-
The object of semasiology.
Two approaches to the study of meaning. -
Types of meaning.
-
Meaning and motivation.
3.1.
The branch of lexicology which studies meaning is called
«semasiology«.
Sometimes the term «semantics»
is used as a synonym to semasiology, but it is ambiguous as it can
stand as well for (1)
the expressive aspect of language in general and (2)
the meaning of one particular word.
Meaning
is certainly the most important property of the word but what is
«meaning»?
Meaning
is one of the most controversial terms in lexicology. At present
there is no generally accepted definition of meaning. Prof.
Smirnitsky defines meaning as «a certain reflection in the mind
of objects, phenomena or relations that makes part of the linguistic
sign, its so-called inner facet, whereas the sound form functions as
its outer facet». Generally speaking, meaning can be described
as a component of the word through which a concept is communicated,
enabling the word to denote objects in the real world.
There are
two
approaches
to the study of meaning: the
referential approach
and the
functional approach.
The former tries to define meaning in terms of relations between the
word (sound form), concept (notion, thought) and referent (object
which the word denotes). They are closely connected and the
relationship between them is represented by «the semiotic
triangle» ( = the basic triangle) of Ogden and Richards (in the
book «The Meaning of Meaning» (1923) by O.K. Ogden and I.A.
Richards).

symbol
referent
(sound form)
This view denies a direct link
between words and things, arguing that the relationship can be made
only through the use of our minds. Meaning is related to a sound
form, concept and referent but not identical with them: meaning is a
linguistic phenomenon while neither concept nor referent is.
The
main criticism of this approach is the difficulty of identifying
«concepts»: they are mental phenomena and purely
subjective, existing
in the minds of individuals. The strongest point of this approach is
that it connects meaning and the process of nomination.
The functional approach to
meaning is less concerned with what meaning is than with how it
works. It is argued, to say that «words have meanings»
means only that they are used in a certain way in a sentence. There
is no meaning beyond that. Ludwig Wittgenstein (1889-1951), in
particular, stressed the importance of this approach in his dictum:
«The meaning of the word is its use in the language». So
meaning is studied by making detailed analyses of the way words are
used in contexts, through their relations to other words in speech,
and not through their relations to concepts or referents.
Actually,
the functional approach is basically confined to the analysis of
sameness or difference of meaning. For example, we can say that in
«take
the bottle»
and «take
to the
bottle»
take
has different meaning as it is used differently, but it does not
explain what the meaning of the verb is. So the functional approach
should
be used not as the theoretical basis for the study of meaning, but
only as complementary to the referential approach.
3.2.
Word meaning is made up of different components, commonly known
as types
of meaning.
The two main types of meaning are grammatical
meaning and
lexical meaning.
Grammatical
meaning
belongs to sets of word-forms and is common to
all words of the given part of speech,
e.g.
girls,
boys, classes, children, mice
express the meaning of
«plurality».
Lexical
meaning
belongs to an individual word in all its forms. It
comprises several components. The two main ones are the
denotational
component and
the connotational component.
The
denotational (
=
denotative)
component,
also called «referential
meaning» or «cognitive meaning», expresses the
conceptual (notional)
content of a word; broadly, it is some information, or knowledge,
of the real-world object that the word denotes.
Basically, this is the component that makes communication possible.
e.g.
notorious
«widely-known»,
celebrated «known
widely».
The
connotational (connotative) component
expresses the attitude of
the speaker to what he is saying, to the object denoted by the word.
This component consists of emotive
connotation and
evaluative connotation.
1) Emotive
connotation
( = «affective meaning», or an emotive charge),
e.g.
In «a
single tree»
single states that there is only one tree,
but
«a
lonely tree»
besides giving the same information, also renders
(conveys) the feeling of sadness.
We
shouldn’t confuse emotive connotations and emotive denotative
meanings
in which some emotion is named, e.g. horror,
love, fear, etc.
2) Evaluative
connotation
labels
the referent as «good» or «bad»,
e.g.
notorious
has a negative evaluative connotation, while
celebrated
a positive one. Cf.: a
notorious criminal/liar/ coward,
etc.
and a
celebrated singer/ scholar/ artist, etc.
It
should be noted that emotive and evaluative connotations are not
individual, they are common to all speakers of the language. But
emotive implications are individual (or common to a group of
speakers),
subjective, depend on personal experience.
e.g.
The word «hospital»
may evoke all kinds of emotions in
different
people (an
architect, a doctor, an invalid, etc.)
Stylistic
connotation,
or stylistic reference, another component of word meaning, stands
somewhat apart from emotive and evaluative connotations. Indeed, it
does not characterize a referent, but rather states how a word should
be used by referring it to a certain functional style of the language
peculiar to a specific sphere of communication. It shows in what
social context, in what communicative situations the word can be
used.
Stylistically,
words can be roughly classified into literary,
or formal
(e.g.
commence, discharge, parent),
neutral
(e.g.
father, begin, dismiss)
and non-literary,
or informal
(e.g.
dad, sack, set off).
3.3.
The term «motivation»
is used to denote the relationship between the
form of the word, i.e. its sound form, morphemic composition and
structural pattern, and its meaning.
There
are three
main types of motivation:
phonetic,
morphological
and
semantic.
1)
Phonetic
motivation
is a direct connection between the sound form
of a word and its meaning. There are two types of phonetic
motivation: sound
imitation and
sound symbolism.
a) Sound
imitation, or
onomatopoeia:
phonetically motivated words are
a direct imitation of the sounds they denote (or the sounds produced
by actions or objects they denote),
e.g.
buzz,
swish, bang, thud, cuckoo.
b) Sound
symbolism.
It’s argued by some linguists that the sounds that make up a word may
reflect or symbolise the properties of the object which the word
refers
to, i.e. they may suggest size, shape, speed, colour, etc.
e.g.
back
vowels
suggest big size, heavy weight, dark colour, front
vowels
suggest lightness, smallness, etc.
Many
words beginning with sl-
are slippery in some way: slide,
slip, slither, sludge,
etc.
or pejorative: slut,
slattern, sly, sloppy, slovenly;
words that end in -ump
almost
all refer to some kind of roundish mass: plump,
chump,
rump, hump, stump.
Certainly, not every word with
these phonetic characteristics will have the meaning suggested. This
is, perhaps, one of the reasons why sound symbolism is not
universally recognized in linguistics.
2) Morphological
motivation
is
a direct connection between the lexical meaning of the component
morphemes, the pattern of their arrangement and the meaning of the
word.
Morphologically motivated
words are those whose meaning is determined by the meaning of their
components,
e.g.
re-write
«write
again»,
ex-wife «former
wife».
The degree
of morphological motivation may be different. Words may be
fully
motivated
(then they are transparent), partially
motivated
and
non-motivated
(idiomatic, or opaque).
a)
If the meaning of the word is determined by the meaning of the
components
and the structural pattern, it is fully
motivated:
e.g. hatless.
b)
If the connection between the morphemic composition of a word and
its meaning is arbitrary, the word is non-motivated,
e.g. buttercup
«yellow-flowered plant».
c)
In hammer
-er
shows that it is an instrument, but what is «hamming«?
«Ham»
has no lexical meaning in this word, thus the word is partially
motivated.
Cf. also cranberry.
Motivation may be lost in the
course of time,
e.g.
in OE wīfman
was
motivated morphologically: wīf
+ man «wife
of a man»; now it is opaque;
its motivation is said to be faded (woman).
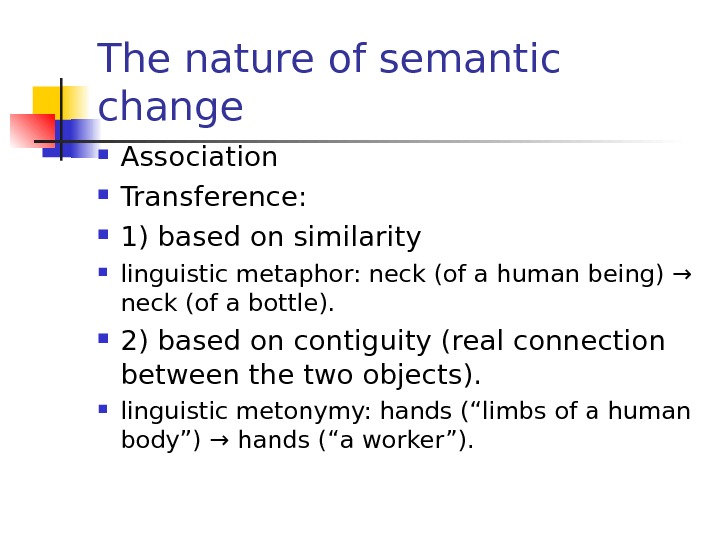
3) Semantic
motivation
is based on co-existence of direct and figurative
meanings of the same word,
e.g.
butterfly
–
1) insect; 2) showy and
frivolous person.( = metaphorical extension of the direct meaning).
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- Размер: 250 Кб
- Количество слайдов: 17
















1. Word Meaning
1. Two schools of thought.
2. Denotation and connotation. Types of
connotation.
3. Polysemy.
4. Semantic changes (metaphor,
metonymy, narrowing /specialization,
broadening /generalization).
5. Secondary ways of semantic change.
2.
• The term semasiology comes from Greek
sema «sign» + semantikos «significant»
• It was introduced into linguistic studies in
1825 by the classical scholar C. Reisig
who set up a new division of grammar
(semasiology, etymology and syntax).
• He regarded semasiology as a historical
discipline that should establish the
principles of governing the
development of meaning.
3.
• In 1883 Michel Breal (the French
philologist) published an article in which
he argued that there ought to be a
science of meaning which he proposed
to call semasiology.
• In 1897 he published his book which
soon spread to other languages and in
1900 after its publication was translated
into English under the title: Semantics:
Studies in the Science of Meaning.
4.
• Another famous book on semantics is The
meaning of meaning by С. К. Ogden and I. A.
Richards published in 1923.
• The term semantics was first used to refer to
the development and change of meaning. It
is originated from Greek word «semantikos»
(«significant“).
• It is the study of meanings – dealing with the
relationship between symbols (words, signs,
etc.) and what they refer to (‘referents’) – and
of behavior in reaction to non-verbal
symbols and verbal symbols (words).
5. Two schools of thought
• relative or
functional
approach
• denotational or
referential
approach
• The relative approach is based on treating the
language as a semiotic system – the theory of
relations .
• The denotational trend of semantic studies
considers a word as a unit possessing its own
meaning.
6. Relative approach
• Each sign achieves a meaning only in
comparison with other signs, its neighbours:
meaning can be studied only through context.
CONTEXT
Extra-linguistic
Linguistic
Lexical
Grammatical
Mixed
7. Referential approach
• The main problem is the relation
between the word, its meaning and the
object in reality which it denotes.
• The basis of the denotational theory is
the double nature (ideal and material) of
the word.
• The material side of the word (symbol),
its meaning, and the referent are
connected with one another.
8.
• The meaning of a word is the reflection of the
objective reality in our consciousness.
Concept-notion
Linguistic sign
Referent
• The word is a form of a notion’s material
existence.
9.
• Every word has two aspects: the outer
aspect (its sound form) and the inner
aspect (its meaning).
• The lexical meaning of a word is the
realization of a notion by means of a
definite language system.
• A word is a language unit, while a
notion is a unit of thinking.
• A notion denotes the reflection in the
mind of real objects and phenomena in
their essential features and relations.
10.
• Notions, as a rule, are international.
• Meanings can be nationally limited.
• The development of lexical
meanings in any language, as well
as the grouping of meanings in
the semantic structure of a word, is
determined by the whole system
of every language.
11.
• Word meaning is made up of various
components. There are 2 important elements
of the meaning:
denotation
connotation
• the denotational – the realization of the notion
(which makes communication possible) and
the connotational – the pragmatic
communicative value of the word.
12.
• The denotation of a word is the direct
explicit meaning that makes
communication possible.
• When we say that a word denotes
something, we mean that it is the name
of a thing.
• To denote is to serve as a linguistic
expression for a concept.
• The conceptual content of a word is
expressed in its denotative meaning.
13.
• The connotation of a word is what the word
implies in addition to its denotational meaning.
It is the set of associations that a word’s use
can evoke:
• a hovel denotes «a small house» and besides
implies that it is a miserable dwelling place,
dirty, in bad repair, and, in general, unpleasant
to live in.
• We call connotation what the word conveys
about the speaker’s attitude to the social
circumstances and the appropriate functional
style, about his approval or disapproval of the
object spoken, or the degree of intensity.
14.
There are 4 main types of connotation:
stylistic (to beat it – to retire, horse –
steed),
emotive (dog – doggie),
evaluative (famous/ well-known –
notorious), and
expressive or intensifying (splendid,
superb, fantastic, beastly, etc. are used
colloquially as terms of exaggeration).
We can also speak of pragmatic
connotations, i.e., those of duration,
manner, attending circumstances, etc.
15.
• The connotation is the idea suggested by its
place near /in association with other words or
phrases.
• Childlike and childish both have the
denotation of «like or characteristic of a
child». However the two words have their own
connotations.
• Childlike suggests the favourable qualities
considered typical of a child: innocence and
trustworthiness.
• Childish connotes the unfavourable
characteristics of a child: foolishness or
immaturity.
16.
• The context of the word can also help to
reveal the general and added meanings.
The context is the part of the statement in
which the word or passage at issue
occurs, that which leads up to and follows
a particular expression:
• The actress captured perfectly the
character’s childlike qualities in her
performance.
• Your childish behaviour is quite
annoying in a grown person.
17.
• Denotative and connotative
components make up the semantic
structure (or semantic paradigm) of a
word which is presented by a structure
of semes.
• A seme is the smallest unit of
meaning.
• Thus, the meaning of the word giggle
includes semes of action, living
being and sex, negative evaluation
and intensity.
18.
• KEY TERMS: semasiology, semantics,
relative, referential, denotation,
connotation, seme.
• Антрушина Г.Б., Афанасьева О.В.,
Морозова Н.Н. Лексикология
английского языка. – стр. 147-151; 193197.
• Елисеева В.В. Лексикология
английского языка.



