As an adult English speaker, you’re expected to have an extensive vocabulary that includes some words that are seldom used in conversational English. You should also be striving to improve your vocabulary. While all these lists are somewhat subjective, they’re a good way to see how good your current vocabulary happens to be, and work on some words you may not know. See how you measure up to this list of 100 intermediate to advanced vocabulary words every adult should know.
Just to make things more interesting, I’ve also peppered a few rather obscure words into the mix, and even though these may rarely be used, they’ll make you an even more dangerous Scrabble player, crossword whizz or other word game player than you already are. Enjoy!
1. Acquiesce
This word means that a person has agreed or assented either verbally or tacitly to something. Even when it is well understood, this word is often misspelled.
2. Aberration
Sometimes, it’s good to be different, but the word “aberration” describes an unwelcome oddity. So, if someone accuses you of aberrant behavior, they aren’t complimenting your originality.
3. Abjure
If you solemnly renounce something, you have abjured it. The word is used in baptism ceremonies in certain churches. The person being baptized declares that he or she abjures Satan and all his works.
4. Abrogate
Abrogation is a situation in which formal or legal measures are taken to do away with something. This would usually be a law or a formal rule that is repealed or temporarily suspended.
5. Acronym
This should have been an easy one for lovers of language. An acronym is an abbreviation consisting of letters. For example, U.S.A for United States of America.
6. Anachronism
I’m sure you will have encountered a few anachronisms during your life. An anachronism is something that is out of date and no longer relevant to the times. If you want to argue that something has lost its relevance by not changing with the times, you can describe it as being anachronistic or an anachronism.
7. Anathema
No, it’s not a rather nice sounding girl’s name. It describes something that you vehemently dislike to the point of total rejection. For example: “He is an atheist; all forms of religion are anathema to him.”
8. Antebellum
A thing that is described as “antebellum” was conceived or constructed prior to an important war. The plantation era before the American Civil War is sometimes referred to as the antebellum era, but the word can apply to anything that preceded a major war.
9. Anthropogenic
Anything that has been caused by human interventions is anthropogenic. The word is usually used in the context of environmental degradation and pollution. Climate change, for example, could be described as an anthropogenic phenomenon.
10. Antithesis
Something or someone that is the diametric opposite of something else. “He was the antithesis of the frivolous millionaire playboy,” would imply that the person was the opposite of what one expect from a happy-go-lucky millionaire. Perhaps he was very serious about current issues, or didn’t like wasting money on status symbols.
11. Assonance
This is the sound a donkey makes. Alright, I’m kidding again, but it does have something to do with sound. It is a technique often used in creative writing and poetry in which similar sounding (but not necessarily rhyming) words are used in close proximity to one another.
12. Benchmarking
Benchmarking involves selecting a certain state as being the norm against which other, similar things will be compared. For example, in vegetation surveys, undisturbed nature would be seen as the benchmark against which vegetation would be evaluated.
13. Bellicose
This is a lovely word for describing people who are aggressive and even willing to fight over an issue. As you can imagine, bellicosity and politics often go hand in hand!
14. Bowdlerize
This is a form of censorship that not only removes the portions of text some might consider risqué, but also weakens the work. The original Bowdler, published an expurgated version of Shakespeare. “Nothing is added to the original text; but those words and expressions omitted which cannot with propriety be read aloud in a family,” he wrote, blithely unaware that his 1818 work would turn his name into a byword for literary slaughter.
15. Chicanery
“Chicanery” alludes to the use of dirty tricks in the financial, political or legal world. If you are ever accused of it, know that you are in deep trouble!
16. Chthonic
You really won’t see this word in everyday use, but it’s a killer if you’re into word games! It refers to caves or the underworld. It is a synonym for the more well-known “subterranean” .
17. Cerulean
You will no doubt have read about cerulean waters or skies and assumed that they were blue. You are right. Specifically, the word refers to a deep, sky-blue.
18. Circumspect
If you are behaving with circumspection, you are watchful, wary or unwilling to take risks. One could almost say it was an antonym or opposite for “bellicose”!
19. Circumlocution
Have you ever talked to someone who explains things in a roundabout way? They are guilty of circumlocution. They literally “talk around” a subject instead of being specific and concise.
20. Cogent
The person who is guilty of circumlocution, should try to be more cogent. In other words, they should be clear, logical and convincing. When you present arguments, you will strive for cogency.
21. Colloquial
This is the kind of language we use every day. It is the “spoken” form of a language, and is not appropriate when you are writing a formal text. That doesn’t mean that colloquial words are wrong or bad. They are simply informal.
22. Conundrum
A conundrum could simply be a riddle, but it is also used to describe any puzzling or difficult question.
23. Crepuscular
This lovely word is used to describe things that resemble or relate to twilight. In its simplest form, it is used to describe creatures that become active at twilight, but I’m sure you know a few people like that too!
24. Deleterious
If something has harmful effects, they can be described as “deleterious effects.” You’ll often find this word being used in medical texts and in psychology. “Harmful” is just as good, but this word is ever so much weightier!
25. Depredation
My mom used to use this word to describe my brother’s activities in the pantry. It describes an act of attack or plunder. Judging from the state of the grocery cupboard once my brother was finished, my mom described what he’d been up to very well.
26. Didactic
In its simplest context, this word describes something that was designed to teach a lesson. For example, a didactic story would have a strong lesson to teach. However, the word can also be used negatively to describe someone who is preachy and patronizing.
27. Egregious
Think of all the words that mean “terribly bad or shocking;” that’s what “egregious” means. Never did a difficult-seeming word have a simpler definition!
28. Enervate
If you are feeling drained, weakened and tired out, you have probably been through some sort of enervating experience. There are good types of tiredness, but this is not one of them.
29. Enfranchise
This means giving people freedom or the right to vote. Nowadays, we worry about disenfranchisement, a situation in which rights or freedoms are taken away.
30. Entomophagy
This word is quite rarely used, but if we were to have a famine, or if certain exotic dishes became popular, we might need it. It means “the eating of insects,” and although it generally applies to animals and birds, there are plenty of people who eat insects as a matter of course! Any word with the suffix “phagy” or “phagous” refers to what an organism eats.
31. Epiphany
An epiphany is an “Aha!” moment, but the word comes from the Christian festival celebrating the revelation of Christ to the magi. If you have a life-changing realization, it could be described as an epiphany.
32. Epitome
A perfect example of something epitomizes it. “Her life so far is the epitome of the American Dream,” makes me think, “Wow, I want one just like it!”
33. Eschatology
A lot of people discuss this quite heatedly without knowing the right word for it. It is a religious doctrine that deals with death, judgement, and what happens to the soul after death. And in case you were wondering – I didn’t know this word before I researched this article, but I thought we needed a few challenges.
34. Eschew
Here’s a useful little word that says more than it seems to. For example, you could say someone doesn’t exercise, but if you say, “He eschewed exercise,” it implies a stronger and more deliberate aversion.
35. Evanescent
If you have literary ambitions, this beautiful word is worth having in your vocabulary. It refers to something that is transitory, or that disappears or fades rapidly.
36. Existential
The word structure says it all. It describes something to do with the nature of existence. If you’re into philosophy, you probably use this word a lot.
37. Exponential
There is a mathematical description of exponents and what can be regarded as “exponential.” I’m not going to go into it here. We more often hear of it in a context that implies rapidly increasing growth. When you hear it, don’t just trust it. Ask for the figures.
38. Facetious
This is one of my all-time favorite words, and I have frequently been accused of facetiousness. It means making inappropriate jokes or taking serious situations too lightly. I wouldn’t say it’s always a good thing, but sometimes, it helps, because there are times when we are way too serious about unimportant things.
39. Fascism
What is it? It sounds great in political arguments, and the word is often bandied about. It is a type of nationalism that sprang up in Europe in the 1920’s, and it led to some pretty authoritarian governments that were known for their right-wing views and intolerance. If you want to know more about the deeper implications of fascism, read some history.
40. Fatuous
A fatuous comment is silly, inane, or just plain stupid. Save this remark for someone who really deserves it, and serve it up cold.
41. Fiduciary
If you encounter this word, it will be in a legal context. It is the term used to describe a trustee who takes care of assets on behalf of one or more beneficiaries.
42. Filibuster
The filibuster is a person who uses a dirty, time-wasting trick to hold up a legislative decision. Without breaking any rules, the filibuster speaks at great length without saying anything useful. The word comes from the old English for “pirate,” and it is not a good thing to be.
43. Fulminate
Let’s use an example: your teacher tells the class that the holiday assignment is a 10,000-word essay. After class, everyone discusses how furious they are, how unfair it is, and so on. They are, in fact, fulminating.
44. Hegemony
Ever since people first got together to live in cities, there have been groups of citizens with differing cultural or social backgrounds. When one group politically dominates all the others, it is called a “hegemony,” and the term can be applied to any form of government that fits the description.
45. Heuristic
If someone once helped you to work something out for yourself, he or she used a heuristic teaching method. You could call it “hands on” learning, but nobody shows you what to do. They just show you how to figure it out, and you get to feel great when you get it right.
46. Holistic
The simplest definition for this would be to say that holism considers various factors that influence each other, and not just one factor, influence or symptom in isolation. The term is most commonly used in philosophy and medicine, but it is getting quite commercialized, and is sometimes used elsewhere too.
47. Homonym
When two words are spelled the same, are pronounced the same, but have different meanings, they are homonyms. For instance, “The man standing beside the pole is a Pole.”
48. Hubris
In Greek mythology, hubris was a state in which mankind defied the gods or thought itself better than the gods. Dreadful consequences predictably followed. Today, it means excessive pride or confidence that could lead to terrible consequences.
49. Incisive
Have you ever tried to explain how you feel about something at length only for your listener to sum it all up in a sentence or two? That’s incisive thinking. It gets to the heart of the matter quickly, showing great insight.
50. Incognito
Are you mysterious? Then you may like being incognito – using another identity or concealing your own identity in some other way.
51. Inculcate
This means teaching someone a principle or habit in such a way that the lesson is fully ingrained and adopted.
52. Interpolate
Interpolating something means inserting it between fixed points. The word is often used to indicate that something has been added to a book or text. Perhaps there are images, or perhaps a third party has added information. It can also be an interruption when someone is talking.
53. Irony
Too easy? Nevertheless, this word is often incorrectly used. Irony means saying the opposite of what you mean for effect. Sometimes, events can be ironic for the same reason: they seem to contradict each other. Many people confuse it with sarcasm.
54. Juxtaposition
When two contrasting situations or thoughts are compared for effect, we have a juxtaposition. It’s a useful technique in both creative and factual writing.
55. Jejune
If someone presents you with a naïve point of view, seems to be oversimplifying, or has only superficial knowledge, you can use this word, both to describe their efforts, and to baffle them.
56. Lionize
When you treat someone as if they were a celebrity, then you are lionizing them. Sometimes, we do this out of genuine respect for what they do, but sometimes, people do it to gain favor.
57. Lucubration
The word “lucubration” could be used to indicate something that has been given a lot of study and deep thought, but it’s also a rather rude way of describing a piece of writing that seems terribly pedantic and overelaborate.
58. Malapropism
The word “malapropism” was coined thanks to a 1755 play by Richard Sheridan. Mrs. Malaprop would often replace words with similar sounding ones with amusing results. If you talk about having “danced the flamingo” you are guilty of a malapropism.
59. Magnanimous
When someone is very generous or forgiving to someone in a less powerful positon, you can call him or her “magnanimous.” It’s a form of generosity that isn’t really necessary, but that shows kindness.
60. Mnemonic
When you use a combination of letters, a rhyme, or a set of associated things to remember a list of names or facts, you are using mnemonics.
61. Motif
A motif could be something as simple as a design on a Tee shirt, or it can be a theme in writing or music. A leitmotif is a “leading motif” that is one of several motifs, but is dominant. In music, it could be a theme tune associated with a particular character.
62. Moiety
In anthropology, this term relates to the groups into which people are divided during important rituals, but it has also come to mean a share, particularly a lesser one.
63. Nihilism
“Nothing matters, everything is trivial, even existence is questionable and could be an illusion. There is no God, and nothing has any importance.” If this depressing philosophy appeals to you, you are a nihilist.
64. Nomenclature
A nomenclature is a system designed for naming things. It could be a set of terminology, a term, or it could refer to a scientific naming system such as that used to identify all living things with two Latin names.
65. Nemesis
You don’t want to meet this person or circumstance. It is an “inescapable agent” that leads to your downfall.
66. Obfuscate
Scenario: you have just been to class. Your teacher has explained something at length in terms that have left you totally confused. Scenario two: you ask a friend why they did something you don’t quite approve of, and they give you a long story that leaves you feeling baffled. Words can be used to clarify, or they can be used to obfuscate facts.
67. Obsequious
People are bowing and scraping and offering every possible tribute to someone in power. You have a feeling they’re being obsequious because of the servile degree of attention they are giving.
68. Oligarchy
A small group of people with very similar interests have absolute control over the destiny of a country or an institution. Does that sound scary? Now you know what to call it!
69. Onomatopoeia
“Bang! Crash! Zoink. Kerflabaflabaflaba!” Words that are meant to imitate sounds are examples of onomatopoeia.
70. Ontology
What is the metaphysical nature of being? Do you have an opinion? That’s ontology! Don’t even ask me about mine…
71. Orthography
How are words spelled? That’s orthography right there!
72. Oxymoron
I’m sure you know a few phrases that are contradictions in terms. Some say that “military intelligence” is one of them. Which oxymoron is your favorite?
73. Paradigm
If you go into business, you will hear this word rather a lot. It means a model that governs the way things are done, and they’ll usually be telling you that you need to shift it, or that there is a new one.
74. Paucity
When there is too little of anything, you are suffering a paucity of it. It’s most often used in relation to facts, but it works just as well and even more uncomfortably with funds.
75. Pecuniary
How remarkable that this word should follow my last incisive remark! Pecuniary considerations are about money. Please do not use them as the sole basis for choosing a career. You will be unhappy, but will have achieved pecuniary gain.
76. Pedantic
Sometimes, it’s good to be fussy or finicky about the way you present information, but if you go too far with it, people will call you “pedantic.”
77. Pedagogy
Pedagogy is teaching, and a pedagogue is a teacher, but this old-fashioned word is often used negatively to describe someone who teaches rather boringly.
78. Pejorative
If you’re inclined to disapprove or disparage something, you are being pejorative. Pejorative words express disapproval.
79. Phonemes
Phonemes are letters that distinguish very similar words from one another. For instance, “pad, pat, bad and bat” are distinguished from each other by phonemes.
80. Plagiarism
As a student, you need to understand plagiarism and know how to avoid it. If you were to copy whole passages from someone else’s work, that’s plagiarism. Of course, plagiarism is something to be avoided whenever you are supposed to be producing original work.
81. Proletariat
If you are an average working class person, you are a member of the proletariat. The word was extensively used in Marxist philosophy, but now it’s fair game for anyone to use.
82. Prolix
When someone calls your written work “prolix,” you should not congratulate yourself. It means you have presented it in an overly complicated, wordy, or rambling fashion. It’s also a great scrabble word. Just imagine the score if you hit “triple word score” with it!
83. Pusillanimous
Cowards, the lily-livered and the generally timid may be deserving of a suitably disparaging adjective. This is it.
84. Quotidian
You could use this word to describe something that is mundane or that happens every day. If you’re looking for a synonym, try “everyday” for size. In medicine, it is used to describe a particularly nasty form of malaria.
85. Reify
Never let it be said that we only looked at long words. This one means turning something abstract into something more real and easier to understand.
86. Rubric
There are three meanings for this word. It could be a statement of purpose or function, a simple heading at the top of a document, or a note in a liturgical book indicating how a ceremony should be performed.
87. Sanguine
I like people with a sanguine disposition. They are upbeat and optimistic. You can, for example, be sanguine about the future, your economic prospects, and so on. Of course, that doesn’t necessarily mean you are being realistic!
88. Scurrilous
Being scurrilous could mean everything from being humorously insulting to being downright libelous and spreading nasty rumors.
89. Sesquipedalian
What could be better than a really long word to describe the use of long words? I have to admit, this is one of my favorites, simply because it seems so appropriate, and rather funny.
90. Soliloquy
Nowadays, if you were to talk to yourself about what your thoughts and feelings, people would think you had gone mad. Nevertheless, the soliloquy has been widely used in drama to give audiences an insight into the character’s thoughts.
91. Tautology
There are two ways to use this word. A tautology could be an unnecessary repetition – repeating the same idea using different words. It could also be used to describe logic that is undeniably correct and proves a truth.
92. Temerity
When you need a word to describe an action that is outrageously cheeky or audacious, this word is perfect for the job, “He had the temerity to decide I wouldn’t mind him copying my work.”
93. Ubiquitous
Anything that is everywhere to be found or seems to be so is “ubiquitous.” “Text speak is becoming so ubiquitous that it may soon be accepted in business letters.”
94. Umami
Your tongue can identify a number of flavors. Umami is a meaty flavor that is not sweet, sour, or salty.
95. Vernacular
The language you speak at home, or the one spoken by a specific group of people in a country or region is its vernacular language. It also refers to architecture that focuses on what is functional.
96. Verisimilitude
Is something real? Is it true? Are you unsure? Then you are doubting its verisimilitude. This word is handy because it combines the concepts of truth and reality.
97. Vitriolic
When people are vitriolic, I either find it very funny (which they don’t intend) or annoying. Vitriolic speech or writing is bitter, caustic and acerbic.
98. Ultracrepidarian
Do you know someone who always has advice for you no matter how little knowledge he or she has? Now you have the right word to describe this person!
99. Unctuous
It’s usually very nice when people admire you, but sometimes you get the feeling that a person is being oily or insincere, and just wants to get into your good books. When this happens, you have just been the object of unctuous behavior.
100. Uxorious
When a man is overly submissive towards his wife, he can be described as “uxorious.” Of course, she might just say that’s just how it should be!
And here are four bonus words:
101. Vacuity
“I admire your vacuity,” he said. “Why, thank you,” she replied, proving the point. Vacuity is empty-headedness and a lack of intelligence.
102. Xeric
Generally, when we see the prefix “Xero” or “Xer” we can associate the word that it introduces with something very dry. A xeric life form can tolerate, and even prefers very dry conditions, and a xerophyte, is a plant that tolerates extremely dry environments.
103. Zymurgy
This is a very helpful scrabble word, but what does it mean? Zymurgy is the art of brewing, wine-making or distilling.
104. Zephyr
A zephyr is a pleasant, light breeze that you’d welcome on a hot summer day. “A passing zephyr rustled through the treetops.” Ah! Poetic!
These examples may contain rude words based on your search.
These examples may contain colloquial words based on your search.
Suggestions
You should know the limits of your equipment.
Независимо от этого, вы должны знать верхний предел вашего оборудования.
You should know there are differences, however.
You should know what I sound like when I…
You should know we slept together.
You should know, the process may change him… somewhat.
Вам следует знать, что во время лечения он может измениться… некоторым образом.
You should know, the process may change him… somewhat.
Вам следует знать, что процесс… может неким образом… изменить его.
You should know what people eat and how they prefer doing it.
Вы должны знать, что люди едят, и как они предпочитают это делать.
You should know I find post hoc negotiation distasteful.
Вы должны знать, что я нахожу переговоры постфактум… неприятными.
You should know your patrons better than anyone else.
Вы должны знать своих заказчиков лучше, чем кто бы то ни было.
You should know more about this little than anybody else.
Вы должны знать больше, чем кто-либо еще знает об этом немногом.
You should know when to stop planning and start doing.
Вы должны знать, когда прекратить думать и начать машинально выполнять удары.
You should know exactly how many competitors you have.
Вы должны знать, с каким количеством конкурентом вам придется столкнуться.
You should know how photons react with different structures.
Вы должны знать, как ведут себя спектроанализаторы разного типа строения.
You should know it never goes their way.
7 Things You should know when planning a…
You should know how to deal with these people.
You should know time moves much faster where your friends are.
Ты должна знать, что время течет гораздо быстрее там, где находятся твои друзья.
You should know, you married her.
You should know your boyfriend has some nasty enemies.
You should know better, but no.
Suggestions that contain You should know
Results: 5412. Exact: 5412. Elapsed time: 496 ms.
Documents
Corporate solutions
Conjugation
Synonyms
Grammar Check
Help & about
Word index: 1-300, 301-600, 601-900
Expression index: 1-400, 401-800, 801-1200
Phrase index: 1-400, 401-800, 801-1200
I mean, you should know who I am,
you
kissed me twice.
Я имею в виду, тебе стоит знать, кто я,
ты
поцеловала меня дважды.
What you should know about this villa.
Что Вам нужно знать о данном объекте недвижимости.
There are a few more things you should know about images.
Вам необходимо знать еще две вещи.
Well, about that, you should know that Daddy cancels his party every year.
Да, насчет этого, тебе стоит знать, что папа отменяет свою вечеринку каждый год.
The first thing you should know about me is that I’m a whore.
Первое, что вам необходимо знать обо мне, это то, что я шлюха.
People also translate
thought
you
should
know
then
you
should
know
you
should
know
how
things
you
should
know
you
should
know
better
so
you
should
know
What you should know about this apartment.
Что Вам нужно знать о данном объекте недвижимости.
Jimmy, there’s something you should know before
you
leave.
Джимми, ты должен узнать кое-что, перед тем, как уедешь.
I think you should know that I’m thinking about marrying Adrian.
Думаю тебе стоит знать что я собираюсь жениться на Эдриан.
Yes. But I thought you should know before the press conference.
Да, но решила, что ты должен узнать до пресс-конференции.
You should know that it is my job to direct the team while solving a case.
Вам необходимо знать, что именно я руковожу командой во время расследования.
you
should
always
know
you
should
just
know
you
should
know
when
you
know
,
you
should
You should know I’m an atheist, so swearing isn’t.
Тебе стоит знать, что я атеистка, поэтому клятва.
I’m sorry that I walked out of dinner, but you should know the reason why.
Прости, что я ушла с ужина, но ты должен узнать, почему.
First of all, I think you should know that I’m having a little get-together.
Во-первых, думаю, тебе стоит знать, что у меня будет небольшая вечеринка.
Some important information that you should know about the use of cookie files 1.
Немного важной информации, которую Вам необходимо знать для использования файлов» Куки» 1.
But you should know, you’re our only lead.
Но вам нужно знать, что
вы
наша единственная зацепка.
I thought you should know that.
Я думаю, вам надо знать, что.
I think you should know Reddington reached out to Agent Keen.
Думаю, Вам надо знать, что Реддингтон связался с агентом Кин.
Well, then, I guess you should know what that means.
Значит, тогда ты должен понимать, что это значит.
There’s probably a few things you should know about me.
Вообще-то есть несколько вещей, которые вам необходимо знать обо мне.
John, before
you
go, you should know.
Перед тем, как
ты
уйдешь, Джон, ты должен узнать.
I just thought you should know of certain potentialities.
Я подумал, что вам нужно знать и о других возможностях.
Maybe you should know me well enough to let it go.
Может тебе следует узнать меня лучше, чтобы отпустить это.
I think you should know what
you
stand for, not just what you’re against.
Думаю, ты должен понимать, за что
ты
борешься, не только- против чего.
You should know that there’s a flip side to this,
Вам надо знать, что есть и другая опасность.
Well, you should know.
Ну тебе лучше знать.
But there are things you should know.
Но есть вещи, которые вам необходимо знать.
No, no, I just thought you should know first.
Нет, нет, я просто подумал, что ты должен узнать первым.
I just told the two of you’cause I figured you should know.
Я просто рассказала
вам,
потому что вам надо знать.
I thought you should know that.
Я подумал, что ты должен узнать.
Basic Facts you should know: Jerusalem Archived January 4,
2013, at the Wayback Machine, Anti-Defamation League, 2007.
Basic Facts you should know: Jerusalem Архивировано 4 января 2013 года.,
Антидиффамационная лига, 2007.
If you want to learn a language, the way to start is by building up a mental “dictionary” of basic words – this is true if
you want to learn English.
While it may sound boring at first, building up a basic English dictionary in your head is the first step to learning enough English to have a conversation.
If you don’t know enough simple English words for daily use, you won’t be able to ask questions and understand the answers.
You also will not be able to convey thoughts or emotions.
Tips For Learning Basic English Words
A quick Google search should provide you with lists of daily use English words with meaning.
Looking through and memorizing these 20 to 100
English words for beginners will help you learn enough to build up your vocabulary enough to have a conversation.
Try reciting the words aloud over and over for yourself.
One of the most efficient ways to learn English words for beginners, however, has got to be to look at lists of basic English words with pictures.
Try and find picture books or other materials for learning basic English words for kids.
Being able to see a picture of what
a basic English word is supposed to means is a great way to imprint it into your memory.
90 Basic English Words That Every English Learner Should Know
Here is our own list of some basic words you should get to know.
There’s also a downloadable PDF file with all these words waiting for you in the end. Let’s dive in!
1. Hello
This is a basic greeting.
2. Goodbye
This is what you say when you are leaving.
3. Yes
This is a word that you say when you agree with something someone has said.
4. No
This is a word that means you disagree with something someone has said.
5. Please
This is a polite way to call someone’s attention. When you are asking someone for a favor you should say “please.”
6. Thank you
When someone does something for you, this is the polite response.
7. Help
If you need someone to do something for you because you can’t do it yourself, you ask for help. If you are in trouble, you should yell “Help!”
8. Sorry
This is what you say if you’ve done something wrong to someone. You can also use it to ask for their attention or interrupt them.
9. Person and People
This is a word that is used when you are talking about humans. A “person” is the singular form, what you use when referring to an individual. “People” is what you call a group.
10. Man and Men
A man is a person who is male. Meanwhile, a group of people who are male are men.
11. Woman and Women
A woman is a person who is female. A group of people who are female are women.
12. He or Him
These are used to refer to a male person. The words “person” or “man” are nouns. “He” and “Him” are pronouns which is a shorter word that is use in place of a noun.
13. She or Her
These are pronouns that are used to refer to a female person. You can use these in place of “woman”.
14. They or Them
These are gender neutral pronouns that you can use to refer to people.
15. I
This is a pronoun you can use to refer to yourself.
16. Me
This is a word you can use to refer to yourself.
17. Mine
This is a word that indicates possession. If you say something in “mine” you are saying it belongs to you.
18. You
This is a gender neutral pronoun that you can use to refer to another person. This is usually what you use when talking directly to someone.
19. We
This is a pronoun that you can use to refer to yourself and other people as a group or collective.
20. Child and Children
These are gender neutral terms that mean a young human or person. A “child” is one young human, while “children” refers to a group of young humans. If someone is below the age of puberty or not yet of legal age, they are usually considered a child.
21. Teenager
If a young human is above the age of puberty, they are referred to as a teenager.
22. Boy
A child or teenager who is male can be called a boy.
23. Girl
A child or teenager who is female can be called a girl.
24. Parent
A parent is someone who takes care of a child. Often this is a blood relation of the child.
25. Father
A father is the male parent
26. Mother
A mother is the female parent.
27. Son
Male offspring.
28. Daughter
Female offspring.
29. Brother
Someone who has the same parent as someone else. If there is more than one male offspring, they will refer to each other as “brother”.
30. Sister
Someone who has the same parent as someone else. If there is more than one female offspring, they will refer to each other as “sister”
31. Thing
An object that is not alive.
32. Animal
A living being that is not human.
33. Plant
A living thing that grows on the earth.
34. This and That
These are pronouns used to refer to things. They can also be used to refer to living things that are not human.
36. These and Those
These are other pronouns used to refer to things. They can also be used to refer to living things that are not human.
37. It
Another pronoun that can be used to refer to things or living things that is not human.
38. Time
This is a concept which means a measurable period when an action happens.
39. Hour
This is a specific unit of time.
40. Day
Can either mean 24 hours of time or the time when the sun is in the sky.
41. Night
The period of time when the sun in not in the sky.
42. When
This is an interrogative word, which is a word that asks a question. When you ask “when” you are looking to know a specific unit of time.
43. Who
This is an interrogative pronoun. The answer to the question “who” refers to a specific person.
44. What
This is an interrogative pronoun. When you ask “what” you are asking about a particular thing.
45. Why
This is an interrogative pronoun. When you ask “why” you are questioning the reason behind a certain action.
46. Place
This means a venue or address where you are, where another person or object is, or where an action or event is taking place.
47. Where
This is an interrogative pronoun. Where you ask “Where” you are asking about a specific place. Often the answer is a specific place at a specific time and date.
48. Here
This refers to the present location. When you are “here”, it refers to where you are at present.
49. Now
This is a word that means the present time. When you say you are somewhere “now”, it is your present location.
50. Later
This word refers to a future time. When you say you will be somewhere “later”, it refers to your location in the near future.
51. From
When you say something is “from” somewhere, you are talking about where it was before it came to its present location.
52. Building
This is a man-made structure, usually consisting of walls, a floor, and a roof.
53. Home
This is a building that is used as by people or a group of people as a residence. Where they eat and sleep on a daily basis.
54. Store
This is a building where good and services are available for sale.
55. Restaurant
This is a building where meals are available for sale. The meals can be eaten there.
56. Eat
This is the act of taking in food or having a meal.
57. Drink
This is the act of taking in liquids.
58. Breakfast
This is a meal that is taken in the morning. Breakfast is usually the first meal of the day.
59. Lunch
This is the meal that is usually taken around mid-day.
60. Dinner
This is a meal that is taken in the evening. It is usually the last meal of the day.
61. Before
This is a word that refers to the past.
62. After
This is a word that refers to a period of time that occurs after an event.
63. To
This is a word that refers to movement. When you go “to” something you are moving closer to it.
64. School
This is a building where education takes place. People gather at a school to either teach of learn lessons.
65. Student
This refers to someone who goes to school to learn. Gender neutral and can be used to refer to an adult, a child, or a teenager.
66. Teacher
This is someone who goes to school to teach students. Gender neutral and usually meant to refer to an adult.
67. Have
This is a verb, which is an action word. “Have” means something you hold.
68. Go
This is another verb. When you or someone “go” you are moving towards something.
69. Do
This is a verb. When you “do” something, you are performing an action.
70. Get
This is a verb. When you or someone else “get” something, you move towards it and hold it.
71. See
This is a verb that refers to vision. If you lay eyes on something, you see it.
72. Smell
This is a verb that refers to odor. When you smell something, you are using your nose.
73. Sound
This is a verb that refers to hearing. You hear a sound.
74. Taste
When you taste something, you know its flavor.
75. Touch
When you touch something, you feel it. Usually with your hands, but if almost anything touches your skin, you will feel its “touch”.
76. Know
When you “know” something, you understand it.
77. Make
This is a verb that refers to creation. When you “make” something, you create it.
78. Come
This is a verb that refers to a future action. When you say you will “come” you are saying that you will be at a venue at a specific time, usually this is sometime in the near future.
79. Use
When you perform an action with something, you use it.
80. With
When you are with someone or something, they or it are with you physically. You are in the same place at the same time.
81. Want
When you want something you desire to have it.
82. For
When you say something if for someone, you are indicating that they possess it.
83. Buy
When you buy something, you give someone else money in order to posses it.
84. Sell
This refers to someone being willing to take money in exchange for an object they posses.
85. Hurt
This refers to feeling bad or being in pain due to an accident.
86. Sick
This refers to feeling bad and maybe being in pain due to illness
87. Doctor
This is someone you should see if you are feeling ill.
89. Hospital
This is a building where you will find a doctor and where you will be taken if you are hurt in an accident.
90. Police
This is a government mandated entity who is supposed to keep peace and security. If you need help you can ask for the police.
Conclusion
While it is possible to
expand your vocabulary by memorizing lists like this, you will still need to know how to use them properly in a conversation. To do so, you need to practice putting the words together and saying them to a native speakers.
This is where and why you need to find a good native English speaking tutor.
Download the PDF file with 90 basic English words below:
90_Basic_English_Words_PDF_List

By
Last updated:
July 26, 2022
15+ Quick English Filler Words You’ll Thank Yourself for Learning
“English is like, totally fun to learn, you know?”
If you take out the words “like,” “totally” and “you know” from that sentence, you’re left with a perfectly understandable sentence: English is fun to learn.
Those words like “totally” and phrases like “you know” are called filler words, and you’ll hear them sometimes in casual English conversations.
That’s why we’ve put together a list of 15+ English filler words which will make you sound like a native speaker.
Contents
- What Are Filler Words?
- When Are Filler Words Used in English?
- Why Should You Learn English Filler Words?
- Use Filler Words in Moderation
- 15+ Common English Filler Words You Should Know
-
- 1. Well
- 2. Um/er/uh
- 3. Hmm
- 4. Like
- 5. Actually/Basically/Seriously
- 6. You see
- 7. You know
- 8. I mean
- 9. You know what I mean?
- 10. At the end of the day
- 11. Believe me
- 12. I guess/I suppose
- 13. Or something
- 14. Okay/so
- 15. Right/mhm/uh huh
Download:
This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you
can take anywhere.
Click here to get a copy. (Download)
What Are Filler Words?
Filler words are words (and phrases) that are used to fill silence when you’re speaking. They’re words that don’t add any real value to the sentence. They simply keep you going while you come up with the rest of your sentence.
Their actual name is “discourse markers,” but they’re much more commonly known as “filler words.”
You might already use filler words without realizing it. When you can’t think of the right word to use in a sentence, you might say “umm.” This gives you a break while you think, without an awkward, silent pause.
Since filler words don’t really add any meaning to the sentence, you don’t need to think about using them. This leaves your brain free to think of other things—like the word you’re trying to remember.
Many filler words actually have other meanings, so not every “like,” for example, is a filler word. We can see a real example of this in the following conversation from the show “Community,” when Pierce tries to stop Shirley from using filler words:
Shirley: Okay. These brownies are, uh—
Pierce: Uh!
Shirley: They, um—
Pierce: Um!
Shirley: These brownies are delicious. They taste like–
Pierce: Like!
Shirley: That’s not a filler word.
One way to finish Shirley’s sentence would be, “They taste like heaven.” In this example, “like” is used to compare brownies to heaven, so it’s not a filler word in this context.
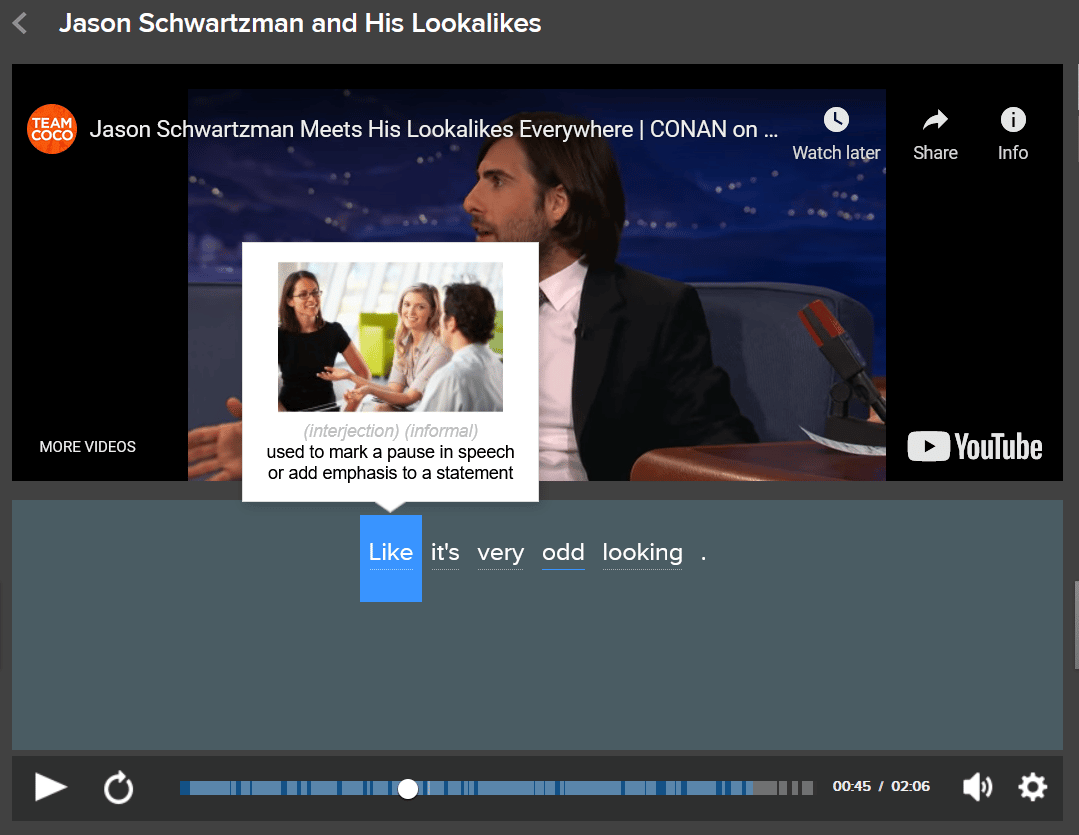
Another example of fillers being used can be seen in this clip of Jason Schwartzman talking to Conan O’Brien on FluentU.
If you hover over the word “like” in that clip (or any other time Jason uses it in the same way, which is often), you’ll see that in this case it’s being used as a filler word. Click on it and the video will pause, showing you a flashcard with example sentences, audio and a definition that all show you the word as a filler.
Plus, you can watch clips from other videos on FluentU where the word is used the same way. Click the arrows to the left or right to move between video examples.
You can find many more filler words and other real, non-textbook English on FluentU, as well as its iOS and Android apps. That’s because the program uses authentic (real, natural) videos of native English, like movie trailers, news segments, interviews, music videos, funny vlogs, commercials and much more.
When Are Filler Words Used in English?
You only need to use filler words when you’re speaking out loud. Generally you won’t use fillers when you’re writing. When you’re speaking out loud, though, you might need some extra time to figure out what to say. That’s when you can use filler words.
Sometimes people use certain filler words (“like,” “literally” or “believe me”) when they’re writing online in website comments, chats or social media. This is fine too, since conversations online are very similar to spoken conversations.
Filler words are used for a number of reasons:
- To show that you’re thinking. Use filler words when you need to think about your answer or statement. For example:
“I have basically… ten more years of college.”
- To make a statement less harsh. When your friend has some broccoli stuck between his teeth, you could just tell him, “You have something in your teeth,” but that might make him embarrassed. It might be nicer to say something more like:
“Well, you have, um, you have a little something in your teeth.”
- To make your statement weaker or stronger. While filler words don’t add anything to sentences, they can be used to change the sentence tone—the attitude of the sentence. See how different these three statements sound:
“I think pugs are cute” is just a regular statement.
“Actually, I think pugs are cute” shows contrast—that someone else doesn’t agree.
“At the end of the day, I think pugs are cute” is something you might say as a conclusion to a discussion about pugs and their ugly (or cute!) wrinkles.
- To stall for time. To stall for time means to do something to try and gain more time. Filler words are an excellent way to stall when you don’t know how to answer a question, or when you don’t want to. For example, if your teacher asks you “Where’s your homework?,” your response might sound a bit like this:
“Uhh. Umm. Well, you see.. My dog ate it.”
- To include the listener in the conversation without ending your sentence. A conversation takes at least two people. Some filler words and phrases can include the other person in the conversation. It’s a bit like reaching out to them as you’re speaking to keep their attention. For example:
“It was a really big bear, you know?”
This sentence includes the listener without ending your speaking turn. Your listener might nod in agreement, allowing you to continue telling him about your pet bear.
Even if you’re just starting to learn English, filler words can make you sound more like an advanced English learner. As you can see, filler words seem useless at first, but they can be really important!
When you think of someone as being a fluent English speaker, you probably think they speak perfectly without stopping. In reality, even native English speakers use filler words, and they use them often. These words are an important part of sounding natural when you speak English.
You’re allowed to pause and think, to be unsure of how to answer, or even to forget the right word to use. The trick is knowing the right filler words to use while you put your thoughts together.
Every language has its own set of filler words. Learning English filler words will help you sound more like a native speaker.
Use Filler Words in Moderation
Like with anything else, you could use filler words too much. Overusing filler words (using too many, too often) can make you sound unprofessional. Even worse, it can make it difficult to follow your sentences. So do use filler words when you speak, but don’t use them too much.
Some people think all filler words are bad, and should be used as little as possible. For an English learner, though, they can be a very helpful way to speak more fluently and confidently. Still, it’s a good idea to use as few filler words as possible in interviews and professional settings.
If you find yourself using too many filler words when you speak, it might be time to either study some more vocabulary or slow down your speech.
With all that in mind, here are some of the most common filler words and phrases used in American English:
15+ Common English Filler Words You Should Know
1. Well
“Well” can be used in a few different ways. You can use it to show that you’re thinking.
“Well, I guess $20 is a good price for a pair of jeans.”
You can also use it to put a pause in a sentence.
“The apples and cinnamon go together like, well, apples and cinnamon.”
You can even use the word to stall.
“Well… fine, you can borrow my car.”
2. Um/er/uh
“Um,” “er” and “uh” are mostly used for hesitation, such as when you don’t know the answer or don’t want to answer.
“Um, er, I uh thought the project was due tomorrow, not today.”
You can use any of the words at any time—they don’t all have to go together.
“Umm… I like the yellow dress better!”
3. Hmm
“Hmm” is a thoughtful sound, and it shows that you’re thinking or trying to decide something.
“Hmm, I like the pink bag but I think I’ll buy the black one instead.”
4. Like
“Like” is sometimes used to mean something is not exact.
“My neighbor has like ten dogs.”
In the above example, the neighbor probably doesn’t have exactly ten dogs. Rather, the neighbor has a lot of dogs.
Usually, though, the word is used when you need a moment to figure out the next word to use.
“My friend was like, completely ready to like kick me out of the car if I didn’t stop using the word ‘like’.”
Keep in mind that the word “like” as a filler is seen as a negative thing. The word is often overused by young females, and can make you sound like you’re not sure what you’re talking about.
5. Actually/Basically/Seriously
“Actually,” “basically” and “seriously” are all adverbs—words that describe actions. Many adverbs (though not all of them) have an “-ly” at the end of the word, which makes it easier to recognize them. All these words can be used as fillers which change the strength of a statement.
For example, the word “actually” is used to point out something you think is true, when others might not agree:
“Actually, pugs are really cute!”
“Basically” and “seriously” change the sentence in slightly different ways too. “Basically” is used when you’re summarizing something, and “seriously” is used to show how strongly you take the statement.
“Basically, the last Batman movie was seriously exciting!”
Other adverbs that are often used as fillers are “totally,” “literally” and “clearly.”
- The word “literally” means “something that is true,” but many times in conversation it’s used with a different meaning: to state strong feelings. For example, you’re not just laughing you’re literally dying from laughter.
- “Totally” means “completely,” and is used to emphasize (show that you feel strongly) about something.
- The word “clearly” means the same as obviously, and is used to state something that is very obviously true.
These three words don’t have to be used together either, but here they are in one sentence:
“Clearly you totally didn’t see me, even though I was literally in front of your face.”
6. You see
“You see” is used to share a fact that you assume the listener doesn’t know.
“I was going to try the app, but you see, I ran out of space on my phone.”
7. You know
“You know” is used to share something that you assume the listener already knows.
“We stayed at that hotel, you know, the one down the street from Times Square.”
It can also be used instead of an explanation, in cases where we feel the listener just understands what you mean.
“When the elevator went down, I got that weird feeling in my ears, you know?”
8. I mean
“I mean” is used to clarify or emphasize how you feel about something.
“I mean, he’s a great guy, I’m just not sure if he’s a good doctor.”
It’s also used to make corrections when you misspeak.
“The duck and the tiger were awesome but scary. I mean, the tiger was scary, not the duck.”
“The cave is two thousand—I mean—twenty thousand years old!”
9. You know what I mean?
“You know what I mean?” is used to make sure the listener is following what you’re saying.
“I really like that girl, you know what I mean?”
10. At the end of the day
“At the end of the day” is a phrase that means “in the end” or “in conclusion.”
“At the end of the day, we’re all just humans, and we all make mistakes.”
11. Believe me
“Believe me” is a way of asking your listener to trust what you’re saying.
“Believe me, I didn’t want this tiny house, but it was the only one I could afford.”
It’s also used to emphasize what you’re about to say.
“Believe me, this is the cheapest, tiniest house ever!”
12. I guess/I suppose
“I guess” and “I suppose” are used to show that you’re hesitant, or not really sure about what you’re saying.
“I was going to eat dinner at home, but I guess I can go eat at a restaurant instead.”
“I guess” is used more often in speech, but “I suppose” can sound classier (a bit smarter).
13. Or something
“Or something” is a sentence ending that means you’re not being exact.
“The cake uses two sticks of butter and ten eggs, or something like that.”
14. Okay/so
“Okay” and “so” are usually used to start sentences, and can be a sign that a new topic is starting.
“So what are you doing next weekend?”
They can also be used to introduce a summary.
“Okay, so we’re going to need to buy supplies for our trip this weekend.”
15. Right/mhm/uh huh
“Right,” “mhm” and “uh huh” are all affirmative responses—they all mean a “yes” response.
“Right, so let’s prepare a list of all the things we’ll need.”
“Uh huh, that’s exactly what he told me too.”
Right, so you should be an expert on filler words by now! Some of these words and phrases can be hard to use correctly, since the meaning is so flexible.
So now you may be wondering: how can I practice using filler words?
To get a deeper sense of how to use these, you should watch English videos. In general, videos made for English speakers are helpful in showing “real” speech. Plus, with videos, you get to see and hear how filler words work in different sentences in different situations.
Movies and TV shows are two great examples. If you have any favorite English shows, watch them again but this time, really pay attention to how the characters talk. See how many filler words you can hear!
Filler words can require a lot of subtlety, but master them and you will be sounding like a native speaker in literally no time.
Download:
This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you
can take anywhere.
Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Building your vocabulary with some of the most common words used in the English language is a great start for your journey in learning this beautiful language.
Not only do these common words expand the English terminology that you know, but they also help you with your English conversation skills since they are indeed words that you hear others use everyday.
If you know 1,000 words, you will be between a functional beginner and conversational level in English. In most of the world’s languages, 500 words will be more than enough to get you through any tourist situations and everyday introductions.
Using everyday common words are the most convenient way to learn English. The more you hear these words, the better it is for you to process and understand them.
And the more you use them, the stronger your English skills become. So it’s a great process of learning from others, and at the same time, learning from yourself, too!
Okay, time to share the list! Remember that with these 1,000 words you’ll be able to ask people how they’re doing, tell them about your day and navigate everyday life situations like shopping and public transit. But also keep in mind that native-like fluency, among many other things, requires about 10,000 vocabulary words.
be – “Will you be my friend?”
and – “You and I will always be friends.”
of – “Today is the first of November.”
a – “I saw a bear today.”
in – “She is in her room.”
to – “Let’s go to the park.”
have – “I have a few questions.”
too – “I like her too.”
it – “It is sunny outside.”
I – “I really like it here.”
that – “That door is open.”
for – “This letter is for you.”
you – “You are really nice.”
he – “He is my brother.”
with – “I want to go with you.”
on – “I watch movies on my iPad.”
do – “What will you do now?”
say – “Can I say something?”
this – “This is my favorite cookie.”
they – “They are here!”
at – “Can you pick me up at the mall?”
but – “I’m sorry but she’s away.”
we – “We are going to watch a movie.”
his – “This is his box.”
from – “This card came from my cousin.”
that – “That’s a really cool trick!”
not – “That’s not what I want.”
can’t – “I can’t open it.”
won’t – “I won’t open it.”
by – “Will you come by and see me?”
she – “She is very happy.”
or – “Do you like blue or yellow?”
as – “Her role as an English teacher is very important.”
what – “What are you thinking of?”
go – “I want to go there.”
their – “This is their house.”
can – “What can I do for you?”
who – “Who can help me?”
get – “Can you get me my eyeglasses?”
if – “What if I fail?”
would – “Would you help me out?”
her – “I have her book.”
all – “All my favorite books are on this shelf.”
my – “My mom is coming to visit.”
make – “Can we make our projects together?”
about – “What is this movie about?”
know – “Do you know where this place is?”
will – “I will help you find that place.”
as – “As soon as she’s here, I’ll talk to her.”
up – “I live up in the mountains.”
one – “She is one of my English teachers.”
time – “There was a time I liked to play golf.”
there – “There are so many things I want to learn.”
year – “This is the year I’m finally going to learn English.”
so – “I am so sorry.”
think – “I think I need to lie down.”
when – “When will I see you again?”
which – “Which of these slippers are yours?”
them – “Please give this to them.”
some – “Please give them some of the apples I brought home.”
me – “Can you give me some apples?”
people – “There are so many people at the mall today.”
take – “Please take home some of these apples”
out – “Please throw the trash out.”
into – “My puppy ran into the woods.”
just – “Just close your eyes.”
see – “Did you see that?”
him – “I heard him singing earlier.”
your – “Your mom is here.”
come – “Can your mom and dad come to the party?”
could – “Could you help me with my project?”
now – “I want to watch this now.”
than – “I like this cake better than the other one you showed me.”
like – “I like this bag better than the other one you showed me.”
other – “I like these shoes better than the other ones you showed me.”
how – “How do I turn this on?”
then – “We had breakfast and then we went to church.”
its – “I need to read its manual.”
our – “This is our home now.”
two – “Two cheeseburgers, please.”
more – “Can I have some more milk shake?”
these – “Do you like these ribbons?”
want – “Do you want these ribbons?”
way – “Can you look this way?”
look – “Please look this way.”
first – “She was my very first teacher.”
also – “She was also my best friend.”
new – “I have new shoes.”
because – “I am crying because I’m sad.”
day – “Today is National Friendship day.”
more – “I have more stickers at home.”
use – “How do I use this?”
no – “There’s no electricity now.”
man – “There’s a man outside looking for you.”
find – “Where can I find rare furniture?”
here – “My mom is here.”
thing – “One thing led to another.”
give – “Give her these pearls.”
many – “We shared many dreams together.”
well – “You know me so well.”
only – “You are my only friend here.”
those – “Those boots belong to my friend.”
tell – “Can you tell me which way to go?”
one – “She’s the one he’s been waiting for.”
very – “I’m very upset right now.”
her – “Her grandmother is sick.”
even – “She can’t even stand on her own.”
back – “I’ll be right back.”
any – “Have you had any luck on your research?”
good – “You’re a good person.”
woman – “That woman looks so polished.”
through – “Your faith will see you through tough times.”
us – “Do you want to go with us?”
life – “This is the best day of my life.”
child – “I just saw a child cross the street by herself.”
there – “Did you go there?”
work – “I have to go to work.”
down – “Let’s go down.”
may – “You may take your seats.”
after – “Let’s have dinner after work.”
should – “Should I buy this dress?”
call – “Call me when you get home, okay?”
world – “I want to travel and see the world.”
over – “I can’t wait for this day to be over.”
school – “My cousin goes to school here.”
still – “I still think you should go.”
try – “Can you try to be nicer to him?”
in – “What’s in that box?”
as – “As soon as I get home, I’m going to start watching that series.”
last – “This is my last slice of cake, I promise!”
ask – “Can you ask the waiter to bring us some wine?”
need – “I need some wine tonight!”
too – “I need some wine, too!”
feel – “I feel so tired, I just need to relax and unwind.”
three – “I have three sisters.”
when – “When was the last time you saw them?”
state – “Check out the state of that shed, it’s falling apart.”
never – “I’m never going to drink wine again.”
become – “Over the years we’ve become really close.”
between – “This is just between you and me.”
high – “Give me a high five!”
really – “I really like your painting!”
something – “I have something for you.”
most – “She’s the most beautiful girl I’ve ever seen.”
another – “I’ll have another glass of wine, please.”
much – “I love you guys so much.”
family – “You are like family to me.”
own – “I want to get my own place.”
out – “Get out of my room.”
leave – “I want you to leave.”
put – “Please put down that book and listen to me.”
old – “I feel so old!”
while – “I can wait for you here while you shop.”
mean – “I didn’t mean to sound so angry.”
on – “Can you turn on the lights?”
keep – “Can we keep the lights on tonight?”
student – “I’ve always been a diligent student.”
why – “This is why I don’t go out anymore.”
let – “Why won’t you let him know how you feel?”
great – “This ice cream place is great for families with kids!”
same – “Hey, we’re wearing the same shirt!”
big – “I have this big crush on Brad Pitt.”
group – “The group sitting across our table is so noisy.”
begin – “Where do I begin with this huge project?”
seem – “She may seem quiet, but she’s really outgoing once you get to know her.”
country – “Japan is such a beautiful country!”
help – “I need help with my Math homework.”
talk – “Can we talk in private?”
where – “Where were you last night?”
turn – “If only I could turn back time.”
problem – “The problem is we think we have plenty of time.”
every – “Every person has his own big goal to fulfill.”
start – “This is a great to start to learn the English language.”
hand – “Don’t let go of my hand.”
might – “This might actually work.”
American – “The American culture is so dynamic.”
show – “Can you show me how to use this vacuum cleaner?”
part – “This is my favorite part of the movie!”
about – “What is the story about?”
against – “I am so against domestic abuse!”
place – “This place is wonderful!”
over – “She kept saying this over and over again.”
such – “He is such an annoying person.”
again – “Can we play that game again?”
few – “Just a few more errands and I’m done!”
case – “What an interesting case you are working on now!”
most – “That’s the most interesting story I’ve ever heard.”
week – “I had a rough week.”
company – “Will you keep me company?”
where – “Where are we going?”
system – “What’s wrong with the airport’s system?”
each – “Can you give each of them an apple?”
right – “I’m right this time.”
program – “This community program for teens is really helpful.”
hear – “Did you hear that?”
so – “I’m so sleepy.”
question – “I have a question for you.”
during – “During the session, I saw him fall asleep.”
work – “I have to work this weekend.”
play – “We can play soccer next weekend instead.”
government – “I hope the government does something about the poverty in this country.”
run – “If you see a bear here, run for your life.”
small – “I have a small favor to ask you.”
number – “I have a number of favors to ask you.”
off – “Please turn off the television.”
always – “I always bring pepper spray with me.”
move – “Let’s move on to the next tourist spot.”
like – “I really like you.”
night – “The night is young.”
live – “I’m going to live like there’s no tomorrow.”
Mr. – “Mr. Morris is here.”
point – “You have a point.”
believe – “I believe in you.”
hold – “Just hold my hand.”
today – “I’m going to see you today.”
bring – “Please bring a pen.”
happen – “What will happen if you don’t submit your report on time?”
next – “This is the next best thing.”
without – “I can’t live without my phone.”
before – “Before I go to bed I always wash my face.”
large – “There’s a large amount of data online about that topic.”
all – “That’s all I know about Dinosaurs.”
million – “I have a million questions about this book.”
must – “We must watch this movie together.”
home – “Can we go home now?”
under – “I hid it under my bed.”
water – “I filled the tub with water.”
room – “His room is at the end of the corridor.”
write – “Can you write me a prescription for this?”
mother – “His mother is a very lovely woman.”
area – “This area of this house needs to be fixed.”
national – “That virus has become a national concern.”
money – “She needs money to buy her medicine.”
story – “She shared her story to the media.”
young – “She is so young and so hopeful.”
fact – “It’s a fact: shopping can improve your mood.”
month – “It’s that time of the month!”
different – “Just because she’s different, it doesn’t mean she’s bad.”
lot – “You have a lot of explaining to do.”
right – “Turn right when you reach the corner.”
study – “Let’s study our English lessons together.
book – “Can I borrow your English book?”
eye – “She has the pink eye.”
job – “I love my job.”
word – “Describe yourself in one word.”
though – “Though you are angry now, I’m sure you will forget about this later.”
business – “His business is thriving.”
issue – “This is not an issue for me.”
side – “Whose side are you on, anyway?”
kind – “Always be kind, even to strangers.”
four – “There are four seasons in a year.”
head – “Let’s head back, it’s freezing out here.”
far – “We’ve gone too far and now we’re lost.”
black – “She has long, black hair.”
long – “She has long, brown hair.”
both – “They both love chocolate ice cream.”
little – “I have two little boys with me now.”
house – “The house is so quiet without you.”
yes – “I hope you say yes.”
after – “After all this time, he has finally learned to love.”
since – “Ever since his mom died, he has been cranky and angry at the world.”
long – “That was such a long time ago.”
provide – “Please provide me with a list of your services.”
service – “Do you have a specific dental service to treat this?”
around – “We went around the block.”
friend – “You’re a good friend.”
important – “You’re important to me.”
father – “My father is so important to me.”
sit – “Let’s sit outside together.”
away – “He’s away right now.”
until – “Until when will you be away?”
power – “With great power comes great responsibility.”
hour – “I’ve been checking his temperature every hour.”
game – “Let’s play a game.”
often – “I buy from his bakery as often as I can.”
yet – “He’s not yet home.”
line – “There’s a long line at the grocery cashier.”
political – “I stay away from political discussions.”
end – “It’s the end of an era.”
among – “Among all my pets, he’s my most favorite.”
ever – “Have you ever tried this cake?”
stand – “Can you stand still for a minute?”
bad – “What you did was so bad.”
lose – “I can’t lose you.”
however – “I want to buy this bag, however, I need to save up for it first.”
member – “She’s a member of the babysitter’s club.”
pay – “Let’s pay for our groceries.”
law – “There’s a law against jay-walking.”
meet – “I want you to meet my aunt.”
car – “Let’s go inside my car.”
city – “This is the city that never sleeps.”
almost – “I’m almost done with my report.”
include – “Did you remember to include the summary in your report?”
continue – “Can we continue working tomorrow?”
set – “Great, let me set an appointment for you.”
later – “I’ll finish it later.”
community – “Our community is very tight knit.”
much – “There’s so much to learn in the English language.”
name – “What’s your name?”
five – “I can give you five reasons why you need to watch that video.”
once – “I once had a puppy named Bark.”
white – “I love my white sneakers.”
least – “She’s the least productive among all the employees.”
president – “She was our class president back in high school.”
learn – “I’d love to learn more about the English language.”
real – “What is her real name?”
change – “What can we change so that things will get better?”
team – “They hired a team to do the design of their new office.”
minute – “She’s laughing every minute of every day.”
best – “This is the best potato salad I’ve ever tasted.”
several – “I have several old clothes I need to donate.”
idea – “It was your idea to go to the beach, remember?”
kid – “I loved that toy when I was a kid.”
body – “She worked out hard to achieve a toned body.”
information – “This is the information I need.”
nothing – “There’s nothing we can do now. “
ago – “Three years ago, I visited Japan for the first time.”
right – “You’re right, I want to go back there.”
lead – “Just lead the way and I’ll follow.”
social – “I feel awkward in these social gatherings.”
understand – “I understand how you feel.”
whether – “Whether in big groups or small groups, I always feel a little shy at first.”
back – “Looking back, I knew I was always an introvert.”
watch – “Let’s watch the sun set on the horizon.”
together – “They’re together now.”
follow – “I’ll follow you home.”
around – “You’ll always have me around.”
parent – “Every parent is trying hard and doing their best.”
only – “You are only allowed to go out today.”
stop – “Please stop that.”
face – “Why is your face so red?”
anything – “You can ask me for anything.”
create – “Did you create that presentation? It was so good.”
public – “This is public property.”
already – “I already asked him to resend his report.”
speak – “Could you speak a little louder?”
others – “The others haven’t arrived yet.”
read – “I read somewhere that this house is haunted.”
level – “What level are you in that game?”
allow – “Do you allow your kids to play outside the house?”
add – “Is it okay if we add a bit of sugar to the tea?”
office – “Welcome to my office.”
spend – “How much did you spend on your last shopping spree?”
door – “You left the door open.”
health – “You must take good care of your health.”
person – “You are a good person.”
art – “This is my work of art.”
sure – “Are you sure you want to do this alone?”
such – “You are such a brave little boy.”
war – “The war has finally ended.”
history – “She is my history professor.”
party – “Are you going to her party tonight?”
within – “We support everyone within our small community.”
grow – “We want everyone to grow and thrive in their careers.”
result – “The result of this outreach program is amazing.”
open – “Are you open to teaching on weekends?”
change – “Where can we change her diaper?”
morning – “It’s such a beautiful morning!”
walk – “Come take a walk with me.”
reason – “You are the reason I came home.”
low – “Her blood pressure has gotten really low.”
win – “We can win this match if we work together.”
research – “How is your research going?”
girl – “That girl is in my class.”
guy – “I’ve seen that guy in school before.”
early – “I come to work so early every day.”
food – “Let’s buy some food, I’m hungry!”
before – “Can I talk to you before you go home?”
moment – “The moment she walked in the room, her puppy started to jump and dance again.”
himself – “He cooked this Turkey himself.”
air – “I am loving the cold night air here.”
teacher – “You are the best teacher ever.”
force – “Don’t force him to play with other kids.”
offer – “Can I offer you a ride home?”
enough – “Boys, that’s enough playing for today.”
both – “You both need to change into your sleep clothes now.”
education – “I just want you to get the best education.”
across – “Your dog ran across the park.”
although – “Although she felt tired, she still couldn’t sleep.”
remember – “Do you think she will still remember me after ten years?”
foot – “Her foot got caught in one of the ropes.”
second – “This is the second time she got late this month.”
boy – “There’s a boy in her class who keeps pulling her hair.”
maybe – “Maybe we can have ice cream for dessert.”
toward – “He took a step toward her.”
able – “Will you be able to send me your report today?”
age – “What is the average marrying age these days?”
off – “The cat ran off with the dog.”
policy – “They have a generous return policy.”
everything – “Everything is on sale.”
love – “I love what you’re wearing!”
process – “Wait, give me time to process everything you’re telling me.”
music – “I love music.”
including – “Around 20 people attended, including Bob and Beth.”
consider – “I hope you consider my project proposal.”
appear – “How did that appear out of nowhere?”
actually – “I’m actually just heading out.”
buy – “I’m going to buy these shoes.”
probably – “He’s probably still asleep.”
human – “Give him a break, he is only human.”
wait – “Is it alright if you wait for a few minutes?”
serve – “This blow dryer has served me well for years.”
market – “Let’s visit the Sunday market.”
die – “I don’t want my cat to die, let’s take him to the vet please.”
send – “Please send the package to my address.”
expect – “You can’t expect much from their poor service.”
home – “I can’t wait to go home!”
sense – “I did sense that something was not okay.”
build – “He is going to build his dream house.”
stay – “You can stay with me for a few weeks.”
fall – “Be careful, you might fall.”
oh – “Oh no, I left my phone at home!”
nation – “We have to act as one nation.”
plan – “What’s your plan this time?”
cut – “Don’t cut your hair.”
college – “We met in college.”
interest – “Music is an interest of mine.”
death – “Death is such a heavy topic for me.”
course – “What course did you take up in college?”
someone – “Is there someone who can go with you?”
experience – “What an exciting experience!”
behind – “I’m scared to check what’s behind that door.”
reach – “I can’t reach him, he won’t answer his phone.”
local – “This is a local business.”
kill – “Smoking can kill you.”
six – “I have six books about Psychology.”
remain – “These remain on the top shelf.”
effect – “Wow, the effect of that mascara is great!”
use – “Can I use your phone?”
yeah – “Yeah, he did call me earlier.”
suggest – “He did suggest that to me.”
class – “We were in the same English class.”
control – “Where’s the remote control?”
raise – “It’s so challenging to discipline kids these days.”
care – “I don’t care about what you think.”
perhaps – “Perhaps we can arrive at a compromise.”
little – “There’s a little bird outside my window.”
late – “I am running late for my doctor’s appointment.”
hard – “That test was so hard.”
field – “He’s over there, by the soccer field.”
else – “Is anyone else coming?”
pass – “Can we pass by the grocery store?”
former – “She was my former housemate.”
sell – “We can sell your old couch online.”
major – “It’s a major issue for the project.”
sometimes – “Sometimes I forget to turn off the porch lights.”
require – “They’ll require you to show your I.D.”
along – “Can I tag along your road trip?”
development – “This news development is really interesting.”
themselves – “They can take care of themselves.”
report – “I read her report and it was great!”
role – “She’s going to play the role of Elsa.”
better – “Your singing has gotten so much better!”
economic – “Some countries are facing an economic crisis.”
effort – “The government must make an effort to solve this.”
up – “His grades have gone up.”
decide – “Please decide where to eat.”
rate – “How would you rate the hotel’s service?”
strong – “They have strong customer service here!”
possible – “Maybe it’s possible to change their bathroom amenities.”
heart – “My heart is so full.”
drug – “She got the patent for the drug she has created to cure cancer.”
show – “Can you show me how to solve this puzzle?”
leader – “You are a wonderful leader.”
light – “Watch her face light up when you mention his name.”
voice – “Hearing his mom’s voice is all he need right now.”
wife – “My wife is away for the weekend.”
whole – “I have the whole house to myself.”
police – “The police have questioned him about the incident.”
mind – “This relaxation technique really eases my mind.”
finally – “I can finally move out from my old apartment.”
pull – “My baby niece likes to pull my hair.”
return – “I give her tickles in return.”
free – “The best things in life are free.”
military – “His dad is in the military.”
price – “This is the price you pay for lying.”
report – “Did you report this to the police?”
less – “I am praying for less stress this coming new year.”
according – “According to the weather report, it’s going to rain today.”
decision – “This is a big decision for me.”
explain – “I’ll explain everything later, I promise.”
son – “His son is so cute!”
hope – “I hope I’ll have a son one day.”
even – “Even if they’ve broken up, they still remain friends.”
develop – “That rash could develop into something more serious.”
view – “This view is amazing!”
relationship – “They’ve taken their relationship to the next level.”
carry – “Can you carry my bag for me?”
town – “This town is extremely quiet.”
road – “There’s a road that leads to the edge of the woods.”
drive – “You can’t drive there, you need to walk.”
arm – “He broke his arm during practice.”
true – “It’s true, I’m leaving the company.”
federal – “Animal abuse is now a federal felony!”
break – “Don’t break the law.”
better – “You better learn how to follow rules.”
difference – “What’s the difference between happiness and contentment?”
thank – “I forgot to thank her for the pie she sent us.”
receive – “Did you receive the pie I sent you?”
value – “I value our friendship so much.”
international – “Their brand has gone international!”
building – “This building is so tall!”
action – “You next action is going to be critical.”
full – “My work load is so full now.”
model – “A great leader is a great model of how to do things.”
join – “He wants to join the soccer team.”
season – “Christmas is my favorite season!”
society – “Their society is holding a fund raiser.”
because – “I’m going home because my mom needs me.”
tax – “How much is the current income tax?”
director – “The director yelled ‘Cut!’”
early – “I’m too early for my appointment.”
position – “Please position your hand properly when drawing.”
player – “That basketball player is cute.”
agree – “I agree! He is cute!”
especially – “I especially like his blue eyes.”
record – “Can we record the minutes of this meeting, please?”
pick – “Did you pick a color theme already?”
wear – “Is that what you’re going to wear for the party?”
paper – “You can use a special paper for your invitations.”
special – “Some special paper are even scented!”
space – “Please leave some space to write down your phone number.”
ground – “The ground is shaking.”
form – “A new island was formed after that big earthquake.”
support – “I need your support for this project.”
event – “We’re holding a big event tonight.”
official – “Our official wedding photos are out!”
whose – “Whose umbrella is this?”
matter – “What does it matter anyway?”
everyone – “Everyone thinks I stole that file.”
center – “I hate being the center of attention.”
couple – “The couple is on their honeymoon now.”
site – “This site is so big!”
end – “It’s the end of an era.”
project – “This project file is due tomorrow.”
hit – “He hit the burglar with a bat.”
base – “All moms are their child’s home base.”
activity – “What musical activity can you suggest for my toddler?”
star – “My son can draw a star!”
table – “I saw him draw it while he was writing on the table.”
need – “I need to enroll him to a good preschool.”
court – “There’s a basketball court near our house.”
produce – “Fresh farm produce is the best.”
eat – “I could eat that all day.”
American – “My sister is dating an American.”
teach – “I love to teach English lessons.”
oil – “Could you buy me some cooking oil at the store?”
half – “Just half a liter please.”
situation – “The situation is getting out of hand.”
easy – “I thought you said this was going to be easy?”
cost – “The cost of fuel has increased!”
industry – “The fuel industry is hiking prices.”
figure – “Will our government figure out how to fix this problem?”
face – “I can’t bear to face this horrendous traffic again and again.”
street – “Let’s cross the street.”
image – “There’s an image of him stored inside my mind.”
itself – “The bike itself is pretty awesome.”
phone – “Plus, it has a phone holder.”
either – “I either walk or commute to work.”
data – “How can we simplify this data?”
cover – “Could you cover for me during emergencies?”
quite – “I’m quite satisfied with their work.”
picture – “Picture this: a lake, a cabin, and lots of peace and quiet.
clear – “That picture is so clear inside my head.”
practice – “Let’s practice our dance number.”
piece – “That’s a piece of cake!”
land – “Their plane is going to land soon.”
recent – “This is her most recent social media post.”
describe – “Describe yourself in one word.”
product – “This is my favorite product in their new line of cosmetics.”
doctor – “The doctor is in.”
wall – “Can you post this up on the wall?”
patient – “The patient is in so much pain now.”
worker – “She’s a factory worker.”
news – “I saw that on the news.”
test – “I have to pass this English test.”
movie – “Let’s watch a movie later.”
certain – “There’s a certain kind of magic in the air now.”
north – “Santa lives up north.”
love – ” l love Christmas!”
personal – “This letter is very personal.”
open – “Why did you open and read it?”
support – “Will you support him?”
simply – “I simply won’t tolerate bad behavior.”
third – “This is the third time you’ve lied to me.”
technology – “Write about the advantages of technology.”
catch – “Let’s catch up soon, please!”
step – “Watch your step.”
baby – “Her baby is so adorable.”
computer – “Can you turn on the computer, please?”
type – “You need to type in your password.”
attention – “Can I have your attention, please?”
draw – “Can you draw this for me?”
film – “That film is absolutely mind-blowing.”
Republican – “He is a Republican candidate.”
tree – “That tree has been there for generations.”
source – “You are my source of strength.”
red – “I’ll wear a red dress tonight.”
nearly – “He nearly died in that accident!”
organization – “Their organization is doing great things for street kids.”
choose – “Let me choose a color.”
cause – “We have to see the cause and effect of this experiment.”
hair – “I’ll cut my hair short for a change.”
look – “Can you look at the items I bought?”
point “What is the point of all this?
century – “We’re living in the 21st century, Mary.”
evidence – “The evidence clearly shows that he is guilty.”
window – “I’ll buy window curtains next week.”
difficult “Sometimes, life can be difficult.”
listen – “You have to listen to your teacher.”
soon – “I will launch my course soon.”
culture – “I hope they understand our culture better.”
billion – “My target is to have 1 billion dollars in my account by the end of the year.”
chance – “Is there any chance that you can do this for me?”
brother – “My brother always have my back.”
energy – “Now put that energy into walking.”
period – “They covered a period of twenty years.”
course – “Have seen my course already?”
summer – “I’ll go to the beach in summer.”
less – “Sometimes, less is more.”
realize – “I just realize that I have a meeting today.”
hundred – “I have a hundred dollars that I can lend you.”
available – “I am available to work on your project.”
plant – “Plant a seed.”
likely – “It was likely a deer trail.”
opportunity – “It was the perfect opportunity to test her theory.”
term – “I’m sure there’s a Latin term for it.”
short – “It was just a short stay at the hotel.”
letter – “I already passed my letter of intent.”
condition – “Do you know the condition I am in?”
choice – “I have no choice.”
place – “Let’s meet out at meeting place.”
single – “I am a single parent.”
rule – “It’s the rule of the law.”
daughter – “My daughter knows how to read now.”
administration – “I will take this up with the administration.”
south – “I am headed south.”
husband – “My husband just bought me a ring for my birthday.”
Congress – “It will be debated at the Congress.”
floor – “She is our floor manager.”
campaign – “I handled their election campaign.”
material – “She had nothing material to report.”
population – “The population of the nearest big city was growing.”
well – “I wish you well.”
call – ” I am going to call the bank.”
economy – “The economy is booming.”
medical -“She needs medical assistance.”
hospital – “I’ll take her to the nearest hospital.”
church – “I saw you in church last Sunday.”
close -“Please close the door.”
thousand – “There are a thousand reasons to learn English!”
risk – “Taking a risk can be rewarding.”
current – “What is your current address?”
fire – “Make sure your smoke alarm works in case of fire.”
future -“The future is full of hope.”
wrong – “That is the wrong answer.”
involve – “We need to involve the police.”
defense – “What is your defense or reason you did this?”
anyone – “Does anyone know the answer?”
increase – “Let’s increase your test score.”
security – “Some apartment buildings have security.”
bank – “I need to go to the bank to withdraw some money.”
myself – “I can clean up by myself.”
certainly – “I can certainly help clean up.”
west – “If you drive West, you will arrive in California.”
sport – “My favorite sport is soccer.”
board – “Can you see the board?”
seek – “Seek and you will find.”
per – “Lobster is $20 per pound.”
subject – “My favorite subject is English!”
officer – “Where can I find a police officer?”
private – “This is a private party.”
rest – “Let’s take a 15 minute rest.”
behavior – “This dog’s behavior is excellent.”
deal – “A used car can be a good deal.”
performance – “Your performance can be affected by your sleep.”
fight – “I don’t want to fight with you.”
throw – “Throw me the ball!”
top – “You are a top student.”
quickly – “Let’s finish reading this quickly.”
past – “In the past, my English was not as good as it is today.”
goal – “My goal is to speak English fluently.”
second – “My second goal is to increase my confidence.”
bed – “I go to bed around 10pm.”
order – “I would like to order a book.”
author – “The author of this series is world-famous.”
fill – “I need to fill (up) my gas tank.”
represent – “I represent my family.”
focus – “Turn off your phone and the TV and focus on your studies!”
foreign – “It’s great having foreign friends.”
drop – “Please don’t drop the eggs!”
plan – “Let’s make a plan.”
blood – “The hospital needs people to give blood.”
upon – “Once upon a time, a princess lived in a castle.”
agency – “Let’s contract an agency to help with marketing.”
push – “The door says ‘push,’ not ‘pull.’”
nature – “I love walking in nature!”
color – “My favorite color is blue.”
no – “‘No’ is one of the shortest complete sentences.”
recently – “I cleaned the bathroom most recently, so I think it’s your turn this time.”
store – “I’m going to the store to buy some bread.”
reduce – “Reduce, reuse, and recycle are the ways to help the environment.”
sound – “I like the sound of wind chimes.”
note – “Please take notes during the lesson.”
fine – “I feel fine.”
before – “Before the movie, let’s buy popcorn!”
near – “Near, far, wherever you are, I do believe that the heart goes on.”
movement – “The environmental movement is an international movement.”
page – “Please turn to page 62.”
enter – “You can enter the building on the left.”
share – “Let me share my idea.”
than – “Ice cream has more calories than water.”
common – “Most people can find something in common with each other.”
poor – “We had a poor harvest this year because it was so dry.”
other – “This pen doesn’t work, try the other one.”
natural – “This cleaner is natural, there aren’t any chemicals in it.”
race – “We watched the car race on TV.”
concern – “Thank you for your concern, but I’m fine.”
series – “What is your favorite TV series?”
significant – “His job earns a significant amount of money.”
similar – “These earrings don’t match, but they are similar.”
hot – “Don’t touch the stove, it’s still hot.”
language – “Learning a new language is fun.”
each – “Put a flower in each vase.”
usually – “I usually shop at the corner store.”
response – “I didn’t expect his response to come so soon.”
dead – “My phone is dead, let me charge it.”
rise – “The sun will rise at 7:00 a.m.”
animal – “What kind of animal is that?”
factor – “Heredity is a factor in your overall health.”
decade – “I’ve lived in this city for over a decade.”
article – “Did you read that newspaper article?”
shoot – “He wants to shoot arrows at the target.”
east – “Drive east for three miles.”
save – “I save all my cans for recycling.”
seven – “There are seven slices of pie left.”
artist – “Taylor Swift is a recording artist.”
away – “I wish that mosquito would go away.”
scene – “He painted a colorful street scene.”
stock – “That shop has a good stock of postcards.”
career – “Retail sales is a good career for some people.”
despite – “Despite the rain, we will still have the picnic.”
central – “There is good shopping in central London.”
eight – “That recipe takes eight cups of flour.”
thus – “We haven’t had any problems thus far.”
treatment – “I will propose a treatment plan for your injury.”
beyond – “The town is just beyond those mountains.”
happy – “Kittens make me happy.”
exactly – “Use exactly one teaspoon of salt in that recipe.”
protect – “A coat will protect you from the cold weather.”
approach – “The cat slowly approached the bird.”
lie – “Teach your children not to lie.”
size – “What size is that shirt?
dog – “Do you think a dog is a good pet?”
fund – “I have a savings fund for college.”
serious – “She is so serious, she never laughs.”
occur – “Strange things occur in that empty house.”
media – “That issue has been discussed in the media.”
ready – “Are you ready to leave for work?”
sign – “That store needs a bigger sign.”
thought – “I’ll have to give it some thought.”
list – “I made a list of things to do.”
individual – “You can buy an individual or group membership.”
simple – “The appliance comes with simple instructions.”
quality – “I paid a little more for quality shoes.”
pressure – “There is no pressure to finish right now.”
accept – “Will you accept my credit card?”
answer – “Give me your answer by noon tomorrow.”
hard – “That test was very hard.”
resource – “The library has many online resources.”
identify – “I can’t identify that plant.”
left – “The door is on your left as you approach.”
meeting – “We’ll have a staff meeting after lunch.”
determine – “Eye color is genetically determined.”
prepare – “I’ll prepare breakfast tomorrow.”
disease – “Face masks help prevent disease.”
whatever – “Choose whatever flavor you like the best.”
success – “Failure is the back door to success.”
argue – “It’s not a good idea to argue with your boss.”
cup – “Would you like a cup of coffee?”
particularly – “It’s not particularly hot outside, just warm.”
amount – “It take a large amount of food to feed an elephant.”
ability – “He has the ability to explain things well.”
staff – “There are five people on staff here.”
recognize – “Do you recognize the person in this photo?”
indicate – “Her reply indicated that she understood.”
character – “You can trust people of good character.”
growth – “The company has seen strong growth this quarter.”
loss – “The farmer suffered heavy losses after the storm.”
degree – “Set the oven to 300 degrees.”
wonder – “I wonder if the Bulls will win the game.”
attack – “The army will attack at dawn.”
herself – “She bought herself a new coat.”
region – “What internet services are in your region?”
television – “I don’t watch much television.”
box – “I packed my dishes in a strong box.”
TV – “There is a good movie on TV tonight.”
training – “The company will pay for your training.”
pretty – “That is a pretty dress.”
trade – “The stock market traded lower today.”
deal – “I got a good deal at the store.”
election – “Who do you think will win the election?”
everybody – “Everybody likes ice cream.”
physical – “Keep a physical distance of six feet.”
lay – “Lay the baby in her crib, please.”
general – “My general impression of the restaurant was good.”
feeling – “I have a good feeling about this.”
standard – “The standard fee is $10.00.”
bill – “The electrician will send me a bill.”
message – “You have a text message on your phone.”
fail – “I fail to see what is so funny about that.”
outside – “The cat goes outside sometimes.”
arrive – “When will your plane arrive?”
analysis – “I’ll give you my analysis when I’ve seen everything.”
benefit – “There are many health benefits to quinoa.”
name – “What’s your name?”
sex – “Do you know the sex of your baby yet?”
forward – “Move the car forward a few feet.”
lawyer – “My lawyer helped me write a will.”
present – “If everyone is present, the meeting can begin.”
section – “What section of the stadium are you sitting in?”
environmental – “Environmental issues are in the news.”
glass – “Glass is much heavier than plastic.”
answer – “Could you answer a question for me?”
skill – “His best skill is woodworking.”
sister – “My sister lives close to me.”
PM – “The movie starts at 7:30 PM.”
professor – “Dr. Smith is my favorite professor.”
operation – “The mining operation employs thousands of people.”
financial – “I keep my accounts at my financial institution.”
crime – “The police fight crime.”
stage – “A caterpillar is the larval stage of a butterfly.”
ok – “Would it be ok to eat out tonight?”
compare – “We should compare cars before we buy one.”
authority – “City authorities make the local laws.”
miss – “I miss you, when will I see you again?”
design – “We need to design a new logo.”
sort – “Let’s sort these beads according to color.”
one – “I only have one cat.”
act – “I’ll act on your information today.”
ten – “The baby counted her ten toes.”
knowledge – “Do you have the knowledge to fix that?”
gun – “Gun ownership is a controversial topic.”
station – “There is a train station close to my house.”
blue – “My favorite color is blue.”
state – “After the accident I was in a state of shock.”
strategy – “Our new corporate strategy is written here.”
little – “I prefer little cars.”
clearly – “The instructions were clearly written.”
discuss – “We’ll discuss that at the meeting.”
indeed – “Your mother does indeed have hearing loss.”
force – “It takes a lot of force to open that door.”
truth – “Please tell me the truth.”
song – “That’s a beautiful song.”
example – “I need an example of that grammar point, please.”
democratic – “Does Australia have a democratic government?”
check – “Please check my work to be sure it’s correct.”
environment – “We live in a healthy environment.”
leg – “The boy broke his leg.”
dark – “Turn on the light, it’s dark in here.”
public – “Masks must be worn in public places.”
various – “That rug comes in various shades of gray.”
rather – “Would you rather have a hamburger than a hot dog?”
laugh – “That movie always makes me laugh.”
guess – “If you don’t know, just guess.”
executive – “The company’s executives are paid well.”
set – “Set the glass on the table, please.”
study – “He needs to study for the test.”
prove – “The employee proved his worth.”
hang – “Please hang your coat on the hook.”
entire – “He ate the entire meal in 10 minutes.”
rock – “There are decorative rocks in the garden.”
design – “The windows don’t open by design.”
enough – “Have you had enough coffee?”
forget – “Don’t forget to stop at the store.”
since – “She hasn’t eaten since yesterday.”
claim – “I made an insurance claim for my car accident.”
note – “Leave me a note if you’re going to be late.”
remove – “Remove the cookies from the oven.”
manager – “The manager will look at your application.”
help – “Could you help me move this table?”
close – “Close the door, please.”
sound – “The dog did not make a sound.”
enjoy – “I enjoy soda.”
network – “Band is the name of our internet network.”
legal – “The legal documents need to be signed.”
religious – “She is very religious, she attends church weekly.”
cold – “My feet are cold.”
form – “Please fill out this application form.”
final – “The divorce was final last month.”
main – “The main problem is a lack of money.”
science – “He studies health science at the university.”
green – “The grass is green.”
memory – “He has a good memory.”
card – “They sent me a card for my birthday.”
above – “Look on the shelf above the sink.”
seat – “That’s a comfortable seat.”
cell – “Your body is made of millions of cells.”
establish – “They established their business in 1942.”
nice – “That’s a very nice car.”
trial – “They are employing her on a trial basis.”
expert – “Matt is an IT expert.”
that – “Did you see that movie?”
spring – “Spring is the most beautiful season.”
firm – “Her ‘no” was very firm, she won’t change her mind.”
Democrat – “The Democrats control the Senate.”
radio – “I listen to the radio in the car.”
visit – “We visited the museum today.”
management – “That store has good management.”
care – “She cares for her mother at home.”
avoid – “You should avoid poison ivy.”
imagine – “Can you imagine if pigs could fly?”
tonight – “Would you like to go out tonight?”
huge – “That truck is huge!”
ball – “He threw the ball to the dog.”
no – “I said ‘no,’ please don’t ask again.”
close – “Close the window, please.”
finish – “Did you finish your homework?”
yourself – “You gave yourself a haircut?”
talk – “He talks a lot.”
theory – “In theory, that’s a good plan.”
impact – “The drought had a big impact on the crops.”
respond – “He hasn’t responded to my text yet.”
statement – “The police chief gave a statement to the media.”
maintain – “Exercise helps you maintain a healthy weight.”
charge – “I need to charge my phone.”
popular – “That’s a popular restaurant.”
traditional – “They serve traditional Italian food there.”
onto – “Jump onto the boat and we’ll go fishing.”
reveal – “Washing off the dirt revealed the boy’s skinned knee.”
direction – “What direction is the city from here?”
weapon – “No weapons are allowed in government buildings.”
employee – “That store only has three employees.”
cultural – “There is cultural significance to those old ruins.”
contain – “The carton contains a dozen egges.”
peace – “World leaders gathered for peace talks.”
head – “My head hurts.”
control – “Keep control of the car.”
base – “The glass has a heavy base so it won’t fall over.”
pain – “I have chest pain.”
apply – “Maria applied for the job.”
play – “The children play at the park.”
measure – “Measure twice, cut once.”
wide – “The doorway was very wide.”
shake – “Don’t shake the can of soda.”
fly – “We can fly to France next year.”
interview – “My job interview went well.”
manage – “Did you manage to find the keys?”
chair – “The table has six matching chairs.”
fish – “I don’t enjoy eating fish.”
particular – “That particular style looks good on you.”
camera – “I use the camera on my phone.”
structure – “The building’s structure is solid.”
politics – “Mitch is very active in politics.”
perform – “The singer will perform tonight.”
bit – “It rained a little bit last night.”
weight – “Keep track of your pet’s weight.”
suddenly – “The storm came up suddenly.”
discover – “You’ll discover treasures at that thrift store.”
candidate – “There are ten candidates for the position.”
top – “The flag flies on the top of that building.”
production – “Factory production has improved over the summer.”
treat – “Give yourself a treat for a job well done.”
trip – “We are taking a trip to Florida in January.”
evening – “I’m staying home this evening.”
affect – “My bank account will affect how much I can buy.”
inside – “The cat stays inside.”
conference – “There will be expert presenters at the conference.”
unit – “A foot is a unit of measure.”
best – “Those are the best glasses to buy.”
style – “My dress is out of style.”
adult – “Adults pay full price, but children are free.”
worry – “Don’t worry about tomorrow.”
range – My doctor offered me a range of options.
mention – “Can you mention me in your story?”
rather – “Rather than focusing on the bad things, let’s be grateful for the good things.”
far – “I don’t want to move far from my family.”
deep – “That poem about life is deep.”
front – “Please face front.”
edge – “Please do not stand so close to the edge of the cliff.”
individual – “These potato chips are in an individual serving size package.”
specific – “Could you be more specific?”
writer – “You are a good writer.”
trouble – “Stay out of trouble.”
necessary – “It is necessary to sleep.”
throughout – “Throughout my life I have always enjoyed reading.”
challenge – “I challenge you to do better.”
fear – “Do you have any fears?”
shoulder – “You do not have to shoulder all the work on your own.”
institution – “Have you attended any institution of higher learning?”
middle – “I am a middle child with one older brother and one younger sister.”
sea – “I want to sail the seven seas.”
dream – “I have a dream.”
bar – “A bar is a place where alcohol is served.”
beautiful – “You are beautiful.”
property – “Do you own property, like a house?”
instead – “Instead of eating cake I will have fruit.”
improve – “I am always looking for ways to improve.”
stuff – “When I moved, I realized I have a lot of stuff!”
claim – “I claim to be a fast reader, but actually I am average.”
These 1000 common words are just a speck of the many English terms you can learn! Aren’t you excited to learn more? For now, focus on familiarizing yourself with these words. And make a conscious effort to use them in your everyday conversations.
The power of everyday English conversations is truly remarkable. And it’s the best way to deepen your learning and love for the language.
If you want more lessons relating to English vocabulary, here’s a great lesson that talks about the different ways you can improve your English vocabulary fast.
Here is a very simple, yet attractive, common noun list. I hope you can start using them soon, if you’re not already!
1. account – an arrangement with a bank to keep your money there and allow you to take it out when you need to.
2. air – the mixture of gases that surrounds the Earth and that we breathe.
3. amount – a collection or mass, especially of something that cannot be counted.
4. animal – something that lives and moves, but is not a human, bird, insect or fish.
5. answer – the receipt and response to a letter, question or phone call.
6. approval – the feeling of having a positive opinion of someone or something.
7. art – the activity of making objects, drawings, music, paintings, sculptures etc that are beautiful or that express feelings.
8. attack – to try to hurt or defeat (mainly referred to physical violence but can also be used to describe verbal or emotional outbursts).
9. attention – notice, thought or interest.
10. back – (adverb) in return, into, towards a previous place or condition, or an earlier time; (noun) the part of your body that is opposite to the front, from your shoulder to your bottom.
11. base – the bottom part of an object, on which it rests, or the lowest part of something.
12. behavior – the way that someone behaves.
13. belief – the feeling of being certain that something exists or is true, something that you believe.
14. birth – the time when a young baby, or young animal comes out of its mother’s body.
15. blood – the red liquid that is sent around the body by the heart.
16. blow – to move and make currents of air, or to make a sound by forcing air out of your mouth.
17. body – the whole physical structure that forms a person or animal.
18. bread – a food made from flour, water and usually yeast, mixed together and baked.
19. breath – the air that goes into and out of your lungs.
20. brother – a man or boy with the same parents as another person.
21. building – a structure with walls and a roof, such as a house or a factory.
22. burn – to be hurt, damaged or destroyed by fire or extreme heat, or to cause this to happen.
23. business – the activity of buying and selling goods and services.
24. butter – a pale yellow food containing a lot of fat that is made from cream, usually spread on bread or used in cooking.
25. care – the process of protecting someone or something, and providing what they need.
26. cause – the reason why something, especially something bad, happens.
27. chance – an occasion that allows something to be done.
28. change – to exchange one thing for another thing, or to make or become different.
29. cloth – a type of woven material, usually used in cleaning to remove dirt, dust or liquid.
30. color/colour – red, blue, green, yellow, red, orange etc.
31. comfort – a pleasant feeling of being relaxed and free from pain.
32. company – an organization that sells goods or services in order to make money.
33. comparison – the act of comparing two or more people or things.
34. competition – a situation in which someone is trying to win something or be more successful than someone else.
35. connection – the state of being related to someone or something.
36. cook – (verb) when you prepare food to be eaten by heating it until it is ready, or (noun) a person who prepares and cooks food.
37. country – an area of land that has its own government, army etc.
38. cover – to put or spread something over something, or to lie on the surface of something.
39. credit – praise, approval or honour.
40. cry – to produce tears as the result of a strong emotion, such as sadness, fear, happiness or pain.
41. current – of the present time.
42. damage – to harm or spoil something.
43. danger – the possibility of harm or death to someone.
44. daughter – your female child.
45. day – a period of 24 hours.
46. death – the end of life.
47. decision – a choice that you make about something after thinking about all the possible options.
48. detail – a single piece of information or fact about something.
49. development – the process in which someone or something grows or changes and becomes more advanced.
50. direction – the position towards which someone or something moves or faces.51. discovery – the process of finding information, a place or an object, especially for the first time.
52. discussion – the activity in which people talk about something and tell each other their ideas or opinions.
53. disease – an illness of people, animals or plants caused by infection or a lack of health.
54. distance – the amount of space between two places.
55. doubt – (a feeling of) not being certain about something, especially how good or true it is.
56. drink – (noun) liquid that is taken into the body through the mouth, or (verb) to take liquid into the body through the mouth.
57. driving – the ability to drive a car, the activity of driving, or the way someone drives.
58. dust – dry dirt in the form of powder that covers surfaces inside a building, or very small dry pieces of soil etc.
59. earth – our planet, the third in order from the sun, between Venus and Mars, the world on which we live. Also another term for soil on the ground.
60. education – the process of teaching or learning in a school or college, or the knowledge that you get from this.
61. effect – the result of a particular influence.
62. end – the part of a place or thing that is the furthest away from the start, or the final part of something such as a period of time, activity or story.
63. error – a mistake.
64. example – a way of helping someone to understand something by showing them how it is used.
65. experience – (the process of getting) knowledge or skill from doing, seeing or feeling things, or something that happens to you which affects how you feel.
66. expert – a person with a high level of knowledge or skill relating to a particular subject or activity.
67. fact – something that is known to have happened or to exist, especially something for which proof exists.
68. fall – to suddenly go down onto the ground or towards the ground without intending to, or by accident.
69. family – a group of people who are related to each other such as a mother, father and their children.
70. father – a male parent.
71. fear – an unpleasant emotion or thought that you have when you are worried or frightened by something dangerous, painful or bad that is happening or may happen.
72. feeling – the fact of feeling something physical, or an emotion.
73. fire – the state of burning that produces flames that send out heat and light, and might produce smoke.
74. flight – a journey in an aircraft.
75. flower – the part of a plant that is often brightly coloured and has a pleasant smell.
76. food – something that people and animals eat or plants absorb, to keep them alive.
77. friend – a person who you know well and like a lot, but who is usually not a member of your family.
78. front – the part of a person’s body, building or object that faces forward, or is most often seen or used.
79. fruit – the soft part containing seeds that is produced by a plant. Many types of fruit are sweet and can be eaten.
80. glass – a hard transparent material used to make windows bottles and other objects.
81. gold – a chemical element that is a valuable, shiny, yellow metal used to make coins and jewellery.
82. government – the group of people that officially control a country.
83. grain – a seed or seeds from a plant, especially a plant like a grass such as rice or wheat.
84. grass – a low, green plant that grows naturally from soil on the Earth’s surface.
85. growth – the growth of a person, animal or plant is its process of increasing in size.
86. guide – written information or a person that gives you the history of, or most important facts about, a particular or subject.
87. harbor/harbour – an area of water next to the coast, often protected from the sea by a thick wall, where ships and boats can shelter.
88. hate – to dislike someone or something very much.
89. hearing – the ability to hear, or an official meeting that is held to collect the facts about an event or problem.
90. heat – the quality of being hot or warm, or the temperature of something.
91. help – to make it possible or easier for someone to do something, by doing part of the work yourself.
92. history – (the study or record of) past events considered together, especially events of a particular period, country or subject.
93. hole – an empty space in an object, usually with an opening to the object’s surface, or an opening that goes completely through an object.
94. hope – to want something to happen or to be true, and usually have a good reason to think that it might.
95. hour – a period of 60 minutes.
96. ice – water that has frozen and become solid, or pieces of this.
97. idea – a suggestion or plan for doing something.
98. increase – to (make something) become larger in amount or size.
99. industry – the companies and activities involved in the process of producing goods for sale, especially in a factory or special area.
100. instrument – an object such as a guitar or drum that is played to produce musical sounds.
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
101. insurance – an agreement in which you pay a company money and they pay your costs if you have an accident or injury.
102. interest – the feeling of wanting to give your attention to something or someone, or wanting to be involved with and to discover more about something.
103. iron – a chemical element that is a common greyish-coloured metal. It is strong, used in making steel, and exists in very small amounts in blood.
104. join – to connect or fasten things together.
105. journey – the act of travelling from one place to another, especially in a vehicle.
106. jump – to push yourself suddenly off the ground and into the air using your legs.
107. kick – to hit someone or something with the foot, or to move the feet and legs suddenly and violently.
108. kiss – to touch another person’s cheek or hand with your lips, especially as a greeting, or to press your mouth onto another person’s mouth in a sexual way.
109. knowledge – understanding of, or information about, a subject that you get by experience or study.
110. land – the surface of the Earth that is not covered by water.
111. language – a system of communication consisting of sounds, words and grammar.
112. laugh – to smile when making sounds with your voice that show you think something is funny or that you are happy.
113. low – not measuring much from the base to the top, close to the ground or the bottom of something.
114. lead – to control a group of people, a country or situation.
115. learning – the activity of obtaining knowledge, or knowledge obtained by study.
116. letter – a written message from one person to another, usually put in an envelope and sent by post.
117. level – the height of something, or the amount or number of something.
118. light – the brightness that comes from the sun, fire and some electrical devices, and that allows things to be seen.
119. limit – the greatest amount, number or level of something that is either possible or allowed.
120. liquid – a substance, such as water, that is not solid or a gas and that can be poured easily.
Read more:
What Happens if You Don’t Drink Enough Water Daily? [Video]
31 House Types ›› Types of houses like apartment, cottage, flat, hut, igloo …
121. look – to direct your eyes in order to see.
122. loss – the fact that you no longer have something, or have less of something.
123. love – to like another adult very much and be romantically and sexually attracted to them, or to have strong feelings of liking a friend or person in your family in a non-sexual way.
124. machine – a piece of equipment with several moving parts that uses power to do a particular type of work.
125. man – an adult male human being.
126. market – the people who might want to buy something, or a part of the world where something is sold, or the business or trade in a particular product.
127. mass – (adjective) having an effect on or involving a large number of people, or forming a large amount. (noun) a large amount of something that has no particular shape or arrangement.
128. meal – an occasion when food is eaten, or the food that is eaten on such an occasion.
129. measure – to discover the exact size or amount of something, or to be of a particular size.
130. meat – the flesh of an animal when it is used for food.
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
131. meeting – an occasion when people come together intentionally, usually in a formal/business sense.
132. memory – the ability to remember information, experiences and people.
133. middle – the central point, position or part.
134. milk – the white liquid produced by cows, goats, sheep, and used by humans as a drink or for making butter and cheese.
135. mind – the part of a person that makes it possible for him or her to think, feel emotions and understand things.
136. mine – the one(s) belonging to or connected with me (the speaker).
137. minute – one of the 60 parts that an hour is divided into, consisting of 60 seconds.
138. mist – thin fog produced by very small drops of water collecting in the air just above an area of ground or water.
139. money – coins or notes that are used to buy things, or the amount of these that one person has.
140. month – a period of about 4 weeks, especially one of the 12 periods into which a year is divided.
141. morning – the part of the day from the time the sun rises or you wake up, until the middle of the day or lunch time.
142. mother – a female parent.
143. mountain – a raised part of the Earth’s surface, much larger than a hill.
144. move – to (cause to) change position.
145. music – a pattern of sounds made by musical instruments, voices or computers, intended to give pleasure to people listening to it.
146. name – the word or words that a person, thing or place is known by.
147. nation – a large aggregate of people united by common descent, history, culture or language, inhabiting a particular country or territory.
148. need – the urge to have something, or want something very much.
149. news – information or reports about recent events.
150. night – the part of every 24-hour period when it is dark, because there is very little light from the sun.
151. noise – a sound or sounds, especially when it is unwanted, unpleasant or loud.
152. number – a unit that forms part of the system of counting or calculating.
153. offer – to ask someone if they would like to have something, or they would like you to do something.
154. oil – a thick liquid that comes from petroleum, used as a fuel, and for making parts of machines move easily.
155. opinion – a thought, belief or judgement about someone or something.
156. order – a request to make, supply or deliver food or goods.
157. organization – a group of people who work together in an organized way for a shared purpose.
158. owner – someone who owns something.
159. page – a side of one of the pieces of paper in a book, magazine or newspaper.
160. pain – a feeling of physical, emotional or mental suffering.
161. paint – a coloured liquid that is put on a surface, such as a wall, to decorate it.
162. paper – thin, flat material made from crushed wood or cloth, used for writing, printing or drawing on.
163. part – some, but not all of a thing.
164. paste – a think, soft, sticky substance made by crushing or mixing things such as fish, fruit or vegetables for food, or a liquid with powder for glue.
165. payment – an amount of money paid or the process of giving money owed to another.
166. peace – free from war and violence, especially when people live and work together happily, without disagreements.
167. person – a man, woman or child.
168. place – an area, town or building.
169. plant – a living thing that grows in earth, or water, usually has a stem, leaves and roots, and produces seeds.
170. play – spending time doing an enjoyable and/or entertaining activity.
171. pleasure – enjoyment, happiness and satisfaction, or something that gives this.
172. position – the place where something or someone is, often in relation to other things.
173. power – ability to control people and events.
174. price – the amount of money for which something is sold.
175. process – a series of actions that you take in order to achieve a result.
176. produce – (verb) to make something or bring something into existence. (noun) food or any other substance that is grown or obtained through farming.
177. profit – money that is earned in trade or business, after paying any costs related to producing selling goods.
178. property – an object/objects, building or land that belong to someone.
179. pull – to move something towards yourself, sometimes with great physical effort.
180. punishment – the act of punishing someone.
181. purpose – why you do something, or why something exists.
182. push – to use physical pressure or force, especially with your hands, in order to move something into a position that is further away from you.
183. quality – how good or bad something is.
184. question – a sentence or phrase used to find out information.
185. rain – drops of water from clouds.
186. reaction – behaviour, a feeling or an action that is the direct result of something.
187. reading – the skill or activity of getting information from books.
188. reason – the cause of an event or situation, something that provides an excuse or explanation.
189. record – (verb) to store sounds or moving pictures using electronic equipment. (noun) the best or fastest ever done. (noun) a flat plastic disc on which music is recorded.
190. regret – a feeling of sadness about something sad or wrong, or about a mistake that you have made.
191. relation – the way in which two people or groups of people feel and behave towards each other.
192. religion – the belief in, and worship of, a god or gods.
193. request – the act of politely or officially asking for something.
194. respect – admiration felt or shown for someone or something that you believe has good ideas or qualities.
195. rest – to stop doing a particular activity in order to relax and regain your strength.
196. reward – something given in exchange for good behaviour or good work.
197. rice – the small seeds of a particular type of grass, cooked and eaten as food.
198. river – a natural wide flow of fresh water across the land into the sea, a lake or another river.
199. road – a long hard man-made surface built for vehicles to travel along.
200. room – a part of the inside of a building that is separated from other parts by walls, floor and ceiling.
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
201. rule – a principle or instruction that states the way things are and how they should be done, and tells you what you are and aren’t allowed to do.
202. run – to move along, faster than walking, by taking quick steps.
203. salt – a common white substance found in sea water and in the ground, used especially to flavour food or to preserve it.
204. sand – a substance that consists of very small grains of rock, found on beaches and deserts.
205. sea – the salty water that covers a large surface of the Earth.
206. seat – a piece of furniture in a building or vehicle, that has been designed for someone to sit on.
207. secretary – someone who works in an office, writing letters, making phone calls and arranging meetings.
208. selection – the act of choosing someone or something.
209. sense – an ability to understand, recognize, value, or react to something, especially any of the five abilities to see, hear, smell, feel and taste.
210. shade – slight darkness caused by something blocking the direct light from the sun.
211. shake – to move or make something or someone move, backwards and forwards or up and down in short quick movements.
212. shame – an uncomfortable feeling of guilt or of being ashamed, because of your own or someone else’s bad behaviour.
213. shock – the emotional or physical reaction to a sudden unexpected and usually unpleasant event or experience.
214. side – a flat outer surface of an object, especially one that is not the top, bottom, the front nor the back.
215. sign – to write your name, usually on a written or printed document, to show that you agree with its contents.
216. silver – a chemical element that is a valuable shiny white metal, used for making cutlery, jewellery, coins or decorative objects.
217. sister – a girl or woman who has the same parents as another person.
218. size – how large or small someone or something is.
219. sky – the area above the earth, in which clouds, the sun, moon and stars can be seen.
220. sleep – the resting state in which the body is not active and the mind is unconscious.
221. slip – to slide without intending to, or to move out of the correct position.
222. smash – to cause something to break noisily into a lot of small pieces.
223. smell – to have a particular quality that others can notice with their noses.
224. smile – a happy or friendly expression on the face in which the ends of the mouth curve up slightly, often with lips parted so that teeth can be seen.
225. smoke – the mixture of gas and very small pieces of carbon that is produced when something burns.
226. sneeze – when you sneeze, air and often small drops of liquid suddenly come out of your mouth and nose in a way that you cannot control.
227. snow – the small soft, white pieces of ice that sometimes fall from the sky when it is extremely cold.
228. soap – a substance used for washing the body, that is usually hard, often has a pleasant smell and produces a mass of bubbles when rubbed with water.
229. society – a large group of people who live together in an organized way. All the people in a country, or in several similar countries, could be referred to as a society.
230. son – someone’s male child.
231. song – a usually short piece of music where words are sung.
232. sort – (noun) a group of things that are of the same type, or that share similar qualities. (verb) to put a number of things in an order, or to separate them into groups.
233. sound – something that you can hear or that can be heard.
234. soup – a usually hot liquid food made from meat, vegetables or fish.
235. space – an empty area that is available to be used. The area around everything that exists, continuing in all directions.
236. start – to begin doing something.
237. step – to move by lifting your foot, and putting it down in a different place, or to put your foot in or on something.
238. stone – a piece of the hard solid substance that is found in the ground, and that is often used for building.
239. stop – to not continue to operate, to not move anymore, or to make someone or something not move anymore.
240. story – a description either true or imagined, of a connected series of events.
241. structure – the way in which the parts of a system or object are arranged or organized, or a system arranged in this way.
242. sugar – a sweet substance especially from the plants sugar cane and sugar beet, used to make food and drinks sweet.
243. suggestion – an idea, plan or action that is suggested, or the act of suggesting it.
244. summer – the season of the year between spring and autumn when the weather is the warmest, lasting from June to September in the UK.
245. surprise – an unexpected event.
246. swim – to move through water by moving parts of your body.
247. talk – to say words aloud; to speak to someone.
248. taste – the flavour of something, or the ability of a person or animal to recognize different flavours.
249. tax – money paid to the government that is based on your income or the cost of goods or services you have bought.
250. teaching – the job of being a teacher; the role/act of educating another person in any particular subject.
251. thing – used to refer in an approximate way to an object or to avoid naming it.
252. thought – the act of thinking about or considering something, an idea or opinion, or a set of ideas about a particular subject.
253. time – the part of existence that is measured in minutes, days or years, or this process considered as a whole.
254. touch – to put your hand or another part of your body lightly onto and off something or someone.
255. trade – the activity of buying and selling or exchanging goods and/or services between people or countries.
256. transport – the movement of people or goods from one place to another.
257. trouble – problems or difficulties, or a negative characteristic of someone.
258. turn – to (cause to) move in a circle round a fixed point or line.
259. use – to put something such as a tool, skill or building to a particular purpose.
260. value – the amount of money that can be received for something.
261. view – an opinion, belief or idea, or a way of thinking about something; what someone can see in their peripheral vision.
262. voice – the sounds that are made when people speak or sing.
263. walk – to move along by putting one foot in front of the other.
264. war – armed fighting between two or more countries or groups, or a particular example of this.
265. wash – to clean something using water and usually soap.
266. waste – an unnecessary or wrong use of things such as money, substances, time, energy or abilities.
267. water – a clear liquid, without colour or taste, that falls from the sky as rain, and is necessary for animal and plant life.
268. way – a route, direction or path.
269. weather – the conditions in the air above the earth such as wind, rain or temperature, especially at a particular time or over a particular area.
270. week – a period of seven days, usually from Monday to Sunday.
271. weight – the amount that someone or something weighs.
272. wind – a current of air moving approximately horizontally, especially one strong enough to be felt.
273. wine – an alcoholic drink generally made from grapes but that can also be made from other fruits or flowers.
274. winter – the season between autumn and spring, when the weather is the coldest.
275. woman – an adult female human being.
276. wood – a hard substance that forms the branches and trunks of trees and can be used as a building material, for making things, or as a fuel.
277. word – a single unit of language that has meaning and can be spoken or written.
278. work – an activity, such as a job, that a person uses physical or mental effort to do, usually for money.
279. writing – a person’s style of writing with a pen on paper that can be recognized as their own.
280. year – a period of twelve months.
If you are already familiar with most of the above words, then you can also click on one of the links below for further suggestions:
Test your vocabulary size
Note: This test is entirely up to you. In order to get correct results, you should choose only words that you know well. If you are not sure you know the word well then do not choose it.
How many words should you know at which level?
| Level | Active Words Range | Passive Words Range |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | 0-300 | 0-600 |
| A2 | 301-750 | 601-1500 |
| B1 | 751-1500 | 1501-3000 |
| B2 | 1501-3000 | 3001-6000 |
| C1 | 3001-5500 | 6001-11000 |
| C2 | 5501-11000 | 11001-20000+ |
CEFR: European Framework of Reference for Languages: Learning, teaching, assessment
Vocabulary has two types of functioning in the individual that are active and passive words. The numbers of active words are less than passives. Because peoeple understand thousands of words on different subjects by listening, reading and seeing, but they can use only the words in line with their interests and the words used commonly (especially when speaking). The words people use to understand are passive, and the words that are used to express and build new structures are called active words.
Expand your vocabulary by pictures