Word for Microsoft 365 Outlook for Microsoft 365 Word 2021 Outlook 2021 Word 2019 Outlook 2019 Word 2016 Outlook 2016 Word 2013 Outlook 2013 Word 2010 Outlook 2010 Word 2007 Outlook 2007 More…Less
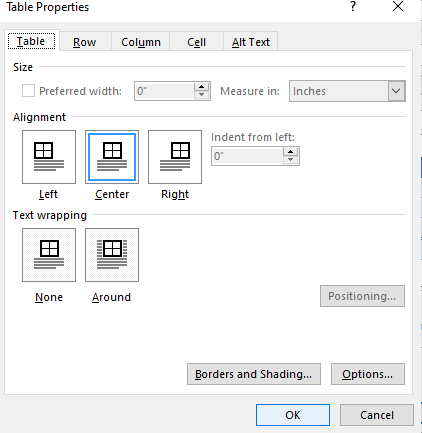
To set or change table options in Word or Outlook, right-click a table and choose Table Properties.
Note: If you want to set properties for a particular row, column, or cell, click in that row, column, or cell before making changes in the Table Properties dialog box.
In this article
-
Table properties
-
Row properties
-
Column properties
-
Cell properties
-
Alt text
Table properties

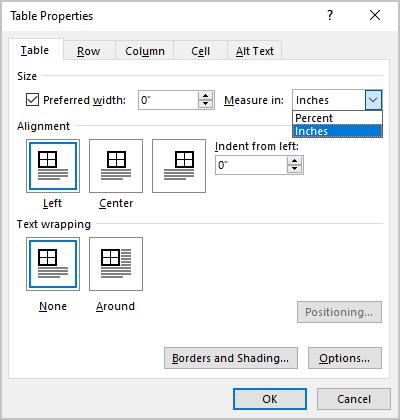
Click the Table tab to apply settings to your entire table:
-
Under Size, set the table’s overall width by selecting Preferred width and choosing a size. In the Measure in box, choose whether you want to measure the width in inches or a percentage of the page.
-
Under Alignment, choose whether you want to align your table to the left, center, or right of page. If you select Left, you can select an indentation distance in the Indent from Left box.
-
Under Text wrapping, select Around if you want nearby text on your page to wrap around your table; you can make text wrapping more precise by clicking Positioning, and then choosing options in the Table Positioning dialog box. If you don’t want text wrapping, select None.
-
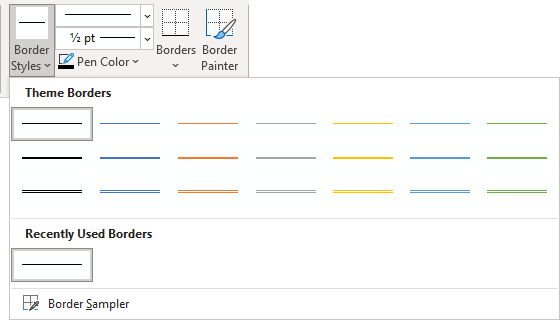
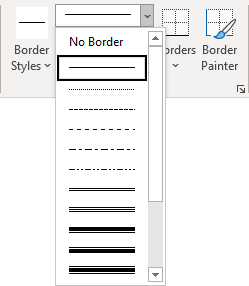
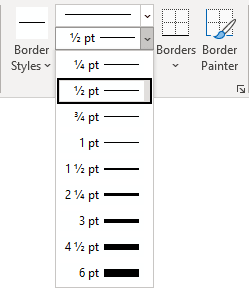
Click Borders and Shading to change the border style, line color, and line width of your table.
-
Click Options to set more table properties, including top and bottom cell margins, cell spacing, and automatic resizing of cell contents.
Top of Page
Row properties
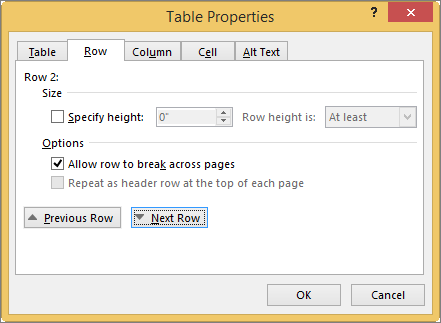
First, click in the row or select the rows you want to change, right-click, choose Table Properties, and then click the Row tab.
-
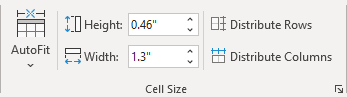
Under Size, set the row’s height by selecting Preferred height and choosing a size; you can further refine the height by selecting an option in the Row height is box.
-
Under Options, select options for breaking rows across pages or creating header rows.
-
To display the currently selected row at the top of the tab and navigate between rows without leaving the Table Properties dialog box, click Previous Row or Next Row.
Top of Page
Column properties
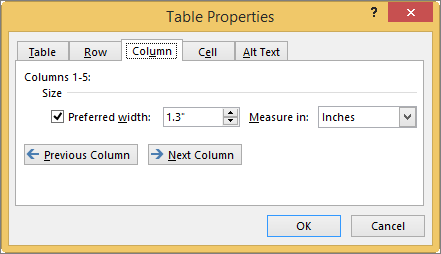
First, click in the column or select the columns you want to change, right-click, choose Table Properties, and then click the Column tab.
-
Under Size, set the column’s width by selecting Preferred width and choosing a size. In the Measure in box, choose whether you want to measure the width in inches or a percentage.
-
To display the currently selected column or columns at the top of the tab and navigate between columns without leaving the Table Properties dialog box, click Previous Column or Next Column.
Top of Page
Cell properties
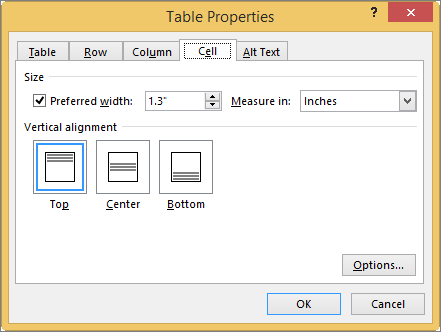
First, click in the cell that you want to change, right-click, choose Table Properties, and then click the Cell tab.
-
Under Size, set the cell’s width by selecting Preferred width and choosing a size. In the Measure in box, choose whether you want to measure the width in inches or a percentage.
-
Under Vertical alignment, choose an alignment option for the cell contents—Top (the default alignment), Center, or Bottom.
-
Click Options to set more cell properties, including top and bottom cell margins and text wrapping and fit options.
Top of Page
Alt text
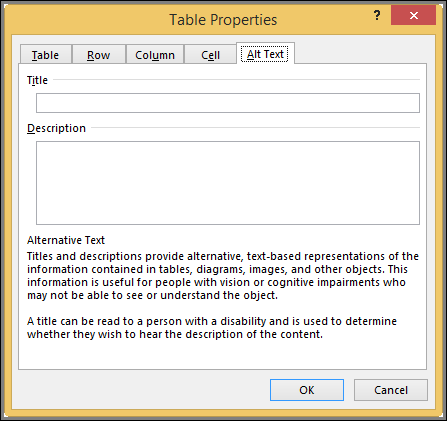
You can create alternative text (alt text) for your table to help people with screen readers understand the content of the table.
-
In the Description box, enter an explanation of the table.
-
In the Title box, enter a brief summary of the table.
Note: Unless you have a complex table, you will usually want to enter text in just the Description box. When you have complex content to describe, filling in the Title field is useful so that reading the full description is not necessary unless desired.
Top of Page
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.
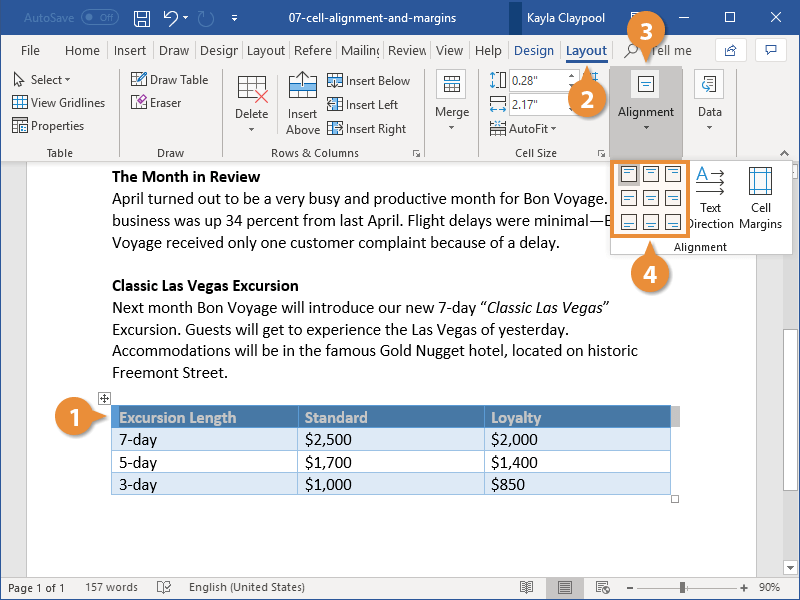
Cell Margins and Cell Spacing are two important settings in any Microsoft Word Table but they aren’t used much and not well understood.
Cell margins are the spaces between your text and the edge of the cell. They can be set separately for the top, bottom, and either side of the cells.
To change the cell margins, we again click in the table and go to the Layout tab on the right. Then click Cell Margins in the Alignment group.
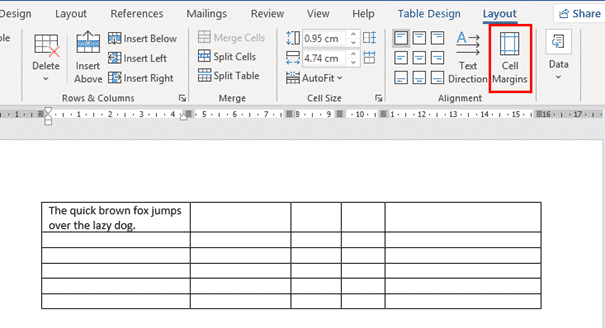
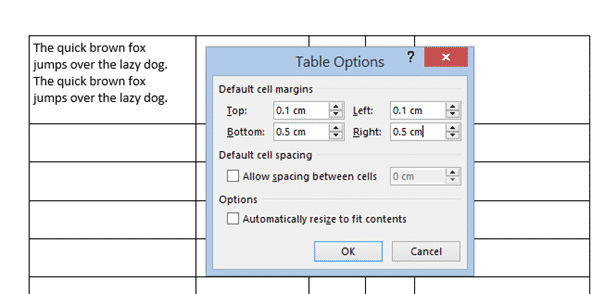
In the Table Options dialog that opens, use the spinners to incrementally change each of the four margins, or simply type in the margin that you want into each field; Top, Bottom, Left or Right.

The margins we’ve selected above are quite large, just to show you clearly how his setting changes your table. Here’s the large cell margins (left) compared to zero cell margins (right).

You can, of course have different margins on different sides:
Individual, Row or Column Cell Margins
Table cell margins can be changed for a row, column or even a single cell, but it’s nowhere near the main Cell Margins ribbon button.
Select the column, row or cell you want to change then go to Table Layout | Table | Properties | Cell | Options. UNcheck the box ‘Same at the whole table’ then change the margin settings.

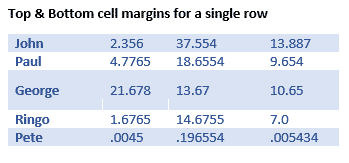
Here’s a single row, highlighted a little by increasing the top & bottom cell margins.
Why Adjust Table Cell Margins?
Cell margins are useful to separate lines in a table, especially when there’s no gridlines. Change the Top & Bottom cell margins to separate the lines and improve readability.

When space is tight, reducing the default left & right cell margins can help fit a table or contents into the available space.
Cell Spacing Tricks in Word Tables
Word’s Table Options have an interesting choice, Cell Spacing. While cell margins are the space between the text and the edge of the cell, cell spacing puts space around each of the cells.
Cell spacing has a surprising effect on the look of a Word Table with single line borders.
Go to Table | Alignment | Cell Margins | Default cell spacing | Allow spacing between cells.
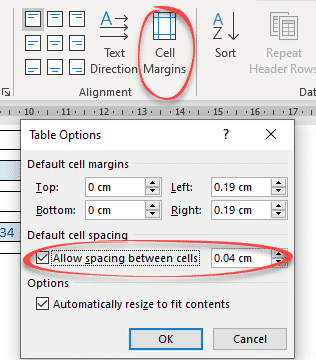
The default is OFF with no spacing.
Here’s how a Table looks using a standard single line border but increasing the cell spacing from the default, Zero.

Changes to Table Borders
As you can see, the single line table border becomes a twin gridline just by adding cell spacing to the same table.

Word table with Footnotes
Merge Cells in Word tables
Word tables for formatting magic
Indexing ‘bug’ in Word tables
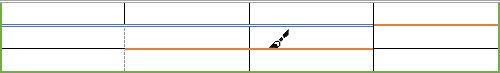
I want to have a spacing between horizonal borders of two adjacent table cells like in this example. I want borders below «Commerce FAculty» and «EBE Faculty» not to touch in order to use horizonal border for grouping. Is this possible?
fixer1234
26.9k61 gold badges72 silver badges116 bronze badges
asked Sep 22, 2015 at 0:24
This will probably depend on the Version of Word you are using, but on mine, I am able to select Table Properties… with a context sensitive click, then under the Table tab choose Options, and then under Options turn on Default Cell Spacing and set it to what you want.
You may have to search for something similar in yours. I am using the Mac version of Word.
answered Sep 22, 2015 at 0:57
AMRAMR
5701 gold badge4 silver badges16 bronze badges
Instructions
- Highlight the relevant cells, after making sure that they have no preexisting overlapping border beforehand (e.g. cell-based bottom border).
- Right click.
- Select ‘Table Properties’.
- Select ‘Borders and Shading’.
- Apply to ‘Paragraph’.
- Add your desired borders (in this case, bottom border).
- Click ‘OK’.
If you do this but the borders are still connected, you need to specify the necessary cell margins, for either the relevant cells or the whole table.
Example table:
This solution is based on: https://wordribbon.tips.net/T013179_Underlining_Cells_Not_Space_Between_Cells.html
answered Jul 12, 2020 at 13:42
ThredolsenThredolsen
1411 silver badge6 bronze badges
Borders always go to the edges of the cells. Two solutions:
-
If you want to use borders, include a narrow dummy column in between that you leave empty. Within the dummy columns, include the borders where you want them and exclude the ones you don’t. This might require a little extra work manipulating column widths.
-
Underscore those headings instead of using a border in that location. The underscore won’t extend beyond the words, which will leave a gap between them.
answered Sep 22, 2015 at 0:40
fixer1234fixer1234
26.9k61 gold badges72 silver badges116 bronze badges
2
Create, Modify and Apply Table Styles in Word Documents
by Avantix Learning Team | Updated August 21, 2022
Applies to: Microsoft® Word® 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021 or 365 (Windows)
You can apply table styles to your Word tables to format them quickly and consistently. Word is shipped with several built-in table styles or you can create your own. You can edit table styles by modifying borders, shading, character formatting, paragraph formatting and table properties. If your document includes multiple tables, table styles can save a lot of time.
Note: Buttons and Ribbon tabs may display in a different way (with or without text) depending on your version of Word, the size of your screen and your Control Panel settings. For newer versionns of Word, Ribbon tabs may appear with different names. For example, the Table Tools Design tab may appear as Table Design.
Recommended article: How to Keep a Microsoft Word Table Together on One Page
Do you want to learn more about Microsoft Word? Check out our virtual classroom or live classroom Word courses >
Table styles and themes
Every Word document uses a document theme which includes a font theme and color theme. The colors used in table styles are based on the color theme.
You can select document themes, color themes and font themes using the Themes, Colors or Fonts drop-down menus on the Design tab in the Ribbon:
You can also create your own custom color themes so your tables can be formatted using your organization’s colors.
Display gridlines
When you are working with tables, it’s a good idea to turn gridlines on. Borders, which are a format, will print. Gridlines do not print.
To display gridlines:
- Click in a table.
- Click the Table Tools Layout or Table Layout tab.
- Click View Gridlines. Gridlines will stay on for all Word documents.
View Gridlines appears on the Table Tools Layout or Table Layout tab when you click in a table:
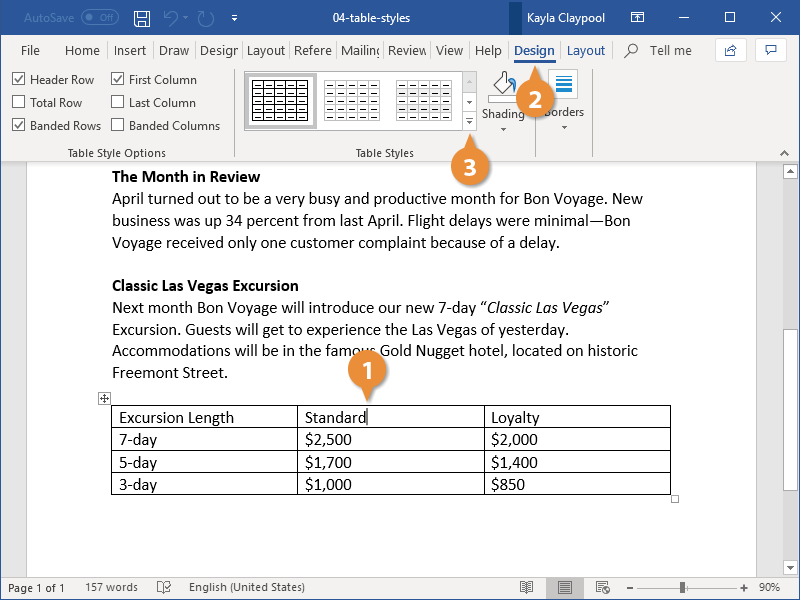
Apply a table style
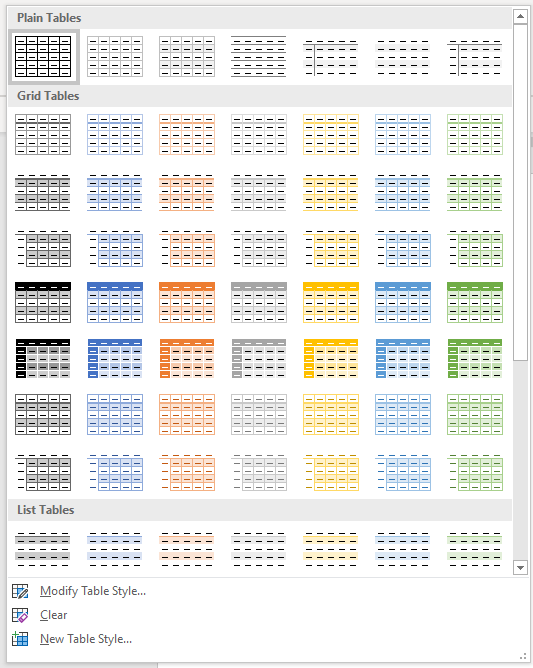
If your Word document contains multiple tables that you want to format in a consistent way, it’s best to use table styles rather than applying manual or direct formatting to each table.
To apply a table style to a table:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon.
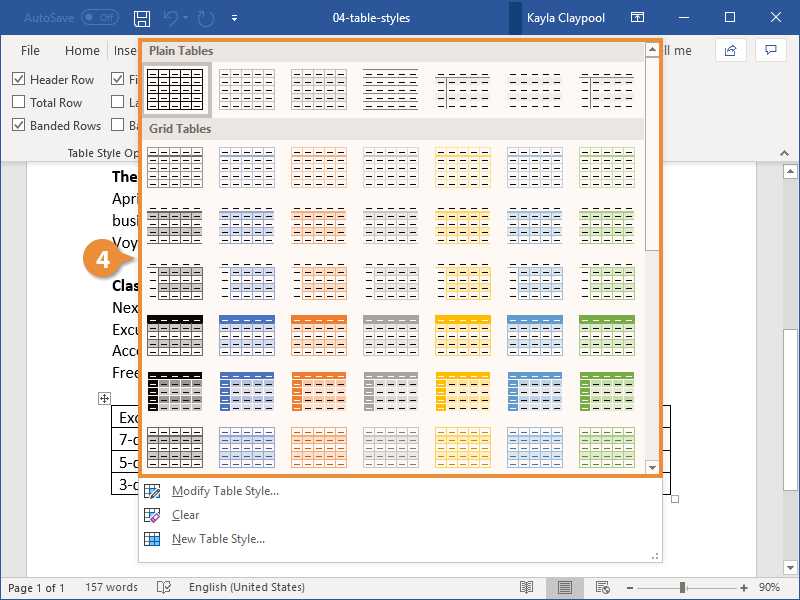
- Click the More down arrow on the bottom right in the Table Styles gallery. A drop-down menu appears.
- Hover over the various table styles. The table formatting will change as you move over different table styles in the gallery.
- Click the table style you want to apply.
Below is the Table Styles gallery (the current theme is the Office theme):
Note: Table styles do not include row height, column width or custom cell formatting for individual cells. If a user applies manual or direct formatting to a table (such as fills and borders) on the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab, this formatting will override the table style.
Apply Table Style Options
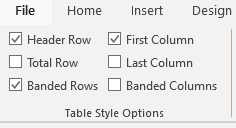
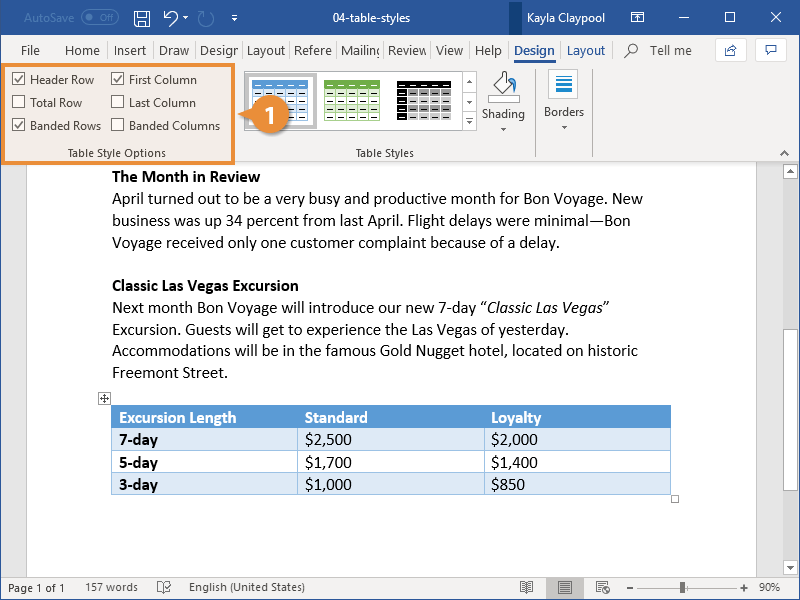
Once you have selected a table style, you can select or check different Table Style Options (which are affected by the formats in the selected table style).
The six Table Style Options that you can apply are: Header Row, Total Row, Banded Rows, First Column, Last Column and Banded Columns. If you have selected a plain table style, you may not notice any changes in the table formatting if you select different Table Style Options.
Table Style Options appear on the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab as follows when you click in a table:
To select Table Style Options:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon.
- In Table Style Options, check or uncheck Header Row. If this option is checked, the header row will be formatted differently from the body rows.
- In Table Style Options, check or uncheck Total Row. If this option is checked, the last row will be formatted differently from the body rows.
- In Table Style Options, check or uncheck Banded Rows or Banded Columns for alternate row or column shading.
- In Table Style Options, check First Column or Last Column if you want the first or last column formatted differently from the other columns.
In the following table, Header Row and Banded Rows are checked in Table Style Options:
Modify a table style
You can modify a table style in a Word document and all tables using that table style will change.
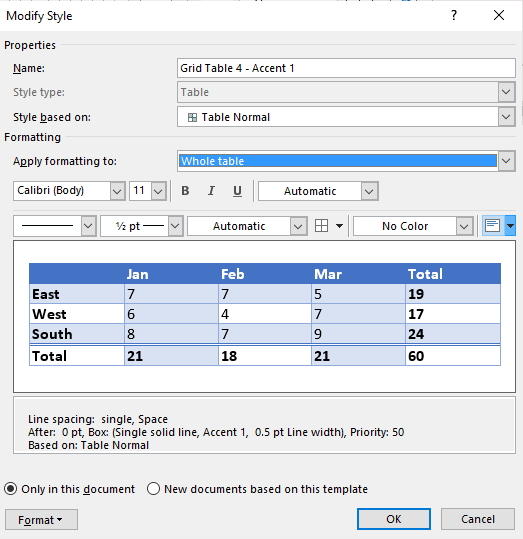
To modify a table style:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon.
- Click the More down arrow on the bottom right in the Table Styles gallery. A drop-down menu appears.
- Click Modify Table Style. A dialog box appears. You can also right-click a table style and select Modify.
- From the Apply Formatting to drop-down menu, select the element that you want to modify (such as Header row).
- Select the desired formatting such as font, font size, font color, fill and border.
- From the Apply Formatting to drop-down menu, select the next element that you want to modify.
- Select the desired formatting such as font, font size, font color, fill and border.
- Repeat for other elements.
- Select Only in this document or New documents based on this template. If you select Only in this document, the modified style will only be available for the current document. If you select New documents based on this template, then the table style will be modified for future documents based on the current template (usually the Normal template).
- Click OK.
Below is the Modify Style dialog box:
You can also click Format at the bottom of the dialog box and choose other options such as Font or Paragraph.
If you modify a table style and the tables using that style do not change, it’s likely that direct or manual formatting has been applied to the table which then overrides the table style. You may need to clear formatting in the table by selecting the table and clicking Clear Formatting on the Home tab in the Font group.
You can also modify Table Properties in a table style. Table properties include table alignment, row settings and cell margins.
To modify Table Properties in a table style:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon.
- Click the More down arrow on the bottom right in the Table Styles gallery. A drop-down menu appears.
- Click Modify Table Style. A dialog box appears. You can also right-click a table style and select Modify.
- Click Format on the bottom left of the dialog box. A drop-down menu appears.
- Click Table Properties. A dialog box appears.
- Click the Table tab and select an Alignment.
- Click the Row tab and select the desired options. For example, turn off Allow row to break across pages.
- Select any other formatting options you want to apply to the entire table.
- Click OK.
- Select Only in this document or New documents based on this template.
- Click OK.
Below is the Table Properties dialog box with the Table tab selected:
Create a new table style
You can also create a new or custom table style.
To create a custom table style:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon.
- Click the More down arrow on the bottom right in the Table Styles gallery. A drop-down menu appears.
- Click a table style to apply it as a base style.
- Click the More down arrow on the bottom right in the Table Styles gallery. A drop-down menu appears.
- Click New Table Style. A dialog box appears.
- Enter a name for the new table style in the Name box.
- Select the desired formatting.
- Select Only in this document or New documents based on this template.
- Click OK.
New Table Style appears at the bottom of the Table Styles gallery:
The new table style will appear in the Table Styles gallery under Custom (at the top of the gallery). If you want to delete it, right-click it in the gallery and select Delete Table Style.
Clear a table style
To clear a table style and remove formatting:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon.
- Click the More down arrow on the bottom right in the Table Styles gallery. A drop-down menu appears.
- Click Clear.
Clear appears at the bottom of the Table Styles gallery:
Set a default table style
You can also set a default table style for new tables in the current document or all new documents.
To set a default table style:
- Click in the table.
- Click the Table Tools Design or Table Design tab in the Ribbon.
- Click the More down arrow on the bottom right in the Table Styles gallery. A drop-down menu appears.
- Right-click the table style you want to use as the default style and select Set as Default from the drop-down menu. A dialog box appears.
- Select This document only or All documents based on the Normal.dotm template (the default template in Word is the Normal template).
- Click OK.
If you are working with documents with multiple tables, formatting with table styles can ensure that your tables are formatted consistently and save a lot of time.
Subscribe to get more articles like this one
Did you find this article helpful? If you would like to receive new articles, JOIN our email list.
More resources
4 Ways to Create a Table in Word
14 Shortcuts to Quickly Select Text in Microsoft Word
How to Create Headings in Word (Using Heading Styles)
How to Quickly Remove Hard Returns in Word Documents
10 Microsoft Word Tips, Tricks and Shortcuts for Selecting in Tables
Related courses
Microsoft Word: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft Excel: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft PowerPoint: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft Word: Long Documents Master Class
Microsoft Word: Styles, Templates and Tables of Contents
Microsoft Word: Designing Dynamic Word Documents Using Fields
VIEW MORE COURSES >
Our instructor-led courses are delivered in virtual classroom format or at our downtown Toronto location at 18 King Street East, Suite 1400, Toronto, Ontario, Canada (some in-person classroom courses may also be delivered at an alternate downtown Toronto location). Contact us at info@avantixlearning.ca if you’d like to arrange custom instructor-led virtual classroom or onsite training on a date that’s convenient for you.
Copyright 2023 Avantix® Learning
Microsoft, the Microsoft logo, Microsoft Office and related Microsoft applications and logos are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in Canada, US and other countries. All other trademarks are the property of the registered owners.
Avantix Learning |18 King Street East, Suite 1400, Toronto, Ontario, Canada M5C 1C4 | Contact us at info@avantixlearning.ca
By default, a table is created with the Table Grid style, which includes a basic black border around each cell in the table. Word includes many built-in styles that provide more visual appeal.
Apply a Table Style
- Click inside the table.
- Click the Design tab in the Table Tools ribbon group.
- (Optional) Click the Table Styles More button to see all the available styles.
- Select a style.
The Table Styles group will show a few table styles, but to see the rest, you’ll need to expand the gallery.
The style is applied to the table, changing the borders, shading, and colors.
You could create a new style by selecting New Table Style or modify an existing one by selecting Modify Table Style and choosing which formatting you’d like.
To remove a Table Style, select Clear from the More Table Styles menu.
Adjust Style Options
You can further customize a table style by changing the table style options.
- Use the check boxes in the Table Style Options group to toggle the following settings:
- Header Row will apply special formatting to the first row of the table. This special formatting can include font effects, or font, background, and border color.
- First Column will apply special formatting to the first column.
- Total Row will add special formatting to the final row of a table, designed to summarize the rows above it.
- Last Column will apply special formatting to the last column to summarize the earlier columns.
- Banded Rows will alternate the background color of rows.
- Banded Columns will alternate the background color of columns.
The special formatting applied by each option is controlled by the style that’s been applied to the table. You can customize these formatting options by clicking the Table Styles More button, then selecting Modify Table Style.
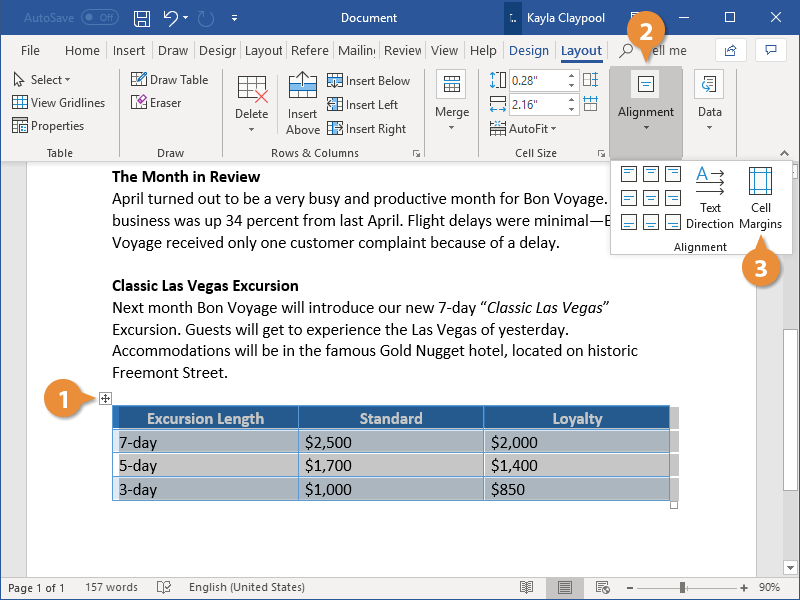
Text Alignment
You can control how text is aligned within a table cell, just like you’d align text on the page.
- Select the cell or cells you want to align.
- Click the Layout tab in the Table Tools ribbon group.
- Expand the Alignment group, if necessary.
- Select an alignment option.
You could also select the entire table if you want to align all the text together.
There are nine alignment options, letting you align the content to either side of a cell, any corner, or center it in the middle of the cell.
The text in the selected cell realigns to the selected side or corner.
You can also select Text Direction to change the text from left-to-right to top-to-bottom or bottom-to-top.
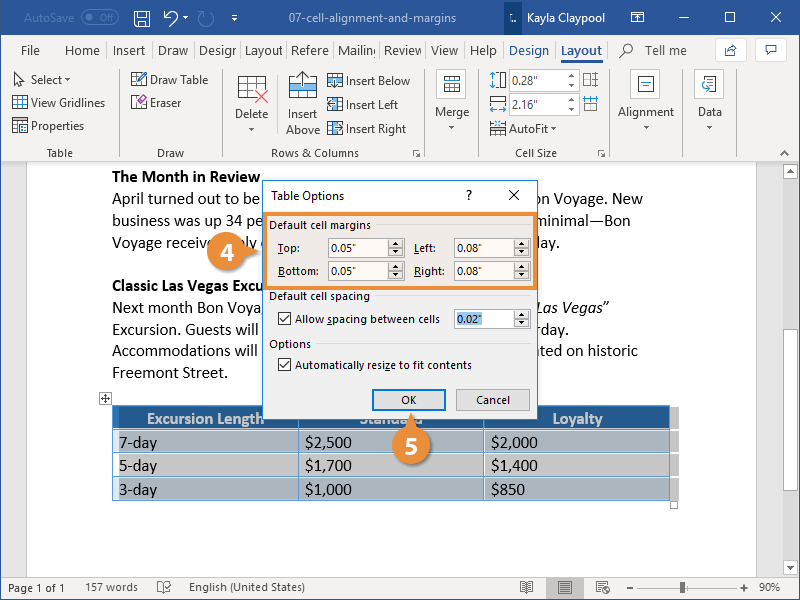
Add Cell Margins
You can also adjust the margins between cell borders and the text within those cells.
- Select cell or cells you want to adjust.
- From the Layout tab, expand the Alignment group, if necessary.
- Click the Cell Margins button.
- Adjust the margins.
- Click OK.
You can select the entire table to adjust all the margins at once.
In the Table Options dialog box, we can adjust the margins for the selected cell or cells. The margin affects how much space there is between the edge of the cell and the contents of that cell.
You can adjust the margin on each side of the cell independently.
The cell margins are changed.
FREE Quick Reference
Click to Download
Free to distribute with our compliments; we hope you will consider our paid training.
If you don’t use tables in your Word documents, you should be! They are one of the 3 content pillars, alongside text and images that allow you to construct any layout and content structure in your documents.
Following this beginners guide to Word tables which covers table basics, this post explores some of the lesser-known features of Word tables, answers the frequently asked questions and tackles the prickly issues.
1. Intro
This post assumes that you know how to create Word tables, add, remove and resize columns and rows and apply some simple formatting. Check out this beginners guide to Word tables if you need a refresher, then come back here and read on!
2. Setting the AutoFit behavior of Word tables
The Autofit behaviour determines the width of the table columns in relation to the page size, contents and margin settings.
- Fixed column width allows you to define an exact width for each of the table columns.
- AutoFit to Contents allow each column width to be condensed to the widest content of the column. Data will never be truncated as a result. It is best to use this option once your table is populated.
- AutoFit to Windows stretches the table to its maximum width to fit within the left ad right margins.
To change the Autofit behaviour of the table:
1. Select the Layout tab under the Table Tools banner at the top of the screen.
2. Click the Autofit icon in the Cell Size group.
3. Choose an Autofit option.
3. Hiding & showing table gridlines
Gridlines allow you to see the row and column divisions of your Word tables, even when the the borders are switched off. When you come to print your document, it will not print gridlines. the only table borders that will print are those you have explicitly turned on.
To toggle the table gridlines on or off:
1. Select any cell in any table.
2. Select the Layout tab under the Table Tools banner.
3. Click the View Gridlines icon in the Table group. When the icon has an orange background, the gridlines are switched on.
If you are not sure how your Word tables will look when they are is printed, click the File tab, then choose Print. Alternatively, press Ctrl P. Don’t worry, it won’t print straight away, but it does provide a preview of how it will look when printed.
4. Merging and splitting cells
Sometimes you need to merge cells (e.g. the header row of a table). At other times you need to split a cell into multiple cells.
To merge cells:
1. Select the cells you wish to merge. The cells must be adjacent (next to each other) and linear (i.e. in a row, in a column or in a block).
2. Select the Layout tab under the Table Tools banner.
3. Click the Merge Cells icon in the Merge group.
To split a cell:
1. Select the cell(s) you wish to split.
2. Select the Layout tab under the Table Tools banner.
3. Click the Split Cells icon in the Merge group.
4. Specify how many rows and columns you wish to split the cell(s) into.
3. Click OK
5. Splitting a Word table into 2 tables
Being able to split Word tables is extremely useful. Perhaps you have a long table that won’t fit on a single page and you want to control where the table splits. Or perhaps you want to split a large table into smaller chunks, maybe creating separate tables for each category, or each group or each department.
Here’s the process:
1. Position the cursor in the row that will become the first row of the new table.
2. Select the Layout tab, under the Table Tools.
3. Click the Split Table icon on the Merge group.
If your table was set with Repeating Headings (see next section), both tables will have identical headings. Otherwise the second table will only show the data cells after the split point.
6. Repeating table headings on every page (automatically)
When you have large tables that flow into a second or third page, the column headings only appear once at the top of the table.
You may be tempted to copy and paste the headings to the top of each subsequent page, but when you insert or delete rows, the copied header row can often appear mid-way down the page.
There is a simple tool that will eliminate this problem.
1. Ensure that the table is a single table, with no manual page breaks in the middle.
2. If there is just one header row, place the cursor in that row.
If two or more rows constitute the table header, select all header rows.
3. Select the Layout tab under the Table Tools banner.
4. Click the Repeat Header Rows icon ion the Data group.
7. Changing the column width
To change the width of a column, there are two methods you can use:
Method 1: Click-and-drag the column divider
1. Position the mouse pointer over a column divider. The pointer will change to a double-headed left-right arrow.
2. Click and drag to the right or the left to resize the column.
3. You can also Best Fit the column by double-clicking the column divider. This reduces the width of the column to the widest content of the column.
Method 2: Manually set each column width (this method is more accurate).
1. Position the cursor in the column you want to change.
2. Select the Layout tab under the Table Tools banner.
3. Click the Properties icon in the Table group.
4. Click the Column tab.
5. Tick the Preferred width box and type in the measurement. The measurement can be fixed width (e.g. 5cm) or a percentage of the table width (e.g. 20%).
6. Click the ← Previous Column or → Next Column buttons to go to the previous or next column, then set the width for each column.
8. Changing the row height
To change the height of a row, there are two methods you can use:
Method 1: Click and drag the row divider.
1. Position the mouse pointer over a row divider. The pointer will change to a double headed up-down arrow.
2. Click and drag upwards or downwards to resize the column.
3. You can also Best Fit the row by double-clicking the row divider. This reduces the height of the column to the highest content of the column.
Method 2: Manually set each row height (this method is more accurate).
1. Position the cursor in the row you want to change.
2. Select the Layout tab under the Table Tools banner.
3. Click the Properties icon in the Table group.
4. Click the Row tab.
5 Tick the Specify height box and type in the measurement.
- Set Row height is to EXACT if you do not want the row height to ever change. Longer content may be truncated.
- Set Row height is to AT LEAST to set a minimum height for the row but allow it to expand to accommodate longer content.
6. Click the Previous Row or Next Row buttons to go to the previous or next row and set the heights for each row.
9. How to prevent row content from splitting over 2 pages
The default setting is to allow rows to break between pages.
To stop that from happening and keep all row content together as a unit:
1. Click in the appropriate row.
2. Click the Layout tab under the Table Tools.
3. Click the Properties icon on the left.
4. Click the Row tab.
5. Untick the box labelled Allow rows to break across pages.
10. Positioning Word tables on a page
To position the table on the page – not the content within the table:
1. Click somewhere in the table.
2. Click the Layout tab under the Table Tools.
3. Click the Properties icon on the left.
4. Click the Tables tab.
5. Select the Center option.
11. Positioning content within a table cell
To align cell content horizontally, simply use the alignment icons in the Paragraph group of the Home tab.
To align cell contents vertically:
1. Select the cell(s) whose contents you wish to align.
2. Select the Layout tab under the Table Tools banner.
3. Locate and select an icon within the group of 9 alignment icons.
From left-to-right and top-to-bottom, these icons represent:
- Top-left, top-middle, top-right.
- Centre-left, centre-middle, centre-right.
- Bottom-left, bottom-middle and bottom-right.
12. Rotating text within a table cell
If you have a lot of columns in your table and you are running out of screen width, you can rotate the text to 90 degrees, so it is displayed vertically.
1. Select the cells whose content you want to rotate.
2. Select the Layout tab under the Table Tools banner
3. Click the Text Direction icon in the Alignment group. Each click of this icon will switch the angle of the text to 0o, 90o and -90o.
13. Why and how to set cell margins
If you need to add some padding to the cells in a table to spread out the contents or compact a crowded table to make it fit the page, then the cell margins give you perfect control.
A cell margin is the gap between the cell border and the cell content.
Cell Margins is a table feature which means the cell margin setting applies to every cell in the table – you cannot have one cell margin measurement in the first cell and a different set of measurements in the second cell.
The default settings for the top and bottom cell margin is 0.
The default setting for the left and right cell margin is 0.19 cm.
1. Select any cell in the table, if necessary.
2. Click the Layout tab under Table Tools.
3. Click the Cell Margins icon in the Alignment group.
14. Converting text into a table
Sometimes you don’t create your tables from scratch.
You may have some data in a list or something you have imported from a CSV (comma separated variable) file.
As long as there is a recognised identifier that can be used to separate each column from the next and each row from the next, you can convert the existing text into a table.
For example, to convert this simple data into a table:
Jan, Feb, Mar
1, 2, 3
4, 5, 6
1. Select the data.
2. Select the Insert tab.
3. Click the Table icon in the Tables group.
4. Choose Convert Text to Table.
A dialog box is displayed (shown right).
5. Start at the bottom. Choose the separator that you are using in your data, e.g. comma.
6. The number of columns is calculated automatically based on the separator you chose.
7. Set the Autofit behaviour, if you want (you can also do this later from the ribbon)
8. Click OK
15. Converting a table into text
To convert a table to regular text:
1. Select the table.
2. Select the Layout tab under the Table Tools.
3. Click the Convert to Text icon in the Data group.
4. In the dialog box, choose the separator that will separate each item of data once it has been converted.
5. Click OK
16. Creating Excel-style formulas within a Word table
Microsoft Word is a document creator. Microsoft Excel is a number cruncher. Therefore, whenever you need to perform mathematical calculations, you should choose Excel. However there is a (rather primitive) feature in Word that allows you to create some simple formulas
In Excel, columns are labelled with a letter and rows are numbered. A cell reference is the intersection of column and row. The same applies in Microsoft Word, except you cannot see the labels.
In this simple example, there are four columns, which are referenced by some invisible letters A, B, C and D and five rows that are referenced by some invisible numbers 1 thru 5.
For example, the Price Per Unit for a Widget is found in cell B2, and the Quantity of Hoojamaflips is found in cell C4.
To create a formula
1. Position the cursor in the answer cell.
2. Select the Layout tab under the Table Tools.
3. Click the Formula icon in the Data group. The Formula dialog box is displayed.
The default formula provided is =SUM(ABOVE) or =SUM(LEFT). This calculates the total of all the cells above the current cell or to the left of the current cell. You can use this or create your own formula. Your formula must start with the equals sign.
The following mathematical symbols can be used:
|
( ) |
Calculate anything in brackets first |
|---|---|
|
^ |
Exponentials (to the power of) |
|
/ |
Divide |
|
* |
Multiply |
|
+ |
Add |
|
— |
Subtract |
So to generate the subtotal for the Widgets order, in the previous example, create a formula in cell D2 which reads = B2 * C2.
You can also apply some basic formatting to the results by opening the Number Format dropdown list
- The # symbol represents a numerical digit position that will only show if the number is big enough.
- The ‘0’ placeholder represents a padding zero. For example a format of 00000 would show the number 123 as 00123.
- The comma represents a thousand separator for numbers over 1,000, 1,000,000 etc.
- The $ formats the number as currency (e.g. $12.34 instead of 12.34).
17. Key Takeaways
- To create a table, select the Insert tab, click the Table icon and choose how many rows and columns you want your starting table to have.
- When a table is created (or selected) Table Tools appear in the commands and ribbon area at the top of the screen. The Table Tools have 2 tabs — Design and Layout
- The AutoFit setting on the Layout ribbon controls how Word table fit on the page. You can autofit to fit the contents, the window (that’s the gap between the margins) or have a fixed width.
- The table gridlines are there to serve as guides and will not be printed. They are useful when working with tables that have no physical borders set. To switch the gridlines on or off, click View
Gridlines on the Layout ribbon. - Multiple cells can be merged, and a single cell can be split. The Merge Cells and Split Cells icons are in the Merge group on the Layout ribbon.
- To repeat the column headings automatically if a table flows into multiple pages, click Repeat Header Rows on the Layout ribbon.
- A single table can be split into multiple tables, each with identical settings, including repeating headings if they were set. Click the Split Table icon on the Layout ribbon.
- The width of columns and the height of rows can be adjusted manually using click-and-drag or set precisely using the Properties icon on the Layout ribbon.
- Row content can be kept together by unticking Allow rows to break across pages (Table Tools | Layout tab | Properties icon | Row tab).
- The table can be positioned within the page using the Properties icon on the Layout ribbon.
- Cell contents can be aligned by clicking one of the 9 alignment
icons on the Layout ribbon. - To rotate text in 90-degree intervals, click the Text Direction icon on the Layout ribbon.
- To add or reduce cell padding within a table, click the Cell Margins icon on the Layout ribbon.
- To convert text to a table, select Insert tab | Table icon | Convert Text
To
Table. - To convert a table to regular text, select the table and click Layout tab | Convert to Text.
- To add Excel-style formulas to a Word table, click the Formula icon on the Layout ribbon.
I hope you found plenty of value in this post. I’d love to hear your biggest takeaway in the comments below together with any questions you may have.
Have a fantastic day.
About the author
Jason Morrell
Jason loves to simplify the hard stuff, cut the fluff and share what actually works. Things that make a difference. Things that slash hours from your daily work tasks. He runs a software training business in Queensland, Australia, lives on the Gold Coast with his wife and 4 kids and often talks about himself in the third person!
SHARE
Getting Started Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to get started with Word 2010. We will understand how to start a Word 2010 application in simple steps. Assuming you have Microsoft Office 2010 installed in your PC, to start the Word application, follow these steps −
Step 1 − Click the Start button.
Step 2 − Click the All Programs option from the menu.
Step 3 − Search for Microsoft Office from the submenu and click it.
Step 4 − Search for Microsoft Word 2010 from the submenu and click it.
This will launch the Microsoft Word 2010 application and you will see the following window.
Explore Window in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will understand how to explore Window in Word 2010. Following is the basic window which you get when you start the Word application. Let us understand the various important parts of this window..
File Tab
The File tab replaces the Office button from Word 2007. You can click it to check the Backstage view. This is where you come when you need to open or save files, create new documents, print a document, and do other file-related operations.
Quick Access Toolbar
This you will find just above the File tab. This is a convenient resting place for the mostfrequently used commands in Word. You can customize this toolbar based on your comfort.
Ribbon
Ribbon contains commands organized in three components −
-
Tabs − These appear across the top of the Ribbon and contain groups of related commands. Home, Insert, Page Layout are examples of ribbon tabs.
-
Groups − They organize related commands; each group name appears below the group on the Ribbon. For example, group of commands related to fonts or group of commands related to alignment, etc.
-
Commands − Commands appear within each group as mentioned above.
Title bar
This lies in the middle and at the top of the window. Title bar shows the program and document titles.
Rulers
Word has two rulers — a horizontal ruler and a vertical ruler. The horizontal ruler appears just beneath the Ribbon and is used to set margins and tab stops. The vertical ruler appears on the left edge of the Word window and is used to gauge the vertical position of elements on the page.
Help
The Help Icon can be used to get word related help anytime you like. This provides nice tutorial on various subjects related to word.
Zoom Control
Zoom control lets you zoom in for a closer look at your text. The zoom control consists of a slider that you can slide left or right to zoom in or out; you can click the + buttons to increase or decrease the zoom factor.
View Buttons
The group of five buttons located to the left of the Zoom control, near the bottom of the screen, lets you switch through the Word’s various document views.
-
Print Layout view − This displays pages exactly as they will appear when printed.
-
Full Screen Reading view − This gives a full screen view of the document.
-
Web Layout view − This shows how a document appears when viewed by a Web browser, such as Internet Explorer.
-
Outline view − This lets you work with outlines established using Word’s standard heading styles.
-
Draft view − This formats text as it appears on the printed page with a few exceptions. For example, headers and footers aren’t shown. Most people prefer this mode.
Document Area
This is the area where you type. The flashing vertical bar is called the insertion point and it represents the location where text will appear when you type.
Status Bar
This displays the document information as well as the insertion point location. From left to right, this bar contains the total number of pages and words in the document, language, etc.
You can configure the status bar by right-clicking anywhere on it and by selecting or deselecting options from the provided list.
Dialog Box Launcher
This appears as very small arrow in the lower-right corner of many groups on the Ribbon. Clicking this button opens a dialog box or task pane that provides more options about the group.
Backstage View in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss the Backstage View in Word 2010. The Backstage view was introduced in Word 2010. This acts as the central place for managing your documents. The backstage view helps in creating new documents, saving and opening documents, printing and sharing documents, and so on.
Getting to the Backstage View is easy: Just click the File tab, located in the upper-left corner of the Word Ribbon. If you already do not have any opened document, then you will see a window listing down all the recently opened documents as follows −
If you already have an opened document, then it will display a window showing detail about the opened document as shown below. Backstage view shows three columns when you select most of the available options in the first column.
The first column of the backstage view will have following options −
| S.No | Option & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Save If an existing document is opened, it will be saved as is, otherwise it will display a dialogue box asking for the document name. |
| 2 |
Save As A dialogue box will be displayed asking for document name and document type, by default it will save in word 2010 format with extension .docx. |
| 3 |
Open This option is used to open an existing word document. |
| 4 |
Close This option is used to close an open document. |
| 5 |
Info This option displays information about the opened document. |
| 6 |
Recent This option lists down all the recently opened documents |
| 7 |
New This option is used to open a new document. |
| 8 |
This option is used to print an open document. |
| 9 |
Save & Send This option will save an open document and will display options to send the document using email, etc. |
| 10 |
Help This option is used to get the required help about Word 2010. |
| 11 |
Options This option is used to set various option related to Word 2010. |
| 12 |
Exit Use this option to close the document and exit. |
Document Information
When you click the Info option available in the first column, it displays the following information in the second column of the backstage view −
-
Compatibility Mode − If the document is not a native Word 2007/2010 document, a Convert button appears here, enabling you to easily update its format. Otherwise, this category does not appear.
-
Permissions − You can use this option to protect your word document. You can set a password so that nobody can open your document, or you can lock the document so that nobody can edit your document.
-
Prepare for Sharing − This section highlights important information you should know about your document before you send it to others, such as a record of the edits you made as you developed the document.
-
Versions − If the document has been saved several times, you may be able to access the previous versions of it from this section.
Document Properties
When you click the Info option available in the first column, it displays various properties in the third column of the backstage view. These properties include the document size, the number of pages in the document, the total number of words in the document, the name of the author etc.
You can also edit various properties by clicking on the property value and if the property is editable, then it will display a text box where you can add your text like title, tags, comments, Author.
Exit Backstage View
It is simple to exit from the Backstage View. Either click on the File tab or press the Esc button on the keyboard to go back to the working mode of Word.
Entering Text — Microsoft Word 2010
In this chapter, let us discuss how to enter text with Microsoft Word 2010. Let us see how easy it is to enter text in a Word document. We assume you know that when you start Word, it displays a new document by default as shown below −
Document area is the area where you type your text. The flashing vertical bar is called the insertion point and it represents the location where the text will appear when you type. keep the cursor at the text insertion point and start typing the text. We typed only two words «Hello Word» as shown below. The text appears to the left of the insertion point as you type −
The following are the two important points that will help you while typing −
-
You do not need to press Enter to start a new line. As the insertion point reaches the end of the line, Word automatically starts a new one. You will need to press Enter, to add a new paragraph.
-
When you want to add more than one space between words, use the Tab key instead of the spacebar. This way you can properly align text by using the proportional fonts.
Move Around in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to move around in Word 2010. Word provides a number of ways to move around a document using the mouse and the keyboard.
To begin with, let us create some sample text. To create a sample text, there is a short cut available. Open a new document and type =rand() and press Enter. Word will create the following content for you −
Moving with Mouse
You can easily move the insertion point by clicking in your text anywhere on the screen. There may be instances when a document is big and you cannot see a place where you want to move. Here, you will have to use the scroll bars, as shown in the following screenshot −
You can scroll through your document by rolling your mouse wheel, which is equivalent to clicking the up-arrow or down-arrow buttons in the scroll bar.
Moving with Scroll Bars
As shown in the above screenshot, there are two scroll bars: one for moving vertically within the document, and one for moving horizontally. Using the vertical scroll bar, you may −
-
Move upward by one line by clicking the upward-pointing scroll arrow.
-
Move downward by one line by clicking the downward-pointing scroll arrow.
-
Move one next page, using the next page button (footnote).
-
Move one previous page, using the previous page button (footnote).
-
Use the Browse Object button to move through the document, going from one chosen object to the next.
Moving with Keyboard
The following keyboard commands, used for moving around your document, also move the insertion point −
| Keystroke | Where the Insertion Point Moves |
|---|---|
 |
Forward one character |
 |
Back one character |
 |
Up one line |

|
Down one line |
| PageUp | To the previous screen |
| PageDown | To the next screen |
| Home | To the beginning of the current line |
| End | To the end of the current line |
You can move word by word or paragraph by paragraph. You would have to hold down the Ctrl key while pressing an arrow key, which moves the insertion point as described here −
| Key Combination | Where the Insertion Point Moves |
|---|---|
Ctrl +  |
To the next word |
Ctrl +  |
To the previous word |
Ctrl +  |
To the start of the previous paragraph |
Ctrl +  |
To the start of the next paragraph |
| Ctrl + PageUp | To the previous browse object |
| Ctrl + PageDown | To the next browse object |
| Ctrl + Home | To the beginning of the document |
| Ctrl + End | To the end of the document |
| Shift + F5 | To the last place you changed in your document. |
Moving with Go To Command
Press the F5 key to use the Go To command. This will display a dialogue box where you will have various options to reach to a particular page.
Normally, we use the page number, the line number or the section number to go directly to a particular page and finally press the Go To button.
Save Document in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to save a document in Word 2010.
Saving New Document
Once you are done with typing in your new Word document, it is time to save your document to avoid losing work you have done on a Word document. Following are the steps to save an edited Word document −
Step 1 − Click the File tab and select the Save As option.
Step 2 − Select a folder where you will like to save the document, Enter the file name which you want to give to your document and Select the Save As option, by default it is the .docx format.
Step 3 − Finally, click on the Save button and your document will be saved with the entered name in the selected folder.
Saving New Changes
There may be an instance when you open an existing document and edit it partially or completely, or an instance where you may like to save the changes in between editing of the document. If you want to save this document with the same name, then you can use either of the following simple options −
-
Just press the Ctrl + S keys to save the changes.
-
Optionally you can click on the floppy icon available at the top left corner and just above the File tab. This option will also help you save the changes.
-
You can also use the third method to save the changes, which is the Save option available just above the Save As option as shown in the above screenshot.
If your document is new and it was never saved so far, then with either of the three options, Word will display a dialogue box to let you select a folder, and enter the document name as explained in case of saving new document.
Opening a Document in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to open a document in Word 2010.
Opening New Document
A new, blank document always opens when you start Microsoft Word. Suppose you want to start another new document while you are working on another document, or you closed an already opened document and want to start a new document. Here are the steps to open a new document −
Step 1 − Click the File tab and select the New option.
Step 2 − When you select the New option from the first column, it will display a list of templates in the second column. Double-click on the Blank document; this is the first option in the template list. We will discuss the other templates available in the list in the following chapters.
You should have your blank document as shown below. The document is now ready for you to start typing your text.
You can use a shortcut to open a blank document anytime. Try using the Ctrl + N keys and you will see a new blank document similar to the one in the above screenshot.
Opening Existing Document
There may be a situation when you open an existing document and edit it partially or completely. Follow the steps given below to open an existing document −
Step 1 − Click the File tab and select the Open option.
Step 2 − This will display the following file Open dialog box. This lets you navigate through different folders and files, and also lets you select a file which you want to open.
Step 3 − Finally, locate and select a file which you want to open and click the small triangle available on the Open button to open the file. You will have different options to open the file, but simply use the Open option.
This will open your selected file. You can use the Open Read-Only option if you are willing just to read the file and you have no intention to modify, i.e., edit the file. Other options can be used for advanced usage.
Closing a Document in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will understand how to close a document in Word 2010. When you finish working with a document, you will proceed to close the document. Closing a document removes it from your computer screen and if you had other documents open, Word displays the last document you used otherwise, you see a blank Word window. Here are simple steps to close an opened document −
Step 1 − Click the File tab and select the Close option.
Step 2 − When you select the Close option and if the document is not saved before closing, it will display the following Warning box asking whether the document should be saved or not.
Step 3 − To save the changes, click Save, otherwise click Don’t Save. To go back to the document, click Cancel. This will close the document and if you have other documents open, Word displays the last document you used, otherwise, you see a blank Word window as shown below −
Context Help in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss Context Help in Word 2010. Microsoft Office provides more than one method for calling up Help when you need it. We will discuss a few important methods in this chapter −
Context Sensitive Help
This is the easiest way of getting help about any of the options available at word screen. You just need to bring your mouse pointer over an option and wait for 2 seconds, MS Word will pop-up a small balloon help giving you detail about the operation. If word has additional help for that option, then it gives the option Press F1 for more help as shown below when you bring your mouse pointer over the color fill option. You can press the F1 key to get further help on this option.
Using F1 Key
You can press the F1 key when you are in the middle of doing something and Office will display the various categories of help as shown below. You can either search a keyword using the Search option or you can browse the listed categories to go through a topic in detail −
Using Help Icon
You can also have similar help window as shown above, by clicking the Help icon located just above the right edge of the ribbon as shown below −
Using Help Option
You can communicate with Microsoft using the Help option available under the File tab.
As shown above, you can use Microsoft Office Help to launch the Help window, or Getting Started link to go to Microsoft’s official website, otherwise use the Contact us option to contact Microsoft via email or phone.
Insert Text in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to insert text in Word 2010. Many times it is required to go back and insert additional text in an existing line. Microsoft Word provides two ways to insert text in existing text and we will show how to use both the methods of inserting text −
Insert and Add Text
First we will see how inserted text will be added into the existing content without replacing any existing content.
Step 1 − Click the location where you wish to insert text; you can also use the keyboard arrows to locate the place where the text needs to be inserted.
Step 2 − Start typing the text that needs to be inserted. Word inserts the text to the left of the insertion point, moving the existing text to the right
Insert and Replace Text
In the Insertion mode, text will be added into the existing content but same time it will over write all the content which comes in its way.
Step 1 − Right-click the status bar and select the Overtype option from the displayed menu.
When you select the Overtype option, the status bar will show the insert mode as shown below −
Step 2 − Click on the Insert text available at the status bar and it will switch to the Overtype mode as shown below −
Step 3 − Now click the location where the text needs to be inserted or you can use the keyboard arrows to locate the place where the text needs to be inserted.
Step 4 − Start typing the text that needs to be inserted. Word will replace the existing text with the newly typed text without moving the position of the exiting test.
Note − Microsoft Word 2010 disabled the functionality of the Insert key and it does nothing, so you will have to follow-up with the above mentioned procedure to turn-on or turn-off the Insert mode.
Select Text in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to select text in Word 2010. Selecting a text is one of the most important skills required while editing a word document. You can perform various operations on a selected text; you can delete the selected text, copy it, move it, apply formatting to it, change its capitalization, etc.
The most common method of selecting a text is to click and drag the mouse over the text you want to select. Following table lists down a few other simple methods that will help you in selecting text in different scenarios −
| S.No | Component & Selection Method |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Selecting text between two points Click at the start of the block of text, hold down Shift, and click at the end of the block. |
| 2 |
Selecting a single word Double-click anywhere on the word you want to select. |
| 3 |
Selecting a paragraph Triple-click anywhere on the paragraph you want to select. |
| 4 |
Selecting a sentence Hold down the Ctrl key and click anywhere in the sentence you want to select. |
| 5 |
Selecting a column of text Hold down Alt, click and hold the mouse button, and drag over the column you want to select. |
Note that only one part of the document can be in the selected state. If you have one portion of the document in selected state and as soon as you try to select any other part of the document, previous part will automatically be de-selected.
Using the Selection Bar
The black shaded area in the following screen shot is called the selection bar. When you bring your cursor in this area, it turns into a rightward-pointing arrow.
You can use the selection bar to select the various components of a document as described in the following table −
| S.No | Component & Selection Method |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Selecting a line Bring your mouse in the selection bar area and click in front of the line you want to select. |
| 2 |
Selecting a paragraph Bring your mouse in the selection bar area and double click in front of the paragraph you want to select. |
| 3 |
Selecting the document Bring your mouse in the selection bar area and triple-click. |
Using the Keyboard
Keyboard provides very good support when you want to select various components of the document as described in the following table −
| S.No | Key & Selection Method Selecting Text |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Ctrl + A Press Ctrl + A keys to select the entire document. |
| 2 |
Shift Keep pressing the Shift key and use any of the arrow keys to select the portion of text. |
| 3 |
F8 Press F8 and then use any of the arrows keys to select the portion of text. |
| 4 |
Ctrl + Shift + F8 Press Ctrl + Shift + F8 and then use any of the arrows keys to select column of the text. |
Delete Text in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to delete text in Word 2010. It is very common to delete text and retype the content in your Word document. You might type something you did not want to type or there is something extra which is not required in the document. Regardless of the reason, Word offers you various ways of deleting the text in partial or complete content of the document.
Using Backspace & Delete Keys
The most basic deletion technique is to delete characters one at a time by pressing either the backspace key or the delete key. Following table describes how you can delete single character or a whole word by using either of these two keys −
| S.No | Keys & Deletion Methods |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Backspace Keep the insertion point just after the character you want to delete and press the Backspace key. Word deletes the character immediately to the left of the insertion point. |
| 2 |
Ctrl + Backspace Keep the insertion point just after the word you want to delete and press Ctrl + Backspace key. Word deletes the whole word immediately to the left of the insertion point. |
| 3 |
Delete Keep the insertion point just before the character you want to delete and press the Delete key. Word deletes the character immediately to the right of the insertion point. |
| 4 |
Ctrl + Delete Keep the insertion point just before the word you want to delete and press Ctrl + Delete key. Word deletes the word immediately to the right of the insertion point. |
Using Selection Method
You have learnt how to select various parts of a Word document. You can make use of that learning to delete those selected parts as described in the following table −
| S.No | Component Selection & Delete Methods |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Deleting text between two points Click at the start of the block of text, hold down the Shift key, and click at the end of the block to select the portion of text and finally press either the Backspace key or the Delete key. |
| 2 |
Deleting a single word Double-click anywhere on the word you want to delete and finally press either the Backspace key or the Delete key. |
| 3 |
Deleting a paragraph Triple-click anywhere on the paragraph you want to delete and finally press either the Backspace key or the Delete key. |
| 4 |
Deleting a sentence Hold down the Ctrl key and click anywhere in the sentence you want to delete and finally press either the Backspace or the Delete key. |
| 5 |
Deleting a column of text Hold down the Alt key, click and hold the mouse button, and drag over the column you want to delete and finally press either the Backspace key or the Delete key. |
| 6 |
Deleting a line Bring your mouse in the selection bar area and click in front of the line you want to delete and finally press either the Backspace key or the Delete key. |
| 7 |
Deleting entire document content Press Ctrl + A keys to delete the entire document and finally press either the Backspace key or the Delete key. |
Note − The black shaded area in the following screen shot is called the selection bar. When you bring your cursor in this area, it turns into a rightward-pointing arrow.
Move Text in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to move text in Word 2010. At times, it is required to move a text from one location to another location in the same document or in any another document. You can move text from one location in a document to another by using the drag-and-drop technique with the help of mouse. This tutorial will teach you how to use the drag and drop technique to move text.
Move within the same document
Step 1 − Select a portion of the text using any of the text selection methods.
Step 2 − Now take your mouse pointer over the selected text and hold the left button of the mouse and keep holding it while moving around the document.
Step 3 − Take your mouse pointer to the place where you want to move the selected text and release the mouse button. You will see that the selected text is moved to the desired location.
Move within different documents
You can move the selected text from one document to another document. Following are some simple steps which will help you in moving text from one document to another document.
Step 1 − Keep both the documents opened and to ensure that both documents are visible, click the Arrange All button on the View tab on the Ribbon.
This will display both the documents as shown below −
Step 2 − Now, select a portion of the text using any of the text selection methods.
Step 3 − Take your mouse pointer over the selected text and hold the left button of the mouse and keep holding it while moving around the document.
Step 4 − Take your mouse pointer at the place in the second document where you want to move the selected text and release the mouse button. You will see that the selected text is moved to the desired location in the second document.
Note − In case you have more than two documents, you can use the Alt + Tab keys to switch through the different documents and select the desired destination document.
Copy & Paste in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to copy, cut and paste in Word 2010. In the previous chapter, we understood how we can select the desired text and move it to any other location in the same document or in any other document. This tutorial will teach you how to use copy, cut and paste techniques to duplicate a text leaving the original text intact or removing the original text completely.
To use copy and paste or cut and paste operations, Word makes use of a temporary memory which is called the clipboard. When you copy or cut a text, it stay on the clipboard temporarily and in the second step you can paste this content at the desired location.
Copy & Paste Operation
The Copy operation will just copy the content from its original place and create a duplicate copy of the content at the desired location without deleting the text from it’s the original location. Following is the procedure to copy the content in word −
Step 1 − Select a portion of the text using any of the text selection methods.
Step 2 − You have various options available to copy the selected text in clipboard. You can make use of any one of the options −
-
Using Right-Click − When you right-click on the selected text, it will display the copy option, click this option to copy the selected content in clipboard.
-
Using Ribbon Copy Button − After selecting text, you can use the copy button available at the ribbon to copy the selected content in clipboard.
-
Using Ctrl + c Keys − After selecting a text, just press Ctrl + c keys to copy the selected content in clipboard.
Step 3 − Finally click at the place where you want to copy the selected text and use either of these two simple options −
-
Using Ribbon Paste Button − Just click the Paste button available at the ribbon to paste the copied content at the desired location.
-
Using Ctrl + v Keys − This is simplest way of pasting the content. Just press Ctrl + v keys to paste the content at the new location.
Note − You can repeat the Paste operation as many times as you like to paste the same content.
Cut & Paste Operation
The Cut operation will cut the content from its original place and move the content from its original location to a new desired location. Following is the procedure to move the content in word −
Step 1 − Select a portion of the text using any of the text selection methods.
Step 2 − Now, you have various options available to cut the selected text and put it in the clipboard. You can make use of one of the options −
-
Using Right-Click − If right-click on the selected portion of text, it will display cut option, just click this option to cut the selected content and keep it in clipboard.
-
Using Ribbon Cut Button − After selecting a portion of text, you can use cut button available at the ribbon to cut the selected content and keep it in clipboard.
-
Using Ctrl + x Keys − After selecting a portion of text, just press Ctrl + x keys to cut the selected content and keep it in clipboard.
Step 3 − Finally, click at the place where you want to move the selected text and use either of these two simple options −
-
Using Ribbon Paste Button − Just click the Paste button available at the ribbon to paste the content at the new location.
-
Using Ctrl + v Keys − This is simplest way of pasting the content. Just press Ctrl + v keys to paste the content at the new location.
Note − You can repeat the Paste operation as many times as you like to paste the same content.
Copy, Cut & Paste in different documents
You can use the same procedure that we discussed above to copy and paste or cut and paste content from one document to another document. This is very simple, just copy or cut the desired content from one document and go into another document where you want to paste the content and use mentioned step to paste the content.
You can use the Alt + Tab keys to switch through the different documents and select the desired destination document.
Find & Replace in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss the Find and Replace operation in Word 2010. While working on editing a document you come across a situation very frequently when you want to search a particular word in your document and many times you will be willing to replace this word with another word at a few or all the places throughout the document. Here, we will understand how to find a word or phrase in a word document and how to replace an existing word with any other word using simple steps.
Find Command
The Find command enables you to locate specific text in your document. Following are the steps to find a word document in the following screen −
Step 1 − Let us work out on a sample text available in our Word document. Just type =rand() and press Enter; the following screen will appear −
Step 2 − Click the Find option in the Editing group on the Home tab or press Ctrl + F to launch the Navigation pane −
Step 3 − Enter a word which you want to search in the Search box, as soon as you finish typing, Word searches for the text you entered and displays the results in the navigation pane and highlights the word in the document as in the following screenshot −
Step 4 − You can click the clear button (X) to clear the search and results and perform another search.
Step 5 − You can use further options while searching for a word. Click the option button to display the options menu and then click the Options option; this will display a list of options. You can select the options like match case to perform case-sensitive search.
Step 6 − Finally, if you are done with the Search operation, you can click the close button (X) to close the Navigation Pane.
Find & Replace Operation
We assume you are an expert in searching a word or phrase in a word document as explained above. This section will teach you how you can replace an existing word in your document. Following are the simple steps −
Step 1 − Click the Replace option in the Editing group on the Home tab or press Ctrl + H to launch the Find and Replace dialog box shown in Step 2 −
Step 2 − Type a word which you want to search. You can also replace the word using the Find and Replace dialog box as in the following screenshot −
Step 3 − Click the Replace button available on the Find and Replace dialog box and you will see the first occurrence of the searched word would be replaced with the replace with word. Clicking again on Replace button would replace next occurrence of the searched word. If you will click Replace All button then it would replace all the found words in one go. You can also use Find Next button just to search the next occurence and later you can use Replace button to replace the found word.
Step 4 − You can use More >> button available on the dialog box to use more options and to make your search more specific like case sensitive search or searching for whole word only etc.
Step 5 − Finally, if you are done with the Find and Replace operation, you can click the Close (X) or Cancel button of the dialog box to close the box.
Spell Check in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to check spelling and grammar in Word 2010. Microsoft Word provides a decent Spelling and Grammar Checker which enables you to search for and correct all spelling and grammar mistakes in your document. Word is intelligent enough to identify misspelled or misused, as well as grammar errors and underlines them as follows.
- A red underline beneath spelling errors.
- A green underline beneath grammar errors.
- A blue line under correctly spelled but misused words.
Check Spelling and Grammar using Review tab
Here is the simple procedure to find out the spelling mistakes and fix them −
Step 1 − Click the Review tab and then click the Spelling & Grammar button.
Step 2 − A Spelling and Grammar dialog box will appear and will display the wrong spellings or errors in grammar. You will also get suggestions to correct as shown below −
Now you have following options to fix the spelling mistakes −
-
Ignore − If you are willing to ignore a word, then click this button and Word ignores the word throughout the document.
-
Ignore All − Like Ignore, but this ignores all occurrences of the same misspelling, not just once but throughout the document.
-
Add to Dictionary − Choose Add to Dictionary to add the word to the Word spelling dictionary.
-
Change − This will change the wrong word using the suggested correct word.
-
Change All − Like Change, but this changes all occurrences of the same misspelling, not just once but throughout the document.
-
AutoCorrect − If you select a suggestion, Word creates an AutoCorrect entry that automatically corrects this spelling error from now on.
Following are the different options in case you have grammatical mistake −
-
Next Sentence − You can click Next Sentence to direct the grammar checker to skip ahead to the next sentence.
-
Explain − The grammar checker displays a description of the rule that caused the sentence to be flagged as a possible error.
-
Options − This will open the Word Options dialog box to allow you to change the behavior of the grammar checker or spelling options.
-
Undo − This will undo the last grammar changed.
Step 3 − Select one of the given suggestions you want to use and click the Change option to fix the spelling or grammar mistake and repeat the step to fix all the spelling or grammar mistake.
Step 4 − Word displays a dialog box when it finishes checking for spelling and grammar mistakes, finally Click OK.
Check Spelling and Grammar using Right Click
If you will right-click the mouse button over a misspelled word, then it will show you the correct suggestions and the above mentioned options to fix the spelling or grammar mistake. Try it yourself.
Zoom In-Out in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to zoom in and zoom out in Word 2010. Microsoft Word provides a functionality to apply zoom-in and zoom-out operations on a document. When we apply the zoom-in operation, it enlarges the size of text whereas applying the zoom-out operation reduces the size of text.
A zoom operation just changes the size of the font on-screen without impacting any other attribute of the document. You can apply the zoom operation in various ways as explained in this chapter.
Zoom-in & Zoom-out using view tab
Here is the simple procedure to apply the zoom-in or the zoom-out operations using the View tab −
Step 1 − Click the View tab and then click the Zoom button as shown below.
Step 2 − When you click the Zoom button, a Zoom dialog box will appear as shown below. This will display the zoom options box to select a value to reduce or increase the size of the document on-screen. By default, it will be 100%; you can select 200% to increase the size of the font or 75% to reduce the size of the font.
You can click the Many pages down arrow and select to display multiple pages.
Step 3 − Once you are done with selecting an option, click OK to apply the changes on the document.
Step 4 − Try different options available, for example Page Width and Text Width.
Zoom-in & Zoom-out using (+) and (-) Buttons
The following screenshot shows two buttons Zoom-out which is the (-) button and Zoom-in which is the (+) button.
Step 1 − Click the Zoom-out button, you will find that your document size will decrease by 10% each time you click the button. Similar way, if you click on Zoom-in button your document size will increase by 10% each time you click the button.
Step 2 − Try this simple operation with different values to see the difference. The above screenshot shows 140% zoom-in view of the document.
Special Symbols in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss the use of special symbols in Word 2010. Your keyboard may not have many characters available but you want to use those characters in your document; in such situations, you have the option to insert Special Symbols the way we will further understand in this chapter.
To insert symbols that are occasionally used, follow the steps in this section. If you find yourself using a particular symbol frequently, you can assign a keyboard shortcut to it.
Insert Special Symbols
Here is a simple procedure to apply zoom-in or zoom-out operation using the View tab −
Step 1 − To insert a special symbol, bring your cursor at the place where you want to insert the symbol. Click the Insert tab. You will find two options under the symbol button (a) Equation and (b) Symbols. Click either of these two options based on your requirement. You will further use equations while preparing mathematical or scientific or any similar document. For now, we are going to understand the use of the Symbol button as shown below.
Step 2 − When you click the Symbol button, a small list of symbols will appear as shown below.
Step 3 − Now click on any of the available symbols in the box to insert that in your document at the selected location. If you do not find the desired symbol in this small box, then you can click at the More Symbols option to have a wide range of symbols as shown below in the symbol dialog box. You can select any of the symbol and then click the Insert button to insert the selected symbol.
Assign Shortcut Key
You can assign a keyboard shortcut to type any of the available symbol. Following are the steps to assign Ctrl + Q key to insert the © symbol which is one of the available symbols in the special symbols list −
Step 1 − Assume you already have the following symbol dialog box opened.
Step 2 − Click the symbol for which a shortcut key needs to be assigned. Now click Shortcut Key button which will display the following Customize Keyboard dialog box.
Step 3 − Now type the selected shortcut key in the shortcut key box. You press Ctrl + Q and then click the Assign button to assign the shortcut key. You will see that the selected key will be added in the list of assigned keys. Finally, use the Close button to close the dialog box.
Step 4 − Now try to type Ctrl + Q using the keyboard directly and you will find that you are able to type © symbol without going into the symbol dialog box.
Undo Changes in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to undo and redo changes in Word 2010. Microsoft word provides two important features called the Undo and the Repeat or Redo. The Undo feature is used to undo the previous action and the Repeat or Redo feature is used to repeat the previous action.
For example, if you mistakenly delete text, you can use the Undo feature to recover it. In a similar way, if you delete a character and you want to delete more characters then you can use the Repeat operation.
How to use Undo & Repeat operations
You can access the Undo and Repeat buttons from the Quick Access toolbar. You should make a note that the Repeat button is also called Redo button and both the operations have the same meaning.
Here is the simple procedure to apply undo or repeat (redo) operations −
Step 1 − Let us type some text in a blank document. Now click the Repeat (Redo) button and you will see that Word will repeat the same operation for you.
Step 2 − Now to examine the undo operation, let us delete the last word operation character by character so that you have the following text remaining in the line.
Step 3 − Let us try to click the Undo button one by one. You will see that Word will recover all the deleted characters one by one after performing a few undo operations.
Shortcuts to use Undo & Repeat operations
Though you can access the Undo and Repeat commands from the Quick Access toolbar, but because these commands are the most frequently used commands, we recommend you memorize their keyboard shortcuts which are as follows −
| S.No | Shortcuts & Operation |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Ctrl + Z Undoes the previous action. |
| 2 |
Ctrl + Y Repeats the previous action. |
Note that if the previous action was Undo, Ctrl+Y redoes the Undone action.
Setting Text Fonts in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to set the text fonts and size in Word 2010. Microsoft word allows you to use different fonts with different size. You can change your document’s appearance by changing the fonts and their size. Usually you use different fonts for paragraphs and headings. It is important to learn how to use different fonts. This chapter will teach you how to change a font and its size in simple steps.
Change the Font Type & Size
We will understand in brief the font buttons that we will further use in this tutorial. Following is a screenshot to show you a few font related buttons.
Step 1 − Select the portion of text the font of which needs to be changed and click the Home tab. Now click the Font Type button to list down all the fonts available as shown below.
Step 2 − Try to move the mouse pointer over the listed fonts. You will see that the text font changes when you move the mouse pointer over different fonts. You can use the Font Scroll Bar to display more fonts available. Finally select a desired font by clicking over the font name in the list. We have selected MV Boli as the font for our sample text.
Step 3 − Similar way, to change the font size, click over the Font Size button which will display a font size list. You will use the same procedure to select a desired font size that you have used while selecting a font type.
Use Shrink and Grow Buttons
You can use a quick way to reduce or enlarge the font size. As shown in the first screenshot, the Shrink Font button can be used to reduce the font size whereas the Grow Font button can be used to enlarge the font size.
Try to click either of these two buttons and you will see the effect. You can click a single button multiple times to apply the effect. Each time you click either of the buttons, it will enlarge or reduce the font size by 1 point.
Clear Formatting Options
All of the setting can be reset to plain text, or the default formatting. To reset text to default settings −
Step 1 − Select the portion of text that you want to reset.
Step 2 − Click the Clear Formatting button in the Home tab Font group, or simply use Ctrl + SPACEBAR.
Text Decoration in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss text decoration in Word 2010. When we use the term decorate, it means decorate by putting the text in italics, underlining the text or making it bold to look more fancy and much more. In this chapter, we will also learn how we can strikethrough a text.
Making text bold
We use bold text to give more emphasis on the sentence. It is very simple to change a selected portion of text into bold font by following two simple steps −
Step 1 − Select the portion of text that the font of which needs to be made bold. You can use any of the text selection methods to select the portion of text.
Step 2 − Click the Font Bold [ B ] button in the Home tab Font group, or simply use Ctrl + B keys to make the selected portion of text bold.
Making Text Italic
An italic text appears with a small inclination and we use the italicized text to differentiate it from other text. It is very simple to change the selected text into italic font by following two simple steps −
Step 1 − Select the portion of text the font of which needs to be italicized. You can use any of the text selection methods to select the portion of text.
Step 2 − Click the Font Italic [ I ] button in the Home tab Font group, or simply use the Ctrl + I keys to convert the portion of text in italic font.
Underline the Text
An underlined portion of text appears with an underline and we use the underlined portion of text to make it more distinguished from other text. It is very simple to change the selected text into underlined font by following two simple steps −
Step 1 − Select the portion of text which needs to be underlined. You can use any of the text selection method to select the portion of text.
Step 2 − Click Font Underline [ U ] button in the Home tab Font group, or simply use the Ctrl + U keys to put an underline under the text.
Strikethrough the Text
Strikethrough portion of text will look as if a line has been drawn through the middle of it. A strikethrough portion of text indicates that it has been deleted and that the portion of text is not required any more. It is very simple to change a selected portion of text into a strikethrough portion of text by following two simple steps −
Step 1 − Select the portion of text that you want to change to a bold font. You can use any of the text selection method to select the portion of text.
Step 2 − Click Font Strikethrough [ abc ] button in the Home tab Font group to put a line in the middle of the text which is called strikethrough the text.
Change Text Case in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to change text cases in Word 2010. You can also capitalize a character you are typing by pressing and holding the SHIFT key while you type. You can also press the CAPS LOCK to have every letter that you type capitalized, and then press the CAPS LOCK again to turn off capitalization.
Change Text to Sentence Case
A sentence case is the case where the first character of every sentence is capitalized. It is very simple to change the selected portion of text into sentence case by following two simple steps −
Step 1 − Select the portion of text that that needs to be put in sentence case. You can use any of the text selection methods to select the portion of text.
Step 2 − Click the Change Case button and then select the Sentence Case option to capitalize the first character of every selected sentence.
Change Text to Lowercase
Changing text to lowercase is where every word of a sentence is in lowercase. It is very simple to change a selected portion of text into lowercase by following two simple steps −
Step 1 − Select the portion of text that needs to be put in lowercase. You can use any of the text selection methods to select the portion of text.
Step 2 − Click the Change Case button and then select Lowercase option to display all the selected words in lowercase.
Change Text to Uppercase
This is where every word of a sentence is in uppercase. It is very simple to change selected text into uppercase by following two simple steps −
Step 1 − Select the portion of text that you want to change to a bold font. You can use any of the text selection method to select the portion of text.
Step 2 − Click the Change Case button and then select UPPERCASE option to display all selected words in all caps. All characters of every selected word will be capitalized.
Capitalize Text
A capitalize case is the case where every first character of every selected word is in capital. This is very simple to change selected text into capitalize by following two simple steps −
Step 1 − Select the portion of text that needs to be capitalized. You can use any of the text selection method to select the portion of text.
Step 2 − Click the Change Case button and then select the Capitalize Each Word option to put a leading cap on each selected word.
Toggle the Text
The Toggle operation will change the case of every character in reverse way. A capital character will become a character in lower case and a character in lower case will become a character in upper case. It is very simple to toggle case of the text by following two simple steps −
Step 1 − Select the portion of text that you want to change to a bold font. You can use any of the text selection method to select the portion of text.
Step 2 − Click the Change Case button and then select the tOGGLE cASE option to change all the words in lowercase into words in uppercase; the words in uppercase words change to words in lowercase.
Change Text Color in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to change text colors in Word 2010. We will also understand how to mark text which should look like it was marked with a highlighter pen. In addition, we will learn how to apply different effects on portions of text.
Change Font Colors
The text that we type comes in black by default; you can always change the color of the font to a color of your choice. It is very simple to change the text color by following two simple steps −
Step 1 − Select the portion of text the font color of which needs to be changed. You can use any of the text selection method to select the portion of text.
Step 2 − Click the Font Color button triangle to display a list of colors. Try to move your mouse pointer over different colors and you will see the text color will change automatically. You can select any of the colors available by simply clicking over it.
If you click at the left portion of the Font Color button, the selected color gets applied to the text automatically; you need to click over the small triangle to display a list of colors.
If you do not find a color of your choice, you can use the More Colors option to display the color pallet box which allows you to select a color from a range of colors.
Highlight Text with Colors
You can highlight a selected portion of text using any color and it will look like it was marked with a highlighter pen. Usually we highlight a text using yellow color. It is very simple to highlight a portion of text with a color by following two simple steps
Step 1 − Select the portion of text that needs to be highlighted with color. You can use any of the text selection method to select the portion of text.
Step 2 − Click the Text Highlight Color button triangle to display a list of colors. Try to move your mouse pointer over different colors and you will see the text color changes automatically. You can select any of the colors available by simply clicking over it.
If you click at the left portion of the Text Highlight Color button, then the selected color gets applied to the portion of text automatically; you need to click over the small triangle to display a list of colors.
Apply Text Effects
Microsoft word provides a list of text effect which add to the beauty of your document, especially to the cover page or the headings of the document. This is very simple to apply various text effects by following two simple steps −
Step 1 − Select the portion of text that you want to change to a bold font. You can use any of the text selection method to select the portion of text.
Step 2 − Click the Text Effect button to display a list of effects including shadow, outline, glow, reflection etc. Try to move your mouse pointer over different effects and you will see the text effect will change automatically. You can select any of the text effect available by simply clicking over it.
Text Alignments in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss text alignments in Word 2010. There are four types of paragraph alignment available in Microsoft Word — left-aligned, center-aligned, rightaligned, and justified.
Left-Aligned Text
A paragraph’s text is left aligned when it is aligned evenly along the left margin. Here is a simple procedure to make a paragraph text left-aligned.
Step 1 − Click anywhere on the paragraph you want to align and click the Align Text Left button available on the Home tab or simply press the Ctrl + L keys.
Center Aligned Text
A paragraph’s text will be said center aligned if it is in the center of the left and right margins. Here is a simple procedure to make a paragraph text center aligned.
Step 1 − Click anywhere on the paragraph you want to align and click the Center button available on the Home tab or simply press the Ctrl + E keys.
Right-Aligned Text
A paragraph’s text is right-aligned when it is aligned evenly along the right margin. Here is a simple procedure to make a paragraph text right-aligned.
Step 1 − Click anywhere on the paragraph you want to align and click the Align Text Right button available on the Home tab or simply press the Ctrl + R keys.
Justified Text
A paragraph’s text is justified when it is aligned evenly along both the left and the right margins. Following is a simple procedure to make a paragraph text justified.
Step 1 − Click anywhere on the paragraph you want to align and click the Justify button available on the Home tab or simply press the Ctrl + J keys.
When you click the Justify button, it displays four options, justify, justify low, justify high and justify medium. You need to select only the justify option. The difference between these options is that low justify creates little space between two words, medium creates a more space than low justify and high creates maximum space between two words to justify the text.
Indent Paragraphs in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss the how to indent paragraphs in Word 2010. As you know the margin settings determine the blank space that appears on each side of a paragraph. You can indent paragraphs in your document from the left margin, the right margin, or both the margins. This chapter will teach you how to indent your paragraphs with or without the first line of the paragraphs.
Left Indentation
Left indentation means to move the left edge of the paragraph inward towards the center of the paragraph. Let us use the following steps to create left indentation.
Step 1 − Click anywhere on the paragraph you want to indent left and click the Increase Indent button available on the Home tab or simply press the Ctrl + M keys. You can click multiple times to create deeper indentation.
Step 2 − You can remove left indentation by clicking the Decrease Indent button available on Home tab or simply press Ctrl + Shift+ M keys. You can click multiple times to remove deeper indentation.
You can also use the Paragraph Dialog Box to set left and right indentations. We will see this dialog box in the last section of this chapter.
Right Indentation
Right indentation means to move the right edge of the paragraph inward towards the center of the paragraph. Let us use the following steps to create right indentation.
Step 1 − Click anywhere on the paragraph you want to indent and then click on the Increase Right Indent spinner available on the Page Layout tab. You can click on the spinner multiple times to create deeper indentation. You can use the Left Indent spinners as well to set left indentation from the same place.
Step 2 − You can remove right indentation by clicking the Decrease Right Indent spinner in the opposite direction.
You can also use the Paragraph Dialog Box to set the left and the right indentations. We will see this dialog box in the next section.
First Line Indentation
You can move the left side of the first line of a paragraph inward toward the center. Let us see the procedure to perform first line indentation.
Step 1 − Click anywhere on the paragraph you want to indent right and click the Paragraph Dialog Box launcher available on the Home tab.
Step 2 − Click the Before Text spinner to set left indentation and select the First Line Option to move the left side of the first line of a paragraph inward toward the center. You can control the movement by setting the Indentation Unit. A preview box will give only the idea and not the indentation status.
Hanging Indentation
You can move the left side of the first line of a paragraph leftward, away from the center which is called the hanging indentation. Let us see the procedure to perform hanging indentation.
Step 1 − Click anywhere on the paragraph you want to indent right and click the Paragraph Dialog Box launcher available on the Home tab.
Step 2 − Click the Before Text spinner to set left indentation and select Hanging Option to move the left side of the first line of a paragraph leftward, away from the center. You can control the movement by setting the Indentation Unit. A preview box will give only the idea and not the indentation status.
You can use the After Text spinner to set the right indentation. You can try it yourself.
Create Bullets in Word 2010
Microsoft word provides bullets and numbers to put a list of items in a nice order. This chapter will teach you simple steps to create either the bulleted or the numbered lists in simple steps.
Create a List from Existing Text
This is very simple to convert a list of lines into a bulleted or numbered list. Following are the simple steps to create either bulleted list or numbered list.
Step 1 − Select a list of text to which you want to assign bullets or numbers. You can use any of the text selection method to select the portion of text.
Step 2 − Click the Bullet Button triangle to display a list of bullets you want to assign to the list. You can select any of the bullet style available by simply clicking over it.
Step 3 − If you are willing to create a list with numbers, then click the Numbering Button triangle instead of the bullet button to display a list of numbers you want to assign to the list. You can select any of the numbering style available by simply clicking over it.
Create a List as You Type
You can create a bulleted list as you type. Word will automatically format it according to your text. Following are the simple steps to create bulleted list as you type.
Step 1 − Type *, and then either press the SPACEBAR or press the TAB key, and then type the rest of what you want in the first item of the bulleted list.
Step 2 − When you are done with typing, press Enter to add the item in the list automatically and go to add next item in the list.
Step 3 − Repeat Step 2 for each list item.
You can create a numbered list as you type. Word will automatically format it according to your text. Following are the simple steps to create numbered list as you type.
Step 1 − Type 1, and then either press the SPACEBAR or press the TAB key, and then type the rest of what you want in the first item of the numbered list.
Step 2 − When you are done with typing, press Enter to add the item in the list automatically and go to add next item in the list.
Step 3 − Repeat Step 2 for each list item.
You can create sub-lists. These sub-lists are called multi-lists. It is simple to create sublists; press the Tab key to put items in sub-list. You can try it yourself.
Set Line Spacing in Word 2010
In this chapter, let us discuss how to set line spacing in Word 2010. A line spacing is the distance between two lines in a Microsoft Word document. You can increase or decrease this distance as per your requirement by following a few simple steps. This chapter will explain how to set the distance between two lines as well as how to set the distance between two paragraphs.
Spacing between Lines
Following are the simple steps to adjust spacing between two lines of the document.
Step 1 − Select the paragraph or paragraphs for which you want to define spacing. You can use any of the text selection method to select the paragraph(s).
Step 2 − Click the Line and Paragraph Spacing Button triangle to display a list of options to adjust space between the lines. You can select any of the option available by simply clicking over it.
Spacing between Paragraphs
You can also set distance between two paragraphs. Following are the simple steps to set this distance.
Step 1 − Select the paragraph or paragraphs for which you want to define spacing and click the Paragraph Dialog Box launcher available on the Home tab.
Step 2 − Click the Before spinner to increase or decrease the space before the selected paragraph. Similar way, click the After spinner to increase or decrease the space after the selected paragraph. Finally, click the OK button to apply the changes.
You can use the Line Spacing option available at the dialog box to set line spacing as we have seen in previous example. You can try it yourself.
Borders and Shades in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to work on borders and shades in Word 2010. Microsoft Word allows you to place a border on any or all of the four sides of selected text, paragraphs, and pages. You can also add different shades to the space occupied by the selected text, paragraphs, and pages. This chapter will teach you how to add any of the borders (left, right, top or bottom) around a text or paragraph or a page and how to add different shadows to them.
Add Borders to Text
Following are the simple steps to add border to any text or paragraph.
Step 1 − Select the portion of text or paragraph to which you want to add border. You can use any of the text selection method to select the paragraph(s).
Step 2 − Click the Border Button to display a list of options to put a border around the selected text or paragraph. You can select any of the option available by simply clicking over it.
Step 3 − Try to add different borders like left, right top or bottom by selecting different options from the border options.
Step 4 − To delete the existing border, simply select the No Border option from the border options.
Note − You can add a horizontal line by selecting the Horizontal Line option from the border options. Otherwise type — (three hyphens) and press ENTER. A single, light horizontal line will be created between the left and the right margins.
Add Borders to Page
You can add borders of your choice to word pages by following the steps given below.
Step 1 − Click the Border Button to display a list of options to put a border. Select the Border and Shading option available at the bottom of the list of options as shown in the above screenshot. This will display a Border and Shading dialog box. This dialog box can be used to set borders and shading around a selected text or page borders.
Step 2 − Click the Page Border tab which will display a list of border settings, styles and options whether this border should be applied to the whole document or just one page or the first page.
Step 3 − You can use the Preview section to disable or enable left, right, top or bottom borders of the page. Follow the instruction given in the preview section itself.
Step 4 − You can customize your border by setting its color, width by using different art available under the style section.
You can have similar or even better borders as given below.
Add Shades to Text
The following steps will help you understand how to add shades on a selected portion of text or a paragraph(s).
Step 1 − Click the Border Button to display a list of options to put a border. Select the Border and Shading option available at the bottom of the list of options as shown in the above screenshot. This will display a Border and Shading dialog box. This dialog box can be used to set borders and shading around a selected portion of text or page borders.
Step 2 − Click the Shading tab; this tab will display the options to select fill, color and style and whether this border should be applied to a paragraph or a portion of text.
Step 3 − You can use the Preview section to have an idea about the expected result. Once you are done, click the OK button to apply the result.
Set Tabs in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to set tabs in Word 2010. Microsoft Word tabs help in setting up information properly within a column. Word enables you to set left, center, right, decimal, or bar tabs to line up columnar information. By default, Word places tabs every .5 inch across the page between the left and right margins.
| S.No | Tab & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Left Left-aligns text at tab stop and this is the default tab. |
| 2 |
Center Centers text over tab stop. |
| 3 |
Right Right-aligns text at tab stop. |
| 4 |
Decimal Aligns numbers at decimal point over tab stop. |
| 5 |
Bar Creates a bar to separate the text. |
Setting a Tab
Following are the simple steps to set the center and the right tabs in a Word document. You can use similar steps but different tabs to set up decimal and bar tabs.
Step 1 − Type some text that you want to line up with the tab stops. Press the Tab key only once between each column of information you to want to line up. I typed the following three lines.
Step 2 − Select a tab type using the Tab button; assume the center tab and finally select the paragraph or paragraphs the tabs of which you want to set. Next click the ruler where you want the tab to appear, a tab will appear at the ruler where you just clicked and the selected portion of text will be adjusted in the center.
Step 3 − Now select the right tab using the Tab Button and click the ruler at the right side where you want to align the text at the right side. A right tab will appear at the ruler where you just clicked and the selected portion of text will be right-aligned.
Moving a Tab
You can move an already set tab at a particular location by following the steps given below.
Step 1 − Click just before the line for which you want to change the tab setting. Drag the tab sign available at the ruler to the left or right.
Step 2 − A vertical line marks its position as you drag and when you click and drag a tab, the text moves with the tab.
Apply Formatting in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to copy and apply formatting in Word 2010. If you already have a well formatted portion of text and you want to apply similar formatting to another portion of text, then Microsoft Word provides a feature to copy and apply a format from one portion of text to another portion of text. This is very useful and a time saving operation.
Copy and Apply of text formatting works for various text attributes; for example, text fonts, text colors, margins, headings, etc.
Copy and Apply Text Formatting
The following steps will help you understand how to copy and apply text formatting from one portion of text in your document to another portion of text in your document.
Step 1 − Select the portion of text containing the formatting that you want to copy. I have selected a text which has bold and underlined font as shown below.
Step 2 − click the Home tab and click the Format Painter button to copy the format of the selected text. As soon as you click the format painter button, the mouse pointer changes to a paint brush when you move the mouse over your document.
Step 3 − Now you are ready to apply the copied text format to any of the selected text. So select a text using mouse where you want to apply the copied text format. While selecting a portion of text, you have to make sure that your mouse pointer is still in paint brush shape. After selecting the text, just release the right-click button of the mouse and you will see that newly selected text is changed to the format used for the original selection. You can click anywhere outside the selection to continue working on your document for further editing.
Copy and Apply Text Formatting multiple times
Step 1 − If you are intended to apply formatting at multiple places, then you will have to double-click the Format Painter button while copying the text format. Later on, you just keep selecting the text where you want to apply the text formatting.
Step 2 − When you are done with applying formatting at all the places, click Format Painter to come out of the format applying operation.
Adjust Page Margins in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to adjust page margins in Word 2010. Margins are the space between the edge of the paper and the text. You can adjust the right, left, top, and bottom margins of your document. By default, Word sets all margins left, right, top, and bottom to 1 inch.
In the screenshot given below, I have shown top, left and right margins, if you will type the complete page, word will leave 1-inch bottom margin as well.
Adjust Margins
The following steps will help you understand how to set margins for an open document.
Step 1 − Open the document the margins of which need to be set. If you want the margins to be applied only to a selected part of a document, select that particular part.
Step 2 − Click the Page Layout tab, and click the Margins button in the Page Setup group. This will display a list of options to be selected but you have to click the Custom Margins option available at the bottom.
You can also select any of the predefined margins from the list, but using custom margins option you will have more control on all the settings.
Step 3 − You will have to display a Page Dialog Box as shown below where you can set top, left, right and bottom margins under the Margins Tab. Select the Apply to: option to apply the margin on selected text or complete document.
Step 4 − If you are going to bind the document and want to add an extra amount of space on one edge for the binding, enter that amount in the Gutter text box, and select the side the gutter is on with the Gutter Position drop-down list. After setting all the desired values for all the margins, click the OK button to apply the margins.
Header and Footer in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to add header and footer in Word 2010. Headers and footers are parts of a document that contain special information such as page numbers and the total number of pages, the document title, company logo, any photo, etc. The header appears at the top of every page, and the footer appears at the bottom of every page.
Add Header and Footer
The following steps will help you understand how to add header and footer in a Word document.
Step 1 − Click the Insert tab, and click either the Header button or the Footer button that which needs to be added first. Assume you are going to add Header; when you click the Header button it will display a list of built-in Headers from where you can choose any of the headers by simply clicking on it.
Step 2 − Once you select any of the headers, it will be applied to the document in editable mode and the text in your document will appear dimmed, Header and Footer buttons appear on the Ribbon and a Close Header and Footer button will also appear at the top-right corner.
Step 3 − Finally, you can type your information whatever you want to have in your document header and once you are done, click Close Header and Footer to come out of the header insertion mode. You will see the final result as follows.
You can follow a similar procedure to add footer in your document.
Edit Header and Footer
The following steps will help you understand how to edit the existing header or footer of your document.
Step 1 − Click the Insert tab, and click either the Header button or Footer button or whatever you want to edit. Assume you are going to edit the Header, so when you click the Header button it will display a list of options including the Edit Header option.
Step 2 − Click on the Edit Header option and Word will display the editable header as shown in the following screenshot.
Step 3 − Now you can edit your document header and once you are done, click Close Header and Footer to come out of the edit header mode.
You can follow a similar procedure to edit the footer in your document.
Add Page Numbers in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to add page numbers in Word 2010. Microsoft Word automatically assigns page numbers on the pages of your document. Typically, page numbers are printed either in header or footer but you have the option that can display the page number in the left or right margins at the top or the bottom of a page.
Add Page Numbers
Following are the simple steps to add page numbers in a Word document.
Step 1 − Click the Insert tab, and click the Page Number button available in the header and footer section. This will display a list of options to display the page number at the top, bottom, current position etc.
Step 2 − When you move your mouse pointer over the available options, it displays further styles of page numbers to be displayed. For example, when I take the mouse pointer at the Bottom of Page option it displays the following list of styles.
Step 3 − Finally, select any one of the page number styles. I selected the Accent Bar 1 style by clicking over it. You will be directed to the Page Footer modification mode. Click the Close Header and Footer button to come out of the Footer Edit mode.
You can format your page numbers using the Format Page Numbers option available under the listed options.
Remove Page Numbers
The following steps will help you remove page numbering from a Word document.
Step 1 − Click the Insert tab, and click the Page Number button available in the header and footer section. This will display a list of options to display page number at the top, bottom, current position, etc. At the bottom, you will have the Remove Page Numbers option. Just click this option and it will delete all the page numbers set in your document.
Insert Page Breaks in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to insert page breaks in Word 2010. Microsoft Word automatically starts a new page when the current page fills with text but you can insert a page break to force Word to start text on a new page. You can insert a page break using either the mouse or the keyboard.
Insert Page Breaks
The following steps will help you insert page breaks in a Word document.
Step 1 − Bring your insertion point immediately before the text that has to appear on a new page.
Step 2 − Click the Insert tab, and click the Page Break button available in the Pages group.
Word inserts a page break and moves all text after the page break onto a new page. You can also use the Ctrl + Enter keys to create a page break at the pointed location.
Delete a Page Break
Just put the insertion point on the previous page of the page break that needs to be deleted. Press the Delete key multiple times until both the pages get merged.
Insert Blank Pages in Word 2010
In this chapter, let us discuss how to insert blank pages in Word 2010. A blank page is a page which does not have any text or any other content over it. This chapter will also make you understand how to delete a blank page from your Microsoft Word document.
Insert Blank Pages
Following are the simple steps to insert blank page in a word document.
Step 1 − Bring your insertion point immediately before the text where you want to insert a blank page.
Step 2 − Click the Insert tab, and click the Blank Page button available in the Pages group.
Word inserts a new blank page and moves all the text after the page break onto a new page.
Delete Blank Pages
The following steps will help you delete blank page from a Word document.
Step 1 − Click the Home tab, and click the Show/Hide ¶ paragraph marks button available in the Paragraph group or simply press the Ctrl + Shift + * keys. This will display all the page breaks as shown below −
Step 2 − Bring your cursor immediately before the Page Break mark available on the blank page and press the Delete Key. This will delete the blank page and again you can click the Show/Hide ¶ paragraph marks button to hide all the paragraph marks.
Cover Pages in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss Almost all the good documents and books have an attractive first page that includes the document title, its subject, author and publisher name etc. This first page is is the Cover Page and Microsoft Word provides an easy way to add a cover page.
Add Cover Pages
Following are the simple steps to add a cover page in a Word document.
Step 1 − Click the Insert tab, and click the Cover Page button available in the Pages group. This will display a list of Built-in Cover Pages as shown below.
Step 2 − Choose a cover page from the options available in the gallery. The selected cover page will be added as the first page of your document which can later be modified according to the requirements. If you want to place the cover page elsewhere except the first page, right-click the cover page in the gallery and select the location you want from the menu that appears.
Delete Cover Pages
The following steps will help you understand how to delete an existing cover page from a Word document.
Step 1 − Click the Insert tab, and click the Cover Page button available in the Pages group. This will display a list of Built-in Cover Pages as shown below. You will find a Remove Current Cover Page option available at the bottom of the cover page gallery.
Step 2 − Click the Remove Current Cover Page option and your cover page will be deleted from your document.
Page Orientation in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss page orientation in Word 2010. Page Orientation is useful when you print your pages. By default, Microsoft Word shows a page in portrait orientation and in this case the width of the page is less than the height of the page; the page will be 8.5 inches × 11 inches.
You can change the page orientation from portrait to landscape orientation. In such case, the width of the page will be more than the height of the page and page will be 11 inches × 8.5 inches.
Change Page Orientation
The following steps will help you understand how to change the page orientation of a word document.
Step 1 − Open the Word document the orientation of which needs to be changed. By default, orientation will be Portrait Orientation as shown below.
Step 2 − Click the Page Layout tab, and click the Orientation button available in the Page Setup group. This will display an Option Menu having both the options (Portrait & Landscape) to be selected.
Step 3 − Click any of the options you want to set to orientation. Because our page is already in portrait orientation, we will click the Landscape option to change my orientation to landscape orientation.
Create a Table in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to create a table in Word 2010. A table is a structure of vertical columns and horizontal rows with a cell at every intersection. Each cell can contain text or graphics, and you can format the table in any way you want. Usually the top row in the table is kept as a table header and can be used to put some informative instruction.
Create a Table
The following steps will help you understand how to create a table in a Word document.
Step 1 − Click the Insert tab followed by the Table button. This will display a simple grid as shown below. When you move your mouse over the grid cells, it makes a table in the table that appears in the document. You can make your table having the desired number of rows and columns.
Step 2 − Click the square representing the lower-right corner of your table, which will create an actual table in your document and Word goes in the table design mode. The table design mode has many options to work with as shown below.
Step 3 − This is an optional step that can be worked out if you want to have a fancy table. Click the Table Styles button to display a gallery of table styles. When you move your mouse over any of the styles, it shows real time preview of your actual table.
Step 4 − To select any of the styles, just click the built-in table style and you will see that the selected style has been applied on your table.
Delete a Table
Following are the simple steps to delete an existing table from a word document.
Step 1 − Click anywhere in the table you want to delete.
Step 2 − Click the Layout tab, and click the Delete Table option under the Delete Table Button to delete the complete table from the document along with its content.
Rows & Columns in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to work with rows and columns in Word 2010. As discussed in the previous chapter, a table is a structure of vertical columns and horizontal rows with a cell at every intersection. A Word table can contain as many as 63 columns but the number of rows is unlimited. This chapter will teach you how to add and delete rows and columns in a table.
Add a Row
Following are the simple steps to add rows in a table of a word document.
Step 1 − Click a row where you want to add an additional row and then click the Layout tab; it will show the following screen.
Step 2 − Now use the Row & Column group of buttons to add any row below or above to the selected row. If you click the Insert Below button, it will add a row just below the selected row as follows.
If you click the Insert Above button, it will add a row just above the selected row.
Delete a Row
The following steps will help you delete rows from a table of a Word document.
Step 1 − Click a row which you want to delete from the table and then click the Layout tab; it will show the following screen.
Step 2 − Click the Layout tab, and then click the Delete Rows option under the Delete Table Button to delete the selected row.
Add a Column
The following steps will help you add columns in a table of a Word document.
Step 1 − Click a column where you want to add an additional column and then click the Layout tab; it will show the following screen.
Step 2 − Now use the Row & Column group of buttons to add any column to the left or right of the selected column. If you click the Insert Left button, it will add a column just left to the selected column as follows.
If you click the Insert Right button, it will add a column just next to the selected column.
Delete a Column
Following are the simple steps to delete columns from a table of a word document.
Step 1 − Click a column which you want to delete from the table and then click the Layout tab; it will show the following screen.
Step 2 − Click the Layout tab, and click the Delete Column option under the Delete Table Button to delete the selected column.
Move a Table in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to move a table in Word 2010. Microsoft Word allows to move a table from one location to another location along with its content. This chapter will give you simple steps to move a table within the same document, though you can move a table from one document to another document using the cut and paste operation.
Move a Table
The following steps will help you move a table within the same Word document.
Step 1 − Bring your mouse pointer over the table which you want to move from one location to another location. As soon as you bring your mouse pointer inside the table, a small Cross Icon will appear at the top-left corner of the table as shown below.
Step 2 − Click over the small Cross Icon which will select the whole table. Once the table is selected, use the Cut button or simply press the Ctrl + X keys to cut the table from its original location.
Step 3 − Bring your insertion point at the location where you want to move the table and use Paste button or simply press Ctrl + V keys to paste the table at the new location.
Resize a Table in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to resize a table in Word 2010. Microsoft Word allows to resize a table to make it smaller and bigger as per your requirement.
Resize a Table
The following steps will help you resize a table available in a Word document.
Step 1 − Bring your mouse pointer over the table which you want to resize. As soon as you bring your mouse pointer inside the table, a small Cross Icon will appear at the top-left corner and a small Resize Icon will appear at the bottom-right corner of the table as shown below.
Step 2 − Bring the mouse pointer over the Resize Icon till it changes to a diagonal doublesided arrow and this is the time when you need to press the left mouse button and keep holding the button while resizing the table. Drag the table up to make it shorter or down to make it larger. You can drag the table diagonally to simultaneously change both the width and the height of the table.
Merging Cells in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to merge table cells in Word 2010. Microsoft Word allows the merging of two or more cells to create one large cell. You will frequently need to merge columns of the top row to create the title of the table. You can merge cells either row-wise or column-wise, rather you cannot merge cells diagonally. This chapter will teach you how to merge multiple rows or columns.
Merging Cells
The following steps will help you merge table cells in a Word document.
Step 1 − Bring your mouse pointer position inside the first cell that you want to merge. Now press the Shift key and click the cells around the cell which you want to merge into the first cell. This will highlight the cells which you click and they will be ready to be merged.
Step 2 − Now click the Layout tab and then click the Merge Cells button which will merge all the selected cells.
After merging the cells, all the content of the cells will be scrambled which you can fix later as you like. For example, you can convert the merged cells text into title or some other description. For example, let us have center-aligned and bigger font text as follows on top of the table.
Split a Table in Word 2010
In this chapter, let us discuss how to split a table in Word 2010. Microsoft Word allows splitting a table into multiple tables but a single operation will always divide a table into two tables. This chapter will teach you how to split a table into two smaller tables.
Split a Table
Following are the simple steps to split a table into two tables in a Word document.
Step 1 − Bring your mouse pointer position anywhere in the row that should appear as the first row of the new table.
Step 2 − Now click the Layout tab and then click the Split Table button which will split the table into two tables and the selected row will become the first row of the lower table.
After splitting the table into two tables, you can further divide it into two parts and you can continue dividing the Word tables as long as a table has more than one row.
Split Cells in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to split table cells in Word 2010. Microsoft Word allows splitting a cell into multiple cells. We will understand how to split a cell into multiple smaller sub-cells.
Split a Cell
The following steps will help you split a cell into two sub-cells of a table available in word document.
Step 1 − Bring your mouse pointer position inside the cell that has to be divided into multiple cells.
Step 2 − Now click the Layout tab and then click the Split Cells button; this will display a dialog box asking for the number of rows and columns to be created from the selected cell.
Step 3 − Select the desired number of rows and columns that have to go into the resultant cell and finally click the OK button to apply the result.
You can divide a cell into multiple cells either row-wise or column-wise or both.
Add Formula in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to add formula to a table in Word 2010. Microsoft Word allows you to use mathematical formula in table cells which can be used to add numbers, to find the average of numbers, or find the largest or the smallest number in table cells you specify. There is a list of formulae, you can choose from the many based on the requirement. This chapter will teach you how to use formula in word tables.
Add a Formula
Following are the simple steps to add formula in a table cell available in Word document.
Step 1 − Consider the following table with the total number of rows. Click in a cell that should contain the sum of the rows.
Step 2 − Now click the Layout tab and then click the Formula button; this will display a Formula Dialog Box which will suggest a default formula, which is =SUM(LEFT) in our case. You can select a number format using Number Format List Box to display the result or you can change the formula using the Formula List Box.
Step 3 − Now click OK to apply the formula and you will see that the left cells have been added and the sum has been put in the total cell where we wanted to have it. You can repeat the procedure to have the sum of other two rows as well.
Cell Formulae
The Formula dialog box provides the following important functions to be used as formula in a cell.
| S.No | Formula & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
AVERAGE( ) The average of a list of cells |
| 2 |
COUNT( ) The number of items in a list of cells |
| 3 |
MAX( ) The largest value in a list of cells |
| 4 |
MIN( ) The smallest value in a list of cells |
| 5 |
PRODUCT( ) The multiplication of a list of cells |
| 6 |
SUM( ) The sum of a list of cells |
We assume you are familiar with how to create a spreadsheet program; you can construct your word cell formula. Word formulae uses a reference system to refer to an individual table cells. Each column is identified by a letter, starting with A for the first column, B for the second column, and so on. After the letter comes the row number. Thus, the first cell in the first row is A1, the third cell in the fourth row is C4, and so on.
Following are useful points to help you in constructing a word cell formula.
| S.No | Cell References and Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | A single cell reference, such as B3 or F7 |
| 2 | A range of cells, such as A4:A9 or C5:C13 |
| 3 | A series of individual cells, such as A3, B4, C5 |
| 4 | ABOVE, referring to all cells in the column above the current cell. |
| 5 | BELOW, referring to all cells in the column below the current cell. |
| 6 | LEFT, referring to all cells in the row to the left of the current cell |
| 7 | RIGHT, referring to all cells in the row to the right of the current cell |
You can also construct simple Math expressions, such as B3+B5*10 by using simple mathematical operators +, -, /, *, %.
Borders & Shades in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to apply table borders and shades in Word 2010. Microsoft Word allows you to place a border on any or all of the four sides of a table very similar to text, paragraphs, and pages. You can also add shades to table rows and columns. This chapter will teach you how to add borders (left, right, top or bottom) around a table and how to add different shades to various rows and columns of the table.
Add Borders to Table
The following steps will help you add borders in a table cell available in Word document.
Step 1 − Select the table to which you want to add border. To select a table, click over the table anywhere which will make the Cross icon visible at the top-left corner of the table. Click this cross icon to select the table.
Step 2 − Click the Border button to display a list of options to put a border around the selected table. You can select any of the option available by simply clicking over it.
Step 3 − Try to add and remove different borders like left, right, top or bottom by selecting different options from the border options.
Step 4 − You can apply border to any of the selected row or column. You can try it yourself.
Step 5 − To delete the existing border, simply select the No Border option from the border options.
Using Border Options
You can add borders of your choice to word table by following the simple steps given below.
Step 1 − Click the Border button to display a list of options to put a border. Select the Border and Shading option available at the bottom of the list of options as shown in the above screenshot. This will display a Border and Shading dialog box. This dialog box can be used to set borders and shading around a selected table.
Step 2 − Click the Border tab; this will display a list of border settings, styles and options whether this border should be applied to the table or text or paragraph.
Step 3 − You can use the Preview section to disable or enable left, right, top or bottom borders of the selected table or row or column. Follow the given instructions in the preview section itself to design the border you like.
Step 4 − You can customize your border by setting its color, width by using different width thickness available under the style section.
Add Shades To Table
The following steps will help you add shades on a selected table or its rows or columns.
Step 1 − Select a row or column where you want to apply a shade of your choice.
Step 2 − Click the Border button to display a list of options to put a border. Select the Border and Shading option available at the bottom of the list of options. This will display a Border and Shading dialog box. This dialog box can be used to set borders and shading around selected row(s) or column(s).
Step 2 − Click the Shading tab which will display options to select fill, color and style and whether this border should be applied to cell or table or selected portion of text.
Step 3 − You can use the Preview section to have an idea about the expected result. Once you are done, click the OK button to apply the result.
Quick Styles in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to apply quick styles in Word 2010. Microsoft Word provides a gallery of Quick Styles that you can apply to headings, titles, text, and lists. Quick styles come with canned formatting choices, such as font, boldface, and color which we will understand in this chapter.
Apply Quick Styles
The following steps will help you understand how to apply quick styles to a selected portion of text.
Step 1 − Select a portion of text to which you want to apply some style. Using style, you can change the selected portion of text as a heading or subheading or title of the document. You can try using different styles on your text based on your requirement.
Step 2 − Click the Home tab and then move your mouse pointer over the available styles in the Style Gallery. You will see that the selected portion of text will change its style based on the selected style. You can display more available styles by clicking the More Style button.
Step 3 − Finally, to apply a selected style, click over the style and you will find that it is has been applied on the selected portion of text.
You can bring a text to its normal appearance by selecting the Normal style available in the Style Gallery.
Change Styles
The Change Style function allows you to change the default font, color, paragraph spacing and style set for a document. The following steps will help you change the default style.
Step 1 − Open the document the style of which needs to be changed. Click the Home tab and then click the Change Styles button; this will show you all the options that can be changed. You can change the Style, the Font, the Color and the Spacing of the paragraph.
Step 2 − If the style set needs to be changed, click the Style Set option; this will display a submenu to select any of the available style set. When you move your mouse over the different style sets, you will get real time text preview to give an idea about the final result.
Step 3 − To apply a selected style set, click over the style set and you will find that it is has been applied on your document.
Similarly, you can try applying Font, Color and Paragraph Spacing. You can try these options yourself.
Use Templates in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to use templates in Word 2010. Microsoft Word template is a collection of styles which defines paragraph styles for regular text paragraphs, a title, and different levels of headings. You can use any of the already existing templates for your Word document or you can design a template which can be used for all your company documents.
Using Existing Template
We will now understand how to use an already existing template for your newly created word document. A template is selected at the time when you create a new blank document.
Step 1 − To start a new document, click the File tab and then click the New option; this will display the Available Templates.
Step 2 − Microsoft Word provides a list of templates arranged under Sample Templates or you can download hundreds of templates from office.com which are arranged in different categories. We will use Sample Templates for our document. For this, we need to click over Sample Templates; this will display a gallery of templates. You can try using the office.com option to select a template based on your requirement.
Step 3 − You can browse a list of available templates and finally select one of them for your document by double-clicking over the template. We will select Equity Report template for our report requirement. While selecting a template for your document, you should select the Document Option available in the third column. This opens your document with predefined setting with which you can modify document title, author name, heading, etc. based on your document requirement.
Create New Template
You can create a fresh new template based on your requirement or you can modify an existing template and save it for later use as a template. A Microsoft Word template file has an extension of .dotx. The following steps will help you create a new template.
Step 1 − To create a new template using an existing template, click the File tab and then click the New option; this will display the Available Templates to be selected. Select any of the available template and open it with the Template Option turned on.
Step 2 − You can now modify an open template as per your requirements and once you are done, you can save this template with a .dotx extension which is a standard extension for Microsoft Word Templates.
You can create a template from a new document as well. Click the File button, and click New option to open a new document. Under Available Templates, double click Blank Document to create a new document template. Save the template with a unique name and .dotx extension.
You can save the created template anywhere you click and whenever you like to use this template, just double-click over the template file and it will open a new template based document for you.
Use Graphics in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to use graphics in Word 2010. You can add beauty to your Microsoft Word documents by inserting a variety of graphics. This chapter will teach you two ways of adding graphics.
Adding Picture in Document
The following steps will help you add an existing picture in your word document. It is assumed that you already have a picture available on your machine before you add this picture in your Word document.
Step 1 − Click on your document where you want to add a picture.
Step 2 − Click the Insert tab and then click the Picture option available in illustrations group, which will display the Insert Picture dialog box.
Step 3 − You can select a required picture using the Insert Picture dialog box. When you will click the Insert button, selected picture will be inserted in your document. You can play with your inserted picture in different ways, like you can apply quick styles to your picture, you can resize it, or you can change its color too. To try it, just -lick your inserted image and Word will give you numerous options available under the Format tab to format your inserted graphics.
You can try yourself to insert other available graphics like Clipart, Different Shapes, Charts and SmartArt or Screenshots.
Adding WordArt in Document
WordArt provides a way to add fancy words in your Word document. You can document your text in a variety of ways. The following steps will help you add WordArt in your document.
Step 1 − Click in your document where you want to add WordArt.
Step 2 − Click the Insert tab and then click the WordArt option available in the Text group; this will display a gallery of WordArt.
Step 3 − You can select any of the WordArt style from the displayed gallery by clicking on it. Now you can modify the inserted text as per your requirement and you can make it further beautiful by using different options available. To try it, just double-click your inserted WordArt and Word will give you numerous options available from the Format tab to format your image. Most frequently used options are Shape Styles and WordArt Styles.
You can try yourself to apply different options on the inserted WordArt by changing its shape styles, colors, WordArt Styles, etc.
Auto Correction in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss auto correction in Word 2010. The AutoCorrect feature automatically corrects common typographical errors when you make them. Let us learn how to use the auto correction option available in Microsoft Word 2010 to correct the spelling automatically as you type the words in your documents.
Setting AutoCorrect
The following steps will help to enable the AutoCorrect feature in Microsoft Word.
Step 1 − Click the File tab, click Options, and then click the Proofing option available in the left most column, it will display the Word Options dialog box.
Step 2 − Click the AutoCorrect Options button which will display the AutoCorrect dialog box and then click the AutoCorrect tab. Now you have to make sure all the options are enabled, especially the Replace Text as you type option. It is also recommended to be careful when you turn off an option.
Step 3 − Select from among the following options, depending on your preferences.
| S.No | Option and Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Show AutoCorrect Options Buttons This option will be used to display a small blue button or bar beneath text that was automatically corrected. Click this button to see a menu, where you can undo the correction or set AutoCorrect options. |
| 2 |
Correct TWo INitial CApitals This option changes the second letter in a pair of capital letters to lowercase. |
| 3 |
Capitalize first letter of sentences This option capitalizes the first letter following the end of a sentence. |
| 4 |
Capitalize first letter of table cells This option will be used to capitalize the first letter of a word in a table cell. |
| 5 |
Capitalize names of days This option will be used to capitalize the names of the days of the week. |
| 6 |
Correct accidental usage of cAPS LOCK key This option will be used to correct capitalization errors that occur when you type with the CAPS LOCK key depressed and turns off this key. |
| 7 |
Replace text as you type This option replaces typographical errors with the correct words as shown in the list beneath it. |
| 8 |
Automatically use suggestions from the spelling checker This option tells Word to replace spelling errors with words from the dictionary as you type. |
Although Word comes preconfigured with hundreds of AutoCorrect entries, you can also manually add entries using the following dialog box and use the Replace and With text boxes to add more entries. I added an entry for Markiting which should be replaced with Marketing. You can use the Add button to add multiple entries.
Step 4 − Click OK to close the AutoCorrect Options dialog box and again click OK to close the Word Options dialog box. Now try to type Markiting and as soon as you type this word, Microsoft Word autocorrects it with the correct word Marketing word.
Auto Formatting in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss auto formatting in Word 2010. The AutoFormat feature automatically formats a document as you type it by applying the associated styles to text. Let us learn how to use the auto format option available in Microsoft Word 2010 to format the typed content. For example, if you type three dashes — and press enter, Word will automatically create a line for you. Similarly, Word will automatically format two dashes — into an em dash (—).
Setting AutoFormat
The following steps will help you set the AutoFormat feature in your Microsoft Word.
Step 1 − Click the File tab, click Options, and then click the Proofing option available in the left most column, it will display the Word Options dialog box.
Step 2 − Click the AutoCrrect Options button; this will display the AutoCorrect dialog box and then click the AutoFormat As You Type tab to determine what items Word will automatically format for you as you type.
Step 3 − Select from among the following options, depending on your preferences.
| S.No | Option and Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
«Straight quotes» with “smart quotes” This option will be used to replace the plain quotation characters with curly quotation characters. |
| 2 |
Fractions (1/2) with fraction character (½) This option will be used to replace the fractions typed with numbers and slashes with fraction characters. |
| 3 |
*Bold* and _italic_ with real formatting This option will be used to format text enclosed within asterisks (*) as bold and text enclosed within underscores ( _ ) as italic. |
| 4 |
Internet and network paths with hyperlinks This option will be used to format e-mail addresses and URLs as clickable hyperlink fields. |
| 5 |
Ordinals (1st) with superscript This option will be used to format ordinal numbers with a superscript like 1st becomes 1st. |
| 6 |
Hyphens (—) with dash (—) This option will be used to replace a single hyphen with an en dash (.) and two hyphens with an em dash (—). |
| 7 |
Automatic bulleted lists This option will be used to apply bulleted list formatting to paragraphs beginning with *, o, or — followed by a space or tab character. |
| 8 |
Automatic numbered lists This option will be used to apply numbered list formatting to paragraphs beginning with a number or letter followed by a space or a tab character. |
| 9 |
Border lines This option will be used to apply paragraph border styles when you type three or more hyphens, underscores, or equal signs (=). |
| 10 |
Tables This option will be used to create a table when you type a series of hyphens with plus signs to indicate the column edges. Try with +——+——+ ) and then press Enter. |
| 11 |
Built-in heading styles This option will be used to apply heading styles to heading text. |
| 12 |
Format beginning of list item like the one before it This option will be used to replace plain quotation characters with curly quotation characters. |
| 13 |
Set left- and first-indent with tabs and backspaces This option sets left indentation on the tab ruler based on the tabs and backspaces you type. |
| 14 |
Define styles based on your formatting This option automatically creates or modifies styles based on manual formatting that you apply to your document. |
Step 4 − Finally click OK to close the AutoCorrect Options dialog box and again click OK to close the Word Options dialog box.
Table of Contents in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to create table of contents in Word 2010. A table of contents (or TOC) is a list of headings in the order in which they appear in the document. You can set a list of headings which should be a part of the table of contents. Let us learn how to create a Table of Contents. A table of content helps in navigating through a Word document by providing associated page numbers and direct links to various headings available on those pages.
Create Table of Contents
The following will help you to create Table of Contents in your Microsoft Word using various levels of headings.
Step 1 − Consider a document having different levels of headings.
Step 2 − You can insert a table of content anywhere in the document, but the best place is always at the beginning of the document. So bring your insertion point at the beginning of the document and then click the References tab followed by the Table of Content button; this will display a list of Table of Contents options.
Step 3 − Select any of the displayed options by simply clicking on it. A table of content will be inserted at the selected location.
Step 4 − You can select number of levels of headings in your table of content. If you click on the Insert Table of Content option available in the option menu, then it will show you a dialog box where you can select the number of levels you want to have in your table of content. You can turn ON or turn OFF the Show Page Numbers option. Once done, click the OK button to apply the options.
Now if you press the Ctrl key and then click over the any link available in the table of content, it will take you directly to the associated page.
Update Table of Contents
When you work on a Word document, then number of pages and their content keep varying and accordingly you need to update your Table of Contents. Following are the simple steps to update an existing Table of Contents in your Microsoft Word.
Step 1 − Consider you already have a table of content as shown above. Click the References tab followed by the Update Table button; this will display the Update Table of Contents dialog box with two options.
Step 2 − If you want to update just the page numbers then select the first option Update page numbers only available in the dialog box but if you want to update page numbers as well, then select the second option Update entire table and you will find your table of content updated with all the latest changes.
Delete Table of Contents
The following steps will help you delete an existing Table of Contents from Microsoft Word.
Step 1 − Consider you already have a table of content as shown above. Click the References tab and next Table of Contents button which will display a list of Table of Contents options along with Remove Table of Contents option available at the bottom.
Step 2 − Click over the Remove Table of Contents option to delete the existing table of contents.
Preview Documents in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss the preview of documents in Word 2010. When you are ready for printing your Word document, it is always recommended to preview the document before you send the document for final printing. During preview of the document you might discover that the set margin is not appropriate or many items may not look good after printing so better to fix them after having a preview of the document. You can also have the option to specify which pages to print, select a printer, specify the paper size on which you want to print, and set the other printing options.
Preview Documents
The following steps will help you preview your Microsoft Word Document.
Step 1 − Open the document the preview of which you want to see.
Step 2 − Click the File tab followed by the Print option; this will display a preview of the document in the right column. You can scroll up or scroll down your document to walk through the document using the given Scrollbar. In the next chapter, we will learn how to print the previewed document and how to set different printing options.
Step 3 − Once you are done with your preview, you can click the Home tab to go to the actual content of the document.
Printing Documents in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to print documents in Word 2010. Consider you are done with previewing and proofing your document and ready for the final printing. This chapter will teach you how to print a part or a complete Microsoft Word document.
Printing Documents
The following steps will help you print your Microsoft Word document.
Step 1 − Open the document for which you want to see the preview. Next click the File tab followed by the Print option which will display a preview of the document in the right column. You can scroll up or scroll down your document to walk through the document using given Scrollbar. The middle column gives various options to be set before you send your document to the printer.
Step 2 − You can set various other printing options available. Select from among the following options, depending on your preferences.
| S.No | Option and Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Copies Set the number of copies to be printed; by default, you will have one copy of the document. |
| 2 |
Print Custom Range This option will be used to print a particular page of the document. Type the number in Pages option, if you want to print all the pages from 7 till 10 then you would have to specify this option as 7-10 and Word will print only 7th, 8th, 9th and 10th pages. |
| 3 |
Print One Sided By default, you print one side of the page. There is one more option where you will turn up your page manually in case you want to print your page on both sides of the page. |
| 4 |
Collated By default, multiple copies will print Collated; if you are printing multiple copies and you want the copies uncollated, select the Uncollated option. |
| 5 |
Orientation By default, page orientation is set to Portrait; if you are printing your document in landscape mode then select the Landscape mode. |
| 6 |
A4 By default, the page size is A4, but you can select other page sizes available in the dropdown list. |
| 7 |
Custom Margin Click the Custom Margins dropdown list to choose the document margins you want to use. For instance, if you want to print fewer pages, you can create narrower margins; to print with more white space, create wider margins. |
| 8 |
1 Page Per Sheet By default, the number of pages per sheet is 1 but you can print multiple pages on a single sheet. Select any option you like from the given dropdown list by clicking over the 1 Page Per Sheet option. |
Step 3 − Once you are done with your setting, click on the Print button which will send your document to the printer for final printing.
Email Documents using Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to email documents using Word 2010. Microsoft Word can be used to send a Word document in an email as an attachment directly at the given email address without opening your email program. This chapter will teach you simple ways of sending email in a variety of formats, including a Word document file (DOC) attachment or a PDF, among others.
Mailing Documents
Following are the simple steps to send a word document as an attachment at the given email address.
Step 1 − Open the document you want to send using e-mail as an attachment.
Step 2 − Click the File tab and then click the Save & Send option from the left most column; this will display a number of options to Save & Send, you will have to select the Send using Email option available in the middle column.
Step 3 − The third column will have various options to send email which allows you to send your document as an attachment in DOC format or you can send your Word document in a PDF format. Click a method to send the document. I’m going to send my document in PDF format.
When you click the Send as PDF option, it displays the following screen where you can type the email address to which you want to send your document, email subject and other additional messages as well. To send email to multiple recipients, separate each e-mail address with a semicolon (;) and a space.
Translate Word 2010 Document
In this chapter, we will discuss how to translate a Word 2010 document. Microsoft Word has an option to translate a complete Word document from one language to another language using simple step. Let us learn how we can translate document content from English to some other language (Spanish).
Translate Document Using Microsoft Translator
The following steps will help you translate a document from one language to another language.
Step 1 − Click the Review tab and then click the Translate button; this will display different options to be selected.
Step 2 − Select the Choose Translation Language option simply by clicking over it. This will display a Translation Language Options dialog box asking for selecting from and to languages. Here From is the source document’s language and To is the target document’s language.
Step 3 − After selecting From Language and To Language, click OK. Now again go to Review tab and then click Translate button which will display different options to be selected. Select top option Translate Document option from the given options, this will display Translate Whole Document dialog box asking for your permission to send your document over the internet to be translated by Microsoft Translator.
Step 4 − To translate your document, you can click the Send button. This will send your document over the internet to be translated and you will have your document translated in your target language.
Step 5 − Now you can copy your translated content manually in any other document and save it for final use.
Compare Documents in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to compare documents in Word 2010. Sometime you modify a Microsoft Word document without turning on the Track Changes mode; in such cases, tracking the changes becomes difficult and you will have to compare the original document with the modified document word by word. But you do not need to compare it manually, Microsoft Word provides an option to compare two documents very easily. Let us see how it can be done.
Compare Two Documents
Let us have the following two documents, (a) Original document (b) Modified version of the same document as follows
Original Document
Modified Document
The following steps will help you compare the two documents.
Step 1 − Click the Review tab and then click the Compare button. This will display the two options to be selected.
Step 2 − Select the Compare option simply by clicking over it. This will display a Compare Documents dialog box asking for the two versions of the Word document that need to be compared with each other.
Step 3 − Select the Original Document and the Revised Document and click the OK button to display the differences in two documents. Left column on the screen would show all the changes done over the course of changes and you will see original as well as modified version of the document on the same screen. You can walk through these changes using the Previous & Next button available under the Review tab.
NOTE − While comparing two documents you can use the different settings available at the Compare Documents dialog box under the More button.
Document Security in Word 2010
Microsoft Word provides a high level of security for your word generated documents. You can set a password for a document to stop unauthorized reading and editing of the document or if you want someone just to read the document then you can set editing restriction on your word document. This chapter will teach you how to make your document password protected and restricted from editing and formatting.
Set Document Password
Once you set a password for a document then you will be able to open the document only if you know the password. If you forget your password, then there is no way to recover it and to open the document. So you need to be careful while setting a password for your important document.
The following steps will help you set a password for a Word document.
Step 1 − Open a Word document for which you want to set a password.
Step 2 − Click the File tab and then click the Info option and finally the Protect Document button which will display a list of options to be selected.
Step 3 − Select the Encrypt with Password option simply by clicking over it. This will display an Encrypt Document dialog box asking for a password to encrypt the document. The same dialog box will appear twice to enter the same password. After entering password each time, click the OK button.
Step 4 − Save the changes, and finally you will have your document password protected. Next time when someone tries to open this document, it will ask for the password before displaying the document content, which confirms that now your document is password protected and you need password to open the document.
Remove Document Password
You can remove a document password only after opening it successfully. The following steps will help you remove password protection from your Word document.
Step 1 − Open a Word document the password of which needs to be removed. You will need the correct password to open the document.
Step 2 − Click the File tab followed by the Info option and finally the Protect Document button which will display a list of options to be selected.
Step 3 − Select the Encrypt with Password option simply by clicking over it. This will display an Encrypt Document dialog box and password which will be in a dotted pattern. You need to remove this dotted pattern from the box and make it clear to remove the password from the document.
Now when you will open your document next time, Word will not ask you for any password because you have removed the password protection from the document.
Set Editing & Formatting Restrictions
The following steps will help you set editing restrictions in a Word document.
Step 1 − Open a Word document for which you want to set editing restrictions.
Step 2 − Click the File tab and then click the Info option and finally the Protect Document button which will display a list of options to be selected.
Step 3 − Select the Restrict Editing option simply by clicking over it. This will open the actual document and it will also give you the option to set editing restrictions in the Restrict Formatting and Editing area. Here you can set formatting as well as editing restrictions on the document.
Step 4 − One you are done with your setting, click the Yes, Start Enforcing Protection button which will display a Start Enforcing Protection dialog box asking for password so that no one else can change the setting. You can enter the password or you can leave it simply blank which means there is no password setting for this protection.
Step 5 − Finally click the OK button and you will find that your document is editing (or formatting if you applied) protected.
Remove Editing & Formatting Restrictions
You can remove the editing restriction from your document using these simple steps.
Step 1 − Open a Word document for which you want to remove the editing restriction.
Step 2 − Click the File tab and then click the Info option and finally the Protect Document button; this will display a list of options to be selected.
Step 3 − Select the Restrict Editing option simply by clicking over it. This will display the Restrict Formatting and Editing area as follows.
Step 4 − Now click the Stop Protection button. If you had set up a password at the time of setting the editing or formatting restrictions, then you will need the same password to remove the editing or formatting restrictions. Word will now ask for the same using the Unprotect Document Dialog box , otherwise it will simply remove the restrictions.
Set Watermark in Word 2010
In this chapter, we will discuss how to set watermark in a Word document. A watermark is a picture that shows up faintly behind the text on a Word document page. When you draft a document, you can watermark the document with Draft Copy stamp, or you can watermark a duplicate document with the Duplicate stamp. Microsoft Word allows you to stamp with watermark using simple steps explained in this chapter.
Set Standard Watermark
The following steps will help you set standard watermark in word document. A standard watermark is the one which is already defined by words and cannot modify their font or color etc.
Step 1 − Open a word document in which you want to add a watermark.
Step 2 − Click the Page Layout tab and then click the Watermark button to display a list of standard watermark options.
Step 3 − You can select any of the available standard watermarks by simply clicking over it. This will be applied to all the pages of the word. Assume we select the Confidential watermark.
Set Custom Watermark
The following steps will help you set custom watermark in word document. A custom watermark is the one which can be modified text and its font, color and size etc.
Step 1 − Open a Word document in which you want to add a watermark.
Step 2 − Click the Page Layout tab and then click the Watermark button to display a list of standard watermark options. At the bottom, you will find the Custom Watermark option.
Step 3 − Click over the Custom Watermark option; this will display the Printed Watermark dialog box.
Step 4 − Now you can set a picture as watermark or you can set predefined text as watermark; you can also type your text in the Text box available at Printed Watermark dialog box. We will set text watermark as DUPLICATE and also set its font color and font size. Once all the parameters are set, click the OK button to set the parameters.
Remove Watermark
The following steps will help you remove an existing watermark from a Word document.
Step 1 − Open a Word document the watermark of which needs to be deleted.
Step 2 − Click the Page Layout tab followed by the Watermark button to display a list of standard watermark options. At the bottom, you will find the Remove Watermark option.
Step 3 − Click Remove Watermark option; this will delete the existing watermark from the document.
Select the table
- Using the mouse: Move the mouse over the table until you see the table selection icons in the upper-left corner of the table and click it:
Note: You can also click on the table selection icon in the bottom-right corner (resizing handle) for the same effect.
- Using the keyboard: To select table elements, on the Table Layout tab, on the Table group, click the Select button, then select the option you prefer:
- Select Cell
- Select Column
- Select Row
- Select Table
Format the table
After positioning the cursor anywhere in a table or selecting a table element, Word shows two tabs: Table Design and Layout. E.g.:
See also Select and format table elements in Word.
Apply a predefined Table style
There are several predefined styles you can use for the table. Styles include a variety of borders, colors, and other attributes that give a table a very professional appearance.
To choose any of the predefined styles, do the following:
1. Select the table.
2. On the Table Design tab, in the Table Styles group, in the Styles Gallery, click the More arrow to see the complete list of styles:
3. Select the table style you want:
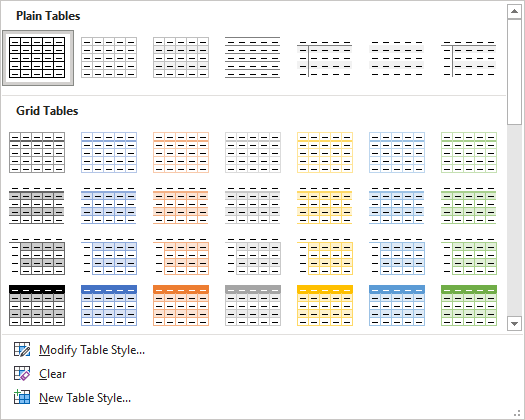
The Table Styles gallery includes three categories of styles:
- Plain Tables have minimal formatting.
- Grid Tables include vertical separators between columns.
- List Tables do not include vertical column separators:

Note: The selected style overrides any previously added style changes for the table.
Modify the table style options
To change the table or selected style, on the Table Design tab, in the Table Style group, click Modify Table Style…:
In the Modify Style dialog box, make changes you want:
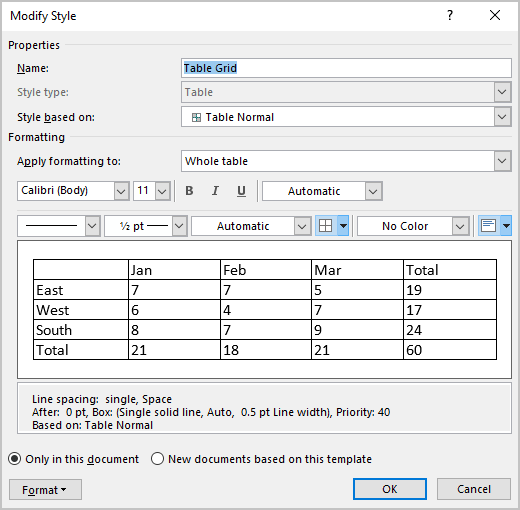
Note: Click the Format button at the bottom of the dialog box to change other options such as Font or Paragraph. See also how to clear formatting.
Customize the table formatting
After applying a table style, you can turn various options on or off to change their appearance. On the Table Design tab, in the Table Style Options group, there are six options:
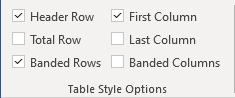
- Header Row is the first row of the table that contains Headers that helps identify the contents of a particular column. Usually, the Header Row is formatted differently and should be repeated at the beginning of each new page for tables that extend beyond one page.
Note: According to most requirements, data tables should have a header row to provide a contextual structure that aids navigation.
- Total Row is the last row of the table. If this option is selected, the last row will be formatted differently from the body rows, designed to summarize the rows above it (see how to insert formulas).
- First Column used special formatting to the column. Usually, the First Column contains the row headings.
- Last Column applies special formatting to the column to summarize the earlier columns (see how to insert formulas).
- Banded Rows and Banded Columns alternate the background color of rows and columns (see how to change the background color for the selected cells below).
Note: Certain Table Style Options may have a different effect depending on the Table Style you’ve chosen. You might need to experiment to get the look you want.
Apply the border styles
To apply and remove cell borders, do the following:
1. Select the cells or entire table to which you want to add a border.
2. On the Table Design tab, in the Borders group, choose the desired Border Styles, Line Style, Line Weight, and Pen Color:
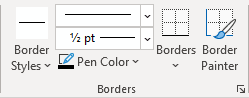
- Select the predefined Line Style, Line Weight, and Line Color from the Border Styles dropdown list:
- Select the Line Style:
- Select a border thickness from the Line Weight dropdown list:
- Select the border color from the Pen Color dropdown list:
- Select the borders from the Borders dropdown list:
Note: Select No Borders from the Borders dropdown list to remove borders from the selected cells.
- Draw the border where you want:
- After selecting border style or color, the Border Painter button is automatically checked, or
- If all that you want is selected already, just click the Border Painter button by yourself:
After any of these actions, your cursor changes to the brush. Now, draw the border where you need it:
Note: Use the Eraser button in the Draw group on the Table Layout tab to remove the unnecessary border:
Apply background colors and shading
To change the background color for some table elements, select them, then on the Table Design tab, in the Table Styles group, click the Shading button, then select the background color you prefer:
Note: To use a pattern instead of a solid color, on the Table Design tab, in the Borders group, click the dialog box launcher:
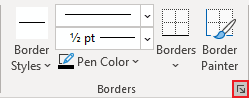
In the Borders and Shading dialog box, on the Shading tab, select a pattern in the Style list:
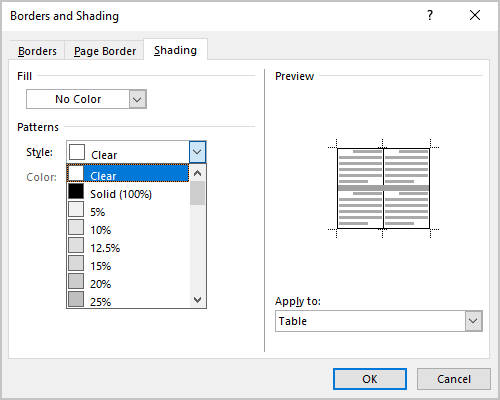
Layout of the table
The Table Layout tab includes commands for changing the entire table format, as well as commands for changing the appearance of individual table components such as cells, columns, rows:
See Select and format table elements in Word for more details.
Resize a table
- Using the mouse: To resize a table in a Word document, move the mouse over the table until you see the table resizing icons (handle) in the bottom-right corner of the table and click it:
Drag the table to the size you need, and then release the handle.
- Using the keyboard: Select a table (see also how to resize individual cells, specific rows, or columns); the do one of the following:
- On the Layout tab, in the Cell Size group, change the values in the Height and Width fields:
- Open the Table Properties dialog box by doing one of the following:
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Table group, click the Properties button:
- Right-click the table and select Table Properties… in the popup menu:
In the Table Properties dialog box, on the Table tab, in the Size section, select the Preferred width check box, then:
- In the Preferred width field, type or select the value you need,
- In the Measure in dropdown list, select one of the items:
- Percent to specify the percentage of the table width,
- Inches to fix the column width:
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Table group, click the Properties button:
- On the Layout tab, in the Cell Size group, change the values in the Height and Width fields:
See how to resize table elements for more details.
Freeze the table
Some Word tables change the width of their columns according to the data. To stop changing the table size when new data is inserted, do the following:
1. Select the table.
2. Open the Table Properties dialog box.
3. In the Table Properties dialog box, on the Table tab, click the Options… button:
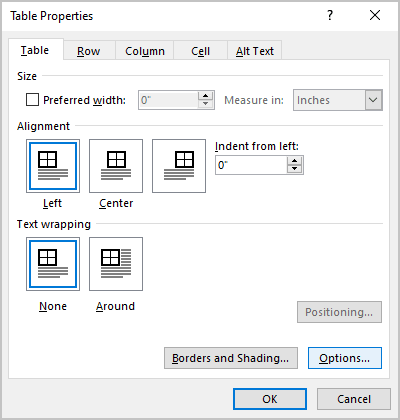
4. In the Table Options dialog box, deselect the Automatically resize to fit contents check box:
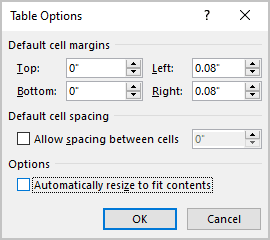
See also how to fix the height of table rows.
Move a table
To move a table to a new page or a new document, select it, then use the Cut and Paste commands. You can also use the Copy command to leave a copy of the table in the original location.