The majority of nouns have distinct plural and singular forms. However, there are a number of special words that are spelled and pronounced exactly the same way in both their singular and plural forms. Here are 101 words that are both singular and plural.
If you are not sure how to convert a singular noun into a plural noun, check out our guide to how to convert a singular noun to a plural noun.
- Accommodation
- Advice
- Alms
- Aircraft
- Aluminum
- Barracks
- Bison
- Binoculars
- Bourgeois
- Breadfruit
- Cannon
- Caribou
- Cattle
- Chalk
- Chassis
- Chinos
- Clippers
- Clothing
- Cod
- Concrete
- Corps
- Correspondence
- Crossroads
- Deer
- Dice
- Doldrums
- Dungarees
- Education
- Eggfruit
- Elk
- Eyeglasses
- Fish (numbers of)
- Flares (clothing)
- Flour
- Food
- Fruit
- Furniture
- Gallows
- Goldfish
- Grapefruit
- Greenfly
- Grouse
- Haddock
- Halibut
- Head (cattle)
- Headquarters
- Help
- Homework
- Hovercraft
- Ides
- Insignia
- Jackfruit
- Jeans
- Knickers
- Knowledge
- Kudos
- Leggings
- Lego
- Luggage
- Moose
- Monkfish
- Mullet
- Nailclippers
- News
- Offspring
- Oxygen
- Pants
- Pyjamas
- Passionfruit
- Pike
- Pliers
- Police
- Premises
- Reindeer
- Rendezvous
- Salmon
- Scissors
- Series
- Shambles
- Sheep
- Shellfish
- Shorts
- Shrimp
- Smithereens
- Spacecraft
- Species
- Squid
- Starfruit
- Stone (weight)
- Sugar
- Swine
- Tongs
- Trousers
- Trout
- Tuna
- Tweezers
- You
- Wheat
- Whitebait
- Wood
Can you think of any words that are both plural and singular? Leave a comment and let us know!
Read a complete list of singular noun and plural noun
Singular and plural noun list a-z
- Army-Armies
- Ass-Asses
- Baby-Babies
- Bamboo-Bamboos
- Bench-Benches
- Bird-Birds
- Boat-Boats
- Bone-Bones
- Box-Boxes
- Boy-Boys
- Brother-in-law- Brothers-in-laws
- Buffalo-Buffaloes
- Bus-Buses
- Bush-Bushes
- Caddy-Caddies
- Calf-Calves
- Car-Cars
- Cat-Cats
- Chair-Chairs
- Chief-Chiefs
- Child-Children
- City-Cities
- Class-Classes
- Class fellow-Class fellows
- Cliff-Cliffs
- Clutch-Clutches
- Copy-Copies
- Country-Countries
- Cow-Cows
- Cry-Cries
- Cuckoo-Cuckoos
- Cup-Cups
- Daughter-in-law- Daughters-in-laws
- Day-Days
- Deci-Decies
- Deer-Deers
- Dog-Dogs
- Donkey-Donkeys
- Dozen-Dozens
- Duty-Duties
- Essay-Essays
- Family-Families
- Father-Fathers
- Father-in-law- Fathers-in-laws
- Fish-Fishes
- Fly-Flies
- Foot-Feet
- Fox-Foxes
- Gas-Gases
- Glass-Glasses
- Grass-Grasses
- Hair-Hairs
- Half-Halves
- Hand-Hands
- Hero-Heroes
- Hoof-Hoofs
- Horse-Horses
- House-Houses
- Inch-Inches
- Jar-Jars
- Key-Keys
- Knife-Knives
- Lady-Ladies
- Lass-Lasses
- Leaf-Leaves
- Leg-Legs
- Life-Lives
- Loaf-Loaves
- Loof-Loofs
- Love-Loves
- Maidservant-Maidservants
- Man-Men
- Mango-Mangoes
- Monkey-Monkeys
- MotherMothers
- Mother-in-law- Mothers-in-laws
- Mouse- Mice
- News-News
- Ox-Oxen
- Pencil-Pencils
- Penny-Pennies
- Person-People
- Pitch-Pitches
- Poetry-Poetries
- Potato-Potatoes
- Proof-Proofs
- Quiz-Quizzes
- Radio-Radios
- Ray-Rays
- River-Rivers
- Scissor-Scissors
- Self-Selves
- Sheep-Sheeps
- Shop-Shops
- Singular-Plural
- Singular noon-Plural noun
- Sister-Sisters
- Sister-in-law- Sister-in-laws
- Sky-Skies
- Son-in-law- Son-in-laws
- Spey- Spies
- Stepson-Stepsons
- Story-Stories
- Table-Tables
- Thief-Thieves
- Tooth-Teeth
- Toy-Toys
- Trouser-Trousers
- Uncle-Uncles
- Watch-Watches
- Wife-Wives
- Wish-Wishes
- Woman-Women
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Army | Armies |
| Ass | Asses |
| Baby | Babies |
| Baby | Baby |
| Bamboo | Bamboos |
| Bench | Benches |
| Bird | Birds |
| Boat | Boats |
| Bone | Bones |
| Box | Boxes |
| Boy | Boys |
| Brother-in-law | Brothers-in-laws |
| Buffalo | Buffaloes |
| Bus | Buses |
| Bush | Bushes |
| Caddy | Caddies |
| Calf | Calves |
| Car | Cars |
| Cat | Cats |
| Chair | Chairs |
| Chief | Chiefs |
| Child | Children |
| City | Cities |
| Class | Classes |
| Class fellow | Class fellows |
| Cliff | Cliffs |
| Clutch | Clutches |
| Copy | Copies |
| Country | Countries |
| Cow | Cows |
| Cry | Cries |
| Cuckoo | Cuckoos |
| Cup | Cups |
| Daughter-in-law | Daughters-in-laws |
| Day | Days |
| Deck | Decks |
| Deer | Deers |
| Dog | Dogs |
| Donkey | Donkeys |
| Dozen | Dozens |
| Duty | Duties |
| Essay | Essays |
| Family | Families |
| Father | Fathers |
| Father-in-law | Fathers-in-laws |
| Fish | Fishes |
| Fly | Flies |
| Foot | Feet |
| Fox | Foxes |
| Gas | Gasses |
| Glass | Glasses |
| Hair | Hairs |
| Half | Halves |
| Hand | Hands |
| Hero | Heroes |
| Hoof | Hoofs |
| Horse | Horses |
| House | Houses |
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Inch | Inches |
| Jar | Jars |
| Key | Keys |
| Knife | Knives |
| Lady | Ladies |
| Lass | Lasses |
| Leaf | Leaves |
| Leg | Legs |
| Life | Lives |
| Loaf | Loaves |
| Loof | Loops |
| Love | Loves |
| Maidservant | Maidservants |
| Man | Men |
| Mango | Mangoes |
| Monkey | Monkeys |
| Mother | Mothers |
| Mother-in-law | Mothers-in-laws |
| Mouse | Mice |
| News | News |
| Ox | Oxen |
| Pencil | Pencils |
| Penny | Pennies |
| Person | People |
| Pitch | Pitches |
| Poetry | Poetries |
| Potato | Potatoes |
| Proof | Proofs |
| Quiz | Quizzes |
| Radio | Radios |
| Ray | Rays |
| River | Rivers |
| Scissor | Scissors |
| Self | Selves |
| Sheep | Sheeps |
| Shop | Shops |
| Singular | Plural |
| Singular noon | Plural noun |
| Sister | Sisters |
| Sister-in-law | Sisters-in-laws |
| Sky | Skies |
| Son-in-law | Sons-in-laws |
| Stepson | Stepsons |
| Story | Stories |
| Table | Tables |
| Thief | Thieves |
| Tooth | Teeth |
| Toy | Toys |
| Trouser | Trousers |
| Uncle | Uncles |
| Watch | Watches |
| Wife | Wives |
| Wish | Wishes |
| Woman | Women |
What is singular noun?
The singular nouns are words that only refer to one person or thing. They can be used as a subject, direct object, indirect object, predicate nominative, or appositive.
For example: “I went to the store.” This sentence is about the speaker and their experience at the store. It’s also possible for a singular noun to be an appositive such as in this sentence: “Tina was wearing her best dress.”
Here, Tina is being described by what she was wearing which is called an appositive.
What is plural noun?
Plural nouns are words that refer to more than one person, place or thing. They are often used in sentences where we want to talk about a group of people, animals, or things.
Let’s take the sentence “I am teaching a class this semester.” We can change it around and say “The students have been working hard all semester long.” In the first sentence, “class” is singular and in the second sentence, “students” is plural. That means you need to use a proper noun (singular or plural) according to the situation.
It may not seem like much of a difference at first but it will make your writing sound awkward if you don’t get it right! The best way is to learn the rules of plural nouns.
We’ll break down the rules so you’ll never get your plural nouns wrong again.
Rule-1
We add ‘-s’ to the end of regular nouns to make them plurals. For examples,
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Chair | Chairs |
| Table | Tables |
| Pencil | Pencils |
| Book | Books |
| Cat | Cats |
Rule-2
In some cases, we add suffix “-es” to the nouns ending in “o”. See examples below.
Examples
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Tomato | Tomatoes |
| Potato | Potatoes |
| Mosquito | Mosquitoes |
| Echo | Echoes |
| Zero | Zeroes |
Rule-3
In some Latin or Greek words (foreign words) ending in “-o”, we add suffix ‘-s’. For example,
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Avocado | Avocados |
| Photo | Photos |
| Video | Videos |
| Studio | Studios |
| Radio | Radios |
Rule-4
When singular noun ends in ‘-us’, we replace ‘-us’ with ‘-i’. Examples are,
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Cactus | Cacti |
| Fungus | Fungi |
| Focus | Foci |
| Nucleus | Nuclei |
Rule-5
In singular noun ending on ‘-y’ (when the letter before -y is vowel), we add ‘-s’ to the end to make the noun plural, for example,
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Boy | Boys |
| Alloy | Alloys |
| Day | Days |
| Ray | Rays |
| Guy | Guys |
Rule-6
In singular noun ending on ‘-y’ (when the letter before -y is consonant), we replace ‘-y’ with ‘-ies’ to make the noun plural, for example
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Lady | Ladies |
| City | Cities |
| Spy | Spies |
| Penny | Pennies |
| Army | Armies |
Rule-7
In some cases, the singular nouns ending in ‘-s’ or ‘-z’, the last letter is doubled plus we add ‘-es’ to the end. See the examples,
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Gas | Gasses |
| Quiz | Quizzes |
| Fez | Fezzes |
Rule-8
In many cases, the singular noun ending in ‘-f’ or ‘-fe’, we replace the ‘-f’ or ‘-fe’ with ‘-ves’. For example,
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Thief | Thieves |
| Wife | Wives |
| Loaf | Loaves |
| Half | Halves |
| Knife | Knives |
There are some exceptions where the rule does not apply, Examples are roof -> roofs, belief -> beliefs, cliff -> cliffs
Rule-9
In case the noun ends in ‘-on’, we replace ‘-on’ with ‘-a’ to make it plural, for example
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Criterion | Criteria |
| Phenomenon | Phenomena |
Rule-10
In case the singular noun is ending in ‘-is’, to make the noun plural, ‘-is’ is replaced with ‘-es’. For examples
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Oasis | Oases |
| Thesis | Theses |
| Basis | Bases |
| Crisis | Crises |
| Diagnosis | Diagnoses |
Rule-11
If the nouns ends in ‘-um’, last letters ‘-um’ are replaced with ‘-a’ in plural form. Examples are
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Datum | Data |
| Agendum | Agenda |
| Medium | Media |
| Bacterium | Bacteria |
| Memorandum | Memoranda |
Rule-12
In some case, the singular noun is ending in ‘-ex’ or ‘-ix’, the plural will end in ‘-ices’ Examples are given below:
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Matrix | Matrices |
| Index | Indices |
| Vertex | Vertices |
| Codex | Codices |
Rule-13
There are several singular nouns which do not follow any of the above rules while making them plural
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Foot | Feet |
| Child | Children |
| Mouse | Mice |
| Louse | Lice |
| Man | Men |
| Woman | Women |
| Goose | Geese |
| People | Person |
| Alumnus | Alumni |
| Genus | Genera |
Rule-14
Many nouns have the same singular and plural form. Fro example, plural nouns for sheep is ‘sheep’. See some more examples.
| Singular | Plural |
|---|---|
| Fish | Fish |
| Tuna | Tuna |
| Salmon | Salmon |
| Deer | Deer |
| Gross | Gross |
| Ice | Ice |
| Species | Species |
Rule-15
Some nouns do not have plural forms. Examples are
- Love
- Hatred
- Lust
- Happiness
- Kindness
Types of Plurals
A lot of people don’t know about the types of plural nouns, but it’s important to understand that there are three types of plurals:-
- Regular Plurals
- Irregular Plurals
- Compound Words
The plural noun rule is one of those things that can trip you up when you’re writing sentences
Regular Plurals
Regular plurals end in s or es. For example, bag -> bags, toy -> toys, pen -> pens etc.
Irregular Plurals
Irregular plurals have a different spelling for their endings than they do for singulars. For example ox -> oxen, goose -> geese etc.
Compound Plurals
Compound words are made up of two words put together to make one word. For example, “bookcase” is a compound word with two parts – book and case. To form the plural form of this word, we would simply add an ‘s’ at the end (bookcases).
It’s easy to remember these rules if you think about them like this – just add an ‘es’ for regular plurals and an ‘s’ for irregular ones!
You can read here further: Regular and Irregular Nouns Rules with Examples
Singular Noun Example Sentences
- Fungus is vicious for human health.
- I need a knife to cut the apple.
- There is only one chair in the hall.
- Runabout is the most popular boat in the United States.
- Tom has been driving the same car for the last ten years.
- Do you think life is so easy?
- I love to eat continental food.
- Tina bought a new house in a colony near the forest.
- My room is spacious and well furnished.
- The chef baked a pie cake for the guests.
- Do you have a camera to record the action?
- The cat is sitting on the roof.
- I avoid junk food because it is unhealthy.
- They booked a table in the restaurant.
- The baby is crying with hunger.
- Do you still listen to radio programs?
- The rug was so dirty that I had to vacuum it.
- I can’t believe you left your clothes on the floor!
- You’re going to have to clean up after yourself if you want dinner tonight.
- In this game, players are given a singular noun and must use it in a sentence.
- It’s time to go home now, so I’ll see you later!
- The most common type of security system is a door alarm that will sound when someone opens your front door.
- I’m going to a party this weekend.
- Who is watching television?
- Our school was founded by a man named John Smith who wanted to create a safe space for children and teenagers who were bullied at their old schools.
Plural Nouns Example Sentences
The plural noun example sentences are often used when you want to refer to a group of people or things.
- Fungi are vicious for human health.
- There are fifty chairs in the hall.
- I avoid oily and high-calorie foods.
- Pakistan is the largest exporters of footballs all over the world.
- Jackson has a great collection of coins and stamps.
- All the friends agreed to spend a day in the jungle camp.
- There are many ways to whiten teeth naturally.
- A fleet of boats was sailing in the river.
- There are 195 countries in the world.
- Men and women are born with 12 pairs of ribs.
- She cut the pizza into equal halves.
- How many subjects have you completed in this syllabus?
- The costs of the new house are high.
- It’s important that you know what the words mean and when they can be used.
- The pencils are sharpened.
- The students have their assignments due tomorrow.
- I think both the computers need to be fixed.
- There is a lot of food for everyone to eat.
- We’ve been waiting on you guys forever!
- As a result of the recent increase in crime rates, many people are opting to buy home security systems.
- These alarms can be easily installed on existing doors with just a few screws and some wiring.
- You don’t need any special tools or equipment – all you’ll need is an electric drill and some patience.
- There are three cats in the yard.
- How many people work for your company?
- A group of students is waiting at the bus stop 30 minutes before school starts.
Worksheet for Singular and Plural Nouns
Following is a worksheet for singular and plural nouns. Answers are given at the end. Mention against each sentence whether highlighted/bold word is a singular or plural noun.
- This is my favorite pizza topping because they give me one every time I order one. (singular/plural)
- The sun is shining. (singular/plural)
- My mom’s favorite color is red. (singular/plural)
- A house has four walls, a roof, and a door. (singular/plural)
- Cars are typically rectangular in shape with sharp corners and flat surfaces. (singular/plural)
- A dog has fur on its back legs to keep it warm during winter months. (singular/plural)
- The cat is under the table. (singular/plural)
- My phone is on my desk. (singular/plural)
- The apple fell from the tree and landed in a pile of leaves. (singular/plural)
- I need to go back to my house because I left my wallet there. (singular/plural)
- That’s an interesting idea, but it won’t work for me. (singular/plural)
- I have two hands and five fingers. (singular/plural)
- You should come over to my place sometime, we’ll have fun together. (singular/plural)
- The books are on the desk. (singular/plural)
- Three dogs were playing outside. (singular/plural)

Answers
- Singular Noun
- Singular Noun
- Singular Noun
- Singular Noun
- Plural Noun
- Singular Noun
- Singular Noun
- Singular Noun
- Singular Noun
- Singular Noun
- Singular Noun
- Plural Noun
- Singular Noun
- Plural Noun
- Plural Noun
Read also
- Singular and Plural Nouns for Kids
- Types of Noun with Examples
- Regular and Irregular Nouns
- Material Nouns
- Abstract Nouns
- Common Nouns
- Proper Nouns
- Countable and Uncountable Nouns
There are some English nouns that can be both plural and singular, depending on the context. This can be confusing for native speakers and non-native speakers alike. But don’t worry! In this lesson, we’ll go over some of the most common examples to help you figure out when to use them. Then we will go over some tips on how to teach English plural nouns.
Some of the most common examples of English nouns that can be both plural and singular include:
- aircraft
- bison
- deer
- fish
- moose
- offspring
- salmon
- sheep
- dice
- series
- species
As you can see, these are all words that can refer to more than one thing, but they can also refer to a single thing. For example, you can say “I saw two deer in my backyard” or “I saw a deer in my backyard”.
Another example is “I caught three fish” or “I caught a fish”.
A Short Story Focusing on Nouns with the Same Singular and Plural Form

Today we go on a walk in the forest. We see many deer and bison. We see some fish in the river. As we walk, a moose in the distance travels with her offspring. Altogether there are twelve moose. We see dozens of salmon swimming upstream. We see many different species of birds.
In the evening, we take out four dice and have two series of games. We play until it’s time for bed.
In the middle of the night, we suddenly hear several aircraft in the sky. They are so loud that they wake us up. We see the lights of the aircraft and watch them until they disappear in the distance.
What a great day! We saw so many different animals and had so much fun!
Test Your Understanding
Uncountable Nouns vs. Nouns with the Same Singular and Plural Form
Uncountable Nouns
When we’re talking about English nouns that can be both plural and singular, we are talking about countable nouns. These are nouns that we can count with numbers. These nouns have two forms: singular and plural.
For example, we can say “I have two cats” or “I have a cat”.
However, there are also many uncountable nouns in English that have only one form. These are words that we cannot count with numbers. For example, we cannot say “I have two water” or “I have a water”. Instead, we can say “I have some water” or “I have a lot of water”.
Here are some more examples of uncountable nouns:
- advice
- information
- news
- money
- tea
- soup
- rice
- sugar
- love
- wisdom
- rain
- silence
A Short Story Focusing on Uncountable Nouns

I am looking for some career advice, so I turn to my wiser friend for help. Useful information is what I need, and thankfully she has loads of it. She is even up-to-date with the latest news in the industry.
We sit down with a cup of tea (with very little sugar) and discuss my options. I have invested a lot of money in my education, so I need to make a wise decision.
“Nevermind that now”, she says. “First have some soup, and a plate of warm rice“.
Rain falls gently against the window. We sit in silence for a while, listening to the rain and eating our soup and rice.
Then she asks me about love (of all things).
“What does love have to do with career advice?” I reply.
My wise friend smiles and says, “Choose a job you love, and you will never have to work a day in your life”.
“That’s deep”, I say. And it is. Deep and true.
“That’s Confucius”, she says and takes away the empty plates of rice.
I finish my soup, thank my friend for her advice, and head out into the rain.
As I walk, the rain stops, and the sun is starting to come out. I think about all the different paths I could take in my life.
Surprisingly, the decision doesn’t seem so hard anymore. I smile, and start walking toward my new future.
So What’s the Difference?
The difference is that uncountable nouns cannot be counted. We cannot say “two rice”, nor “two rices”. There is only one form (in this case “rice”), and it refers to some amount of the thing, not a specific number of things.
In contrast, nouns with identical singular and plural forms are countable nouns, which can be counted. For example, we can say “Bob sold a sheep”. We can also say “Bob sold 30 sheep”.
Summary
To sum up, there are English nouns that can be both plural and singular. These are countable nouns that have the same form in both the singular and plural. In contrast, there are uncountable nouns that have only one form and cannot be counted.
Test Your Understanding
Final Test
You finished the lesson! Good job! ☺️
Click here to get full access to all our lessons and courses.

See Also
Sample Self-Study Lessons (Short Form)
Sample Self-Study Lessons (Long Form)
self-study online English courses
Singular and Plural Nouns
Nouns are the words used as the names of persons, animals, places, things, ideas or events.
There are two types of nouns in English Grammar. One refers to the singular noun and the other refers to the plural noun.
These two nouns are also otherwise called the singular number and the plural number.
Singular Noun Definition:
When a noun refers to one person or thing, it is said to be in the Singular Noun/Number.
Singular Noun Examples:
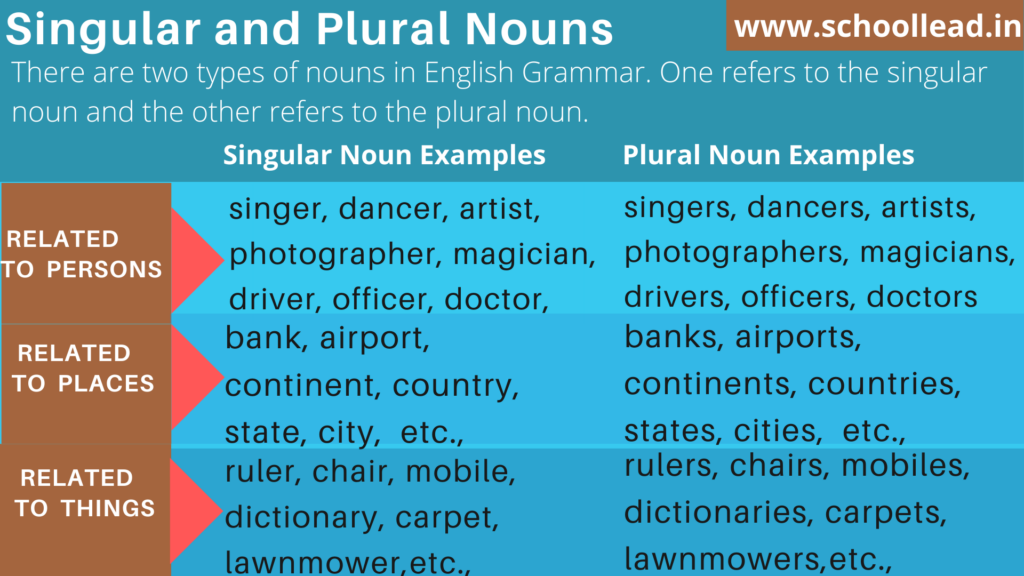
These Singular Nouns can be categorised in the following manner.
- Singular Nouns related to one person:
singer, dancer, artist, photographer, magician, driver, officer, doctor, engineer, principal, peon, labor, nurse, shopkeeper, gatekeeper, sweeper, salesman, philosopher, teacher, minister, president, businessperson, writer, student, friend, boy, girl, toddler, baby, teenager, woman, man, person etc.,
- Singular Nouns related to one place:
bank, airport, continent, country, state, city, town, village, hotel, school, classroom, university, college, park, shop, coffee shop, zoo, water park, mall, supermarket, post office, police station, house, laboratory, library, museum, stadium, building, restaurant, temple, mosque, church, etc.,
- Singular Nouns related to one thing:
ruler, chair, mobile, dictionary, carpet, lawnmower, bus, computer, courage, telephone, spade, printer, hammer, bicycle, pen, table, ship, calculator, crayon, sofa, truck, television, pencil, fridge, book, lamp, ladder, train, cooker, whiteboard, marker, duster, register, map, globe etc.,
Plural Noun Definition:
When a noun refers to more than one person or thing, it is said to be in the Plural Noun/Number.
Plural Noun Examples:
rooms, tables, computers, pieces of chalk, students, teachers, parents, books, pens, stories etc.,
Forming of Plural Noun:
There are various RULES to form plural nouns from singular. Most of the rules have been provided here.
They are as follows:
Rule No 1: Most of the Nouns in English form their plural noun by adding ‘s’ at the end of a singular noun.
Examples:
- actor – actors
- animal – animals
- answer – answers
- boat – boats
- book – books
- bottle – bottles
- car – cars
- cat – cats
- cap – caps
- cow – cows
- day – days
- desk – desks
- dog – dogs
- example – examples
- fact- facts
- goat – goats
- group – groups
- girl -girls
- house – houses
- lake – lakes
- pencil – pencils
- pen – pens
- school – schools
- snake – snakes
- system – systems
- teacher – teachers
- thing – things
Rule No 2: When Nouns end in –’o’, we generally add –’es’ to form plurals:
Examples:
- buffalo – buffaloes
- cargo – cargoes
- echo – echoes
- hero – heroes
- mango – mangoes
- mosquito – mosquitoes
- negro – negroes
- potato – potatoes
- tomato – tomatoes
- torpedo – torpedoes
- veto – vetoes
- volcano – volcanoes
- zero – zeroes
Exception 1: Though some nouns end in –’o’, we add only ‘s’.
- canto – cantos
- commando – commandos
- Eskimo – Eskimos
- logo – logos
- memento – mementos
- memo – memos
- photo – photos
- piano – pianos
- pro – pros
- solo – solos
Exception 2: But for some nouns, we can add ‘s’ and ‘es’. Both are correct.
- buffalo – buffalos/buffaloes
- cargo – cargos/cargoes
- commando – commandos/commandoes
- memento – mementos/mementoes
- mosquito – mosquitos/mosquitoes
- portico – porticos/porticoes
- volcano – volcanos/volcanoes
Rule No 3: When a noun ends in –’o’ but preceded by a vowel, we add only “s”.
Examples:
- bamboo – bamboos
- cuckoo – cuckoos
- cameo – cameos
- folio – folios
- kangaroo – kangaroos
- portfolio – portfolios
- radio – radios
- studio – studios
- video – videos
Rule No 4: When Nouns end in -s, -sh, -ch (soft), or -x, we add -’es’ to form plurals:
Examples:
- access – accesses
- address – addresses
- atlas – atlases
- ax – axes
- beach – beaches
- bench – benches
- box – boxes
- branch – branches
- brush – brushes
- bunch – bunches
- bus – buses
- church – churches
- class – classes
- congress – congresses
- crash – crashes
- dish – dishes
- dress – dresses
- fox – foxes
- gas – gases
- kiss – kisses
- lunch – lunches
- mass – masses
- match – matches
- patch – patches
- radish – radishes
- research – researches
- search – searches
- sketch – sketches
- speech – speeches
- stress – stresses
- status – statuses
- stitch – stitches
- success – successes
- tax – taxes
- touch: touches
- watch – watches
- wish – wishes
- witch – witches
Rule No 5: When Nouns end in –’y’ and –’y’ is preceded by a consonant, we change the ‘y’ into ‘i’ and add -’es’ to form plurals.
Examples:
- berry – berries
- cherry – cherries
- city – cities
- colony – colonies
- copy – copies
- country – countries
- daisy – daisies
- duty – duties
- dictionary – dictionaries
- enemy – enemies
- fairy – fairies
- family – families
- fly – flies
- gallery – galleries
- hobby – hobbies
- injury – injuries
- lady – ladies
- lorry – lorries
- lily – lilies
- party – parties
- penny – pennies
- pony – ponies
- puppy – puppies
- reply – replies
- story – stories
- study – studies
- theory – theories
- trophy – trophies
- university – universities
- victory – victories
Exception: But, in case –’y’ is preceded by a vowel, we add only –’s’.
- boy – boys
- day – days
- delay – delays
- donkey – donkeys
- essay – essays
- guy – guys
- holiday – holidays
- joy – joys
- key – keys
- monkey – monkeys
- play – plays
- ray – rays
- storey – storeys
- toy – toys
- tray – trays
- valley – valleys
Rule No 6: When Nouns end in -’ch’ and ‘ch’ is pronounced as ‘k’, we add –’s’ to form the plural.
Examples:
- hierarch – hierarchs
- epoch – epochs
- eunuch – eunuchs
- monarch – monarchs
- patriarch – patriarchs
- matriarch – matriarchs
- stomach – stomachs
- hierarch – hierarchs
Rule No 7: When Nouns end in ‘f’ or ‘fe’, we replace it with –‘v’ and then add -‘es’ to form the plural.
Examples:
- calf – calves
- elf – elves
- half – halves
- hoof – hooves
- knife – knives
- leaf – leaves
- life – lives
- leaf – leaves
- loaf – loaves
- scarf – scarves
- self – selves
- sheaf – sheaves
- shelf – shelves
- thief – thieves
- wife – wives
- wolf – wolves
Exception 1: The following nouns become plural when we add only ‘s’.
- belief – beliefs
- brief – briefs
- chief – chiefs
- cliff – cliffs
- cuff – cuffs
- gulf – gulfs
- grief – griefs
- proof – proofs
- roof – roofs
- safe – safes
- scarf – scarfs
- serf – serfs
- strife – strifes
- turf – turfs
Exception 2: But for some nouns, we can add both -’s’ or –’ves’. Both are correct.
- dwarf – dwarfs or dwarves
- hoof – hoofs or hooves
- scarf – scarfs or scarves
- kerchief – kerchief or kerchieves
- wharf – wharfs or wharves
Rule No 8: We change inside vowels of some nouns to make them plural
Examples:
- dormouse – dormice
- goose – geese
- foot – feet
- louse – lice
- man – men
- mouse – mice
- person – people
- tooth – teeth
- woman – women
Exception: We add -’en’ to a few nouns to make them plural.
- child – children
- ox – oxen
- brother – brethren (brothers also correct)
- cow – kine (cows also correct)
- sister – sistren (sisters also correct)
Rule No 9: Some nouns are the same in singular and plural.
Examples:
- aircraft – aircraft
- barracks – barracks
- deer – deer
- dozen – dozen
- gross – gross
- pair -pair
- score – score
- series – series
- sheep – sheep
- spacecraft – spacecraft
- species – species
Rule No 10: Some nouns have two types of plural forms
Examples:
- antelope – antelope or antelopes
- fish – fish or fishes
- reindeer – reindeer or reindeers
- herring – herring or herrings
Rule No 11: Some nouns are used only in the plural form
Names of certain tools and things:
bellows, scissors, spectacles, binoculars, glasses, goggles, sunglasses
headphones, pliers, tweezers, tongs, pincers, chopsticks etc.
Names of clothes and footwear:
shorts, trousers, panties, briefs, drawers, tights, jeans, pants, pyjamas, clothes, shoes, sandals, gloves, slippers, boots, socks etc.
Note: We can use ‘a pair of’ with these plural nouns.
Examples:
a pair of trousers, a pair of pants, a pair of glasses, a pair of scissors, a pair of chopsticks, a pair of sandals, a pair of gloves etc.,
Certain other different nouns:
earnings, belongings, assets, congratulations, thanks, annals,
outskirts, premises, surroundings, environs, alms, riches, eaves etc.,
Certain Collective Nouns:
Poultry, cattle, vermin, people, gentry, children etc.,
Rule No 12: Some nouns are used only in the singular form
Names of subjects and others:
mathematics, physics, economics, electronics, news, innings, politics, wages, ethics etc.,
Names of some common diseases:
measles, mumps, rickets etc.,
Names of some games:
billiards, draughts, carroms etc.,
Certain Collective Nouns:
knowledge, information, stationery, luggage, furniture, homework, scenery, bread, expenditure money, power etc.,
Some nouns that refer to number, weight etc., if preceded by numerals.
dozen, gross, hundred, thousand, horse-power, million-foot etc.,
Examples:
- Two dozen bananas
- Two gross of pencils
- Three hundred rupees
- A three-foot stick
- Four thousand dollars
Note: But, we add –’s’ to these nouns if they are used without numerals and are followed by ‘of’.
Examples:
- Dozens of bananas
- Hundreds of rupees
- Thousands of people
- The tree is 30 feet high.
Rule No 13: Change of Compound Nouns into plural:
Examples:
| Compound Nouns in Singular | Compound Nouns in Plural |
| By adding -’s’ to the base or important word | |
| Governor-general | Governors-general |
| Doctor Of Philosophy | Doctors Of Philosophy |
| Commander-in-chief | Commanders-in-chief |
| Brother-in-law | Brothers-in-law |
| Father-in-law | Fathers-in-law |
| Mother-in-law | Mothers-in-law |
| Sister-in-law | Sisters-in-law |
| Son-in-law | Sons-in-law |
| Passer-by | Passers-by |
| Looker-on | Lookers -on |
| Sergeant Major | Sergeants Major |
| Heir Apparent | Heirs Apparent |
| By removing -’y’ and adding -’ies’ to the base or important word | |
| Attorney-general | Attorneys-general |
| Assistant Secretary Of State | Assistant Secretaries Of State |
| Notary Public | Notaries Public |
| Lady-in-waiting | ladies-in-waiting |
| lily-of-the-valley | lilies-of-the-valley |
| By adding -’s’ or -’es’ to the word ending | |
| Step-parent | Step-parents |
| Step-daughter | Step-daughters |
| Step-mother | Step-mothers |
| Maid-servant | Maid-servants |
| General Staff | General Staff(s) |
| Court-Martial | Court-Martials / Courts-Martial |
| Vice-Principal | Vice-Principals |
| Book-case | Book-cases |
| Go-between | Go-betweens |
| Has-been | Has-beens |
| Good-for-nothing | Good-for-nothings |
| Forget-me-not | Forget-me-nots |
| Higher-up | Higher-ups |
| Grown-up | Grown-ups |
| Mix-up | Mix-ups |
| Takeoff | Takeoffs |
| Armful | Armfuls |
| Handful | Handfuls |
| Cupful | Cupfuls |
| Mouthful | Mouthfuls |
| Tablespoonful | Tablespoonfuls |
| Blackboard | Blackboards |
| Bystander | Bystanders |
| Toothbrush | Toothbrushes |
| By changing both the words | |
| Man-servant | Men-servants |
| Man-driver | Men-drivers |
| Woman-writer | Women-writers |
| Woman-teacher | Women-teachers |
| Woman-doctor | Woman-doctors (Women-doctors) |
| By changing words ‘man and woman’ into ‘men and women’ | |
| Fisherman | Fishermen |
| Workman | Workmen |
| Boatman | Boatmen |
| Man-of-war | Men-of-war |
| Saleswoman | Saleswomen |
| Workingwoman | Workingwomen |
| By adding -’s’ to the word ‘man’, when it refers to any ethnic group, race or civilian | |
| Mussalman | Mussalmans |
| German | Germans |
| Norman | Normans |
| Brahman | Brahmans |
| Other phrases | |
| Many Stops For Buses | Many Bus Stops |
| 150 Trees With Oranges | 150 Orange Trees |
Rule No 14: In the case of letters, numbers, and abbreviations, we add an apostrophe and -’s’ to make them plural.
Examples:
- Akshay, write your q’s and p’s clearly.
- Mohini, add two 8’s and subtract three 2’s.
- Ten M.A.’s and only two B.E.’s have attended the interview.
Rule No 15: Some Greek and Latin Nouns can form their plurals in the following manner:
1.Some nouns can be added –’es’ in place of –’is’ to make them plural
Examples:
|
|
2. Some Nouns that end in -’a’ can be added -’e’ to make the plural
Examples:
- antenna – antennae or antennas
- alga – algae
- formula – formulae
- larva – larvae
- nebula – nebulae
- vertebra – vertebrae
3. Some nouns can be added –’i’ in place of –’us’ to make them plural
Examples:
- cactus – cacti
- focus – foci
- fungus – fungi
- nucleus – nuclei
- radius – radii
- syllabus – syllabi
- terminus – termini
4. Some nouns can be added –’a’ in place of –’um’ to make them plural
Examples:
- agendum (agenda) – agenda (nowadays, agenda is used mostly as a singular form)
- aquarium – aquaria or aquariums
- bacterium – bacteria
- curriculum – curricula
- corrigendum – corrigenda
- datum – data
- erratum – errata
- forum – fora
- gymnasium – gymnasia or gymnasiums
- maximum – maxima or maximums
- medium – media
- memorandum – memoranda or memorandums
- millennium – millennia
- moratorium – moratoria or moratoriums
- podium – podia or podiums
- referendum – referenda or referendums
- stratum – strata
4. Some nouns can be added –’ices’ in place of –’ex/ix’ to make them plural
Examples:
- appendix – appendices or appendixes
- index – indices or indexes
- matrix – matrices
- vertex – vertices
6. Some nouns can be added –’a’ in place of –’on’ to make them plural
Examples:
- automaton – automata or automatons
- criterion – criteria
- ganglion – ganglia or ganglions
- polyhedron – polyhedra
- phenomenon – phenomena
7. Some nouns that end in –’ma’ can be added –’ta’ to make them plural
Examples:
- dogma – dogmata
- stigma – stigmata
8. The following words are from French:
Examples:
- madame (madam) – mesdames
- monsieur – messieurs
Greek and Latin Nouns Worksheets
Rule No 16: Some Nouns have two plural forms each with a different meaning.
Examples:
| Singular | Plural | Meaning |
| brother | brothers | sons of the same parent |
| brethren | members of a society or a community | |
| Cloth | cloths | pieces of cloth |
| clothes | dresses or garments | |
| Die | dies | stamps for coining |
| dice | small cubes used in games | |
| Index | indexes | tables of contents to books |
| indices |
signs used in algebra |
|
| Penny | pennies | number of coins |
| pence | amount in value | |
| fish | fish | denote the same kind of two or more fish |
| fishes | denote the different kinds of fish | |
| genius | geniuses | intelligent or talented persons |
| genii |
spirits or ghosts |
Rule No 17: Some Nouns have two meanings in the singular but only one in the plural:
Examples:
| Singular | Meaning | Plural | Meaning |
| people | 1. nation
2. men or women |
peoples | nations |
| powder | 1.dust
2. a dose of medicine |
powders | doses of medicine |
| practice | 1. habit
2. exercise of a profession |
practices | habits |
| light | 1.a lamp
2. radiance |
lights | lamps |
Rule No 18: Some nouns have one meaning in the singular, but two in the plural.
Examples:
| Singular | Meaning | Plural | Meaning |
| arm | upper limb | arms | 1.upper limbs
2.weapons |
| colour | hue | colours | 1.hues
2. the flags of a regiment |
| custom | habit | customs | 1.habits
2.duties levied on imports |
| manner | method | manners | 1.methods
2.correct behaviour |
| minute | A unit of time | minutes | 1.units of time
2.proceedings of a meeting |
| moral | a moral lesson | morals | 1.moral lessons
2.conduct |
| number | a quantity | numbers | 1.quantities
2.verses |
| effect | result | effects | 1) results
2) property |
| pain | suffering | pains | 1.suffering
2.care, exertion |
| quarter | fourth part | quarters | 1.fourth parts
2.lodgings |
| spectacle | a sight | spectacles | 1.sights
2.eye-glasses |
| premise | proposition | premises | 1. propositions
2. buildings |
| letter | 1.a letter of the alphabet
2.epistle |
letters | 1.letters of the alphabet
2.epistles 3.literature |
Rule No 19: Some nouns have different meanings in the singular and in the plural.
Examples:
| Singular | Meaning | Plural | Meaning |
| advice | counsel | advices | information |
| air | atmosphere | airs | affected manners |
| authority | power | authorities | persons in power |
| beef | flesh of ox | beeves | bulls, cattle and cows |
| blind | unable to see because of injury, disease, or a congenital condition | blinds | a screen for a window |
| good | benefit, well-being | goods | merchandise |
| compass | extent, range | compasses | in an instrument for drawing circles |
| iron | a metal | irons | fetters |
| physic | medicine | physics | natural science |
| character | the mental and moral qualities distinctive to an individual. | characters | a person in a novel, play, or film |
| respect | regard | respects | compliments |
| force | strength | forces | troops |
| return | coming back | returns | statistics |
| vesper | evening | vespers | evening prayers |
| sand | a kind of matter | sands | a desert |
| wood | the hard fibrous material that forms the main substance of the trunk or branches of a tree or shrub, used for fuel or timber. | woods | a small forest |
Rule No 20: Some nouns are normally used in the plural.
1.Proper Nouns:
India, Telangana, Warangal, Ashoka, Mary, Ganga etc
Note.1 When a Proper Noun is used in the plural, it becomes a Common Noun.
He is a Bruce Lee in fighting.
Kalidasa is called the Shakespeare of India
Note.2 But Some Nouns can be used in Plural like
The United States of America, The Alps, The Himalayas etc.,
2.Abstract Nouns:
Hope, charity, love, kindness, friendship, death, beauty etc.,
Note: When the Abstract Noun is used in the plural, it becomes a Common Noun.
Truly, the beauties of Kashmir are enticing.
3.Material Nouns:
Copper, iron, tin, wood, glass, rice, oil etc.,
Note: When a Material Noun is used in the plural, it becomes a Common Noun
Examples:
He does not have any coppers with him. (copper coins)
The convict has been found in irons. (fetters)
Last summer, we enjoyed ourselves in the nearby woods. (forests)
- Types of Nouns
- Proper Nouns
- Common Nouns
- Collective Nouns
- Nouns of Multitude
- Material Nouns
- Abstract Nouns
- Compound Nouns
- The Noun – Case
- Gender of the Noun
- Possessive Nouns
- A list of Partitives
- Appositive
- List of Countable and Uncountable Nouns
- Countable and Uncountable Nouns