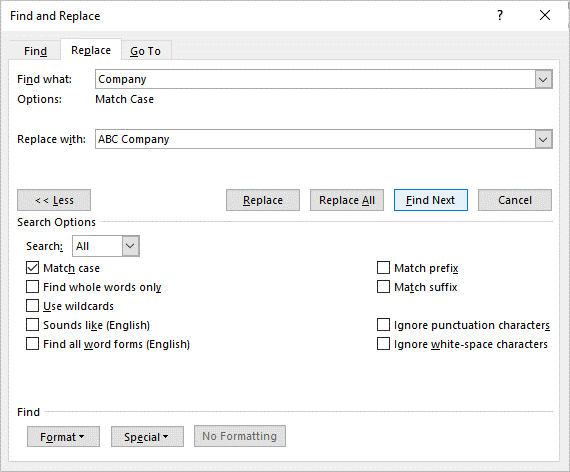
Find and replace text
-
Go to Home > Replace.
-
Enter the word or phrase you want to replace in Find what.
-
Enter your new text in Replace with.
-
Choose Replace All to change all occurrences of the word or phrase. Or, select Find Next until you find the one you want to update, and then choose Replace.
-
To specify only upper or lowercase in your search, select More > Match case. There are several other ways to search in this menu.
For other options, see Find and replace text
Find and replace basic text
In the upper-right corner of the document, in the search box 
To replace found text:
-
Select the magnifying glass, and then select Replace.
-
In the Replace With box, type the replacement text.
-
Select Replace All or Replace.
Tips:
-
You can also open the basic Find and Replace pane with the keyboard shortcut CONTROL + H.
-
When you replace text, it’s a good idea to select Replace instead of Replace All. That way you can review each item before replacing it.
-
You can find text with special formatting, such as bold or highlight, by using the Format menu.
-
Select View > Navigation Pane.
-
In the Navigation Pane, select the magnifying glass.
-
Select Settings
, and then select Advanced Find & Replace.
Notes:
-
Select the arrow at the bottom of the Find and Replace dialog box to show all options.
-
-
-
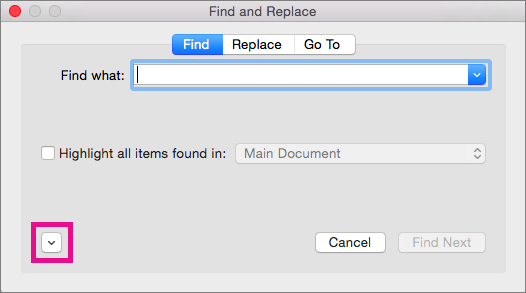
On the Format menu, select the option that you want.
If a second dialog box opens, select the options that you want, and then select OK.
-
In the Find and Replace dialog box, select Find Next or Find All.
You can find and replace text with special formatting, such as bold or highlight, by using the Format menu.
-
Select View > Navigation Pane.
-
In the Navigation Pane, select the magnifying glass.
-
Select Settings
, and then select Advanced Find & Replace.
-
At the top of the dialog box, select Replace.
Notes:
-
Select the arrow at the bottom of the Find and Replace dialog box to show all options.
-
-
-
On the Find what box, type the text that you want to find.
-
On the Format menu, select the formatting that you want to find.
If a second dialog box opens, select the options that you want, and then select OK.
-
Select in the box next to Replace with.
-
On the Format menu, select the replacement formatting. If a second dialog box appears, select the formats that you want, and then select OK.
-
Select Replace, Replace All, or Find Next.
-
Select View > Navigation Pane.
-
In the Navigation Pane, select the magnifying glass.
-
Select Settings
, and then select Advanced Find & Replace.
Notes:
-
Select the arrow at the bottom of the Find and Replace dialog box to show all options.
-
-
-
On the Special menu, select the special character that you want to find.
-
Select Find Next.
-
Select View > Navigation Pane.
-
In the Navigation Pane, select the magnifying glass.
-
Select Settings
, and then select Advanced Find & Replace.
Notes:
-
Select the arrow at the bottom of the Find and Replace dialog box to show all options.
-
-
-
At the top of the Find and Replace dialog box, select Replace and then select in the Find What box, but don’t type anything there. Later, when you select a special character, Word will automatically put the character code in the box for you.
Note: Select the arrow at the bottom of the Find and Replace dialog box to show all options.
-
On the Special menu, select the special character that you want to find.
-
Select in the Replace with box.
-
On the Special menu, select the special character that you want to use as a replacement.
-
Select Replace or Find Next.
-
Select View > Navigation Pane.
-
In the Navigation Pane, select the magnifying glass.
-
Select Settings
, and then select Advanced Find & Replace.
-
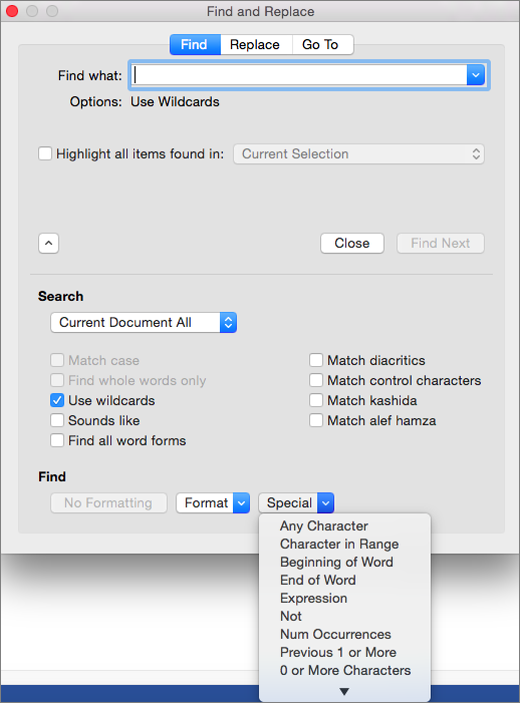
Select the Use wildcards check box.
If you don’t see the Use wildcards check box, select
.
-
Select the Special menu, select a wildcard character, and then type any additional text in the Find what box.
-
Select Find Next.
Tips:
-
To cancel a search in progress, press
+ PERIOD.
-
You can also enter a wildcard character directly in the Find what box instead of selecting an item from the Special pop-up menu.
-
To search for a character that’s defined as a wildcard character, type a backslash () before the character. For example, type ? to find a question mark.
-
You can use parentheses to group the wildcard characters and text and to indicate the order of evaluation. For example, search for <(pre)*(ed)> to find «presorted» and «prevented.»
-
You can search for an expression and use the n wildcard character to replace the search string with the rearranged expression. For example, type (Newman) (Belinda) in the Find what box and 2 1 in the Replace with box. Word will find «Newman Belinda» and replace it with «Belinda Newman.»
-
-
To replace found text:
-
Select the Replace tab, and then select the Replace with box.
-
Select Special, select a wildcard character, and then type any additional text in the Replace with box.
-
Select Replace All, Replace, or Find Next.
Tip: When you replace text, it’s a good idea to select Replace instead of Replace All. That way you can confirm each replacement to make sure that it’s correct.
-
You can refine a search by using any of the following wildcard characters.
|
To find |
Use this |
For example |
|---|---|---|
|
Any single character |
? |
s?t finds «sat» and «set.» |
|
Any string of characters |
* |
s*d finds «sad» and «started.» |
|
One of the specified characters |
[ ] |
w[io]n finds «win» and «won.» |
|
Any single character in this range |
[-] |
[r-t]ight finds «right» and «sight» and «tight.» Ranges must be in ascending order. |
|
Any single character except the characters inside the brackets |
[!] |
m[!a]st finds «mist» and «most» but not «mast.» |
|
Any single character except characters in the range inside the brackets |
[!x-z] |
t[!a-m]ck finds «tock» and «tuck» but not «tack» or «tick.» Ranges must be in ascending order. |
|
Exactly n occurrences of a character or expression |
{ n} |
fe{2}d finds «feed» but not «fed.» |
|
At least n occurrences of a character or expression |
{ n,} |
fe{1,}d finds «fed» and «feed.» |
|
A range of occurrences of a character or expression |
{ n, n} |
10{1,3} finds «10,» «100,» and «1000.» |
|
One or more occurrences of a character or expression |
@ |
lo@t finds «lot» and «loot.» |
|
The beginning of a word |
< |
<(inter) finds «interesting» and «intercept» but not «splintered.» |
|
The end of a word |
> |
(in)> finds «in» and «within,» but not «interesting.» |
Word for the web lets you find and replace basic text. You can match case or fine whole words only. For more varied options, open your document in Word for the desktop.
Need more help?
In addition to searching for and replacing text, you can search for and replace Word’s special characters,
such as paragraph and tab marks.
To find and replace special characters, follow these steps:
1. On the Home tab, in the Editing group, click
Replace:
2. In the Find and Replace dialog box, click the
More > > button:
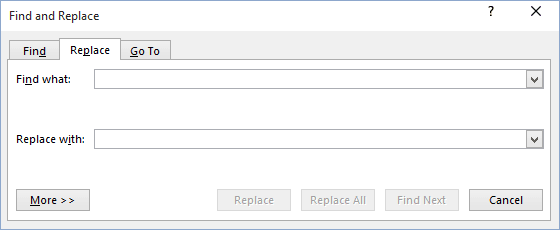
3. Click the Special button, and select the special character or
item you want to find and any text for which you want to search.
4. Position the insertion point in the Replace With text box.
5. Click the Special button, and select the special character or
item to add to the Replace With text box. You can add more than one special character to the text
box, and you can also add text before or after a special character in the Replace With text box.
6. Make sure that the All option is selected in the
Search list box. If you want to limit the search to text before or after the insertion point,
choose the Up or Down option in the Search box.
7. Do one of the following:
- To confirm each replacement on a one-by-one basis, click Find Next. Then click Replace
to replace the text or Find Next to skip to the next occurrence. - To replace all occurrences of the search text without confirmation, click Replace All.
8. When the replace session for the entire document is complete, a
dialog box informs you how many replacements were made. Click OK or press Enter to close
the dialog box.
9. Click Close in the Find and Replace dialog box to end
the session.
Characters in the Special Menu
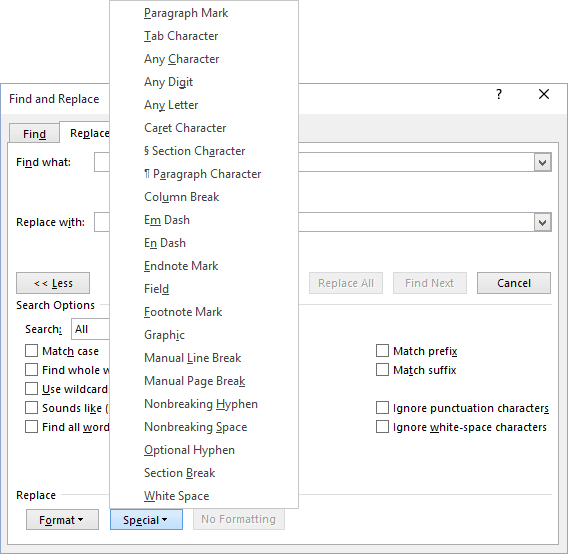
- ^p — Paragraph Mark
- ^t — Tab Character
- ^? — Any Character
- ^# — Any Digit
- ^$ — Any Letter
- ^^ — Caret Character
- ^u — Section Character
- ^v — Paragraph Character
- ^c — Clipboard Contents
- ^n — Column Break
- ^+ — Em Dash
- ^= — En Dash
- ^e — Endnote Mark
- ^d — Field
- ^& — Find What Text
- ^f — Footnote Mark
- ^g — Graphic
- ^l — Manual Line Break
- ^m — Manual Page Break
- ^~ — Nonbreaking Hyphen
- ^s — Nonbreaking Space
- ^- — Optional Hyphen
- ^b — Section Break
- ^w — White Space
See also this tip in French:
Remplacer les caractères spéciaux.
To do this, we need to open WORD and find the word «replace» on the top panel, in the corner. Click on it and a window will open in which we can change the Russian letter to an identical English one. The same will happen if you use the hotkeys (CRTL + H).
Finding and replacing text
- Go to Home> Replace or press CTRL + H.
- In the Find box, enter your search word or phrase.
- In the Replace box, enter your new text.
- Click the Find Next button until you reach the word you want to change.
- Click the Replace button.
How to find English letters in Russian text Word?
You need to use the Find and Replace dialog box (Ctrl + H), in which in the Find field set the format Language: English. English texts will be found. But note that the Russian text that was inserted into the document with the English keyboard layout will also be highlighted.
How to italicize only English letters in Word?
You can use Ctrl + H in the «Find» line in the font settings to select Language / English. In the replacement line, select only formatting — italics.
How to replace Russian letters with English in Excel?
Now if you select a range on the sheet and run our macro with the Alt + F8 keyboard shortcut or on the Developer → Macros tab, then all English letters found in the selected cells will be replaced with Russian equivalent to them.
In the Replace box, type: ^ & and press Ctrl + AND (this stands for bold) and then click Replace All. Numbers in the text will be bold.
How to find Latin letters in a Word?
Usually these are ALT + SHIFT hotkeys, less often CTRL + SHIFT. That is, the method is very simple — hold down the Shift key and type the number we need (more precisely, Latin letters).
How to determine the language of the text in the Word?
In versions 2010, 2013, and 2016 of Word and Outlook
- Open a new document or email message.
- On the Review tab, in the Language group, click the Language button.
- Select Set Spell Check Language.
- In the Language dialog box, select the Detect language automatically check box.
How to select only Russian text in a Word?
Press CTRL + H.
How to skip all spelling mistakes in a Word?
How to do this is described below. On the File tab, select Options, open the Spelling section, clear the Check spelling automatically check box, and then click OK. To re-enable the spell checker, repeat the above process and select the Check spelling automatically check box.
How to select all the same letters in a Word?
Edit-> Find-> The “Find” field is empty -> “Format” button -> from the drop-down list select “Highlight” -> “Find next” button. The transition to all selected text fragments will be performed.
How to select all the letters A in a Word?
In Word, you can select all text in a document (CTRL + A) or specific text or table elements using your mouse or keyboard.
How to replace the Cyrillic alphabet with the Latin alphabet in Excel?
Replace the Cyrillic alphabet with the Latin alphabet (rschu -> home) -> the program will replace all the Cyrillic letters with the Latin letters corresponding to the same keyboard keys; Replace Latin with Cyrillic (vfvf -> mother) -> the program will replace all Latin letters with Cyrillic letters corresponding to the same keys on the keyboard.
How to replace Russian characters with English ones?
To do this, we need to open WORD and find the word «replace» on the top panel, in the corner. Click on it and a window will open in which we can change the Russian letter to an identical English one. The same will happen if you use the hotkeys (CRTL + H).
How to bypass Antiplagiat letter replacement?
Replacing Russian letters with English — anti-plagiarism
- LIFEHACK
- The fastest and most effective way to cheat anti-plagiarism is file encoding. …
- You check the uniqueness of the new file for free, make sure of the high percentage of originality, and then we send a check for payment.
Find and Replace Text and Numbers in Word
by Avantix Learning Team | Updated March 7, 2022
Applies to: Microsoft® Word® 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021 or 365 (Windows)
You can find and replace in Word using the Find and Replace dialog box as well as the Navigation Pane. If you use the dialog box, you can find and replace text and numbers and use wildcards for more advanced find and replace tasks. Wildcards are useful when you are not able to find an exact match. You can display the Find and Replace dialog box using a keyboard shortcut or the Home tab in the Ribbon.
Recommended article: How to Quickly Remove Hard Returns in Word Documents
Do you want to learn more about Microsoft Word? Check out our virtual classroom or in-person Word courses >
Note: Screenshots in this article are from Word 365 but are similar in previous versions of Word.
The Replace command appears on the Home tab in the Ribbon in the Editing group:
Using the Find and Replace dialog box to replace words or characters (and match case)
You can perform simple find and replace tasks using the Replace dialog box in its collapsed state. To access more advanced options, you will need to click More in the Replace dialog box to expand it.
To use the Find and Replace dialog box to find and replace text in Word (words or characters) and match case if needed:
- Click the Home tab in the Ribbon.
- In the Editing group, click Replace to display the Replace dialog box. Alternatively, press Ctrl + H if you prefer to use a keyboard shortcut to open the Replace dialog box.
- Enter the text you want to find in the Find What box. You can specify whether Word should locate only matches with the exact capitalization by clicking More and then selecting or checking Match case.
- Enter the text you want to replace in the Replace box.
- Click Find Next and then click Replace for each occurrence or click Replace All.
- Click Close.
In the following example, the Replace dialog box has been expanded to display other options including Match case:
Finding and replacing using wildcards
To use wildcards, you will need to use the Find and Replace dialog box and expand it to display more options. You can then select the option to Use wildcards. A wildcard can replace one or more characters in a string of text or numbers. The most common wildcard is the asterisk (*).
It’s important to note that wildcard searches are case sensitive. Also, Word uses «lazy» pattern matching so it will stop matching as soon as possible. This means that you could enter part of a word and find that part without using wildcards.
To find and replace text using wildcards in Word:
- Position the cursor at the location in the document where you want to start finding and replacing. If you want to start at the beginning of the document, you can press Ctrl + Home.
- Click the Home tab in the Ribbon.
- In the Editing group, click Replace. Alternatively, press Ctrl + H. A dialog box appears.
- Select More to expand the dialog box.
- Click in the Find What box.
- Select or check the Use wildcards checkbox.
- Enter the text and wildcard(s) you want to use. For example, enter s*l to find any text starting with s and ending with l.
- Click in the Replace with box.
- Enter the text you want to use to replace the text in the Find what box.
- Click Find Next to find the first instance of the characters you want to find.
- Click Replace or Replace All. If you click Replace, Word will select the next matching characters in the Find what box. If you click Replace All, Word will display a dialog box with the number of replacements. In this case, click OK.
- If necessary, click Replace again. Repeat for each instance.
- Click Close to close the dialog box.
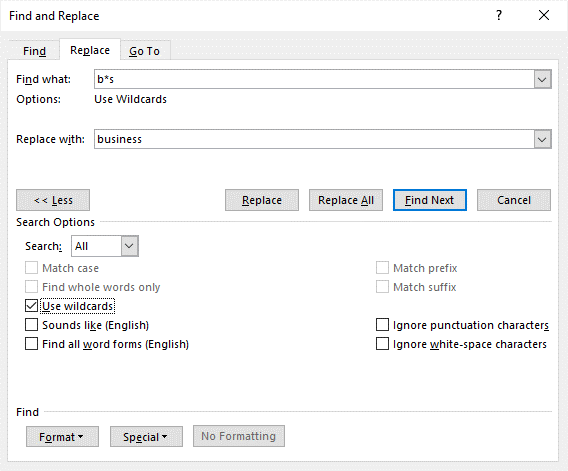
In the following example, b*s has been entered in the Find what box to find any word starting with starting with b and ending with s:
If you want to undo a Replace or Replace All action, close the dialog box and press Ctrl + Z.
Using common wildcards
The most common wildcards you can use in the Find and Replace dialog box are the asterisk (*) to find multiple characters and the question mark (?) to find a single character.
For example:
b*l will find ball and barrel (a character followed any characters and ending with a specific character)
h?ll will find hill and hall (a character followed by any single character and then followed by 2 characters)
Using wildcards to find one or more instances of the same character
You can also use @ as a wildcard to find one or more instances of the same character.
For example:
catchal@ will find catchal or catchall
Using wildcards for alternate characters and ranges
You can also use wildcards to find alternate characters or ranges of characters. These are entered in square brackets [ ] and may be combined with other wildcards.
[ ] can be used to find each of a set of characters
[ – ] can be used to find each of a set of characters in a range
You can use any character or series of characters in a range within the square brackets (including the space character). Characters are processed in alphanumeric order from lowest to highest.
For example:
[abc] will find any of the letters a, b, or c
[G] will find the upper case letter G
[A-Z] will find any upper case letter
[0-9] will find any single number
[13579] will find any odd number
[0-9A-z] will find any number or letter
f[ai]n will find each of the characters in square brackets such as fan or fin
[b-f]at will find each of a range of characters such as bat, cat, and fat
Using wildcards to omit characters
If you want to omit specific characters, you can use an exclamation mark (!) combined with square brackets.
For example:
[!f]ast will find last and past but not fast
Using wildcards to find the beginning or end of a word
You can use the less than symbol (<) to find the beginning of a word and the greater than symbol (>) to find the end of a word. These wildcards are combined with characters in round brackets or parentheses.
For example,
<(watch) will find watching or watchman
(all)> will find wall or stall
These wildcards can be problematic if you are using a wildcard and you want to find > or < as characters in the document. If this is the case, enter a backslash () in front of the character so that it is not treated as a wildcard.
For example,
<*> will find <h1> or <h2>
Using wildcards to find instances of a character
You can use curly brackets { } to specify the number of instances of a character. These brackets can be combined with a comma to specify the number of instances. Counting can be used with individual characters or with sets of characters.
{n} is used to find the number of instances of a character
{n,} is used to find at least n instances of a character
{n,m} is used to find between n and m instances of a character
For example:
^p{2} will find two consecutive paragraph marks or hard returns (^p is a special character for a paragraph mark in Word)
{3} will find three spaces (there is a space entered before the first curly bracket)
30{2,} will find at least 2 instances of the preceding character such as 3000 or 30000
30{3,4} will find between 3 and 4 instances of the preceding character such as 30000 or 300000 not 300
These last wildcards are particularly useful if you are finding and replacing numbers in Word.
The Find and Replace dialog box offers more functionality as well. For example, you can also Find and Replace Formatting in Word.
Subscribe to get more articles like this one
Did you find this article helpful? If you would like to receive new articles, join our email list.
More resources
How to Add Page Numbers in Word (Step by Step)
How to View Document Statistics in Microsoft Word
How to Update All Figure Numbers in Microsoft Word
How to Check Word Count in Microsoft Word (4 Ways)
How to Superscript or Subscript in Word (with Shortcuts)
Related courses
Microsoft Word: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft Word: Designing Dynamic Word Documents Using Fields
Microsoft Word: Long Documents Master Class
Microsoft Word: Accessible Word Documents
Microsoft Excel: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft PowerPoint: Intermediate / Advanced
VIEW MORE COURSES >
Our instructor-led courses are delivered in virtual classroom format or at our downtown Toronto location at 18 King Street East, Suite 1400, Toronto, Ontario, Canada (some in-person classroom courses may also be delivered at an alternate downtown Toronto location). Contact us at info@avantixlearning.ca if you’d like to arrange custom instructor-led virtual classroom or onsite training on a date that’s convenient for you.
Copyright 2023 Avantix® Learning
Microsoft, the Microsoft logo, Microsoft Office and related Microsoft applications and logos are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in Canada, US and other countries. All other trademarks are the property of the registered owners.
Avantix Learning |18 King Street East, Suite 1400, Toronto, Ontario, Canada M5C 1C4 | Contact us at info@avantixlearning.ca
Exchange one text string for another in any version of Word
Updated on October 29, 2021
What to Know
- Open the Find and Replace tool in Word with the keyboard shortcut CTRL+H.
- Find and Replace doesn’t take capitalization into account unless you specifically tell it to.
- To replace capitalization, select More in the Find and Replace box, then Match Case > Replace or Replace All > OK.
All editions of Microsoft Word offer a feature called Find and Replace. Use this tool to search for a specific word, number, or phrase in a document and replace it with something else. You can also make several replacements at once—like changing a name or fixing something you’ve consistently misspelled. Use it, also, to replace numbers or punctuation and cap or uncap words.
If you turn on Track Changes before you begin, you can reject the replacement or deletion of any unintended word.
Find and Replace a Word
The Microsoft Word Find and Replace dialog box, in its simplest form, prompts you to type the word you’re looking for and the word you want to replace it with. Then, click Replace, and either allow Word to change every entry for you or, go through them one at a time.
To open the tool, press Ctrl+H (Cmd+H on Mac).
Change Capitalization in Microsoft Word
The Find and Replace feature doesn’t take into account anything about capitalization unless you specifically tell it to. To get to that option you’ll need to click the More option in the Find and Replace dialog box:
- Open the Find and Replace dialog box using your favorite method. We prefer Ctrl+H.
- Click More.
- Type the appropriate entry in the Find What and Replace With lines.
- Click Match Case.
- Click Replace and Replace again, or, click Replace All.
- Click OK.
Advanced Options
When you select the More expander in the Search and Replace dialog box, you’ll encounter several customizations. The list of items varies according to which version of Word you’re running.
Search Options
Select the check boxes to include or exclude things like punctuation, white-space characters, or substrings. Plus, apply tools like word-form matching (i.e., walked also matches walking) and Soundex matching (Karin matches Karen).
Replace Options
Word supports more advanced substitutions, too. Use special characters to substitute text markup with symbols. For example, replace a character code like & with an ampersand. This approach is useful for de-cluttering pasted HTML text that uses HTML codes to render certain symbols.
Thanks for letting us know!
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Subscribe


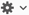 , and then select Advanced Find & Replace.
, and then select Advanced Find & Replace.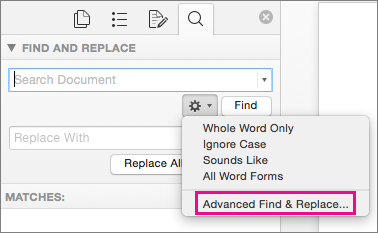

 .
.
 + PERIOD.
+ PERIOD.