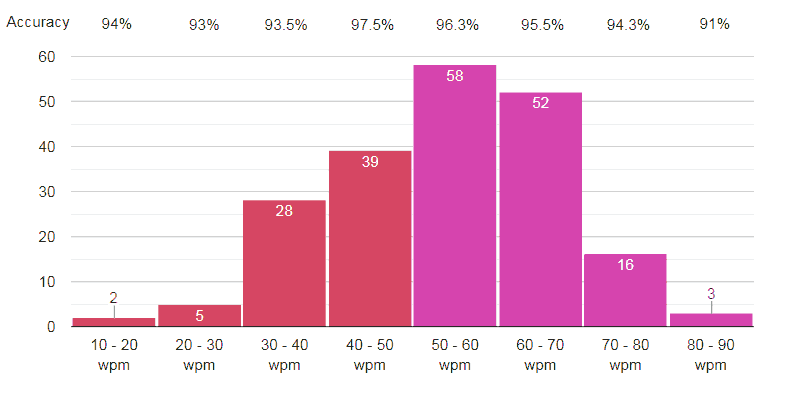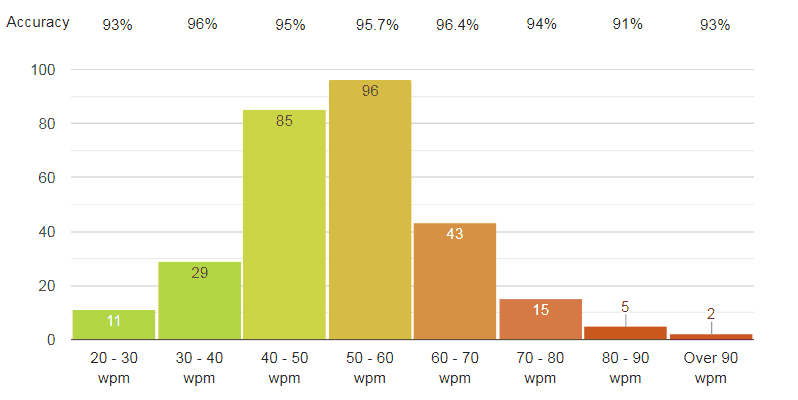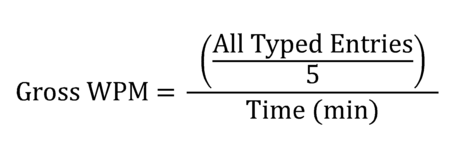Universe of great insights
Typing skills? Check. Take the next step and make your online communication outstanding.
Visit Learning Space
How to Improve Your Typing Speed
Take a deep breath, relax your fingers, and take it slow. You need to be focused and not annoyed when attempting the typing speed test. The best thing you can do to start typing faster is to type more. The more practice you get under your belt, the faster your ‘typing-fu’ will be. It’s all about developing muscle memory. Just make sure you are reinforcing good habits and not ones that will leave your fingers hurting after an intense typing session.
What Is the Best 10-Finger Typing Layout?
Of course, you should use ten fingers for typing, but you can start with a layout that’s the most comfortable for you. The small bumps on the F and J keys will help your fingers locate the correct position without looking. This setup should give you a full range of motion. The more you type, the faster you will get. There are a few alternative layouts that propose a more ergonomic approach to typing. You could also take the big leap and try out the Dvorak keyboard, but that’s a different story.
Who Invented the Qwerty Keyboard?
The QWERTY keyboard was invented in 1868 by Christopher Latham Sholes. He also designed the first successful typewriter. The order of the keys was decided by listing the most common letter combinations and making sure that they were not placed next to each other. He did this to avoid problems that often happened when two neighboring keys were pressed consecutively. The QWERTY keyboard is used to this day and is the most widely used keyboard available.
Word per Minute (WPM) Typing Test
What is the WPM typing test? There are different types of tests for typing. This one is a typing test that expresses your typing skills in words per minute. The more you practice typing, and the more you test your typing speed, the higher your WPM score will be. Some online typing tests and typing test games focus only on WPM typing. The disadvantage of the WPM typing test is that you are only learning how to type fast. WPM typing tests do not show your accuracy.
Is This Really a Free Typing Test You Can Use?
As the makers of LiveChat, customer service software for businesses, we wanted to provide the community of our customers and live chat agents with a free typing test. This way, they can consistently practice typing and improve their typing skills. We’ve also made this tool accessible to every visitor of our page. Our tool is a free typing speed test with a WPM score, but it can be also used as a typing speed test for kids.
How Can You Upgrade Your Typing Skills?
Practice typing as much as you can. Type a lot, type tests, and practice typing tests. Improve your words per minute typing results, and test your typing speed often. Our typing speed test will keep track of all typing tests that you’ve taken in the past so you will be able to see the improvements over time. You will be able to see how your speed typing has changed. If you can do a five-minute typing test every day, your typing skills will increase dramatically.
How Are the Words From the Test Chosen?
We’ve decided to use the 1,000 most common words in the English language. Additionally, we wanted to include words that you can find in our blog articles. You can think of it as a touch of LiveChat’s flavor to make the typing test a bit more interesting. This free typing speed test focuses on typing itself, so words appear randomly. Reading full sentences may influence your typing speed.
Why Have We Prepared This Typing Test?
We prepared this free typing test to give you a quick and easy way to test your typing speed. You can use it when practicing your typing skills to get an idea of how well you are progressing. Businesses can use this test to get an idea about the typing skills of potential hires or to help existing employees develop their typing speed. This typing speed test is one of our free tools, just like the UTM Builder or our Privacy Policy Generator.
Why Is Typing Speed Important to Everyone?
The faster you type, the faster you will be able to communicate with others. You will be able to save a ton of time on any kind of work that requires typing. At first, it will be a couple of extra minutes that you won’t really notice. Over time, the minutes will turn into hours of saved time that you can spend on other activities.
What Is the Average Typing Speed?
The average person types between 38 and 40 words per minute (WPM). That translates into between 190 and 200 characters per minute (CPM). However, professional typists type a lot faster, averaging between 65 and 75 WPM.
What Is CPM and How Can You Calculate It?
The CPM stands for the number of characters you type per minute, including all the mistakes. “Corrected” scores count only correctly typed words. WPM is just the corrected CPM divided by five. This is the de facto international standard.
How Many Words per Minute Is a Good Score?
An average professional typist usually types around 65 to 75 WPM. More advanced positions require 80 to 95 (this is typically the minimum required for dispatch positions and other time-sensitive typing jobs). There are also some advanced typists whose work requires speeds above 120 WPM.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
«wpm» redirects here. For other uses, see WPM.
Words per minute, commonly abbreviated wpm (sometimes uppercased WPM), is a measure of words processed in a minute, often used as a measurement of the speed of typing, reading or Morse code sending and receiving.
Alphanumeric entry[edit]
Since words vary in length, for the purpose of measurement of text entry the definition of each «word» is often standardized to be five characters or keystrokes long in English,[1] including spaces and punctuation. For example, under such a method applied to plain English text the phrase «I run» counts as one word, but «rhinoceros» and «let’s talk» would both count as two.
Karat et al. found in one study of average computer users in 1999 that the average rate for transcription was 32.5 words per minute, and 19.0 words per minute for composition.[2] In the same study, when the group was divided into «fast», «moderate», and «slow» groups, the average speeds were 40 wpm, 35 wpm, and 23 wpm, respectively.
With the onset of the era of desktop computers, fast typing skills became much more widespread.
Typically, professional typists type at speeds of 43 to 80 wpm, while some positions can require 80 to 95 (usually the minimum required for dispatch positions and other time-sensitive typing jobs), and some advanced typists work at speeds above 120 wpm.[3] Two-finger typists, sometimes also referred to as «hunt and peck» typists, commonly reach sustained speeds of about 37 wpm for memorized text and 27 wpm when copying text, but in bursts may be able to reach much higher speeds.[4] From the 1920s through the 1970s, typing speed (along with shorthand speed) was an important secretarial qualification, and typing contests were popular and often publicized by typewriter companies as promotional tools.
Stenotype[edit]
Stenotype keyboards enable the trained user to input text as fast as 360 wpm at very high accuracy for an extended period, which is sufficient for real-time activities such as court reporting or closed captioning. While training dropout rates are very high — in some cases only 10% or even fewer graduate — stenotype students are usually able to reach speeds of 100–120 wpm within six months, which is faster than most alphanumeric typists. Guinness World Records gives 360 wpm with 97.23% accuracy as the highest achieved speed using a stenotype.[5]
Numeric entry[edit]
The numeric entry or 10-key speed is a measure of one’s ability to manipulate the numeric keypad found on most modern separate computer keyboards. It is used to measure speed for jobs such as data entry of number information on items such as remittance advice, bills, or checks, as deposited to lock boxes. It is measured in keystrokes per hour (KPH). Many jobs require a certain KPH, often 8,000 or 10,000.[citation needed]
Handwriting[edit]
For an adult population (age range 18–60) the average speed of copying is 40 letters per minute (approximately 8 wpm), with the range from a minimum of 26 to a maximum of 113 letters per minute (approximately 5 to 20 wpm).[citation needed]
A study of police interview records showed that the highest speed fell in the range 120–155 characters per minute, the highest possible limit being 190 characters per minute.[6]
According to various studies the speed of handwriting of 3–7 graders varies from 25 to 94 letters per minute.[7]
Using stenography (shorthand) methods, this rate increases greatly. Handwriting speeds up to 350 words per minute have been achieved in shorthand competitions.[8]
Reading and comprehension[edit]
Words per minute is a common metric for assessing reading speed and is often used in the context of remedial skills evaluation, as well as in the context of speed reading, where it is a controversial measure of reading performance.
A word in this context is the same as in the context of speech.
Research done in 2012[9] measured the speed at which subjects read a text aloud, and found the typical range of speeds across 17 different languages to be 184±29 wpm or 863±234 characters per minute. However, the number of wpm varied between languages, even for languages that use the Latin or Cyrillic alphabets: as low as 161±18 for Finnish and as high as 228±30 for English. This was because different languages have different average word lengths (longer words in such languages as Finnish and shorter words in English). However, the number of characters per minute tends to be around 1000 for all the tested languages. For the tested Asian languages that use particular writing systems (Arabic, Hebrew, Chinese, Japanese) these numbers are lower.
Scientific studies have demonstrated that reading—defined here as capturing and decoding all the words on every page—faster than 900 wpm is not feasible given the limits set by the anatomy of the eye.[10]
While proofreading materials, people are able to read English at 200 wpm on paper, and 180 wpm on a monitor.[11] [Those numbers from Ziefle, 1998, are for studies that used monitors prior to 1992. See Noyes & Garland 2008 for a modern tech view of equivalence.]
Speech and listening[edit]
Audiobooks are recommended to be 150–160 words per minute, which is the range that people comfortably hear and vocalize words.[12]
Slide presentations tend to be closer to 100–125 wpm for a comfortable pace,[13] auctioneers can speak at about 250 wpm,[citation needed] and the fastest speaking policy debaters speak from 350[14] to over 500 words per minute.[15] Internet speech calculators show that various things influence words per minute including nervousness.[citation needed]
John Moschitta, Jr., was listed in Guinness World Records, for a time, as the world’s fastest speaker, being able to talk at 586 wpm.[16] He has since been surpassed by Steve Woodmore, who achieved a rate of 637 wpm.[17]
Sign language[edit]
In the realm of American Sign Language, the American Sign Language University (ASLU) specifies a cutoff proficiency for students who clock a signing speed of 110-130 wpm.[18]
Morse code[edit]
Morse code uses variable length sequences of short and long duration signals (dits and dahs, colloquially called dots and dashes) to represent source information[19] e.g., sequences for the letter «K» and numeral «2» are respectively ( ▄▄▄ ▄ ▄▄▄ ) and ( ▄ ▄ ▄▄▄ ▄▄▄ ▄▄▄ ). This variability complicates the measurement of Morse code speed rated in words per minute. Using telegram messages, the average English word length is about five characters, each averaging 5.124 dot durations or baud. Spacing between words should also be considered, being seven dot durations in the USA and five in British territories. So the average British telegraph word was 30.67 dot times.[20] So the baud rate of a Morse code is 50⁄60 × word per minute rate.
It is standard practice to use two different such standard words to measure Morse code speeds in words per minute. The standard words are: «PARIS» and «CODEX». In Morse code «PARIS» has a dot duration of 50, while «CODEX» has 60.
Although many countries no longer require it for licensing, Morse is still widely used by amateur radio («ham») operators. Experienced hams routinely send Morse at 20 words per minute, using manually operated hand telegraph keys; enthusiasts such as members of The CW Operators’ Club routinely send and receive Morse code at speeds up to 60 wpm. The upper limit for Morse operators attempting to write down Morse code received by ear using paper and pencil is roughly 20 wpm. Many skilled Morse code operators can receive Morse code by ear mentally without writing down the information at speeds up to 70 wpm.[21] To write down the Morse code information manually at speeds higher than 20 wpm it is usual for the operators to use a typewriter or computer keyboard to enable higher speed copying.
In the United States a commercial radiotelegraph operator’s license is still issued, although there is almost no demand for it, since for long distance communication ships now use the satellite-based Global Maritime Distress and Safety System. Besides a written examination, proficiency at receiving Morse at 20 wpm plain language and 16 wpm in code groups must be demonstrated.[22]
High-speed telegraphy contests are still held. The fastest Morse code operator was Theodore Roosevelt McElroy copying at 75.6 wpm using a typewriter at the 1939 world championship.[23]
See also[edit]
- Colemak keyboard
- Dvorak keyboard
- Instructograph
- Keystroke dynamics
- Morse code
- Speed typing contest
- Touch typing
References[edit]
- ^ Ahmed Sabbir Arif and Wolfgang Stuerzlinger. 2009.»Analysis of Text Entry Performance Metrics». In Proceedings of the IEEE Toronto International Conference–Science and Technology for Humanity (TIC-STH ’09). IEEE, Washington, D.C., US, pp. 100-105.
- ^ Karat CM, Halverson C, Horn D, Karat J (1999). «Patterns of entry and correction in large vocabulary continuous speech recognition systems». Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI ’99). New York, NY, US: ACM. pp. 568–575. doi:10.1145/302979.303160. ISBN 0-201-48559-1.
- ^ Ayres, Robert U; Martinás, Katalin (2005), «120 wpm for very skilled typist», On the Reappraisal of Microeconomics: Economic Growth and Change in a Material World, Cheltenham, UK & Northampton, Massachusetts: Edward Elgar Publishing, p. 41, ISBN 978-1-84542-272-1, retrieved 22 November 2010
- ^ Brown, C. Marlin (1988). Human-computer interface design guidelines. USA: Ablex Pub. Corp. ISBN 0893913324.
- ^ «Fastest realtime court reporter (stenotype writing)». Guinnessworldrecords.com. 2004-07-30. Retrieved 2014-05-13.
- ^ Hardcastle, R. A.; Matthews, C. J. (January 1991). «Speed of writing». Journal of the Forensic Science Society. 31 (1): 21–29. doi:10.1016/s0015-7368(91)73114-9.
- ^ Zaviani, Jenny; Wallen, Margaret (2006). «The Development of Graphomotor Skills». In Henderson, Anne; Pehoski, Charlane (eds.). Hand Function in the Child: Foundations for Remediation (2nd ed.). St. Louis, MO: Mosby. p. 228. ISBN 0323031862.
- ^ «New World’S Record For Shorthand Speed» (PDF). New York Times. 1922-12-30. Retrieved 2014-05-13.
- ^ Trauzettel-Klosinski, Susanne; Dietz, Klaus (August 2012). «Standardized Assessment of Reading Performance: The New International Reading Speed Texts IReST». Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 53 (9): 5452–61. doi:10.1167/iovs.11-8284. PMID 22661485.
- ^ Bremer, Rod (2016-01-20). The Manual: A Guide to the Ultimate Study Method (2 ed.). Fons Sapientiae Publishing. ISBN 978-0-9934964-0-0.
- ^ Ziefle, M (December 1998). «Effects of display resolution on visual performance». Human Factors. 40 (4): 554–68. doi:10.1518/001872098779649355. PMID 9974229. S2CID 33065301.
- ^ Williams, J. R. (1998). Guidelines for the use of multimedia in instruction, Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society 42nd Annual Meeting, 1447–1451
- ^ Wong, Linda (2014). Essential Study Skills. Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-1285965628.
- ^ Chafets, Zev (2006-03-19). «Ministers of Debate». The New York Times.
- ^ Smillie, Dirk (2008-07-22). Falwell Inc.: Inside a Religious, Political, Educational, and Business Empire — Dirk Smillie — Google Boeken. ISBN 9780312376291. Retrieved 2014-04-20.
- ^ «John Moschitta set record for fast talking… May 24 in History». Brainyhistory.com. 1988-05-24. Retrieved 2014-04-20.
- ^ «World’s Fastest Talker — Steve Woodmore». YouTube. 2011-02-05. Archived from the original on 2021-12-12. Retrieved 2014-04-20.
- ^ «How fast should I sign?». American Sign Language University. 2014-02-09. Retrieved 2020-07-30.
- ^ International Telecommunication Union, ITU. «International Morse Code Recommendation» (PDF). ITU.
- ^ Morsh, Joseph E.; Stannard, A. F. B. (1947). «Studies in international Morse Code. II. A simplified method of determining code speed». Canadian Journal of Psychology. 1 (2): 67–70. doi:10.1037/h0084027.
- ^ Morse Code at 140 WPM
- ^ Commercial Radio Operator Types of Licenses
- ^ «Morse code page of Roger J. Wendell — WBŘJNR (WB0JNR)». Rogerwendell.com. Retrieved 2014-04-20.
Download Article
Download Article
Curious how efficient of a communicator you are? Words per minute (WPM for short) is a measurement that defines how quickly you are able to form and recognize words in your communication with others. Whether you’re looking to figure out how quickly you type, speak, or read, the basic formula for finding your WPM is the same: (# words)/(# minutes).
-
1
For the quickest results, use an online typing tester. Today, the easiest way to figure out how many words you can type per minute is usually to use a program online specifically made to test this. It’s easy to find dozens of these programs with a search engine term like «words per minute typing test.» Though there are many of these types of programs available, most work the same way: you type a list of words within a certain time limit and the program uses your performance to calculate your WPM.
- One great program for this is available at 10fastfingers.com.[1]
The test on this page is simple: just type each word on the screen, putting a space between each, until the minute timer counts down. - In addition to learning your WPM, this typing test will also tell you the number of mistakes you made and tell you which percentage of test-takers you scored in.
- One great program for this is available at 10fastfingers.com.[1]
-
2
Alternatively, open a word processor and set a timer. You can also determine your typed WPM manually — for this, you’ll need a computer program you can type in (like a word processor or notepad program), a timer or stopwatch, and a source of text you can copy.
- Set the timer for any length of time (in general, the longer you test yourself for, the less vulnerable you’ll be to fluke performances.)
- Your text should be long enough that you won’t reach the end before your timer finishes.
- If you don’t have a word processor installed on your device, you can access one for free with a Google account at drive.google.com.[2]
Advertisement
-
3
Start the timer and start typing. When you’re all ready to go, start the timer, then begin copying the text. Try to be as accurate as you can — if you notice a mistake while you’re typing a word, fix it, but you don’t need to fix mistakes in words that you’ve already finished. Keep copying the text until the timer goes off, then stop immediately.
-
4
Divide the number of words by the number of minutes. Now, finding your WPM is easy. Divide the number of words you typed by the number of minutes that you originally set your timer for. The final answer you get is your WPM.[[3]
[Image:Calculate Words Per Minute Step 4.jpg|center]]- Note that nearly all modern word processors have a «word count» feature, so you don’t need to count your words manually.
- For example, let’s say that we type 102 words in 1 minute and 30 seconds. To find our WPM, we would divide 102 words/1.5 minutes to get 68 WPM.
Advertisement
-
1
Use an online test. If you’re trying to figure out how many words per minute you can read, once again, your best bet is generally to use an online speed reading test program. These are a little less common than typing speed tests but plenty of good ones can still be found with search engine queries like «reading words per minute.»
- One great program is available at readingsoft.com.[4]
In this program, you time yourself while you read a text of predetermined length. Once you finish, the program calculates your WPM based on how quickly you reached the end.
- One great program is available at readingsoft.com.[4]
-
2
Alternatively, grab a stopwatch and copy a long stretch of text into a word processor. As above, it’s also possible to find the WPM you read manually. To do this, you’ll want to open a word processor, paste a page or two of text into it (preferably something you haven’t read before), then get ready to start a stopwatch.[5]
- Before you begin, use your word processor’s «word count» feature to determine how many words are in your text selection. Record this number — you’ll need it at the end.
- A good place to find long text selections you haven’t read before is on your favorite news website. Since the news is constantly updated, you won’t have to wait long to find something you haven’t read yet.
-
3
Start the stopwatch and start reading. When you’re ready, start timing yourself and begin reading the text at your normal reading speed. Unless you’re specifically trying to see your maximum reading speed, you shouldn’t rush yourself — this won’t give you an accurate picture of how fast you read in your day-to-day life.
-
4
Divide the number of words by the time it took you to read the text. Stop the stopwatch as soon as you read the very last word in the text. Now, just use the same formula as above to find your WPM: # words/# minutes.[6]
- For example, if it took us three minutes to read a 1,100-word news article, we would find our WPM by dividing 1,100/3 = 366.7 WPM.
Advertisement
-
1
Grab a stopwatch and find a speech with a known number of words. Figuring out your WPM while speaking is a little more difficult than the two methods above. Most noticeably, there aren’t any good online programs that can make the calculations for you. However, with a little effort, you can still find your speaking WPM manually. Start by copying a speech (preferably a reasonably short one that you haven’t read before) into your word processor, then finding the number of words in it with the processor’s «word count» feature. You’ll also need a stopwatch for this test.
- A list of major historical speeches is available at historyplace.com.[7]
Many of these speeches (like, for instance, George Graham Vest’s «Tribute to the Dog») aren’t well-known by the general public, making them great for this test.
- A list of major historical speeches is available at historyplace.com.[7]
-
2
Time yourself as you deliver the speech. Start the stopwatch and begin reading the text out loud. Talk at your normal speaking rate — again, unless you’re trying to figure out your maximum speaking rate, going quickly has no purpose. Speak with a moderate, conversational pace, pausing whenever feels natural.
-
3
Divide the number of words in the speech by the minutes it took to deliver. When you finish the speech, stop the stopwatch. Once again, your WPM is given by dividing the number of words in the speech by the number of minutes it took for you to speak it.[8]
- For example, if it took us five minutes to deliver a 1,000-word speech, we would find our WPM by dividing 1,000/5 = 200 WPM.
-
4
Use a recording of a natural conversation for a more accurate WPM. The test above is alright for determining your WPM, but it’s not perfectly accurate. The way we speak when delivering a speech is a little different than the way we speak when we’re actually talking in our day-to-day life — many people, for instance, deliberately talk more slowly and clearly when reading aloud. In addition, since you’re reading from a written text, the test is also partly a test of your reading speed and not your natural speaking speed.
- To get the most accurate results, you’ll want to record yourself speaking to someone else in a semi-casual setting for a long, uninterrupted stretch of time, count the words manually, and divide by the number of words by the number of minutes. This is fairly painstaking, but it’s the most accurate measure of your actual speaking speed.
- One good way to get yourself talking for a long stretch of time is to gather a group of friends and tell them a long, detailed story that you know well and have told before. This way, you won’t need to pause to remember how the story goes — you’ll only be limited by your natural speaking speed.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
I am having trouble with a homework assignment. My teacher wants me to read 106 words at 50 wpm, how do I calculate this so that I can complete this project?
Maybe this will answer your question: 106 words read at 50 wpm should take you just over 2 minutes (about 2.1 minutes or about 2 minutes and 6 seconds). If it were just 100 words (not 106), it would take exactly 2 minutes.
-
Question
What if I took less than a mintue to speak the text I was given? How do I calculate from seconds to mintues?
You should divide the number of words read by 60 to get wps (words per second). Or instead, you could calculate your wpm like this: Divide the words read by the fraction of a minute it took. For example, 6 seconds is 0.1 of a minute. If it took 48 seconds to read your words, that would be 8/10 or 0.8 minutes. In that case, divide your number of words by 0.8 to get your wpm.
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
-
Once you find your words per minute, multiply by 60 to find your words per hour (WPH).
-
Keep in mind that the text you use for your test can affect your results. Texts with lots of long, complicated words will slow you down and give you a lower WPM, while texts with mostly short, easier words will give you a higher WPM.
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
Advertisement
About This Article
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 132,614 times.
Did this article help you?
12 May 2020Admin
We wrote this original article on the 10th of November 2019, based on our survey data. In March 2020, we have completed our second survey to find out average words per minute speed with more people with different age group and job title.
We also include the old survey result so that we can get the average WPM in a large volume. First of all, if you are here to increase your average typing speed, I suggest you read this article: How to increase typing speed?
Contents
- What is the average typing speed?
- Average words per minute of students (Age 13 to 27)
- Average wpm of office workers (Age – 24 to 47)
- Average wpm of Programmers
- Average wpm of typist
- Average typing speed of teenagers
- What is a good typing speed?
- Fastest typing speed in the world
- How to increase typing speed?
People ask me a question several times, what is the average typing speed of a person. You may also think the same question sometimes. People are interested to know others’ typing speed to set an example and improve their typing skill.
So, in this post, I am going to share some of the statistical data related to the average words per minute speed.
What is the average typing speed?
Survey report of March 2020
In last month we surveyed thousands of people of several occupations. We did the same type of survey earlier in the year 2019, but this time we did it on a vast scale.
We have divided the participants into four classes, back-office workers, students, typists and programmers. In this article, we will revile the detailed analyses of that survey.
Before scolding the survey result, I want to clarify that we conducted this survey online on our website. The participates of different age and occupation join this survey from different parts of the world.
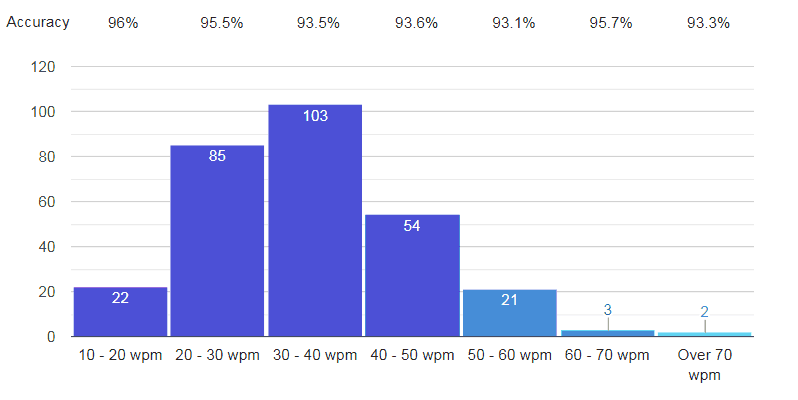
Students (Age 13 to 27)
Average words per minute
Nearly 300 students participate in this survey. And all the students aged between 13 to 27 years. As you can see in this graph, 103(35.5%) students out of 290 have the typing speed between 30 to 40 WPM. 107 (36.8%) students have the typing speed bellow 30 WPM. And only 5(1.7%) students have the typing speed over 60 WPM.
So in this report, it is apparent that over 83% of students has the words per minute speed between 20 to 50 WPM. Now come to the next category, back-office workers.
Accuracy rate
It is really vital to track the accuracy rate besides typing speed. As, a good typing speed has the value only when you have an excellent accuracy rate. In our survey, we found that the average accuracy rate of students is 94.38%. Weather, the accuracy rate of students who scored below 30 WPM, is 95.75%.
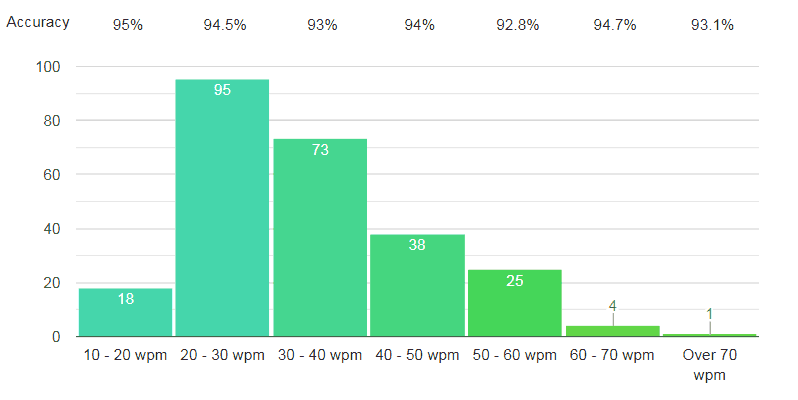
Back-office workers (Age group – 24 to 47)
Average words per minute
The report is also not very impressive here. Over 37% general office workers have the typing speed between 20 to 30 WPM. 28.7% peoples have a speed between 30 to 40 WPM. 14.9% office workers have typing speed around 40 to 50 WPM. And only 11.8% of them have over 50 WPM speed.
That’s mean, according to this survey, it’s very clear that most of the office workers don’t see typing as a serious matter.
Accuracy rate
The average accuracy rate of back-office workers is 93.8%. That’s mean students has slightly better accuracy rate than the office workers. Although 93.8% also is not a very bad rate.
Programmers (Age group 22 to 53)
Average WPM
On the other side, we found that programmers are pretty good at typing. As a programmer spends most of their time on typing codes, it’s natural that they have a good typing speed. In our test, approximately 73% of coders have typing speed between 40 to 70 WPM. Only 3.4% of coders have typing speed below 30 WPM. And 9.3% has speeded over 70 WPM. That’s really impressive.
Accuracy
The average exactness of programmers is 94.38%. While the accuracy rate of coders who have typing speed between 40 to 70 WPM is 96.43% which is an excellent rate.
Professional typist (Age group 23 to 61)
Average WPM
Now the typist, but you have to understand that the typist attended the survey are all not professional typists. Many people just started their career as a typist and DTP worker.
You can see clearly in this graph that 94% of typist has typing speed over 40 WPM. It’s definitely better than programmers, office workers and the students. Nearly 8.4% of typist has WPM rate over 70. And only 4% of typist has WPM speed bellow 30.
Accuracy
94.26% is the average exactness rate of professional typists and DTP personals.
Conclusion
So it’s apparent that typist and programmers generally have a better typing skill then the students and office workers. And the final result that we got in our survey is, the average typing speed of students is around 34.44 WPM, approx 33.93 words per minute for office workers, programmers average WPM is 53.76, and typists have the average typing speed of 52.20 WPM.
Average typing speed (Gender wise)
We found an interesting fact that girls’ average typing speed is a little lesser than the boys. But among those who score above 60 WPM, girls are 65%. It is pretty interesting.
Average typing speed of teenagers
In our survey, we found that the average words per minute of teenagers are around 38 which is a little more than the average WPM of students. But their accuracy rate is a little less than the others.
What is a good typing speed?
Now a very important question, what is a good typing speed, and what WPM should we target? We can say that the speed that is above average is good. That’s mean if you are a student; we can say that, over 35 words per minute is a good typing speed (as the average typing speed of students is around 34.44 WPM).
But if you wanna be a good typist or a programmer you must have a WPM speed over 60. On average we can say 50 – 60 WPM is a good speed. According to a survey done by Microsoft Corporation, many HR, Managers expect their employees to be able to type above 50 WPM speed. So if you are preparing for a job you should target at least 50 WPM.
In our survey, we found that a 14 years old girl achieve 83 WPM speed. That’s mean it’s not necessary that students must have a typing speed between 35 to 50 WPM. There is no limit, so practice more and more to improve your typing further.
Fastest typing speed in the world
The record of being the fastest typist is in the name of Stella Pajunas Garnand. She made this record in 1946 by typing 216 words in one minute. She used an IBM model an electric typewriter to make this record. It is the fastest typing speed ever recorded in the world using a QWERTY layout.
According to some journals and The Guinness World Records, the fastest typist is Barbara Blackburn. Who made this record in 2005 by using a Dvorak keyboard. Her top speed was 212 wpm.
Women achieve both the records, so it’s entirely a wrong myth that the typing speed of girls is lower than the boys.
I hope this detailed report will encourage you to practice typing more and improve your typing speed. Remember the average typing speed of a professional typist is around 60 WPM with more than 98% accuracy rate.
How to increase typing speed?
If you are a student, a teacher, an office representative or a programmer, in a simple word, if you are in a profession where you need to use a computer, a good typing speed can save a lot of time for you. That’s why people are getting interested to learn to type.
And the most common question that people ask, how I could increase my average typing speed. So here we will tell you how you could improve average words per minute speed.
Typing method
One of the main reasons for a slow typing speed is the wrong typing method. Generally, people use the Hunt & Peck typing method to type. In this method, the typist looks at the keyboard, find the key, and then press the key. It is a long process, so it takes some time to look at the keyboard and find the right key.
On the other side, the touch typing method is a way of typing where the typist memorizes the keyboard layout and type without looking at the keyboard. So this method can save a lot of time and make your typing fast. To learn touch typing click on this link: Learn touch typing.
The schedule
So if you are going to learn the touch typing method you have to memorize the keyboard layout which may be a tough job for you. To make it simple, you have to understand the layout and practice from scratch. You may join our free typing lessons to start practicing from the basics. We have designed this course to practice touch typing from the basic level to the advance level.
In free time you may play typing games as it is helpful to set the fingers on the keyboard. Also, if you don’t want to join 30 days long course, you may try our English typing test program. Using this you can practice and check your typing speed in just 5 minutes.
But the most important thing is consistency. If you are not consistent, no typing lesson can teach you to type. So, it is necessary to make a schedule and follow it. Keep at least one hour every day for practice.
If you can follow the schedule for 30 days, your average typing speed will increase a lot. Lastly, accuracy is more important than speed. So don’t ignore typing accuracy while you focus on the speed.
If you want to learn touch typing and increase your typing speed, you may join our 30 days of free typing lessons. If you follow this lesson properly your typing skill will definitely improve a lot.
The average typing speed is around 40 words per minute. To achieve a high level of productivity, aim for 60 to 70 words per minute instead. The following table presents different levels of assessment for an adult.
| Targets for an adult | Words per minute (wpm) | Characters per minute (cpm) |
|---|---|---|
| Average speed | 40 wpm and over | 200 cpm and over |
| Above average speed | 50 wpm and over | 250 cpm and over |
| Productive speed | 60 wpm and over | 300 cpm and over |
| High speed | 70 wpm and over | 350 cpm and over |
| Competitive speed | 120 wpm and over | 600 cpm and over |
Which speed target should you set?
The right speed target depends on your age and your goals. And speed isn’t everything when it comes to learning! It is just as important to develop accuracy. This table provides some guidelines to help you set the right goals for training.
| Age range | Beginner | Intermediate | Expert |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 to 11 years old | 15 wpm (75 cpm) 80% accuracy |
25 wpm (125 cpm) 85% accuracy |
35 wpm (175 cpm) 90% accuracy |
| 12 to 16 years old | 30 wpm (150 cpm) 85% accuracy |
40 wpm (200 cpm) 90% accuracy |
50 wpm (250 cpm) 95% accuracy |
| 17 years old and over | 45 wpm (225 cpm) 90% accuracy |
55 wpm (275 cpm) 95% accuracy |
65 wpm (325 cpm) 100% accuracy |
Do you use Typing Pal at school? See our typing accuracy lesson plan to better instruct your students on the subject.
Do you want to improve your typing speed?
Typing faster means learning how to properly position your hands, use all the fingers, hit the right keys without looking at them and avoiding mistakes. If you don’t fully master at least one of these aspects, you could benefit from typing training.
Typing Pal’s training covers all aspects of good typing technique and offers you a complete and personalized program with hundreds of activities suitable for beginners and advanced users.
Trust our method tested by millions of users to help you achieve your goals. Try it for free!
WPM Calculator
There are some formulas and typing equations used to calculate your typing statistics during the free typing test. Let’s check the following formulas and typing equations:
Gross WPM
Gross is also called Raw WPM, which calculates how fast you can type without penalty for mistakes. In the Gross Typing Speed formula, your total typed words are divided by total time (one minute), and the final result is your WPM.
When typing speed is calculating, a word that contains five characters, such as “I love my computer, don’t you?” would be counted as 6 words, not just 5, for example, (30 characters / 5). In this example, except keys such as backspace or shift to work, all other characters are counted, including spaces, letters, numbers, and punctuation.
This way, it is easier to calculate all the numbers in the word. To get the number of words you type, simply count all the typed entries and divide them into 5. For example, in 1 minute, you typed 200 characters, then your typing speed would be 40 WPM according to this formula: (200 characters / 5) / 1 min = 40 WPM. However, if you typed 200 characters in 30 seconds, your net speed would be 80 WPM. Would you really like to test by applying this formula?
Furthermore, a Net WPM calculation formula for measuring typing speed is considered more accurate. In the Gross formula, all your typing mistakes included will give you a complete picture of your true typing abilities. But in Net WPM calculation, Gross WPM is used to provide more accurate results.
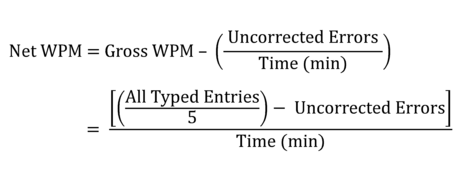
Net WPM
Net WPM is a more accurate and useful tool in gauging typing abilities. Typing mistakes play a part in its calculation, so it also measures your typing productivity instead of count only typing speed. In other words, if you are a fast typist but make a mistake, you will get a lower WPM score than a slower but more accurate typist.
This means that it takes up more time to correct errors and proof-reading than simply to type a passage correctly in the first place. However, fewer mistakes mean less chance of error during typing and proof-reading.
To calculate net WPM, you first need to calculate your Gross WPM and then subtract the total gross WPM results from the total amount of your error that you typed in the one-minute test (also known as error rate). If you don’t know how to calculate your error rates, simply divide the number of mistakes by the total typed characters. For example, in a 2-minute typing test with 80 WPM gross typing speed, you made 8 mistakes, then your error rate would be (8 errors / 2 mins) = 4 errors per minute. However, your net typing speed would be (80 – 4) = 76 WPM. One thing always remembers, your typing speed goes down by 1 WPM on every mistake you make per minute typing speed.
This is a simple equation that deciding which types of mistakes should be counted. However, there are two kinds of mistakes.
- 1. Mistakes that are made and corrected
- 2. Mistakes that are made and not corrected
The first requirement is to count all the mistakes, regardless of the reforms, and another argument is why only uncorrected mistakes should be counted.
1) The mistakes correction during the typing test not only messes up the typist’s concentration but also causes a brief pause. Besides, function keys such as shift and delete keys take time to press and don’t count as characters. This means that your mistake already counted before processing the error correction; even your timer penalty does not stop.
Furthermore, the time penalty also discourages the typist from mistakes correction in the first place. While typists should be encouraged at all costs to avoid mistakes. Errors left uncorrected are much more undesirable and devastating than immediately errors resolved while typing.
2) Now, we will look at a number of errors that were corrected later. For example, in a one-minute typing test with 20 WPM typing speed, you were made a total of 20 errors, but you immediately correct all of them. But we calculate 0 WPM as net speed after considering all errors and take the total number of typed characters and all are free of errors (20 * 5 – 20 = 80 characters to be exact), then the typing speed of 0 WPM indicates that no word was ever typed. If errors are left uncorrected, typically typing a word incorrectly and then waste time in correction would be a blunder, and 0 WPM would be acceptable, but the text resulting would be useless.
Still, typists encourage minimized mistakes because if they don’t waste their time on the correction of 20 errors, they can type much faster than 20 WPM.
These are the two main points that proved that the only errors left uncorrected should be penalized.
Accuracy
Typing accuracy is considered to be the percentage of correct entries out of the total entries typed. It’s easy to calculate; your total typed correct characters divided by the total numbers and then multiplied by 100% and get the accurate percentage. For example, if out of 100 characters, you type 90 characters correctly, which means you typed with 90% accuracy.
It is more interesting to note in this accuracy calculation that whether you correct your mistakes or not, all errors are counted, unlike the net WPM calculation. This is because, In the calculation of accuracy, you see your errors directly so that the next character is typed correctly regardless of whether it will be corrected or not.
(Visited 274,524 times, 6 visits today)
Just start typing and dont use Backslash to correct your
mistakes. Your mistakes will be marked and shown below the writing box. Good luck!
Tip!
- Word Per Minute (WPM) is measured by calculating how many words you can type in 1 minute.
- Character Per Minute (CPM) calculates how many characters are typed per minute.
- The top typing speed was achieved by Stella Pajunas in 1946, whereas Mrs. Barbara Blackburn has averaged
150 wpm in 50 minutes and her top speed was 212 wpm.
Average typing speed
0 — 20 Slow
20 — 40 Average
40 — 60 Fast
60 — 80 Professional
80 — 100+ Top
Calculating WPM Typing:- Inquisitive how productive of a communicator you are? Words Per Minute (WPM for short) is an estimation that characterizes how rapidly you can frame and perceive words in your correspondence with others. Whether you hope to sort out how you type, talk, and read, a recipe for finding your WPM is similar.
i. For the fastest outcomes, utilize a web-based typing analyzer. Today, the most straightforward method for sorting out the number of words you that can type Per Minute is typically to utilize a program online explicitly made to test this. It’s not difficult to track down many of these projects with a web index term like “words Per Minute typing test.” However there are many of these sorts of projects accessible, most work the same way: you type a rundown of words inside a specific time limit and the program utilizes your presentation to compute your WPM.
- One extraordinary program for this is accessible at 10fastfingers.com. The test on this page is basic: simply type a word on screens, putting space, until the moment’s clock counts.
- As well as learning your WPM, this typing test will likewise let you know the number of errors you made and let you know what level of test-takers you scored in.
ii. On the other hand, open a word processor and set a clock. You can likewise decide your composed WPM physically — for this, you’ll require a PC program you can type in (like a word processor or notebook program) a clock or stopwatch, and a wellspring of text you can duplicate.
- Set the clock for any period (as a rule; the more you test yourself, the less weak you’ll accident exhibition.)
- Your text ought to be long enough that you won’t arrive at the end before your clock wraps up.
- On the off chance that you don’t have a word processor introduced on your gadget, you can get to one for nothing with a Google account at drive.google.com.
iii. Begin the clock and begin typing. At the point when you’re all set, begin the clock, then, at that point, start replicating the text. Attempt to be as exact as possible — assuming you notice a misstep while you’re typing a word, fix it, however you don’t have to fix botches in words that you’ve proactively wrapped up. Continue to duplicate the text until the clock goes off, then stop right away.
iv. Partition the number of words by the number of minutes. Presently, it is not difficult to track down your WPM. Partition the number of words you composed by the number of minutes that you initially set your clock for. The last response you get is your WPM.
- Note that essentially all cutting-edge word processors have a “word count” included, so you don’t have to count your words physically.
- For instance, suppose that we type 102 words in 1 moment and 30 seconds. To find our WPM, we would isolate 102 words/1.5 minutes to get 68 WPM.
Finding Words Read Per Minute: Calculating WPM Typing
I. Utilize a web-based test. Assuming that you’re attempting to sort out the number of words Per Minute you can peruse, by and by, your smartest choice is by and large to utilize a web-based speed-perusing test program. These are somewhat less normal than typing speed tests however a lot of good ones can in any case be found with web search tool questions like “perusing words Per Minute.”
- One extraordinary program is accessible at readingsoft.com. In this program, you time yourself while you read a text of foreordained length. When you finish, the program computes your WPM in light of how rapidly you arrived at the end.
ii. On the other hand, snatch a stopwatch and duplicate an extended length of text into a word processor. As over, it’s additionally conceivable to find the WPM you read physically. To do this, you’ll need to open a word processor, glue a page or two of text into it (ideally something you haven’t perused previously), and then, at that point, prepare to begin a stopwatch.
- Before you start, utilize your assertion processor’s “statement count” element to decide the number of words that are in your text choice. Record this number — you’ll require it toward the end.
- A decent spot to find long text determinations you haven’t perused before is on your #1 news site. Since the news is continually refreshed, you will not need to stand by lengthy to find something you haven’t perused at this point.
iii. Begin the stopwatch and begin perusing. At the point when you’re prepared, begin timing yourself and start perusing the text at your typical understanding pace. Except if you’re explicitly attempting to see your most extreme understanding velocity, you shouldn’t rush yourself — this won’t provide you with a precise image of how quickly you read in your everyday life.
iv. Partition the number of words when it took you to peruse the text. Stop the stopwatch when you read the absolute final say regarding the text. Presently, simply utilize a similar recipe as above to track down your WPM: # words/# minutes.
- For instance, if it took us three minutes to peruse a 1,100-word news story, we would track down our WPM by isolating 1,100/3 = 366.7 WPM.
Finding Words Verbally expressed Per Minute: Calculating WPM Typing
I. Get a stopwatch and track down a discourse with a known number of words. Sorting out your WPM while talking is somewhat more troublesome than the two strategies above. Most discernibly, there aren’t any great web-based programs that can make the estimations for you. Notwithstanding, with a touch of exertion, you can find your speaking WPM physically. Begin by replicating a discourse (ideally a sensibly short one that you haven’t perused previously) into your promise processor, then, at that point, track down the number of words in it with the processor’s “statement count” highlight. You’ll likewise require a stopwatch for this test.
- A rundown of major verifiable talks is accessible at historyplace.com. A large number of these discourses (like, for example, George Graham Vest’s “Recognition for the Canine”) aren’t notable by the overall population, making them incredible for this test.
ii. Time yourself as you convey the discourse. Begin the stopwatch and start reciting the text without holding back. Talk at your ordinary talking rate — Once more, except if you’re attempting to sort out your most incredible talking rate, going rapidly has no reason. Talk with a moderate, conversational speed, stopping at whatever point feels regular.
iii. Partition the number of words in the discourse continuously it took to convey. At the point when you finish the discourse, stop the stopwatch. Once more your WPM is given by separating no. of words in the discourse by the number of minutes it took for you to talk about it.
- For instance, on the off chance that it took us five minutes to convey a 1,000-word discourse, we would track down our WPM by separating 1,000/5 = 200 WPM.
iv. Utilize a recording of a characteristic discussion for a more exact WPM. The test above is okay for deciding your WPM, yet entirely it’s not precise. How we talk while conveying a discourse is somewhat not the same as how we talk when we’re talking in our everyday life — many individuals, for example, purposely talk all the more leisurely and obviously while perusing resoundingly. Moreover, since you’re perusing from a composed text, the test is likewise part of the way a trial of your understanding pace and not your regular talking speed.
- To come by the most dependable outcomes, you’ll need to record yourself addressing another person in a semi-relaxed environment for a long, continuous time frame, count the words physically, and partition the number of words by the number of minutes. This is genuinely caring, however, it’s the most reliable proportion of your genuine talking speed.
- One effective method for making yourself talk for a significant length of time is to assemble a gathering of companions and let them know a long, itemized story that you know well and have told previously. Along these lines, you won’t have to respite to recall how the story goes — you’ll just be restricted by your regular talking speed.
Computing Words Per Minute (WPM): Calculating WPM Typing
In Type to Learn, because a ton of the illustrations don’t need typing actual words, we characterize a “word” as any five characters, including spaces, numbers, letters, and accentuation, however NOT capability keys like Shift or Delete.
In this manner, the quantity of words is determined by separating the number of characters composed by 5. The quantity of “words” is then separated by the complete slip by time (in minutes). The following is the real computation.
- Absolute Number of Words = Complete Keys Squeezed/5
- WPM = Absolute Number of Words/Time Slipped by in Minutes (adjusted down)
Model:
- Absolute Keys Squeezed = 200
- Time Slipped by in Minutes = 1.5
- WPM = ( (200/5)/1.5 ) = 26
Computing Accuracy:
In Type to Learn, Precision is characterized as the level of right keys squeezed out of the all-out number of keys squeezed. We ascertain this by separating no. of right keys pressed by the complete no of keys pressed, increasing by 100.
Model:
- All out Keys Squeezed = 200
- Right Keys Squeezed = 190
- Accuracy = (190/200) * 100 = 95%
Ascertaining Changed Words Per Minute (AWPM): Calculating WPM Typing
Changed Words Per Minute is your speed adapted to the number of mistakes made during the illustration or action. This is finished by duplicating the understudy’s WPM score by their Accuracy rate. This information point is a solitary number that considers both speed and Accuracy.
- AWPM = WPM x Accuracy (adjusted down)
Model:
- WPM = 26
- Accuracy = 85%
- AWPM = 26 x .85 = 22
Suggested Tags:- Free Computer Institute Registration in India.
< Shubham >
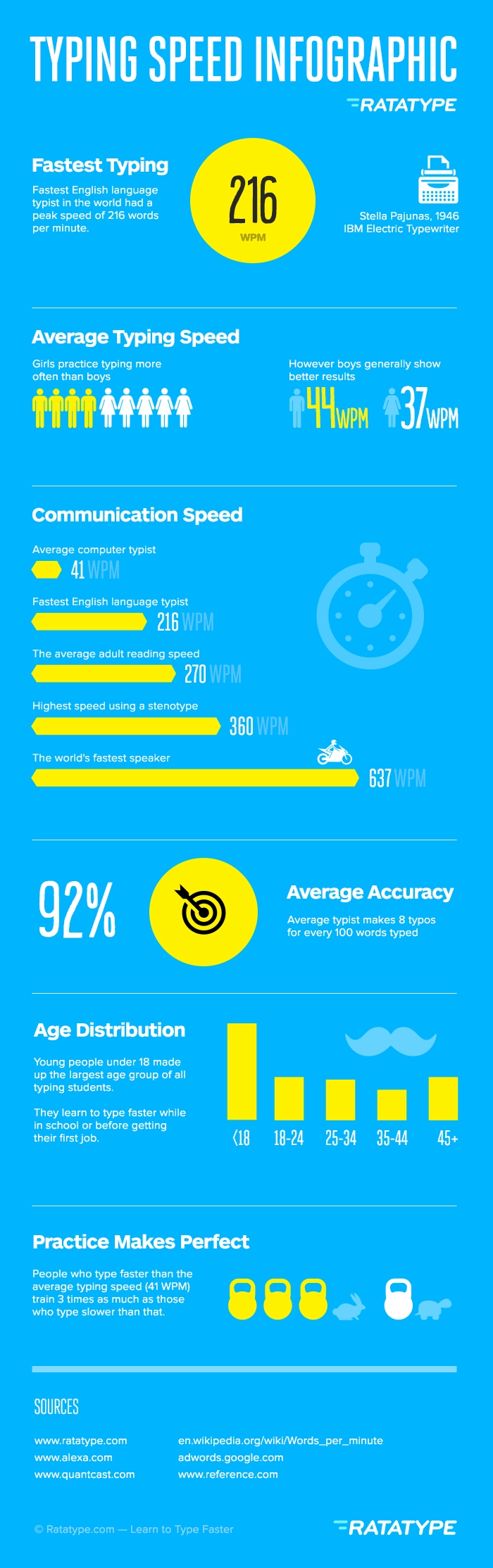
What is the average typing speed on the keyboard? Who types the fastest? How can your typing speed help you get a better job offer? You will get the answer to all these questions and more in this infographic.
The Fastest Typing Speed
The highest typing speed ever recorded was 216 words per minute (wpm), set by Stella Pajunas in 1946, using an IBM electric typewriter. Currently, the fastest English language typist is Barbara Blackburn, who reached a peak typing speed of 212 wpm during a test in 2005, using a Dvorak simplified keyboard.
The average wpm speed is only 41.4 words in one minute. This is far below the speeds of the record holders, or even the speeds that are needed to be successful in the working world. However, it is considered a good typing speed.
Who Types Faster?
The average typing speed for boys is 44 words per minute. This is slightly faster than for girls, who clock in at 37 wpm, a full 7 word per minute slower. This seems a little odd, because statistics show that girls actually enjoy practicing their typing skills more than boys do.
You can take a typing test online at any time to test your skills and find out if you are faster than the average typist.
Any Typos?
The average accuracy for a typist is around 92%, meaning they make 8 mistakes for every 100 words typed. The desired accuracy for professional typing positions is around 97% or higher.
Above the Average
Practice is the key factor in becoming a professional typist, or a typist of any appreciable skill. Let’s repeat that, just to make sure it sinks in. Practice, practice, practice. Activity analysis has shown that people who type faster than average tend to practice 3 times longer than those who have average or below average wpm speeds.
When to Start Learning
Developed typing skills can help young people get better study results in school or college, and get better job offers once they have finished school. 65% of people who learn how to touch type faster are under the age of 24. The main goal of learning to touch type or improving touch typing skills, after age 25 is to become more successful in current job.
Motivation
Improving touch typing skills is a must for every person under 18, but everyone can benefit from some time spent practicing. Average typing speed is one of the key skills listed on your resume. Spend some more time practicing and get better results with Ratatype.
Embed This Image On Your Site
(copy code below):
See also:
-
How to save 21 days per year while typing
-
8 mistakes that prevent you from learning how to touch type fast