Hello Learners, Today we will know the important features of the word processor.
In this post, I will explain in features of word processing software in detail.
This Article is the Best on the whole internet.
If you read this article carefully you will understand all about the word processor — features, uses, and advantages.
I Guaranteed you, after reading this article you will not need to read any other Articles. In fact, our readers are satisfied with this blog post.
Note — The only purpose of this article is to tell you about word processor features in very simple language. This article has been written by an expert, if you think this article can be improved further, then you must give us feedback.
What is Word Processor?
Word Processor is system software. With the help of word processor software, you can easily create any type of document. This software is very helpful for office work. There are various office employees who use this software to do their own work.
Microsoft Word is a very popular word processor software.
What are the Features of Word Processor?
There are various important features of word processor software, which features names are given below.
1. Easy Typing
You can type very easily using a word processor. Word processor provides you with many features to create a document so that you can type any type of document.
Word processor gives you more features in typing anything than typewriter-like — word processor has unlimited pages. You keep typing and as soon as the first page is over, the word processor lets you type on the new page.
While you are typing on the typewriter, you have to enter another page as soon as the page ends.
Everything you type in the word processor is visible to you so that you can also correct it if the wrong word is typed. But there is no such facility in the typewriter that you can correct the wrong word.
2. Text Copy
Copy is also a great feature of the word processor, using which you can copy any text. The copy feature is there in all types of word processors.
With the use of copy features, you can use the same text multiple times in the document without writing it, which saves you time as well.
3. Text Cut
The cut is also a great feature of the word processor, using which you can cut any text in the document. The cut feature is completely different from the copy feature.
For example, by using the copy feature, the copied text is in both the places in the document, such as — from where you copied your text and where you pasted the text, while the cut text is removed from the part of the document where The text is cut from.
4. Paste
The paste is also a great feature of the word processor, using which you can paste any copied or cut text on any part of the document. Any text is copied or cut only for pasting.
5. Multimedia
Multimedia is also a great feature of the word processor, using which you make your document more attractive.
Using multimedia features, you can insert multimedia in your document like — clip art, charts, images, pictures, video, etc.
6. Text formatting
Text formatting is also a great feature of the word processor, using which you can make your document more beautiful.
Using text formatting features, you can change the font of the text of your document, the size of the text, and the color of the text and you can also bold, italicize, and underline your text.
7. Spelling and Grammar
Spelling and Grammar is also a great feature of the word processor, using which you can check the spelling and grammar errors of the document.
8. Adjust the Layout
Adjusting the layout is also a great feature of the word processor, using which you can modify the margins, size, and layout of the document according to your need.
9. Find
Find is also a great feature of the word processor, using which you can find any word or sentence in the document. This feature helps you a lot, just imagine if your document is 100 to 150 pages.
If you have to find any word or sentence, then it will take you a lot of time, but you can find that word or sentence in a few seconds using the find features.
10. Search and Replace
Search and Replace is also a great feature of the word processor, using which you can find any word or sentence in the document and replace that word with a new word using the replace feature.
If your document is 100 to 500 pages, then imagine how much time and effort it will take to manually replace a word. But using the Search and Replace feature, you can replace any word or sentence with a new word or sentence in a few seconds.
11. Indentation and lists
Indentation and lists are also a great feature of the word processor, using which you can add tabs, bullet lists, and number lists to the document so that your document looks more beautiful.
12. Insert tables
Insert tables is also a great feature of the word processor, using which you can insert tables in the document.
13. Multiple Windows
Multiple windows are also a very good feature of a word processor, using which you can open multiple windows in word processor software. This feature is used by people to use more than one-word processors windows at the same time.
In a word processor, you have to press the ctrl and N buttons simultaneously to open more than one window.
14. AutoCorrect
AutoCorrect is also a great feature of word processors using which to automatically correct any common errors in your document like — (typing «teh» and having it autocorrected to «the»).
15. Headers and Footers
Headers and footers are also a great feature of the word processor, using which you can add anything according to your need in the headers and footers of your document like — page numbers, dates, footnotes, etc.
16. Mail Merge
If we want to send the same information to different people at the same time, then there is a feature in the word processor using which we can do that and that feature is named mail merge.
Using mail merge, the body of the letter is typed once and it is sent to different addresses.
There are various advantages of word processor software, which are given below.
- Quality
- Storage of Text
- Security
1. Quality
Word processor helps us to create error free documents. Every document prepared through word processor is absolutely correct in spelling and grammar, there is no possibility in it, and word processor allows us to make many copies of the same format.
2. Storage of Text
In word processor we can create of any number of page document and in word processor we can copy any word or sentence any number of times.
You can also use it by making some changes in any old word file in the word processor, for which we do not need to create a new word file.
3. Security
In a word processor, we can secure any document while creating it. As soon as someone opens that document, he asks for password before opening the document, and only after entering the correct password, the document will open.
Uses of Word Processor
There are various uses of word processor software, and this word processor are used in different fields which are — education field, planning or business-related works, for making assignments and home, etc.
With the use of this word processor software, you can do many things, whose names are given below.
- Memos.
- Making Card.
- Letter writing
- Legal Copies.
- Making resume/CV.
- Letters and letterhead.
- Reference documents.
- writing short stories.
I hope you understand this.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A word processor program is a computer program that provides word processing functions. Originally a separate type of application to desktop publishing, the two program types now overlap, with many word processors now including what were once desktop publishing functions.
History[edit]
The first known electronic word processor program was Electric Pencil, released in 1976, as a tool for programmers to write documentation and manuals for their code. Electric pencil featured basic formatting and navigation, and supported external devices such as cassette recorders and printers. Electric Pencil II was released shortly after, targeting the CP/M operating system. Several other word processing programs were released shortly after, including EasyWriter and WordStar.[1]
A screenshot of WordStar 3.0 in use
WordStar was created in four months by Seymour Rubinstein after founding MicroPro International in 1978. WordStar is commonly attributed as the first WYSIWYG (what you see is what you get) editor, as the WordStar editor replicated the printed output. Inspired by the success of WordStar, many competitors began to release their offerings, including WordPerfect in 1979, MultiMate in 1982, and Microsoft Word in 1983.[1][2]
List of word processors[edit]
Notable programs include:
- Electric Pencil (1976)
- WordStar (1978)
- WordPerfect (1979)
- EasyWriter (1979)
- IBM DisplayWrite (1981)
- MultiMate (1982)
- Volkswriter (1982)
- Microsoft Word (1983)
- Lotus Manuscript (1986)
- TextMaker (1987)
- Sprint (word processor) (1987)
- IBM Lotus Word Pro (1988)
- InPage (1994)
- WordPad (1995)
- TextEdit (1996)
- Ability Write (1996)
- KWord (1998)
- AbiWord (1998)
- Adobe InCopy (1999)
- Atlantis Word Processor (2000)
- Jarte (2001)
- Pages (2005)
- JWPce (2005)
- Google Docs (2006)
- Scrivener (software) (2007)
- WordGrinder (2007)
- PolyEdit (2010)
- LibreOffice Writer (2011)
- Apache OpenOffice Writer (2012)
- Calligra Words (2012)
A word processing function is an essential part of any office suite, and may be provided as a stand-alone program (for example Word in Microsoft Office) or as a function of a more general program (for example LibreOffice Writer in LibreOffice) or other (for example
TextMaker in SoftMaker). With the emergence of the internet, different cloud-based word processor programs began to emerge, which allow people to work faster and more efficiently.
See also[edit]
- Word processor
- Word processor (electronic device)
References[edit]
- ^ a b Bergin, Thomas J. (October 2006). «The Origins of Word Processing Software for Personal Computers: 1976-1985». IEEE Annals of the History of Computing. 28 (4): 32–47. doi:10.1109/MAHC.2006.76. ISSN 1934-1547. S2CID 18895790. Retrieved 29 June 2022.
- ^ Bergin, Thomas J. (October 2006). «The Proliferation and Consolidation of Word Processing Software: 1985-1995». IEEE Annals of the History of Computing. 28 (4): 48–63. doi:10.1109/MAHC.2006.77. ISSN 1934-1547. S2CID 20785663. Retrieved 29 June 2022.
External links[edit]
Microsoft Word is not an example of system software. On the contrary, it is an example of application software, which requires system software to function.
Windows, on the other hand, is an example of system software. Windows provides a platform for application software like Microsoft Word to operate.
It’s important to note that both the desktop version of Microsoft Word and the web version are examples of application software.
The difference is that the downloadable desktop version runs on a local server (your device). The online version of Microsoft Word runs on a web server and is accessible through an internet connection and a browser, like Chrome (also an application software).
- What Is Software? Software vs Hardware
-
What Is System Software? System Software vs Application Software
-
Examples Of System Software
- Examples Of Application Software
-
Examples Of System Software
-
Other Types Of Software
- What Is Microsoft Word? Is Microsoft Word An Example Of System Software?
If you’re just learning about different types of software, you may be wondering whether Microsoft Word is an example of system software. Being one of the most popular desktop programs, it’s natural to wonder which software category to place it in.
Before understanding whether Microsoft Word is system software, however, it is critical to understand what exactly system software is. It’s also essential to have a good grasp of the various types of software in general.
The two main types of software are system software and application software. First, I’ll explain exactly what software is and the differences between system and application software.
Then, I’ll talk about Microsoft Word and explain why it is not an example of system software. Let’s get into it.
What Is Software? Software vs Hardware
Image by Gerd Altmann from Pixabay
Before we can delve into the differences between system and application software, we need to understand what software is and what makes it different from hardware.
Many people confuse system software and hardware, but they’re two very different things.
Software is a set of code that tells your computer what to do. Think of it as a set of instructions that tell the computer how to run or execute a specific task.
Various programs, applications, and scripts, such as Microsoft Word, fall under the category of software.
The difference between software and hardware is that hardware refers to the physical parts of your computer. That includes your mouse, screen, keyboard, CPU, and any other hard part you can touch with your hand – hence the term hardware.
Also Read: Best WPS Office Alternatives
Photo by Pok Rie from Pexels
However, without software, hardware is useless, like a brick. It’s like a dead body, without any capabilities or functions.
We need system software to get the hardware to operate as a functional computer. System software instructs the hardware how to operate, turn on, show a display, perform tasks, and so on.
It may be helpful to think of system software as the brain and hardware as the body, although it’s not a perfect analogy.
What Is System Software? System Software vs Application Software
Now that we understand what hardware and software are, it’s time to explain the difference between system software and application software.
As mentioned, system software is code that tells the hardware how to operate. Windows is an example of system software.
If you don’t have Windows, Linux, or another operating system installed on your hardware, you won’t be able to do much with it.
System software provides the platform for application software to run on. It interacts closely with the hardware of your computer, and it’s written in a low-level language, so the hardware can understand its instructions.
System software has a more general purpose – instead of being there to help you perform a particular task, it’s there to help you perform a wide range of tasks.
Application software, on the other hand, has a more specific purpose. Each software has a different purpose and is designed to help you perform a particular task or set of tasks.
Image by Peggy und Marco Lachmann-Anke from Pixabay
Application software is usually written in a high-level language.
That’s because while system software interacts with the hardware, application software provides a program interface for the user (you) to interact with. You don’t interact closely with the system software itself.
Low-level language is written for machines (like your hardware) to understand. High-level language is for programs designed for humans.
You install system software on your hardware when you install an operating system, like Windows or Linux. Once installed, it will run at all times when your computer is on, and it will be interacting with the hardware and instructing it how to operate.
System software is essential; without it, you can’t do much with your laptop. On the other hand, you can uninstall and reinstall application software without impacting the capabilities and functions of other application software.
Examples Of System Software
Image by MasterTux from Pixabay
You’re probably familiar with at least some system software, at least if you have a computer or a phone. For desktop computers and laptops, the most common system software includes Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Lesser-used system software for laptops includes Raspberry Pi and Chrome OS. Chrome OS is the system software used on Chromebooks, and it’s based on Linux.
For mobile phones and tablets, the most common system software are Android and iOS. Windows Mobile was a popular operating system that has since been discontinued, as has the Blackberry OS, which stopped operating at the beginning of 2022.
As you can see, all software have one thing in common: They allow the hardware of the device, whether that’s a laptop or phone, to operate. We have also created a list of top system software examples that you can check.
Examples Of Application Software
Image by Pixaline from Pixabay
Application software programs are more user-specific. Here are some examples of the most popular application software:
- Microsoft Word
- Photoshop
- Google Chrome
- Firefox
- Safari Browser
- Windows Media Player
Even applications that come preinstalled on your device don’t necessarily fall into the category of system software. If they can be disabled and not interfere with the functionality of the device, and if they have a specific use case, they’re still application software.
For example, Android phones might come with the Google Maps app installed. However, that’s still application software.
Other Types Of Software
Image by James Osborne from Pixabay
To understand whether Microsoft Word is system software, you only need to know about system and application software. However, other types of software do exist, although many of them fall into either the system or application software category.
- Firmware: Firmware is low-level software embedded into the hardware. Firmware helps tell the hardware what to do and facilitates interaction between the system software and hardware. You don’t need to buy it separately like Windows.
- Utility software: Utility software includes antivirus programs and disk cleanup tools. They help the system operate smoothly, but they aren’t exactly system software. You don’t need an antivirus to run Windows.
- Language translators: Programming language translators translate programs from one code to another, such as from high-level code to low-level code, to make it possible for the machine to read it.
The following types of software can be either system or application software:
- Open-source software: This is software for which the source code is public. Linux is open-source system software.
- Freeware: Freeware isn’t necessarily open source, but it’s free.
- Shareware: Shareware is only free for evaluation – for example, it might have a free trial.
- Proprietary software: Proprietary software isn’t public like open-source software but owned by an entity. It could be freeware, shareware, or paid software.
Now that you have a good grasp of the different types of software and what system software is, let’s go back to our original question.
First, we need to understand what Microsoft Word is. Most of you already know this, but let’s quickly go over it.
Microsoft Word is a word processor application that people can use to write documents, edit documents, check text for errors, and so on.
Knowing what we know about system and application software, here are some questions to ask:
- Is Microsoft Word essential for the operating system? No, it’s not. You can use Windows without it.
- Does Microsoft Word provide an operating system for other applications to run on? No, it does not.
- Is Microsoft Word written in a low-level language? No, Microsoft Office applications like Word are written in C languages, which are high-level languages.
As such, we can conclude that Microsoft Word is not a good example of system software.
So, is Microsoft Word a good example of application software? Here are some questions to ask yourself:
- Does it exist for a specific use case? Yes, it does – it allows users to do specific tasks like writing documents.
- Can you execute it at will, instead of needing it to run at all times the operating system is on? Yes, you can use it only when you need it.
- Does it require system software to operate? Yes, you need a system software like Windows to run Microsoft Word.
- Is it written in a high-level language? Yes, it is.
As such, we can safely conclude that Microsoft Word is a good example of application software. Specifically, it is proprietary software – the source code is not public; it is instead owned by Microsoft.
Also Read: Best MS Office Alternatives For Windows
Benjamin Levin is a digital marketing professional with 4+ years of experience with inbound and outbound marketing. He helps small businesses reach their content creation, social media marketing, email marketing, and paid advertising goals. His hobbies include reading and traveling.
A word processor is software or a device that allows users to create, edit, and print documents. It enables you to write text, store it electronically, display it on a screen, modify it by entering commands and characters from the keyboard, and print it.
Of all computer applications, word processing is the most common. Today, most word processors are delivered either as a cloud service or as software that users can install on a PC or mobile device.
Word Processor Checklist
Jump to a topic in this article:
- What is the History of Word Processing?
- What are Standard Features of Word Processors?
- Full-featured Word Processors
- Word Processors vs. Text Editors vs. Desktop Publishing Systems
What is the History of Word Processing?
The earliest word processors were standalone machines similar to electric typewriters that debuted in the 1960s. The great advantage of these early machines over using a typewriter was that you could make changes without retyping the entire document. Over time, the devices acquired more advanced features, such as the ability to save documents on a disk, elaborate formatting options, and spell-checking.
While there are still some standalone word processors in use today, word processing began to move to personal computers in the 1980s. In the early days of the PC, a word processor called WordPerfect became one of the most widely used applications of any kind. Over time, however, What You See Is What You Get (WYSIWYG) word processors that showed users exactly what would print on their final documents became more popular. One of those WYSISWG word processors, Microsoft Word, became dominant in the 1990s.
Image: The first version of Microsoft Word was developed in 1981. The current version is Microsoft Word 16 (released in 2016).
With the advent of cloud computing in the 2000s, word processing changed again. The cloud allowed users to do their word processing via a browser-based application. While these cloud-based word processors lacked the advanced functionality of software installed on a device, they allowed users to store their documents in a remote data center and access them from any Internet-connected PC or mobile device. They also made it easier for geographically separated teams of people to work together on the same document. Many users found that cloud-based word processors offered enough features to meet their needs, as well as greater convenience, mobility, and collaboration support.
What are Standard Features of Word Processors?
Word processors vary considerably, but all word processors, whether cloud-based or installed on a system, support the following basic features:
insert text: Allows you to insert text anywhere in the document.
delete text: Allows you to erase characters, words, lines, or pages.
cut and paste: Allows you to remove (cut) a section of text from one place in a document and insert (paste) it somewhere else.
copy: Allows you to duplicate a section of text.
page size and margins: Allows you to define various page sizes and margins, and the word processor will automatically readjust the text so that it fits.
search and replace: Allows you to direct the word processor to search for a particular word or phrase. You can also direct the word processor to replace one group of characters with another everywhere that the first group appears.
word wrap: Automatically moves to the next line when you have filled one line with text, and it will readjust text if you change the margins.
print: Allows you to send a document to a printer to get hard copy.
file management: Provides file management capabilities that allow you to create, delete, move, and search for files.
font specifications: Allows you to change fonts within a document. For example, you can specify bold, italics, and underlining. Most word processors also let you change the font size and even the typeface.
windows: Allows you to edit two or more documents at the same time. Each document appears in a separate window. This is particularly valuable when working on a large project that consists of several different files.
spell checking: Identifies words that don’t appear in a standard dictionary.
Full-Featured Word Processors
Most installable modern word processor software supports additional features that enable you to manipulate and format documents in more sophisticated ways. Full-featured word processors usually support the following advanced features, and cloud-based word processors may have some of these features as well:
grammar checking: Identifies sentences, paragraphs, and punctuation that doesn’t appear to meet commonly recognized rules of grammar.
footnotes and cross-references: Automates the numbering and placement of footnotes and enables you to easily cross-reference other sections of the document.
automated lists: Automatically creates bulleted or numbered lists, including multi-level outlines.
graphics: Allows you to embed illustrations, graphs, and possibly even videos into a document. Some word processors let you create the illustrations within the word processor; others let you insert an illustration produced by a different program.
headers, footers, and page numbering: Allows you to specify customized headers and footers that the word processor will put at the top and bottom of every page. The word processor automatically keeps track of page numbers so that the correct number appears on each page.
layout: Allows you to specify different margins within a single document and to specify various methods for indenting paragraphs.
macros: Enables users to define and run macros, a character or word that represents a series of keystrokes. The keystrokes can represent text or commands. The ability to define macros allows you to save yourself a lot of time by replacing common combinations of keystrokes.
merge: Allows you to merge text from one file into another file. This is particularly useful for generating many files that have the same format but different data. Generating mailing labels is the classic example of using merges.
tables of contents and indexes: Allows you to automatically create a table of contents and index based on special codes that you insert in the document.
thesaurus: Allows you to search for synonyms without leaving the word processor.
collaboration: Allows users to track changes to the document when more than one person is editing. Some cloud-based word processors also allow multiple users to edit the same document at the same time.
internet features: Allows users to embed Web links into their documents and format their documents for the Web. Some also link to Web services that can help users create their documents.
translation and speech: As artificial intelligence capabilities become more commonplace, some word processors have gained the ability to read text aloud, to accept voice commands, and to translate text from one language to another.
Read also: What is a Spreadsheet?
Word Processors vs. Text Editors vs. Desktop Publishing Systems
Word processors are very similar to two other categories of software: text editors and desktop publishing applications. An example of a word processor is offered by Zoho.
Applications that support only the basic features from the first list above (and maybe a few others) are sometimes called text editors. Office workers sometimes use text editors to create simple documents that don’t require a full-featured word processor. However, text editors are more commonly used by programmers who use special text editors with features designed for writing code.
Desktop publishing systems, on the other hand, are generally more advanced and complex than word processors. The line dividing word processors from desktop publishing systems is constantly shifting as word processors become more advanced. In general, though, desktop publishing applications support finer control over layout, especially for documents with a lot of graphics, and they offer more support for full-color printing options.
This article was updated April 2021 by Jenna Phipps
Updated: 07/06/2021 by
Sometimes abbreviated as WP, a word processor is a software program capable of creating, storing, and printing typed documents. Today, the word processor is one of the most frequently used software programs on a computer, with Microsoft Word being a popular choice.
Word processors can create multiple types of files, including text files (.txt), rich text files (.rtf), HTML files (.htm & .html), and Word files (.doc & .docx). Some word processors can also be used to create XML files (.xml).
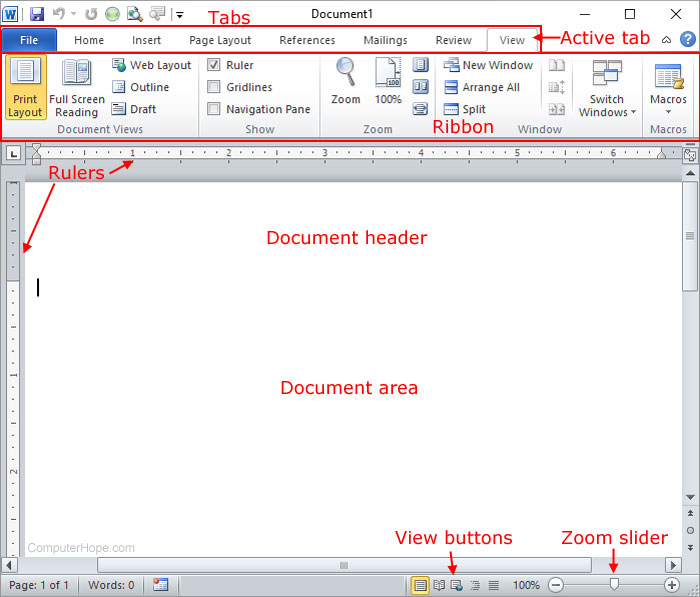
Overview of Word
In a word processor, you are presented with a blank white sheet as shown below. The text is added to the document area and after it has been inserted formatted or adjusted to your preference. Below is an example of a blank Microsoft Word window with areas of the window highlighted.
Features of a word processor
Unlike a basic plaintext editor, a word processor offers several additional features that can give your document or other text a more professional appearance. Below is a listing of popular features of a word processor.
Note
Some more advanced text editors can perform some of these functions.
- Text formatting — Changing the font, font size, font color, bold, italicizing, underline, etc.
- Copying, cutting, and pasting — Once text is entered into a document, it can be copied or cut and pasted in the current document or another document.
- Multimedia — Insert clip art, charts, images, pictures, and video into a document.
- Spelling and Grammar — Checks for spelling and grammar errors in a document.
- Adjust the layout — Capable of modifying the margins, size, and layout of a document.
- Find — Word processors give you the ability to quickly find any word or text in any size of the document.
- Search and Replace — You can use the Search and Replace feature to replace any text throughout a document.
- Indentation and lists — Set and format tabs, bullet lists, and number lists.
- Insert tables — Add tables to a document.
- Word wrap — Word processors can detect the edges of a page or container and automatically wrap the text using word wrap.
- Header and footer — Being able to adjust and change text in the header and footer of a document.
- Thesaurus — Look up alternatives to a word without leaving the program.
- Multiple windows — While working on a document, you can have additional windows with other documents for comparison or move text between documents.
- AutoCorrect — Automatically correct common errors (e.g., typing «teh» and having it autocorrected to «the»).
- Mailers and labels — Create mailers or print labels.
- Import data — Import and format data from CSV, database, or another source.
- Headers and footers — The headers and footers of a document can be customized to contain page numbers, dates, footnotes, or text for all pages or specific pages of the document.
- Merge — Word processors allow data from other documents and files to be automatically merged into a new document. For example, you can mail merge names into a letter.
- Macros — Setup macros to perform common tasks.
- Collaboration — More modern word processors help multiple people work on the same document at the same time.
Examples and top uses of a word processor
A word processor is one of the most used computer programs because of its versatility in creating a document. Below is a list of the top examples of how you could use a word processor.
- Book — Write a book.
- Document — Any text document that requires formatting.
- Help documentation — Support documentation for a product or service.
- Journal — Keep a digital version of your daily, weekly, or monthly journal.
- Letter — Write a letter to one or more people. Mail merge could also be used to automatically fill in the name, address, and other fields of the letter.
- Marketing plan — An overview of a plan to help market a new product or service.
- Memo — Create a memo for employees.
- Report — A status report or book report.
- Résumé — Create or maintain your résumé.
Examples of word processor programs
Although Microsoft Word is popular, there are other word processor programs. Below is a list of some popular word processors in alphabetical order.
- Abiword.
- Apple iWork — Pages.
- Apple TextEdit — Apple macOS included word processor.
- Corel WordPerfect.
- Dropbox Paper (online and free).
- Google Docs (online and free).
- LibreOffice -> Writer (free).
- Microsoft Office -> Microsoft Word.
- Microsoft WordPad.
- Microsoft Works (discontinued).
- SoftMaker FreeOffice -> TextMaker (free).
- OpenOffice -> Writer (free).
- SSuite -> WordGraph (free).
- Sun StarOffice (discontinued).
- Textilus (iPad and iPhone).
- Kingsoft WPS Office -> Writer (free).
Word processor advantages over a typewriter
See our typewriter page for a listing of advantages a computer with a word processor has over a typewriter.
Computer acronyms, Doc, Microsoft Word, Software terms, Untitled, Word processing, Word processor terms, WordStar, Write