На чтение 16 мин. Просмотров 14.8k.

Malcolm Gladwell
Мечтатель начинает с чистого листа бумаги и переосмысливает мир
Эта статья содержит полное руководство по использованию Excel
VBA Worksheet в Excel VBA. Если вы хотите узнать, как что-то сделать быстро, ознакомьтесь с кратким руководством к рабочему листу VBA ниже.
Если вы новичок в VBA, то эта статья — отличное место для начала. Мне нравится разбивать вещи на простые термины и объяснять их на простом языке.
Вы можете прочитать статью от начала до конца, так как она написана в логическом порядке. Или, если предпочитаете, вы можете использовать оглавление ниже и перейти непосредственно к теме по вашему выбору.
Содержание
- Краткое руководство к рабочему листу VBA
- Вступление
- Доступ к рабочему листу
- Использование индекса для доступа к рабочему листу
- Использование кодового имени рабочего листа
- Активный лист
- Объявление объекта листа
- Доступ к рабочему листу в двух словах
- Добавить рабочий лист
- Удалить рабочий лист
- Цикл по рабочим листам
- Использование коллекции листов
- Заключение
Краткое руководство к рабочему листу VBA
В следующей таблице приведен краткий обзор различных методов
Worksheet .
Примечание. Я использую Worksheet в таблице ниже, не указывая рабочую книгу, т.е. Worksheets, а не ThisWorkbook.Worksheets, wk.Worksheets и т.д. Это сделано для того, чтобы примеры были понятными и удобными для чтения. Вы должны всегда указывать рабочую книгу при использовании Worksheets . В противном случае активная рабочая книга будет использоваться по умолчанию.
| Задача | Исполнение |
| Доступ к рабочему листу по имени |
Worksheets(«Лист1») |
| Доступ к рабочему листу по позиции слева |
Worksheets(2) Worksheets(4) |
| Получите доступ к самому левому рабочему листу |
Worksheets(1) |
| Получите доступ к самому правому листу |
Worksheets(Worksheets.Count) |
| Доступ с использованием кодового имени листа (только текущая книга) |
Смотри раздел статьи Использование кодового имени |
| Доступ по кодовому имени рабочего листа (другая рабочая книга) |
Смотри раздел статьи Использование кодового имени |
| Доступ к активному листу | ActiveSheet |
| Объявить переменную листа | Dim sh As Worksheet |
| Назначить переменную листа | Set sh = Worksheets(«Лист1») |
| Добавить лист | Worksheets.Add |
| Добавить рабочий лист и назначить переменную |
Worksheets.Add Before:= Worksheets(1) |
| Добавить лист в первую позицию (слева) |
Set sh =Worksheets.Add |
| Добавить лист в последнюю позицию (справа) |
Worksheets.Add after:=Worksheets(Worksheets.Count) |
| Добавить несколько листов | Worksheets.Add Count:=3 |
| Активировать рабочий лист | sh.Activate |
| Копировать лист | sh.Copy |
| Копировать после листа | sh1.Copy After:=Sh2 |
| Скопировать перед листом | sh1.Copy Before:=Sh2 |
| Удалить рабочий лист | sh.Delete |
| Удалить рабочий лист без предупреждения |
Application.DisplayAlerts = False sh.Delete Application.DisplayAlerts = True |
| Изменить имя листа | sh.Name = «Data» |
| Показать/скрыть лист | sh.Visible = xlSheetHidden sh.Visible = xlSheetVisible sh.Name = «Data» |
| Перебрать все листы (For) | Dim i As Long For i = 1 To Worksheets.Count Debug.Print Worksheets(i).Name Next i |
| Перебрать все листы (For Each) | Dim sh As Worksheet For Each sh In Worksheets Debug.Print sh.Name Next |
Вступление
Три наиболее важных элемента VBA — это Рабочая книга, Рабочий лист и Ячейки. Из всего кода, который вы пишете, 90% будут включать один или все из них.
Наиболее распространенное использование Worksheet в VBA для доступа к его ячейкам. Вы можете использовать его для защиты, скрытия, добавления, перемещения или копирования листа.
Тем не менее, вы будете в основном использовать его для выполнения некоторых действий с одной или несколькими ячейками на листе.
Использование Worksheets более простое, чем использование рабочих книг. С книгами вам может потребоваться открыть их, найти, в какой папке они находятся, проверить, используются ли они, и так далее. С рабочим листом он либо существует в рабочей книге, либо его нет.
Доступ к рабочему листу
В VBA каждая рабочая книга имеет коллекцию рабочих листов. В этой коллекции есть запись для каждого рабочего листа. Эта коллекция называется просто Worksheets и используется очень похоже на коллекцию Workbooks. Чтобы получить доступ к рабочему листу, достаточно указать имя.
Приведенный ниже код записывает «Привет Мир» в ячейках A1 на листах: Лист1, Лист2 и Лист3 текущей рабочей книги.
Sub ZapisVYacheiku1()
' Запись в ячейку А1 в листе 1, листе 2 и листе 3
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Лист1").Range("A1") = "Привет Мир"
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Лист2").Range("A1") = "Привет Мир"
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Лист3").Range("A1") = "Привет Мир"
End Sub
Коллекция Worksheets всегда принадлежит книге. Если мы не
указываем рабочую книгу, то активная рабочая книга используется по умолчанию.
Sub ZapisVYacheiku1()
' Worksheets относятся к рабочим листам в активной рабочей книге.
Worksheets("Лист1").Range("A1") = "Привет Мир"
Worksheets("Лист2").Range("A1") = "Привет Мир"
Worksheets("Лист3").Range("A1") = "Привет Мир"
End Sub
Скрыть рабочий лист
В следующих примерах показано, как скрыть и показать лист.
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Лист1").Visible = xlSheetHidden
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Лист1").Visible = xlSheetVisible
Если вы хотите запретить пользователю доступ к рабочему
листу, вы можете сделать его «очень скрытым». Это означает, что это может быть
сделано видимым только кодом.
' Скрыть от доступа пользователя
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Лист1").Visible = xlVeryHidden
' Это единственный способ сделать лист xlVeryHidden видимым
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Лист1").Visible = xlSheetVisible
Защитить рабочий лист
Другой пример использования Worksheet — когда вы хотите защитить его.
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Лист1").Protect Password:="Мойпароль"
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Лист1").Unprotect Password:="Мойпароль"
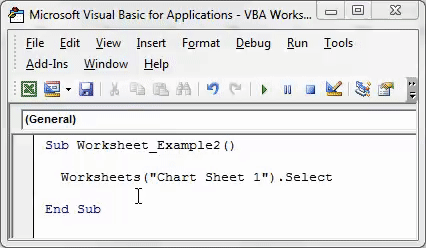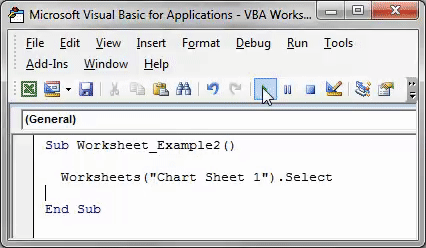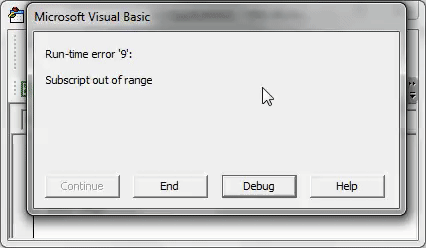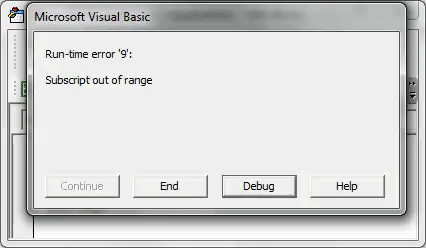
Индекс вне диапазона
При использовании Worksheets вы можете получить сообщение об
ошибке:
Run-time Error 9 Subscript out of Range
Это означает, что вы пытались получить доступ к рабочему листу, который не существует. Это может произойти по следующим причинам:
- Имя Worksheet , присвоенное рабочим листам, написано неправильно.
- Название листа изменилось.
- Рабочий лист был удален.
- Индекс был большим, например Вы использовали рабочие листы (5), но есть только четыре рабочих листа
- Используется неправильная рабочая книга, например Workbooks(«book1.xlsx»).Worksheets(«Лист1») вместо
Workbooks(«book3.xlsx»).Worksheets («Лист1»).
Если у вас остались проблемы, используйте один из циклов из раздела «Циклы по рабочим листам», чтобы напечатать имена всех рабочих листов коллекции.
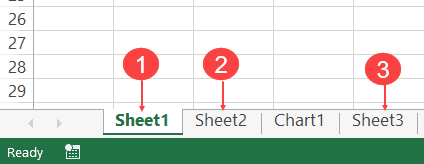
Использование индекса для доступа к рабочему листу
До сих пор мы использовали имя листа для доступа к листу.
Указатель относится к положению вкладки листа в рабочей книге. Поскольку
положение может быть легко изменено пользователем, не рекомендуется
использовать это.
В следующем коде показаны примеры использования индекса.
' Использование этого кода является плохой идеей, так как
' позиции листа все время меняются
Sub IspIndList()
With ThisWorkbook
' Самый левый лист
Debug.Print .Worksheets(1).Name
' Третий лист слева
Debug.Print .Worksheets(3).Name
' Самый правый лист
Debug.Print .Worksheets(.Worksheets.Count).Name
End With
End Sub
В приведенном выше примере я использовал Debug.Print для печати в Immediate Window. Для просмотра этого окна выберите «Вид» -> «Immediate Window » (Ctrl + G).
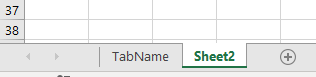
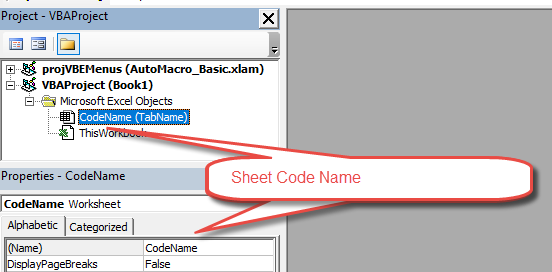
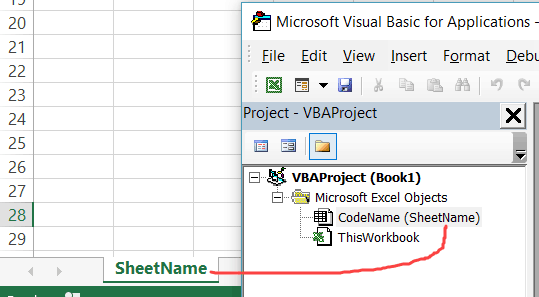
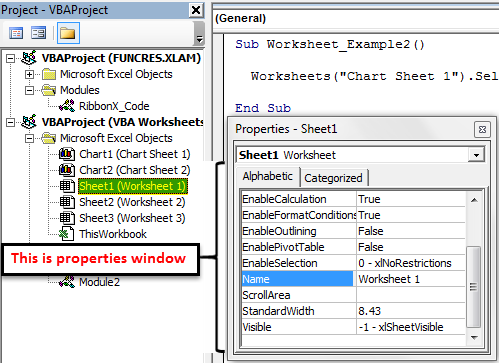
Использование кодового имени рабочего листа
Лучший способ получить доступ к рабочему листу —
использовать кодовое имя. Каждый лист имеет имя листа и кодовое имя. Имя листа
— это имя, которое отображается на вкладке листа в Excel.
Изменение имени листа не приводит к изменению кодового имени, что означает, что ссылка на лист по кодовому имени — отличная идея.
Если вы посмотрите в окне свойств VBE, вы увидите оба имени.
На рисунке вы можете видеть, что кодовое имя — это имя вне скобок, а имя листа
— в скобках.
Вы можете изменить как имя листа, так и кодовое имя в окне
свойств листа (см. Изображение ниже).
Если ваш код ссылается на кодовое имя, то пользователь может
изменить имя листа, и это не повлияет на ваш код. В приведенном ниже примере мы
ссылаемся на рабочий лист напрямую, используя кодовое имя.
Sub IspKodImya2()
' Используя кодовое имя листа
Debug.Print CodeName.Name
CodeName.Range("A1") = 45
CodeName.Visible = True
End Sub
Это делает код легким для чтения и безопасным от изменения
пользователем имени листа.
Кодовое имя в других книгах
Есть один недостаток использования кодового имени. Он относится только к рабочим листам в рабочей книге, которая содержит код, т.е. ThisWorkbook.
Однако мы можем использовать простую функцию, чтобы найти
кодовое имя листа в другой книге.
Sub ИспЛист()
Dim sh As Worksheet
' Получить рабочий лист под кодовым именем
Set sh = SheetFromCodeName("CodeName", ThisWorkbook)
' Используйте рабочий лист
Debug.Print sh.Name
End Sub
' Эта функция получает объект листа из кодового имени
Public Function SheetFromCodeName(Name As String, bk As Workbook) As Worksheet
Dim sh As Worksheet
For Each sh In bk.Worksheets
If sh.CodeName = Name Then
Set SheetFromCodeName = sh
Exit For
End If
Next sh
End Function
Использование приведенного выше кода означает, что если
пользователь изменит имя рабочего листа, то на ваш код это не повлияет.
Существует другой способ получения имени листа внешней
рабочей книги с использованием кодового имени. Вы можете использовать элемент
VBProject этой Рабочей книги.
Вы можете увидеть, как это сделать, в примере ниже. Я включил это, как дополнительную информацию, я бы рекомендовал использовать метод из предыдущего примера, а не этот.
Public Function SheetFromCodeName2(codeName As String _
, bk As Workbook) As Worksheet
' Получить имя листа из CodeName, используя VBProject
Dim sheetName As String
sheetName = bk.VBProject.VBComponents(codeName).Properties("Name")
' Используйте имя листа, чтобы получить объект листа
Set SheetFromCodeName2 = bk.Worksheets(sheetName)
End Function
Резюме кодового имени
Ниже приведено краткое описание использования кодового имени:
- Кодовое имя рабочего листа может быть
использовано непосредственно в коде, например. Sheet1.Range - Кодовое имя будет по-прежнему работать, если имя
рабочего листа будет изменено. - Кодовое имя может использоваться только для
листов в той же книге, что и код. - Везде, где вы видите ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
(«имя листа»), вы можете заменить его кодовым именем рабочего листа. - Вы можете использовать функцию SheetFromCodeName
сверху, чтобы получить кодовое имя рабочих листов в других рабочих книгах.
Активный лист
Объект ActiveSheet ссылается на рабочий лист, который в данный момент активен. Вы должны использовать ActiveSheet только в том случае, если у вас есть особая необходимость ссылаться на активный лист.
В противном случае вы должны указать рабочий лист, который
вы используете.
Если вы используете метод листа, такой как Range, и не
упоминаете лист, он по умолчанию будет использовать активный лист.
' Написать в ячейку A1 в активном листе
ActiveSheet.Range("A1") = 99
' Активный лист используется по умолчанию, если лист не используется
Range("A1") = 99
Объявление объекта листа
Объявление объекта листа полезно для того, чтобы сделать ваш
код более понятным и легким для чтения.
В следующем примере показан код для обновления диапазонов
ячеек. Первый Sub не объявляет объект листа. Вторая подпрограмма объявляет
объект листа, и поэтому код намного понятнее.
Sub NeObyavObektList()
Debug.Print ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Лист1").Name
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Лист1").Range("A1") = 6
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Лист1").Range("B2:B9").Font.Italic = True
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Лист1").Range("B2:B9").Interior.Color = rgbRed
End Sub
Sub ObyavObektList()
Dim sht As Worksheet
Set sht = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Лист1")
sht.Range("A1") = 6
sht.Range("B2:B9").Font.Italic = True
sht.Range("B2:B9").Interior.Color = rgbRed
End Sub
Вы также можете использовать ключевое слово With с объектом
листа, как показано в следующем примере.
Sub ObyavObektListWith()
Dim sht As Worksheet
Set sht = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Лист1")
With sht
.Range("A1") = 6
.Range("B2:B9").Font.Italic = True
.Range("B2:B9").Interior.Color = rgbRed
End With
End Sub
Доступ к рабочему листу в двух словах
Из-за множества различных способов доступа к рабочему листу вы можете быть сбитыми с толку. Так что в этом разделе я собираюсь разбить его на простые термины.
- Если вы хотите использовать тот лист, который активен в данный момент, используйте ActiveSheet.
ActiveSheet.Range("A1") = 55
2. Если лист находится в той же книге, что и код, используйте кодовое имя.
3. Если рабочая таблица находится в другой рабочей книге, сначала получите рабочую книгу, а затем получите рабочую таблицу.
' Получить рабочую книгу
Dim wk As Workbook
Set wk = Workbooks.Open("C:ДокументыСчета.xlsx", ReadOnly:=True)
' Затем получите лист
Dim sh As Worksheet
Set sh = wk.Worksheets("Лист1")
Если вы хотите защитить пользователя от изменения имени листа, используйте функцию SheetFromCodeName из раздела «Имя кода».
' Получить рабочую книгу
Dim wk As Workbook
Set wk = Workbooks.Open("C:ДокументыСчета.xlsx", ReadOnly:=True)
' Затем получите лист
Dim sh As Worksheet
Set sh = SheetFromCodeName("sheetcodename",wk)
Добавить рабочий лист
Примеры в этом разделе показывают, как добавить новую
рабочую таблицу в рабочую книгу. Если вы не предоставите никаких аргументов для
функции Add, то новый
рабочий лист будет помещен перед активным рабочим листом.
Когда вы добавляете рабочий лист, он создается с именем по умолчанию, например «Лист4». Если вы хотите изменить имя, вы можете легко сделать это, используя свойство Name.
В следующем примере добавляется новый рабочий лист и изменяется имя на «Счета». Если лист с именем «Счета» уже существует, вы получите сообщение об ошибке.
Sub DobavitList()
Dim sht As Worksheet
' Добавляет новый лист перед активным листом
Set sht = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets.Add
' Установите название листа
sht.Name = "Счета"
' Добавляет 3 новых листа перед активным листом
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets.Add Count:=3
End Sub
В предыдущем примере вы добавляете листы по отношению к
активному листу. Вы также можете указать точную позицию для размещения листа.
Для этого вам нужно указать, какой лист новый лист должен
быть вставлен до или после. Следующий код показывает вам, как это сделать.
Sub DobavitListPervPosl()
Dim shtNew As Worksheet
Dim shtFirst As Worksheet, shtLast As Worksheet
With ThisWorkbook
Set shtFirst = .Worksheets(1)
Set shtLast = .Worksheets(.Worksheets.Count)
' Добавляет новый лист на первую позицию в книге
Set shtNew = Worksheets.Add(Before:=shtFirst)
shtNew.Name = "FirstSheet"
' Добавляет новый лист к последней позиции в книге
Set shtNew = Worksheets.Add(After:=shtLast)
shtNew.Name = "LastSheet"
End With
End Sub
Удалить рабочий лист
Чтобы удалить лист, просто вызовите Delete.
Dim sh As Worksheet
Set sh = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Лист12")
sh.Delete
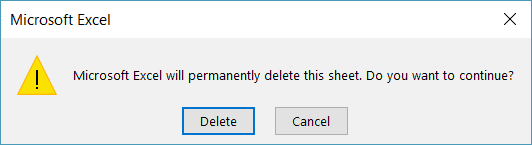
Excel отобразит предупреждающее сообщение при удалении листа. Если вы хотите скрыть это сообщение, вы можете использовать код ниже:
Application.DisplayAlerts = False sh.Delete Application.DisplayAlerts = True
Есть два аспекта, которые нужно учитывать при удалении таблиц.
Если вы попытаетесь получить доступ к рабочему листу после
его удаления, вы получите ошибку «Subscript out of Range», которую мы видели в
разделе «Доступ к рабочему листу».
Dim sh As Worksheet
Set sh = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Лист2")
sh.Delete
' Эта строка выдаст «Subscript out of Range», так как «Лист2» не существует
Set sh = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Лист2")
Вторая проблема — когда вы назначаете переменную листа. Если вы попытаетесь использовать эту переменную после удаления листа, вы получите ошибку автоматизации, подобную этой:
Run-Time error -21147221080 (800401a8′) Automation Error
Если вы используете кодовое имя рабочего листа, а не
переменную, это приведет к сбою Excel,
а не к ошибке автоматизации.
В следующем примере показано, как происходят ошибки автоматизации.
sh.Delete ' Эта строка выдаст ошибку автоматизации Debug.Assert sh.Name
Если вы назначите переменную Worksheet действительному рабочему листу, он будет работать нормально.
sh.Delete
' Назначить sh на другой лист
Set sh = Worksheets("Лист3")
' Эта строка будет работать нормально
Debug.Assert sh.Name
Цикл по рабочим листам
Элемент «Worksheets» — это набор рабочих листов, принадлежащих рабочей книге. Вы можете просмотреть каждый лист в коллекции рабочих листов, используя циклы «For Each» или «For».
В следующем примере используется цикл For Each.
Sub CiklForEach()
' Записывает «Привет Мир» в ячейку A1 для каждого листа
Dim sht As Worksheet
For Each sht In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
sht.Range("A1") = "Привет Мир"
Next sht
End Sub
В следующем примере используется стандартный цикл For.
Sub CiklFor()
' Записывает «Привет Мир» в ячейку A1 для каждого листа
Dim i As Long
For i = 1 To ThisWorkbook.Worksheets.Count
ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(i).Range("A1") = "Привет Мир"
Next sht
End Sub
Вы видели, как получить доступ ко всем открытым рабочим книгам и как получить доступ ко всем рабочим листам в ThisWorkbook. Давайте сделаем еще один шаг вперед — узнаем, как получить доступ ко всем рабочим листам во всех открытых рабочих книгах.
Примечание. Если вы используете код, подобный этому, для записи на листы, то сначала сделайте резервную копию всего, так как в итоге вы можете записать неверные данные на все листы.
Sub NazvVsehStr()
' Печатает рабочую книгу и названия листов для
' всех листов в открытых рабочих книгах
Dim wrk As Workbook
Dim sht As Worksheet
For Each wrk In Workbooks
For Each sht In wrk.Worksheets
Debug.Print wrk.Name + ":" + sht.Name
Next sht
Next wrk
End Sub
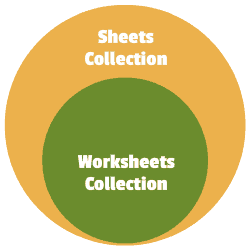
Использование коллекции листов
Рабочая книга имеет еще одну коллекцию, похожую на Worksheets под названием Sheets. Это иногда путает пользователей. Чтобы понять, в первую очередь, вам нужно знать о типе листа, который является диаграммой.
В Excel есть возможность создать лист, который является диаграммой. Для этого нужно:
- Создать диаграмму на любом листе.
- Щелкнуть правой кнопкой мыши на графике и выбрать «Переместить».
- Выбрать первый вариант «Новый лист» и нажмите «ОК».
Теперь у вас есть рабочая книга, в которой есть типовые листы и лист-диаграмма.
- Коллекция «Worksheets » относится ко всем рабочим листам в рабочей книге. Не включает в себя листы типа диаграммы.
- Коллекция Sheets относится ко всем листам, принадлежащим книге, включая листы типовой диаграммы.
Ниже приведены два примера кода. Первый проходит через все
листы в рабочей книге и печатает название листа и тип листа. Второй пример
делает то же самое с коллекцией Worksheets.
Чтобы опробовать эти примеры, вы должны сначала добавить лист-диаграмму в свою книгу, чтобы увидеть разницу.
Sub KollSheets()
Dim sht As Variant
' Показать название и тип каждого листа
For Each sht In ThisWorkbook.Sheets
Debug.Print sht.Name & " is type " & TypeName(sht)
Next sht
End Sub
Sub KollWorkSheets()
Dim sht As Variant
' Показать название и тип каждого листа
For Each sht In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
Debug.Print sht.Name & " is type " & TypeName(sht)
Next sht
End Sub
Если у вас нет листов диаграмм, то использование коллекции Sheets — то же самое, что использование коллекции WorkSheets.
Заключение
На этом мы завершаем статью о Worksheet VBA. Я надеюсь, что было полезным.
Три наиболее важных элемента Excel VBA — это рабочие книги, рабочие таблицы, диапазоны и ячейки.
Эти элементы будут использоваться практически во всем, что вы делаете. Понимание их сделает вашу жизнь намного проще и сделает изучение VBA увлекательнее.
In this Article
- Sheets Vs. Worksheets
- Referencing Sheets
- ActiveSheet
- Sheet Name
- Sheet Index Number
- Sheet “Code Name”
- Referencing Sheets in Other Workbooks
- Activate vs. Select Sheet
- Activate a Sheet
- Select a Sheet
- Select Multiple Sheets
- Worksheet Variable
- Loop Through All Sheets in Workbook
- Worksheet Protection
- Workbook Protection
- Worksheet Protection
- Protect Worksheet
- Unprotect Worksheet
- Worksheet Visible Property
- Unhide Worksheet
- Hide Worksheet
- Very Hide Worksheet
- Worksheet-Level Events
- Worksheet Activate Event
- Worksheet Change Event
- Worksheet Cheat Sheet
- VBA Worksheets Cheatsheet
This is the ultimate guide to working with Excel Sheets / Worksheets in VBA.
At the bottom of this guide, we’ve created a cheat sheet of common commands for working with sheets.
Sheets Vs. Worksheets
There are two ways to reference Sheets using VBA. The first is with the Sheets object:
Sheets("Sheet1").ActivateThe other is with the Worksheets object:
Worksheets("Sheet1").Activate99% of the time, these two objects are identical. In fact, if you’ve searched online for VBA code examples, you’ve probably seen both objects used. Here is the difference:
The Sheets Collection contains Worksheets AND Chart Sheets.
So use Sheets if you want to include regular Worksheets AND Chart Sheets. Use Worksheets if you want to exclude Chart Sheets. For the rest of this guide we will use Sheets and Worksheets interchangeably.
Referencing Sheets
There are several different ways to reference Sheets:
- ActiveSheet
- Sheet Tab Name
- Sheet Index Number
- Sheet Code Name
ActiveSheet
The ActiveSheet is the Sheet that’s currently active. In other words, if you paused your code and looked at Excel, it’s the sheet that is visible. The below code example will display a MessageBox with the ActiveSheet name.
MsgBox ActiveSheet.NameSheet Name
You are probably most familiar with referencing Sheets by their Tab Name:
Sheets("TabName").ActivateThis is the sheet name that’s visible to Excel users. Enter it into the sheets object, as a string of text, surrounded by quotations.
Sheet Index Number
The Sheet Index number is the sheet position in the workbook. 1 is the first sheet. 2 is the second sheet etc.:
Sheets(1).ActivateSheet Index Number – Last Sheet in Workbook
To reference the last Sheet in the workbook, use Sheets.Count to get the last Index Number and activate that sheet:
Sheets(Sheets.Count).ActivateSheet “Code Name”
The Sheet Code Name is it’s Object name in VBA:
CodeName.ActivateVBA Coding Made Easy
Stop searching for VBA code online. Learn more about AutoMacro — A VBA Code Builder that allows beginners to code procedures from scratch with minimal coding knowledge and with many time-saving features for all users!
Learn More
Referencing Sheets in Other Workbooks
It’s also easy to reference Sheets in other Workbooks. To do so, you need to use the Workbooks Object:
Workbooks("VBA_Examples.xlsm").Worksheets("Sheet1").ActivateImportant: The Workbook must be open before you can reference its Sheets.
Activate vs. Select Sheet
In another article we discuss everything about activating and selecting sheets. The short version is this:
When you Activate a Sheet it becomes the ActiveSheet. This is the sheet you would see if you looked at your Excel program. Only one sheet may be activate at a time.
Activate a Sheet
Sheets("Sheet1").ActivateWhen you select a Sheet, it also becomes the ActiveSheet. However, you can select multiple sheets at once. When multiple sheets are selected at once, the “top” sheet is the ActiveSheet. However, you can toggle the ActiveSheet within selected sheets.
VBA Programming | Code Generator does work for you!
Select a Sheet
Sheets("Sheet1").SelectSelect Multiple Sheets
Use an array to select multiple sheets at once:
Worksheets(Array("Sheet2", "Sheet3")).SelectWorksheet Variable
Assigning a worksheet to an object variable allows you to reference the worksheet by it’s variable name. This can save a lot of typing and make your code easier to read. There are also many other reasons you might want to use variables.
To declare a worksheet variable:
Dim ws as worksheetAssign a worksheet to a variable:
Set ws = Sheets("Sheet1")Now you can reference the worksheet variable in your code:
ws.ActivateLoop Through All Sheets in Workbook
Worksheet variables are useful when you want to loop through all the worksheets in a workbook. The easiest way to do this is:
Dim ws as Worksheet
For Each ws in Worksheets
MsgBox ws.name
Next wsThis code will loop through all worksheets in the workbook, displaying each worksheet name in a message box. Looping through all the sheets in a workbook is very useful when locking / unlocking or hiding / unhiding multiple worksheets at once.
Worksheet Protection
AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Workbook Protection
Workbook protection locks the workbook from structural changes like adding, deleting, moving, or hiding worksheets.
You can turn on workbook protection using VBA:
ActiveWorkbook.Protect Password:="Password"or disable workbook protection:
ActiveWorkbook.UnProtect Password:="Password"Note: You can also protect / unprotect without a password by omitting the Password argument:
ActiveWorkbook.ProtectWorksheet Protection
Worksheet-level protection prevents changes to individual worksheets.
Protect Worksheet
Worksheets("Sheet1").Protect "Password"Unprotect Worksheet
Worksheets("Sheet1").Unprotect "Password"There are a variety of options when protecting worksheets (allow formatting changes, allow user to insert rows, etc.) We recommend using the Macro Recorder to record your desired settings.
We discuss worksheet protection in more detail here.
AutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Worksheet Visible Property
You might already know that worksheets can be hidden:
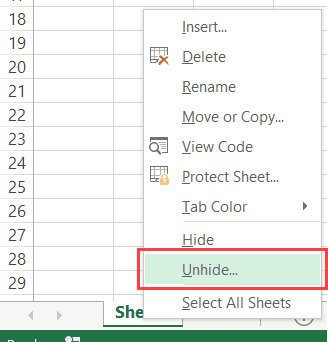
There are actually three worksheet visibility settings: Visible, Hidden, and VeryHidden. Hidden sheets can be unhidden by any regular Excel user – by right-clicking in the worksheet tab area (shown above). VeryHidden sheets can only be unhidden with VBA code or from within the VBA Editor. Use the following code examples to hide / unhide worksheets:
Unhide Worksheet
Worksheets("Sheet1").Visible = xlSheetVisibleHide Worksheet
Worksheets("Sheet1").visible = xlSheetHiddenVery Hide Worksheet
Worksheets("Sheet1").Visible = xlSheetVeryHiddenAutoMacro | Ultimate VBA Add-in | Click for Free Trial!
Worksheet-Level Events
Events are triggers that can cause “Event Procedures” to run. For example, you can cause code to run every time any cell on a worksheet is changed or when a worksheet is activated.
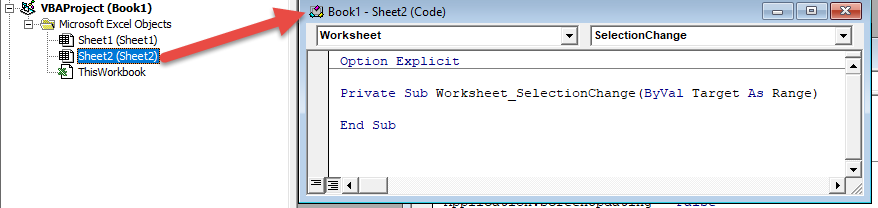
Worksheet event procedures must be placed in a worksheet module:
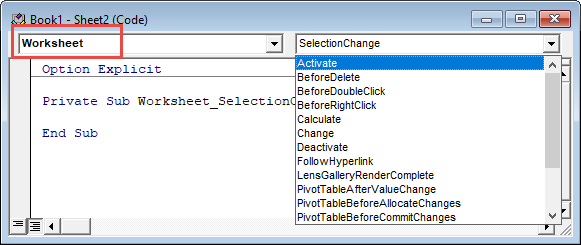
There are numerous worksheet events. To see a complete list, go to a worksheet module, select “Worksheet” from the first drop-down. Then selecting an event procedure from the second drop-down to insert it into the module.
Worksheet Activate Event
Worksheet activate events run each time the worksheet is opened.
Private Sub Worksheet_Activate()
Range("A1").Select
End SubThis code will select cell A1 (resetting the view area to the top-left of the worksheet) each time the worksheet is opened.
Worksheet Change Event
Worksheet change events run whenever a cell value is changed on the worksheet. Read our tutorial about Worksheet Change Events for more information.
Worksheet Cheat Sheet
Below you will find a cheat sheet containing common code examples for working with sheets in VBA
VBA Worksheets Cheatsheet
VBA worksheets Cheatsheet
| Description | Code Example |
|---|---|
| Referencing and Activating Sheets | |
| Tab Name | Sheets(«Input»).Activate |
| VBA Code Name | Sheet1.Activate |
| Index Position | Sheets(1).Activate |
| Select Sheet | |
| Select Sheet | Sheets(«Input»).Select |
| Set to Variable | Dim ws as Worksheet Set ws = ActiveSheet |
| Name / Rename | ActiveSheet.Name = «NewName» |
| Next Sheet | ActiveSheet.Next.Activate |
| Loop Through all Sheets | Dim ws as Worksheet
For each ws in Worksheets |
| Loop Through Selected Sheets | Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In ActiveWindow.SelectedSheets |
| Get ActiveSheet | MsgBox ActiveSheet.Name |
| Add Sheet | Sheets.Add |
| Add Sheet and Name | Sheets.Add.Name = «NewSheet» |
| Add Sheet With Name From Cell | Sheets.Add.Name = range(«a3»).value |
| Add Sheet After Another | Sheets.Add After:=Sheets(«Input») |
| Add Sheet After and Name | Sheets.Add(After:=Sheets(«Input»)).Name = «NewSheet» |
| Add Sheet Before and Name | Sheets.Add(Before:=Sheets(«Input»)).Name = «NewSheet» |
| Add Sheet to End of Workbook | Sheets.Add After:=Sheets(Sheets.Count) |
| Add Sheet to Beginning of Workbook | Sheets.Add(Before:=Sheets(1)).Name = «FirstSheet» |
| Add Sheet to Variable | Dim ws As Worksheet Set ws = Sheets.Add |
| Copy Worksheets | |
| Move Sheet to End of Workbook | Sheets(«Sheet1»).Move After:=Sheets(Sheets.Count) |
| To New Workbook | Sheets(«Sheet1»).Copy |
| Selected Sheets To New Workbook | ActiveWindow.SelectedSheets.Copy |
| Before Another Sheet | Sheets(«Sheet1»).Copy Before:=Sheets(«Sheet2») |
| Before First Sheet | Sheets(«Sheet1»).Copy Before:=Sheets(1) |
| After Last Sheet | Sheets(«Sheet1»).Copy After:=Sheets(Sheets.Count) |
| Copy and Name | Sheets(«Sheet1»).Copy After:=Sheets(Sheets.Count) ActiveSheet.Name = «LastSheet» |
| Copy and Name From Cell Value | Sheets(«Sheet1»).Copy After:=Sheets(Sheets.Count) ActiveSheet.Name = Range(«A1»).Value |
| To Another Workbook | Sheets(«Sheet1»).Copy Before:=Workbooks(«Example.xlsm»).Sheets(1) |
| Hide / Unhide Sheets | |
| Hide Sheet | Sheets(«Sheet1»).visible = False or Sheets(«Sheet1»).visible = xlSheetHidden |
| Unhide Sheet | Sheets(«Sheet1»).Visible = True or Sheets(«Sheet1»).Visible = xlSheetVisible |
| Very Hide Sheet | Sheets(Sheet1).Visible = xlSheetVeryHidden |
| Delete or Clear Sheets | |
| Delete Sheet | Sheets(«Sheet1»).Delete |
| Delete Sheet (Error Handling) | On Error Resume Next Sheets(«Sheet1»).Delete On Error GoTo 0 |
| Delete Sheet (No Prompt) | Application.DisplayAlerts = False Sheets(«Sheet1»).Delete Application.DisplayAlerts = True |
| Clear Sheet | Sheets(«Sheet1»).Cells.Clear |
| Clear Sheet Contents Only | Sheets(«Sheet1»).Cells.ClearContents |
| Clear Sheet UsedRange | Sheets(«Sheet1»).UsedRange.Clear |
| Protect or Unprotect Sheets | |
| Unprotect (No Password) | Sheets(«Sheet1»).Unprotect |
| Unprotect (Password) | Sheets(«Sheet1»).Unprotect «Password» |
| Protect (No Password) | Sheets(«Sheet1»).Protect |
| Protect (Password) | Sheets(«Sheet1»).Protect «Password» |
| Protect but Allow VBA Access | Sheets(«Sheet1»).Protect UserInterfaceOnly:=True |
| Unprotect All Sheets | Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In Worksheets |
Home / VBA / VBA Objects / VBA Worksheet Object -Working with Excel Worksheet in VBA
In VBA, the worksheet object represents a single worksheet that is a part of the workbook’s worksheets (or sheets) collection. Using the worksheet object, you can refer to the worksheet in a VBA code, and refer to a worksheet you can also get access to the properties, methods, and events related to it.
Here’s a small snapshot of where a worksheet stands in the Excel object hierarchy.
Application ➪ Workbook ➪ Worksheets ➪ Worksheet
In this tutorial, we will learn about using and referring to a worksheet in Excel using a VBA code.
Helpful Links: Run a Macro – Macro Recorder – Visual Basic Editor – Personal Macro Workbook
Sheets Vs. Worksheets
First thing first. This is important to understand the difference between a worksheet and a sheet. In Excel, you have types of sheets that you can insert into a workbook, and a worksheet is one of those types. As you can see in the below snapshot when you insert a new sheet Excel asks you to select the sheet type.
Here’s the point to understand: When you use the word “Sheets” you are referring to all the sheets (Worksheets, Macro Sheets, and Chart Sheets), but when you use the word “Worksheet” you are referring only to the worksheets (see also).

Accessing a Worksheet (Sheet) using VBA
VBA gives you different ways to access a worksheet from a workbook, and ahead, we will see different ways to do that.
1. Refer to a Sheet using the Name
Every sheet has its name to identify it, and you can use it to refer to that sheet as well. Let’s say you want to refer to the “Sheet1”, the code would be:

Sheets(“Sheet1”)
Worksheets(“Sheet1”)Both above codes refer to the “Sheet1”.
2. Refer to Sheet using Number
You can also use a sheet’s number to refer to it. Let’s if a sheet is at the fifth position in the workbook then you can use this number to refer to it.
Sheets (5)
Worksheets (5)Now here above two lines of code work in two different ways. The first line refers to the 5th sheet, and the second line refers to the 5th worksheet in the workbook.

3. Refer to the ActiveSheet
If a sheet is already active, then you can refer to it, using the keyword “Activesheet” instead of its name.
ActiveSheetIf you want to perform an activity in the ActiveSheet, you can use the “Activesheet” object, but if you skip using it, VBA will still perform the activity in the active sheet.
Read: Select a Range using VBA
4. Refer to a Sheet using Code Window Name
Each sheet has its code window, and there’s a name to that code window. Usually, a user can change the sheet name from the tab, but the name that you have in the code window can’t be changed unless you do it from the properties.
Open the Visual Basic Editor from the Developer Tab, and in the properties section, you can see the name of the sheet that you have selected.

And you can also change this name from the properties section.

Now you can refer to it by using the code window name.
mySheet5. Refer to More than One Sheet
You can also refer to more than one sheet in one go using a single line of code. For this, you can use an array, just like the following code.
Sheets(Array("Sheet1", "Sheet2"))This code refers to “Sheet1” and “Sheet2”, but, there’s one thing that you need to understand when you refer to more than one sheet, there are a few methods and properties that you can’t use.
6. Refer to Sheet in a Different Workbook
A worksheet or a sheet is a part of the worksheets collection in a workbook, and if you want to refer to a specific sheet other than the active workbook, then you need to refer to that workbook first.
Workbooks("Book1").Sheets("Sheet1")To run this code, you need to have “Book1” open.
Properties, Methods, and Events Related to a Sheet or a Worksheet
In VBA, each Excel object has some properties, methods, and events that you can use, and in the same way, you can access the properties and methods that come with it. Once you specify a worksheet, type a dot (.), and you’ll get the list.

In this list, all the icons where you can see a hand are properties, and where you have green brick are methods.
Property Example
Let’s say you want to change the color of the worksheet’s tab, in this case, you can use the TAB property of the worksheet.
mySheet.Tab.ThemeColor = xlThemeColorAccent2In the above line of code, you have the tab property and further theme color property to change the tab color of the worksheet.
Method Example
In the same way, you can use the methods that come with worksheets. One of the most common methods is the “Select” method that you can use to select a sheet.
mySheet.SelectThe moment you run this code, it selects the “mySheet” from the active workbook.
Event Example
Some events are associated with a worksheet. For example, when you activate a sheet, that’s an event, and in the same way, when you change something within the sheet. See the following code where you have code to run when an event (change in the worksheet) happens.

Private Sub Worksheet_SelectionChange(ByVal Target As Range)
Range("A1").Value = Range("A1").Value + 1
End SubThis code enters a value in the cell A1 of the sheet every time you make a change in the worksheet.
Declaring a Worksheet Object
You can also declare a variable as a worksheet, making it easy to use that worksheet in a VBA code. First, use the DIM keyword, and then the name of the variable. After that, specify the object type as a worksheet.

More on VBA Worksheets
Activate a Sheet | Add a New Sheet | Copy a Sheet | Rename a Sheet | Hide a Sheet | Delete Sheet | Protect Sheet | Clear a Sheet | Check IF Sheet Exists | Loop Through Each Sheet in the Workbook | Count Sheets
- VBA Tutorial
Apart from cells and ranges, working with worksheets is another area you should know about to use VBA efficiently in Excel.
Just like any object in VBA, worksheets have different properties and methods associated with it that you can use while automating your work with VBA in Excel.
In this tutorial, I will cover ‘Worksheets’ in detail and also show you some practical examples.
So let’s get started.
All the codes I mention in this tutorial need to be placed in the VB Editor. Go to the ‘Where to Put the VBA Code‘ section to know how it works.
If you’re interested in learning VBA the easy way, check out my Online Excel VBA Training.
Difference between Worksheets and Sheets in VBA
In VBA, you have two collections that can be a bit confusing at times.
In a workbook, you can have worksheets and as well as chart sheets. The example below has three worksheets and one chart sheet.
In Excel VBA:
- The ‘Worksheets’ collection would refer to the collection of all the worksheet objects in a workbook. In the above example, the Worksheets collection would consist of three worksheets.
- The ‘Sheets’ collection would refer to all the worksheets as well as chart sheets in the workbook. In the above example, it would have four elements – 3 Worksheets + 1 Chart sheet.
If you have a workbook that only has worksheets and no chart sheets, then ‘Worksheets’ and ‘Sheets’ collection is the same.
But when you have one or more chart sheets, the ‘Sheets’ collection would be bigger than the ‘Worksheets’ collection
Sheets = Worksheets + Chart Sheets
Now with this distinction, I recommend being as specific as possible when writing a VBA code.
So if you have to refer to worksheets only, use the ‘Worksheets’ collection, and if you have to refer to all sheets (including chart sheets), the use the ‘Sheets’ collection.
In this tutorial, I will be using the ‘Worksheets’ collection only.
Referencing a Worksheet in VBA
There are many different ways you can use to refer to a worksheet in VBA.
Understanding how to refer to worksheets would help you write better code, especially when you’re using loops in your VBA code.
Using the Worksheet Name
The easiest way to refer to a worksheet is to use its name.
For example, suppose you have a workbook with three worksheets – Sheet 1, Sheet 2, Sheet 3.
And you want to activate Sheet 2.
You can do that using the following code:
Sub ActivateSheet()
Worksheets("Sheet2").Activate
End Sub
The above code asks VBA to refer to Sheet2 in the Worksheets collection and activate it.
Since we are using the exact sheet name, you can also use the Sheets collection here. So the below code would also do that same thing.
Sub ActivateSheet()
Sheets("Sheet2").Activate
End Sub
Using the Index Number
While using the sheet name is an easy way to refer to a worksheet, sometimes, you may not know the exact name of the worksheet.
For example, if you’re using a VBA code to add a new worksheet to the workbook, and you don’t know how many worksheets are already there, you would not know the name of the new worksheet.
In this case, you can use the index number of the worksheets.
Suppose you have the following sheets in a workbook:
The below code would activate Sheet2:
Sub ActivateSheet() Worksheets(2).Activate End Sub
Note that we have used index number 2 in Worksheets(2). This would refer to the second object in the collection of the worksheets.
Now, what happens when you use 3 as the index number?
It will select Sheet3.
If you’re wondering why it selected Sheet3, as it’s clearly the fourth object.
This happens because a chart sheet is not a part of the worksheets collection.
So when we use the index numbers in the Worksheets collection, it will only refer to the worksheets in the workbook (and ignore the chart sheets).
On the contrary, if you’re using Sheets, Sheets(1) would refer to Sheets1, Sheets(2) would refer to Sheet2, Sheets(3) would refer to Chart1 and Sheets(4) would refer to Sheet3.
This technique of using index number is useful when you want to loop through all the worksheets in a workbook. You can count the number of worksheets and then loop through these using this count (we will see how to do this later in this tutorial).
Note: The index number goes from left to right. So if you shift Sheet2 to the left of Sheet1, then Worksheets(1) would refer to Sheet2.
Using the Worksheet Code Name
One of the drawbacks of using the sheet name (as we saw in the section above) is that a user can change it.
And if the sheet name has been changed, your code wouldn’t work until you change the name of the worksheet in the VBA code as well.
To tackle this problem, you can use the code name of the worksheet (instead of the regular name that we have been using so far). A code name can be assigned in the VB Editor and doesn’t change when you change the name of the sheet from the worksheet area.
To give your worksheet a code name, follow the below steps:
- Click the Developer tab.
- Click the Visual Basic button. This will open the VB Editor.
- Click the View option in the menu and click on Project Window. This will make the Properties pane visible. If the Properties pane is already visible, skip this step.
- Click on the sheet name in the project explorer that you want to rename.
- In the Properties pane, change the name in the field in front of (Name). Note that you can’t have spaces in the name.
The above steps would change the name of your Worksheet in the VBA backend. In the Excel worksheet view, you can name the worksheet whatever you want, but in the backend, it will respond to both the names – the sheet name and the code name.
In the above image, the sheet name is ‘SheetName’ and the code name is ‘CodeName’. Even if you change the sheet name on the worksheet, the code name still remains the same.
Now, you can use either the Worksheets collection to refer to the worksheet or use the codename.
For example, both the line will activate the worksheet.
Worksheets("Sheetname").Activate
CodeName.Activate
The difference in these two is that if you change the name of the worksheet, the first one wouldn’t work. But the second line would continue to work even with the changed name. The second line (using the CodeName) is also shorter and easier to use.
Referring to a Worksheet in a Different Workbook
If you want to refer to a worksheet in a different workbook, that workbook needs to be open while the code runs, and you need to specify the name of the workbook and the worksheet that you want to refer to.
For example, if you have a workbook with the name Examples and you want to activate Sheet1 in the Example workbook, you need to use the below code:
Sub SheetActivate()
Workbooks("Examples.xlsx").Worksheets("Sheet1").Activate
End Sub
Note that if the workbook has been saved, you need to use the file name along with the extension. If you’re not sure what name to use, take help from Project Explorer.
In case the workbook has not been saved, you don’t need to use the file extension.
Adding a Worksheet
The below code would add a worksheet (as the first worksheet – i.e., as the leftmost sheet in the sheet tab).
Sub AddSheet() Worksheets.Add End Sub
It takes the default name Sheet2 (or any other number based on how many sheets are already there).
If you want a worksheet to be added before a specific worksheet (say Sheet2), then you can use the below code.
Sub AddSheet()
Worksheets.Add Before:=Worksheets("Sheet2")
End Sub
The above code tells VBA to add a sheet and then uses the ‘Before’ statement to specify the worksheet before which the new worksheet should to be inserted.
Similarly, you can also add a sheet after a worksheet (say Sheet2), using the below code:
Sub AddSheet()
Worksheets.Add After:=Worksheets("Sheet2")
End Sub
If you want the new sheet to be added to the end of the sheets, you need to first know how many sheets are there. The following code first counts the number of sheets, and the adds the new sheet after the last sheet (to which we refer using the index number).
Sub AddSheet() Dim SheetCount As Integer SheetCount = Worksheets.Count Worksheets.Add After:=Worksheets(SheetCount) End Sub
Deleting a Worksheet
The below code would delete the active sheet from the workbook.
Sub DeleteSheet() ActiveSheet.Delete End Sub
The above code would show a warning prompt before deleting the worksheet.
If you don’t want to see the warning prompt, use the below code:
Sub DeleteSheet() Application.DisplayAlerts = False ActiveSheet.Delete Application.DisplayAlerts = True End Sub
When Application.DisplayAlerts is set to False, it will not show you the warning prompt. If you use it, remember to set it back to True at the end of the code.
Remember that you can’t undo this delete, so use the above code when you’re absolutely sure.
If you want to delete a specific sheet, you can do that using the following code:
Sub DeleteSheet()
Worksheets("Sheet2").Delete
End Sub
You can also use the code name of the sheet to delete it.
Sub DeleteSheet() Sheet5.Delete End Sub
Renaming the Worksheets
You can modify the name property of the Worksheet to change its name.
The following code will change the name of Sheet1 to ‘Summary’.
Sub RenameSheet()
Worksheets("Sheet1").Name = "Summary"
End Sub
You can combine this with the adding sheet method to have a set of sheets with specific names.
For example, if you want to insert four sheets with the name 2018 Q1, 2018 Q2, 2018 Q3, and 2018 Q4, you can use the below code.
Sub RenameSheet() Dim Countsheets As Integer Countsheets = Worksheets.Count For i = 1 To 4 Worksheets.Add after:=Worksheets(Countsheets + i - 1) Worksheets(Countsheets + i).Name = "2018 Q" & i Next i End Sub
In the above code, we first count the number of sheets and then use a For Next loop to insert new sheets at the end. As the sheet is added, the code also renames it.
Assigning Worksheet Object to a Variable
When working with worksheets, you can assign a worksheet to an object variable, and then use the variable instead of the worksheet references.
For example, if you want to add a year prefix to all the worksheets, instead of counting the sheets and the running the loop that many numbers of times, you can use the object variable.
Here is the code that will add 2018 as a prefix to all the worksheet’s names.
Sub RenameSheet() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In Worksheets Ws.Name = "2018 - " & Ws.Name Next Ws End Sub
The above code declares a variable Ws as the worksheet type (using the line ‘Dim Ws As Worksheet’).
Now, we don’t need to count the number of sheets to loop through these. Instead, we can use ‘For each Ws in Worksheets’ loop. This will allow us to go through all the sheets in the worksheets collection. It doesn’t matter whether there are 2 sheets or 20 sheets.
While the above code allows us to loop through all the sheets, you can also assign a specific sheet to a variable.
In the below code, we assign the variable Ws to Sheet2 and use it to access all of Sheet2’s properties.
Sub RenameSheet()
Dim Ws As Worksheet
Set Ws = Worksheets("Sheet2")
Ws.Name = "Summary"
Ws.Protect
End Sub
Once you set a worksheet reference to an object variable (using the SET statement), that object can be used instead of the worksheet reference. This can be helpful when you have a long complicated code and you want to change the reference. Instead of making the change everywhere, you can simply make the change in the SET statement.
Note that the code declares the Ws object as the Worksheet type variable (using the line Dim Ws as Worksheet).
Hide Worksheets Using VBA (Hidden + Very Hidden)
Hiding and Unhiding worksheets in Excel is a straightforward task.
You can hide a worksheet and the user would not see it when he/she opens the workbook. However, they can easily unhide the worksheet by right-clicking on any sheet tab.
But what if you don’t want them to be able to unhide the worksheet(s).
You can do this using VBA.
The code below would hide all the worksheets in the workbook (except the active sheet), such that you can not unhide it by right-clicking on the sheet name.
Sub HideAllExcetActiveSheet() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets If Ws.Name <> ActiveSheet.Name Then Ws.Visible = xlSheetVeryHidden Next Ws End Sub
In the above code, the Ws.Visible property is changed to xlSheetVeryHidden.
- When the Visible property is set to xlSheetVisible, the sheet is visible in the worksheet area (as worksheet tabs).
- When the Visible property is set to xlSheetHidden, the sheet is hidden but the user can unhide it by right-clicking on any sheet tab.
- When the Visible property is set to xlSheetVeryHidden, the sheet is hidden and cannot be unhidden from worksheet area. You need to use a VBA code or the properties window to unhide it.
If you want to simply hide sheets, that can be unhidden easily, use the below code:
Sub HideAllExceptActiveSheet() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets If Ws.Name <> ActiveSheet.Name Then Ws.Visible = xlSheetHidden Next Ws End Sub
The below code would unhide all the worksheets (both hidden and very hidden).
Sub UnhideAllWoksheets() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets Ws.Visible = xlSheetVisible Next Ws End Sub
Related Article: Unhide All Sheets In Excel (at one go)
Hide Sheets Based on the Text in it
Suppose you have multiple sheets with the name of different departments or years and you want to hide all the sheets except the ones that have the year 2018 in it.
You can do this using a VBA INSTR function.
The below code would hide all the sheets except the ones with the text 2018 in it.
Sub HideWithMatchingText() Dim Ws As Worksheet For Each Ws In Worksheets If InStr(1, Ws.Name, "2018", vbBinaryCompare) = 0 Then Ws.Visible = xlSheetHidden End If Next Ws End Sub
In the above code, the INSTR function returns the position of the character where it finds the matching string. If it doesn’t find the matching string, it returns 0.
The above code checks whether the name has the text 2018 in it. If it does, nothing happens, else the worksheet is hidden.
You can take this a step further by having the text in a cell and using that cell in the code. This will allow you to have a value in the cell and then when you run the macro, all the sheets, except the one with the matching text in it, would remain visible (along with the sheets where you’re entering the value in the cell).
Sorting the Worksheets in an Alphabetical Order
Using VBA, you can quickly sort the worksheets based on their names.
For example, if you have a workbook that has sheets for different department or years, then you can use the below code to quickly sort these sheets in an ascending order.
Sub SortSheetsTabName() Application.ScreenUpdating = False Dim ShCount As Integer, i As Integer, j As Integer ShCount = Sheets.Count For i = 1 To ShCount - 1 For j = i + 1 To ShCount If Sheets(j).Name < Sheets(i).Name Then Sheets(j).Move before:=Sheets(i) End If Next j Next i Application.ScreenUpdating = True End Sub
Note that this code works well with text names and in most of the cases with years and numbers too. But it can give you the wrong results in case you have the sheet names as 1,2,11. It will sort and give you the sequence 1, 11, 2. This is because it does the comparison as text and considers 2 bigger than 11.
Protect/Unprotect All the Sheets at One Go
If you have a lot of worksheets in a workbook and you want to protect all the sheets, you can use the VBA code below.
It allows you to specify the password within the code. You will need this password to unprotect the worksheet.
Sub ProtectAllSheets() Dim ws As Worksheet Dim password As String password = "Test123" 'replace Test123 with the password you want For Each ws In Worksheets ws.Protect password:=password Next ws End Sub
The following code would unprotect all the sheets in one go.
Sub ProtectAllSheets() Dim ws As Worksheet Dim password As String password = "Test123" 'replace Test123 with the password you used while protecting For Each ws In Worksheets ws.Unprotect password:=password Next ws End Sub
Creating a Table of Contents of All Worksheets (with Hyperlinks)
If you have a set of worksheets in the workbook and you want to quickly insert a summary sheet which has the links to all the sheets, you can use the below code.
Sub AddIndexSheet() Worksheets.Add ActiveSheet.Name = "Index" For i = 2 To Worksheets.Count ActiveSheet.Hyperlinks.Add Anchor:=Cells(i - 1, 1), _ Address:="", SubAddress:=Worksheets(i).Name & "!A1", _ TextToDisplay:=Worksheets(i).Name Next i End Sub
The above code inserts a new worksheet and names it Index.
It then loops through all the worksheets and creates a hyperlink for all the worksheets in the Index sheet.
Where to Put the VBA Code
Wondering where the VBA code goes in your Excel workbook?
Excel has a VBA backend called the VBA editor. You need to copy and paste the code into the VB Editor module code window.
Here are the steps to do this:
- Go to the Developer tab.
- Click on the Visual Basic option. This will open the VB editor in the backend.
- In the Project Explorer pane in the VB Editor, right-click on any object for the workbook in which you want to insert the code. If you don’t see the Project Explorer go to the View tab and click on Project Explorer.
- Go to Insert and click on Module. This will insert a module object for your workbook.
- Copy and paste the code in the module window.
You May Also Like the Following Excel VBA Tutorials:
- Working with Workbooks using VBA.
- Using IF Then Else Statements in VBA.
- For Next Loop in VBA.
- Creating a User-Defined Function in Excel.
- How to Record a Macro in Excel.
- How to Run a Macro in Excel.
- Excel VBA Events – An Easy (and Complete) Guide.
- How to Create an Add-in in Excel.
- How to Save and Reuse Macro using Excel Personal Macro Workbook.
- Using Active Cell in VBA in Excel (Examples)
- How to Open Excel Files Using VBA (Examples)
Excel VBA Worksheets
Excel is a workbook. In that workbook, it contains worksheets or sheets. Understanding the concept of Worksheets in VBA is important because we all work with worksheets. In a normal Excel file, we call it sheets, but in VBA terminology, it is called a “Worksheet.” All the collections of a worksheet are called “Worksheets.”
In VBA, a Worksheet is an object. Therefore, there are two ways of referring to the worksheet, one using the “Worksheet” object and another using the “Sheets” object.
We know your question is what the difference between them is. We can see two sheets in Excel: regular worksheets and chart sheets.
The “worksheet” tab in excel considers only the worksheets in the workbook except for chart sheets. On the other hand, “Sheets” considers all the worksheets in the workbook, including the chart sheet. For example, look at the below image.
In the above, we have a total of 5 sheets. Of these 5 sheets, 3 are worksheets, and 2 are chart sheets.
Here, the “Worksheet” count is 3, and the “Sheets” count is 2.
Now, look at the below image.
All the sheets are worksheets, so the count of both “Worksheets” and “Sheets” is 3.
So, as part of the code, if you want to use worksheets, and objects, remember this point.
Table of contents
- Excel VBA Worksheets
- Syntax of VBA Worksheets
- How to use Worksheets Object in VBA?
- Example #1
- Example #2 – Select Worksheets by Name
- Example #3 – Problem with Worksheet Name
- Example #4 – Get the Count of Total Sheets in the Workbook
- Example #5 – Methods Using Worksheet Object
- Recommended Articles
Syntax of VBA Worksheets
As we said, the worksheet is an object variable. However, this has syntax too.
The index is nothing that is the worksheet number we are referring to. However, as you can see in the end, it is referred to as an Object.
For example, Worksheet(1).Select means to select the first worksheet of the workbook. It doesn’t matter what the worksheet’s name is; whatever the worksheet inserted first in the workbook will be selected.
We can also refer to the worksheet by its name. We need to mention the complete as it is a worksheet name in double quotes.
For example, Worksheet(“Sales Sheet”).Select means select the sheet named “Sales Sheet.” Here it doesn’t matter what the number of the worksheet it always selects is.
How to use Worksheets Object in VBA?
You can download this VBA Worksheet Object Template here – VBA Worksheet Object Template
Example #1
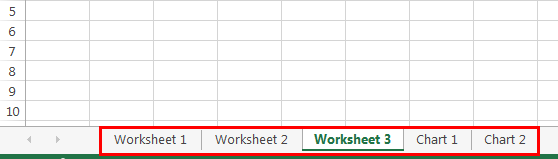
Assume you have a total of 5 sheets in your workbook. The name of those worksheets is “Worksheet 1”, “Worksheet 2”, “Worksheet 3”, “Chart Sheet 1”, and “Chart Sheet 2.”
If we use the numbering to select the worksheet, then we can use the number as the worksheet reference.
Worksheet(2). Select means it will select the second worksheet of the workbook.
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Example1() Worksheets(2).Select End Sub
We will run this code using the F5 key or manually and see the result.
Now, we will change the sheet number to 3.
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Example1() Worksheets(3).Select End Sub
Now, see what happens when you run the code manually or using the F5 key code.
If you look at the above image, it selected the 4th worksheet when we asked to select the 3rd one.
That is because we have used the Worksheet object, not the Sheets object. As we told earlier, the “Worksheets” object considers only worksheets, not chart sheets.
Use the Sheets object to select the third sheet of all the sheets in the workbook.
Code:
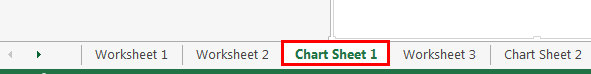
Sub Worksheet_Example1()
Sheets(3).Select
End Sub
Now, it will select the exact third sheet.
Example #2 – Select Worksheets by Name
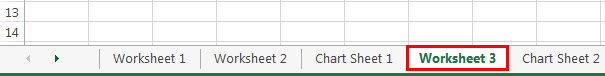
Selecting the sheets by their name is an accurate way of referring to the sheet. For example, if we want to select the sheet “Worksheet 3,” you can use the code below.
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Example2() Worksheets("Worksheet 3").Select End Sub
It will select the exact sheet. It doesn’t matter where placed in the workbook.
But if you try to access the chart sheet with the “Worksheets” object, we will get a “Subscript out of range errorSubscript out of range is an error in VBA that occurs when we attempt to reference something or a variable that does not exist in the code. For example, if we do not have a variable named x but use the msgbox function on x, we will receive a subscript out of range error.read more.”
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Example2() Worksheets("Chart Sheet 1").Select End Sub
Run this code through the F5 key or manually and see the result.
Example #3 – Problem with Worksheet Name
There is one more problem with referring to the sheets by their name. If someone changes the worksheet’s name, we will get the “Subscript out of range error.”
To solve this issue go to the basic visual editor by pressing the ALT + F11 key.
Select the sheet name and press the F4 key to see the “Properties” window.
The window changes the worksheet’s name to your name in these properties.
One interesting thing is that even though we have changed the worksheet’s name from “Worksheet 1” to “WS1,” we can still see the same name in the workbook.
Now, we can refer to this sheet by the “WS1” name.
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Example2() Worksheets("WS1").Select End Sub
Now, it doesn’t matter who changes the name of the worksheet. Still, our code refers to the same sheet as long as it is not changing in the Visual Basic Editor.
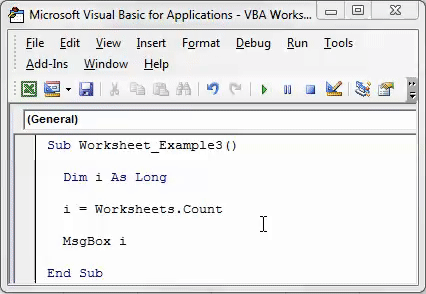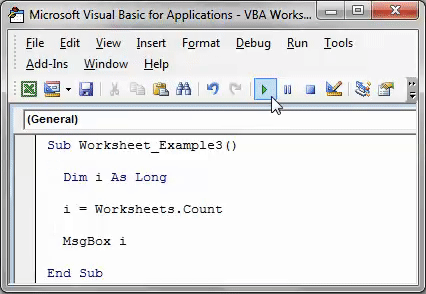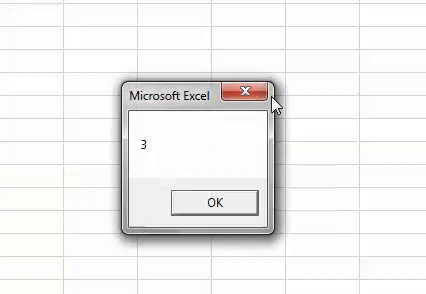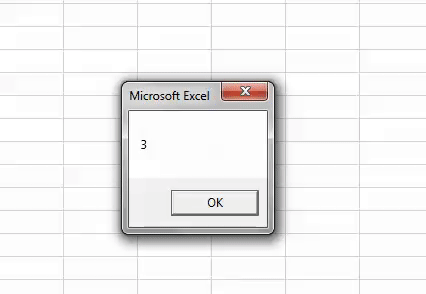
Example #4 – Get the Count of Total Sheets in the Workbook
A worksheet is an object. We can use all the properties and methods associated with it. So what do we do with worksheets?
We insert worksheets. We rename worksheets. We delete worksheets and many other things we do with them.
Enter the object “Worksheets” and put a dot to see all the options with them.
To get the count of the worksheets, use VBA Count PropertyThe count function in VBA counts how many cells have values in them. Cells with numbers or text enclosed in double quotes are counted, as are those whose values are typed directly. However, cells that contain random data that Excel is unable to translate are not counted.read more.
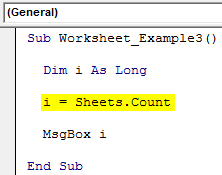
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Example3() Dim i As Long i = Worksheets.Count MsgBox i End Sub
It will show the count of the worksheets.
Even though there are 5 sheets, we got the count as 3 because the other 2 sheets are chart sheets.
To get the overall count of sheets, use the “Sheets” object.
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Example3() Dim i As Long i = Sheets.Count MsgBox i End Sub
It will show the full count of the sheets.
Example #5 – Methods Using Worksheet Object
After entering the worksheet object, we can access all the associated properties and objects. For example, we can add a new sheet. We can delete, etc.
To Add New Sheet.
Worksheet.Add
To Delete Worksheet
Worksheet(“Sheet Name”).Delete
To Change the Name of the Worksheet
Worksheet(“Sheet Name”).Name = “New Name”
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to VBA Worksheets. Here, we learn how to use the VBA Worksheet object to find, select, and get the count of total worksheets in Excel, along with some simple to advanced examples. Below are some useful Excel articles related to VBA: –
- GetObject in VBA
- VBA Delete All Excel Files
- Excel VBA Worksheet Function
- VBA New Line