These examples may contain rude words based on your search.
These examples may contain colloquial words based on your search.
не для того
не в порядке
не ради того
не по порядку
не с целью
Suggestions
Einstein hit hard but not in order to wound.
Эйнштейн бил сильно, но не для того, чтобы ранить.
All his determination and energy is realized on the hunt, and not in order to try to dominate the master.
Вся его решительность и энергия реализуется на охоте, а не для того, чтобы попытаться доминировать над хозяином.
The list is not in order of preference.
Those whose papers were not in order were held for further investigation.
Тех, у кого не в порядке документы, задерживаем для дальнейшего выяснения.
I can tell you absolutely confidently, not in order to throw someone bream.
Я могу сказать абсолютно уверенно, не ради того, чтобы закинуть кому-то леща.
Japanese engineers decided to get the car to rise above the carpet is not in order to teach it to fly.
Но японские инженеры решили заставить автомобиль приподниматься над покрытием вовсе не ради того, чтобы научить его летать.
I looked at it not in order to forget.
Such persons could be deported if their residency documents were not in order.
Такие лица могли быть депортированы, если их документы на проживание были не в порядке.
That’s for rescue dawn, fighter and machinist (not in order).
Это для спасательного рассвета, истребителя и машиниста (не в порядке).
So it seemed to her that she dresses for herself, not in order to deliver someone pleasure.
Так ей казалось, что она одевается для себя, а не для того, чтобы доставить кому-то удовольствие.
You travel, not in order to prove that you live better.
Ты путешествуешь не для того, чтобы доказать, что ты живешь лучше.
Here people live not for the sake of tourists and not in order to earn money for visitors.
Здесь люди живут не ради туристов и не для того, чтобы заработать денег на приезжих.
I say this not in order to condemn those women who sell their bodies.
Я это говорю вовсе не для того, чтобы осудить тех женщин, которые торгуют собственным телом.
Your papers are not in order, please get off at the next station.
У вас документы не в порядке; извольте сойти на ближайшей станции.
Feminists start such conversations not in order to scandalize or let out negative emotions.
Американки начинают такие разговоры не для того, чтобы поскандалить или выплеснуть негативные эмоции.
Of course, not in order to play.
Sometimes that thyroid is not in order, will know only when examining about other diseases.
Иногда о том, что щитовидка не в порядке, узнают только при обследовании по поводу других болезней.
But not in order to possess her.
If the graphics card was initially not in order, then with a longer artificial load, the card may finally break.
Если видеокарта изначально была не в порядке, то при большем времени искусственных нагрузок карта может окончательно сломаться.
After all, people come here for communication, and not in order to watch commercials or distribute spam.
Ведь люди приходят сюда за общением, а не для того, чтобы смотреть на рекламные ролики или распространять спам.
Suggestions that contain not in order
Results: 473. Exact: 473. Elapsed time: 697 ms.
Documents
Corporate solutions
Conjugation
Synonyms
Grammar Check
Help & about
Word index: 1-300, 301-600, 601-900
Expression index: 1-400, 401-800, 801-1200
Phrase index: 1-400, 401-800, 801-1200
How to pronounce not in order?
How to say not in order in sign language?
Numerology
-
Chaldean Numerology
The numerical value of not in order in Chaldean Numerology is: 6
-
Pythagorean Numerology
The numerical value of not in order in Pythagorean Numerology is: 6
Examples of not in order in a Sentence
-
Ivan Sigal:
Facebook your house is not in order.
-
Angelos Tsiaras:
But of course this is not in order to find a place where we could go. This is still science fiction.
-
Ludwig Wittgenstein:
I don’t know why we are here, but I’m pretty sure that it is not in order to enjoy ourselves.
-
Miguel de Unamuno:
We need God, not in order to understand the why, but in order to feel and sustain the ultimate wherefore, to give a meaning to the universe.
Translation
Find a translation for the not in order definition in other languages:
Select another language:
- — Select —
- 简体中文 (Chinese — Simplified)
- 繁體中文 (Chinese — Traditional)
- Español (Spanish)
- Esperanto (Esperanto)
- 日本語 (Japanese)
- Português (Portuguese)
- Deutsch (German)
- العربية (Arabic)
- Français (French)
- Русский (Russian)
- ಕನ್ನಡ (Kannada)
- 한국어 (Korean)
- עברית (Hebrew)
- Gaeilge (Irish)
- Українська (Ukrainian)
- اردو (Urdu)
- Magyar (Hungarian)
- मानक हिन्दी (Hindi)
- Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Italiano (Italian)
- தமிழ் (Tamil)
- Türkçe (Turkish)
- తెలుగు (Telugu)
- ภาษาไทย (Thai)
- Tiếng Việt (Vietnamese)
- Čeština (Czech)
- Polski (Polish)
- Bahasa Indonesia (Indonesian)
- Românește (Romanian)
- Nederlands (Dutch)
- Ελληνικά (Greek)
- Latinum (Latin)
- Svenska (Swedish)
- Dansk (Danish)
- Suomi (Finnish)
- فارسی (Persian)
- ייִדיש (Yiddish)
- հայերեն (Armenian)
- Norsk (Norwegian)
- English (English)
Word of the Day
Would you like us to send you a FREE new word definition delivered to your inbox daily?
Citation
Use the citation below to add this definition to your bibliography:
Are we missing a good definition for not in order? Don’t keep it to yourself…
-
#1
I understand that all the following sentences are correct:
«He got up early to have time to pack»
«He got up early in order to have time to pack»
«He got up early so as to have time to pack»
But what about their negatives?
«He got up early NOT to be late»
«He got up early in order NOT to be late»
«He got up early so as NOT to be late»
-
#2
I understand that all the following sentences are correct:
«He got up early to have time to pack»
«He got up early in order to have time to pack»
«He got up early so as to have time to pack»But what about their negatives?
«He got up early NOT to be late»
«He got up early in order NOT to be late»
«He got up early so as NOT to be late»
The last one is probably the most idiomatic.
-
#3
Then I suppose that «NOT to» as used in the following 1903 poem is only used as an old-fashioned form and not in use any longer. Am I right?
«1By such an all-embalming summer day
2As sweetens now among the mountain pines
3Down to the cornland yonder and the vines,
4To where the sky and sea are mixed in gray,
5How do all things together take their way
6Harmonious to the harvest, bringing wines
7And bread and light and whatsoe’er combines
8In the large wreath to make it round and gay.
9To me my troubled life doth now appear
10Like scarce distinguishable summits hung
11Around the blue horizon: places where
12Not even a traveller purposeth to steer, —
13Whereof a migrant bird in passing sung,
14And the girl closed her window not to hear.»
-
#4
Not to be late creo que es correcto, el infinitivo en negativo es NOT TO.cheers
-
#5
Then I suppose that «NOT to» as used in the following 1903 poem is only used as an old-fashioned form and not in use any longer. Am I right?
[…]
14And the girl closed her window not to hear.»
It may have only been acceptable in poetic usage even then.
-
#6
«
«He got up early NOT to be late»
It sounds strange, but I’m not sure that I would say it’s incorrect. By incorrect, I mean an impossible combination, not a violation of a prescriptive rule. The most natural way for me to express the idea is to say, ‘he got up early so he wouldn’t be late’.It’s an interesting point to ponder.
-
#7
I understand that all the following sentences are correct:
«He got up early to have time to pack»
«He got up early in order to have time to pack»
«He got up early so as to have time to pack»But what about their negatives?
«He got up early NOT to be late»
«He got up early in order NOT to be late»
«He got up early so as NOT to be late»
-
#8
http://www.bbc.co.uk/worldservice/learningenglish/youmeus/learnit/learnitv146.shtml
In order to is normal before a negative infinitive. We do not usually use to by itself here:
- In order not to oversleep, I set the alarm for seven o’clock.
- I walked very slowly across the room with the drinks in order not to spill them
Compare the following:
- He’s staying on in Australia for nine more months so that he can perfect his English.
- He’s staying on in Australia for nine more months in order to perfect his English.
- We’re going to leave by three so that we don’t get stuck in the rush-hour traffic.
- We’re going to leave by three so as not to get stuck in the rush-hour traffic.
- Jamie had an afternoon nap so that he wouldn’t fall asleep at the concert later.
- Jamie had an afternoon nap in order not to fall asleep at the concert later.
- In order that you may pass the exam, we recommend you read through all your notes. (Very formal.)
- In order to pass the exam, we recommend you read through all your notes. (Less formal.)
uplasep.
Chile.
Verb
They ordered everyone out of the house.
The soldiers were ordered back to the base.
“Stop! Drop your weapon!” ordered the officer.
The court threw out the conviction and ordered a new trial.
The judge ordered that the charges be dismissed.
He was accused of ordering the murder of his wife.
I ordered the books from the company’s website.
The shirt you ordered should arrive in the mail in a couple of days.
To order, call the number at the bottom of your screen.
Order now and receive a free gift!
Noun
That’s an order, not a request!
Failing to comply with an order will result in the loss of your job.
She received an order to appear in court.
They can’t close down the school without an order from the governor’s office.
The mayor gave an order to evacuate the city.
It’s not his fault. He was only following orders.
I’m not taking orders from you! You’re not my boss.
The city was evacuated by order of the mayor.
The store received an order for 200 roses this morning.
They had trouble filling large customer orders.
See More
Recent Examples on the Web
For the past three seasons, Fox has ordered more episodes around mid-May.
—
That sum is in addition to the more than $293,000 that Daniels had been ordered to pay after losing a libel case against the former president in federal district court and $245,000 for unsuccessfully pursuing an earlier appeal.
—
In addition to probation, Miles and Butler must complete 40 hours of community service, and they were fined $200 and ordered to pay $300 in victims’ compensation.
—
Customers who order via the app or El Pollo Loco website will get free delivery.
—
That ruling, which came out of a district court in Texas in early 2022, ordered the U.S. to pay $230 million to victims of the shooting in Sutherland Springs, a ruling that was contested by the federal government.
—
The judge later ordered the federal government to pay more than $230 million in damages to roughly 80 victims and relatives of those killed.
—
The settlement is less than the $230 million that Rodriguez had ordered the government to pay families and the victims last year, but the Justice Department appealed that ruling.
—
If approved by Attorney General Merrick Garland, the settlement would end the government’s appeal of a judge’s verdict last year ordering the feds to pay more than $230 million in damages.
—
When the shelter-in-place order went into effect in 2020, biophilic tones like browns and greens mimicked the connection with the great outdoors that so many people desperately craved.
—
Hernandez drove in three of the Bobcats’ seven runs out of the 9-hole in the order.
—
In the sixth inning, the Phillies didn’t turn to their bench to replace any of the three lefties at the bottom of their order.
—
However, Boeing said the issue was limited to certain 787s while the FAA order would cover all of them.
—
The hexagons were talismans of order and plenty.
—
The order was introduced at the beginning of the pandemic and allows for the rapid expulsion of migrants at the border.
—
Texas guard transfer Junior Angilau is still limited, explaining the order at left guard.
—
The height of the Galactic Empire, this period is also known as the Golden Age of the Jedi, a time when the ancient order was at its peak.
—
See More
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word ‘order.’ Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Скачать материал

Скачать материал




- Сейчас обучается 268 человек из 64 регионов


- Сейчас обучается 396 человек из 63 регионов


Описание презентации по отдельным слайдам:
-
1 слайд
Word Meaning
Lecture # 6
Grigoryeva M. -
2 слайд
Word Meaning
Approaches to word meaning
Meaning and Notion (понятие)
Types of word meaning
Types of morpheme meaning
Motivation
-
3 слайд
Each word has two aspects:
the outer aspect
( its sound form)
catthe inner aspect
(its meaning)
long-legged, fury animal with sharp teeth
and claws -
4 слайд
Sound and meaning do not always constitute a constant unit even in the same language
EX a temple
a part of a human head
a large church -
5 слайд
Semantics (Semasiology)
Is a branch of lexicology which studies the
meaning of words and word equivalents -
6 слайд
Approaches to Word Meaning
The Referential (analytical) approachThe Functional (contextual) approach
Operational (information-oriented) approach
-
7 слайд
The Referential (analytical) approach
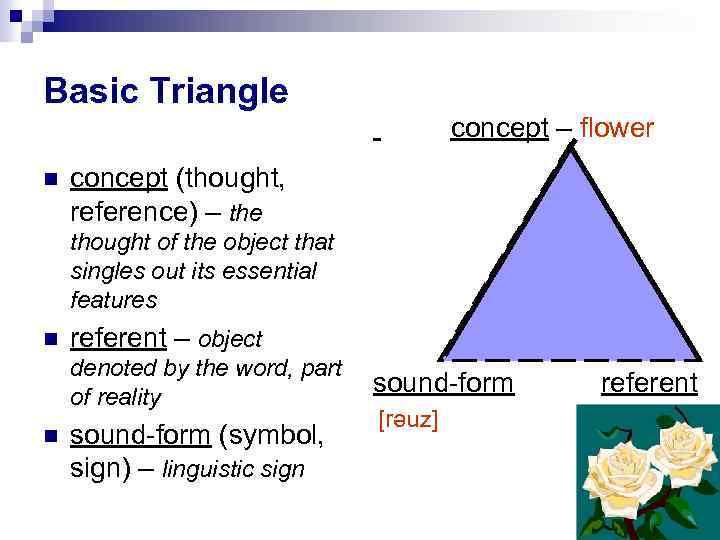
formulates the essence of meaning by establishing the interdependence between words and things or concepts they denotedistinguishes between three components closely connected with meaning:
the sound-form of the linguistic sign,
the concept
the actual referent -
8 слайд
Basic Triangle
concept (thought, reference) – the thought of the object that singles out its essential features
referent – object denoted by the word, part of reality
sound-form (symbol, sign) – linguistic sign
concept – flowersound-form referent
[rәuz] -
9 слайд
In what way does meaning correlate with
each element of the triangle ?In what relation does meaning stand to
each of them? -
10 слайд
Meaning and Sound-form
are not identical
different
EX. dove — [dΛv] English sound-forms
[golub’] Russian BUT
[taube] German
the same meaning -
11 слайд
Meaning and Sound-form
nearly identical sound-forms have different meanings in different languages
EX. [kot] Russian – a male cat
[kot] English – a small bed for a childidentical sound-forms have different meanings (‘homonyms)
EX. knight [nait]
night [nait] -
12 слайд
Meaning and Sound-form
even considerable changes in sound-form do not affect the meaningEX Old English lufian [luvian] – love [l Λ v]
-
13 слайд
Meaning and Concept
concept is a category of human cognitionconcept is abstract and reflects the most common and typical features of different objects and phenomena in the world
meanings of words are different in different languages
-
14 слайд
Meaning and Concept
identical concepts may have different semantic structures in different languagesEX. concept “a building for human habitation” –
English Russian
HOUSE ДОМ+ in Russian ДОМ
“fixed residence of family or household”
In English HOME -
15 слайд
Meaning and Referent
one and the same object (referent) may be denoted by more than one word of a different meaning
cat
pussy
animal
tiger -
16 слайд
Meaning
is not identical with any of the three points of the triangle –
the sound form,
the concept
the referentBUT
is closely connected with them. -
17 слайд
Functional Approach
studies the functions of a word in speech
meaning of a word is studied through relations of it with other linguistic units
EX. to move (we move, move a chair)
movement (movement of smth, slow movement)The distriution ( the position of the word in relation to
others) of the verb to move and a noun movement is
different as they belong to different classes of words and
their meanings are different -
18 слайд
Operational approach
is centered on defining meaning through its role in
the process of communicationEX John came at 6
Beside the direct meaning the sentence may imply that:
He was late
He failed to keep his promise
He was punctual as usual
He came but he didn’t want toThe implication depends on the concrete situation
-
19 слайд
Lexical Meaning and Notion
Notion denotes the reflection in the mind of real objectsNotion is a unit of thinking
Lexical meaning is the realization of a notion by means of a definite language system
Word is a language unit -
20 слайд
Lexical Meaning and Notion
Notions are international especially with the nations of the same cultural levelMeanings are nationally limited
EX GO (E) —- ИДТИ(R)
“To move”
BUT !!!
To GO by bus (E)
ЕХАТЬ (R)EX Man -мужчина, человек
Она – хороший человек (R)
She is a good person (E) -
21 слайд
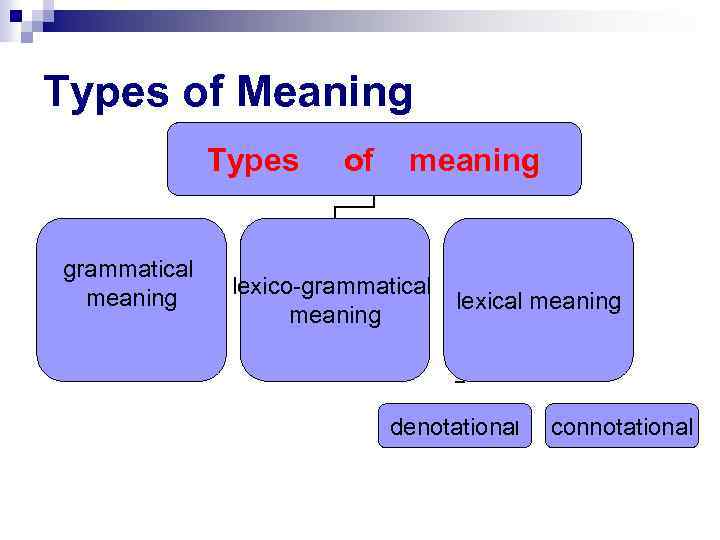
Types of Meaning
Types of meaninggrammatical
meaninglexico-grammatical
meaning
lexical meaning
denotational
connotational -
22 слайд
Grammatical Meaning
component of meaning recurrent in identical sets of individual forms of different wordsEX. girls, winters, toys, tables –
grammatical meaning of pluralityasked, thought, walked –
meaning of past tense -
23 слайд
Lexico-grammatical meaning
(part –of- speech meaning)
is revealed in the classification of lexical items into:
major word classes (N, V, Adj, Adv)
minor ones (artc, prep, conj)words of one lexico-grammatical class have the same paradigm
-
24 слайд
Lexical Meaning
is the meaning proper to the given linguistic unit in all its forms and distributionsEX . Go – goes — went
lexical meaning – process of movement -
25 слайд
PRACTICE
Group the words into 3 column according to the grammatical, lexical or part-of –speech meaning
Boy’s, nearest, at, beautiful,
think, man, drift, wrote,
tremendous, ship’s, the most beautiful,
table, near, for, went, friend’s,
handsome, thinking, boy,
nearer, thought, boys,
lamp, go, during. -
26 слайд
Grammatical
The case of nouns: boy’s, ship’s, friend’s
The degree of comparison of adj: nearest, the most beautiful
The tense of verbs: wrote, went, thoughtLexical
Think, thinking, thought
Went, go
Boy’s, boy, boys
Nearest, near, nearer
At, for, during (“time”)
Beautiful, the most beautifulPart-of-speech
Nouns—verbs—adj—-prep -
27 слайд
Aspects of Lexical meaning
The denotational aspectThe connotational aspect
The pragmatic aspect
-
28 слайд
Denotational Meaning
“denote” – to be a sign of, stand as a symbol for”establishes the correlation between the name and the object
makes communication possibleEX booklet
“a small thin book that gives info about smth” -
29 слайд
PRACTICE
Explain denotational meaningA lion-hunter
To have a heart like a lion
To feel like a lion
To roar like a lion
To be thrown to the lions
The lion’s share
To put your head in lion’s mouth -
30 слайд
PRACTICE
A lion-hunter
A host that seeks out celebrities to impress guests
To have a heart like a lion
To have great courage
To feel like a lion
To be in the best of health
To roar like a lion
To shout very loudly
To be thrown to the lions
To be criticized strongly or treated badly
The lion’s share
Much more than one’s share
To put your head in lion’s mouth -
31 слайд
Connotational Meaning
reflects the attitude of the speaker towards what he speaks about
it is optional – a word either has it or notConnotation gives additional information and includes:
The emotive charge EX Daddy (for father)
Intensity EX to adore (for to love)
Imagery EX to wade through a book
“ to walk with an effort” -
32 слайд
PRACTICE
Give possible interpretation of the sentencesShe failed to buy it and felt a strange pang.
Don’t be afraid of that woman! It’s just barking!
He got up from his chair moving slowly, like an old man.
The girl went to her father and pulled his sleeve.
He was longing to begin to be generous.
She was a woman with shiny red hands and work-swollen finger knuckles. -
33 слайд
PRACTICE
Give possible interpretation of the sentences
She failed to buy it and felt a strange pang.
(pain—dissatisfaction that makes her suffer)
Don’t be afraid of that woman! It’s just barking!
(make loud sharp sound—-the behavior that implies that the person is frightened)
He got up from his chair moving slowly, like an old man.
(to go at slow speed—was suffering or was ill)
The girl went to her father and pulled his sleeve.
(to move smth towards oneself— to try to attract smb’s attention)
He was longing to begin to be generous.
(to start doing— hadn’t been generous before)
She was a woman with shiny red hands and work-swollen finger knuckles.
(colour— a labourer involved into physical work ,constant contact with water) -
34 слайд
The pragmatic aspect of lexical meaning
the situation in which the word is uttered,
the social circumstances (formal, informal, etc.),
social relationships between the interlocutors (polite, rough, etc.),
the type and purpose of communication (poetic, official, etc.)EX horse (neutral)
steed (poetic)
nag (slang)
gee-gee (baby language) -
35 слайд
PRACTICE
State what image underline the meaningI heard what she said but it didn’t sink into my mind.
You should be ashamed of yourself, crawling to the director like that.
They seized on the idea.
Bill, chasing some skirt again?
I saw him dive into a small pub.
Why are you trying to pin the blame on me?
He only married her for her dough. -
36 слайд
PRACTICE
State what image underline the meaning
I heard what she said but it didn’t sink into my mind.
(to understand completely)
You should be ashamed of yourself, crawling to the director like that.
(to behave humbly in order to win favour)
They seized on the idea.
(to be eager to take and use)
Bill, chasing some skirt again?
(a girl)
I saw him dive into a small pub.
(to enter suddenly)
Why are you trying to pin the blame on me?
(to blame smb unfairly)
He only married her for her dough.
(money) -
37 слайд
Types of Morpheme Meaning
lexical
differential
functional
distributional -
38 слайд
Lexical Meaning in Morphemes
root-morphemes that are homonymous to words possess lexical meaning
EX. boy – boyhood – boyishaffixes have lexical meaning of a more generalized character
EX. –er “agent, doer of an action” -
39 слайд
Lexical Meaning in Morphemes
has denotational and connotational components
EX. –ly, -like, -ish –
denotational meaning of similiarity
womanly , womanishconnotational component –
-ly (positive evaluation), -ish (deragotary) женственный — женоподобный -
40 слайд
Differential Meaning
a semantic component that serves to distinguish one word from all others containing identical morphemesEX. cranberry, blackberry, gooseberry
-
41 слайд
Functional Meaning
found only in derivational affixes
a semantic component which serves to
refer the word to the certain part of speechEX. just, adj. – justice, n.
-
42 слайд
Distributional Meaning
the meaning of the order and the arrangement of morphemes making up the word
found in words containing more than one morpheme
different arrangement of the same morphemes would make the word meaningless
EX. sing- + -er =singer,
-er + sing- = ? -
43 слайд
Motivation
denotes the relationship between the phonetic or morphemic composition and structural pattern of the word on the one hand, and its meaning on the othercan be phonetical
morphological
semantic -
44 слайд
Phonetical Motivation
when there is a certain similarity between the sounds that make up the word and those produced by animals, objects, etc.EX. sizzle, boom, splash, cuckoo
-
45 слайд
Morphological Motivation
when there is a direct connection between the structure of a word and its meaning
EX. finger-ring – ring-finger,A direct connection between the lexical meaning of the component morphemes
EX think –rethink “thinking again” -
46 слайд
Semantic Motivation
based on co-existence of direct and figurative meanings of the same wordEX a watchdog –
”a dog kept for watching property”a watchdog –
“a watchful human guardian” (semantic motivation) -
-
48 слайд
Analyze the meaning of the words.
Define the type of motivation
a) morphologically motivated
b) semantically motivatedDriver
Leg
Horse
Wall
Hand-made
Careless
piggish -
49 слайд
Analyze the meaning of the words.
Define the type of motivation
a) morphologically motivated
b) semantically motivated
Driver
Someone who drives a vehicle
morphologically motivated
Leg
The part of a piece of furniture such as a table
semantically motivated
Horse
A piece of equipment shaped like a box, used in gymnastics
semantically motivated -
50 слайд
Wall
Emotions or behavior preventing people from feeling close
semantically motivated
Hand-made
Made by hand, not machine
morphologically motivated
Careless
Not taking enough care
morphologically motivated
Piggish
Selfish
semantically motivated -
51 слайд
I heard what she said but it didn’t sink in my mind
“do down to the bottom”
‘to be accepted by mind” semantic motivationWhy are you trying to pin the blame on me?
“fasten smth somewhere using a pin” –
”to blame smb” semantic motivationI was following the man when he dived into a pub.
“jump into deep water” –
”to enter into suddenly” semantic motivationYou should be ashamed of yourself, crawling to the director like that
“to move along on hands and knees close to the ground” –
“to behave very humbly in order to win favor” semantic motivation
Найдите материал к любому уроку, указав свой предмет (категорию), класс, учебник и тему:
6 210 150 материалов в базе
- Выберите категорию:
- Выберите учебник и тему
- Выберите класс:
-
Тип материала:
-
Все материалы
-
Статьи
-
Научные работы
-
Видеоуроки
-
Презентации
-
Конспекты
-
Тесты
-
Рабочие программы
-
Другие методич. материалы
-
Найти материалы
Другие материалы
- 22.10.2020
- 141
- 0
- 21.09.2020
- 530
- 1
- 18.09.2020
- 256
- 0
- 11.09.2020
- 191
- 1
- 21.08.2020
- 197
- 0
- 18.08.2020
- 123
- 0
- 03.07.2020
- 94
- 0
- 06.06.2020
- 73
- 0
Вам будут интересны эти курсы:
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Формирование компетенций межкультурной коммуникации в условиях реализации ФГОС»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Клиническая психология: теория и методика преподавания в образовательной организации»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Введение в сетевые технологии»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «История и философия науки в условиях реализации ФГОС ВО»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Основы построения коммуникаций в организации»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Организация практики студентов в соответствии с требованиями ФГОС медицинских направлений подготовки»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Правовое регулирование рекламной и PR-деятельности»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Организация маркетинга в туризме»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Источники финансов»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Техническая диагностика и контроль технического состояния автотранспортных средств»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Осуществление и координация продаж»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Технический контроль и техническая подготовка сварочного процесса»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Управление качеством»
Inversion
Inversion
is a syntactic phenomenon of the deliberate changing of word order in
the initial sentence model. Word order is a crucial syntactical
problem in many languages. In English it has peculiarities which have
been caused by the concrete and specific way the language has
developed. The English language has developed a fixed word order
which in the great majority of cases shows without fails what is the
Subject of the sentence. This fixed word order is Subject— Verb
(Predicate) — Object (S—P—O).
This
predominance of fixed word order makes conspicuous any change in the
structure of the sentence and inevitably calls forth a modification
in the stylistic meanings.
There
are two types of inversion: grammatical and stylistic. Grammatical
inversion is aimed at the change of the communicative type of
sentence and has no stylistic value.
Stylistic
inversion is aimed at logical or emotional intensification of a
certain sentence element. It attaches the additional emotional
colouring to the surface meaning of the utterance. It is always
semantically and stylistically motivated:
Talent
Mr. Micawber has; capital Mr. Micawber has not (Ch. Dickens).
Rude
am I in my speech… ( W.Shakespeare).
Of
his own class he saw nothing (J. London).
Безбожний
царю, творче зла,
Правди
гонителю жестокий (Т. Шевченко).
Detachment
A
specific arrangement of sentence members is observed in detachment.
Detachment
(відокремлення)
is a stylistic device based on singling out structurally and
semantically a secondary member of the sentence with the help of
punctuation: dashes, commas or even a full stop. When placed in a
certain syntactic position, a detached sentence component may seem
formally independent of the words it refers to, though the word order
may not be violated and semantic connections between the elements
remain strong:
He
had been nearly killed, ingloriously, in a jeep accident (I. Show).
I
have to beg you for money. Daily (S. Lewis).
There
was a world of anticipation in her voice and of confidence too, as
she walked past me on to the terrace (D. du Maurier).
Горіли
свічки, сяяли в рушниках ікони…Але це
відійшло, розтануло разом з ладанними
димами, зостався…лише цей довершений
архітектурний витвір, оця симфонія
пластики (О. Гончар).
Due
to the detachment the adverbial modifiers ingloriously
and daily
and attributive construction
of
confidence in
the English examples and the subject оця
симфонія пластики
in the Ukrainian one have
become foregrounded into the reader’s focus of attention.
Stylistic
function of detachment is determined by the syntactic role of the
isolated element, its place in the sentence, general linguistic and
stylistic context of the utterance.
Detachment
is aimed at foregrounding of the isolated sentence element which
according to author’s standpoint acquires greater emotional or
logical importance. Detachment is used in descriptive and narrative
discourses in order to make a written text akin to the spoken one,
live and emotionally charged. Detachment is one of the most powerful
means of rendering speaker’s emotions or mirroring character’s
emotional /psychological state. It is used in descriptions of nature,
events, situations in order to impress the reader and to create the
presence effect:
Володькові
очі все ширшають і ширшають, на щоках
з’явились
рум’янці.
Щось дуже сильне тягне його туди. Так
хотілося б, так дуже хотілося б… Бачити.
Чути. Знати (У. Самчук).
Марта
ревнувала Антона. Уперто, затаєнно,
сильно, до всіх і до всього (М. Коцюбинський).
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
Word Meaning Lecture # 6 Grigoryeva M.
Word Meaning Approaches to word meaning Meaning and Notion (понятие) Types of word meaning Types of morpheme meaning Motivation
Each word has two aspects: the outer aspect ( its sound form) cat the inner aspect (its meaning) long-legged, fury animal with sharp teeth and claws
Sound and meaning do not always constitute a constant unit even in the same language EX a temple a part of a human head a large church
Semantics (Semasiology) Is a branch of lexicology which studies the meaning of words and word equivalents
Approaches to Word Meaning The Referential (analytical) approach The Functional (contextual) approach Operational (information-oriented) approach
The Referential (analytical) approach formulates the essence of meaning by establishing the interdependence between words and things or concepts they denote distinguishes between three components closely connected with meaning: the sound-form of the linguistic sign, the concept the actual referent
Basic Triangle concept – flower concept (thought, reference) – the thought of the object that singles out its essential features referent – object denoted by the word, part of reality sound-form (symbol, sign) – linguistic sign sound-form [rәuz] referent
In what way does meaning correlate with each element of the triangle ? • In what relation does meaning stand to each of them? •
Meaning and Sound-form are not identical different EX. dove — [dΛv] English [golub’] Russian [taube] German sound-forms BUT the same meaning
Meaning and Sound-form nearly identical sound-forms have different meanings in different languages EX. [kot] Russian – a male cat [kot] English – a small bed for a child identical sound-forms have different meanings (‘homonyms) EX. knight [nait]
Meaning and Sound-form even considerable changes in sound-form do not affect the meaning EX Old English lufian [luvian] – love [l Λ v]
Meaning and Concept concept is a category of human cognition concept is abstract and reflects the most common and typical features of different objects and phenomena in the world meanings of words are different in different languages
Meaning and Concept identical concepts may have different semantic structures in different languages EX. concept “a building for human habitation” – English Russian HOUSE ДОМ + in Russian ДОМ “fixed residence of family or household” In English HOME
Meaning and Referent one and the same object (referent) may be denoted by more than one word of a different meaning cat pussy animal tiger
Meaning is not identical with any of the three points of the triangle – the sound form, the concept the referent BUT is closely connected with them.
Functional Approach studies the functions of a word in speech meaning of a word is studied through relations of it with other linguistic units EX. to move (we move, move a chair) movement (movement of smth, slow movement) The distriution ( the position of the word in relation to others) of the verb to move and a noun movement is different as they belong to different classes of words and their meanings are different
Operational approach is centered on defining meaning through its role in the process of communication EX John came at 6 Beside the direct meaning the sentence may imply that: He was late He failed to keep his promise He was punctual as usual He came but he didn’t want to The implication depends on the concrete situation
Lexical Meaning and Notion denotes the Lexical meaning is reflection in the realization of a mind of real objects notion by means of a definite language system Notion is a unit of Word is a language thinking unit
Lexical Meaning and Notions are Meanings are internationally limited especially with the nations of the same EX GO (E) —- ИДТИ(R) cultural level “To move” BUT !!! To GO by bus (E) ЕХАТЬ (R) EX Man -мужчина, человек Она – хороший человек (R) She is a good person (E)
Types of Meaning Types grammatical meaning of meaning lexico-grammatical meaning lexical meaning denotational connotational
Grammatical Meaning component of meaning recurrent in identical sets of individual forms of different words EX. girls, winters, toys, tables – grammatical meaning of plurality asked, thought, walked – meaning of past tense
Lexico-grammatical meaning (part –of- speech meaning) is revealed in the classification of lexical items into: major word classes (N, V, Adj, Adv) minor ones (artc, prep, conj) words of one lexico-grammatical class have the same paradigm
Lexical Meaning is the meaning proper to the given linguistic unit in all its forms and distributions EX. Go – goes — went lexical meaning – process of movement
PRACTICE Group the words into 3 column according to the grammatical, lexical or part-of –speech meaning • • Boy’s, nearest, at, beautiful, think, man, drift, wrote, tremendous, ship’s, the most beautiful, table, near, for, went, friend’s, handsome, thinking, boy, nearer, thought, boys, lamp, go, during.
• Grammatical 1. The case of nouns: boy’s, ship’s, friend’s 2. The degree of comparison of adj: nearest, the most beautiful 3. The tense of verbs: wrote, went, thought • Lexical 1. Think, thinking, thought 2. Went, go 3. Boy’s, boys 4. Nearest, nearer 5. At, for, during (“time”) 6. Beautiful, the most beautiful • Part-of-speech Nouns—verbs—adj—-prep
Aspects of Lexical meaning The denotational aspect The connotational aspect The pragmatic aspect
Denotational Meaning “denote” – to be a sign of, stand as a symbol for” establishes the correlation between the name and the object makes communication possible EX booklet “a small thin book that gives info about smth”
PRACTICE Explain denotational meaning • • A lion-hunter To have a heart like a lion To feel like a lion To roar like a lion To be thrown to the lions The lion’s share To put your head in lion’s mouth
PRACTICE • A lion-hunter A host that seeks out celebrities to impress guests • To have a heart like a lion To have great courage • To feel like a lion To be in the best of health • To roar like a lion To shout very loudly • To be thrown to the lions To be criticized strongly or treated badly • The lion’s share Much more than one’s share • To put your head in lion’s mouth
Connotational Meaning reflects the attitude of the speaker towards what he speaks about it is optional – a word either has it or not Connotation gives additional information and includes: The emotive charge EX Daddy (for father) Intensity EX to adore (for to love) Imagery EX to wade through a book “ to walk with an effort”
PRACTICE Give possible interpretation of the sentences • She failed to buy it and felt a strange pang. • Don’t be afraid of that woman! It’s just barking! • He got up from his chair moving slowly, like an old man. • The girl went to her father and pulled his sleeve. • He was longing to begin to be generous. • She was a woman with shiny red hands and workswollen finger knuckles.
PRACTICE Give possible interpretation of the sentences • She failed to buy it and felt a strange pang. (pain—dissatisfaction that makes her suffer) • Don’t be afraid of that woman! It’s just barking! (make loud sharp sound—-the behavior that implies that the person is frightened) • He got up from his chair moving slowly, like an old man. (to go at slow speed—was suffering or was ill) • The girl went to her father and pulled his sleeve. (to move smth towards oneself— to try to attract smb’s attention) • He was longing to begin to be generous. (to start doing— hadn’t been generous before) • She was a woman with shiny red hands and work-swollen finger knuckles. (colour— a labourer involved into physical work , constant contact with water)
The pragmatic aspect of lexical meaning the situation in which the word is uttered, the social circumstances (formal, informal, etc. ), social relationships between the interlocutors (polite, rough, etc. ), the type and purpose of communication (poetic, official, etc. ) EX horse (neutral) steed (poetic) nag (slang) gee-gee (baby language)
PRACTICE State what image underline the meaning • I heard what she said but it didn’t sink into my mind. • You should be ashamed of yourself, crawling to the director like that. • They seized on the idea. • Bill, chasing some skirt again? • I saw him dive into a small pub. • Why are you trying to pin the blame on me? • He only married her for her dough.
PRACTICE State what image underline the meaning • I heard what she said but it didn’t sink into my mind. • (to understand completely) • You should be ashamed of yourself, crawling to the director like that. (to behave humbly in order to win favour) • They seized on the idea. (to be eager to take and use) • Bill, chasing some skirt again? (a girl) • I saw him dive into a small pub. (to enter suddenly) • Why are you trying to pin the blame on me? (to blame smb unfairly) • He only married her for her dough. (money)
Types of Morpheme Meaning lexical differential functional distributional
Lexical Meaning in Morphemes root-morphemes that are homonymous to words possess lexical meaning EX. boy – boyhood – boyish affixes have lexical meaning of a more generalized character EX. –er “agent, doer of an action”
Lexical Meaning in Morphemes has denotational and connotational components EX. –ly, -like, -ish – denotational meaning of similiarity womanly , womanish connotational component – -ly (positive evaluation), -ish (deragotary) женственный женоподобный
Differential Meaning a semantic component that serves to distinguish one word from all others containing identical morphemes EX. cranberry, blackberry, gooseberry
Functional Meaning found only in derivational affixes a semantic component which serves to refer the word to the certain part of speech EX. just, adj. – justice, n.
Distributional Meaning the meaning of the order and the arrangement of morphemes making up the word found in words containing more than one morpheme different arrangement of the same morphemes would make the word meaningless EX. sing- + -er =singer, -er + sing- = ?
Motivation denotes the relationship between the phonetic or morphemic composition and structural pattern of the word on the one hand, and its meaning on the other can be phonetical morphological semantic
Phonetical Motivation when there is a certain similarity between the sounds that make up the word and those produced by animals, objects, etc. EX. sizzle, boom, splash, cuckoo
Morphological Motivation when there is a direct connection between the structure of a word and its meaning EX. finger-ring – ring-finger, A direct connection between the lexical meaning of the component morphemes EX think –rethink “thinking again”
Semantic Motivation based on co-existence of direct and figurative meanings of the same word EX a watchdog – ”a dog kept for watching property” a watchdog – “a watchful human guardian” (semantic motivation)
• PRACTICE
Analyze the meaning of the words. Define the type of motivation a) morphologically motivated b) semantically motivated • Driver • Leg • Horse • Wall • Hand-made • Careless • piggish
Analyze the meaning of the words. Define the type of motivation a) morphologically motivated b) semantically motivated • Driver Someone who drives a vehicle morphologically motivated • Leg The part of a piece of furniture such as a table semantically motivated • Horse A piece of equipment shaped like a box, used in gymnastics semantically motivated
• Wall Emotions or behavior preventing people from feeling close semantically motivated • Hand-made Made by hand, not machine morphologically motivated • Careless Not taking enough care morphologically motivated • Piggish Selfish semantically motivated
what she said but it didn’t sink in my mind “do down to the bottom” ‘to be accepted by mind” semantic motivation I heard Why are you trying to pin the blame on me? “fasten smth somewhere using a pin” – ”to blame smb” semantic motivation I was following the man when he dived into a pub. “jump into deep water” – ”to enter into suddenly” semantic motivation You should be ashamed of yourself, crawling to the director like that “to move along on hands and knees close to the ground” – “to behave very humbly in order to win favor” semantic motivation










![Meaning and Sound-formare not identical
different
EX. dove - [dΛv]... Meaning and Sound-formare not identical
different
EX. dove - [dΛv]...](https://documents.infourok.ru/2d0c9b9d-1c12-4da2-8c1e-80496902c301/slide_10.jpg)

















































![Meaning and Sound-form are not identical different EX. dove - [dΛv] English [golub’] Russian Meaning and Sound-form are not identical different EX. dove - [dΛv] English [golub’] Russian](https://present5.com/presentation/54919015_285694613/image-10.jpg)
![Meaning and Sound-form nearly identical sound-forms have different meanings in different languages EX. [kot] Meaning and Sound-form nearly identical sound-forms have different meanings in different languages EX. [kot]](https://present5.com/presentation/54919015_285694613/image-11.jpg)