import java.io.File;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class WriteDataToExcel {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
XSSFSheet spreadsheet
= workbook.createSheet(" Student Data ");
XSSFRow row;
Map<String, Object[]> studentData
= new TreeMap<String, Object[]>();
studentData.put(
"1",
new Object[] { "Roll No", "NAME", "Year" });
studentData.put("2", new Object[] { "128", "Aditya",
"2nd year" });
studentData.put(
"3",
new Object[] { "129", "Narayana", "2nd year" });
studentData.put("4", new Object[] { "130", "Mohan",
"2nd year" });
studentData.put("5", new Object[] { "131", "Radha",
"2nd year" });
studentData.put("6", new Object[] { "132", "Gopal",
"2nd year" });
Set<String> keyid = studentData.keySet();
int rowid = 0;
for (String key : keyid) {
row = spreadsheet.createRow(rowid++);
Object[] objectArr = studentData.get(key);
int cellid = 0;
for (Object obj : objectArr) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellid++);
cell.setCellValue((String)obj);
}
}
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(
new File("C:/savedexcel/GFGsheet.xlsx"));
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
}
}
Learn to read excel, write excel, evaluate formula cells and apply custom formatting to the generated excel files using Apache POI library with examples.
If we are building software for the HR or Finance domain, there is usually a requirement for generating excel reports across management levels. Apart from reports, we can also expect some input data for the applications coming in the form of excel sheets and the application is expected to support this requirement.
Apache POI is a well-trusted library among many other open-source libraries to handle such usecases involving excel files. Please note that, in addition, we can read and write MS Word and MS PowerPoint files also using the Apache POI library.
This Apache POI tutorial will discuss some everyday excel operations in real-life applications.
- 1. Maven Dependency
- 2. Important Classes in POI Library
- 3. Writing an Excel File
- 4. Reading an Excel File
- 5. Add and Evaluate Formula Cells
- 6. Formatting the Cells
- 7. Conclusion
1. Maven Dependency
If we are working on a maven project, we can include the Apache POI dependencies in pom.xml file using this:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2</version>
</dependency>2. Important Classes in POI Library
-
HSSF, XSSF and XSSF classes
Apache POI main classes usually start with either HSSF, XSSF or SXSSF.
- HSSF – is the POI Project’s pure Java implementation of the Excel 97(-2007) file format. e.g., HSSFWorkbook, HSSFSheet.
- XSSF – is the POI Project’s pure Java implementation of the Excel 2007 OOXML (.xlsx) file format. e.g., XSSFWorkbook, XSSFSheet.
- SXSSF (since 3.8-beta3) – is an API-compatible streaming extension of XSSF to be used when huge spreadsheets have to be produced and heap space is limited. e.g., SXSSFWorkbook, SXSSFSheet. SXSSF achieves its low memory footprint by limiting access to the rows within a sliding window, while XSSF gives access to all rows in the document.
-
Row and Cell
Apart from the above classes, Row and Cell interact with a particular row and a particular cell in an excel sheet.
-
Styling Related Classes
A wide range of classes like CellStyle, BuiltinFormats, ComparisonOperator, ConditionalFormattingRule, FontFormatting, IndexedColors, PatternFormatting, SheetConditionalFormatting etc. are used when you have to add formatting to a sheet, primarily based on some rules.
-
FormulaEvaluator
Another helpful class FormulaEvaluator is used to evaluate the formula cells in an excel sheet.
3. Writing an Excel File
I am taking this example first so we can reuse the excel sheet created by this code in further examples.
Writing excel using POI is very simple and involves the following steps:
- Create a workbook
- Create a sheet in workbook
- Create a row in sheet
- Add cells to sheet
- Repeat steps 3 and 4 to write more data
It seems very simple, right? Let’s have a look at the code doing these steps.
Java program to write an excel file using Apache POI library.
package com.howtodoinjava.demo.poi;
//import statements
public class WriteExcelDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//Blank workbook
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
//Create a blank sheet
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Employee Data");
//This data needs to be written (Object[])
Map<String, Object[]> data = new TreeMap<String, Object[]>();
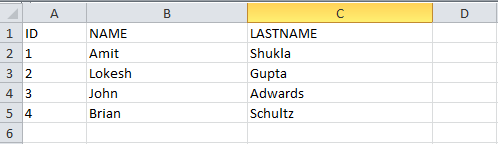
data.put("1", new Object[] {"ID", "NAME", "LASTNAME"});
data.put("2", new Object[] {1, "Amit", "Shukla"});
data.put("3", new Object[] {2, "Lokesh", "Gupta"});
data.put("4", new Object[] {3, "John", "Adwards"});
data.put("5", new Object[] {4, "Brian", "Schultz"});
//Iterate over data and write to sheet
Set<String> keyset = data.keySet();
int rownum = 0;
for (String key : keyset)
{
Row row = sheet.createRow(rownum++);
Object [] objArr = data.get(key);
int cellnum = 0;
for (Object obj : objArr)
{
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellnum++);
if(obj instanceof String)
cell.setCellValue((String)obj);
else if(obj instanceof Integer)
cell.setCellValue((Integer)obj);
}
}
try
{
//Write the workbook in file system
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(new File("howtodoinjava_demo.xlsx"));
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
System.out.println("howtodoinjava_demo.xlsx written successfully on disk.");
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
See Also: Appending Rows to Excel
4. Reading an Excel File
Reading an excel file using POI is also very simple if we divide this into steps.
- Create workbook instance from an excel sheet
- Get to the desired sheet
- Increment row number
- iterate over all cells in a row
- repeat steps 3 and 4 until all data is read
Let’s see all the above steps in code. I am writing the code to read the excel file created in the above example. It will read all the column names and the values in it – cell by cell.
Java program to read an excel file using Apache POI library.
package com.howtodoinjava.demo.poi;
//import statements
public class ReadExcelDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try
{
FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream(new File("howtodoinjava_demo.xlsx"));
//Create Workbook instance holding reference to .xlsx file
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(file);
//Get first/desired sheet from the workbook
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
//Iterate through each rows one by one
Iterator<Row> rowIterator = sheet.iterator();
while (rowIterator.hasNext())
{
Row row = rowIterator.next();
//For each row, iterate through all the columns
Iterator<Cell> cellIterator = row.cellIterator();
while (cellIterator.hasNext())
{
Cell cell = cellIterator.next();
//Check the cell type and format accordingly
switch (cell.getCellType())
{
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue() + "t");
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue() + "t");
break;
}
}
System.out.println("");
}
file.close();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Program Output:
ID NAME LASTNAME
1.0 Amit Shukla
2.0 Lokesh Gupta
3.0 John Adwards
4.0 Brian Schultz See Also: Apache POI – Read an Excel File using SAX Parser
5. Add and Evaluate Formula Cells
When working on complex excel sheets, we encounter many cells with formulas to calculate their values. These are formula cells. Apache POI also has excellent support for adding formula cells and evaluating already present formula cells.
Let’s see one example of how to add formula cells in excel?
The sheet has four cells in a row and the fourth one in the multiplication of all the previous 3 rows. So the formula will be: A2*B2*C2 (in the second row)
Java program to add formula in an excel file using Apache POI library.
public static void main(String[] args)
{
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Calculate Simple Interest");
Row header = sheet.createRow(0);
header.createCell(0).setCellValue("Pricipal");
header.createCell(1).setCellValue("RoI");
header.createCell(2).setCellValue("T");
header.createCell(3).setCellValue("Interest (P r t)");
Row dataRow = sheet.createRow(1);
dataRow.createCell(0).setCellValue(14500d);
dataRow.createCell(1).setCellValue(9.25);
dataRow.createCell(2).setCellValue(3d);
dataRow.createCell(3).setCellFormula("A2*B2*C2");
try {
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(new File("formulaDemo.xlsx"));
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
System.out.println("Excel with foumula cells written successfully");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}Similarly, we want to read a file with formula cells and use the following logic to evaluate formula cells.
Java program to evaluate formula in an excel file using Apache POI library.
public static void readSheetWithFormula()
{
try
{
FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream(new File("formulaDemo.xlsx"));
//Create Workbook instance holding reference to .xlsx file
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(file);
FormulaEvaluator evaluator = workbook.getCreationHelper().createFormulaEvaluator();
//Get first/desired sheet from the workbook
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
//Iterate through each rows one by one
Iterator<Row> rowIterator = sheet.iterator();
while (rowIterator.hasNext())
{
Row row = rowIterator.next();
//For each row, iterate through all the columns
Iterator<Cell> cellIterator = row.cellIterator();
while (cellIterator.hasNext())
{
Cell cell = cellIterator.next();
//Check the cell type after eveluating formulae
//If it is formula cell, it will be evaluated otherwise no change will happen
switch (evaluator.evaluateInCell(cell).getCellType())
{
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue() + "tt");
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue() + "tt");
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA:
//Not again
break;
}
}
System.out.println("");
}
file.close();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}Program Output:
Pricipal RoI T Interest (P r t)
14500.0 9.25 3.0 402375.0 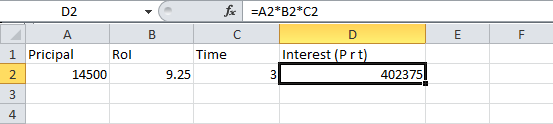
6. Formatting the Cells
So far we have seen examples of reading/writing and excel files using Apache POI. But, when creating a report in an excel file, it is essential to add formatting on cells that fit into any pre-determined criteria.
This formatting can be a different coloring based on a specific value range, expiry date limit etc.
In the below examples, we are taking a couple of such cell formatting examples for various purposes.
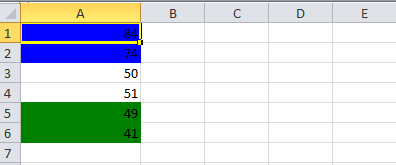
6.1. Cell value in a specific range
This code will color any cell in a range whose value is between a configured range. [e.g., between 50 and 70]
static void basedOnValue(Sheet sheet)
{
//Creating some random values
sheet.createRow(0).createCell(0).setCellValue(84);
sheet.createRow(1).createCell(0).setCellValue(74);
sheet.createRow(2).createCell(0).setCellValue(50);
sheet.createRow(3).createCell(0).setCellValue(51);
sheet.createRow(4).createCell(0).setCellValue(49);
sheet.createRow(5).createCell(0).setCellValue(41);
SheetConditionalFormatting sheetCF = sheet.getSheetConditionalFormatting();
//Condition 1: Cell Value Is greater than 70 (Blue Fill)
ConditionalFormattingRule rule1 = sheetCF.createConditionalFormattingRule(ComparisonOperator.GT, "70");
PatternFormatting fill1 = rule1.createPatternFormatting();
fill1.setFillBackgroundColor(IndexedColors.BLUE.index);
fill1.setFillPattern(PatternFormatting.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
//Condition 2: Cell Value Is less than 50 (Green Fill)
ConditionalFormattingRule rule2 = sheetCF.createConditionalFormattingRule(ComparisonOperator.LT, "50");
PatternFormatting fill2 = rule2.createPatternFormatting();
fill2.setFillBackgroundColor(IndexedColors.GREEN.index);
fill2.setFillPattern(PatternFormatting.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
CellRangeAddress[] regions = {
CellRangeAddress.valueOf("A1:A6")
};
sheetCF.addConditionalFormatting(regions, rule1, rule2);
}
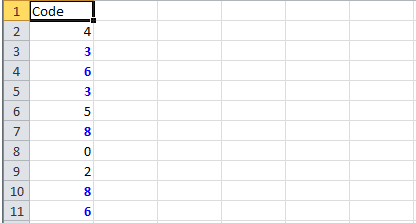
6.2. Highlight Duplicate Values
Highlight all cells which have duplicate values in observed cells.
static void formatDuplicates(Sheet sheet) {
sheet.createRow(0).createCell(0).setCellValue("Code");
sheet.createRow(1).createCell(0).setCellValue(4);
sheet.createRow(2).createCell(0).setCellValue(3);
sheet.createRow(3).createCell(0).setCellValue(6);
sheet.createRow(4).createCell(0).setCellValue(3);
sheet.createRow(5).createCell(0).setCellValue(5);
sheet.createRow(6).createCell(0).setCellValue(8);
sheet.createRow(7).createCell(0).setCellValue(0);
sheet.createRow(8).createCell(0).setCellValue(2);
sheet.createRow(9).createCell(0).setCellValue(8);
sheet.createRow(10).createCell(0).setCellValue(6);
SheetConditionalFormatting sheetCF = sheet.getSheetConditionalFormatting();
// Condition 1: Formula Is =A2=A1 (White Font)
ConditionalFormattingRule rule1 = sheetCF.createConditionalFormattingRule("COUNTIF($A$2:$A$11,A2)>1");
FontFormatting font = rule1.createFontFormatting();
font.setFontStyle(false, true);
font.setFontColorIndex(IndexedColors.BLUE.index);
CellRangeAddress[] regions = {
CellRangeAddress.valueOf("A2:A11")
};
sheetCF.addConditionalFormatting(regions, rule1);
sheet.getRow(2).createCell(1).setCellValue("<== Duplicates numbers in the column are highlighted. " +
"Condition: Formula Is =COUNTIF($A$2:$A$11,A2)>1 (Blue Font)");
}
6.3. Alternate Color Rows in Different Colors
A simple code to color each alternate row in a different color.
static void shadeAlt(Sheet sheet) {
SheetConditionalFormatting sheetCF = sheet.getSheetConditionalFormatting();
// Condition 1: Formula Is =A2=A1 (White Font)
ConditionalFormattingRule rule1 = sheetCF.createConditionalFormattingRule("MOD(ROW(),2)");
PatternFormatting fill1 = rule1.createPatternFormatting();
fill1.setFillBackgroundColor(IndexedColors.LIGHT_GREEN.index);
fill1.setFillPattern(PatternFormatting.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
CellRangeAddress[] regions = {
CellRangeAddress.valueOf("A1:Z100")
};
sheetCF.addConditionalFormatting(regions, rule1);
sheet.createRow(0).createCell(1).setCellValue("Shade Alternating Rows");
sheet.createRow(1).createCell(1).setCellValue("Condition: Formula Is =MOD(ROW(),2) (Light Green Fill)");
}
6.4. Color amounts that are going to expire in the next 30 days
A handy code for financial projects which keeps track of deadlines.
static void expiryInNext30Days(Sheet sheet)
{
CellStyle style = sheet.getWorkbook().createCellStyle();
style.setDataFormat((short)BuiltinFormats.getBuiltinFormat("d-mmm"));
sheet.createRow(0).createCell(0).setCellValue("Date");
sheet.createRow(1).createCell(0).setCellFormula("TODAY()+29");
sheet.createRow(2).createCell(0).setCellFormula("A2+1");
sheet.createRow(3).createCell(0).setCellFormula("A3+1");
for(int rownum = 1; rownum <= 3; rownum++) sheet.getRow(rownum).getCell(0).setCellStyle(style);
SheetConditionalFormatting sheetCF = sheet.getSheetConditionalFormatting();
// Condition 1: Formula Is =A2=A1 (White Font)
ConditionalFormattingRule rule1 = sheetCF.createConditionalFormattingRule("AND(A2-TODAY()>=0,A2-TODAY()<=30)");
FontFormatting font = rule1.createFontFormatting();
font.setFontStyle(false, true);
font.setFontColorIndex(IndexedColors.BLUE.index);
CellRangeAddress[] regions = {
CellRangeAddress.valueOf("A2:A4")
};
sheetCF.addConditionalFormatting(regions, rule1);
sheet.getRow(0).createCell(1).setCellValue("Dates within the next 30 days are highlighted");
}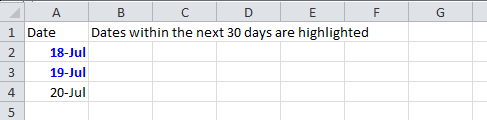
I am ending this apache poi tutorial here to keep the post within a limit.
7. Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned to read excel, write excel, set and evaluate formula cells, and format the cells with color codings using the Apache POI library.
Happy Learning !!
Source Code on Github
I want to read and write an Excel file from Java with 3 columns and N rows, printing one string in each cell. Can anyone give me simple code snippet for this? Do I need to use any external lib or does Java have built-in support for it?
I want to do the following:
for(i=0; i <rows; i++)
//read [i,col1] ,[i,col2], [i,col3]
for(i=0; i<rows; i++)
//write [i,col1], [i,col2], [i,col3]
Paolo Forgia
6,5328 gold badges46 silver badges58 bronze badges
asked Oct 4, 2009 at 10:54
1
Try the Apache POI HSSF. Here’s an example on how to read an excel file:
try {
POIFSFileSystem fs = new POIFSFileSystem(new FileInputStream(file));
HSSFWorkbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook(fs);
HSSFSheet sheet = wb.getSheetAt(0);
HSSFRow row;
HSSFCell cell;
int rows; // No of rows
rows = sheet.getPhysicalNumberOfRows();
int cols = 0; // No of columns
int tmp = 0;
// This trick ensures that we get the data properly even if it doesn't start from first few rows
for(int i = 0; i < 10 || i < rows; i++) {
row = sheet.getRow(i);
if(row != null) {
tmp = sheet.getRow(i).getPhysicalNumberOfCells();
if(tmp > cols) cols = tmp;
}
}
for(int r = 0; r < rows; r++) {
row = sheet.getRow(r);
if(row != null) {
for(int c = 0; c < cols; c++) {
cell = row.getCell((short)c);
if(cell != null) {
// Your code here
}
}
}
}
} catch(Exception ioe) {
ioe.printStackTrace();
}
On the documentation page you also have examples of how to write to excel files.
answered Oct 4, 2009 at 10:59
rogeriopvlrogeriopvl
50.8k8 gold badges54 silver badges58 bronze badges
7
Apache POI can do this for you. Specifically the HSSF module. The quick guide is most useful. Here’s how to do what you want — specifically create a sheet and write it out.
Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook();
//Workbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook();
CreationHelper createHelper = wb.getCreationHelper();
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet("new sheet");
// Create a row and put some cells in it. Rows are 0 based.
Row row = sheet.createRow((short)0);
// Create a cell and put a value in it.
Cell cell = row.createCell(0);
cell.setCellValue(1);
// Or do it on one line.
row.createCell(1).setCellValue(1.2);
row.createCell(2).setCellValue(
createHelper.createRichTextString("This is a string"));
row.createCell(3).setCellValue(true);
// Write the output to a file
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("workbook.xls");
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.close();
answered Oct 4, 2009 at 10:57
Brian AgnewBrian Agnew
267k36 gold badges333 silver badges441 bronze badges
2
First add all these jar files in your project class path:
- poi-scratchpad-3.7-20101029
- poi-3.2-FINAL-20081019
- poi-3.7-20101029
- poi-examples-3.7-20101029
- poi-ooxml-3.7-20101029
- poi-ooxml-schemas-3.7-20101029
- xmlbeans-2.3.0
- dom4j-1.6.1
Code for writing in a excel file:
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Blank workbook
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
//Create a blank sheet
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Employee Data");
//This data needs to be written (Object[])
Map<String, Object[]> data = new TreeMap<String, Object[]>();
data.put("1", new Object[]{"ID", "NAME", "LASTNAME"});
data.put("2", new Object[]{1, "Amit", "Shukla"});
data.put("3", new Object[]{2, "Lokesh", "Gupta"});
data.put("4", new Object[]{3, "John", "Adwards"});
data.put("5", new Object[]{4, "Brian", "Schultz"});
//Iterate over data and write to sheet
Set<String> keyset = data.keySet();
int rownum = 0;
for (String key : keyset)
{
//create a row of excelsheet
Row row = sheet.createRow(rownum++);
//get object array of prerticuler key
Object[] objArr = data.get(key);
int cellnum = 0;
for (Object obj : objArr)
{
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellnum++);
if (obj instanceof String)
{
cell.setCellValue((String) obj);
}
else if (obj instanceof Integer)
{
cell.setCellValue((Integer) obj);
}
}
}
try
{
//Write the workbook in file system
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(new File("C:\Documents and Settings\admin\Desktop\imp data\howtodoinjava_demo.xlsx"));
workbook.write(out);
out.close();
System.out.println("howtodoinjava_demo.xlsx written successfully on disk.");
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
Code for reading from excel file
/*
* To change this template, choose Tools | Templates
* and open the template in the editor.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream(new File("C:\Documents and Settings\admin\Desktop\imp data\howtodoinjava_demo.xlsx"));
//Create Workbook instance holding reference to .xlsx file
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(file);
//Get first/desired sheet from the workbook
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
//Iterate through each rows one by one
Iterator<Row> rowIterator = sheet.iterator();
while (rowIterator.hasNext())
{
Row row = rowIterator.next();
//For each row, iterate through all the columns
Iterator<Cell> cellIterator = row.cellIterator();
while (cellIterator.hasNext())
{
Cell cell = cellIterator.next();
//Check the cell type and format accordingly
switch (cell.getCellType())
{
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue() + "t");
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue() + "t");
break;
}
}
System.out.println("");
}
file.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
answered Aug 2, 2013 at 9:15
0
You can also consider JExcelApi. I find it better designed than POI. There’s a tutorial here.
answered Oct 4, 2009 at 13:06
javashlookjavashlook
10.3k1 gold badge26 silver badges33 bronze badges
3
There is a new easy and very cool tool (10x to Kfir): xcelite
Write:
public class User {
@Column (name="Firstname")
private String firstName;
@Column (name="Lastname")
private String lastName;
@Column
private long id;
@Column
private Date birthDate;
}
Xcelite xcelite = new Xcelite();
XceliteSheet sheet = xcelite.createSheet("users");
SheetWriter<User> writer = sheet.getBeanWriter(User.class);
List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>();
// ...fill up users
writer.write(users);
xcelite.write(new File("users_doc.xlsx"));
Read:
Xcelite xcelite = new Xcelite(new File("users_doc.xlsx"));
XceliteSheet sheet = xcelite.getSheet("users");
SheetReader<User> reader = sheet.getBeanReader(User.class);
Collection<User> users = reader.read();
answered Dec 23, 2014 at 8:21
Ran AdlerRan Adler
3,52128 silver badges27 bronze badges
0
For reading a xlsx file we can use Apache POI libs
Try this:
public static void readXLSXFile() throws IOException
{
InputStream ExcelFileToRead = new FileInputStream("C:/Test.xlsx");
XSSFWorkbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook(ExcelFileToRead);
XSSFWorkbook test = new XSSFWorkbook();
XSSFSheet sheet = wb.getSheetAt(0);
XSSFRow row;
XSSFCell cell;
Iterator rows = sheet.rowIterator();
while (rows.hasNext())
{
row=(XSSFRow) rows.next();
Iterator cells = row.cellIterator();
while (cells.hasNext())
{
cell=(XSSFCell) cells.next();
if (cell.getCellType() == XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_STRING)
{
System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue()+" ");
}
else if(cell.getCellType() == XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC)
{
System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue()+" ");
}
else
{
//U Can Handel Boolean, Formula, Errors
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
answered Apr 13, 2017 at 8:16
.csv or POI will certainly do it, but you should be aware of Andy Khan’s JExcel. I think it’s by far the best Java library for working with Excel there is.
answered Oct 4, 2009 at 12:50
duffymoduffymo
304k44 gold badges368 silver badges558 bronze badges
2
A simple CSV file should suffice
answered Oct 4, 2009 at 11:01
John La RooyJohn La Rooy
292k53 gold badges363 silver badges501 bronze badges
8
String path="C:\Book2.xlsx";
try {
File f = new File( path );
Workbook wb = WorkbookFactory.create(f);
Sheet mySheet = wb.getSheetAt(0);
Iterator<Row> rowIter = mySheet.rowIterator();
for ( Iterator<Row> rowIterator = mySheet.rowIterator() ;rowIterator.hasNext(); )
{
for ( Iterator<Cell> cellIterator = ((Row)rowIterator.next()).cellIterator() ; cellIterator.hasNext() ; )
{
System.out.println ( ( (Cell)cellIterator.next() ).toString() );
}
System.out.println( " **************************************************************** ");
}
} catch ( Exception e )
{
System.out.println( "exception" );
e.printStackTrace();
}
and make sure to have added the jars poi and poi-ooxml (org.apache.poi) to your project
instinct
4301 gold badge7 silver badges24 bronze badges
answered Apr 11, 2014 at 10:24
ToumiToumi
2,8673 gold badges37 silver badges30 bronze badges
For reading data from .xlsx workbooks we need to use XSSFworkbook classes.
XSSFWorkbook xlsxBook = new XSSFWorkbook(fis);
XSSFSheet sheet = xlsxBook.getSheetAt(0); etc.
We need to use Apache-poi 3.9 @ http://poi.apache.org/
For detailed info with example visit
: http://java-recent.blogspot.in
CuberChase
4,4305 gold badges33 silver badges52 bronze badges
answered Jun 18, 2013 at 1:47
1
Sure , you will find the code below useful and easy to read and write. This is a util class which you can use in your main method and then you are good to use all methods below.
public class ExcelUtils {
private static XSSFSheet ExcelWSheet;
private static XSSFWorkbook ExcelWBook;
private static XSSFCell Cell;
private static XSSFRow Row;
File fileName = new File("C:\Users\satekuma\Pro\Fund.xlsx");
public void setExcelFile(File Path, String SheetName) throws Exception
try {
FileInputStream ExcelFile = new FileInputStream(Path);
ExcelWBook = new XSSFWorkbook(ExcelFile);
ExcelWSheet = ExcelWBook.getSheet(SheetName);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw (e);
}
}
public static String getCellData(int RowNum, int ColNum) throws Exception {
try {
Cell = ExcelWSheet.getRow(RowNum).getCell(ColNum);
String CellData = Cell.getStringCellValue();
return CellData;
} catch (Exception e) {
return "";
}
}
public static void setCellData(String Result, int RowNum, int ColNum, File Path) throws Exception {
try {
Row = ExcelWSheet.createRow(RowNum - 1);
Cell = Row.createCell(ColNum - 1);
Cell.setCellValue(Result);
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream(Path);
ExcelWBook.write(fileOut);
fileOut.flush();
fileOut.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw (e);
}
}
}
answered May 6, 2015 at 14:58
satendersatender
1,16913 silver badges12 bronze badges
using spring apache poi repo
if (fileName.endsWith(".xls")) {
File myFile = new File("file location" + fileName);
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(myFile);
org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook workbook = null;
try {
workbook = WorkbookFactory.create(fis);
} catch (InvalidFormatException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
Iterator<Row> rowIterator = sheet.iterator();
while (rowIterator.hasNext()) {
Row row = rowIterator.next();
Iterator<Cell> cellIterator = row.cellIterator();
while (cellIterator.hasNext()) {
Cell cell = cellIterator.next();
switch (cell.getCellType()) {
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue());
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_BOOLEAN:
System.out.print(cell.getBooleanCellValue());
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue());
break;
}
System.out.print(" - ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
goto
7,79110 gold badges48 silver badges58 bronze badges
answered Feb 22, 2017 at 9:53
I edited the most voted one a little cuz it didn’t count blanks columns or rows well not totally, so here is my code i tested it and now can get any cell in any part of an excel file. also now u can have blanks columns between filled column and it will read them
try {
POIFSFileSystem fs = new POIFSFileSystem(new FileInputStream(Dir));
HSSFWorkbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook(fs);
HSSFSheet sheet = wb.getSheetAt(0);
HSSFRow row;
HSSFCell cell;
int rows; // No of rows
rows = sheet.getPhysicalNumberOfRows();
int cols = 0; // No of columns
int tmp = 0;
int cblacks=0;
// This trick ensures that we get the data properly even if it doesn't start from first few rows
for(int i = 0; i <= 10 || i <= rows; i++) {
row = sheet.getRow(i);
if(row != null) {
tmp = sheet.getRow(i).getPhysicalNumberOfCells();
if(tmp >= cols) cols = tmp;else{rows++;cblacks++;}
}
cols++;
}
cols=cols+cblacks;
for(int r = 0; r < rows; r++) {
row = sheet.getRow(r);
if(row != null) {
for(int c = 0; c < cols; c++) {
cell = row.getCell(c);
if(cell != null) {
System.out.print(cell+"n");//Your Code here
}
}
}
}} catch(Exception ioe) {
ioe.printStackTrace();}
answered Oct 4, 2015 at 20:16
If column number are varing you can use this
package com.org.tests;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.*;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ExcelSimpleTest
{
String path;
public FileInputStream fis = null;
private XSSFWorkbook workbook = null;
private XSSFSheet sheet = null;
private XSSFRow row =null;
private XSSFCell cell = null;
public ExcelSimpleTest() throws IOException
{
path = System.getProperty("user.dir")+"\resources\Book1.xlsx";
fis = new FileInputStream(path);
workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fis);
sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
}
public void ExelWorks()
{
int index = workbook.getSheetIndex("Sheet1");
sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(index);
int rownumber=sheet.getLastRowNum()+1;
for (int i=1; i<rownumber; i++ )
{
row = sheet.getRow(i);
int colnumber = row.getLastCellNum();
for (int j=0; j<colnumber; j++ )
{
cell = row.getCell(j);
System.out.println(cell.getStringCellValue());
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
ExcelSimpleTest excelwork = new ExcelSimpleTest();
excelwork.ExelWorks();
}
}
The corresponding mavendependency can be found here
Ohmen
6,1343 gold badges26 silver badges35 bronze badges
answered Aug 26, 2016 at 6:06
1
Another way to read/write Excel files is to use Windmill. It provides a fluent API to process Excel and CSV files.
Import data
try (Stream<Row> rowStream = Windmill.parse(FileSource.of(new FileInputStream("myFile.xlsx")))) {
rowStream
// skip the header row that contains the column names
.skip(1)
.forEach(row -> {
System.out.println(
"row n°" + row.rowIndex()
+ " column 'User login' value : " + row.cell("User login").asString()
+ " column n°3 number value : " + row.cell(2).asDouble().value() // index is zero-based
);
});
}
Export data
Windmill
.export(Arrays.asList(bean1, bean2, bean3))
.withHeaderMapping(
new ExportHeaderMapping<Bean>()
.add("Name", Bean::getName)
.add("User login", bean -> bean.getUser().getLogin())
)
.asExcel()
.writeTo(new FileOutputStream("Export.xlsx"));
answered Sep 30, 2017 at 15:07
amanteauxamanteaux
1,95319 silver badges23 bronze badges
You need Apache POI library and this code below should help you
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Iterator;
//*************************************************************
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
//*************************************************************
public class AdvUse {
private static Workbook wb ;
private static Sheet sh ;
private static FileInputStream fis ;
private static FileOutputStream fos ;
private static Row row ;
private static Cell cell ;
private static String ExcelPath ;
//*************************************************************
public static void setEcxelFile(String ExcelPath, String SheetName) throws Exception {
try {
File f= new File(ExcelPath);
if(!f.exists()){
f.createNewFile();
System.out.println("File not Found so created");
}
fis = new FileInputStream("./testData.xlsx");
wb = WorkbookFactory.create(fis);
sh = wb.getSheet("SheetName");
if(sh == null){
sh = wb.getSheet(SheetName);
}
}catch(Exception e)
{System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
//*************************************************************
public static void setCellData(String text , int rowno , int colno){
try{
row = sh.getRow(rowno);
if(row == null){
row = sh.createRow(rowno);
}
cell = row.getCell(colno);
if(cell!=null){
cell.setCellValue(text);
}
else{
cell = row.createCell(colno);
cell.setCellValue(text);
}
fos = new FileOutputStream(ExcelPath);
wb.write(fos);
fos.flush();
fos.close();
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
//*************************************************************
public static String getCellData(int rowno , int colno){
try{
cell = sh.getRow(rowno).getCell(colno);
String CellData = null ;
switch(cell.getCellType()){
case STRING :
CellData = cell.getStringCellValue();
break ;
case NUMERIC :
CellData = Double.toString(cell.getNumericCellValue());
if(CellData.contains(".o")){
CellData = CellData.substring(0,CellData.length()-2);
}
break ;
case BLANK :
CellData = ""; break ;
}
return CellData;
}catch(Exception e){return ""; }
}
//*************************************************************
public static int getLastRow(){
return sh.getLastRowNum();
}
answered Mar 30, 2019 at 16:48
Abdo BmzAbdo Bmz
6221 gold badge10 silver badges24 bronze badges
You can not read & write same file in parallel(Read-write lock). But, we can do parallel operations on temporary data(i.e. Input/output stream). Write the data to file only after closing the input stream. Below steps should be followed.
- Open the file to Input stream
- Open the same file to an Output Stream
- Read and do the processing
- Write contents to output stream.
- Close the read/input stream, close file
- Close output stream, close file.
Apache POI — read/write same excel example
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
public class XLSXReaderWriter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
File excel = new File("D://raju.xlsx");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(excel);
XSSFWorkbook book = new XSSFWorkbook(fis);
XSSFSheet sheet = book.getSheetAt(0);
Iterator<Row> itr = sheet.iterator();
// Iterating over Excel file in Java
while (itr.hasNext()) {
Row row = itr.next();
// Iterating over each column of Excel file
Iterator<Cell> cellIterator = row.cellIterator();
while (cellIterator.hasNext()) {
Cell cell = cellIterator.next();
switch (cell.getCellType()) {
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue() + "t");
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue() + "t");
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_BOOLEAN:
System.out.print(cell.getBooleanCellValue() + "t");
break;
default:
}
}
System.out.println("");
}
// writing data into XLSX file
Map<String, Object[]> newData = new HashMap<String, Object[]>();
newData.put("1", new Object[] { 1d, "Raju", "75K", "dev",
"SGD" });
newData.put("2", new Object[] { 2d, "Ramesh", "58K", "test",
"USD" });
newData.put("3", new Object[] { 3d, "Ravi", "90K", "PMO",
"INR" });
Set<String> newRows = newData.keySet();
int rownum = sheet.getLastRowNum();
for (String key : newRows) {
Row row = sheet.createRow(rownum++);
Object[] objArr = newData.get(key);
int cellnum = 0;
for (Object obj : objArr) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellnum++);
if (obj instanceof String) {
cell.setCellValue((String) obj);
} else if (obj instanceof Boolean) {
cell.setCellValue((Boolean) obj);
} else if (obj instanceof Date) {
cell.setCellValue((Date) obj);
} else if (obj instanceof Double) {
cell.setCellValue((Double) obj);
}
}
}
// open an OutputStream to save written data into Excel file
FileOutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(excel);
book.write(os);
System.out.println("Writing on Excel file Finished ...");
// Close workbook, OutputStream and Excel file to prevent leak
os.close();
book.close();
fis.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException fe) {
fe.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException ie) {
ie.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
answered Jul 20, 2018 at 21:46
RajuRaju
2,8628 gold badges38 silver badges57 bronze badges
Please use Apache POI libs and try this.
try
{
FileInputStream x = new FileInputStream(new File("/Users/rajesh/Documents/rajesh.xls"));
//Create Workbook instance holding reference to .xlsx file
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(x);
//Get first/desired sheet from the workbook
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
//Iterate through each rows one by one
for (Iterator<Row> iterator = sheet.iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
Row row = (Row) iterator.next();
for (Iterator<Cell> iterator2 = row.iterator(); iterator2
.hasNext();) {
Cell cell = (Cell) iterator2.next();
System.out.println(cell.getStringCellValue());
}
}
x.close();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Majid Laissi
19k19 gold badges65 silver badges105 bronze badges
answered Nov 28, 2014 at 11:41
When using the apache poi 4.1.2. The celltype changes a bit. Below is an example
try {
File excel = new File("/home/name/Downloads/bb.xlsx");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(excel);
XSSFWorkbook book = new XSSFWorkbook(fis);
XSSFSheet sheet = book.getSheetAt(0);
Iterator<Row> itr = sheet.iterator();
// Iterating over Excel file in Java
while (itr.hasNext()) {
Row row = itr.next();
Iterator<Cell> cellIterator = row.cellIterator();
while (cellIterator.hasNext()) {
Cell cell = cellIterator.next();
switch (cell.getCellType()) {
case STRING:
System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue() + "t");
break;
case NUMERIC:
System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue() + "t");
break;
case BOOLEAN:
System.out.print(cell.getBooleanCellValue() + "t");
break;
default:
}
}
System.out.println("");}
}catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}
answered May 22, 2020 at 8:44
mumbasamumbasa
5526 silver badges11 bronze badges
If you go for third party library option, try using Aspose.Cells API that enables Java Applications to create (read/write) and manage Excel spreadsheets efficiently without requiring Microsoft Excel.
e.g
Sample code:
1.
//Load sample workbook
Workbook wb = new Workbook(dirPath + "sample.xlsx");
//Access first worksheet
Worksheet ws = wb.getWorksheets().get(0);
//Access cells iterator
Iterator itrat = ws.getCells().iterator();
//Print cells name in iterator
while(itrat.hasNext())
{
Cell cell = (Cell)itrat.next();
System.out.println(cell.getName() + ": " + cell.getStringValue().trim());
}
Workbook book = new Workbook("sample.xlsx");
Worksheet sheet = book.getWorksheets().get(0);
Range range = sheet.getCells().getMaxDisplayRange();//You may also create your desired range (in the worksheet) using, e.g sheet.getCells().createRange("A1", "J11");
Iterator rangeIterator = range.iterator();
while(rangeIterator.hasNext())
{
Cell cell = (Cell)rangeIterator.next();
//your code goes here.
}
Hope, this helps a bit.
PS. I am working as Support developer/ Evangelist at Aspose.
answered Sep 2, 2020 at 19:29
Amjad SahiAmjad Sahi
1,7531 gold badge9 silver badges15 bronze badges
If you need to do anything more with office documents in Java, go for POI as mentioned.
For simple reading/writing an excel document like you requested, you can use the CSV format (also as mentioned):
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CsvWriter {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
String fileName = "test.xls";
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter(fileName));
out.println("a,b,c,d");
out.println("e,f,g,h");
out.println("i,j,k,l");
out.close();
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(fileName));
String line = null;
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(line);
String sep = "";
while (scanner.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(sep + scanner.next());
sep = ",";
}
}
in.close();
}
}
answered Oct 4, 2009 at 12:02
Adriaan KosterAdriaan Koster
15.8k5 gold badges45 silver badges60 bronze badges
This will write a JTable to a tab separated file that can be easily imported into Excel. This works.
If you save an Excel worksheet as an XML document you could also build the XML file for EXCEL with code. I have done this with word so you do not have to use third-party packages.
This could code have the JTable taken out and then just write a tab separated to any text file and then import into Excel. I hope this helps.
Code:
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.swing.JTable;
import javax.swing.table.TableModel;
public class excel {
String columnNames[] = { "Column 1", "Column 2", "Column 3" };
// Create some data
String dataValues[][] =
{
{ "12", "234", "67" },
{ "-123", "43", "853" },
{ "93", "89.2", "109" },
{ "279", "9033", "3092" }
};
JTable table;
excel() {
table = new JTable( dataValues, columnNames );
}
public void toExcel(JTable table, File file){
try{
TableModel model = table.getModel();
FileWriter excel = new FileWriter(file);
for(int i = 0; i < model.getColumnCount(); i++){
excel.write(model.getColumnName(i) + "t");
}
excel.write("n");
for(int i=0; i< model.getRowCount(); i++) {
for(int j=0; j < model.getColumnCount(); j++) {
excel.write(model.getValueAt(i,j).toString()+"t");
}
excel.write("n");
}
excel.close();
}catch(IOException e){ System.out.println(e); }
}
public static void main(String[] o) {
excel cv = new excel();
cv.toExcel(cv.table,new File("C:\Users\itpr13266\Desktop\cs.tbv"));
}
}
answered Feb 26, 2014 at 22:58
Doug HaufDoug Hauf
3,0158 gold badges45 silver badges69 bronze badges
1
Рассказывает автор блога javarevisited.blogspot.ru
Из этой статьи вы сможете узнать о записи и чтении данных из Excel файлов в Java (будет рассмотрен как XLS, так и XLSX формат). Мы будем использовать библиотеку Apache POI и сосредоточимся на работе с типами String и Date, работа с последним происходит достаточно хитро. Напомню, что работу с числами мы уже рассмотрели в другой статье.
Библиотеку poi-XX.jar вы можете использовать для всех старых (xls, doc, ppt) файлов Microsoft Office, для новых (xlsx, docx, pptx) вам понадобится poi-ooxml-XX.jar. Очень важно понимать, что к чему относится, т.к. используемые классы тоже разные — для старых расширений это HSSFWorkbook, а для новых — XSSFWorkbook.
Подготовка: загрузка библиотек и зависимостей
Конечно, существует достаточно много открытых библиотек, которые позволяют работать с Excel файлами в Java, например, JXL, но мы будем использовать имеющую самый обширный API и самую популярную — Apache POI. Чтобы её использовать, вам нужно скачать jar файлы и добавить их через Eclipse вручную, или вы можете предоставить это Maven.
Во втором случае вам нужно просто добавить следующие две зависимости:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>3.12</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>3.12</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Самое удобное в Maven — что он загрузит не только указанные poi.jar и poi-ooxml.jar, но и все jar файлы, которые используются внутри, то есть xmlbeans-2.6.0.jar, stax-api-1.0.1.jar, poi-ooxml-schemas-3.12.jar и commons-codec-1.9.jar.
Если вы будете добавлять библиотеки вручную — не забудьте о вышеназванных файлах. Скачать всё можно отсюда. Помните — если вы загрузите только poi-XX.jar, то ваш код скомпилируется без ошибок, но потом упадёт с java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/apache/xmlbeans/XmlObject, так как внутри будет вызываться xmlbeans.jar.
Запись
В этом примере мы запишем в xls файл следующие данные: в первую ячейку — строку с именем, а во вторую — дату рождения. Вот пошаговая инструкция:
- Создаём объект
HSSFWorkBook; - Создаём лист, используя на объекте, созданном в предыдущем шаге,
createSheet(); - Создаём на листе строку, используя
createRow(); - Создаём в строке ячейку —
createCell(); - Задаём значение ячейки через
setCellValue(); - Записываем
workbookвFileчерезFileOutputStream; - Закрываем
workbook, вызываяclose().
Для записи строк или чисел этого вполне достаточно, но чтобы записать дату, нам понадобится сделать ещё кое-что:
- Создать
DateFormat; - Создать
CellStyle; - Записать
DateFormatвCellStyle; - Записать
CellStyleв ячейку; - Теперь в эту ячейку можно записать объект
Dateчерез всё тот жеsetCellValue; - Чтобы дата поместилась в ячейку, нам нужно добавить столбцу свойство автоматически менять размер:
sheet.autoSizeColumn(1).
Всё вместе это будет выглядеть так:
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public static void writeIntoExcel(String file) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException{
Workbook book = new HSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = book.createSheet("Birthdays");
// Нумерация начинается с нуля
Row row = sheet.createRow(0);
// Мы запишем имя и дату в два столбца
// имя будет String, а дата рождения --- Date,
// формата dd.mm.yyyy
Cell name = row.createCell(0);
name.setCellValue("John");
Cell birthdate = row.createCell(1);
DataFormat format = book.createDataFormat();
CellStyle dateStyle = book.createCellStyle();
dateStyle.setDataFormat(format.getFormat("dd.mm.yyyy"));
birthdate.setCellStyle(dateStyle);
// Нумерация лет начинается с 1900-го
birthdate.setCellValue(new Date(110, 10, 10));
// Меняем размер столбца
sheet.autoSizeColumn(1);
// Записываем всё в файл
book.write(new FileOutputStream(file));
book.close();
}
Чтение
Теперь мы считаем из только что созданного файла то, что мы туда записали.
- Для начала создадим
HSSFWorkBook, передав в конструкторFileInputStream; - Получаем лист, передавая в
getSheet()его номер или название; - Получаем строку, используя
getRow(); - Получаем ячейку, используя
getCell(); - Узнаём тип ячейки, используя на ней
getCellType(); - В зависимости от типа ячейки, читаем её значения, используя
getStringCellValue(),getNumericCellValue()илиgetDateCellValue(); - Закрываем
workbookиспользуяclose().
Напомню, что дату Excel хранит как числа, т.е. тип ячейки всё равно будет CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC.
В виде кода это будет выглядеть следующим образом:
public static void readFromExcel(String file) throws IOException{
HSSFWorkbook myExcelBook = new HSSFWorkbook(new FileInputStream(file));
HSSFSheet myExcelSheet = myExcelBook.getSheet("Birthdays");
HSSFRow row = myExcelSheet.getRow(0);
if(row.getCell(0).getCellType() == HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_STRING){
String name = row.getCell(0).getStringCellValue();
System.out.println("name : " + name);
}
if(row.getCell(1).getCellType() == HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC){
Date birthdate = row.getCell(1).getDateCellValue();
System.out.println("birthdate :" + birthdate);
}
myExcelBook.close();
}
В заключение
Как уже упомналось выше, чтение из xlsx файлов ничем принципиально не отличается — нужно только вместо HSSFWorkBook, HSSFSheet, HSSFRow (и прочих) из poi-XX.jar использовать XSSFWorkBook, XSSFSheet, XSSFRow из poi-ooxml-XX.jar. Это всё, что вам нужно знать для чтения и записи в файлы Excel. Разумеется, с помощью библиотеки Apache POI вы можете сделать гораздо больше, но эта статья должна помочь вам быстрее в ней освоиться.
Перевод статьи «How to Read Write Excel file in Java — POI Example»
- Details
- Written by
- Last Updated on 30 May 2019 | Print Email
In this tutorial, I’d love to share with you guys some examples of writing data to Excel files using the Apache POI library. If today is the first day you get to know Apache POI and you haven’t written any code snippet to read/write Excel files yet, I recommend you to read the sections 1 and 2 in the tutorial How to Read Excel Files in Java using Apache POI to understand the fundamentals of Apache POI.
Or if you are a kind of person who likes getting your hands-dirty first, let jump directly into the following examples.
1. Apache POI API Basics for Writing Excel Files
The fundamental interfaces include Workbook, Sheet, Row and Cell. For basic formatting, use the CellStyle and Font interfaces. Concrete implementing classes include:
- Excel 2003: HSSFWorkbook, HSSFSheet, HSSFRow, HSSFCell, etc.
- Excel 2007: XSSFWorkbook, XSSFSheet, XSSFRow, XSSFCell, etc.
But I recommend using the common interfaces for greater flexibility with both Excel formats 2003 (XLS) and 2007(XLSX).
Here are the basic steps for writing an Excel file:
- Create a Workbook.
- Create a Sheet.
- Repeat the following steps until all data is processed:
- Create a Row.
- Create Cellsin a Row. Apply formatting using CellStyle.
- Write to an OutputStream.
- Close the output stream.
Now, let’s see some examples that demonstrate writing a list of books to an Excel file.
2. A Simple Example to create an Excel file in Java
The following code snippet is a very simple program that demonstrates writing a list of books to an Excel file in the simplest and dirty form:
package net.codejava.excel;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
/**
* A very simple program that writes some data to an Excel file
* using the Apache POI library.
* @author www.codejava.net
*
*/
public class SimpleExcelWriterExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Java Books");
Object[][] bookData = {
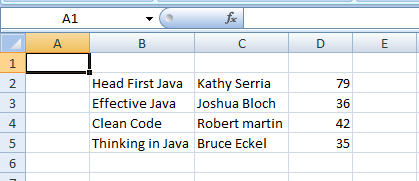
{"Head First Java", "Kathy Serria", 79},
{"Effective Java", "Joshua Bloch", 36},
{"Clean Code", "Robert martin", 42},
{"Thinking in Java", "Bruce Eckel", 35},
};
int rowCount = 0;
for (Object[] aBook : bookData) {
Row row = sheet.createRow(++rowCount);
int columnCount = 0;
for (Object field : aBook) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(++columnCount);
if (field instanceof String) {
cell.setCellValue((String) field);
} else if (field instanceof Integer) {
cell.setCellValue((Integer) field);
}
}
}
try (FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("JavaBooks.xlsx")) {
workbook.write(outputStream);
}
}
}
This program creates an Excel 2007 document which looks like the following screenshot (File: JavaBooks.xlsx):
3. A More Object-Oriented Example to create an Excel file in Java
The following code snippets demonstrate a nicer program that focuses on OOP approach. That makes the program more flexible and easy to extend or upgrade in the future.
- Create the model class (Book.java):
package net.codejava.excel; public class Book { private String title; private String author; private float price; public Book() { } public Book(String title, String author, double price) { this.title = title; this.author = author; this.price = price; } // getters and setters } - The method that writes a list of books to an Excel file (in 2003 format):
public void writeExcel(List<Book> listBook, String excelFilePath) throws IOException { Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(); Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet(); int rowCount = 0; for (Book aBook : listBook) { Row row = sheet.createRow(++rowCount); writeBook(aBook, row); } try (FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(excelFilePath)) { workbook.write(outputStream); } } - The method that writes information of a book to cells:
private void writeBook(Book aBook, Row row) { Cell cell = row.createCell(1); cell.setCellValue(aBook.getTitle()); cell = row.createCell(2); cell.setCellValue(aBook.getAuthor()); cell = row.createCell(3); cell.setCellValue(aBook.getPrice()); } - The following method creates some dummy data (a list of books):
private List<Book> getListBook() { Book book1 = new Book("Head First Java", "Kathy Serria", 79); Book book2 = new Book("Effective Java", "Joshua Bloch", 36); Book book3 = new Book("Clean Code", "Robert Martin", 42); Book book4 = new Book("Thinking in Java", "Bruce Eckel", 35); List<Book> listBook = Arrays.asList(book1, book2, book3, book4); return listBook; } - And the following code snippet is for testing:
NiceExcelWriterExample excelWriter = new NiceExcelWriterExample(); List<Book> listBook = excelWriter.getListBook(); String excelFilePath = "NiceJavaBooks.xls"; excelWriter.writeExcel(listBook, excelFilePath);
4. Formatting Cells of the Excel file
Of course you may need to format the Excel file to make it looks nicely and professionally. Formatting is diversity and quite complex so in this introductory tutorial, I just show you how to format the basics like setting font style. Here are the steps:
- Create a CellStyle object what holds formatting information:
CellStyle cellStyle = sheet.getWorkbook().createCellStyle();
- Invoke the appropriate setters to apply the formatting you want. For example:
cellStyle.setAlignment(CellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER); cellStyle.setFont(font); cellStyle.setWrapText(true);
For example, the following method writes a header row for the document with font style bold and size is 16:
private void createHeaderRow(Sheet sheet) {
CellStyle cellStyle = sheet.getWorkbook().createCellStyle();
Font font = sheet.getWorkbook().createFont();
font.setBold(true);
font.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 16);
cellStyle.setFont(font);
Row row = sheet.createRow(0);
Cell cellTitle = row.createCell(1);
cellTitle.setCellStyle(cellStyle);
cellTitle.setCellValue("Title");
Cell cellAuthor = row.createCell(2);
cellAuthor.setCellStyle(cellStyle);
cellAuthor.setCellValue("Author");
Cell cellPrice = row.createCell(3);
cellPrice.setCellStyle(cellStyle);
cellPrice.setCellValue("Price");
}
You can see the complete program (FormattedExcelWriterExample.java) which can be found in the source code attached to this article.
5. Writing both Excel 2003 and Excel 2007 formats in Java
For better flexibility (supporting both common Excel formats), I recommend writing a factory method that either returns a HSSFWorkbook or XSSFWorkbook, depending on the extension of the file (.xls or .xlsx). Here’s the method:
private Workbook getWorkbook(String excelFilePath)
throws IOException {
Workbook workbook = null;
if (excelFilePath.endsWith("xlsx")) {
workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
} else if (excelFilePath.endsWith("xls")) {
workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The specified file is not Excel file");
}
return workbook;
}
You can see the complete program (FlexibleExcelWriterExample.java) which can be found in the source code attached to this article.
That’s how to read Excel files in Java programmatically. To learn more in-depth about Java programming, this Java software developers course would be good choice.
Related Java Excel Tutorials:
- How to Read Excel Files in Java using Apache POI
- Java Example to Read Password-protected Excel Files Using Apache POI
- Java Example to Update Existing Excel Files Using Apache POI
- Working with Formula Cells in Excel using Apache POI
References
- Apache POI — the Java API for Microsoft Documents
- POI API Documentation (Javadocs)
- Apache POI Quick Guide
- Apache POI HOWTO
About the Author:

Add comment
Apache POI is a powerful Java library to work with different Microsoft Office file formats such as Excel, Power point, Visio, MS Word etc. The name POI was originally an acronym for Poor Obfuscation Implementation, referring humorously to the fact that the file formats seemed to be deliberately obfuscated, but poorly, since they were successfully reverse-engineered. In this tutorial we will use Apache POI library to perform different functions on Microsoft Excel spreadsheet. Let’s get started.
Tools & Technologies:
- Java JDK 1.5 or above
- Apache POI library v3.8 or above (download)
- Eclipse 3.2 above (optional)
1. Add Apache POI dependency
Make sure to include apache poi jar file to your project. If your project uses Maven as dependency management, add following in your Pom.xml file.
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId> <artifactId>poi</artifactId> <version>3.8</version> </dependency>
If you are not using Maven then you can directly add required JAR files in your classpath.
- Download
poi-2.5.1.jar(or in this case 3.8) jar file. - Include this file in your projects class path.
- Create new java project in eclipse with auto generated main function.
2. Read Excel File
To read an excel file, Apache POI provides certain easy-to-use APIs. In below sample code we use different classes from POI library to read content of cell from excel file. This is for quick reference.
Code language: Java (java)
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet; import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook; //.. FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream(new File("C:\test.xls")); //Get the workbook instance for XLS file HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(file); //Get first sheet from the workbook HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0); //Get iterator to all the rows in current sheet Iterator<Row> rowIterator = sheet.iterator(); //Get iterator to all cells of current row Iterator<Cell> cellIterator = row.cellIterator();
Notice how each class in POI library starts with HSSF prefix! e.g. HSSFWorkbook, HSSFSheet etc. HSSF stands for Horrible SpreadSheet Format! I’m not kidding.. It really is. Similar to HSSF, POI has different prefix for other file formats too:
- HSSF (Horrible SpreadSheet Format) – reads and writes Microsoft Excel (XLS) format files.
- XSSF (XML SpreadSheet Format) – reads and writes Office Open XML (XLSX) format files.
- HPSF (Horrible Property Set Format) – reads “Document Summary” information from Microsoft Office files.
- HWPF (Horrible Word Processor Format) – aims to read and write Microsoft Word 97 (DOC) format files.
- HSLF (Horrible Slide Layout Format) – a pure Java implementation for Microsoft PowerPoint files.
- HDGF (Horrible DiaGram Format) – an initial pure Java implementation for Microsoft Visio binary files.
- HPBF (Horrible PuBlisher Format) – a pure Java implementation for Microsoft Publisher files.
- HSMF (Horrible Stupid Mail Format) – a pure Java implementation for Microsoft Outlook MSG files
- DDF (Dreadful Drawing Format) – a package for decoding the Microsoft Office Drawing format.
Working with .xlsx files
The classes we used in above code snippet, HSSFWorkbook and HSSFSheet works for .xls format. In order to work with newer xls format viz .xlsx, you need to see newer POI classes like:
Code language: Java (java)
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet; import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet; //.. FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream(new File("C:\test.xlsx")); //Get the workbook instance for XLS file XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook (file); //Get first sheet from the workbook XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0); //Get iterator to all the rows in current sheet Iterator<Row> rowIterator = sheet.iterator(); //Get iterator to all cells of current row Iterator<Cell> cellIterator = row.cellIterator();
Use XSSFWorkbook and XSSFSheet class in all of the below examples in order to make them work with .xlsx files. Consider a sample excel file: test.xls
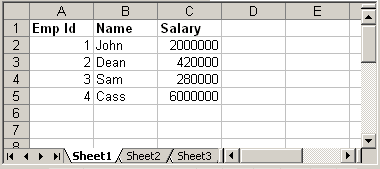
We will read above xls file using Apache POI and prints the data.
Code language: Java (java)
try { FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream(new File("C:\test.xls")); //Get the workbook instance for XLS file HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(file); //Get first sheet from the workbook HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0); //Iterate through each rows from first sheet Iterator < Row > rowIterator = sheet.iterator(); while (rowIterator.hasNext()) { Row row = rowIterator.next(); //For each row, iterate through each columns Iterator < Cell > cellIterator = row.cellIterator(); while (cellIterator.hasNext()) { Cell cell = cellIterator.next(); switch (cell.getCellType()) { case Cell.CELL_TYPE_BOOLEAN: System.out.print(cell.getBooleanCellValue() + "tt"); break; case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC: System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue() + "tt"); break; case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING: System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue() + "tt"); break; } } System.out.println(""); } file.close(); FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(new File("C:\test.xls")); workbook.write(out); out.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
The above code is self explanatory. It read the sheet from workbook and iterate through each row and cell to print its values. Just note how we use different methods like getBooleanCellValue, getNumericCellValue etc to read cell value. Before reading a cell content, we need to first determine its type using method cell.getCellType() and then call appropriate method to read content. Output:
Code language: CSS (css)
Emp Id Name Salary 1.0 John 2000000.0 2.0 Dean 420000.0 3.0 Sam 280000.0 4.0 Cass 6000000.0
3. Create New Excel File
Let us create a new excel file and write data in it. Following is the API which we will use for this purpose.
Code language: Java (java)
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet; import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook; //.. HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(); HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Sample sheet"); //Create a new row in current sheet Row row = sheet.createRow(0); //Create a new cell in current row Cell cell = row.createCell(0); //Set value to new value cell.setCellValue("Blahblah");
Below is the complete code that writes a new excel with dummy data:
Code language: Java (java)
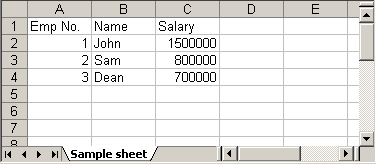
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(); HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Sample sheet"); Map < String, Object[] > data = new HashMap < String, Object[] > (); data.put("1", new Object[] { "Emp No.", "Name", "Salary" }); data.put("2", new Object[] { 1 d, "John", 1500000 d }); data.put("3", new Object[] { 2 d, "Sam", 800000 d }); data.put("4", new Object[] { 3 d, "Dean", 700000 d }); Set < String > keyset = data.keySet(); int rownum = 0; for (String key: keyset) { Row row = sheet.createRow(rownum++); Object[] objArr = data.get(key); int cellnum = 0; for (Object obj: objArr) { Cell cell = row.createCell(cellnum++); if (obj instanceof Date) cell.setCellValue((Date) obj); else if (obj instanceof Boolean) cell.setCellValue((Boolean) obj); else if (obj instanceof String) cell.setCellValue((String) obj); else if (obj instanceof Double) cell.setCellValue((Double) obj); } } try { FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(new File("C:\new.xls")); workbook.write(out); out.close(); System.out.println("Excel written successfully.."); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
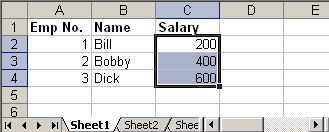
Output:
new.xls
4. Update Existing Excel File
Updating an existing excel file is straight forward. Open the excel using different API that we discussed above and set the cell’s value. One thing we need to note here is that we can update the excel file only when we close it first.
update.xls
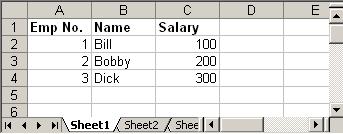
Following Java code read the above excel file and doubles the salary of each employee:
Code language: Java (java)
try { FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream(new File("C:\update.xls")); HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(file); HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0); Cell cell = null; //Update the value of cell cell = sheet.getRow(1).getCell(2); cell.setCellValue(cell.getNumericCellValue() * 2); cell = sheet.getRow(2).getCell(2); cell.setCellValue(cell.getNumericCellValue() * 2); cell = sheet.getRow(3).getCell(2); cell.setCellValue(cell.getNumericCellValue() * 2); file.close(); FileOutputStream outFile = new FileOutputStream(new File("C:\update.xls")); workbook.write(outFile); outFile.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
Steps to update excel file will be:
- Open excel file in input mode (inputstream)
- Use POI API and read the excel content
- Update cell’s value using different
setCellValuemethods. - Close the excel input file (inputstream)
- Open same excel file in output mode (outputstream)
- Write content of updated workbook in output file
- Close output excel file
Output:
update.xls
5. Adding Formulas
Apache POI provides API to add excel formulas to cell programmatically. Following method that comes handy for this:
Code language: Java (java)
cell.setCellFormula("someformula")
For example:
Code language: Java (java)
cell.setCellFormula("A2*B2*C5") //or cell.setCellFormula("SUM(A1:A7)")
Note: Formula string should not start with equal sign (=) Thus, following is incorrect way of adding formula:
Code language: Java (java)
cell.setCellFormula("=A2*B2*C5") //Ops! Won't work
The above code will throw:
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)
org.apache.poi.ss.formula.FormulaParseException: The specified formula '=A2*B2*C5' starts with an equals sign which is not allowed.
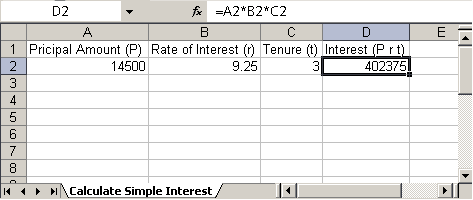
Following Java code creates a new excel sheet which calculates Simple Interest. It defines Principal amount, Rate of Interest and Tenure. We add an excel formula to calculate interest.
Code language: Java (java)
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(); HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Calculate Simple Interest"); Row header = sheet.createRow(0); header.createCell(0).setCellValue("Pricipal Amount (P)"); header.createCell(1).setCellValue("Rate of Interest (r)"); header.createCell(2).setCellValue("Tenure (t)"); header.createCell(3).setCellValue("Interest (P r t)"); Row dataRow = sheet.createRow(1); dataRow.createCell(0).setCellValue(14500 d); dataRow.createCell(1).setCellValue(9.25); dataRow.createCell(2).setCellValue(3 d); dataRow.createCell(3).setCellFormula("A2*B2*C2"); try { FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(new File("C:\formula.xls")); workbook.write(out); out.close(); System.out.println("Excel written successfully.."); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
Output:
formula.xls
Triggering Existing Excel Formulas
In certain cases your excel file might have formula defined and you may want to trigger those formulas since you updated it using POI. Following code snippet will do the trick.
Code language: Java (java)
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("/somepath/test.xls"); Workbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook(fis); //or new XSSFWorkbook("C:\test.xls") FormulaEvaluator evaluator = wb.getCreationHelper().createFormulaEvaluator(); for (int sheetNum = 0; sheetNum < wb.getNumberOfSheets(); sheetNum++) { Sheet sheet = wb.getSheetAt(sheetNum); for (Row r: sheet) { for (Cell c: r) { if (c.getCellType() == Cell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA) { evaluator.evaluateFormulaCell(c); } } } }
We use FormulaEvaluator class to evaluate formula defined in each of the cell.
6. Adding Styles to Cell
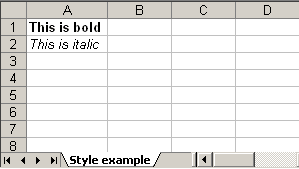
Adding style to a cell is also piece of cake. Check following example which creates two new cell one with bold font and another with italic and add text to it.
Code language: Java (java)
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(); HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("Style example"); HSSFFont font = workbook.createFont(); font.setBoldweight(HSSFFont.BOLDWEIGHT_BOLD); HSSFCellStyle style = workbook.createCellStyle(); style.setFont(font); Row row = sheet.createRow(0); Cell cell = row.createCell(0); cell.setCellValue("This is bold"); cell.setCellStyle(style); font = workbook.createFont(); font.setItalic(true); style = workbook.createCellStyle(); style.setFont(font); row = sheet.createRow(1); cell = row.createCell(0); cell.setCellValue("This is italic"); cell.setCellStyle(style); try { FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(new File("C:\style.xls")); workbook.write(out); out.close(); System.out.println("Excel written successfully.."); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
Output:
style.xls
6.1 Add Background Color to the cell
Changing background color of the cell is a bit tricky. Ideally we assume setting background color will have some API like setFillBackgroundColor, but surprisingly to set background color of a cell, we have to set the foreground color :D. See below API.
Code language: Java (java)
cellStyle.setFillForegroundColor(HSSFColor.GREY_25_PERCENT.index);
So use setFillForegroundColor method to set the background color of given cell. I hope this article is useful.
No matter how Microsoft is doing in comparison with Google, Microsoft Office is still the most used application in software world. Other alternatives like OpenOffice and LiberOffice have failed to take off to challenge MS Office. What this mean to a Java application developer? Because of huge popularity of MS office products you often need to support Microsoft office format such as word, Excel, PowerPoint and additionally Adobe PDF. If you are using JSP Servlet, display tag library automatically provides Excel, Word and PDF support. Since JDK doesn’t provide direct API to read and write Microsoft Excel and Word document, you have to rely on third party library to do your job. Fortunately there are couple of open source library exists to read and write Microsoft Office XLS and XLSX file format, Apache POI is the best one. It is widely used, has strong community support and it is feature rich.
You can find lot of examples of how to do with Excel using Apache POI online, which means you will never feel alone and has instant Google support if you stuck there. In this article, we will learn how to read and write excel files in Java. As I said, Excel files has two popular format .XLS (produced by Microsoft Officer version prior to 2007 e.g. MS Office 2000 and 2003) and .XLSX (created by Microsoft Office 2007 onwards e.g. MS Office 2010 and 2013).
Fortunately Apache POI supports both format, and you can easily create, read, write and update Excel files using this library. It uses terms like workbook, worksheet, cell, row to keep itself aligned with Microsoft Excel and that’s why it is very easy to use. Apache POI also provides different implementation classes to handle both XLS and XLSX file format.
One interesting thing with POI is that (I don’t know whether it’s intentional, accidentally or real) it has got some really funny names for its workbook implementations like
- XSSF (XML SpreadSheet Format) – Used to reading and writting Open Office XML (XLSX) format files.
- HSSF (Horrible SpreadSheet Format) – Use to read and write Microsoft Excel (XLS) format files.
- HWPF (Horrible Word Processor Format) – to read and write Microsoft Word 97 (DOC) format files.
- HSMF (Horrible Stupid Mail Format) – pure Java implementation for Microsoft Outlook MSG files
- HDGF (Horrible DiaGram Format) – One of the first pure Java implementation for Microsoft Visio binary files.
- HPSF (Horrible Property Set Format) – For reading “Document Summary” information from Microsoft Office files.
- HSLF (Horrible Slide Layout Format) – a pure Java implementation for Microsoft PowerPoint files.
- HPBF (Horrible PuBlisher Format) – Apache’s pure Java implementation for Microsoft Publisher files.
- DDF (Dreadful Drawing Format) – Apache POI package for decoding the Microsoft Office Drawing format.
It’s very important that you know full form of these acronyms, otherwise it would be difficult to keep track of which implementation is for which format. If you are only concerned about reading Excel files then at-least remember XSSF and HSSF classes e.g. XSSFWorkBook and HSSFWorkBook.
How to Read Excel File (XLSX) in Java
In our first example, we will learn about reading the current popular Excel file format i.e. file with extension .XLSX. This is a XML spreadsheet format and other spreadsheet software like OpenOffice and LiberOffice also use this format. In order to read Excel file, you need to first download Apache POI Jar files, without these your code will neither compiler nor execute.
If you hate to maintain JARs by yourself, use Maven. In Eclipse IDE, you can download M2Eclipse plug-in to setup Maven project. Once you done that, add the following dependencies in your pom.xml (project object model) file.
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId> <artifactId>poi</artifactId> <version>3.11-beta2</version> </dependency>
By the way, as Norbert pointed out, The classes for OOXML format (such as XSSF for reading .xlsx format) are in a different Jar file. You need to include the poi-ooxml jar in your project, along with the dependencies for it. When you add poi-ooxml JAR as dependency via Maven, it will also add other required dependencies by itself. For example, adding below XML snippet in pom.xml will download four JAR files
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId> <artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId> <version>3.11-beta2</version> </dependency>
poi-ooxml-3.11-beta2.jar
poi-ooxml-schemas-3.11-beta2.jar
xmlbeans-2.6.0.jar
stax-api-1.0.1.jar
If you are not using Maven then add the following JAR files in your Java program’s classpath
poi-3.11-beta2.jar
commons-codec-1.9.jar
poi-ooxml-3.11-beta2.jar
poi-ooxml-schemas-3.11-beta2.jar
xmlbeans-2.6.0.jar
stax-api-1.0.1.jar
Here is how our sample Excel 2013 File looks like, remember this has saved in .xlsx format.
add here is code to read that Excel file. The first two lines are very common, they are to read file from the file system in Java, real code starts from 3rd line. Here we are passing a binary InputStream to create an instance of XSSFWorkBook class, which represents an Excel workbook.
The next line gives us a worksheet from the book, and from there we are just going through each row and then each column. Cell represents a block in Excel, also known as cell. This is where we read or write data.
A cell can be any type e.g. String, numeric or boolean. Before reading the value you must ascertain the correct type of cell. After that just call corresponding value method e.g. getStringValue() or getNumericValue() to read data from cell.
This how exactly you read rows and columns from an Excel file in Java. You can see we have used two for loop, one to iterate over all rows and the inner loop is to go through each column.
File myFile = new File("C://temp/Employee.xlsx"); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(myFile); // Finds the workbook instance for XLSX file XSSFWorkbook myWorkBook = new XSSFWorkbook (fis); // Return first sheet from the XLSX workbook XSSFSheet mySheet = myWorkBook.getSheetAt(0); // Get iterator to all the rows in current sheet Iterator<Row> rowIterator = mySheet.iterator(); // Traversing over each row of XLSX file while (rowIterator.hasNext()) { Row row = rowIterator.next(); // For each row, iterate through each columns Iterator<Cell> cellIterator = row.cellIterator(); while (cellIterator.hasNext()) { Cell cell = cellIterator.next(); switch (cell.getCellType()) { case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING: System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue() + "t"); break; case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC: System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue() + "t"); break; case Cell.CELL_TYPE_BOOLEAN: System.out.print(cell.getBooleanCellValue() + "t"); break; default : } } System.out.println(""); }
Let me know if you have trouble understanding any of lines. They are very simple and self-explanatory but if you need additional detail, just drop us a comment.
How to write XLSX File in Java
Writing into Excel file is also similar to reading, The workbook and worksheet classes will remain same, all you will do is to create new rows, columns and cells. Once you are done creating new rows in your Excel file in memory, you need to open an output stream to write that data into your Excel File.
This will save all updates you made in an existing file or in a new file which is created by Java’s File class.
Here is a step by step code of updating an existing Excel file in Java. In first couple of lines we are creating rows in form of object array and storing them as values in HashMap with key as row number.
After that, we loop through HashMap and insert each row at the end of the last row, in other words we are appending rows in our Excel file. Just like before reading we need to determine type of cell, we also need to do the same thing before writing data into cell.
This is done by using instanceof keyword of Java. Once you are done with appending all rows form Map to Excel file, save the file by opening a FileOutputStream and saving data into file system.
// Now, let’s write some data into our XLSX file
Map<String, Object[]> data = new HashMap<String, Object[]>(); data.put("7", new Object[] {7d, "Sonya", "75K", "SALES", "Rupert"}); data.put("8", new Object[] {8d, "Kris", "85K", "SALES", "Rupert"}); data.put("9", new Object[] {9d, "Dave", "90K", "SALES", "Rupert"}); // Set to Iterate and add rows into XLS file Set<String> newRows = data.keySet(); // get the last row number to append new data int rownum = mySheet.getLastRowNum(); for (String key : newRows) { // Creating a new Row in existing XLSX sheet Row row = mySheet.createRow(rownum++); Object [] objArr = data.get(key); int cellnum = 0; for (Object obj : objArr) { Cell cell = row.createCell(cellnum++); if (obj instanceof String) { cell.setCellValue((String) obj); } else if (obj instanceof Boolean) { cell.setCellValue((Boolean) obj); } else if (obj instanceof Date) { cell.setCellValue((Date) obj); } else if (obj instanceof Double) { cell.setCellValue((Double) obj); } } } // open an OutputStream to save written data into XLSX file FileOutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(myFile); myWorkBook.write(os); System.out.println("Writing on XLSX file Finished ..."); Output Writing on XLSX file Finished ...
Here is how our updated Excel file looks after adding three more rows
How to read Excel (XLS) file in Java
Reading XLS file is no different than reading an XLSX format file, all you need to do is to use correct workbook implementation for XLS format e.g. instead of using XSSFWorkbook and XSSFSheet , you need to use HSSFWorkbook and HSSFSheet classes from Apache POI library. As I said before, POI has got some really funny names for different XLS formats e.g. Horrible SpreadSheet Format to represent old Microsoft Excel file format (.xls). Remembering them can be hard but you can always refer to their online Javadoc. You can reuse rest of code given in this example, for example you can use same code snippet to iterate over rows, columns and from reading/writing into a particular cell. Given they are two different format, some features will not be available on XLS file processors but all basic stuff remain same.
Error and Exception
If you happen to use incorrect classes e.g. instead of using XSSFWorkbook to read XLSX file, if you use HSSFWorkbook then you will see following error :
Exception in thread "main" org.apache.poi.poifs. filesystem.OfficeXmlFileException: The supplied data appears to be in the Office 2007+ XML. You are calling the part of POI that deals with OLE2 Office Documents. You need to call a different part of POI to process this data (eg XSSF instead of HSSF) at org.apache.poi.poifs.storage.HeaderBlock.<init>(HeaderBlock.java:131) at org.apache.poi.poifs.storage.HeaderBlock.<init>(HeaderBlock.java:104) at org.apache.poi.poifs.filesystem.POIFSFileSystem.<init>(POIFSFileSystem.java:128) at org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook.<init>(HSSFWorkbook.java:361) at org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook.<init>(HSSFWorkbook.java:342) at App.main(App.java:25)
Java Program to Read/Write Excel Files using Apache POI
Here is our full Java program to read/write from existing Excel files in Java. If you are using Eclipse IDE, just create a Java Project, copy the code and paste it there. No need to create proper package structure and Java source file with the same name, Eclipse will take care of that. If you have Maven and Eclipse plugins installed, instead create a Maven Java project, this will also help you to download Apache POI Jar files.
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.sql.Date; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell; import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row; import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet; import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook; /** * Sample Java program to read and write Excel file in Java using Apache POI * */ public class XLSXReaderWriter { public static void main(String[] args) { try { File excel = new File("C://temp/Employee.xlsx"); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(excel); XSSFWorkbook book = new XSSFWorkbook(fis); XSSFSheet sheet = book.getSheetAt(0); Iterator<Row> itr = sheet.iterator(); // Iterating over Excel file in Java while (itr.hasNext()) { Row row = itr.next(); // Iterating over each column of Excel file Iterator<Cell> cellIterator = row.cellIterator(); while (cellIterator.hasNext()) { Cell cell = cellIterator.next(); switch (cell.getCellType()) { case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING: System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue() + "t"); break; case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC: System.out.print(cell.getNumericCellValue() + "t"); break; case Cell.CELL_TYPE_BOOLEAN: System.out.print(cell.getBooleanCellValue() + "t"); break; default: } } System.out.println(""); } // writing data into XLSX file Map<String, Object[]> newData = new HashMap<String, Object[]>(); newData.put("7", new Object[] { 7d, "Sonya", "75K", "SALES", "Rupert" }); newData.put("8", new Object[] { 8d, "Kris", "85K", "SALES", "Rupert" }); newData.put("9", new Object[] { 9d, "Dave", "90K", "SALES", "Rupert" }); Set<String> newRows = newData.keySet(); int rownum = sheet.getLastRowNum(); for (String key : newRows) { Row row = sheet.createRow(rownum++); Object[] objArr = newData.get(key); int cellnum = 0; for (Object obj : objArr) { Cell cell = row.createCell(cellnum++); if (obj instanceof String) { cell.setCellValue((String) obj); } else if (obj instanceof Boolean) { cell.setCellValue((Boolean) obj); } else if (obj instanceof Date) { cell.setCellValue((Date) obj); } else if (obj instanceof Double) { cell.setCellValue((Double) obj); } } } // open an OutputStream to save written data into Excel file FileOutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(excel); book.write(os); System.out.println("Writing on Excel file Finished ..."); // Close workbook, OutputStream and Excel file to prevent leak os.close(); book.close(); fis.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException fe) { fe.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException ie) { ie.printStackTrace(); } } } Output ID NAME SALARY DEPARTMENT MANGER 1.0 John 70K IT Steve 2.0 Graham 80K DATA Carl 3.0 Sodhi 60K IT Ram 4.0 Ram 100K IT Alex 5.0 Carl 150K DATA Alex 7.0 Sonya 75K SALES Rupert 9.0 Dave 90K SALES Rupert 8.0 Kris 85K SALES Rupert Writing on Excel file Finished ...
That’s all about how to read and write Excel files in Java. We have learned to read/write both XLS and XLSX format in Java, which is key to support old Microsoft Excel files created using the Microsoft Office version prior to 2007. Though there are couple of other alternative libraries to read Excel files from Java program, but Apache POI is the best one and you should use it whenever possible. Let me know if you face any problem while running this program in your Eclipse IDE or from command prompt. Just make sure to include right set of JAR in your CLASSPATH, alternatively used Maven to download JAR.