You all must have worked with Excel at some time in your life and must have felt the need for automating some repetitive or tedious task. Don’t worry in this tutorial we are going to learn about how to work with Excel using Python, or automating Excel using Python. We will be covering this with the help of the Openpyxl module.
Getting Started
Openpyxl is a Python library that provides various methods to interact with Excel Files using Python. It allows operations like reading, writing, arithmetic operations, plotting graphs, etc.
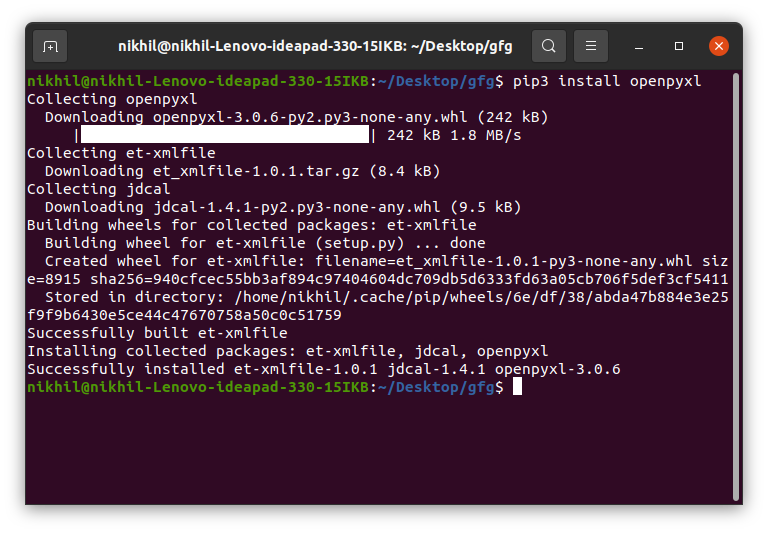
This module does not come in-built with Python. To install this type the below command in the terminal.
pip install openpyxl
Reading from Spreadsheets
To read an Excel file you have to open the spreadsheet using the load_workbook() method. After that, you can use the active to select the first sheet available and the cell attribute to select the cell by passing the row and column parameter. The value attribute prints the value of the particular cell. See the below example to get a better understanding.
Note: The first row or column integer is 1, not 0.
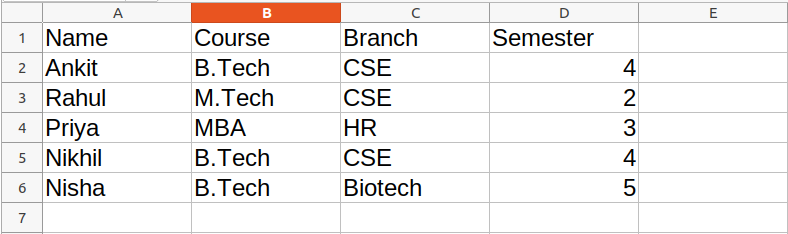
Dataset Used: It can be downloaded from here.
Example:
Python3
import openpyxl
path = "gfg.xlsx"
wb_obj = openpyxl.load_workbook(path)
sheet_obj = wb_obj.active
cell_obj = sheet_obj.cell(row = 1, column = 1)
print(cell_obj.value)
Output:
Name
Reading from Multiple Cells
There can be two ways of reading from multiple cells.
Method 1: We can get the count of the total rows and columns using the max_row and max_column respectively. We can use these values inside the for loop to get the value of the desired row or column or any cell depending upon the situation. Let’s see how to get the value of the first column and first row.
Example:
Python3
import openpyxl
path = "gfg.xlsx"
wb_obj = openpyxl.load_workbook(path)
sheet_obj = wb_obj.active
row = sheet_obj.max_row
column = sheet_obj.max_column
print("Total Rows:", row)
print("Total Columns:", column)
print("nValue of first column")
for i in range(1, row + 1):
cell_obj = sheet_obj.cell(row = i, column = 1)
print(cell_obj.value)
print("nValue of first row")
for i in range(1, column + 1):
cell_obj = sheet_obj.cell(row = 2, column = i)
print(cell_obj.value, end = " ")
Output:
Total Rows: 6 Total Columns: 4 Value of first column Name Ankit Rahul Priya Nikhil Nisha Value of first row Ankit B.Tech CSE 4
Method 2: We can also read from multiple cells using the cell name. This can be seen as the list slicing of Python.
Python3
import openpyxl
path = "gfg.xlsx"
wb_obj = openpyxl.load_workbook(path)
sheet_obj = wb_obj.active
cell_obj = sheet_obj['A1': 'B6']
for cell1, cell2 in cell_obj:
print(cell1.value, cell2.value)
Output:
Name Course Ankit B.Tech Rahul M.Tech Priya MBA Nikhil B.Tech Nisha B.Tech
Refer to the below article to get detailed information about reading excel files using openpyxl.
- Reading an excel file using Python openpyxl module
Writing to Spreadsheets
First, let’s create a new spreadsheet, and then we will write some data to the newly created file. An empty spreadsheet can be created using the Workbook() method. Let’s see the below example.
Example:
Python3
from openpyxl import Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
workbook.save(filename="sample.xlsx")
Output:
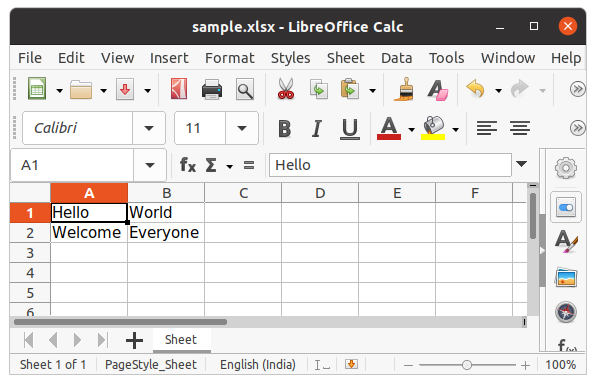
After creating an empty file, let’s see how to add some data to it using Python. To add data first we need to select the active sheet and then using the cell() method we can select any particular cell by passing the row and column number as its parameter. We can also write using cell names. See the below example for a better understanding.
Example:
Python3
import openpyxl
wb = openpyxl.Workbook()
sheet = wb.active
c1 = sheet.cell(row = 1, column = 1)
c1.value = "Hello"
c2 = sheet.cell(row= 1 , column = 2)
c2.value = "World"
c3 = sheet['A2']
c3.value = "Welcome"
c4 = sheet['B2']
c4.value = "Everyone"
wb.save("sample.xlsx")
Output:
Refer to the below article to get detailed information about writing to excel.
- Writing to an excel file using openpyxl module
Appending to the Spreadsheet
In the above example, you will see that every time you try to write to a spreadsheet the existing data gets overwritten, and the file is saved as a new file. This happens because the Workbook() method always creates a new workbook file object. To write to an existing workbook you must open the file with the load_workbook() method. We will use the above-created workbook.
Example:
Python3
import openpyxl
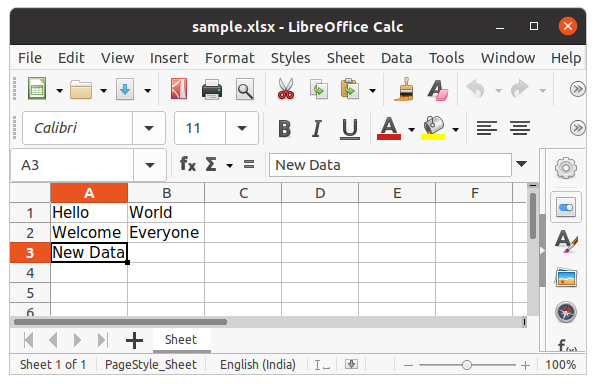
wb = openpyxl.load_workbook("sample.xlsx")
sheet = wb.active
c = sheet['A3']
c.value = "New Data"
wb.save("sample.xlsx")
Output:
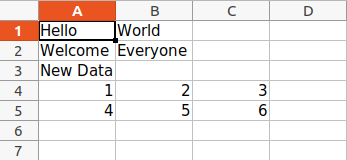
We can also use the append() method to append multiple data at the end of the sheet.
Example:
Python3
import openpyxl
wb = openpyxl.load_workbook("sample.xlsx")
sheet = wb.active
data = (
(1, 2, 3),
(4, 5, 6)
)
for row in data:
sheet.append(row)
wb.save('sample.xlsx')
Output:
Arithmetic Operation on Spreadsheet
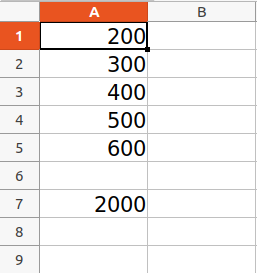
Arithmetic operations can be performed by typing the formula in a particular cell of the spreadsheet. For example, if we want to find the sum then =Sum() formula of the excel file is used.
Example:
Python3
import openpyxl
wb = openpyxl.Workbook()
sheet = wb.active
sheet['A1'] = 200
sheet['A2'] = 300
sheet['A3'] = 400
sheet['A4'] = 500
sheet['A5'] = 600
sheet['A7'] = '= SUM(A1:A5)'
wb.save("sum.xlsx")
Output:
Refer to the below article to get detailed information about the Arithmetic operations on Spreadsheet.
- Arithmetic operations in excel file using openpyxl
Adjusting Rows and Column
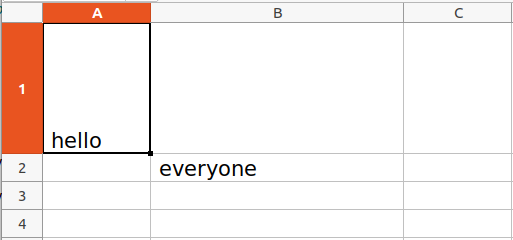
Worksheet objects have row_dimensions and column_dimensions attributes that control row heights and column widths. A sheet’s row_dimensions and column_dimensions are dictionary-like values; row_dimensions contains RowDimension objects and column_dimensions contains ColumnDimension objects. In row_dimensions, one can access one of the objects using the number of the row (in this case, 1 or 2). In column_dimensions, one can access one of the objects using the letter of the column (in this case, A or B).
Example:
Python3
import openpyxl
wb = openpyxl.Workbook()
sheet = wb.active
sheet.cell(row = 1, column = 1).value = ' hello '
sheet.cell(row = 2, column = 2).value = ' everyone '
sheet.row_dimensions[1].height = 70
sheet.column_dimensions['B'].width = 20
wb.save('sample.xlsx')
Output:
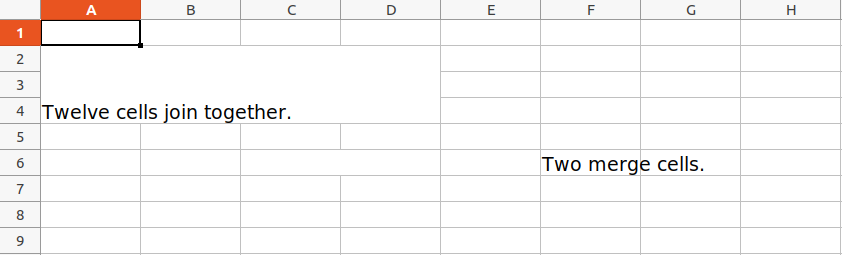
Merging Cells
A rectangular area of cells can be merged into a single cell with the merge_cells() sheet method. The argument to merge_cells() is a single string of the top-left and bottom-right cells of the rectangular area to be merged.
Example:
Python3
import openpyxl
wb = openpyxl.Workbook()
sheet = wb.active
sheet.merge_cells('A2:D4')
sheet.cell(row = 2, column = 1).value = 'Twelve cells join together.'
sheet.merge_cells('C6:D6')
sheet.cell(row = 6, column = 6).value = 'Two merge cells.'
wb.save('sample.xlsx')
Output:
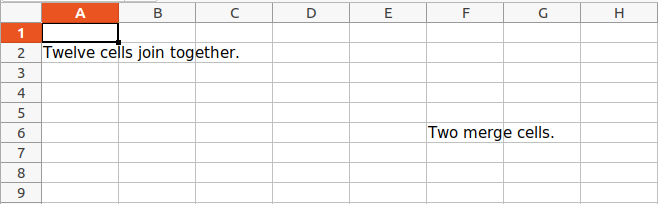
Unmerging Cells
To unmerge cells, call the unmerge_cells() sheet method.
Example:
Python3
import openpyxl
wb = openpyxl.load_workbook('sample.xlsx')
sheet = wb.active
sheet.unmerge_cells('A2:D4')
sheet.unmerge_cells('C6:D6')
wb.save('sample.xlsx')
Output:
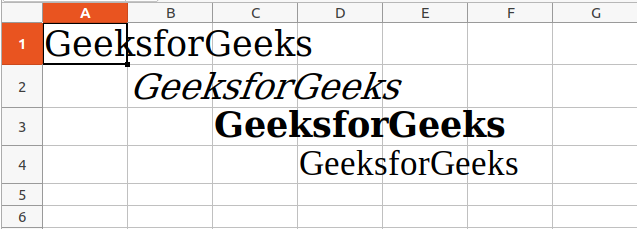
Setting Font Style
To customize font styles in cells, important, import the Font() function from the openpyxl.styles module.
Example:
Python3
import openpyxl
from openpyxl.styles import Font
wb = openpyxl.Workbook()
sheet = wb.active
sheet.cell(row = 1, column = 1).value = "GeeksforGeeks"
sheet.cell(row = 1, column = 1).font = Font(size = 24 )
sheet.cell(row = 2, column = 2).value = "GeeksforGeeks"
sheet.cell(row = 2, column = 2).font = Font(size = 24, italic = True)
sheet.cell(row = 3, column = 3).value = "GeeksforGeeks"
sheet.cell(row = 3, column = 3).font = Font(size = 24, bold = True)
sheet.cell(row = 4, column = 4).value = "GeeksforGeeks"
sheet.cell(row = 4, column = 4).font = Font(size = 24, name = 'Times New Roman')
wb.save('sample.xlsx')
Output:
Refer to the below article to get detailed information about adjusting rows and columns.
- Adjusting rows and columns of an excel file using openpyxl module
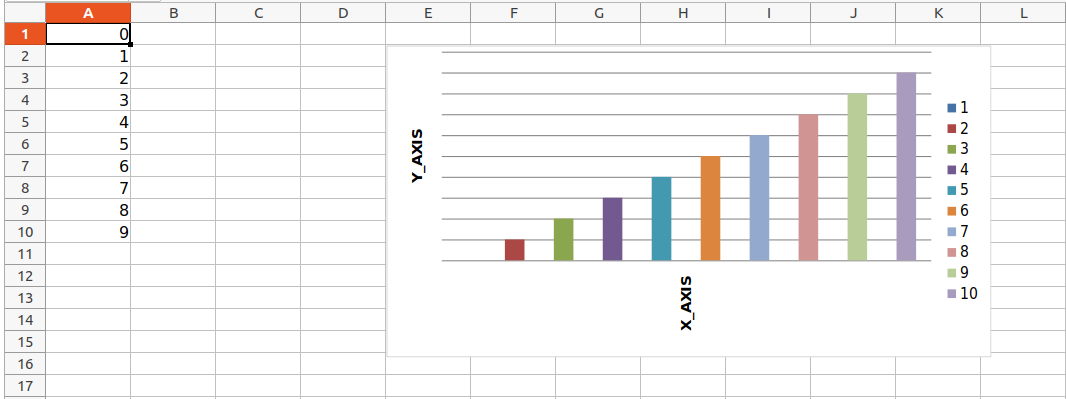
Plotting Charts
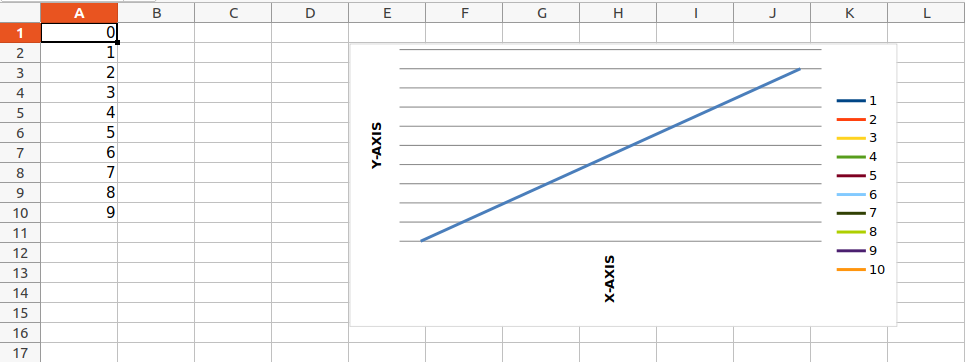
Charts are composed of at least one series of one or more data points. Series themselves are comprised of references to cell ranges. For plotting the charts on an excel sheet, firstly, create chart objects of specific chart class( i.e BarChart, LineChart, etc.). After creating chart objects, insert data in it, and lastly, add that chart object in the sheet object.
Example 1:
Python3
import openpyxl
from openpyxl.chart import BarChart, Reference
wb = openpyxl.Workbook()
sheet = wb.active
for i in range(10):
sheet.append([i])
values = Reference(sheet, min_col=1, min_row=1,
max_col=1, max_row=10)
chart = BarChart()
chart.add_data(values)
chart.title = " BAR-CHART "
chart.x_axis.title = " X_AXIS "
chart.y_axis.title = " Y_AXIS "
sheet.add_chart(chart, "E2")
wb.save("sample.xlsx")
Output:
Example 2:
Python3
import openpyxl
from openpyxl.chart import LineChart, Reference
wb = openpyxl.Workbook()
sheet = wb.active
for i in range(10):
sheet.append([i])
values = Reference(sheet, min_col=1, min_row=1,
max_col=1, max_row=10)
chart = LineChart()
chart.add_data(values)
chart.title = " LINE-CHART "
chart.x_axis.title = " X-AXIS "
chart.y_axis.title = " Y-AXIS "
sheet.add_chart(chart, "E2")
wb.save("sample.xlsx")
Output:
Refer to the below articles to get detailed information about plotting in excel using Python.
- Plotting charts in excel sheet using openpyxl module | Set 1
- Plotting charts in excel sheet using openpyxl module | Set 2
- Plotting charts in excel sheet using openpyxl module | Set 3
Adding Images
For the purpose of importing images inside our worksheet, we would be using openpyxl.drawing.image.Image. The method is a wrapper over PIL.Image method found in PIL (pillow) library. Due to which it is necessary for the PIL (pillow) library to be installed in order to use this method.
Image Used:
Example:
Python3
import openpyxl
from openpyxl.drawing.image import Image
wb = openpyxl.Workbook()
sheet = wb.active
sheet.append([10, 2010, "Geeks", 4, "life"])
img = Image("geek.jpg")
sheet.add_image(img, 'A2')
wb.save('sample.xlsx')
Output:
Refer to the below article to get detailed information about adding images.
- Openpyxl – Adding Image
Some More Functionality of Excel using Python
- How to delete one or more rows in excel using Openpyxl?
- Trigonometric operations in excel file using openpyxl
- How to copy data from one excel sheet to another
- How to Automate an Excel Sheet in Python?
I believe you have used Microsoft Excel on some occasions. It is very powerful when it comes to working with spreadsheets, tables, charts, etc. But what does Python have to do with that?
Python is a game-changer when it comes to Excel files because it can automate daunting stuff you might encounter in an Excel-related task. For instance, you may be required to look for some information in hundreds of spreadsheets of the company’s budgets. Very daunting, isn’t it? In this tutorial, I will show you how Python can be used easily to work with Excel documents.
Oh, don’t worry if you don’t have Microsoft Excel installed on your machine. You can use other alternatives to walk through this tutorial, such as LibreOffice Calc and OpenOffice Calc.
Let’s get started!
OpenPyXL
OpenPyXL is a library used to read and write Excel 2010 .xlsx/.xlsm/.xltx/.xltm files. This is the library we will be using in this tutorial to work with Excel documents.
The first thing we need to do in order to make use of this library is install OpenPyXL.
Installing OpenPyXL
In order to install OpenPyXL, we will be using pip, which is (based on Wikipedia):
A package management system used to install and manage software packages written in Python. Many packages can be found in the Python Package Index (PyPI).
You can follow the steps mentioned in the Python Packaging User Guide for installing pip, but if you have Python 2.7.9 and higher, or Python 3.4 and higher, you already have pip!
OpenPyXL now can be simply installed by typing the following command (in macOS’s Terminal):
Opening an Excel Document
After installing OpenPyXL, we are ready to start working with Excel documents. The first normal task we would perform on an Excel document is to open that document. Go ahead and download the Excel file sample.xlsx in order to follow along with the tutorial, or you can use whichever Excel file you like.
Before we can use OpenPyXL, we need to import it, as follows:
The method we need in order to open the Excel document is load_workbook(). If you are wondering what is meant by a workbook, it is simply the Excel spreadsheet document. The script that we thus need to open an Excel document is as follows:
1 |
import openpyxl |
2 |
excel_document = openpyxl.load_workbook('sample.xlsx') |
Let’s now see the type returned from the load_workbook() method. This can be done as follows:
1 |
print type(excel_document) |
This will return the following:
1 |
<class 'openpyxl.workbook.workbook.Workbook'> |
As we can see, the object returned is Workbook, of data type workbook. The Workbook object here represents the Excel file.
Sheet Names
Sheets in Excel consist of columns (with letters starting from A, B, C, etc.) and rows (starting from 1, 2, 3, etc.). In order to check what sheets we have in our Excel document, we use the get_sheet_names() method as follows:
1 |
print(excel_document.sheetnames) |
If we print the above command, we get the following:
Thus showing that we have one sheet, called Sheet1.
If you have multiple sheets, you can access a specific sheet by its name using this method: get_sheet_by_name(). For example, to get the current sheet:
1 |
print(excel_document. get_sheet_by_name('Sheet1')) |
The output will be:
Accessing Cells
Now that we have learned how to open an Excel file and get the sheet, let’s see how easy it is to access a cell in that sheet. All you have to do is retrieve that sheet, and then determine the location (coordinate) of the cell. Let’s say that we want to access column A row 2 in the Excel document we have, that is A2. This can be implemented as follows:
1 |
sheet = excel_document['Sheet1'] |
2 |
print(sheet['A2'].value) |
In this case, you will have the following value returned:
We can also use a row-column notation. For instance, if we want to access the cell at row 5 and column 2, we type the following:
1 |
sheet.cell(row = 5, column = 2).value |
The output in this case will be programmer.
If we want to see the object type representing the cell, we can type:
1 |
print(type(sheet['A2'])) |
In this case, you would get the following output:
1 |
<class 'openpyxl.cell.cell.Cell'> |
which means that the object is of type Cell.
Accessing a Range of Cells
What if you were interested in accessing a range of cells rather than only one cell? Let’s say we want to access the cells from A1 to B3, which look like this in our Excel document?
This can be done using the following script:
1 |
multiple_cells = sheet['A1':'B3'] |
2 |
for row in multiple_cells: |
3 |
for cell in row: |
4 |
print(cell.value) |
In this case, you will get the following output:
1 |
Name |
2 |
Profession |
3 |
Abder |
4 |
Student |
5 |
Bob |
6 |
Engineer |
Accessing All Rows and Columns
OpenPyXL enables you to access all the rows and columns in your Excel document, using the rows() and columns() methods, respectively.
In order to access all the rows, we can do the following:
1 |
for row in sheet.rows: |
2 |
print(row) |
The output of the above script would be as follows:
1 |
(<Cell 'Sheet1'.A1>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B1>) |
2 |
(<Cell 'Sheet1'.A2>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B2>) |
3 |
(<Cell 'Sheet1'.A3>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B3>) |
4 |
(<Cell 'Sheet1'.A4>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B4>) |
5 |
(<Cell 'Sheet1'.A5>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B5>) |
6 |
(<Cell 'Sheet1'.A6>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B6>) |
7 |
(<Cell 'Sheet1'.A7>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B7>) |
On the other hand, if we want to access all the columns, we simply do the following:
1 |
for column in sheet.columns: |
2 |
print(column) |
In which case, you will get the following output:
1 |
(<Cell 'Sheet1'.A1>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.A2>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.A3>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.A4>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.A5>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.A6>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.A7>) |
2 |
(<Cell 'Sheet1'.B1>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B2>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B3>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B4>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B5>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B6>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B7>) |
There is of course more that you can do with Excel documents, as you can see in the OpenPyXL documentation.
Conclusion
From this tutorial, we have noticed how flexible it can be to work with Excel documents using Python. Remember the scenario mentioned at the beginning of the tutorial? It’s worth trying as a project!
This post has been updated with contributions from Esther Vaati. Esther is a software developer and writer for Envato Tuts+.
Did you find this post useful?
Dr. Aber-Rahman Ali is a researcher who uses machine learning and image processing in medical image analysis.
He also likes writing about Python!
Watch Now This tutorial has a related video course created by the Real Python team. Watch it together with the written tutorial to deepen your understanding: Editing Excel Spreadsheets in Python With openpyxl
Excel spreadsheets are one of those things you might have to deal with at some point. Either it’s because your boss loves them or because marketing needs them, you might have to learn how to work with spreadsheets, and that’s when knowing openpyxl comes in handy!
Spreadsheets are a very intuitive and user-friendly way to manipulate large datasets without any prior technical background. That’s why they’re still so commonly used today.
In this article, you’ll learn how to use openpyxl to:
- Manipulate Excel spreadsheets with confidence
- Extract information from spreadsheets
- Create simple or more complex spreadsheets, including adding styles, charts, and so on
This article is written for intermediate developers who have a pretty good knowledge of Python data structures, such as dicts and lists, but also feel comfortable around OOP and more intermediate level topics.
Before You Begin
If you ever get asked to extract some data from a database or log file into an Excel spreadsheet, or if you often have to convert an Excel spreadsheet into some more usable programmatic form, then this tutorial is perfect for you. Let’s jump into the openpyxl caravan!
Practical Use Cases
First things first, when would you need to use a package like openpyxl in a real-world scenario? You’ll see a few examples below, but really, there are hundreds of possible scenarios where this knowledge could come in handy.
Importing New Products Into a Database
You are responsible for tech in an online store company, and your boss doesn’t want to pay for a cool and expensive CMS system.
Every time they want to add new products to the online store, they come to you with an Excel spreadsheet with a few hundred rows and, for each of them, you have the product name, description, price, and so forth.
Now, to import the data, you’ll have to iterate over each spreadsheet row and add each product to the online store.
Exporting Database Data Into a Spreadsheet
Say you have a Database table where you record all your users’ information, including name, phone number, email address, and so forth.
Now, the Marketing team wants to contact all users to give them some discounted offer or promotion. However, they don’t have access to the Database, or they don’t know how to use SQL to extract that information easily.
What can you do to help? Well, you can make a quick script using openpyxl that iterates over every single User record and puts all the essential information into an Excel spreadsheet.
That’s gonna earn you an extra slice of cake at your company’s next birthday party!
Appending Information to an Existing Spreadsheet
You may also have to open a spreadsheet, read the information in it and, according to some business logic, append more data to it.
For example, using the online store scenario again, say you get an Excel spreadsheet with a list of users and you need to append to each row the total amount they’ve spent in your store.
This data is in the Database and, in order to do this, you have to read the spreadsheet, iterate through each row, fetch the total amount spent from the Database and then write back to the spreadsheet.
Not a problem for openpyxl!
Learning Some Basic Excel Terminology
Here’s a quick list of basic terms you’ll see when you’re working with Excel spreadsheets:
| Term | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Spreadsheet or Workbook | A Spreadsheet is the main file you are creating or working with. |
| Worksheet or Sheet | A Sheet is used to split different kinds of content within the same spreadsheet. A Spreadsheet can have one or more Sheets. |
| Column | A Column is a vertical line, and it’s represented by an uppercase letter: A. |
| Row | A Row is a horizontal line, and it’s represented by a number: 1. |
| Cell | A Cell is a combination of Column and Row, represented by both an uppercase letter and a number: A1. |
Getting Started With openpyxl
Now that you’re aware of the benefits of a tool like openpyxl, let’s get down to it and start by installing the package. For this tutorial, you should use Python 3.7 and openpyxl 2.6.2. To install the package, you can do the following:
After you install the package, you should be able to create a super simple spreadsheet with the following code:
from openpyxl import Workbook
workbook = Workbook()
sheet = workbook.active
sheet["A1"] = "hello"
sheet["B1"] = "world!"
workbook.save(filename="hello_world.xlsx")
The code above should create a file called hello_world.xlsx in the folder you are using to run the code. If you open that file with Excel you should see something like this:
Woohoo, your first spreadsheet created!
Reading Excel Spreadsheets With openpyxl
Let’s start with the most essential thing one can do with a spreadsheet: read it.
You’ll go from a straightforward approach to reading a spreadsheet to more complex examples where you read the data and convert it into more useful Python structures.
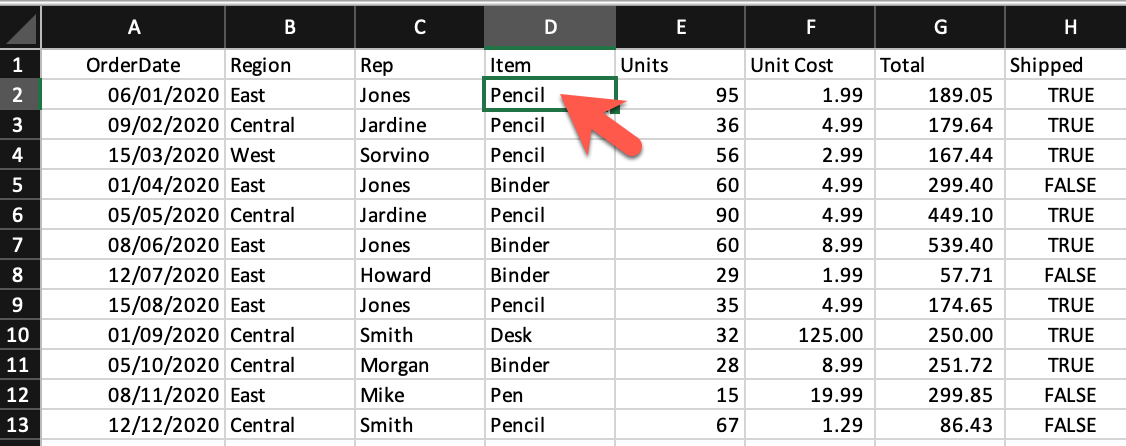
Dataset for This Tutorial
Before you dive deep into some code examples, you should download this sample dataset and store it somewhere as sample.xlsx:
This is one of the datasets you’ll be using throughout this tutorial, and it’s a spreadsheet with a sample of real data from Amazon’s online product reviews. This dataset is only a tiny fraction of what Amazon provides, but for testing purposes, it’s more than enough.
A Simple Approach to Reading an Excel Spreadsheet
Finally, let’s start reading some spreadsheets! To begin with, open our sample spreadsheet:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl import load_workbook
>>> workbook = load_workbook(filename="sample.xlsx")
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Sheet 1']
>>> sheet = workbook.active
>>> sheet
<Worksheet "Sheet 1">
>>> sheet.title
'Sheet 1'
In the code above, you first open the spreadsheet sample.xlsx using load_workbook(), and then you can use workbook.sheetnames to see all the sheets you have available to work with. After that, workbook.active selects the first available sheet and, in this case, you can see that it selects Sheet 1 automatically. Using these methods is the default way of opening a spreadsheet, and you’ll see it many times during this tutorial.
Now, after opening a spreadsheet, you can easily retrieve data from it like this:
>>>
>>> sheet["A1"]
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A1>
>>> sheet["A1"].value
'marketplace'
>>> sheet["F10"].value
"G-Shock Men's Grey Sport Watch"
To return the actual value of a cell, you need to do .value. Otherwise, you’ll get the main Cell object. You can also use the method .cell() to retrieve a cell using index notation. Remember to add .value to get the actual value and not a Cell object:
>>>
>>> sheet.cell(row=10, column=6)
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.F10>
>>> sheet.cell(row=10, column=6).value
"G-Shock Men's Grey Sport Watch"
You can see that the results returned are the same, no matter which way you decide to go with. However, in this tutorial, you’ll be mostly using the first approach: ["A1"].
The above shows you the quickest way to open a spreadsheet. However, you can pass additional parameters to change the way a spreadsheet is loaded.
Additional Reading Options
There are a few arguments you can pass to load_workbook() that change the way a spreadsheet is loaded. The most important ones are the following two Booleans:
- read_only loads a spreadsheet in read-only mode allowing you to open very large Excel files.
- data_only ignores loading formulas and instead loads only the resulting values.
Importing Data From a Spreadsheet
Now that you’ve learned the basics about loading a spreadsheet, it’s about time you get to the fun part: the iteration and actual usage of the values within the spreadsheet.
This section is where you’ll learn all the different ways you can iterate through the data, but also how to convert that data into something usable and, more importantly, how to do it in a Pythonic way.
Iterating Through the Data
There are a few different ways you can iterate through the data depending on your needs.
You can slice the data with a combination of columns and rows:
>>>
>>> sheet["A1:C2"]
((<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.B1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.C1>),
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A2>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.B2>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.C2>))
You can get ranges of rows or columns:
>>>
>>> # Get all cells from column A
>>> sheet["A"]
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A1>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A2>,
...
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A99>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A100>)
>>> # Get all cells for a range of columns
>>> sheet["A:B"]
((<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A1>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A2>,
...
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A99>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A100>),
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B1>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B2>,
...
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B99>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B100>))
>>> # Get all cells from row 5
>>> sheet[5]
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A5>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B5>,
...
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.N5>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.O5>)
>>> # Get all cells for a range of rows
>>> sheet[5:6]
((<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A5>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B5>,
...
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.N5>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.O5>),
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A6>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B6>,
...
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.N6>,
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.O6>))
You’ll notice that all of the above examples return a tuple. If you want to refresh your memory on how to handle tuples in Python, check out the article on Lists and Tuples in Python.
There are also multiple ways of using normal Python generators to go through the data. The main methods you can use to achieve this are:
.iter_rows().iter_cols()
Both methods can receive the following arguments:
min_rowmax_rowmin_colmax_col
These arguments are used to set boundaries for the iteration:
>>>
>>> for row in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=1,
... max_row=2,
... min_col=1,
... max_col=3):
... print(row)
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.B1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.C1>)
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A2>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.B2>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.C2>)
>>> for column in sheet.iter_cols(min_row=1,
... max_row=2,
... min_col=1,
... max_col=3):
... print(column)
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.A2>)
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.B1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.B2>)
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.C1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.C2>)
You’ll notice that in the first example, when iterating through the rows using .iter_rows(), you get one tuple element per row selected. While when using .iter_cols() and iterating through columns, you’ll get one tuple per column instead.
One additional argument you can pass to both methods is the Boolean values_only. When it’s set to True, the values of the cell are returned, instead of the Cell object:
>>>
>>> for value in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=1,
... max_row=2,
... min_col=1,
... max_col=3,
... values_only=True):
... print(value)
('marketplace', 'customer_id', 'review_id')
('US', 3653882, 'R3O9SGZBVQBV76')
If you want to iterate through the whole dataset, then you can also use the attributes .rows or .columns directly, which are shortcuts to using .iter_rows() and .iter_cols() without any arguments:
>>>
>>> for row in sheet.rows:
... print(row)
(<Cell 'Sheet 1'.A1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.B1>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.C1>
...
<Cell 'Sheet 1'.M100>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.N100>, <Cell 'Sheet 1'.O100>)
These shortcuts are very useful when you’re iterating through the whole dataset.
Manipulate Data Using Python’s Default Data Structures
Now that you know the basics of iterating through the data in a workbook, let’s look at smart ways of converting that data into Python structures.
As you saw earlier, the result from all iterations comes in the form of tuples. However, since a tuple is nothing more than an immutable list, you can easily access its data and transform it into other structures.
For example, say you want to extract product information from the sample.xlsx spreadsheet and into a dictionary where each key is a product ID.
A straightforward way to do this is to iterate over all the rows, pick the columns you know are related to product information, and then store that in a dictionary. Let’s code this out!
First of all, have a look at the headers and see what information you care most about:
>>>
>>> for value in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=1,
... max_row=1,
... values_only=True):
... print(value)
('marketplace', 'customer_id', 'review_id', 'product_id', ...)
This code returns a list of all the column names you have in the spreadsheet. To start, grab the columns with names:
product_idproduct_parentproduct_titleproduct_category
Lucky for you, the columns you need are all next to each other so you can use the min_column and max_column to easily get the data you want:
>>>
>>> for value in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=2,
... min_col=4,
... max_col=7,
... values_only=True):
... print(value)
('B00FALQ1ZC', 937001370, 'Invicta Women's 15150 "Angel" 18k Yellow...)
('B00D3RGO20', 484010722, "Kenneth Cole New York Women's KC4944...)
...
Nice! Now that you know how to get all the important product information you need, let’s put that data into a dictionary:
import json
from openpyxl import load_workbook
workbook = load_workbook(filename="sample.xlsx")
sheet = workbook.active
products = {}
# Using the values_only because you want to return the cells' values
for row in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=2,
min_col=4,
max_col=7,
values_only=True):
product_id = row[0]
product = {
"parent": row[1],
"title": row[2],
"category": row[3]
}
products[product_id] = product
# Using json here to be able to format the output for displaying later
print(json.dumps(products))
The code above returns a JSON similar to this:
{
"B00FALQ1ZC": {
"parent": 937001370,
"title": "Invicta Women's 15150 ...",
"category": "Watches"
},
"B00D3RGO20": {
"parent": 484010722,
"title": "Kenneth Cole New York ...",
"category": "Watches"
}
}
Here you can see that the output is trimmed to 2 products only, but if you run the script as it is, then you should get 98 products.
Convert Data Into Python Classes
To finalize the reading section of this tutorial, let’s dive into Python classes and see how you could improve on the example above and better structure the data.
For this, you’ll be using the new Python Data Classes that are available from Python 3.7. If you’re using an older version of Python, then you can use the default Classes instead.
So, first things first, let’s look at the data you have and decide what you want to store and how you want to store it.
As you saw right at the start, this data comes from Amazon, and it’s a list of product reviews. You can check the list of all the columns and their meaning on Amazon.
There are two significant elements you can extract from the data available:
- Products
- Reviews
A Product has:
- ID
- Title
- Parent
- Category
The Review has a few more fields:
- ID
- Customer ID
- Stars
- Headline
- Body
- Date
You can ignore a few of the review fields to make things a bit simpler.
So, a straightforward implementation of these two classes could be written in a separate file classes.py:
import datetime
from dataclasses import dataclass
@dataclass
class Product:
id: str
parent: str
title: str
category: str
@dataclass
class Review:
id: str
customer_id: str
stars: int
headline: str
body: str
date: datetime.datetime
After defining your data classes, you need to convert the data from the spreadsheet into these new structures.
Before doing the conversion, it’s worth looking at our header again and creating a mapping between columns and the fields you need:
>>>
>>> for value in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=1,
... max_row=1,
... values_only=True):
... print(value)
('marketplace', 'customer_id', 'review_id', 'product_id', ...)
>>> # Or an alternative
>>> for cell in sheet[1]:
... print(cell.value)
marketplace
customer_id
review_id
product_id
product_parent
...
Let’s create a file mapping.py where you have a list of all the field names and their column location (zero-indexed) on the spreadsheet:
# Product fields
PRODUCT_ID = 3
PRODUCT_PARENT = 4
PRODUCT_TITLE = 5
PRODUCT_CATEGORY = 6
# Review fields
REVIEW_ID = 2
REVIEW_CUSTOMER = 1
REVIEW_STARS = 7
REVIEW_HEADLINE = 12
REVIEW_BODY = 13
REVIEW_DATE = 14
You don’t necessarily have to do the mapping above. It’s more for readability when parsing the row data, so you don’t end up with a lot of magic numbers lying around.
Finally, let’s look at the code needed to parse the spreadsheet data into a list of product and review objects:
from datetime import datetime
from openpyxl import load_workbook
from classes import Product, Review
from mapping import PRODUCT_ID, PRODUCT_PARENT, PRODUCT_TITLE,
PRODUCT_CATEGORY, REVIEW_DATE, REVIEW_ID, REVIEW_CUSTOMER,
REVIEW_STARS, REVIEW_HEADLINE, REVIEW_BODY
# Using the read_only method since you're not gonna be editing the spreadsheet
workbook = load_workbook(filename="sample.xlsx", read_only=True)
sheet = workbook.active
products = []
reviews = []
# Using the values_only because you just want to return the cell value
for row in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=2, values_only=True):
product = Product(id=row[PRODUCT_ID],
parent=row[PRODUCT_PARENT],
title=row[PRODUCT_TITLE],
category=row[PRODUCT_CATEGORY])
products.append(product)
# You need to parse the date from the spreadsheet into a datetime format
spread_date = row[REVIEW_DATE]
parsed_date = datetime.strptime(spread_date, "%Y-%m-%d")
review = Review(id=row[REVIEW_ID],
customer_id=row[REVIEW_CUSTOMER],
stars=row[REVIEW_STARS],
headline=row[REVIEW_HEADLINE],
body=row[REVIEW_BODY],
date=parsed_date)
reviews.append(review)
print(products[0])
print(reviews[0])
After you run the code above, you should get some output like this:
Product(id='B00FALQ1ZC', parent=937001370, ...)
Review(id='R3O9SGZBVQBV76', customer_id=3653882, ...)
That’s it! Now you should have the data in a very simple and digestible class format, and you can start thinking of storing this in a Database or any other type of data storage you like.
Using this kind of OOP strategy to parse spreadsheets makes handling the data much simpler later on.
Appending New Data
Before you start creating very complex spreadsheets, have a quick look at an example of how to append data to an existing spreadsheet.
Go back to the first example spreadsheet you created (hello_world.xlsx) and try opening it and appending some data to it, like this:
from openpyxl import load_workbook
# Start by opening the spreadsheet and selecting the main sheet
workbook = load_workbook(filename="hello_world.xlsx")
sheet = workbook.active
# Write what you want into a specific cell
sheet["C1"] = "writing ;)"
# Save the spreadsheet
workbook.save(filename="hello_world_append.xlsx")
Et voilà, if you open the new hello_world_append.xlsx spreadsheet, you’ll see the following change:
Notice the additional writing 
C1.
Writing Excel Spreadsheets With openpyxl
There are a lot of different things you can write to a spreadsheet, from simple text or number values to complex formulas, charts, or even images.
Let’s start creating some spreadsheets!
Creating a Simple Spreadsheet
Previously, you saw a very quick example of how to write “Hello world!” into a spreadsheet, so you can start with that:
1from openpyxl import Workbook
2
3filename = "hello_world.xlsx"
4
5workbook = Workbook()
6sheet = workbook.active
7
8sheet["A1"] = "hello"
9sheet["B1"] = "world!"
10
11workbook.save(filename=filename)
The highlighted lines in the code above are the most important ones for writing. In the code, you can see that:
- Line 5 shows you how to create a new empty workbook.
- Lines 8 and 9 show you how to add data to specific cells.
- Line 11 shows you how to save the spreadsheet when you’re done.
Even though these lines above can be straightforward, it’s still good to know them well for when things get a bit more complicated.
One thing you can do to help with coming code examples is add the following method to your Python file or console:
>>>
>>> def print_rows():
... for row in sheet.iter_rows(values_only=True):
... print(row)
It makes it easier to print all of your spreadsheet values by just calling print_rows().
Basic Spreadsheet Operations
Before you get into the more advanced topics, it’s good for you to know how to manage the most simple elements of a spreadsheet.
Adding and Updating Cell Values
You already learned how to add values to a spreadsheet like this:
>>>
>>> sheet["A1"] = "value"
There’s another way you can do this, by first selecting a cell and then changing its value:
>>>
>>> cell = sheet["A1"]
>>> cell
<Cell 'Sheet'.A1>
>>> cell.value
'hello'
>>> cell.value = "hey"
>>> cell.value
'hey'
The new value is only stored into the spreadsheet once you call workbook.save().
The openpyxl creates a cell when adding a value, if that cell didn’t exist before:
>>>
>>> # Before, our spreadsheet has only 1 row
>>> print_rows()
('hello', 'world!')
>>> # Try adding a value to row 10
>>> sheet["B10"] = "test"
>>> print_rows()
('hello', 'world!')
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, 'test')
As you can see, when trying to add a value to cell B10, you end up with a tuple with 10 rows, just so you can have that test value.
Managing Rows and Columns
One of the most common things you have to do when manipulating spreadsheets is adding or removing rows and columns. The openpyxl package allows you to do that in a very straightforward way by using the methods:
.insert_rows().delete_rows().insert_cols().delete_cols()
Every single one of those methods can receive two arguments:
idxamount
Using our basic hello_world.xlsx example again, let’s see how these methods work:
>>>
>>> print_rows()
('hello', 'world!')
>>> # Insert a column before the existing column 1 ("A")
>>> sheet.insert_cols(idx=1)
>>> print_rows()
(None, 'hello', 'world!')
>>> # Insert 5 columns between column 2 ("B") and 3 ("C")
>>> sheet.insert_cols(idx=3, amount=5)
>>> print_rows()
(None, 'hello', None, None, None, None, None, 'world!')
>>> # Delete the created columns
>>> sheet.delete_cols(idx=3, amount=5)
>>> sheet.delete_cols(idx=1)
>>> print_rows()
('hello', 'world!')
>>> # Insert a new row in the beginning
>>> sheet.insert_rows(idx=1)
>>> print_rows()
(None, None)
('hello', 'world!')
>>> # Insert 3 new rows in the beginning
>>> sheet.insert_rows(idx=1, amount=3)
>>> print_rows()
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
(None, None)
('hello', 'world!')
>>> # Delete the first 4 rows
>>> sheet.delete_rows(idx=1, amount=4)
>>> print_rows()
('hello', 'world!')
The only thing you need to remember is that when inserting new data (rows or columns), the insertion happens before the idx parameter.
So, if you do insert_rows(1), it inserts a new row before the existing first row.
It’s the same for columns: when you call insert_cols(2), it inserts a new column right before the already existing second column (B).
However, when deleting rows or columns, .delete_... deletes data starting from the index passed as an argument.
For example, when doing delete_rows(2) it deletes row 2, and when doing delete_cols(3) it deletes the third column (C).
Managing Sheets
Sheet management is also one of those things you might need to know, even though it might be something that you don’t use that often.
If you look back at the code examples from this tutorial, you’ll notice the following recurring piece of code:
This is the way to select the default sheet from a spreadsheet. However, if you’re opening a spreadsheet with multiple sheets, then you can always select a specific one like this:
>>>
>>> # Let's say you have two sheets: "Products" and "Company Sales"
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Products', 'Company Sales']
>>> # You can select a sheet using its title
>>> products_sheet = workbook["Products"]
>>> sales_sheet = workbook["Company Sales"]
You can also change a sheet title very easily:
>>>
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Products', 'Company Sales']
>>> products_sheet = workbook["Products"]
>>> products_sheet.title = "New Products"
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['New Products', 'Company Sales']
If you want to create or delete sheets, then you can also do that with .create_sheet() and .remove():
>>>
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Products', 'Company Sales']
>>> operations_sheet = workbook.create_sheet("Operations")
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Products', 'Company Sales', 'Operations']
>>> # You can also define the position to create the sheet at
>>> hr_sheet = workbook.create_sheet("HR", 0)
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['HR', 'Products', 'Company Sales', 'Operations']
>>> # To remove them, just pass the sheet as an argument to the .remove()
>>> workbook.remove(operations_sheet)
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['HR', 'Products', 'Company Sales']
>>> workbook.remove(hr_sheet)
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Products', 'Company Sales']
One other thing you can do is make duplicates of a sheet using copy_worksheet():
>>>
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Products', 'Company Sales']
>>> products_sheet = workbook["Products"]
>>> workbook.copy_worksheet(products_sheet)
<Worksheet "Products Copy">
>>> workbook.sheetnames
['Products', 'Company Sales', 'Products Copy']
If you open your spreadsheet after saving the above code, you’ll notice that the sheet Products Copy is a duplicate of the sheet Products.
Freezing Rows and Columns
Something that you might want to do when working with big spreadsheets is to freeze a few rows or columns, so they remain visible when you scroll right or down.
Freezing data allows you to keep an eye on important rows or columns, regardless of where you scroll in the spreadsheet.
Again, openpyxl also has a way to accomplish this by using the worksheet freeze_panes attribute. For this example, go back to our sample.xlsx spreadsheet and try doing the following:
>>>
>>> workbook = load_workbook(filename="sample.xlsx")
>>> sheet = workbook.active
>>> sheet.freeze_panes = "C2"
>>> workbook.save("sample_frozen.xlsx")
If you open the sample_frozen.xlsx spreadsheet in your favorite spreadsheet editor, you’ll notice that row 1 and columns A and B are frozen and are always visible no matter where you navigate within the spreadsheet.
This feature is handy, for example, to keep headers within sight, so you always know what each column represents.
Here’s how it looks in the editor:
Notice how you’re at the end of the spreadsheet, and yet, you can see both row 1 and columns A and B.
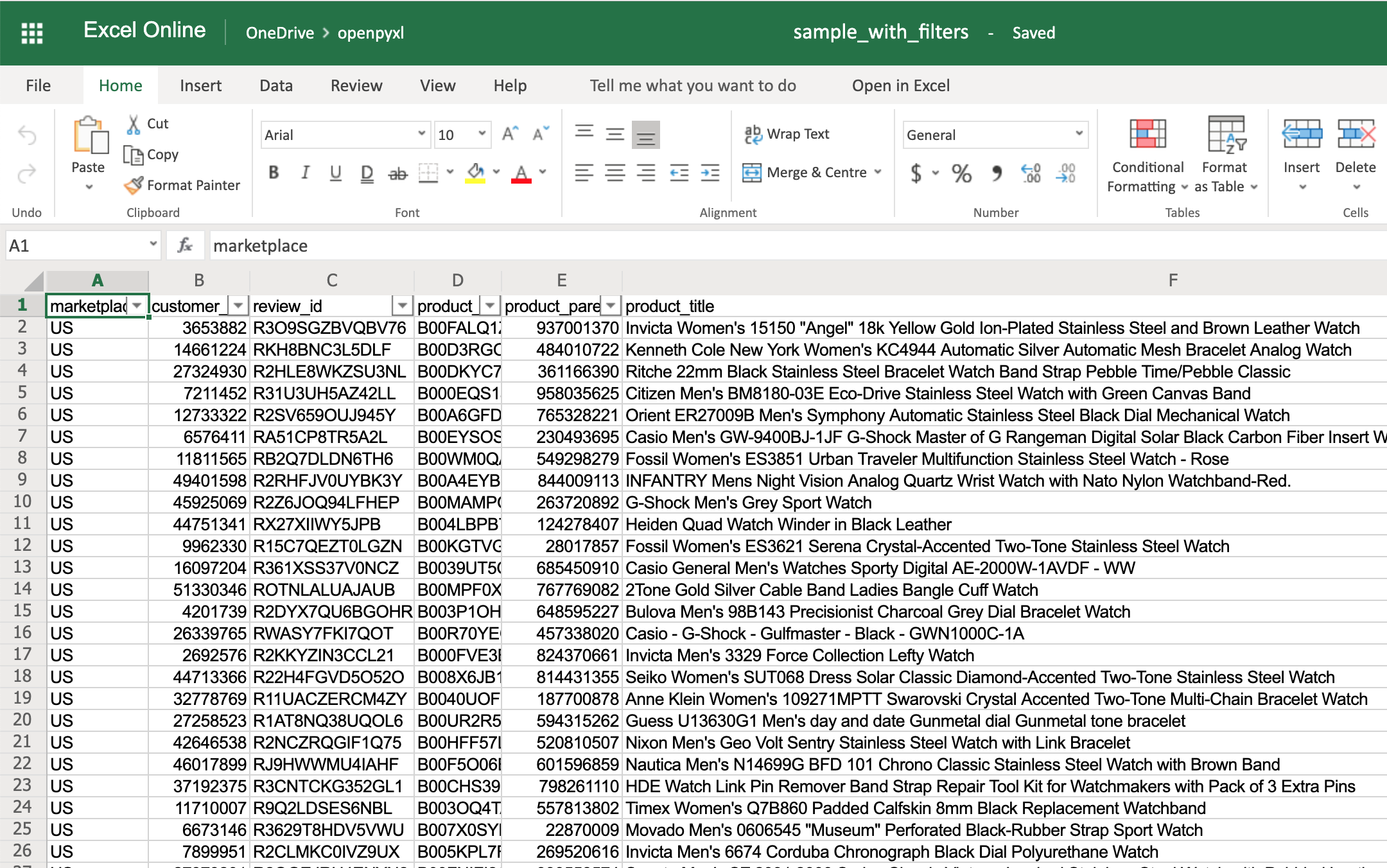
Adding Filters
You can use openpyxl to add filters and sorts to your spreadsheet. However, when you open the spreadsheet, the data won’t be rearranged according to these sorts and filters.
At first, this might seem like a pretty useless feature, but when you’re programmatically creating a spreadsheet that is going to be sent and used by somebody else, it’s still nice to at least create the filters and allow people to use it afterward.
The code below is an example of how you would add some filters to our existing sample.xlsx spreadsheet:
>>>
>>> # Check the used spreadsheet space using the attribute "dimensions"
>>> sheet.dimensions
'A1:O100'
>>> sheet.auto_filter.ref = "A1:O100"
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_with_filters.xlsx")
You should now see the filters created when opening the spreadsheet in your editor:
You don’t have to use sheet.dimensions if you know precisely which part of the spreadsheet you want to apply filters to.
Adding Formulas
Formulas (or formulae) are one of the most powerful features of spreadsheets.
They gives you the power to apply specific mathematical equations to a range of cells. Using formulas with openpyxl is as simple as editing the value of a cell.
You can see the list of formulas supported by openpyxl:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl.utils import FORMULAE
>>> FORMULAE
frozenset({'ABS',
'ACCRINT',
'ACCRINTM',
'ACOS',
'ACOSH',
'AMORDEGRC',
'AMORLINC',
'AND',
...
'YEARFRAC',
'YIELD',
'YIELDDISC',
'YIELDMAT',
'ZTEST'})
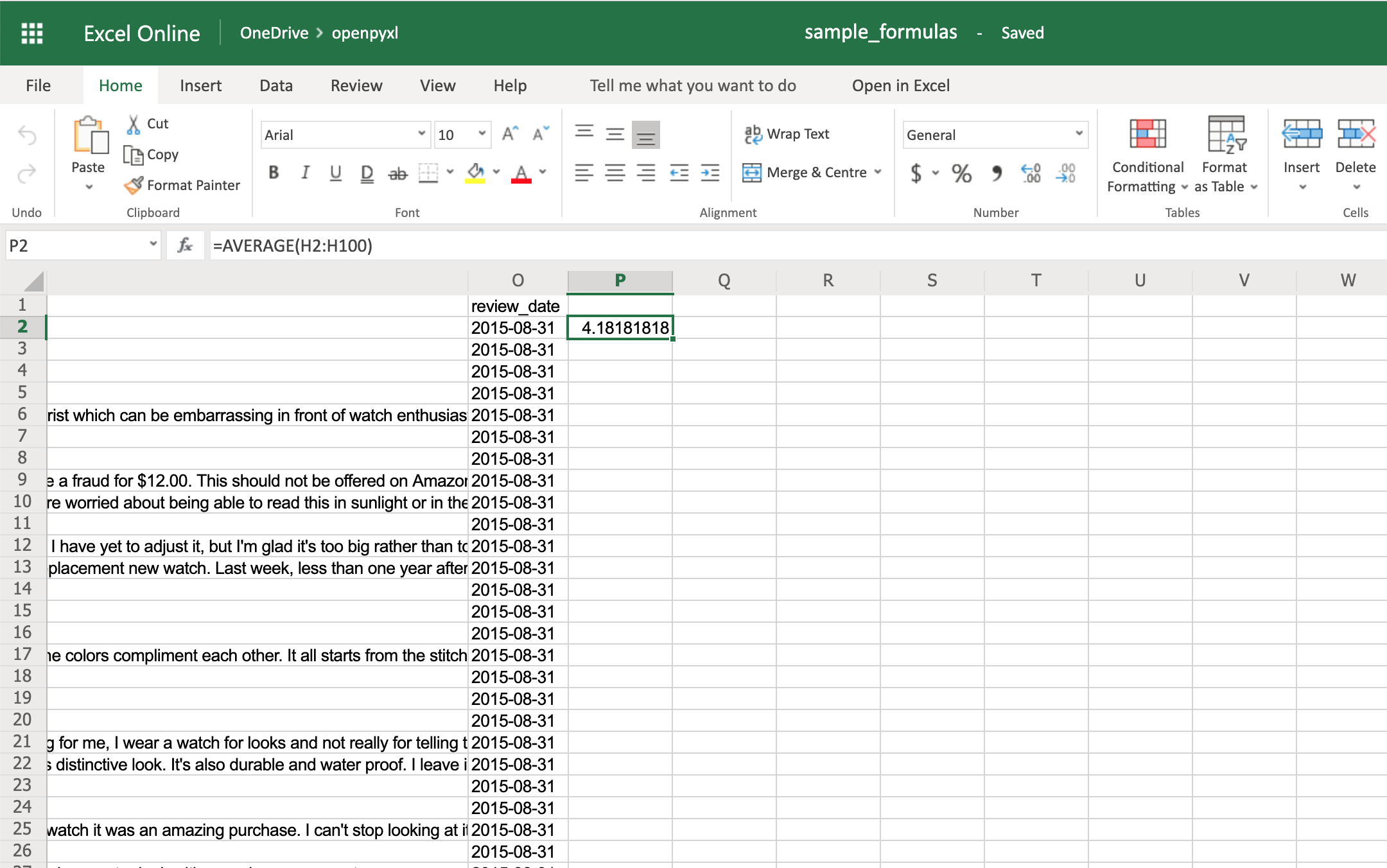
Let’s add some formulas to our sample.xlsx spreadsheet.
Starting with something easy, let’s check the average star rating for the 99 reviews within the spreadsheet:
>>>
>>> # Star rating is column "H"
>>> sheet["P2"] = "=AVERAGE(H2:H100)"
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_formulas.xlsx")
If you open the spreadsheet now and go to cell P2, you should see that its value is: 4.18181818181818. Have a look in the editor:
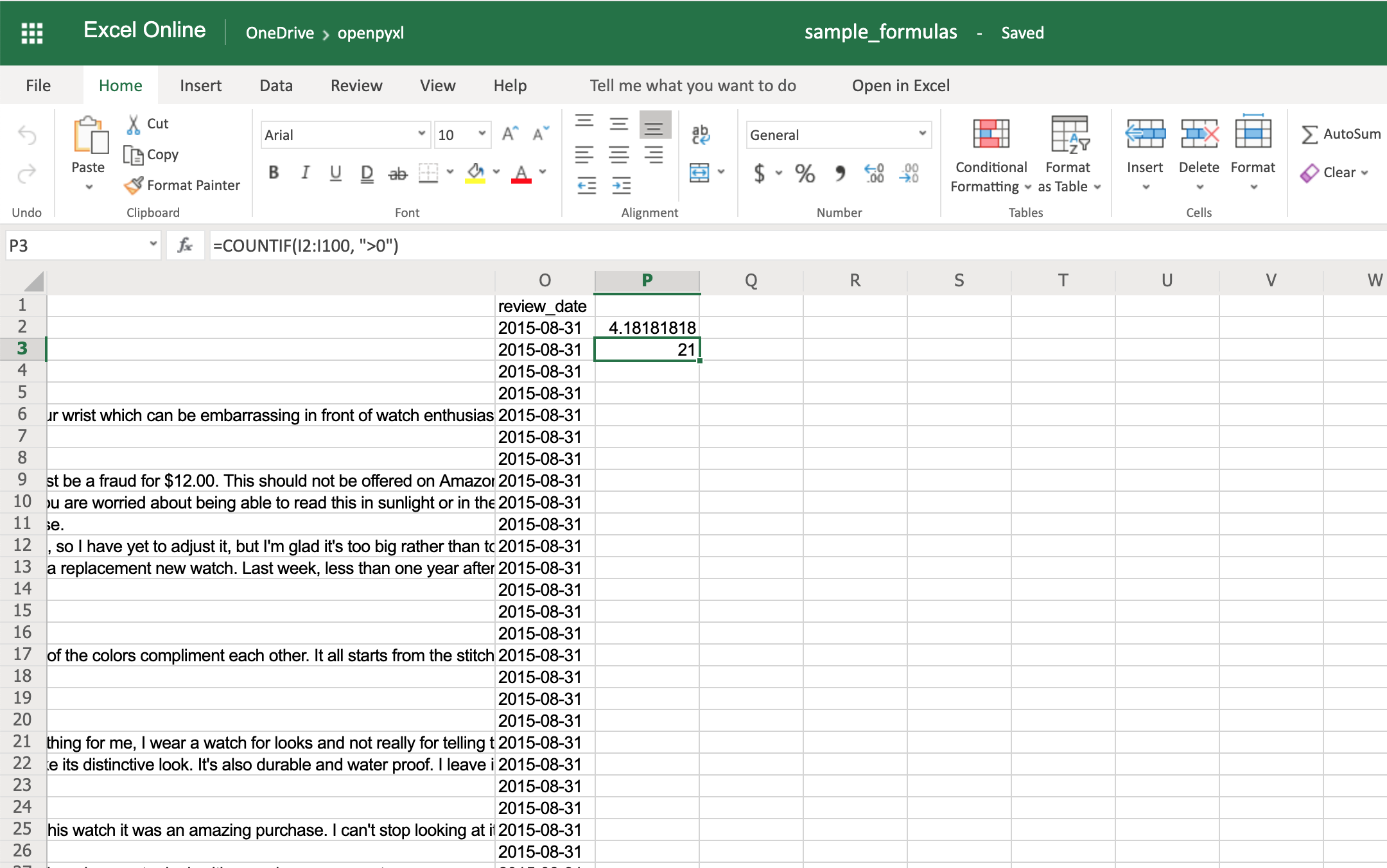
You can use the same methodology to add any formulas to your spreadsheet. For example, let’s count the number of reviews that had helpful votes:
>>>
>>> # The helpful votes are counted on column "I"
>>> sheet["P3"] = '=COUNTIF(I2:I100, ">0")'
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_formulas.xlsx")
You should get the number 21 on your P3 spreadsheet cell like so:
You’ll have to make sure that the strings within a formula are always in double quotes, so you either have to use single quotes around the formula like in the example above or you’ll have to escape the double quotes inside the formula: "=COUNTIF(I2:I100, ">0")".
There are a ton of other formulas you can add to your spreadsheet using the same procedure you tried above. Give it a go yourself!
Adding Styles
Even though styling a spreadsheet might not be something you would do every day, it’s still good to know how to do it.
Using openpyxl, you can apply multiple styling options to your spreadsheet, including fonts, borders, colors, and so on. Have a look at the openpyxl documentation to learn more.
You can also choose to either apply a style directly to a cell or create a template and reuse it to apply styles to multiple cells.
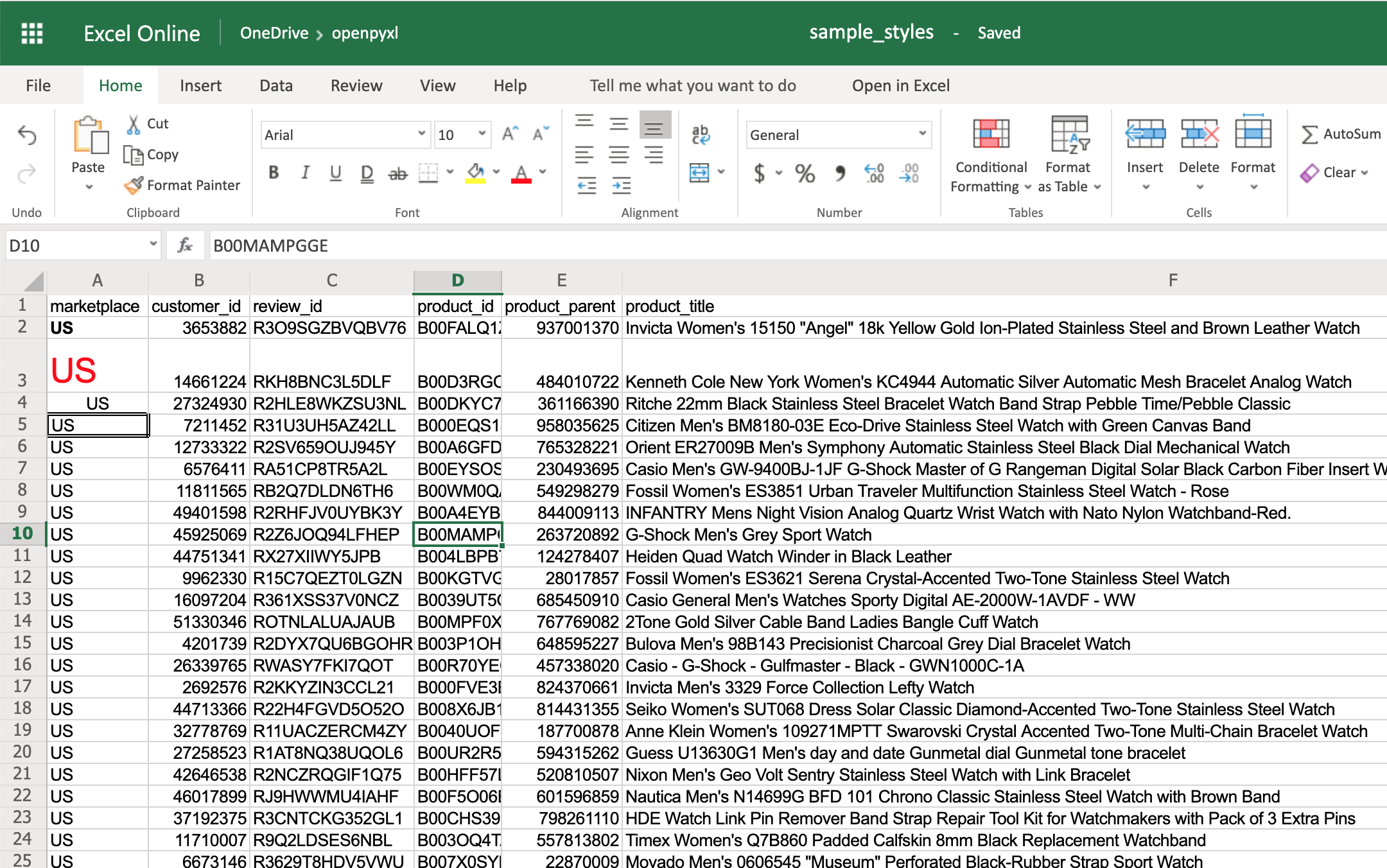
Let’s start by having a look at simple cell styling, using our sample.xlsx again as the base spreadsheet:
>>>
>>> # Import necessary style classes
>>> from openpyxl.styles import Font, Color, Alignment, Border, Side
>>> # Create a few styles
>>> bold_font = Font(bold=True)
>>> big_red_text = Font(color="00FF0000", size=20)
>>> center_aligned_text = Alignment(horizontal="center")
>>> double_border_side = Side(border_style="double")
>>> square_border = Border(top=double_border_side,
... right=double_border_side,
... bottom=double_border_side,
... left=double_border_side)
>>> # Style some cells!
>>> sheet["A2"].font = bold_font
>>> sheet["A3"].font = big_red_text
>>> sheet["A4"].alignment = center_aligned_text
>>> sheet["A5"].border = square_border
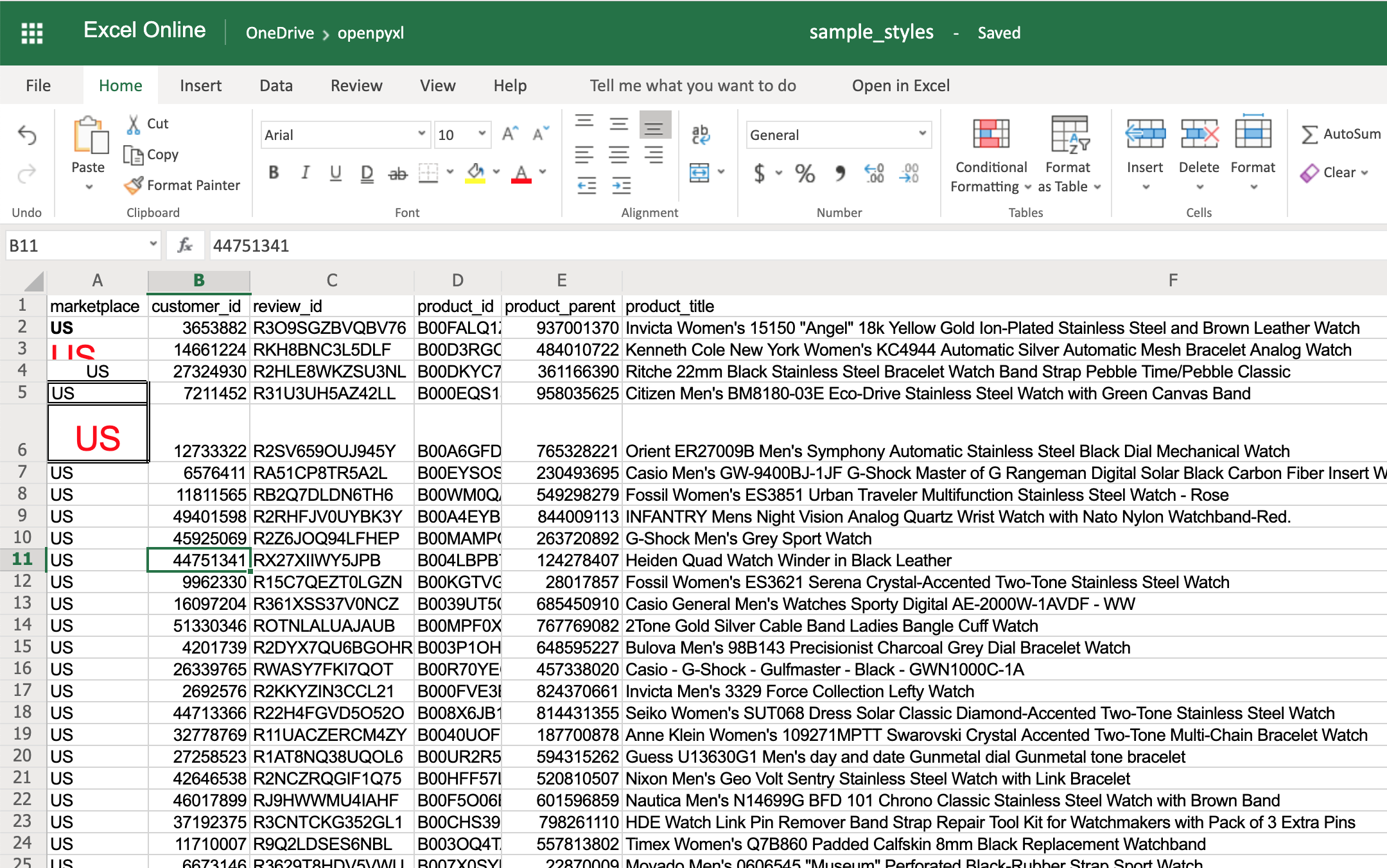
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_styles.xlsx")
If you open your spreadsheet now, you should see quite a few different styles on the first 5 cells of column A:
There you go. You got:
- A2 with the text in bold
- A3 with the text in red and bigger font size
- A4 with the text centered
- A5 with a square border around the text
You can also combine styles by simply adding them to the cell at the same time:
>>>
>>> # Reusing the same styles from the example above
>>> sheet["A6"].alignment = center_aligned_text
>>> sheet["A6"].font = big_red_text
>>> sheet["A6"].border = square_border
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_styles.xlsx")
Have a look at cell A6 here:
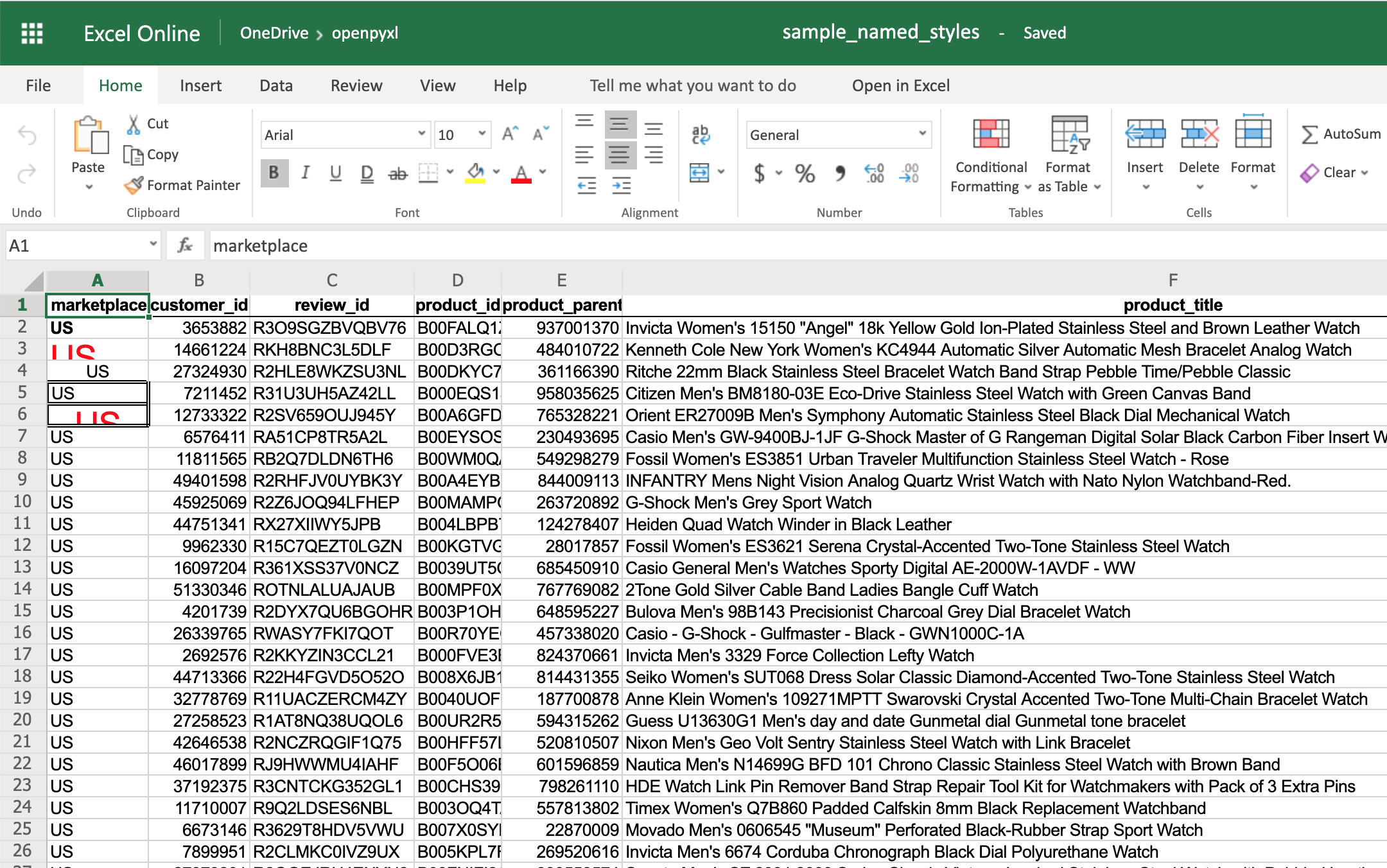
When you want to apply multiple styles to one or several cells, you can use a NamedStyle class instead, which is like a style template that you can use over and over again. Have a look at the example below:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl.styles import NamedStyle
>>> # Let's create a style template for the header row
>>> header = NamedStyle(name="header")
>>> header.font = Font(bold=True)
>>> header.border = Border(bottom=Side(border_style="thin"))
>>> header.alignment = Alignment(horizontal="center", vertical="center")
>>> # Now let's apply this to all first row (header) cells
>>> header_row = sheet[1]
>>> for cell in header_row:
... cell.style = header
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_styles.xlsx")
If you open the spreadsheet now, you should see that its first row is bold, the text is aligned to the center, and there’s a small bottom border! Have a look below:
As you saw above, there are many options when it comes to styling, and it depends on the use case, so feel free to check openpyxl documentation and see what other things you can do.
Conditional Formatting
This feature is one of my personal favorites when it comes to adding styles to a spreadsheet.
It’s a much more powerful approach to styling because it dynamically applies styles according to how the data in the spreadsheet changes.
In a nutshell, conditional formatting allows you to specify a list of styles to apply to a cell (or cell range) according to specific conditions.
For example, a widespread use case is to have a balance sheet where all the negative totals are in red, and the positive ones are in green. This formatting makes it much more efficient to spot good vs bad periods.
Without further ado, let’s pick our favorite spreadsheet—sample.xlsx—and add some conditional formatting.
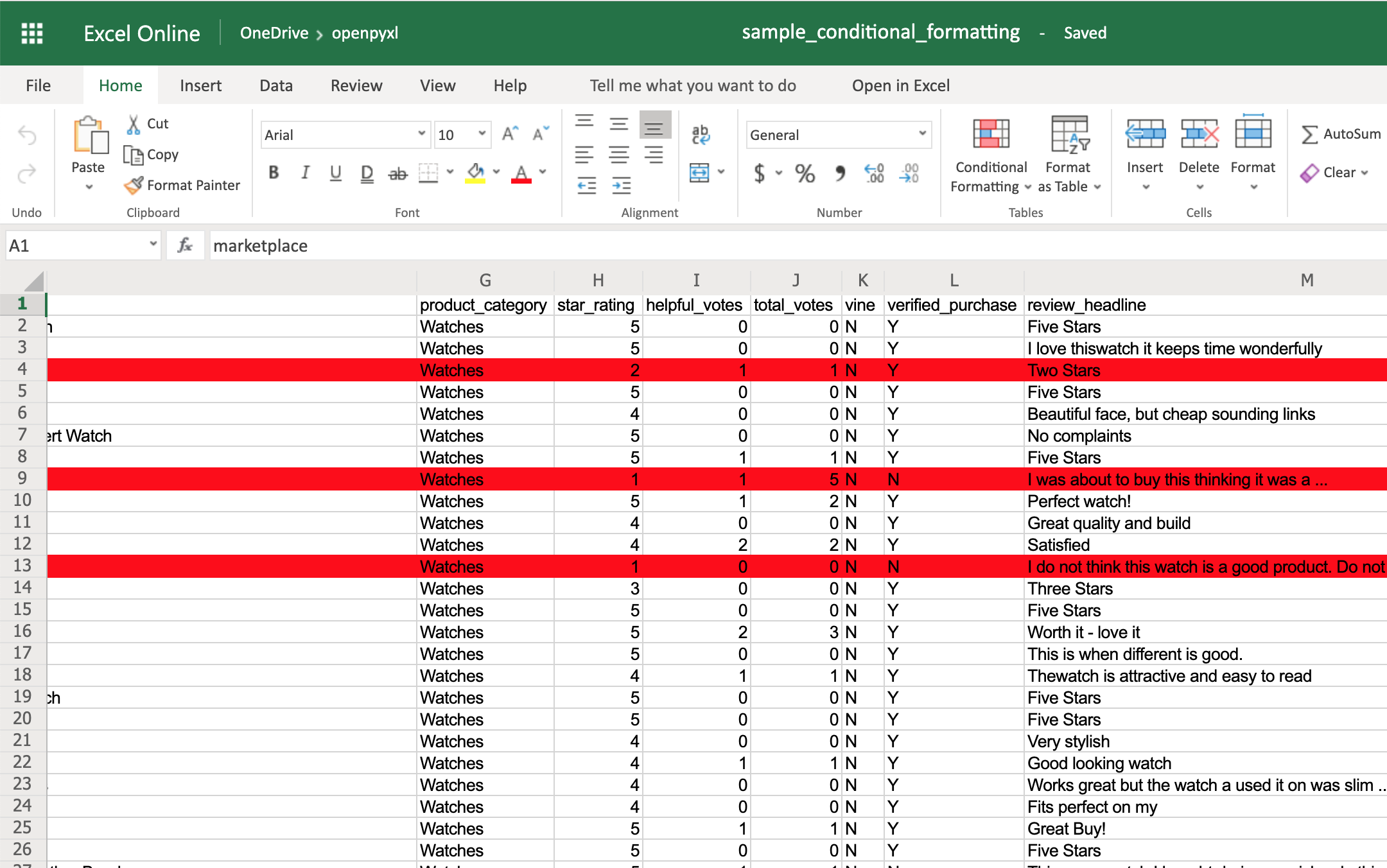
You can start by adding a simple one that adds a red background to all reviews with less than 3 stars:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl.styles import PatternFill
>>> from openpyxl.styles.differential import DifferentialStyle
>>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import Rule
>>> red_background = PatternFill(fgColor="00FF0000")
>>> diff_style = DifferentialStyle(fill=red_background)
>>> rule = Rule(type="expression", dxf=diff_style)
>>> rule.formula = ["$H1<3"]
>>> sheet.conditional_formatting.add("A1:O100", rule)
>>> workbook.save("sample_conditional_formatting.xlsx")
Now you’ll see all the reviews with a star rating below 3 marked with a red background:
Code-wise, the only things that are new here are the objects DifferentialStyle and Rule:
DifferentialStyleis quite similar toNamedStyle, which you already saw above, and it’s used to aggregate multiple styles such as fonts, borders, alignment, and so forth.Ruleis responsible for selecting the cells and applying the styles if the cells match the rule’s logic.
Using a Rule object, you can create numerous conditional formatting scenarios.
However, for simplicity sake, the openpyxl package offers 3 built-in formats that make it easier to create a few common conditional formatting patterns. These built-ins are:
ColorScaleIconSetDataBar
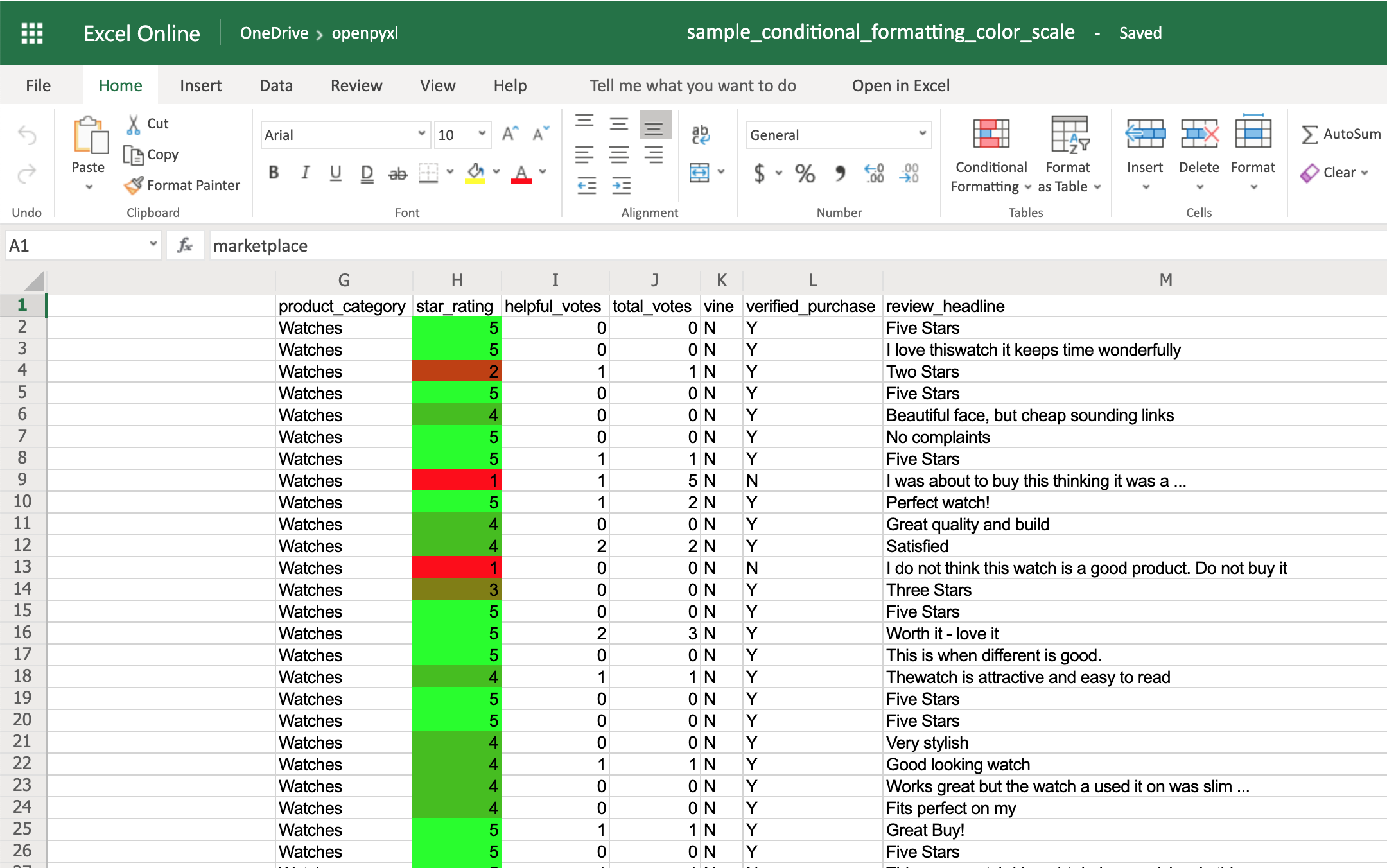
The ColorScale gives you the ability to create color gradients:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import ColorScaleRule
>>> color_scale_rule = ColorScaleRule(start_type="min",
... start_color="00FF0000", # Red
... end_type="max",
... end_color="0000FF00") # Green
>>> # Again, let's add this gradient to the star ratings, column "H"
>>> sheet.conditional_formatting.add("H2:H100", color_scale_rule)
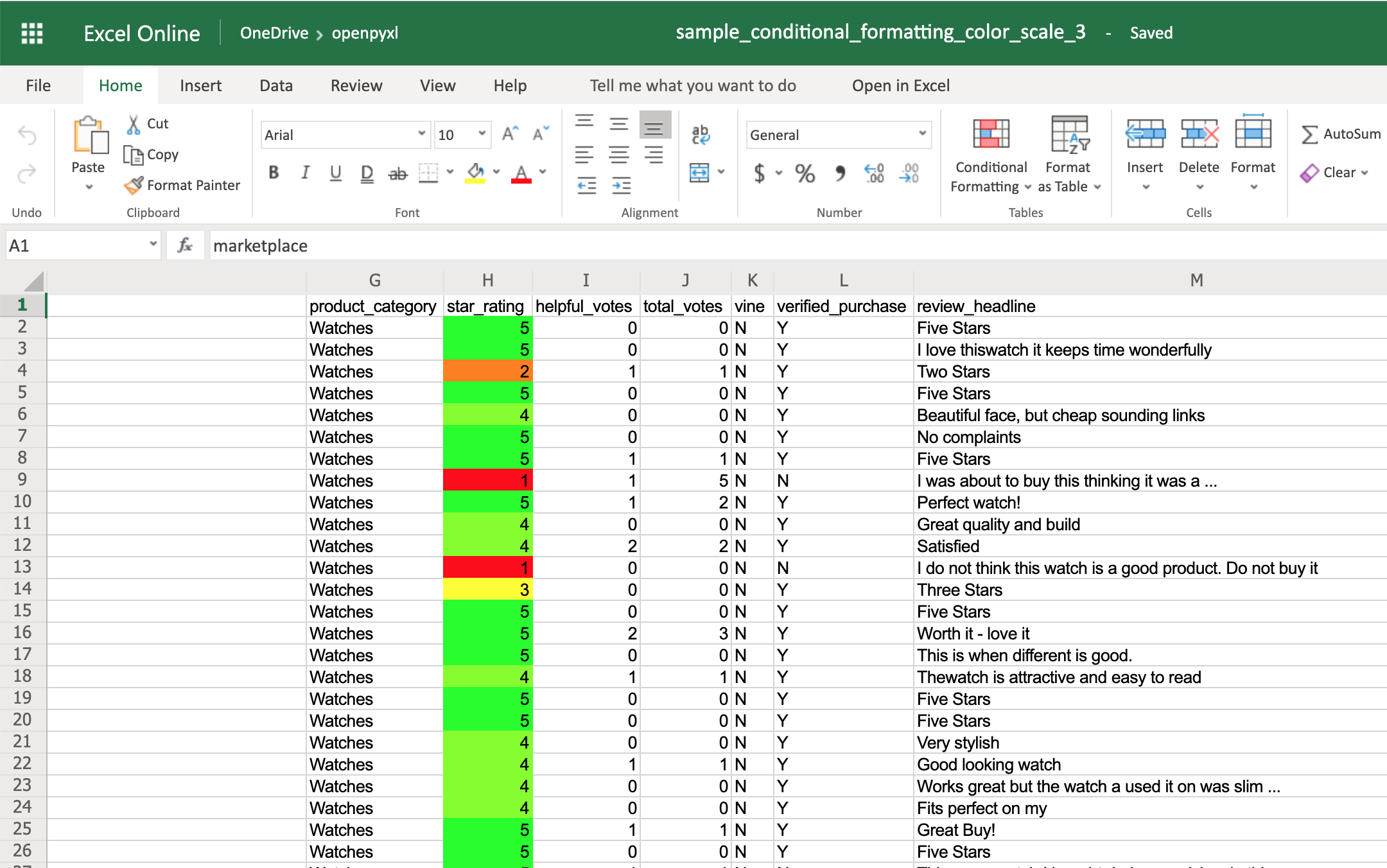
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_conditional_formatting_color_scale.xlsx")
Now you should see a color gradient on column H, from red to green, according to the star rating:
You can also add a third color and make two gradients instead:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import ColorScaleRule
>>> color_scale_rule = ColorScaleRule(start_type="num",
... start_value=1,
... start_color="00FF0000", # Red
... mid_type="num",
... mid_value=3,
... mid_color="00FFFF00", # Yellow
... end_type="num",
... end_value=5,
... end_color="0000FF00") # Green
>>> # Again, let's add this gradient to the star ratings, column "H"
>>> sheet.conditional_formatting.add("H2:H100", color_scale_rule)
>>> workbook.save(filename="sample_conditional_formatting_color_scale_3.xlsx")
This time, you’ll notice that star ratings between 1 and 3 have a gradient from red to yellow, and star ratings between 3 and 5 have a gradient from yellow to green:
The IconSet allows you to add an icon to the cell according to its value:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import IconSetRule
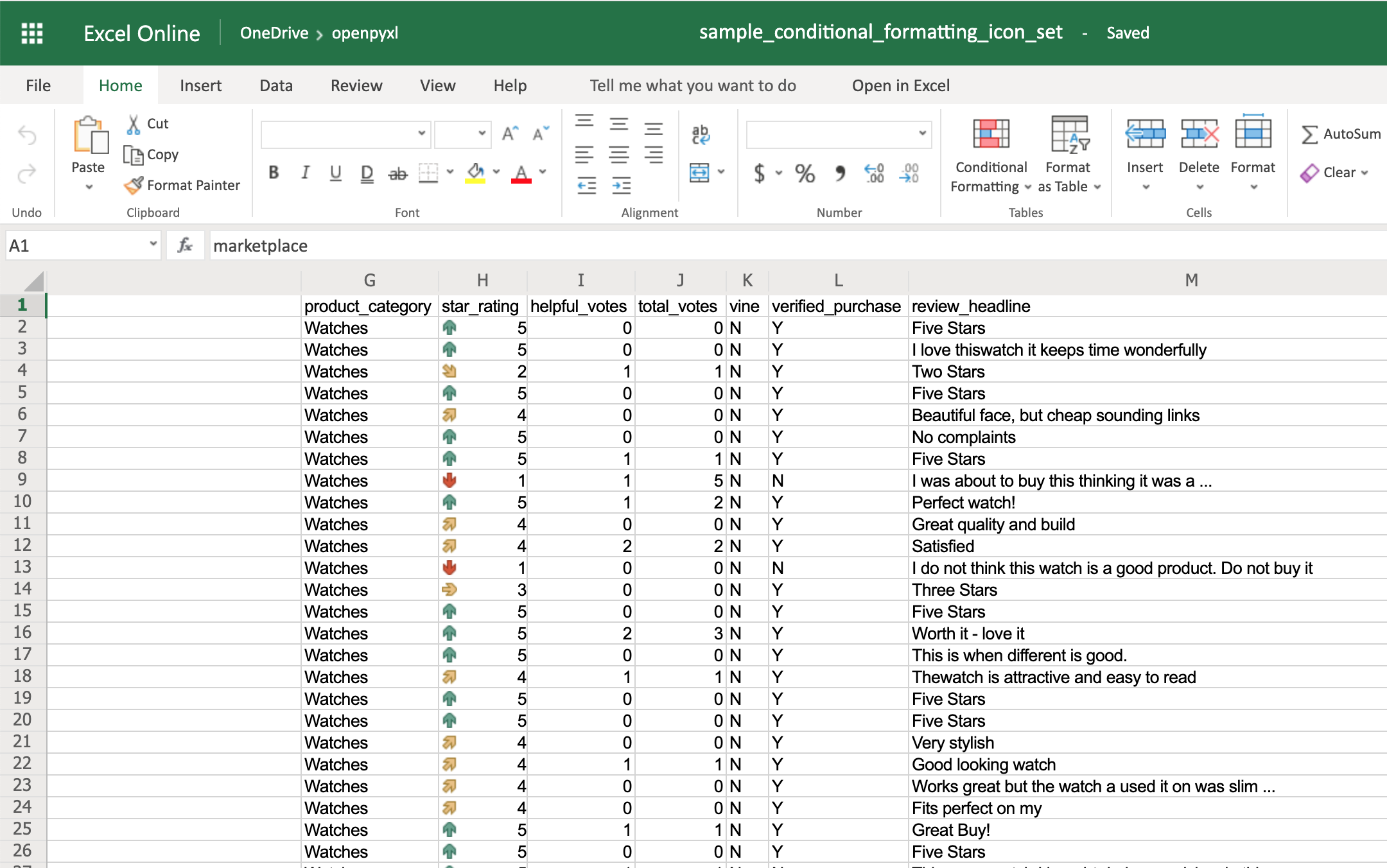
>>> icon_set_rule = IconSetRule("5Arrows", "num", [1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
>>> sheet.conditional_formatting.add("H2:H100", icon_set_rule)
>>> workbook.save("sample_conditional_formatting_icon_set.xlsx")
You’ll see a colored arrow next to the star rating. This arrow is red and points down when the value of the cell is 1 and, as the rating gets better, the arrow starts pointing up and becomes green:
The openpyxl package has a full list of other icons you can use, besides the arrow.
Finally, the DataBar allows you to create progress bars:
>>>
>>> from openpyxl.formatting.rule import DataBarRule
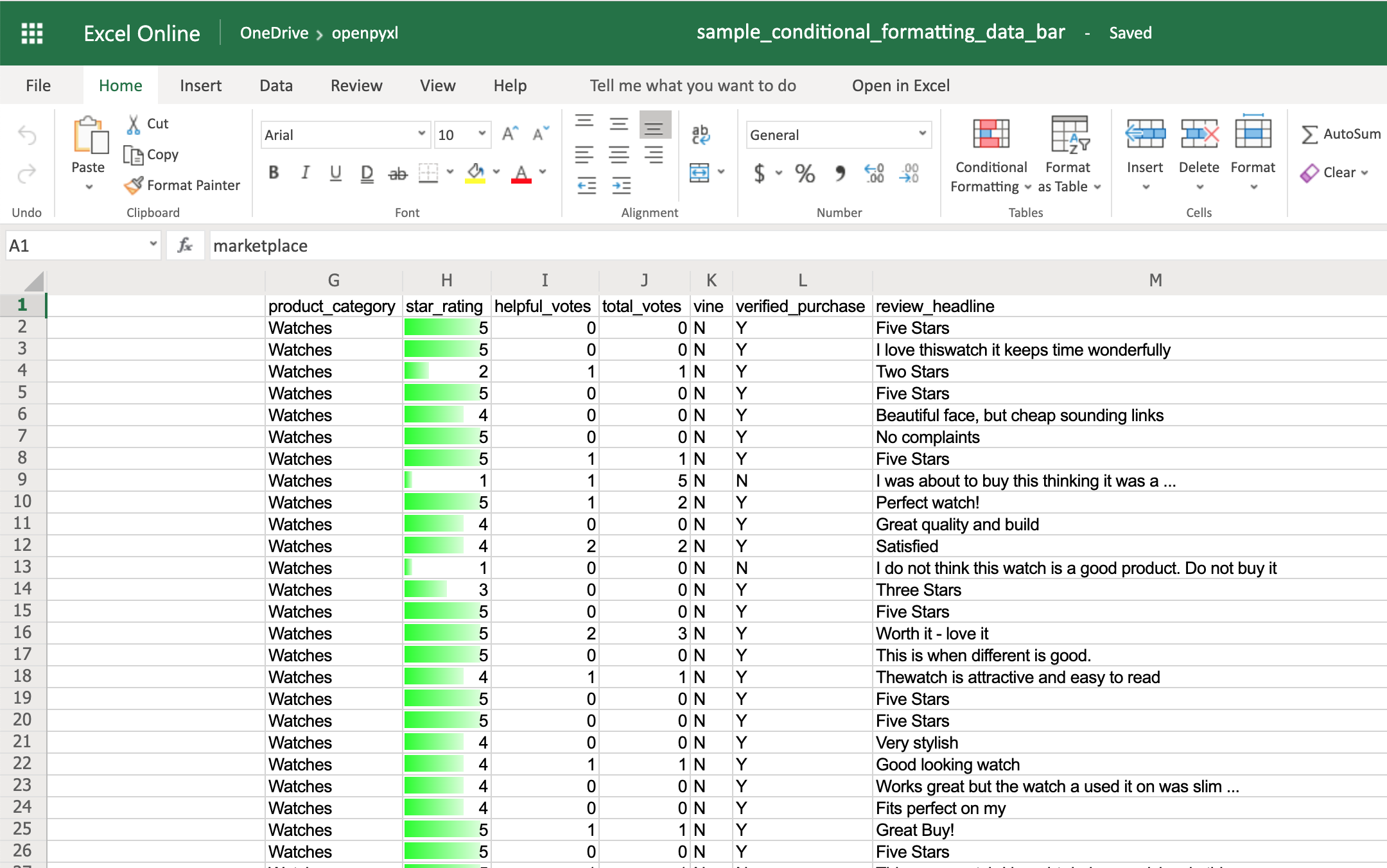
>>> data_bar_rule = DataBarRule(start_type="num",
... start_value=1,
... end_type="num",
... end_value="5",
... color="0000FF00") # Green
>>> sheet.conditional_formatting.add("H2:H100", data_bar_rule)
>>> workbook.save("sample_conditional_formatting_data_bar.xlsx")
You’ll now see a green progress bar that gets fuller the closer the star rating is to the number 5:
As you can see, there are a lot of cool things you can do with conditional formatting.
Here, you saw only a few examples of what you can achieve with it, but check the openpyxl documentation to see a bunch of other options.
Adding Images
Even though images are not something that you’ll often see in a spreadsheet, it’s quite cool to be able to add them. Maybe you can use it for branding purposes or to make spreadsheets more personal.
To be able to load images to a spreadsheet using openpyxl, you’ll have to install Pillow:
Apart from that, you’ll also need an image. For this example, you can grab the Real Python logo below and convert it from .webp to .png using an online converter such as cloudconvert.com, save the final file as logo.png, and copy it to the root folder where you’re running your examples:
Afterward, this is the code you need to import that image into the hello_word.xlsx spreadsheet:
from openpyxl import load_workbook
from openpyxl.drawing.image import Image
# Let's use the hello_world spreadsheet since it has less data
workbook = load_workbook(filename="hello_world.xlsx")
sheet = workbook.active
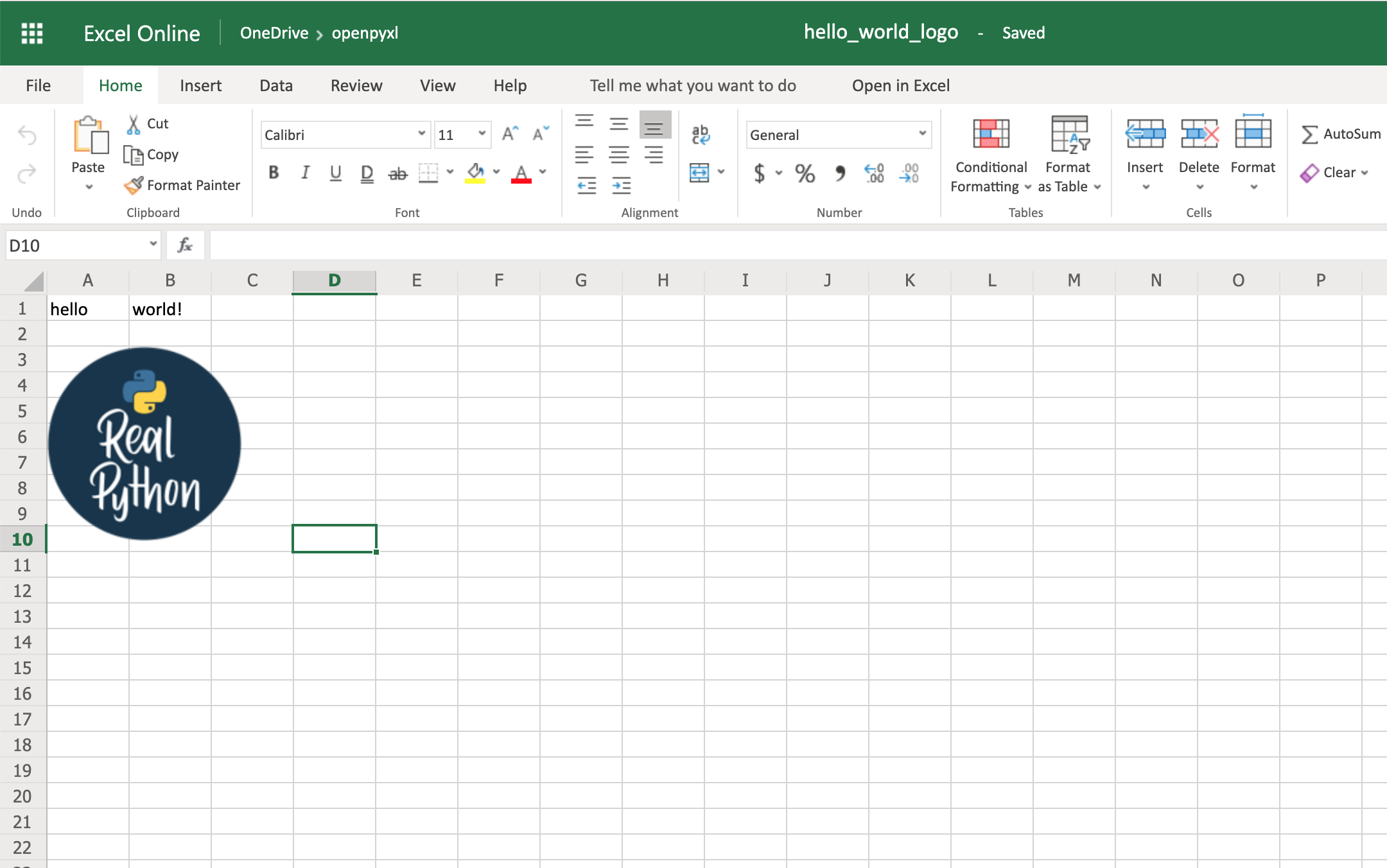
logo = Image("logo.png")
# A bit of resizing to not fill the whole spreadsheet with the logo
logo.height = 150
logo.width = 150
sheet.add_image(logo, "A3")
workbook.save(filename="hello_world_logo.xlsx")
You have an image on your spreadsheet! Here it is:
The image’s left top corner is on the cell you chose, in this case, A3.
Adding Pretty Charts
Another powerful thing you can do with spreadsheets is create an incredible variety of charts.
Charts are a great way to visualize and understand loads of data quickly. There are a lot of different chart types: bar chart, pie chart, line chart, and so on. openpyxl has support for a lot of them.
Here, you’ll see only a couple of examples of charts because the theory behind it is the same for every single chart type:
For any chart you want to build, you’ll need to define the chart type: BarChart, LineChart, and so forth, plus the data to be used for the chart, which is called Reference.
Before you can build your chart, you need to define what data you want to see represented in it. Sometimes, you can use the dataset as is, but other times you need to massage the data a bit to get additional information.
Let’s start by building a new workbook with some sample data:
1from openpyxl import Workbook
2from openpyxl.chart import BarChart, Reference
3
4workbook = Workbook()
5sheet = workbook.active
6
7# Let's create some sample sales data
8rows = [
9 ["Product", "Online", "Store"],
10 [1, 30, 45],
11 [2, 40, 30],
12 [3, 40, 25],
13 [4, 50, 30],
14 [5, 30, 25],
15 [6, 25, 35],
16 [7, 20, 40],
17]
18
19for row in rows:
20 sheet.append(row)
Now you’re going to start by creating a bar chart that displays the total number of sales per product:
22chart = BarChart()
23data = Reference(worksheet=sheet,
24 min_row=1,
25 max_row=8,
26 min_col=2,
27 max_col=3)
28
29chart.add_data(data, titles_from_data=True)
30sheet.add_chart(chart, "E2")
31
32workbook.save("chart.xlsx")
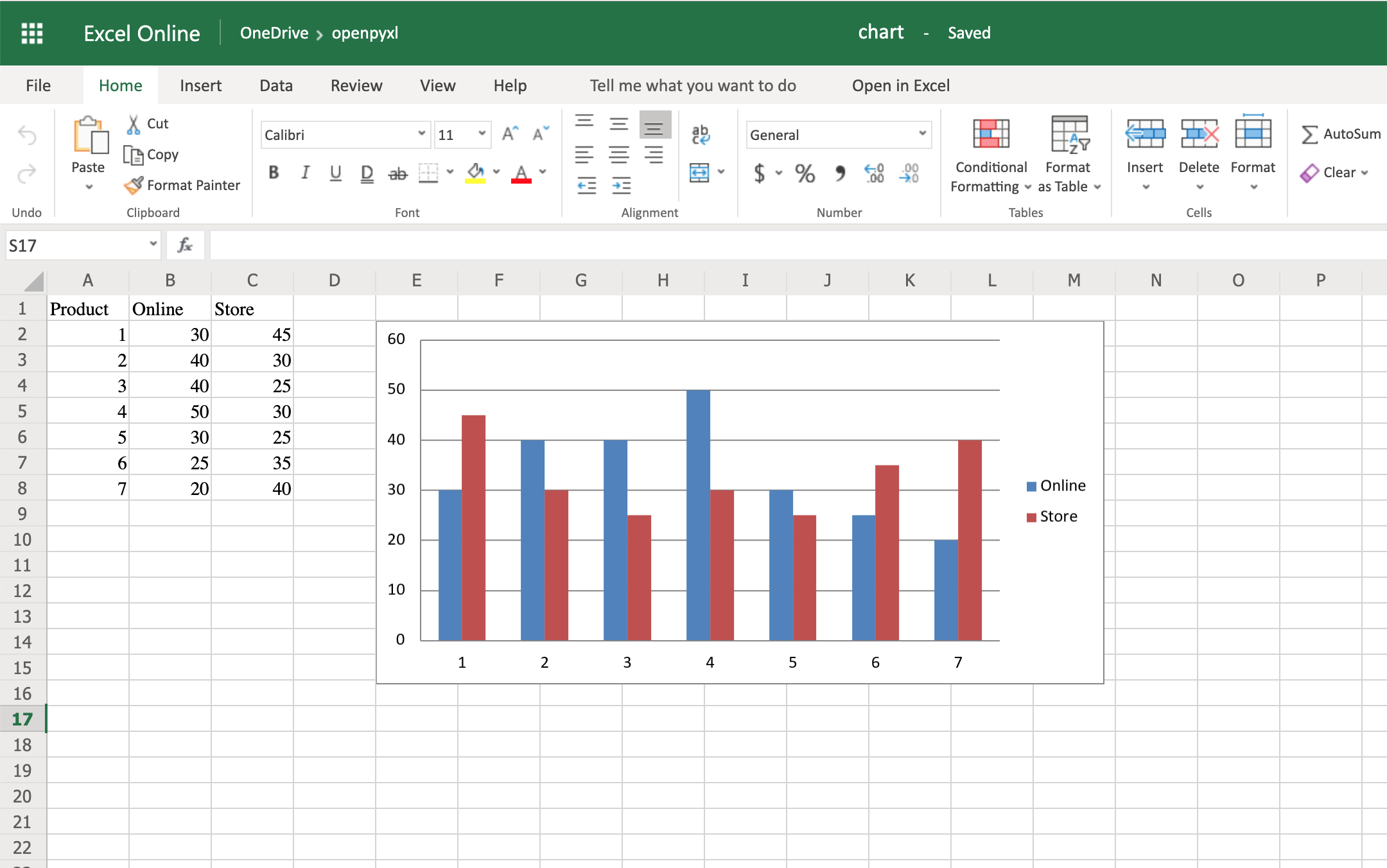
There you have it. Below, you can see a very straightforward bar chart showing the difference between online product sales online and in-store product sales:
Like with images, the top left corner of the chart is on the cell you added the chart to. In your case, it was on cell E2.
Try creating a line chart instead, changing the data a bit:
1import random
2from openpyxl import Workbook
3from openpyxl.chart import LineChart, Reference
4
5workbook = Workbook()
6sheet = workbook.active
7
8# Let's create some sample sales data
9rows = [
10 ["", "January", "February", "March", "April",
11 "May", "June", "July", "August", "September",
12 "October", "November", "December"],
13 [1, ],
14 [2, ],
15 [3, ],
16]
17
18for row in rows:
19 sheet.append(row)
20
21for row in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=2,
22 max_row=4,
23 min_col=2,
24 max_col=13):
25 for cell in row:
26 cell.value = random.randrange(5, 100)
With the above code, you’ll be able to generate some random data regarding the sales of 3 different products across a whole year.
Once that’s done, you can very easily create a line chart with the following code:
28chart = LineChart()
29data = Reference(worksheet=sheet,
30 min_row=2,
31 max_row=4,
32 min_col=1,
33 max_col=13)
34
35chart.add_data(data, from_rows=True, titles_from_data=True)
36sheet.add_chart(chart, "C6")
37
38workbook.save("line_chart.xlsx")
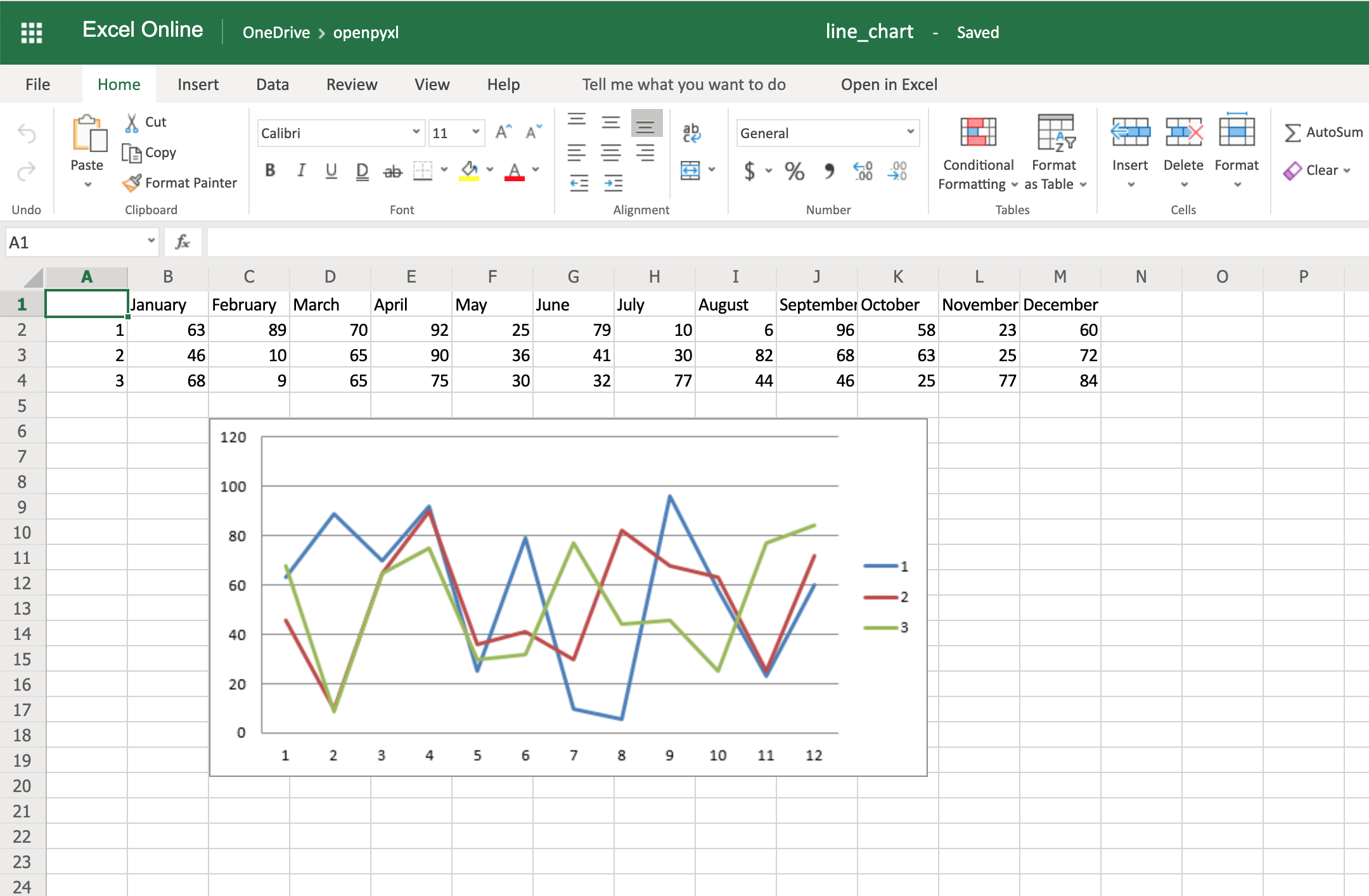
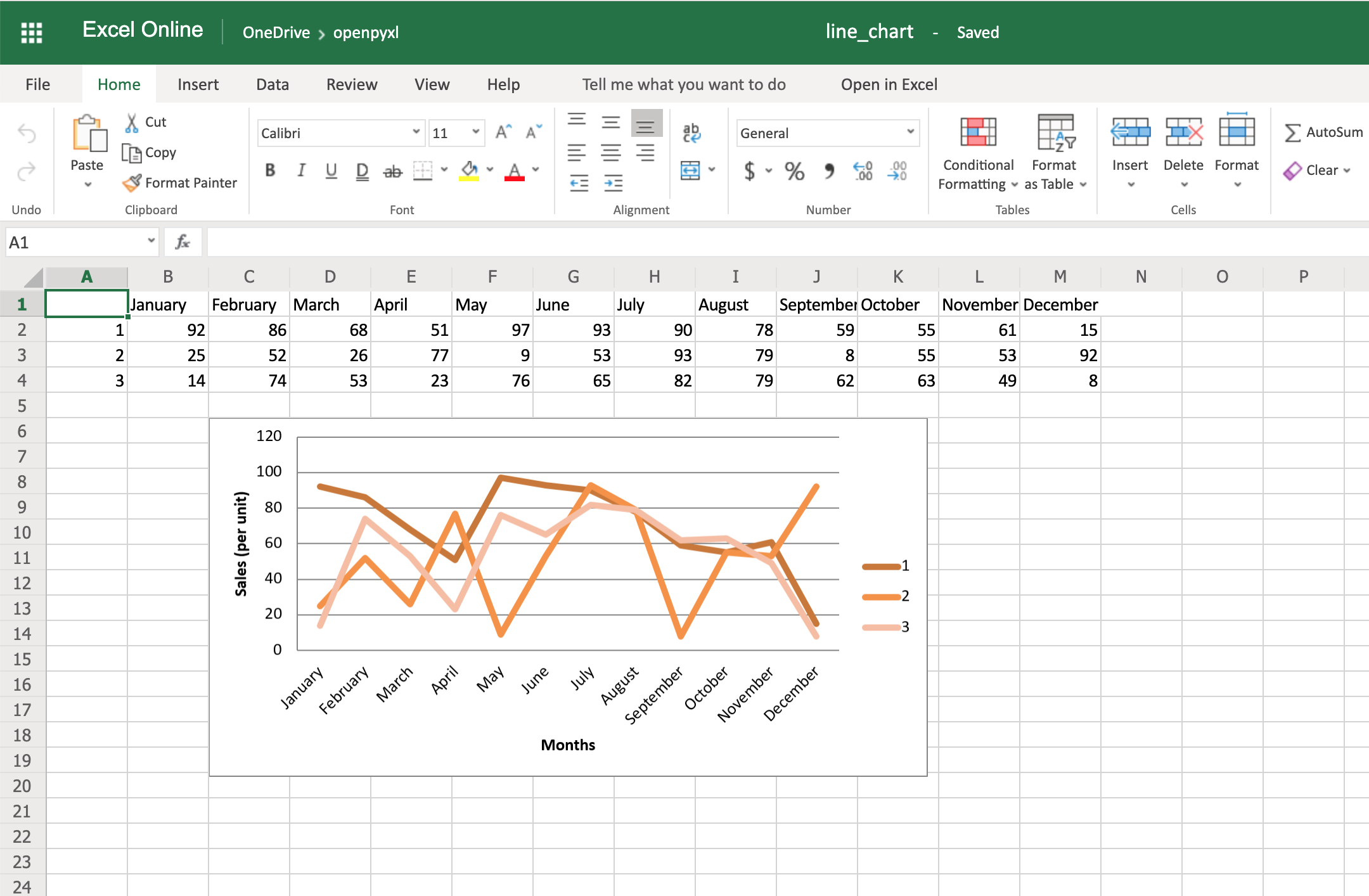
Here’s the outcome of the above piece of code:
One thing to keep in mind here is the fact that you’re using from_rows=True when adding the data. This argument makes the chart plot row by row instead of column by column.
In your sample data, you see that each product has a row with 12 values (1 column per month). That’s why you use from_rows. If you don’t pass that argument, by default, the chart tries to plot by column, and you’ll get a month-by-month comparison of sales.
Another difference that has to do with the above argument change is the fact that our Reference now starts from the first column, min_col=1, instead of the second one. This change is needed because the chart now expects the first column to have the titles.
There are a couple of other things you can also change regarding the style of the chart. For example, you can add specific categories to the chart:
cats = Reference(worksheet=sheet,
min_row=1,
max_row=1,
min_col=2,
max_col=13)
chart.set_categories(cats)
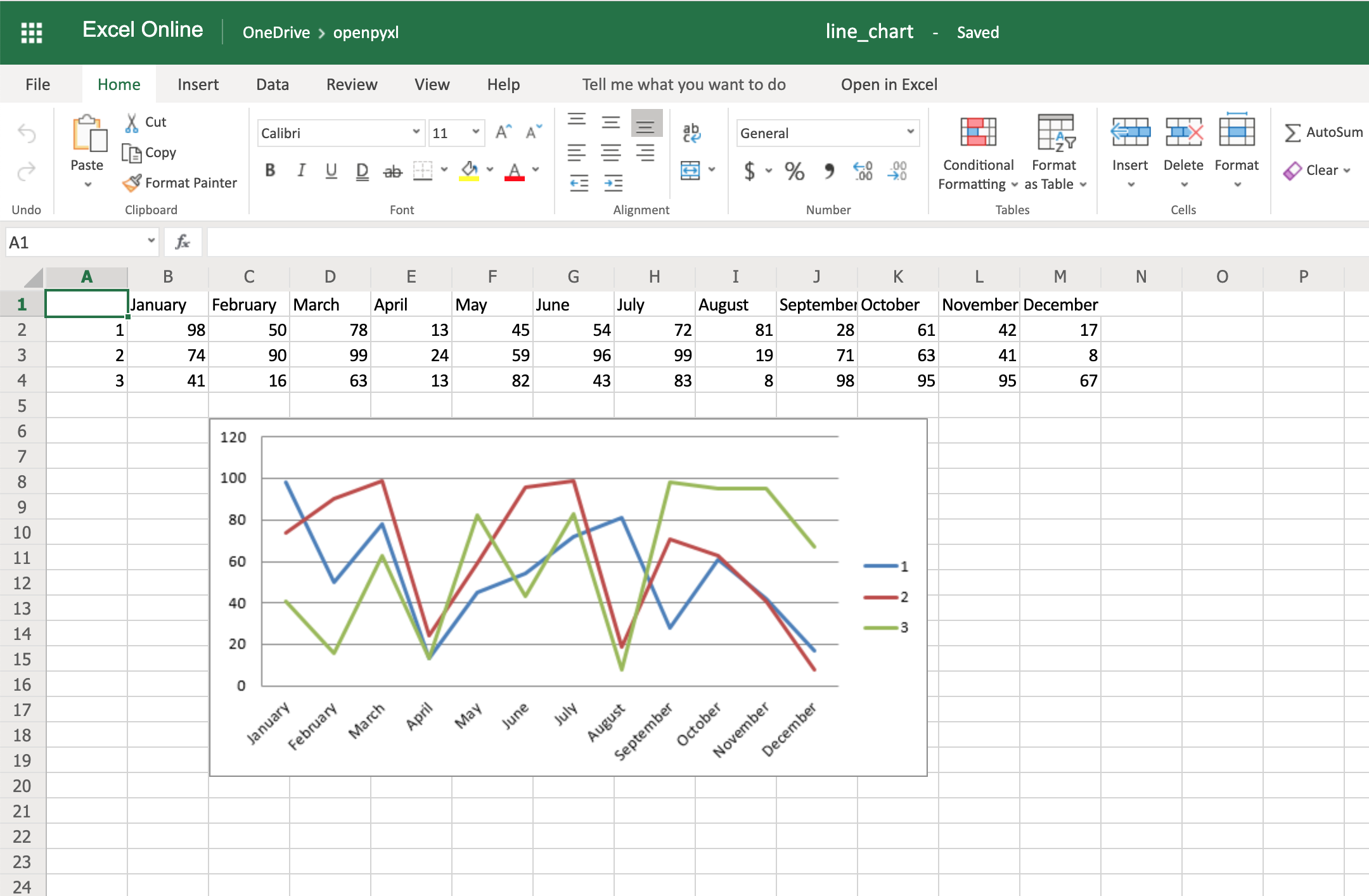
Add this piece of code before saving the workbook, and you should see the month names appearing instead of numbers:
Code-wise, this is a minimal change. But in terms of the readability of the spreadsheet, this makes it much easier for someone to open the spreadsheet and understand the chart straight away.
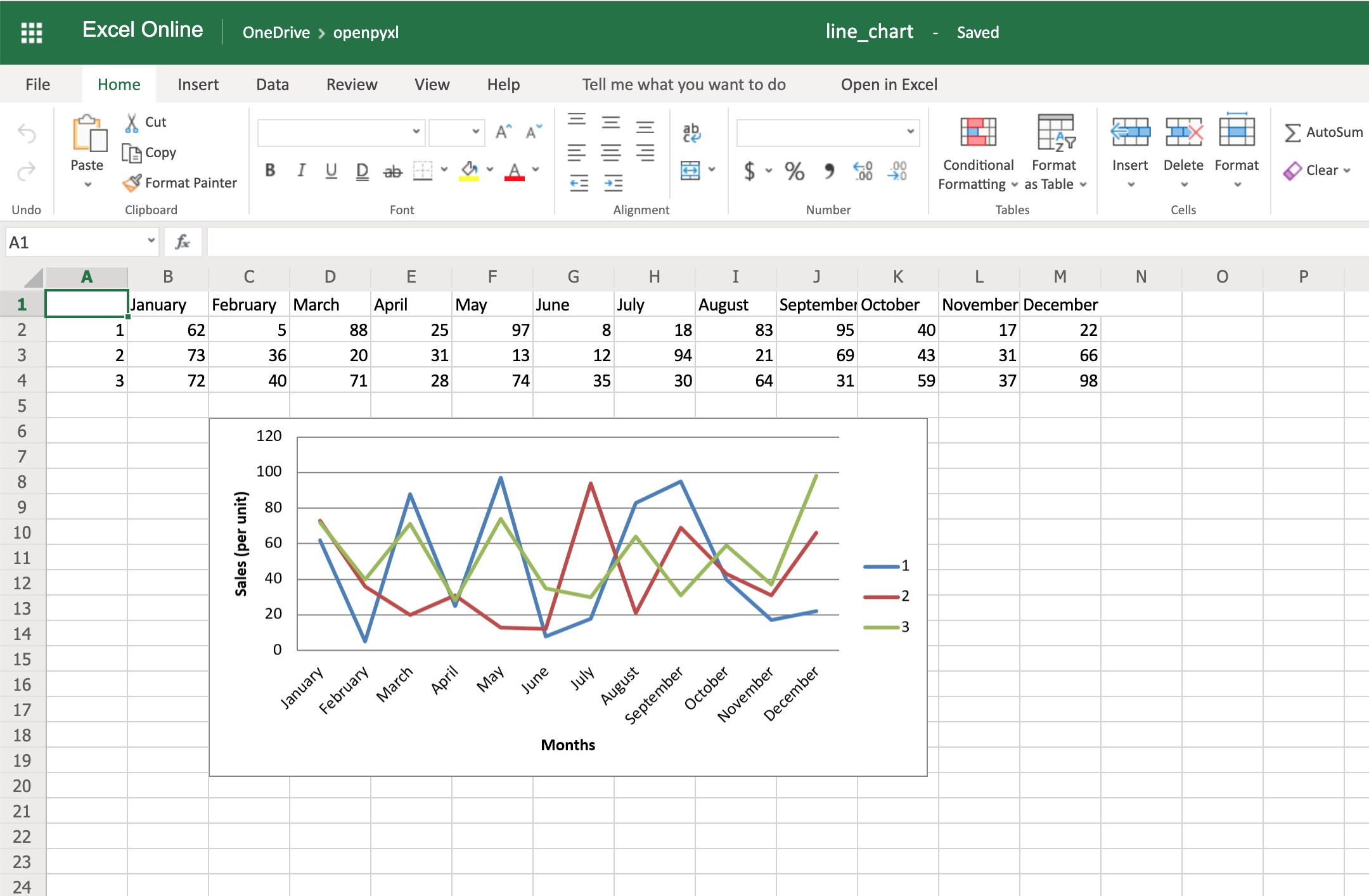
Another thing you can do to improve the chart readability is to add an axis. You can do it using the attributes x_axis and y_axis:
chart.x_axis.title = "Months"
chart.y_axis.title = "Sales (per unit)"
This will generate a spreadsheet like the below one:
As you can see, small changes like the above make reading your chart a much easier and quicker task.
There is also a way to style your chart by using Excel’s default ChartStyle property. In this case, you have to choose a number between 1 and 48. Depending on your choice, the colors of your chart change as well:
# You can play with this by choosing any number between 1 and 48
chart.style = 24
With the style selected above, all lines have some shade of orange:
There is no clear documentation on what each style number looks like, but this spreadsheet has a few examples of the styles available.
Here’s the full code used to generate the line chart with categories, axis titles, and style:
import random
from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.chart import LineChart, Reference
workbook = Workbook()
sheet = workbook.active
# Let's create some sample sales data
rows = [
["", "January", "February", "March", "April",
"May", "June", "July", "August", "September",
"October", "November", "December"],
[1, ],
[2, ],
[3, ],
]
for row in rows:
sheet.append(row)
for row in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=2,
max_row=4,
min_col=2,
max_col=13):
for cell in row:
cell.value = random.randrange(5, 100)
# Create a LineChart and add the main data
chart = LineChart()
data = Reference(worksheet=sheet,
min_row=2,
max_row=4,
min_col=1,
max_col=13)
chart.add_data(data, titles_from_data=True, from_rows=True)
# Add categories to the chart
cats = Reference(worksheet=sheet,
min_row=1,
max_row=1,
min_col=2,
max_col=13)
chart.set_categories(cats)
# Rename the X and Y Axis
chart.x_axis.title = "Months"
chart.y_axis.title = "Sales (per unit)"
# Apply a specific Style
chart.style = 24
# Save!
sheet.add_chart(chart, "C6")
workbook.save("line_chart.xlsx")
There are a lot more chart types and customization you can apply, so be sure to check out the package documentation on this if you need some specific formatting.
Convert Python Classes to Excel Spreadsheet
You already saw how to convert an Excel spreadsheet’s data into Python classes, but now let’s do the opposite.
Let’s imagine you have a database and are using some Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) to map DB objects into Python classes. Now, you want to export those same objects into a spreadsheet.
Let’s assume the following data classes to represent the data coming from your database regarding product sales:
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import List
@dataclass
class Sale:
quantity: int
@dataclass
class Product:
id: str
name: str
sales: List[Sale]
Now, let’s generate some random data, assuming the above classes are stored in a db_classes.py file:
1import random
2
3# Ignore these for now. You'll use them in a sec ;)
4from openpyxl import Workbook
5from openpyxl.chart import LineChart, Reference
6
7from db_classes import Product, Sale
8
9products = []
10
11# Let's create 5 products
12for idx in range(1, 6):
13 sales = []
14
15 # Create 5 months of sales
16 for _ in range(5):
17 sale = Sale(quantity=random.randrange(5, 100))
18 sales.append(sale)
19
20 product = Product(id=str(idx),
21 name="Product %s" % idx,
22 sales=sales)
23 products.append(product)
By running this piece of code, you should get 5 products with 5 months of sales with a random quantity of sales for each month.
Now, to convert this into a spreadsheet, you need to iterate over the data and append it to the spreadsheet:
25workbook = Workbook()
26sheet = workbook.active
27
28# Append column names first
29sheet.append(["Product ID", "Product Name", "Month 1",
30 "Month 2", "Month 3", "Month 4", "Month 5"])
31
32# Append the data
33for product in products:
34 data = [product.id, product.name]
35 for sale in product.sales:
36 data.append(sale.quantity)
37 sheet.append(data)
That’s it. That should allow you to create a spreadsheet with some data coming from your database.
However, why not use some of that cool knowledge you gained recently to add a chart as well to display that data more visually?
All right, then you could probably do something like this:
38chart = LineChart()
39data = Reference(worksheet=sheet,
40 min_row=2,
41 max_row=6,
42 min_col=2,
43 max_col=7)
44
45chart.add_data(data, titles_from_data=True, from_rows=True)
46sheet.add_chart(chart, "B8")
47
48cats = Reference(worksheet=sheet,
49 min_row=1,
50 max_row=1,
51 min_col=3,
52 max_col=7)
53chart.set_categories(cats)
54
55chart.x_axis.title = "Months"
56chart.y_axis.title = "Sales (per unit)"
57
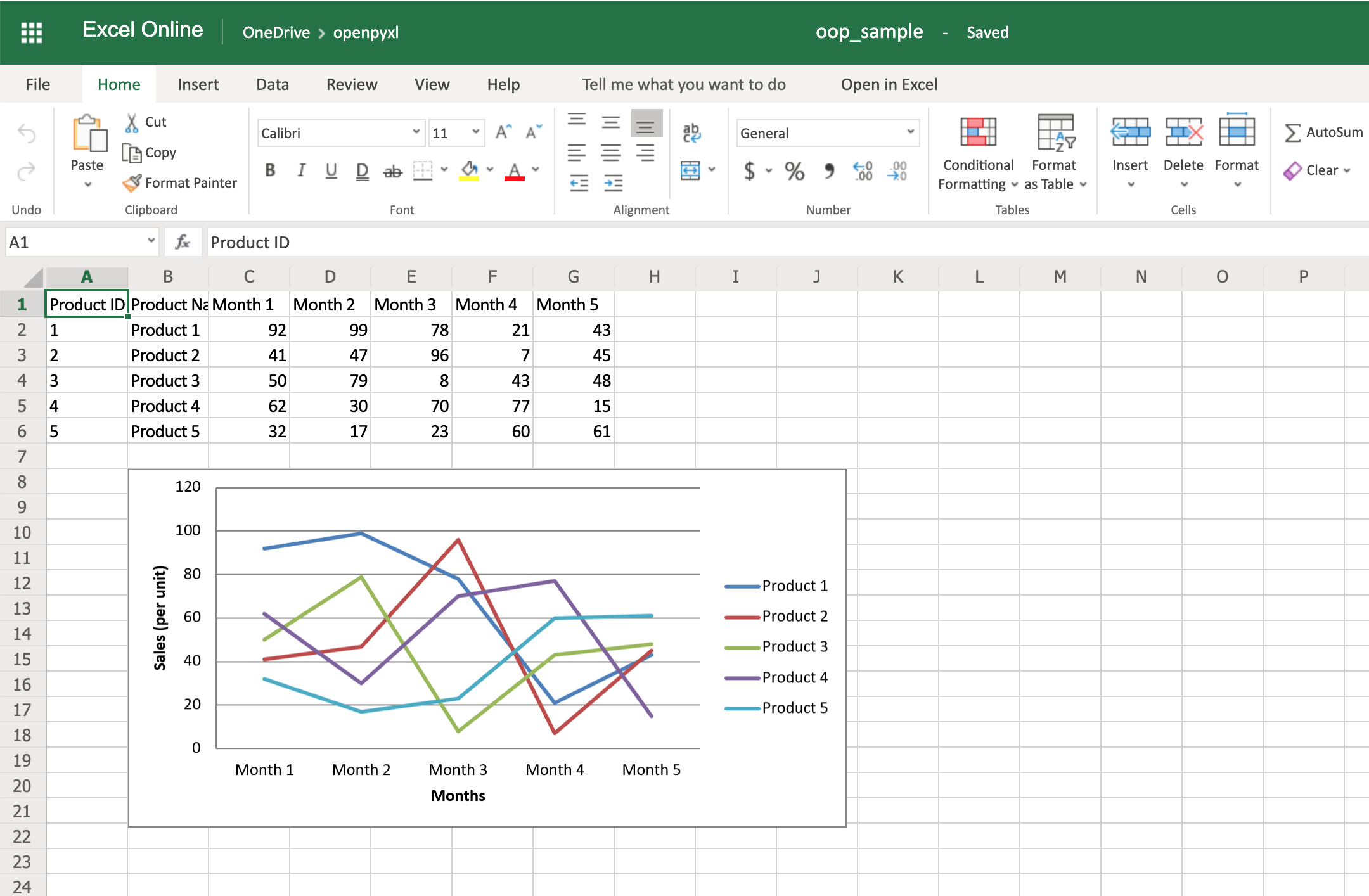
58workbook.save(filename="oop_sample.xlsx")
Now we’re talking! Here’s a spreadsheet generated from database objects and with a chart and everything:
That’s a great way for you to wrap up your new knowledge of charts!
Bonus: Working With Pandas
Even though you can use Pandas to handle Excel files, there are few things that you either can’t accomplish with Pandas or that you’d be better off just using openpyxl directly.
For example, some of the advantages of using openpyxl are the ability to easily customize your spreadsheet with styles, conditional formatting, and such.
But guess what, you don’t have to worry about picking. In fact, openpyxl has support for both converting data from a Pandas DataFrame into a workbook or the opposite, converting an openpyxl workbook into a Pandas DataFrame.
First things first, remember to install the pandas package:
Then, let’s create a sample DataFrame:
1import pandas as pd
2
3data = {
4 "Product Name": ["Product 1", "Product 2"],
5 "Sales Month 1": [10, 20],
6 "Sales Month 2": [5, 35],
7}
8df = pd.DataFrame(data)
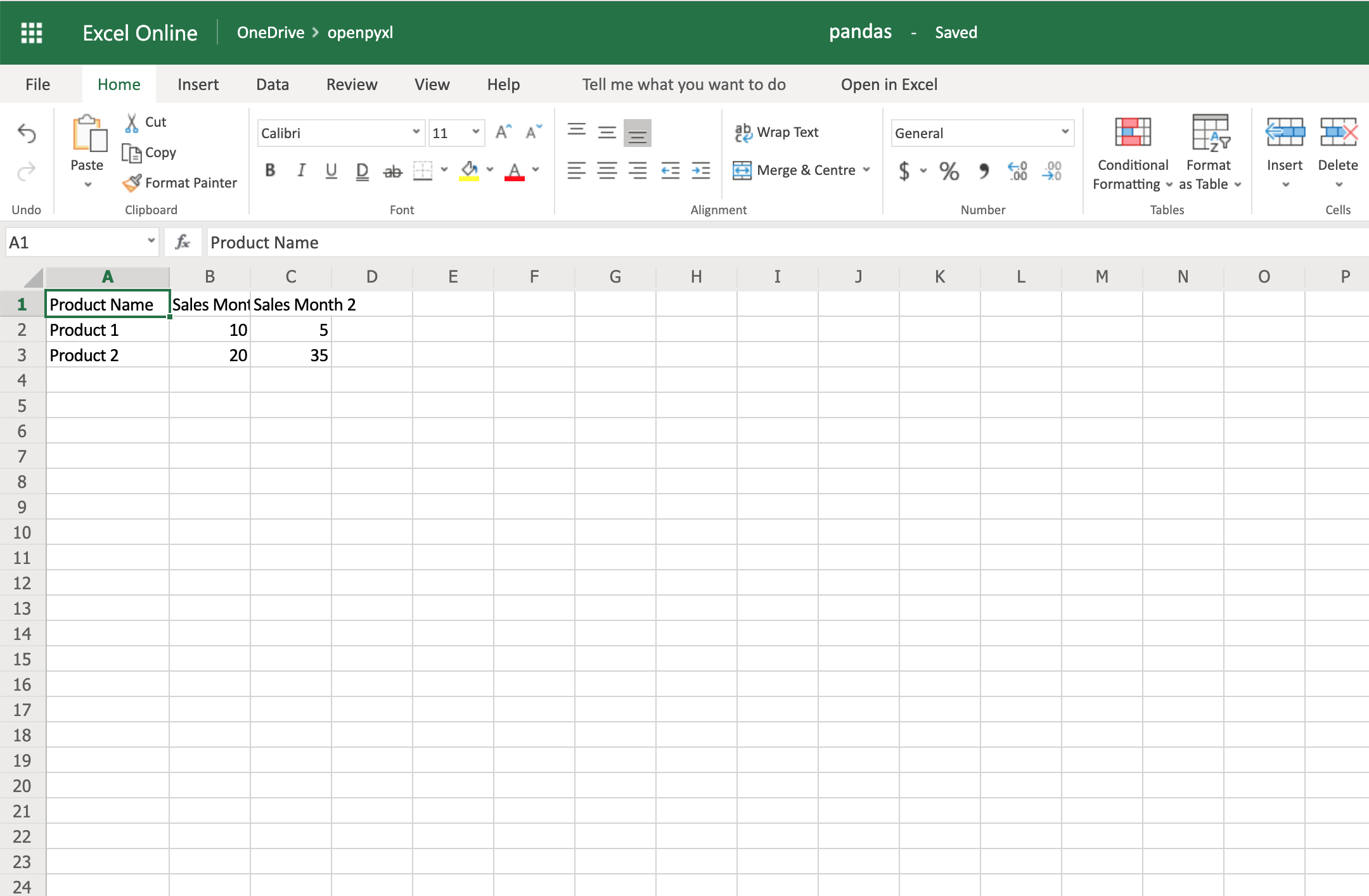
Now that you have some data, you can use .dataframe_to_rows() to convert it from a DataFrame into a worksheet:
10from openpyxl import Workbook
11from openpyxl.utils.dataframe import dataframe_to_rows
12
13workbook = Workbook()
14sheet = workbook.active
15
16for row in dataframe_to_rows(df, index=False, header=True):
17 sheet.append(row)
18
19workbook.save("pandas.xlsx")
You should see a spreadsheet that looks like this:
If you want to add the DataFrame’s index, you can change index=True, and it adds each row’s index into your spreadsheet.
On the other hand, if you want to convert a spreadsheet into a DataFrame, you can also do it in a very straightforward way like so:
import pandas as pd
from openpyxl import load_workbook
workbook = load_workbook(filename="sample.xlsx")
sheet = workbook.active
values = sheet.values
df = pd.DataFrame(values)
Alternatively, if you want to add the correct headers and use the review ID as the index, for example, then you can also do it like this instead:
import pandas as pd
from openpyxl import load_workbook
from mapping import REVIEW_ID
workbook = load_workbook(filename="sample.xlsx")
sheet = workbook.active
data = sheet.values
# Set the first row as the columns for the DataFrame
cols = next(data)
data = list(data)
# Set the field "review_id" as the indexes for each row
idx = [row[REVIEW_ID] for row in data]
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=idx, columns=cols)
Using indexes and columns allows you to access data from your DataFrame easily:
>>>
>>> df.columns
Index(['marketplace', 'customer_id', 'review_id', 'product_id',
'product_parent', 'product_title', 'product_category', 'star_rating',
'helpful_votes', 'total_votes', 'vine', 'verified_purchase',
'review_headline', 'review_body', 'review_date'],
dtype='object')
>>> # Get first 10 reviews' star rating
>>> df["star_rating"][:10]
R3O9SGZBVQBV76 5
RKH8BNC3L5DLF 5
R2HLE8WKZSU3NL 2
R31U3UH5AZ42LL 5
R2SV659OUJ945Y 4
RA51CP8TR5A2L 5
RB2Q7DLDN6TH6 5
R2RHFJV0UYBK3Y 1
R2Z6JOQ94LFHEP 5
RX27XIIWY5JPB 4
Name: star_rating, dtype: int64
>>> # Grab review with id "R2EQL1V1L6E0C9", using the index
>>> df.loc["R2EQL1V1L6E0C9"]
marketplace US
customer_id 15305006
review_id R2EQL1V1L6E0C9
product_id B004LURNO6
product_parent 892860326
review_headline Five Stars
review_body Love it
review_date 2015-08-31
Name: R2EQL1V1L6E0C9, dtype: object
There you go, whether you want to use openpyxl to prettify your Pandas dataset or use Pandas to do some hardcore algebra, you now know how to switch between both packages.
Conclusion
Phew, after that long read, you now know how to work with spreadsheets in Python! You can rely on openpyxl, your trustworthy companion, to:
- Extract valuable information from spreadsheets in a Pythonic manner
- Create your own spreadsheets, no matter the complexity level
- Add cool features such as conditional formatting or charts to your spreadsheets
There are a few other things you can do with openpyxl that might not have been covered in this tutorial, but you can always check the package’s official documentation website to learn more about it. You can even venture into checking its source code and improving the package further.
Feel free to leave any comments below if you have any questions, or if there’s any section you’d love to hear more about.
Watch Now This tutorial has a related video course created by the Real Python team. Watch it together with the written tutorial to deepen your understanding: Editing Excel Spreadsheets in Python With openpyxl
Время на прочтение
10 мин
Количество просмотров 290K
Первая часть статьи была опубликована тут.
Как читать и редактировать Excel файлы при помощи openpyxl
ПЕРЕВОД
Оригинал статьи — www.datacamp.com/community/tutorials/python-excel-tutorial
Автор — Karlijn Willems
Эта библиотека пригодится, если вы хотите читать и редактировать файлы .xlsx, xlsm, xltx и xltm.
Установите openpyxl using pip. Общие рекомендации по установке этой библиотеки — сделать это в виртуальной среде Python без системных библиотек. Вы можете использовать виртуальную среду для создания изолированных сред Python: она создает папку, содержащую все необходимые файлы, для использования библиотек, которые потребуются для Python.
Перейдите в директорию, в которой находится ваш проект, и повторно активируйте виртуальную среду venv. Затем перейдите к установке openpyxl с помощью pip, чтобы убедиться, что вы можете читать и записывать с ним файлы:
# Activate virtualenv
$ source activate venv
# Install `openpyxl` in `venv`
$ pip install openpyxl
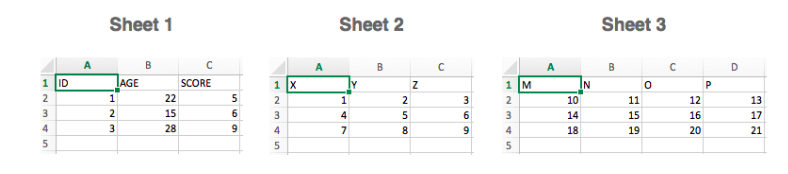
Теперь, когда вы установили openpyxl, вы можете начать загрузку данных. Но что именно это за данные? Например, в книге с данными, которые вы пытаетесь получить на Python, есть следующие листы:
Функция load_workbook () принимает имя файла в качестве аргумента и возвращает объект рабочей книги, который представляет файл. Это можно проверить запуском type (wb). Не забудьте убедиться, что вы находитесь в правильной директории, где расположена электронная таблица. В противном случае вы получите сообщение об ошибке при импорте.
# Import `load_workbook` module from `openpyxl`
from openpyxl import load_workbook
# Load in the workbook
wb = load_workbook('./test.xlsx')
# Get sheet names
print(wb.get_sheet_names())Помните, вы можете изменить рабочий каталог с помощью os.chdir (). Фрагмент кода выше возвращает имена листов книги, загруженной в Python. Вы можете использовать эту информацию для получения отдельных листов книги. Также вы можете проверить, какой лист активен в настоящий момент с помощью wb.active. В приведенном ниже коде, вы также можете использовать его для загрузки данных на другом листе книги:
# Get a sheet by name
sheet = wb.get_sheet_by_name('Sheet3')
# Print the sheet title
sheet.title
# Get currently active sheet
anotherSheet = wb.active
# Check `anotherSheet`
anotherSheetНа первый взгляд, с этими объектами Worksheet мало что можно сделать. Однако, можно извлекать значения из определенных ячеек на листе книги, используя квадратные скобки [], к которым нужно передавать точную ячейку, из которой вы хотите получить значение.
Обратите внимание, это похоже на выбор, получение и индексирование массивов NumPy и Pandas DataFrames, но это еще не все, что нужно сделать, чтобы получить значение. Нужно еще добавить значение атрибута:
# Retrieve the value of a certain cell
sheet['A1'].value
# Select element 'B2' of your sheet
c = sheet['B2']
# Retrieve the row number of your element
c.row
# Retrieve the column letter of your element
c.column
# Retrieve the coordinates of the cell
c.coordinateПомимо value, есть и другие атрибуты, которые можно использовать для проверки ячейки, а именно row, column и coordinate:
Атрибут row вернет 2;
Добавление атрибута column к “С” даст вам «B»;
coordinate вернет «B2».
Вы также можете получить значения ячеек с помощью функции cell (). Передайте аргументы row и column, добавьте значения к этим аргументам, которые соответствуют значениям ячейки, которые вы хотите получить, и, конечно же, не забудьте добавить атрибут value:
# Retrieve cell value
sheet.cell(row=1, column=2).value
# Print out values in column 2
for i in range(1, 4):
print(i, sheet.cell(row=i, column=2).value)Обратите внимание: если вы не укажете значение атрибута value, вы получите <Cell Sheet3.B1>, который ничего не говорит о значении, которое содержится в этой конкретной ячейке.
Вы используете цикл с помощью функции range (), чтобы помочь вам вывести значения строк, которые имеют значения в столбце 2. Если эти конкретные ячейки пусты, вы получите None.
Более того, существуют специальные функции, которые вы можете вызвать, чтобы получить другие значения, например get_column_letter () и column_index_from_string.
В двух функциях уже более или менее указано, что вы можете получить, используя их. Но лучше всего сделать их явными: пока вы можете получить букву прежнего столбца, можно сделать обратное или получить индекс столбца, перебирая букву за буквой. Как это работает:
# Import relevant modules from `openpyxl.utils`
from openpyxl.utils import get_column_letter, column_index_from_string
# Return 'A'
get_column_letter(1)
# Return '1'
column_index_from_string('A')Вы уже получили значения для строк, которые имеют значения в определенном столбце, но что нужно сделать, если нужно вывести строки файла, не сосредотачиваясь только на одном столбце?
Конечно, использовать другой цикл.
Например, вы хотите сосредоточиться на области, находящейся между «A1» и «C3», где первый указывает левый верхний угол, а второй — правый нижний угол области, на которой вы хотите сфокусироваться. Эта область будет так называемой cellObj, которую вы видите в первой строке кода ниже. Затем вы указываете, что для каждой ячейки, которая находится в этой области, вы хотите вывести координату и значение, которое содержится в этой ячейке. После окончания каждой строки вы хотите выводить сообщение-сигнал о том, что строка этой области cellObj была выведена.
# Print row per row
for cellObj in sheet['A1':'C3']:
for cell in cellObj:
print(cells.coordinate, cells.value)
print('--- END ---')Обратите внимание, что выбор области очень похож на выбор, получение и индексирование списка и элементы NumPy, где вы также используете квадратные скобки и двоеточие чтобы указать область, из которой вы хотите получить значения. Кроме того, вышеприведенный цикл также хорошо использует атрибуты ячейки!
Чтобы визуализировать описанное выше, возможно, вы захотите проверить результат, который вернет вам завершенный цикл:
('A1', u'M')
('B1', u'N')
('C1', u'O')
--- END ---
('A2', 10L)
('B2', 11L)
('C2', 12L)
--- END ---
('A3', 14L)
('B3', 15L)
('C3', 16L)
--- END ---Наконец, есть некоторые атрибуты, которые вы можете использовать для проверки результата импорта, а именно max_row и max_column. Эти атрибуты, конечно, являются общими способами обеспечения правильной загрузки данных, но тем не менее в данном случае они могут и будут полезны.
# Retrieve the maximum amount of rows
sheet.max_row
# Retrieve the maximum amount of columns
sheet.max_column
Это все очень классно, но мы почти слышим, что вы сейчас думаете, что это ужасно трудный способ работать с файлами, особенно если нужно еще и управлять данными.
Должно быть что-то проще, не так ли? Всё так!
Openpyxl имеет поддержку Pandas DataFrames. И можно использовать функцию DataFrame () из пакета Pandas, чтобы поместить значения листа в DataFrame:
# Import `pandas`
import pandas as pd
# Convert Sheet to DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(sheet.values)
Если вы хотите указать заголовки и индексы, вам нужно добавить немного больше кода:
# Put the sheet values in `data`
data = sheet.values
# Indicate the columns in the sheet values
cols = next(data)[1:]
# Convert your data to a list
data = list(data)
# Read in the data at index 0 for the indices
idx = [r[0] for r in data]
# Slice the data at index 1
data = (islice(r, 1, None) for r in data)
# Make your DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=idx, columns=cols)Затем вы можете начать управлять данными при помощи всех функций, которые есть в Pandas. Но помните, что вы находитесь в виртуальной среде, поэтому, если библиотека еще не подключена, вам нужно будет установить ее снова через pip.
Чтобы записать Pandas DataFrames обратно в файл Excel, можно использовать функцию dataframe_to_rows () из модуля utils:
# Import `dataframe_to_rows`
from openpyxl.utils.dataframe import dataframe_to_rows
# Initialize a workbook
wb = Workbook()
# Get the worksheet in the active workbook
ws = wb.active
# Append the rows of the DataFrame to your worksheet
for r in dataframe_to_rows(df, index=True, header=True):
ws.append(r)Но это определенно не все! Библиотека openpyxl предлагает вам высокую гибкость в отношении того, как вы записываете свои данные в файлы Excel, изменяете стили ячеек или используете режим только для записи. Это делает ее одной из тех библиотек, которую вам точно необходимо знать, если вы часто работаете с электронными таблицами.
И не забудьте деактивировать виртуальную среду, когда закончите работу с данными!
Теперь давайте рассмотрим некоторые другие библиотеки, которые вы можете использовать для получения данных в электронной таблице на Python.
Готовы узнать больше?
Чтение и форматирование Excel файлов xlrd
Эта библиотека идеальна, если вы хотите читать данные и форматировать данные в файлах с расширением .xls или .xlsx.
# Import `xlrd`
import xlrd
# Open a workbook
workbook = xlrd.open_workbook('example.xls')
# Loads only current sheets to memory
workbook = xlrd.open_workbook('example.xls', on_demand = True)Если вы не хотите рассматривать всю книгу, можно использовать такие функции, как sheet_by_name () или sheet_by_index (), чтобы извлекать листы, которые необходимо использовать в анализе.
# Load a specific sheet by name
worksheet = workbook.sheet_by_name('Sheet1')
# Load a specific sheet by index
worksheet = workbook.sheet_by_index(0)
# Retrieve the value from cell at indices (0,0)
sheet.cell(0, 0).value
Наконец, можно получить значения по определенным координатам, обозначенным индексами.
О том, как xlwt и xlutils, соотносятся с xlrd расскажем дальше.
Запись данных в Excel файл при помощи xlrd
Если нужно создать электронные таблицы, в которых есть данные, кроме библиотеки XlsxWriter можно использовать библиотеки xlwt. Xlwt идеально подходит для записи и форматирования данных в файлы с расширением .xls.
Когда вы вручную хотите записать в файл, это будет выглядеть так:
# Import `xlwt`
import xlwt
# Initialize a workbook
book = xlwt.Workbook(encoding="utf-8")
# Add a sheet to the workbook
sheet1 = book.add_sheet("Python Sheet 1")
# Write to the sheet of the workbook
sheet1.write(0, 0, "This is the First Cell of the First Sheet")
# Save the workbook
book.save("spreadsheet.xls")Если нужно записать данные в файл, то для минимизации ручного труда можно прибегнуть к циклу for. Это позволит немного автоматизировать процесс. Делаем скрипт, в котором создается книга, в которую добавляется лист. Далее указываем список со столбцами и со значениями, которые будут перенесены на рабочий лист.
Цикл for будет следить за тем, чтобы все значения попадали в файл: задаем, что с каждым элементом в диапазоне от 0 до 4 (5 не включено) мы собираемся производить действия. Будем заполнять значения строка за строкой. Для этого указываем row элемент, который будет “прыгать” в каждом цикле. А далее у нас следующий for цикл, который пройдется по столбцам листа. Задаем условие, что для каждой строки на листе смотрим на столбец и заполняем значение для каждого столбца в строке. Когда заполнили все столбцы строки значениями, переходим к следующей строке, пока не заполним все имеющиеся строки.
# Initialize a workbook
book = xlwt.Workbook()
# Add a sheet to the workbook
sheet1 = book.add_sheet("Sheet1")
# The data
cols = ["A", "B", "C", "D", "E"]
txt = [0,1,2,3,4]
# Loop over the rows and columns and fill in the values
for num in range(5):
row = sheet1.row(num)
for index, col in enumerate(cols):
value = txt[index] + num
row.write(index, value)
# Save the result
book.save("test.xls")В качестве примера скриншот результирующего файла:
Теперь, когда вы видели, как xlrd и xlwt взаимодействуют вместе, пришло время посмотреть на библиотеку, которая тесно связана с этими двумя: xlutils.
Коллекция утилит xlutils
Эта библиотека в основном представляет собой набор утилит, для которых требуются как xlrd, так и xlwt. Включает в себя возможность копировать и изменять/фильтровать существующие файлы. Вообще говоря, оба этих случая подпадают теперь под openpyxl.
Использование pyexcel для чтения файлов .xls или .xlsx
Еще одна библиотека, которую можно использовать для чтения данных таблиц в Python — pyexcel. Это Python Wrapper, который предоставляет один API для чтения, обработки и записи данных в файлах .csv, .ods, .xls, .xlsx и .xlsm.
Чтобы получить данные в массиве, можно использовать функцию get_array (), которая содержится в пакете pyexcel:
# Import `pyexcel`
import pyexcel
# Get an array from the data
my_array = pyexcel.get_array(file_name="test.xls")
Также можно получить данные в упорядоченном словаре списков, используя функцию get_dict ():
# Import `OrderedDict` module
from pyexcel._compact import OrderedDict
# Get your data in an ordered dictionary of lists
my_dict = pyexcel.get_dict(file_name="test.xls", name_columns_by_row=0)
# Get your data in a dictionary of 2D arrays
book_dict = pyexcel.get_book_dict(file_name="test.xls")Однако, если вы хотите вернуть в словарь двумерные массивы или, иными словами, получить все листы книги в одном словаре, стоит использовать функцию get_book_dict ().
Имейте в виду, что обе упомянутые структуры данных, массивы и словари вашей электронной таблицы, позволяют создавать DataFrames ваших данных с помощью pd.DataFrame (). Это упростит обработку ваших данных!
Наконец, вы можете просто получить записи с pyexcel благодаря функции get_records (). Просто передайте аргумент file_name функции и обратно получите список словарей:
# Retrieve the records of the file
records = pyexcel.get_records(file_name="test.xls")Записи файлов при помощи pyexcel
Так же, как загрузить данные в массивы с помощью этого пакета, можно также легко экспортировать массивы обратно в электронную таблицу. Для этого используется функция save_as () с передачей массива и имени целевого файла в аргумент dest_file_name:
# Get the data
data = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
# Save the array to a file
pyexcel.save_as(array=data, dest_file_name="array_data.xls")Обратите внимание: если указать разделитель, то можно добавить аргумент dest_delimiter и передать символ, который хотите использовать, в качестве разделителя между “”.
Однако, если у вас есть словарь, нужно будет использовать функцию save_book_as (). Передайте двумерный словарь в bookdict и укажите имя файла, и все ОК:
# The data
2d_array_dictionary = {'Sheet 1': [
['ID', 'AGE', 'SCORE']
[1, 22, 5],
[2, 15, 6],
[3, 28, 9]
],
'Sheet 2': [
['X', 'Y', 'Z'],
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]
[7, 8, 9]
],
'Sheet 3': [
['M', 'N', 'O', 'P'],
[10, 11, 12, 13],
[14, 15, 16, 17]
[18, 19, 20, 21]
]}
# Save the data to a file
pyexcel.save_book_as(bookdict=2d_array_dictionary, dest_file_name="2d_array_data.xls")Помните, что когда используете код, который напечатан в фрагменте кода выше, порядок данных в словаре не будет сохранен!
Чтение и запись .csv файлов
Если вы все еще ищете библиотеки, которые позволяют загружать и записывать данные в CSV-файлы, кроме Pandas, рекомендуем библиотеку csv:
# import `csv`
import csv
# Read in csv file
for row in csv.reader(open('data.csv'), delimiter=','):
print(row)
# Write csv file
data = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
outfile = open('data.csv', 'w')
writer = csv.writer(outfile, delimiter=';', quotechar='"')
writer.writerows(data)
outfile.close()Обратите внимание, что NumPy имеет функцию genfromtxt (), которая позволяет загружать данные, содержащиеся в CSV-файлах в массивах, которые затем можно помещать в DataFrames.
Финальная проверка данных
Когда данные подготовлены, не забудьте последний шаг: проверьте правильность загрузки данных. Если вы поместили свои данные в DataFrame, вы можете легко и быстро проверить, был ли импорт успешным, выполнив следующие команды:
# Check the first entries of the DataFrame
df1.head()
# Check the last entries of the DataFrame
df1.tail()Note: Используйте DataCamp Pandas Cheat Sheet, когда вы планируете загружать файлы в виде Pandas DataFrames.
Если данные в массиве, вы можете проверить его, используя следующие атрибуты массива: shape, ndim, dtype и т.д.:
# Inspect the shape
data.shape
# Inspect the number of dimensions
data.ndim
# Inspect the data type
data.dtypeЧто дальше?
Поздравляем, теперь вы знаете, как читать файлы Excel в Python 
Если вы хотите глубже погрузиться в тему — знакомьтесь с PyXll, которая позволяет записывать функции в Python и вызывать их в Excel.
Узнайте, как читать и импортировать файлы Excel в Python, как записывать данные в эти таблицы и какие библиотеки лучше всего подходят для этого.
Известный вам инструмент для организации, анализа и хранения ваших данных в таблицах — Excel — применяется и в data science. В какой-то момент вам придется иметь дело с этими таблицами, но работать именно с ними вы будете не всегда. Вот почему разработчики Python реализовали способы чтения, записи и управления не только этими файлами, но и многими другими типами файлов.
Из этого учебника узнаете, как можете работать с Excel и Python. Внутри найдете обзор библиотек, которые вы можете использовать для загрузки и записи этих таблиц в файлы с помощью Python. Вы узнаете, как работать с такими библиотеками, как pandas, openpyxl, xlrd, xlutils и pyexcel.
Данные как ваша отправная точка
Когда вы начинаете проект по data science, вам придется работать с данными, которые вы собрали по всему интернету, и с наборами данных, которые вы загрузили из других мест — Kaggle, Quandl и тд
Но чаще всего вы также найдете данные в Google или в репозиториях, которые используются другими пользователями. Эти данные могут быть в файле Excel или сохранены в файл с расширением .csv … Возможности могут иногда казаться бесконечными, но когда у вас есть данные, в первую очередь вы должны убедиться, что они качественные.
В случае с электронной таблицей вы можете не только проверить, могут ли эти данные ответить на вопрос исследования, который вы имеете в виду, но также и можете ли вы доверять данным, которые хранятся в электронной таблице.
Проверяем качество таблицы
- Представляет ли электронная таблица статические данные?
- Смешивает ли она данные, расчеты и отчетность?
- Являются ли данные в вашей электронной таблице полными и последовательными?
- Имеет ли ваша таблица систематизированную структуру рабочего листа?
- Проверяли ли вы действительные формулы в электронной таблице?
Этот список вопросов поможет убедиться, что ваша таблица не грешит против лучших практик, принятых в отрасли. Конечно, этот список не исчерпывающий, но позволит провести базовую проверку таблицы.
Лучшие практики для данных электронных таблиц
Прежде чем приступить к чтению вашей электронной таблицы на Python, вы также должны подумать о том, чтобы настроить свой файл в соответствии с некоторыми основными принципами, такими как:
- Первая строка таблицы обычно зарезервирована для заголовка, а первый столбец используется для идентификации единицы выборки;
- Избегайте имен, значений или полей с пробелами. В противном случае каждое слово будет интерпретироваться как отдельная переменная, что приведет к ошибкам, связанным с количеством элементов на строку в вашем наборе данных. По возможности, используйте:
- подчеркивания,
- тире,
- горбатый регистр, где первая буква каждого слова пишется с большой буквы
- объединяющие слова
- Короткие имена предпочтительнее длинных имен;
- старайтесь не использовать имена, которые содержат символы ?, $,%, ^, &, *, (,), -, #,? ,,, <,>, /, |, , [,], {, и };
- Удалите все комментарии, которые вы сделали в вашем файле, чтобы избежать добавления в ваш файл лишних столбцов или NA;
- Убедитесь, что все пропущенные значения в вашем наборе данных обозначены как NA.
Затем, после того, как вы внесли необходимые изменения или тщательно изучили свои данные, убедитесь, что вы сохранили внесенные изменения. Сделав это, вы можете вернуться к данным позже, чтобы отредактировать их, добавить дополнительные данные или изменить их, сохранив формулы, которые вы, возможно, использовали для расчета данных и т.д.
Если вы работаете с Microsoft Excel, вы можете сохранить файл в разных форматах: помимо расширения по умолчанию .xls или .xlsx, вы можете перейти на вкладку «Файл», нажать «Сохранить как» и выбрать одно из расширений, которые указаны в качестве параметров «Сохранить как тип». Наиболее часто используемые расширения для сохранения наборов данных в data science — это .csv и .txt (в виде текстового файла с разделителями табуляции). В зависимости от выбранного варианта сохранения поля вашего набора данных разделяются вкладками или запятыми, которые образуют символы-разделители полей вашего набора данных.
Теперь, когда вы проверили и сохранили ваши данные, вы можете начать с подготовки вашего рабочего окружения.
Готовим рабочее окружение
Как убедиться, что вы все делаете хорошо? Проверить рабочее окружение!
Когда вы работаете в терминале, вы можете сначала перейти в каталог, в котором находится ваш файл, а затем запустить Python. Убедитесь, что файл лежит именно в том каталоге, к которому вы обратились.
Возможно, вы уже начали сеанс Python и у вас нет подсказок о каталоге, в котором вы работаете. Тогда можно выполнить следующие команды:
# Import `os`
import os
# Retrieve current working directory (`cwd`)
cwd = os.getcwd()
cwd
# Change directory
os.chdir("/path/to/your/folder")
# List all files and directories in current directory
os.listdir('.')Круто, да?
Вы увидите, что эти команды очень важны не только для загрузки ваших данных, но и для дальнейшего анализа. А пока давайте продолжим: вы прошли все проверки, вы сохранили свои данные и подготовили рабочее окружение.
Можете ли вы начать с чтения данных в Python?
Установите библиотеки для чтения и записи файлов Excel
Даже если вы еще не знаете, какие библиотеки вам понадобятся для импорта ваших данных, вы должны убедиться, что у вас есть все, что нужно для установки этих библиотек, когда придет время.
Подготовка к дополнительной рабочей области: pip
Вот почему вам нужно установить pip и setuptools. Если у вас установлен Python2 ⩾ 2.7.9 или Python3 ⩾ 3.4, то можно не беспокоиться — просто убедитесь, что вы обновились до последней версии.
Для этого выполните следующую команду в своем терминале:
# Для Linux/OS X
pip install -U pip setuptools
# Для Windows
python -m pip install -U pip setuptoolsЕсли вы еще не установили pip, запустите скрипт python get-pip.py, который вы можете найти здесь. Следуйте инструкциям по установке.
Установка Anaconda
Другой вариант для работы в data science — установить дистрибутив Anaconda Python. Сделав это, вы получите простой и быстрый способ начать заниматься data science, потому что вам не нужно беспокоиться об установке отдельных библиотек, необходимых для работы.
Это особенно удобно, если вы новичок, но даже для более опытных разработчиков это способ быстро протестировать некоторые вещи без необходимости устанавливать каждую библиотеку отдельно.
Anaconda включает в себя 100 самых популярных библиотек Python, R и Scala для науки о данных и несколько сред разработки с открытым исходным кодом, таких как Jupyter и Spyder.
Установить Anaconda можно здесь. Следуйте инструкциям по установке, и вы готовы начать!
Загрузить файлы Excel в виде фреймов Pandas
Все, среда настроена, вы готовы начать импорт ваших файлов.
Один из способов, который вы часто используете для импорта ваших файлов для обработки данных, — с помощью библиотеки Pandas. Она основана на NumPy и предоставляет простые в использовании структуры данных и инструменты анализа данных Python.
Эта мощная и гибкая библиотека очень часто используется дата-инженерами для передачи своих данных в структуры данных, очень выразительных для их анализа.
Если у вас уже есть Pandas, доступные через Anaconda, вы можете просто загрузить свои файлы в Pandas DataFrames с помощью pd.Excelfile():
# импорт библиотеки pandas
import pandas as pd
# Загружаем ваш файл в переменную `file` / вместо 'example' укажите название свого файла из текущей директории
file = 'example.xlsx'
# Загружаем spreadsheet в объект pandas
xl = pd.ExcelFile(file)
# Печатаем название листов в данном файле
print(xl.sheet_names)
# Загрузить лист в DataFrame по его имени: df1
df1 = xl.parse('Sheet1')Если вы не установили Anaconda, просто выполните pip install pandas, чтобы установить библиотеку Pandas в вашей среде, а затем выполните команды, которые включены в фрагмент кода выше.
Проще простого, да?
Для чтения в файлах .csv у вас есть аналогичная функция для загрузки данных в DataFrame: read_csv(). Вот пример того, как вы можете использовать эту функцию:
# Импорт библиотеки pandas
import pandas as pd
# Загрузить csv файл
df = pd.read_csv("example.csv") Разделитель, который будет учитывать эта функция, по умолчанию является запятой, но вы можете указать альтернативный разделитель, если хотите. Перейдите к документации, чтобы узнать, какие другие аргументы вы можете указать для успешного импорта!
Обратите внимание, что есть также функции read_table() и read_fwf() для чтения файлов и таблиц с фиксированной шириной в формате DataFrames с общим разделителем. Для первой функции разделителем по умолчанию является вкладка, но вы можете снова переопределить это, а также указать альтернативный символ-разделитель. Более того, есть и другие функции, которые вы можете использовать для получения данных в DataFrames: вы можете найти их здесь.
Как записать Pandas DataFrames в файлы Excel
Допустим, что после анализа данных вы хотите записать данные обратно в новый файл. Есть также способ записать ваши Pandas DataFrames обратно в файлы с помощью функции to_excel().
Но, прежде чем использовать эту функцию, убедитесь, что у вас установлен XlsxWriter, если вы хотите записать свои данные в несколько листов в файле .xlsx:
# Установим `XlsxWriter`
pip install XlsxWriter
# Указать writer библиотеки
writer = pd.ExcelWriter('example.xlsx', engine='xlsxwriter')
# Записать ваш DataFrame в файл
yourData.to_excel(writer, 'Sheet1')
# Сохраним результат
writer.save()Обратите внимание, что в приведенном выше фрагменте кода вы используете объект ExcelWriter для вывода DataFrame.
Иными словами, вы передаете переменную Writer в функцию to_excel() и также указываете имя листа. Таким образом, вы добавляете лист с данными в существующую рабочую книгу: вы можете использовать ExcelWriter для сохранения нескольких (немного) разных DataFrames в одной рабочей книге.
Все это означает, что если вы просто хотите сохранить один DataFrame в файл, вы также можете обойтись без установки пакета XlsxWriter. Затем вы просто не указываете аргумент движка, который вы передаете в функцию pd.ExcelWriter(). Остальные шаги остаются прежними.
Аналогично функциям, которые вы использовали для чтения в файлах .csv, у вас также есть функция to_csv() для записи результатов обратно в файл, разделенный запятыми. Он снова работает так же, как когда вы использовали его для чтения в файле:
# Запишите DataFrame в csv
df.to_csv("example.csv")Если вы хотите иметь файл, разделенный табуляцией, вы также можете передать t аргументу sep. Обратите внимание, что есть другие функции, которые вы можете использовать для вывода ваших файлов. Вы можете найти их все здесь.
Пакеты для разбора файлов Excel и обратной записи с помощью Python
Помимо библиотеки Pandas, который вы будете использовать очень часто для загрузки своих данных, вы также можете использовать другие библиотеки для получения ваших данных в Python. Наш обзор основан на этой странице со списком доступных библиотек, которые вы можете использовать для работы с файлами Excel в Python.
Далее вы увидите, как использовать эти библиотеки с помощью некоторых реальных, но упрощенных примеров.
Использование виртуальных сред
Общий совет для установки — делать это в Python virtualenv без системных пакетов. Вы можете использовать virtualenv для создания изолированных сред Python: он создает папку, содержащую все необходимые исполняемые файлы для использования пакетов, которые потребуются проекту Python.
Чтобы начать работать с virtualenv, вам сначала нужно установить его. Затем перейдите в каталог, в который вы хотите поместить свой проект. Создайте virtualenv в этой папке и загрузите в определенную версию Python, если вам это нужно. Затем вы активируете виртуальную среду. После этого вы можете начать загрузку в другие библиотеки, начать работать с ними и т. д.
Совет: не забудьте деактивировать среду, когда закончите!
# Install virtualenv
$ pip install virtualenv
# Go to the folder of your project
$ cd my_folder
# Create a virtual environment `venv`
$ virtualenv venv
# Indicate the Python interpreter to use for `venv`
$ virtualenv -p /usr/bin/python2.7 venv
# Activate `venv`
$ source venv/bin/activate
# Deactivate `venv`
$ deactivateОбратите внимание, что виртуальная среда может показаться немного проблемной на первый взгляд, когда вы только начинаете работать с данными с Python. И, особенно если у вас есть только один проект, вы можете не понять, зачем вам вообще нужна виртуальная среда.
С ней будет гораздо легче, когда у вас одновременно запущено несколько проектов, и вы не хотите, чтобы они использовали одну и ту же установку Python. Или когда ваши проекты имеют противоречащие друг другу требования, виртуальная среда пригодится!
Теперь вы можете, наконец, начать установку и импорт библиотек, о которых вы читали, и загрузить их в таблицу.
Как читать и записывать файлы Excel с openpyxl
Этот пакет обычно рекомендуется, если вы хотите читать и записывать файлы .xlsx, xlsm, xltx и xltm.
Установите openpyxl с помощью pip: вы видели, как это сделать в предыдущем разделе.
Общий совет для установки этой библиотеки — делать это в виртуальной среде Python без системных библиотек. Вы можете использовать виртуальную среду для создания изолированных сред Python: она создает папку, которая содержит все необходимые исполняемые файлы для использования библиотек, которые потребуются проекту Python.
Перейдите в каталог, в котором находится ваш проект, и повторно активируйте виртуальную среду venv. Затем продолжите установку openpyxl с pip, чтобы убедиться, что вы можете читать и записывать файлы с ним:
# Активируйте virtualenv
$ source activate venv
# Установим `openpyxl` в `venv`
$ pip install openpyxlТеперь, когда вы установили openpyxl, вы можете загружать данные. Но что это за данные?
Доспутим Excel с данными, которые вы пытаетесь загрузить в Python, содержит следующие листы:
Функция load_workbook() принимает имя файла в качестве аргумента и возвращает объект рабочей книги, который представляет файл. Вы можете проверить это, запустив type (wb). Убедитесь, что вы находитесь в том каталоге, где находится ваша таблица, иначе вы получите error при импорте.
# Import `load_workbook` module from `openpyxl`
from openpyxl import load_workbook
# Load in the workbook
wb = load_workbook('./test.xlsx')
# Get sheet names
print(wb.get_sheet_names())Помните, что вы можете изменить рабочий каталог с помощью os.chdir().
Вы видите, что фрагмент кода выше возвращает имена листов книги, загруженной в Python.Можете использовать эту информацию, чтобы также получить отдельные листы рабочей книги.
Вы также можете проверить, какой лист в настоящее время активен с wb.active. Как видно из кода ниже, вы можете использовать его для загрузки другого листа из вашей книги:
# Get a sheet by name
sheet = wb.get_sheet_by_name('Sheet3')
# Print the sheet title
sheet.title
# Get currently active sheet
anotherSheet = wb.active
# Check `anotherSheet`
anotherSheetНа первый взгляд, с этими объектами рабочего листа вы не сможете многое сделать.. Однако вы можете извлечь значения из определенных ячеек на листе вашей книги, используя квадратные скобки [], в которые вы передаете точную ячейку, из которой вы хотите получить значение.
Обратите внимание, что это похоже на выбор, получение и индексирование массивов NumPy и Pandas DataFrames, но это не все, что вам нужно сделать, чтобы получить значение. Вам нужно добавить атрибут value:
# Retrieve the value of a certain cell
sheet['A1'].value
# Select element 'B2' of your sheet
c = sheet['B2']
# Retrieve the row number of your element
c.row
# Retrieve the column letter of your element
c.column
# Retrieve the coordinates of the cell
c.coordinateКак вы можете видеть, помимо значения, есть и другие атрибуты, которые вы можете использовать для проверки вашей ячейки, а именно: row, column и coordinate.
Атрибут row вернет 2;
Добавление атрибута column к c даст вам ‘B’
coordinate вернет ‘B2’.
Вы также можете получить значения ячеек с помощью функции cell(). Передайте row и column, добавьте к этим аргументам значения, соответствующие значениям ячейки, которую вы хотите получить, и, конечно же, не забудьте добавить атрибут value:
# Retrieve cell value
sheet.cell(row=1, column=2).value
# Print out values in column 2
for i in range(1, 4):
print(i, sheet.cell(row=i, column=2).value)Обратите внимание, что если вы не укажете атрибут value, вы получите <Cell Sheet3.B1>, который ничего не говорит о значении, которое содержится в этой конкретной ячейке.
Вы видите, что вы используете цикл for с помощью функции range(), чтобы помочь вам распечатать значения строк, имеющих значения в столбце 2. Если эти конкретные ячейки пусты, вы просто вернете None. Если вы хотите узнать больше о циклах for, пройдите наш курс Intermediate Python для Data Science.
Есть специальные функции, которые вы можете вызывать для получения некоторых других значений, например, get_column_letter() и column_index_from_string.
Две функции указывают примерно то, что вы можете получить, используя их, но лучше сделать их четче: хотя вы можете извлечь букву столбца с предшествующего, вы можете сделать обратное или получить адрес столбца, когда вы задаёте букву последнему. Вы можете увидеть, как это работает ниже:
# Импорт необходимых модулей из `openpyxl.utils`
from openpyxl.utils import get_column_letter, column_index_from_string
# Вывод 'A'
get_column_letter(1)
# Return '1'
column_index_from_string('A')Вы уже получили значения для строк, которые имеют значения в определенном столбце, но что вам нужно сделать, если вы хотите распечатать строки вашего файла, не сосредотачиваясь только на одном столбце? Использовать другой цикл, конечно!
Например, вы говорите, что хотите сфокусироваться на области между «А1» и «С3», где первая указывает на левый верхний угол, а вторая — на правый нижний угол области, на которой вы хотите сфокусироваться. ,
Эта область будет так называемым cellObj, который вы видите в первой строке кода ниже. Затем вы говорите, что для каждой ячейки, которая находится в этой области, вы печатаете координату и значение, которое содержится в этой ячейке. После конца каждой строки вы печатаете сообщение, которое указывает, что строка этой области cellObj напечатана.
# Напечатать строчку за строчкой
for cellObj in sheet['A1':'C3']:
for cell in cellObj:
print(cells.coordinate, cells.value)
print('--- END ---')Еще раз обратите внимание, что выбор области очень похож на выбор, получение и индексирование списка и элементов массива NumPy, где вы также используете [] и : для указания области, значения которой вы хотите получить. Кроме того, вышеприведенный цикл также хорошо использует атрибуты ячейки!
Чтобы сделать вышеприведенное объяснение и код наглядным, вы можете проверить результат, который вы получите после завершения цикла:
('A1', u'M')
('B1', u'N')
('C1', u'O')
--- END ---
('A2', 10L)
('B2', 11L)
('C2', 12L)
--- END ---
('A3', 14L)
('B3', 15L)
('C3', 16L)
--- END ---Наконец, есть некоторые атрибуты, которые вы можете использовать для проверки результата вашего импорта, а именно max_row и max_column. Эти атрибуты, конечно, и так — общие способы проверки правильности загрузки данных, но они все равно полезны.
# Вывести максимальное количество строк
sheet.max_row
# Вывести максимальное количество колонок
sheet.max_columnНаверное, вы думаете, что такой способ работы с этими файлами сложноват, особенно если вы еще хотите манипулировать данными.
Должно быть что-то попроще, верно? Так и есть!
openpyxl поддерживает Pandas DataFrames! Вы можете использовать функцию DataFrame() из библиотеки Pandas, чтобы поместить значения листа в DataFrame:
# Import `pandas`
import pandas as pd
# конвертировать Лист в DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(sheet.values)Если вы хотите указать заголовки и индексы, вам нужно добавить немного больше кода:
# Put the sheet values in `data`
data = sheet.values
# Indicate the columns in the sheet values
cols = next(data)[1:]
# Convert your data to a list
data = list(data)
# Read in the data at index 0 for the indices
idx = [r[0] for r in data]
# Slice the data at index 1
data = (islice(r, 1, None) for r in data)
# Make your DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=idx, columns=cols)Затем вы можете начать манипулировать данными со всеми функциями, которые предлагает библиотека Pandas. Но помните, что вы находитесь в виртуальной среде, поэтому, если библиотека еще не представлена, вам нужно будет установить ее снова через pip.
Чтобы записать ваши Pandas DataFrames обратно в файл Excel, вы можете легко использовать функцию dataframe_to_rows() из модуля utils:
# Import `dataframe_to_rows`
from openpyxl.utils.dataframe import dataframe_to_rows
# Initialize a workbook
wb = Workbook()
# Get the worksheet in the active workbook
ws = wb.active
# Append the rows of the DataFrame to your worksheet
for r in dataframe_to_rows(df, index=True, header=True):
ws.append(r)Но это точно не все! Библиотека openpyxl предлагает вам высокую гибкость при записи ваших данных обратно в файлы Excel, изменении стилей ячеек или использовании режима write-only. Эту библиотеку обязательно нужно знать, когда вы часто работаете с электронными таблицами ,
Совет: читайте больше о том, как вы можете изменить стили ячеек, перейти в режим write-only или как библиотека работает с NumPy здесь.
Теперь давайте также рассмотрим некоторые другие библиотеки, которые вы можете использовать для получения данных вашей электронной таблицы в Python.
Прежде чем закрыть этот раздел, не забудьте отключить виртуальную среду, когда закончите!
Чтение и форматирование Excel-файлов: xlrd
Эта библиотека идеально подходит для чтения и форматирования данных из Excel с расширением xls или xlsx.
# Import `xlrd`
import xlrd
# Open a workbook
workbook = xlrd.open_workbook('example.xls')
# Loads only current sheets to memory
workbook = xlrd.open_workbook('example.xls', on_demand = True)Когда вам не нужны данные из всей Excel-книги, вы можете использовать функции sheet_by_name() или sheet_by_index() для получения листов, которые вы хотите получить в своём анализе
# Load a specific sheet by name
worksheet = workbook.sheet_by_name('Sheet1')
# Load a specific sheet by index
worksheet = workbook.sheet_by_index(0)
# Retrieve the value from cell at indices (0,0)
sheet.cell(0, 0).valueТакже можно получить значение в определённых ячейках с вашего листа.
Перейдите к xlwt и xlutils, чтобы узнать больше о том, как они относятся к библиотеке xlrd.
Запись данных в Excel-файлы с xlwt
Если вы хотите создать таблицу со своими данными, вы можете использовать не только библиотеку XlsWriter, но и xlwt. xlwt идеально подходит для записи данных и форматирования информации в файлах с расширением .xls
Когда вы вручную создаёте файл:
# Import `xlwt`
import xlwt
# Initialize a workbook
book = xlwt.Workbook(encoding="utf-8")
# Add a sheet to the workbook
sheet1 = book.add_sheet("Python Sheet 1")
# Write to the sheet of the workbook
sheet1.write(0, 0, "This is the First Cell of the First Sheet")
# Save the workbook
book.save("spreadsheet.xls")Если вы хотите записать данные в файл, но не хотите делать все самостоятельно, вы всегда можете прибегнуть к циклу for, чтобы автоматизировать весь процесс. Составьте сценарий, в котором вы создаёте книгу и в которую добавляете лист. Укажите список со столбцами и один со значениями, которые будут заполнены на листе.
Далее у вас есть цикл for, который гарантирует, что все значения попадают в файл: вы говорите, что для каждого элемента в диапазоне от 0 до 4 (5 не включительно) вы собираетесь что-то делать. Вы будете заполнять значения построчно. Для этого вы указываете элемент строки, который появляется в каждом цикле. Далее у вас есть еще один цикл for, который будет проходить по столбцам вашего листа. Вы говорите, что для каждой строки на листе, вы будете смотреть на столбцы, которые идут с ним, и вы будете заполнять значение для каждого столбца в строке. Заполнив все столбцы строки значениями, вы перейдете к следующей строке, пока не останется строк.
# Initialize a workbook
book = xlwt.Workbook()
# Add a sheet to the workbook
sheet1 = book.add_sheet("Sheet1")
# The data
cols = ["A", "B", "C", "D", "E"]
txt = [0,1,2,3,4]
# Loop over the rows and columns and fill in the values
for num in range(5):
row = sheet1.row(num)
for index, col in enumerate(cols):
value = txt[index] + num
row.write(index, value)
# Save the result
book.save("test.xls")На скриншоте ниже представлен результат выполнения этого кода:
Теперь, когда вы увидели, как xlrd и xlwt работают друг с другом, пришло время взглянуть на библиотеку, которая тесно связана с этими двумя: xlutils.
Сборник утилит: xlutils
Эта библиотека — сборник утилит, для которого требуются и xlrd и xlwt, и которая может копировать, изменять и фильтровать существующие данные. О том, как пользоваться этими командами рассказано в разделе по openpyxl.
Вернитесь в раздел openpyxl, чтобы получить больше информации о том, как использовать этот пакет для получения данных в Python.
Использование pyexcel для чтения .xls или .xlsx файлов
Еще одна библиотека, которую можно использовать для чтения данных электронных таблиц в Python — это pyexcel; Python Wrapper, который предоставляет один API для чтения, записи и работы с данными в файлах .csv, .ods, .xls, .xlsx и .xlsm. Конечно, для этого урока вы просто сосредоточитесь на файлах .xls и .xls.
Чтобы получить ваши данные в массиве, вы можете использовать функцию get_array(), которая содержится в пакете pyexcel:
# Import `pyexcel`
import pyexcel
# Get an array from the data
my_array = pyexcel.get_array(file_name="test.xls")Вы также можете получить свои данные в упорядоченном словаре списков. Вы можете использовать функцию get_dict():
# Import `OrderedDict` module
from pyexcel._compact import OrderedDict
# Get your data in an ordered dictionary of lists
my_dict = pyexcel.get_dict(file_name="test.xls", name_columns_by_row=0)
# Get your data in a dictionary of 2D arrays
book_dict = pyexcel.get_book_dict(file_name="test.xls")Здесь видно, что если вы хотите получить словарь двумерных массивов или получить все листы рабочей книги в одном словаре, вы можете прибегнуть к get_book_dict().
Помните, что эти две структуры данных, которые были упомянуты выше, массивы и словари вашей таблицы, позволяют вам создавать DataFrames ваших данных с помощью pd.DataFrame(). Это облегчит обработку данных.
Кроме того, вы можете просто получить записи из таблицы с помощью pyexcel благодаря функции get_records(). Просто передайте аргумент file_name в функцию, и вы получите список словарей:
# Retrieve the records of the file
records = pyexcel.get_records(file_name="test.xls")Чтобы узнать, как управлять списками Python, ознакомьтесь с примерами из документации о списках Python.
Запись в файл с pyexcel
С помощью этой библиотеки можно не только загружать данные в массивы, вы также можете экспортировать свои массивы обратно в таблицу. Используйте функцию save_as() и передайте массив и имя файла назначения в аргумент dest_file_name:
# Get the data
data = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
# Save the array to a file
pyexcel.save_as(array=data, dest_file_name="array_data.xls")Обратите внимание, что если вы хотите указать разделитель, вы можете добавить аргумент dest_delimiter и передать символ, который вы хотите использовать в качестве разделителя между «».
Однако если у вас есть словарь, вам нужно использовать функцию save_book_as(). Передайте двумерный словарь в bookdict и укажите имя файла:
# The data
2d_array_dictionary = {'Sheet 1': [
['ID', 'AGE', 'SCORE']
[1, 22, 5],
[2, 15, 6],
[3, 28, 9]
],
'Sheet 2': [
['X', 'Y', 'Z'],
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]
[7, 8, 9]
],
'Sheet 3': [
['M', 'N', 'O', 'P'],
[10, 11, 12, 13],
[14, 15, 16, 17]
[18, 19, 20, 21]
]}
# Save the data to a file
pyexcel.save_book_as(bookdict=2d_array_dictionary, dest_file_name="2d_array_data.xls")При использовании кода, напечатанного в приведенном выше примере, важно помнить, что порядок ваших данных в словаре не будет сохранен. Если вы не хотите этого, вам нужно сделать небольшой обход. Вы можете прочитать все об этом здесь.
Чтение и запись .csv файлов
Если вы все еще ищете библиотеки, которые позволяют загружать и записывать данные в файлы .csv, кроме Pandas, лучше всего использовать пакет csv:
# import `csv`
import csv
# Read in csv file
for row in csv.reader(open('data.csv'), delimiter=','):
print(row)
# Write csv file
data = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
outfile = open('data.csv', 'w')
writer = csv.writer(outfile, delimiter=';', quotechar='"')
writer.writerows(data)
outfile.close()Обратите внимание, что в пакете NumPy есть функция genfromtxt(), которая позволяет загружать данные, содержащиеся в файлах .csv, в массивы, которые затем можно поместить в DataFrames.
Финальная проверка данных
Когда у вас есть данные, не забудьте последний шаг: проверить, правильно ли загружены данные. Если вы поместили свои данные в DataFrame, вы можете легко и быстро проверить, был ли импорт успешным, выполнив следующие команды:
# Check the first entries of the DataFrame
df1.head()
# Check the last entries of the DataFrame
df1.tail()Если у вас есть данные в массиве, вы можете проверить их, используя следующие атрибуты массива: shape, ndim, dtype и т.д .:
# Inspect the shape
data.shape
# Inspect the number of dimensions
data.ndim
# Inspect the data type
data.dtype
Что дальше?
Поздравляем! Вы успешно прошли наш урок и научились читать файлы Excel на Python.
Если вы хотите продолжить работу над этой темой, попробуйте воспользоваться PyXll, который позволяет писать функции в Python и вызывать их в Excel.
Microsoft Excel is one of the most powerful spreadsheet software applications in the world, and it has become critical in all business processes. Companies across the world, both big and small, are using Microsoft Excel to store, organize, analyze, and visualize data.
As a data professional, when you combine Python with Excel, you create a unique data analysis bundle that unlocks the value of the enterprise data.
In this tutorial, we’re going to learn how to read and work with Excel files in Python.
After you finish this tutorial, you’ll understand the following:
- Loading Excel spreadsheets into pandas DataFrames
- Working with an Excel workbook with multiple spreadsheets
- Combining multiple spreadsheets
- Reading Excel files using the
xlrdpackage
In this tutorial, we assume you know the fundamentals of pandas DataFrames. If you aren’t familiar with the pandas library, you might like to try our Pandas and NumPy Fundamentals – Dataquest.
Let’s dive in.
Reading Spreadsheets with Pandas
Technically, multiple packages allow us to work with Excel files in Python. However, in this tutorial, we’ll use pandas and xlrd libraries to interact with Excel workbooks. Essentially, you can think of a pandas DataFrame as a spreadsheet with rows and columns stored in Series objects. Traversability of Series as iterable objects allows us to grab specific data easily. Once we load an Excel workbook into a pandas DataFrame, we can perform any kind of data analysis on the data.
Before we proceed to the next step, let’s first download the following spreadsheet:
Sales Data Excel Workbook — xlsx ver.
The Excel workbook consists of two sheets that contain stationery sales data for 2020 and 2021.
NOTE
Although Excel spreadsheets can contain formula and also support formatting, pandas only imports Excel spreadsheets as flat files, and it doesn’t support spreadsheet formatting.
To import the Excel spreadsheet into a pandas DataFrame, first, we need to import the pandas package and then use the read_excel() method:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_excel('sales_data.xlsx')
display(df)| OrderDate | Region | Rep | Item | Units | Unit Cost | Total | Shipped | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2020-01-06 | East | Jones | Pencil | 95 | 1.99 | 189.05 | True |
| 1 | 2020-02-09 | Central | Jardine | Pencil | 36 | 4.99 | 179.64 | True |
| 2 | 2020-03-15 | West | Sorvino | Pencil | 56 | 2.99 | 167.44 | True |
| 3 | 2020-04-01 | East | Jones | Binder | 60 | 4.99 | 299.40 | False |
| 4 | 2020-05-05 | Central | Jardine | Pencil | 90 | 4.99 | 449.10 | True |
| 5 | 2020-06-08 | East | Jones | Binder | 60 | 8.99 | 539.40 | True |
| 6 | 2020-07-12 | East | Howard | Binder | 29 | 1.99 | 57.71 | False |
| 7 | 2020-08-15 | East | Jones | Pencil | 35 | 4.99 | 174.65 | True |
| 8 | 2020-09-01 | Central | Smith | Desk | 32 | 125.00 | 250.00 | True |
| 9 | 2020-10-05 | Central | Morgan | Binder | 28 | 8.99 | 251.72 | True |
| 10 | 2020-11-08 | East | Mike | Pen | 15 | 19.99 | 299.85 | False |
| 11 | 2020-12-12 | Central | Smith | Pencil | 67 | 1.29 | 86.43 | False |
If you want to load only a limited number of rows into the DataFrame, you can specify the number of rows using the nrows argument:
df = pd.read_excel('sales_data.xlsx', nrows=5)
display(df)| OrderDate | Region | Rep | Item | Units | Unit Cost | Total | Shipped | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2020-01-06 | East | Jones | Pencil | 95 | 1.99 | 189.05 | True |
| 1 | 2020-02-09 | Central | Jardine | Pencil | 36 | 4.99 | 179.64 | True |
| 2 | 2020-03-15 | West | Sorvino | Pencil | 56 | 2.99 | 167.44 | True |
| 3 | 2020-04-01 | East | Jones | Binder | 60 | 4.99 | 299.40 | False |
| 4 | 2020-05-05 | Central | Jardine | Pencil | 90 | 4.99 | 449.10 | True |
Skipping a specific number of rows from the begining of a spreadsheet or skipping over a list of particular rows is available through the skiprows argument, as follows:
df = pd.read_excel('sales_data.xlsx', skiprows=range(5))
display(df)| 2020-05-05 00:00:00 | Central | Jardine | Pencil | 90 | 4.99 | 449.1 | True | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2020-06-08 | East | Jones | Binder | 60 | 8.99 | 539.40 | True |
| 1 | 2020-07-12 | East | Howard | Binder | 29 | 1.99 | 57.71 | False |
| 2 | 2020-08-15 | East | Jones | Pencil | 35 | 4.99 | 174.65 | True |
| 3 | 2020-09-01 | Central | Smith | Desk | 32 | 125.00 | 250.00 | True |
| 4 | 2020-10-05 | Central | Morgan | Binder | 28 | 8.99 | 251.72 | True |
| 5 | 2020-11-08 | East | Mike | Pen | 15 | 19.99 | 299.85 | False |
| 6 | 2020-12-12 | Central | Smith | Pencil | 67 | 1.29 | 86.43 | False |
The code above skips the first five rows and returns the rest of the data. Instead, the following code returns all the rows except for those with the mentioned indices:
df = pd.read_excel('sales_data.xlsx', skiprows=[1, 4,7,10])
display(df)| OrderDate | Region | Rep | Item | Units | Unit Cost | Total | Shipped | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2020-02-09 | Central | Jardine | Pencil | 36 | 4.99 | 179.64 | True |
| 1 | 2020-03-15 | West | Sorvino | Pencil | 56 | 2.99 | 167.44 | True |
| 2 | 2020-05-05 | Central | Jardine | Pencil | 90 | 4.99 | 449.10 | True |
| 3 | 2020-06-08 | East | Jones | Binder | 60 | 8.99 | 539.40 | True |
| 4 | 2020-08-15 | East | Jones | Pencil | 35 | 4.99 | 174.65 | True |
| 5 | 2020-09-01 | Central | Smith | Desk | 32 | 125.00 | 250.00 | True |
| 6 | 2020-11-08 | East | Mike | Pen | 15 | 19.99 | 299.85 | False |
| 7 | 2020-12-12 | Central | Smith | Pencil | 67 | 1.29 | 86.43 | False |
Another useful argument is usecols, which allows us to select spreadsheet columns with their letters, names, or positional numbers. Let’s see how it works:
df = pd.read_excel('sales_data.xlsx', usecols='A:C,G')
display(df)| OrderDate | Region | Rep | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2020-01-06 | East | Jones | 189.05 |
| 1 | 2020-02-09 | Central | Jardine | 179.64 |
| 2 | 2020-03-15 | West | Sorvino | 167.44 |
| 3 | 2020-04-01 | East | Jones | 299.40 |
| 4 | 2020-05-05 | Central | Jardine | 449.10 |
| 5 | 2020-06-08 | East | Jones | 539.40 |
| 6 | 2020-07-12 | East | Howard | 57.71 |
| 7 | 2020-08-15 | East | Jones | 174.65 |
| 8 | 2020-09-01 | Central | Smith | 250.00 |
| 9 | 2020-10-05 | Central | Morgan | 251.72 |
| 10 | 2020-11-08 | East | Mike | 299.85 |
| 11 | 2020-12-12 | Central | Smith | 86.43 |
In the code above, the string assigned to the usecols argument contains a range of columns with : plus column G separated by a comma. Also, we’re able to provide a list of column names and assign it to the usecols argument, as follows:
df = pd.read_excel('sales_data.xlsx', usecols=['OrderDate', 'Region', 'Rep', 'Total'])
display(df)| OrderDate | Region | Rep | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2020-01-06 | East | Jones | 189.05 |
| 1 | 2020-02-09 | Central | Jardine | 179.64 |
| 2 | 2020-03-15 | West | Sorvino | 167.44 |
| 3 | 2020-04-01 | East | Jones | 299.40 |
| 4 | 2020-05-05 | Central | Jardine | 449.10 |
| 5 | 2020-06-08 | East | Jones | 539.40 |
| 6 | 2020-07-12 | East | Howard | 57.71 |
| 7 | 2020-08-15 | East | Jones | 174.65 |
| 8 | 2020-09-01 | Central | Smith | 250.00 |
| 9 | 2020-10-05 | Central | Morgan | 251.72 |
| 10 | 2020-11-08 | East | Mike | 299.85 |
| 11 | 2020-12-12 | Central | Smith | 86.43 |
The usecols argument accepts a list of column numbers, too. The following code shows how we can pick up specific columns using their indices:
df = pd.read_excel('sales_data.xlsx', usecols=[0, 1, 2, 6])
display(df)| OrderDate | Region | Rep | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2020-01-06 | East | Jones | 189.05 |
| 1 | 2020-02-09 | Central | Jardine | 179.64 |
| 2 | 2020-03-15 | West | Sorvino | 167.44 |
| 3 | 2020-04-01 | East | Jones | 299.40 |
| 4 | 2020-05-05 | Central | Jardine | 449.10 |
| 5 | 2020-06-08 | East | Jones | 539.40 |
| 6 | 2020-07-12 | East | Howard | 57.71 |
| 7 | 2020-08-15 | East | Jones | 174.65 |
| 8 | 2020-09-01 | Central | Smith | 250.00 |
| 9 | 2020-10-05 | Central | Morgan | 251.72 |
| 10 | 2020-11-08 | East | Mike | 299.85 |
| 11 | 2020-12-12 | Central | Smith | 86.43 |
Working with Multiple Spreadsheets
Excel files or workbooks usually contain more than one spreadsheet. The pandas library allows us to load data from a specific sheet or combine multiple spreadsheets into a single DataFrame. In this section, we’ll explore how to use these valuable capabilities.
By default, the read_excel() method reads the first Excel sheet with the index 0. However, we can choose the other sheets by assigning a particular sheet name, sheet index, or even a list of sheet names or indices to the sheet_name argument. Let’s try it:
df = pd.read_excel('sales_data.xlsx', sheet_name='2021')
display(df)| OrderDate | Region | Rep | Item | Units | Unit Cost | Total | Shipped | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2021-01-15 | Central | Gill | Binder | 46 | 8.99 | 413.54 | True |
| 1 | 2021-02-01 | Central | Smith | Binder | 87 | 15.00 | 1305.00 | True |
| 2 | 2021-03-07 | West | Sorvino | Binder | 27 | 19.99 | 139.93 | True |
| 3 | 2021-04-10 | Central | Andrews | Pencil | 66 | 1.99 | 131.34 | False |
| 4 | 2021-05-14 | Central | Gill | Pencil | 53 | 1.29 | 68.37 | False |
| 5 | 2021-06-17 | Central | Tom | Desk | 15 | 125.00 | 625.00 | True |
| 6 | 2021-07-04 | East | Jones | Pen Set | 62 | 4.99 | 309.38 | True |
| 7 | 2021-08-07 | Central | Tom | Pen Set | 42 | 23.95 | 1005.90 | True |
| 8 | 2021-09-10 | Central | Gill | Pencil | 47 | 1.29 | 9.03 | True |
| 9 | 2021-10-14 | West | Thompson | Binder | 57 | 19.99 | 1139.43 | False |
| 10 | 2021-11-17 | Central | Jardine | Binder | 11 | 4.99 | 54.89 | False |
| 11 | 2021-12-04 | Central | Jardine | Binder | 94 | 19.99 | 1879.06 | False |
The code above reads the second spreadsheet in the workbook, whose name is 2021. As mentioned before, we also can assign a sheet position number (zero-indexed) to the sheet_name argument. Let’s see how it works:
df = pd.read_excel('sales_data.xlsx', sheet_name=1)
display(df)| OrderDate | Region | Rep | Item | Units | Unit Cost | Total | Shipped | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2021-01-15 | Central | Gill | Binder | 46 | 8.99 | 413.54 | True |
| 1 | 2021-02-01 | Central | Smith | Binder | 87 | 15.00 | 1305.00 | True |
| 2 | 2021-03-07 | West | Sorvino | Binder | 27 | 19.99 | 139.93 | True |
| 3 | 2021-04-10 | Central | Andrews | Pencil | 66 | 1.99 | 131.34 | False |
| 4 | 2021-05-14 | Central | Gill | Pencil | 53 | 1.29 | 68.37 | False |
| 5 | 2021-06-17 | Central | Tom | Desk | 15 | 125.00 | 625.00 | True |
| 6 | 2021-07-04 | East | Jones | Pen Set | 62 | 4.99 | 309.38 | True |
| 7 | 2021-08-07 | Central | Tom | Pen Set | 42 | 23.95 | 1005.90 | True |
| 8 | 2021-09-10 | Central | Gill | Pencil | 47 | 1.29 | 9.03 | True |
| 9 | 2021-10-14 | West | Thompson | Binder | 57 | 19.99 | 1139.43 | False |
| 10 | 2021-11-17 | Central | Jardine | Binder | 11 | 4.99 | 54.89 | False |
| 11 | 2021-12-04 | Central | Jardine | Binder | 94 | 19.99 | 1879.06 | False |
As you can see, both statements take in either the actual sheet name or sheet index to return the same result.
Sometimes, we want to import all the spreadsheets stored in an Excel file into pandas DataFrames simultaneously. The good news is that the read_excel() method provides this feature for us. In order to do this, we can assign a list of sheet names or their indices to the sheet_name argument. But there is a much easier way to do the same: to assign None to the sheet_name argument. Let’s try it:
all_sheets = pd.read_excel('sales_data.xlsx', sheet_name=None)Before exploring the data stored in the all_sheets variable, let’s check its data type:
type(all_sheets)dictAs you can see, the variable is a dictionary. Now, let’s reveal what is stored in this dictionary:
for key, value in all_sheets.items():
print(key, type(value))2020 <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
2021 <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>The code above shows that the dictionary’s keys are the Excel workbook sheet names, and its values are pandas DataFrames for each spreadsheet. To print out the content of the dictionary, we can use the following code:
for key, value in all_sheets.items():
print(key)
display(value)2020| OrderDate | Region | Rep | Item | Units | Unit Cost | Total | Shipped | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2020-01-06 | East | Jones | Pencil | 95 | 1.99 | 189.05 | True |
| 1 | 2020-02-09 | Central | Jardine | Pencil | 36 | 4.99 | 179.64 | True |
| 2 | 2020-03-15 | West | Sorvino | Pencil | 56 | 2.99 | 167.44 | True |
| 3 | 2020-04-01 | East | Jones | Binder | 60 | 4.99 | 299.40 | False |
| 4 | 2020-05-05 | Central | Jardine | Pencil | 90 | 4.99 | 449.10 | True |
| 5 | 2020-06-08 | East | Jones | Binder | 60 | 8.99 | 539.40 | True |
| 6 | 2020-07-12 | East | Howard | Binder | 29 | 1.99 | 57.71 | False |
| 7 | 2020-08-15 | East | Jones | Pencil | 35 | 4.99 | 174.65 | True |
| 8 | 2020-09-01 | Central | Smith | Desk | 32 | 125.00 | 250.00 | True |
| 9 | 2020-10-05 | Central | Morgan | Binder | 28 | 8.99 | 251.72 | True |
| 10 | 2020-11-08 | East | Mike | Pen | 15 | 19.99 | 299.85 | False |
| 11 | 2020-12-12 | Central | Smith | Pencil | 67 | 1.29 | 86.43 | False |
2021| OrderDate | Region | Rep | Item | Units | Unit Cost | Total | Shipped | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2021-01-15 | Central | Gill | Binder | 46 | 8.99 | 413.54 | True |
| 1 | 2021-02-01 | Central | Smith | Binder | 87 | 15.00 | 1305.00 | True |
| 2 | 2021-03-07 | West | Sorvino | Binder | 27 | 19.99 | 139.93 | True |
| 3 | 2021-04-10 | Central | Andrews | Pencil | 66 | 1.99 | 131.34 | False |
| 4 | 2021-05-14 | Central | Gill | Pencil | 53 | 1.29 | 68.37 | False |
| 5 | 2021-06-17 | Central | Tom | Desk | 15 | 125.00 | 625.00 | True |
| 6 | 2021-07-04 | East | Jones | Pen Set | 62 | 4.99 | 309.38 | True |
| 7 | 2021-08-07 | Central | Tom | Pen Set | 42 | 23.95 | 1005.90 | True |
| 8 | 2021-09-10 | Central | Gill | Pencil | 47 | 1.29 | 9.03 | True |
| 9 | 2021-10-14 | West | Thompson | Binder | 57 | 19.99 | 1139.43 | False |
| 10 | 2021-11-17 | Central | Jardine | Binder | 11 | 4.99 | 54.89 | False |
| 11 | 2021-12-04 | Central | Jardine | Binder | 94 | 19.99 | 1879.06 | False |
Combining Multiple Excel Spreadsheets into a Single Pandas DataFrame
Having one DataFrame per sheet allows us to have different columns or content in different sheets.
But what if we prefer to store all the spreadsheets’ data in a single DataFrame? In this tutorial, the workbook spreadsheets have the same columns, so we can combine them with the concat() method of pandas.
If you run the code below, you’ll see that the two DataFrames stored in the dictionary are concatenated:
combined_df = pd.concat(all_sheets.values(), ignore_index=True)
display(combined_df)| OrderDate | Region | Rep | Item | Units | Unit Cost | Total | Shipped | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2020-01-06 | East | Jones | Pencil | 95 | 1.99 | 189.05 | True |
| 1 | 2020-02-09 | Central | Jardine | Pencil | 36 | 4.99 | 179.64 | True |
| 2 | 2020-03-15 | West | Sorvino | Pencil | 56 | 2.99 | 167.44 | True |
| 3 | 2020-04-01 | East | Jones | Binder | 60 | 4.99 | 299.40 | False |
| 4 | 2020-05-05 | Central | Jardine | Pencil | 90 | 4.99 | 449.10 | True |
| 5 | 2020-06-08 | East | Jones | Binder | 60 | 8.99 | 539.40 | True |
| 6 | 2020-07-12 | East | Howard | Binder | 29 | 1.99 | 57.71 | False |
| 7 | 2020-08-15 | East | Jones | Pencil | 35 | 4.99 | 174.65 | True |
| 8 | 2020-09-01 | Central | Smith | Desk | 32 | 125.00 | 250.00 | True |
| 9 | 2020-10-05 | Central | Morgan | Binder | 28 | 8.99 | 251.72 | True |
| 10 | 2020-11-08 | East | Mike | Pen | 15 | 19.99 | 299.85 | False |
| 11 | 2020-12-12 | Central | Smith | Pencil | 67 | 1.29 | 86.43 | False |
| 12 | 2021-01-15 | Central | Gill | Binder | 46 | 8.99 | 413.54 | True |
| 13 | 2021-02-01 | Central | Smith | Binder | 87 | 15.00 | 1305.00 | True |
| 14 | 2021-03-07 | West | Sorvino | Binder | 27 | 19.99 | 139.93 | True |
| 15 | 2021-04-10 | Central | Andrews | Pencil | 66 | 1.99 | 131.34 | False |
| 16 | 2021-05-14 | Central | Gill | Pencil | 53 | 1.29 | 68.37 | False |
| 17 | 2021-06-17 | Central | Tom | Desk | 15 | 125.00 | 625.00 | True |
| 18 | 2021-07-04 | East | Jones | Pen Set | 62 | 4.99 | 309.38 | True |
| 19 | 2021-08-07 | Central | Tom | Pen Set | 42 | 23.95 | 1005.90 | True |
| 20 | 2021-09-10 | Central | Gill | Pencil | 47 | 1.29 | 9.03 | True |
| 21 | 2021-10-14 | West | Thompson | Binder | 57 | 19.99 | 1139.43 | False |
| 22 | 2021-11-17 | Central | Jardine | Binder | 11 | 4.99 | 54.89 | False |
| 23 | 2021-12-04 | Central | Jardine | Binder | 94 | 19.99 | 1879.06 | False |
Now the data stored in the combined_df DataFrame is ready for further processing or visualization. In the following piece of code, we’re going to create a simple bar chart that shows the total sales amount made by each representative. Let’s run it and see the output plot:
total_sales_amount = combined_df.groupby('Rep').Total.sum()
total_sales_amount.plot.bar(figsize=(10, 6))Reading Excel Files Using xlrd
Although importing data into a pandas DataFrame is much more common, another helpful package for reading Excel files in Python is xlrd. In this section, we’re going to scratch the surface of how to read Excel spreadsheets using this package.
NOTE
The xlrd package doesn’t support xlsx files due to a potential security vulnerability. So, we use the xls version of the sales data. You can download the xls version from the link below:
Sales Data Excel Workbook — xls ver.
Let’s see how it works:
import xlrd
excel_workbook = xlrd.open_workbook('sales_data.xls')Above, the first line imports the xlrd package, then the open_workbook method reads the sales_data.xls file.
We can also open an individual sheet containing the actual data. There are two ways to do so: opening a sheet by index or by name. Let’s open the first sheet by index and the second one by name:
excel_worksheet_2020 = excel_workbook.sheet_by_index(0)
excel_worksheet_2021 = excel_workbook.sheet_by_name('2021')Now, let’s see how we can print a cell value. The xlrd package provides a method called cell_value() that takes in two arguments: the cell’s row index and column index. Let’s explore it:
print(excel_worksheet_2020.cell_value(1, 3))PencilWe can see that the cell_value function returned the value of the cell at row index 1 (the 2nd row) and column index 3 (the 4th column).
The xlrd package provides two helpful properties: nrows and ncols, returning the number of nonempty spreadsheet’s rows and columns respectively:
print('Columns#:', excel_worksheet_2020.ncols)
print('Rows#:', excel_worksheet_2020.nrows)Columns#: 8
Rows#: 13Knowing the number of nonempty rows and columns in a spreadsheet helps us with iterating over the data using nested for loops. This makes all the Excel sheet data accessible via the cell_value() method.
Conclusion
This tutorial discussed how to load Excel spreadsheets into pandas DataFrames, work with multiple Excel sheets, and combine them into a single pandas DataFrame. We also explored the main aspects of the xlrd package as one of the simplest tools for accessing the Excel spreadsheets data.
Introduction
Excel is ubiquitous. Many software projects originate from some company or process overgrowing the Excel spreadsheets that were being employed to manage it. As application developers, more than once we’ve had to reverse-engineer Excel files and translate them into a software application. Exploring working with Excel in Python is the goal of this article.
Excel is also quite common as an export format for data, and sometimes also as an input format. And while Excel is not by any means a domain-specific language, we can sometimes consider it as part of the “notation” that some domain experts use to formalize their problems. Thus, software that can “speak” Excel is often closer to its users. Even when the long-term objective is to convert them to an application or to a domain-specific language (DSL), it’s often a good idea to provide an automated migration path from Excel, as well as borrowing notation from Excel.
For example, an application could consume existing Excel files that people use to exchange among themselves as part of the project, effectively gaining the ability to “speak the same language” as the users. Or, it could produce a spreadsheet as the output of some query or calculation, because some users may want to further expand on it to compile a report with additional charts and formulas.
In this tutorial, we’ll explore working with Excel spreadsheets in Python, using the openpyxl library and other tools. In particular, we’ll learn how to:
- Process Excel files as input, with various methods to access the data in them;
- Evaluate formulas;
- Write Excel files as output.
Note: here, we’re talking about “modern” (2010) XML-based Excel files only, that have a .xlsx extension. Openpyxl does not support legacy binary Excel files (.xls). There are other solutions for that that we won’t explore in this tutorial.
All the sample code shown in this tutorial is available in our GitHub repository.
Setup
In the following, we assume a UNIX-like environment – Linux, OSX, or WSL, the Windows Substrate for Linux. As the first step, we’ll create a directory to hold our project:
mkdir python-excel cd python-excel
Alternatively, if we plan to push our code on GitHub, we may create a repository on GitHub first, and clone it on our local machine:
git clone <repo-url> python-excel cd python-excel
This will give us the option to have GitHub generate a .gitignore file for Python, a README file, and a license file for us.
After we’ve created the project root directory, we can use pip to install openpyxl. We may want to set a virtual environment up so that we don’t pollute our system’s Python installation:
python -m venv .venv source .venv/bin/activate
Having activated the environment, we should see it reflected in our shell prompt, like this:
(.venv) python-excel (main*) »
We’ll then write a requirements.txt file that lists our dependencies:
echo openpyxl > requirements.txt
Even if we only have a single dependency right now, explicitly listing it in a file that can be interpreted by the machine will make it easier for other developers to work on our project – including a future version of ourselves that has long forgotten about it.
Then, we’ll install the required dependencies with pip:
python -m pip install -r requirements.txt
We can also easily automate these steps in our CI pipeline, such as GitHub actions.
Loading an Excel File
In Openpyxl, an Excel file is called a “workbook” and is represented by an instance of the class openpyxl.workbook.Workbook. Opening one is super easy:
wb = load_workbook(path)
Openpyxl opens workbooks for reading and for writing at the same time unless we specify that we want a read-only workbook with read_only=True as an argument to load_workbook.
When we finish working with an Excel file, we have to close it:
wb.close()
Unfortunately, a Workbook is not a “context manager”, so we cannot use Python’s with statement to automatically close it when we’re done. Instead, we have to manually arrange to close it even in case of exceptions:
wb = load_workbook(path)
try:
# Use wb...
finally:
wb.close()
Processing an Excel File – Common Cases
In general, workbooks may contain multiple sheets, so in order to access the data in an Excel file, we first need to choose a sheet to work on.
Later on, we’ll see how to process multiple worksheets, but for now, we’ll assume that the data that we’re interested in is in the active sheet – the one that the user will see when they open the file in their spreadsheet application:
sheet = wb.active
This is quite often the only sheet in the document, actually.
Now that we have a sheet, we can access the data in its cells in several ways.
Iterating over rows. We can process the data one row at a time, using a Pythonic generator:
for row in sheet.rows():
# Do something with the row
The rows that rows() yields are themselves generators, and we can iterate through them:
for row in sheet.rows():
for cell in row:
# Do something with the cell
Or we can access them by index:
for row in sheet.rows():
header = row[2]
Actually, the sheet itself is iterable in row order, so we can omit rows altogether:
for row in sheet:
pass
Iterating over columns. Similarly, we can iterate by column using the cols method:
for col in sheet.cols():
# Use the column
Columns work the same as rows: they are themselves iterable and addressable by index.
Accessing cells by address. If we need a piece of data that is in one specific cell, we don’t need to iterate through the whole sheet until we encounter it; we can use Excel-style coordinates to access the cell:
cell = sheet['C5']
We can also obtain a generator for a row, column, or a range of cells; we’ll show that in a later section.
Processing Cells
In any case, to process the data in a spreadsheet we have to deal with individual cells. In Openpyxl, a cell has a value and a bunch of other information that is mostly interesting only for writing, such as style information.
Conveniently, we work with cell values as Python objects (numbers, dates, strings, and so on) as Openpyxl will translate them to Excel types and back appropriately. So, cell contents are not restricted to be strings. Here, for example, we read the contents of a cell as a number:
tax_percentage = sheet['H16'].value tax_amount = taxable_amount * tax_percentage
However, we have no guarantee that the user actually put a number in that cell; if it contains the string “bug”, in the lucky case, we’ll get a runtime error when we run the code above:
TypeError: can't multiply sequence by non-int of type 'float'
However, in the not-so-lucky case, i.e. when taxable_amount is an integer – as it should be, since we’re dealing with money in the example – we’ll get a long string of “bug” repeated taxable_amount times. That’s because Python overloads the * operator for strings and integers to mean “repeat the string n times”. This will potentially result in further type errors down the line, or in a memory error when Python cannot allocate such a big string.
Therefore, we should always validate the input to our program, including Excel files. In this particular case, we can check the type of the value of a cell with Python’s isinstance function:
if isinstance(cell.value, numbers.Number):
# Use the value
Or we can ask the cell for which type of data it contains:
if cell.data_type == TYPE_NUMERIC:
# Use the numeric value
Advanced Addressing of Cells
So far, we’ve explored the simplest, most straightforward ways of accessing cells. However, that doesn’t cover all the use cases that we may encounter; let’s have a look at more complex access schemes.
Sheets other than the active one. We can obtain sheets by access them by name from the workbook:
sheet = wb['2020 Report']
Then we can access cells in the sheet as we’ve seen earlier.
Ranges of cells. We’re not limited to addressing cells one by one – we can also obtain cell ranges:
sheet['D']is a whole row (D in this case)sheet[7]is a whole column (7 in this case)sheet['B:F']represents a range of rowssheet['4:10']represents a range of columnssheet['C3:H5']is the most versatile option, representing an arbitrary range of cells.
In any of the above cases, the result is an iterable of all the cells, in row order (except when the range represents one or more columns, in which case, cells are arranged in column order):
for cell in sheet['B2:F10']:
# B2, B3, ..., F1, F2, ..., F10
for cell in sheet['4:10']:
# A4, B4, ..., A10, B10, ...
for cell in sheet['B2:F10']for cell in sheet['4:10']
Cell Iterators
If the above addressing schemes don’t suit our problem, we can resort to the lower-level methods iter_rows and iter_columns, that return generators – respectively by row and by column – over a range of cells.
In particular, both methods take 5 named parameters:
- min_row – the number of the starting row (1 is A, 2 is B, etc.)
- min_col – the starting column
- max_row – the number of the last row
- max_col – the last column
- values_only – if true, the generator will yield only the value of each cell, rather than the entire cell object. So, we won’t have to spell
cell.value, justvalue. On the other hand, we won’t have access to the other properties of the cell, such as its data_type.
So, for example, if we want to iterate over the range B2:F10 by column we’ll write:
for cell in sheet.iter_columns(min_row=2, min_col=2, max_row=6, max_col=10):
# Use the cell
Writing an Excel File
To write an Excel file, we just call the save method on our workbook:
wb.save('someFile.xlsx')
There’s not much to say about that. It’s more interesting to know how to modify a workbook before saving it. This can be a workbook that has been loaded from a file or a brand new workbook created in Python with the new operator.
Modifying Individual Cells
We can alter the value of a cell simply by assigning to it:
cell.value = 42
Note that this will automatically update the cell’s data type to reflect the new value. Besides the obvious primitive types (integer, float, string), the available types include various classes in the datetime module, as well as NumPy numeric types if NumPy is installed.
Not just values and types, we can set other properties of cells, notably style information (font, color, …), which is useful if we’re set on producing a good-looking report. The documentation of Openpyxl contains a thorough explanation of working with styles so we’ll just refer to that.
Adding and Removing Sheets
So far we’ve seen that we can address some objects – particularly workbooks and worksheets – as if they were dictionaries, to access their components: worksheets, rows, columns, individual cells, cell ranges. We’ll now see how we can add new information to the dictionaries and how to replace existing information. We’ll start with sheets.
To create a worksheet, we use the create_sheet method on a workbook:
new_sheet = wb.create_sheet()
This will add a new sheet to the workbook, after the other sheets, and will return it. We can also give it a title:
new_sheet = wb.create_sheet(title = 'My new sheet')
If we want to place the sheet at another position in the list, we can specify its index (which is zero-based, zero being the first):
# The new sheet will be inserted as the third sheet new_sheet = wb.create_sheet(index = 2)
To delete a sheet, instead, we have two options. We can delete it by name in accordance with the dictionary abstraction:
del wb['My sheet']
We can check if a sheet with a given name is present in the workbook using the in operator:
name = 'My sheet'
if name in workbook:
del workbook[name]
Alternatively, we can call the remove method with the sheet as the argument:
wb.remove(sheet)
Adding and Removing Rows, Columns, and Cells
Similarly, we have methods for adding or removing rows, columns, or individual cells in a worksheet. Let’s see some examples.
First and foremost, by simply accessing a cell, we cause the creation of all rows and columns needed to make room for it:
wb = Workbook() # Initially, an empty worksheet has a single row and column, A and 1 self.assertEqual(wb.active.max_row, 1) self.assertEqual(wb.active.max_column, 1) # We set the value of the cell at C3; # openpyxl creates rows B, C and columns 2, 3 automatically wb.active['C3'].value = 12 # Now the sheet has 3 rows and columns self.assertEqual(wb.active.max_row, 3) self.assertEqual(wb.active.max_column, 3) wb.close()
Additionally, we can use the insert_rows and insert_cols methods to add rows or columns in the middle of the sheet. Existing cells are automatically moved after the newly inserted rows/columns:
wb = Workbook() self.assertEqual(wb.active.max_row, 1) wb.active['A1'].value = 11 # Insert 3 rows, starting at index 0 (i.e. row 1) wb.active.insert_rows(0, 3) self.assertEqual(wb.active.max_row, 4) # Note how the cell, A1, has automatically moved by 3 rows to A4 self.assertEqual(wb.active['A4'].value, 11)
We have the corresponding delete_rows and delete_cols to remove rows/columns instead:
# Delete 2 columns, starting from index 1, i.e. column B sheet.delete_columns(1, 2)
Working With Formulas
Spreadsheets are powerful because they support formulas to compute cell values. Calculated cells automatically update their value when other cells change. Let’s see how we can work with formulas in Openpyxl.
First of all, we can ignore formulas altogether if we just want to read an Excel file. In that case, opening it in “data only” mode will hide formulas, presenting all cells with a concrete value – as computed the last time Excel opened the file:
wb = load_workbook(filename, data_only=True)
Only when modifying an Excel file we may want to recalculate formulas. While openpyxl has some support for parsing formulas, that we could use to analyze them (e.g., to check if they’re only calling known functions), it doesn’t know how to evaluate formulas by itself. So, we have to resort to a third-party library if we want to compute formulas.
Enter the library called, well, “formulas”. Let’s add it to our requirements.txt file and install it:
$ cat requirements.txt openpyxl formulas pip install -r requirements.txt
With the formulas library, we have two options:
- calculating the values of all the formulas in a workbook, recursively following dependencies, the way Excel does it;
- compiling individual formulas to Python functions that we can then invoke with different arguments.
Calculating the Values of All Formulas
The first use case is not the most interesting in the context of this tutorial because it overlaps with the data_only approach we’ve seen earlier. In fact, in that mode, we cannot load a workbook, modify it, and then recompute the formulas in it. We’d have to:
- save the modified workbook to a file;
- have formulas load the file again;
- calculate formula values with an API call;
- save the file with the calculated values;
- open the file with openpyxl in data_only mode and finally see the computed values.
Not really efficient use of developer and computer time!
That said, this feature of the formulas library does have its value, because it supports some advanced use cases:
- Calculating formulas across multiple workbooks. In Excel, it’s possible to have a formula refer to another file. formulas can load multiple workbooks as part of the same set so as to resolve these cross-file references, which is a pretty rarely used feature of Excel that, e.g., Apple’s Numbers doesn’t support.
- Compiling an entire Excel workbook into a Python function. We can define certain cells as input cells, others as output cells, and obtain a function that, given the inputs, computes the formulas in the workbook and returns the values it finds in the output cells after the calculation.
However, to keep it simple, we’ll leave those out of this tutorial.
Compiling Individual Formulas as Python Functions
Let’s concentrate on individual formulas, that we can better integrate with our work based on openpyxl. As per formulas’ documentation, the incantation for compiling an Excel formula into a Python function is the following:
func = formulas.Parser().ast(value)[1].compile()
Note the [1] there – for some reason, the ast method returns a tuple of two objects of which the second, the builder, is the most useful. Even though this is documented, apparently it’s a piece of internal API that would need to be wrapped in a more user-friendly interface.
Anyway, when we evaluate the code above, the resulting func will be a function with as many arguments as the inputs of the formula:
func = formulas.Parser().ast('=A1+B1')[1].compile()
func(1, 2) == 3 # True
Handling Dependencies of Formulas
So, we can compile the formula of a single cell into a function. However, what happens when the formula depends on other cells that contain formulas themselves? The formulas library doesn’t help us in that regard; we have to compute all the inputs recursively if they are themselves formulas. Let’s see how we might do that.
First of all, how do we distinguish between a cell with a formula and a cell with a regular value? Openpyxl doesn’t offer a method to do that, so we have to check if the value of the cell starts with an equal character:
def has_formula(cell: Cell)
return isinstance(cell.value, str) and cell.value.startswith('=')
Therefore, we know how to compute the values of cells that don’t contain formulas:
def compute_cell_value(cell: Cell):
if not has_formula(cell):
return cell.value
Now, the interesting thing is how to compute the value when the cell does contain a formula:
func = formulas.Parser().ast(cell.value)[1].compile() args = [] # TODO: compute function arguments return func(*args)
We compile the formula into a Python function and then we invoke it on its inputs. Since the inputs are references to cells, we recursively invoke compute_cell_value in order to get their values:
sheet = cell.parent for key in func.inputs.keys(): args.append(compute_cell_value(sheet[key]))
We leverage the fact that every cell keeps a reference to its parent, i.e., the sheet that contains it. We also make use of introspection information retained by formulas, that allows us to inspect the inputs of a function – a dictionary of cell references.
Note that this doesn’t support references across sheets or, for that matter, files.
Computing Formulas Over Cell Ranges
So far, our compute_cell_value function successfully computes the values of cells without formulas and with formulas that may depend on other cells. However, what about formulas that depend, not on individual cells, but on cell ranges?
Well, in that case, the input of a function is a range expression, such as A1:Z1 in =SUM(A1:Z1). When we call compute_cell_value recursively, we pass it the following:
sheet[key]
When the key is the address of a single cell, we obtain a cell object; but when it refers to a range of cells, we obtain a tuple with one entry per cell. Our compute_cell_value doesn’t know how to deal with such input, so we have to modify it to handle that case:
if isinstance(input, Tuple): return tuple(map(compute_cell_value, input))
Then, the complete version of the function becomes:
def compute_cell_value(input: Union[Cell, Tuple]):
if isinstance(input, Tuple):
return tuple(map(compute_cell_value, input))
if not has_formula(input):
return input.value
func = formulas.Parser().ast(input.value)[1].compile()
args = []
sheet = input.parent
for key in func.inputs.keys():
args.append(compute_cell_value(sheet[key]))
return func(*args)
Adding New Formula Functions
formulas supports many built-in Excel functions, but not all of them. And of course it doesn’t know about user-defined functions in VBA. However, we can register new Python functions with it so that they can be called in formulas:
def is_number(number): ... # This is actually defined in formulas, but strangely not exposed as the Excel function FUNCTIONS = formulas.get_functions() FUNCTIONS['ISNUMBER'] = is_number
Simple as that. The inputs to the function are its actual arguments as native Python values, so strings, numbers, dates, etc. – not instances of the Cell class.
Also, compared to a regular Python function, we have to guard against XlError, which represents errors in calculations such as #DIV/0! or #REF! (we typically see those in Excel when we’ve made some mistake in writing a formula):
def is_number(number):
if isinstance(number, XlError):
return False
...
Conclusions
We can work productively with Excel in Python with the aid of two mature open-source libraries, openpyxl and formulas. Consuming and producing complex Excel files is a valuable capability in applications whose users routinely work with Excel.
In this tutorial, we’ve learned how to read and write Excel files that may contain formulas. We didn’t talk about styling, charts, merging cells, and other possibilities you may want to read about.
All the sample code shown in this tutorial is available in our GitHub repository.
Read more:
To discover more about how to write a python parser, you can read Parsing In Python: Tools And Libraries
The Best Programming Languages
Get the guide to the best programming languages to use in each situation delivered to your email and read it when you want on the device you want
Microsoft Excel is probably one of the highly used data storage applications. A huge proportion of small to medium size businesses fulfill their analytics requirement using Excel.
However, analyzing huge amount of data in Excel can become highly tedious and time-consuming. You could build customized data processing and analytics application using Visual Basic(VBA), the language that powers the Excel sheets. However, learning VBA could be difficult and perhaps, not worth it.
However, if you have a little knowledge of Python, you could build highly professional Business Intelligence using Excel data, without the need of a database. Using Python with Excel could be a game changer for your business.
Sections Covered
- Basic Information about Excel
- What is Openpyxl and how to install it?
- Reading data from Excel in Python
- Reading multiple cells from Excel in Python
- Find the max row and column number of an Excel sheet in Python
- How to iterate over Excel rows and columns in Python?
- Create a new Excel file with Python
- Writing data to Excel in Python
- Appending data to Excel in Python
- Manipulating Excel Sheets in Python
- Practical usage example of data analysis of Excel sheets in Python
Basic Information about Excel
Before beginning this Openpyxl tutorial, you need to keep the following details in mind.
- Excel files are called Workbooks.
- Each Workbook can contain multiple sheets.
- Every sheet consists of rows starting from 1 and columns starting from A.
- Rows and columns together make up a cell.
- Any type of data can be stored.
What is Openpyxl and how to install it?
The Openpyxl module in Python is used to handle Excel files without involving third-party Microsoft application software. It is arguably, the best python excel library that allows you to perform various Excel operations and automate excel reports using Python. You can perform all kinds of tasks using Openpyxl like:-
- Reading data
- Writing data
- Editing Excel files
- Drawing graphs and charts
- Working with multiple sheets
- Sheet Styling etc.
You can install Openpyxl module by typing pip install openpyxl in your command line.
pip install openpyxlReading data from Excel in Python
To import an excel file in Python, use the load_workbook method from Openpyxl library.
Let’s import an Excel file named wb1.xlsx in Python using Openpyxl module. It has the following data as shown in the image below.
Step 1 — Import the load_workbook method from Openpyxl.
from openpyxl import load_workbook
Step 2 — Provide the file location for the Excel file you want to open in Python.
wb = load_workbook('wb1.xlsx')If your Excel file is present in the same directory as the python file, you don’t need to provide to entire file location.
Step 3 — Choose the first active sheet present in the workbook using wb.active attribute.
sheet = wb.activeThe above points are a standard way of accessing Excel sheets using Python. You will see them being used multiple times through out this article.
Let’s read all the data present in Row 1 (header row).
Method 1 — Reading data through Excel cell name in Python
Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('wb1.xlsx')
sheet = wb.active
print(sheet["A1"].value)
print(sheet["B1"].value)
print(sheet["C1"].value)
print(sheet["D1"].value)Output
ProductId
ProductName
Cost per Unit
QuantityMethod 2 — Reading data from Excel using cell() method in Python
Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('wb1.xlsx')
sheet = wb.active
print(sheet.cell(row=1, column=1).value)
print(sheet.cell(row=1, column=2).value)
print(sheet.cell(row=1, column=3).value)
print(sheet.cell(row=1, column=4).value)Output
ProductId
ProductName
Cost per Unit
QuantityReading Multiple Cells from Excel in Python
You can also read multiple cells from an Excel workbook. Let’s understand this through various examples. Refer to the image of the wb1.xlsx file above for clarity.
Method 1 — Reading a range of cells in Excel using cell names
To read the data from a specific range of cells in your Excel sheet, you need to slice your sheet object through both the cells.
Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('wb1.xlsx')
sheet = wb.active
# Access all cells from A1 to D11
print(sheet["A1:D11"])Output
((<Cell 'Sheet1'.A1>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B1>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C1>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.D1>),
(<Cell 'Sheet1'.A2>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B2>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C2>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.D2>),
(<Cell 'Sheet1'.A3>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B3>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C3>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.D3>),
(<Cell 'Sheet1'.A4>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B4>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C4>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.D4>),
(<Cell 'Sheet1'.A5>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B5>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C5>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.D5>),
(<Cell 'Sheet1'.A6>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B6>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C6>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.D6>),
(<Cell 'Sheet1'.A7>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B7>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C7>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.D7>),
(<Cell 'Sheet1'.A8>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B8>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C8>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.D8>),
(<Cell 'Sheet1'.A9>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B9>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C9>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.D9>),
(<Cell 'Sheet1'.A10>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B10>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C10>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.D10>),
(<Cell 'Sheet1'.A11>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.B11>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.C11>, <Cell 'Sheet1'.D11>))You can see that by slicing the sheet data from A1:D11, it returned us tuples of row data inside a tuple. In order to read the values of every cell returned, you can iterate over each row and use .value.
Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('wb1.xlsx')
sheet = wb.active
# Access all cells from A1 to D11
for row in sheet["A1:D11"]:
print ([x.value for x in row])Output
['ProductId', 'ProductName', 'Cost per Unit', 'Quantity']
[1, 'Pencil', '$0.5', 200]
[2, 'Pen', '$1', 500]
[3, 'Eraser', '$0.25', 100]
[4, 'Sharpner', '$0.75', 100]
[5, 'Files', '$3', 50]
[6, 'A4 Size Paper', '$9', 10]
[7, 'Pencil Box', '$12', 20]
[8, 'Pen Stand', '$5.5', 10]
[9, 'Notebook', '$2', 50]
[10, 'Marker', '$1', 75]Method 2 — Reading a single row in Excel using cell name
To read a single row in your Excel sheet, just access the single row number from your sheet object.
Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('wb1.xlsx')
sheet = wb.active
# Access all cells in row 1
for data in sheet["1"]:
print(data.value)Output
ProductId
ProductName
Cost per Unit
QuantityMethod 3 — Reading all rows in Excel using rows attribute
To read all the rows, use sheet.rows to iterate over rows with Openpyxl. You receive a tuple element per row by using the sheet.rows attribute.
Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('wb1.xlsx')
sheet = wb.active
# Access all cells in row 1
for row in sheet.rows:
print([data.value for data in row])Output
['ProductId', 'ProductName', 'Cost per Unit', 'Quantity']
[1, 'Pencil', '$0.5', 200]
[2, 'Pen', '$1', 500]
[3, 'Eraser', '$0.25', 100]
[4, 'Sharpner', '$0.75', 100]
[5, 'Files', '$3', 50]
[6, 'A4 Size Paper', '$9', 10]
[7, 'Pencil Box', '$12', 20]
[8, 'Pen Stand', '$5.5', 10]
[9, 'Notebook', '$2', 50]
[10, 'Marker', '$1', 75]Method 4 — Reading a single column in Excel using cell name
Similar to reading a single row, you can read the data in a single column of your Excel sheet by its alphabet.
Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('wb1.xlsx')
sheet = wb.active
# Access all cells in column A
for data in sheet["A"]:
print(data.value)Output
ProductId
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10Method 5 — Reading all the columns in Excel using columns attribute
To read all the data as a tuple of the columns in your Excel sheet, use sheet.columns attribute to iterate over all columns with Openpyxl.
Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('wb1.xlsx')
sheet = wb.active
# Access all columns
for col in sheet.columns:
print([data.value for data in col])Output
['ProductId', 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
['ProductName', 'Pencil', 'Pen', 'Eraser', 'Sharpner', 'Files', 'A4 Size Paper', 'Pencil Box', 'Pen Stand', 'Notebook', 'Marker']
['Cost per Unit', '$0.5', '$1', '$0.25', '$0.75', '$3', '$9', '$12', '$5.5', '$2', '$1']
['Quantity', 200, 500, 100, 100, 50, 10, 20, 10, 50, 75]Method 6 — Reading all the data in Excel
To read all the data present in your Excel sheet, you don’t need to index the sheet object. You can just iterate over it.
Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('wb1.xlsx')
sheet = wb.active
# Access all cells in Excel
for row in sheet:
print([data.value for data in row])Output
['ProductId', 'ProductName', 'Cost per Unit', 'Quantity']
[1, 'Pencil', '$0.5', 200]
[2, 'Pen', '$1', 500]
[3, 'Eraser', '$0.25', 100]
[4, 'Sharpner', '$0.75', 100]
[5, 'Files', '$3', 50]
[6, 'A4 Size Paper', '$9', 10]
[7, 'Pencil Box', '$12', 20]
[8, 'Pen Stand', '$5.5', 10]
[9, 'Notebook', '$2', 50]
[10, 'Marker', '$1', 75]Find the max row and column number of an Excel Sheet in Python
To find the max row and column number from your Excel sheet in Python, use sheet.max_row and sheet.max_column attributes in Openpyxl.
Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('wb1.xlsx')
sheet = wb.active
print(f"Max row in the active sheet is {sheet.max_row}")
print(f"Max column in the active sheet is {sheet.max_column}")Output
Max row in the active sheet is 11
Max column in the active sheet is 4Note — If you update a cell with a value, the sheet.max_row and sheet.max_column values also change, even though you haven’t saved your changes.
Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('pylenin.xlsx')
sheet = wb.active
sheet["A1"].value = "Lenin"
print(sheet.max_row)
sheet["A2"].value = "Mishra"
print(sheet.max_row)
# wb.save('pylenin.xlsx')Output
1
2How to iterate over Excel rows and columns in Python?
Openpyxl offers two commonly used methods called iter_rows and iter_cols to iterate over Excel rows and columns in Python.
iter_rows()— Returns one tuple element per row selected.iter_cols()— Returns one tuple element per column selected.
Both the above mentioned methods can receive the following arguments for setting boundaries for iteration:
- min_row
- max_row
- min_col
- max_col
Example 1 — iter_rows()
Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('wb1.xlsx')
sheet = wb.active
# Access all cells from between
# "Row 1 and Row 2" and "Column 1 and Column 3"
for row in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=1,
max_row=2,
min_col=1,
max_col=3):
print([data.value for data in row])Output
['ProductId', 'ProductName', 'Cost per Unit']
[1, 'Pencil', '$0.5']As you can see, only the first 3 columns of the first 2 rows are returned. The tuples are row based.
You can also choose to not pass in some or any arguments in iter_rows method.
Code — Not passing min_col and max_col
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('wb1.xlsx')
sheet = wb.active
# min_col and max_col arguments are not provided
for row in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=1,
max_row=2):
print([data.value for data in row])Output
['ProductId', 'ProductName', 'Cost per Unit', 'Quantity']
[1, 'Pencil', '$0.5', 200]All the columns from the first 2 rows are being printed.
Example 2 — iter_cols()
Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('wb1.xlsx')
sheet = wb.active
# Access all cells from A1 to D11
for row in sheet.iter_cols(min_row=1,
max_row=2,
min_col=1,
max_col=3):
print([data.value for data in row])Output
['ProductId', 1]
['ProductName', 'Pencil']
['Cost per Unit', '$0.5']The tuples returned are column based on using iter_cols() method.
You can also choose to not pass in some or any arguments in iter_cols() method.
Code — Not passing any argument
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('wb1.xlsx')
sheet = wb.active
# min_col and max_col arguments are not provided
for row in sheet.iter_cols():
print([data.value for data in row])Output
['ProductId', 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
['ProductName', 'Pencil', 'Pen', 'Eraser', 'Sharpner', 'Files', 'A4 Size Paper', 'Pencil Box', 'Pen Stand', 'Notebook', 'Marker']
['Cost per Unit', '$0.5', '$1', '$0.25', '$0.75', '$3', '$9', '$12', '$5.5', '$2', '$1']
['Quantity', 200, 500, 100, 100, 50, 10, 20, 10, 50, 75]Create a new Excel file with Python
To create a new Excel file in Python, you need to import the Workbook class from Openpyxl library.
Code
from openpyxl import Workbook
wb = Workbook()
sheet = wb.active
sheet['A1'] = "Pylenin"
sheet['B1'] = "loves"
sheet['C1'] = "Python"
wb.save("pylenin.xlsx")This should create a new Excel workbook called pylenin.xlsx with the provided data.
Writing data to Excel in Python
There are multiple ways to write data to an Excel file in Python.
Method 1 — Writing data to Excel using cell names
Code
from openpyxl import Workbook
wb = Workbook()
sheet = wb.active
sheet['A1'] = "Pylenin"
sheet['B1'] = "loves"
sheet['C1'] = "Python"
wb.save("pylenin.xlsx")Output
Method 2 — Writing data to Excel using the cell() method
Code
from openpyxl import Workbook
wb = Workbook()
sheet = wb.active
sheet.cell(row=1, column=1).value = "Pylenin"
sheet.cell(row=1, column=2).value = "loves"
sheet.cell(row=1, column=3).value = "Python"
wb.save("pylenin.xlsx")Output
Method 3 — Writing data to Excel by iterating over rows
Code — Example 1
from openpyxl import Workbook
wb = Workbook()
sheet = wb.active
for row in sheet["A1:D3"]:
row[0].value = "Pylenin"
row[1].value = "loves"
row[2].value = "Python"
wb.save("pylenin.xlsx")Output
You can also use methods like iter_rows() and iter_cols() to write data to Excel.
Code — Example 2 — using iter_rows() method
from openpyxl import Workbook
wb = Workbook()
sheet = wb.active
for row in sheet.iter_rows(min_row=1,
max_row=3,
min_col=1,
max_col=3):
row[0].value = "Pylenin"
row[1].value = "loves"
row[2].value = "Python"
wb.save("pylenin.xlsx")Output
Code — Example 3 — using iter_cols() method
from openpyxl import Workbook
wb = Workbook()
sheet = wb.active
for col in sheet.iter_cols(min_row=1,
max_row=3,
min_col=1,
max_col=3):
col[0].value = "Pylenin"
col[1].value = "loves"
col[2].value = "Python"
wb.save("pylenin.xlsx")Output
Appending data to Excel in Python
Openpyxl provides an append() method, which is used to append values to an existing Excel sheet in Python.
Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('pylenin.xlsx')
sheet = wb.active
data = (
("Pylenin", "likes", "icecream"),
("Pylenin", "likes", "Cricket")
)
for row in data:
sheet.append(row)
wb.save('pylenin.xlsx')Output
Manipulating Excel Sheets in Python
Each Excel workbook can contain multiple sheets. To get a list of all the sheet names in an Excel workbook, you can use the wb.sheetnames.
Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('pylenin.xlsx')
print(wb.sheetnames)Output
['Sheet']As you can see, pylenin.xlsx has only one sheet.
To create a new sheet in Python, use the create_sheet() method from the Openpyxl library.
Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('pylenin.xlsx')
wb.create_sheet('Pylenin')
wb.save('pylenin.xlsx')Output
You can also create sheets at different positions in the Excel Workbook.
Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('pylenin.xlsx')
# insert sheet at 2nd to last position
wb.create_sheet('Lenin Mishra', -1)
wb.save('pylenin.xlsx')Output
If your Excel workbook contains multiple sheets and you want to work with a particular sheet, you can refer the title of that sheet in your workbook object.
Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('pylenin.xlsx')
ws = wb["Pylenin"]
ws["A1"].value = "Pylenin"
ws["A2"].value = "loves"
ws["A3"].value = "Python"
wb.save('pylenin.xlsx')Output
Practical usage example of data analysis of Excel sheets in Python
Let’s perform some data analysis with wb1.xlsx file as shown in the first image.
Objective
- Add a new column showing
Total Price per Product. - Calculate the
Total Costof all the items bought.
The resulting Excel sheet should look like the below image.
Step 1 — Find the max row and max column of the Excel sheet
As mentioned before, you can use the sheet.max_row and sheet.max_column attributes to find the max row and max column for any Excel sheet with Openpyxl.
Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('wb1.xlsx')
sheet = wb.active
print(f"Max row in the active sheet is {sheet.max_row}")
print(f"Max column in the active sheet is {sheet.max_column}")Output
Max row in the active sheet is 11
Max column in the active sheet is 4Step 2 — Add an extra column in Excel with Python
To add an extra column in the active Excel sheet, with calculations, you need to first create a new column header in the first empty cell and then iterate over all rows to multiply Quantity with Cost per Unit.
Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('wb1.xlsx')
sheet = wb.active
# Add new column header
sheet.cell(row=1, column=sheet.max_column+1).value = "Total Price per Product"
wb.save("wb1.xlsx")Output
Now that an extra column header has been created, the sheet.max_column value will change to 5.
Now you can calculate the Total Price per Product using iter_rows() method.
Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('wb1.xlsx')
sheet = wb.active
# Calculate Total Price per Product
for id, row in enumerate(sheet.iter_rows(min_row=2,
max_row = sheet.max_row)):
row_number = id + 2 # index for enumerate will start at 0
product_name = row[1].value
cost_per_unit = row[2].value
quantity = row[3].value
print(f"Total cost for {product_name} is {cost_per_unit*quantity}")
# Update cell value in the last column
current_cell = sheet.cell(row=row_number, column=sheet.max_column)
current_cell.value = cost_per_unit*quantity
# Format cell from number to $ currency
current_cell.number_format = '$#,#0.0'
print("nSuccesfully updated Excel")
wb.save('wb1.xlsx')Output
Total cost for Pencil is 100.0
Total cost for Pen is 500
Total cost for Eraser is 25.0
Total cost for Sharpner is 75.0
Total cost for Files is 150
Total cost for A4 Size Paper is 90
Total cost for Pencil Box is 240
Total cost for Pen Stand is 55.0
Total cost for Notebook is 100
Total cost for Marker is 75
Succesfully updated ExcelStep 3 — Calculate sum of a column in Excel with Python
The last step is to calculate the Total Cost of the last column in the Excel file.
Access the last column and add up all the cost.
You can read the last column by accessing the sheet.columns attribute. Since it returns a generator, you first convert it to a python list and access the last column.
last_column_data = list(sheet.columns)[-1]
# Ignore header cell
total_cost = sum([x.value for x in last_column_data[1:]])Create a new row 2 places down from the max_row and fill in Total Cost.
max_row = sheet.max_row
total_cost_descr_cell = sheet.cell(row = max_row +2, column = sheet.max_column -1)
total_cost_descr_cell.value = "Total Cost"
total_cost_cell = sheet.cell(row = max_row +2, column = sheet.max_column)
total_cost_cell.value = total_costImport Font class from openpyxl.styles to make the last row Bold.
# Import the Font class from Openpyxl
from openpyxl.styles import Font
bold_font = Font(bold=True)
total_cost_descr_cell.font = bold_font
total_cost_cell.font = bold_font
total_cost_cell.number_format = "$#,#0.0"Final Code
Code
from openpyxl import load_workbook
wb = load_workbook('wb1.xlsx')
sheet = wb.active
last_column_data = list(sheet.columns)[-1]
# Ignore header cell
total_cost = sum([x.value for x in last_column_data[1:]])
max_row = sheet.max_row
total_cost_descr_cell = sheet.cell(row = max_row + 2, column = sheet.max_column -1)
total_cost_descr_cell.value = "Total Cost"
total_cost_cell = sheet.cell(row = max_row + 2, column = sheet.max_column)
total_cost_cell.value = total_cost
# Import the Font class from Openpyxl
from openpyxl.styles import Font
bold_font = Font(bold=True)
total_cost_descr_cell.font = bold_font
total_cost_cell.font = bold_font
total_cost_cell.number_format = "$#,#0.0"
print("nSuccesfully updated Excel")
wb.save('wb1.xlsx')When you run the above code, you should see all the relevant updates to your Excel sheet.