Presentation on theme: «Word Stress in English.»— Presentation transcript:
1
Word Stress in English
2
Word Stress in English Word stress is your magic key to understanding spoken English. Native speakers of English use word stress naturally. Word stress is so natural for them that they don’t even know they use it. Non-native speakers who speak English to native speakers without using word stress, encounter two problems: They find it difficult to understand native speakers, especially those speaking fast. 2.The native speakers may find it difficult to understand them.
3
Understanding Syllables
To understand word stress, it helps to understand syllables. Every word is made from syllables. Each word has one, two, three or more syllables. word number of syllables Dog 1 Green Quite Quiet Qui-et 2 Orange Or-ange Table Ta-ble Expensive Ex-pen-sive 3 Interesting In-ter-est-ing 4 realistic Re-al-is-tic unexceptional Un-ex-cep-tion-al 5 Notice that (with a few rare exceptions) every syllable contains at least one vowel (a, e, i, o or u) or vowel sound.
4
What is Word Stress? In English, we do not say each syllable with the same force or strength. In one word, we accentuate ONE syllable. We say one syllable very loudly (big, strong, important) and all the other syllables very quietly. Let’s take 3 words: photograph, photographer and photographic. Do they sound the same when spoken? No. Because we accentuate (stress) ONE syllable in each word. And it is not always the same syllable. So the shape of each word is different. click word to hear shape total syllables stressed syllable PHO TO GRAPH 3 #1 PHO TO GRAPH ER 4 #2 PHO TO GRAPH IC #3
5
This happens in ALL words with 2 or more syllables: TEACHer, JaPAN, CHINa, aBOVE, converSAtion, INteresting, imPORtant, deMAND, etCETera, etCETera, etCETera The syllables that are not stressed are ‘weak’ or ‘small’ or ‘quiet’. Native speakers of English listen for the STRESSED syllables, not the weak syllables. If you use word stress in your speech, you will instantly and automatically improve your pronunciation and your comprehension. Try to hear the stress in individual words each time you listen to English — on the radio, or in films for example. Your first step is to HEAR and recognise it. After that, you can USE it! There are two very important rules about word stress: One word, one stress. (One word cannot have two stresses. So if you hear two stresses, you have heard two words, not one word.) The stress is always on a vowel.
6
Why is Word Stress Important?
Word stress is not used in all languages. Some languages, Japanese or French for example, pronounce each syllable with eq-ual em-pha-sis. Other languages, English for example, use word stress. Word stress is not an optional extra that you can add to the English language if you want. It is part of the language! English speakers use word stress to communicate rapidly and accurately, even in difficult conditions. If, for example, you do not hear a word clearly, you can still understand the word because of the position of the stress. Think again about the two words photograph and photographer. Now imagine that you are speaking to somebody by telephone over a very bad line. You cannot hear clearly. In fact, you hear only the first two syllables of one of these words, photo… Which word is it, photograph or photographer? Of course, with word stress you will know immediately which word it is because in reality you will hear either PHOto… or phoTO… So without hearing the whole word, you probably know what the word is (PHOto…graph or phoTO…grapher). It’s magic! (Of course, you also have the ‘context’ of your conversation to help you.) This is a simple example of how word stress helps us understand English. There are many, many other examples, because we use word stress all the time, without thinking about it.
7
Where do I Put Word Stress?
There are some rules about which syllable to stress. But…the rules are rather complicated! Probably the best way to learn is from experience. Listen carefully to spoken English and try to develop a feeling for the «music» of the language. When you learn a new word, you should also learn its stress pattern. If you keep a vocabulary book, make a note to show which syllable is stressed. If you do not know, you can look in a dictionary. All dictionaries give the phonetic spelling of a word. This is where they show which syllable is stressed, usually with an apostrophe (‘) just before or just after the stressed syllable. (The notes at the front of the dictionary will explain the system used.) Look at (and listen to) this example for the word plastic. There are 2 syllables. Syllable #1 is stressed. example phonetic spelling: dictionary A phonetic spelling: dictionary B PLAS TIC /plæs’tIk/ /’plæs tIk/
8
Rules of Word Stress in English
There are two very simple rules about word stress: One word has only one stress. (One word cannot have two stresses. If you hear two stresses, you hear two words. Two stresses cannot be one word. It is true that there can be a «secondary» stress in some words. But a secondary stress is much smaller than the main [primary] stress, and is only used in long words.) We can only stress vowels, not consonants. Here are some more, rather complicated, rules that can help you understand where to put the stress. But do not rely on them too much, because there are many exceptions. It is better to try to «feel» the music of the language and to add the stress naturally.
9
Stress on first syllable
rule example Most 2-syllable nouns PRESent, EXport, CHIna, TAble Most 2-syllable adjectives PRESent, SLENder, CLEVer, HAPpy 2. Stress on last syllable rule example Most 2-syllable verbs to preSENT, to exPORT, to deCIDE, to beGIN There are many two-syllable words in English whose meaning and class change with a change in stress. The word present, for example is a two-syllable word. If we stress the first syllable, it is a noun (gift) or an adjective (opposite of absent). But if we stress the second syllable, it becomes a verb (to offer). More examples: the words export, import, contract and object can all be nouns or verbs depending on whether the stress is on the first or second syllable.
10
Stress on penultimate syllable (penultimate = second from end)
rule example Words ending in -ic GRAPHic, geoGRAPHic, geoLOGic Words ending in -sion and -tion teleVIsion, reveLAtion For a few words, native English speakers don’t always «agree» on where to put the stress. For example, some people say teleVIsion and others say TELevision. Another example is: CONtroversy and conTROversy.
11
Stress on ante-penultimate syllable
(ante-penultimate = third from end) rule example Words ending in -cy, -ty, -phy and -gy deMOcracy, dependaBIlity, phoTOgraphy, geOLogy Words ending in -al CRItical, geoLOGical 5. Compound words (words with two parts) rule example For compound nouns, the stress is on the first part BLACKbird, GREENhouse For compound adjectives, the stress is on the second part bad-TEMpered, old-FASHioned For compound verbs, the stress is on the second part to underSTAND, to overFLOW
Скачать материал

Скачать материал




- Сейчас обучается 268 человек из 64 регионов




Описание презентации по отдельным слайдам:
-
1 слайд
Word stress in English
-
2 слайд
Nature of word stress
The sequence of syllables in the word is not pronounced identically.
The syllable or syllables which are uttered with more prominence than the other syllables of the word are said to be stressed or accented. -
3 слайд
Accentual structure of the word or its stress pattern
the correlation of varying prominences of syllables in a word -
4 слайд
Definition of stress
is different by different authors:
an increase of energy, accompanied by an increase of expiratory and articulatory activity (B.A. Bogoroditsky).
the degree of force, which is accompanied by a strong force of exhalation and gives an impression of loudness (D. Jones). -
5 слайд
Definition of stress
stress is connected with the force of breath (H. Sweet).
the effect of prominence is achieved by any or all of four factors: force, tone, length and vowel colour (A.C. Gimson). -
6 слайд
The dynamic stress implies greater force with which the syllable is pronounced.
↓ ↓
articulation of the stressed syllable → greater muscular energy is produced by the speaker. -
7 слайд
Stress in different languages
English, German, French, Russian → possess predominantly dynamic word stress.
In Scandinavian languages the word stress is considered to be both dynamic and musical. For instance, in Swedish, the word komma (comma) is distinguished from the word komma (come) by a difference in tones.
The musical (or tonic) word stress is observed in Chinese, Japanese, Vietnamese. -
8 слайд
Types of word stress
special prominence in a stressed syllable is achieved mainly through the intensity of articulation → dynamic, or force stress.
special prominence in a stressed syllable is achieved mainly through the change of pitch, or musical tone → musical, or tonic. -
9 слайд
Types of word stress
special prominence in a stressed syllable is achieved through the changes in the quantity of the vowels, which are longer in the stressed syllables than in the unstressed ones quantitative.
changes in the quality of the vowel under stress → qualitative -
10 слайд
English word stress or accent is a complex phenomenon
traditionally defined as dynamic, but the special prominence of the stressed syllables is manifested also through the changes in the vowel quantity, consonant and vowel quality and pitch of the voice.
↓ ↓ -
11 слайд
English word stress
is marked by the variations in
force,
pitch,
quantity,
quality. -
12 слайд
contract [‘kσntrækt], to contract [kən’trækt]
in the stressed syllable:
the force is greater, which is connected with more energetic articulation;
the pitch of voice is higher, which is connected with stronger tenseness of the vocal cords and the walls of the resonance chamber; -
13 слайд
contract [‘kσntrækt], to contract [kən’trækt]
the quantity of the vowel [æ] in [kən’trækt] is greater, the vowel becomes longer;
the quality of the vowel [æ] in the stressed syllable is different from the quality of this vowel in the unstressed position, in which it is more narrow than [æ]. -
14 слайд
Three groups of words with identical spelling
A.C.Gimson
words represent different parts of speech which are opposed by means of shifting of the stress. -
15 слайд
First group
A small group of words where the noun is differentiated from a verb by the opposition of the accentual pattern of the word alone
increase [‘ınkri:s] – [ın’kri:s]
insult [‘ınsʌlt] – [ın’sʌlt] -
16 слайд
Second group
The shifting of the stress which means the change of the accentual pattern of the word may be or may not be accompanied by the reduction of the vowel in the unstressed syllable of the verbs
transport [‘trænspo:t] – [træns’po:t] or [trǝns’po:t]
torment [‘to:ment] – [to:’ment] or [tǝ’ment] -
17 слайд
Third group
The largest group manifests the change of their accentual pattern together with the qualitative reduction of the unstressed vowel
combine [‘kombaın] – [kǝm’baın]
conduct [‘kondʌkt] – [kǝn’dʌkt] -
18 слайд
A terminological confusion
heaviness, sound pressure, force, power, strength, intensity, amplitude, prominence, emphasis, accent, stress → are used synonymously by most writers
↓ ↓
drawback of any theory of stress based on production of speech → gives a partial explanation, does not analyze on the perceptive level. -
19 слайд
On the acoustic level
the counterpart of force is the intensity of the vibrations of the vocal cords of the speaker which is perceived by the listener as loudness
→ the greater energy is associated by the listener with greater loudness.
The acoustic counterparts of voice pitch and length are frequency and duration respectively. -
20 слайд
Russian accentual structure English accentual structure
-
21 слайд
The stressed syllables → the most prominent syllables
the notions «stressed» and «prominent» should not be used synonymically (G.P. Torsuev)
The effect of prominence is created by some phonetic features of sounds which have nothing to do with word or sentence stress. -
22 слайд
Sounds of speech have different degrees of sonority
Vowels are more sonorous than consonants.
Open vowels are more sonorous than close ones.
→ inner quality of vowels
→ not directly connected with the accentual structure of words but with other articulatory characteristics
→ it contributes to the effect of prominence. -
23 слайд
Historical (traditional) length of vowels
also adds to the effect of prominence but is not connected with the word stress
↓ ↓
prominence in speech is a broader term than stress -
24 слайд
Stress difficulties peculiar to the accentual structure
are connected with the vowel special and inherent prominence.
In identical positions the intensity of English vowels is different.
The highest in intensity is [a:], then go [о:, з:, i:, u:, æ, σ, e, υ, ı]. -
25 слайд
Peculiarities of sounds in accented syllables
[ə] is never stressed
[i, e, υ] tend to occur in unstressed syllables
Syllables with the syllabic [l, m, n] are never stressed
Unstressed diphthongs may partially lose their glide quality.
In stressed syllables English stops have complete closure, fricatives have full friction, and features of fortis/lenis distinction are clearly defined.
Найдите материал к любому уроку, указав свой предмет (категорию), класс, учебник и тему:
6 210 158 материалов в базе
- Выберите категорию:
- Выберите учебник и тему
- Выберите класс:
-
Тип материала:
-
Все материалы
-
Статьи
-
Научные работы
-
Видеоуроки
-
Презентации
-
Конспекты
-
Тесты
-
Рабочие программы
-
Другие методич. материалы
-
Найти материалы
Другие материалы
- 27.12.2020
- 3366
- 1
- 27.12.2020
- 4749
- 2
- 27.12.2020
- 4947
- 11
- 27.12.2020
- 5785
- 13
- 27.12.2020
- 5022
- 9
- 27.12.2020
- 4057
- 1
- 27.12.2020
- 3882
- 0
- 27.12.2020
- 3905
- 1
Вам будут интересны эти курсы:
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Организация и предоставление туристских услуг»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Клиническая психология: теория и методика преподавания в образовательной организации»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Организация практики студентов в соответствии с требованиями ФГОС юридических направлений подготовки»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Этика делового общения»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Правовое регулирование рекламной и PR-деятельности»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Использование активных методов обучения в вузе в условиях реализации ФГОС»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Мировая экономика и международные экономические отношения»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Организация деятельности специалиста оценщика-эксперта по оценке имущества»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Организация деятельности по водоотведению и очистке сточных вод»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Международные валютно-кредитные отношения»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Осуществление и координация продаж»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Гражданско-правовые дисциплины: теория и методика преподавания в образовательной организации»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Управление качеством»
Lecture 5
Изображение слайда
General Notes on Word Stress.
Types of Word Stress.
Degrees of Word Stress.
Placement of Word Stress.
Common Rules of Word Stress in English.
Functions of Word Stress.
Изображение слайда
3
Слайд 3: The Nature of Word Stress
Изображение слайда
4
Слайд 4: The Nature of Word Stress
Word Stress
is a greater degree of prominence of a syllable or syllables as compared to the other syllables of the word
Изображение слайда
5
Слайд 5: The Nature of Word Stress
Scientists about Word Stress:
D. Jones: Word Stress is the degree of force, which is accompanied by a strong force of exhalation and gives an impression of loudness.
A. C. Gimson: English word stress or accent is a complex phenomenon, marked by the variations in force, pitch, quality and quantity.
Изображение слайда
6
Слайд 6: The Nature of Word Stress
Scientists about Word Stress:
B. A. Bogoroditsky : Stress as an increase of energy, accompanied by an increase of expiratory and articulatory activity.
S. F. Leontyeva : Word stress can be defined as the singling out of one or more syllables in a word, which is accompanied by the change of the force of utterance, pitch of the voice, qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the sound which is usually a vowel.
Изображение слайда
7
Слайд 7: The Nature of Word Stress
The effect of prominence of the stressed syllable is achieved by a number of phonetic parameters:
Pitch
Loudness
Length
Vowel Quality
These 4 factors usually work together in combination, but they are not equally important. The strongest effect is produced by pitch and length.
Изображение слайда
8
Слайд 8: The Nature of Word Stress
In the stressed syllable:
the force of utterance is greater, which is connected with more energetic articulation;
the pitch of the voice is higher, which is connected with stronger tenseness of the vocal cords and the walls of resonance cavity;
the quantity of the vowel is greater, the vowel becomes longer;
the quality of the vowel is different (in unstressed syllables it is usually narrow).
Изображение слайда
9
Слайд 9: The Nature of Word Stress
Word Stress
is singling out of one or more syllables in a word, which is accompanied by the change of the force of utterance, pitch of the voice, qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the sound, which is usually a vowel.
Изображение слайда
10
Слайд 10: Types of Word Stress
Изображение слайда
11
Слайд 11: Types of Word Stress
We distinguish the following types of Word Stress:
dynamic (force) stress is achieved by greater force with which the syllable is pronounced (Russian, English, French, German);
musical (tonic) stress is achieved through the change of pitch/musical tone (Japanese, Korean);
quantitative stress is achieved through the changes in the quantity of the vowels, which are longer in the stressed syllables (Russian);
qualitative stress is achieved through the changes in the quality of the vowel (Russian).
Изображение слайда
12
Слайд 12: Types of Word Stress
English Word Stress
is traditionally defined as dynamic, but in fact, the special prominence of the stressed syllables is manifested not only through the increase of intensity, but also through the changes in the vowel quantity, consonant and vowel quality and pitch of the voice.
Изображение слайда
13
Слайд 13: Degrees of Word Stress
Изображение слайда
14
Слайд 14: Degrees of Word Stress
The syllables in a word are characterized by different degrees of prominence. There are as many degrees of stress in a word as there are syllables.
In English there are 3 degrees of stress :
primary (strong, main, principal);
secondary (half-stressed, half-strong);
weak (unstressed).
Изображение слайда
15
Слайд 15: Degrees of Word Stress
In American English there are 4 degrees of stress :
primary (strong, main, principal);
secondary (half-stressed, half-strong);
tertiary (on the last but one syllable in the words with suffixes -ary, -ory, -ony : ´ dictio ˏ nary.
weak (unstressed).
Изображение слайда
16
Слайд 16: Degrees of Word Stress
In transcription stress is indicated by placing the stress mark before the symbol of the first sound of the stressed syllable.
Primary stress is marked by a raised short vertical stroke and secondary stress is marked by a lowered one:
examination [ɪg ˏ zᴂmɪ ´ neɪʃ(ǝ)n]
Изображение слайда
17
Слайд 17: Placement of Word Stress
Изображение слайда
18
Слайд 18: Placement of Word Stress
According to its placement in a word,
stress can be:
fixed
free
shifting
Изображение слайда
19
Слайд 19: Placement of Word Stress
Fixed
(the position of the word stress is always the same,
it is restricted to a particular syllable):
in French (the last syllable),
in Finnish and Czech (the first syllable),
in Polish (the last but one syllable).
Изображение слайда
20
Слайд 20: Placement of Word Stress
Free
(the location of the word stress is not
confined to a specific position,
it can fall on any syllable of the word):
English, Russian, Italian, Greek, Spanish, etc.
Изображение слайда
21
Слайд 21: Placement of Word Stress
Shifting
(the word stress can change
its position in different forms
of the word and its derivatives):
´ music — mu ´ sician
Изображение слайда
22
Слайд 22: Placement of Word Stress
To define the position of word stress
it is necessary to take into account
a number of factors :
phonological structure of the syllable;
the number of syllables in a word;
morphological factor;
the part of speech the word belongs to;
the semantic factor.
Изображение слайда
23
Слайд 23: Placement of Word Stress
The phonological structure of the syllable is related to the status of a particular syllables in terms of the degree of sonority.
The sounds that possess a greater degree of sonority contribute to the greater prominence of the syllable. A syllable is strong when it contains a long vowel or a diphthong or a short vowel followed by two consonants:
a ´ rrive — de ´ velop
Изображение слайда
24
Слайд 24: Placement of Word Stress
The number of syllables in a word influences the number of stresses and the position of stress.
There are stress patterns typical of two-syllable words, three-syllable words and so on.
In multi-syllable words there appears secondary stress.
Изображение слайда
25
Слайд 25: Placement of Word Stress
Morphological factor shows that in complex words the placement of stress depends on the type of suffix.
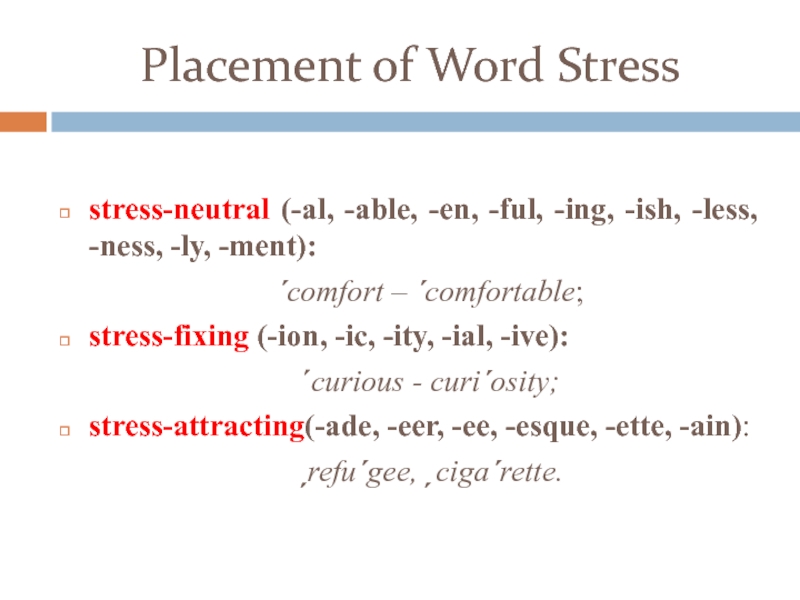
Suffixes are divided into:
stress-neutral (which do not affect the stress placement in the stem);
stress-fixing (which influence stress in the stem);
stress-attracting (which carry stress themselves).
Изображение слайда
26
Слайд 26: Placement of Word Stress
stress-neutral (-al, -able, -en, — ful, — ing, — ish, -less, — ness, — ly, — ment ):
´ comfort – ´ comfortable ;
stress-fixing (-ion, — ic, — ity, — ial, — ive ):
´ curious — curi ´ osity ;
stress-attracting (- ade, — eer, — ee, — esque, — ette, — ain ) :
ˏ refu ´ gee, ˏ ciga ´ rette.
Изображение слайда
27
Слайд 27: Placement of Word Stress
The grammatical category the word belongs to:
´contrast – to con´trast
´habit – ha´bitual
´music – mu´sician
´insult – to in´sult
´record – to re´cord
´present – to pre´sent
Изображение слайда
28
Слайд 28: Placement of Word Stress
The semantic factor (for compound words and words with the so-called separable prefixes).
The majority of such words have two equally strong stresses, both stressed parts are considered to be of equal semantic importance:
compound adjectives: ´ hard- ´ working, ´ blue- ´ eyed,
verbs with post positions : ´ sit ´ down, ´ take ´ off,
numerals from 13 to 19: ´ four ´ teen, ´ six ´ teen.
Изображение слайда
29
Слайд 29: Common Rules of Word Stress
Изображение слайда
30
Слайд 30: Common Rules of Word Stress
Two-syllable words (verbs, adjectives, adverbs):
the second syllable is stressed if it contains a long vowel or a diphthong, or if it ends with more than one consonant: a ´ pply, a ´ ssist. But! ´ hone st.
the first syllable is stressed if the final syllable contains a short vowel and one (or no) final consonant: ´ enter, ´ open.
Two-syllable words (nouns):
the first syllable is stressed if the second syllable contains a short vowel: ´ money ;
the second syllable is stressed if the second syllable contains a long vowel or a diphthong : es ´ tate.
Изображение слайда
31
Слайд 31: Common Rules of Word Stress
Three-syllable words (verbs):
the last but one syllable is stressed if the last syllable contains a short vowel and ends with one consonant: de ´ termine.
the final syllable is stressed if it contains a long vowel or a diphthong, or ends with more than one consonant: enter´tain.
Изображение слайда
32
Слайд 32: Common Rules of Word Stress
Three-syllable words (nouns, adjectives):
the middle syllable is stressed if the syllable preceding the final syllable contains a long vowel or a diphthong, or if it ends with more than one consonant:
di ´ saster ;
the first syllable is stressed if the final syllable contains a short vowel and the middle syllable contains a short vowel and ends with not more than one consonant:
´ cinema
´insolent
Изображение слайда
33
Слайд 33: Common Rules of Word Stress
Words with prefixes:
in words with prefixes the primary stress typically falls on the syllable following the prefix:
im ´ possible, re ´ call ;
in words with prefixes with their own meaning, the place of secondary stress is on the prefix:
ˏ ex- ´ minister.
in prefixal verbs which are distinguished from similarly spelt nouns and adjectives, the second syllable is stressed:
to in ´ crease – ´ increase.
Изображение слайда
34
Слайд 34: Common Rules of Word Stress
Words with suffixes:
suffixes -esce, -esque, -ate, -ize, -fy, -ette, -ique, -ee, -eer, — ade have stress on themselves or the preceding syllable:
ˏ mari ´ nade, ˏ specia ´ lize ;
suffixes -ical, -ic, -ion, -ity, -ial, -cient, -iency, -eous,-ual, -uous, -ety, -itous, -ive, -ative, -itude, -ident, -inal, -wards have stress on the preceding syllable:
eco ´ nomic, ma ´ jority.
Изображение слайда
35
Слайд 35: Common Rules of Word Stress
Words of 4 or more syllables:
The stress is on the antepenultimate syllable (third from the end):
e ´ mergency
his ´ torical
Изображение слайда
36
Слайд 36: Common Rules of Word Stress
Compound words:
The first element is stressed when:
Compounds are written as one word : ´ bedroom.
Nouns are compounded of a verb and an adv.: ´ make-up.
The second element is stressed when:
Food items have the first element which is of a material used in manufacturing the whole : ˏ apple ´ tart.
Parts of the house are implied : ˏ front ´ door.
Изображение слайда
37
Слайд 37: Common Rules of Word Stress
Compound words:
The first element is stressed when:
Adjectives with past participle characterize people :
ˏ thick- ´ skinned.
Nouns ending in -er, -ing are followed by adverbs :
ˏ passer ´ by.
The first element of compounds is a number:
second- ´ class, three — ´ wheeler.
Compound function as an adverb :
head- ´ first.
Изображение слайда
38
Слайд 38: Common Rules of Word Stress
The most common types of English stress pattern
´_ _ (´after)
_´_ (be´fore)
´_ _ _ (´family)
_´_ _ (im´portance)
Some words have 2 variants of stress:
ki ´ lometer – ´ kilometer
Изображение слайда
39
Слайд 39: Functions of Word Stress
Изображение слайда
Изображение слайда
41
Слайд 41: Functions of Word Stress
The constitutive function:
word stress organizes the syllables into a word
The recognitive ( identicatory ) function:
word stress makes it possible to identify and recognize a word in the chain of speech.
The distinctive function:
word stress is capable of differentiating the meaning of words or their forms: ´ import — im ´ port.
Изображение слайда
What is WORD STRESS?
What types of word stress do you know?
How does stress perform constitutive, distinctive and recognitive function?
What is the terminology suggested by different authors to distinguish between different degrees of word stress?
What factors determine the place of word stress?
Изображение слайда
Леонтьева С.Ф. Теоретическая фонетика современного английского языка (на англ. яз.) /С.Ф. Леонтьева.- М., 2002. – 336 с.
Соколова М.А. Практическая фонетика английского языка /М.А. Соколова. – М.: Гуманит. изд. центр ВЛАДОС, 1997. – 384 с.
O’Connor L.D. Phonetics /L.D. O’Connor. Penguin, 1977.
Sokolova M.A. English Phonetics. A theoretical course /M.A. Sokolova. M., 1996. – 286 p.
Vassilyev V.A. English Phonetics: A theoretical Course /V.A. Vassilyev. M., 1980. – 323 p.
Изображение слайда
44
Последний слайд презентации: Word Stress: Thank you for your attention!
Изображение слайда
- Размер: 52.5 Кб
- Количество слайдов: 25











![contract ['kσntrækt], to contract [k n'trækt]ə in the stressed syllable: • the contract ['kσntrækt], to contract [k n'trækt]ə in the stressed syllable: • the](https://present5.com/docs//12_word_stress_in_english_images/12_word_stress_in_english_11.jpg)
![contract ['kσntrækt], to contract [k n'trækt]ə • the quantity of the vowel [æ] contract ['kσntrækt], to contract [k n'trækt]ə • the quantity of the vowel [æ]](https://present5.com/docs//12_word_stress_in_english_images/12_word_stress_in_english_12.jpg)











![Peculiarities of sounds in accented syllables • [ ] is never stressedə • Peculiarities of sounds in accented syllables • [ ] is never stressedə •](https://present5.com/docs//12_word_stress_in_english_images/12_word_stress_in_english_24.jpg)
Оцените презентацию от 1 до 5 баллов!
-
Тип файла:
ppt / pptx (powerpoint)
-
Всего слайдов:
16 слайдов
-
Для класса:
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11
-
Размер файла:
202.59 kB
-
Просмотров:
55
-
Скачиваний:
5
-
Автор:
неизвестен
Слайды и текст к этой презентации:
№1 слайд
Содержание слайда: Word stress
Stress is the relative emphasis that may be given to certain syllables in a word, or to certain words in a phrase or sentence. The term is also used for similar patterns of phonetic prominence inside syllables. The word accent is sometimes also used with this sense.
№2 слайд
Содержание слайда: SO…
Word stress (WS) can be defined as the
singling out of one or more syllables in a
word, which is accompanied by the
change of the force of utterance, pitch of
the voice, qualitative and quantitative
characteristics of the sound which is usually
a vowel.
№3 слайд
Содержание слайда: If we compare stressed and unstressed syllables in the two contract, we may note that in the stressed syllable:
the force of utterance is greater, which is connected with more energetic articulation;
the pitch of the voice is higher, which is connected with stronger tenseness of the vocal cords and the walls of the resonance chamber
the quantity of the vowel is greater, a vowel becomes longer;
the quality of the vowel !& in the stressed syllable is different from the quality of this vowel in the unstressed position, in why it is more narrow than.
№4 слайд
Содержание слайда: The phonetic manifestation of stress varies from language to language. In different languages one of the factors constituting word stress is usually more significant than the others. According to the most salient feature the following types of word stress are distinguished in different languages:
dynamic or force stress if special prominence in a stressed syllable(syllables) is achieved mainly through the intensity of articulation;
musical or tonic stress if special prominence is achieved mainly through the change of pitch, or musical tone.
quantitative stress if special prominence is achieved through the changes in the quantity of the vowels, which are longer in the stressed syllables than in the unstressed ones.
qualitative stress if special prominence is achieved through the changes in the quality of the vowel under stress. Vowel reduction is often used as a manipulation of quality in unstressed syllables.
№5 слайд
Содержание слайда: Place and degrees of Word Stress
One of the ways of reinitiating the
prominence of syllables is
manipulating the degree of stress.
There is controversy about degrees
of WS in English and their
terminology. Strictly speaking,
polysyllabic word has as many
degrees of stress as there are
syllables in it.
Designating strongest syllable by 1, the second strongest by 2, etc., we may represent the distribution Jesses in the following example:
examination indivisibility
igzemineSin indivizibiloti
32415 2536174
№6 слайд
Содержание слайда: The American scholars bloch & trager distinguish 4 types of WS
Other American linguists also distinguish four degrees of word stress but term them:
Loud
Reduced loud
Medial
Weak
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Weak
№7 слайд
Содержание слайда: Stress can be characterized as fixed and free. In languages with fixed type of stress the place of stress is always the same.
In English and Russian word-stress is free, that is it may fall any syllable in a word;
Stress in English and in Russian is not only free but also shifting. In both languages the place of stress may shift, which helps to differentiate different parts of speech, e.g. `insult—to in`sult, `import—to im`port.
№8 слайд
Содержание слайда: Examples of shifting:
preSENT (verb) – PRESent (noun)
reFER (verb) – REFerence (noun)
exTRACT (verb) – EXtract (noun)
inCREASE (verb) – INcrease (noun)
OBject (noun) – obJECT (verb)
№9 слайд
Содержание слайда: Functions and tendencies of the English stress
1. Word stress constitutes a word, it organizes
the syllables of a word Into a language unit
having a definite accentual structure, that is
a pattern of relationship among the syllables;
a word does not exist without the word stress.
Thus the word stress performs the constitutive
function. Sound continuum becomes a phrase
when it is divided into units organized by word
stress into words.
№10 слайд
Содержание слайда: 2. Word stress enables a person to identify a
2. Word stress enables a person to identify a
succession of syllables as a definite accentual
pattern of a word. This function of word stress
as known as identificatory(or recognitive).
Correct accentuation helps the listener to make the process of communication easier, whereas the distortedaccentual pattern of words, misplaced word stresses prevent normal understanding.
№11 слайд
Содержание слайда: 3. Word stress alone is capable of differentiating the meaning of words or their forms, thus performing its distinctive function. The accentual patterns of words or the degrees of word stress and their positions form oppositions, e.g. ‘import — im’port, ‘billow — below.
3. Word stress alone is capable of differentiating the meaning of words or their forms, thus performing its distinctive function. The accentual patterns of words or the degrees of word stress and their positions form oppositions, e.g. ‘import — im’port, ‘billow — below.
№12 слайд
Содержание слайда: T
e
n
d
e
n
c
I
e
s
of WS
Recessive. The accentual structure of English words is liable to instability due to the different origin of several layers in the Modern English word-stock. In Germanic languages the word stress originally fell on the initial syllable or the second syllable, the root syllable in the English words with prefixes. It is seen in the native English words having no prefix, e.g. mother, daughter, brother, swallow; in assimilated French borrowings, e.g. reason, colour, restaurant etc.
Rhythmical. The rhythm of alternating stressed and unstressed syllables gave birth to the rhythmical tendency in the present-day English which caused the appearance of the secondary stress in the multisyllabic French borrowings, e.g. revolution, organi’sation, assimilation, etc.
Retentive. Was traced in the instability of the accentual structure of English word stress: a derivative often retains the stress of the original or parent word, e.g. ‘similar — as’simitate, recom’mend — recommen ‘dation.
№13 слайд
Содержание слайда: Typology of accentual structures
The numerous variations of English word stress are systematized in the typology of accentual structure of English words worked out by G.P. Torsuyev. He classifies them according to the number of stressed syllables, their degree or character (the main and the secondary stress). The distribution of stressed syllables within the word accentual types forms accentual structures of words. Accentual types and accentual structures are closely connected with the morphological type of words, with the number of syllables, the semantic value of the root and the prefix of the word.
№14 слайд
Содержание слайда: 1. [‘___]. This accentual type marks both simple and compound words. The accentual structures of this type may include two and more syllables,
1. [‘___]. This accentual type marks both simple and compound words. The accentual structures of this type may include two and more syllables,
e.g. ‘fafher, ‘possibly, ‘mother-in-law, ‘gas-pipe.
2. [ ‘_ ‘_ ]. The accentual type is commonly realized in compound words, most of them are with separable prefixes,
e.g. ‘radio-‘active, ‘re’write, ‘diso’bey.
3. [ ‘_’ _ ‘_ ] and
4. [‘_’ _ ‘_ ‘_]. The accentual types are met in initial compound abbreviations
e.g. ‘U’S’A, ‘U’S’S’R.
5. [‘_ ,___]. The type is realized both in simple and compound words, very common among compound words,
e.g. ‘hair-,dresser, ‘substructure.
6. [, _’___]. The accentual type marks a great number of simple words and some compound words as well. In simple words the stresses fall onto:
e.g.1. the prefix and the root: maga’zine;
2. the root and the suffix: ,hospi’tality;
3. the prefix and the suffix: disorganization.
№15 слайд
Содержание слайда: The other five types are rare and found in small number of words.
The other five types are rare and found in small number of words.
The most widely spread among the enumerated accentual types are supposed to be Type 1, Type 2, Type 5 and Type 6.
The variability of the word accentual structure is multiplied in
connected speech. The accentual structure of words may be
altered under the influence of rhythm, e.g. An ‘unpolished ‘stone
but: The ‘stone was un’polished.
The tempo of speech may influence the accentual pattern of words.
With the quickening of the speed the carefulness of articulation is
diminished, the vowels are reduced or elided, the secondary stress
may be dropped, e.g. The ‘whole organi’zation of the ‘meeting
was ‘faulty.
№16 слайд
1. The stress pattern of English words.
The nature of English words stress.
The functions of word stress.
2. The nature of English words stress.
A word, as a meaningful language
unit, has a definite phonetic
structure.
The phonetic structure of a word
comprises not only the sounds that
the word is composed of and not
only the syllabic structure that these
sounds form, it also has a definite
stress pattern.
3. The nature of English words stress.
There may be one prominent syllable in a word as compared to
the rest of the syllables of the same word (as in «important»),
there may be two equally prominent syllables (as in
«misbehave»), two unequally prominent syllables (as in
«e,xami’nation») or more prominent syllables (as in ‘
unre,lia’bility»).
4. The nature of English words stress
• And this correlation of
degrees of prominence of
the syllables in a word
forms the stress pattern of
the word, which is often
called the accentual
structure of a word.
Monosyllabic words
have no stress pattern,
because there can be
established no
correlation of
prominence within it.
Yet as lexical units
monosyllables are
regarded as stressed
5. The nature of English words stress
The stress patterns of
words are generally
perceived without
difficulty.
Actual speech does
not consist of isolated
words. And the stress
pattern of a word is
deduced from how
the word is accented
in connected speech.
6. The nature of English words stress
On the other hand, the stress pattern of a word is only its potential
pattern in an utterance. Though English words generally retain their
stress patterns in connected speech, there occur numerous
instances when the stress pattern, of a word is altered
7. The nature of English words stress
Cf. ‘un̍happy — He was ̍so unˋhappy.
Thus, word stress may be said to be a word—level concept,
which should not be confused with utterance stress. Word
stress be tangs to the word when said in isolation.
Whereas utterance stress belongs to the utterance.
He ̍remembered those ˋunhappy ̍days.
8. The nature of English words stress
The placement of
utterance stress is
primarily
conditioned by the
situational and
linguistic context.
It is also conditioned
by subjective factors:
by the speaker’s
intention to bring out
words which are
considered by him to
be semantically
important in the
situational context.
9. The nature of English words stress
• As for the stress pattern of a word, it is
conditioned only by objective
factors: pronunciation tendencies and the
orthoepic norm.
10. The nature of English words stress
In different languages stress may
be achieved by various
combinations of these
parameters. Depending upon
which parameter is the principal
one in producing the effect of
stress, word stress in languages
may be of different types.
11. Different types of word stress
There are languages with dynamic word
stress. Stress in such languages is mainly
achieved by a greater force of articulation
which results in greater loudness, on the
auditory level, and greater intensity on the
acoustic level. The stressed syllables are
louder than the unstressed ones.
In languages with musical word stress
prominence is mainly achieved by variations
in pitch level, the main acoustic parameter
being fundamental frequency. Chinese,
Japanese, Vietnamese are languages with
musical word stress (or tonic word stress).
12. Different types of word stress
In languages with quantitative word stress the effect of
stress is mainly based on the quantity of the sound, i.e. its
duration. In such languages vowels in the stressed syllables
are always longer than vowels in unstressed syllables.
13. THE FUNCTIONS OF WORD STRESS.
THE FUNCTIONS OF WORD
STRESS.
Word stress has a
constitutive function, as
it moulds syllables into a
word by forming its
stress pattern. Without
a definite stress pattern
a word ceases to be a
word and becomes a
sequence of syllables.
Word stress has a
distinctive function in
English, because there
exist different words in
English with analogous
sound structure which
are differentiated in
speech only by their
stress patterns
14. THE FUNCTIONS OF WORD STRESS.
THE FUNCTIONS OF WORD
STRESS.
Noun
Adjective
‘accent
̗̗
or
‘accent
Verb
‘insult
‘ab̗stract
ac’cent
or
acʹcent
in’sult ,
̗ ab’stract
or ab’stract
15. Is it the different degrees of stress or rather the stress patterns that distinguish one word from another?
Is it the different degrees of stress or rather
the stress patterns that distinguish one word
from another?
There exist different views of the problem. Some linguists (G. Trager,
A. Hill) regard degrees of word stress as phonological units, which
can distinguish words. They consider degrees of word stress to be
separate phonemes.
16.
Alongside the generally accepted
phonemes they have introduced into
the phonemic’ inventory 4 stress
phonemes: primary (or loud),
secondary (or reduced loud), tertiary
{or medial) and weak stress
phonemes.
17.
Another view is expressed by G. Torsuyev, H. Kurath, A. Gimson and others. They think
that it is the stress patterns of words that contrast with each other rather than
degrees of stress. Moreover, in one stress pattern secondary stress may be stronger
than primary stress in another stress pattern.
18. Questions
1) What types of word stress do you know?
2) What functions of word stress?
1
2
Word stress (WS) can be defined as the singling out of one or more syllables in a word, which is accompanied by the change of the force of utterance, pitch of the voice, qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the sound which is usually a vowel.
3
the force of utterance is greater, which is connected with more energetic articulation; the pitch of the voice is higher, which is connected with stronger tenseness of the vocal cords and the walls of the resonance chamber the quantity of the vowel is greater, a vowel becomes longer; the quality of the vowel !& in the stressed syllable is different from the quality of this vowel in the unstressed position, in why it is more narrow than.
4
dynamic or force stress if special prominence in a stressed syllable(syllables) is achieved mainly through the intensity of articulation; musical or tonic stress if special prominence is achieved mainly through the change of pitch, or musical tone. quantitative stress if special prominence is achieved through the changes in the quantity of the vowels, which are longer in the stressed syllables than in the unstressed ones. qualitative stress if special prominence is achieved through the changes in the quality of the vowel under stress. Vowel reduction is often used as a manipulation of quality in unstressed syllables.
5
One of the ways of reinitiating the prominence of syllables is manipulating the degree of stress. There is controversy about degrees of WS in English and their terminology. Strictly speaking, polysyllabic word has as many degrees of stress as there are syllables in it. Designating strongest syllable by 1, the second strongest by 2, etc., we may represent the distribution Jesses in the following example: examination indivisibility igzemineSin indivizibiloti The majority of British phoneticians (D. Jones, Kingdon, A. C. Gimson among them) and Russian phoneticians (V. A. Vassilyev, Shakhbagova) consider that there are three degrees of word-stress in English: primary — the strongest secondary — the second strongest, partial, and weak — all the other degrees. The syllables bearing either primary or secondary stress are termed stressed, while syllables with weak stress are called, somewhat inaccurately, unstressed.
6
Loud Reduced loud Medial Weak Primary Secondary Tertiary Weak
7
In English and Russian word-stress is free, that is it may fall any syllable in a word; Stress in English and in Russian is not only free but also shifting. In both languages the place of stress may shift, which helps to differentiate different parts of speech, e.g. `insult—to in`sult, `import—to im`port.
8
preSENT (verb) – PRESent (noun) reFER (verb) – REFerence (noun) exTRACT (verb) – EXtract (noun) inCREASE (verb) – INcrease (noun) OBject (noun) – obJECT (verb)
9
1. Word stress constitutes a word, it organizes the syllables of a word Into a language unit having a definite accentual structure, that is a pattern of relationship among the syllables; a word does not exist without the word stress. Thus the word stress performs the constitutive function. Sound continuum becomes a phrase when it is divided into units organized by word stress into words.
10
2. Word stress enables a person to identify a succession of syllables as a definite accentual pattern of a word. This function of word stress as known as identificatory(or recognitive). Correct accentuation helps the listener to make the process of communica tion easier, whereas the distortedaccentual pattern of words, misplaced word stresses prevent normal understanding.
11
3. Word stress alone is capable of differentiating the meaning of words or their forms, thus performing its distinctive function. The accentual patterns of words or the degrees of word stress and their positions form oppositions, e.g. ‘import im’port, ‘billow below.
12
Recessive. The accentual structure of English words is liable to instability due to the different origin of several layers in the Modern English word-stock. In Germanic languages the word stress originally fell on the initial syllable or the second syllable, the root syllable in the English words with prefixes. It is seen in the native English words having no prefix, e.g. mother, daughter, brother, swallow; in assimilated French borrowings, e.g. reason, colour, restaurant etc. Rhythmical. The rhythm of alternating stressed and unstressed syllables gave birth to the rhythmical tendency in the present-day English which caused the appearance of the secondary stress in the multisyllabic French borrowings, e.g. revolution, organi’sation, assimilation, etc. Retentive. Was traced in the instability of the accentual structure of English word stress: a derivative often retains the stress of the original or parent word, e.g. ‘similar as’simitate, recom’mend recommen ‘dation.
13
The numerous variations of English word stress are systematized in the typology of accentual structure of English words worked out by G.P. Torsuyev. He classifies them according to the number of stressed syllables, their degree or character (the main and the secondary stress). The distribution of stressed syllables within the word accentual types forms accentual structures of words. Accentual types and accentual structures are closely connected with the morphological type of words, with the number of syllables, the semantic value of the root and the prefix of the word.
14
The accentual types are: 1. [‘___]. This accentual type marks both simple and compound words. The accentual structures of this type may include two and more syllables, e.g. ‘fafher, ‘possibly, ‘mother-in-law, ‘gas-pipe. 2. [ ‘_ ‘_ ]. The accentual type is commonly realized in compound words, most of them are with separable prefixes, e.g. ‘radio-‘active, ‘re’write, ‘diso’bey. 3. [ ‘_’ _ ‘_ ] and 4. [‘_’ _ ‘_ ‘_]. The accentual types are met in initial compound abbreviations e.g. ‘U’S’A, ‘U’S’S’R. 5. [‘_,___]. The type is realized both in simple and compound words, very common among compound words, e.g. ‘hair-,dresser, ‘substructure. 6. [, _’___]. The accentual type marks a great number of simple words and some compound words as well. In simple words the stresses fall onto: e.g.1. the prefix and the root: maga’zine; 2. the root and the suffix:,hospi’tality; 3. the prefix and the suffix: disorganization.
15
The other five types are rare and found in small number of words. The most widely spread among the enumerated accentual types are supposed to be Type 1, Type 2, Type 5 and Type 6. The variability of the word accentual structure is multiplied in connected speech. The accentual structure of words may be altered under the influence of rhythm, e.g. An ‘unpolished ‘stone but: The ‘stone was un’polished. The tempo of speech may influence the accentual pattern of words. With the quickening of the speed the carefulness of articulation is diminished, the vowels are reduced or elided, the secondary stress may be dropped, e.g. The ‘whole organi’zation of the ‘meeting was ‘faulty.
16
Слайд 2Plan
General Notes on Word Stress.
Types of Word Stress.
Degrees of Word
Stress.
Placement of Word Stress.
Common Rules of Word Stress in English.
Functions
of Word Stress.

Слайд 4The Nature of Word Stress
Word Stress
is a greater degree of
prominence of a syllable or syllables as compared to the
other syllables of the word

Слайд 5The Nature of Word Stress
Scientists about Word Stress:
D. Jones: Word
Stress is the degree of force, which is accompanied by
a strong force of exhalation and gives an impression of loudness.
A. C. Gimson: English word stress or accent is a complex phenomenon, marked by the variations in force, pitch, quality and quantity.

Слайд 6The Nature of Word Stress
Scientists about Word Stress:
B. A. Bogoroditsky:
Stress as an increase of energy, accompanied by an increase
of expiratory and articulatory activity.
S. F. Leontyeva: Word stress can be defined as the singling out of one or more syllables in a word, which is accompanied by the change of the force of utterance, pitch of the voice, qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the sound which is usually a vowel.

Слайд 7The Nature of Word Stress
The effect of prominence of the
stressed syllable is achieved by a number of phonetic parameters:
Pitch
Loudness
Length
Vowel
Quality
These 4 factors usually work together in combination, but they are not equally important. The strongest effect is produced by pitch and length.

Слайд 8The Nature of Word Stress
In the stressed syllable:
the force of
utterance is greater, which is connected with more energetic articulation;
the
pitch of the voice is higher, which is connected with stronger tenseness of the vocal cords and the walls of resonance cavity;
the quantity of the vowel is greater, the vowel becomes longer;
the quality of the vowel is different (in unstressed syllables it is usually narrow).

Слайд 9The Nature of Word Stress
Word Stress
is singling out
of one or more syllables in a word, which is
accompanied by the change of the force of utterance, pitch of the voice, qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the sound, which is usually a vowel.

Слайд 11Types of Word Stress
We distinguish the following types of Word
Stress:
dynamic (force) stress is achieved by greater force with which
the syllable is pronounced (Russian, English, French, German);
musical (tonic) stress is achieved through the change of pitch/musical tone (Japanese, Korean);
quantitative stress is achieved through the changes in the quantity of the vowels, which are longer in the stressed syllables (Russian);
qualitative stress is achieved through the changes in the quality of the vowel (Russian).

Слайд 12Types of Word Stress
English Word Stress
is traditionally
defined as dynamic, but in fact, the special prominence of
the stressed syllables is manifested not only through the increase of intensity, but also through the changes in the vowel quantity, consonant and vowel quality and pitch of the voice.

Слайд 14Degrees of Word Stress
The syllables in a word are characterized
by different degrees of prominence. There are as many degrees
of stress in a word as there are syllables.
In English there are 3 degrees of stress:
primary (strong, main, principal);
secondary (half-stressed, half-strong);
weak (unstressed).

Слайд 15Degrees of Word Stress
In American English there are 4 degrees
of stress:
primary (strong, main, principal);
secondary (half-stressed, half-strong);
tertiary (on the last
but one syllable in the words with suffixes -ary, -ory, -ony: ´dictioˏnary.
weak (unstressed).

Слайд 16Degrees of Word Stress
In transcription stress is indicated by placing
the stress mark before the symbol of the first sound
of the stressed syllable.
Primary stress is marked by a raised short vertical stroke and secondary stress is marked by a lowered one:
examination [ɪgˏzᴂmɪ´neɪʃ(ǝ)n]

Слайд 18Placement of Word Stress
According to its placement in a word,
stress can be:
fixed
free
shifting

Слайд 19Placement of Word Stress
Fixed
(the position of the word stress is
always the same,
it is restricted to a particular syllable):
in French (the last syllable),
in Finnish and Czech (the first syllable),
in Polish (the last but one syllable).

Слайд 20Placement of Word Stress
Free
(the location of the word stress is
not
confined to a specific position,
it can fall on
any syllable of the word):
English, Russian, Italian, Greek, Spanish, etc.

Слайд 21Placement of Word Stress
Shifting
(the word stress can change
its position
in different forms
of the word and its derivatives):
´music
— mu´sician

Слайд 22Placement of Word Stress
To define the position of word stress
it is necessary to take into account
a number of
factors:
phonological structure of the syllable;
the number of syllables in a word;
morphological factor;
the part of speech the word belongs to;
the semantic factor.

Слайд 23Placement of Word Stress
The phonological structure of the syllable is
related to the status of a particular syllables in terms
of the degree of sonority.
The sounds that possess a greater degree of sonority contribute to the greater prominence of the syllable. A syllable is strong when it contains a long vowel or a diphthong or a short vowel followed by two consonants:
a´rrive — de´velop

Слайд 24Placement of Word Stress
The number of syllables in a word
influences the number of stresses and the position of stress.
There
are stress patterns typical of two-syllable words, three-syllable words and so on.
In multi-syllable words there appears secondary stress.

Слайд 25Placement of Word Stress
Morphological factor shows that in complex words
the placement of stress depends on the type of suffix.
Suffixes
are divided into:
stress-neutral (which do not affect the stress placement in the stem);
stress-fixing (which influence stress in the stem);
stress-attracting (which carry stress themselves).

Слайд 26Placement of Word Stress
stress-neutral (-al, -able, -en, -ful, -ing, -ish,
-less, -ness, -ly, -ment):
´comfort – ´comfortable;
stress-fixing (-ion, -ic, -ity,
-ial, -ive):
´curious — curi´osity;
stress-attracting(-ade, -eer, -ee, -esque, -ette, -ain):
ˏrefu´gee, ˏciga´rette.
Слайд 27Placement of Word Stress
The grammatical category the word belongs to:
´contrast
– to con´trast
´habit – ha´bitual
´music – mu´sician
´insult – to in´sult
´record
– to re´cord
´present – to pre´sent

Слайд 28Placement of Word Stress
The semantic factor (for compound words and
words with the so-called separable prefixes).
The majority of such
words have two equally strong stresses, both stressed parts are considered to be of equal semantic importance:
compound adjectives: ´hard-´working, ´blue-´eyed,
verbs with post positions : ´sit´down, ´take´off,
numerals from 13 to 19: ´ four´teen, ´six´teen.

Слайд 30
Common Rules of Word Stress
Two-syllable words (verbs, adjectives, adverbs):
the second
syllable is stressed if it contains a long vowel or
a diphthong, or if it ends with more than one consonant: a´pply, a´ssist. But! ´honest.
the first syllable is stressed if the final syllable contains a short vowel and one (or no) final consonant: ´enter, ´open.
Two-syllable words (nouns):
the first syllable is stressed if the second syllable contains a short vowel: ´money;
the second syllable is stressed if the second syllable contains a long vowel or a diphthong: es´tate.

Слайд 31
Common Rules of Word Stress
Three-syllable words (verbs):
the last but one
syllable is stressed if the last syllable contains a short
vowel and ends with one consonant: de´termine.
the final syllable is stressed if it contains a long vowel or a diphthong, or ends with more than one consonant: enter´tain.

Слайд 32
Common Rules of Word Stress
Three-syllable words (nouns, adjectives):
the middle syllable
is stressed if the syllable preceding the final syllable contains
a long vowel or a diphthong, or if it ends with more than one consonant:
di´saster;
the first syllable is stressed if the final syllable contains a short vowel and the middle syllable contains a short vowel and ends with not more than one consonant:
´cinema
´insolent

Слайд 33
Common Rules of Word Stress
Words with prefixes:
in words with prefixes
the primary stress typically falls on the syllable following the
prefix:
im´possible, re´call ;
in words with prefixes with their own meaning, the place of secondary stress is on the prefix:
ˏex-´minister.
in prefixal verbs which are distinguished from similarly spelt nouns and adjectives, the second syllable is stressed:
to in´crease – ´increase.

Слайд 34
Common Rules of Word Stress
Words with suffixes:
suffixes -esce, -esque, -ate,
-ize, -fy, -ette, -ique, -ee, -eer, — ade have stress
on themselves or the preceding syllable:
ˏmari´nade, ˏspecia´lize;
suffixes -ical, -ic, -ion, -ity, -ial, -cient, -iency, -eous,-ual, -uous, -ety, -itous, -ive, -ative, -itude, -ident, -inal, -wards have stress on the preceding syllable:
eco´nomic, ma´jority.

Слайд 35
Common Rules of Word Stress
Words of 4 or more syllables:
The
stress is on the antepenultimate syllable (third from the end):
e´mergency
his´torical

Слайд 36
Common Rules of Word Stress
Compound words:
The first element is stressed
when:
Compounds are written as one word: ´bedroom.
Nouns are compounded of
a verb and an adv.:´make-up.
The second element is stressed when:
Food items have the first element which is of a material used in manufacturing the whole: ˏapple ´tart.
Parts of the house are implied: ˏfront ´door.

Слайд 37
Common Rules of Word Stress
Compound words:
The first element is stressed
when:
Adjectives with past participle characterize people:
ˏthick-´skinned.
Nouns ending in -er, -ing
are followed by adverbs:
ˏpasser´by.
The first element of compounds is a number:
second-´class, three -´wheeler.
Compound function as an adverb:
head-´first.

Слайд 38
Common Rules of Word Stress
The most common types of English
stress pattern
´_ _ (´after)
_´_ (be´fore)
´_ _ _ (´family)
_´_ _ (im´portance)
Some words have 2 variants of stress:
ki´lometer – ´kilometer

Слайд 41
Functions of Word Stress
The constitutive function:
word stress organizes the
syllables into a word
The recognitive (identicatory) function:
word stress makes it
possible to identify and recognize a word in the chain of speech.
The distinctive function:
word stress is capable of differentiating the meaning of words or their forms: ´import — im´port.

Слайд 42Questions:
What is WORD STRESS?
What types of word stress do
you know?
How does stress perform constitutive, distinctive and recognitive function?
What
is the terminology suggested by different authors to distinguish between different degrees of word stress?
What factors determine the place of word stress?

Слайд 43
Literature
Леонтьева С.Ф. Теоретическая фонетика современного английского языка (на
англ. яз.) /С.Ф. Леонтьева.- М., 2002. – 336 с.
Соколова
М.А. Практическая фонетика английского языка /М.А. Соколова. – М.: Гуманит. изд. центр ВЛАДОС, 1997. – 384 с.
O’Connor L.D. Phonetics /L.D. O’Connor. Penguin, 1977.
Sokolova M.A. English Phonetics. A theoretical course /M.A. Sokolova. M., 1996. – 286 p.
Vassilyev V.A. English Phonetics: A theoretical Course /V.A. Vassilyev. M., 1980. – 323 p.

© 2023 Prezi Inc.
Terms & Privacy Policy











![contract ['kσntrækt], to contract [kən'trækt] in the stressed syllable:
th... contract ['kσntrækt], to contract [kən'trækt] in the stressed syllable:
th...](https://documents.infourok.ru/c64815f0-6016-41bc-b5c6-fb6c141d54db/slide_12.jpg)
![contract ['kσntrækt], to contract [kən'trækt]the quantity of the vowel [æ] in... contract ['kσntrækt], to contract [kən'trækt]the quantity of the vowel [æ] in...](https://documents.infourok.ru/c64815f0-6016-41bc-b5c6-fb6c141d54db/slide_13.jpg)











![Peculiarities of sounds in accented syllables [ə] is never stressed
[i, e, υ]... Peculiarities of sounds in accented syllables [ə] is never stressed
[i, e, υ]...](https://documents.infourok.ru/c64815f0-6016-41bc-b5c6-fb6c141d54db/slide_25.jpg)