Word-building in
English, major means of WB in English:
a) affixation;
b) conversion;
c) composition; types
of compounds.
WB
is the process of creating new words in a language with the help of
its inner sources.
Two
types of WB proper :
-
Word derivation when 1 stem undergoes different changes;
-
Word composition when 2 or more stems are put together.
The most important means of word derivation are:
a) affixation;
b) conversion;
c) composition; types of compounds.
Affixation,
conversion, composition are the most productive or major means of WB
in modern English.
Shortening
occupies the intermediate position between major & “minor” or
less productive & unproductive means of WB.
Minor
means of word-building are:
-
Back formation = reversion;
-
Blending = telescoping;
-
Reduplication = doubling the stem;
-
Sound immitation;
-
Sound interchange;
-
Shift of stress, etc.
Affixation is the most productive means of word-building in English.
Affixation is the formation of new words by adding a derivational
affix to a derivational base.
Affixation is subdivided into:
-
Suffixation
-
Prefixation.
The essential differences between suffixes &
preffixes is that preffixes as a rule only modify the lexical meaning
of a word without changing the part of speech to which the word
belongs
e.g. to tie – to untie
However, some preffixes form new words in a
different part of speech:
e.g. friend – N., to be friend-V., adj.- little., V.-
to be little.
Suffixes do not only modify the lexical meaning of a word but also
form a word belonging to a different part of speech.
Suffixes are usually classified according to the part of speech they
form:
-
Noun-forming suffixes ( to read – reader, dark – darkness);
-
Adjective-forming (power-powerful);
-
Verb-forming ( to organize, to purify);
-
Adverbal-forming (quick-quickly).
Prefixes are usually classified according to their meaning:
-
Negative prefixes (-un; -non; -in; -dis…);
-
Reversative = privative (-un; -de; -dis..);
-
Pejorative (уничижительные)
(mis-; mal- (maltreat-дурно
обращаться); pseudo-); -
Preffixes of time & order (fore-(foretell); pre-(prewar); post-;
ex-(ex-wife); -
Prefixes of repetition (re- rewrite);
-
Locative prefixes (super-; sub-subway; into-; trans –atlantic))
The 2 main criteria, according to which all the affixes are
subdivided are:
1)
origin;
2) productivity.
As to their origin (etymology) affixes are:
-
Native;
-
Borrowed.
Borrowed affixes may be classified according to the source of
borrowing (Greek, Latin, etc.) According to their productivity, i.e.
the ability to build new words at the present time, English affixes
are:
-
Productive or living affixes, used to build new words now;
-
Non-productive = unproductive affixes, not used in the word-building
now, or used very rarely.
Productivity shouldn’t be confused with frequency. What is frequent
may turn out to be non-productive (-some (adj.)-handsome is very
frequent, but not productive).
Some native prefixes still productive in English
are: — fore; -out (grow); over (estimate); -un (able); -up
(bringing); -under, -mis, etc.
Productive foreign prefixes are: -dis (like); -en (close); -re(call);
-super (natural); -pre (war); -non (drinking); -anti (noise).
Native noun-forming suffixes in modern English are: -er (writer);
-ster (youngster), -ness(brightness), etc.
Adjective-forming native suffixes (productive in English) are: -y
(rocky); -ish (Turkish), ful; -ed (cultured); -less (useless), etc.
Foreign productive noun-forming suffixes are: -ee
(employee); -tion (revolution); -ism(Gr., realism); -ist, etc.
Borrowed productive verb-forming suffixes of
Romanic origin are: -ise,ize (organize), -fy, ify (signify).
Prefixation is more typical of adjectives & verbs. Suffixation is
approximately evenly used in all parts of speech.
There are 2 types of semantic relations between affixes:
-
Homonymy;
-
Synonymy.
Homonymous prefixes are: -in: inactive, to inform.
Homonymous suffixes are: -ful1
(adjective-forming), -ful2
(noun-forming-spoonful), -ly1
(adj.-forming-friendly), -ly2
(adverb-forming-quickly).
Some affixes make a chain of synonyms: the native
suffix –er denoting an agent, is synonymous to suffix –ist
(Gr.)-socialist & to suffix –eer – also denoting an agent
(engineer) but often having a derrogatory force (`sonneteer-
стихоплёт, profiteer –
спекулянт, etc.)
Some affixes are polysemantic: the noun-forming suffix –er has
several meanings:
-
An agent or doer of the action –giver, etc.
-
An instrument –boiler, trailer
-
A profession, occupation –driver;
-
An inhabitant of some place –londoner.
b)
Conversion
is one of the most productive word-building means in English. Words,
formed by means of conversion have identical phonetic & graphic
initial forms but belong to different parts of speech (noun –
doctor; verb –to doctor). Conversion
is a process of coining (создание)
a new word in a different part of speech & with different
distribution characteristic but without adding any derivative
elements, so that the basic form of the original & the basic form
of the derived words are homonymous (identical). (Arnold)
The
main reason for the widespread conversion in English is its
analytical character, absence of scarcity of inflections. Conversion
is treated differently in linguistic literature. Some linguists
define conversion as a non-affixal way of word-building (Marchened
defines conversion as the formation of new words with the help of a
zero morpheme, hence the term zero derivation)
Some
American & English linguists define conversioon as a functional
shift from one part of speech to another, viewing conversion as a
purely syntactical process. Accoding to this point of view, a word
may function as 2 or more different parts of speech at the same time,
which is impossible. Professor Smernitsky treats conversion as a
morphological way of word-building. According to him conversion is
the formation of a new word through the changes in its paradigm.
Some
other linguists regard conversion as a morphological syntactical way
of word-building, as it involves both a change of the paradigm &
the alterration of the syntactic function of the word.
But
we shouldn’t overlook the semantic change, in the process of
conversion. All the morphological & syntactical changes, only
accompany the semantic process in conversion. Thus, conversion may be
treated as a semantico-morphologico-syntactical process.
As a word within the conversion pair is
semantically derived from the other there are certain semantic
relationswithin a conversion pair.
De-nominal words (от
глагола) make up the largest group &
display the following semantic relations with the nouns:
-
action characteristic of the thing: -a butcher; to butcher
-
instrumental use of the thing: -a whip; to wheep
-
acquisition of a thing: a coat; to coat
-
deprivation of a thing: skin – to skin.
Deverbal substantives (отглаг.сущ)they
may denote:
-
instance of the action: to move – a move;
-
agent of the action: to switch – a switch;
-
place of the action: to walk- a walk;
-
object or result of the action: to find – a find.
The English vocabulary abounds mostly in verbs,
converted from nouns( or denominal verbs) & nouns, converted from
verbs (deverbal substances): pin –to pin; honeymoon-to honeymoon.
There are also some other cases of conversion: batter-to batter, up –
to up, etc.
c)
Composition is one of the most productive word-building
means in modern English. Composition is the production of a new word
by means of uniting 2 or more stems which occur in the language as
free forms (bluebells, ice-cream).
According
to the type of composition & the linking element, there are
following types of compounds:
-
neutral compounds; (1)
-
morphological compounds; (2)
-
syntactical compounds. (3)
(1)
Compounds built by means of stem junction (juxt – opposition)
without any morpheme as a link, are called neutral compounds. The
subtypes of neutral compounds according to the structure of immediate
constituents:
a)
simple neutral compounds (neutral compounds proper) consisting of 2
elements (2 simple stems): sky –blue;film-star.
b) derived compounds (derivational compounds) –
include at least one derived stem: looking-glass, music-lover,
film-goer, mill-owner derived compounds or derivational should be
distinguished from compound derivatives, formed by means of a suffix,
which reffers to the combination of stems as a whole. Compound
derivatives (сложно-произв.слова)
are the result of 2 acts of word-building composition &
derivation. ( golden-haired, broad-shouldered, honey-mooner,
first-nighter).
c)
contracted compounds which have a shortened stem or a simple stem in
their structure, as “V-day” (victory), G-man (goverment), H-bag
(hand-bag).
d)
compounds, in which at least 1 stem is compound (waterpaper(comp)
–basket(simple))
(2)
Compounds with a specific morpheme as a link (comp-s with a linking
element = morphological compounds). E.g. Anglo-Saxon, Franko-German,
speedometer, statesman, tradespeople, handicraft, handiwork.
(3)
Compounds formed from segments of speech by way of isolating speech
sintagmas are sometimes called syntactic compounds, or compounds with
the linking element(s) represented as a rule by the stems of
form-words (brother-in-law, forget-me-not, good-in-nothing).
II.
Compounds may be classified according to a part of speech they belong
& within each part of speech according to their structural
pattern (structural types of compound-nouns):
-
compounds nouns formed of an adjectival stem + a noun stem A+N.
e.g.blackberry, gold fish
-
compound nouns formed of a noun-stem +a noun stem N+N
e.g. waterfall, backbone, homestead, calhurd
III.
Semantically compounds may be: idiomatic (non-motivated),
non-idiomatic
(motivated).
The compounds whose meanings can be derived from the meanings of
their component stems, are called non-idiomatic, e.g. classroom,
handcuff, handbag, smoking-car.
The
compounds whose meanings cannot be derived from the meanings of their
component stems are called idiomatic, e.g. lady-bird, man of war,
mother-of-pearls.
The
critiria applied for distinguishing compounds from word combinations
are:
-
graphic;
-
phonetic;
-
grammatical (morphological, syntactic);
-
semantic.
The graphic criteria can be relied on when
compounds are spelled either sollidly, or with or with a hyphen, but
it fails when the compound is spelled as 2 separate words,
e.g.
blood(-)vessel
(крово-сосудистый)
The phonetic criterium is applied to comp-s which
have either a high stress on the first component as in “hothead”
(буйная голова),
or a double stress “ `washing-ma`chine”, but it’s useless when
a compound has a level stress on both components, as in “
`arm-chair, `ice-cream” etc.
If we apply morphological & syntactical
criterium, we’ll see that compounds consisting of stems, possess
their structural integrity. The components of a compound are
grammatically invariable. No word can be inserted between the
components, while the components of a word-group, being independant
words, have the opposite features (tall-boy(высокий
комод), tall boy (taller&
cleverer,tallest)).
One of the most reliable criteria is the semantic
one. Compounds generally possess the higher degree of semantic
cohesion (слияние) of its elements
than word-groups. Compounds usually convey (передавать)
1 concep. (compare: a tall boy – 2 concepts, & a tallboy – 1
concept). In most cases only a combination of different criteria can
serve to distinguish a compound word from a word combination.
Lecture 3. Word-building: affixation, conversion, composition, abbreviation. THE WORD-BUILDING SYSTEM OF ENGLISH 1. Word-derivation 2. Affixation 3. Conversion 4. Word-composition 5. Shortening 6. Blending 7. Acronymy 8. Sound interchange 9. Sound imitation 10. Distinctive stress 11. Back-formation Word-formation is a branch of Lexicology which studies the process of building new words, derivative structures and patterns of existing words. Two principle types of wordformation are distinguished: word-derivation and word-composition. It is evident that wordformation proper can deal only with words which can be analyzed both structurally and semantically. Simple words are closely connected with word-formation because they serve as the foundation of derived and compound words. Therefore, words like writer, displease, sugar free, etc. make the subject matter of study in word-formation, but words like to write, to please, atom, free are irrelevant to it. WORD-FORMATION WORD-DERIVATION AFFIXATION WORD-COMPOSITION CONVERSION 1. Word-derivation. Speaking about word-derivation we deal with the derivational structure of words which basic elementary units are derivational bases, derivational affixes and derivational patterns. A derivational base is the part of the word which establishes connection with the lexical unit that motivates the derivative and determines its individual lexical meaning describing the difference between words in one and the same derivative set. For example, the individual lexical meaning of the words singer, writer, teacher which denote active doers of the action is signaled by the lexical meaning of the derivational bases: sing-, write-, teach-. Structurally derivational bases fall into 3 classes: 1. Bases that coincide with morphological stems of different degrees оf complexity, i.e., with words functioning independently in modern English e.g., dutiful, day-dreamer. Bases are functionally and semantically distinct from morphological stems. Functionally the morphological stem is a part of the word which is the starting point for its forms: heart – hearts; it is the part which presents the entire grammatical paradigm. The stem remains unchanged throughout all word-forms; it keeps them together preserving the identity of the word. A derivational base is the starting point for different words (heart – heartless – hearty) and its derivational potential outlines the type and scope of existing words and new creations. Semantically the stem stands for the whole semantic structure of the word; it represents all its lexical meanings. A base represents, as a rule, only one meaning of the source word. 2. Bases that coincide with word-forms, e.g., unsmiling, unknown. The base is usually represented by verbal forms: the present and the past participles. 3. Bases that coincide with word-groups of different degrees of stability, e.g., blue-eyed, empty-handed. Bases of this class allow a rather limited range of collocability, they are most active with derivational affixes in the class of adjectives and nouns (long-fingered, blue-eyed). Derivational affixes are Immediate Constituents of derived words in all parts of speech. Affixation is generally defined as the formation of words by adding derivational affixes to different types of bases. Affixation is subdivided into suffixation and prefixation. In Modern English suffixation is mostly characteristic of nouns and adjectives coining, while prefixation is mostly typical of verb formation. A derivational pattern is a regular meaningful arrangement, a structure that imposes rigid rules on the order and the nature of the derivational base and affixes that may be brought together to make up a word. Derivational patterns are studied with the help of distributional analysis at different levels. Patterns are usually represented in a generalized way in terms of conventional symbols: small letters v, n, a, d which stand for the bases coinciding with the stems of the respective parts of speech: verbs, etc. Derivational patterns may represent derivative structure at different levels of generalization: - at the level of structural types. The patterns of this type are known as structural formulas, all words may be classified into 4 classes: suffixal derivatives (friendship) n + -sf → N, prefixal derivatives (rewrite), conversions (a cut, to parrot) v → N, compound words (musiclover). - at the level of structural patterns. Structural patterns specify the base classes and individual affixes thus indicating the lexical-grammatical and lexical classes of derivatives within certain structural classes of words. The suffixes refer derivatives to specific parts of speech and lexical subsets. V + -er = N (a semantic set of active agents, denoting both animate and inanimate objects - reader, singer); n + -er = N (agents denoting residents or occupations Londoner, gardener). We distinguish a structural semantic derivationa1 pattern. - at the level of structural-semantic patterns. Derivational patterns may specify semantic features of bases and individual meaning of affixes: N + -y = A (nominal bases denoting living beings are collocated with the suffix meaning "resemblance" - birdy, catty; but nominal bases denoting material, parts of the body attract another meaning "considerable amount" - grassy, leggy). The basic ways of forming new words in word-derivation are affixation and conversion. Affixation is the formation of a new word with the help of affixes (heartless, overdo). Conversion is the formation of a new word by bringing a stem of this word into a different paradigm (a fall from to fall). 2. Affixation Affixation is generally defined as the formation of words by adding derivational affixes to different types of bases. Affixation includes suffixation and prefixation. Distinction between suffixal and prefixal derivates is made according to the last stage of derivation, for example, from the point of view of derivational analysis the word unreasonable – un + (reason- + -able) is qualified as a prefixal derivate, while the word discouragement – (dis- + -courage) + -ment is defined as a suffixal derivative. Suffixation is the formation of words with the help of suffixes. Suffixes usually modify the lexical meaning of the base and transfer words to a different part of speech. Suffixes can be classified into different types in accordance with different principles. According to the lexico-grammatical character suffixes may be: deverbal suffixes, e.d., those added to the verbal base (agreement); denominal (endless); deadjectival (widen, brightness). According to the part of speech formed suffixes fall into several groups: noun-forming suffixes (assistance), adjective-forming suffixes (unbearable), numeral-forming suffixes (fourteen), verb-forming suffixes (facilitate), adverb-forming suffixes (quickly, likewise). Semantically suffixes may be monosemantic, e.g. the suffix –ess has only one meaning “female” – goddess, heiress; polysemantic, e.g. the suffix –hood has two meanings “condition or quality” falsehood and “collection or group” brotherhood. According to their generalizing denotational meaning suffixes may fall into several groups: the agent of the action (baker, assistant); collectivity (peasantry); appurtenance (Victorian, Chinese); diminutiveness (booklet). Prefixation is the formation of words with the help of prefixes. Two types of prefixes can be distinguished: 1) those not correlated with any independent word (un-, post-, dis-); 2) those correlated with functional words (prepositions or preposition-like adverbs: out-, up-, under-). Diachronically distinction is made between prefixes of native and foreign origin. Prefixes can be classified according to different principles. According to the lexico-grammatical character of the base prefixes are usually added to, they may be: deverbal prefixes, e.d., those added to the verbal base (overdo); denominal (unbutton); deadjectival (biannual). According to the part of speech formed prefixes fall into several groups: noun-forming prefixes (ex-husband), adjective-forming prefixes (unfair), verb-forming prefixes (dethrone), adverb-forming prefixes (uphill). Semantically prefixes may be monosemantic, e.g. the prefix –ex has only one meaning “former” – ex-boxer; polysemantic, e.g. the prefix –dis has four meanings “not” disadvantage and “removal of” to disbrunch. According to their generalizing denotational meaning prefixes may fall into several groups: negative prefixes – un, non, dis, a, in (ungrateful, nonpolitical, disloyal, amoral, incorrect); reversative prefixes - un, de, dis (untie, decentralize, disconnect); pejorative prefixes – mis, mal, pseudo (mispronounce, maltreat, pseudo-scientific); prefix of repetition (redo), locative prefixes – super, sub, inter, trans (superstructure, subway, intercontinental, transatlantic). 3. Conversion Conversion is a process which allows us to create additional lexical terms out of those that already exist, e.g., to saw, to spy, to snoop, to flirt. This process is not limited to one syllable words, e.g., to bottle, to butter, nor is the process limited to the creation of verbs from nouns, e.g., to up the prices. Converted words are extremely colloquial: "I'll microwave the chicken", "Let's flee our dog", "We will of course quiche and perrier you". Conversion came into being in the early Middle English period as a result of the leveling and further loss of endings. In Modern English conversion is a highly-productive type of word-building. Conversion is a specifically English type of word formation which is determined by its analytical character, by its scarcity of inflections and abundance of mono-and-de-syllabic words in different parts of speech. Conversion is coining new words in a different part of speech and with a different distribution but without adding any derivative elements, so that the original and the converted words are homonyms. Structural Characteristics of Conversion: Mostly monosyllabic words are converted, e.g., to horn, to box, to eye. In Modern English there is a marked tendency to convert polysyllabic words of a complex morphological structure, e.g., to e-mail, to X-ray. Most converted words are verbs which may be formed from different parts of speech from nouns, adjectives, adverbs, interjections. Nouns from verbs - a try, a go, a find, a loss From adjectives - a daily, a periodical From adverbs - up and down From conjunctions - but me no buts From interjection - to encore Semantic Associations / Relations of Conversion: The noun is the name of a tool or implement, the verb denotes an action performed by the tool, e.g., to nail, to pin, to comb, to brush, to pencil; The noun is the name of an animal, the verb denotes an action or aspect of behavior considered typical of this animal, e.g., to monkey, to rat, to dog, to fox; When the noun is the name of a part of a human body, the verb denotes an action performed by it, e.g., to hand, to nose, to eye; When the noun is the name of a profession or occupation, the verb denotes the activity typical of it, e.g., to cook, to maid, to nurse; When the noun is the name of a place, the verb will denote the process of occupying the place or by putting something into it, e.g., to room, to house, to cage; When the word is the name of a container, the verb will denote the act of putting something within the container, e.g., to can, to pocket, to bottle; When the word is the name of a meal, the verb means the process of taking it, e.g., to lunch, to supper, to dine, to wine; If an adjective is converted into a verb, the verb may have a generalized meaning "to be in a state", e.g., to yellow; When nouns are converted from verbs, they denote an act or a process, or the result, e.g., a try, a go, a find, a catch. 4. Word-composition Compound words are words consisting of at least two stems which occur in the language as free forms. Most compounds in English have the primary stress on the first syllable. For example, income tax has the primary stress on the in of income, not on the tax. Compounds have a rather simple, regular set of properties. First, they are binary in structure. They always consist of two or more constituent lexemes. A compound which has three or more constituents must have them in pairs, e.g., washingmachine manufacturer consists of washingmachine and manufacturer, while washingmachine in turn consists of washing and machine. Compound words also usually have a head constituent. By a head constituent we mean one which determines the syntactic properties of the whole lexeme, e.g., the compound lexeme longboat consists of an adjective, long and a noun, boat. The compound lexeme longboat is a noun, and it is а noun because boat is a noun, that is, boat is the head constituent of longboat. Compound words can belong to all the major syntactic categories: • Nouns: signpost, sunlight, bluebird, redwood, swearword, outhouse; • Verbs: window shop, stargaze, outlive, undertake; • Adjectives: ice-cold, hell-bent, undersized; • Prepositions: into, onto, upon. From the morphological point of view compound words are classified according to the structure of immediate constituents: • Compounds consisting of simple stems - heartache, blackbird; • Compounds where at least one of the constituents is a derived stem -chainsmoker, maid-servant, mill-owner, shop-assistant; • Compounds where one of the constituents is a clipped stem - V-day, A-bomb, Xmas, H-bag; • Compounds where one of the constituents is a compound stem - wastes paper basket, postmaster general. Compounds are the commonest among nouns and adjectives. Compound verbs are few in number, as they are mostly the result of conversion, e.g., to blackmail, to honeymoon, to nickname, to safeguard, to whitewash. The 20th century created some more converted verbs, e.g., to weekend, to streamline,, to spotlight. Such converted compounds are particularly common in colloquial speech of American English. Converted verbs can be also the result of backformation. Among the earliest coinages are to backbite, to browbeat, to illtreat, to housekeep. The 20th century gave more examples to hitch-hike, to proof-read, to mass-produce, to vacuumclean. One more structural characteristic of compound words is classification of compounds according to the type of composition. According to this principle two groups can be singled out: words which are formed by a mere juxtaposition without any connecting elements, e.g., classroom, schoolboy, heartbreak, sunshine; composition with a vowel or a consonant placed between the two stems. e.g., salesman, handicraft. Semantically compounds may be idiomatic and non-idiomatic. Compound words may be motivated morphologically and in this case they are non-idiomatic. Sunshine - the meaning here is a mere meaning of the elements of a compound word (the meaning of each component is retained). When the compound word is not motivated morphologically, it is idiomatic. In idiomatic compounds the meaning of each component is either lost or weakened. Idiomatic compounds have a transferred meaning. Chatterbox - is not a box, it is a person who talks a great deal without saying anything important; the combination is used only figuratively. The same metaphorical character is observed in the compound slowcoach - a person who acts and thinks slowly. The components of compounds may have different semantic relations. From this point of view we can roughly classify compounds into endocentric and exocentric. In endocentric compounds the semantic centre is found within the compound and the first element determines the other as in the words filmstar, bedroom, writing-table. Here the semantic centres are star, room, table. These stems serve as a generic name of the object and the determinants film, bed, writing give some specific, additional information about the objects. In exocentric compound there is no semantic centre. It is placed outside the word and can be found only in the course of lexical transformation, e.g., pickpocket - a person who picks pockets of other people, scarecrow an object made to look like a person that a farmer puts in a field to frighten birds. The Criteria of Compounds As English compounds consist of free forms, it's difficult to distinguish them from phrases, because there are no reliable criteria for that. There exist three approaches to distinguish compounds from corresponding phrases: Formal unity implies the unity of spelling solid spelling, e.g., headmaster; with a hyphen, e.g., head-master; with a break between two components, e.g., head master. Different dictionaries and different authors give different spelling variants. Phonic principal of stress Many compounds in English have only one primary stress. All compound nouns are stressed according to this pattern, e.g., ice-cream, ice cream. The rule doesn't hold with adjectives. Compound adjectives are double-stressed, e.g., easy-going, new-born, sky-blue. Stress cannot help to distinguish compounds from phrases because word stress may depend on phrasal stress or upon the syntactic function of a compound. Semantic unity Semantic unity means that a compound word expresses one separate notion and phrases express more than one notion. Notions in their turn can't be measured. That's why it is hard to say whether one or more notions are expressed. The problem of distinguishing between compound words and phrases is still open to discussion. According to the type of bases that form compounds they can be of : 1. compounds proper – they are formed by joining together bases built on the stems or on the ford-forms with or without linking element, e.g., door-step; 2. derivational compounds – by joining affixes to the bases built on the word-groups or by converting the bases built on the word-groups into the other parts of speech, e.g., longlegged → (long legs) + -ed, a turnkey → (to turn key) + conversion. More examples: do-gooder, week-ender, first-nighter, house-keeping, baby-sitting, blue-eyed blond-haired, four-storied. The suffixes refer to both of the stems combined, but not to the final stem only. Such stems as nighter, gooder, eyed do not exist. Compound Neologisms In the last two decades the role of composition in the word-building system of English has increased. In the 60th and 70th composition was not so productive as affixation. In the 80th composition exceeded affixation and comprised 29.5 % of the total number of neologisms in English vocabulary. Among compound neologisms the two-component units prevail. The main patterns of coining the two-component neologisms are Noun stem + Noun stem = Noun; Adjective stem + Noun stem = Noun. There appeared a tendency to coin compound nouns where: The first component is a proper noun, e.g., Kirlian photograph - biological field of humans. The first component is a geographical place, e.g., Afro-rock. The two components are joined with the help of the linking vowel –o- e.g., bacteriophobia, suggestopedia. The number of derivational compounds increases. The main productive suffix to coin such compound is the suffix -er - e.g., baby-boomer, all nighter. Many compound words are formed according to the pattern Participle 2 + Adv = Adjective, e.g., laid-back, spaced-out, switched-off, tapped-out. The examples of verbs formed with the help of a post-positive -in -work-in, die-in, sleep-in, write-in. Many compounds formed by the word-building pattern Verb + postpositive are numerous in colloquial speech or slang, e.g., bliss out, fall about/horse around, pig-out. ATTENTION: Apart from the principle types there are some minor types of modern wordformation, i.d., shortening, blending, acronymy, sound interchange, sound imitation, distinctive stress, back-formation, and reduplicaton. 5. Shortening Shortening is the formation of a word by cutting off a part of the word. They can be coined in two different ways. The first is to cut off the initial/ middle/ final part: Aphaeresis – initial part of the word is clipped, e.g., history-story, telephone-phone; Syncope – the middle part of the word is clipped, e.g., madam- ma 'am; specs spectacles Apocope – the final part of the word is clipped, e.g., professor-prof, editored, vampirevamp; Both initial and final, e.g., influenza-flu, detective-tec. Polysemantic words are usually clipped in one meaning only, e.g., doc and doctor have the meaning "one who practices medicine", but doctor is also "the highest degree given by a university to a scholar or scientist". Among shortenings there are homonyms, so that one and the same sound and graphical complex may represent different words, e.g., vac - vacation/vacuum, prep — preparation/preparatory school, vet — veterinary surgeon/veteran. 6. Blending Blending is a particular type of shortening which combines the features of both clipping and composition, e.g., motel (motor + hotel), brunch (breakfast + lunch), smog (smoke + fog), telethon (television + marathon), modem , (modulator + demodulator), Spanglish (Spanish + English). There are several structural types of blends: Initial part of the word + final part of the word, e.g., electrocute (electricity + execute); initial part of the word + initial part of the word, e.g., lib-lab (liberal+labour); Initial part of the word + full word, e.g., paratroops (parachute+troops); Full word + final part of the word, e.g., slimnastics (slim+gymnastics). 7. Acronymy Acronyms are words formed from the initial letters of parts of a word or phrase, commonly the names of institutions and organizations. No full stops are placed between the letters. All acronyms are divided into two groups. The first group is composed of the acronyms which are often pronounced as series of letters: EEC (European Economic Community), ID (identity or identification card), UN (United Nations), VCR (videocassette recorder), FBI (Federal Bureau of Investigation), LA (Los Angeles), TV (television), PC (personal computer), GP (General Practitioner), ТВ (tuberculosis). The second group of acronyms is composed by the words which are pronounced according to the rules of reading in English: UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization), AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome), ASH (Action on Smoking and Health). Some of these pronounceable words are written without capital letters and therefore are no longer recognized as acronyms: laser (light amplification by stimulated emissions of radiation), radar (radio detection and ranging). Some abbreviations have become so common and normal as words that people do not think of them as abbreviations any longer. They are not written in capital letters, e.g., radar (radio detection and ranging), laser (light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation) yuppie, gruppie, sinbads, dinkies. Some abbreviations are only written forms but they are pronounced as full words, e.g., Mr, Mrs, Dr. Some abbreviations are from Latin. They are used as part of the language etc. - et cetera, e.g., (for example) — exampli gratia, that is - id est. Acromymy is widely used in the press, for the names of institutions, organizations, movements, countries. It is common to colloquial speech, too. Some acronyms turned into regular words, e.g., jeep -came from the expression general purpose car. There are a lot of homonyms among acronyms: MP - Member of Parliament/Military Police/Municipal Police PC - Personal Computer/Politically correct 8. Sound-interchange Sound-interchange is the formation of a new word due to an alteration in the phonemic composition of its root. Sound-interchange falls into two groups: 1) vowel-interchange, e.g., food – feed; in some cases vowel-interchange is combined with suffixation, e.g., strong – strength; 2) consonant-interchange e.g., advice – to advise. Consonant-interchange and vowel-interchange may be combined together, e.g., life – to live. This type of word-formation is greatly facilitated in Modern English by the vast number of monosyllabic words. Most words made by reduplication represent informal groups: colloquialisms and slang, hurdy-gurdy, walkie-talkie, riff-raff, chi-chi girl. In reduplication new words are coined by doubling a stem, either without any phonetic changes as in bye-bye or with a variation of the root-vowel or consonant as in ping-pong, chit-chat. 9. Sound imitation or (onomatopoeia) It is the naming of an action or a thing by more or less exact reproduction of the sound associated with it, cf.: cock-a-do-doodle-do – ку-ка-ре-ку. Semantically, according to the source sound, many onomatopoeic words fall into the following definitive groups: 1) words denoting sounds produced by human beings in the process of communication or expressing their feelings, e.g., chatter; 2) words denoting sounds produced by animals, birds, insects, e.g., moo, buzz; 3) words imitating the sounds of water, the noise of metallic things, movements, e.g., splash, whip, swing. 10. Distinctive stress Distinctive stress is the formation of a word by means of the shift of the stress in the source word, e.g., increase – increase. 11. Back-formation Backformation is coining new words by subtracting a real or supposed suffix, as a result of misinterpretation of the structure of the existing word. This type of word-formation is not highly productive in Modern English and it is built on the analogy, e.g., beggar-to beg, cobbler to cobble, blood transfusion — to blood transfuse, babysitter - to baby-sit.
СЛОВООБРАЗОВАНИЕ (WORD-BUILDING)
В английском языке имеется несколько способов словообразования:
1) конверсия (образование новых слов без изменения их написания и произношения)
2) словосложение (образование нового слова путем сложения двух слов в одно)
3) изменение ударения в слове (и получение нового слова другой части речи).
4) аффиксация (прибавление к корню суффикса или префикса)
Конверсия. Словосложение. Изменение ударения.
Иногда слово может менять свое значение и выполнять новую синтаксическую функцию в предложении, не изменяя при этом написания и произношения (конверсия). Наиболее распространенным является образование глаголов от существительных: master (хозяин) — to master (управлять), house (дом) — to house (размещать), water (вода) — to water (поливать). Но глаголы могут быть образованы и от прилагательных: empty (пустой) — to empty (опустошать) white (белый) — to white (белить).
Словосложение — это объединение полнозначных слов или их основ в сложное слово. Вновь образованное сложное слово пишется слитно или через дефис: airfield — аэродром (air — воздух, field — поле), air-base — авиабаза (air — воздух, base — база), airman — авиатор (air — воздух, man — мужчина), schoolday — школьный день (school — школа, day — день), birthplace — место рождения (birth — рождение, place — место).
Сложные слова могут состоять из двух существительных, первое из которых приобретает значение прилагательного. В этом случае слова пишутся отдельно. Например: service dress — форменная одежда, одежда для службы (service — служба, dress — платье), shop window — витрина (shop — магазин, window — окно), skim milk — снятое молоко (to skim — снимать (накипь и т.д.), milk — молоко).
Многие существительные совпадают по форме с глаголами, но отличаются ударением. Как правило, в существительных ударение падает на первый слог, а в соответствующих глаголах — на второй: export (экспорт) — to export (экспортировать) present (подарок) — to present (дарить).
Словообразование с помощью аффиксации.
Образование новых слов может происходить при помощи присоединения к основе слова суффиксов или префиксов (приставок). Префиксы присоединяются к корню слова в начале, а суффиксы — в конце. Слова, образованные с помощью префиксов или суффиксов, в отличие от простых слов, называются производными.
Префиксы, как и суффиксы, могут присоединяться к различным частям речи, изменяя при этом значение основы слова, например: happy (счастливый) — unhappy (несчастный) — happiness (счастье) — happily (счастливо); help (помощь) — helper (помощник) — helpful (полезный) — helpless (беспомощный).
Наиболее употребительные приставки (префиксы) и их значения:
1. Префикс со значением “снова”, “заново”, “вновь”, “пере”:
|
re- |
to construct (строить) — to reconstruct (перестроить), to read (читать) — to reread (перечитать), to write (писать) — to rewrite (переписать) |
2. Префиксы, которые придают слову противоположное значение или обозначают противоположное действие:
|
un- dis- de- anti- counter- contra- |
to dress (одеваться) — to undress (раздеваться), to tie (связывать) — to untie (развязывать) to appear (появляться) — to disappear (исчезать) formation (формирование) — deformation (деформация) fascist (фашист) — anti-fascist (антифашист) attack (атака) — counterattack (контратака) to contradict (противоречить, возражать) |
3. Префиксы, имеющие отрицательное значение:
|
a- ab- un- im- in- ir- il- dis- mis- non- |
amoral (аморальный, безнравственный) absent (отсутствующий), abnormal (ненормальный) kind (добрый) — unkind (недобрый) possible (возможный) — impossible (невозможный) ability (способность) — inability (неспособность) regular (регулярный) — irregular (нерегулярный) legal (легальный) — illegal (нелегальный) honest (честный) — dishonest (нечестный), to understand (понимать) — to misunderstand (неправильно понять) interference (вмешательство) — non-interference (невмешательство) |
! NOTE ! Приставка, которая начинается на “i” изменяется в зависимости от того, какая за ней стоит буква: il + l, ir + r, im + b, m, p. |
4. Префиксы, имеющие значение “сверх”, “пере”, “чрезмерно”:
|
over- super- ultra- extra- |
to pay (платить) — to overpay (переплатить) human (человеческий) — superhuman (сверхчеловеческий) short (короткий) — ultra-short (ультракороткий) extraordinary (необычный) |
5. Префиксы со значением “между”, “взаимно”:
|
со- inter- |
existence (существование) — co-existence (сосуществование) national (национальный) — international (интернациональный) |
6. Префиксы, которые переводятся как
а) “перед”:
|
рге- fore- |
war (война) — pre-war (довоенный), historic (исторический) — prehistoric (доисторический) to foresee (предвидеть) |
б) “после”:
|
post- |
war (война,) — post-war (послевоенный), revolutionary (революционный) — post-revolutionary (послереволюционный) |
в) “недостаточно”, “недо-“:
|
under- |
to pay (платить) — to underpay (оплачивать низко, т.е. недостаточно оплачивать, недоплачивать), production (производство) — underproduction (недопроизводство) |
г) “под”:
|
sub- |
division (разделение) — subdivision (подразделение), committee (комиссия, комитет) — subcommittee (подкомиссия) |
д) “экс”, “бывший”:
|
ex- |
champion (чемпион) — ex-champion (бывший чемпион) |
е) само-, авто-
|
auto- |
autobiography (автобиография), automatic (автоматический) |
ж) полу-
|
semi- |
semifinal (полуфинал), semicircle (полукруг) |
з) через-, транс-
|
trans- |
transatlantic (трансатлантический) |
и) вверх, кверху, наверху
|
up- |
upstairs (вверх по лестнице), upside (верхняя часть), to uproot (вырывать с корнем) |
к) двойной, два, дважды
|
bi- |
bilingual (двуязычный), bi-monthly (выходящий два раза в месяц) |
л) имеющий дело с книгами
|
bibli(o)- |
bibliography (библиография) |
м) относящийся к жизни
|
bio- |
biography (биография) |
н) второстепенное значение
|
by- |
by-street (переулок, улочка) |
о) много-, мульти-, поли-
|
multi- poly- |
multicolored (многоцветный), multimillionaire (мультимиллионер) polyglot (полиглот), polytechnic (политехнический) |
п) второстепенное значение
|
by- |
by-street (переулок, улочка) |
7. Префикс глагола, имеющий значение “делать”:
|
en- |
large (большой) — to enlarge (увеличивать, делать больше), danger (опасность) — to endanger (подвергать опасности), force (сила) — to enforce (принуждать, настаивать) |
Основные суффиксы существительных:
1. Суффиксы, обозначающие принадлежность к
а) политическому направлению профессии или нации:
|
-ist -an, -ian |
Communist (коммунист), Marxist (марксист}, materialist (материалист); artist (художник), typist (машинистка), pianist (пианист), historian (историк), librarian (библиотекарь), musician (музыкант); Russian (русский), Bulgarian (болгарин) |
2. Суффикс, обозначающий учение, теорию, качество:
|
-ism |
marxism (марксизм), heroism (героизм) |
3. Суффиксы, обозначающие действующее лицо, его занятие или должность:
|
-ег, -or -ee, -eer |
to teach (учить) — teacher (учитель), to direct (руководить) — director (руководитель) employee (служащий), refugee (беженец, эмигрант), auctioneer (аукционер), |
4. Суффикс, обозначающий результат действия:
|
-ment -ade |
achievement (достижение), agreement (согласие), government (правительство) lemonade (лимонад), blockade (блокада) |
5. Суффиксы, обозначающие
а) состояние:
|
-hood -ship -cy, -acy |
brotherhood (братство), childhood (детство), manhood (мужественность) dictatorship (диктатура), friendship (дружба), leadership (руководство) accuracy (точность), infancy (младенчество), supremacy (превосходство) |
б) действие, состояние:
|
-age -ing -ence -ance -ion, -tion -ition, -ation -sion -al |
shortage (нехватка), marriage (брак, супружество), voyage (путешествие) hunting (охота), crossing (пересечение, перекресток), living (житье) silence (молчание), difference (различие) importance (важность), resistance (сопротивление) collection (собрание, коллекция), dictation (диктант, диктовка) competition (соревнование), hesitation (сомнение, колебание) decision (решение) removal ( удаление), arrival (прибытие), refusal (отказ), approval (одобрение) |
в) качество или состояние:
|
-dom -ness -ty |
freedom (свобода), kingdom (королевство), wisdom (мудрость) coldness (холод), darkness (темнота), kindness (доброта), weakness (слабость) activity (активность), safety (безопасность) |
г) место действия, занятие или состояние
|
-ery |
bakery (булочная), surgery (кабинет хирурга), cookery (кулинария), slavery (рабство) |
д) род занятий, отрасль науки
|
-ics |
physics (физика), politics (политика) |
Основные суффиксы прилагательных:
1. Суффикс, образующий прилагательные от существительных и обозначающий национальную принадлежность или слабую степень качества:
|
-ese -ish |
Chinese (китаец, китайский), Japanese (японец, японский) Pole (поляк) — Polish (польский), Scott (шотландец) — Scottish (шотландский) red (красный) — reddish (красноватый), child (ребенок) — childish (ребячливый, детский) |
2. Суффиксы, образующие прилагательные от глаголов и обозначающие наличие качества:
|
-ive -ent -ant |
to act (действовать) — active (активный), to talk (разговаривать) – talkative (разговорчивый) to differ (различать) — different (различный), to insist (настаивать) — insistent (настойчивый) to observe (наблюдать, замечать) — observant (наблюдательный, внимательный) |
3. Суффиксы, образующие прилагательные от существительных
и обозначающие наличие качества, свойства:
|
-ic -al -ful -ous -у |
base (основа) — basic (основной), economy (экономика) — economic (экономический) centre (центр) — central (центральный) culture (культура) — cultural (культурный), beauty (красота) — beautiful (красивый) peace (мир) — peaceful (мирный), fame (слава) — famous (знаменитый) cloud (облако) — cloudy (облачный), sun (солнце) — sunny (солнечный) |
4. Суффиксы, образующие прилагательные от различных частей
речи и обозначающие
а) качество, свойство:
|
-аrу -огу |
element (элемент) — elementary (элементарный) illusion (иллюзия) — illusory (обманчивый, иллюзорный) |
б) способность что-либо сделать, состояние, качество:
|
-able — ible |
to change (изменить) — changeable (изменчивый) to eat (есть) — eatable (съедобный), reason (разум) — reasonable (разумный) |
в) отсутствие качества:
|
-less |
useless (бесполезный), windless (безветренный) |
Основные суффиксы глаголов:
|
-ate -en -fy, -ify -ize, -ise |
active (активный) — to activate (активизировать) short (короткий) — to shorten (укоротить) pure (чистый) — to purify (очищать), simple (простой) — to simplify (упрощать) character (характер) — to characterize (характеризовать) |
Основные суффиксы наречий
Суффиксы, образующие наречия от
а) прилагательных, иногда — существительных, порядковых числительных и причастий:
|
-ly |
bad (плохой) — badly (плохо), part (часть) — partly (частично), first (первый) — firstly (во-первых) |
б) существительных и наречий и обозначающие направление (или направленность):
|
-wards -ward |
North (север) — northward(s) (к северу, на север), after (после) — afterwards (впоследствии, позже, потом), back (обратно, назад) — backward(s) (назад, в обратном направлении) home (дом, домой) — homeward (к дому, по направлению к дому) |
NOTE! В английском языке большое место занимают слова, заимствованные из других языков. Такие слова называются интернациональными. По корню этих слов легко догадаться об их значении. Например: telegram (телеграмма), orchestra (оркестр), concert (концерт) и др. Умение подмечать интернациональные слова в значительной степени облегчает работу по переводу текста.
WORD-BUILDING (exercises)
Ex. 1. Переведите следующие слова, выделите в них суффиксы и префиксы:
Untrue, prehistoric, ultramodern, postwar, ex-champion, anti-body, decompose, decode, deform, depart, discover, disappearance, reread, reconstruct, coauthor, unequal, misunderstand, undress, disarm, anti-fascist, cooperation, co-existence, interaction, superhuman, ultra-violet.
Ex. 2. Определите, к какой части речи относятся следующие слова. Переведите их:
Achievement — achieve, resistance — resistant, assistance — assist — assistant, celebration — celebrate, difference — different, city — citizen, nation — national — nationality, measure — measurement, develop — development, act — active — activity, contain — container, discover — discovery — discoverer, literature — literary, graduate — graduation — undergraduate — post-graduate, educate — education, progress — progressive, act — action — activity — active, govern — governor — government.
Ex. З. Образуйте от данных глаголов существительные с помощью суффикса -ег или -or. Переведите на русский язык:
To lead, to write, to read, to visit, to speak, to sleep, to act, to direct, to conduct, to drive, to fight, to mine, to report, to sing, to skate, to swim, to teach, to travel, to sail, to invent, to found, to compose.
Ex. 4. Образуйте от данных слов существительные с помощью суффикса -ist, -ism, -ian. Переведите на русский язык:
Special, social, art, capital, economy, international, piano, technic, mathematics, statistics, politics, music, electric, Russia, Hungary, Canada, India.
Ex. 5. Образуйте от данных глаголов существительные с помощью суффикса -ment. Переведите на русский язык:
Develop, achieve, move, arrange, treat, state, improve, agree, equip, govern, require, measure, announce, pave.
Ex. 6. Образуйте прилагательные с помощью суффиксов -ful и -less, переведите их на русский язык:
Beauty, thank, hope, doubt, care, aim, use, shape, fruit, power, thought, harm, colour.
Ex. 7. Образуйте прилагательные с помощью суффиксов -able, -ible, переведите их на русский язык:
Change, convert, prevent, break, compare, desire, profit, read, comfort, respect, expect.
Ex. 8. Найдите и выделите суффиксы в данных словах и определите, к какой части речи эти слова относятся:
British, foolish, understandable, heartless, pitiless, successful, experiment, function, musician, socialist, artist, capitalism, professional, fundamental, industrial, doubtful, useful, different, treatment, creative, attractive, peaceful, dangerous, elementary, childish, active, economic, director, worker, passage, marriage, silence, freedom, kingdom.
Ex. 9. Образуйте глаголы с помощью суффикса -en:
Red, tight, soft, deep, short, dark, bright, weak, black, white, sweet, sharp, strength.
Ex. 10. Образуйте наречия с помощью суффикса -1у и переведите их:
Bad, first, part, quick, strong, short, silent, rapid, wide, extreme, cruel, kind, happy.
Ex. 11. Образуйте глаголы от данных существительных. Переведите их:
Turn, smile, smoke, snow, start, stay, step, stop, study, talk, visit, rest, air, paper, cover, handle, cause, watch, act, address, answer, brush, clean, cross, crowd, wave, wish, work, dance, doubt, dress, end, fight, help, hope, joke, laugh, lift, light, love, mind, paper, pencil, place, plan, play, post, reply, report, return, sail, show.
Ex. 12. Переведите на русский язык. Выделите словообразующие элементы. Определите, к какой части речи относятся данные слова:
React, reaction, reactor, reactivity; science, scientific, scientist; industry, industrial, industrious; cold, coldly, coldness; dark, darkness, darken; happy, happily, happiness, unhappy; equal, equally, unequal, equality; free, freedom, freely; attention, attentive, attentively; sun, sunny, sunless; care, careful, careless, carefully, carelessness; to differ, different, difference, indifferent; England, English, Englishman; fame, famous.
Ex. 13. Переведите следующие сложные слова:
Airport, armchair, bathroom, bedroom, bookcase, bookshelf, classroom, custom-house, dining-room, drawing-room, fireplace, folksong, gentleman, hairbrush, icebox, newspaper, notebook, postcard, post-office, raincoat, sportsman, sunshine, writing-table.
Ex. 14. Прочтите следующие пары слов, соблюдая ударения. Переведите их:
An accent — to accent, a contract — to contract, a content — to content, a contest — to contest, a convoy — to convoy, a convict — to convict, a perfect — to perfect, a record — to record.
Ex. 15. Определите, к каким частям речи относятся выделенные слова:
1. Не works as a teacher. 2. I saw one of his works at the exhibition. 3. I was waiting for your report. 4. They report the results of their experiment every Monday. 5. His report contains some of his thoughts about the experiment. 6. You’ll make progress if you work hard. 7. He thought about his new work. 8. I have a present for you. 9. I am busy at present. 10. He presented me with a book.
Ex. 16. Проанализируйте состав следующих слов. Определите части речи. Дайте начальную форму. Переведите слова:
Powerful, inventor, high-quality, network, demoralize, profitable, dislike, disagree, movement, shorten, incorrect, electricity, fruitful, fruitless, happiness, dangerous, noisy, sunny, rainy, badly, strongly, reading, teaching, rebuild, retell, leader, teacher, unhappy, unusual, translation, cooperation, schoolboy, icebreaker.
Ex. 17. Напишите сложные существительные, исходя из объяснений.
Например: A machine for drying hair – hair drier.
1. A thing for opening tins — … . 2. A machine for playing records — … . 3. A machine for mixing food — … . 4. A thing that times eggs (when they are boiling) — … . 5. Things for warming people’s legs — … . 6. Stuff that kills flies — … . 7. A liquid that removes paint — … . 8. A tool that opens bottles — … . 9. A thing for peeling potatoes — … . 10. A liquid for removing eye makeup — … . 11. Stuff for freshening the air — … .
Ex. 18. Напишите словосочетания по модели число+ существительное+существительное (! не забывайте что число и первое существительное соединяется дефисом и что это существительное обычно стоит в единственном числе)
Например: a walk lasting for three miles – a three-mile walk.
1. A girl who has just celebrated her sixteenth birthday — … . 2. A flight lasting for ten hours — … . 3. A note that is worth twenty pounds — … . 4. A language course that lasts four weeks — … . 5. A drive that takes three hours — … . 6. A meal that consists of three courses — … . 7. A holiday that lasts two weeks — … . 8. A delay at the airport that went on for two hours — … . 9. A letter that goes on for ten pages — … . 10. A university course that takes three years — … . 11. A prison sentence of ten years — … . 12. A hotel with five stars — … . 13. A speed limit of 30 miles an hour — … . 14. A house that was built two hundred years ago — … .
Ex. 19. Распределите прилагательные по трем группам: 1) люди, 2) места, 3) вещи:
Obstinate, unspoilt, hand-made, waterproof, easy-going, breathtaking, aggressive, deserted, overgrown, overcrowded, cunning, picturesque, arrogant, long-lasting, spoilt, automatic, accurate, artificial.
Ex. 20. Выберите слово с нужным по смыслу префиксом или суффиксом.
1. I know Jim Kerry is very popular but I find him totally childish / childlike. 2. I couldn’t work out whom the letter was from. The signature was childish / childlike. 3. Sarah is so childish / childlike. She always plays trick on her friends. 4. It was wonderful to watch the tiny lambs playing. I got such childish / childlike pleasure from the experience. 5. Sophie is extremely sensitive / sensible at the moment. Anything you say seems to upset her. 6. Karen is not a very sensitive / sensible person. She wore high-heeled shoes for our four-mile walk. 7. I’ve never known her to tell a lie. She’s a very true / truthful person. 8. I can never watch sad films that are based on true / truthful a story. They always make me cry. 9. Susan is so intolerable / intolerant of other people. She never accepts anyone else’s opinion, and she always thinks she knows best. 10. I find Mark’s behaviour intolerable / intolerant. It’s unfair to be so selfish. 11. We’re having an economic / economical crisis at the moment. James has lost his job and I don’t know how we are going to pay the rent. 12. It’s more economic / economical to drive slowly. You can do a lot more miles to the gallop.
Ex. 21. Подберите к каждой тройке слов такое, чтобы с его помощью образовать составные существительные, используйте слова: board, green, paper, book, birthday, blood, rain, site, road, sports, ice, water, day, night, hand, case, sun, bag.
Например: camp…, building…, bomb… – campsite, building site, bomb-site.
1. …test, …pressure, …donor. 2. …fall, …melon, …skiing. 3. …house, …grocer, …salad. 4. …club, …mare, …shift. 5. brief…, suit…, book… . 6. paper…, plastic…, shoulder… . 7. …bow, …coat, …drop. 8. …shine, …rise, …set. 9. …works, …sign, …rage. 10. black…, floor…, notice… . 11. …light, …break, …dream. 12. …shake, …writing, …book. 13. …cube, …berg, …rink. 14. …cake, …present, …card. 15. …scape, …lady, …slide. 16. …car, …center, …ground. 17. address…, visitor’s…, note… .
Ex. 22. Дополните предложения сложными существительными в скобках (это могут быть и составные существительные, и существительные в притяжательном падеже в простой или аналитической форме).
1. Your coat is on the … (back, chair). 2. You’ve just spilt the … (milk, cat). 3. Can you buy some … (paper, toilet). 4. I never listened to my … (advise, parents). 5. Can you buy a … (wine, bottle) to have with supper? 6. What did that … (road, sigh) say? Did you see it? 7. It’s such a mess in here. There are empty … (wine, bottles) everywhere. 8. The … (Prime Minister, duties) include entertaining heads of the state. 9. The … (my shoe, heel) has come off. 10. Can I borrow your … (brush, hair)? 11. What happened at the … (film, end)? 12. Here is … (today, news). 13. Where is the nearest … (Metro, station)? 14. It’s my … (anniversary, parents, wedding) next week. 15. The … (company, success) is due to its efficiency. 16. I’ve got a … (fortnight, holiday) next month. 17. The … (government, economic policy) is confusing. 18. My children go to the local … (school, state). 19. The annual … (rate, inflation) is about 4 percent. 20. Are there any … (coffee, cups) in your bedroom? There are none in the kitchen. 21. Do you want a … (coffee, cup)?
Ex. 22. Заполните пропуски глаголом или существительным: advice – to advise, use – to use, abuse – to abuse, belief – to believe, relief – to relieve, grief – grieve, excuse – to excuse, breath – to breathe, half – to halve, house – to house, safe – to save, bath – to bathe.
1. It is my personal … that this man is innocent. 2. Let me listen to your chest. Take a deep … and say “Ah”. 3. You should put your valuables in the … . 4. Drug … is a terrible problem all over the world. 5. I know it isn’t good for my skin, but I love sun … . 6. I’ve been so worried about you! It’s such a … to see you at last! 7. “What are we going to do with this cake?” “Cut it in two. You take … and I’ll take … .” 8. Can you show me how to … this new coffee machine? 9. The refugees are … in temporary accommodation. 10. She apologizes for her behavior, and said it was because she’d had a busy day, but that’s no … for breaking all the plates. 11. People need time to … after the death of someone they love. 12. Take my … . Never marry for money. Marry for love.
Ex. 22. Напишите слово противоположное по значению, используя префикс
Kind, honest, credible, appear, fair, equal, pleased, continue, fasten, normal, employed, friendly, trust, professional, known, cover, safe, use, probable, important, emotional.
WORD-BUILDING (Test)
1. Определите, к какой части речи относятся данные слова. Переведите их:
Beautiful, function, artist, musician, heartless, economic, worker, badly, act, action, active, basic, fruitless, population, movement, historic, democratic, work, daily, literature, picture, organization, friendship, highly, leader, fight, fighter, national, impressive, hopeful, hopeless, beautiful, special, specialist, define, definition, humanism, humanist, humanistic, use, useful, useless.
2. Переведите слова на русский язык. Определите префикс и его значение:
Coauthor, undress, disarm, postwar, illegal, unkind, reconstruct, deformation, prewar, antibody, ex-champion, superhuman, ultrashort.
3. Образуйте прилагательные от существительных при помощи следующих суффиксов: -al, -ful, -ous, -у, -able, -ible, -ic, -less, -ish. Переведите пары слов.
Reason, beauty, hope, doubt, care, aim, use, desire, boy, success, heart, experiment, form, office, danger, fame, electron, base, nature, cloud, sun, child, Scott, history, home.
4. Переведите предложения. Определите, к каким частям речи относятся выделенные слова. Назовите сложные слова:
1. Many pupils study English. 2. My grandfather has a large study. 3. Who ruled this country? 4. All sportsmen must obey the rules of the game. 5. The Soviet Union is tied by friendship with India in their work for peace. 6. All peace-loving people work for peace for the whole of mankind.
5. Назовите глаголы, от которых образованы следующие существительные:
Protection, show, writer, worker, movement, investigation, achievement, statement, reader, department, equipment, construction, organization, reporter, arrival, improvement, conductor, establishment, development, education, definition, regulation, assistance, agreement.
6. Переведите без словаря. Определите, к какой части речи относятся слова:
a) Specialist, institute, university, culture, central, national, nation, international, organization, Soviet, minister, nature, natural, traditional, progressive, moral, social, socialist, public, programmer, popular, modern, revolution, revolutionary, final, talent, continent, festival, political, experiment, experimentation, electricity, technical, transformation, system, systematically, practice, practical, seminar, lecture, lecturer, period, historic, history, professor, complex, form, acceleration, instrument, philosopher, idea, basic, fundamental, conceptions, mass, class, element, motor, method, problem, energy, radio, text, material, temperature, progress, television.
b) 1. France and England are European countries. 2. In the evening we like to listen to classical music. 3. We saw a comedy at the Drama Theatre last night. 4. Your train leaves from platform two. 5. This jazz orchestra gave several concerts in our town. 6. In 1610 Galileo constructed the first telescope in the world. 7. This was a dangerous experiment.
7. Проанализируйте следующие слова, какие они? Определите их составляющие. Переведите на русский язык:
Ice-hockey, world-wide, bedroom, newspaper, long-term, birthplace, sportsman, apple-pie, peace-loving, schoolchildren, football, highland, television, underground, north-west, sometimes, lowland, landscape, well-known, multinational, network, vice-president.
8. Поставьте слово, указанное в скобках, в нужную форму.
1. My father is very … (act) even though he’s seventy. 2. I’ve always wanted to work in the theatre, but … (act) it isn’t a very secure profession. 3. I … (hope), we’ll soon find a solution to the problem. 4. Look … (care) to the left and to the right before crossing the road. 5. It was very … (care) of you to lose my watch. 6. I take two … (day) newspapers and three Sunday papers. 7. You’ve broken my camera! Look at it! It’s … (use)! 8. Thanks for the advice. It was really … (use). 9. I have some very … (noise) neighbours. 10. She became … (fame) as a result of her invention.
WORD-BUILDING IN ENGLISH
Word-formation l process of creating new words from resources of a particular language according to certain semantic and structural patterns existing in the language
Word-formation l branch of Lexicology l studies the patterns on which the English language builds words l may be studied synchronically and diachronically
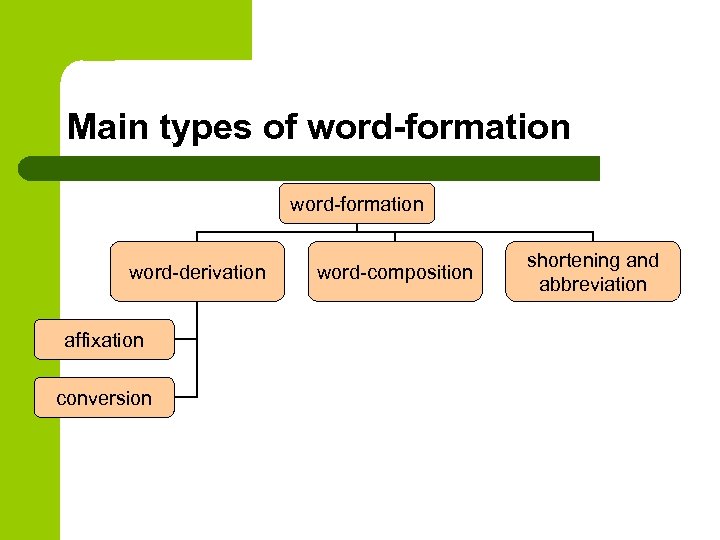
Main types of word-formation word-derivation affixation conversion word-composition shortening and abbreviation
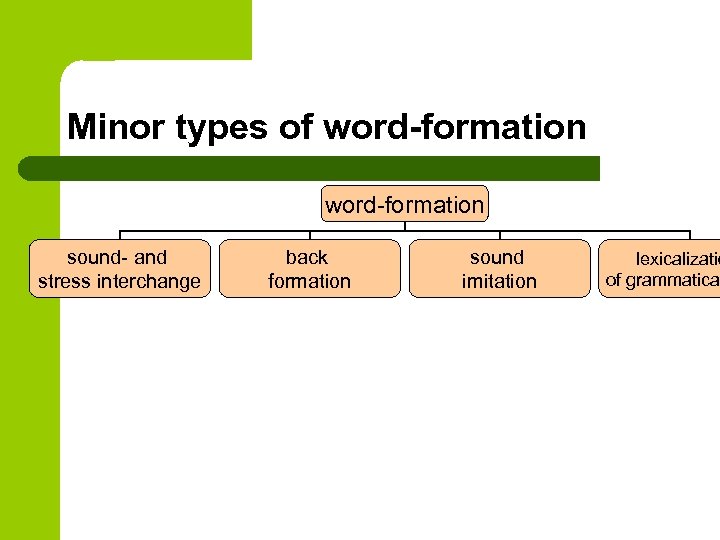
Minor types of word-formation sound- and stress interchange back formation sound imitation lexicalizatio of grammatical
Derivational Pattern is a meaningful combination of stems and affixes l regularly reproduced l indicates the grammatical part-of-speech meaning e. g. verbal stem + -ee = noun (‘one who is V-ed’) examine + -ee = examinee addressee, employee, divorcee l
Affixation l l formation of words by adding derivational affixes to stems one of the most productive ways of wordbuilding
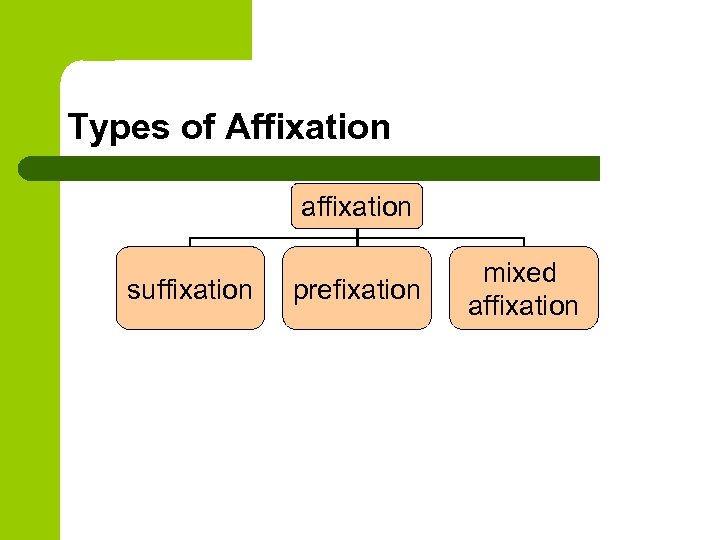
Types of Affixation affixation suffixation prefixation mixed affixation
Affixation Suffixation l words are formed with the help of suffixes l changes a part-of-speech meaning (e. g. work – worker) l transfers a word into a different semantic group (e. g. child – childhood) l is characteristic of noun and adjective formation Prefixation l words are formed with the help of prefixes l does not change a part-ofspeech meaning (e. g. usual – unusual) l about 25 prefixes form one part of speech from another (e. g. head – to behead) l is characteristic of verb formation
Mixed Affixation l l l formation by both prefixation and suffixation semantic structure becomes more limited the more affixes added the less polysemantic the word becomes e. g. speak – unspeakable place – irreplaceable
Conversion l l process of creating a new word in a different part of speech with different distributional characteristic but without adding any affixes so that the basic form of the original and the basic form of a derived word are homonymous
Conversion A new word: l has a meaning different from the original one l has a new paradigm peculiar to its new category as a part of speech l the morphemic shape of the original word remains unchanged
Conversion l l face, noun -s, pl. -’s, poss. c. , sg -s’, poss. c. , pl a front part of the head from the forehead to the chin l l to face, verb -s, 3 rd p. sg. -ed, past ind. , past part. -ing, pres. part. , gerund to turn the face towards sb/smth
Reasons for the widespread development of conversion absence of morphological elements which mark the part of speech of the word e. g. back (noun) – If you use mirrors you can see the l back of your head to back – Their houses back onto the river. back (adverb) – Put the book back on the shelf. back (adjective) – a back garden, back teeth
Reasons for the widespread development of conversion l simplicity of paradigms of English parts of speech l a great number of one-syllable words that are mobile and flexible
Conversion in Present-Day English l l l typical of one-syllable words not common to affixed words (e. g. a commission – to commission) the predominant way of verb formation verbs are mainly formed from nouns and rarely from other parts of speech highly productive
Conversion in Different Parts of Speech l noun verb e. g. an eye – to eye, a bag – to bag, a room – to room l verb noun e. g. to jump – a jump, to do – a do l adjective verb e. g. pale – to pale l adjective noun e. g. private – a private, blind – the blind
Conversion in Different Parts of Speech form word noun e. g. He was familiar with ups and downs of life. I shan’t go into whys and wherefores. l affix noun e. g. Freudism, existentialism and all other ‘isms’ of l modern life. interjection verb e. g. pooh – to pooh-pooh l
Conversion and Other Types of Word. Formation l conversion and composition e. g. pin-point — to pin point, black-list – to blacklist l composition, conversion and shortening e. g. to drive in – a drive-in theater – a drive-in l conversion and composition in phrases and sentences e. g. Old man what-do-you-call-him’s book is on sale.
Traditional and Occasional Conversion Traditional Conversion l the use of a word is recorded in the dictionary e. g. to cook, to look, find, aim, etc. Occasional Conversion l the use of a word is not registered by the dictionary l occurs momentarily, through the immediate need of the situation, brings out the meaning more vividly e. g. If anybody oranges me again tonight, I’ll knock his face off!
Shortening l a way of word-formation when part of the original word or word group is taken away
Shortening A new word: l l l belongs to the same part of speech as a the original word (e. g. demo – demonstration) has the same lexical meaning as the original word capable of being used as a free form can take functional affixes (e. g. a bikes) mostly monosemantic
Shortening A new word: l may serve as basis for further word-formation by derivation and composition e. g. fancy (noun) fantasy (shortening) fancy (noun) to fancy (conversion) fancy (noun) fancier, fanciful (derivation) fancy (noun) fancy-ball, fancy-dress (composition)
Shortening A new word: l differs from the original word stylistically or emotionally, characteristic of colloquial speech e. g. Becky Rebecca (diminutive) Japs the Japanese examination (college slang) hanky handkerchief (nursery word) o’er over (bookish, poetic style)
Shortening in Different Parts of Speech l l nouns e. g. professor verbs e. g. to revolve adjectives (very few) e. g. dilly delightful (jargonism) interjection e. g. Shun! attention
Types of Shortening final clipping (apocope) — a word is shortened at the end e. g. ed editor, referee l initial clipping (apheresis) – a word is shortened at the beginning e. g. phone telephone, chute parachute l
Types of Shortening medial clipping (syncope) – some syllables or sounds are omitted from the middle of a word e. g. maths mathematics spectacles fancy fantasy l
Types of Shortening l a word is clipped both at the end at the beginning e. g. flu tec fridge influenza detective refridgerator
Abbreviation (graphical shortening) l l shortening of word or word-groups in written speech in speech the corresponding full forms are used e. g. lb — pound e. g. – for example i. e. – that is Dr. – Doctor Oct. — October
Composition l l is the way of word-building when a word is formed by joining two or more stems to form one word one of the most productive ways of wordbuilding in Modern English
Compound Words consist of at least two stems which occur in the language as free forms e. g. a brother-in-law, airbus, snow-white l
Criteria for Distinguishing between a Compound a Word-combination l l Compound Word graphic criterion: solid or hyphenated spelling e. g. sunbeam, warship semantic criterion: conveys one concept e. g. a green-house l l Word-Combination graphic criterion: spelling with a break e. g. a tall boy semantic criterion: conveys more than one concept e. g. a green house
Criteria for Distinguishing between a Compound a Word-combination Compound Word l phonetic criterion: a single uniting stress e. g. a ´greenhouse Word-Combination l phonetic criterion: each word in a group has a stress e. g. a ´green ´house
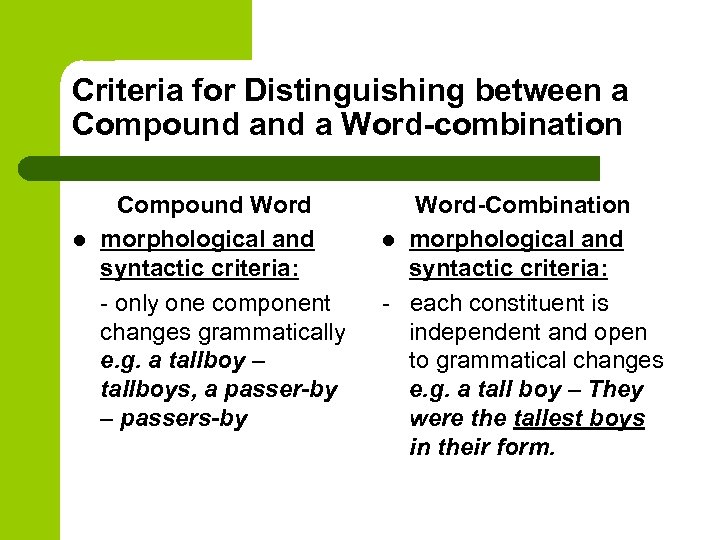
Criteria for Distinguishing between a Compound a Word-combination l Compound Word morphological and syntactic criteria: — only one component changes grammatically e. g. a tallboy – tallboys, a passer-by – passers-by Word-Combination l morphological and syntactic criteria: — each constituent is independent and open to grammatical changes e. g. a tall boy – They were the tallest boys in their form.
Criteria for Distinguishing between a Compound a Word-combination l Compound Word morphological and syntactic criteria: — no word can be inserted between the components Word-Combination l morphological and syntactic criteria: — other words may be inserted between the constituent parts e. g. a tall handsome boy
Classifications of Compounds l l l according to the parts of speech according to the joining element according to the structure of compounds according to the degree of semantic independence according to the order of components according to the motivation of the meaning of compounds
Classification of compounds according to the part of speech nouns and adjectives e. g. baby-sitter, power-hungry (энергоемкий) l adverbs and prepositions e. g. indoors, within, outside l verbs (formed by means of conversion or backformation) e. g. to handcuff hand-cuffs, to babysit baby-sitter l
Classification according to the joining element l neutral compounds are formed by joining two stems together without any joining morpheme e. g. classroom, dancing-hall l syntactical compounds – components are joined by means of form-word stems e. g. here-and-now, free-for-all
Classification according to the joining element l morphological compounds – components are joined by a linking element: — vowel “o”, “I” e. g. speedometer, handicraft — consonant “s” e. g. sportsman
Classification according to the structure of compounds l l compound words proper – formed by juxtaposition of two stems without any linking element e. g. top-notch (первоклассный), tiptop compound-affixed words – e. g. honeymooner
Classification according to the structure of compounds l l compound words consisting of three or more stems — e. g. eggshell-thin, cornflower-blue compound-shortened words – e. g. V-day, landsat
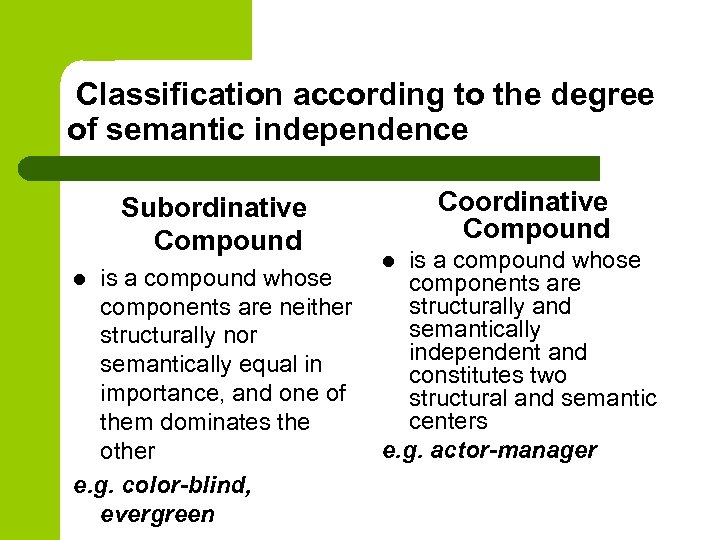
Classification according to the degree of semantic independence Subordinative Compound is a compound whose components are neither structurally nor semantically equal in importance, and one of them dominates the other e. g. color-blind, evergreen l Coordinative Compound is a compound whose components are structurally and semantically independent and constitutes two structural and semantic centers e. g. actor-manager l
Classification according to the order of components Syntactic Compound l is a compound that conforms to grammatical patterns current in the language e. g. northwest, for-free, maybe, killjoy, seashore Asyntactic Compound l is a compound that does not conform to grammatical patterns current in the language e. g. to babysit (to sit with a baby), rope-like (like a rope)
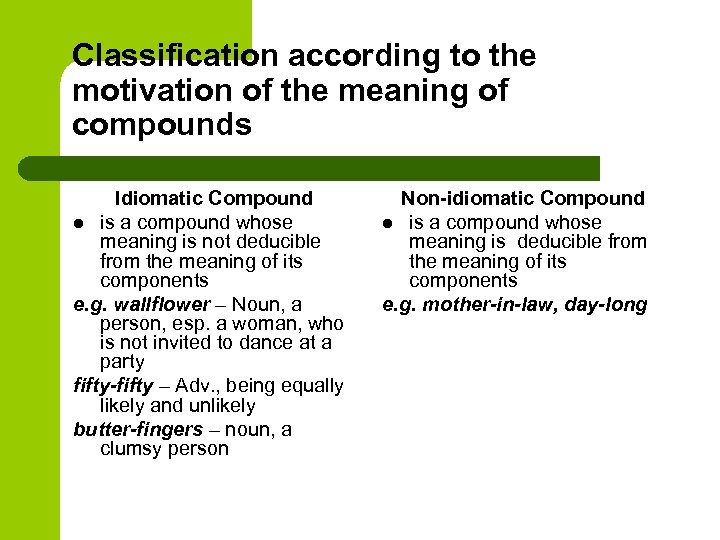
Classification according to the motivation of the meaning of compounds Idiomatic Compound l is a compound whose meaning is not deducible from the meaning of its components e. g. wallflower – Noun, a person, esp. a woman, who is not invited to dance at a party fifty-fifty – Adv. , being equally likely and unlikely butter-fingers – noun, a clumsy person Non-idiomatic Compound l is a compound whose meaning is deducible from the meaning of its components e. g. mother-in-law, day-long
Ways of forming compound words l l l reduplication – e. g. too-too, hush-hush partial conversion from word-groups e. g. can-do (исполнительный и энергичный) can do backformation from compound nouns and wordgroups e. g. to baby-sitter vowel interchange (ablaut compounds) e. g. chit-chat (сплетни), tip-top, riff-raff (сброд) rhyme compounds – e. g. willy-nilly (волей-неволей), hoity-toity(надменный)
Peculiarities of English Compounds l l l all components of compound words are free forms, can be used independently with a distinct meaning of their own e. g. motherland, day-off, everybody usually are two-stem compounds attributive compounds e. g. last-minute changes, four-year course
Sound Interchange l way of forming new words with the help of change of sounds within a word
Types of Sound Interchange l l l vowel change – e. g. full – to fill, blood – to bleed consonant interchange – e. g. to speakspeech, advice – to advise the combination of vowel and consonant change – e. g. life – to live, strong strength
Stress Interchange l e. g. ´import — to im´port, ´suspect – to sus´pect
Lexicalization of Grammatical Form l way of creating new words with the help of suffix “s” e. g. glass – glasses, custom – customs, colour — colours
Backformation l way of creating new words by subtracting a real or supposed suffix from the original word e. g. to beggar, to editor, to burgler
Sound Imitation (Onomatopoeia) l way of forming new words by imitating different kinds of sounds that may be produced by animals, birds, insects, human being and inanimate objects e. g. buzz, croak, moo, mew, purr, roar e. g. clink, whip, splash, bubble e. g. giggle, mutter, babble