Is the category for this document correct?
- Foreign Language
- English (Language)
Thank you for your participation!

No more boring flashcards learning!
Learn languages, math, history, economics, chemistry and more with free Studylib Extension!
- Distribute all flashcards reviewing into small sessions
- Get inspired with a daily photo
- Import sets from Anki, Quizlet, etc
- Add Active Recall to your learning and get higher grades!
Add to Chrome
It’s free
Learning root words in English is not only helpful to fetch good marks in the verbal ability section of competitive exams but also help to hone up the English vocabulary skills in general.
English is one of the important sections of various Government exams like Bank, SSC, RRB, etc. and aspirants preparing for these examinations are required to have a good vocabulary to ace this section.
Now, the English language being vast and comprehensive, it is difficult to memorise each and every word and their meaning. So, English root words can help you to understand the meaning of all the words easily.
Therefore, this article will provide the list of root words with detailed explanation. Candidates will also be able to download the root words pdf for convenient preparation.
English Root Words PDF:-Download PDF Here
To understand vocabulary, we need to understand each word and history attached to it. English is considered as a global language because it is a culmination of all popular languages like Spanish, Latin, Greek etc. Learning the root words will make it easy for the aspirants to work out the meaning of the new words as they encounter them.
What is the root word?
A root word is a word that forms the basis of new words by adding affixes (prefixes or suffixes). It is the most basic part of any word.
The basic structure of roots are either affixed or suffixed and then they become a new word. An understanding of the usual root words will help make a good guess about the meaning of newly known words and will, in turn, strengthen your vocabulary.
Check out General English for competitive exams for various conceptual based topics along with their explanations.
Let’s check out various root words in English, their combination and different new words formed by them.
Candidates can go through the video on English Vocabulary – Root Words to understand the concept.
English Root Word List
- Root Word – Mal – a Latin word, Meaning – bad or evil.
English words having ‘mal’ root word –
- Malignment – defame something badly
- Malice – evil intention
- Maltreat. – Treat someone/something badly
- Malfunction – working badly
- Dismal – A gloomy situation
- Maleficent – Someone who deliberately try causing harm to someone
*All the words having ‘mal’ root word gives a negative connotation.
Candidates can check the List of Homophones/Homonyms in the given link to prepare for the English section.
2. Root Word – Phobia, Meaning – Fear or dislike
English words formed of it –
- Demophobia – demo is people so one who fears public speaking have demophobia
- Zoophobia – people who fear animals.
- Theophobia – Thei is God/Religion, so a person who fears religion has theophobia.
- Pedophobia – Pedo means child, so a person who doesn’t like children has pedophobia.
- Gynophobia – a person who dislikes girls/women because Gyno is a girl/woman.
You can check the List of Phobias in the given link which is important for the general awareness section as well.
3. Root word – Fin – a Latin word, Meaning – to end something, limit, or boundary.
English words containing ‘Fin’ in them –
- Infinity – No limit
- Infinitesimal – immeasurably small
- Confinement – concluding state of pregnancy
- Definite – Precise
We can see, the words mean to end or limit something. Examples: We take a final exam at the end of the course. The one who watches reality TV Shows, see the Finale episode or the final episode of the season.In a race, the Finish line is known as the end of it.
4. Root word – Phil – a Greek word, Meaning – to Love.
English word with root word ‘Phil’-
- Bibliophile – the one who loves books
- Philologist – word lover who is a scholar of language
- Philanthropist – is a person who loves mankind.
- Philosopher – A person who will love wisdom
- Philodendron – A tree that curls up while growing and are called love trees.
So we can see all the words with root words are associated with love. Did you know the city of Philadelphia actually means the city of brotherly love.
5. Root word – Logy a Greek word, Meaning – to study something
Words formed with the root word ‘logy’ are –
- Analogy – the study of comparison of two or more things
- Anthropology – the study of human beings as ‘anthrop’ means human.
- Theology – ‘theo’ means God/religion so theology is the study of religion
- Morphology – the study of structures is morphology. Morph means structures.
The above-given examples for ‘logy’ root words form a part of one-word substitution which is again an important topic to study in the English language section. Candidates can go the category-wise list of one-word substitution for assistance in preparation.
6. Root word – Thie, a Greek word – Meaning – God/Religion
English words formed using the root word ‘Thei’ are –
- Theist – ‘ist’ is follower, so theist is one who believes in God
- Atheist – A [person who do not believe in God
- Pantheist – Pan means that is all over, so the person who believes in all God across all religion is Pantheist
- Monotheist – Mono connotes one, so those who believe in one god are monotheists.
Also, check the One Word substitution Questions & Answers asked in various government exams.
7. Root word – Fact – coming from the Latin language – Meaning – something that is “made” or “done”. Let’s check the different words with this root word –
- Factory: is a place where something is “made”.
- Manufactured: A place where something is made too. Manufactured originally means something that is made in large scale.
- Artifact – something that is made by human skills
- Factor – is a “maker”. For example, a beautiful painting done by someone is a deciding factor who gained the rank of a master- painter.
- Benefactor – Someone who does good for other people
- Stupefaction – something that made you completely surprised
- Petrifaction – a superpower that makes people turn into stones by just gazing at them
- Malefactor – someone that does evil to human
- Satisfaction – done enough
All the words formed of the root word ‘fact’ connotes something done or made.
8. Root Word – Dict/Dic – a Latin word – Meaning– Say
English words containing Dict/Dic in them –
- Prediction – say something beforehand.
- Dictated – say something to someone
- Verdict – speaking or saying the truth
- Indicate – make known about something by saying
- Contradict – say something against
- Dictionary – a book that tells us how to say a certain word correctly.
- Addicted – when we want to say or declare that we are in love with certain things.
Candidates preparing for various government exams can check the following topics for preparation:
- Idioms And Phrases
- List of Synonyms and Antonyms
- Letter Writing Format
- Active And Passive Voice Rules
9. Root Word – Cide, a Latin word, Meaning a person or something that kills, Act of killing.
There are many words in the English language formed with the root word Cide –
- Patricide – Patri means Father, so the killing of one’s father is Patricide
- Uxoricide – Husband who kills his wife, Uxor means Wife.
- Maritricide – Marit is husband, so Maritricide is killing of one’s husband
- Infanticide – Infant is a child, the killing of a child is infanticide.
So, it can be understood that the words with root word Cide connote killing of someone or something.
10. Root Word – Anti, a Greek word, Meaning – Opposite or against
The English words formed of the root word ‘Anti’ –
- Antiseptic – working against infection
- Antidote – working against the effect of the poison
- Antisocial – opposite to social norms
- Antioxidants – compounds that work against the chemical reactions that damage the cells of an organism.
Remember, anything with the root word ‘anti’ is supposed to do against or opposite of something.
Given below are a few links that give questions and answers of important verbal ability topics that are asked in various government examinations, candidates can check these for practice and revision.
For more such questions and answers on different topics or to get more concepts and rules-based explanations of various topics covered in the Verbal Ability section, check the linked page.
Root Words That are Common English Words
There are certain root words that form a standalone word of its own or as part of other common words in the English language. Given below are some common English words that are root words as well:
- Act – meaning – to move or do, other English words- actor, acting, reenact
- Crypt – Meaning – to hide, other English words – cryptic, apocryphal, cryptography
- Ego – meaning – Self-importance, Other words formed of it egotist, egocentric, egomaniac
- Legal – meaning – related to the law, other words in English – illegal, legalities, paralegal
- Form – meaning – shape, words formed from it – conform, reform, formulate
- Phobia – meaning – fear – words formed from this root word are already discussed above.
- Norm – meaning – typical, other English words – abnormal, paranormal, normality.
Given below is the Root words list that originates from either Latin or Greek words and forms the basis of different English words.
| Root Words from the Greek Language | ||
| Root Words | Meaning | Examples |
| meter/metr | measure | thermometer, perimeter |
| tele | far off | television, telephone |
| psycho | soul; spirit | psychology, psychic |
| therm | heat | thermal, thermometer |
| techno | art; science; skill | technique, technological |
| pseudo | not genuine, false | pseudonym, pseudoscience |
| morph | form; shape | morphology, morphing |
| photo/phos | light | photograph, phosphorous |
| phon | sound | phone, symphony |
| hydr | water | hydration, dehydrate |
| mono | one | monologue, monotonous |
| mis/miso | hate | misanthrope, misogyny |
| micro | small | microbe, microscope |
| hetero | different | heteronym, heterogeneous |
| scope | viewing instrument | microscope, telescope |
| hypo | below; beneath | hypothermia, hypothetical |
| homo | same | homonym, homogenous |
| chron | time | chronological, chronic |
| gram | thing written | epigram, telegram |
| auto | self | autobiography, automobile |
| dyna | power | dynamic, dynamite |
| bio | life | biology, biography |
| dys | bad; hard; unlucky | dysfunctional, dyslexic |
| phobia | fear | claustrophobia, phobic |
| logy | study of | biology, psychology |
| graph | writing | graphic, phonograph |
| nym | name | antonym, synonym |
| anthrop | man; human; humanity | anthropologist, philanthropy |
Candidates preparing for various government exams can check the relevant links given below:
- Free Online Mock Tests For Government exams
- Previous Year Question Papers WIth Solution For Government exams
The table below gives the English root words taken from the Latin language:
| English Root Words From the Latin Language | ||
| Root Words | Meaning | Examples |
| aqua | water | aquarium, aquamarine |
| bene | good | benefactor, benevolent |
| circum | around | circumference, circumstance |
| duc/duct | to lead | conduct, induce |
| cent | one hundred | century, percent |
| mal | bad | malevolent, malefactor |
| mater | mother | material, maternity |
| form | shape | conform, reform |
| ambi | both | ambiguous, ambidextrous |
| dict | to say | dictation, dictator |
| mit | to send | transmit, admit |
| fort | strength | fortitude, fortress |
| fract | to break | fracture, fraction |
| struct | to build | destruction, restructure |
| scrib/scribe | to write | inscription, prescribe |
| ject | throw | projection, rejection |
| multi | many | multimedia, multiple |
| fac | to do; to make | factory, manufacture |
| aud | to hear | audience, audition |
| sect/sec | to cut | bisect, section |
| jud | judge | judicial, prejudice |
| mort | death | mortal, mortician |
| pater | father | paternal, paternity |
| port | to carry | portable, transportation |
| contra/counter | against | contradict, encounter |
| rupt | to break | bankrupt, disruption |
| voc | voice; to call | vocalize, advocate |
| spect | to look | inspection, spectator |
| vid/vis | to see | video, televise |
| sent | to feel; to send | consent, resent |
English Root Words List:-Download PDF Here
Candidates preparing for the various government exams can refer to the detailed exam syllabus in the links given below:

By
Last updated:
April 2, 2023
How do you feel about shortcuts?
By learning short and simple pieces of English words, also known as word roots, you can unlock an understanding of thousands of words and boost your English vocabulary!
In this post, we’re going to share 30 English word roots from Latin and Greek to help you improve your comprehension of English by providing a shortcut to learning.
Contents
- What is a Root?
- 30 Common English Word Roots from Greek and Latin
-
- Roots of Greek Origin
- Roots of Latin Origin
- How to Use Roots to Form and Understand English Words
-
- The Top 10 Suffixes You’ll See with Roots
- The Top 10 Prefixes You’ll See with Roots
- The Matching Game for Practicing English Roots, Suffixes and Prefixes
Download:
This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you
can take anywhere.
Click here to get a copy. (Download)
What is a Root?
First, we should talk about what “root” means.
A root is the basic unit of a word.
Linguists, scientists who study language, refer to the root as the base or foundation of a word. If you really think about it, the name “root” makes sense. A real, literal root is the base of a tree, connecting the tree to the ground. The root of a word connects that word to some meaning.
To learn about other parts of words and their relationships with roots, check out this informative page.
30 Common English Word Roots from Greek and Latin
If you aren’t sure that you want to memorize hundreds of roots, then memorize just these 30 roots. These are some of the most useful and common roots that you’ll learn!
You’ll see these popping up everywhere in words you both know and don’t know. If you wouldn’t have had any idea what they meant before you had learned the roots, then you’ll see the value of learning roots.
Roots of Greek Origin
| Greek Root | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Psych | Mind | Psychology (the study of the mind) |
| Phil | Love | Cinephile (movie lover) |
| Mega | Great, large | Megaphone (a large device which makes your voice louder) |
| Mono | Single | Monochromatic (having only one color) |
| Chron | Time | Chronological (organized by time of occurrence) |
| Bio | Life | Biology (the study of living things) |
| Theo | God | Theology (the study of religion) |
| Phone | Sound | Telephone (a device used to talk with other people) |
| Auto | Self | Automatic (happens on its own) |
| Poly | Many | Polyglot (person who can speak many languages) |
Roots of Latin Origin
| Latin Root | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Struc | Build | Structure (parts or pieces built into something complex) |
| Vac | Empty | Vacuous (having an empty mind, not thinking) |
| Ver | True | Veritable (real, true, authentic) |
| Scrib/Scrip | Write | Prescription (a written note signed by a doctor which provides instructions for medicine or treatment) |
| Luc | Light | Lucid (bright, clear) |
| Mal | Bad | Malevolent (wanting to do bad or evil things) |
| Mar | Sea | Marina (a port or harbor for boats and ships) |
| Manu/Mani | Hand | Manicure (a treatment to make your hands look clean, neat and polished) |
| Min | Small | Miniscule (very small in size) |
| Fort | Strong | Fortitude (strength) |
| Mort | Death | Mortician (someone who prepares dead bodies to be buried) |
| Nas/Nat | Birth | Nascent (coming into existence, something just recently created) |
| Trans | Across | Transatlantic (something which crosses the Atlantic Ocean) |
| Voc/Vos | Voice | Vociferous (loud, someone who speaks loudly or talks a lot) |
| Aqua | Water | Aquarium (a tank of water where fish are kept as pets) |
| Bene | Good | Benevolent (wanting good things for people, generous, kind) |
| Omni | All | Omniscient (knowing everything) |
| Sens/Sent | Feel | Sentimental (emotional, attaching emotional value to things) |
| Terr | Earth | Terrarium (a container for land animals kept as pets, often containing rocks, dirt or sand) |
| Vid/Vis | See | Visible (able to be seen) |
How to Use Roots to Form and Understand English Words
Now that you have a list of great roots to memorize, you’ll need a list of the most common prefixes and suffixes to go with it.
Why?
Prefixes and suffixes are two things that can be attached to roots to form words.
Suffixes can be attached at the ends of roots to change either the definition or the part of speech (noun, verb, adjective, etc.) of the word. So, suffixes can change verbs into nouns, nouns into adjectives and so on.
To create words you put a root together with either a suffix or prefix. Examples:
photo (root for light) + graph (suffix for written) = photograph (light that is written)
re (prefix for again) + flect (root for bend) = reflect (to bend again)
Now you might think these are funny ways to define the words “photograph” and “reflect.” This is because using Latin to define words means that you’re using very direct, literal translations.
However funny these translations might sound, there’s always a clue there that shows what the true meaning is in English.
The Top 10 Suffixes You’ll See with Roots
Top Greek Suffixes
| Greek Suffix | Meaning |
|---|---|
| phil/phile | fear, fearing |
| chrome | color |
| logy | study of |
| ism | act, practice or result of |
| some | body |
| meter | a measurement |
| nomy | systematized knowledge of |
Top Latin Suffixes
| Latin Suffix | Meaning |
|---|---|
| able | is, can be |
| act | state, quality |
| cidal/cide | killer, a killing |
The Top 10 Prefixes You’ll See with Roots
Top Greek Prefixes
| Greek Prefix | Meaning |
|---|---|
| amphi | both, about, around |
| andro | man, male |
| anti | against, opposed |
| mono | one, single, alone |
Top Latin Prefixes
| Latin Prefix | Meaning |
|---|---|
| ad | to, attached to |
| semi | half |
| non | not |
| pre | before |
| inter | between |
| co | with, together |
As you can see, learning roots, suffixes and prefixes is a quick shortcut to learn and understand words in English.
Immersing yourself in the language and seeing how it’s used by native speakers is a great way to learn vocabulary and see word roots. There are many great TV shows in English that you could watch, or you could even try a language-learning program like FluentU.
FluentU features an array of bite-sized authentic English videos, like inspiring talks and movie trailers, each with interactive subtitles that you can hover over to see more information about the words used. The subtitles will help you identify new vocabulary that you can add to your personalized flashcard decks to practice.
By immersing yourself in native media, not only will you be able to expand your vocabulary by identifying roots and common trends, but you’ll also get to see them used in context!
The Matching Game for Practicing English Roots, Suffixes and Prefixes
As you know, practice makes perfect, and this also applies when learning roots, suffixes and prefixes.
Play this with a partner to see who can win the most points!
a. Make flashcards of the roots, suffixes and prefixes you want to memorize. You’ll also need a dictionary.
b. Mix up the flashcards into two groups, keeping suffixes and prefixes together in one group with the roots in another separate group.
c. Place the two groups in two separate piles face down in their separate groups. You’ll now have all the roots on the right side and prefixes/suffixes on the left side.
d. Pick a card from each group and turn both cards face up.
e. Form a word and write down what you think the definition should be according to the meaning of the root and the suffix or prefix you chose. Also write down whether you believe it is or isn’t a real word in the English language.
f. Once you’ve made your two guesses, look the word up in the dictionary to see if it really exists. If it does and the meaning you guessed is correct, then two points for you! If it’s not a real word, but you got the root and prefix/suffix meanings correct, then one point for you.
So there you have it, folks.
You’ve got a great guide to English word roots and how to use them!
Get out there and see how much English you understand now.
Download:
This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you
can take anywhere.
Click here to get a copy. (Download)
PRONUNCIATION OF ROOT WORD
GRAMMATICAL CATEGORY OF ROOT WORD
Root word is a noun.
A noun is a type of word the meaning of which determines reality. Nouns provide the names for all things: people, objects, sensations, feelings, etc.
WHAT DOES ROOT WORD MEAN IN ENGLISH?
Root (linguistics)
A root, or root word, is a word that does not have a prefix or a suffix. The root word is the primary lexical unit of a word, and of a word family, which carries the most significant aspects of semantic content and cannot be reduced into smaller constituents. Content words in nearly all languages contain, and may consist only of root morphemes. However, sometimes the term «root» is also used to describe the word minus its inflectional endings, but with its lexical endings in place. For example, chatters has the inflectional root or lemma chatter, but the lexical root chat. Inflectional roots are often called stems, and a root in the stricter sense may be thought of as a monomorphemic stem. The traditional definition allows roots to be either free morphemes or bound morphemes. Root morphemes are essential for affixation and compounds. However, in polysynthetic languages with very high levels of inflectional morphology, the term «root» is generally synonymous with «free morpheme». Many such languages have a very restricted number of morphemes that can stand alone as a word: Yup’ik, for instance, has no more than two thousand.
Definition of root word in the English dictionary
The definition of root word in the dictionary is the form of a word after all affixes are removed.
WORDS THAT RHYME WITH ROOT WORD
TRANSLATION OF ROOT WORD
Find out the translation of root word to 25 languages with our English multilingual translator.
The translations of root word from English to other languages presented in this section have been obtained through automatic statistical translation; where the essential translation unit is the word «root word» in English.
Translator English — Chinese
字根
1,325 millions of speakers
Translator English — Spanish
raíz de la palabra
570 millions of speakers
Translator English — Hindi
मूल शब्द
380 millions of speakers
Translator English — Arabic
جذر الكلمة
280 millions of speakers
Translator English — Russian
корень слова
278 millions of speakers
Translator English — Portuguese
palavra de raiz
270 millions of speakers
Translator English — Bengali
রুট শব্দ
260 millions of speakers
Translator English — French
racine du mot
220 millions of speakers
Translator English — Malay
Kata akar
190 millions of speakers
Translator English — German
Wortstamm
180 millions of speakers
Translator English — Japanese
語根
130 millions of speakers
Translator English — Korean
루트 단어
85 millions of speakers
Translator English — Javanese
Tembung ROOT
85 millions of speakers
Translator English — Vietnamese
từ gốc
80 millions of speakers
Translator English — Tamil
ரூட் சொல்
75 millions of speakers
Translator English — Marathi
मूळ शब्द
75 millions of speakers
Translator English — Turkish
kelime kökü
70 millions of speakers
Translator English — Italian
radice
65 millions of speakers
Translator English — Polish
słowo korzeń
50 millions of speakers
Translator English — Ukrainian
корінь слова
40 millions of speakers
Translator English — Romanian
cuvânt rădăcină
30 millions of speakers
Translator English — Greek
ρίζα της λέξης
15 millions of speakers
Translator English — Afrikaans
wortel woord
14 millions of speakers
Translator English — Swedish
rotordet
10 millions of speakers
Translator English — Norwegian
root ord
5 millions of speakers
TENDENCIES OF USE OF THE TERM «ROOT WORD»
The term «root word» is quite widely used and occupies the 46.318 position in our list of most widely used terms in the English dictionary.

FREQUENCY
Quite widely used
The map shown above gives the frequency of use of the term «root word» in the different countries.
Principal search tendencies and common uses of root word
List of principal searches undertaken by users to access our English online dictionary and most widely used expressions with the word «root word».
FREQUENCY OF USE OF THE TERM «ROOT WORD» OVER TIME
The graph expresses the annual evolution of the frequency of use of the word «root word» during the past 500 years. Its implementation is based on analysing how often the term «root word» appears in digitalised printed sources in English between the year 1500 and the present day.
10 ENGLISH BOOKS RELATING TO «ROOT WORD»
Discover the use of root word in the following bibliographical selection. Books relating to root word and brief extracts from same to provide context of its use in English literature.
1
Active Word Play: Games and Activities that Build Vocabulary
Root Word-Definition Cards Blank Card Template Cross-index of Games and
Activities Arts and 60 ACTIVE WORD PLAY. ROOT WORD ROOT WORD ROOT
WORD AGRI ANTHROPO AQUA DEFINITION FIELD DEFINITION DEFINITION …
2
CAHSEE-English Language Arts: California High School Exit Exam
Many words begin with or contain a part of a word that is the same as another
word and that is called a root word. With the knowledge of root words,
understanding the basic background and meaning of many other words is made
much easier.
3
Medical Terminology Component Glossary
A combining form is the combining vowel plus the root word. between a root word
and another root word or between a root word and a suffix. For example in these
cases: ELECTROCARDIOGRAM the combining forms in this word are …
4
Spelling: A Phonetic Approach
Students will also learn how the addirion ot the prefix changes the meaning of the
root word. Spelling Words: unusual, unhappy, unfair, refill, replace, redo,
disappear, disagree, incorrect, invisible Rule: Prefixes are small word parts thar
are …
5
How to Improve Your Vocabulary
Each word meaning begins with a base or root word. The base or root word
alone has meaning, but it is generally combined with at least one other word part.
A prefix is a word part added at the beginning of a root word, while a suf fix is a
word …
Sarah Kartchner Clark, 1999
6
Pass the Nelson Denny: NDRT Study Guide and Practice Test …
A The stem root word lumin- means light, for example illumination and luminous.
24. D The stem root word nutri- means nourish, for example nutrient. 25. C The
stem root word oct- means eight, for example octagon and octahedron. 26.
Complete Test Preparation Team
7
HOBET Test Strategy: Winning Multiple Choice Strategies for …
B The stem root word lax- means not tense, for example laxative and relaxation. 2
1. C The stem root word mania- means relating to mental illness, for example
kleptomania and maniac. 22. C The stem root word maj- means greater, …
Complete Test Preparation Team
8
Elsevier’s Veterinary Assisting Textbook
When joined to the root word natal, meaning “birth,” the result becomes the
medical word: PREnatal. Prenatal means “before birth.” The prefix pre used
alone means nothing to the reader. Root Word A root word is the subject part of
the word …
9
Word by Word: Comprehensive Word Study Program
‘portare’ is a root word meaning ‘to carry’ 3.3.3.3.3. List more words that contain
the root word ‘cycl’. List more words that contain the root word ‘cycl’. List more
words that contain the root word ‘cycl’. List more words that contain the root word
…
Ric Publications Staff, 1997
10
Indo-European Language and Culture: An Introduction
Besides the attachment of suffixes (and sometimes, but more rarely, prefixes and
infixes – affixes added into the middle of a root), word— formation in PIE often
required modification of the shape of the root itself, in ways to be discussed
further …
Benjamin W. Fortson, IV, 2011
2 NEWS ITEMS WHICH INCLUDE THE TERM «ROOT WORD»
Find out what the national and international press are talking about and how the term root word is used in the context of the following news items.
Bright Lights, Big Dictionaries: What It Was Like to Compete in Scripps
You have to rely on skills beyond rote memorization: root words, that kind of thing. You’re allowed to ask three questions: language of origin, part of speech, and … «Jezebel, May 15»
What Is A Parable? A Bible Definition
The word parable is from the root word “paraballo” or in the Greek “parabole.” This compound word comes from “para” which means “to come along side or … «Patheos, May 14»
Root Words! The English language has its roots in languages like Greek and Latin. An understanding of the common root words will help us make educated guesses about the meaning of new words and substantially strengthen our vocabulary.
Given below is a list of commonly used root words, their meanings and some examples of words formed using these root words.
Geek Root Words
List of Greek root words with meanings and examples:
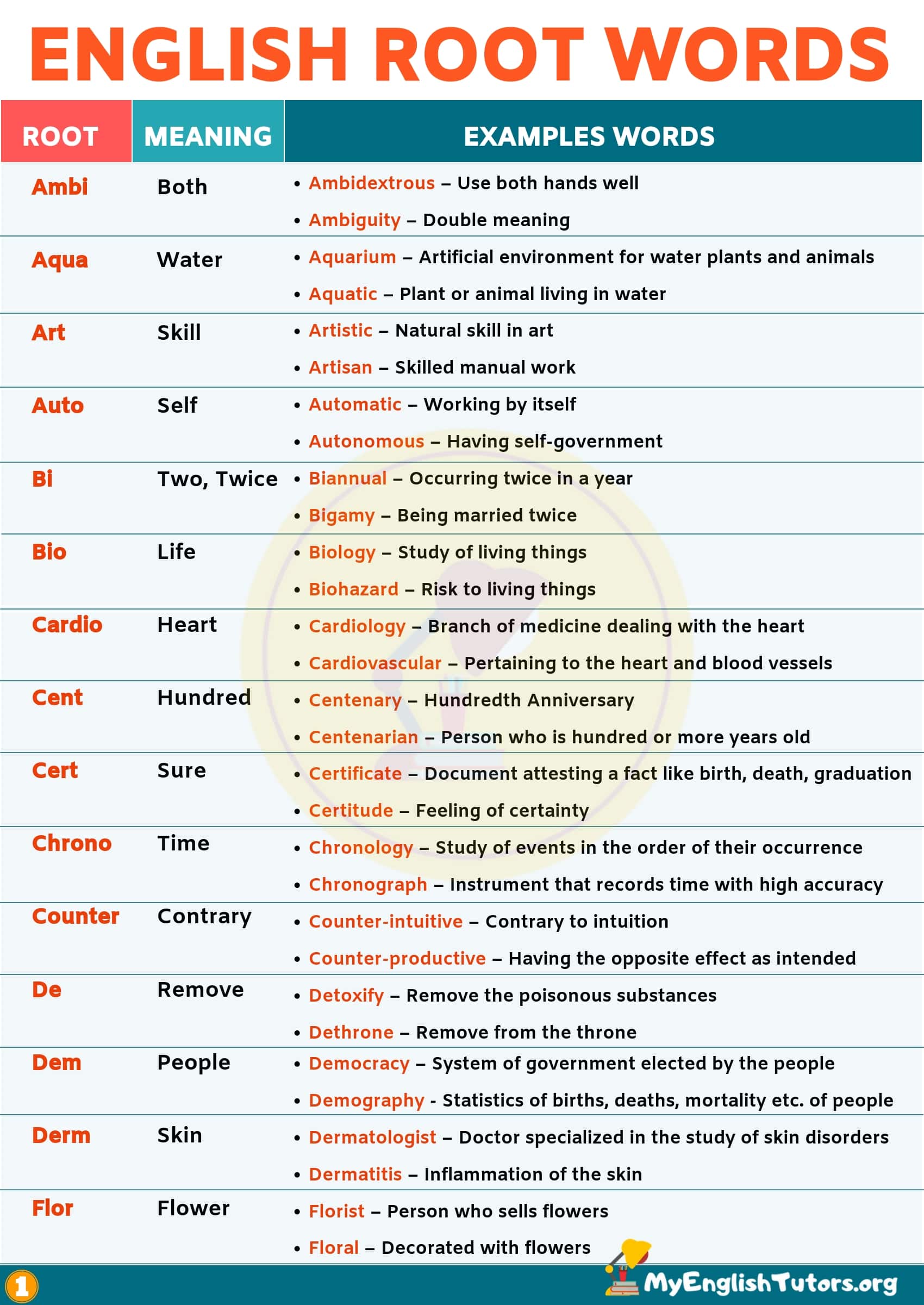
- Ambi
Meaning: Both
Examples:
- Ambidextrous – Use both hands well
- Ambiguity – Double meaning, can be interpreted in more than one way
- Aqua
Meaning: Water
Examples:
- Aquarium – Artificial environment for water plants and animals
- Aquatic – Plant or animal living in water
- Art
Meaning: Skill
Examples:
- Artistic – Natural skill in art
- Artisan – Skilled manual work
- Auto
Meaning: Self
Examples:
- Automatic – Working by itself
- Autonomous – Having self-government
- Bi
Meaning: Two, Twice
Examples:
- Biannual – Occurring twice in a year
- Bigamy – Being married twice
- Bio
Meaning: Life
Examples:
- Biology – Study of living things
- Biohazard – Risk to living things
- Cardio
Meaning: Heart
Examples:
- Cardiology – Branch of medicine dealing with the heart
- Cardiovascular – Pertaining to the heart and blood vessels
- Cent
Meaning: Hundred
Examples:
- Centenary – Hundredth Anniversary
- Centenarian – Person who is hundred or more years old
- Cert
Meaning: Sure
Examples:
- Certificate – Document attesting a fact like birth, death, graduation, marriage etc
- Certitude – Feeling of certainty
- Chrono
Meaning: Time
Examples:
- Chronology – Study of events in the order of their occurrence
- Chronograph – Instrument that records time with high accuracy
- Counter
Meaning: Contrary
Examples:
- Counter-intuitive – Contrary to intuition
- Counter-productive – Having the opposite effect as intended
- De
Meaning: Remove
Examples:
- Detoxify – Remove the poisonous substances
- Dethrone – Remove from the throne
- Dem
Meaning: People
Examples:
- Democracy – System of government elected by the people
- Demography – Statistics of births, deaths, mortality etc. of people
- Derm
Meaning: Skin
Examples:
- Dermatologist – Doctor specialized in the study of skin disorders
- Dermatitis – Inflammation of the skin
- Flor
Meaning: Flower
Examples:
- Florist – Person who sells flowers
- Floral – Decorated with flowers
- Gastro
Meaning: Stomach
Examples:
- Gastritis – Inflammation of the stomach lining
- Gastroenterologist – Doctor specialized in the study of stomach and intestinal disorders
- Grat
Meaning: Pleasing
Examples:
- Gratify – Delight or please someone
- Gratuity – Tip, token of appreciation
- Hepa
Meaning: Liver
Examples:
- Hepatitis – Inflammation of the liver
- Hepatic – Relating to the liver
- Hept
Meaning: Seven
Examples:
- Heptagon – Figure with seven sides
- Heptathlon – Athletic event having seven events
- Hex
Meaning: Six
Examples:
- Hexagon – Figure with six sides
- Hexavalent – Having a valency of six
- Inter
Meaning: Between
Examples:
- Interconnect – Connect with each other
- Interdepend – Depend on each other
- Iso
Meaning: Equal
Examples:
- Isosceles – Triangle having two equal sides
- Isobar – Line on map connecting points of equal barometer pressures
- Jud
Meaning: Law
Examples:
- Judiciary – Collective of judges
- Judgement – Decision of a court
- Kilo
Meaning: Thousand
Examples:
- Kilogram – Thousand grams
- Kilolitre – Thousand litres
- Lacto
Meaning: Milk
Examples:
- Lactic – Obtained from mil
- Lactose – Sugar occurring in milk
- Mal
Meaning: Bad
Examples:
- Malevolent – Wishing bad things on others
- Malice – Intention to do evil
- Mort
Meaning: Death
Examples:
- Mortuary – Place where dead bodies are kept until they are cremated or buried
- Mortician – Undertaker
- Narr
Meaning: Tell
Examples:
- Narrate – To tell a story
- Narrator – Person who tells a story.
- Nov
Meaning: New
Examples:
- Novelty – Newness or originality
- Novice – Beginner
- Oct
Meaning: Eight
Examples:
- Octagon – Figure with eight sides
- Octave – Stanza of eight lines
- Ocu
Meaning: Eye
Examples:
- Ocular – Connected with the eyes
- Oculist – Specialist in the medical treatment of eye disorders
- Omni
Meaning: All
Examples:
- Omnipresent – Present everywhere at the same time
- Omnivorous – Eating all kinds of foods
- Ortho
Meaning: Straight
Examples:
- Orthodontics – Dealing with straightening of teeth
- Orthopaedics – Dealing with the straightening of bones
- Pan
Meaning: All
Examples:
- Panorama – An all-around view
- Pandemic – Prevalent all over a country or world
- Ped
Meaning: Foot
Examples:
- Pedicure – Treatment of the feet
- Pedal – Foot operated lever
- Poly
Meaning: Many
Examples:
- Polygon – Figure with many sides
- Polygamy – Having more than one husband or wife at the same time
- Psych
Meaning: Mind
Examples:
- Psychiatry – Study of mental diseases
- Psych – Prepare oneself mentally for a task
- Quad
Meaning: Four
Examples:
- Quadruple – Increase four times
- Quadrangle – Figure having four sides
- Quin
Meaning: Five
Examples:
- Quintuple – Increase five times
- Quintuplet – Five children born at the same time
- Semi
Meaning: Half
Examples:
- Semi-circle – Half of a circle
- Semiaquatic – Animal living partly on land and partly in water
- Sept
Meaning: Seven
Examples:
- Septuplet – Seven children born at the same time
- Septuagenarian – People aged before 70 and 79
- Trans
Meaning: Across
Examples:
- Transpacific – Across the Pacific Ocean
- Transnational – Across national boundaries
- Tri
Meaning: Three
Examples:
- Triangle – Figure with three sides
- Triathlon – Athletic event having three events
- Uni
Meaning: One
Examples:
- Unitarian – People who believes God is one person
- Unique – One of a kind
- Vince
Meaning: Conquer
Examples:
- Invincible – One who cannot be conquered
- Convince – Persuade a person
Learn more with a big list of suffixes and prefixes in English with examples.
Root Words List | Infographic
Root Words List | Infographic 1
Root Words List | Infographic 2

Root Words List | Infographic 3

4.8
12
votes
Article Rating
-Jan-21-2021-05-13-39-91-PM.png?width=1080&name=Title_%20How%20to%20Study%20Efficiently%20for%20Hours%20On%20End%20(With%20the%20Help%20of%20a%20Tomato)-Jan-21-2021-05-13-39-91-PM.png)
We often call these fragments roots, because other words grow from them like plants. Greek and Latin roots are most useful to learn; since I study the latter language, I’ll be focusing on Latin roots in this post.
The root of a word won’t give you the word’s exact definition, but rather clues to its meaning. These clues can help you retain exact definitions by triggering your memory when you see the part of the word that comes from the root.
Here’s a classic example: the root mal- comes from the Latin word for bad. If you speak Romance languages, like Spanish or French, you’ll probably recognize this root. You’ll also have an advantage in learning English vocabulary because Romance languages developed from Latin. (Can you figure out the root of Romance by thinking about the people who first spoke Latin?)
You can see the root mal- in English words like
- malice (desire to cause pain)
- malign (as an adjective: evil; as a verb: to speak badly of someone)
- malefactor (evildoer)
- malevolent (having ill-will or producing evil)
You can also see the root as a prefix in the word maladjusted (poorly adjusted). You can even see it in made-up names like Maleficent from Sleeping Beauty.
Knowing the root word mal- helps your learning in at least four ways.
- If you study a particular word like malice, the root can trigger your memory when you see the word again. You’ll think: the definition has something to do with badness.
- If you encounter an unfamiliar word that contains mal, you can make an educated guess as to its definition.
- You can remember a cluster of related words like the ones above. This accelerates your vocabulary acquisition.
- You can start to grasp how English words are put together, which is cool!
A lot of English teachers will do what I just did: they’ll introduce a root—or several—with relevant English words. This method is useful, but it restricts your vocabulary to what fits in a list of previously assembled roots. I’ll show you how you can use roots for the vocabulary you need to learn.
Instead of tailoring your vocabulary to a list of roots, you can tailor your roots to a list of vocabulary. The secret to this method is etymology, the study of where words come from (and how their meanings have changed). We say that we’ve found a word’s etymology when we can trace its development backwards through time, to a probable origin. When English words have Latin roots, you can usually trace them back through French, and then to Latin.
A word’s origin is usually listed as a full word in another language, not necessarily the most basic root. We can usually figure out the root by looking at the origin word—but hey, I’m getting ahead of myself. Let’s start at the beginning.
Step One: Choose and define your word.
Choose a word you want to study. If you are looking for a word’s root, you can start by finding its etymology. Look up the word in an etymology dictionary: I recommend the Online Etymology Dictionary.
If you make a successful search, you’ll get the word’s dictionary entry. This will usually start with the word’s current (and sometimes historical) definitions. Then you’ll see a word like “from,” which signals the journey back to the word’s origins.
Let’s say we want to define and remember the adjective primeval. When we look it up in our etymology dictionary, we first get the definition: “of or belonging to the first age.” So, something primeval is ancient, from the world’s earliest times.
Let’s note down what we’ve found in a table.
|
Word |
Definition |
|
Primeval |
From the world’s earliest times |
Step Two: Find an origin for the word.
In the entry, we keep reading through some stuff about the 1650s and then we see the word “from»! As you read the part of the entry after “from,” imagine that you’re going further back in time, possibly through a few other languages. Here, we’re focusing on words with Latin roots. You should stop at the last Latin word because that’s usually the origin closest to a root we’re looking for. As I said before, the origin is usually a full word, not a basic root.
Before you move on, check to see how the meaning of the origin word relates to the word you’re studying. Remember, this relationship is the motivation for learning words this way!
Here’s where we are so far:
|
Word |
Definition |
|
Primeval |
From the world’s earliest ages |
We’ve just gotten to “from” in the word’s entry, and we now see “from primus “first” + aevum “an age.”” So, we have two origin words in Latin. I’m going to underline and focus on primus because I can already think of related words (like primary). If you’re doing this process for another word and also find two origins, you can try doing the next steps with both origins and see what happens.
|
Word |
Definition |
Origin |
|
Primeval |
From the world’s earliest ages |
Primus: first (Aevum: an age) |
Step Three: Find a root.
To find the root, it’s useful to have a list of roots, or a root guide. You can try putting “list of Greek and Latin roots” into a search engine to find your own, but here is one I like to use.
Since the root is usually at the beginning of the origin, you can look for a root to match your origin by scrolling alphabetically, or you can use ctrl-F and start slowly typing the origin word. It might take you a few tries to find a root matching your origin word, and you might even need to type “root for primus” into your search engine.
Here’s where we are so far:
|
Word |
Definition |
Origin |
|
Primeval |
From the world’s earliest ages |
Primus: first (Aevum: an age) |
If we go to the row of roots that start with “P” in the root word guide, we’ll find an entry for “prim-” meaning first. So now we understand that the “prim” in primus signifies meaning, and the “us” signifies something else (a masculine nominative ending, for those of you studying Latin).
|
Word |
Definition |
Origin |
Root |
|
Primeval |
From the world’s earliest ages |
Primus: first (Aevum: an age) |
Prim- : first |
Step Four: Find related words.
Now for the fun part! Once you’ve found a root, see if there are other English words that come from the root. They might be words you already know or words you want to define to supplement your vocabulary.
By looking at the entry for “prim-” we can see the additional words primary and primitive. I can also think of primordial.
|
Word |
Definition |
Origin |
Root |
Related Words |
|
Primeval |
From the world’s earliest ages |
Primus: first (Aevum: an age) |
Prim- : first |
Primary (of chief importance; earliest in time or order) Primitive (relating to an early stage in development) |
Using this method, you can define new words for yourself, find their roots, and connect them to other, related words. I recommend keeping a section in the back of your notebook for a table like the one I’ve modeled above.
I wrote out the method in a lot of detail, so it seems like a long process. Once you start practicing, though, the process shouldn’t take very long. You can do it as you learn new vocabulary and reap the benefits of knowing roots!
Practice:
I’ve tested each word on the following list using the method above and the resources (etymology dictionary and root guide) I’ve recommended. You should be able to find definitions, origin words, roots, and related words for the following:
- Circumscribe
- Commemorate
- Corpulent
- Credulous
- Culpable
- Derisive
- Ignominy
- Insular
- Marinate
- Tangible
- Tenable
- Terrestrial
Many words in the English language are formed by taking base words or root words and adding combinations of prefixes and suffixes to them.
A root word is the primary form of a word. While root words may contain the core meaning of the word, they cannot stand alone. For example, “bene” is the root in the word “beneficial.”
A base word is slightly different from a root because a base is the basic form of a word that can stand on its own. For example, “commit” is the base in the word “commitment.” To differentiate the two, just remember that a base can have affixes attached to it, but it does not have to; a root must have an affix (prefix or suffix), or another root, attached to it in order to make it a whole word.
A prefix is a word part that is placed at the beginning of a word to change or enhance its meaning. For example, “dis—” is the prefix of the word “disagree.”
A suffix is a word part that is placed at the end of a word to change or enhance its meaning. For example, “—ful” is the suffix of the word “thankful.”
Most English words are actually derivatives of ancient Greek and Latin words. Knowing Greek and Latin roots is an essential reading comprehension strategy for students because they could determine the meaning of an unknown word if they were familiar with any of the prefixes, suffixes, or root words attached to it. When context clues fail, breaking down words into their smallest parts can ensure your students will be successful.
For example, students might not know what the word “contradict” means, but if they know that “contra” means against and “dict” means speak, they can determine that contradict means: to assert the opposite against what someone has said. Another example is the word “incredulous.” If students know that “in” means not, “cred” means believe, and “ous” means having, then they could conclude incredulous means: not having a readiness to believe things easily.
Greek and Latin word parts are a tool you want your students to have in their academic tool belt because having a strong vocabulary helps students tremendously with reading, writing, listening, and speaking skills. Below you can find a FREE, downloadable copy of the 300 most commonly used Greek and Latin root words, suffixes, and prefixes. You can choose particular word parts from the list below to use in your classroom or provide students with this comprehensive list to keep for reference.














