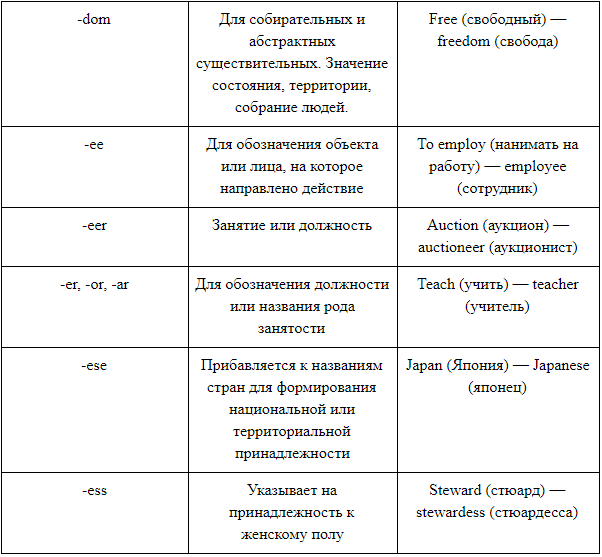
способность,
inability
неспособность;
disability
нетрудоспособность
способный, умелый
unable
неспособный
disabled
искалеченный; инвалид
дать возможность
disable
делать неспособным, калечить
умело, искусно
абсурдность
абсурдный
приемлемость
приемлемый
unacceptable
неприемлемый
принимать, соглашаться
доступ
accessibility
доступность
доступный
доступно
случай, случайность
случайный
нечаянно, случайно
действие
actor
актер
actress
актриса
activity
активность
activities
деятельность
acting
представление
активный
acting
действующий, работающей
действовать
активно
достижение
достигать
привычка, приверженность, увлеченность
addict
увлеченный человек, имеющий стойкую привычку
способный вызывать привычку
увлекаться, предаваться
восхищение
восхитительный
восхищаться
восхитительно
совет
рекомендуемый
советовать
притворство, искусственность
affection
привязанность, любовь
притворный
affectionate
любящий
affective
эмоциональный
воздействовать, влиять; притворяться
соглашение, согласие
disagreement
разногласие, несогласие
соответствующий, приятный
соглашаться
disagree
не соглашаться
соответственно
агрессия
aggressor
агрессору зачинщик
агрессивный
нападать
агрессивно
цель
бесцельный
целиться, намереваться
бесцельно
то, что может быть позволено
unaffordable
то, что невозможно себе позволить
позволять себе
развлечение
приятно изумленный
amusing
забавный
развлекать, забавлять
изумленно
внешность; появление
disappearance
исчезновение
появляться
disappear
исчезать
назначение; деловая встреча
disappointment
разочарование, досада
назначенный
disappointed
огорченный
disappointing
разочаровывающий
назначать
disappoint
разочаровывать
одобрение
одобренный
approving
одобрительный
одобрять
одобрительно
соглашение; расположение
приведенный в порядок
приводить в порядок, организовывать
аргумент, довод
argumentation
аргументация
доказуемый (в споре)
argumentative
спорный, конфликтный
утверждать, спорить, ссориться
доказательно
присвоение; ассигнование
подходящий, соответствующий
inappropriate
несоответствущий, неуместный
присваивать, предназначать
соответственно, подходяще
прибытие
прибывать, приезжать
притяжение, привлекательность
привлеченный
attractive
привлекательный
привлекать
привлекательно
избежание, отмена
то, чего можно избежать
unavoidable
неизбежный
избегать
неизбежно
красота; красавица
красивый
украшать
красиво
роды
сносный, допустимый
unbearable
невыносимый
носить; терпеть
невыносимо
вера
вероятный, правдоподобный
unbelievable
невероятный
верить
выгода
выгодный
получать выгоду
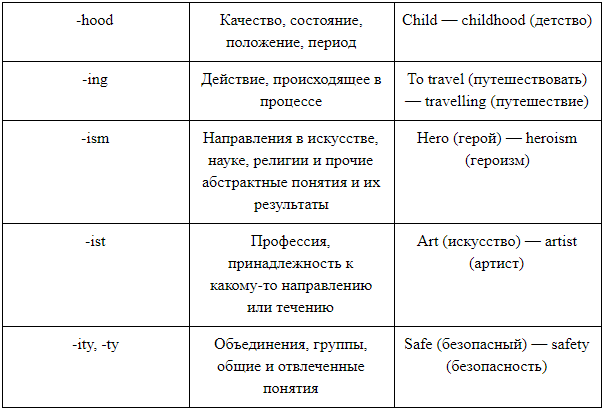
зануда
boredom
скука
испытывающий скуку
boring
скучный, надоедливый
надоедать
скучно
дыхание, дуновение
breathing
дыхание
breather
короткая передышка
дышащий
breathless
бездыханный
дышать
затаив дыхание
дело
businessman
деловой мужчина
businesswoman
деловая женщина
занятой
businesslike
деловой, практичный
занимать делом
деловито, по-деловому
забота, уход
заботливый
careless
небрежный
заботиться, любить
заботливо
carelessly
небрежно
празднование
celebrity
знаменитость
знаменитый, прославленный
праздновать, прославлять
определенность
uncertainty
неопределенность, неуверенность
определенный
uncertain
неопределенный
определенно, уверенно
изменение; мелочь, сдача
изменчивый
changed
изменившийся
changeless
неизменный
unchanged
не изменившийся
менять; обменивать(ся)
неизменно
характер
характерный, типичный
характеризовать
выбор
разборчивый
выбирать
ребенок
children
дети
детский; ребяческий
очистка; устранение препятствий
четкий, ясный
очищать, расчищать
четко, ясно
облако
облачный
cloudless
безоблачный
собрание; коллекция
collector
сборщик
коллективный, совокупный
собирать; коллекционировать
колония
колониальный
колонизировать
цвет
цветной
colourless
бесцветный
multi-coloured
разноцветный
раскрашивать
комфорт; утешение
discomfort
беспокойство; неудобство
удобный, комфортабельный
uncomfortable
неудобный
утешать, успокаивать
удобно
uncomfortably
неудобно
община, общество
общественный, коллективный
сообщение
communicator
коммуникатор, переговорщик
использующийся в общении; коммуникативный
сообщать; общаться
сравнение
сравниваемый
comparative
сравнительный
сравнивать
сравнительно, относительно
соревнование; конкуренция
competitor
конкурент, соперник
соревновательный
соревноваться, конкурировать
в форме соревнования, конкуренции
завершение, окончание
законченный
complete
полный, завершенный
incomplete
неполный, назавершенный
заканчивать, завершать
полностью
поздравление
поздравлять
соединение, объединение
связанный, соединенный
соединять
disconnect
разъединять
внимание; рассмотрение, обсуждение
значительный
considerate
внимательный, деликатный, тактичный
inconsiderate
неосмотрительный; невнимательный к другим
считать, полагать; рассматривать
значительно
совесть
совестливый, добросовестный
conscientiousless
бессовестный
добросовестно
сознание
осознающий
unconscious
без сознания
сознательно, осознанно
консультация
consultant
консультант
консультирующий
консультировать
вместилище, контейнер
содержащий
содержать, вмещать
непрерывность
продолжающийся, длящийся
продолжать
непрерывно
управление, руководство
поддающийся управлению
uncontrollable
неподдающийся управлению
controlled
управляемый
uncontrolled
неуправляемый
управлять, регулировать
бесконтрольно
убеждение
убедительный
convinced
убежденный
убеждать
убедительно
повар
cooker
плита, духовка
переваренный
under-cooked
недоваренный
готовить еду
исправление
corrector
корректор
правильный
incorrect
неправильный
исправлять
правильно
прилавок
discount
скидка
accountant
бухгалтер
исчисляемый
uncountable
неисчисляемый
считать
немеряно, без счета
храбрость
храбрый
encouraged
воодушевленный
encouraging
подбадривающий
discouraged
обескураженный
приободрять, поддерживать
discourage
отговаривать, обескураживать
смело, храбро
создание
creativity
творчество
creator
творец, создатель
creature
творение; живое существо
творческий
создавать, творить
творчески
вера, доверие
вероятный, заслуживающий доверия
incredible
невероятный
вероятно
incredibly
невероятно
критик
criticism
критика
критический; переломный; рискованный
критиковать
критично, критически
культивация, обработка
культивированный, обработанный
обрабатывать
культура
культурный, воспитанный
cultural
культурный (как часть культуры)
культурно
лекарство; лечение
излечимый
incurable
неизлечимый
вылечивать, исцелять
неизлечимо
опасность
опасный
угрожать
опасно
день
ежедневный
ежедневно
обман, заблуждение
обманчивый
deceitful
обманчивый, лживый
обманывать
обманчиво, предательски
решение
определенный, явный
undecided
нерешительный, неясный
decisive
решительный, убежденный, убедительный
решать, принимать решение
решительно, определенно
определение
четкий, определенный
indefinite
неопределенный
определять, давать определение
определенно, ясно
indefinitely
нечетко, неопределенно
восторг, наслаждение
восхитительный
delighted
польщенный
восхищаться
с восторгом
доставка, поставка
доставленный
доставлять
зависимость
independence
независимость
зависимый
independent
независимый
зависеть
независимо
депрессия, подавленность
депрессивный, вызывающий депрессию
depressed
подавленный
подавлять
описание
описательный, наглядный
описывать
проект, дизайн
designer
дизайнер, проектировщик
проектировать
желание, стремление
желательный, желаемый
undesirable
нежелательный
желать, стремиться
желательно
разрушение
разрушенный
разрушать, уничтожать
решительность; определение
решительный
решать, определять
развитие
developer
разработчик
развитой
developing
развивающийся
undeveloped
неразвитый
развивать(ся)
умирающий
умирать
разница, различие
indifference
безразличие
другой, отличающийся
indifferent
безразличный
отличаться
по-другому
indifferently
с безразличием
тревога, беспокойство; нарушение тишины, порядка
обеспокоенный
disturbing
беспокоящий
беспокоить, мешать
сомнение
сомнительный
doubtless
несомненный
undoubted
бесспорный
сомневаться
с сомнением
doubtlessly
не сомневаясь
undoubtedly
без сомнения
легкость, свобода
disease
болезнь
легкий
uneasy
неловкий, тревожный
облегчать, ослаблять
легко
uneasily
неловко
хозяйство
экономический
economical
экономный
экономить
экономически; экономно
воспитатель, педагог
education
образование
образованный
uneducated
необразованный
educative
образовательный
воспитывать, давать образование
следствие, результат
effectiveness
эффективность
эффективный, действующий
производить, выполнять
эффективно, действенно
электричество
electrician
электрик
электрический
электрифицировать
империя
empiror
император
имперский
empiric / empirical
исходящий из опыта, эмпирический
служба, работа
unemployment
безработица
employer
наниматель, работодатель
employee
работающий по найму
нанятый, занятый
unemployed
безработный
нанимать
конец, окончание
бесконечный
unending
нескончаемый
конец, окончание
бесконечно
окружающая среда
природный
развлечение
развлекательный
развлекать
энтузиазм, восторг
enthusiast
энтузиаст, восторженный человек
восторженный
с восторгом
оборудование
снаряженный, оборудованный
снаряжать
сущность
главный, основной
главным образом
экзамен; медосмотр
проэкзаменованный; осмотренный врачом
экзаменовать; осматривать
возбуждение, волнение
возбуждающий
excitable
возбудимый
excited
возбужденный, взволнованный
возбуждать, волновать
взволнованно, возбужденно
ожидание, предчувствие
ожидаемый
unexpected
неожиданный
ожидать, предчувствовать
расход(ы), затраты
дорогой
inexpensive
недорогой
тратить, расходовать
дорого
опыт, опытность
inexperience
неопытность
experiment
эксперимент
опытный
inexperienced
неопытный
experimental
эспериментальный
испытывать
взрыв
explosive
взрывчатое вещество
взрывчатый
взрываться
выражение
выразительный
выражать
выразительно
пространство, степень
длительный,обширный
extensive
обширный
простираться, тянуться
обширно, протяженно
крайняя степень, крайность
крайний, чрезвычайный
крайне
очарование, обаяние
чарующий
fascinated
очарованный
очаровывать
справедливость; порядочность
порядочный, справедливый
unfair
несправедливый
справедливо, честно; довольно-таки
финансы
финансовый
финансировать
финансово
твердость
твердый
утверждать
твердо
физическая форма, физическое состояние
находящийся в хорошей форме; подходящий
unfit
неподходящий
подгонять, подстраивать
следующий
следовать
глупыш, дурак
глупый
обманывать
глупо
забываемый
unforgettable
незабываемый
forgetful
забывчивый
forgotten
забытый
забывать
прощение
прощающий
forgivable
простительный
unforgivable
непростительный
прощать
с прощением
судьба, счастье; богатство, состояние
счастливый
unfortunate
несчастный
к счастью
unfortunately
к сожалению
свобода
свободный; бесплатный
свободно
частота
частый
часто посещать
часто
друг
friendship
дружба
friendliness
дружелюбие
дружеский, дружелюбный
unfriendly
недружеский
дружелюбно
страх, испуг
страшный
frightened
испуганный
frightening
пугающий
пугать, устрашать
страшно; испуганно
щедрость
щедрый
щедро
джентльмен
мягкий, нежный
мягко, нежно
привидение, призрак
похожий на привидение
трава
травяной
привычка, обычай
habitant
обитатель
habitat
естественная среда
habitation
жилище, обиталище
привычный
приучать
обычно
рука; рабочий
handful
горсть
удобный (для использования)
handmade
изготовленный вручную
вручать
счастье
unhappiness
несчастье
счастливый
unhappy
несчастный
счастливо
unhappily
несчастливо
вред
вредный
harmless
безвредный
повредить, навредить
вредно
здоровье
здоровый
unhealthy
нездоровый
дом, жилище
бездомный
честь
почетный
почитать, чтить
почетно
надежда
hopefulness
оптимизм, надежда
надеющийся
hopeless
безнадежный
надеяться
с надеждой
человечество
человеческий
humane
гуманный
inhuman
бесчеловечный
humanitarian
гуманитарный
юмор
юмористический
с юмором
спешка
торопливый, спешащий
hurried
торопливый
торопиться
торопливо
лед
ледяной
важность
важный
unimportant
незначительный
важно
впечатление
впечатленный
impressive
впечатляющий
unimpressed
безучастный
производить впечатление
впечатляюще
улучшение
улучшенный
улучшать
толчок, побуждение
импульсивный
импульсивно
несчастный случай; конфликт, инцидент
случайный
случайно
рост, увеличение
растущий
увеличивать(ся)
с ростом
промышленность
промышленный
industrious
трудолюбивый. усердный
индустриализовать
в промышленном отношении
сообщение, информация
informant
осведомитель
formality
формальность
осведомленный
well-informed
знающий, хорошо информированный
misinformed
неверно информированный
formal
формальный, официальный
informal
неофициальный
информировать
misinform
неверно сообщать; дезинформировать
информационно
интенсивность
интенсивный
интенсифицировать
интенсивно
интерес
заинтересованный
interesting
интересный
интересовать
изобретатель
invention
изобретение
изобретательный
изобретать
изобретательно
приглашение
приглашенный
приглашать
вдохновение
вдохновленный
inspiring
вдохновляющий
вдохновлять
знание
acknowledgement
признание; расписка
признанный
признавать, подтверждать
законность, легальность
юридический, законный
illegal
незаконный, подпольный
легализовать
законно
illegally
незаконно
сходство, подобие
приятный
unlike
непохожий
like
аналогичный
относиться хорошо
dislike
относиться отрицательно
вероятно
unlikely
невероятно
unlike
в отличие
жизнь
living
жизнь
оживленный, веселый
live
актуальный, реальный
жить
оживленно
литература
буквальный
literary
литературный
literate
грамотный
illiterate
неграмотный
буквально
место, поселение
местный
размещать
в определенном месте
одиночество
одинокий; один
удача
удачливый
unlucky
неудачливый, неудачный
к счастью
роскошь
шикарный
большинство
главный, основной
управляющий, руководитель
управленческий
управлять; справляться
женитьба
женатый / замужняя
unmarried
неженатый / незамужняя
жениться
встреча; собрание
встречать, знакомиться
память
memorial
мемориал
памятный
заучивать наизусть
нищета
нищенский, ничтожный
месяц
ежемесячный
ежемесячно
движение
неподвижный
показывать жестом
тайна, загадка
таинственный, загадочный
таинственно, загадочно
необходимость
необходимый
unnecessary
ненужный
необходимо
нерв
нервный
нервировать
нервно
число; количество
многочисленный
numerate
умеющий считать
innumerate
неумеющий считать
обозначать цифрами
объект, предмет
objective
цель; возражение
объективный
возражать
объективно
упрямый
упрямо
случай, происшествие
происходить
операция; оперирование, приведение в действие
управлять, действовать
возможность
opportunist
оппортунист
своевременный, подходящий
оппозиция, противостояние
opponent
оппонент, противник
напротив
opposed
противоположный
противопосталять
владелец, хозяин
собственный
владеть
боль
болезненный
painless
безболезненный
болезненно
painlessly
безболезненно
терпение
impatience
нетерпение
patient
пациент
терпеливый
impatient
нетерпеливый
терпеливо
impatiently
нетерпеливо
участник
participation
участие
участвующий
принимать участие
подробности
особенный
особенно
совершенство
совершенный, идеальный
imperfect
несовершенный
совершенствовать, улучшать
отлично, безупречно
период, срок
периодический
периодически
представление; исполнение
performer
исполнитель
исполнять, выполнять, совершать
мир, спокойствие
мирный
мирно
разрешение
permissiveness
вседозволенность
permit
пропуск
позволяющий
позволять
с позволением
удовольствие
приятный
pleased
довольный
displeased
недовольный
доставлять удовольствие
приятно
точка; пункт
остроконечный, нацеленный
pointful
уместный, удачный
pointless
бесцельный
указывать, направлять
остро, по существу
вежливость
вежливый
impolite
невежливый
вежливо
популярность
популярный
unpopular
непопулярный
популяризировать
владение, собственность
possessor
обладатель, владелец
собственнический
владеть, обладать
вероятность, возможность
возможный
impossible
невозможный
возможно
сила, мощь
мощный
powerless
бессильный
уполномочивать
предпочтение
предпочтительный
preferential
пользующийся препочтением
предпочитать
предпочтительно
подготовка
подготовленный
unprepared
неподготовленный
подготовить
с готовностью
престиж
престижный
престижно
профессия
профессиональный
профессионально
выгода
выгодный
unprofitable
не приносящий выгоды
получать выгоду
выгодно
прогресс, продвижение
прогрессивный
продвигаться вперед
постепенно, продвигаясь вперед
предложение
предложенный
делать предложение
процветание
процветающий
процветать
процветающе
общественность
общественный
разглашать
открыто, публично
быстрота
быстрый
убыстрять
быстро
реальность
realization
реализация, осуществление
реальный, настоящий
unreal
нереальный
реализовать, осуществлять
действительно, в самом деле
признание, узнавание
признанный
узнавать; признавать
снижение, понижение
уменьшенный; сниженный
снижать; сбавлять
отдых, расслабление
расслабленный
relaxing
отдыхающий; расслабляющий
отдыхать, расслабляться
расслабленно
надежность
надежный
unreliable
ненадежный
доверять, полагаться
надежно
религия
религиозный
нежелание, неохота
неохотный
неохотно
регулярность
irregularity
нерегулярность
регулярный, правильный
irregular
неправильный; нестандартный
регулировать
регулярно
замечание
замечательный
замечать, отмечать
замечательно
представление
representative
представитель
представительный
представлять
упрек
безупречный
упрекать
с упреком
репутация
имеющий хорошую репутацию, почтенный
disreputable
имеющий плохую репутацию
давать репутацию
disrepute
компрометироватъ
сопротивление
ударопрочный;
irresistible
неотразимый
resistant
прочный
сопротивляться
неотразимо
уважение
уважительный
уважать
с уважением
отдых
беспокойный
отдыхать
беспокойно
награда
стоящий награды
unrewarded
невознагражденный
награждать
богатства
richness
богатство
богатый
обогащать
богато
риск
рискованный
рисковать
грусть
грустный
огорчать
грустно
сейф
safety
безопасность
безопасный
unsafe
опасный
спасать; экономить
безопасно
удовлетворение
dissatisfaction
неудовлетворенность; недовольство
довольный
dissatisfied
недовольный
satisfactory
удовлетворительный
unsatisfactory
неудовлетворительный
удовлетворять
dissatisfy
разочаровывать; огорчать
исследование
искать, осуществлять поиск
безопасность
безопасный
insecure
находящийся в опасности
охранять, гарантировать
безопасно
серьезность
серьезный
серьезно
наука
scientist
ученый
научный
научно
чувство
insensibility
отсутствие чувствительности
чувствительный
insensitive
несочувствующий
sensible
разумный
insensible
нечувствительный, неосознающий
ощущать
чувствительно
sensibly
разумно
услуга, обслуживание
servant
слуга
обслуженный; поданный на стол
служить, обслуживать, подавать на стол
значительный
insignificant
незначительный
иметь значение
значительно
сходство, похожесть
похожий, подобный
похоже, подобно
искренность
искренний
insincere
неискренний
искренне
шорты
короткий
укорачивать
кратко
сон
sleeper
спящий; спальный вагон
спящий
sleepless
бессонный
спать
без сна
решение; раствор
решенный; растворенный
решать; находить выход; растворять
специальность; фирменное блюдо
specialty
особенность
особенный; специальный
specific
специфический
точно определять
specialize
специализировать(ся)
специально
specifically
специфично
сила
сильный
укреплять
сильно
стресс
стрессовый
ударять, ставить ударение
в состоянии стресса
успех
успешный
unsuccessful
безуспешный
преуспевать
успешно
достаточность
insufñcience
недостаточность
достаточный
insufficient
недостаточный
быть достаточным
достаточно
подходящий
unsuitable
неподходящий
подходить, устраивать
предложение
предлагать
подозреваемый
подозрительный
подозревать
подозрительно
пловец
swimming
плавание
плавающий, плавательный
плавать
сочувствие, понимание
сочувствующий
сочувствовать
с пониманием; сочувственно
уверенность
уверенный
unsure
неуверенный
assured
обеспеченный; уверенный
self-assured
уверенный в себе
обеспечивать; гарантировать
assure
уверять, обеспечивать
конечно; уверенно
assuredly
с уверенностью
окружение
окруженный
окружать
беседа, разговор
разговорчивый
беседовать
вкус
distaste
отсуствие вкуса
сделанный со вкусом; обладающий вкусом
tasteless
безвкусный
пробовать
со вкусом
tastelessly
без вкуса
террор
terrorist
террорист
ужасный
terrific
потрясающий
terrifying
ужасающий
terrified
напуганный
ужасать
ужасно
terrifically
потрясающе
жажда
испытывать жажду
колготки
плотный, тесный
сжимать, натягивать
тесно, плотно
мысль
задумчивый
thoughtless
бездумный
думать, иметь мнение
задумчиво
трагедия
трагичный
tragical
трагический
трагично
путешествие
traveller
путешественник
путешествующий
путешествовать
правда
untruth
неправда
правильный; настоящий
untrue
неверный, не соответствующий действительности
truthful
правдивый
по-настоящему, искренне
truthfully
правдиво
ценность
ценимый
valuable
ценный
ценить, оценивать
разнообразие
variability
изменчивость, непостоянство
изменяемый
invariable
неизменный
менять, разнообразить
неизменно
год
ежегодный
ежегодно
понимание
misunderstanding
непонимание; недоразумение
понятный
понимать
польза
misuse
неправильное использование;
usage
использование
полезный
useless
бесполезный
used
использованный
unused
неиспользованный
использовать, пользоваться
полезно
uselessly
бесполезно
неделя
еженедельный
еженедельно
ширина
широкий
расширять
широко
воля, желание; завещание
жаждущий, желающий
unwilling
не желающий
проявлять волю, желать
охотно, с удовольствием
unwillingly
неохотно
ветер
ветренный
windless
безветренный
мудрость
мудрый
unwise
неблагоразумный
мудро
unwisely
неблагоразумно
стоимость, ценность
достойный
worthless
не имеющий ценности
1. Add –ness to form nouns from adjectives
The suffix –ness forms nouns from adjectives. Not all adjectives can have –ness added to them, but it is a common form – especially with adjectives ending in y (though note the spelling change, to –iness), hard consonant sounds like d, and many adjectives ending in ful. Common examples are:
- ready – They questioned her readiness for the test.
- happy – It is important to create happiness for everyone.
- weak – Eating too much cake was a major weakness of his.
- sad – The closure of the post office brought sadness to the community.
- mad – The decision to drive in the snow was pure madness.
- forgetful – Forgetfulness comes with old age.
2. Add –ity to form nouns from adjectives
The suffix –ity forms nouns from adjectives. Again, this is only for certain adjectives, though it is common adjectives ending in –ble or with soft –s sounds. To form nouns with –ity, changes in spelling often occur, such as replacing the last few letters of the adjective. Common examples are:
- responsible – Your children are not my responsibility.
- possible – Nuclear war seemed like a real possibility.
- scarce – The scarcity of drinks became problematic during the party.
- hilarious – They reacted to the joke with much hilarity.
- probable – It’s hard to guess the probability of her passing the test.
3. Add –ance or –ence to form nouns from adjectives or verbs
The suffix –ance (or –ence) can be added to either adjectives or verbs to form nouns. This is particularly used for adjectives ending in –ent or –ant (where the spelling changes to replace t with -ce) and various verbs. Common examples include:
- independent – Having a car has improved my independence.
- important – Never underestimate the importance of studying.
- silent – Enjoy the silence while the children are away.
- appear – The appearance of a second singer improved the concert.
- resist – The home team put up a strong resistance against their opponents
4. Add –ment to form nouns from adjectives or verbs
The suffix –ment can be added to either adjectives or verbs to form nouns. It is mostly used with verbs, of many kinds, but occasionally also with adjectives with soft endings (such as y endings). This suffix normally does not change the spelling of the core word (though y may change to i). Common examples include:
- appoint – I need to make an appointment with my doctor.
- assign – The final essay was a very big assignment.
- enjoy – Don’t let the rain affect your enjoyment of this walk.
- merry – The children found a lot of merriment in the clown’s antics.
- replace – Our replacement teacher was much better than the first one.
5. Add –tion or –sion to form nouns from verbs
The suffix –tion (or –sion) can be added to verbs to form nouns. They follow many different verb forms, and often change spellings to fit comfortably (for example adding an additional vowel or changing a consonant to sound more natural).
- inform – There is not enough information about foxes in our area.
- decide – The committee will make a formal decision this Friday.
- describe – The police have a good description of the thief.
- multiply – I like addition and subtraction but multiplication is difficult.
- admit – The criminal’s admission of guilt got him in trouble.
Note that a lot of the changes from adjective or verb to noun will need to be learned individually, and spelling rules will not always help you – even if you know how to choose the right suffix, the spelling to connect it to the core word may not be simple.
Admit is a good example of this, as it can be used as a verb with two different meanings, and each one forms a noun with a different suffix:
- Admit – to confess – The criminal’s admission.
- Admit – to give access – Admittance to the top floor is prohibited.
6. Use –ship or –hood to form nouns from other nouns
The suffixes –ship and –hood can be used to create nouns from other nouns. Nouns with –ship added to the end create an abstract noun that shows a relationship (relationship itself is an example!).
- friend – Our friendship is very strong.
- partner – We are in partnership with a major organisation.
Nouns with –hood added to the end are abstract nouns to show groupings, which can refer to grouped people, areas or, more abstractly, periods of time:
- priest – Entering the priesthood is a very serious commitment.
- neighbour – Our neighbourhood is thankfully very quiet.
- child – My childhood was a fun and productive time!
This is a quick introduction to using suffixes to form new nouns from other words. There are many exceptions, and these are patterns rather than rules, so often it is necessary to learn examples individually. However, these patterns can quickly build your vocabulary, and will help you understand what a new noun means when you are familiar with its root. The suffixes also give useful signals to identify a word as a noun. If you have any questions, do comment below!
Suffixes in English: 40 Most Common
Hey.
Source: https://corp.lingualeo.com/ru/2016/11/16/suffiksyi-v-angliyskom-yazyike/
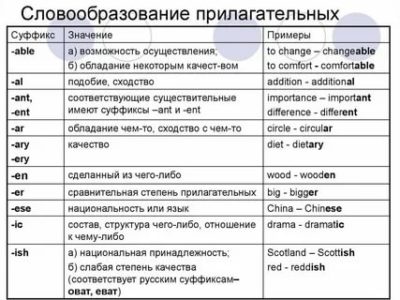
Formation of adjectives in English
The formation of adjectives in English is a rather important and interesting topic. Of course, you can speak English at a fairly high level without going into such details, but such information will not be superfluous.
As in Russian, English adjectives can be derived from other parts of speech. These are usually verbs and nouns. Adjectives are formed using suffixes and prefixes. So, first things first.
Formation of English adjectives using prefixes
Prefixes, or prefixes, are added at the beginning of a word and change its meaning. Usually they change the meaning of the adjective to the opposite, negative. A few examples:
- un— (unlucky)
- in— (invisible)
- dis— (discontent)
- il— (illegal)
- ir— (irrational)
- im— (immovable)
There are several prefixes that change the meaning of a word, but without a negative meaning:
- pre— (pre-emptive)
- hyper— (hypertensive, hyperactive)
Formation of English adjectives using suffixes
There are a lot of varieties of English adjectives formed in the suffix way. As an example, there is a picture with the main suffixes, as well as a few examples of words.
- ful (wonderful, graceful)
- less (pointless, careless)
- able (vulnerable, tolerable)
- ible (terrible, permissible)
- ant (pleasant, hesitant)
- ent (different, patient)
- ic (scientific, iconic)
- ive (active, impressive)
- y (angry, dirty)
- ing (interesting, worrying)
- ed (confused, excited)
- al (general, typical)
- (i) an (Victorian, American)
- You reprise the theme of the (gorgeous, famous)
- ish (childish, Irish)
There is also a classification of English adjectives according to the parts of speech from which they are derived. Adjectives can be formed from nouns, verbs, as well as from other adjectives using various suffixes and prefixes, examples of which have already been considered. The very form of the word may also change. For example, the adjective long is formed from the noun length with a change at the root of the word.
Source: https://english-bird.ru/forming-adjectives/
Suffixes in English — types, education, application
›Learning a language› Vocabulary ›Word formation› Suffixes in English with different parts of speech
Remember those moments in Russian lessons when you were asked to parse a word by defining its prefix, root, suffix and ending? Perhaps this event only caused you headaches, but fear not, everything will be different in English. Let’s not analyze the entire morphological analysis at once, but consider only the suffixes in the English language, which have many interesting features.
A suffix or just the English suffix is a morpheme for word formation in English, which usually comes after the root. In simple words, a suffix is one or more letters, thanks to which a word can change its part of speech, for example, from a verb to a noun:
| Verb | Noun |
| read | reader (reader) |
Or, in general, acquire a different meaning:
| Noun / Verb | Noun |
| bruise (bruise / wrinkle) | bruiser (fighter) |
There are no specific rules regarding suffixes in English. That is, you cannot take one suffix, which, for example, forms nouns, and use it with all words in a row. Suffixes are not always attached to words that look similar or have the same root letter. Nevertheless, a certain logic in their use shines through, and therefore, knowing the suffixes and their functions, you can learn to intuitively form words.
English suffixes: location
As mentioned earlier, English suffixes, like Russian ones, follow immediately after the root:
| Root | Suffix |
| length | en |
| lengthen |
Suffixes can be followed by an ending:
| Root | Suffix | End |
| direct | or | s |
| Directors |
One sentence can contain both a prefix and a suffix:
| Console | Root | Suffix |
| im | patient | ly |
| impatiently |
The suffix can change if the word is used in plural:
| Singular | Plural |
| opportunity (opportunity) | opportunities |
Having dealt with the peculiarities of the location and use of suffixes in the word, let’s move on to their types.
Suffixes in English: species
Suffixes can be used to form almost all independent parts of speech. Based on this, they are divided into 5 categories:
- Noun suffixes
- Vertex suffixes
- Adjective suffixes
- Adverb suffixes
- Numeral suffixes
Let’s analyze each group separately. Note that there are very, very many suffixes in the English language, and therefore we will consider only the most used of them.
Noun suffixes
The group of suffixes for the formation of nouns is perhaps the most voluminous. It includes:
- participate in the formation of inanimate nouns from verbs. Table for clarity:
| Verb | Noun |
| printer (a printer) | |
| ventilate | ventilationor (fan) |
| project (project) | projector (projector) |
- and also in the formation of nouns expressing a person who is engaged in what the verb denotes. To make it clearer, let’s turn to examples:
| Verb | Noun |
| —er | |
| chase (to chase) | chaser |
| run | runner |
| call (to call) | caller (caller) |
| -gold | |
| object (object) | objector (objector / objector) |
| compete (to compete) | competitor |
| survive | survivor |
Often these suffixes are used to form vocabulary words:
| rescue | rescuer |
| sail | sailor |
| teach | teacher (teacher) |
| act (play / act) | actor (actor) |
| wait | waiter |
- A couple of these professions can be used in conjunction with the -ess (-ress) suffix, perhaps the only feminine suffix used in English:
| Masculine nouns | Feminine nouns |
| actor (actor) | actress (actress) |
| waiter | waitress (waitress) |
| steward (steward) | stewardess |
- In addition to professions, the following nouns can be changed using the suffix:
| Masculine nouns | Feminine nouns |
| God | goddess |
| prince | princess |
| count (count) | countess (countess) |
| lion (lion) | lioness (lioness) |
- — of — a suffix that is used to indicate the person to whom the action is directed, that is, this suffix is the opposite of the -er and -or suffixes:
| -er / -or | — of |
| interviewer | interviewee (interviewee) |
| employer | employee |
| addresser (addresser / sender) | addressee (addressee / recipient) |
- -ian — another suffix with which you can express the type of activity. Words are formed from nouns, examples:
| Nouns | Nouns with -ian |
| sparrowic (music) | musician (musician) |
| academy | academicician (academician) |
| Physic (medicine) | physician |
| history | historian (historian) |
The same functions are performed by suffixes:
| Nouns | Suffixed nouns |
| -ent | |
| study (study) | student |
| residency (residence) | resident |
| -ant | |
| account | accountant |
| merchantry (trade) | merchant |
- -ist, is usually used with professions related to the scientific field:
| Nouns | Nouns with -ist |
| science | scientist |
| zoology | zoologist |
| cynology (cynology) | cynologist |
And with music:
| guitar (guitar) | guitarist (guitarist) |
| cello (cello) | cellist |
| piano | pianist (pianist) |
Although this suffix is often found in nouns that express supporters of some views and their perception of the world. In this case, the English suffix performs the same function as the Russian suffix -ist, forming almost identical words:
| Buddhist |
| realist |
| nihilist |
| atheist |
- -ism Is another English suffix that is similar to Russian -ism. It denotes concepts related to the ideological currents and beliefs of a person:
| Catholicism |
| liberalism (liberalism) |
| Marxism |
Source: https://speakenglishwell.ru/suffiksy-v-anglijskom-yazyke/
Enjoy learning English online with Puzzle English for free
For knowledge of a foreign language, a wealth of vocabulary is no less important than an understanding of grammar. The more words a person speaks, the freer he feels in a foreign language environment.
The variety of vocabulary is largely determined by the richness of word formation in the English language. The construction of new words is based on general principles. And the one who knows these principles feels much more confident among unfamiliar vocabulary.
The structure of the word and its change
New words are learned gradually. Most often, at first we only understand them in texts or someone else’s speech, and only then we begin to actively use them in ours. Therefore, mastering new vocabulary is a long process and requires patience from the student, active practice of reading, listening and working with a dictionary.
One of the methods to quickly expand your vocabulary is to master the ways of word formation in English. Having understood the principles by which words are built, it is possible to derive the meanings of its cognate words from an already known word.
The building blocks for every word are the root, prefixes and suffixes. The root is the part of the word that carries the main meaning. A word cannot exist without a root. Whereas prefixes and suffixes are an optional part, however, when added to the root, it is they that help form new words. Therefore, when describing word formation in English, we will separate prefix and suffix methods.
All prefixes and suffixes have their own meaning. It is usually quite blurry and serves to change the basic meaning of the word. When a prefix or suffix (or both) is added to the root, their value is added to the root value. This is how a new word turns out.
The formation of new words can lead not only to a change in meaning, but also to change parts of speech. Suffixes are more common in this function. By adding to the root, they translate a word from one part of speech to another, for example, they make an adjective from a verb or a verb from a noun.
So, from one root a whole group can be formed, all the elements of which are interconnected. Therefore, word formation helps learners of English to see the semantic relationships between words and better navigate the variety of vocabulary.
You can get a new word not only through prefixes and suffixes. Another way is compounding, in which two roots are combined into one word, forming a new meaning. In addition, word formation includes the reduction of words and the creation of abbreviations.
Prefixes as a way of word formation in English
A prefix (the term «prefix» is also used) is an element of a word that is placed before the root. Prefix word formation is rarely used by the English language to change parts of speech (as an exception, the prefix «en-» / «em-» for the formation of verbs can be called). But prefixes are actively used to change the meaning of a word. The prefixes themselves can have different meanings, but among them there is a large group of prefixes with a similar function: to change the meaning of a word to the opposite.
1. Prefixes with negative values:
- un-: unpredictable (unpredictable), unable (unable)
- dis-: disapproval, disconnection
Source: https://puzzle-english.com/directory/wordbuilding
Features of word formation in English
Good afternoon friends! Today I and the teacher of English, Ekaterina, would like to tell you what word formation in English is. The processes of the emergence of new words can be observed in every language.
And in languages related by origin, the methods of replenishing the dictionary will be very similar, and may even have the same names in the meaning. British and Russian have a number of similar techniques for forming new words.
Let’s dwell on each of them in more detail, and you will see that Word Formation in English is very similar to Russian, and in some respects even simpler.
Plus suffix
Affixing is one of the most common and well-known ways to get new words. You just need to add a suitable suffix or prefix — and the new word is ready.
But if it seems to you that in Russian adding morphemes to the root of a word is very easy, then remember that the most frequent mistakes that we make in spelling words are found in suffixes, and there are a lot of spelling rules for their spelling, not to mention exceptions …
Compared to Russian, the British affixation is very simple: for each part of speech, separate types of morphemes are characteristic:
- Verb suffixes — help to form a predicate from adjectives, nouns.
— en or -ize, -ise you add to words in order to give them the meaning of «becoming like the original word»: thick (thick) — thicken (thicken, become thick);
modern (new) — modernize (modernized, modernize);
— ify, fy will help you get a word that means transformation into what the original word said: simple (simple) — simplify (simplify).
— ate is attached to nouns to denote transformation into something or when we show that we are exposed to the initial word: granule (granules) — granulate (granulate).
- Suffixes of nouns — are needed to get the names of objects, professions, phenomena from words denoting a sign of an object and an action.
- By adding -er, -or will get the person doing this action or profession:
Run (run) — runner (runner), act (play) — actor (actor). - A verbal noun denoting a process can be denoted by using –ing: dance (to dance) — dancing (to dance)
- The two suffixes –ness and –ty / -ity will help to form words from adjectives that mean a property or quality, state or condition: kind (kind) — kindness (kindness), major (large) — majority (majority).
- Abstract concepts meaning concepts related to the original word can be obtained using a number of suffix morphemes: -ment, — ance (y) / — ence (y), -dom, -ion / -tion / -sion / -ssion, -ure, -hood, -ship, -th: neighbor — neighborhood, move — movement, translate — translation, educate — education , friend (friend) — friendship (friendship).
- Nationality or professional identity can be specified using -an / -ian: Italia — Italian (Italian)
- It is possible to show that a person belongs to a certain movement or profession by adding –ist — just like in Russian: piano (piano) — pianist (pianist).
The correct use of morphemes to form nouns will help you greatly increase your vocabulary. Often, it is possible to understand which affix should be added at the level of intuition and auditory perception of the language.
Exercises will help you develop these skills. Try the following activity and check your hearing. It is necessary to form new words using the indicated bases and morphemes.
Well, how did it work? If you are in doubt about the correctness of adding an affix, try entering the resulting word into an electronic translator. And of course, try to remember the resulting lexical units.
All these rules will come in handy when preparing for international exams in English.
- To indicate a trait, quality or property of an item, you will need the following morphemes:
-al, -ic, -ical, — ous, -ful, -ly / -y (for nouns), -ant / -ent, -ive, -able / -ible, -ite (for actions), -ary, -ate, -ed. - Lack of quality or feature is always indicated with –less: use — useless.
• as part of a word in an adjective indicates the similarity bird (bird) — bird- (similar to a bird). - Nationality can be shown by several suffixes, for which there is no specific rule for their use. These are –ish, -ese, -ian / -an: Spain — Spanish.
- By adding –ern to the cardinal point, you get the same adjective: south — southern.
Consider the examples in the table to better understand the principles of adding morphemes:
- Separately, we can single out the prefix way of forming words. Each prefix has its own meaning, as in Russian:
You also need to know how to form a verb in English, and there is a separate article about this.
Changing nothing
Conversion words are very common in English. This is not a characteristic feature of the appearance of new words for Russian, but it allows you to significantly increase your vocabulary, simply by looking at all the meanings of a word in the dictionary.
Conversion as a way of word formation consists in the fact that the whole word, completely unchanged, passes from one part of speech to another. Therefore, often in the dictionary opposite a foreign word, you can see several translations with the signs adj (adjective), n (noun), v (verb), adv (adverb), which mean different parts of speech.
For example plant (plant, plant) — to plant (plant).
One plus one makes one
Another common way of word formation is word composition. For us to understand its meaning is very simple: merged two roots — got a new meaning: smoke-free (smokeless). These roots can be written together or with a hyphen.
Strokes and sounds
You can get a new part of speech by changing the stress in the word or one of the sounds: export (export) — to export (export).
And you certainly can’t help but stop at the abbreviation, because the British are so fond of abbreviating words and even whole phrases, replacing letters with an apostrophe. As a result of this reduction, we all got the well-known e-mail, which was originally an electronic mail (electronic message).
Now that you have plenty of exercise, sit back and check out the article on England’s coastline with beaches and the Titanic Museum.
Now you see that it is not so difficult to increase your vocabulary, you just need to remember the words you know and try to form other parts of speech from them.
Marina Rusakova’s school will help you improve your English. You will be able to memorize words without memorization by the method of associations, these words you will remember for 10 years, even if you do not learn the language. Understand rules with verbs, prepositions, times. Learn to comprehend English by ear, you will understand what bloggers, anchors in the news are saying and you will understand films.
I hope my story today was helpful to you.
Subscribe and learn languages with us! You will also receive as a gift a basic phrasebook in three languages, English, German and French. Russian transcription will tell you the pronunciation of words, even if you don’t know the language.
I was with you, Natalya Glukhova, I wish you a good day!
Don’t forget to tell your friends about it! You will find new interesting and useful information in my blog.
(2 4,50 of 5)
- Payments in Germany in connection with the coronavirus for pensioners
Source: https://vivaeurope.ru/languages/english/gramatika/slovoobrasovanije
The ending is ous in English. Suffixes in adjectives in English: the nuances of word-formation definitions
A large number of new words in the English language are formed by attaching suffixes and prefixes to the root of a word.
Suffixing is the process of forming new words using suffixes, prefixing is a similar process where prefixes are involved.
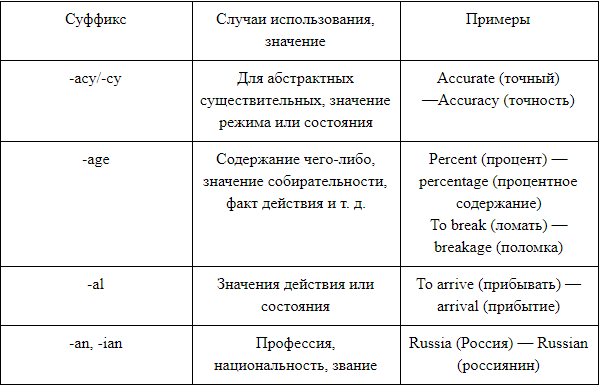
Common noun suffixes:
- The suffix -age forms, which show the action or its result (leakage — leakage, coverage — coverage), and nouns expressing the essence of a concept or quantity (acreage — area in acres, voltage — voltage). Due to the ambiguity of some neologisms, the meaning can expand to the name of the place (orphanage — orphanage).
- Suffix—al added to some verbs to form abstract nouns that denote an action or its result: arrival — arrival, recital — presentation, referral — direction.
- The suffix -ance (with its variants -ence / -ancy / -ency), when attached mainly to verbs, forms action names: absorbance — absorption, riddance — elimination.
This suffix is closely related to -cy / -ce, which are involved in the formation of nouns from adjectives that have suffixes -ant / -ent.
- Suffix -ant forms that are related to a person (especially in the technical or business sphere: applicant — candidate, defendant — defendant) or to substances involved in biological, chemical or physical processes: attractant — attractant, dispersant — dispersant.
Most of the producing words are verbs of Latin origin.
- Suffixes -cy / -ce join productively with adjectives ending in -ant / -ent (convergence — interaction, efficiency — efficiency) and nouns ending in -ant / -ent: agency, agency, presidency, presidency.
- Suffix -dom semantically similar to -hood and -ship, which denote similar concepts.
This suffix is attached to nouns to form common nouns, which denote regions, kingdoms or territories: kingdom — kingdom, maoridom — Maori kingdom.
- The suffix -ee participates in the formation of nouns, which denote persons who inadvertently appear in a context without volitional action on their part: biographee — the one about whom the biography is being written; standee — a person who is forced to stand (for example, on a bus).
- Suffix -eer forms nouns, the meaning of which can be expressed as follows: «a person who has business or is associated with someone / something»: auctioneer — auctioneer, budgeter — budgetary, mountaineer — climber, cameleer — camel driver.
- The suffix -er in derivative words indicates that persons from the context are active participants in the events: teacher — teacher, singer — singer.
Also, this suffix is used to form nouns indicating the place of origin or residence: Londoner — a resident of London, Highlander — Scottish Highlander.
- Suffix— (e) ry forms nouns with the meaning of a place where certain actions are performed or specific services can be provided: bakery — bakery, carwashery — washing.
- Derivatives with a suffix — (e) ry can also denote aggregate concepts: confectionery — confectionery, pottery — earthenware.
- The -ess suffix refers to a small number of derivative nouns that denote female people and animals: princess — princess, tigress — tigress.
- Suffix -ful indicates that the noun acts as a divisible object that has a capacity: cupful — a full cup, handful — a handful, tumblerful — 240 ml, a measure of the volume of liquid.
- The suffix -hood forms nouns that denote states and aggregate concepts: childhood — childhood, beggarhood — poverty.
- Suffix -ism forms nouns from this part of speech and adjectives denoting state, position, attitude, belief, system of theories: Parkinsonism — Parkinsonism, conservatism — conservatism, Marxism — Marxism.
- The -ist suffix forms words that in most cases have a matching -ism noun pair.
Semantically, this suffix denotes a person who is dealing with something: a careerist is a careerist, a fundamentalist is a fundamentalist.
- Suffix -ity forms nouns that denote quantity, state or quality and are mainly of Latin origin: curiosity — curiosity, profundity — depth.
- The -ness suffix is the most productive in the English language and can be attached to almost any adjective: witness — wisdom, darkness — darkness.
- Suffix -ship forms nouns that denote state or position: friendship — friendship, membership — membership.
Verb → noun
| -AL | Refuse-refusal |
| -ANCE/ENCE | |
| -ATION/TION | Locate location |
| -SION | Impress-impression |
| -URE | Press pressure |
| -MENT | Punish Punishment |
| -AGE |
Source: https://chemistry-gid.ru/kapitanskaya-dochka/okonchanie-ous-v-angliiskom-yazyke-suffiksy-v-prilagatelnyh-v.html
Suffixes in English — Learn All
There can be confusion between suffixes and endings in English (both are often called word endings), besides, English terminology in this matter is slightly different from Russian. Therefore, let’s start with the basic concepts.
The ending is an inflectional morpheme. It changes the form of a word, but not its meaning, and at the same time carries a grammatical load:
- pencil — pencils (ending indicates plural)
- work — worked (the ending indicates the elapsed time)
The suffix, in turn, is a derivational morpheme. Suffixes in English create new words, either by changing the meaning of the original one, or by converting one part of speech to another:
- red — reddish (red — reddish)
- teach — teacher (teach — teacher)
There are very few endings in English — these are -s (-es), -ed and -ing. There are a lot of suffixes in English. In this article, we will consider only the most common ones.
Profession and occupation suffixes (-er, -ent, -ess)
The -er suffix is perhaps the most common and productive for «doers.» With it, you can form a noun from almost any verb.
- write> writer — write> writer
- bake> baker — oven> baker
- paint> painter — paint> painter
Most modern words denoting the performer of an action are formed precisely with his help. This also applies to inanimate objects.
- printer — printer
- scanner — scanner
Many words that come from French and Latin have the -or suffix:
- doctor — doctor
- tailor — tailor
- actor — actor
The English suffix -ist often denotes an activity related to science and medicine:
- scientist — scientist
- dentist — dentist
- biologist — biologist
It also denotes an adherent of any views and beliefs:
- pacifist — pacifist
- communist — communist
- realist — realist
Other suffixes in English of words of Latin and Greek origin:
Suffix -ian:
- musician — musician
- librarian — librarian
- mathematician — mathematician
Suffix -ent:
- student — student
- resident — resident, resident
- agent — agent
Suffix -ant:
- informant — informant
- assistant — assistant
- confidant — confidant
The -ess suffix is one of the few «feminine» suffixes in English:
- waitress — waitress
- actress — actress
- princess — princess
Process, action, phenomenon suffixes (-ment, -ion, -ism)
The suffix in English -ment is needed when forming verbal nouns and means an action or its result:
- movement — movement
- entertainment — entertainment
- concealment — concealment
The -ion suffix also denotes an action, process, or result of that process:
- revolution — revolution
- isolation — isolation
- restriction — restriction
The suffix -ism denotes a system of views, beliefs:
- racism — racism
- communism — communism
- pacifism — pacifism
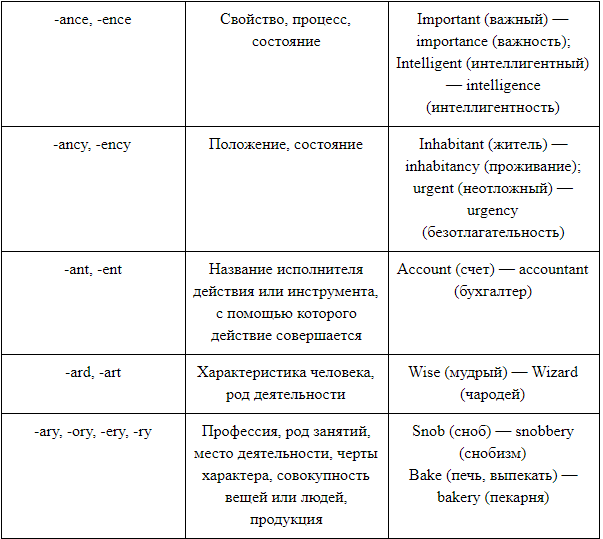
State, quality, property suffixes (-ance / -ence, -dom, -hood, -ity, -ness, -ship, -th)
The -ance / -ence suffix in a noun usually matches the -ant / -ent suffix in an adjective:
- different — difference
- important — importance (important — importance)
- independent — independence
The suffixes in English -hood and -ship mean a person’s condition associated with his age, social relations, and sometimes activity; or a group of people united by this state.
- childhood — childhood
- motherhood — motherhood
- priesthood — clergy
- friendship — friendship
- internship — internship, internship
The suffix -dom means states and properties of a broader meaning:
- freedom — freedom
- wisdom — wisdom
- martyrdom — Martyrdom
The suffix in English -ness means possession of some quality and serves to form nouns from adjectives:
- kindness — kindness
- usefulness — usefulness
- vastness — vastness
The -th suffix more often means physical properties:
- strength — strength
- length — length
- warmth — warm
The suffix -ity means property, quality, and is common for words of Latin origin:
- brevity — brevity
- velocity — speed
- purity — purity
Adjective suffixes
The suffix -ful in English means possession of quality (and is related to the adjective full — «full»):
- beautiful — beautiful
- useful — useful
The -less suffix is opposite in meaning to the previous one and means lack of quality:
- careless — carefree
- harmless — harmless
The suffix -able, -ible characterizes the property or accessibility for any action:
- edible — edible
- portable — portable, portable
- admirable — admirable
The suffixes -ic and -al mean «related, related»:
- heroic — heroic
- mythic — mythical
- cultural — cultural
- musical — musical
The -ous suffix also carries a characteristic:
- dangerous — dangerous
- nutritious — nutritious
The English suffix -ish has several meanings:
expresses similarity (in terms of appearance, behavior)
- girlish — girlish
- childich — childish, childish
- foolish — stupid
weakens the meaning of an adjective
- reddish — reddish
- narrowish — narrowish
means nationality, language or country
- English — English
- Swedish — Swedish
The suffix -ive means possession of a property, the ability:
- attractive — attractive
- sedative — sedative
The English suffix -y is used to form many simple adjectives:
- rainy — rainy
- dirty — dirty
- sunny — sunny
Vertex suffixes
Verb suffixes are not so diverse and almost all have the meaning of «doing something» or «becoming something.»
Suffix -ate
- motivate — to motivate
- activate — activate
Suffix -en
- lengthen — lengthen
- strengthen — strengthen
Suffix -ify
- verify — confirm
- clarify — to clarify
Suffix -ize, -ise
- visualize — render
- neutralize — neutralize
Adverb suffix
Adverbs are formed with just one suffix in English -ly:
- loudly — loudly
- beautifully — beautifully
- politely — politely
We read further:
10 ways to tell an adjective from an adverb in English
What are the types of sentences in English
5 simple rules for word order in English
Adverb, know your place!
Source: https://skyeng.ru/articles/chto-vy-ne-znali-o-suffiksah-v-anglijskom
Formation of nouns in English: suffixes, prefixes, etc.
To do it right assignments 26 — 31 from section «Grammar and Vocabulary» on the Unified State Exam in English, You need to know the most used prefixes and suffixes of nouns.
I want to say right away that the article will be long, so be patient and read it to the end.
Helpful advice:
Be sure to learn all the words from this article, as they are selected from real assignments of past years, which were proposed for implementation on the exam in English.
Work separately with each block, spelling out the words, even if they seem familiar to you.
Remember that in assignments 26 — 31 along with your ability to form new words using various affixes, your spelling skills are assessed!
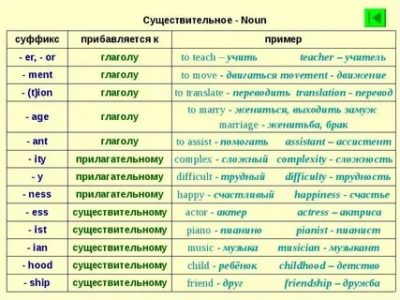
Education model: Verb + er = Noun
When adding a suffix — er to a verb or noun, a noun is formed, denoting a profession, occupation of a person, as well as the names of some objects:
To write — writer, to sing — singer, to drive — driver, to teach — teacher, to examine — examiner, to learn — learner, to build — builder, to loaf — loafer (quitter)
Trumpet — trumpeter (trumpeter), bank — banker (banker), finance — financier (financier)
To contain — container (container), to dust — duster (duster), to grate — grater (grater), to mix — mixer (mixer), to shake — shaker (shaker), to blend — blender (blender), to open — opener (can-opener)
Mince (minced meat) — mincer (meat grinder)
Exception: to lie (lie) — LIAR (liar / liar)
Education model:Verb + or = noun
When adding a suffix — or a noun denoting a profession, occupation of a person is formed to the verb (these are mainly nouns of Latin and French origin):
To act — actor (actor), to advise — advisor / —er (advisor, consultant), to animate — animator (animator), to conduct — conductor (conductor), to create — creator (creator), to decorate — decorator (decorator, painter, wallpaper passer), to direct — director (director, director), to educate — educator (teacher), to illustrate — illustrator (illustrator), to invent — inventor (inventor), to invest — investor (investor, contributor), to instruct — instructor (instructor), to translate — translator (translator), to sail — sailor (sailor), to visit — visitor (visitor), to conquer — coqueror (conqueror)
Here are some more nouns with the suffix —or, to remember:
doctor, professionalor, sculptureor, sponsor, ancestor (ancestor), tutor, mentor (mentor)
Education model: Noun + ist = Noun
When adding a suffix -ist a noun is formed to the noun, denoting a profession, occupation of a person:
art — art (artist), cello — cell (cellist), chemistry — chem (chemist, pharmacist), drama — dramat (playwright), ecology — ecolog (ecologist), economics — econom (economist), geology — geolog (geologist), genetics — genetic (geneticist), guitar — guitar (guitarist), journal — journal (journalist), medal — medal (medalist), meteorology — meteorolog (meteorologist), optimism — optim
Source: https://crownenglishclub.ru/dlya-nachinayushhih/obrazovanie-sushhestvitelnyh-v-anglijskom-yazyke-suffiksy-pristavki-i-dr.html
Plural in English — online lessons for beginners
Read the entire lesson and do a short, easy listening exercise (a translation is shown after each assignment). In the second block of the exercise, you will be asked to write the same phrases under dictation, so listen and read carefully the phrases that you compose in the first block.
Start exercise
In most cases, the plural in English is formed very simply — the ending “-s» or «-Is«, which read differently depending on the consonant in front of it — voiced or voiceless:
For words ending in «s, ss, ch, tch, x» (hissing or whistling sounds), the ending «-Is«, Which reads loudly [of].
In a side-by-side exercise (see the main exercise below), an English noun is shown; to see it in the plural, just click on the word.
In the lesson exercise, beginners will be able to compose phrases on their own — click on the English words to translate the phrase proposed in Russian. A few words that we will meet in the exercise:
- to want [that uOnt] — to want (the verb following the verb «to want» requires the use of a particle «to«- I want to help you — I want to help you) to have [tu hEv] — to have one [uan] — one
Features of the use of plural nouns
Grammatical addition: in English, the plural can be in «countable nouns«. There are a number of nouns that are used only in the singular (we emphasize, in English; the use of words in Russian and English can both coincide and diverge, but we need to get out of the habit of making comparisons with the native language, and plunge into the logic of English):
- money [mani] — money hair [hea] — hair advice [adv] — advice
A number of other nouns are used only in the plural form:
- glasses [glAsiz] — glassesgoods [goodz] — goods trousers [trauzez] — trousers people [people] — people (singular, but implies the plural)
A number of English nouns form the plural in a special way:
- man — men [men] — [men] — man / men, people woman — women [umen] — [wiming] — woman / women (we prepare the organs of speech for pronouncing [y], but immediately pronounce the next sound) child — children [child] — [chIldren] — child / children
A separate lesson will be devoted to these features of the plural in English; now it is important for beginners to remember the basic rule for the formation of the plural.
Plural adjectives
Adjectives in english do not change in the plural and do not change by gender:
- good guy [good boy] — good boy good boys [good boys] — good boys good girl [good girl] — good girl good girls [good girls] — good girls
A noun before another noun can act as an adjective; in this case, it is not used in the plural:
- life situations — life situations
▲ Start online exercise
Next: Articles A, AN, THE and a bit of TO. • Tutor: preparation for the exam and exam, passing international exams.
• «My day» / «Working day» / «My day off»
• TEST elementary / intermediate
Source: http://english.prolingvo.info/beginner/plural.php
Suffixes in English — how to spell English suffixes correctly? — SPEAK ENGLISH
English suffixes, like Russian ones, are the elements of a word following the root. They help us form new words. Some suffixes change the part of speech, for example, turning a verb into a noun. You should also not forget about those suffixes that, changing the form of a word, do not affect its very meaning.
If you have at least a little understanding of the suffixes table in English, then any word-formation «delights» in English will seem like child’s play.
Moreover, having understood the principles of constructing new words using prefixes and suffixes (by the way, prefixes are significantly inferior to suffixes in terms of flexibility and prevalence), a language learner can easily translate masculine nouns into feminine ones, form a nationality or profession.
It turns out that it is not at all necessary to set records for the number of words learned. Indeed, in English, as in Russian, there is the concept of «single-root words» that differ from each other only by suffixes and prefixes. Therefore, knowing, for example, the meaning of the verb paint (to paint, to paint), you will easily understand that a painter is an artist.
Word-building and form-building suffixes: differences
Some English suffixes are considered by Russian speakers as endings. For example, some English textbooks call the suffix -ed an ending. All Suffixes in English are divided into two large groups: form-building and word-building. Thanks to the first, the word does not change its meaning, only the form changes. Compare short and shorter.
Word-forming suffixes in English form a new word with a different meaning, albeit often similar to the meaning of the original word. For example, neighbor is a neighborhood.
Shaping suffixes in english
So, in English, unlike Russian, one word can take not so many forms. This is due to the fact that in English many grammatical meanings of a word, such as gender, verb tense, etc., are expressed not by the word itself, but by various auxiliary elements (articles, auxiliary verbs, etc.).
In Russian, an adjective alone (depending on case, number, gender) can have more than 20 forms. For example, beloved — beloved — beloved — beloved, etc. In English, the adjective favorite (beloved) may not change at all, but we can guess about its exact form from the context (environment): This is my favorite book (This is my favorite book) ).
— He is my favorite writer.
However, in some cases, English words do change shape. And for this, there are five formative suffixes in English that are important to remember: -ed, -est, -ing, -s (-es), -er.
Now it’s worth understanding English words that can take different forms. So, the English suffix -ed is needed in order to form the second and third forms of the regular verb. For example, finish is finished.
The suffixes -er and -est in English are used to form comparative forms of adjectives. We use these suffixes with short adjectives like close (close), big (big), etc. The suffix -er is used for the comparative form, and -est for the excellent one. For example, close — closer — closest.
Among English suffixes, -s and -es are widespread.
They apply in the following cases:
Source: https://ekaterina-alexeeva.ru/nachinayushhim/suffiksy-v-anglijskom-yazyke-kak-pravilno-pisat-anglijskie-suffiksy.html
Word formation. Noun suffixes in English (grade 9)
This is a lesson from the cycle «Word formation in English» and in it we will consider the common noun suffixes: -er / or, -tion, -ing, -ness, -ence / ance (5). Exercises on word formation of a noun will help you understand how nouns are formed in English using suffixes, as well as prepare for English exams in the form of the OGE and USE.
for posting on other Internet resources is prohibited. EnglishInn.ru.
Basic noun suffixes in English (grade 9)
Remember 5 main noun suffixes.
- er / or (worker)
- tion (informaproduction)
- ing (reading)
- ness (happyness)
- ence / ance (difference)
Next, let’s dwell in more detail on each of them.
1. Suffixes of nouns formed from a verb
- -er / or (doer suffix) dance — dancer work — workercollect — collector
invent — inventor
- -tion (process suffix) collect — collection
invent — invention
- -ingsuffer — suffering warn — warning
mean — meaning
Remember three suffixes -er (-or), -tion, -ing, with the help of which nouns are formed from the verb.
2. Suffixes of nouns formed from an adjective
- -nessill — illness
kind — kindness
- -ance / -ence (corresponding adjectives have suffixes: -ant / -ent) important — importance
different — difference
Remember two suffixes: -ness, -ence (ance), with the help of which nouns are formed from an adjective.
Suffixes of nouns in English. Exercises
Suffixes -ness & -tion Are the most common noun suffixes.
Exercise 1. Suffix -ness. Translate these nouns and indicate the adjectives from which they are derived.
foolishness, happiness, seriousness, illness, readiness, richness, strangeness, carelessness, whiteness, cleverness, greatness, brightness
Note.
Source: http://englishinn.ru/slovoobrazovanie-suffiksyi-sushhestvitelnyih-v-angliy.html
Methods of forming nouns in English
How to replenish vocabulary more than 3 times without memorizing? Adopt this method and — voila! Vocabulary enlarged before our eyes.
This method is word formation. How does this work for nouns?
Briefly — about the main thing Usually the topic is studied indefinitely. There is a more effective method: covering the entire «puzzle» at a time. Seeing a clear picture, you can easily refine the little things without negativity.
So, the formation of nouns in English assumes skills:
- convert a noun from a verb and vice versa;
- use affixes;
- put a different emphasis;
- replace the consonant at the root;
- form compound words.
Many do not assume how many words they ALREADY know. They simply do not know how to use this wealth competently.
Having learned 5 skills, you can refer to the dictionary just to check it.
1. Conversion
Nouns in English are related to verbs in an interesting way: they can be the same word. This method is called conversion… This is the first skill. Using it, it is easy to guess about the translation of 60% of English words. Moreover, verbs can be converted not only into nouns, but also into adjectives.
The examples below will help you understand the phenomenon of conversion.
Example: love = to love / love.
Verb convergent word noun
| dream, dream | dream | dream |
| call | name | name, title |
| lift up | lift | lift, lift |
| to send | ||
| milk | milk | milk |
| pour | water | water |
| mind | mind | mind, opinion |
Many are embarrassed that in translation into Russian, both words are not the same root. But the language is different.
It’s funny, but the British created it for themselves! For native speakers, these are absolutely identical words: to milk — milk (milk), to name — name (name — name).
2. Affixation
This «scary» word means suffixes plus prefixes. All prefixes are of two types: negative and significant.
Acquaintance with negative ones has already taken place through borrowing: dysfunction, antispam, deflation. Significant — different in meaning, but amenable to logic.
Prefixes
2 groups of prefixes will allow you to find the meaning of a word by context without a dictionary. If you learn the meaning of each prefix separately, the brain starts to panic, it looks for the right algorithm. It takes time, and speech slows down.
And most importantly, the desire to study the language at all disappears.
Example: everyone knows the prefixes «dis-«, «de-«, «anti-«. But for some reason they do not notice them in English!
An important detail: most negative prefixes of nouns work with verbs.
Negative prefixes
| Console | Examples |
| anti- | Antistress, antipode, antispam. |
| dis- | Disharmony, disqualification. |
| de- | Depiction, departure. |
| mis- | Misfortune, misunderstanding. |
| as- | Sedition, separation. |
| not- | Nonconformist, nonstop. |
Significant prefixes
Most are present in their native language, in borrowings.
You can check the skill of forming nouns in English using a dictionary, but after an independent attempt.
For example, form words: disqualification, pseudoscience, professional, extraordinary, hyperactive, and others. Such training is enjoyable and helps to understand the language.
| Attachment type | Examples of prefixes |
| involvement | Anti-, co-, con-, contra-, vice-. |
| censures |
Source: https://www.study.ru/courses/elementary/obrazovanie-sushchestvitelnyh
Plural of Nouns
In English, everything countable nouns * used both in the singular and in the plural.
* Countable Nouns denote items that can be counted (one, two, three, four, five, etc.): one apple, two apples, three apples; one story, two stories, three stories.
Countable and uncountable nouns
The main way of forming the plural
In English, the plural of nouns is formed by attaching an ending -s (-es) to a noun in the singular:
a pen — pens (handle — handles)
a book — books (book — books)
a box — boxes (box — boxes)
Features of attaching the ending -s (-es)
If a noun ends in -s, -ss, -sh, -ch, -tch, -z, -x, then the ending is added -Is:
a bus — buses (bus — buses)
a glass — glasses (glass — glasses)
a bush — bushes (bush — bushes)
a bench — benches (bench — benches)
a match — Played (match — matches)
a fox — foxes (fox — foxes)
If a noun ends in consonant + y, then -y changes to i, and added -Is:
a baby — babies (baby — babies)
a story — stories (story — stories)
a city — cities (city — cities)
If a noun ends in vowel + y, then the ending is simply added -s:
a toy — toys (toy — toys)
a tray — trays (tray — trays)
a monkey — m (monkey — monkeys)
If a noun ends in -f or -faiththen -f changes to -v, and added -Is:
a leaf — leaves (leaf — leaves)
a thief — thieves (thief — thieves)
a wife — wives (wife — wives)
a knife — knives (knife — knives)
But in some cases, nouns ending in -f, the ending is simply added -s:
a roof — roofs (roof — roofs)
a cliff — cliffs (rock — rocks)
a chief — chiefs (leader — leaders)
a dwarf — dwarfs (gnome — gnomes)
If a noun ends in -o, then the ending is added -Is:
a tomato — tomatoes (tomato — tomatoes)
a hero — heroes (hero — heroes)
In some cases, for nouns ending in -o, the ending is added -s:
a photo — beautiful photos (photography — photographs)
a kilo — kilos (kilogram — kilograms)
a piano — pianos (piano — multiple pianos)
a radio — radios (radio — multiple radio)
a video — videos (video — several videos)
a studio — (studio — studios)
There are also nouns on -o, the plural of which can be formed by adding -s or -Is, while the -es form is used more often:
a memento — mementoes / mements (souvenir — souvenirs)
a mosquito — mosquitoes / Mosquitoes (mosquito — mosquitoes)
a tornado — tornadoes / torandos (hurricane — hurricanes)
a volcano — volcanoes / volcanoes (volcano — volcanoes)
a zero — zeoroes / zeroes (zero — zeros)
Special plural forms of nouns
There are nouns in English, the plural of which must be remembered:
a man [mæn] — men (man — men)
a woman [ˈwʊmən] — women [ˈWɪmɪn] (woman — women)
a child [tʃaɪld] — children [ˈTʃɪl.
drən] (child — children)
a tooth [tuːθ] — teeth [tiːθ] (tooth — teeth)
a foot [fʊt] — feet [fiːt] (foot — feet)
a mouse [maʊs] — mice [maɪs] (mouse — mice)
a goose [ɡuːs] — geese [ɡiːs] (goose — geese)
a louse [laʊs] — face [laɪs] (louse — lice)
an ox [ɒks] — oxen [ˈⱰksn] (bull — bulls)
Remember also nouns in which the plural form coincides with the singular form:
one deer — two deer (one deer — two deer)
one fish — two fish (one fish — two fish)
one sheep — two sheep (one ram — two rams)
one series — two series (one episode — two episodes)
one species — two species (one kind — two kinds)
one aircraft — two aircraft (one plane — two planes)
one spacecraft — two spacecraft (one spaceship — two spaceships)
one salmon — two salmon (one salmon — two salmon)
one cod — two code (one cod — two cod)
one moose — two mosses (one moose — two moose)
one means — two means (one remedy — two remedies)
one offspring — two Offspring (one offspring — two offspring)
Please note that the same noun can be either countable or uncountable, depending on its lexical meaning. For example, salmon (salmon) in the meaning of «kind of fish» is a countable noun, therefore, has the plural form:
I was very excited when I caught a salmon… — I was delighted when I caught the salmon.
I was very excited when I caught two salmon… — I was delighted when I caught two salmon.
Source: https://myefe.ru/reference/nouns/plurals
Adverb in English
An adverb is a word that defines the meaning of a verb, adjective, other adverb, or noun phrase. Most adverbs are formed by adding the suffix –ly to the adjective.
Rules for the formation of adverbs in English
1. To form an adverb in English from an adjective that ends in — l, you need to add the suffix –ly.
Example: careful-carefully.
2.Adjectives ending in — y, when forming an adverb in English, take the suffix — ily.
Will take: lucky-luckily.
3. The suffix Ble is changed to bly.
Example: responsible-responsibly.
Mode of action adverb
The adverb of the mode of action characterizes the verb. It describes the way in which an action is performed.
Example: She did the work carefully. Carefully characterizes the verb to describe the quality of the action.
Adverb of place or location
The adverb of place indicates where the action takes place.
Example: They live locally. (She lives in this area.)
Adverb of time
The adverb of time indicates when an action is performed or its duration, or how often this action is performed.
Example:
— He did it yesterday. (When) — He did it yesterday. (When)
— They are permanently busy. (Duration) — They are constantly busy. (Duration)
— She never does it. (Frequency) — She never does that. (How often)
Adverb of Degree in English
The degree adverb increases or decreases the effect of the verb.
Example: I completely agree with you. (I totally agree with you.) This increases the effect of the verb, while the adverb `partially` decreases it.
Adverbs characterizing adjectives
An adjective can be defined by an adverb. It usually comes before the adjective, with the exception of the adverb enough, which follows it.
Example:
— That`s really good. (This is really good.)
— It was a terribly difficult time for all of us. (It was a terribly difficult time for all of us.)
— It wasn`t good enough. (It wasn’t good enough.) The word enough follows the adjective.
Adverbs characterizing adverbs
An adverb can define another adverb. As with adjectives, the adverb comes before the adverb it defines, while enough is the exception.
Example:
— She did it really well. (She did it very well.)
— He didn`t come last night, funnily enough. (He didn’t show up last night, which is funny enough.)
Noun adverb
An adverb can characterize a noun to indicate a time or place.
Example:
— The concert tomorrow. (Tomorrow’s concert)
Source: http://www.the-world.ru/narechie
Ways of word formation in English
Learning English vocabulary is much easier if you understand how words are formed and what parts they consist of. Today we will look at the main ways of word formation in English. By understanding the basic principles and ways of forming words, you will not get lost in all the variety of English vocabulary.
1. Affixation
Affixation Is the formation of new words by adding prefixes and suffixes. In linguistics, prefixes and suffixes are called affixes, which is why this method of word formation bears this name. Affixation is the most common way to create new words.
Depending on what exactly is added to the word stem (prefix or suffix), prefix and suffix are distinguished. If both are added, then the method of formation is prefix-suffix.
The advantage of affixing is that suffixes and prefixes give us a lot of information about a word.
Suffixes indicate part of speech. If you carefully analyze English words, then you probably noticed that there are special suffixes for nouns, adjectives, adverbs, verbs, thanks to which you immediately determine which part of speech is in front of you. In addition, suffixes can give additional meanings to words. In this article, I will not dwell on the meanings of all suffixes, but I will give a few examples of how suffixes work in English:
teacher — suffix –Er indicates that the word is a noun, and also that it is the name of a profession or occupation
Beautiful — suffix –Ful indicates that the word is an adjective
Lucky — suffix –Ate also adjective suffix
fortunately — suffix –Ly indicates that the word is an adverb
information — suffix –Ation indicates that the word is a noun
informative — suffix –Ive indicates that this is an adjective
informatively — suffix –Ly indicates that the word is an adverb
stability — suffix –Ity indicates that the word is a noun
stabilizes — suffix –Ise indicates that we have a verb
Please note that not one, but two suffixes can be added to the stem, as, for example, when forming an adverb from an adjective that already has a suffix.
As for the prefixes, they do not change the part of speech, but affect the meaning of the word. For example, they make the word negative:
dishonest — dishonest
irrational — irrational
unimportant — unimportant
In addition to changing the sign from plus to minus, prefixes can give words a variety of shades of meaning. There are a lot of prefixes in English, each of them can be devoted to a separate article. Here I will give just a few examples to illustrate how the set-top boxes work:
prehistoric — prehistoric
overeat Overeat
replace — move
international — international
Knowing the meanings of prefixes and suffixes, you can increase your active and passive vocabulary. Firstly, you will be able to independently form new parts of speech, and change the meanings of words. And secondly, you will easily guess what the new words that you come across mean.
2. Composition
There are many so-called compounds in the English language. These words are formed by the fusion of two stems. A word constructed in this way takes on a new meaning. Many verbs, nouns, adjectives are formed by word composition:
hair + to cut = the haircut — a haircut
driving + license = a driving license — rights
baby + to sit = to babysit — look after the child
brain + to wash = to brainwash — brainwash
well + dressed = well-dressed — well dressed
green + eye = green-eyed — green-eyed
Some adverbs and pronouns are also formed in this way:
every + where = everywhere — everywhere, everywhere
any + time = anytime — Anytime
some+body= somebody — somebody
3. Conversion
Sometimes you know a word and you know it’s a verb. And suddenly you meet him again — and it is a noun. This is how it works conversion — the transition of a word from one part of speech to another. In this case, the spelling and pronunciation of the word does not change. This can be confusing, but the good news is that, although the meaning of a word changes with the transition, it still often remains close to the original word.
There are different types of conversion. The most common of these is the transition from noun to verb and from verb to noun:
an email — to email a host — to host a name — to name to call — a call to visit — a visit (to visit — visit)
to date — a date (to date — the one with whom you are dating: a guy or a girl)
Adjectives can be converted to verbs and nouns:
to empty — empty dry — to dry clean — to clean final — a final
rich — the rich
4. Changing stress
To my surprise, many have never heard of this word formation method and confuse it with conversion. Although some linguists consider it as an example of conversion, in order to avoid mistakes, it is more expedient to consider it separately.
When we perceive a word in a text, at first glance it seems that it simply «passed» into another part of speech, because it is written in the same way as the corresponding verb or noun.
However, not all so simple. Some words do not just convert, but also change the stress! Surprised? Let’s look at some examples, you may have mispronounced many of them:
to permit
Source: https://enginform.com/article/slovoobrazovanie-v-angliyskom
Английские суффиксы, как и русские — это следующие за корнем элементы слова. Они помогают нам образовывать новые слова. Некоторые суффиксы меняют часть речи, превращая, например, глагол в существительное. Не стоит также забывать и о тех суффиксах, которые, изменяя форму слова, не влияют на само его значение.
Если вы будете иметь хотя бы небольшое представление о таблице suffixes in English, то любые словообразовательные «изыски» в английском покажутся детской забавой. Более того, поняв принципы построения новых слов с помощью приставок и суффиксов (кстати, приставки значительно уступают суффиксам по гибкости и распространенности), изучающий язык без проблем сможет переводить существительные мужского рода в женский, образовывать национальность или профессию.
Оказывается, совершенно не обязательно ставить рекорды по количеству выученных слов. Ведь в английском, как и в русском, существует понятие «однокоренные слова», отличающиеся друг от друга лишь суффиксами и приставками. Поэтому, зная, например, значение глагола paint (красить, заниматься живописью), вы легко поймете, что painter — это художник.
Словообразующие и формообразующие суффиксы: отличия
Некоторые английские суффиксы русскоговорящие считают окончаниями. Например, суффикс -ed некоторые учебники английского называют окончанием. Все Suffixes in English делится на две большие группы: формообразующие и словообразующие. Благодаря первым, слово не меняет своего значения, изменяется лишь форма. Сравните, short (короткий) и shorter (короче).
Словообразующие суффиксы в английском формируют новое слово с иным значением, пусть часто и сходным со значением изначального слова. Например, neighbor (сосед) — neighborhood (соседство).
Формообразующие суффиксы в английском
Итак, в английском языке, в отличие от русского, одно слово может принимать не так уж много форм. Это обусловлено тем, что в английском многие грамматические значения слова, такие, как род, время глагола и прочее, выражаются не самим словом, а различными вспомогательными элементами (артиклями, вспомогательными глаголами и т.д.). В русском языке у одного только прилагательного (в зависимости от падежа, числа, рода), может быть более 20 форм. Например, любимый — любимая — любимые — любимого и т. п. В английском же прилагательное favorite (любимый) может вообще не изменяться, но о его точной форме мы догадываемся из контекста (окружения): This is my favorite book (Это моя любимая книга). — He is my favorite writer (Он мой любимый писатель).
Однако в некоторых случаях английские слова все-таки меняют форму. И для этого в английском есть пять формообразующих суффиксов, которые важно запомнить: -ed, -est, -ing, -s (-es), -er.
Теперь стоит разобраться в английских словах, способных принимать разные формы. Итак, английский суффикс -ed нужен для того, чтобы образовать вторую и третью форму правильного глагола. Например, finish (заканчивать, завершать) — finished (завершил).
Суффиксы -er и -est в английском языке применяются при образовании сравнительных форм прилагательных. Эти суффиксы мы используем с короткими прилагательными, вроде close (близкий), big (большой) и т. п. Для сравнительной формы применяется суффикс -er, а для превосходной — -est. Например, close (близкий) — closer (более близкий) — closest (самый близкий).
Среди английских суффиксов широко распространены -s и -es. Они применяются в следующих случаях:
- для образования притяжательной формы одушевленного существительного — father (отец) — father’s house (отцовский дом);
- для образования множественного числа существительного — face (лицо) — faces (лица);
- для формирования 3 лица единственного числа глагола (в Present Simple) — run (бегать) — runs (бежит).
Наконец, английский суффикс -ing применяется для образования временных форм Continuous, причастия 1-го типа, отглагольного существительного и герундия: to run (бежать) — I am running (Я бегу) — running (бегая, бегающий, бег). Подробнее об этом — в статье Окончание ing.
Суффиксы, образующие существительные
Словообразующие суффиксы в английском языке способствуют формированию целого ряда существительных. Именно им мы обязаны появлению названий многих профессий. Список суффиксов для существительных достаточно обширен.
Суффиксы в английском языке: таблица для существительных
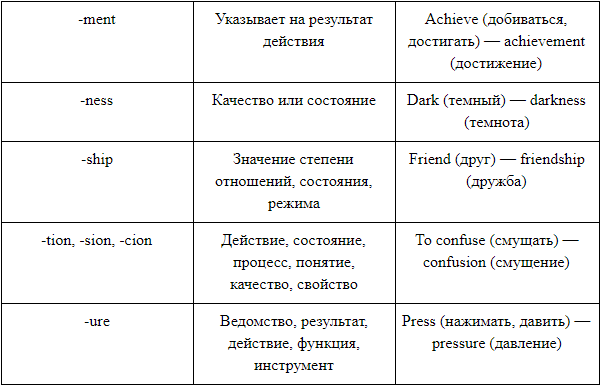
Суффиксы прилагательных в английском языке
Огромное количество прилагательных в английском образованы из существительных и глаголов. Некоторые суффиксы используются для образования и существительных, и прилагательных (например, -al, -ing). Но большинство суффиксов, которые мы встречаем с частью речи, отвечающей на вопрос «какой», не встречаются в существительных или глаголах. Например, суффикс less в английском языке характерен только для прилагательных.
Список суффиксов прилагательных в английском языке, так же, как и в случае с существительными, достаточно обширен.
- -able, -ible. Возможность совершения, выполнения какого-либо действия. Чтобы получилось прилагательное, суффикс добавляют к глаголу. Например, to forget (забывать) — forgettable (незапоминающийся).
- -al. Используется для обозначения признака. Например, accident (случай) — accidental (случайный).
- -ant. Прилагательные, образованные при помощи этого суффикса от глаголов и существительных, означают «передающий качества». Например, please (радовать) — pleasant (приятный).
- -ar. При образовании прилагательных этот суффикс часто прибавляют к существительным или основам латинского происхождения. -Ar используется в значении «иметь качество чего-то» (например, луны, солнца, полюса): lunar (лунный), solar (солнечный), polar (полярный).
- -ary, ory. Используются в обозначении характеристики, качества или отношения к чему-либо. Например, diet (диета) — dietary (диетический).
- -ate. Значение прилагательных с суффиксом -ate, как правило, можно выразить словосочетанием «обладать каким-либо качеством»: affection — affectionate (привязанность — любящий, привязчивый). Этот суффикс также указывает на характеристику. Например, fortune (счастье, удача) — fortunate (счастливый, удачный).
- -ed. Прилагательные с этим суффиксом обычно описывают влияние, оказанное на кого-то или что-то: amaze (поражать, изумлять) — amazed (изумленный).
- -ent. Используется в значении качества: to differ (различаться) — different (разный).
- -ern. Применяется при указании на часть света: south (юг) — southern (южный).
- -ese. Обозначает национальность или территориальную принадлежность. Например, China (Китай) — Chinese (китайский).
- -ful. Этот суффикс в английском превращает существительное в прилагательное, обозначающее «быть наделенным чем-либо, каким-либо свойством». Например, beauty (красота) — beautiful (красивый).
- -ian, ean. Эти суффиксы в английском языке встречаются в прилагательных, выражающих национальную или территориальную принадлежность: Italy (Италия) — Italian (итальянский).
- -ic. Добавляется к существительному и описывает качество: majesty (величие) — majestic (величественный).
- -ical. Обозначает признак: myth (миф) — mythical (мифический).
- -ing. Для образования прилагательных и причастий со значением качества и свойства. Например, to miss (скучать, упускать) — missing (потерянный, отсутствующий).
- -ish. Суффикс используется в прилагательных в значении «приблизительно», также встречается в названиях национальностей, иногда выражает похожесть или принадлежность к чему-либо. Например, child (ребенок) — childish (детский).
- -ive. Употребляется в значении качества, способности: attract (привлекать) — attractive (привлекательный).
- -less. Суффикс less в английском языке служит антонимом суффиксу ful и указывает на отсутствие какого-либо качества: home (дом) — homeless (бездомный).
- -like. Означает похожесть на что-либо, сходство: wave (волна) — wavelike (волнообразный).
- -ly. Для обозначения качества: friend (друг) — friendly (дружелюбный).
- —ous — суффикс, выражающий характеристику: poison (яд) — poisonous (ядовитый).
- -y. Используется в значении «иметь признак»: dirt (грязь) — dirty (грязный).
Глагольные суффиксы
С помощью суффиксов в английском языке из существительных и прилагательных образуется целый ряд глаголов.
Глагольные суффиксы в английском языке: таблица с примерами
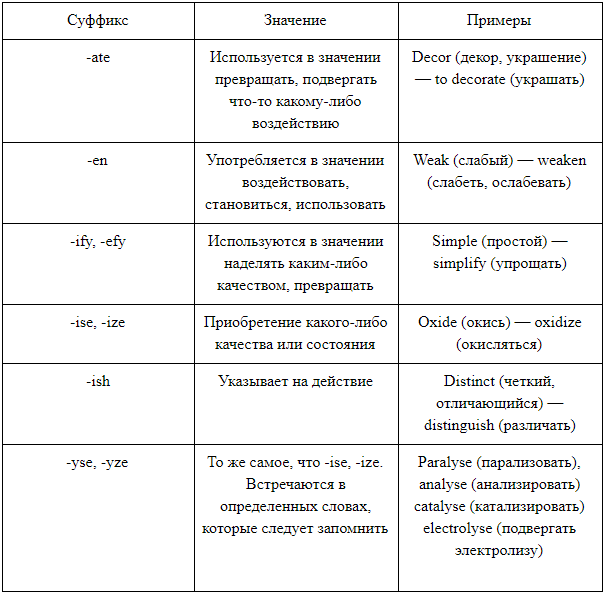
Суффиксы наречий
Словообразование наречий в английском языке — это гораздо более легкий процесс, чем создание существительных и прилагательных. Для того, чтобы получить часть речи, отвечающие на вопросы как, каким образом, обычно достаточно применить один из представленных ниже суффиксов:
- -ly
- wise
- ward/wards
Суффикс ward используется в значении направления: home (дом, дача) — homeward (домой). -Ly указывает на образ действия. Например, true (честный) — truly (честно). -Wise означает способ действия: other (другой) — otherwise (иначе).
Конечно же, вам совершенно необязательно запоминать все суффиксы в английском языке. Постоянная разговорная практика способствует тому, что обучающийся со временем начинает видеть составные части в словах, легко определяя суффиксы, приставки и корни. А понимание основы нового слова позволяет догадаться о его функции в предложении.
List of Verbs, Nouns, Adjectives and Adverbs
List of Verbs, Nouns, Adjectives and Adverbs
It is very important to know how the words will change from one part of speech to another. For example, a noun beauty can be written as beautiful in adjective form beautifully in adverb form and beautify in the verb form. This kind of change will take place when we add suffixes and prefixes to the root word. Here, you will find a huge list of Verbs, Nouns, Adjectives, and Adverbs with the added prefixes and suffixes for the modification.
A suffix is a letter or group of letters added at the end of a word to make a new word. Suffix changes a word from one part of speech to another like a noun to an adjective.
A prefix is a letter or group of letters placed at the beginning of a word to modify or change its meaning.
List of Verbs, Nouns, Adjectives, and Adverbs:
| 1. | Verbs | Nouns | Adjectives | Adverbs |
| 2. | enable | ability | able | ably |
| 3. | accept | acceptance | acceptable | acceptably |
| 4. | accuse | accusation | accusing | accusingly |
| 5. | achieve | achievement | achievable | |
| 6. | act | act, action, activity | active | actively |
| 7. | add | addition | additional | additionally |
| 8. | admire | admiration | admirable | admirably |
| 9. | advise | advice | advisable | advisably |
| 10. | agree | agreement | agreeable | agreeably |
| 11. | anger | anger | angry | angrily |
| 12. | appreciate | appreciation | appreciable, appreciative | appreciatively |
| 13. | approve | approval | approving | approvingly |
| 14. | approximate | approximation | approximate | approximately |
| 15. | argue | argument | arguable, argumentative | arguably |
| 16. | attend | attention | attentive | attentively |
| 17. | attract | attraction | attractive | attractively |
| 18. | base | base, basis | basic | basically |
| 19. | beautify | beauty | beautiful | beautifully |
| 20. | believe | belief | believable | believably |
| 21. | bore | bore, boredom | bored, boring | boringly |
| 22. | breathe | breath | breathless | breathlessly |
| 23. | calm | calm, calmness | calm | calmly |
| 24. | care | care | careful, caring | carefully, carelessly |
| 25. | centralize | centre, centralization | central, centralized | centrally |
| 26. | characterize | character | characteristic | characteristically |
| 27. | circulate | circulation | circular | |
| 28. | clean | cleanliness | clean | cleanly |
| 29. | clear | clarity, clearance | clear | clearly |
| 30. | collect | collection | collective | collectively |
| 31. | colour | colour | coloured | colourfully |
| 32. | comfort | comfort | comfortable | comfortably |
| 33. | compare | comparison | comparable, comparative | comparatively |
| 34. | compete | competition | competitive, uncompetitive | competitively |
| 35. | complete | completion | complete | completely |
| 36. | conclude | conclusion | conclusive | conclusively |
| 37. | condition | condition | conditional | conditionally, |
| 38. | confide | confidence | confident, confidential | confidently, confidentially |
| 39. | confuse | confusion | confused, confusing | confusingly |
| 40. | consider | consideration | considerable, considerate | considerably |
| 41. | continue | continuation, continuity | continual, continuous | continually, continuously |
| 42. | cool | cool, coolness | cool | coolly |
| 43. | correct | correction, correctness | correct, corrective | correctly |
| 44. | create | creation, creativity | creative | creatively |
| 45. | criticize | critic | critical | critically |
| 46 | accustom | custom | customary | customarily |
| 47. | dare | dare | daring | daringly |
| 48. | darken | dark, darkness | dark, darkened, darkening | darkly |
| 49. | deaden | death | dead, deadly, deathly | deadly, deathly |
| 50. | deceive | deceit, deception | deceitful, deceptive | deceptively |
| 51. | decide | decision | decided, decisive | decidedly, decisively |
| 52. | decorate | decoration | decorative | decoratively |
| 53. | deepen | deep, depth | deep, deepening | deeply |
| 54. | defend | defence | defensive | defensively |
| 55. | define | definition | definite | definitely |
| 56. | demonstrate | demonstration | demonstrable, demonstrative | demonstrably |
| 57. | depend | dependent, dependence | dependable | dependably |
| 58. | describe | description | describable | descriptively |
| 59. | destroy | destruction | destructive | destructively |
| 60. | determine | determination | determined | determinedly |
| 61. | differ, differentiate | difference | different | differently |
| 62. | direct | direction | direct | directly |
| 63. | disagree | disagreement | disagreeable | disagreeably |
| 64.. | disappoint | disappointment | disappointed, disappointing | disappointingly |
| 65. | distance | distance | distant | distantly |
| 66. | disturb | disturbance | disturbed, disturbing | disturbingly |
| 67. | doubt | doubt | doubtful | doubtfully |
| 68. | dream | dream | dreamless, dreamy | dreamily |
| 69. | dress | dress | dressed, dressy | dressily |
| 70. | drink | drink, drunkenness | drunk, drunken | drunkenly |
| 71. | ease | ease, easiness | easy | easily |
| 72. | educate | education | educated, educational | educationally |
| 73. | effect | effect, effectiveness | effective | effectively |
| 74. | electrify | electricity | electric, electrical | electrically |
| 75. | embarrass | embarrassment | embarrassed, embarrassing | embarrassingly |
| 76. | emphasize | emphasis | emphatic | emphatically |
| 77. | encourage | encouragement | encouraged, encouraging | encouragingly |
| 78. | end | end | unending, endless | endlessly |
| 80. | energize | energy | energetic | energetically |
| 81. | enjoy | enjoyment | enjoyable | enjoyably |
| 82. | entertain | entertainment | entertaining | entertainingly |
| 83. | enthuse | enthusiasm | enthusiastic | enthusiastically |
| 84. | equalize | equality | equal | equally |
| 85. | excel | excellence | excellent | excellently |
| 86. | excite | excitement | excitable, excited, exciting | excitedly, excitingly |
| 87. | excuse | excuse | excusable | excusably |
| 88. | expect | expectation | expectant | expectantly, |
| 89. | expend | expenditure, expense | expensive | expensively |
| 90. | experiment | experiment | experimental | experimentally |
| 91. | explain | explanation | explanatory, explicable | inexplicably |
| 92. | explode | explosion | explosive | explosively |
| 93. | express | expression | expressive | expressively |
| 94. | familiarize | familiarity | familiar | familiarly |
| 95. | fashion | fashion | fashionable | fashionably |
| 96. | fear | fear | fearful, fearless, fearsome | fearfully, fearlessly |
| 97. | finalize | final | final | finally |
| 98. | fish | fish, fishing | fishy | fishily |
| 99. | fit | fit | fitted | fittingly |
| 100. | force | force | forceful, forcible | forcefully, forcibly |
| 101. | forget | forgetfulness | forgetful | forgetfully |
| 102. | formalize | formality | formal | formally |
| 103. | frequent | frequency | frequent | frequently |
| 104. | freshen | freshness | fresh | freshly |
| 105. | frighten | fright | frightened, frightening, frightful | frighteningly, frightfully |
| 106. | harden | hardship | hard | hard, hardly |
| 107. | harm | harm, harmfulness | harmful, harmless | harmfully, harmlessly |
| 108. | heat, overheat | heat | heated | heatedly |
| 109. | help | help | helpful, helpless | helpfully, helplessly |
| 110. | hope | hope | hopeful, hopeless | hopefully, hopelessly |
| 111. | hurry | hurry | hurried | hurriedly |
| 112. | hurt | hurt | hurtful | hurtfully |
| 113. | ice | ice | icy | icily |
| 114. | imagine | imagination | imaginable, imaginative | unimaginably, imaginatively |
| 115. | impress | impression | impressive | impressively |
| 116. | increase | increase | increased | increasingly |
| 117. | infect | infection | infectious | infectiously |
| 118. | insist | insistence | insistent | insistently |
| 119. | instruct | instruction | instructive | instructively |
| 120. | intend | intent, intention | intended, intentional, | intentionally |
| 121. | interest | interest | interested, disinterested, uninterested, interesting | interestingly |
| 122. | invent | invention | inventive | inventively |
| 123. | invite | invitation, invite | inviting | invitingly |
| 124. | know | knowledge | knowledgeable, known | knowingly, knowledgeably |
| 125. | enlarge | enlargement | large | largely |
| 126. | laugh | laugh | laughable | laughably |
| 127. | outlaw | law | lawful | lawfully |
| 128. | legalize | legality | legal | legally |
| 129. | lengthen | length | lengthy | lengthily |
| 130. | light, lighten | light | light | lightly |
| 131. | locate, | location | local | locally |
| 132. | love | love | lovable, lovely | lovingly |
| 133. | lower | low | low, lower | low |
| 134. | man | man, mankind | manly | mannishly, manfully |
| 135. | mark | mark | marked | markedly |
| 136. | match | match | matchless | matchlessly |
| 137 | materialize | material,
materialism |
immaterial, materialistic | materially |
| 138. | mean | meaning,
meaningfulness |
meaningful, meaningless | meaningfully,
meaninglessly |
| 139. | measure | measurement | measurable | immeasurably |
| 140. | memorize | memory | memorable | memorably |
| 141. | mind | mind, mindlessness | mindless, mindful | mindlessly |
| 142. | minimize | minimum | minimal | minimally |
| 143. | mistake | mistake | mistaken | mistakenly |
| 144. | moralize | moral, morality | moral, moralistic | morally |
| 145. | mother | mother, motherhood | motherly | |
| 146 | move | move, movement | movable, moving | movingly |
| 147. | murder | murder | murderous | murderously |
| 148. | name, rename | name | named, unnamed, nameless | namely |
| 149. | nationalize | nation, nationalization, nationality | national, nationalistic | nationally |
| 150. | naturalize | nature, naturalist, naturalization, | natural,
naturalistic |
naturally |
| 151. | necessitate | necessity | necessary | necessarily |
| 152. | need | need | needy | needlessly |
| 153. | unnerve | nerve, nervousness | nervous, nervy, | nervously, nervelessly |
| 154. | renew | news, newness | new, renewable | newly, anew |
| 155. | normalize | normality | normal | normally |
| 156. | notice | notice | noticeable | noticeably |
| 157. | obey | obedience | obedient | obediently |
| 158. | offend | offence | offensive | offensively |
| 159. | officiate | office | official | officially |
| 160. | open | openness | open | openly |
| 161. | operate, cooperate | operation | operational,
operative |
operationally |
| 162. | opt | option | optional | optionally |
| 163. | originate | origin | original | originally |
| 164. | pain | pain | painful, painless | painfully, painlessly |
| 165. | part, impart | part, partition | partial, impartial | partially, partly |
| 166. | pacify | peace | peaceful | peacefully |
| 167. | perfect | perfection | perfect | perfectly |
| 168. | personalize, personify | person, personality | personal, personalized | personally |
| 169. | persuade | persuasion, persuasiveness | persuasive | persuasively |
| 170. | play, outplay | play, playfulness | playful, playable | playfully |
| 171. | please | pleasure | pleasant, pleasurable | pleasantly, unpleasantly |
| 172. | point | point, pointlessness | pointed, pointless | pointlessly, pointedly |
| 173. | politicize | politics | political, politicized | politically |
| 174. | popularize | popularity | popular | popularly |
| 175. | power, empower | power | powerful, powerless | powerfully |
| 176. | prefer | preference | preferable, preferred | preferably |
| 177. | present | presence, presentation, | present, presentable | presently |
| 178. | privatize | privacy, privatization | private | privately |
| 179. | profit | profit, profitability | profitable | profitably |
| 180. | progress | progress, progression | progressive | progressively |
| 181. | provide | provision | provisional | provisionally |
| 182. | publicize | public, publicity | public | publicly |
| 183. | punish | punishment | punishable, punishing | punishingly |
| 184. | purify | purification, purity | pure | purely |
| 185. | question | question | questionable | questionably |
| 186. | quieten | quiet | quiet | quietly |
| 187. | race | race | racial | racially |
| 188. | realize | realism, reality | real, realistic | really, realistically |
| 189. | reason | reason | reasonable | reasonably |
| 190. | receive | receipt, reception, | receptive, reciprocal | reciprocally |
| 191. | recognize | recognition | recognizable | recognizably |
| 192. | reflect | reflection | reflective | reflectively |
| 193. | regret | regret | regrettable, regretful | regrettably, regretfully |
| 194. | regulate | regular, regularity | regular | regularly |
| 195. | relate | relation, relationship | related, relative | relatively |
| 196. | rely | reliability | reliable | reliably |
| 197. | remark | remark | remarkable | remarkably |
| 198. | repair | repair | irreparable | irreparably |
| 199. | repeat | repeat, repetition | repeated, repetitive | repeatedly, repetitively |
| 200. | report | report | reported | reportedly |
| 201. | respect | respect | respectable, respectful, respective | respectably, respectfully, respectively |
| 202. | respond | response, responsiveness | responsive | responsively |
| 203. | rest | rest | restless, rested, restful | restlessly |
| 204. | enrich | riches, richness | rich | richly |
| 205. | right | right, rightness, | righteous, rightful | right, rightly, rightfully |
| 206. | romanticize | romance, romanticism | romantic, romanticized | romantically |
| 207. | roughen | rough, roughness | rough | roughly |
| 208. | round | round | round, rounded | roundly |
| 209. | sadden | sadness | sad, saddened | sadly |
| 210. | satisfy | satisfaction | satisfactory, | satisfactorily |
| 211. | school | school, pre-school | scholastic | scholastically |
| 212. | search, research | search, research | searchable | searchingly |
| 213. | sense, sensitize | sense, sensibility, sensitivity, sensitiveness | sensible, sensitive, sensory | sensibly, sensitively |
| 214. | separate | separation | separable, separate | separately |
| 215. | shake | shake, shakiness | shaky | shakily |
| 216. | shape | shape | shapely, shaped | shapelessly |
| 217. | sharpen | sharpness | sharp | sharply, sharpish |
| 218. | shock | shock | shocking, shockable | shockingly |
| 219. | shorten | short, shortness | short, shortish | shortly |
| 220. | shy | shyness | shy | shyly |
| 221. | sicken | sick, sickness | sick, sickly | sickeningly |
| 222. | signify | significance | significant | significantly |
| 223. | silence | silence | silent | silently |
| 224. | simplify | simplicity, simplification | simplistic | simply |
| 225. | single | single | singular | singly |
| 226. | sleep | sleep, sleepiness | asleep, sleepy | sleepily |
| 227. | socialize | society, | sociable, social | socially |
| 228. | soften | softness | soft | softly |
| 229. | solidify | solid, solidity | solid | solidly |
| 230. | specialize | specialty | special, specialized | specially |
| 231. | speed | speed, speediness | speedy | speedily |
| 232. | spot | spot | spotted, spotty | spotlessly |
| 233. | stand, withstand | stand, standstill | standing, outstanding | outstandingly |
| 234. | steepen | steepness | steep | steeply |
| 235. | stiffen | stiffness | stiff | stiffly |
| 236. | strengthen | strength | strong | strongly |
| 237. | strike | strike | striking | strikingly |
| 238. | structure | structure, structuralism | structural | structurally |
| 239. | study | student, study | studious | studiously |
| 240. | style | style, stylishness | stylish, stylistic | stylishly, stylistically |
| 241. | substantiate | substance | substantial, substantive | substantially |
| 242. | succeed | success, succession | successful, successive | successfully |
| 243. | suggest | suggestion | suggestive, suggestible | suggestively |
| 244. | support | support, supportiveness | supportive, supporting | supportively |
| 245. | suppose, presuppose | supposition | supposed | supposedly |
| 246. | surprise | surprise | surprised, surprising | surprisingly |
| 247. | suspect | suspect, suspicion | suspected, suspicious | suspiciously |
| 248. | sweeten | sweet, sweetness | sweet | sweetly |
| 249. | symbolize | symbol, symbolism | symbolic | symbolically |
| 250. | sympathize | sympathy | sympathetic | sympathetically |
| 251. | systematize | system, systematization | systematic | systematically |
| 252. | talk | talk, talks | talkative | talkatively |
| 253. | taste | taste | tasteful, tasty | tastefully |
| 254. | thank | thanks, thankfulness | thankful | thankfully |
| 255. | theorize | theory, theorem | theoretical | theoretically |
| 256. | thicken | thick, thickness | thick | thickly |
| 257. | thin | thinness | thin | thinly |
| 258. | think | thought, thoughtfulness, | thoughtful | thoughtfully |
| 259. | threaten | threat | threatening | threateningly |
| 260. | tighten | tightness | tight | tight, tightly |
| 261. | tire | tiredness | tired, tiresome,
tiring |
tiredly, tiresomely |
| 262. | touch | touch | touched, touching, touchy | touchingly, touchily |
| 263. | trouble | trouble | troublesome, troubling | troublingly |
| 264. | trust, entrust | trust, trusteeship | trusting, trustworthy | trustfully |
| 265. | typify | type | typical | typically |
| 266. | understand | understanding | understandable | understandably |
| 267. | use | usage, use | used, useful | usefully |
| 268. | vary | variant, variety, variation | variable, varied, various | invariably, variously |
| 269. | violate | violence | violent | violently |
| 270. | wrong | wrong | wrongful | wrongly, wrongfully |
| 271. | warm | warmth | warm | warmly |
| 272. | waste | wastage, waste | waste, wasteful | wastefully |
| 273. | watch | watch, watchfulness | watchful | watchfully |
| 274. | weaken | weakness | weak | weakly |
| 275. | weigh, outweigh | weight | weighty, weightless | weightlessly |
| 276. | widen | width | wide | widely |
| 277. | wonder | wonder | wonderful | wonderfully |
| 278. | worry | worry | worried, worrying, worrisome | worryingly |
| 279. | write, rewrite | writing | written |
End of the list of Verbs, Nouns, Adjectives, and Adverbs:
Recommended links to Read:
Apart from this list of Verbs, Nouns, Adjectives and Adverbs, you can also refer to the following topics.
- Proper Adjectives
- Adjectives of Quality (Qualitative Adjectives/Descriptive Adjectives)
- Adjectives of Quantity (Quantitative Adjectives)
- Adjectives of Number (Numeral Adjectives)
- Demonstrative Adjectives
- Interrogative Adjectives
- Distributive Adjectives
- Possessive Adjectives (Pronominal)
- Emphasizing Adjectives
- Exclamatory Adjectives
- Participle Adjectives
- Relative Adjectives
- Compound Adjectives
- Formation of Adjectives