FreeDictionary explains about adverbs that
If we use more than one adverb to describe a verb, there is a general order in which the different categories of adverbs should appear—this is known as the order of adverbs (sometimes called the royal order of adverbs):
- Manner
- Place
- Frequency
- Time
- Purpose
But the post goes on to affirm that:
There is a great deal of flexibility regarding where in a sentence an adverb can appear, regardless of its content and the rules of order that we looked at above. While the order of adverbs is useful to keep in mind, it is a guide, rather than a law.
Looking at your sentences
Plants were exposed to freezing temperatures for 2 hours.
follows the guide rule of standard word order, and is therefore the most neutral way of putting it. As for
Plants were exposed for 2 hours to freezing temperatures.
Here more stress falls on for 2 hours, as it changed its routine place in the sentence without however changing the meaning of the sentence. So the sentence is correct and can be used unambiguously.
Yet, since you say ‘no particular emphasis needed’, the answer to your question is that your first sentence is standard word order.
1. What is Word Order?
Word order is important: it’s what makes your sentences make sense! So, proper word order is an essential part of writing and speaking—when we put words in the wrong order, the result is a confusing, unclear, and an incorrect sentence.
2.Examples of Word Order
Here are some examples of words put into the correct and incorrect order:
I have 2 brothers and 2 sisters at home. CORRECT
2 brothers and 2 sisters have I at home. INCORRECT
I am in middle school. CORRECT
In middle school I am. INCORRECT
How are you today? CORRECT
You are how today? INCORRECT
As you can see, it’s usually easy to see whether or not your words are in the correct order. When words are out of order, they stand out, and usually change the meaning of a sentence or make it hard to understand.
3. Types of Word Order
In English, we follow one main pattern for normal sentences and one main pattern for sentences that ask a question.
a. Standard Word Order
A sentence’s standard word order is Subject + Verb + Object (SVO). Remember, the subject is what a sentence is about; so, it comes first. For example:
The dog (subject) + eats (verb) + popcorn (object).
The subject comes first in a sentence because it makes our meaning clear when writing and speaking. Then, the verb comes after the subject, and the object comes after the verb; and that’s the most common word order. Otherwise, a sentence doesn’t make sense, like this:
Eats popcorn the dog. (verb + object + subject)
Popcorn the dog eats. (object + subject + verb)
B. Questions
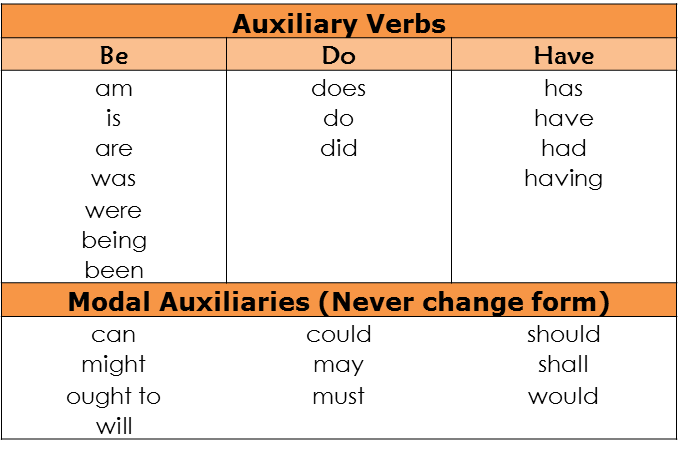
When asking a question, we follow the order auxiliary verb/modal auxiliary + subject + verb (ASV). Auxiliary verbs and modal auxiliaries share meaning or function, many which are forms of the verb “to be.” Auxiliary verbs can change form, but modal auxiliaries don’t. Here’s a chart to help you:
As said, questions follow the form ASV; or, if they have an object, ASVO. Here are some examples:
Can he cook? “Can” (auxiliary) “he” (subject) “cook” (verb)
Does your dog like popcorn? “Does” (A) “your dog” (S) “like” (V) “popcorn” (O)
Are you burning the popcorn? “Are” (A) “you” (S) “burning” (V) “popcorn” (O)
4. Parts of Word Order
While almost sentences need to follow the basic SVO word order, we add other words, like indirect objects and modifiers, to make them more detailed.
a. Indirect Objects
When we add an indirect object, a sentence will follow a slightly different order. Indirect objects always come between the verb and the object, following the pattern SVIO, like this:
I fed the dog some popcorn.
This sentence has “I” (subject) “fed” (verb) “dog” (indirect object) “popcorn” (direct object).
b. Prepositional Phrases
Prepositional phrases also have special positions in sentences. When we use the prepositions like “to” or “for,” then the indirect object becomes part of a prepositional phrase, and follows the order SVOP, like this:
I fed some popcorn to the dog.
Other prepositional phrases, determining time and location, can go at either the beginning or the end of a sentence:
He ate popcorn at the fair. -Or- At the fair he ate popcorn.
In the morning I will go home. I will go home in the morning.
c. Adverbs
Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs, adding things like time, manner, degree; and often end in ly, like “slowly,” “recently,” “nearly,” and so on. As a rule, an adverb (or any modifier) should be as close as possible to the thing it is modifying. But, adverbs are special because they can usually be placed in more than one spot in the sentence and are still correct. So, there are rules about their placement, but also many exceptions.
In general, when modifying an adjective or adverb, an adverb should go before the word it modifies:
The dog was extremely hungry. CORRECT adverb modifies “hungry”
Extremely, the dog was hungry. INCORRECT misplaced adverb
The extremely dog was hungry. INCORRECT misplaced adverb
The dog was hungry extremely. INCORRECT misplaced adverb
As you can see, the word “extremely” only makes sense just before the adjective “hungry.” In this situation, the adverb can only go in one place.
When modifying a verb, an adverb should generally go right after the word it modifies, as in the first sentence below. BUT, these other uses are also correct, though they may not be the best:
The dog ran quickly to the fair. CORRECT * BEST POSITION
Quickly the dog ran to the fair. CORRECT
The dog quickly ran to the fair. CORRECT
The dog ran to the fair quickly. CORRECT
For adverbs expressing frequency (how often something happens) the adverb goes directly after the subject:
The dog always eats popcorn.
He never runs slowly.
I rarely see him.
Adverbs expressing time (when something happens) can go at either the beginning or of the end of the sentence, depending what’s important about the sentence. If the time isn’t very important, then it goes at the beginning of the sentence, but if you want to emphasize the time, then the adverb goes at the end of the sentence:
Now the dog wants popcorn. Emphasis on “the dog wants popcorn”
The dog wants popcorn now. Emphasis on “now”
5. How to Use Avoid Mistakes with Word Order
Aside from following the proper SVO pattern, it’s important to write and speak in the way that is the least confusing and the most clear. If you make mistakes with your word order, then your sentences won’t make sense. Basically, if a sentence is hard to understand, then it isn’t correct. Here are a few key things to remember:
- The subject is what a sentence is about, so it should come first.
- A modifier (like an adverb) should generally go as close as possible to the thing it is modifying.
- Indirect objects can change the word order from SVO to SVIO
- Prepositional phrases have special positions in sentences
Finally, here’s an easy tip: when writing, always reread your sentences out loud to make sure that the words are in the proper order—it is usually pretty easy to hear! If a sentence is clear, then you should only need to read it once to understand it.
Normally, sentences in the English language take a simple form. However, there are times it would be a little complex. In these cases, the basic rules for how words appear in a sentence can help you.
Word order typically refers to the way the words in a sentence are arranged. In the English language, the order of words is important if you wish to accurately and effectively communicate your thoughts and ideas.
Although there are some exceptions to these rules, this article aims to outline some basic sentence structures that can be used as templates. Also, the article provides the rules for the ordering of adverbs and adjectives in English sentences.
Basic Sentence Structure and word order rules in English
For English sentences, the simple rule of thumb is that the subject should always come before the verb followed by the object. This rule is usually referred to as the SVO word order, and then most sentences must conform to this. However, it is essential to know that this rule only applies to sentences that have a subject, verb, and object.
For example
Subject + Verb + Object
He loves food
She killed the rat
Sentences are usually made of at least one clause. A clause is a string of words with a subject(noun) and a predicate (verb). A sentence with just one clause is referred to as a simple sentence, while those with more than one clause are referred to as compound sentences, complex sentences, or compound-complex sentences.
The following is an explanation and example of the most commonly used clause patterns in the English language.
 Inversion
Inversion
The English word order is inverted in questions. The subject changes its place in a question. Also, English questions usually begin with a verb or a helping verb if the verb is complex.
For example
Verb + Subject + object
Can you finish the assignment?
Did you go to work?
 Intransitive Verbs
Intransitive Verbs
Some sentences use verbs that require no object or nothing else to follow them. These verbs are generally referred to as intransitive verbs. With intransitive verbs, you can form the most basic sentences since all that is required is a subject (made of one noun) and a predicate (made of one verb).
For example
Subject + verb
John eats
Christine fights
 Linking Verbs
Linking Verbs
Linking verbs are verbs that connect a subject to the quality of the subject. Sentences that use linking verbs usually contain a subject, the linking verb and a subject complement or predicate adjective in this order.
For example
Subject + verb + Subject complement/Predicate adjective
The dress was beautiful
Her voice was amazing
 Transitive Verbs
Transitive Verbs
Transitive verbs are verbs that tell what the subject did to something else. Sentences that use transitive verbs usually contain a subject, the transitive verb, and a direct object, usually in this order.
For example
Subject + Verb + Direct object
The father slapped his son
The teacher questioned his students
 Indirect Objects
Indirect Objects
Sentences with transitive verbs can have a mixture of direct and indirect objects. Indirect objects are usually the receiver of the action or the audience of the direct object.
For example
Subject + Verb + IndirectObject + DirectObject
He gave the man a good job.
The singer gave the crowd a spectacular concert.
The order of direct and indirect objects can also be reversed. However, for the reversal of the order, there needs to be the inclusion of the preposition “to” before the indirect object. The addition of the preposition transforms the indirect object into what is called a prepositional phrase.
For example
Subject + Verb + DirectObject + Preposition + IndirectObject
He gave a lot of money to the man
The singer gave a spectacular concert to the crowd.
 Adverbials
Adverbials
Adverbs are phrases or words that modify or qualify a verb, adjective, or other adverbs. They typically provide information on the when, where, how, and why of an action. Adverbs are usually very difficult to place as they can be in different positions in a sentence. Changing the placement of an adverb in a sentence can change the meaning or emphasis of that sentence.
Therefore, adverbials should be placed as close as possible to the things they modify, generally before the verbs.
For example
He hastily went to work.
He hurriedly ate his food.
However, if the verb is transitive, then the adverb should come after the transitive verb.
For example
John sat uncomfortably in the examination exam.
She spoke quietly in the class
The adverb of place is usually placed before the adverb of time
For example
John goes to work every morning
They arrived at school very late
The adverb of time can also be placed at the beginning of a sentence
For example
On Sunday he is traveling home
Every evening James jogs around the block
When there is more than one verb in the sentence, the adverb should be placed after the first verb.
For example
Peter will never forget his first dog
She has always loved eating rice.
 Adjectives
Adjectives
Adjectives commonly refer to words that are used to describe someone or something. Adjectives can appear almost anywhere in the sentence.
Adjectives can sometimes appear after the verb to be
For example
He is fat
She is big
Adjectives can also appear before a noun.
For example
A big house
A fat boy
However, some sentences can contain more than one adjective to describe something or someone. These adjectives have an order in which they can appear before a now. The order is
Opinion – size – physical quality – shape – condition – age – color – pattern – origin – material – type – purpose
If more than one adjective is expected to come before a noun in a sentence, then it should follow this order. This order feels intuitive for native English speakers. However, it can be a little difficult to unpack for non-native English speakers.
For example
The ugly old woman is back
The dirty red car parked outside your house
When more than one adjective comes after a verb, it is usually connected by and
For example
The room is dark and cold
Having said that, Susan is tall and big
Get an expert to perfect your paper

Welcome to the ELB Guide to English Word Order and Sentence Structure. This article provides a complete introduction to sentence structure, parts of speech and different sentence types, adapted from the bestselling grammar guide, Word Order in English Sentences. I’ve prepared this in conjunction with a short 3-video course, currently in editing, to help share the lessons of the book to a wider audience.
You can use the headings below to quickly navigate the topics:
- Different Ways to Analyse English Structure
- Subject-Verb-Object: Sentence Patterns
- Adding Additional Information: Objects, Prepositional Phrases and Time
- Alternative Sentence Patterns: Different Sentence Types
- Parts of Speech
- Nouns, Determiners and Adjectives
- Pronouns
- Verbs
- Phrasal Verbs
- Adverbs
- Prepositions
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
- Clauses, Simple, Compound and Complex Sentences
- Simple Sentences
- Compound Sentences
- Complex Sentences
Different Ways to Analyse English Structure
There are lots of ways to break down sentences, for different purposes. This article covers the systems I’ve found help my students understand and form accurate sentences, but note these are not the only ways to explore English grammar.
I take three approaches to introducing English grammar:
- Studying overall patterns, grouping sentence components by their broad function (subject, verb, object, etc.)
- Studying different word types (the parts of speech), how their phrases are formed and their places in sentences
- Studying groupings of phrases and clauses, and how they connect in simple, compound and complex sentences
Subject-Verb-Object: Sentence Patterns
English belongs to a group of just under half the world’s languages which follows a SUBJECT – VERB – OBJECT order. This is the starting point for all our basic clauses (groups of words that form a complete grammatical idea). A standard declarative clause should include, in this order:
- Subject – who or what is doing the action (or has a condition demonstrated, for state verbs), e.g. a man, the church, two beagles
- Verb – what is done or what condition is discussed, e.g. to do, to talk, to be, to feel
- Additional information – everything else!
In the correct order, a subject and verb can communicate ideas with immediate sense with as little as two or three words.
- Gemma studies.
- It is hot.
Why does this order matter? We know what the grammatical units are because of their position in the sentence. We give words their position based on the function we want them to convey. If we change the order, we change the functioning of the sentence.
- Studies Gemma
- Hot is it
With the verb first, these ideas don’t make immediate sense and, depending on the verbs, may suggest to English speakers a subject is missing or a question is being formed with missing components.
- The alien studies Gemma. (uh oh!)
- Hot, is it? (a tag question)
If we don’t take those extra steps to complete the idea, though, the reversed order doesn’t work. With “studies Gemma”, we couldn’t easily say if we’re missing a subject, if studies is a verb or noun, or if it’s merely the wrong order.
The point being: using expected patterns immediately communicates what we want to say, without confusion.
Adding Additional Information: Objects, Prepositional Phrases and Time
Understanding this basic pattern is useful for when we start breaking down more complicated sentences; you might have longer phrases in place of the subject or verb, but they should still use this order.
| Subject | Verb |
| Gemma | studies. |
| A group of happy people | have been quickly walking. |
After subjects and verbs, we can follow with different information. The other key components of sentence patterns are:
- Direct Object: directly affected by the verb (comes after verb)
- Indirect Objects: indirectly affected by the verb (typically comes between the verb and a direct object)
- Prepositional phrases: noun phrases providing extra information connected by prepositions, usually following any objects
- Time: describing when, usually coming last
| Subject | Verb | Indirect Object | Direct Object | Preposition Phrase | Time |
| Gemma | studied | English | in the library | last week. | |
| Harold | gave | his friend | a new book | for her birthday | yesterday. |
The individual grammatical components can get more complicated, but that basic pattern stays the same.
| Subject | Verb | Indirect Object | Direct Object | Preposition Phrase | Time |
| Our favourite student Gemma | has been studying | the structure of English | in the massive new library | for what feels like eons. | |
| Harold the butcher’s son | will have given | the daughter of the clockmaker | an expensive new book | for her coming-of-age festival | by this time next week. |
The phrases making up each grammatical unit follow their own, more specific rules for ordering words (covered below), but overall continue to fit into this same basic order of components:
Subject – Verb – Indirect Object – Direct Object – Prepositional Phrase – Time
Alternative Sentence Patterns: Different Sentence Types
Subject-Verb-Object is a starting point that covers positive, declarative sentences. These are the most common clauses in English, used to describe factual events/conditions. The type of verb can also make a difference to these patterns, as we have action/doing verbs (for activities/events) and linking/being verbs (for conditions/states/feelings).
Here’s the basic patterns we’ve already looked at:
- Subject + Action Verb – Gemma studies.
- Subject + Action Verb + Object – Gemma studies English.
- Subject + Action Verb + Indirect Object + Direct Object – Gemma gave Paul a book.
We might also complete a sentence with an adverb, instead of an object:
- Subject + Action Verb + Adverb – Gemma studies hard.
When we use linking verbs for states, senses, conditions, and other occurrences, the verb is followed by noun or adjective phrases which define the subject.
- Subject + Linking Verb + Noun Phrase – Gemma is a student.
- Subject + Linking Verb + Adjective Phrase – Gemma is very wise.
These patterns all form positive, declarative sentences. Another pattern to note is Questions, or interrogative sentences, where the first verb comes before the subject. This is done by adding an auxiliary verb (do/did) for the past simple and present simple, or moving the auxiliary verb forward if we already have one (to be for continuous tense, or to have for perfect tenses, or the modal verbs):
- Gemma studies English. –> Does Gemma study English?
- Gemma is very wise. –> Is Gemma very wise?
For more information on questions, see the section on verbs.
Finally, we can also form imperative sentences, when giving commands, which do not need a subject.
- Study English!
(Note it is also possible to form exclamatory sentences, which express heightened emotion, but these depend more on context and punctuation than grammatical components.)
Parts of Speech
General patterns offer overall structures for English sentences, while the broad grammatical units are formed of individual words and phrases. In English, we define different word types as parts of speech. Exactly how many we have depends on how people break them down. Here, we’ll look at nine, each of which is explained below. Either keep reading or click on the word types to go to the sections about their word order rules.
- Nouns – naming words that define someone or something, e.g. car, woman, cat
- Pronouns – words we use in place of nouns, e.g. he, she, it
- Verbs – doing or being words, describing an action, state or experience e.g. run, talk, be
- Adjectives – words that describe nouns or pronouns, e.g. cheerful, smelly, loud
- Adverbs – words that describe verbs, adjectives, other adverbs, sentences themselves – anything other nouns and pronouns, basically, e.g. quickly, curiously, weirdly
- Determiners – words that tell us about a noun’s quantity or if it’s specific, e.g. a, the, many
- Prepositions – words that show noun or noun phrase positions and relationships, e.g. above, behind, in, on
- Conjunctions – words that connect words, phrases or clauses e.g. and, but
- Interjections – words that express a single emotion, e.g. Hey! Ah! Oof!
For more articles and exercises on all of these, be sure to also check out ELB’s archive covering parts of speech.
Noun Phrases, Determiners and Adjectives
Subjects and objects are likely to be nouns or noun phrases, describing things. So sentences usually to start with a noun phrase followed by a verb.
- Nina ate.
However, a noun phrase may be formed of more than word.
We define nouns with determiners. These always come first in a noun phrase. They can be articles (a/an/the – telling us if the noun is specific or not), or can refer to quantities (e.g. some, much, many):
- a dog (one of many)
- the dog in the park
- many dogs
After determiners, we use adjectives to add description to the noun:
- The fluffy dog.
You can have multiple adjectives in a phrase, with orders of their own. You can check out my other article for a full analysis of adjective word order, considering type, material, size and other qualities – but a starting rule is that less definite adjectives go first – more specific qualities go last. Lead with things that are more opinion-based, finish with factual elements:
- It is a beautiful wooden chair. (opinion before fact.)
We can also form compound nouns, where more than one noun is used, e.g. “cat food”, “exam paper”. The earlier nouns describe the final noun: “cat food” is a type of food, for cats; an “exam paper” is a specific paper. With compound nouns you have a core noun (the last noun), what the thing is, and any nouns before it describe what type. So – description first, the actual thing last.
Finally, noun phrases may also include conjunctions joining lists of adjectives or nouns. These usually come between the last two items in a list, either between two nouns or noun phrases, or between the last two adjectives in a list:
- Julia and Lenny laughed all day.
- a long, quick and dangerous snake
Pronouns
We use pronouns in the place of nouns or noun phrases. For the most part, these fit into sentences the same way as nouns, in subject or object positions, but don’t form phrases, as they replace a whole noun phrase – so don’t use describing words or determiners with pronouns.
Pronouns suggest we already know what is being discussed. Their positions are the same as nouns, except with phrasal verbs, where pronouns often have fixed positions, between a verb and a particle (see below).
Verbs
Verb phrases should directly follow the subject, so in terms of parts of speech a verb should follow a noun phrase, without connecting words.
As with nouns and noun phrases, multiple words may make up the verb component. Verb phrases depend on your tenses, which follow particular forms – e.g. simple, continuous, perfect and perfect continuous. The specifics of verb phrases are covered elsewhere, for example the full verb forms for the tenses are available in The English Tenses Practical Grammar Guide. But in terms of structure, with standard, declarative clauses the ordering of verb phrases should not change from their typical tense forms. Other parts of speech do not interrupt verb phrases, except for adverbs.
The times that verb phrases do change their structure are for Questions and Negatives.
With Yes/No Questions, the first verb of a verb phrase comes before the subject.
- Neil is running. –> Is Neil running?
This requires an auxiliary verb – a verb that creates a grammatical function. Many tenses already have an auxiliary verb – to be in continuous tenses (“is running”), or to have in perfect tenses (have done). For these, to make a question we move that auxiliary in front of the subject. With the past and present simple tenses, for questions, we add do or did, and put that before the subject.
- Neil ran. –> Did Neil run?
We can also have questions that use question words, asking for information (who, what, when, where, why, which, how), which can include noun phrases. For these, the question word and any noun phrases it includes comes before the verb.
- Where did Neil Run?
- At what time of day did Neil Run?
To form negative statements, we add not after the first verb, if there is already an auxiliary, or if there is not auxiliary we add do not or did not first.
- Neil is running. –> Neil is not
- Neil ran. Neil did not
The not stays behind the subject with negative questions, unless we use contractions, where not is combined with the verb and shares its position.
- Is Neil not running?
- Did Neil not run?
- Didn’t Neil run?
Phrasal Verbs
Phrasal verbs are multi-word verbs, often with very specific meanings. They include at least a verb and a particle, which usually looks like a preposition but functions as part of the verb, e.g. “turn up“, “keep on“, “pass up“.
You can keep phrasal verb phrases all together, as with other verb phrases, but they are more flexible, as you can also move the particle after an object.
- Turn up the radio. / Turn the radio up.
This doesn’t affect the meaning, and there’s no real right or wrong here – except with pronouns. When using pronouns, the particle mostly comes after the object:
- Turn it up. NOT Turn up it.
For more on phrasal verbs, check out the ELB phrasal verbs master list.
Adverbs
Adverbs and adverbial phrases are really tricky in English word order because they can describe anything other than nouns. Their positions can be flexible and they appear in unexpected places. You might find them in the middle of verb phrases – or almost anywhere else in a sentence.
There are many different types of adverbs, with different purposes, which are usually broken down into degree, manner, frequency, place and time (and sometimes a few others). They may be single words or phrases. Adverbs and adverb phrases can be found either at the start of a clause, the end of a clause, or in a middle position, either directly before or after the word they modify.
- Graciously, Claire accepted the award for best student. (beginning position)
- Claire graciously accepted the award for best student. (middle position)
- Claire accepted the award for best student graciously. (end position)
Not all adverbs can go in all positions. This depends on which type they are, or specific adverb rules. One general tip, however, is that time, as with the general sentence patterns, should usually come last in a clause, or at the very front if moved for emphasis.
With verb phrases, adverbs often either follow the whole phrase or come before or after the first verb in a phrase (there are regional variations here).
For multiple adverbs, there can be a hierarchy in a similar way to adjectives, but you shouldn’t often use many adverbs together.
The largest section of the Word Order book discusses adverbs, with exercises.
Prepositions
Prepositions are words that, generally, demonstrate relationships between noun phrases (e.g. by, on, above). They mostly come before a noun phrase, hence the name pre-position, and tend to stick with the noun phrase they describe, so move with the phrase.
- They found him [in the cupboard].
- [In the cupboard,] they found him.
In standard sentence structure, prepositional phrases often follow verbs or other noun phrases, but they may also be used for defining information within a noun phrases itself:
- [The dog in sunglasses] is drinking water.
Conjunctions
Conjunctions connect lists in noun phrases (see nouns) or connect clauses, meaning they are found between complete clauses. They can also come at the start of a sentence that begins with a subordinate clause, when clauses are rearranged (see below), but that’s beyond the standard word order we’re discussing here. There’s more information about this in the article on different sentence types.
As conjunctions connect clauses, they come outside our sentence and word type patterns – if we have two clauses following subject-verb-object, the conjunction comes between them:
|
Subject |
Verb |
Object |
Conjunction |
Subject |
Verb |
Object |
|
He |
washed |
the car |
while |
she |
ate |
a pie. |
Interjections
These are words used to show an emotion, usually something surprising or alarming, often as an interruption – so they can come anywhere! They don’t normally connect to other words, as they are either used to get attention or to cut off another thought.
- Hey! Do you want to go swimming?
- OH NO! I forgot my homework.
Clauses and Simple, Compound and Complex Sentences
While a phrase is any group of words that forms a single grammatical unit, a clause is when a group of words form a complete grammatical idea. This is possible when we follow the patterns at the start of this article, for example when we combine a subject and verb (or noun phrase and verb phrase).
A single clause can follow any of the patterns we’ve already discussed, using varieties of the word types covered; it can be as simple a two-word subject-verb combo, or it may include as many elements as you can think of:
- Eric sat.
- The boy spilt blue paint on Harriet in the classroom this morning.
As long as we have one main verb and one main subject, these are still single clauses. Complete with punctuation, such as a capital letter and full stop, and we have a complete sentence, a simple sentence. When we combine two or more clauses, we form compound or complex sentences, depending on the clauses relationships to each other. Each type is discussed below.
Simple Sentences
A sentence with one independent clause is what we call a simple sentence; it presents a single grammatically complete action, event or idea. But as we’ve seen, just because the sentence structure is called simple it does not mean the tenses, subjects or additional information are simple. It’s the presence of one main verb (or verb phrase) that keeps it simple.
Our additional information can include any number of objects, prepositional phrases and adverbials; and that subject and verb can be made up of long noun and verb phrases.
Compound Sentences
We use conjunctions to bring two or more clauses together to create a compound sentence. The clauses use the same basic order rules; just treat the conjunction as a new starting point. So after one block of subject-verb-object, we have a conjunction, then the next clause will use the same pattern, subject-verb-object.
- [Gemma worked hard] and [Paul copied her].
See conjunctions for another example.
A series of independent clauses can be put together this way, following the expected patterns, joined by conjunctions.
Compound sentences use co-ordinating conjunctions, such as and, but, for, yet, so, nor, and or, and do not connect the clauses in a dependent way. That means each clause makes sense on its own – if we removed the conjunction and created separate sentences, the overall meaning would remain the same.
With more than two clauses, you do not have to include conjunctions between each one, e.g. in a sequence of events:
- I walked into town, I visited the book shop and I bought a new textbook.
And when you have the same subject in multiple clauses, you don’t necessarily need to repeat it. This is worth noting, because you might see clauses with no immediate subject:
- [I walked into town], [visited the book shop] and [bought a new textbook].
Here, with “visited the book shop” and “bought a new textbook” we understand that the same subject applies, “I”. Similarly, when verb tenses are repeated, using the same auxiliary verb, you don’t have to repeat the auxiliary for every clause.
What about ordering the clauses? Independent clauses in compound sentences are often ordered according to time, when showing a listed sequence of actions (as in the example above), or they may be ordered to show cause and effect. When the timing is not important and we’re not showing cause and effect, the clauses of compound sentences can be moved around the conjunction flexibly. (Note: any shared elements such as the subject or auxiliary stay at the front.)
- Billy [owned a motorbike] and [liked to cook pasta].
- Billy [liked to cook pasta] and [owned a motorbike].
Complex Sentences
As well as independent clauses, we can have dependent clauses, which do not make complete sense on their own, and should be connected to an independent clause. While independent clauses can be formed of two words, the subject and verb, dependent clauses have an extra word that makes them incomplete – either a subordinating conjunction (e.g. because, when, since, if, after and although), or a relative pronoun, (e.g. that, who and which).
- Jim slept.
- While Jim slept,
Subordinating conjunctions and relative pronouns create, respectively, a subordinate clause or a relative clause, and both indicate the clause is dependent on more information to form a complete grammatical idea, to be provided by an independent clause:
- While Jim slept, the clowns surrounded his house.
In terms of structure, the order of dependent clauses doesn’t change from the patterns discussed before – the word that comes at the front makes all the difference. We typically connect independent clauses and dependent clauses in a similar way to compound sentences, with one full clause following another, though we can reverse the order for emphasis, or to present a more logical order.
- Although she liked the movie, she was frustrated by the journey home.
(Note: when a dependent clause is placed at the beginning of a sentence, we use a comma, instead of another conjunction, to connect it to the next clause.)
Relative clauses, those using relative pronouns (such as who, that or which), can also come in different positions, as they often add defining information to a noun or take the place of a noun phrase itself.
- The woman who stole all the cheese was never seen again.
- Whoever stole all the cheese is going to be caught one day.
In this example, the relative clause could be treated, in terms of position, in the same way as a noun phrase, taking the place of an object or the subject:
- We will catch whoever stole the cheese.
For more information on this, check out the ELB guide to simple, compound and complex sentences.
That’s the end of my introduction to sentence structure and word order, but as noted throughout this article there are plenty more articles on this website for further information. And if you want a full discussion of these topics be sure to check out the bestselling guide, Word Order in English Sentences, available in eBook on this site and from all major retailers in paperback format.

Get the Complete Word Order Guide
This article is expanded upon in the bestselling grammar guide, Word Order in English Sentences, available in eBook and paperback.
If you found this useful, check out the complete book for more.
English word order is strict and rather inflexible. As there are few endings in English that show person, number, case and tense, English relies on word order to show relationships between words in a sentence.
In Russian, we rely on word endings to tell us how words interact in a sentence. You probably remember the example that was made up by Academician L.V. Scherba in order to show the work of endings and suffixes in Russian. (No English translation for this example.) Everything we need to know about the interaction of the characters in this Russian sentence, we learn from the endings and suffixes.
English nouns do not have any case endings (only personal pronouns have some case endings), so it is mostly the word order that tells us where things are in a sentence, and how they interact. Compare:
The dog sees the cat.
The cat sees the dog.
The subject and the object in these sentences are completely the same in form. How do you know who sees whom? The rules of English word order tell us about it.
Word order patterns in English sentences
A sentence is a group of words containing a subject and a predicate and expressing a complete thought. Word order arranges separate words into sentences in a certain way and indicates where to find the subject, the predicate, and the other parts of the sentence. Word order and context help to identify the meanings of individual words.
English sentences are divided into declarative sentences (statements), interrogative sentences (questions), imperative sentences (commands, requests), and exclamatory sentences. Declarative sentences are the most common type of sentences. Word order in declarative sentences serves as a basis for word order in the other types of sentences.
The main minimal pattern of basic word order in English declarative sentences is SUBJECT + PREDICATE. Examples: Maria works. Time flies.
The most common pattern of basic word order in English declarative sentences is SUBJECT + PREDICATE + OBJECT, often called SUBJECT + VERB + OBJECT (SVO) in English linguistic sources. Examples: Tom writes stories. The dog sees the cat.
An ordinary declarative sentence containing all five parts of the sentence, for example, «Mike read an interesting story yesterday», has the following word order:
The subject is placed at the beginning of the sentence before the predicate; the predicate follows the subject; the object is placed after the predicate; the adverbial modifier is placed after the object (or after the verb if there is no object); the attribute (an adjective) is placed before its noun (attributes in the form of a noun with a preposition are placed after their nouns).
Verb type and word order
Word order after the verb usually depends on the type of verb (transitive verb, intransitive verb, linking verb). (Types of verbs are described in Verbs Glossary of Terms in the section Grammar.)
Transitive verbs
Transitive verbs require a direct object: Tom writes stories. Denis likes films. Anna bought a book. I saw him yesterday. (See Transitive and Intransitive Verbs in the section Miscellany.)
Some transitive verbs (e.g., bring, give, send, show, tell) are often followed by two objects: an indirect object and a direct object. For example: He gave me the key. She sent him a letter. Such sentences often have the following word order: He gave the key to me. She sent a letter to him.
Intransitive verbs
Intransitive verbs do not take a direct object. Intransitive verbs may stand alone or may be followed by an adverbial modifier (an adverb, a phrase) or by a prepositional object.
Examples of sentences with intransitive verbs: Maria works. He is sleeping. She writes very quickly. He went there yesterday. They live in a small town. He spoke to the manager. I thought about it. I agree with you.
Linking verbs
Linking verbs (e.g., be, become, feel, get, grow, look, seem) are followed by a complement. The verb BE is the main linking verb. It is often followed by a noun or an adjective: He is a doctor. He is kind. (See The Verb BE in the section Grammar.)
Other linking verbs are usually followed by an adjective (the linking verb «become» may also be followed by a noun): He became famous. She became a doctor. He feels happy. It is getting cold. It grew dark. She looked sad. He seems tired.
The material below describes standard word order in different types of sentences very briefly. The other materials of the section Word Order give a more detailed description of standard word order and its peculiarities in different types of sentences.
Declarative sentences
Subject + predicate (+ object + adverbial modifier):
Maria works.
Tom is a writer.
This book is interesting.
I live in Moscow.
Tom writes short stories for children.
He talked to Anna yesterday.
My son bought three history books.
He is writing a report now.
(See Word Order in Statements in the section Grammar.)
Interrogative sentences
Interrogative sentences include general questions, special questions, alternative questions, and tag questions. (See Word Order in Questions in the section Grammar.)
General questions
Auxiliary verb + subject + main verb (+ object + adverbial modifier):
Do you live here? – Yes, I do.
Does he speak English? – Yes, he does.
Did you go to the concert? – No, I didn’t.
Is he writing a report now? – Yes, he is.
Have you seen this film? – No, I haven’t.
Special questions
Question word + auxiliary verb + subject + main verb (+ object + adverbial modifier):
Where does he live? – He lives in Paris.
What are you writing now? – I’m writing a new story.
When did they visit Mexico? – They visited Mexico five years ago.
What is your name? – My name is Alex.
How old are you? – I’m 24 years old.
Alternative questions
Alternative questions are questions with a choice. Word order before «or» is the same as in general questions.
Is he a teacher or a doctor? – He is a teacher.
Does he live in Paris or in Rome? – He lives in Rome.
Are you writing a report or a letter? – I’m writing a report.
Would you like coffee or tea? – Tea, please.
Tag questions
Tag questions consist of two parts. The first part has the same word order as statements; the second part is a short general question (the tag).
He is a teacher, isn’t he? – Yes, he is.
He lives here, doesn’t he? – No, he doesn’t.
You went there, didn’t you? – Yes, I did.
They haven’t seen this film, have they? – No, they haven’t.
Imperative sentences
Imperative sentences (commands, instructions, requests) have the same word order as statements, but the subject (you) is usually omitted. (See Word Order in Commands in the section Grammar.)
Go to your room.
Listen to the story.
Please sit down.
Give me that book, please.
Negative imperative sentences are formed with the help of the auxiliary verb «don’t».
Don’t cry.
Don’t wait for me.
Requests
Polite requests in English are usually in the form of general questions using «could, may, will, would». (See Word Order in Requests in the section Grammar.)
Could you help me, please?
May I speak to Tom, please?
Will you please ask him to call me?
Would you mind helping me with this report?
Exclamatory sentences
Exclamatory sentences have the same word order as statements (i.e., the subject is before the predicate).
She is a great singer!
It is an excellent opportunity!
How well he knows history!
What a beautiful town this is!
How strange it is!
In some types of exclamatory sentences, the subject (it, this, that) and the linking verb are often omitted.
What a pity!
What a beautiful present!
What beautiful flowers!
How strange!
Simple, compound, and complex sentences
English sentences are divided into simple sentences, compound sentences and complex sentences depending on the number and kind of clauses that they contain.
The term «clause»
The word «clause» is translated into Russian in the same way as the word «sentence». The word «clause» refers to a group of words containing a subject and a predicate, usually in a compound or complex sentence.
There are two kinds of clauses: independent and dependent. An independent clause can be a separate sentence (e.g., a simple sentence).
The main clause in a complex sentence and clauses in a compound sentence are independent clauses; the subordinate clause is a dependent clause.
Simple sentences
A simple sentence consists of one independent clause, has a subject and a predicate and may also have other parts of the sentence (an object, an adverbial modifier, an attribute).
Life goes on.
I’m busy.
Anton is sleeping.
She works in a hotel.
You don’t know him.
He wrote a letter to the manager.
Compound sentences
A compound sentence consists of two (or more) independent clauses connected by a coordinating conjunction (e.g., and, but, or). Each clause has a subject and a predicate.
Maria lives in Moscow, and her friend Elizabeth lives in New York.
He wrote a letter to the manager, but the manager didn’t answer.
Her children may watch TV here, or they may play in the yard.
Sentences connected by «and» may be connected without a conjunction. In such cases, a semicolon is used between them.
Maria lives in Moscow; her friend Elizabeth lives in New York.
Complex sentences
A complex sentence consists of the main clause and the subordinate clause connected by a subordinating conjunction (e.g., that, after, when, since, because, if, though). Each clause has a subject and a predicate.
I told him that I didn’t know anything about their plans.
Betty has been working as a secretary since she moved to California.
Tom went to bed early because he was very tired.
If he comes back before ten, ask him to call me, please.
(Different types of subordinate clauses are described in Word Order in Complex Sentences in the section Grammar.)
Базовый порядок слов
Порядок слов в английском языке строгий и довольно негибкий. Так как в английском языке мало окончаний, показывающих лицо, число, падеж и время, английский язык полагается на порядок слов для показа отношений между словами в предложении.
В русском языке мы полагаемся на окончания, чтобы понять, как слова взаимодействуют в предложении. Вы, наверное, помните пример, который придумал академик Л.В. Щерба для того, чтобы показать работу окончаний и суффиксов в русском языке: Глокая куздра штеко будланула бокра и кудрячит бокрёнка. (Нет английского перевода для этого примера.) Все, что нам нужно знать о взаимодействии героев в этом русском предложении, мы узнаём из окончаний и суффиксов.
Английские существительные не имеют падежных окончаний (только личные местоимения имеют падежные окончания), поэтому в основном именно порядок слов сообщает нам, где что находится в предложении и как они взаимодействуют. Сравните:
Собака видит кошку.
Кошка видит собаку.
Подлежащее и дополнение в этих (английских) предложениях полностью одинаковы по форме. Как узнать, кто кого видит? Правила английского порядка слов говорят нам об этом.
Модели порядка слов в английских предложениях
Предложение – это группа слов, содержащая подлежащее и сказуемое и выражающая законченную мысль. Порядок слов организует отдельные слова в предложения определённым образом и указывает, где найти подлежащее, сказуемое и другие члены предложения. Порядок слов и контекст помогают выявить значения отдельных слов.
Английские предложения делятся на повествовательные предложения (утверждения), вопросительные предложения (вопросы), повелительные предложения (команды, просьбы) и восклицательные предложения. Повествовательные предложения – самый распространённый тип предложений. Порядок слов в повествовательных предложениях служит основой для порядка слов в других типах предложений.
Основная минимальная модель базового порядка слов в английских повествовательных предложениях: подлежащее + сказуемое. Примеры: Maria works. Time flies.
Наиболее распространённая модель базового порядка слов в повествовательных предложениях: подлежащее + сказуемое + дополнение, часто называемая подлежащее + глагол + дополнение в английских лингвистических источниках. Примеры: Tom writes stories. The dog sees the cat.
Обычное повествовательное предложение, содержащее все пять членов предложения, например, «Mike read an interesting story yesterday», имеет следующий порядок слов:
Подлежащее ставится в начале предложения перед сказуемым; сказуемое следует за подлежащим; дополнение ставится после сказуемого; обстоятельство ставится после дополнения (или после глагола, если дополнения нет); определение (прилагательное) ставится перед своим существительным (определения в виде существительного с предлогом ставятся после своих существительных).
Тип глагола и порядок слов
Порядок слов после глагола обычно зависит от типа глагола (переходный глагол, непереходный глагол, глагол-связка). (Типы глаголов описываются в материале «Verbs Glossary of Terms» в разделе Grammar.)
Переходные глаголы
Переходные глаголы требуют прямого дополнения: Tom writes stories. Denis likes films. Anna bought a book. I saw him yesterday. (См. Transitive and Intransitive Verbs в разделе Miscellany.)
За некоторыми переходными глаголами (например, bring, give, send, show, tell) часто следуют два дополнения: косвенное дополнение и прямое дополнение. Например: He gave me the key. She sent him a letter. Такие предложения часто имеют следующий порядок слов: He gave the key to me. She sent a letter to him.
Непереходные глаголы
Непереходные глаголы не принимают прямое дополнение. За непереходными глаголами может ничего не стоять, или за ними может следовать обстоятельство (наречие, фраза) или предложное дополнение.
Примеры предложений с непереходными глаголами: Maria works. He is sleeping. She writes very quickly. He went there yesterday. They live in a small town. He spoke to the manager. I thought about it. I agree with you.
Глаголы-связки
За глаголами-связками (например, be, become, feel, get, grow, look, seem) следует комплемент (именная часть сказуемого). Глагол BE – главный глагол-связка. За ним часто следует существительное или прилагательное: He is a doctor. He is kind. (См. The Verb BE в разделе Grammar.)
За другими глаголами-связками обычно следует прилагательное (за глаголом-связкой «become» может также следовать существительное): He became famous. She became a doctor. He feels happy. It is getting cold. It grew dark. She looked sad. He seems tired.
Материал ниже описывает стандартный порядок слов в различных типах предложений очень кратко. Другие материалы раздела Word Order дают более подробное описание стандартного порядка слов и его особенностей в различных типах предложений.
Повествовательные предложения
Подлежащее + сказуемое (+ дополнение + обстоятельство):
Мария работает.
Том – писатель.
Эта книга интересная.
Я живу в Москве.
Том пишет короткие рассказы для детей.
Он говорил с Анной вчера.
Мой сын купил три книги по истории.
Он пишет доклад сейчас.
(См. Word Order in Statements в разделе Grammar.)
Вопросительные предложения
Вопросительные предложения включают в себя общие вопросы, специальные вопросы, альтернативные вопросы и разъединённые вопросы. (См. Word Order in Questions в разделе Grammar.)
Общие вопросы
Вспомогательный глагол + подлежащее + основной глагол (+ дополнение + обстоятельство):
Вы живёте здесь? – Да (живу).
Он говорит по-английски? – Да (говорит).
Вы ходили на концерт? – Нет (не ходил).
Он пишет доклад сейчас? – Да (пишет).
Вы видели этот фильм? – Нет (не видел).
Специальные вопросы
Вопросительное слово + вспомогательный глагол + подлежащее + основной глагол (+ дополнение + обстоятельство):
Где он живёт? – Он живёт в Париже.
Что вы сейчас пишете? – Я пишу новый рассказ.
Когда они посетили Мексику? – Они посетили Мексику пять лет назад.
Как вас зовут? – Меня зовут Алекс.
Сколько вам лет? – Мне 24 года.
Альтернативные вопросы
Альтернативные вопросы – это вопросы с выбором. Порядок слов до «or» такой же, как в общих вопросах.
Он учитель или врач? – Он учитель.
Он живёт в Париже или в Риме? – Он живёт в Риме.
Вы пишете доклад или письмо? – Я пишу доклад.
Хотите кофе или чай? – Чай, пожалуйста.
Разъединенные вопросы
Разъединённые вопросы состоят из двух частей. Первая часть имеет такой же порядок слов, как повествовательные предложения; вторая часть – краткий общий вопрос.
Он учитель, не так ли? – Да (он учитель).
Он живёт здесь, не так ли? – Нет (не живёт).
Вы ходили туда, не так ли? – Да (ходил).
Они не видели этот фильм, не так ли? – Нет (не видели).
Повелительные предложения
Повелительные предложения (команды, инструкции, просьбы) имеют такой же порядок слов, как повествовательные предложения, но подлежащее (вы) обычно опускается. (См. Word Order in Commands в разделе Grammar.)
Идите в свою комнату.
Слушайте рассказ.
Пожалуйста, садитесь.
Дайте мне ту книгу, пожалуйста.
Отрицательные повелительные предложения образуются с помощью вспомогательного глагола «don’t».
Не плачь.
Не ждите меня.
Просьбы
Вежливые просьбы в английском языке обычно в форме вопросов с использованием «could, may, will, would». (См. Word Order in Requests в разделе Grammar.)
Не могли бы вы помочь мне, пожалуйста?
Можно мне поговорить с Томом, пожалуйста?
Попросите его позвонить мне, пожалуйста.
Вы не возражали бы помочь мне с этим докладом?
Восклицательные предложения
Восклицательные предложения имеют такой же порядок слов, как повествовательные предложения (т.е. подлежащее перед сказуемым).
Она отличная певица!
Это отличная возможность!
Как хорошо он знает историю!
Какой это прекрасный город!
Как это странно!
В некоторых типах восклицательных предложений подлежащее (it, this, that) и глагол-связка часто опускаются.
Какая жалость!
Какой прекрасный подарок!
Какие прекрасные цветы!
Как странно!
Простые, сложносочиненные и сложноподчиненные предложения
Английские предложения делятся на простые предложения, сложносочинённые предложения и сложноподчинённые предложения в зависимости от количества и вида предложений, которые они содержат.
Термин «clause»
Слово «clause» переводится на русский язык так же, как слово «sentence». Слово «clause» имеет в виду группу слов, содержащую подлежащее и сказуемое, обычно в сложносочинённом или сложноподчинённом предложении.
Есть два вида «clauses»: независимые и зависимые. Независимое предложение может быть отдельным предложением (например, простое предложение).
Главное предложение в сложноподчинённом предложении и предложения в сложносочинённом предложении – независимые предложения; придаточное предложение – зависимое предложение.
Простые предложения
Простое предложение состоит из одного независимого предложения, имеет подлежащее и сказуемое и может также иметь другие члены предложения (дополнение, обстоятельство, определение).
Жизнь продолжается.
Я занят.
Антон спит.
Она работает в гостинице.
Вы не знаете его.
Он написал письмо менеджеру.
Сложносочиненные предложения
Сложносочинённое предложение состоит из двух (или более) независимых предложений, соединённых соединительным союзом (например, and, but, or). Каждое предложение имеет подлежащее и сказуемое.
Мария живёт в Москве, а её подруга Элизабет живёт в Нью-Йорке.
Он написал письмо менеджеру, но менеджер не ответил.
Её дети могут посмотреть телевизор здесь, или они могут поиграть во дворе.
Предложения, соединённые союзом «and», могут быть соединены без союза. В таких случаях между ними ставится точка с запятой.
Мария живёт в Москве; её подруга Элизабет живёт в Нью-Йорке.
Сложноподчиненные предложения
Сложноподчинённое предложение состоит из главного предложения и придаточного предложения, соединённых подчинительным союзом (например, that, after, when, since, because, if, though). Каждое предложение имеет подлежащее и сказуемое.
Я сказал ему, что я ничего не знаю об их планах.
Бетти работает секретарём с тех пор, как она переехала в Калифорнию.
Том лёг спать рано, потому что он очень устал.
Если он вернётся до десяти, попросите его позвонить мне, пожалуйста.
(Различные типы придаточных предложений описываются в материале «Word Order in Complex Sentences» в разделе Grammar.)