Presentation on theme: «Using Word Processing, Spreadsheet, and Database Software»— Presentation transcript:
1
Using Word Processing, Spreadsheet, and Database Software
Integrating Educational Technology into Teaching
2
General Word Processing Features and Capabilities
Storing documents for later use. Erasing and inserting text. Searching and replacing text. Moving or copying text. Inserting carriage returns — word wraparound. Changing the style and appearance of text easily. Justifying text on both margins. Creating headers, footers, and numbering pages — pagination.
3
General Word Processing Features and Capabilities (cont.)
Inserting text prepared on other word processors. Checking and correcting spelling. Suggesting words. Reviewing style and grammar. Allowing the insertion of graphics. Merging text with database files.
4
Advantages of Word Processing for Education
Saving time. Creating professional looking documents. Sharing text among multiple users.
5
Benefits of Word Processing: Findings from Research
Do students write better with word processing? ‘It depends’ (IETIT p131) Generally, studies seem to suggest that students who are using word processing are improving their writing and their attitude toward writing only if it is used in the context of good writing instruction and if students have enough time to learn word processing features. Teachers should not expect their student’s writing quality to improve automatically if the teachers use word processing software with their students.
6
Applying Word Processing in Various Instructional Ways
Writing processes. Students can write, edit, and illustrate stories by using word processing. Dynamic group products. A group of students can write a poem or letter together, adding and changing lines anytime. Individual language, writing, and reading exercises. Encouraging writing across the curriculum.
7
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions when Learning Word Processing
Forgetting to move the cursor before typing. Forgetting to highlight before changing a format. ‘Losing’ part of the document. Forgetting automatic wraparound at the end of lines.
8
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions when Learning Word Processing
Problems naming and saving files. Incorrect spacing at the top or bottom of the document. —Loading paper in the printer. —Extra lines in the document. Problems searching and replacing text.
9
Spreadsheet Software in Teaching and Learning
Spreadsheet are also called worksheets. Spreadsheets were the earliest application software available for microcomputers. A spreadsheet program can be a stand alone package or it can be part of an integrated package such as Microsoft Works. Teachers use spreadsheets in gradebooks or gradekeeping packages to store and calculate grades.
10
Spreadsheet Features and Capabilities
Calculations and comparisons. Spreadsheets can calculate and manipulate stored numbers in lots of ways by using different formulas. Automatic recalculation. Copying cells.
11
Spreadsheet Features and Capabilities
Placing information in column-row formats for easy reading and interpretation. Creating graphs that correspond to data. Using worksheets prepared with other programs.
12
Advantages of Spreadsheets
Time savings. Creating charts. Answering “what if” questions. Motivation.
13
Teacher Productivity — Applications of Spreadsheets
Gradekeeping. Club and/or classroom budgets. Computerized checkbooks for clubs or other organizations.
14
Teacher Productivity — Applications of Spreadsheets
Attendance charts. Performance assessment checklist. Class inventory.
15
Teaching and Learning Activities — Applications of Spreadsheets
Demonstrations. Student products. Problem solving activities. Storing and analyzing data. Projecting grades.
16
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions Learning Spreadsheets
Forgetting to highlight cells to be formatted. Difficulty developing formulas and using predefined functions.
17
Database Defined Allow users to store, organize, and manipulate information, including text and numerical data. Allow the user to locate information through key word searches. “ People often use the term database to refer both to the computer program and the product it creates. However, database products are also sometimes called files.
18
Types of Database Programs and Products
Single application: dBase, Microsoft Word Integrated package: ClarisWorks, Microsoft Works Database software: dBase, Microsoft Works Prepared database: ERIC on Disc or online
19
Types of Database Programs and Products
Flat filing system: ClarisWorks, Microsoft Works Relational filing system: dBase, Fox Pro, Oracle Non-programmable systems: ClarisWorks, Microsoft Works Programmable DBMS systems: dBase, Fox Pro, Oracle
20
General Database Features and Capabilities
Allowing changes to information. Sorting information alphabetically or numerically. Searching for information. Creating & Retrieving reports or summaries of information. Merging with word processing documents.
21
Advantages of Databases
Reducing data redundancy and error. Saving time locating and/or updating information. Allowing comparisons of information through queries. Rapid information retrieval.
22
Issues Related to Databases
Privacy Act of 1974 The Act also limits the kind of information that can be kept on citizens, and requires that people be told what information the government keeps on them. Teachers must recognize their responsibility to safeguard student information and protect it from unauthorized access. Teachers have to keep disks in secure places, make sure passwords remain secret, and delete information at the request of parents or students.
23
Teacher Productivity — Database Software
Teachers may use databases to help them prepare classroom materials and other tasks they would otherwise have to do by hand or couldn’t do at all. Inventorying and locating instructional resources. Using information on students to plan instruction and enhance motivation. Using information on students to respond to questions or perform required tasks.
24
Teaching and Learning Activities — Database Software
Teaching research and study skills. Teaching organization skills. Understanding the power of information “pictures.” Posing and testing hypotheses.
25
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions when Learning Databases
Confusing spreadsheet and database features. Difficulties with keyword searches. Decisions about which fields to include.
26
The End
Introduction
Why Use Software Tools?
- Improved Productivity
- Improved Appearance
- Improved Accuracy
The “Basic Three”
Word Processing, Spreadsheet, and Database Programs
Recent Developments in Software Tools
- Web-based software tools
- Open-source software
- PDA tools
- Web-enabled features
- Better file-exchange compatibility
- Software suites and integrated packages
Using Word Processing Software in Teaching and Learning
Word processing programs allow people to produce typed documents on a computer screen.
The Impact of Word Processing in Education
Why Teachers Use Word Processing
- Saves time
- Enhances document appearance
- allows sharing of documents
- allows collaboration of documents
Research in the Impact of Word Processing
- mixed results
- best if used in the context of good instruction and prior word processing skills
Issues in Using Word Processing
- When should students start word processing?
- Is it necessary to teach keyboarding skills?
- What effects does word processing have on hand-writing?
- What impact does word processing have on assessment?
Word Processing in the Classroom: Productivity and Teaching Strategies
Productivity Strategies
- prepare instructional materials, lesson plans, notes, reports, letters, etc.
- save documents as template to update and reuse
Instructional Integration Strategies for Word Processing
- supporting the learning of writing processes
- using a dynamic group product approach
- assigning individual language, writing, and reading exercises
- encouraging writing through the curriculum
Teaching Word Processing Skills: Recommended Skills and Activities
Suggested Steps for Introducing Word Processing to Students
- Prepare for teaching
- Demonstrate the basics
- Assign individual practice
- Demonstrate formatting features
- Assign more individual practice
- Demonstrate procedures with new files
Using Spreadsheet Software in Teaching and Learning
Spreadsheets are programs designed to organize and manipulate numerical data.
The Impact of Spreadsheets in Education
Why Teachers Use Spreadsheets
- Save time
- Organize displays of information
- Support asking “what if” questions
- Increase motivation to work with mathematics
Research on the Impact of Spreadsheet Use
- Spreadsheets widely believed to help students visualize numerical concepts
- few studies
Issues in Using Spreadsheets
- Use spreadsheets to keep grades or rely on grade-keeping software
Spreadsheets in the Classroom: Productivity and Teaching Strategies
Productivity Strategies
- prepare classroom materials
- complete calculations
Instructional Integration Strategies for Spreadsheets
- Making possible teaching demonstrations
- Supporting student products
- Supporting mathematical problem solving
- Storing and analyzing data
- Projecting grades
Teaching Spreadsheet Skills: Recommended Skills and Activities
Suggested Steps for Introducing Spreadsheets to Students
- Prepare for teaching
- Demonstrate the basics
- Assign individual practice
- Demonstrate formatting features
- Assign more individual practice
Using Database Software in Teaching and Learning
Databases are computer programs that allow users to store, organize, and manipulate information, including both text and numerical data.
The Impact of Databases in Educaton
Why Teachers Use Databases
- Reducing data redundancy
- Saving time and/or updating information
- Allowing comparisons of information through searches across files
- Helping reveal relationships among data
Research on the Instructional Uses of Databases
- students can acquire useful skills in searching for and using information
- students need guidance in asking relevant questions and analyzing results
- useful in teaching inquiry and problem-solving skills
- may increase quality of internet use
Issues in Using Databases
- Simplified access versus privacy
- Coping with information overload
Databases in the Classroom: Productivity and teaching Strategies
Productivity Strategies
- Inventorying and locating instructional resources
- Data mining for planning and reporting
- Sending personalized letters to parents and others
Instructional Integration Strategies for Databases
- Teaching research and study skills
- Teaching organization skills
- Understanding the power of information “pictures”
- Posing and testing hypotheses
- Searching for information during research
Teaching Database Skills: Recommended Skills and Activities
Suggested Steps for Introducing Database Programs to Students
- Prepare for teaching
- Demonstrate the basics
- Assign individual practice
- Demonstrate database creation and use
- Assign more individual practice
A Summary of Software Tool Integration Strategies
- Software tools address productivity and instructional needs
- reduce labor involved in preparing student products
- remove logistical barriers to learning
Pirillo & Fitz. (2007). Notepad [Image], Retrieved Sept. 25, 2011, from http://checkengineusa.com/dennislembree/blog/media/runs_notepad_fast.gif
Roblyer, M.D. and Doering, A. (2010). Integrating Educational Technology into Teaching (5th Ed.). Boston, MA: Pearson Education, Inc.
At this lesson we will speak about such application software as word processors, spreadsheets, databases, about the future of softwear and will
become a developer for a while.

Reading
Skim the text.
Ознакомьтесь с текстом.
Word processing

Spreadsheets and databases
A spreadsheet program helps you manage personal and business finances. Spreadsheets, or worksheets, are mathematical tables which show figures in
rows and columns.
A cell can hold three types of data: text, numbers and formulae.
Formulae are entries that have an equation which calculates the value to display; we can use them to calculate totals,
percentages, discounts, etc.

Spreadsheets have many built-in functions, pre-written instructions that can be carried out by referring to the function by name. For example, =SUM(D2:D7)
means add up all the values in the cell range D2 to D7.
The format menu lets you choose font, alignment, borders, etc.
Parts of a database

Database basics
A database is essentially a computerized record-keeping system.
Each unit of information you create is called a record and each record is made up of a collection of fields. Typically, a
single record consists of a set of field names like: Title, FirstName, Surname, JobTitle, TelNo and ID. You fill in a form with the relevant information for each field
to add a new record to the database. There are different data types.
• Text — holds letters and numbers not used in calculations
• Number — can only hold numbers used in calculations and reports
• Memo — can store long texts
• Date/Time — a date or time or combination of both
• AutoNumber — assigns a number to each record
• OLE Object — (object linking and embedding) holds sounds and pictures
• Yes/No — for alternative values like true/false, yes/no, on/off, etc.
• Hyperlink — adds a link to a website
Once you have added data to a set of records, indexes must be created to help the database find specific records and sort
(classify) records faster. An index performs the same function as in the back of a book or in a library. For example, if you regularly search your database by surname, the index
should be defined on this field.
Relational databases
Two database files can be related or joined as long as they hold a piece of data in common. A file of employee names, for example, could
include a field called ‘DEPARTMENT NUMBER’ and another file, containing details of the department itself, could include the same field. This common field can then be used to
link the two files together.
Extracting information from a database is known as performing a query. For example, if you want to know all customers that spend more than £9,000
per month, the program will search the name field and the money field simultaneously.
| Слово | Транскрипция | Перевод |
| toolbar | ˈtəʊlbɑːr | панель инструментов |
| menu bar | ˈmenjuː bɑː | главное меню |
| undo reverse action | ˈʌnˈduː rɪˈvɜːs ækʃn | действие отмены-повтора |
| typeface | ˈtaɪpfeɪs | тип шрифта |
| font | fɔnt | шрифт |
| alignment | əˈlaɪnmənt | выравнивание |
| header | ˈhedə | верхний колонтитул, заголовок |
| footer | ˈfʊtə | нижний колонтитул, подвал страницы |
| bold text | bəʊld tekst | жирный шрифт текста |
| italic text | ɪˈtælɪk tekst | курсив |
| inserted hyperlink | ɪnˈsɜːtɪd ˈhaɪpəlɪŋk | вставленная гиперссылка |
| Word processing | ||
| a word processor | wɜːd ˈprəʊsesər | текстовый редактор |
| to enable | ɪˈneɪbl | позволять, давать возможность |
| word processing | wɜːd ˈprəʊsesɪŋ | обработка текста |
| a typewriter | ˈtaɪpraɪtə | печатная машинка |
| to retype | rɪˈtaɪp | перепечатать |
| entire | ɪnˈtaɪə | целый, весь |
| a mistake | mɪsˈteɪk | ошибка |
| to back up | bæk ʌp | возвращать |
| to delete | dɪˈliːt | удалить |
| to remove | rɪˈmuːv | убирать, удалять, стирать |
| to leave a trace | liːv ə treɪs | оставить след |
| equally | ˈiːkwəlɪ | также, в равной мере, одинаково |
| to insert | ˈɪnsət | вставить |
| a feature | ˈfiːʧə | свойство, функция |
| word wrap | wɜːd ræp | перенос слов |
| layout | ˈleɪaʊt | ориентация листа |
| merge | mɜːʤ | формат по образцу |
| spell checker | spel ˈʧekə | проверка орфографии |
| line | laɪn | зд. граница |
| desktop publishing system (DTP) | ˈdesktɒp ˈpʌblɪʃɪŋ ˈsɪstɪm | настольная издательская система |
| to shift | ʃɪft | сдвигаться, перемещаться |
| full-colour | fʊl-ˈkʌlə | полноцветный |
| Spreadsheets and databases | ||
| a spreadsheet, a worksheet | ˈspredʃiːt, ˈwɜːkʃiːt | электронная таблица |
| a database | ˈdeɪtəbeɪs | база данных |
| a spreadsheet program | ˈspredʃiːt ˈprəʊgræm | программа электронных таблиц |
| a table | teɪbl | таблица |
| a row | rəʊ | строка |
| a column | ˈkɔləm | столбец |
| a cell | sel | ячейка |
| an entry | ˈentrɪ | запись |
| an equation | ɪˈkweɪʃn | уравнение, равенство |
| a value | ˈvæljuː | значение |
| a total | təʊtl | сумма, итог |
| percentage | pəˈsentɪʤ | процентное отношение |
| a cell range | sel reɪnʤ | диапазон ячеек |
| format menu | ˈfɔːmæt ˈmenjuː | меню форматирования |
| font | fɔnt | шрифт |
| alignment | əˈlaɪnmənt | выравнивание |
| а border | ˈbɔːdə | граница |
| Parts of a database | ||
| a record-keeping system | ˈrekɔːd ˈkiːpɪŋ ˈsɪstɪm | система учета |
| a record | ˈrekɔːd | запись |
| a field | поле | |
| single | sɪŋgl | отдельный |
| a set of | set ɔv | набор, ряд |
| relevant | ˈrelɪvənt | соответствующий |
| to add | æd | добавить |
| a data type | ˈdeɪtə taɪp | тип данных |
| hyperlink | ˈhaɪpəlɪŋk | гиперссылка |
| an index | ˈɪndeks | индекс, код |
| to sort | sɔːt |
сортировать, отбирать, классифицировать |
| related, joined | rɪˈleɪtɪd, ˈʤɔɪnd | связанный |
| as long as | æz lɔŋ æz | при условии, до тех пор |
| in common | ɪn ˈkɔmən | совместно, вместе |
| to link | lɪŋk | связывать, соединять |
| to extract | ˈekstrækt | извлекать, выбирать |
| a query | ˈkwɪərɪ | запрос |
Grammar
Времена группы Continuous (Progressive)
Времена группы Continuous, или Progressive, обозначают действие, которое происходило, происходит или произойдёт в точно указанное время. Другими словами,
они показывают действие в процессе. Слово «continuous» переводится как «длительное», а «progressive» как «продолженное».
Дополнительные характеристики этих действий — незаконченность и динамичность.
Время Present Continuous (Present Progressive) указывает на длительное действие или процесс, который происходит в данный момент
времени, в момент речи, и не является законченным действием. Present Continuous употребляется со словами now (сейчас), at the moment (в данный
момент).
Прежде, чем построить предложение в Present Сontinuous вспомним спряжение глагола to be в Present
Simple:
| Утверждение | Отрицание | Вопрос | Ответ | |
|
P r. S i m. |
I am He (She, It) is We are You are They are |
I am not (I’m not) He (She, It) is not (He isn’t) We are not (We aren’t) You are not (You aren’t) They are not (They aren’t) |
Am I ? Is he (she, it) ? Are we ? Are you ? Are they ? |
Yes, I am. Yes, he (she, it) is. Yes, we are. Yes, you are. Yes, they are. |
Теперь, к вышеприведённому спряжению глагола to be, который становится вспомогательным глаголом, прибавим основной глагол с окончанием
-ing, и получим предложение в Present Сontinuous.
Рассмотрим на примере глагола to play (играть).
| Утверждение | Отрицание | Вопрос | |
|
P r. C o n t. |
I am playing (Я играю) He (she, it) is playing We are playing You are playing They are playing |
I am not playing (Я не играю) He (she, it) is not playing We are not playing You are not playing They are not playing |
Is he (she, it) playing? Are we playing? Are you playing? Are they playing? |
Ответом на вопрос будет Yes, he is. или No, he isn’t. Другие примеры:
Don’t bother me. I’m trying to concentrate. — Не отвлекай меня. Я пытаюсь сконцентрироваться.
Sally is doing her homework at the moment. — Салли делает домашнее задание в данный момент.
Dad and me are fishing now. — Папа и я рыбачим сейчас.
Время Past Continuous (Past Progressive) указывает на процесс, длившийся в определённый момент в прошлом. При этом должно быть указано точное время или период, когда
совершалось действие, или же это должно быть четко понятно из контекста. Для того, чтобы построить предложение в Past Continuous, необходимо вспомнить спряжение глагола to be в
Past Simple:
| Утверждение | Отрицание | Вопрос | Ответ | |
|
P a s t S. |
I was He (She) was We were You were They were |
I was not
He (She) was not We were not You were not They were not |
Was I ?
Was he (she) ? Were we ? Were you ? Were they ? |
Yes, I was.
Yes, he (she) was. Yes, we were. Yes, you were. Yes, they were. |
Добавив к вышеприведенной схеме основной глагол с окончанием -ing, получим предложение в Past Continuous. Рассмотрим на примере глагола to read (читать):
| Утверждение | Отрицание | Вопрос | |
|
P a s t C o n. |
I was reading (Я читал) He (she, it) was reading We were reading You were reading They were reading |
I was not reading (Я не читал) He (she, it) was not reading We were not reading You were not reading They were not reading |
Was he (she, it) reading? Were we reading? Were you reading? Were they reading? |
Ответим на вопрос Yes, he was. или No, he wasn’t. Приведем другие примеры:
Brooke was cooking at 6 p.m. — Брук готовила в 6 часов вечера.
At midnight I was reading a book. — В полночь я читал книгу.
When you called I was taking a shower. — Когда ты позвонил, я принимала душ.
Предложения в Future Continuous (Future Progressive) строятся по схеме: Сущ.(местоим.) + will be + основной глагол с окончанием
-ing. Пример с глаголом to walk (гулять):
| Утверждение | Отрицание | Вопрос | |
|
F u t. C o n. |
I will be walking (Я буду гулять) He (she) will be walking We will be walking You will be walking They will be walking |
I will not be walking (Я не буду гулять) He (she) will not be walking We will not be walking You will not be walking They will not be walking |
Will I be walking? Will he (she) be walking? Will we be walking? Will you be walking? Will they be walking? |
Ответ на вопрос будет либо Yes, I will, либо No, I won’t.
Другие примеры:
Trevor will be watching a football match tomorrow at 8 p.m. — Тревор будет смотреть футбол завтра в 8 часов вечера.
Tomorrow this time I will be flying to New York. — Завтра в это же время, я буду лететь в Нью-Йорк.
Don’t disturb me in the evening, I’ll be preparing for exam. — Не мешайте мне вечером, я буду готовиться к экзамену.
Некоторые глаголы, называемые статичными глаголами (stative verbs), не употребляются во временах группы Continuous в силу своей специфичности. Для обозначения длительного
действия они употребляются в форме Simple.
Статичные глаголы:
-
глаголы восприятия — to see (видеть), to hear (слышать), to smell (пахнуть), to notice (замечать), to feel (чувствовать), to recognize (узнавать), to taste (иметь
вкус); -
глаголы умственного процесса — to know (знать), to think/to consider/to suppose (считать, полагать), to believe / to trust (верить), to expect (ожидать), to remember
(помнить), to recollect (вспоминать), to understand (понимать); -
глаголы эмоционального состояния — to want (хотеть), to wish / to desire (желать), to adore (восхищаться), to like (нравиться), to dislike (не нравиться), to hate
(ненавидеть), to detest (презирать), to refuse (отказываться), to fear (бояться), to forgive (прощать), to respect (уважать), to care for (заботиться); -
глаголы обладания и отношения — to own/to possess (обладать), to belong (принадлежать), to resemble (иметь сходство), to fit (подходить), to contain (содержать), to
involve (включать в себя), to consist (состоять), to keep (хранить), to appear (появляться), to seem (казаться), to signify (выражать), to matter (значить).
Разница в употреблении Present Simple и Present Continuous
| Present Simple | Present Continuous |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Listening
Listen to the following radio talk show called Computer Forecast, in which Barry Harris, the host, is discussing the
future of software technology with ths two guests.
Прослушайте аудиозапись ток-шоу Computer Forecast, в котором ведущий Барри Харрис обсуждает будущее программных средств со своими
двумя гостями.

Ex. 6. Are the following sentences true or false? Choose the correct variant.
Нижеследующие предложения верны или нет? Выберите правильный вариант.
Speaking
Ex. 7. Answer the following questions.
Ответьте на следующие вопросы.
- What are your most favourite and least favourite pieces of software?
- What piece of software do you regularly use? What are its main advantages and disadvantages?
- What is the best freeware application you have downloaded from the Internet?
- What application programs would be used and for what purpose by a museum, by publishers of a subscription-only magazine, by police headquarters?
- Which data fields would you include in the database of the patients of a hospital, in the database of a library catalogue?
- What do you think about the future of software technology?
Writing
Ex. 8. If you were a developer of software, what kind of software program would you develop? Why? Write an essay (100-150 words).
So, you’have revised the structures of word processors, spreadsheets and databases. Also, you’ve learned Continuous Tense and may speak
about progressive actions. Moreover, you’ve listened to the speacialists’ opinions to the future of softwear and have expressed your opinion. Finally, you’ve been in developer’s shoes and thought
about your own softwear program.
Skip to content
If you’ve already produced a spreadsheet containing a list of advice, and you must make more entries to the list, here’s a fast and effortless way to better the information already entered on your spreadsheet. In summary, in the event that you simply must see the recorder, and you’re operating a modern version of Windows, then utilize Excel Viewer for best possibility of compatibility. At times developing a recorder requires a good deal of time, hence the templates that are also available in word format can help to pile up your information in an efficient method. The spreadsheet was made by John Sterling so as to supply the birding community using an easily-accessible single supply of county lists. Simple Spreadsheet is a beneficial tool for those users who ought to create spreadsheets and tables without installing complex applications. Our gambling pool spreadsheet is rather simple to use.
Spreadsheets usually supply the ability to portray information relationships graphically. Budget Spreadsheets have the right to be used for organization, institution, institution purposes and even for private documentation. It’s extremely simple to earn a blank budget spreadsheet, due to this simple accessibility to free blank spreadsheet templates that may be downloaded at no cost from several sites on the web.
Spreadsheets are frequently utilized to take care of data. Naturally, as with OpenOffice, there may be some compatibility problems, but the majority of the spreadsheets should open seamlessly. The subsequent downloadable spreadsheet consists of the template used to perform non-linear regression utilizing Microsoft Excel.
When you sit in on a virtual conference or when your boss starts firing off their favorite productivity tips, what do you do? You open a digital document and take notes. 📝
…probably with the same word processing software you’ve used since the ninth grade. 👀
Word processing software isn’t what it used to be—it’s better.
These tools have evolved beyond the boring blank screens we felt forced to use. Now, word processing can actually be fun!
Rich text editing, dynamic formatting, intuitive writing assistance, and collaboration features are some of the greatest benefits to using top word processing software. But the best part? It’s also incredibly affordable.
Follow along as we dive into every must-have word-processing feature and the 10 best word-processing software for every team, writing style, and use case! Complete with detailed feature comparisons, pros and cons, pricing, ratings, and more!
What is a Word Processing Software?
Word processing software is an application used to capture, format, and edit any form of writing—whether it be your general thoughts, meeting notes, SOPs, or email drafts. Your mind may immediately go to typewriters, but the benefits of word-processing software extend much further than that.

Thanks to the modern development of project management software, collaboration tools, and intuitive design, word processing software can do more than you ever thought possible! You can edit one document alongside your peers, arrange documents by category, share them via simple links, and flex your creativity with rich formatting. And these days, that’s just the bare minimum!
The thing is, there are a ton of word processing software to choose from these days.
In fact, we’d bet our bottom dollar that you can think of a few off the top of your head as we speak! You might even have a top three!
But with the number of new, flexible, and exciting features being added to word processing tools each day, it’s important to know what to look for in your go-to software in order to best serve your use case and to get the most bang for your buck.
What Should You Look for in Word Processing Software?
All this talk about advanced features makes you wonder—what does this functionality actually look like?
You don’t have to settle for the basic features we grew up struggling with. You also don’t have to fork over an arm and a leg to access powerful software that can take your documents so much further!

Here is a list of our favorite, must-have features to look for in your next word-processing software:
- Ease of use: Make sure your software is easy to learn, share with others, and efficiently supports your most-used functions
- Cloud-based and a reliable offline mode: Things happen! You might lose your wifi connection, need to switch devices, or be asked to share your documents on the spot. Cloud-based software and offline functionality ensure these hurdles won’t pose any real problem
- Collaboration features: These features make it possible for you to edit and develop documents in real-time with the team! With clarity and without overlap. And consider it a bonus if you can also tag your team or comment on your text
- Custom permissions and sharing: Especially if you often work with stakeholders, clients, or other departments, it’s important to have the ability to choose who can edit, view, or give access to your work
- Version history: This is your way of keeping a digital paper trail. Plus, if you make a mistake, you’ll have the power to go back and restore your text
- Integrations: The more integrations, the more information you can pull into your documents! Plus, it goes both ways, multiple integrations with your chosen word processing software means you can also access your documents from virtually anywhere and from any other tool
The 10 Best Word-Processing Software
There’s no reason why your word-processing software can’t be exciting, dynamic, or collaborative.
Digital editors and document sharing have come a long way in the past decade and we have tons of software to show for that growth! The challenge then becomes finding a tool that’s tailored to your unique needs and aligns with your work style.
So what do you do? You refer back to this list!
We’ve researched and tested the best word-processing software to bring you 10 of our favorites based on their best features, limitations, pricing, ratings, and more!
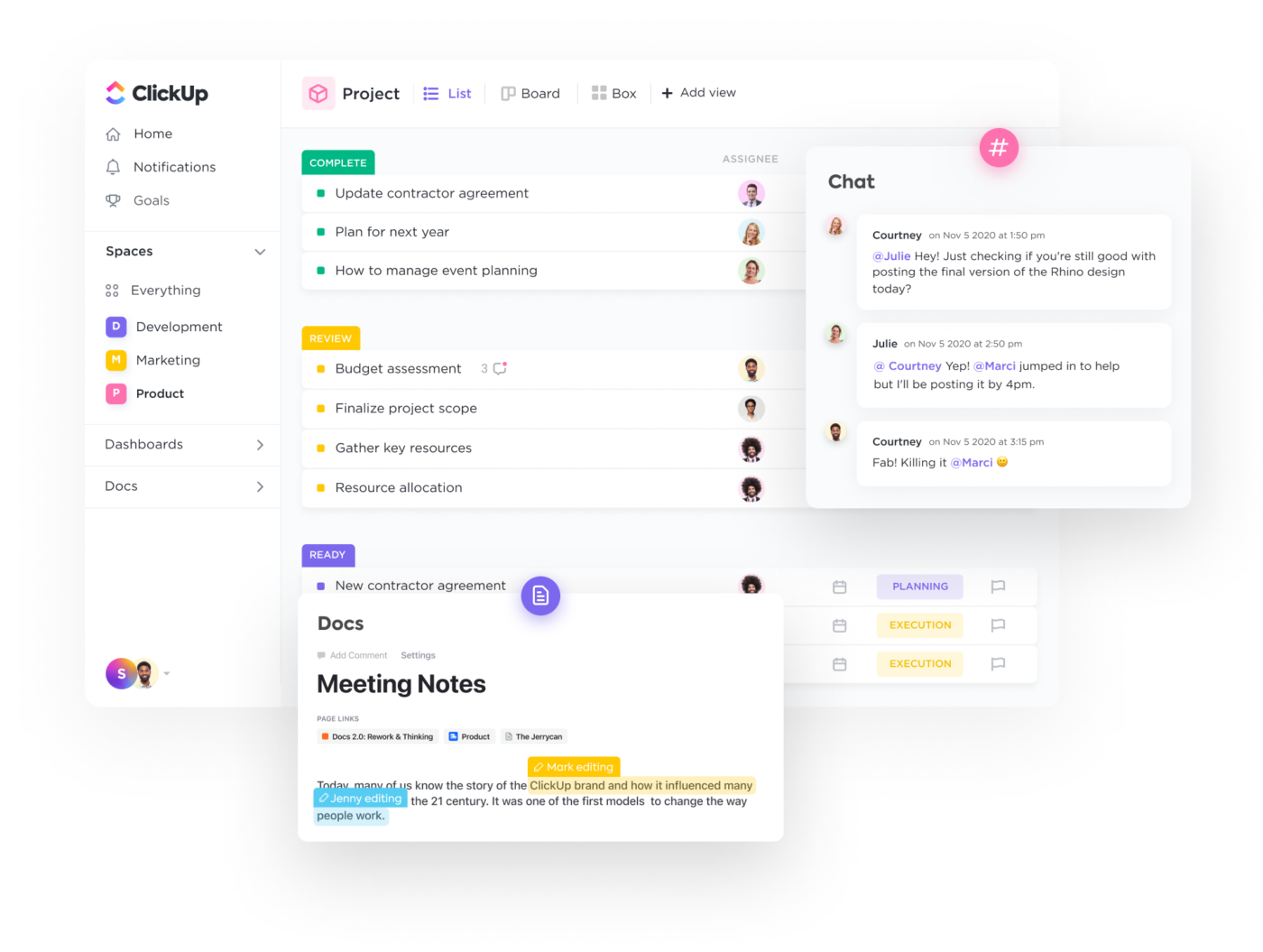
1. ClickUp

ClickUp is the ultimate all-in-one productivity tool for teams across industries to centralize their work into one collaborative platform. ClickUp is known for its rich set of fully customizable features, including a built-in document editor to create everything from simple to-do lists to detailed wikis, then connect them directly to your workflow.
With the ability to convert text into actionable tasks, embed data from virtually any other work tool, and collaborate on documents in real-time, ClickUp Docs is the ideal word processing tool for teams, students, and enterprise companies alike.
ClickUp best features
- Advanced word processing and work management features across every pricing plan, even Free Forever
- Embed media, tables, bookmarks, and even other documents into ClickUp Docs to bring more context and value into your roadmaps and knowledge bases
- Live detection in ClickUp Docs lets teams edit, contribute, and comment on the same document in real-time
- Link Docs to tasks and add widgets to automatically update workflows from your document editor
- Turn highlighted text into action items and delegate them to the team with threaded comments and @mentions
- Hundreds of templates for any use case, including several created specifically for ClickUp Docs
- Easy and secure sharing via URL for any guest, collaborator, or even public access
- Over 1,000 integrations to embed work into ClickUp Docs from virtually anywhere
- Nested pages and styling options to create visual hierarchies within every Doc
ClickUp cons
- There can be a bit of an adjustment period learning all of ClickUp’s advanced features
- Some views are not yet offered on the mobile app
ClickUp pricing
- Free Forever
- Unlimited: $5 per user, per month
- Business: $12 per user, per month
- Business Plus: $19 per user, per month
- Enterprise: Contact ClickUp for custom pricing
ClickUp ratings and reviews
- G2: 4.7/5 (5,680+ reviews)
- Capterra: 4.7/5 (3,540+ reviews)
2. Microsoft Word
Microsoft Word is a powerful word processor for anyone to create Word documents, spreadsheets, emails, and more. It’s part of the Microsoft Office Suite, which makes it easy to integrate with other Microsoft products like Excel and PowerPoint.
Word offers various features to help you stay organized, such as template options for different types of formal documents and advanced editing tools. You can add images, tables, charts, hyperlinks, and other media to enhance the look of your MS Word documents. The program also provides many features to help make creating documents more efficient, such as a spellchecker, auto-corrector, and thesaurus.
Microsoft Word best features
- OneDrive storage to save and access documents from anywhere
- Real-time collaboration to share and edit with others
- Spelling and grammar checker
- Mobile app
Microsoft Word limitations
- Functions on the toolbar are different from version to version
- Many features of Word forms don’t transfer and cause the format to break when printing documents
Microsoft Word pricing
- Microsoft Word is available as a standalone version for $159.99 or with a Microsoft 365 subscription
Microsoft Word ratings and reviews
- Capterra: 4.7/5 (1,600+ reviews)
- G2: 4.7/5 (1,000+ reviews)
3. Google Docs
Google Docs is an online word processor that makes it easy to create and edit professional documents. With real-time collaboration tools, Google Docs provides a platform for groups of people to collaborate on a single project, ensuring that everyone stays up-to-date with the document’s progress. Features like templated and automated formatting are also available to make your document look professional.
With Google Docs, users can track changes, comments, and suggestions as they make revisions and edits. All of the documents you create in Google Docs are automatically saved in the cloud, so you can access them from any device at any time. So whether you’re on your desktop or mobile device, you can continue working!
Google Docs best features
- @Mentions to pull relevant people, files, and events
- Smart Compose helps you write faster with fewer errors
- Third-party applications with project management tools
- Comment replies from Gmail
Google Docs limitations
- Limitations on document sizes
- Not suitable as a scalable knowledge base system
Google Docs pricing
- Google Docs is free with a Google account
Google Docs ratings and reviews
- Capterra: 4.7/5 (27,000+ reviews)
- G2: N/A
4. Grammarly
Grammarly is an AI-powered writing assistant. It helps you identify and fix grammar, spelling, punctuation, and other writing errors quickly. Grammarly offers suggestions while you’re using desktop apps or websites, including Gmail, ClickUp, LinkedIn, Google Docs, and more!
With Grammarly, you get feedback on your writing in real-time so you can improve it instantly. Plus, with its deep understanding of grammar topics and linguistics, you can trust your next report or project will be polished and professional. Grammarly makes it easy to focus on what’s important—creating strong, compelling content.
Discover the top content collaboration software!
Grammarly best features
- Style Guide to capture voice and style for consistent documents
- Text snippets to insert sentences and paragraphs in all workflows
- Tone Detector for effective communication
- In-app editor to upload documents
Grammarly limitations
- Doesn’t work for all apps and websites
- Expensive monthly subscriptions
Grammarly pricing
- Free plan
- Premium: $12/month
- Business: $15/member per month
Grammarly ratings and reviews
- Capterra: 4.7/5 (6,000+ reviews)
- G2: 4.6/5 (1,200+ reviews)
5. WPS Office
WPS Office is a comprehensive office suite that provides you with the tools and features necessary to manage all your documents, files, and presentations efficiently. It supports popular file formats and is compatible with PC and mobile devices. With WPS Office, users can create and edit text documents, spreadsheets, and slide shows in an intuitive and user-friendly interface.
It also includes powerful document management tools such as colorful themes, annotation, split PDF documents, and file format conversion. The software also has advanced collaboration capabilities that allow multiple users to work on the same file simultaneously.
WPS Office best features
- 100,000+ templates organized by categories
- Multiple language support
- Text extraction
- Watermark creation
WPS Office limitations
- Limited ability to handle different work styles and preferences
- A free plan is not available
WPS Office pricing
- WPS Premium: $18.99 for 6 months or $29.99 for 1 year
- WPS Business (WPS Cloud Pro): Starts at $5.99/user per month
WPS Office ratings and reviews
- Capterra: 4.5/5 (1,200+ reviews)
- G2: 4.4/5 (200+ reviews)
6. Dropbox Paper
Dropbox Paper offers a simple way to start a project. The drag–and–drop feature allows users to break down complex tasks into easily manageable chunks. By inviting teammates to collaborate on projects, everyone can contribute to the conversation, comment on each other’s work, and brainstorm in real-time.
The Master Doc feature allows anyone to create a hub for other docs. For complex or long-term projects, organizing documents from the start will boost productivity. It provides you with an efficient way to access and manage all the related documents by creating links to them. You don’t need to spend extra time searching for files. Search or navigate within the master document!
Dropbox Paper best features
- Search bar to find publicly viewable docs associated with a team member’s email address
- Keyboard shortcuts to highlight specific text
- Custom templates to standard forms
- Auto-generated table of contents
Dropbox Paper limitations
- Limitations on file upload sizes in a Dropbox account
- Basic users can only be signed into three devices at a time
Dropbox Paper pricing
- Plus: $9.99/month for 1 user
- Family: $16.99/family per month for up to 6 users
- Professional: $16.58/month for 1 user
- Standard: $15/user per month for 3+ users
- Advanced: $24/user per month for 3+ users
- Enterprise: Contact Dropbox for pricing
Dropbox Paper ratings and reviews
- Capterra: 4.4/5 (100+ reviews)
- G2: 4.1/5 (4,400+ reviews)
7. Notion
Notion is a document-based workspace for your notes, tasks, documents, and databases. It’s a versatile tool as a word processor to track any information, from project milestones and task reminders to travel plans and personal ideas.
Notion’s operating system makes it easy to organize whatever you need to keep track of. With its intuitive drag-and-drop interface, you can quickly set up custom workspaces tailored to whatever type of project or goal. Plus, Notion allows you to link between different databases and notes, create checklists, embed media, and more.
Check out the best Notion alternatives!
Notion best features
- iOS, Windows, web browser, MacOS platforms
- Calendar, Kanban boards, lists, and gallery views
- Real-time collaboration
- Bidirectional linking
Notion limitations
- Pricey premium plans compared to other word processors on this list
- Limited project and task management features
Notion pricing
- Free plan
- Plus: $8/user per month, billed annually
- Business: $15/user per month, billed annually
- Enterprise: Contact Notion for pricing
Notion ratings and reviews
- Capterra: 4.7/5 (1,100+ reviews)
- G2: 4.6/5 (1,000+ reviews)
8. Coda
Coda is a powerful document editor for creating and managing content. With Coda, you can create documents from scratch, edit existing ones, track changes, collaborate with others in real-time, and share them securely. The editor provides a range of tools to help you write fluently and quickly—including text formatting, image editing, tables, and hyperlinks.
Coda also comes with built-in collaboration features, so you can invite people to join in on projects and discuss changes easily. With its easy-to-use interface and intuitive tools, Coda is a word processor solution for anyone looking to build professional documents!
Coda best features
- Building blocks to upgrade documents into boards
- Dashboards to view connected data
- Google Calendar and Slack integrations
- Drag-and-drop basic templates
Coda limitations
- Not scalable as a document database compared to other word processors
- Limited integrations with other apps
Coda pricing
- Free plan
- Pro: $10/month per Doc Maker, billed annually
- Team: $30/month per Doc Maker, billed annually
- Enterprise: Contact Coda for pricing
Coda ratings and reviews
- Capterra: 4.6/5 (40+ reviews)
- G2: 4.7/5 (300+ reviews)
Bonus: Compare Coda Vs. Airtable
9. Evernote
Evernote is an online note-taking application to help you be more productive and organized. With Evernote, you can store anything from text-based notes to images, videos, and audio recordings. You can even add reminders and read web pages offline. Evernote is available for various platforms, including mobile devices. Plus, it has a Web Clipper browser extension!
No matter what type of project you’re working on, Evernote makes managing the details easier. Whether it’s brainstorming new content ideas or planning a business meeting, Evernote gives you the freedom to capture, organize and sync all your information. With features like searchable tags and categories, you’ll have the tools to find what you need, when you need it.
Connect Evernote and ClickUp to manage your notes in one place!
Evernote best features
- Calendar view to connect schedules and notes
- Document scanner to go paperless
- Due dates and reminders functionality
- Google Calendar integration
Evernote limitations
- Limited number of saved templates on all plans
- Evernote Teams account has a shared 30 GB of uploads per month
Evernote pricing
- Free plan
- Personal: $6.67/month, billed annually
- Professional: $9.17/month, billed annually
- Teams: $14.99/month per user
Evernote ratings and reviews
- Capterra: 4.4/5 (7,700+ reviews)
- G2: 4.4/5 (1,900+ reviews)
10. LibreOffice
LibreOffice is a free open source office suite designed to make completing everyday tasks easier. It’s an open-source product, meaning that it’s free and available to all users. LibreOffice includes programs for word processing, presentation building, spreadsheet editing, database manipulation, formula editing, drawing, and more.
Together these tools provide an intuitive user experience and help individuals create their best work. With LibreOffice, you can develop financial reports, spreadsheets, presentations, and more. If you want more functionality, extensions are available through the LibreOffice repository.
LibreOffice best features
- Formula editor to insert mathematical and scientific formulas
- LanguageTool APIs for grammar checking
- OpenDocument Format (ODF) extensions
- Custom templates
LibreOffice limitations
- Outdated interface compared to other free word processing programs
- Not scalable as a long-term document database
LibreOffice pricing
- LibreOffice is free
LibreOffice ratings and reviews
- Capterra: 4.3/5 (1,600+ reviews)
- G2: 4.3/5 (200+ reviews)
ClickUp—More Than the Average Word Processor
It’s time to ask for more from your word processing software, ClickUp Docs will show you how. 🙂
Edit with the team, turn your thoughts into actionable tasks, and connect your documents directly to your workflow, all without leaving your editor! No other word processor can enhance the value of your documents like ClickUp can. But the best part? ClickUp does it all for free.
Access ClickUp Docs, unlimited tasks, tons of templates and resources, more than 1,000 integrations, and so much more when you sign up for ClickUp today.
Download

Skip this Video
Loading SlideShow in 5 Seconds..
Using Word Processing, Spreadsheet, and Database Software PowerPoint Presentation
Download Presentation
Using Word Processing, Spreadsheet, and Database Software
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — E N D — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
Presentation Transcript
-
Using Word Processing, Spreadsheet, and Database Software Integrating Educational Technology into Teaching
-
General Word Processing Features and Capabilities • Storing documents for later use. • Erasing and inserting text. • Searching and replacing text. • Moving or copying text. • Inserting carriage returns — word wraparound. • Changing the style and appearance of text easily. • Justifying text on both margins. • Creating headers, footers, and numbering pages — pagination.
-
General Word Processing Features and Capabilities (cont.) • Inserting text prepared on other word processors. • Checking and correcting spelling. • Suggesting words. • Reviewing style and grammar. • Allowing the insertion of graphics. • Merging text with database files.
-
Advantages of Word Processing for Education • Saving time. • Creating professional looking documents. • Sharing text among multiple users.
-
Benefits of Word Processing: Findings from Research • Do students write better with word processing? ‘It depends’ (IETIT p131) • Generally, studies seem to suggest that students who are using word processing are improving their writing and their attitude toward writing only if it is used in the context of good writing instruction and if students have enough time to learn word processing features. • Teachers should not expect their student’s writing quality to improve automatically if the teachers use word processing software with their students.
-
Applying Word Processing in Various Instructional Ways • Writing processes. Students can write, edit, and illustrate stories by using word processing. • Dynamic group products. A group of students can write a poem or letter together, adding and changing lines anytime. • Individual language, writing, and reading exercises. • Encouraging writing across the curriculum.
-
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions when Learning Word Processing • Forgetting to move the cursor before typing. • Forgetting to highlight before changing a format. • ‘Losing’ part of the document. • Forgetting automatic wraparound at the end of lines.
-
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions when Learning Word Processing • Problems naming and saving files. • Incorrect spacing at the top or bottom of the document. —Loading paper in the printer. —Extra lines in the document. • Problems searching and replacing text.
-
Spreadsheet Software in Teaching and Learning • Spreadsheet are also called worksheets. • Spreadsheets were the earliest application software available for microcomputers. • A spreadsheet program can be a stand alone package or it can be part of an integrated package such as Microsoft Works. • Teachers use spreadsheets in gradebooks or gradekeeping packages to store and calculate grades.
-
Spreadsheet Features and Capabilities • Calculations and comparisons. Spreadsheets can calculate and manipulate stored numbers in lots of ways by using different formulas. • Automatic recalculation. • Copying cells.
-
Spreadsheet Features and Capabilities • Placing information in column-row formats for easy reading and interpretation. • Creating graphs that correspond to data. • Using worksheets prepared with other programs.
-
Advantages of Spreadsheets • Time savings. • Creating charts. • Answering “what if” questions. • Motivation.
-
Teacher Productivity — Applications of Spreadsheets • Gradekeeping. • Club and/or classroom budgets. • Computerized checkbooks for clubs or other organizations.
-
Teacher Productivity — Applications of Spreadsheets • Attendance charts. • Performance assessment checklist. • Class inventory.
-
Teaching and Learning Activities — Applications of Spreadsheets • Demonstrations. • Student products. • Problem solving activities. • Storing and analyzing data. • Projecting grades.
-
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions Learning Spreadsheets • Forgetting to highlight cells to be formatted. • Difficulty developing formulas and using predefined functions.
-
Database Defined • Allow users to store, organize, and manipulate information, including text and numerical data. • Allow the user to locate information through key word searches. • “ People often use the term database to refer both to the computer program and the product it creates. However, database products are also sometimes called files.
-
Types of Database Programs and Products • Single application: dBase, Microsoft Word • Integrated package: ClarisWorks, Microsoft Works • Database software: dBase, Microsoft Works • Prepared database: ERIC on Disc or online
-
Types of Database Programs and Products • Flat filing system: ClarisWorks, Microsoft Works • Relational filing system: dBase, Fox Pro, Oracle • Non-programmable systems: ClarisWorks, Microsoft Works • Programmable DBMS systems: dBase, Fox Pro, Oracle
-
General Database Features and Capabilities • Allowing changes to information. • Sorting information alphabetically or numerically. • Searching for information. • Creating & Retrieving reports or summaries of information. • Merging with word processing documents.
-
Advantages of Databases • Reducing data redundancy and error. • Saving time locating and/or updating information. • Allowing comparisons of information through queries. • Rapid information retrieval.
-
Issues Related to Databases • Privacy Act of 1974 • The Act also limits the kind of information that can be kept on citizens, and requires that people be told what information the government keeps on them. • Teachers must recognize their responsibility to safeguard student information and protect it from unauthorized access. • Teachers have to keep disks in secure places, make sure passwords remain secret, and delete information at the request of parents or students.
-
Teacher Productivity — Database Software • Teachers may use databases to help them prepare classroom materials and other tasks they would otherwise have to do by hand or couldn’t do at all. • Inventorying and locating instructional resources. • Using information on students to plan instruction and enhance motivation. • Using information on students to respond to questions or perform required tasks.
-
Teaching and Learning Activities — Database Software • Teaching research and study skills. • Teaching organization skills. • Understanding the power of information “pictures.” • Posing and testing hypotheses.
-
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions when Learning Databases • Confusing spreadsheet and database features. • Difficulties with keyword searches. • Decisions about which fields to include.
-
The End———-