Описание презентации по отдельным слайдам:
-
1 слайд
Порядок слов в вопросительном предложении
Вопросы имеют строгий порядок слов. Давайте посмотрим, какой именно!
e.g.
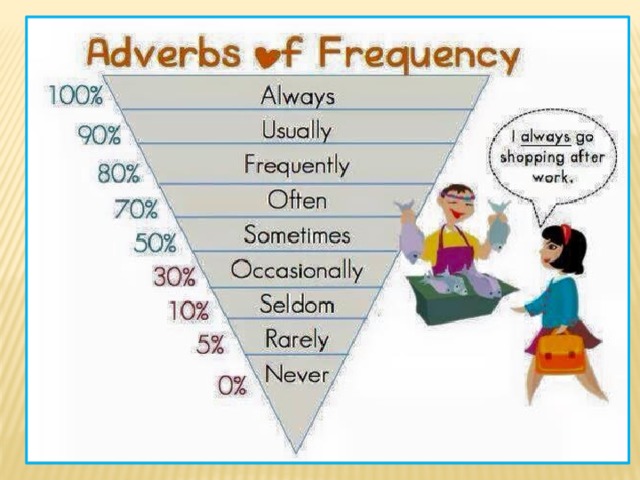
What do you do in the morning?
What time do you get up?
Do you like ice-cream? -
2 слайд
Порядок слов в вопросительном предложении
Итак давайте посмотрим какой именно порядок слов в вопросе:
e.g.
What do you do in the morning?
(o) ① ② ③ -
3 слайд
Word Order in Questions
What do you do in the morning?
(o) ① ② ③
(o) question word – на нулевой позиции стоит вопросительное слово;
① auxiliary verb (operator) — вспомогательный глагол (оператор) стоит на первом месте;
[og’zıljərı və:b]
② subject – подлежащее на втором месте;
③ main verb — смысловой глагол на третьем месте.
[meın və:b] -
4 слайд
Типы вопросов
Рассмотрим два типа вопросительных предложений:
① General question – общий вопрос
Общий вопрос — это вопрос, на который можно ответить «да» или «нет»;
② Special question – специальный вопрос
Специальный вопрос — это вопрос, на который нужно дать развёрнутый ответ.
1.
1A
word order in questions
questions with do / does / did in present simple and past simple
question word
auxiliary
subject
infinitive (= verb)
Do
you
live with your parents?
Did
you
have a holiday last year?
Where
does
your sister
work?
When
did
you
start studying English?
What
did
they
talk about?
• Use ASI (Auxiliary, Subject, Infinitive) and QUASI (Question word,
Auxiliary, Subject, Infinitive) to remember word order in questions.
2.
1A
word order in questions
questions with be
question word
be
subject
adjective, noun, etc.
Are
you
hungry?
Is
there
a bank near here?
What
was
that
noise?
Where
are
you
from?
were
you
born?
• Make questions with the verb be by inverting the verb and the subject.
She is a teacher. Is she a teacher?
© 2023 Prezi Inc.
Terms & Privacy Policy
Презентация выполнена преподавателем английского языка ГБПОУ «Нижегородский Губернский колледж» Кузнецовой Светланой Ивановной
Word Order in English Sentences (Порядок слов в английском предложении)
Subject
Predicate
Supplement,
and if more than one, first is indirectly without an excuse, then direct, indirect ends with a preposition.
Fact, it is still possible to place before the subject at the beginning of sentences.
To visualize this scheme, we use such a designation order of words
in the English sentence
If we are talking about the order of words in the English issue (word order in questions), then we define for themselves what question word we always will be placed at the head of proposal, followed by the auxiliary verb will follow. Then look at the scheme and working again as a proposal in the affirmative. For example: «How much does this jacket?». Note that the subject is at the end of sentences. The order of words in the English language, this will not allow.
We translate:
How much does this jacket cost?
All the formalities are met.
Put the sentences in the correct order.
1. him / I / about the accident / told _____________________________________________
2. a mask / on Halloween / Kim / wore _____________________________________________
3. tomorrow / we / going / are / to the movie _____________________________________________
4. cub / the lion / playing / is / with his _____________________________________________
5. Bill Gates / a / famous / person / is _______________________________________
Basic Word Order
Базовый порядок слов
English word order is strict and rather inflexible. As there are few endings in English that show person, number, case and tense, English relies on word order to show relationships between words in a sentence.
Порядок слов в английском языке строгий и довольно негибкий. Так как в английском языке мало окончаний, показывающих лицо, число, падеж и время, английский язык полагается на порядок слов для показа отношений между словами в предложении.
In Russian, we rely on word endings to tell us how words interact in a sentence. You probably remember the example made up by Academician L.V. Scherba in order to show the work of endings and suffixes in Russian. (No English translation for this example.) Everything we need to know about the interaction of the characters in this Russian sentence, we learn from the endings and suffixes.
В русском языке мы полагаемся на окончания, чтобы понять, как слова взаимодействуют в предложении. Вы, наверное, помните пример, придуманный академиком Л.В. Щербой для того, чтобы показать работу окончаний и суффиксов в русском языке: Глокая куздра штеко будланула бокра и кудрячит бокрёнка. (Нет английского перевода для этого примера.) Все, что нам нужно знать о взаимодействии героев в этом русском предложении, мы узнаём из окончаний и суффиксов.
English nouns do not have any case endings (only personal pronouns have some case endings), so it is mostly the word order that tells us where things are in a sentence, and how they interact. Compare:
Английские существительные не имеют падежных окончаний (только личные местоимения имеют падежные окончания), поэтому в основном именно порядок слов сообщает нам, где что находится в предложении и как они взаимодействуют. Сравните:
The dog sees the cat.
Собака видит кошку.
The cat sees the dog.
Кошка видит собаку.
The subject and the object in these sentences are completely the same in form. How do you know who sees whom? The rules of English word order tell us about it.
Подлежащее и дополнение в этих (английских) предложениях полностью одинаковы по форме. Как узнать, кто кого видит? Правила английского порядка слов говорят нам об этом.
Word order patterns in English sentences
Модели порядка слов в английских предложениях
A sentence is a group of words containing a subject and a predicate and expressing a complete thought. Word order arranges separate words into sentences in a certain way and indicates where to find the subject, the predicate, and the other parts of the sentence. Word order and context help to identify the meanings of individual words.
Предложение – это группа слов, содержащая подлежащее и сказуемое и выражающая законченную мысль. Порядок слов организует отдельные слова в предложения определённым образом и указывает, где найти подлежащее, сказуемое и другие члены предложения. Порядок слов и контекст помогают выявить значения отдельных слов.
English sentences are divided into declarative sentences (statements), interrogative sentences (questions), imperative sentences (commands, requests), and exclamatory sentences . Declarative sentences are the most common type of sentences. Word order in declarative sentences serves as a basis for word order in the other types of sentences.
Английские предложения делятся на повествовательные предложения (утверждения), вопросительные предложения (вопросы), повелительные предложения (команды, просьбы) и восклицательные предложения. Повествовательные предложения – самый распространенный тип предложений. Порядок слов в повествовательных предложениях служит основой для порядка слов в других типах предложений.
The main minimal pattern of basic word order in English declarative sentences is SUBJECT + PREDICATE. Examples: Maria works. Time flies.
Основная минимальная модель базового порядка слов в английских повествовательных предложениях: подлежащее + сказуемое. Примеры: Maria works. Time flies.
The most common pattern of basic word order in English declarative sentences is SUBJECT + PREDICATE + OBJECT, often called SUBJECT + VERB + OBJECT (SVO) in English linguistic sources. Examples: Tom writes stories. The dog sees the cat.
Наиболее распространённая модель базового порядка слов в повествовательных предложениях: подлежащее + сказуемое + дополнение, часто называемая подлежащее + глагол + дополнение в английских лингвистических источниках. Примеры: Tom writes stories. The dog sees the cat.
An ordinary declarative sentence containing all five parts of the sentence, for example, «Mike read an interesting story yesterday», has the following word order:
Обычное повествовательное предложение, содержащее все пять членов предложения, например, «Mike read an interesting story yesterday», имеет следующий порядок слов:
The subject is placed at the beginning of the sentence before the predicate; the predicate follows the subject; the object is placed after the predicate; the adverbial modifier is placed after the object (or after the verb if there is no object); the attribute (an adjective) is placed before its noun (attributes in the form of a noun with a preposition are placed after their nouns).
Подлежащее ставится в начале предложения перед сказуемым; сказуемое следует за подлежащим; дополнение ставится после сказуемого; обстоятельство ставится после дополнения (или после глагола, если дополнения нет); определение (прилагательное) ставится перед своим существительным (определения в виде существительного с предлогом ставятся после своих существительных).
Transitive verbs
Переходные глаголы
Transitive verbs require a direct object: Tom writes stories. Denis likes films. Anna bought a book. I saw him yesterday.
Переходные глаголы требуют прямого дополнения: Tom writes stories. Denis likes films. Anna bought a book. I saw him yesterday.
Some transitive verbs (e.g., bring, give, send, show, tell) are often followed by two objects: an indirect object and a direct object. For example: He gave me the key. She sent him a letter. Such sentences often have the following word order: He gave the key to me. She sent a letter to him.
За некоторыми переходными глаголами (например, bring, give, send, show, tell) часто следуют два дополнения: косвенное дополнение и прямое дополнение. Например: He gave me the key. She sent him a letter. Такие предложения часто имеют следующий порядок слов: He gave the key to me. She sent a letter to him.
Intransitive verbs
Непереходные глаголы
Intransitive verbs do not take a direct object. Intransitive verbs may stand alone or may be followed by an adverbial modifier (an adverb, a phrase) or by a prepositional object.
Непереходные глаголы не принимают прямое дополнение. За непереходными глаголами может ничего не стоять, или за ними может следовать обстоятельство (наречие, фраза) или предложное дополнение.
Examples of sentences with intransitive verbs: Maria works. He is sleeping. She writes very quickly. He went there yesterday. They live in a small town. He spoke to the manager. I thought about it. I agree with you.
Примеры предложений с непереходными глаголами: Maria works. He is sleeping. She writes very quickly. He went there yesterday. They live in a small town. He spoke to the manager. I thought about it. I agree with you.
Linking verbs
Глаголы-связки
Linking verbs (e.g., be, become, feel, get, grow, look, seem) are followed by a complement. The verb BE is the main linking verb. It is often followed by a noun or an adjective: He is a doctor. He is kind.
За глаголами-связками (например, be, become, feel, get, grow, look, seem) следует комплемент (именная часть сказуемого). Глагол BE – главный глагол-связка. За ним часто следует существительное или прилагательное: He is a doctor. He is kind.
Other linking verbs are usually followed by an adjective (the linking verb «become» may also be followed by a noun): He became famous. She became a doctor. He feels happy. It is getting cold. It grew dark. She looked sad. He seems tired.
За другими глаголами-связками обычно следует прилагательное (за глаголом-связкой «become» может также следовать существительное): He became famous. She became a doctor. He feels happy. It is getting cold. It grew dark. She looked sad. He seems tired.
Declarative sentences
Повествовательные предложения
Subject + predicate (+ object + adverbial modifier):
Подлежащее + сказуемое (+ дополнение + обстоятельство):
Maria works.
Мария работает.
Tom is a writer.
Том писатель.
This book is interesting.
I live in Moscow.
Эта книга интересная.
Я живу в Москве.
Tom writes short stories for children.
Том пишет короткие рассказы для детей.
He talked to Anna yesterday.
Он говорил с Анной вчера.
My son bought three history books.
Мой сын купил три книги по истории.
He is writing a report now.
Он пишет доклад сейчас.
General questions
Общие вопросы
Auxiliary verb + subject + main verb (+ object + adverbial modifier):
Вспомогательный глагол + подлежащее + основной глагол (+ дополнение + обстоятельство):
Do you live here? – Yes, I do.
Вы живёте здесь? – Да (живу).
Does he speak English? – Yes, he does.
Он говорит по-английски? – Да (говорит).
Did you go to the concert? – No, I didn’t.
Вы ходили на концерт? – Нет (не ходил).
Is he writing a report now? – Yes, he is.
Он пишет доклад сейчас? – Да (пишет).
Have you seen this film? – No, I haven’t.
Вы видели этот фильм? – Нет (не видел).
Special questions
Специальные вопросы
Question word + auxiliary verb + subject + main verb (+ object + adverbial modifier):
Вопросительное слово + вспомогательный глагол + подлежащее + основной глагол (+ дополнение + обстоятельство):
Where does he live? – He lives in Paris.
Где он живет? – Он живёт в Париже.
What are you writing now? – I’m writing a new story.
Что вы сейчас пишете? – Я пишу новый рассказ.
When did they visit Mexico? – They visited Mexico five years ago.
Когда они посетили Мексику? – Они посетили Мексику пять лет назад.
What is your name? – My name is Alex.
Как вас зовут? – Меня зовут Алекс.
How old are you? – I’m 24 years old.
Сколько вам лет? – Мне 24 года.
Alternative questions
Альтернативные вопросы
Alternative questions are questions with a choice. Word order before «or» is the same as in general questions.
Альтернативные вопросы – это вопросы с выбором. Порядок слов до «or» такой же, как в общих вопросах.
Is he a teacher or a doctor? – He is a teacher.
Он учитель или врач? – Он учитель.
Does he live in Paris or in Rome? – He lives in Rome.
Он живет в Париже или в Риме? – Он живёт в Риме.
Are you writing a report or a letter? – I’m writing a report.
Вы пишете доклад или письмо? – Я пишу доклад.
Would you like coffee or tea? – Tea, please.
Хотите кофе или чай? – Чай, пожалуйста.
Tag questions
Разделительные вопросы
Tag questions consist of two parts. The first part has the same word order as statements; the second part is a short general question (the tag).
Разделительные вопросы состоят из двух частей. Первая часть имеет такой же порядок слов, как повествовательные предложения; вторая часть – краткий общий вопрос.
He is a teacher, isn’t he? – Yes, he is.
Он учитель, не так ли? – Да (он учитель).
He lives here, doesn’t he? – No, he doesn’t.
Он живет здесь, не так ли? – Нет (не живёт).
You went there, didn’t you? – Yes, I did.
Вы ходили туда, не так ли? – Да (ходил).
They haven’t seen this film, have they? – No, they haven’t.
Они не видели этот фильм, не так ли? – Нет (не видели).
Imperative sentences
Повелительные предложения
Imperative sentences (commands, instructions, requests) have the same word order as statements, but the subject (you) is usually omitted.
Повелительные предложения (команды, инструкции, просьбы) имеют такой же порядок слов, как повествовательные предложения, но подлежащее (вы) обычно опускается.
Go to your room.
Идите в свою комнату.
Listen to the story.
Слушайте рассказ.
Please sit down.
Пожалуйста, садитесь.
Give me that book, please.
Дайте мне ту книгу, пожалуйста.
Negative imperative sentences are formed with the help of the auxiliary verb «don’t».
Отрицательные повелительные предложения образуются с помощью вспомогательного глагола «don’t».
Don’t cry.
Не плачь.
Don’t wait for me.
Не ждите меня.
Exclamatory sentences
Восклицательные предложения
Exclamatory sentences have the same word order as statements (i.e., the subject is before the predicate).
Восклицательные предложения имеют такой же порядок слов, как повествовательные предложения (т.е. подлежащее перед сказуемым).
She is a great singer!
Она отличная певица!
It is an excellent opportunity!
Это отличная возможность!
How well he knows history!
Как хорошо он знает историю!
What a beautiful town this is!
How strange it is!
Какой это прекрасный город!
Как это странно!
In some types of exclamatory sentences, the subject (it, this, that) and the linking verb are often omitted.
В некоторых типах восклицательных предложений подлежащее (it, this, that) и глагол-связка часто опускаются.
What a pity!
Какая жалость!
What a beautiful present!
Какой прекрасный подарок!
What beautiful flowers!
Какие прекрасные цветы!
How strange!
Как странно!
Requests
Просьбы
Polite requests in English are usually in the form of general questions using «could, may, will, would».
Вежливые просьбы в английском языке обычно в форме вопросов с использованием «could, may, will, would».
Could you help me, please?
Не могли бы вы помочь мне, пожалуйста?
May I speak to Tom, please?
Можно мне поговорить с Томом, пожалуйста?
Will you please ask him to call me?
Попросите его позвонить мне, пожалуйста.
Would you mind helping me with this report?
Вы не возражали бы помочь мне с этим докладом?
Compound sentences
Сложносочиненные предложения
A compound sentence consists of two (or more) simple sentences connected by a coordinating conjunction (e.g., and, but, or). Each simple sentence has a subject and a predicate.
Сложносочинённое предложение состоит из двух независимых предложений, соединённых соединительными союзами (например, and, but, or). Каждое предложение имеет подлежащее и сказуемое.
Maria lives in Moscow, and her friend Elizabeth lives in New York.
Мария живёт в Москве, а ее подруга Элизабет живёт в Нью-Йорке.
He wrote a letter to the manager, but the manager didn’t answer.
Он написал письмо менеджеру, но менеджер не ответил.
Her children may watch TV here, or they may play in the yard.
Её дети могут посмотреть телевизор здесь, или они могут поиграть во дворе.
Simple sentences connected by «and» may be connected without a conjunction. In such cases, a semicolon is used between the sentences in a compound sentence.
Простые предложения, соединённые союзом «and», могут быть соединены без союза. В таких случаях между двумя предложениями в сложноподчинённом предложении ставится точка с запятой.
Maria lives in Moscow; her friend Elizabeth lives in New York.
Мария живёт в Москве; ее подруга Элизабет живёт в Нью-Йорке.
Complex sentences
Сложноподчиненные предложения
A complex sentence consists of the main clause and the subordinate clause connected by a subordinating conjunction (e.g., that, after, when, since, because, if, though). Each clause has a subject and a predicate.
Сложноподчинённое предложение состоит из главного предложения и придаточного предложения, соединённых подчинительными союзами (например, that, after, when, since, because, if, though). Каждое предложение имеет подлежащее и сказуемое.
I told him that I didn’t know anything about their plans.
Я сказал ему, что я ничего не знаю об их планах.
Betty has been working as a secretary since she moved to California.
Бетти работает секретарём с тех пор, как она переехала в Калифорнию.
Tom went to bed early because he was very tired.
Том лёг спать рано, потому что он очень устал.
If he comes back before ten, ask him to call me, please.
Если он вернётся до десяти, попросите его позвонить мне, пожалуйста.
Great is the struggle,
and great is also the prize.
Notes
The normal order of words in a sentence is sometimes altered for emphasis.
Sweet are the uses of adversity. (Here the subject ‘the uses of adversity’ comes at the end of the sentence.)
Fallen, fallen is Babylon .
Uneasy lies the head
that wears a crown.
Word Order in Negative Sentences
Arrange the words to make negative sentences. Place time expressions at the end of the sentences.
- our holiday / will / at home / we / not / spend / next year
- did / I / him / see / not / last night / at the disco
- to a party / not / we / tonight / going / are
- will / a letter / not / next week / send / you / she
- not / the truth / did / he / tell / you
- to the cinema / we / want / not / do / tonight / to go
- play / in the bar / did / he / last week / not / the piano
- not / now / she / in England / is
- eat / in winter / ice-cream / do / not / I
- right now / have / not / we / time / do
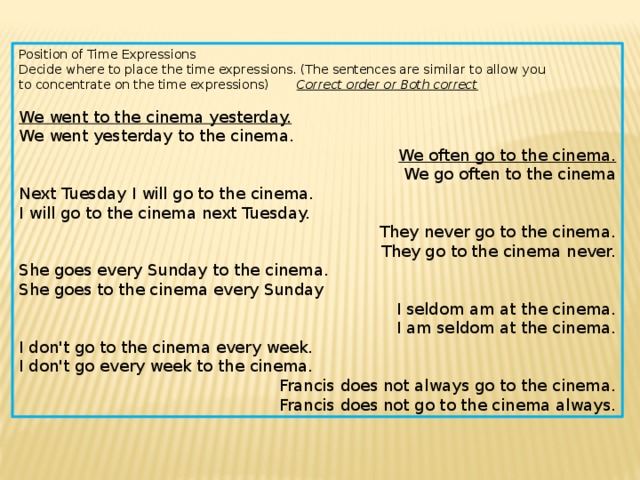
Position of Time Expressions
Decide where to place the time expressions. (The sentences are similar to allow you
to concentrate on the time expressions) Correct order or Both correct
We went to the cinema yesterday.
We went yesterday to the cinema.
We often go to the cinema.
We go often to the cinema
Next Tuesday I will go to the cinema.
I will go to the cinema next Tuesday.
They never go to the cinema.
They go to the cinema never.
She goes every Sunday to the cinema.
She goes to the cinema every Sunday
I seldom am at the cinema.
I am seldom at the cinema.
I don’t go to the cinema every week.
I don’t go every week to the cinema.
Francis does not always go to the cinema.
Francis does not go to the cinema always.
Слайд 1
порядок слов в английском предложении
Слайд 2
Понять, как между собой взаимодействуют слова внутри предложения, в русском языке помогают суффиксы и окончания. В английском языке слова практически не изменяются В русском языке – свободный порядок слов — показать взаимосвязь слов внутри предложения может только порядок слов . Именно поэтому он фиксированный и строгий.
Слайд 3
Порядок слов в утвердительных предложениях:
Слайд 4
S = subject = подлежащее = кто?/что ? Подлежащее — кто выполняет действие V = verb = глагол = что делает? Английское предложение, как правило, не может существовать без глагола, даже там, где в русском переводе его нет: « D ogs are cute » («собаки -милые »). O = object = дополнение = кого?/что? Если в предложении есть дополнение, оно обязательно будет связано с глаголом: «I had a dream » («Мне приснился сон »). Дополнений может быть сразу несколько: «I had a dream about my family » («Мне приснился сон про мою семью»). M = manner = образ действия = как? Наречия в английском часто заканчиваются на — ly : slowly (медленно), quietly (тихо), seriously (серьезно). Но: fast (быстро), hard (сложно), late (поздно), well (хорошо).
Слайд 5
P = place = место = где? Когда вы уточнили, как именно происходит действие, следует сказать, где оно происходит: « We walk in the park » T = time = время = when ? Информация о том, когда происходит действие, как правило, идет в самый конец предложения: « We walk in the park in the evening » Можно запоминить эту схему в виде вопросов: who ? do ? what ? how ? where ? when ? (кто? делает? что? как? где? когда?).
Слайд 6
Есть исключения из этой схемы : Например, чтобы сделать акцент на месте или времени, эту информацию выносят в начало предложения: « For 5 years , I’ve been learning English, but I can’t express myself effectively » Наречия на — ly могут стоять перед глаголом: « I seriously believe he can do this job » Конструкция there is / there are . Если нужно сказать о наличии определенного предмета в определенном месте, то такие предложения строятся по схеме: There is / There are + существительное + обстоятельство места. « There is a flower in the vase »
Слайд 7
ПСДО — ещё один способ запомнить порядок слов П — подлежащее , С — сказуемое , Д — дополнение, О — обстоятельство . I like this movie very much.
Слайд 8
Вопросительные предложения: Утвердительные предложения:
Слайд 10
Ex. 1 Put the words in the right order. usually / at 10 o’clock / out of the garage / in the morning / drives / his bike / Fred a shower / after dinner / often / Mrs Lewis / takes a parking place / near the library / we / find / seldom to / I / on / a / night-club / sometimes / Saturdays / go fly / my parents / to Australia / sometimes / I / in winter / and enjoys / very much / swimming / in the pool / always / Mary hardly / last year / could / skate / I is / near / house / there / new / a / our / cinema got / my / problems / I / with / have / home-task / some well / think / your / very / I / don’t / sister / drives to / parents / once / the theatre / month / my / a / go his / car / two / ago / Jim / sold / years necklace / can’t / anywhere / Cindy / her / find been / to / India / Mike / has / year / already / this lunch / never / weekdays / she / has / on
Слайд 11
Ответы: Fred usually drives his bike out of the garage at 10 o’clock in the morning. ( Фред обычно выезжает из гаража на своем байке в 10 часов утра.) Lewis often takes a shower after dinner. ( Миссис Льюис часто принимает душ после ужина.) We seldom find a parking place near the library. ( Мы редко находим место для парковки у библиотеки.) I sometimes go to a night-club on Saturdays. ( Иногда я хожу в ночной клуб по субботам.) My parents and I sometimes fly to Australia in winter. ( Мы с родителями иногда летаем в Австралию зимой.) Mary always enjoys swimming in the pool very much. ( Мэри всегда очень нравится плавать в бассейне.) I could hardly skate last year. ( Я с трудом мог кататься на коньках в прошлом году.) There is a new cinema near our house. ( Возле нашего дома есть новый кинотеатр.) I have got some problems with my home-task. ( У меня есть проблемы с домашним заданием.) I don’t think your sister drives very well. ( Не думаю, что твоя сестра очень хорошо водит машину.) My parents go to the theatre once a month. ( Мои родители ходят в театр раз в месяц.) Jim sold his car two years ago. ( Джим продал свою машину два года назад.) Cindy can’t find her necklace anywhere. ( Синди нигде не может найти свое ожерелье.) Mike has already been to India this year. ( Майк уже был в Индии в этом году.) She never has lunch on weekdays. ( Она никогда не обедает в будние дни.)
Слайд 12
Ex. 2 . Translate the sentences into English . Телевизор я смотрю редко. На улице темно, и я скоро поду спать. Они что-то очень шумно обсуждают в спальне. Он медленно шел вдоль реки. На уроках мы часто поем песни. Я тихо закрыла дверь и сразу же пошла в ванну. Мой дядя очень любит рыбалку. Анна умеет хорошо играть в теннис. Она все время кричит на детей. Твои книги я положу на стол. Я недостаточно хорошо его знаю. По телевизору много хороших фильмов сегодня. В парке есть красивый фонтан. В прошлый вторник было очень ветрено. Эти туфли я купила в Италии.
Слайд 13
I seldom watch TV. It’s dark outside and I am going to bed soon. They are discussing something very loudly in the bedroom. He was walking slowly along the river. We often sing songs at the lessons. I shut the door quietly and went to the bathroom immediately. My uncle loves fishing very much. Ann can play tennis well. She is shouting at the kids all the time. I will put your books on the table. I don’t know him well enough. There are a lot of good films on TV today. There is a nice fountain in the park. It was very windy last Tuesday. I bought these shoes in Italy. Ответы:
Слайд 14
Ex.3 . Find out mistakes and correct them I think, I’ll tomorrow in the evening go to cinema. She very much loves her parents. In Paris we were in July last year. I’m sure, they will in these competitions win. Yesterday I too late went to bed. James very well speaks English. I’ll call in private my coach. We don’t like at all cooking. Last Friday very interesting cartoons children watched. I think, I’ll go to cinema tomorrow in the evening. She loves her parents very much. We were in Paris in July last year. I’m sure, they will win in these competitions. I went to bed too late yesterday. James speaks English very well. I’ll call my coach in private. We don’t like cooking at all. Children watched very interesting cartoons last Friday.
Слайд 15
https ://s- english.ru / Презентация подготовлена учителем английского языка Хохловой И.В .
Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Презентация на тему Типы вопросительных предложений английского языка
Содержание
-
1.
Типы вопросительных предложений английского языка -
2.
THERE ARE FIVE TYPES OF QUESTIONS IN ENGLISHYES/NO QUESTIONSSPECIAL QUESTIONSSUBJECT QUESTIONSQUESTION TAGSALTERNATIVE QUESTIONS -
3.
YES/NO QUESTIONS(questions without questions words, questions are -
4.
WORD ORDER IN YES/NO QUESTIONS (ПОРЯДОК СЛОВ В ОБЩИХ ВОПРОСАХ) -
5.
SPECIAL QUESTIONS(start with a question word)Who did -
6.
QUESTION WORDSWho-кто?Where-где?What-что?When-когда?Why-почему?How-как?Whose-чей? -
7.
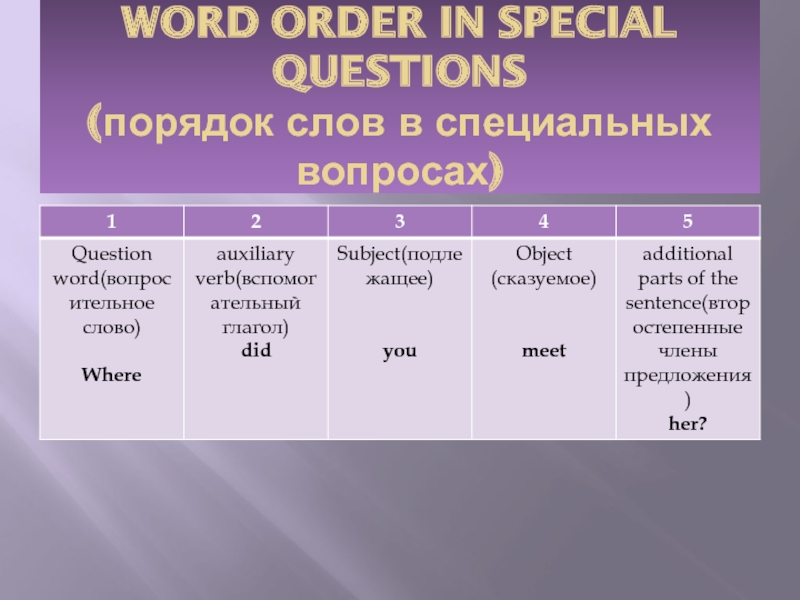
WORD ORDER IN SPECIAL QUESTIONS (порядок слов в специальных вопросах) -
8.
SUBJECT QUESTIONS(If who, which or what are -
9.
WORD ORDER IN SUBJECT QUESTIONS (порядок слов в вопросах к подлежащему) -
10.
QUESTION TAGS(We use them for confirmation of -
11.
WORD ORDER IN QUESTION TAGS (порядок слов в разделительных вопросах) -
12.
THE RULES OF FORMATION QUESTIONS TAGS -
13.
ALTERNATIVE QUESTIONSBegin with an auxiliary verb + -
14.
WORD ORDER IN ALTERNATIVE QUESTIONS(порядок слов в альтернативных вопросах) -
15.
Скачать презентанцию
THERE ARE FIVE TYPES OF QUESTIONS IN ENGLISHYES/NO QUESTIONSSPECIAL QUESTIONSSUBJECT QUESTIONSQUESTION TAGSALTERNATIVE QUESTIONS
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1TYPES OF QUESTIONS IN ENGLISH
Подготовила преподаватель английского языка «Пинковичской средней
школы имени Якуба Коласа» Пинского района Лящук Елена Геннадьевна

Слайд 2THERE ARE FIVE TYPES OF QUESTIONS IN ENGLISH
YES/NO QUESTIONS
SPECIAL QUESTIONS
SUBJECT
QUESTIONS
QUESTION TAGS
ALTERNATIVE QUESTIONS

Слайд 3YES/NO QUESTIONS
(questions without questions words, questions are usually formed by
changing the word order; this means the auxiliary or modal
verb comes before the subject).
Can she type?
Will you help me?

Слайд 4WORD ORDER IN YES/NO QUESTIONS
(ПОРЯДОК СЛОВ В ОБЩИХ ВОПРОСАХ)

Слайд 5SPECIAL QUESTIONS
(start with a question word)
Who did you go out?
Where
did you meet her?
What is your name?

Слайд 6QUESTION WORDS
Who-кто?
Where-где?
What-что?
When-когда?
Why-почему?
How-как?
Whose-чей?

Слайд 7WORD ORDER IN SPECIAL QUESTIONS
(порядок слов в специальных вопросах)
Слайд 8SUBJECT QUESTIONS
(If who, which or what are the subject of
the question)
subject
object
Harry loves Jane.
Who loves Jane?
Subject object
Marry helped George.
Who did Mary help?

Слайд 9WORD ORDER IN SUBJECT QUESTIONS
(порядок слов в вопросах к подлежащему)

Слайд 10QUESTION TAGS
(We use them for confirmation of or agreement to
our statement. We form question tags with an auxiliary verb
and a personal pronoun.)
He can drive, can’t he?

Слайд 11WORD ORDER IN QUESTION TAGS
(порядок слов в разделительных вопросах)

Слайд 12THE RULES OF FORMATION QUESTIONS TAGS

Слайд 13ALTERNATIVE QUESTIONS
Begin with an auxiliary verb + “or”
Does he help
you every day or every other day?

Слайд 14WORD ORDER IN ALTERNATIVE QUESTIONS(порядок слов в альтернативных вопросах)
-
Скачать презентацию (0.36 Мб)
-
152 загрузки -
4.2 оценка
Ваша оценка презентации
Оцените презентацию по шкале от 1 до 5 баллов
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Комментарии
Добавить свой комментарий
Аннотация к презентации
Интересует тема «Типы вопросительных предложений английского языка (Types of Questions in English)»? Лучшая powerpoint презентация на эту тему представлена здесь! Данная презентация состоит из 14 слайдов. Средняя оценка: 4.2 балла из 5. Также представлены другие презентации по иностранным языкам для 7 класса. Скачивайте бесплатно.
Содержание
-
Слайд 1
TYPES OF QUESTIONS IN ENGLISH
Подготовила преподаватель английского языка «Пинковичской средней школы имени Якуба Коласа» Пинского района Лящук Елена Геннадьевна
-
Слайд 2
THERE ARE FIVE TYPES OF QUESTIONS IN ENGLISH
YES/NO QUESTIONS
SPECIAL QUESTIONS
SUBJECT QUESTIONS
QUESTION TAGS
ALTERNATIVE QUESTIONS -
Слайд 3
YES/NO QUESTIONS
(questions without questions words, questions are usually formed by changing the word order; this means the auxiliary or modal verb comes before the subject).
Can she type?
Will you help me? -
Слайд 4
WORD ORDER IN YES/NO QUESTIONS(ПОРЯДОК СЛОВ В ОБЩИХ ВОПРОСАХ)
-
Слайд 5
SPECIAL QUESTIONS
(start with a question word)
Who did you go out?
Where did you meet her?
What is your name? -
Слайд 6
QUESTION WORDS
Who-кто?
Where-где?
What-что?
When-когда?
Why-почему?
How-как?
Whose-чей? -
Слайд 7
WORD ORDER IN SPECIAL QUESTIONS(порядок слов в специальных вопросах)
-
Слайд 8
SUBJECT QUESTIONS
(If who, which or what are the subject of the question)
subject object
Harry loves Jane.
Who loves Jane?
Subject object
Marry helped George.Who did Mary help?
-
Слайд 9
WORD ORDER IN SUBJECT QUESTIONS(порядок слов в вопросах к подлежащему)
-
Слайд 10
QUESTION TAGS
(We use them for confirmation of or agreement to our statement. We form question tags with an auxiliary verb and a personal pronoun.)
He can drive, can’t he? -
Слайд 11
WORD ORDER IN QUESTION TAGS(порядок слов в разделительных вопросах)
-
Слайд 12
THE RULES OF FORMATION QUESTIONS TAGS
-
Слайд 13
ALTERNATIVE QUESTIONS
Begin with an auxiliary verb + “or”
Doeshe help you every day or every other day?
-
Слайд 14
WORD ORDER IN ALTERNATIVE QUESTIONS(порядок слов в альтернативных вопросах)
Посмотреть все слайды
Сообщить об ошибке
Похожие презентации












Спасибо, что оценили презентацию.
Мы будем благодарны если вы поможете сделать сайт лучше и оставите отзыв или предложение по улучшению.
Добавить отзыв о сайте
Изображение слайда
2
Слайд 2: THERE ARE FIVE TYPES OF QUESTIONS IN ENGLISH
YES/NO QUESTIONS
SPECIAL QUESTIONS
SUBJECT QUESTIONS
QUESTION TAGS
ALTERNATIVE QUESTIONS
Изображение слайда
3
Слайд 3: YES/NO QUESTIONS
(questions without questions words, questions are usually formed by changing the word order; this means the auxiliary or modal verb comes before the subject).
Can she type?
Will you help me?
Изображение слайда
4
Слайд 4: WORD ORDER IN YES/NO QUESTIONS ( ПОРЯДОК СЛОВ В ОБЩИХ ВОПРОСАХ)
1
2
3
4
Auxiliary verb
( вспомогательный глагол)
Will
subject
(подлежащее)
you
object
(сказуемое)
help
additional parts of the sentence
(второстепенные члены предложения)
me?
Изображение слайда
5
Слайд 5: SPECIAL QUESTIONS
(start with a question word)
Who did you go out?
Where did you meet her?
What is your name?
Изображение слайда
6
Слайд 6: QUESTION WORDS
Who- кто?
Where -где?
What- что?
When- когда?
Why- почему?
How- как?
Whose- чей?
Изображение слайда
7
Слайд 7: WORD ORDER IN SPECIAL QUESTIONS ( порядок слов в специальных вопросах)
1
2
3
4
5
Question word( вопросительное слово)
Where
auxiliary verb (вспомогательный глагол)
did
Subject (подлежащее)
you
Object ( сказуемое)
meet
additional parts of the sentence( второстепенные члены предложения)
her?
Изображение слайда
8
Слайд 8: SUBJECT QUESTIONS
(If who, which or what are the subject of the question)
s ubject object
Harry loves Jane.
Who loves Jane?
Subject object
Marry helped George.
Who did Mary help?
Изображение слайда
9
Слайд 9: WORD ORDER IN SUBJECT QUESTIONS ( порядок слов в вопросах к подлежащему)
1
2
Begin with “who, what, which…”
Начинаются с « who, what, which… »
Who
Direct word order
Прямой порядок слов
loves Jane?
Изображение слайда
10
Слайд 10: QUESTION TAGS
(We use them for confirmation of or agreement to our statement. We form question tags with an auxiliary verb and a personal pronoun.)
He can drive, can’t he ?
Изображение слайда
11
Слайд 11: WORD ORDER IN QUESTION TAGS ( порядок слов в разделительных вопросах)
1
2
Direct word order
( прямой порядок слов)
He can drive,
“a tag”
(хвостик)
can’t he?
Изображение слайда
12
Слайд 12: THE RULES OF FORMATION QUESTIONS TAGS
1
2
+
He can drive,
—
can’t he?
—
He can’t drive,
+
can he?
Изображение слайда
13
Слайд 13: ALTERNATIVE QUESTIONS
Begin with an auxiliary verb + “or”
Does he help you every day or every other day?
Изображение слайда
14
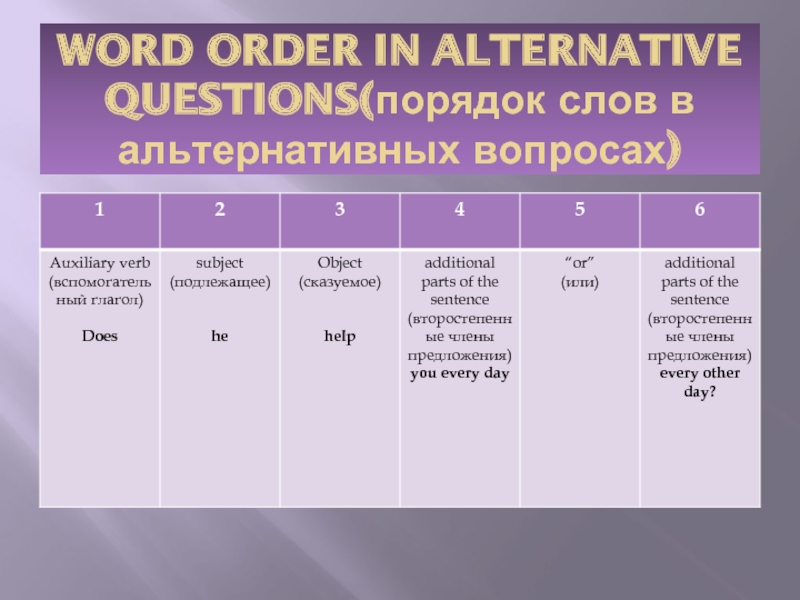
Последний слайд презентации: TYPES OF QUESTIONS IN ENGLISH: WORD ORDER IN ALTERNATIVE QUESTIONS( порядок слов в альтернативных вопросах)
1
2
3
4
5
6
Auxiliary verb
( вспомогательный глагол)
Does
subject
(подлежащее)
he
Object
(сказуемое)
help
additional parts of the sentence
(второстепенные члены предложения)
you every day
“or”
(или)
additional parts of the sentence
(второстепенные члены предложения)
every other day?
Изображение слайда
TYPES OF QUESTIONS IN ENGLISH
Подготовила преподаватель английского языка
Пятигорского техникума торговли, технологий и сервиса
Валуева О.В.
THERE ARE FIVE TYPES OF QUESTIONS IN ENGLISH
- YES/NO QUESTIONS
- SPECIAL QUESTIONS
- SUBJECT QUESTIONS
- QUESTION TAGS
- ALTERNATIVE QUESTIONS
YES/NO QUESTIONS
(questions without questions words, questions are usually formed by changing the word order; this means the auxiliary or modal verb comes before the subject).
Can she type?
Will you help me?
WORD ORDER IN YES/NO QUESTIONS
(ПОРЯДОК СЛОВ В ОБЩИХ ВОПРОСАХ)
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
Auxiliary verb (вспомогательный глагол) Will |
subject (подлежащее) you |
object (сказуемое) help |
additional parts of the sentence (второстепенные члены предложения) me? |
SPECIAL QUESTIONS
(start with a question word)
Who did you go out?
Where did you meet her?
What is your name?
QUESTION WORDS
Who-кто?
Where-где?
What-что?
When-когда?
Why-почему?
How-как?
Whose-чей?
WORD ORDER IN SPECIAL QUESTIONS
(порядок слов в специальных вопросах)
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
Question word(вопросительное слово) Where |
auxiliary verb(вспомогательный глагол) did |
Subject(подлежащее) you |
Object (сказуемое) meet |
additional parts of the sentence(второстепенные члены предложения) her? |
SUBJECT QUESTIONS
(If who, which or what are the subject of the question)
subject object
Harry loves Jane.
Who loves Jane?
Subject object
Marry helped George.
Who did Mary help?
WORD ORDER IN SUBJECT QUESTIONS
(порядок слов в вопросах к подлежащему)
|
1 |
2 |
|
Begin with “who, what, which…” Начинаются с «who, what, which…» Who |
Direct word order Прямой порядок слов loves Jane? |
QUESTION TAGS
(We use them for confirmation of or agreement to our statement. We form question tags with an auxiliary verb and a personal pronoun.)
He can drive, can’t he?
WORD ORDER IN QUESTION TAGS
(порядок слов в разделительных вопросах)
|
1 |
2 |
|
Direct word order (прямой порядок слов) He can drive, |
“a tag” (хвостик) can’t he? |
THE RULES OF FORMATION QUESTIONS TAGS
|
1 |
2 |
|
+ He can drive, |
— can’t he? |
|
— He can’t drive, |
+ can he? |
ALTERNATIVE QUESTIONS
Begin with an auxiliary verb + “or”
Does he help you every day or every other day?
WORD ORDER IN ALTERNATIVE QUESTIONS(порядок слов в альтернативных вопросах)
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
Auxiliary verb (вспомогательный глагол) Does |
subject (подлежащее) he |
Object (сказуемое) help |
additional parts of the sentence (второстепенные члены предложения) you every day |
“or” (или) |
additional parts of the sentence (второстепенные члены предложения) every other day? |