple vs. Present Continuous
- Present Simple Wh Questions
- Present Simple Yes/No Questions
- Present Tense Review
- Question Words
- Relative Clauses
- Reported Speech
- Subject-Verb Agreement
- Tag Questions
- There is & There are
- Used to
- Verb to be
- Wh Questions
- Parts of Speech
- Abstract Nouns
- Adjectives
- Adjective-Noun Collocations
- Adjectives of Feeling & Emotion
- Adjectives of Opinion
- Adjectives of Quantity
- Adjective Opposites
- Adjective Order
- Adjective-Preposition Collocations
- -ed and -ing Adjectives
- Adverb-Adjective Collocations
- Adverb Order
- Adverbs of Affirmation & Negation
- Adverbs of Degree
- Adverbs of Frequency
- Adverbs of Manner
- Adverbs of Place
- Adverbs of Time
- Articles — a, an, the
- Causative Verbs
- Collective Nouns
- Common & Proper Nouns
- Compound Adjectives
- Compound Nouns
- Concrete Nouns
- Conjunctions
- Countable & Uncountable Nouns
- Demonstrative Adjectives
- Demonstrative Pronouns
- Dependent Prepositions
- Indefinite Pronouns
- Intensifiers & Mitigators
- Interjections
- Modal Verbs of Ability
- Modals of Deduction & Speculation
- Modals of Necessity
- Modals of Obligation & Prohibition
- Modals of Possibility & Certainty
- Onomatopoeia
- Parts of Speech
- Phrasal Verbs
- Possessives
- Prefixes
- Prepositions of Movement
- Prepositions of Place
- Prepositions of Time
- Proper Adjectives
- Quantifiers
- Reflexive Pronouns
- Sense Verbs and Adjectives
- Singular & Plural Nouns
- So and Such
- Subject & Object Pronouns
- Suffixes
- Too and Enough
- Transition Words
- Verb-Noun Collocations
- Verbs
- Functional Language
- Agreeing & Disagreeing
- Air Travel
- Asking Permission
- At the Dentist’s
- At the Doctor’s
- Being Polite
- Classroom Language
- Complaining & Apologizing
- Complimenting
- Critical Thinking & Problem Solving
- Describing Character & Personality
- Describing People’s Appearance
- Describing Places
- Describing Things
- Emailing
- Etiquette and Manners
- Getting Around
- Getting to Know You
- Giving Advice
- Giving Directions
- Giving Opinions
- Giving Personal Information
- Greetings & Introductions
- Holidays
- Indirect Questions
- Likes and Dislikes
- Making Arrangements
- Making Decisions
- Making Excuses
- Making Invitations
- Making Offers & Promises
- Making Requests
- Making Suggestions
- Online Communication
- Ordering Food & Drink
- Shopping
- Small Talk
- Social Media
- Telephoning
- Times and Dates
- Travel
- General English
- Animals
- Christmas
- Cities & Towns
- Clothes & Fashion
- Colours
- Computers & Smartphones
- Countries & Nationalities
- Crime, Law & Punishment
- Cultural Celebrations
- Easter
- Family & Relationships
- Food & Drink
- Going Out & Entertainment
- Halloween
- Health & Fitness
- Hobbies & Free Time
- Houses, Rooms & Furniture
- Idioms
- Jobs & the Workplace
- Modes of Transport
- Money
- Music
- Numbers
- Parts of the Body
- Reading Comprehension
- Seasons
- Space
- Sports
- The Natural World
- Time Expressions
- TV & Film
- Valentine’s Day
- Weather
- Academic English
- Academic Collocations
- Academic Reading Comprehension
- AWL Sublist 1 & 2
- Cause and Effect Essays
- Compare and Contrast Essays
- Debating
- Discussion Essays
- Discussions
- Essay Writing
- Paragraph Writing
- Persuasive Essays
- Presentation Skills
- Problem Solution Essays
- Punctuation
- Reading Skills
- Referenced Essays
- Study Skills
- The Writing Process
- Business English
- Business Emails
- Business Meetings
- Business Negotiations
- Talking About Jobs
- Games
- Answer Games
- Brainstorming Games
- Category Games
- Classic Childhood Games
- Counting Games
- Describing Games
- Drawing Games
- Drilling Activity Games
- First Day of Class Games
- Flashcard Games
- Grammar Games
- Hangman Games
- Listening Games
- Miming Games
- Music Games
- Question & Answer Games
- Quiz Games
- Sentence Race Games
- Spelling Games
- TV Game Shows
- Verb Games
- Vocabulary Games
- Word Association Games
- Word Games
- Yes/No Question Games
- Ideas
- Classroom Interaction Patterns
- Classroom Management
- Concept Checking
- Cultural Awareness
- Developing Students’ Listening Skills
- Developing Students’ Reading Skills
- Developing Students’ Speaking Skills
- Eliciting Techniques
- ESL Dictations
- How to Introduce a Lesson
- How to Use Music in ESL Class
- Lesson Planning
- Making Teaching Materials Relevant
- Problems Learning English
- Teaching English Idioms
- Teaching English Vocabulary
- Teaching Large Classes
- Teaching Mixed-Ability Classes
- Teaching Small Classes
- The First Day of Class
- Using Correction in Class
- Using Song Gap Fills
- Membership
- Online Membership
- ESL Essentials eBook Series
Parts of Speech ESL Games, Worksheets and Activities
- Pre-intermediate (A2)
- Intermediate (B1)
- Upper-intermediate (B2)
- Advanced (C1)
Silly Sentences
ESL Parts of Speech Activity — Vocabulary and Grammar: Brainstorming, Categorising, Forming Sentences — Pair Work — Pre-intermediate (A2) — 25 minutes
This parts of speech activity helps students learn and practice how to use nouns, verbs, adjectives and adverbs in sentences. Brainstorm nouns, verbs, adjectives and adverbs as a class. Students then copy down the words into the word bank on their worksheet. In pairs, students then take it in turns to choose a word from the word bank to complete each sentence with the parts of speech indicated. Students say each word to their partner, and both students cross it off in the word bank, and write it in the space provided. Each word can only be used once. When the students have finished, review the sentences they came up with together as a class.
Verbs, Nouns, Adjectives, and Adverbs
ESL Parts of Speech Worksheet — Vocabulary Exercises: Categorising, Unscrambling, Binary Choice, Error Correction, Gap-fill — Speaking Game: Forming Sentences — Pair Work — Pre-intermediate (A2) — 30 minutes
This free parts of speech worksheet helps students learn how to identify verbs, nouns, adjectives, and adverbs and use them in sentences. First, students read a sentence and put the words in the correct parts of speech category. Students then read sentences describing verbs, nouns, adjectives and adverbs and indicate which part of speech is being described in each one. Next, students put words into the correct parts of speech category and put words in the correct order to make sentences. Students then move on to read sentences and underline the correct part of speech to be used in each one. Afterwards, students rewrite sentences, correcting the mistakes. Next, students read sentences and fill in gaps with the correct parts of speech using their own ideas. Lastly, in pairs, students take it in turns to say a letter of the alphabet and then the word verb, noun, adjective or adverb. Their partner then has 30 seconds to think of a suitable word and use it in a sentence. Students score one point for each correct sentence. The student with the most points at the end of the game wins.
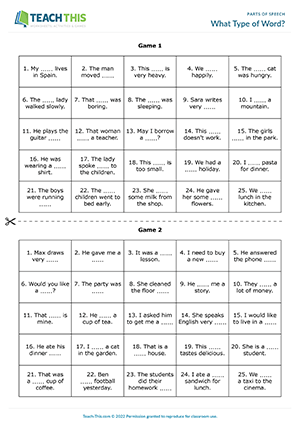
What Type of Word?
ESL Parts of Speech Game- Grammar: Gap-fill, Guessing, Sentence Completion, Freer Practice — Group Work — Pre-intermediate (A2) — 25 minutes
Here is a fun parts of speech game to help students identify the position of verbs, nouns, adjectives and adverbs in sentences. In groups of three, two students play the first game and one student acts as judge. The players take it in turns to choose a square and identify the missing part of speech in the sentence. The student acting as judge checks the answer sheet. If the part of speech is correct, the player chooses a suitable word to complete the sentence. If the judge agrees the word is appropriate, the player marks the square with an ‘O’ or an ‘X’ accordingly. It is then the other player’s turn to choose a square. The first player to get five squares in a row wins the game. Afterwards, students play a second game, giving the student who acted as judge a chance to play.
Crucial Combinations
ESL Parts of Speech Game — Vocabulary: Identifying, Gap-fill, Guessing — Pair Work — Intermediate (B1) — 25 minutes
In this parts of speech game, students race to guess missing parts of speech in sentences. First, in two groups, students identify the two missing parts of speech in each sentence on their worksheet, writing down their answers. Next, students pair up with someone from the other group. Students then take turns reading each sentence to their partner using the word ‘blank’ for the missing words and then asking for the two parts of speech they need to complete the sentence, e.g. ‘I need a verb and a noun’. Their partner checks the word pairs in the box on their worksheet for the appropriate words and reads them aloud. If the student agrees the answers are correct, they write the words in the sentence and their partner crosses them out. When a pair has completed all their sentences, they put up their hands to have their answers checked. The first pair to complete all their sentences correctly wins.
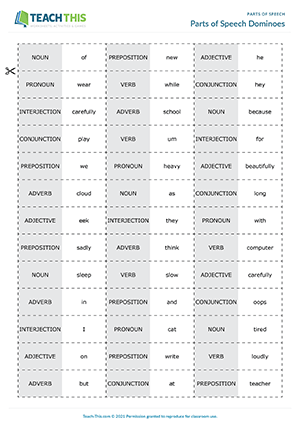
Parts of Speech Dominoes
ESL Parts of Speech Game — Grammar, Vocabulary and Speaking: Matching, Forming Sentences from Prompts — Group Work — Intermediate (B1) — 25 minutes
In this free parts of speech game, students match words with parts of speech and make sentences using the words. The first player places one of their dominoes at either end of the domino on the table, matching a word with a part of speech or vice versa. The player then makes a sentence using the word they just matched with the part of speech. For example, if a student matched the word of with preposition, they might say ‘Windows are made of glass’. The other group members listen and judge the sentence. If the other students agree the sentence is correct and uses the part of speech appropriately, the domino remains in place. If not, the player must take back the domino. Play then passes to the next student and so on. The first player to get rid of all their dominoes wins the game.
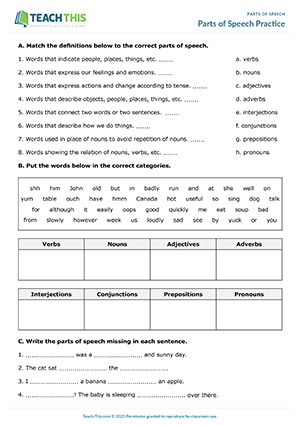
Parts of Speech Practice
ESL Parts of Speech Worksheet- Grammar and Vocabulary Exercises: Matching, Categorizing, Identifying, Gap-fill — Intermediate (B1) — 30 minutes
Here is a parts of speech worksheet to help students learn and practice the eight parts of speech. Students start by matching definitions to the correct parts of speech. Next, students put words into their parts of speech categories. Students then decide which parts of speech are missing from sentences. After that, students complete sentences with words from Exercise B. Following that, students identify and underline the word that does not belong in each word group. Lastly, students complete sentences with their own words.
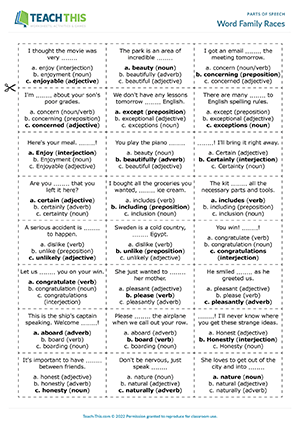
Word Family Races
ESL Parts of Speech Game — Grammar and Vocabulary: Multiple Choice, Identifying, Matching — Group Work — Upper-intermediate (B2) — 20 minutes
In this parts of speech game, students identify which of several related words is the correct part of speech to complete sentences. In groups, students take turns picking up a card and reading out the sentence on the card using the word ‘blank’ for the missing word in the sentence, e.g. I thought the movie was very ‘blank’. Next, the student reads out three words from a word family, e.g. enjoy, enjoyment, enjoyable. The other group members listen and race to choose the correct word to complete the sentence, along with correctly identifying the word’s part of speech. The first student to say the correct word and part of speech wins and keeps the card. Students get one guess per round. If no one gets the correct word and part of speech, the card is placed at the bottom of the pile to be used again later in the game. The student with the most cards at the end of the game wins.
Word Wizard
ESL Parts of Speech Worksheet — Grammar Exercises: Gap-fill, Identifying, Categorising, Error Correction, Unscrambling — Upper-intermediate (B2) — 35 minutes
In this parts of speech worksheet, students identify parts of speech and use them to construct grammatically correct sentences. Students start by completing sentences with words from a box. Next, students sort the underlined words in the sentences by their parts of speech. After that, students identify parts of speech errors in sentences and rewrite them so that they are correct. Finally, students use their knowledge of parts of speech to unscramble sentences.
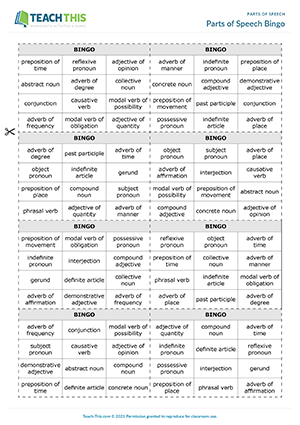
ESL Parts of Speech Game — Vocabulary and Listening: Matching — Group Work — Advanced (C1) — 20 minutes
In this parts of speech game, students play bingo by matching advanced parts of speech with words. You or a student reads a word at random from the caller’s sheet. There are four words to choose from for each part of speech. Students look at their bingo cards to see if they can match the word with a part of speech shown on their card. If they can, they cross off the part of speech. The game continues until a student has crossed off all the parts of speech on their card. When this happens, the student shouts ‘Bingo!’ and reads out the parts of speech they crossed off. If they match with the words that were called out, the student wins the game. Play several rounds, making sure students receive a different bingo card each time.
- Home
- Grammar
- Adverbial Clauses
- Adverbial Phrases
- Be Going To Statements
- Be Going To Wh Questions
- Be Going To Yes/No Questions
- Be Going To & Present Continuous
- Comparatives
- Superlatives
- Comparatives & Superlatives
- Zero Conditional
- First Conditional
- Second Conditional
- Third Conditional
- Mixed Conditionals
- Future Continuous
- Future Continuous vs. Future Perfect
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect Simple
- Future Simple
- Future Time Clauses
- Mixed Future Tenses
- Gerunds & Infinitives
- Have got & Has got
- I wish & If only
- Imperatives
- Irregular Verbs
- Narrative Tenses
- Noun Clauses
- Noun Phrases
- Passive Voice
- Past Continuous
- Past Perfect
- Past Perfect Continuous
- Past Perfect Simple & Continuous
- Past Simple Affirmative & Negative
- Past Simple Passive
- Past Simple Regular Verbs
- Past Simple vs. Past Continuous
- Past Simple Was and Were
- Past Simple Wh Questions
- Past Simple Yes/No Questions
- Past Tense Review
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect — Ever and Never
- Present Perfect — For and Since
- Present Perfect — Just, Yet & Already
- Present Perfect vs. Past Simple
- Present Perfect Continuous
- Present Simple Affirmative & Negative
- Present Simple Passive
- Present Simple vs. Present Continuous
- Present Simple Wh Questions
- Present Simple Yes/No Questions
- Present Tense Review
- Question Words
- Relative Clauses
- Reported Speech
- Subject-Verb Agreement
- Tag Questions
- There is & There are
- Used to
- Verb to be
- Wh Questions
- Parts of Speech
- Abstract Nouns
- Adjectives
- Adjective-Noun Collocations
- Adjectives of Feeling & Emotion
- Adjectives of Opinion
- Adjectives of Quantity
- Adjective Opposites
- Adjective Order
- Adjective-Preposition Collocations
- -ed and -ing Adjectives
- Adverb-Adjective Collocations
- Adverb Order
- Adverbs of Affirmation and Negation
- Adverbs of Degree
- Adverbs of Frequency
- Adverbs of Manner
- Adverbs of Time
- Adverbs of Place
- Articles — a, an, the
- Causative Verbs
- Collective Nouns
- Common & Proper Nouns
- Compound Adjectives
- Compound Nouns
- Concrete nouns
- Conjunctions
- Countable & Uncountable Nouns
- Demonstrative Adjectives
- Demonstrative Pronouns
- Dependent Prepositions
- Indefinite Pronouns
- Intensifiers & Mitigators
- Interjections
- Modal Verbs of Ability
- Modals of Deduction & Speculation
- Modals of Necessity
- Modals of Obligation & Prohibition
- Onomatopoeia
- Modals of Possibility & Certainty
- Parts of Speech
- Phrasal Verbs
- Possessives
- Prefixes
- Prepositions of Movement
- Prepositions of Place
- Prepositions of Time
- Proper Adjectives
- Quantifiers
- Reflexive Pronouns
- Sense Verbs & Adjectives
- Singular & Plural Nouns
- So and Such
- Subject & Object Pronouns
- Suffixes
- Too and Enough
- Transition Words
- Verb-Noun Collocations
- Verbs
- Functional Language
- Agreeing & Disagreeing
- Air Travel
- Asking Permission
- At the Dentist’s
- At the Doctor’s
- Being Polite
- Classroom Language
- Complaining & Apologizing
- Complimenting
- Critical Thinking & Problem Solving
- Describing Character & Personality
- Describing People’s Appearance
- Describing Places
- Describing Things
- Emailing
- Etiquette and Manners
- Getting Around
- Getting to Know You
- Giving Advice
- Giving Directions
- Giving Opinions
- Giving Personal Information
- Greetings & Introductions
- Holidays
- Indirect Questions
- Likes and Dislikes
- Making Decisions
- Making Arrangements
- Making Excuses
- Making Invitations
- Making Offers & Promises
- Making Requests
- Making Suggestions
- Online Communication
- Ordering Food & Drink
- Shopping
- Small Talk
- Social Media
- Telephoning
- Times and Dates
- Travel
- General English
- Animals
- Christmas
- Cities & Towns
- Clothes & Fashion
- Colours
- Computers & Smartphones
- Countries & Nationalities
- Crime, Law & Punishment
- Cultural Celebrations
- Easter
- Family & Relationships
- Food & Drink
- Going Out & Entertainment
- Halloween
- Health & Fitness
- Hobbies & Free Time
- Houses, Rooms & Furniture
- Idioms
- Jobs & the Workplace
- Modes of Transport
- Money
- Music
- Numbers
- Parts of the Body
- Reading Comprehension
- Seasons
- Space
- Sports
- The Natural World
- Time Expressions
- TV & Film
- Valentine’s Day
- Weather
- Academic English
- Academic Collocations
- Academic Reading Comprehension
- AWL Sublist 1 and 2
- Cause and Effect Essays
- Compare and Contrast Essays
- Debating
- Discussion Essays
- Discussions
- Essay Writing
- Paragraph Writing
- Persuasive Essays
- Presentation Skills
- Problem Solution Essays
- Punctuation
- Reading Skills
- Referenced Essays
- Study Skills
- The Writing Process
- Business English
- Business Emails
- Business Meetings
- Business Negotiations
- Talking about Jobs
- ESL Games
- Brainstorming Games
- Category Games
- Classic Childhood Games
- Counting Games
- Describing Games
- Drawing Games
- Drilling Activity Games
- First Day of Class Games
- Flashcard Games
- Answer Games
- Grammar Games
- Hangman Games
- Listening Games
- Miming Games
- Music Games
- Question & Answer Games
- Quiz Games
- Sentence Race Games
- Spelling Games
- TV Game Shows
- Verb Games
- Vocabulary Games
- Word Association Games
- Word Games
- Yes/No Question Games
- Ideas
- Classroom Interaction Patterns
- Classroom Management
- Concept Checking
- Cultural Awareness
- Developing Students’ Listening Skills
- Developing Students’ Reading Skills
- Developing Students’ Speaking Skills
- Eliciting Techniques
- ESL Dictations
- How to Introduce a Lesson
- How to Use Music in ESL Class
- Lesson Planning
- Making Teaching Materials Relevant
- Problems Learning English
- Teaching English Idioms
- Teaching English Vocabulary
- Teaching Large Classes
- Teaching Mixed-Ability Classes
- Teaching Small Classes
- The First Day of Class
- Using Correction in Class
- Using Song Gap Fills
- Online Membership
- ESL Essentials eBook Series
- Online Platform Tutorial
- TEFL Certification & Courses
- Join our Team
- Contact Us / FAQ
- About Us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use