When students engage in “word analysis” or “word study,” they break words down into their smallest units of meaning — morphemes. Each morpheme has a meaning that contributes to our understanding of the whole word.
What does word analysis mean?, Word analysis is a process of learning more about word meanings by studying their origins and parts. A “morpheme” is the smallest meaningful part of a word. Other terms for word analysis: Morphemic analysis.
Furthermore, How do you analyze a word?, In “word analysis” or “word study,” students break words down into morphemes, their smallest units of meaning. Each morpheme has a meaning that contributes to the whole word. Students’ knowledge of morphemes helps them to identify the meaning of words and builds their vocabulary.
Finally, What is analysis of word structure?, Structural analysis is the process of breaking words down into their basic parts to determine word meaning. … When using structural analysis, the reader breaks words down into their basic parts: Prefixes – word parts located at the beginning of a word to change meaning. Roots – the basic meaningful part of a word.
Frequently Asked Question:
How do you teach the word meaning?
How to teach:
- Introduce each new word one at a time. Say the word aloud and have students repeat the word. …
- Reflect. …
- Read the text you’ve chosen. …
- Ask students to repeat the word after you’ve read it in the text. …
- Use a quick, fun activity to reinforce each new word’s meaning. …
- Play word games. …
- Challenge students to use new words.
How do you understand words meaning?
To understand a word without a dictionary, try re-reading the entire sentence to see if the context helps you to find out what the word means. If it’s unclear, try to figure it out by thinking about the meaning of the words you’re familiar with, since the unknown word might have a similar meaning.
How do you teach word concepts?
The first step with Concept of Word Instruction is to teach the poem to the students. They need to have the poem memorized, so that they can accurately match the memorized words to the print they see. Teachers can use pictures that represent the text or hand motions with common nursery rhymes and finger plays.
How do you teach words with multiple meanings?
Play word games that ask students to recognize words‘ multiple meanings. For example, create—or have students illustrate—pairs of cards to tell or show two meanings of a specific word. Use the cards to play a matching game. Students should collect both pictures for a word and give a verbal definition of each picture.
How can we help students to understand meaning?
Follow these steps and try some different techniques in your classroom:
- Choose a lesson from your textbook. …
- Before the lesson, select some words that you think your students won’t know. …
- Decide how you could help your students understand these words. …
- Before your students read the lesson, write the words on the board.
What does structural analysis mean?
STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS is a strategy that is used to facilitate decoding as students become more proficient readers. These advanced decoding strategies help students learn parts of words so they can more easily decode unknown multi-‐syllabic words. In structural analysis, students are taught to read prefixes and suffixes.
What is structure in structural analysis?
1.1 Structural Analysis Defined. A structure, as it relates to civil engineering, is a system of interconnected members used to support external loads. Structural analysis is the prediction of the response of structures to specified arbitrary external loads.
What is word analysis?
When students engage in “word analysis” or “word study,” they break words down into their smallest units of meaning — morphemes. Each morpheme has a meaning that contributes to our understanding of the whole word.
What are the types of structural analysis?
What are the types of Structural Analysis?
- Hand Calculations. Hand Calculations in Structural Analysis. …
- Finite Element Analysis. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) …
- Structural Analysis Software.
What is structural analysis of words?
Structural analysis is the process of breaking words down into their basic parts to determine word meaning. … When using structural analysis, the reader breaks words down into their basic parts: Prefixes – word parts located at the beginning of a word to change meaning. Roots – the basic meaningful part of a word.
How do I teach word study?
A cycle of instruction for word study might include the following:
- introduce the spelling pattern by choosing words for students to sort.
- encourage students to discover the pattern in their reading and writing.
- use reinforcement activities to help students relate this pattern to previously acquired word knowledge.
How do you teach the word meaning?
How to teach:
- Introduce each new word one at a time. Say the word aloud and have students repeat the word. …
- Reflect. …
- Read the text you’ve chosen. …
- Ask students to repeat the word after you’ve read it in the text. …
- Use a quick, fun activity to reinforce each new word’s meaning. …
- Play word games. …
- Challenge students to use new words.
What are some strategies for breaking words apart to get their meaning?
5 Ways To Have K-2 Students Practice Breaking Apart Words
- Segment the sounds in a CVC (consonant-vowel-consonant) word.
- Read the onset and rime of a word (i.e. sh-ip)
- Recognize and read word families.
- Read “smaller” words inside compound words.
- Derive meaning from root words, prefixes, and suffixes.
What is word analysis?
When students engage in “word analysis” or “word study,” they break words down into their smallest units of meaning — morphemes. Each morpheme has a meaning that contributes to our understanding of the whole word.
How do you analyze a word?
In “word analysis” or “word study,” students break words down into morphemes, their smallest units of meaning. Each morpheme has a meaning that contributes to the whole word. Students’ knowledge of morphemes helps them to identify the meaning of words and builds their vocabulary.
What is analysis example?
The definition of analysis is the process of breaking down a something into its parts to learn what they do and how they relate to one another. Examining blood in a lab to discover all of its components is an example of analysis. noun.
What is Analysis sentence?
The purpose of analysis is to make the complete grammatical structure of a sentence clear. Each part of the sentence is identified, its function des- cribed, and its relationship to the other parts of the sentence explained. There are different ways of presenting a sentence analysis.
- Lexicology is the part of linguistics which studies words, their nature(?) and meaning, words’ elements(?), relations between words (semantical relations), word groups and the whole lexicon.
The word «lexicology» derives from the Greek «λεξικόν» (lexicon), neut. of «λεξικός» (lexikos), «of or for words»,[1] from «λέξις» (lexis), «speech», «word»,[2] (in turn from «λέγω» lego «to say», «to speak»[3]) + «-λογία», (-logia), «the study of», a suffix derived from «λόγος» (logos), amongst others meaning «speech, oration, discourse, quote, study, calculation, reason»,[4] it turn also from «λέγω».
The term first appeared in the 1820s, though there were lexicologists in essence before the term was coined.
- General — the general study of words, irrespective of the specific features of any particular language
Special — the description of the vocabulary of a given language
Historical — the study of the evolution of a vocabulary as well as of its elements. This branch discusses the origin of words, their change and development.
Descriptive — deals with the description of the vocabulary of a given language at a given stage of its development.
- English vocabulary as a system
Modern English Lexicology aims at giving a systematic description of the word-stock of Modern English. It treats the following basic problems:
— Basic problems
— Semasiology;
— Word-Structure;
— Word-Formation;
— Etymology of the English Word-Stock;
— Word-Groups and Phraseological Units;
— Variants, dialects of the E. Language;
— English Lexicography.
System is a set of competing possibilities in language, together with the rules for choosing them.
Structuralism recognized that a language is best viewed as a system of elements, with each element being chiefly defined by its place within the system, by the way it is related to other elements.
Language systems:
— speech
— syntactic
— lexical
— morphological
— phonetical
Modern approaches to the problem of study of a language system are characterised by two different levels of study: syntagmatic and paradigmatic.
Paradigmatic relations are the relation between set of linguistic items, which in some sense, constitute choices, so that only one of them may be present at a time in a given position. On the paradigmatic level, the word is studied in its relationships with other words in the vocabulary system.
So, a word may be studied in comparison with other words of similar meaning (e. g. work, n. — labour, n.; to refuse, v. — to reject v. — to decline, v.), of opposite meaning (e. g. busy, adj. — idle, adj.; to accept, v, — to reject, v.), of different stylistic characteristics (e. g. man, n. — chap, n. — bloke, n. — guy, n.).
Consequently, the main problems of paradigmatic studies of vocabulary are:
— synonymy
— hyponymy
— antonymy
— functional styles
Syntagmatic relations
On the syntagmatic level, the semantic structure of the word is analysed in its linear relationships with neighbouring words in connected speech. In other words, the semantic characteristics of the word are observed, described and studied on the basis of its typical contexts, in speech:
— phrases
— collocations
Some collocations are totally predictable, such as spick with span, others are much less so: letter collocates with a wide range of lexemes, such as alphabet and spelling, and (in another sense) box, post, and write.
Collocations differ greatly between languages, and provide a major difficulty in mastering foreign languages. In English, we ‘face’ problems and ‘interpret’ dreams; but in modern Hebrew, we have to ‘stand in front of problems and ‘solve’ dreams.
The more fixed a collocation is, the more we think of it as an ‘idiom’ — a pattern to be learned as a whole, and not as the ‘sum of its parts’.
Combination of paradigmatic and syntagmatic relations in lexical system determines vocabulary as a system.
- One of the earliest and most obvious non-semantic grouping is the alphabetical organization of the word-stock, which is represented in most dictionaries. It is of great practical value in the search for the necessary word, but its theoretical value is almost null, because no other property of the word can be predicted from the letter or letters the word begins with.
Morphological groupings.
On the morphological level words are divided into four groups according to their morphological structure:
1) root or morpheme words (dog, hand);
2) derivatives, which contain no less than two morphemes (dogged (ynpямый), doggedly; handy, handful);
3) compound words consisting of not less than two free morphemes (dog-cheap-«very cheap», dog-days — «hottest part of the year»; handbook, handball)
4) compound derivatives (dog-legged — «crooked or bent like a dog’s hind leg», left-handed).
This grouping is considered to be the basis for lexicology.
Another type of traditional lexicological grouping as known as word-families such as: hand, handy, handicraft, handbag, handball, handful, hand-made,handsome, etc.
A very important type of non-semantic grouping for isolated lexical units is based on a statistical analysis of their frequency. Frequency counts carried out for practical purposes of lexicology, language teaching and shorthand show important correlations between quantative and qualitative characteristics of lexical units, the most frequent words being polysemantic and stylistically neutral. The frequency analysis singles out two classes:
1) notional words;
2) form (or functional) words.
Notional words constitute the bulk of the existing word-stock, according to the recent counts given for the first 1000 most frequently occurring words they make up 93% of the total number.
All notional lexical units are traditionally subdivided into parts of speech: nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs. Nouns numerically make the largest class — about 39% of all notional words; verbs come second — 25% of words; they are followed by adjectives — 17% and adverbs — 12%.
Form or functional words — the remaining 7% of the total vocabulary — are prepositions, articles, conjunctions, which primarily denote various relations between notional words. Their grammatical meaning dominates over their lexical meaning. They make a specific group of about 150 units.
Lexico-grammatical grouping.
By a lexico-grammatical group we understand a class of words which have a common lexico-grammatical meaning, a common paradigm, the same substituting elements and possibly a characteristic set of suffixes rendering the lexico-grammatical meaning.
Lexico-grammatical groups should not be confused with parts of speech. For instance, audience and honesty belong to the same part of speech but to different lexico-grammatical groups because their lexico-grammatical meaning is different.
Common Denominator of Meaning, Semantic Fields.
Words may also be classified according to the concepts underlying their meaning. This classification is closely connected with the theory of semantic fields. By the term «semantic fields» we understand closely knit sectors of vocabulary each characterized by a common concept. The words blue, red, yellow, black, etc. may be described as making up the semantic field of colours, the words mother, father, sister, cousin, etc. — as members of the semantic field of kinship terms, the words joy, happiness, gaiety, enjoyment, etc. as belonging to the field of pleasurable emotions, and so on.
The members of the semantic fields are not synonymous but all of them are joined together by some common semantic component — the concept of colours or the concept of kinship, etc. This semantic component common to all members of the field is sometimes described as the common denominator of meaning. All members of the field are semantically interdependent as each member helps to delimit and determine the meaning of its neighbours and is semantically delimited and determined by them. It follows that the word meaning is to a great extent determined by the place it occupies in its semantic field.
It is argued that we cannot possibly know the exact meaning of the word if we do not know the structure of the semantic field to which the word belongs, the number of the members and the concepts covered by them, etc. The meaning of the word captain, e.g. cannot be properly understood until we know the semantic field in which this term operates — the army, the navy, or the merchant service. It follows that the meaning of the word captain is determined by the place it occupies among the terms of the relevant rank system. In other words we know what captain means only if we know whether his subordinate is called mate or first officer (merchant service), commander (navy) or lieutenant (army).
Semantic dependence of the word on the structure of me field may be also illustrated by comparing members of analogous conceptual fields in different languages. Comparing, e.g. kinship terms in Russian and in English we observe that the meaning of the English term mother-in-law is different from either the Russian тёща or свекровь, as the English term covers the whole area which in Russian is divided between the two words. The same is true of the members of the semantic field of colours (cf. blue — синий, голубой), of human body (cf. hand, arm — рука) and others.
The theory of semantic field is severely criticized by Soviet linguists mainly on philosophical grounds as some of the proponents of the semantic-field theory hold the idealistic view that language is a kind of self-contained entity standing between man and the world of reality (Zwischenwelt). The followers of this theory argue that semantic fields reveal the fact that human experience is analysed and elaborated in a unique way, differing from one language to another. Broadly speaking they assert that people speaking different languages actually have different concepts, as it is through language that we see the real world around us. In short, they deny the primacy of matter forgetting that our concepts are formed not only through linguistic experience, but primarily through our actual contact with the real world. We know what hot means not only because we know the word hot, but also because we burn our fingers when we touch something very hot. A detailed critical analysis of the theory of semantic fields is the subject-matter of general linguists. Here we are concerned with the theory only as a means of semantic classification of vocabulary items.
Two more points should be discussed in this connection. Firstly, semantic groups may be very extensive and may cover big conceptual areas, e.g. man-universe, etc. There may be, however, comparatively small lexical groups of words linked by a common denominator of meaning. The words bread, cheese, milk, meat, etc. make up the semantic field with the concept of food as the common denominator of meaning. Such smaller lexical groups seem to play a very important role in determining individual meanings of polysemantic words in lexical contexts. Analysing polysemantic verbs we see that the verb take, e.g. in combination with the lexical group denoting means of transportation is synonymous with the verb go (take the tram, the bus, etc.). When combined with members of another lexical group possessing another semantic denominator, the same verb is synonymous with to drink (to take tea, coffee, etc.). Such word-groups are often used not only in scientific lexicological analysis, but also in practical class-room teaching. In a number of textbooks we find words with some common denominator of meaning listed under the headings Flower, Fruit, Domestic Animals, and so on.
In other words lexical or semantic field is the organization of related words and expressions into a system which shows their relationship to one another.
For example, kinship terms such as father, mother, sister, brother, uncle, aunt belong to a lexical field whose relevant features include generation, sex, membership of the father’s or mother’s side of the family, etc.
The absence of a word in a particular place in a lexical field of a language is called a lexical gap.
For example, in English there is no singular noun that covers both cow and bull as hoarse covers stallion and mare.
Common Contextual Associations. Thematic Groups.
Another type of classification almost universally used in practical class-room teaching is known as thematic grouping. Classification of vocabulary items into thematic groups is based on the co-occurrence of words in certain repeatedly used contexts.
In linguistic contexts co-occurrence may be observed on different levels. On the level of word-groups the word question, e.g., is often found in collocation with the verbs raise, put forward, discuss, etc., with the adjectives urgent, vital, disputable and so on. The verb accept occurs in numerous contexts together with the nouns proposal, invitation, plan and others.
As a rule, thematic groups deal with contexts on the level of the sentence (or utterance). Words in thematic groups are joined together by common contextual associations within the framework of the sentence and reflect the interlinking words, e.g. tree-grow-green; journey-train-taxi-bags-ticket or sun-shine-brightly-blue-sky, is due to the regular co-occurrence of these words in similar sentences. Unlike members of synonymic sets or semantic fields, words making up a thematic group belong to different parts of speech and do not possess any common denominator of meaning.
Contextual associations formed by the speaker of a language are usually conditioned by the context of situation which necessitates the use of certain words. When watching a play, e.g., we naturally speak of the actors who act the main parts, of good (or bad) staging of the play, of the wonderful scenery and so on. When we go shopping it is usual to speak of the prices, of the goods we buy, of the shops, etc. (In practical language learning thematic groups are often listed under various headings, e.g. At the Theatre, At School, Shopping, and are often found in text-books and courses of conversational English).
Thematic and ideographic organization of a vocabulary.
It is a further subdivision within the lexico-grammatical grouping. The basis of grouping is not only linguistic but also extra-linguistic. The words are associated because the things they name occur together and are closely connected in reality, e.g., terms of kinship. Names of parts of the human body, colour terms, etc.
The ideographic groupings are independent of classification into parts of speech, as grammatical meaning is not taken into consideration. Words and expressions are here classed not according to their lexico-grammatical meaning but strictly according to their signification, i.e. to their system of logical notions. These subgroups may compare nouns, verbs adjectives and adverbs together, provided they refer to the same notion. Under alphabetical order the words which in the human mind go close together (father, brother, uncle, etc.) are placed in various parts of a dictionary. So, some lexicographers place such groups of lexical units in the company they usually keep in every day life, in our minds. These dictionaries are called ideographical or ideological.
Synonymic grouping is a special case of lexico-grammatical grouping based on semantic proximity of words belonging to the same part of speech. Taking up similarity of meaning and contrasts of phonetic shape we observe that every language in its vocabulary has a variety of words kindred (родственный) or similar in meaning but distinct in morphemic composition, phonetic shape and usage. These words express the most delicate shades of thought, feelings and are explained in the dictionaries of synonyms.
Antonyms have been traditionally defined as words of opposite meaning. Their distinction from synonyms is semantic polarity. The English language is rich in synonyms and antonyms, their study reveals the systematic character of the English vocabulary.
Special terminology.
Sharply defined extensive semantic fields are found in terminological systems. Terminology constitutes the greatest part of every language vocabulary. A term is a word or word-group used to name a notion characteristic of some special field of knowledge, e.g., linguistics, cybernetics, industry, culture, informatics. Almost every system of terms is nowadays fixed and analyzed in numerous special dictionaries of the English language. ?
Hyponymy (включение).
Another type of paradigmatic relation is hyponymy. The notion of hyponymy is traditional enough; it has been long recognized as one of the main-principles in the organization of the vocabulary off all languages. For instance, animal is a generic term as compared to the specific names: wolf, dog, mouse. Dog, in its tern, may serve as a generic term for different breeds such as bull-dog, collie, poodle.
In other words, this type of relationship means the «inclusion» of a more specific term in a more general term, which has been established by some scientists in terms of logic of classes*. For example, the meaning of tulips is said to be included in the meaning of «flower», and so on.
So, the word-stock is not only a sum total of all the words of a language, but a very complicated set of various relationships between different groupings, layers, between the vocabulary as a whole and isolated individual lexical units.
- The importance of English lexicology is based not on the size of its vocabulary, however big it is, but on the fact that at present it is the world’s most widely used language. One of the most fundamental works on the English language of the present — «A Grammar of Contemporary English” by R. Quirk, S. Greenbaum, G. Leech and J. Svartvik (1978) — gives the following data: it is spoken as a native language by nearly three hundred million people in Britain, the United States, Ireland, Australia, Canada, New Zealand, South Africa and some other countries. The knowledge of English is widely spread geographically — it is in fact used in all continents. It is also spoken in many countries as a second language and used in official and business activities there. This is the case in India, Pakistan and many other former British colonies. English is also one of the working languages of the United Nations and the universal language of international aviation. More than a half world’s scientific literature is published in English and 60% of the world’s radio broadcasts are in English. For all these reasons it is widely studied all over the world as a foreign language. The theoretical value of lexicology becomes obvious if we realise that it forms the study of one of the three main aspects of language, i.e. its vocabulary, the other two being its grammar and sound system. The theory of meaning was originally developed within the limits of philosophical science. The relationship between the name and the thing named has in the course of history constituted one of the key questions in gnostic theories and therefore in the struggle of materialistic and idealistic trends. The idealistic point of view assumes that the earlier forms of words disclose their real correct meaning, and that originally language was created by some superior reason so that later changes of any kind are looked upon as distortions and corruption. The materialistic approach considers the origin, development and current use of words as depending upon the needs of social communication. The dialectics of its growth is determined by its interaction with the development of human practice and mind. In the light of V. I. Lenin’s theory of reflection we know that the meanings of words reflect objective reality. Words serve as names for things, actions, qualities, etc. and by their modification become better adapted to the needs of the speakers. This proves the fallacy of one of the characteristic trends in modern idealistic linguistics, the so-called Sapir-Whorf thesis according to which the linguistic system of one’s native language not only expresses one’s thoughts but also determines them. This view is incorrect, because our mind reflects the surrounding world not only through language but also directly. Lexicology came into being to meet the demands of many different branches of applied linguistics, namely of lexicography, standardisation of terminology, information retrieval, literary criticism and especially of foreign language teaching. Its importance in training a would-be teacher of languages is of a quite special character and cannot be overestimated as it helps to stimulate a systematic approach to the facts of vocabulary and an organised comparison of the foreign and native language. It is particularly useful in building up the learner’s vocabulary by an effective selection, grouping and analysis of new words. New words are better remembered if they are given not at random but organised in thematic groups, word-families, synonymic series, etc. A good knowledge of the system of word-formation furnishes a tool helping the student to guess and retain in his memory the meaning of new words on the basis of their motivation and by comparing and contrasting them with the previously learned elements and patterns. The knowledge, for instance, of the meaning of negative, reversative and pejorative prefixes and patterns of derivation may be helpful in understanding new words. For example such words as immovable a, deforestation n and miscalculate v will be readily understood as ‘that cannot be moved’, ‘clearing land from forests’ and ‘to calculate wrongly’. By drawing his pupils’ attention to the combining characteristics of words the teacher will prevent many mistakes.1 It will be word-groups falling into patterns, instead of lists of unrelated items, that will be presented in the classroom. A working knowledge and understanding of functional styles and stylistic synonyms is indispensable when literary texts are used as a basis for acquiring oral skills, for analytical reading, discussing fiction and translation. Lexicology not only gives a systematic description of the present make-up of the vocabulary, but also helps students to master the literary standards of word usage. The correct use of words is an important counterpart of expressive and effective speech. An exact knowledge of the vocabulary system is also necessary in connection with technical teaching means. Lexicology plays a prominent part in the general linguistic training of every philologist by summing up the knowledge acquired during all his years at the foreign language faculty. It also imparts the necessary skills of using different kinds of dictionaries and reference books, and prepares for future independent work on increasing and improving one’s vocabulary.
- The treatment of words in lexicology cannot be divorced from the study of all the other elements in the language system to which words belong. It should be always borne in mind that in reality, in the actual process of communication, all these elements are interdependent and stand in definite relations to one another. We separate them for convenience of study, and yet to separate them for analysis is pointless, unless we are afterwards able to put them back together to achieve a synthesis and see their interdependence and development in the language system as a whole. The word, as it has already been stated, is studied in several branches of linguistics and not in lexicology only, and the latter, in its turn, is closely connected with general linguistics, the history of the language, phonetics, stylistics, grammar and such new branches of our science as sociolinguistics, paralinguistics, pragmalinguistics and some others.1 The importance of the connection between lexicology and phonetics stands explained if we remember that a word is an association of a given group of sounds with a given meaning, so that top is one word, and tip is another. Phonemes have no meaning of their own but they serve to distinguish between meanings. Their function is building up morphemes, and it is on the level of morphemes that the form-meaning unity is introduced into language. We may say therefore that phonemes participate in signification. Word-unity is conditioned by a number of phonological features. Phonemes follow each other in a fixed sequence so that [pit] is different from [tip]. The importance of the phonemic make-up may be revealed by the substitution test which isolates the central phoneme of hope by setting it against hop, hoop, heap or hip. An accidental or jocular transposition of the initial sounds of two or more words, the so-called spoonerisms illustrate the same point. Cf. our queer old dean for our dear old queen, sin twister for twin sister, May I sew you to a sheet? for May I show you to a seat?, a half-warmed fish for a half-formed wish, etc.1 Discrimination between the words may be based upon stress: the word ‘import is recognised as a noun and distinguished from the verb im’port due to the position of stress. Stress also distinguishes compounds from otherwise homonymous word-groups: ‘blackbird : : ‘black ‘bird. Each language also possesses certain phonological features marking word-limits. Historical phonetics and historical phonology can be of great use in the diachronic study of synonyms, homonyms and polysemy. When sound changes loosen the ties between members of the same word-family, this is an important factor in facilitating semantic changes. The words whole, heal, hail, for instance, are etymologically related.2 The word whole originally meant ‘unharmed’, ;unwounded’. The early verb whole meant 4to make whole’, hence ‘heal’. Its sense of ‘healthy’ led to its use as a salutation, as in hail! Having in the course of historical development lost their phonetic similarity, these words cannot now exercise any restrictive influence upon one another’s semantic development. Thus, hail occurs now in the meaning of ‘call’, even with the purpose to stop and arrest (used by sentinels). Meaning in its turn is indispensable to phonemic analysis because to establish the phonemic difference between [ou] and [o] it is sufficient to know that [houp] means something different from [hop]. All these considerations are not meant to be in any way exhaustive, they can only give a general idea of the possible interdependence of the two branches of linguistics. Stylistics, although from a different angle, studies many problems treated in lexicology. These are the problems of meaning, connotations, synonymy, functional differentiation of vocabulary according to the sphere of communication and some other issues. For a reader without some awareness of the connotations and history of words, the images hidden in their root and their stylistic properties, a substantial part of the meaning of a literary text, whether prosaic or poetic, may be lost. Thus, for instance, the mood of despair in O. Wilde’s poem «Taedium Vitae” (Weariness of Life) is felt due to an accumulation of epithets expressed by words with negative, derogatory connotations, such as: desperate, paltry, gaudy, base, lackeyed, slanderous, lowliest, meanest. An awareness of all the characteristic features of words is not only rewarded because one can feel the effect of hidden connotations and imagery, but because without it one cannot grasp the whole essence of the message the poem has to convey. The difference and interconnection between grammar and lexicology is one of the important controversial issues in linguistics and as it is basic to the problems under discussion in this book, it is necessary to dwell upon it a little more than has been done for phonetics and stylistics. A close connection between lexicology and grammar is conditioned by the manifold and inseverable ties between the objects of their study. Even isolated words as presented in a dictionary bear a definite relation to the grammatical system of the language because they belong to some part of speech and conform to some lexico-grammatical characteristics of the word class to which they belong. Words seldom occur in isolation. They are arranged in certain patterns conveying the relations between the things for which they stand, therefore alongside with their lexical meaning they possess some grammatical meaning. Сf. head of the committee and to head a committee. The two kinds of meaning are often interdependent. That is to say, certain grammatical functions and meanings are possible only for the words whose lexical meaning makes them fit for these functions, and, on the other hand, some lexical meanings in some words occur only in definite grammatical functions and forms and in definite grammatical patterns. For example, the functions of a link verb with a predicative expressed by an adjective cannot be fulfilled by every intransitive verb but are often taken up by verbs of motion: come true, fall ill, go wrong, turn red, run dry and other similar combinations all render the meaning of ‘become sth’. The function is of long standing in English and can be illustrated by a line from A. Pope who, protesting against blank verse, wrote: It is not poetry, but prose run mad.1 On the other hand the grammatical form and function of the word affect its lexical meaning. A well-known example is the same verb go when in the continuous tenses, followed by to and an infinitive (except go and come), it serves to express an action in the near and immediate future, or an intention of future action: You’re not going to sit there saying nothing all the evening, both of you, are you? (Simpson) Participle II of the same verb following the link verb be denotes absence: The house is gone. In subordinate clauses after as the verb go implies comparison with the average: … how a novel that has now had a fairly long life, as novels go, has come to be written (Maugham). The subject of the verb go in this construction is as a rule an inanimate noun. The adjective hard followed by the infinitive of any verb means ‘difficult’: One of the hardest things to remember is that a man’s merit in one sphere is no guarantee of his merit in another. Lexical meanings in the above cases are said to be grammatically conditioned, and their indicating context is called syntactic or mixed. The point has attracted the attention of many authors.1 The number of words in each language being very great, any lexical meaning has a much lower probability of occurrence than grammatical meanings and therefore carries the greatest amount of information in any discourse determining what the sentence is about. W. Chafe, whose influence in the present-day semantic syntax is quite considerable, points out the many constraints which limit the co-occurrence of words. He considers the verb as of paramount importance in sentence semantic structure, and argues that it is the verb that dictates the presence and character of the noun as its subject or object. Thus, the verbs frighten, amuse and awaken can have only animate nouns as their objects. The constraint is even narrower if we take the verbs say, talk or think for which only animate human subjects are possible. It is obvious that not all animate nouns are human. This view is, however, if not mistaken, at least one-sided, because the opposite is also true: it may happen that the same verb changes its meaning, when used with personal (human) names and with names of objects. Compare: The new girl gave him a strange smile (she smiled at him) and The new teeth gave him a strange smile. These are by no means the only relations of vocabulary and grammar. We shall not attempt to enumerate all the possible problems. Let us turn now to another point of interest, namely the survival of two grammatically equivalent forms of the same word when they help to distinguish between its lexical meanings. Some nouns, for instance, have two separate plurals, one keeping the etymological plural form, and the other with the usual English ending -s. For example, the form brothers is used to express the family relationship, whereas the old form brethren survives in ecclesiastical usage or serves to indicate the members of some club or society; the scientific plural of index, is usually indices, in more general senses the plural is indexes. The plural of genius meaning a person of exceptional intellect is geniuses, genius in the sense of evil or good spirit has the plural form genii. It may also happen that a form that originally expressed grammatical meaning, for example, the plural of nouns, becomes a basis for a new grammatically conditioned lexical meaning. In this new meaning it is isolated from the paradigm, so that a new word comes into being. Arms, the plural of the noun arm, for instance, has come to mean ‘weapon’. E.g. to take arms against a sea of troubles (Shakespeare). The grammatical form is lexicalised; the new word shows itself capable of further development, a new grammatically conditioned meaning appears, namely, with the verb in the singular arms metonymically denotes the military profession. The abstract noun authority becomes a collective in the term authorities and denotes ‘a group of persons having the right to control and govern’. Compare also colours, customs, looks, manners, pictures, works which are the best known examples of this isolation, or, as it is also called, lexicalisation of a grammatical form. In all these words the suffix -s signals a new word with a new meaning. It is also worthy of note that grammar and vocabulary make use of the same technique, i.e. the formal distinctive features of some derivational oppositions between different words are the same as those of oppositions contrasting different grammatical forms (in affixation, juxtaposition of stems and sound interchange). Compare, for example, the oppositions occurring in the lexical system, such as work :: worker, power :: will-power, food :: feed with grammatical oppositions: work (Inf.) :: worked (Past Ind.), pour (Inf.) :: will pour (Put. Ind.), feed (Inf.) :: fed (Past Ind.). Not only are the methods and patterns similar, but the very morphemes are often homonymous. For example, alongside the derivational suffixes -en, one of which occurs in adjectives (wooden), and the other in verbs (strengthen), there are two functional suffixes, one for Participle II (written), the other for the archaic plural form (oxen). Furthermore, one and the same word may in some of its meanings function as a notional word, while in others it may be a form word, i.e. it may serve to indicate the relationships and functions of other words. Compare, for instance, the notional and the auxiliary do in the following: What you do’s nothing to do with me, it doesn’t interest me. Last but not least all grammatical meanings have a lexical counterpart that expresses the same concept. The concept of futurity may be lexically expressed in the words future, tomorrow, by and by, time to come, hereafter or grammatically in the verbal forms shall come and will come. Also plurality may be described by plural forms of various words: houses, boys, books or lexically by the words: crowd, party, company, group, set, etc. The ties between lexicology and grammar are particularly strong in the sphere of word-formation which before lexicology became a separate branch of linguistics had even been considered as part of grammar. The characteristic features of English word-building, the morphological structure of the English word are dependent upon the peculiarity of the English grammatical system. The analytical character of the language is largely responsible for the wide spread of conversion1 and for the remarkable flexibility of the vocabulary manifest in the ease with which many nonce-words2 are formed on the spur of the moment. This brief account of the interdependence between the two important parts of linguistics must suffice for the present. In future we shall have to return to the problem and treat some parts of it more extensively.
No matter what aspect of language
a scholar is looking into, he or she will adhere to the principles of
scientific method: observation, classification, generalization,
predictions, and verification. “The procedures by which researchers
go about their work of describing, explaining and predicting
phenomena are called research methodology. It is also defined as the
study of methods by which knowledge is gained” (Rajasekar,
Philominathan, & Chinnathambi, 2006, p.2). Observations do not
always give a clear sense of what data may be relevant and what data
are not. Accurate observation is especially critical in lexicology
when the phenomena under investigation appear to be anomalous.
Classification includes an orderly arrangement of data obtained
through observation. It also includes arrangement of some anomalous
data.
The next principle includes
generalization. The collected data are analyzed, and on this basis,
certain hypotheses are offered to explain the phenomena. Theory and
hypothesis are two concepts that are associated with explanations in
lexicology. A theory may be a well-developed and well-confirmed body
of explanatory material. Some
scholars believe that predictions are a part of the hypothesis, and
once predictions are made, the hypothesis can be tested (Perry, p.
17). Verification involves
confirmation or rejection of the hypothesis.
R. S. Ginzburg , S. S. Khidekel,
G. Y. Knyazeva, and A. A. Sankin (1979)
propose the following methods and procedures of linguistic
analyses:
contrastive analysis; statistical methods of analysis; immediate
constituents analysis; distributional analysis and co-occurrence;
transformational analysis; componential analysis; and method of
semantic differential.
Comparative and contrastive
analysis involves the
systematic comparison of two or more philogenically-related and
non-related languages with the aim of finding the similarities and
differences between or among them. The term ‘comparative’ was
first used by Sir William Jones in 1786, in a speech at the Royal
Asiatic Society in Calcutta, India. In his speech, he compared
Sanskrit, Greek, Latin, and Gothic and pointed out that some words
shared similarities. “The comparative method is a technique of
linguistic analysis that compares lists of related words in a
selection of languages” (Denham & Lobeck, 2011, p.361). This
method also helps individuals study the structure of a target
language by comparing it to the structure of their native language.
Specialists
in the field of applied linguistics believe that the most effective
teaching materials are those that are based upon a scientific
description of the target language, carefully compared with a
parallel description of the native language of the learner (Fries,
1957). The
contrastive analysis
is the prediction that a contrastive analysis of structural
differences between two or more languages will allow individuals to
identify areas of contrast and predict where there will be some
difficulty and errors on the part of a second-language learner. The
method helps to predict and explain difficulties individuals may
experience while learning a second language.
The second approach is
statistical,
or quantitative.
It has originated mainly from “the field of psychology where there
has been heavy emphasis on the use of statistics to make
generalizations from samples to populations” (Perry, 2011, p. 79).
A quantitative method is used to represent data in numbers; it is a
study that uses numerical data with emphasis on statistics to answer
the research questions. A quantitative
method differs from a
qualitative method.
Qualitative research does not highlight statistical data. It is a
research done in “a natural setting, involving intensive holistic
data collection through observation at a very close personal level
without the influence of prior theory and contains mostly verbal
analysis” (Perry, 2011, p. 257). A qualitative method may be used
in case studies and discourse analysis.
The term immediate
constituents (IC) was
first used by Leonard Bloomfield in his book, Language.
“The principle of immediate constituents leads us to observe the
structural order, which may differ from their actual sequence”
(Bloomfield, 1935, p. 210). Ginzburg et
al. (1979)
further develop the theory of immediate constituents, and they try to
determine
the ways in which lexical units are relevantly related to one
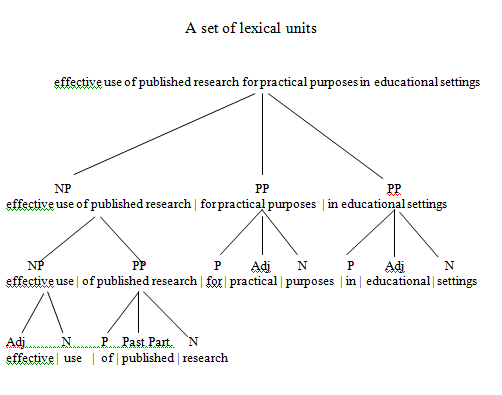
another. For example, the phrase effective
use of published research for practical purposes in educational
settings
may be divided into
the following successive layers – immediate constituents, which in
turn are subdivided into further immediate constituents:
The
purpose of IC analysis is to segment a set of lexical units into
independent sequences, or ICs, thus revealing the hierarchical
structure of this set. “Successive segmentation results in Ultimate
Constituents (UC), i.e. two-facet units that cannot be segmented into
smaller units having both sound-form and meaning” (Ginzburg,
Khidekel,
Knyazeva,
& Sankin,
1979, p. 246).
In the distributional
analysis and
co-occurrence, the term ‘distribution’ means “the occurrence of
a lexical unit relative to other lexical units of the same level
(words relative to words / morphemes relative to morphemes, etc.)
(1979,
p. 246). Lexemes occupy certain positions in a sentence, and if words
are polysemous, they realize their meanings in the context, in
different distributional patterns; for example, compare the verb
chase
in
the phrases chase
around after someone
(to seek someone or something in different places), chase
after someone or something
(to pursue or hunt for someone), chase
someone or something away from some place
(to drive someone or something out of some place), chase
someone or something down
(to track down and seize someone or something), chase
someone in(to) some place
(to drive someone or some creature into a place), and chase
someone and something up
(to seek someone or something out; to look high and low for someone
or something. So, the term ‘distribution’ is “the aptness of a
word in one of its meanings to collocate or to co-occur with a
certain group, or certain groups of words having some common semantic
component” (1979, p. 249). V.
Fromkin, R. Rodman, N. Hyams, and K. M. Hummel (2010)
term this analysis as collocation
analysis when the
presence of one word in the text affects the occurrence of other
words, so a collocation is “the occurrence of two or more words
within a short space of each other in a corpus” (p.432).
Transformational
analysis
in lexicological investigations is the “re-patterning of various
distributional structures in order to discover difference or
similarity of meaning of practically identical distributional
patterns” (Ginzburg,
Khidekel,
Knyazeva,
& Sankin,
1979, p.251). In a number of cases, distributional patterns are
polysemous; therefore, transformational procedures will help to
analyze the semantic similarity
or difference
of the lexemes under examination and the factors that account for
their polysemy. If we compare the compound words highball,
highland, highlight,
and high-rise,
we see that the distributional pattern of stems is identical, and it
may be represented as adj+n
pattern. The first part of the stems modifies or describes the second
part, and these compounds may be assumed as ‘a kind of ball,’ ‘a
kind of land,’ ‘a kind of light,’ and ‘a kind of rise.’
However, this assumption may be wrong because the semantic
relationship between the stems is different; therefore, the lexical
meanings of the words are also different. A transformational
procedure shows that highland
is semantically equivalent to ‘an area of high ground’; highball
is
not a kind of ball but corresponds to “whiskey
and water or soda with ice, served in a tall glass’ or ‘a
railroad signal for a train to proceed at full speed’;
highlight semantically
equals to ‘the part of the surface that catches more light’; and
high-rise
is semantically the same as ‘a building with many stories (Br.
storeys).’ Although distributional structure of these compound
words is similar, the transformational analysis of these words shows
that the semantic relationship between the stems and the lexical
meanings of the words is different. This same approach may be applied
to the analysis of the word-groups, and the result will be the same:
“word-groups of identical distributional structure when
re-patterned also show that the semantic relationship between words
and consequently the meaning of word-groups may be different”
(Ibid,
p.252).
Structural
linguists take a seemingly different approach to the analysis of
lexemes, known as componential
analysis—that
is an analysis in terms of components. This view to the depiction of
meaning of words and phrases is based upon “the thesis that the
sense of every lexeme can be analyzed in terms of a set of more
general sense components (or semantic features)” (Lyons, 1987,
p.317). This term was first used by N.Trubetzkoi (1939) who
introduced componential analysis to phonology. Later, Hjelmslev and
Jakobson applied it to grammar and semantics. In America,
componential analysis was proposed by “anthropologists as a
technique for describing and comparing the vocabulary of kinship in
various languages (as cited in Lyons, 1978, p. 318), and only later
American linguists adopted the method and integrated it into
semantics and syntax. Componential analysis is useful when
identifying similarities and differences among words with related
meanings. F.R. Palmer suggests that sex provides a set of components
for kinship terms. We can add here other components as well:
|
Human |
Male |
Female |
Adult |
Child |
Lineality |
Generation |
|
|
grandmother |
+ |
— |
+ |
+ |
— |
direct |
G1 |
|
grandfather |
+ |
+ |
— |
+ |
— |
direct |
G1 |
|
mother |
+ |
— |
+ |
+ |
— |
direct |
G2 |
|
father |
+ |
+ |
— |
+ |
— |
direct |
G2 |
|
aunt |
+ |
— |
+ |
+ |
— |
collineal |
G2 |
|
uncle |
+ |
+ |
— |
+ |
— |
collineal |
G2 |
|
daughter |
+ |
— |
+ |
+ |
+ |
direct |
G4 |
|
son |
+ |
+ |
— |
+ |
+ |
direct |
G4 |
|
granddaughter |
+ |
— |
+ |
+ |
+ |
direct |
G5 |
|
grandson |
+ |
+ |
— |
+ |
+ |
direct |
G5 |
|
sister |
+ |
— |
+ |
+ |
+ |
collineal |
G3 |
|
brother |
+ |
+ |
— |
+ |
+ |
collineal |
G3 |
|
niece |
+ |
— |
+ |
+ |
+ |
collineal |
G4 |
|
nephew |
+ |
+ |
— |
+ |
+ |
collineal |
G4 |
|
cousin |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
+ |
ablineal |
G3 |
If
we apply componential analysis to living creatures that represent
some kind of ‘proportional’ relationship, the most characteristic
is a three-fold division with many words that refer to living
creatures (Palmer, 1990, p. 109):
|
Man |
Woman |
Child |
Man |
Woman |
Child |
|
cock |
hen |
chick |
gander |
goose |
gosling |
|
bull |
cow |
calf |
lion |
lioness |
cub |
|
boar |
sow |
piglet |
peacock |
peahen |
chick, |
|
buck |
doe |
fawn |
ram |
ewe |
lamb |
The
characteristic of componential analysis is that it attempts “as far
as possible to treat components in terms of binary oppositions”
(Palmer, 1990, p.111), e.g., between an adult and a child, a male and
female, parent and child, animate and inanimate, and other
oppositions.
Words are
related to semantic meaning not only in denotation, as the above
analyses show, but also in connotation. The analysis of the
connotational meanings of words is difficult to do because their
nuances are slight and difficult to grasp, and they do not yield
themselves easily to objective investigation and verification.
Semantic differential, the technique introduced by psycholinguists
Charles Egerton
Osgood, George J. Suci, and Percy H. Tannenbaum,
has been proven to be very effective in establishing and displaying
these differences. “The semantic differential is a combination of
controlled association and scaling procedures” (1957, p. 20). The
participants are provided “a concept to be differentiated and a set
of bipolar adjectival scales against which to do it” (1957, p.20),
and they are tasked to rate a concept, or a term, on a 7-scale
semantic differential for the concept, with the poles described by
two antonymic adjectives (e.g. ‘beautiful’ and ‘ugly’). The
following example illustrates this technique:
Woman
Although
the participants will apply their subjective evaluation, this method
proves to be objective because the procedures are explicit and can be
replicated (1957, p.125).
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
Word-formation: morphological structure and its analysis Lecture 7.
§ 1. The grammar of lexicon When a word first comes into existence it is built out according to the existing patterns of the elements available in the language. Word-formation is that branch of lexicology that studies the derivative structure of existing words and the patterns on which a language builds new words. Words can be divided into smaller sense units which are generally referred to as morphemes (Greek morphe ‘form’ + -erne ‘the smallest distinctive unit’).
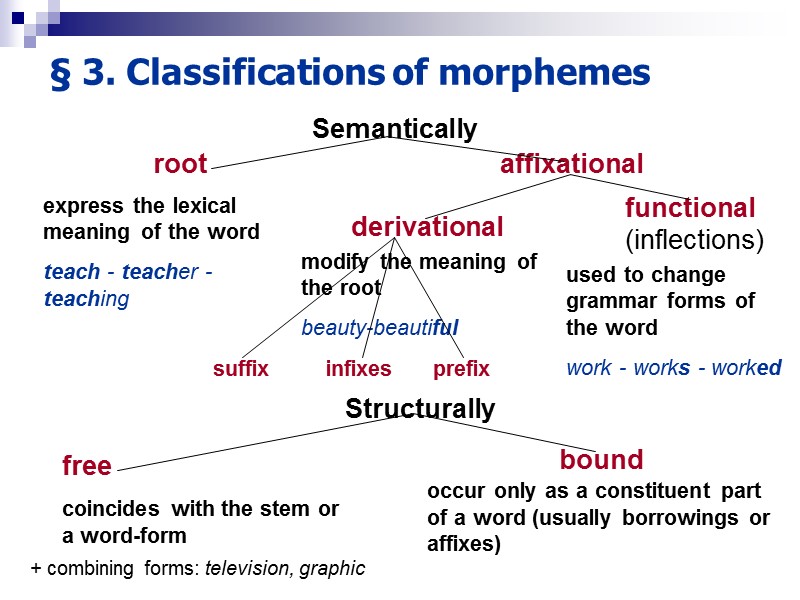
§ 2. Morpheme, allomorph Morphemes are the smallest indivisible two-facet language units not independent (used as parts of words) minimum meaningful language unit (indivisible into smaller meaningful units) abstract meaning Allomorphs (from Greek altos ‘other’) is a positional variant of that or this morpheme occurring in a specific environment. Ex. im- occurs before bilabials (impossible), ir- before r (irregular), il- before I (illegal), in- before all other consonants and vowels (indirect, inability) Ex. [iz] in dishes, [z] in dreams and [s] in books
§ 3. Classifications of morphemes Semantically root affixational express the lexical meaning of the word teach — teacher — teaching derivational functional (inflections) modify the meaning of the root beauty-beautiful used to change grammar forms of the word work — works — worked Structurally free coincides with the stem or a word-form bound occur only as a constituent part of a word (usually borrowings or affixes) suffix prefix infixes + combining forms: television, graphic
§ 4. Morphological types of words simple (root) words — one root morpheme and an inflexion (boy, warm, law, tables, tenth); derived words — one root morpheme, one or several affixes and an inflexion (unmanageable, lawful); compound words — two or more root morphemes and an inflexion (boyfriend, outlaw); compound-derivatives and derivative compounds — two or more root morphemes, one or more affixes and an inflexion (left-handed, warm-hearted, blue-eyed).
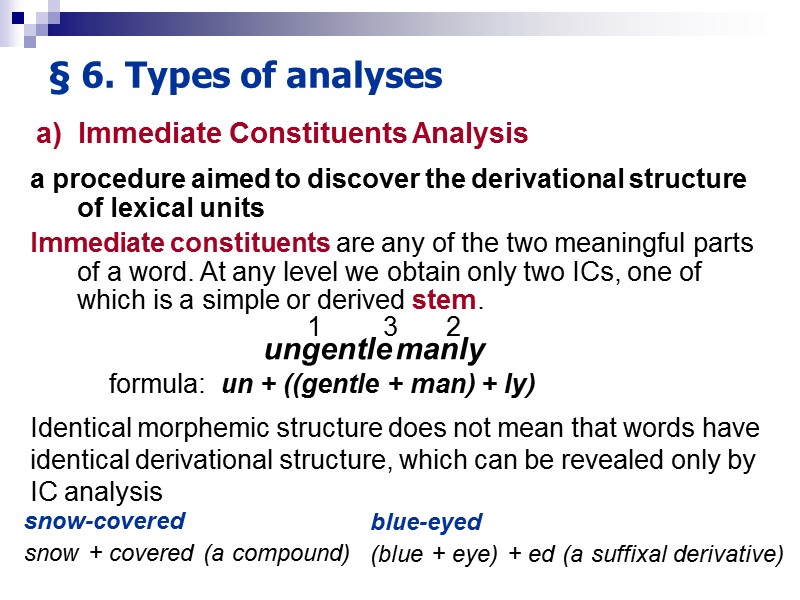
§ 6. Types of analyses a procedure aimed to discover the derivational structure of lexical units Immediate constituents are any of the two meaningful parts of a word. At any level we obtain only two ICs, one of which is a simple or derived stem. formula: un + ((gentle + man) + ly) 2 3 un gentle man ly Identical morphemic structure does not mean that words have identical derivational structure, which can be revealed only by IC analysis snow-covered snow + covered (a compound) blue-eyed (blue + eye) + ed (a suffixal derivative) a) Immediate Constituents Analysis 1
b) Structural Word-formation Analysis studies the structural correlation with other words, the structural patterns or rules on which words are built girl :: girlish = child :: childish = spinster :: spinsterish c) Mоrphemiс Analysis states the number and type of morphemes that make up the word
He gave me the heartiest welcome ever Simple, free, nominal stem coinciding with the root Functional morpheme with the meaning of superlative degree of comparison An allomorph of the morpheme –y, which is a denominal, adjective-forming, bound, derivational morpheme He greeted me cordially Derived, free, adjectival stem De-adjectival, adverb-forming, bound, derivational morpheme Simple, bound, nominal stem = root morpheme De-nominal, adjective-forming, bound, derivational morpheme
§ 5. Types of word-formation Main types Derivation Composition Conversion Minor types Shortening Abbreviation, acronymy Blending Sound interchange Sound imitation Distinctive stress Back-formation
Practical task # 5 1. What term describes the morphemes highlighted in each pair of words: assistance, reference unbearable, audible Homonyms Allomorphs Synonyms
2. Give a TRUE or FALSE answer: Functional morphemes are used to modify lexical meaning of words. Immediate constituents analysis shows how the word was formed. Stems always coincide with foot morphemes.
7 Ways to Teach Word Analysis Every Day
I love teaching word analysis skills because they help kids become stronger readers. Learning strategies to figure out the meaning of new words helps students become more confident and independent in their reading. And as they increase their vocabularies, their reading comprehension improves.
But with increasingly harder vocabulary in the upper elementary grades, word analysis can be really challenging for students. So how can we make time for students to practice and improve their word-solving skills all year long?
What Are Word Analysis Skills?
When students use word analysis skills, they are independently using strategies and resources to figure out what unfamiliar words and phrases mean.
Here are specific word analysis skills you might teach to 3rd, 4th, and 5th graders:
- use context clues
- differentiate among multiple meanings of words
- use knowledge of roots, prefixes, suffixes, synonyms, antonyms, and homophones
- use word reference materials (dictionary, glossary, thesaurus)
- identify figurative language

.
How Do We Make Word Analysis Part of the Daily Routine?
Here are some ways that I’ve made word analysis instruction a part of the daily routine so students keep using these skills all year long:
Get Kids Reading
The single best thing kids can do is read different types of text (fiction, nonfiction, poetry, literary nonfiction, functional text, etc.) at different levels. Independent reading, guided reading groups, and literature circles are all opportunities to use vocabulary skills.
As they’re reading, students can use sticky notes and graphic organizers to show the word analysis strategies they used to figure out different words.
Read Aloud
A daily read-aloud is an easy place to incorporate word analysis practice. As you read a chapter book or mentor text, you can model how you stop at an unfamiliar word and infer its meaning using different clues and strategies. After a few examples, you can have students try this out.
Use Anchor Charts and Word Walls
I LOVE using word analysis anchor charts. I use them when I first teach all of the different strategies and keep them up all year long so students can refer back to them. Mini anchor charts in reading notebooks also work if you’re short on wall space!

You can also create a word wall for synonym and antonym pairs, homophone pairs, and common affixes. I like using interactive word walls that students can add to when they find examples in their reading. They can jot them on a sticky note and add them to the wall.
Use Warmup Questions
Starting each day with a word analysis question is a quick and easy spiral review method. I love showing a daily warmup question on the interactive whiteboard and having students answer on their own whiteboards. Stand-alone analysis questions (questions that don’t require reading a passage) are also great to use as time fillers when you have a few extra minutes.
Need help coming up with questions? Grab a free word analysis question stems list below!

Try a Vocabulary Word of the Day
A vocabulary word of the day is another great activity. You can ask students to segment a word into its root word and affixes, come up with a synonym or antonym for a word, etc. It can go up on your whiteboard, be included in a morning message, or even be an “entrance ticket” to enter the classroom. You can make it more fun by challenging students to use the word in their normal conversations.
This is also a good way to review previously taught vocabulary words. Multiple exposures to words in different scenarios will help expand kids’ vocabularies and get them reviewing all those word-solving skills!
Use Literacy Station Activities
If you have word work stations, morning work bins, early finisher options, or centers, you can easily add some quick individual or partner activities that get kids using their word analysis strategies. Here are a few ideas to try:
- file folder games
- crosswords and word searches
- task cards
- sorting activities
- vocabulary word scavenger hunts
- poem of the day/week
- holiday/seasonal themed activities
- board games like Scrabble

If you have laptops or iPads handy, you can also have students practice using online word reference tools. But keep in mind that they’re set up differently than print resources. My students always needed needed a lot of practice with both.
Bring Other Content Areas into Language Arts
Students are certainly going to come across new words in areas like science, social studies, and math. Using short, leveled content-focused passages in reading groups is a helpful way to introduce vocabulary they’ll need to learn. The key is making sure they have enough background knowledge to grasp the majority of the content. We don’t want every word to be new!
I also like to have students create a class glossary or dictionary of terms they learn throughout a unit.
The biggest way to incorporate word analysis skills in your classroom all year long is to have kids read, read, read and to read, read, read to them! The more they come across new words and phrases, the more opportunities they have to figure out what they mean. Doing a spiral review of word solving skills like using context clues, word parts, and word reference sources will keep kids actively working to solve those unknown word meanings all year long.