-
#1
I’ve been wondering how to put the time, day and date in the right order.
Can anybody help me?
I’d like to make an appointment for Friday at 2:00 on Feb. 28.
I’d like to make an appointment at 2:00 on Friday Feb. 28.
I’d like to make an appointment at 2:00 Friday Feb.28.
-
#2
Spoken: I’d like to make an appointment for Friday, February 28th, at 2pm.
-
#3
Or, I’d like to make an appointment for 2 pm on Friday, February 28th.
The time should not separate the day of the week and the date. Whether it comes first or last is a matter of style. Just don’t put it in the middle.
There are a few things that seem off with your original sentence:
I would like to meet you at 5pm this Sunday in KFC on the first floor in USA Shopping center.
First, the order of adverbials is off. As the Cambridge dictionary says, adverbials of time should follow adverbials of place.
When there is more than one of the three types of adverb together, they usually go in the order: manner, place, time.
An example from there is:
James played brilliantly [manner] in the match [place] on Saturday [time]. (preferred to James played brilliantly on Saturday in the match.)
So in your sentence, the order of the adverbs needs to be reversed:
I would like to meet you in KFC on the first floor in USA Shopping center at 5pm this Sunday.
That is immediately much better. The two sets of adverbials are in the right order (place, then time).
Within each set, you have already arranged each of them from most specific to most general: 5pm is more specific than this Sunday, for example. You could choose to arrange from most general to most specific too: this Sunday at 5pm. But in that case you should probably rearrange the place adverbs too, to go from most general (USA Shopping Center) to most specific (KFC). That is a matter of preference and style rather than a rule per se. The way you have them arranged is fine.
The rest of the tweaks don’t have to do directly with your question about the arrangement of adverbials, but are needed to make the sentence idiomatic. Consider the following conversation:
«Where did you eat?»
«KFC.»
«The one on Foo Road?»
«No, the one in USA Shopping Center.»
When you are specifying which KFC, you need the definite article. You can say I’ll see you in KFC, but once you’re narrowing it down to a specific one, you have to say I’ll meet you in the KFC on the first floor.
I would like to meet you in the KFC on the first floor in USA Shopping center at 5pm this Sunday.
Next, idiomatically we say the nth floor of a building rather than in:
I would like to meet you in the KFC on the first floor of USA Shopping center at 5pm this Sunday.
Finally, is the name of the mall USA Shopping Center? If so, capitalize accordingly:
I would like to meet you in the KFC on the first floor of USA Shopping Center at 5pm this Sunday.
If the shopping center is called just USA, and you’re adding the shopping center for disambiguation (the first floor of USA seems, um, rather vast) then you need to lose the capital S and add a definite article. It’s a bit tricky to explain, but I’ll try. Suppose I’ve been trying to choose between Harmon-Kardon and Bose speakers. Once I am sure, I might say:
I’ve decided to buy the Bose speakers.
Here, I’m using Bose to specify which speakers among the ones I was considering. Since it’s a specification, I need the definite article. It works just like the green bag or some other specification using an adjective.
Similarly, if the mall is just named USA, you are specifying which shopping center, and its name functions adjectivally. So you would need the definite article:
I would like to meet you in the KFC on the first floor of the USA shopping center at 5pm this Sunday.
®Ros
A simple rule is that you can put time expressions such as “Tomorrow,” “Last week,” or “Two days ago” at the beginning of your sentence or at the end of your sentence.
Here are some correct examples:
1 Tomorrow we’ll have an important meeting.
Or:
We’ll have an important meeting tomorrow.
Not: We’ll tomorrow have an important meeting.
And not: We’ll have tomorrow an important meeting.
2 Last week I saw Jen with Enzo.
I saw Jen with Enzo last week.
3 Two days ago I made an appointment with my dentist.
I made an appointment with my dentist two days ago.
And not: I made two days ago an appointment with my dentist.
Please note: This rule doesn’t count for always, never, sometimes, usually and rarely. For the rule of these, have a look at this article.
So to recap:
Put time expressions at the beginning or at the end of your sentence.
Easy, isn’t it?
Please have a look at some more examples:
4 Early in the evening we went for a walk on the beach.
We went for a walk on the beach early in the evening.
5 Yesterday night Alexandra worked the night shift.
Alexandra worked the night shift yesterday night.
6 At a quarter to six the bell rang.
The bell rang at a quarter to six.
7 In the summer of 1995 Desiree wasn’t born yet.
Desiree wasn’t born yet in the summer of 1995.
So now try the quiz.
Quiz
You can do the quiz online here.
Put in the time expressions according to the instructions between brackets.
Example 1:
Mat worked all day (today, end).
Answer:
Mat worked all day today.
Example 2:
Farhad did his laundry (yesterday, beginning).
Answer:
Yesterday Farhad did his laundry.
1 Robin quit smoking (last year, beginning).
2 The stars are bright (tonight, beginning).
3 Mr Eastlander is out (this afternoon, end).
4 Spring starts early (this year, beginning).
5 The sun goes down (at five o’clock, end).
6 The birds build a nest (when it gets warm, end).
7 I need to remove the clothes from the line (before it gets dark, beginning).
8 She falls asleep on top of her book (when she feels tired, beginning).
9 The neighbours will start renovating their flat (in December, end).
10 The toast will be ready (in five minutes, beginning).
Did you like this quiz? Why not order some more?
10000+ results for ‘word order time’
Word Order Reisen
Unjumble
by Iarichardson
Y10
German
Word Order
Separable Verbs — SORT — Correct/Incorrect
Whack-a-mole
by Iarichardson
Y10
German
Word Order
Free Time Activities word order
Unjumble
by Commone07s
High school
KS3
Y7
Y8
Y9
French
BBa 10De Time word order
Unjumble
by Bbar4809
KS4
German
Ordering Units of Time
Rank order
by U75573030
KS1
Maths
Time
Word Order German
Missing word
by Judithshand
German
Internet word order time manner place
Unjumble
by Sandiefillingha
unjumble,The word order is subject +day + time
Unjumble
by Ddeseulin2
Y8
French
Past Tense with Time Phrases Word Order
Unjumble
by Lbrown19
Y7 Adverbs of time word order
Unjumble
by Cni4032
Word order
Rank order
by U49266076
Word Order
Unjumble
by Michaelelliott
Days of the Week
Quiz
by Ffpsmissc
KS1
Maths
Time
Et quart , moins le quart et heure.
Quiz
by Elsaseulin
French
time
O’clock Practice
Quiz
by Boddam45
Y1
Y2
Maths
time
Time chase
Maze chase
by Ffpsmissc
KS1
Maths
Time
Match the clocks
Find the match
by Vbwoodman
Y5
Maths
Time
o’clock / half past / quarter past /quarter to
Quiz
by Ffpsmissc
KS1
Maths
Time
Time — sort into order
Rank order
by Fad2
Order units of time
Rank order
by Victoria568
Academy Stars 2 Reading Time 1 (Order)
Rank order
by Kikhayaa
Elementary School
children
Y2
Y3
English
Academy Stars 2
Reaction time order
Rank order
by Clare20
2 Adjectives Word Order
Unjumble
by Karenmoss
word order
Unjumble
by Gabmilicz77
Word order 1
Rank order
by Arthurmckeown
it is time! Find the right word order.
Unjumble
by Elsaseulin
Y6
French
Days of the week and time word order
Unjumble
by Cni4032
Word order 2
Rank order
by Arthurmckeown
simple hour.
Match up
by Elsaseulin
Y7
French
time
Week 21 GER — Year 9 Word order with time phrases
Unjumble
by Clare20
KS3
German
Alphabetical order
Rank order
by Laurajackson
E2
E3
E1
Alphabetical Order
English
Word order (предложения БЕЗ глагола действия)
Unjumble
by Babrasin
English
Sentence word order
Question word order
Unjumble
by Traceyunwin
Comparatives — word order
Unjumble
by Mafaldagiudice
English
ESOL
Word order in questions
Missing word
by Leighanne
Mi familia
Random wheel
by Kingecgbert
KS3
Spanish
Time
Word Order
Unjumble
by Pamtosh
High school
Y9
Y10
Spanish
J1 time sequencers Logical Order
Rank order
by Shiva568
Word order
Unjumble
by Serious
Word order
Unjumble
by Achidzey
PE Months of the year in order
Rank order
by Lgegg
Adult Education
ESL
Time
German word order
Unjumble
by Marielaaffum
KS3
German
Word order
Unjumble
by Rachelswhitfield
University
Word Order
Unjumble
by Sijingni2020
Word Order
Unjumble
by Beckywootton
Word order
Unjumble
by Jageary1
Dutch
Units of Time
Higher or lower
by U75573030
KS1
Maths
Time
Word Order
Unjumble
by Keh
word order
Unjumble
by Cdavey2
Word order
Unjumble
by Esolworcester
English Word Order
Unjumble
by U22352817
Adult Education
English
ESL
Word order
Unjumble
by Arthurmckeown
Adult Education
English
Word Order
Unjumble
by Shahrourahmed
Word order
Unjumble
by Liptakandrea
Word order
Unjumble
by Charismphillips
WORD ORDER
Unjumble
by Salinaann999
English
Word order
Unjumble
by Leighanne
Word order
Unjumble
by Woodlouse100
Word Order
Unjumble
by U49266076
Word order
Unjumble
by U77406923
Essential grammar
in use
Word order Adverbs Prepositions of Time
Word order
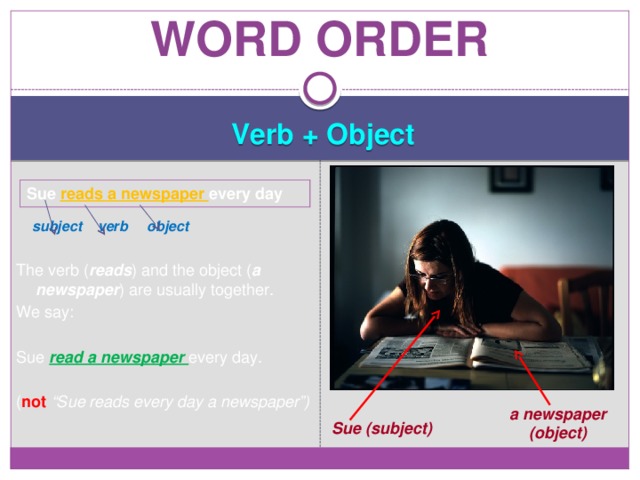
Verb + Object
subject verb object
The verb ( reads ) and the object ( a newspaper ) are usually together.
We say:
Sue read a newspaper every day.
( not “Sue reads every day a newspaper”)
Sue reads a newspaper every day
a newspaper (object)
Sue (subject)
Word order
Verb + Object
Correct
Incorrect
He speaks English very well.
He speaks very well English.
I like Chinese food very much.
I like very much Chinese food.
Paul often wears a black hat.
Paul wears often a black hat.
Did you watch TV all evening?
Did you watch all evening TV?
We invited a lot of people to the party.
We invited to the party a lot of people.
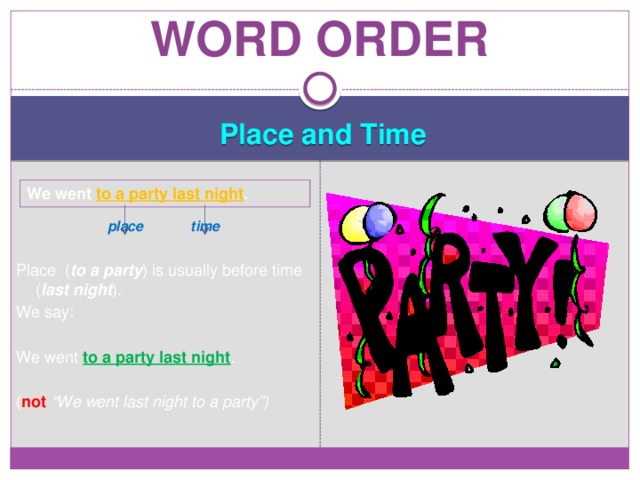
Word order
Place and Time
place time
Place ( to a party ) is usually before time ( last night ).
We say:
We went to a party last night .
( not “We went last night to a party”)
We went to a party last night .
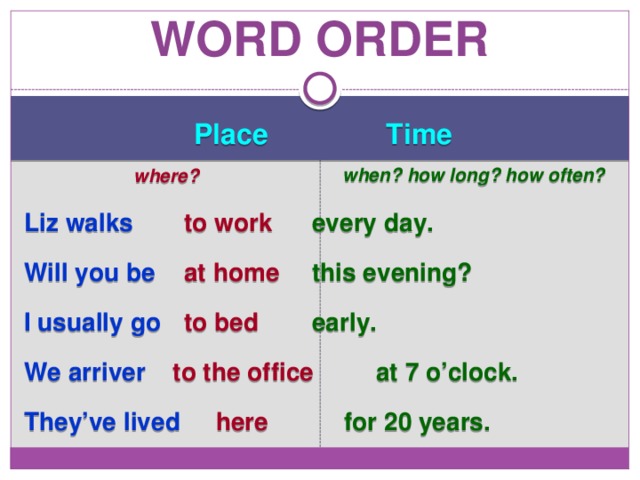
Word order
Place Time
when? how long? how often?
where?
Liz walks to work every day.
Will you be at home this evening?
I usually go to bed early.
We arriver to the office at 7 o’clock.
They’ve lived here for 20 years.
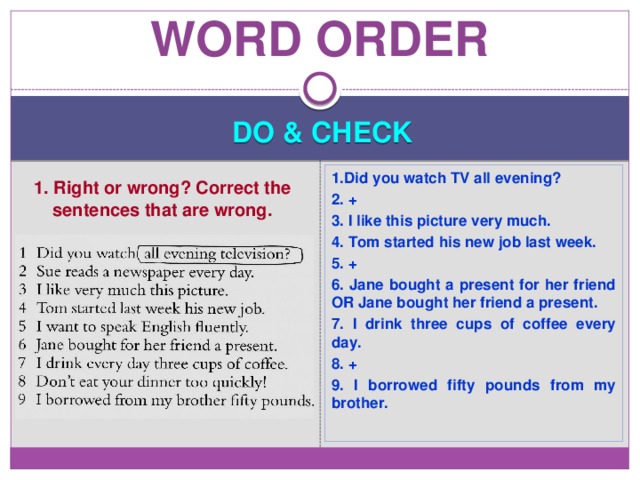
Word order
DO & CHECK
1.Did you watch TV all evening?
2. +
3. I like this picture very much.
4. Tom started his new job last week.
5. +
6. Jane bought a present for her friend OR Jane bought her friend a present.
7. I drink three cups of coffee every day.
8. +
9. I borrowed fifty pounds from my brother.
1. Right or wrong? Correct the sentences that are wrong.
Word order
DO & CHECK
1. I opened the door quietly.
2. I wrote two letters this morning.
3. Paul passed the exams easily.
4. Ann doesn’t speak French very well.
5. I did a lot of work yesterday.
6. Do you know London well?
7. We enjoyed the party very much.
8. I explained the problem carefully.
9. We met some friends at the airport.
10. Did you buy that jacket in England?
11. We do the same things every day.
12. I don’t like football very much.
2. Put the words in order.
Word order
DO & CHECK
- (to work/ every day/ walks/ Liz)
- (at the hotel/early/ we/ arrived)
- (goes/ every year/ to Italy/ Julia)
- (we/ since 1998/ here/ have lived)
- (in London/ Sue/ in 2004/ was born)
- (didn’t go/ yesterday/ Paul/ to work)
- (to the bank/ yesterday afternoon/ went/ Ann)
- (I/ in bed/ this morning/ my breakfast/ had)
- (in October/ Barbara/ to university/ is going)
- (I/ a beautiful bird/ this morning/ in the garden/ saw)
- (many times/ have been/ my parents/ to the United States)
- (my umbrella/ I/ last night/ left/ in the restaurant)
- (to the cinema/ tomorrow evening/ are you going?)
- (the children/ I/ took/ this morning/ to school)
3. Put the words in order.
Word order
DO & CHECK
- Liz walks to work every day.
- We arrived at the hotel early.
- Julia goes to Italy every year.
- We have lived here since 1998.
- Sue was born in London in 2004.
- Paul didn’t go to work yesterday.
- Ann went to the bank yesterday afternoon.
- I had my breakfast in bed this morning.
- Barbara is going to university in October.
- I saw a beautiful bird in the garden this morning.
- My parents have been to the United States many times.
- I left my umbrella in the restaurant last night.
- Are you going to the cinema tomorrow evening?
- I took the children to school this morning.
adverbs
Adverbs often go with the verb in the middle of a sentence.
My brother never speaks to me.
always often
She’s always late.
ever rarely
Do you often go to restaurants?
already also
I sometimes eat too much. (or Sometimes I eat too much.)
usually all
I don’t want to go to the cinema.
never sometimes seldom just
I’ve already seen the film.
still both
I’ve got three sisters. They’re all married.
adverbs
Always, often, never go BEFORE the verb
Correct
Incorrect
I always go to work by car.
I go always to work by car.
Ann often plays tennis.
Ann plays often tennis.
You sometimes look unhappy.
You look sometimes unhappy.
They usually have dinner at 7.
I watch rarely/seldom TV.
I rarely/seldom watch TV.
He plays also tennis and volleyball.
Richard is a good footballer. He also plays tennis and volleyball.
adverbs
Always, often, never go AFTER the verb BE
Correct
Incorrect
I am never ill.
I never am ill.
They are usually at home at 8.
They usually are at home at 8.
It is often very cold here in winter.
It often is very cold here in winter.
When I was a child, I was always late for school.
When I was a child, I always was late for school.
adverbs
Adverbs go BETWEEN two verbs
Correct
Incorrect
I will always remember you.
I always will remember you.
It doesn’t often rain here.
It doesn’t rain often here.
Do you usually go to work by car?
Do you go usually to work by car?
I can never find my keys.
I never can find my keys.
Have you ever been to Rome?
Have ever you been to Rome?
Ann just has gone out.
Ann has just gone out.
1. Write these sentences with the words in brackets (…).
adverbs
1. My brother speaks to me (never)
2. Susan is polite. (always)
3. I finish work at 5 o’clock. (usually)
4. Jill has started a new job. (just)
5. I go to bed before midnight. (rarely)
6. The bus isn’t late. (usually)
7. I don’t eat fish. (often)
8. I will forget what you said. (never)
9. Have you lost your passport? (ever)
10. Do you work in the same place? (still)
11. They stay in the same hotel. (always)
12. Diane doesn’t work on Saturday (usually)
13. Is Tina here? (already)
14. What do you have for breakfast? (usually)
15. I can remember his name (never)
DO
&
CHECK
adverbs
1. My brother never speaks to me.
2. Susan is always polite.
3. I usually finish work at 5 o’clock.
4. Jill has just started a new job.
5. I rarely go to bed before midnight.
6. The bus isn’t usually late.
7. I don’t often eat fish.
8. I will never forget what you said.
9. Have you ever lost your passport?
10. Do you still work in the same place?
11. They always stay in the same hotel.
12. Diane doesn’t usually work on Saturday
13. Is Tina already here?
14. What do you usually have for breakfast?
15. I can never remember his name.
DO
&
CHECK
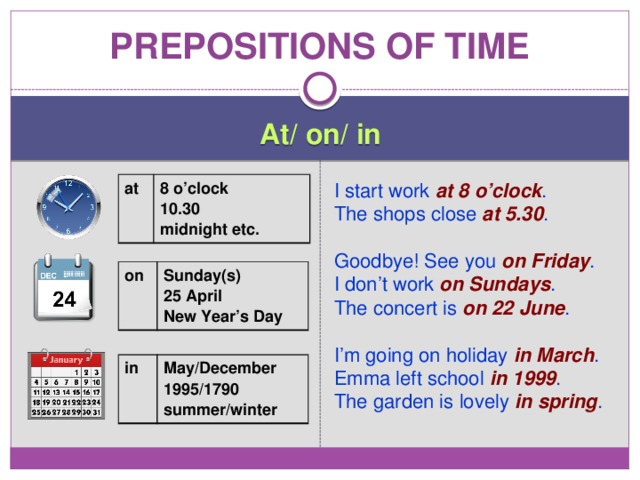
Prepositions of time
At/ on/ in
I start work at 8 o’clock .
The shops close at 5.30 .
Goodbye! See you on Friday .
I don’t work on Sundays .
The concert is on 22 June .
at
8 o’clock
I’m going on holiday in March .
10.30
Emma left school in 1999 .
midnight etc.
The garden is lovely in spring .
on
Sunday(s)
25 April
New Year’s Day
in
May/December
1995/1790
summer/winter
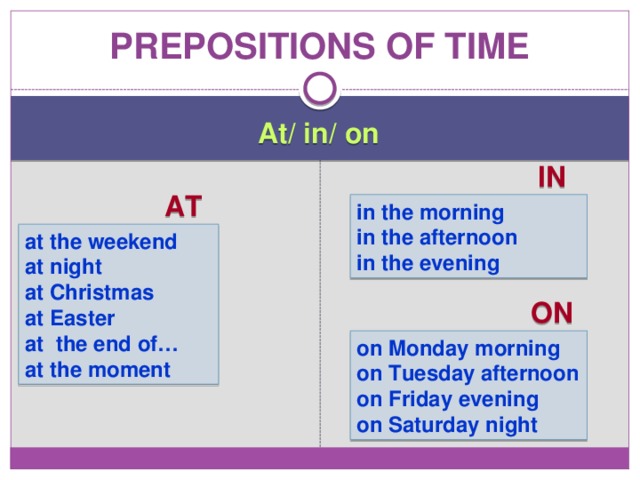
Prepositions of time
At/ in/ on
IN
AT
in the morning
in the afternoon
in the evening
at the weekend
at night
at Christmas
at Easter
at the end of…
at the moment
ON
on Monday morning
on Tuesday afternoon
on Friday evening
on Saturday night
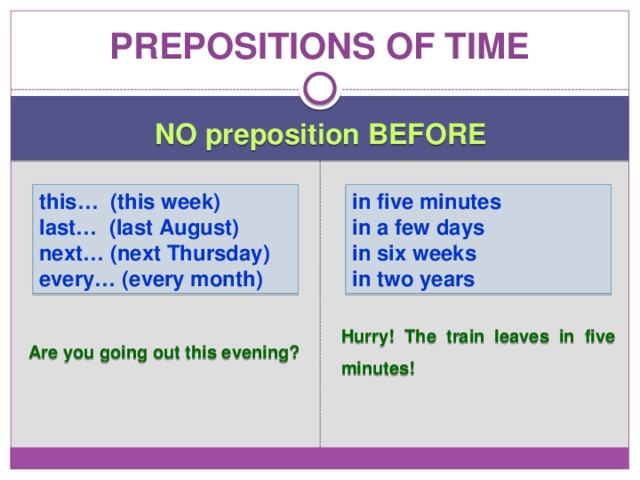
Prepositions of time
NO preposition BEFORE
this… (this week)
in five minutes
last… (last August)
in a few days
next… (next Thursday)
in six weeks
every… (every month)
in two years
Hurry! The train leaves in five minutes!
Are you going out this evening?
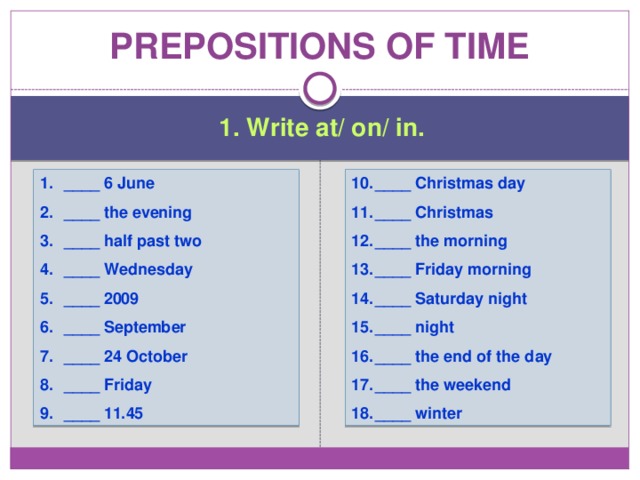
Prepositions of time
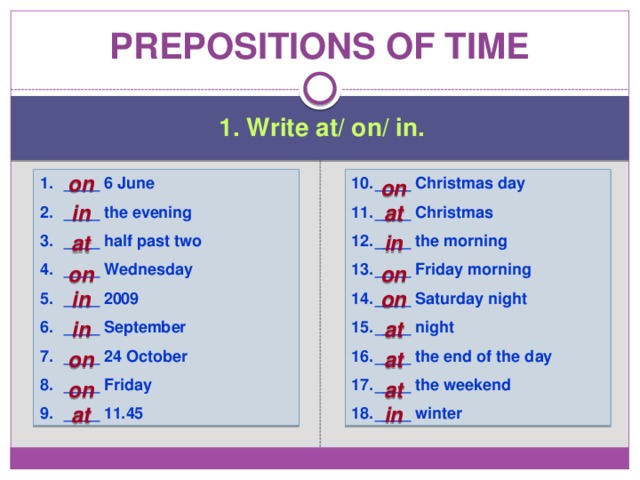
1. Write at/ on/ in.
- ____ 6 June
- ____ the evening
- ____ half past two
- ____ Wednesday
- ____ 2009
- ____ September
- ____ 24 October
- ____ Friday
- ____ 11.45
- ____ Christmas day
- ____ Christmas
- ____ the morning
- ____ Friday morning
- ____ Saturday night
- ____ night
- ____ the end of the day
- ____ the weekend
- ____ winter
Prepositions of time
1. Write at/ on/ in.
- ____ 6 June
- ____ the evening
- ____ half past two
- ____ Wednesday
- ____ 2009
- ____ September
- ____ 24 October
- ____ Friday
- ____ 11.45
- ____ Christmas day
- ____ Christmas
- ____ the morning
- ____ Friday morning
- ____ Saturday night
- ____ night
- ____ the end of the day
- ____ the weekend
- ____ winter
on
on
at
in
at
in
on
on
in
on
at
in
on
at
on
at
at
in
Prepositions of time
2. Write at/ on/ in.
1. Where were you ___ 28 February?
10. I often go away ___ the weekend
2. I got up ___ 8 a.m. this morning.
11. I’m starting my new job ___ 3 July.
3. I like getting up early ___ in the morning.
12. We often go to the beach ___ summer.
13. George isn’t here ___ the moment.
4. My sister got married ___ May.
5. Diana and I first met ___ 1999.
14. Julia’s birthday is ___ January.
6. Did you go out ___ Tuesday?
15. Do you work ___ Saturdays.
16. The company started ___ 1969.
7. Did you go out ___ Tuesday evening?
17. I like to look at the stars ___ night.
8. Do you often go out ___ evening?
9. Let’s meet ___ 7.30 tomorrow evening.
18. I’ll send you the money ___ the end of the month.
Prepositions of time
2. Write at/ on/ in.
1. Where were you ___ 28 February?
10. I often go away ___ the weekend
2. I got up ___ 8 a.m. this morning.
11. I’m starting my new job ___ 3 July.
on
12. We often go to the beach ___ summer.
3. I like getting up early ___ the morning.
4. My sister got married ___ May.
13. George isn’t here ___ the moment.
5. Diana and I first met ___ 1999.
14. Julia’s birthday is ___ January.
15. Do you work ___ Saturdays.
6. Did you go out ___ Tuesday?
16. The company started ___ 1969.
7. Did you go out ___ Tuesday evening?
8. Do you often go out ___ evening?
17. I like to look at the stars ___ night.
18. I’ll send you the money ___ the end of the month.
9. Let’s meet ___ 7.30 tomorrow evening.
at
at
on
in
in
at
in
in
in
on
on
in
on
at
at
in
at
Prepositions of time
3. Write at/ on/ in if necessary. Sometimes there is no preposition.
- I’m leaving ___ Friday.
- I’m leaving ___ next Friday.
- I always feel tired ___ the evening.
- Will you be at home ___ this evening?
- They went to France ___ last summer.
- Laura was born ___ 1978.
- What are you doing ___ the weekend?
- I call Nick ___ every Monday.
- Shell we play tennis ___ next Sunday?
- I can’t go to the party ___ Saturday
- I’ll be back ___ an hour.
- I don’t often go out ___ night.
Prepositions of time
3. Write at/ on/ in if necessary. Sometimes there is no preposition.
- I’m leaving ___ Friday.
- I’m leaving ___ next Friday.
- I always feel tired ___ the evening.
- Will you be at home ___ this evening?
- They went to France ___ last summer.
- Laura was born ___ 1978.
- What are you doing ___ the weekend?
- I call Nick ___ every Monday.
- Shell we play tennis ___ next Sunday?
- I can’t go to the party ___ Saturday
- I’ll be back ___ an hour.
- I don’t often go out ___ night.
on
at
—
in
—
—
—
on
—
in
in
at
Авторская страничка
За основу использовано учебное пособие
- Murphy Raymond, Essential Grammar In Use, Cambridge University Press, 2000
Изображения:
- http://cdn1.iconfinder.com/data/icons/general12/png/256/calendar.png
- http://contently.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2012/02/calendar_icon3.png
- http://clipartist.net/RSS/openclipart.org/Unity/clock_wall_paper_art-555px.png
Составила:
Левенцева Т.А.,
учитель английского языка
МОУ «Гимназия №3» г.Воркуты
2013г.
So you have some curiosity about time order words? The short answer is that time order words establish the sequence in which events happen and are some of the most important words in the English language.
What are Time Order Words?
Time order words set the scene in academic writing as well as fiction. They are the compass and the time keeper to help keep the listener on track. The most popular place to find time order words is at the start of a paragraph, but they can come anywhere in a sentence.
So maybe you’re still wondering why time order words are important? They provide the context and grounding in the English language. Without them, you are most likely to be a little bit lost and possible assume something that is not true or part of the story.
Time Order Words List
Here are some examples broken down into categories to help make some sense of time order words.
BEFORE
- Earlier
- Formerly
- In the past
- Not long ago
- Once
- Preceding
- Previously
- Prior to
- Up until that time
- Yesterday
FIRST
- At first
- At the beginning
- At the onset
- Before
- Commence
- Embark
- From this point
- In the first place
- Starting with
- To begin
NEXT
- After
- After a few days
- After a while
- After that
- As soon as
- Consequently
- Following
- Henceforth
- In time
- In turn
- Later
- Momentarily
- Not long after
- Right after
- Second
- Third
- Shortly
- Since
- Soon
- Soon after
- Then
- Tomorrow
- When
- Presently
SOMETIMES
- At times
- From time to time
- Gradually
- Occasionally
- Periodically
- Rarely
- Seldom
- Some of the time
LAST
- Afterward
- At last
- At the end
- Eventually
- Final
- Finally
- Hereafter
- In conclusion
- In the end
- Last of all
- Later on
- Thereafter
- To conclude
- To finish
- Until
Time Order Sentence Examples
- In the past, I had been taught to bake cookies.
- At first, I was a bit nervous about speaking in front of the committee.
- The maiden has learned from her earlier experiences.
- Before they became trendy, overalls were formerly only worn by farm workers.
- We’re going to Thailand at the beginning of the winter to avoid the snow.
- Mary began to prepare the meal, starting with peeling the potatoes and carrots.
- Henceforth you must pay a toll to cross this bridge.
- If beaches are your jam, then you must go surfing with me.
- After a while, the conversation turns to the meaning of life.
- I like to eat ice cream for breakfast, from time to time.
- Let’s go to the concert first and then eat dinner afterward.
- To conclude, I agree with everything everyone has said here tonight.
- To begin with, I’m not always so scared of the dark.
- Not long ago I learned that most sharks are not predatory towards humans.
- As soon as I save up enough money, I’m taking a trip to Mexico.
- Periodically, I don’t like being around people and need to be alone.
- Eventually, the sun rose and everything was back to normal.
- Presently, we have enough grain to supply the farm for the rest of the month.
- From this point, let’s count our blessings and let go of the losses.
Time Order Words | Image
Pin
Last Updated on June 22, 2022
Please note: This original post has been updated and replaced by a new version of Writing Dates and Times.
Rule: The following examples apply when using dates:
The meeting is scheduled for June 30.
The meeting is scheduled for the 30th of June.
We have had tricks played on us on April 1.
The 1st of April puts some people on edge. (Some prefer to write it out: The first of April)
Rule: There are differing policies for expressing decades using numerals. Some write the 1980s and the ’80s, others write the 1980’s and the 80’s. However, using two apostrophes (the ’80’s) is awkward and is not recommended.
Correct:
During the ’80s, the world’s economy grew.
During the 1980s, the world’s economy grew.
During the 1980’s, the world’s economy grew.
Not Advised:
During the ’80’s, the world’s economy grew.
Rule: Some writers spell out the time of day, others prefer numbers.
Example: She gets up at four thirty before the baby wakes up.
Example: The baby wakes up at 5 o’clock in the morning.
Rule: Some use numerals with the time of day when exact times are being emphasized.
Example: Her flight leaves at 6:22 a.m.
Example: Please arrive by 12:30 p.m. sharp.
Rule: It is clearer to use noon and midnight rather than 12:00 p.m. or 12:00 a.m.
Note: You may use AM and PM, A.M. and P.M., am and pm, or a.m. and p.m.
Some put a space after the numeral, others do not.
Example: Her flight leaves at 6:22 a.m.
Example: Her flight leaves at 6:22am.
Example: Please arrive by 12:30 P.M. sharp.
Pop Quiz: Correct or Incorrect?
1. The last outbreak of smallpox occurred in the late seventy’s.
2. Can you get here by 12:00 midnight?
3. Please deliver the package by August 1st.
Pop Quiz Answers:
1. The last outbreak of smallpox occurred in the late seventies.
2. Can you get here by midnight? (leave out 12:00)
3. Please deliver the package by August 1. (OR by the first of August OR by the 1st of August)
Are you ready for the quiz?
Writing Dates and Times Quiz
Advertisement
If the article or the existing discussions do not address a thought or question you have on the subject, please use the «Comment» box at the bottom of this page.
Time Order Words or Phrases tell when events happen and in what order. Here are some useful time order words in English.
List of Time Order Words
These are time-order transition words in English you should know…
BEFORE
- Earlier
- Formerly
- In the past
- Not long ago
- Once
- Preceding
- Previously
- Prior to
- Up until that time
- Yesterday
FIRST
- At first
- At the beginning
- At the onset
- Before
- Commence
- Embark
- From this point
- In the first place
- Starting with
- To begin
NEXT
- After
- After a few days
- After a while
- After that
- As soon as
- Consequently
- Following
- Henceforth
- In time
- In turn
- Later
- Momentarily
- Not long after
- Right after
- Second
- Third
- Shortly
- Since
- Soon
- Soon after
- Then
- Tomorrow
- When
- Presently
SOMETIMES
- At times
- From time to time
- Gradually
- Occasionally
- Periodically
- Rarely
- Seldom
- Some of the time
LAST
- Afterward
- At last
- At the end
- Eventually
- Final
- Finally
- Hereafter
- In conclusion (In Conclusion Synonym)
- In the end
- Last of all
- Later on
- Thereafter
- To conclude
- To finish
- Until
Time Order Transition Words Examples
- In the past, the exam had been overemphasized.
- He was cross at first, but later he relented.
- The general had served as a soldier in the earlier war.
- Smocks were formerly worn by farm workers.
- We’re going to Japan at the beginning of July.
- Franco began to prepare the ground, starting with the Falange.
- Henceforth I expect you to be punctual for the meeting.
- She started to sing, and then the others chimed in.
- After a while, we naturally started talking about the children.
- I like to buy myself little luxuries from time to time.
- Let’s go to the theatre first and eat afterward.
- To conclude, I’d like to express my thanks to my family.
- To begin with, I don’t like his attitude.
- Not long ago I had read that each atom was a sort of solar system.
- As soon as we can afford it, we’ll move out to the suburbs.
- Periodically, Congress has made half-hearted attempts at finance reform.
- Eventually, Roberto backed down and apologized.
- Presently, a young woman in a white coat came in.
- From this point, we can apply our usual analysis.
Time Order Transition Words | Infographic
Useful List of Time Order Words in English
Last Updated on August 16, 2019
| Word order: place and time | ||
| subject + verb | place | time / when |
| I cycle | to school | every day. |
| We left | home | at 8 o’clock. |
| He arrived | at our house | an hour ago. |
| She has lived | in the town | since 1975. |
| Place usually comes before time:
I went to London last year. I went last year to London. |
Practise this grammar
Word order: subject, verb, object (ex. 1) >>
Word order: subject, verb, object (ex. 2) >>