From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
WordPerfect, a word processor first released for minicomputers in 1979 and later ported to microcomputers, running on Windows XP
A word processor (WP)[1][2] is a device or computer program that provides for input, editing, formatting, and output of text, often with some additional features.
Early word processors were stand-alone devices dedicated to the function, but current word processors are word processor programs running on general purpose computers.
The functions of a word processor program fall somewhere between those of a simple text editor and a fully functioned desktop publishing program. However, the distinctions between these three have changed over time and were unclear after 2010.[3][4]
Background[edit]
Word processors did not develop out of computer technology. Rather, they evolved from mechanical machines and only later did they merge with the computer field.[5] The history of word processing is the story of the gradual automation of the physical aspects of writing and editing, and then to the refinement of the technology to make it available to corporations and Individuals.
The term word processing appeared in American offices in early 1970s centered on the idea of streamlining the work to typists, but the meaning soon shifted toward the automation of the whole editing cycle.
At first, the designers of word processing systems combined existing technologies with emerging ones to develop stand-alone equipment, creating a new business distinct from the emerging world of the personal computer. The concept of word processing arose from the more general data processing, which since the 1950s had been the application of computers to business administration.[6]
Through history, there have been three types of word processors: mechanical, electronic and software.
Mechanical word processing[edit]
The first word processing device (a «Machine for Transcribing Letters» that appears to have been similar to a typewriter) was patented by Henry Mill for a machine that was capable of «writing so clearly and accurately you could not distinguish it from a printing press».[7] More than a century later, another patent appeared in the name of William Austin Burt for the typographer. In the late 19th century, Christopher Latham Sholes[8] created the first recognizable typewriter although it was a large size, which was described as a «literary piano».[9]
The only «word processing» these mechanical systems could perform was to change where letters appeared on the page, to fill in spaces that were previously left on the page, or to skip over lines. It was not until decades later that the introduction of electricity and electronics into typewriters began to help the writer with the mechanical part. The term “word processing” (translated from the German word Textverarbeitung) itself was created in the 1950s by Ulrich Steinhilper, a German IBM typewriter sales executive. However, it did not make its appearance in 1960s office management or computing literature (an example of grey literature), though many of the ideas, products, and technologies to which it would later be applied were already well known. Nonetheless, by 1971 the term was recognized by the New York Times[10] as a business «buzz word». Word processing paralleled the more general «data processing», or the application of computers to business administration.
Thus by 1972 discussion of word processing was common in publications devoted to business office management and technology, and by the mid-1970s the term would have been familiar to any office manager who consulted business periodicals.
Electromechanical and electronic word processing[edit]
By the late 1960s, IBM had developed the IBM MT/ST (Magnetic Tape/Selectric Typewriter). This was a model of the IBM Selectric typewriter from the earlier part of this decade, but it came built into its own desk, integrated with magnetic tape recording and playback facilities along with controls and a bank of electrical relays. The MT/ST automated word wrap, but it had no screen. This device allowed a user to rewrite text that had been written on another tape, and it also allowed limited collaboration in the sense that a user could send the tape to another person to let them edit the document or make a copy. It was a revolution for the word processing industry. In 1969, the tapes were replaced by magnetic cards. These memory cards were inserted into an extra device that accompanied the MT/ST, able to read and record users’ work.
In the early 1970s, word processing began to slowly shift from glorified typewriters augmented with electronic features to become fully computer-based (although only with single-purpose hardware) with the development of several innovations. Just before the arrival of the personal computer (PC), IBM developed the floppy disk. In the early 1970s, the first word-processing systems appeared which allowed display and editing of documents on CRT screens.
During this era, these early stand-alone word processing systems were designed, built, and marketed by several pioneering companies. Linolex Systems was founded in 1970 by James Lincoln and Robert Oleksiak. Linolex based its technology on microprocessors, floppy drives and software. It was a computer-based system for application in the word processing businesses and it sold systems through its own sales force. With a base of installed systems in over 500 sites, Linolex Systems sold 3 million units in 1975 — a year before the Apple computer was released.[11]
At that time, the Lexitron Corporation also produced a series of dedicated word-processing microcomputers. Lexitron was the first to use a full-sized video display screen (CRT) in its models by 1978. Lexitron also used 51⁄4 inch floppy diskettes, which became the standard in the personal computer field. The program disk was inserted in one drive, and the system booted up. The data diskette was then put in the second drive. The operating system and the word processing program were combined in one file.[12]
Another of the early word processing adopters was Vydec, which created in 1973 the first modern text processor, the «Vydec Word Processing System». It had built-in multiple functions like the ability to share content by diskette and print it.[further explanation needed] The Vydec Word Processing System sold for $12,000 at the time, (about $60,000 adjusted for inflation).[13]
The Redactron Corporation (organized by Evelyn Berezin in 1969) designed and manufactured editing systems, including correcting/editing typewriters, cassette and card units, and eventually a word processor called the Data Secretary. The Burroughs Corporation acquired Redactron in 1976.[14]
A CRT-based system by Wang Laboratories became one of the most popular systems of the 1970s and early 1980s. The Wang system displayed text on a CRT screen, and incorporated virtually every fundamental characteristic of word processors as they are known today. While early computerized word processor system were often expensive and hard to use (that is, like the computer mainframes of the 1960s), the Wang system was a true office machine, affordable to organizations such as medium-sized law firms, and easily mastered and operated by secretarial staff.
The phrase «word processor» rapidly came to refer to CRT-based machines similar to Wang’s. Numerous machines of this kind emerged, typically marketed by traditional office-equipment companies such as IBM, Lanier (AES Data machines — re-badged), CPT, and NBI. All were specialized, dedicated, proprietary systems, with prices in the $10,000 range. Cheap general-purpose personal computers were still the domain of hobbyists.
Japanese word processor devices[edit]
In Japan, even though typewriters with Japanese writing system had widely been used for businesses and governments, they were limited to specialists who required special skills due to the wide variety of letters, until computer-based devices came onto the market. In 1977, Sharp showcased a prototype of a computer-based word processing dedicated device with Japanese writing system in Business Show in Tokyo.[15][16]
Toshiba released the first Japanese word processor JW-10 in February 1979.[17] The price was 6,300,000 JPY, equivalent to US$45,000. This is selected as one of the milestones of IEEE.[18]
Toshiba Rupo JW-P22(K)(March 1986) and an optional micro floppy disk drive unit JW-F201
The Japanese writing system uses a large number of kanji (logographic Chinese characters) which require 2 bytes to store, so having one key per each symbol is infeasible. Japanese word processing became possible with the development of the Japanese input method (a sequence of keypresses, with visual feedback, which selects a character) — now widely used in personal computers. Oki launched OKI WORD EDITOR-200 in March 1979 with this kana-based keyboard input system. In 1980 several electronics and office equipment brands entered this rapidly growing market with more compact and affordable devices. While the average unit price in 1980 was 2,000,000 JPY (US$14,300), it was dropped to 164,000 JPY (US$1,200) in 1985.[19] Even after personal computers became widely available, Japanese word processors remained popular as they tended to be more portable (an «office computer» was initially too large to carry around), and become necessities in business and academics, even for private individuals in the second half of the 1980s.[20] The phrase «word processor» has been abbreviated as «Wa-pro» or «wapuro» in Japanese.
Word processing software[edit]
The final step in word processing came with the advent of the personal computer in the late 1970s and 1980s and with the subsequent creation of word processing software. Word processing software that would create much more complex and capable output was developed and prices began to fall, making them more accessible to the public. By the late 1970s, computerized word processors were still primarily used by employees composing documents for large and midsized businesses (e.g., law firms and newspapers). Within a few years, the falling prices of PCs made word processing available for the first time to all writers in the convenience of their homes.
The first word processing program for personal computers (microcomputers) was Electric Pencil, from Michael Shrayer Software, which went on sale in December 1976. In 1978 WordStar appeared and because of its many new features soon dominated the market. However, WordStar was written for the early CP/M (Control Program–Micro) operating system, and by the time it was rewritten for the newer MS-DOS (Microsoft Disk Operating System), it was obsolete. Suddenly, WordPerfect dominated the word processing programs during the DOS era, while there was a large variety of less successful programs.
Early word processing software was not as intuitive as word processor devices. Most early word processing software required users to memorize semi-mnemonic key combinations rather than pressing keys such as «copy» or «bold». Moreover, CP/M lacked cursor keys; for example WordStar used the E-S-D-X-centered «diamond» for cursor navigation. However, the price differences between dedicated word processors and general-purpose PCs, and the value added to the latter by software such as “killer app” spreadsheet applications, e.g. VisiCalc and Lotus 1-2-3, were so compelling that personal computers and word processing software became serious competition for the dedicated machines and soon dominated the market.
Then in the late 1980s innovations such as the advent of laser printers, a «typographic» approach to word processing (WYSIWYG — What You See Is What You Get), using bitmap displays with multiple fonts (pioneered by the Xerox Alto computer and Bravo word processing program), and graphical user interfaces such as “copy and paste” (another Xerox PARC innovation, with the Gypsy word processor). These were popularized by MacWrite on the Apple Macintosh in 1983, and Microsoft Word on the IBM PC in 1984. These were probably the first true WYSIWYG word processors to become known to many people.
Of particular interest also is the standardization of TrueType fonts used in both Macintosh and Windows PCs. While the publishers of the operating systems provide TrueType typefaces, they are largely gathered from traditional typefaces converted by smaller font publishing houses to replicate standard fonts. Demand for new and interesting fonts, which can be found free of copyright restrictions, or commissioned from font designers, occurred.
The growing popularity of the Windows operating system in the 1990s later took Microsoft Word along with it. Originally called «Microsoft Multi-Tool Word», this program quickly became a synonym for “word processor”.
From early in the 21st century Google Docs popularized the transition to online or offline web browser based word processing, this was enabled by the widespread adoption of suitable internet connectivity in businesses and domestic households and later the popularity of smartphones. Google Docs enabled word processing from within any vendor’s web browser, which could run on any vendor’s operating system on any physical device type including tablets and smartphones, although offline editing is limited to a few Chromium based web browsers. Google Docs also enabled the significant growth of use of information technology such as remote access to files and collaborative real-time editing, both becoming simple to do with little or no need for costly software and specialist IT support.
See also[edit]
- List of word processors
- Formatted text
References[edit]
- ^ Enterprise, I. D. G. (1 January 1981). «Computerworld». IDG Enterprise. Archived from the original on 2 January 2019. Retrieved 1 January 2019 – via Google Books.
- ^ Waterhouse, Shirley A. (1 January 1979). Word processing fundamentals. Canfield Press. ISBN 9780064537223. Archived from the original on 2 January 2019. Retrieved 1 January 2019 – via Google Books.
- ^ Amanda Presley (28 January 2010). «What Distinguishes Desktop Publishing From Word Processing?». Brighthub.com. Archived from the original on 1 April 2019. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
- ^ «How to Use Microsoft Word as a Desktop Publishing Tool». PCWorld. 28 May 2012. Archived from the original on 19 August 2017. Retrieved 3 May 2018.
- ^ Price, Jonathan, and Urban, Linda Pin. The Definitive Word-Processing Book. New York: Viking Penguin Inc., 1984, page xxiii.
- ^ W.A. Kleinschrod, «The ‘Gal Friday’ is a Typing Specialist Now,» Administrative Management vol. 32, no. 6, 1971, pp. 20-27
- ^ Hinojosa, Santiago (June 2016). «The History of Word Processors». The Tech Ninja’s Dojo. The Tech Ninja. Archived from the original on 6 May 2018. Retrieved 6 May 2018.
- ^ See also Samuel W. Soule and Carlos Glidden.
- ^ The Scientific American, The Type Writer, New York (August 10, 1872)
- ^ W.D. Smith, “Lag Persists for Business Equipment,” New York Times, 26 Oct. 1971, pp. 59-60.
- ^ Linolex Systems, Internal Communications & Disclosure in 3M acquisition, The Petritz Collection, 1975.
- ^ «Lexitron VT1200 — RICM». Ricomputermuseum.org. Archived from the original on 3 January 2019. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
- ^ Hinojosa, Santiago (1 June 2016). «The History of Word Processors». The Tech Ninja’s Dojo. Archived from the original on 24 December 2018. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
- ^ «Redactron Corporation. @ SNAC». Snaccooperative.org. Archived from the original on 15 December 2018. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
- ^ «日本語ワードプロセッサ». IPSJコンピュータ博物館. Retrieved 2017-07-05.
- ^ «【シャープ】 日本語ワープロの試作機». IPSJコンピュータ博物館. Retrieved 2017-07-05.
- ^ 原忠正 (1997). «日本人による日本人のためのワープロ». The Journal of the Institute of Electrical Engineers of Japan. 117 (3): 175–178. Bibcode:1997JIEEJ.117..175.. doi:10.1541/ieejjournal.117.175.
- ^ «プレスリリース;当社の日本語ワードプロセッサが「IEEEマイルストーン」に認定». 東芝. 2008-11-04. Retrieved 2017-07-05.
- ^
«【富士通】 OASYS 100G». IPSJコンピュータ博物館. Retrieved 2017-07-05. - ^ 情報処理学会 歴史特別委員会『日本のコンピュータ史』ISBN 4274209334 p135-136
Word Processing
Andrew Prestage, in Encyclopedia of Information Systems, 2003
I. An Introduction to Word Processing
Word processing is the act of using a computer to transform written, verbal, or recorded information into typewritten or printed form. This chapter will discuss the history of word processing, identify several popular word processing applications, and define the capabilities of word processors.
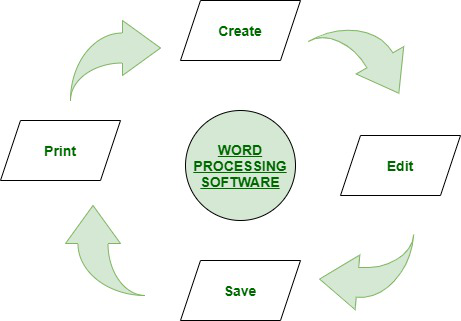
Of all the computer applications in use, word processing is by far the most common. The ability to perform word processing requires a computer and a special type of computer software called a word processor. A word processor is a program designed to assist with the production of a wide variety of documents, including letters, memoranda, and manuals, rapidly and at relatively low cost. A typical word processor enables the user to create documents, edit them using the keyboard and mouse, store them for later retrieval, and print them to a printer. Common word processing applications include Microsoft Notepad, Microsoft Word, and Corel WordPerfect.
Word processing technology allows human beings to freely and efficiently share ideas, thoughts, feelings, sentiments, facts, and other information in written form. Throughout history, the written word has provided mankind with the ability to transform thoughts into printed words for distribution to hundreds, thousands, or possibly millions of readers around the world. The power of the written word to transcend verbal communications is best exemplified by the ability of writers to share information and express ideas with far larger audiences and the permanency of the written word.
The increasingly large collective body of knowledge is one outcome of the permanency of the written word, including both historical and current works. Powered by decreasing prices, increasing sophistication, and widespread availability of technology, the word processing revolution changed the landscape of communications by giving people hitherto unavailable power to make or break reputations, to win or lose elections, and to inspire or mislead through the printed word.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B0122272404001982
Computers and Effective Security Management1
Charles A. Sennewald, Curtis Baillie, in Effective Security Management (Sixth Edition), 2016
Word Processing
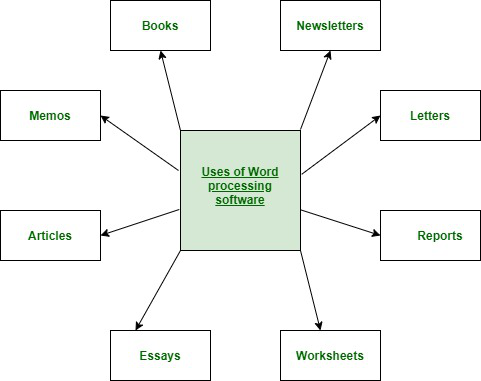
Word processing software can easily create, edit, store, and print text documents such as letters, memoranda, forms, employee performance evaluations (such as those in Appendix A), proposals, reports, security surveys (such as those in Appendix B), general security checklists, security manuals, books, articles, press releases, and speeches. A professional-looking document can be easily created and readily updated when necessary.
The length of created documents is limited only by the storage capabilities of the computer, which are enormous. Also, if multiple copies of a working document exist, changes to it should be promptly communicated to all persons who use the document. Specialized software, using network features, can be programmed to automatically route changes to those who need to know about updates.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128027745000241
Globalization
Jennifer DeCamp, in Encyclopedia of Information Systems, 2003
II.D.2.c. Rendering Systems
Special word processing software is usually required to correctly display languages that are substantially different from English, for example:
- 1.
-
Connecting characters, as in Arabic, Persian, Urdu, Hindi, and Hebrew
- 2.
-
Different text direction, as in the right-to-left capability required in Arabic, Persian, Urdu, and Hindi, or the right-to-left and top-to-bottom capability in formal Chinese
- 3.
-
Multiple accents or diacritics, such as in Vietnamese or in fully vowelled Arabic
- 4.
-
Nonlinear text entry, as in Hindi, where a vowel may be typed after the consonant but appears before the consonant.
Alternatives to providing software with appropriate character rendering systems include providing graphic files or elaborate formatting (e.g., backwards typing of Arabic and/or typing of Arabic with hard line breaks). However, graphic files are cumbersome to download and use, are space consuming, and cannot be electronically searched except by metadata. The second option of elaborate formatting often does not look as culturally appropriate as properly rendered text, and usually loses its special formatting when text is added or is upgraded to a new system. It is also difficult and time consuming to produce. Note that Microsoft Word 2000 and Office XP support the above rendering systems; Java 1.4 supports the above rendering systems except for vertical text.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B0122272404000800
Text Entry When Movement is Impaired
Shari Trewin, John Arnott, in Text Entry Systems, 2007
15.3.2 Abbreviation Expansion
Popular word processing programs often include abbreviation expansion capabilities. Abbreviations for commonly used text can be defined, allowing a long sequence such as an address to be entered with just a few keystrokes. With a little investment of setup time, those who are able to remember the abbreviations they have defined can find this a useful technique. Abbreviation expansion schemes have also been developed specifically for people with disabilities (Moulton et al., 1999; Vanderheiden, 1984).
Automatic abbreviation expansion at phrase/sentence level has also been investigated: the Compansion (Demasco & McCoy, 1992; McCoy et al., 1998) system was designed to process and expand spontaneous language constructions, using Natural Language Processing to convert groups of uninflected content words automatically into full phrases or sentences. For example, the output sentence “John breaks the window with the hammer” might derive from the user input text “John break window hammer” using such an approach.
With the rise of text messaging on mobile devices such as mobile (cell) phones, abbreviations are increasingly commonplace in text communications. Automatic expansion of many abbreviations may not be necessary, however, depending on the context in which the text is being used. Frequent users of text messaging can learn to recognize a large number of abbreviations without assistance.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123735911500152
Case Studies
Brett Shavers, in Placing the Suspect Behind the Keyboard, 2013
Altered evidence and spoliation
Electronic evidence in the form of word processing documents which were submitted by a party in litigation is alleged to have been altered. Altered electronic evidence has become a common claim with the ability to determine the changes becoming more difficult. How do you know if an email has been altered? What about a text document?
Case in Point
Odom v Microsoft and Best Buy, 2006
The Odom v Microsoft and Best Buy litigation primarily focused on Internet access offered to customers in which the customers were automatically billed for Internet service without their consent. One of the most surprising aspects of this case involved the altering of electronic evidence by an attorney for Best Buy. The attorney, Timothy Block, admitted to altering documents prior to producing the documents in discovery to benefit Best Buy.
Investigative Tips: All evidence needs to be validated for authenticity. The weight given in legal hearings depends upon the veracity of the evidence. Many electronic files can be quickly validated through hash comparisons. An example seen in Figure 11.4 shows two files with different file names, yet their hash values are identical. If one file is known to be valid, perhaps an original evidence file, any file matching the hash values would also be a valid and unaltered copy of the original file.
Figure 11.4. Two files with different file names, but having the same hash value, indicating the contents of the files are identical.
Alternatively, Figure 11.5 shows two files with the same file name but having different hash values. If there were a claim that both of these files are the same original files, it would be apparent that one of the files has been modified.
Figure 11.5. Two files with the same file names, but having different hash values, indicating the contents are not identical.
Finding the discrepancies or modifications of an electronic file can only be accomplished if there is a comparison to be made with the original file. Using Figure 11.5 as an example, given that the file having the MD5 hash value of d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e is the original, and where the second file is the alleged altered file, a visual inspection of both files should be able to determine the modifications. However, when only file exists, proving the file to be unaltered is more than problematic, it is virtually impossible.
In this situation of having a single file to verify as original and unaltered evidence, an analysis would only be able to show when the file was modified over time, but the actual modifications won’t be known. Even if the document has “track changed” enabled, which logs changes to a document, that would only capture changes that were tracked, as there may be more untracked and unknown changes.
As a side note to hash values, in Figure 11.5, the hash values are completely different, even though the only difference between the two sample files is a single period added to the text. Any modification, no matter how minor, results in a drastic different hash value.
The importance in validating files in relation to the identification of a suspect that may have altered a file is that the embedded metadata will be a key point of focus and avenue for case leads. As a file is created, copied, modified, and otherwise touched, the file and system metadata will generally be updated.
Having the dates and times of these updates should give rise to you that the updates occurred on some computer system. This may be on one or more computers even if the file existed on a flash drive. At some point, the flash drive was connected to a computer system, where evidence on a system may show link files to the file. Each of these instances of access to the file is an opportunity to create a list of possible suspects having access to those systems in use at each updated metadata fields.
In the Microsoft Windows operating systems, Volume Shadow Copies may provide an examiner with a string of previous versions of a document, in which the modifications between each version can be determined. Although not every change may have been incrementally saved by the Volume Shadow Service, such as if the file was saved to a flash drive, any previous versions that can be found will allow to find some of the modifications made.
Where a single file will determine the outcome of an investigation or have a dramatic effect on the case, the importance of ‘getting it right’ cannot be overstated. Such would be the case of a single file, modified by someone in a business office, where many persons had common access to the evidence file before it was known to be evidence. Finding the suspect that altered the evidence file may be simple if you were at the location close to the time of occurrence. Interviews of the employees would be easier as most would remember their whereabouts in the office within the last few days. Some may be able to tell you exactly where other employees were in the office, even point the suspect out directly.
But what if you are called in a year later? How about 2 or more years later? What would be the odds employees remembering their whereabouts on a Monday in July 2 years earlier? To identify a suspect at this point requires more than a forensic analysis of a computer. It will probably require an investigation into work schedules, lunch schedules, backup tapes, phone call logs, and anything else to place everyone somewhere during the time of the file being altered.
Potentially you may even need to examine the hard drive of a copy machine and maybe place a person at the copy machine based on what was copied at the time the evidence file was being modified. When a company’s livelihood is at stake or a person’s career is at risk, leave no stone unturned. If you can’t place a suspect at the scene, you might be able to place everyone else at a location, and those you can’t place, just made your list of possible suspects.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9781597499859000113
When, How, and Why Do We Trust Technology Too Much?
Patricia L. Hardré, in Emotions, Technology, and Behaviors, 2016
Trusting Spelling and Grammar Checkers
We often see evidence that users of word processing systems trust absolutely in spelling and grammar checkers. From errors in business letters and on resumes to uncorrected word usage in academic papers, this nonstrategy emerges as epidemic. It underscores a pattern of implicit trust that if a word is not flagged as incorrect in a word processing system, then it must be not only spelled correctly but also used correctly. The overarching error is trusting the digital checking system too much, while the underlying functional problem is that such software identifies gross errors (such as nonwords) but cannot discriminate finer nuances of language requiring judgment (like real words used incorrectly). Users from average citizens to business executives have become absolutely comfortable with depending on embedded spelling and grammar checkers that are supposed to autofind, trusting the technology so much that they often do not even proofread. Like overtrust of security monitoring, these personal examples are instances of reduced vigilance due to their implicit belief that the technology is functionally flawless, that if the technology has not found an error, then an error must not exist.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128018736000054
Establishing a C&A Program
Laura Taylor, Matthew Shepherd Technical Editor, in FISMA Certification and Accreditation Handbook, 2007
Template Development
Certification Packages consist of a set of documents that all go together and complement one another. A Certification Package is voluminous, and without standardization, it takes an inordinate amount of time to evaluate it to make sure all the right information is included. Therefore, agencies should have templates for all the documents that they require in their Certification Packages. Agencies without templates should work on creating them. If an agency does not have the resources in-house to develop these templates, they should consider outsourcing this initiative to outside consultants.
A template should be developed using the word processing application that is the standard within the agency. All of the relevant sections that the evaluation team will be looking for within each document should be included. Text that will remain constant for a particular document type also should be included. An efficient and effective C&A program will have templates for the following types of C&A documents:
- ▪
-
Categorization and Certification Level Recommendation
- ▪
-
Hardware and Software Inventory
- ▪
-
Self-Assessment
- ▪
-
Security Awareness and Training Plan
- ▪
-
End-User Rules of Behavior
- ▪
-
Incident Response Plan
- ▪
-
Security Test and Evaluation Plan
- ▪
-
Privacy Impact Assessment
- ▪
-
Business Risk Assessment
- ▪
-
Business Impact Assessment
- ▪
-
Contingency Plan
- ▪
-
Configuration Management Plan
- ▪
-
System Risk Assessment
- ▪
-
System Security Plan
- ▪
-
Security Assessment Report
The later chapters in this book will help you understand what should be included in each of these types of documents. Some agencies may possibly require other types of documents as required by their information security program and policies.
Templates should include guidelines for what type of content should be included, and also should have built-in formatting. The templates should be as complete as possible, and any text that should remain consistent and exactly the same in like document types should be included. Though it may seem redundant to have the exact same verbatim text at the beginning of, say, each Business Risk Assessment from a particular agency, each document needs to be able to stand alone and make sense if it is pulled out of the Certification Package for review. Having similar wording in like documents also shows that the packages were developed consistently using the same methodology and criteria.
With established templates in hand, it makes it much easier for the C&A review team to understand what it is that they need to document. Even expert C&A consultants need and appreciate document templates. Finding the right information to include the C&A documents can by itself by extremely difficult without first having to figure out what it is that you are supposed to find—which is why the templates are so very important. It’s often the case that a large complex application is distributed and managed throughout multiple departments or divisions and it can take a long time to figure out not just what questions to ask, but who the right people are who will know the answers.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9781597491167500093
Speech Recognition
John-Paul Hosom, in Encyclopedia of Information Systems, 2003
I.B. Capabilities and Limitations of Automatic Speech Recognition
ASR is currently used for dictation into word processing software, or in a “command-and-control” framework in which the computer recognizes and acts on certain key words. Dictation systems are available for general use, as well as for specialized fields such as medicine and law. General dictation systems now cost under $100 and have speaker-dependent word-recognition accuracy from 93% to as high as 98%. Command-and-control systems are more often used over the telephone for automatically dialing telephone numbers or for requesting specific services before (or without) speaking to a human operator. Telephone companies use ASR to allow customers to automatically place calls even from a rotary telephone, and airlines now utilize telephone-based ASR systems to help passengers locate and reclaim lost luggage. Research is currently being conducted on systems that allow the user to interact naturally with an ASR system for goals such as making airline or hotel reservations.
Despite these successes, the performance of ASR is often about an order of magnitude worse than human-level performance, even with superior hardware and long processing delays. For example, recognition of the digits “zero” through “nine” over the telephone has word-level accuracy of about 98% to 99% using ASR, but nearly perfect recognition by humans. Transcription of radio broadcasts by world-class ASR systems has accuracy of less than 87%. This relatively low accuracy of current ASR systems has limited its use; it is not yet possible to reliably and consistently recognize and act on a wide variety of commands from different users.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B0122272404001647
Prototyping
Rex Hartson, Pardha Pyla, in The UX Book (Second Edition), 2019
20.7 Software Tools for Making Wireframes
Wireframes can be sketched using any drawing or word processing software package that supports creating and manipulating shapes. While many applications suffice for simple wireframing, we recommend tools designed specifically for this purpose. We use Sketch, a drawing app, to do all the drawing. Craft is a plug-in to Sketch that connects it to InVision, allowing you to export Sketch screen designs to InVision to incorporate hotspots as working links.
In the “Build mode” of InVision, you work on one screen at a time, adding rectangular overlays that are the hotspots. For each hotspot, you specify what other screen you go to when someone clicks on that hotspot in “Preview mode.” You get a nice bonus using InVision: In the “operate” mode, you, or the user, can click anywhere in an open space in the prototype and it highlights all the available links. These tools are available only on Mac computers, but similar tools are available under Windows.
Beyond this discussion, it’s not wise to try to cover software tools for making prototypes in this kind of textbook. The field is changing fast and whatever we could say here would be out of date by the time you read this. Plus, it wouldn’t be fair to the numerous other perfectly good tools that didn’t get cited. To get the latest on software tools for prototyping, it’s better to ask an experienced UX professional or to do your research online.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128053423000205
Design Production
Rex Hartson, Partha S. Pyla, in The UX Book, 2012
9.5.3 How to Build Wireframes?
Wireframes can be built using any drawing or word processing software package that supports creating and manipulating shapes, such as iWork Pages, Keynote, Microsoft PowerPoint, or Word. While such applications suffice for simple wireframing, we recommend tools designed specifically for this purpose, such as OmniGraffle (for Mac), Microsoft Visio (for PC), and Adobe InDesign.
Many tools and templates for making wireframes are used in combination—truly an invent-as-you-go approach serving the specific needs of prototyping. For example, some tools are available to combine the generic-looking placeholders in wireframes with more detailed mockups of some screens or parts of screens. In essence they allow you to add color, graphics, and real fonts, as well as representations of real content, to the wireframe scaffolding structure.
In early stages of design, during ideation and sketching, you started with thinking about the high-level conceptual design. It makes sense to start with that here, too, first by wireframing the design concept and then by going top down to address major parts of the concept. Identify the interaction conceptual design using boxes with labels, as shown in Figure 9-4.
Take each box and start fleshing out the design details. What are the different kinds of interaction needed to support each part of the design, and what kinds of widgets work best in each case? What are the best ways to lay them out? Think about relationships among the widgets and any data that need to go with them. Leverage design patterns, metaphors, and other ideas and concepts from the work domain ontology. Do not spend too much time with exact locations of these widgets or on their alignment yet. Such refinement will come in later iterations after all the key elements of the design are represented.
As you flesh out all the major areas in the design, be mindful of the information architecture on the screen. Make sure the wireframes convey that inherent information architecture. For example, do elements on the screen follow a logical information hierarchy? Are related elements on the screen positioned in such a way that those relationships are evident? Are content areas indented appropriately? Are margins and indents communicating the hierarchy of the content in the screen?
Next it is time to think about sequencing. If you are representing a workflow, start with the “wake-up” state for that workflow. Then make a wireframe representing the next state, for example, to show the result of a user action such as clicking on a button. In Figure 9-6 we showed what happens when a user clicks on the “Related information” expander widget. In Figure 9-7 we showed what happens if the user clicks on the “One-up” view switcher button.
Once you create the key screens to depict the workflow, it is time to review and refine each screen. Start by specifying all the options that go on the screen (even those not related to this workflow). For example, if you have a toolbar, what are all the options that go into that toolbar? What are all the buttons, view switchers, window controllers (e.g., scrollbars), and so on that need to go on the screen? At this time you are looking at scalability of your design. Is the design pattern and layout still working after you add all the widgets that need to go on this screen?
Think of cases when the windows or other container elements such as navigation bars in the design are resized or when different data elements that need to be supported are larger than shown in the wireframe. For example, in Figures 9-5 and 9-6, what must happen if the number of photo collections is greater than what fits in the default size of that container? Should the entire page scroll or should new scrollbars appear on the left-hand navigation bar alone? How about situations where the number of people identified in a collection are large? Should we show the first few (perhaps ones with most number of associated photos) with a “more” option, should we use an independent scrollbar for that pane, or should we scroll the entire page? You may want to make wireframes for such edge cases; remember they are less expensive and easier to do using boxes and lines than in code.
As you iterate your wireframes, refine them further, increasing the fidelity of the deck. Think about proportions, alignments, spacing, and so on for all the widgets. Refine the wording and language aspects of the design. Get the wireframe as close to the envisioned design as possible within the constraints of using boxes and lines.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123852410000099
Goals
- Students will recognize the major types of word processing programs.
- Students will discriminate the types of problems that are best solved
with various types of word processors. - Students will recognize the major tools that are available in word
processor application programs. - Students will use a text editor to create and modify a simple ASCII
text file. - Students will use a high end word processing program to practice
common text formatting problems.
Prereqs
- Comfort with the keyboard and mouse
- Experience with the STAIR process for solving problems
- Familiarity with principles of data encoding
- Familiarity with differences between hardware and software
- Understanding of the attributes of RAM
- Familiarity with operating systems, file names and directories
Discussion
Word processing is one of the most common applications for computers
today. It would be difficult to spend a day in a modern office or
university without coming into contact with a word processing program.
Most people have had some contact with word processing. We shall
examine the concept in some detail, so you will be familiar with a
number of levels of word processing software applications, the types
of tools such programs make available to you, and so you will know
what kinds of problems are best solved with this type of program.
How Word Processors Work
The advantages of word processing programs can best be illustrated by
thinking of some of the disadvantages of typewriters. When we use a
typewriter to create a document, there is a direct connection between
the keys and the paper. As soon as you press a key on the keyboard,
there is an impact on the paper, and the document has been modified.
If you catch a mistake quickly, you can fix it with correction tape or
white-out. If your mistake is more than one character long, it is
much harder to fix. If you want to add a word, move a
paragraph, or change the margins, you have to completely retype the
page. Sometimes this necessitates changes on other pages as well. A
one word change could lead to retyping an entire document.
Word processing is a type of software that focuses on the ability to
handle text. The computer does this by assigning each letter of the
alphabet and each other character on the keyboard a specific numeric
code. These numeric codes are translated into computer machine language,
and stored in the computer’s memory. Because the information is in memory,
it is very easy to change and manipulate. This is the key to the
success of word processing.
Example
Information in memory can be moved very quickly and easily. If we
want to change a word in a document, what happens in the computer is
something like this:
Imagine Darlene has started out her resume with the following word:
REUME
Obviously she has forgotten a letter. If she were using a typewriter,
the page would be trashed, and she would have to start over. Since
this is a word processor, Darlene can manipulate the memory containing
codes for the word «REUME» and add the «S» to it. When she tries, the
following things happen:
She moves her cursor to the spot in the text where she wants the S to
show up. The «cursor» is a special mark on the screen that indicates
at which place in the document the computer is currently focused. In this
case, Darlene wants to put an S between the E and the U. Her word
processor won’t let her put the cursor between two letters (although
some will), so she puts it on the U.
By moving the cursor, Darlene is telling the program to move around in
memory as well. When she place her cursor on the U on the screen, she
is telling the program to point to the corresponding spot in the
computer’s memory. The computer is now concentrating on the memory
cell that contains the code for the character «U».
She checks to be sure she is in insert mode (more on that later),
and she types the letter «S».
When Darlene does this, the computer shifts all the letters one memory
cell to the right, and inserts the code for the S in its proper
place.
Word processors and RAM
It sounds like a lot is happening. That’s true, but computers do all
these things so quickly that it seems instantaneous to us. You don’t
really have to know exactly where the stuff is in memory, or how it
gets moved around. The important thing to understand is that all the
information in your document is stored in some kind of digital
format in the computer’s memory. When you modify a document, you are really
modifying the computer’s memory. A word processing program handles
all the messy memory manipulation, so all you have to do is concentrate
on writing your paper.
RAM (Random Access Memory), where all the action is happening, has
one serious drawback. It only lasts as long as the computer is receiving
electrical power. Obviously this will cause some problems, because you
can’t just carry a computer around to show people your documents.
(Imagine the extension cord!) You also might run into some serious
problems if your computer were suddenly hit by a monsoon or something,
and you lost electrical power. In short, you cannot count on RAM memory
alone.
Word processing programs (as well as almost every type of program) are
designed to allow you to copy your information. Computer scientists
refer to the information your program is using as data. The data in
RAM can easily be duplicated to floppy disks or a hard drive. This is
called saving. Copying the data from RAM to a printer is called
printing. You can also copy data from other places to RAM. Copying the data
from the disk is referred to as loading the data. You might already
know what saving and printing are. We don’t mean to insult you by
telling you again. We just want to illustrate that it all boils down
to copying binary information to and from RAM.
Types of Word Processing Programs
There are many flavors of word processing programs. Different
programs are better for different types of jobs. One common problem
is deciding which program you will use to do a certain type of job.
It is important to know your options.
Text Editors
The simplest programs that do word processing are known as text
editors. These programs are designed to be small, simple, and cheap.
Almost every operating system made has at least one built in text
editor. Most text editors save files in a special format called
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange — Whew!)
ASCII is a coding convention that almost all computers understand.
Each letter is assigned a numeric value that will fit in eight digits
of binary notation. «a» is 97 in ASCII, and «A» is 65. All the
numeric digits, and most punctuation marks also have numeric values in
ASCII. You certainly don’t need to memorize all the codes, (That’s
the text editor’s job.) but you should recognize the word « ASCII».
The biggest advantage of this scheme is that almost any program
can read and write ASCII text.
Text editors can be wonderful programs. The biggest advantage is the
price. There is probably already one or more installed on your
computer. You can find a number of text editors for free on the
Internet. Text editors are generally very easy to learn. Since they don’t
do a lot of fancy things, they are generally less intimidating than
full fledged word processor packages with all kinds of features.
Finally, text editors are pretty universal. Since they almost all use
the ASCII standard, you can read a text file written on any text
editor with just about any text editor. This is often not the case
when using fancier programs.
The ability to write ASCII text is the biggest benefit of text
editors. ASCII is also the biggest disadvantage of most text editors.
It is a very good way of storing text information, but it has no way
of handling more involved formatting. Text editors generally do not
allow you to do things like change font sizes or styles, spell
checking, or columns. (If you don’t know what those things are, stay
tuned. We will talk about them later in this chapter.)
Text editors aren’t all simple, though. Text editors are actually the
workhorses of the computing world. Most computer programs and web
pages are written with specialized text editors, and these programs
can be quite involved. You won’t need to learn any hard-core text editors
for this class, but you may end up learning one down the road.
If all you want to do is get text written, and you aren’t too
concerned about how fancy it looks, text editors are fine. (In fact,
this book was written entirely in emacs, a unix-based text editor.)
Common text editor programs:
- Windows: Notepad
- Macintosh: SimpleText
- Linux: vi, emacs
- Multi-platform: notepad++, jedit, synedit, many more
Integrated Packages
Frequently these software packages are included when a person buys a
new computer system. An integrated package is a huge program that
contains a word processor, a spreadsheet, a database tool, and other
software applications in the same program. (Don’t worry if you don’t
know what a spreadsheet or a database is. We’ll get there soon
enough!) An integrated application package is kind of like a «Swiss
army knife» of software.
The advantages of an integrated package derive from the fact that all
the applications are part of the same program, and were written by the
same company. It should be relatively easy to use the parts of an
integrated package together. These programs tend to be smaller, older
versions of larger programs, so they might be less complicated to use.
Since they were presumably written together, they should all have the
same general menu structure, and similar commands. (The command to
save a file would be the same set of keystrokes in all the programs,
for example.) Integrated packages are often designed with casual
users in mind. This might make them easier to use than more robust
programs. The word processor built into an integrated package is
probably more powerful than a typical text editor. Integrated
packages are often already installed on new computers, so they might
not cost you any more than the original purchase price of the
computer. The word processor on an integrated package will almost
certainly give you some features you would not expect to find on plain
text editors.
Integrated packages have some disadvantages. With the advent of
graphic user interfaces and modern operating systems, programs have
become more and more standard even if they were written by completely
different companies. Almost every program for Windows uses Alt-F-S to
save, for example. Also, as in the Swiss army knife analogy, the
programmers had to make some compromises in order to make all the
applications fit in one program. A Swiss army knife does contain a
saw, but if you had to cut down a tree, wouldn’t you rather use a real
saw? The programs in an integrated package are usually stripped down
or older versions of the company’s high end software. They certainly
have fewer features, and might be less friendly. Word processing
programs that are part of integrated packages generally have their own
special code for storing text information, although they can usually
read and write ASCII as well. (However, if you choose to save in
ASCII, you cannot save all the special formatting commands).
Common Integrated Packages:
- Microsoft Works
- Lotus Works
- Claris Works
Today the trend is to package all the high-level programs together, so
MS-Office and OpenOffice.org both contain fully-featured Word
Processors, Databases, Spreadsheets, and more.
High-End Word Processors
Word processing programs have evolved a great deal from the early
days of computing. A modern word processing program can do many
things besides simply handling text.
Since the early ’90s, most word processors feature a WYSIWYG
interface. WYSIWYG (pronounced «whizeewig») stands for «What You See
Is What You Get.» This means that the screen will look reasonably
like the printed document. This feature is important because the
real strength of word processors is in the formatting they allow.
Formatting is the manipulation of characters, paragraphs, pages, and
documents. Most of the word processor features we will discuss below
are various ways of formatting the text, or changing the way it looks
on the page. Formatting was possible before WYSIWYG, but it required
more imagination from the writer, because you couldn’t see the effects
of the formatting until you printed out the document.
Modern word processors also are designed to have numerous features for
advanced users. Since a large portion of most people’s computer time
is spent with a word processing program, it is important that these
programs have features to make editing documents easier. Some of the
additional features that one can expect to find on a modern word
processor are spelling and grammar checkers, ability to handle
graphics, tables, and mathematical formulas, and outline editors. The
word processing market is a very competitive one, and the major
software companies are always competing to have the word processor
with the most advanced features available.
Software companies are also interested in making their programs as
easy to learn as possible. With this goal in mind, most word
processors come with tutorial programs, extensive on-line help, and
clear menus.
These full featured word processors sound wonderful, and they are.
You might wonder if they have any drawbacks. Of course they do.
Word processing programs as have been described often cost hundreds of
dollars. The cost seems prohibitive for something that doesn’t even
have a physical presence! Many of the features of full-fledged
word processors are not needed by casual users. Sometimes the sheer
number of unneeded features can be intimidating. Using a full-power
word processor just to write a couple of letters a week is like
killing flies with a chain saw. You simply might not need that much
power to do the job properly. High end word processing programs
almost always save documents in special proprietary codes rather than
as ASCII code. This means the programs can save all the special
formatting that ASCII cannot handle (like font sizes, columns,
graphics, and so on.) It also means that if you write a document in
WordPerfect, you may not be able to read it in Word. Even
different versions of the same program might not be able to read each
other’s documents directly. There are ways you can work around this
problem, but you should know it exists.
High-end Word Processing Packages:
- WordPerfect
- Microsoft Word
- OpenOffice.org Write
Ironically, there is now a trend away from WYSIWYG towards
«semantic markup.» The idea is not to put all the formatting details
in place, but to explain the meaning of the text in the document. The
actual markup of each meaning is defined in a separate document. For
example, here’s the semantic markup of this paragraph:
<p class = "update"> Ironically, there is now a trend away from WYSIWYG towards "semantic markup." The idea is not to put all the formatting details in place, but to explain the meaning of the text in the document. The actual markup of each meaning is defined in a separate document. For example, here's the semantic markup of this paragraph: </p>
In another part of the document I describe how to format «updates»:
.update {
border: 1px black solid;
background-color: #FFFFCC;
padding-left: .5em;
}
It’s completely OK if you don’t understand any of the code. The
important idea is how markup can be separated from meaning.
Desktop Publishing
Another classification of programs you should know about has an
uncertain future. These programs are called desktop publishing
applications. Desktop publishing takes text that has already been
created, and applies powerful formatting features to that text.
Traditionally, applications that allowed the integration of text and
graphics, and allowed the development of style sheets were thought of
as desktop publishing. Such a program makes it easy to create other
kinds of documents rather than just plain pages. With a desktop
publisher, there are already style sheets developed to help you create
pamphlets, cards, signs, and other types of documents that you wouldn’t
be able to create on a typewriter.
The higher end word processing programs give you most of the features
you could want in a desktop publishing program. It is possible to do
many of the same things. Desktop Publishers are still very popular in
certain specialty fields (graphic arts, printing, and publishing,) but
the effects can be duplicated with skillful use of a word processing
program.
Common Desktop Publishing programs:
- Pagemaker
- Microsoft Publisher
Sign / Banner Programs
Another level of desktop publishing that has become very popular is
the advent of specialty printing programs such as «The Print Shop» or
«Print Master +». These programs are designed specifically to help the
user create signs, banners, and greeting cards. They are very easy to
use, and much less expensive than full-feature desktop publishing
applications, but again the effects can be duplicated with a higher
end word processor.
How Do You Choose Which Word Processor You Use?
As always, the critical question is: «What kinds of problems are you
trying to solve?» For most beginners, the lower end word processor
that came with their computer is a fine start. If it does what you
need, and you are happy with it, don’t spend money unnecessarily.
Many people find that if they do a lot of writing, they begin to yearn
for the features of a more powerful word processing program. As you
gain experience, you will find a favorite program and learn its
commands and idiosyncrasies well. You will find if you concentrate on
the concepts, that all word processors of a certain level are pretty
much the same, although the exact layout and command structure may
differ. You will also probably discover if you do a lot of writing
with the computer that you have several programs you use
interchangeably. A skilled computer user often chooses the program to
solve a specific problem much like a golfer chooses a different club
for each type of shot. Sometimes a text editor is sufficient, and
sometimes only the best, most powerful, and most expensive program
will do the job properly. Learning what is best for you is part of
the process.
Layout of Word Processors
Word processing programs of any type usually share the most basic
features. They universally reserve most of the screen for the text
being edited. Most word processing programs also contain a
menu structure with most of the programs commands available in a
hierarchical organization scheme. Many word processors have graphic
toolbars with icons representing the most critical commands. Almost
all such programs have scroll bars or some other mechanism for
allowing the user to move around in large documents. All word
processors also have a cursor, which is usually a small box or line,
which shows the user where in the document she is currently typing.
Commands Available In Most Word Processing Programs:
Different types of word processing programs will have different
commands available. Generally, text editors have the fewest commands.
More complex programs often start with the same types of commands and
add to them. Commands may be available in a number of ways; by
locating them on the menu system, by looking up shortcut keys, or by
pressing an icon on a graphic tool bar. If in doubt, utilize the
on-line help to locate the command you want.
File Handling Commands
Any level of text editor or word processor will have commands to save,
load, and print your text. These commands are so frequent that you
will usually see many ways to invoke them.
- Save Document
-
Allows you to save your document onto some kind of disk.
If you have already saved this document at least once, it will save
the document to the same drive, directory, and file name you used last
time. Saving a document really means making a copy of the codes in
memory that represent the document, and copying those codes onto a
disk file. If you have never given this document a name, a Save
command often acts like a Save As. (see below) You might also look for
a Write command, a picture of a disk, or a Save As command. - Save As…
-
Often you will see this command in addition to a save command. There
is a subtle difference between the two commands. Save As {it always}
asks you for the name and location of your file. Most of the time,
the Save command does not ask for this information. If the Save
command does not know what to call the file (because you have never
saved it before) it will automatically invoke a Save As. The only
time you absolutely must use a Save As is when you want to load a
file, make some changes to it, and save it as a NEW file with a
DIFFERENT name. If you use the Save command, the new changes will be
written on top of the old document. With Save As, you can force the
changed document to be in a new file. This really doesn’t happen very
much. Many people spend their whole lives using nothing but Save. - Load or Open
-
You will almost always see a command that allows you to open or load a
document. These terms usually mean the same thing. You will usually
get some sort of a dialog box asking you for the directory and file
name of a text document, and the program goes to the disk, grabs the
file, and loads it into the editing area of the screen. (Actually, it
loads the file into memory, and then shows a copy of the memory onto
the screen.) -
A print command takes the document and copies it to the printer.
Obviously, for this to work, you must have a printer attached to your
machine. There are occasional variations to this command. You might
get a dialog box that asks you which pages to print, how many copies you
want, which printer you want to use (if more than one is set up on
your computer), and so on. You might also see a Print Preview command
that shows a picture of what the page will look like when printed.
This is especially useful when you are using a program that does not
support WYSIWYG.
Editing Commands and Block Manipulation
There are a number of commands you will find on nearly any word
processor that enable you to manipulate text in special ways.
Frequently you will find these commands on an Edit menu. The editing
commands are based on a concept called block manipulation.
Block manipulation simply means taking a «chunk» of text and marking
it in some way so it can be treated as one unit. Once a block of text
is marked as such, it can be deleted or manipulated easily.
- Marking a Block
-
Many modern programs allow you to mark a block of text with the mouse.
Simply point the mouse at the beginning of the text you want to mark,
hold down the mouse button, and drag to the end of the block. You
will probably see the text you have dragged over change color. Some
programs put highlighted text in inverse video. Many programs also
allow you to select text with the Shift key and the arrow keys in
combination. This is sometimes more precise than the mouse
techniques. Some older programs require you to move the cursor to the
beginning of the text, mark it as the beginning of a block, move to
the end of the text you want to manipulate, and mark it as the end of
the block. Learn how your program does it. It is worth the effort. - Copying a Block
-
You will usually find some kind of command called Copy. It only works
after you have marked a block of text. Copy by itself doesn’t do
anything on the screen, but it is still a very important command.
What it does is to take the block of text and make a copy of it in a
special part of memory called the clipboard (or sometimes the buffer).
The copy command does not change the original text; it just places a
copy of the text in the clipboard. - Cutting a Block
-
Cutting is very similar to copying. You must start by marking a block
of text. When you activate a cut command, the original block will
disappear. It isn’t gone forever, though. A copy of it has been made
in the clipboard. - Pasting a Block
-
The paste command doesn’t make much sense until you have cut or copied
a block of text into the clipboard. The paste command copies the
contents of the clipboard into the document at whatever point the
cursor was sitting when the paste command was activated. - How Block Manipulation Works
-
These commands really need to be used together to be useful. Which
ones you use depend on the kind of problem you are trying to solve.
If you had to write «I will not talk out in class» 100 times, you
might write the phrase once, mark it as a block, copy it, and then
paste it 99 times.
If you have written a document and realize that the last line really
belongs at the beginning of the document, you might mark the line you
want to move as a block, cut the block move the cursor to the
beginning of the document, and activate the paste command.
Formatting Commands
Another set of commands are found less frequently on text editors, but
are common on higher-level word processors. These commands are for
formatting various elements of a document. You may find a format
menu. Many of these commands also are available on toolbars.
Formatting a Character
A character is one letter or other symbol. There are many ways to
format characters in word processing programs. It is possible to make
characters bold, italic, underlined, or perhaps some other attribute.
Not all word processors will do all these things, but most will do
bold, italic, and underline. Often you activate the command by
choosing it from a menu, clicking on a toolbar icon, or activating a
key sequence. Once you have started the command, anything you type
will be typed in that style. When you want to go back to standard
letters, you activate the same command again. Commands that turn off
and on like this are called toggles, because they are reminiscent of
toggle switches. Many word processors allow you to enter the text
without any format, then to select a set of characters as a block
(like you did to copy and paste), then to activate the command.
Experiment with your word processor to see how it works.
Word processors that feature WYSIWYG frequently support the use of
fonts. A font is defined in computing as a combination of a special
character set and type size. In the typewriter world, you were pretty
much stuck with the size and style of letters the typewriter came
with. Some of the later typewriters had the characters on a ball you
could change, but you still had very little control of exactly how the
letters looked. In a modern word processing application, you have a
great deal of control. You can choose different type faces that look
like script, handwriting, Old English, or whatever. After you have
chosen a basic look for your letters, you can choose what size the
letters are.
Fonts are measured by typesetters in points. 72.25 points is
equivalent to an inch. Most standard text is 10 points. A newspaper
headline might be 200 points. You may be able to control other
attributes of each letter, such as its color, a shadow, and other advanced
features.
Formatting Paragraphs}
Most writing is organized into paragraphs. These divisions make a
document easier to read. There are ways you can control how
paragraphs look on the screen. You can control how your program
handles indention. You can often force the computer to indent the
first line of every paragraph automatically. You can also frequently
control the line spacing inside the paragraph, the amount of spacing
between paragraphs, and the justification.
Justification refers to how the text is lined up between the margins.
Most documents created with a typewriter or word processor are
left-justified. That means that the left margin is lined up perfectly, but
the right margin is a little ragged. The computer keeps track of the
right margin for you when you use a word processor, so you don’t have
to press the «Enter» key at the end of every line (in fact you
shouldn’t press «Enter» at the end of every line. The only time you
should press «Enter» is when you want to end a paragraph!) The
automatic process the computer uses to send text to the next line is
called word wrap. If you want to have the right margin line up
cleanly, but let the left one be a little ragged (Maybe as you type
the return address and date of a business letter) you can choose a
right justify command. If you look at books and magazines, you will
see that both the right and left columns are justified. Many word
processors will allow you to justify both margins. This works by
adjusting the amount of space between letters and words so the margins
work out perfectly. The computer does it automatically when you ask
it to do so. Another form of justification is centering. When you
center a line, you tell the program to give it equal left and right
margins, regardless of the length of the line. Centering is useful
for headlines, but is often distracting when used for body text.
The other major element of a document is the page. There are some
page formatting commands you should be able to find in any word
processor as well. You will probably have some way to adjust the
margins of the page. Note that there are top and bottom margins, as
well as left and right margins.
You can also frequently find some kind of header/footer command.
Headers and footers are special areas at the top and bottom,
respectively, of the page. These areas are not used for regular text,
but reserved for special things like a title at the top of every page,
page numbers, and footnotes. You will have to experiment a little
to see how your word processor handles these features, but they are
well worth learning. You will never go back to the old way of writing
footnotes once you have mastered using footers to automate the
process.
One more page formatting command you might find useful is page
orientation. Many word processors allow you to choose how information
is printed on the page. The «up and down» orientation we are used to
seeing on typewritten documents is called portrait mode. (If you
think about painted portraits, they are usually up-and-down rectangles.)
When your document is printed «sideways» it is referred to as landscape
mode. (Landscape paintings are often oriented in this way.)
__________
| ___ | ________________
| /o o | | |
|| L | | | /WWW |
||___/| | | / |
| / | |/ |
|_/_____| |______________|
Portrait Landscape
mode mode
Most of the time you should use portrait mode, but sometimes landscape
mode is appropriate, especially when you are doing something special
like tables, graphics, or fancy desktop publishing.
Commands Found in More Advanced Programs
High-End Formatting Tools
There are a few more elaborate formatting tools generally found
only in the higher end word processors. These tools border on desktop
publishing, and allow you better control of your document. You
probably won’t use them every day, but they are wonderful when you
need them.
- Tables
-
On a typewriter, creating a table required judicious use of the TAB
key and very careful planning. Most advanced word processors allow
you to create tables very easily. You can usually select the number
of rows and columns, change the size and format of rows and columns,
and easily copy and paste specific cells. The table tool is worth
learning. - Columns
-
Sometimes you will want to have a page formatted into two or more
vertical columns. This was quite tedious on a typewriter, but there
is usually some kind of tool to make column creation easier on a
modern word processor. - Lists
-
You will frequently find tools for making lists. Lists can have
automatic numbering (like an outline) or each list item might have a
small icon marking, called a bullet. Most modern word processing
programs have some kind of tool to make list management easier. - Graphics
-
Most high-end word processing programs enable you to incorporate
graphics into text documents with relative ease. Often they
incorporate small painting programs so you can generate your own
graphics as well. To make graphics and text easier to work with, many
word processing programs include frames, which are boxes on the screen
that can hold text and graphics. When you mix text and graphics on a
page, you may want to investigate frames in the on-line help so you can
have more control over how the text and graphics interact.
Composition Tools
Many word processors have other advanced features that help a writer
with the mechanics of writing properly. These tools can be
instrumental in avoiding common writing mistakes.
- Spell Checking
-
A spell checker is a program that looks at a document and compares
each word in the document to an electronic dictionary. If it finds
the word in the dictionary, it moves on to the next word. If it does
not find the word, it stops and asks the user for guidance. Good
spell checkers try to guess what word the user was trying to type and
make suggestions. Even if you are a very good speller, you should get
in the habit of running your materials through a spell checker. It is
a quick and relatively painless way to keep typos from marring your
paper.Keep in mind that spelling checkers are not perfect, and they cannot
catch every mistake. The following poem excerpt points out the
problem:Ode To The Spell Checker I have a spelling checker. It came with my PC. It plane lee marks four my revue, Miss steaks aye can know sea. Eye ran this poem threw it, Your sure reel glad two no. Its vary polished in it's weigh, My checker tooled me sew.(This poem can be found in its entirety at:
http://selma.ucd.ie/~pdurkin/Jokes/spellcheck.html It is attributed
to Jerry Zar, the Dean of the Graduate School, NW Ill. U) - Grammar Checkers
-
There are also tools available on most high end word processors that
will check your grammar for common mistakes. Grammar checkers are
wonderful at catching mechanical problems like incomplete sentences
and subject-verb agreement. Grammar tends to be more subjective
than spelling, so the advice of a grammar checker might or might not
be useful to you. It is worth running to check your mistakes, but it
will never replace the lessons you learned from your English teachers
or a skilled editor. When grammar checkers first came on the market,
a reporter tried testing the Gettysburg Address by Abraham Lincoln.
The program gave the speech extremely poor marks. Many people
consider it to be one of the most beautiful passages of American
English ever. Use a grammar checker if you have one, but also use
your judgment. - Outline Editors
-
These features allow you to organize your thoughts in outline format.
The advantage is that you can choose to see only your main ideas or
headings, and have all the text hidden. This feature allows you to
move the main headings around and all the text associated with the
headings will automatically move appropriately. If you are going to
do term papers or other serious writing, you should investigate this
feature.
Vocabulary/Important Ideas
- Word Processing
-
A type of software that specializes in handling text. Word processing
programs typically contain commands for handling and formatting text
documents. - Insert/Overwrite Modes
-
Most word processors allow you to choose one of these modes. When you
are in {bf insert} mode, any text you type is inserted into the
document at the cursor position. {it Overwrite} mode also types text
at the cursor position, but it writes over the top of existing text,
much like a typewriter with correcting tape. Most experienced word
processor users prefer insert mode for most of their work. - Text Editors
-
A classification of word processing software characterized by its low
cost, ready availability, tendency to work only in ASCII format, and
inability to do high-powered formatting. - ASCII
-
American Standard C}ode for Information
Interchange. A standard convention used to encode text, numbers, and
common punctuation in numeric format so they can be stored in a
computer’s memory. Nearly all computers and programs can work with
some form of ASCII. Text editors are designed especially to work with
ASCII-based documents. - Integrated Packages
-
Programs that contain all the major applications within one «super
application». These programs are useful, but often lack some of the
more advanced features of full-fledged application packages. - WYSIWYG
-
What You See is What You Get.
A capability often found on higher-level word processing
programs. The screen mimics the output of the printer, so the typist
can see pretty much what the final output of the document will be. - Proprietary
-
The term {it proprietary} is frequently used when discussing software to
denote a certain idea that is particular to a specific brand of
software. When a program uses a proprietary scheme to save word
processing documents, for example, other programs may not be able to
read these documents without some kind of translation. - Desktop Publishing
-
A classification of word processing software that concentrates on
incorporation of graphics, powerful formatting, and development of
complex styles including newsletters, signs, and pamphlets. - Style Sheet
-
In desktop publishing, a template that specifies how a certain type of
document will be created. Style sheets are used to define a uniform
look and feel for documents of the same general type. For example, a
company might issue a standard style sheet for intra-corporation
memoranda. Many high-end word processors incorporate this feature.
Sometimes style sheets are referred to as templates. - Scroll Bars
-
Horizontal or vertical bars which indicate the cursor position in a
document. Usually scroll bars can be used with the mouse to
facilitate moving through the document. - Cursor
-
A small mark on the screen, usually a rectangle, underline, or
I-shaped design. The cursor indicates the exact position within the document
(and memory) where any commands and typing will be executed. - Save
-
The Save command saves a document without prompting for the file
name, unless the file has never been saved before. If this is the
case, it invokes a Save As command instead. - Save As
-
This command always prompts for a file name. It is used when
you want to save the changes to file without changing the file already
saved on the disk. - Load (or Open)
-
This command prompts the user for a file name, then loads the document
into the application. -
A print command is used to send a copy of the document to the
printer. - Print Preview
-
This command is especially useful in non-WYSIWYG environments. It
allows you to see a preview of the document exactly as it will be
printed. It is often a good idea to invoke this command before you
print a document, to be sure it will turn out exactly as you plan. - Block Manipulation
-
The process of defining a section of text so it can be copied, pasted,
or otherwise manipulated as one unit. - Copy
-
A copy command takes a block of text and copies it to a memory
buffer without removing the original text. Used to it
duplicate sections of a document. - Cut
-
This command copies a block of text to a memory buffer, and removes
the original text from the document. Used to {it move} sections of a
document. - Paste
-
This command takes the block of text last placed in the buffer by a
cut or copy command, and inserts it into the document at the current
cursor position. - Formatting
-
The process of defining how a document will look. Formatting can
occur at the character level, as well as at the paragraph and page
level. - Character Attributes
-
The special modifications to letters, such as {bf boldface} and {it
italic} - Font
-
The combination of character set and size that defines how an
individual character looks. Most word processing packages allow the
user to choose from many fonts. - Toggle
-
A command is referred to as a {it toggle} if repeated execution of
the command causes something to switch between two modes. Insert
and Overwrite modes are good examples of toggles. Often character
attributes are also considered toggles. - Point
-
A point is a type setter’s measurement of character size. Officially,
there are 72.25 points to an inch. - Justification
-
The way the lines of text are arranged on the page. The usual options
are left-justified, right-justified, centered, and both-justified. - Left-Justified
-
The text is lined up so that the left margin is even. The right
margin will not be even in left-justified text. - Right-Justified
-
The text is lined up so that the left margin is ragged, but the right
margin is even. Often used to line up dates and return addresses on
business letters. - Both-Justified
-
The text is lined up so that both the left and right margins are lined
up, as in a newspaper or magazine. - Centered
-
The text is lined up with an equal distance from the left and right
margins. Usually used in headlines. - Word Wrap
-
A behavior of word processing programs which automatically moves words
too large to fit the current line onto a new line. Eliminates the
need to press «return» at the end of each line. - Headers, Footers
-
Special areas at the top and bottom of word processing documents.
These sections are reserved for information that will appear on {it
each page} of the document. Usually page numbers, document name, or
document author will be in the header/footer area. The footer is
also useful for holding footnotes. - Landscape Mode
-
Documents in this mode print the long part of the page horizontally, as
in a landscape painting. - Portrait Mode
-
Documents in this mode print the long part of the page vertically,
as in a portrait painting. - Table
-
A section of a document organized into rows and columns. Higher-end
word processors often have a number of tools to help make tables
easier to create and manage. - Column
-
Vertical separation of text into two or more sections. Newspapers and
newsletters are often arranged in columns. High-end word processing
programs and desktop publishing programs usually include some tools to
make column manipulation easier. - Spell Checker
-
A feature of higher-end word processing programs that compares each
word in a document to a dictionary of proper spellings. Most spell
checkers «guess» which word the user was trying to type and give the
user some guesses to choose from. - Grammar Checker
-
A feature in word processing programs that checks a document for
common grammatical errors. Grammar checkers can also grade documents
for readability and complexity. Sometimes grammar checkers are
separate programs. - Outline Editors
-
A feature or program that easily enables the user to create and
manipulate outlines. Most of these programs allow you to hide the
body text so you can see and modify the subject headings. The
associated body text is automatically moved with the appropriate heading.
Summary
Word processing programs are a type of software that make
it easier to create and modify text documents. Word Processing
applications are organized into a number of categories according to
their complexity: Simple programs that manipulate ASCII are called
Text Editors. More complex programs that feature formatting commands
are called Word Processors. Some word processors are included in
integrated application packages, which also feature other application
programs. Such packages are convenient, but may not have all the
features of larger programs. Full-featured word processing programs
contain many options for formatting text and documents. They also
might contain special utilities for more complex formatting and
composition. Desktop publishing programs are designed for more
complex formatting, especially the integration of text and graphics.
Most word processing programs contain the same types of commands,
although the exact ways to access these commands may vary. You will
almost always see file handling commands, including commands to Load,
Save, Save As, and Print. Frequently, you will also see commands for block
manipulation, including Copy, Cut, and Paste. More advanced programs
may contain special commands for formatting characters and paragraphs,
as well as other commands to deal with tables, columns, and lists.
The fanciest word processing programs may also contain commands to
assist with composition, such as spelling and grammar checkers and
outline editors.
Word processing software helps you manipulate a text document and create or edit a text document.
-
Best 15 Word Processing Software Examples
- 1. Microsoft Word
- 2. iWork Pages
- 3. OpenOffice Writer
- 4. WordPerfect
- 5. FocusWriter
- 6. LibreOffice Writer
- 7. AbiWord
-
8. WPS Word
- 9. Polaris Docs
- 10. Writemonkey
-
11. Dropbox Paper
- 12. Scribus
- 13. SoftMaker FreeOffice TextMaker
- 14. Zoho Docs Writer
- 15. Google Docs
- Conclusion
A quality word processing software can also provide output options such as printing or exporting a text document into other formats.
Without word processing software, you would have difficulty processing paragraphs, pages, and even papers.
Not many people know that early word processing software was standalone devices, but word processors come as lightweight software that’s easy to install with technological advancements.
Another great advantage of word processing software is that it allows you to store documents electronically, display them across screens, or fully modify documents before printing them.
Even though word processing software isn’t complex to learn, it might take a bit of time to learn how to take full advantage of the software with so many functions.
Also, keep in mind that some word processing software comes from the office bundle that includes other processing software.
In this article, you’ll learn more about word processing software and see 15 of the best examples.
Whether you’re a writer, editor, or only need quality word processing software to prepare your documents pre-printing, at least one of these 15 software will be a good pick!
Even though most word processing software has similar features and offers similar benefits, the small but significant differences between these word processing software examples can make a huge difference for personal use.
1. Microsoft Word
The most known word processing software is Microsoft Word, and chances are high you’ve used it at least on one occasion to process or create text documents.
Word is the most known word processing software because the creator of Windows creates it and it often comes integrated with the Windows operating system.
However, Word is also known for the benefits it offers. Improved search and navigational experience combined with the ability to work with others simultaneously are just some of the benefits.
Along with that, Word gives you the ability to access, share, and work on your documents from almost anywhere.
With plenty of options to create, edit, and process text, Word also has additional visual effects, turning text into diagrams, and combining visual aspects into text documents.
Instant help when creating documents is another great integration that especially helps writers. Exporting and having document flexibility is helpful when producing specific documents for your studies or work, and it’s just one of many benefits of Word.
2. iWork Pages
iWork Pages is a must-have word processing software for Apple users. Even though Microsoft Word is available for macOS, iWork is a great native alternative that helps Apple users process, create, and work with word documents.
iWork Pages was previously known as AppleWorks, and it is part of the official Apple iWork suite.
Not only Pages can help you create documents, but they can also help you to collaborate with others efficiently, create animated documents from your data, and even build interactive charts from your text.
What’s great about Pages is that it comes with built-in help and sample formulas, so you don’t always have to create a document from scratch. Instead, you can use templates or benefit from function suggestions to improve the way you work.
With over 30 spreadsheet templates, you won’t have to create text documents from scratch unless you enjoy creating your work from scratch. Templates can help you spend less time formatting and creating the basics of your document and yet leave you with more time to focus on your text.
3. OpenOffice Writer
Among the paid word processing software, there are a couple of free gems such as OpenOffice.
OpenOffice is a free and open productivity suite that includes Writer, the perfect software for word processing.
Whether you’re trying to draft a quick letter or working on complex text documents (maybe even writing a book), the writer is a reliable and fully equipped word processing software to handle all needed tasks.
What’s great about Writer is that it is very easy to use, so you won’t have to spend hours learning the ins and outs of the software to take full advantage of it.
Instead, you will be able to focus on producing documents of all types and letting Writer help you along the way.
With built-in features such as AutoCorrect or AutoComplete, you can quickly write your documents without having to worry about making mistakes.
Along with these two features, OpenOffice Writer comes with a table of contents, references, multi-page display, and notes to help you annotate and review documents, as well as create well-structured text documents.
Lastly, exporting isn’t going to be a problem since Writer can help you export your text document into other formats such as HTML, PDF, or even .odt.
Also, keep in mind that OpenOffice provides templates you can download and use with Writer to make your drafts easier.
4. WordPerfect
WordPerfect is described as the Microsoft Office alternative. It is an all-in-one suite that focuses on productivity and efficiency when working with digital documents (especially text documents).
Inside the WordPerfect Office, you will have access to a neat and efficient word processor that can help you quickly draft new documents, create letters or brochures, write resumes, and even start writing a book.
What’s so special about WordPerfect is that it supports collaboration with about 60 file formats, so you can import and export documents from any third-party software.
With the help of Reveal Codes, WordPerfect provides seamless formatting after you import documents from any source.
And if you’re looking to “spice up” your text documents, you can do so easily with the help of built-in PDF forms into this powerful and versatile word processing software.
5. FocusWriter
If you spend a lot of time writing documents in your word processing software, and yet you find it hard to concentrate and focus on the words, FocusWriter is a great pick.
FocusWriter is a very simple word processing software that utilizes a versatile interface hidden away from the most important part of the software. This way, you can focus on the page and text, and whenever you need to use any integrated feature, all you have to do is swipe your cursor across the edges to open the hidden menu.
With integrated features such as timers, alarms, daily goals, fully customizable themes, and even the ability to use typewriter sound effects, this word processing software will help you stay on track and get things done.
Along with these features, FocusWriter has optional features such as live statistics, spell-checking, and even the ability to use FocusWriter in 20 different languages.
These features aim to improve the user experience and make word processing tasks fun and more productive since you can set your own goals.
This is a word processing software that adds improved features that aren’t very common among its competitors.
6. LibreOffice Writer
When you are a very organized person and need word processing software that will match this, LibreOffice Writer is worth trying.
LibreOffice Writer is a modern word processing software that ensures you can edit any document quickly with the help of integrated features.
Therefore, Writer is good enough for doing quick and simple edits. Still, it’s also more than enough to finish books, edit many content pages, add diagrams, and even feature indexes into your documents.
The user interface is very neat and even though there are many features they’re hidden away so you can focus on the most important aspect of word processing: the text.
7. AbiWord
When you require a very similar word processing software to Word, and yet you’re on a budget, AbiWord is a good choice.
AbiWord is compatible with the latest operating systems and interface-wise, it is very similar to Microsoft Word. Even though it’s not the “prettiest” word processing software, it has everything you might need to get the work done efficiently, and it won’t cost you a penny.
With compatibility to work with all standard text documents, AbiWord also allows you to share your documents with others easily or even merge your letters directly with your email.
Even though AbiWord might not have all features other word processing software include, AbiWord is built on the extensible plugin architecture, so you can always find plugins to include features you might be missing.
On top of that, I should mention that AbiWord is available in 30 different languages, and it is still getting updates so that you won’t be relying on an outdated version.
8. WPS Word
WPS offers a suite similar to Microsoft Office that includes three components: the Word, Excel, and Presentation.
Word is a word processing software that is highly compatible with almost all compatible document formats, and it is even compatible with all operations systems.
Creating documents from scratch with Word is very simple, and yet with standard formatting tools everyone is familiar with, editing documents is even easier.
On top of that, Word includes many extras that are rarely found in other word processing software, such as hundreds of document templates. Therefore, if you don’t feel like creating documents from scratch, basing your documents on pre-existing templates can save you a lot of time and work.
Combining media with text is highly possible, and viewing multiple documents simultaneously improves efficiency when working with multiple documents.
With collaboration tools, password protection for chosen documents, and automatic spell-checking tools, you can easily get your work done without worrying about accuracy.
9. Polaris Docs
Polaris Office is a combination of tools that includes Docs, a highly versatile version that’s very similar to a combination of Microsoft Word and Google Docs.
It’s a very versatile word processing software that allows you to work on your documents wherever you are.
Not only is it available as computer software, but it also has a dedicated web browser version and even the app version suitable for Android and iOS smartphones.
Collaboration is guaranteed with such versatility, and when it comes down to getting the work done, Polaris Docs supports all types of documents, including sheets, slides, and more.
Saved documents can be worked on in groups, meaning that more than one person can edit the document in real-time. And if you ever decide to collaborate on a document with someone, you can invite them with a link and keep the communication open with an integrated chat in the Polaris Docs.
Feature-wise, Polaris Docs is packed with the most standard features you would expect from a word processing software, and yet the main improvement is the way you can collaborate with others and work on the same document in real-time.
10. Writemonkey
If you search for a word processing document that will leave you on your own with your words and yet will hide all functionalities in a very minimalistic and simple interface, Writemonkey makes a great choice.
Writemonkey might look like a coding interface at first, but it is a stripped-down word processing software that helps you focus on your writing.
Of course, Writemonkey is also ideal for making quick edits and even reading.
This is probably one of the lightest and smallest word processing software that is very easy to install and even easier to get used to.
What’s also great is that you have full control over the interface to customize it to your needs. On top of that, you can set timed writing or even feature a visual progress bar to make your writing work feel like a breeze.
And if you ever end up missing something in Writemonkey, you can always introduce third-party upgrades to this word processing software via plugins.
11. Dropbox Paper
When you need a versatile, reliable, and quick word processing software that’s perhaps web-based, Dropbox Paper is worth considering.
Dropbox Paper is a lightweight web-based word processing software that allows simple editing and collaboration between teams.
With Dropbox Paper, you can create documents from scratch or import existing documents to easily track any edits or changes made by your team members. On top of that, with this light word processing software, you can keep everything organized, ensure feedback is properly given, and even improve your documents.
You can do almost everything in Dropbox Paper that you would do in other word processing software. However, Paper can also serve as a co-editing software.
Whether you’re trying to improve communication in your team, improve collaboration between team members, or you’re writing a book with your partner, Paper is the place to stay productive, organized, and efficient.
12. Scribus
If you require professional word processing software to handle your business/work documents or edit and prepare your book for publishing, Scribus is a great choice.
Even though it’s a bit different from standard word processing software, Scribus allows you to choose one of the designed layouts, set your typesetting, and even improve your written documents with professional-looking quality images.
With Scribus, you can also create animations that you can place directly inside your document, or you can turn your text documents into interactive PDF presentations.
On top of that, the creation of forms or questionnaires is very simple. With OpenType support, you can now edit your existing documents with advanced features such as advanced typography.
While Scribus is a great fit for simple editing and personal documents, it excels at creating magazine covers, newspaper front pages, preparing the books for publishing, and even manufacturing artwork.
It might not be the standard word processing software most people are looking for, but it will fit professional needs easily for a very fair price.
13. SoftMaker FreeOffice TextMaker
When you need a simple word processing software, SoftMaker FreeOffice is a great stepping stone that won’t cost you anything, and yet it includes almost everything you might need for personal or business use.
In the FreeOffice, you will get TextMaker included. TextMaker is a small but efficient word processing software that allows you to create all types of documents and edit existing documents that you can easily import.
What’s unique about TextMaker is that it doesn’t only focus on written documents. Instead, it also offers great features for processing words on graphics. Therefore, you can use TextMaker to create great text for your images, logos, or even banners.
With many different fonts, styles, and even wrapping options, TextMaker will make all your graphics look professional and attractive yet easy to read.
Since TextMaker can import almost all types of documents, you can also export your work in the most standard formats, such as Word DOC and DOCX. However, what’s also great about TextMaker is that it allows you to create PDF files from your documents.
You can even create an EPUB eBook with the help of TextMaker, which is a great feature, considering that SoftMaker provides the TextMaker for free.
14. Zoho Docs Writer
Zoho Docs Writer is a perfect example of an online word processing software that is easy to use and easy to access. Yet, in return, you will get very reliable and advanced features you can use on any of your documents.
The writer allows you to focus on your words in a distraction-free interface, yet you can work with others in an effortless document sharing.
With the most standard features, you would expect a word processing software packed in the interface you can access via the web browser and even get unlimited versions of your document.
These versions help you compare differences and find differences after collaboration with others.
One of the most advanced yet convenient features is publishing your documents directly (if you are a content creator).
If not, Zoho Docs Writer can help you electronically sign documents and even fill out PDF forms (or edit PDFs) without a problem.
15. Google Docs
Suppose you are not a fan of standalone word processing documents or don’t consider your computer reliable enough for your work. In that case, Google Docs is one of the most reliable web-based word processing software than most others in this space that you can get your hands on.
Along with the Sheets, Slides, and Forms, Docs allows you to not only create documents from scratch or import and edit existing documents, but it also allows you to store all your documents in the cloud for free.
You can easily access your documents from any device, as long as you’re signed in to your Google account, and yet you will easily get used to the functionality and features of the Docs.
On top of that, Docs is very flexible, so you can export them in many different formats just the way you can import documents. However, one thing to keep in mind is that you will need an internet connection at all times to access your documents or work on them.
Conclusion
Even though Microsoft Word is one of the most known word processing software globally, there is much other software that is as good and worth giving it a try.
One couldn’t do without quality word processing software, but you even get the chance to find the one that will fit your needs the most with so many choices.
Even though each one of these is similar, there are differences in the interface, functionality, and even features that the software provides.
With that being said, you can easily choose according to your needs and purpose, which I highly recommend!
Tom loves to write on technology, e-commerce & internet marketing.
Tom has been a full-time internet marketer for two decades now, earning millions of dollars while living life on his own terms. Along the way, he’s also coached thousands of other people to success.
Word processing generally means the task of creating printed materials like letters, reports, thesis, books and so on. It involves the tasks such as entering text, editing, formatting, proofing, and printing.
Word processing nowadays is the use of computer to produce documents consisting primarily of text or words (as distinguished from numbers). Word processor is a general application software used for producing such text documents.
In the initial days of development, the computer was primarily used for performing mathematical calculations. The documents produced on computers consisted of recording the results of the calculation with a very little textual material. With the development, special computers and computer software were developed to produce documents such as letters and reports. Such computers were used in the printing industry for composing the material for printing.
These days, it is common that the computers are used extensively for word processing, and has almost replaced conventional typewriters across the world.
Of all computer applications, word processing is probably the most common. To perform word processing, you need a computer, a special program called a word processor, and a printer. A word processor enables you to create a document, store it electronically on a disk, display it on a screen, modify it by entering commands and characters from the keyboard, and print it on a printer.
The great advantage of word processing over using a typewriter is that you can make changes without retyping the entire document. If you make a typing mistake, you simply back up the cursor and correct your mistake. If you want to delete a paragraph, you simply remove it, without leaving a trace. It is equally easy to insert a word, sentence, or paragraph in the middle of a document. Word processors also make it easy to move sections of text from one place to another within a document, or between documents. When you have made all the changes you want, you can send the file to a printer to get a hard-copy or disk to store for future purpose.
Basic Features of Word Processors
There are various Word processors, but all word processors support the following basic features:
- Insert text: Lets you to insert text anywhere in the document.
- Delete text: You can remove characters, words, lines, or pages from document easily and without leaving any trace.
- Cut and paste : It has facilities to move the selected text by removing (cut) it from one place of document and inserting (paste) it somewhere else.
- Copy : Supports creating duplicate of a selection of text without any trouble.
- Page size and margins : It has options to define and change among various page sizes and margins, and the word processor will automatically readjust the text so that it fits in new layout.
- Search and replace : Allows you to search for a particular word or phrase in document. You can also replace one text with another and optionally everywhere that the match occurs.
- Word wrap : Word processor has this feature to automatically moves to the next line after you complete a line. This is also known as soft line break or auto line break. Word wrap also readjust text if you change the margins, paper orientation or page size.
- Print: Word processor supports various printers to send a document for printout.
Word processors that support only these features (and maybe a few others) are called text editors. Most word processors, however, support additional features that enable you to manipulate and format documents in more sophisticated ways. These more advanced word processors are sometimes called full-featured word processors.
Additional Features of Full-featured Word Processors
- File management : Many word processors contain file management capabilities that allow you to create, delete, move, and search for files. File menu is MS Word has commands for this task.
- Font specifications: Allows you to change typeface (fonts) within a document. You can specify font, font size, font styles such as bold, italics, and underlining and different effects like superscript, subscript, outline, strike-through etc.
- Footnotes and cross-references: Automates the numbering and placement of footnotes and enables you to easily cross-reference other sections of the document.
- Graphics: Allows you to embed illustrations (images) and graphs into a document. Some word processors let you create the illustrations within the word processor (using autoshapes and drawing tools); others let you insert an illustration produced by a different program.
- Headers , footers , and page numbering: Allows you to specify customized headers and footers that the word processor will place at the top and bottom of every page. It can keeps track of page numbers so that the correct number appears on each page.
- Layout : Supports different page size, margins and page orientation within a single document. It also has facility to apply various indentation to paragraphs.
- Macros : A macro is a character or word that represents a series of keystrokes. The keystrokes can represent text or commands. The ability to define macros allows you to save yourself a lot of time by replacing common combinations of keystrokes.
- Merges: Allows you to merge text from one file into another file. This is particularly useful for generating many files that have the same format and structure but different data. Generating mailing labels is the classic example of using merges.
- Spell checker : A utility that allows you to check the spelling of words. It will mark any word having spelling mistake or that it does not recognize. Spell checkers have ability to produce a list of suggested word to make you easier to correct mistakes.
- Table of contents and indexes: Word processors have features to automatically create a table of contents and index based on special codes that you insert in the document.
- Thesaurus: Word processors have a built-in thesaurus that allows you to search for synonyms without leaving the document.
- Windows : Lets you to edit two or more documents at the same time. Each document appears in a separate window. This is particularly valuable when working on a large project that consists of several different files.
- WYSIWYG (what you see is what you get): With WYSIWYG, a document appears on the display screen exactly as it will look when printed.
Word Processors And Desktop Publishing Systems
Desktop publishing is as good as having a mini-printing press within a personal computer. Publishing software helps design the page layout for each document. Tools in desktop publishing applications can help the user to configure the layout, where things are printed in the final design and how things are printed.
The line dividing word processors from desktop publishing (DTP) systems is constantly shifting. In general, though, desktop publishing applications support finer control over layout, and more support for full-color documents.
Both word processing and desktop publishing are similar in many ways but different in areas that cover the publication of documents.
Similarities between Word Processors and Desktop Publishing Systems
- Both the word processor and DTP systems deal with text that can be formatted.
- Word processors and desktop publishing systems work with tables and pictures.
- Both tools have many similar features like WordArt, Clip Art, and text styles.
The differences between Word Processors and DTP Systems
Word processing involves creation, editing, and printing of text while desktop publishing involves production of documents that combine text with graphics.
- Word processing is difficult to layout and design as compared to desktop publishing. Thus, desktop publishing is used to work on things like newsletters, magazines, adverts, and brochures where layout is important. Word processing documents are common for simple memos, letters, manuscripts, and resumes.
- When creating a desktop publisher, the first page is blank and a text frame must be added to add text. This is unlike the word processing in which text can be directly entered into the blank page.
- With desktop publishing, users can easily manipulate text and graphics and try new ideas. In contrast to this, word processing tools are adding more page layout features. Thus, the line that draws the difference between the two hardly exists now.
- Though there are many differences between the two, more word processing applications are coming out with enhanced features that mimic many of the desktop publishing tools on the market today. So, whether you choose to use word processing or desktop publishing software all depends on your document publishing needs and what application your are most comfortable using
Types of Word Processing
Word Processing applications are organized into a number of categories according to their complexity: Simple programs that manipulate ASCII are called Text Editors. More complex programs that feature formatting commands are called Word Processors. Some word processors are included in integrated application packages, which also feature other application programs. Such packages are convenient, but may not have all the features of larger programs. Full – featured word processing programs contain many options for formatting text and documents. They also might contain special utilities for more complex formatting and composition. Desktop publishing programs are designed for more complex formatting, especially the integration of text and graphics.
Text Editors
The simplest programs that do word processing are known as text editors. These programs are designed to be small, simple, and cheap. Almost every operating system comes with at least one text editor built in. Most text editors save files in a special format called ASCII. The biggest advantage of this scheme is that almost any program can read and write ASCII text.
The biggest advantage of text editors is the price. There is probably already one or more installed on your computer. You can find a number of text editors for free on the Internet. The ability to write ASCII text is the biggest benefit of text editors. It is a very good way of storing text information, but it has no way of handling more involved formatting. Text editors generally do not allow you to do things like change font sizes or styles, spell checking, or columns.
Windows: Notepad, DOS: Edit, Macintosh: SimpleText etc are some common text editor programs:
Integrated Packages
An integrated package is a huge program that contains a word processor, a spreadsheet, a database tool, and other software applications in the same program. The advantages of an integrated package derive from the fact that all the applications are part of the same program, and were written by the same company. Since they were presumably written together, they should all have the same general menu structure, and similar commands. The word processor built into an integrated package is probably more powerful than a typical text editor.
Integrated packages have some disadvantages. With the advent of GUI and modern operating systems, programs have become more and more standard even if they were written by completely different companies. The programmers had to make some compromises in order to make all the applications fit in one program. Word processing programs that are part of integrated packages generally have their own special code for storing text information, although they can usually read and write ASCII as well. However, if you choose to save in ASCII, you cannot save all the special formatting commands.
Microsoft Works, Microsoft Office Suite, Lotus Works, Claris Works are some examples of integrated packages.
High-end Word Processors
Word processing programs have evolved a great deal from the early days of computing. A modern word processing program can do many things besides simply handling text.
Since the early ’90s, most word processors feature a WYSIWYG interface. This feature is important because the real strength of word processors is in the formatting they allow. Formatting is the manipulation of characters, paragraphs, pages, and documents.
Modern word processors also are designed to have numerous features for advanced users. Some of the additional features that one can expect to find on a modern word processor are spelling and grammar checkers, ability to handle graphics, tables, and mathematical formulas, and outline editors.
These full-featured word processors sound wonderful, and they are. You might wonder if they have any drawbacks.
- Word processing programs as I have described often cost hundreds of dollars.
- Many of the features of full – fledged word processors are not needed by casual users.
- High-end word processing programs almost always save documents in special proprietary codes rather than as ASCII code. This makes the document incompatible with other applications. If you write a document in WordPerfect, you may not be able to read it in Word.
WordPerfect, Microsoft Word are some examples of commercial Word Processing packages
Desktop Publishing
Another classification of word processing you should know about has an uncertain future. These programs are called desktop publishing applications. Desktop publishing is taking the text that already been created, and applying powerful formatting features to that text. Traditionally, applications that allowed the integration of text and graphics, and allowed the development of style sheets were thought of as desktop publishing. Such a program makes it easy to create other kinds of documents than plain pages. With a desktop publisher, there are already style sheets developed to help you create pamphlets, cards, signs, and other types of documents that you wouldn’t be able to create on a typewriter.
The higher end word processing programs give you most of the features you could want in a desktop publishing program. It is possible to do many of the same things. Desktop Publishers are still very popular in certain specialty fields (graphic arts, printing, and publishing,) but the effects can be duplicated with skillful use of a word processing program.
Adobe Pagemaker, Adobe Illustrator, Microsoft Publisher are the example of some common Desktop Publishing programs.
Sign / Banner Programs
Another level of desktop publishing that has become very popular is the advent of specialty printing programs such as ‘The Print Shop’ or ‘Print Master +.’ These programs are designed specifically to help the user create signs, banners, and greeting cards. They are very easy to use, and much less expensive than full-feature desktop publishing applications, but again the effects can be duplicated with a higher end word processor.
Points to Remember
- Word processing did not develop out of computer technology. It evolved from the needs of writers rather than those of mathematicians, only later merging with the computer field
- The term word processing was invented by IBM in the late 1960s.
- A word processor is a computer application used for the production (including composition, editing, formatting, and possibly printing) of any sort of printable material.
- Word processor may also refer to a type of stand-alone office machine, popular in the 1970s and 1980s, combining the keyboard text-entry and printing functions of an electric typewriter with a dedicated processor (like a computer processor) for the editing of text.
- Microsoft Word is the most widely used word processing software. Many other word processing applications exist, including WordPerfect (which dominated the market from the mid-1980s to early-1990s on computers running MS-DOS operating system) and open source applications OpenOffice.org Writer, LibreOffice Writer, AbiWord, KWord, and LyX. Web-based word processors, such as Office Web Apps or Google Docs, are a relatively new category.
- Desktop publishing applications support finer control over layout and more support for full-color documents where as the word processing systems focus on editing and formatting of text.
- Text Editors, Integrated Packages, High-end Word Processors, Desktop Publishing, Sign / Banner Programs are the different types of word processors.
References:
- Webopedia – http://www.webopedia.com
- Wikipedia – http://en.wikipedia.org
- Bright Hub – http://www.brighthub.com
- IUPUI, Department of Computer and Information Science – http://cs.iupui.edu/
Recommended Reading:
- A brief history of WordProcessing
- WordProcessors: Stupid and Inefficient by Allin Cottrell
- Desktop Publishing: by Szu-chia Wang
Word processing is the process of adding text to a word processing unit such as a computer or typewriter. The typed words are stored in the computer or word processor temporarily to allow for editing before a hard copy of the document. The term «word processing» is a fairly general term, so it may refer to several types of writing without the use of pen and paper. Typewriters, for example, process words directly onto a paper without storing the data, while computers use specific programs to store the typed data before printing.
Modified typewriters have been commonly used in the past for word processing. The typewriter would store the data — usually with the use of a computer chip — before printing the words onto a page. The person using the word processor could then check the writing for errors before printing the final draft. When computers became common in the workplace and at home, word processors became mostly obsolete, though some models are still used for a wide range of purposes, including as educational devices for students with special needs.
Computers have generally taken over word processing duties. The computers feature specific programs in which a person can type manuscripts of any length. The data is stored as an electronic document that can be opened, closed, saved, and edited at any time. This allows the user to make corrections or changes to a document multiple times before printing out a hard copy of the document. In many cases, the document is not printed out onto hard copy paper at all; instead, it can be used on the internet, in e-mails, or for other digital purposes.
Simpler programs, such as text editors or notepads, can be used to record text quickly without excess formatting options, such as multiple fonts or font sizes. Such programs are easy to use and do not come loaded with formatting features, such as color, multiple fonts, line spacing options, and so on. They are meant to be used for quick word processing that will not need to be formatted for presentation.
Word processing software often includes several features unavailable on typewriters or older word processors. Such features may include the ability to manipulate the layout of the text, the size and color of the font, the type of font used, line spacing, margin adjustments, and the ability to insert photos, web links, graphs, charts, and other objects directly into the document.
Improve Article
Save Article
Like Article
Improve Article
Save Article
Like Article
Word Processing Software :
The word “word processor” means it processes words with pages and paragraphs. Word processors are of 3 types which are electronic, mechanical, and software.
The word processing software is used to apply the basic editing and design and also helps in manipulating the text to your pages whereas the word processor, is a device that provides editing, input, formatting, and output of the given text with some additional features.
It is a type of computer software application or an electronic device. In today’s generation, the word processor has become the word processing software or programs that are running on general-purpose computers.
Examples or Applications of a Word Processing Software :
- Wordpad
- Microsoft Word
- Lotus word pro
- Notepad
- WordPerfect (Windows only),
- AppleWorks (Mac only),
- Work pages
- OpenOffice Writer
Features :
- They are stand-alone devices that are dedicated to the function.
- Their programs are running on general-purpose computers
- It is easy to use
- Helps in changing the shape and style of the characters of the paragraphs
- Basic editing like headers & footers, bullets, numbering is being performed by it.
- It has a facility for mail merge and preview.
Functions :
- It helps in Correcting grammar and spelling of sentences
- It helps in storing and creating typed documents in a new way.
- It provides the function of Creating the documents with basic editing, saving, and printing of it or same.
- It helps in Copy the text along with moving deleting and pasting the text within a given document.
- It helps in Formatting text like bold, underlining, font type, etc.
- It provides the function of creating and editing the formats of tables.
- It helps in Inserting the various elements from some other types of software.
Advantages :
- It benefits the environment by helping in reducing the amount of paperwork.
- The cost of paper and postage waste is being reduced.
- It is used to manipulate the document text like a report
- It provides various tools like copying, deleting and formatting, etc.
- It helps in recognizing the user interface feature
- It applies the basic design to your pages
- It makes it easier for you to perform repetitive tasks
- It is a fully functioned desktop publishing program
- It is time-saving.
- It is dynamic in nature for exchanging the data.
- It produces error-free documents.
- Provide security to our documents.
Disadvantages :
- It does not give you complete control over the look and feel of your document.
- It did not develop out of computer technology.
Like Article
Save Article
Word Processing[edit | edit source]
Introduction and Overview
Word processing is probably the most common among the «productivity» software applications in use. The computer was certainly adopted quickly as a replacement for the typewriter when users had increased access to computers and discovered its advantages in document creation, editing, formatting and saving — that is, its word processing capabilities. This is especially true when it comes to making changes to previously created documents. No longer is it necessary to re-type entire pages and/or documents in order to add, delete and make corrections, among other things. It has become as simple as retrieving the originally typed document from the computer (or storage device), making the necessary changes and either printing it with the «push of a button» (or few keystrokes) or putting the new version back into a file on the computer or on a storage device. In fact, there should be less chance of errors and typos because of such features as spelling and grammar checking options.
Possibly the greatest advantage in word processing is the «word wrap» feature which eliminates the need for time consuming «carriage returns,» therefore also decreasing the expenditure of energy in the typing process. In order to do «word processing,» one needs a computer and a program called a «word processor» (http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/W/word_processing.html Retrieved Oct 2, 2006).
Computers are generally sold with factory installed word processing software, but often this software is not the product or version desired by the customer. For example, the functionality of the software (e.g., Notepad) is more limited compared to the likes of Microsoft Word. As a result, purchasers tend to purchase, install and upgrade to a more common and familiar word processor.
In the early 1980s, word processing software such as DW3 (DisplayWriter) was command based and, as a result, more dependent upon «function» keys for implementing commands. Since the 1990s, users are not required to remember specific functions because the programs tend to be more ‘user friendly’ in terms of providing icons and drop-down menu options for the user’s convenience. Although it may take one some time to find the appropriate command, a user can search and/or browse even request «help» from the program itself — to find what they wish to accomplish in their document.
Perhaps the most common and familiar to computer users are such word processing software as Microsoft Word and WordPerfect. In fact, word processing has advanced to the point of being within a «suite» of productivity software applications and, as a result, can utilize the interconnectivity of the programs in this «suite» to produce advanced word document presentations with such features as ‘linked’ tables, maps and websites.
For more technical documents, there’s an option to utilize a feature called «Cite While You Write» which inserts commands into the menu (i.e., ‘Tools’) of the word processing program (e.g., Microsoft Word) to give the user direct access to references and enables the bibliographic software (e.g., EndNote or ProCite) to conduct bibliographic formatting during the writing stage in the open document (Thomson ISI ResearchSoft, 2003, «EndNote 7 … Bibliographies & More Made Easy,» p. 38; ISI ResearchSoft, 2000, «ProCite,» pp. 63-64).
Today, rather than purchasing word processing software, there is the option to use Free Software (e.g., AbiWord). Many word processors can open and save Microsoft Word Document files [and] …. suitable for a wide variety of word processing tasks [and] … available for a number of languages and operating systems» (http://www.abisource.com/ Retrieved Oct 3, 2006).. Another option is to make use of web based word processors (e.g., Writely). One can «share documents instantly & collaborate [in] real-time … edit your documents from anywhere … store your documents securely online … [and is] easy to use … [because it provides] a familiar, desktop feel» (https://www.google.com/accounts/ServiceLogin?service=writely&passive=true&continue=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.writely.com%2F<mpl=homepage&nui=0 Retrieved Oct 2, 2006).
While there are many word processors available, each and everyone has the ability to perform the basics. That is, word processors enable the user to create or type a document, edit (make additions and corrections, as well as check spelling and grammar, move, copy and paste text), format (e.g., change spacing and capitalization, bold, italicize and underline text), print and save (http://www.compusmart.ab.ca/alummis/beginnerword/index.htm Retrieved Oct 2, 2006). Word processors can be quite complicated and provide the user with very advanced functions (as noted above), but the following discussions will begin by focusing on the basics for the benefit of all users.
Since 2007 Windows Vista has speech recognition included with Microsoft Word. The Speech Recognition allows you to issue commands to your computer with your voice. You can launch programs, switch between open programs, close a window, etc with a microphone connected to the computer. With Microsoft Word, you can dictate text, edit and format the text. Once it is set up, there a many possibilities for commands you can use like waking a “sleeping” system, selecting or correcting words in a document or even requesting for a list of possible commands to use.
You do need to train the Speech Recognition feature to learn your voice accurately through an interactive tutorial before you begin using it, it is highly suggested to use a good quality microphone so the computer can hear you better which will reduce errors. The dictation mode allows you to easily speak what’s on your mind and have Microsoft Word do all the work for you, dramatically reducing the use of your keyboard and mouse, it will also allow you to navigate between screens and applications with ease. The Speech Recognition feature is not very useful though for those who often work with text that is not grammatical, such as computer programmers, accountants, and computer administrators.(http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb530325.aspx)
Microsoft Word 2007 attempts to change the de facto word (and office) document file format, but the Open Document is used across more word processors and is gaining in popularity faster.
Microsoft’s newest update to the application is Word 2010 which was released in June of 2010. The application included a release of a free online version that works on an applet on most browsers that could be accessed through Microsoft’s online email client, Live or Hotmail. The new version also replaced what once was Microsoft Works with Office Starter 2010 offering a more basic word processor in the suite which comes pre-installed on most computers.The new version of Word most noticeable change could have been the look of the «Orb» which was the icon for the File option which is now a tab icon with the word File on it. Along with these changes and other the application does offer more features for common to power users. (Wikipedia Office 2010)
Document Creation
When you enter text onto a new Word document by a use of a keyboard, you are not only inputting data into the computer but you are also forcing the computer to begin working in a new document (William.B & Sawyer.S, 2007. Using Information Technology. The McGraw-Hill Publishing Inc: New York). Three functions of word processing assist you with the process of what is called creating or starting a new document.
The most integral function is the cursor. This small arrow or vertical line that appears on the screen allows you to see where you are located in the document. It allows you to navigate through the document so that you do not loose your place.
On the left or right side of your document you will also find a scrolling device that allows you to quickly move back and forth through the document from beginning to end. This device allows you to preview the beginning and end of the document while saving a vast amount of time (William.B & Sawyer.S, 2007. Using Information Technology. The McGraw-Hill Publishing Inc: New York).
When it comes to creating a document the easiest package that comes to mind is Microsoft Word. With Microsoft Word you are able to create, edit, spell check, print, and save professional looking documents, calendars, brochures, etc. In addition to creating, editing, spell checking, printing, and saving professional looking documents you can import other applications into Microsoft Word including spreadsheets, PowerPoint presentations, and database directly into Microsoft Word maximizing all the specifications of other applications.
There are similar packages out there that will do basically the same as Microsoft Word. They include Word Perfect, Open Office, and Lotus to name a few.
Document Revision
Editing is the process of making changes or modifications to an existing document. In word processors there are many features that can assist you with editing your document. Word processing allows people to spend less time with editing and formatting which in turn allows them to put more time into the piece they are writing (http://office.microsoft.com/en-ca/word/HA101650321033.aspx, Retrieved December 5, 2006). Information technology has greatly improved the process of human editing but also has allowed us to become “editing inept” as we the computer just does it for us with the touch of a button. Essentially an English professor may say we have become lazy in our approach to English.
Part of the reason we have become lazy is due to the fact that word processing has made it so easy for us to edit. Instead of whiteout or erasing if we make a mistake we can use the insert & delete button. If we feel we want to make additions to the document we can use the insert button and start typing wherever we place the cursor. All other text will shift (William.B & Sawyer.S, 2007. Using Information Technology. The McGraw-Hill Publishing Inc: New York). You can also replace text in a document. For example, if you have typed one word throughout the whole document but realize you made a mistake you can find all instances of the words and then replace them with the word you meant. This feature saves the average writer an enormous amount of time. Making a mistake used to be a great annoyance in those handwriting days because it meant using an eraser, whiteout or even starting over. However, now with the Undo command you can undo the last mistake you made just by using a touch of a button or simple command — Control Z on the keyboard. (William.B & Sawyer.S, 2007. Using Information Technology. The McGraw-Hill Publishing Inc: New York).
Editing a word processor document also allows you to cut and paste which used to be accomplished with scissors and glue. However, you can do this on the computer now with a touch of a button. Word processing allows you to copy a word, paragraph or picture and paste to another location or another file.
If you are having trouble thinking of a synonym all you have to do is use the built in thesaurus which is part of most word processors today.
The last two elements of word processing that we have become to increasingly rely on in our daily careers, schooling and writing is spelling and grammar check. The computer will scan your document and pick up any miss-spelled word or grammar issues you may have in your writing. This technique is and was one that you would spend hours and hours on in your English class learning however now the computer will automatically check and fix for you. Be careful with the spell check feature as if the word is spelled correctly but in the wrong context it will not pick it up. These features are good but still need the human eye to totally understand the language.
Formatting Options
Two very useful tools in Microsoft Word are Templates and Wizards. There are numerous pre-made Templates you have access to in Microsoft Word; ranging from certain types of business and personal Templates. There is also an option to create your own personalized Template. The purpose of these Templates is to save you time when creating specific documents you may use with the same outlines just different body information. Template can contain formatting, styles, headers, footers, and graphics. The Wizard is a tool that can save a lot of time formatting, printing, and mail merging. In Microsoft Office 2010 both of these tools can be accessed through the File tab.
Morley, Deborah, and Charles S. Parker. Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow. Boston, MA: Course Technology, Cengage Learning, 2011. Print.
The use of templates in word processing has become very popular. Templates are extremely helpful whether you are working in a Fortune 500 company or own your own small business. The templates that are available are wide spread and include fax cover sheets, resumes, calendars, business cards and memos to name just a few. I think that the resume templates are most helpful whether you are a recent college graduate or if you are returning to work. The templates give you many different options to choose from, but also give you the ability to customize them to make them your own.
(Understanding Computers Today and Tomorrow/13th Edition/Morley and Parker page 29)
Styles vs Direct Formatting
It is always a good idea, especially for longer documents of more than one page, to use the Header1, Header2, Header3 markup rather than using direct formatting. The advantage of building a document using styles is that when it comes to outputting to PDF, the word processor will build an outline view of the document and this will be handy in finding Chapters and Sections in a longer document.
Styles are beneficial also when you want to change the text properties of your headings. For example, if you have set your sub-sections to 14pt Arial and have a 20 page document. If you want to change the typeface to something else, using direct formatting it will be necessary to manually go thru the complete document changing the typeface to «Liberation Serif». Using the style for Heading1 you go into a dialog box and change the properties of Heading1 — font-size, font-weight, color, etc… This step alone will save a lot of time.
A word processor is software or a device that allows users to create, edit, and print documents. It enables you to write text, store it electronically, display it on a screen, modify it by entering commands and characters from the keyboard, and print it.
Of all computer applications, word processing is the most common. Today, most word processors are delivered either as a cloud service or as software that users can install on a PC or mobile device.
Word Processor Checklist
Jump to a topic in this article:
- What is the History of Word Processing?
- What are Standard Features of Word Processors?
- Full-featured Word Processors
- Word Processors vs. Text Editors vs. Desktop Publishing Systems
What is the History of Word Processing?
The earliest word processors were standalone machines similar to electric typewriters that debuted in the 1960s. The great advantage of these early machines over using a typewriter was that you could make changes without retyping the entire document. Over time, the devices acquired more advanced features, such as the ability to save documents on a disk, elaborate formatting options, and spell-checking.
While there are still some standalone word processors in use today, word processing began to move to personal computers in the 1980s. In the early days of the PC, a word processor called WordPerfect became one of the most widely used applications of any kind. Over time, however, What You See Is What You Get (WYSIWYG) word processors that showed users exactly what would print on their final documents became more popular. One of those WYSISWG word processors, Microsoft Word, became dominant in the 1990s.
Image: The first version of Microsoft Word was developed in 1981. The current version is Microsoft Word 16 (released in 2016).
With the advent of cloud computing in the 2000s, word processing changed again. The cloud allowed users to do their word processing via a browser-based application. While these cloud-based word processors lacked the advanced functionality of software installed on a device, they allowed users to store their documents in a remote data center and access them from any Internet-connected PC or mobile device. They also made it easier for geographically separated teams of people to work together on the same document. Many users found that cloud-based word processors offered enough features to meet their needs, as well as greater convenience, mobility, and collaboration support.
What are Standard Features of Word Processors?
Word processors vary considerably, but all word processors, whether cloud-based or installed on a system, support the following basic features:
insert text: Allows you to insert text anywhere in the document.
delete text: Allows you to erase characters, words, lines, or pages.
cut and paste: Allows you to remove (cut) a section of text from one place in a document and insert (paste) it somewhere else.
copy: Allows you to duplicate a section of text.
page size and margins: Allows you to define various page sizes and margins, and the word processor will automatically readjust the text so that it fits.
search and replace: Allows you to direct the word processor to search for a particular word or phrase. You can also direct the word processor to replace one group of characters with another everywhere that the first group appears.
word wrap: Automatically moves to the next line when you have filled one line with text, and it will readjust text if you change the margins.
print: Allows you to send a document to a printer to get hard copy.
file management: Provides file management capabilities that allow you to create, delete, move, and search for files.
font specifications: Allows you to change fonts within a document. For example, you can specify bold, italics, and underlining. Most word processors also let you change the font size and even the typeface.
windows: Allows you to edit two or more documents at the same time. Each document appears in a separate window. This is particularly valuable when working on a large project that consists of several different files.
spell checking: Identifies words that don’t appear in a standard dictionary.
Full-Featured Word Processors
Most installable modern word processor software supports additional features that enable you to manipulate and format documents in more sophisticated ways. Full-featured word processors usually support the following advanced features, and cloud-based word processors may have some of these features as well:
grammar checking: Identifies sentences, paragraphs, and punctuation that doesn’t appear to meet commonly recognized rules of grammar.
footnotes and cross-references: Automates the numbering and placement of footnotes and enables you to easily cross-reference other sections of the document.
automated lists: Automatically creates bulleted or numbered lists, including multi-level outlines.
graphics: Allows you to embed illustrations, graphs, and possibly even videos into a document. Some word processors let you create the illustrations within the word processor; others let you insert an illustration produced by a different program.
headers, footers, and page numbering: Allows you to specify customized headers and footers that the word processor will put at the top and bottom of every page. The word processor automatically keeps track of page numbers so that the correct number appears on each page.
layout: Allows you to specify different margins within a single document and to specify various methods for indenting paragraphs.
macros: Enables users to define and run macros, a character or word that represents a series of keystrokes. The keystrokes can represent text or commands. The ability to define macros allows you to save yourself a lot of time by replacing common combinations of keystrokes.
merge: Allows you to merge text from one file into another file. This is particularly useful for generating many files that have the same format but different data. Generating mailing labels is the classic example of using merges.
tables of contents and indexes: Allows you to automatically create a table of contents and index based on special codes that you insert in the document.
thesaurus: Allows you to search for synonyms without leaving the word processor.
collaboration: Allows users to track changes to the document when more than one person is editing. Some cloud-based word processors also allow multiple users to edit the same document at the same time.
internet features: Allows users to embed Web links into their documents and format their documents for the Web. Some also link to Web services that can help users create their documents.
translation and speech: As artificial intelligence capabilities become more commonplace, some word processors have gained the ability to read text aloud, to accept voice commands, and to translate text from one language to another.
Read also: What is a Spreadsheet?
Word Processors vs. Text Editors vs. Desktop Publishing Systems
Word processors are very similar to two other categories of software: text editors and desktop publishing applications. An example of a word processor is offered by Zoho.
Applications that support only the basic features from the first list above (and maybe a few others) are sometimes called text editors. Office workers sometimes use text editors to create simple documents that don’t require a full-featured word processor. However, text editors are more commonly used by programmers who use special text editors with features designed for writing code.
Desktop publishing systems, on the other hand, are generally more advanced and complex than word processors. The line dividing word processors from desktop publishing systems is constantly shifting as word processors become more advanced. In general, though, desktop publishing applications support finer control over layout, especially for documents with a lot of graphics, and they offer more support for full-color printing options.
This article was updated April 2021 by Jenna Phipps