Are there any words that have this meaning?
One of many, as in a person out of many people.
Clarification:
The single individual or item is similar to the group and not unique in any way.
asked Jun 21, 2017 at 17:19
AzizAziz
1111 gold badge1 silver badge5 bronze badges
14
Specimen — An individual animal, plant, piece of a mineral, etc. used as an example of its species or type for scientific study or display.
‘Carla could not help feeling a degree of reluctant admiration for
this odd female specimen’
ODO.
answered Jun 21, 2017 at 18:05
Depending on context, the word clone might suit. One of the definitions given in the Oxford Dictionary online is:
clone
1.1 A person or thing regarded as an exact copy of another.
‘guitarists who are labelled Hendrix clones’
(Whatever a Hendrix may be.)
However it is a neologism, and I would not advise its use in formal writing.
Another possibility (again reflecting my scientific background) is instance.
instance
1 An example or single occurrence of something.
‘the search finds every instance where the word appears’
answered Jun 21, 2017 at 17:49
DavidDavid
12.2k7 gold badges23 silver badges59 bronze badges
2
I’m not sure if this is the context you mean it in, but in the network communication sense, the word you are looking for is «Anycast».
A unicast communication is a message from one person to one person. (one to one)
A broadcast communication is a message from one person to all people. (one to all)
A multicast communication is a message from one person to all members of a group of people. (one to many)
An anycast communication is a message from one person to a single member of a group of people. (one of many)
Another way of describing it is what is sometimes referred to as a phone number to a «hunt group». For instance, if I need to speak to someone in support, I can call the support «hunt group» and it will direct the call to a single member of the entire support group. If that member is unavailable, it will direct my phone call to another single member of the entire support group.
answered Jun 21, 2017 at 18:03
EddieEddie
4331 gold badge6 silver badges15 bronze badges
1
As I understand the question I prefer the noun select or selected depending on the situation. My dictionary says the definition of selected is; to choose in preference to another or others; pick out.
answered Jun 21, 2017 at 18:00
The closest definition to this word that I have found is humility. I think that I understand what the question is… As in, an employee among employees, a friend among friends, a civilian among civilians, not seeking to be better than or less than or separate from others, but just one among many. I personally don’t think that humility is the best definition, but it’s the closest one that I have found.
answered May 14, 2021 at 21:52
1
-
The object of semasiology.
Two approaches to the study of meaning. -
Types of meaning.
-
Meaning and motivation.
3.1.
The branch of lexicology which studies meaning is called
«semasiology«.
Sometimes the term «semantics»
is used as a synonym to semasiology, but it is ambiguous as it can
stand as well for (1)
the expressive aspect of language in general and (2)
the meaning of one particular word.
Meaning
is certainly the most important property of the word but what is
«meaning»?
Meaning
is one of the most controversial terms in lexicology. At present
there is no generally accepted definition of meaning. Prof.
Smirnitsky defines meaning as «a certain reflection in the mind
of objects, phenomena or relations that makes part of the linguistic
sign, its so-called inner facet, whereas the sound form functions as
its outer facet». Generally speaking, meaning can be described
as a component of the word through which a concept is communicated,
enabling the word to denote objects in the real world.
There are
two
approaches
to the study of meaning: the
referential approach
and the
functional approach.
The former tries to define meaning in terms of relations between the
word (sound form), concept (notion, thought) and referent (object
which the word denotes). They are closely connected and the
relationship between them is represented by «the semiotic
triangle» ( = the basic triangle) of Ogden and Richards (in the
book «The Meaning of Meaning» (1923) by O.K. Ogden and I.A.
Richards).

symbol
referent
(sound form)
This view denies a direct link
between words and things, arguing that the relationship can be made
only through the use of our minds. Meaning is related to a sound
form, concept and referent but not identical with them: meaning is a
linguistic phenomenon while neither concept nor referent is.
The
main criticism of this approach is the difficulty of identifying
«concepts»: they are mental phenomena and purely
subjective, existing
in the minds of individuals. The strongest point of this approach is
that it connects meaning and the process of nomination.
The functional approach to
meaning is less concerned with what meaning is than with how it
works. It is argued, to say that «words have meanings»
means only that they are used in a certain way in a sentence. There
is no meaning beyond that. Ludwig Wittgenstein (1889-1951), in
particular, stressed the importance of this approach in his dictum:
«The meaning of the word is its use in the language». So
meaning is studied by making detailed analyses of the way words are
used in contexts, through their relations to other words in speech,
and not through their relations to concepts or referents.
Actually,
the functional approach is basically confined to the analysis of
sameness or difference of meaning. For example, we can say that in
«take
the bottle»
and «take
to the
bottle»
take
has different meaning as it is used differently, but it does not
explain what the meaning of the verb is. So the functional approach
should
be used not as the theoretical basis for the study of meaning, but
only as complementary to the referential approach.
3.2.
Word meaning is made up of different components, commonly known
as types
of meaning.
The two main types of meaning are grammatical
meaning and
lexical meaning.
Grammatical
meaning
belongs to sets of word-forms and is common to
all words of the given part of speech,
e.g.
girls,
boys, classes, children, mice
express the meaning of
«plurality».
Lexical
meaning
belongs to an individual word in all its forms. It
comprises several components. The two main ones are the
denotational
component and
the connotational component.
The
denotational (
=
denotative)
component,
also called «referential
meaning» or «cognitive meaning», expresses the
conceptual (notional)
content of a word; broadly, it is some information, or knowledge,
of the real-world object that the word denotes.
Basically, this is the component that makes communication possible.
e.g.
notorious
«widely-known»,
celebrated «known
widely».
The
connotational (connotative) component
expresses the attitude of
the speaker to what he is saying, to the object denoted by the word.
This component consists of emotive
connotation and
evaluative connotation.
1) Emotive
connotation
( = «affective meaning», or an emotive charge),
e.g.
In «a
single tree»
single states that there is only one tree,
but
«a
lonely tree»
besides giving the same information, also renders
(conveys) the feeling of sadness.
We
shouldn’t confuse emotive connotations and emotive denotative
meanings
in which some emotion is named, e.g. horror,
love, fear, etc.
2) Evaluative
connotation
labels
the referent as «good» or «bad»,
e.g.
notorious
has a negative evaluative connotation, while
celebrated
a positive one. Cf.: a
notorious criminal/liar/ coward,
etc.
and a
celebrated singer/ scholar/ artist, etc.
It
should be noted that emotive and evaluative connotations are not
individual, they are common to all speakers of the language. But
emotive implications are individual (or common to a group of
speakers),
subjective, depend on personal experience.
e.g.
The word «hospital»
may evoke all kinds of emotions in
different
people (an
architect, a doctor, an invalid, etc.)
Stylistic
connotation,
or stylistic reference, another component of word meaning, stands
somewhat apart from emotive and evaluative connotations. Indeed, it
does not characterize a referent, but rather states how a word should
be used by referring it to a certain functional style of the language
peculiar to a specific sphere of communication. It shows in what
social context, in what communicative situations the word can be
used.
Stylistically,
words can be roughly classified into literary,
or formal
(e.g.
commence, discharge, parent),
neutral
(e.g.
father, begin, dismiss)
and non-literary,
or informal
(e.g.
dad, sack, set off).
3.3.
The term «motivation»
is used to denote the relationship between the
form of the word, i.e. its sound form, morphemic composition and
structural pattern, and its meaning.
There
are three
main types of motivation:
phonetic,
morphological
and
semantic.
1)
Phonetic
motivation
is a direct connection between the sound form
of a word and its meaning. There are two types of phonetic
motivation: sound
imitation and
sound symbolism.
a) Sound
imitation, or
onomatopoeia:
phonetically motivated words are
a direct imitation of the sounds they denote (or the sounds produced
by actions or objects they denote),
e.g.
buzz,
swish, bang, thud, cuckoo.
b) Sound
symbolism.
It’s argued by some linguists that the sounds that make up a word may
reflect or symbolise the properties of the object which the word
refers
to, i.e. they may suggest size, shape, speed, colour, etc.
e.g.
back
vowels
suggest big size, heavy weight, dark colour, front
vowels
suggest lightness, smallness, etc.
Many
words beginning with sl-
are slippery in some way: slide,
slip, slither, sludge,
etc.
or pejorative: slut,
slattern, sly, sloppy, slovenly;
words that end in -ump
almost
all refer to some kind of roundish mass: plump,
chump,
rump, hump, stump.
Certainly, not every word with
these phonetic characteristics will have the meaning suggested. This
is, perhaps, one of the reasons why sound symbolism is not
universally recognized in linguistics.
2) Morphological
motivation
is
a direct connection between the lexical meaning of the component
morphemes, the pattern of their arrangement and the meaning of the
word.
Morphologically motivated
words are those whose meaning is determined by the meaning of their
components,
e.g.
re-write
«write
again»,
ex-wife «former
wife».
The degree
of morphological motivation may be different. Words may be
fully
motivated
(then they are transparent), partially
motivated
and
non-motivated
(idiomatic, or opaque).
a)
If the meaning of the word is determined by the meaning of the
components
and the structural pattern, it is fully
motivated:
e.g. hatless.
b)
If the connection between the morphemic composition of a word and
its meaning is arbitrary, the word is non-motivated,
e.g. buttercup
«yellow-flowered plant».
c)
In hammer
-er
shows that it is an instrument, but what is «hamming«?
«Ham»
has no lexical meaning in this word, thus the word is partially
motivated.
Cf. also cranberry.
Motivation may be lost in the
course of time,
e.g.
in OE wīfman
was
motivated morphologically: wīf
+ man «wife
of a man»; now it is opaque;
its motivation is said to be faded (woman).
3) Semantic
motivation
is based on co-existence of direct and figurative
meanings of the same word,
e.g.
butterfly
–
1) insect; 2) showy and
frivolous person.( = metaphorical extension of the direct meaning).
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
CAMBRIDGE
ENGLISH VOCABULARY IN USE ADVANCED
UNIT 91
One word, many meanings
|
A |
Polysemy A Look
You |
||||||||
|
B |
Being aware of polysemy It • • • • Language The |
EXERCISES
|
91.1 |
Find 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
91.2 |
What Write |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
91.3 |
Here 1 The Their 2 Don’t Parliament 3 Let’s My 4 The Why 5 Sales You’ve 6 Do Thanks |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
91.4 |
Look |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
91.5 |
What
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
91.6 |
Explain 1 2 3 4 |
ANSWER KEY
91.1
1
intend: I didn’t mean to hurt you.
2 exactly: She finished the exercise in five minutes flat.
3 proper, just: It’s only fair that we should share the housework.
4 city with the seat of government: Wellington is the capital of New
Zealand.
5 light in colour: I’ve got fair hair and burn easily in the sun.
6 unkind: You shouldn’t be so mean to your little sister.
7 fixed: To join the Fitness Club you pay a flat fee of £500.
8 neither very good nor very bad: His marks in his final exams ranged from
excellent to fair.
9 money: You need plenty of capital to open a restaurant.
10 unwilling to spend money: He’s far too mean to buy her flowers.
91.2
It’s
only fair: adjective (right)
The Frankfurt Book Fair: noun (large show)
the weather to stay fair: adjective (pleasant)
I’ve got fair skin: adjective (light)
ranged from excellent to fair: adjective (satisfactory)
the burning third-floor flat: noun (apartment)
terribly flat and boring: adjective (level)
a flat fee of £500: adjective (fixed)
B flat minor: noun (♭ =
a note that is a semitone lower than B itself)
in
five minutes flat: adverb (only; emphasises how quick a time is)
in capital letters: adjective (upper case)
the capital of New Zealand: noun (city where the country’s government
sits)
capital to open a restaurant: noun (money)
Capital punishment: adjective (punishable by death)
‘coagulate’ mean: verb (convey a meaning, express an idea)
mean to hurt you: verb (intend)
too mean to buy her flowers: adjective (opposite of generous)
be so mean: adjective (unkind)
91.3
1
match 4 post
2
bill 5 mark
3
set 6 run
91.4
a
an instrument a dentist uses to make holes in your teeth
b
training for marching
c
a powerful tool used for making holes in a road
d
an exercise practising grammar in a fairly mechanical way
91.5
1
a the list on which students are marked present or absent every day
b to send a letter or parcel in a special way so it has protection against
being lost
2 a how much performers might appeal to the public
b money earned on an investment or paid for a loan
3 a to cut up into small cubes (usually vegetables)
b a cube with a number from one to six on each side
4 a throwing the ball into the air and hitting it at the start of a turn
b the attention given to customers by staff
5 a specific problem being dealt with by lawyers
b a piece of luggage
6 a the long stick that players use in snooker or billiards
b the words or actions that tell an actor that it is his or her turn to speak
91.6
1
Then it hit me! This means ‘then I suddenly understood and then the ball
suddenly struck my body.’
2 This is based on the traditional saying that babies are delivered to a home
by a big bird called a
stork. A crane is another kind of large bird rather like a stork. But a crane
can also be a piece of
heavy machinery used to lift heavy objects.
3 In the first sentence, flies is a verb and like is a
preposition – the sentence is comparing the flight
of time with that of an arrow. In the second sentence, flies is a noun
and like is a verb and the
sentence says that fruit flies [very small insects] enjoy bananas.
4 As well as being a preposition, down is the word for very soft
feathers used to stuff, for example,
pillows or winter jackets. If prices are up, they have risen and if
they are down they have fallen.
- Top Definitions
- Synonyms
- Quiz
- Related Content
- Examples
- British
- Idioms And Phrases
This shows grade level based on the word’s complexity.
This shows grade level based on the word’s complexity.
adjective, more, most.
constituting or forming a large number; numerous: many people.
noting each one of a large number (usually followed by a or an): For many a day it rained.
noun
a large or considerable number of persons or things: A good many of the beggars were blind.
the many, the greater part of humankind.
pronoun
many persons or things: Many of the beggars were blind. Many were unable to attend.
QUIZ
CAN YOU ANSWER THESE COMMON GRAMMAR DEBATES?
There are grammar debates that never die; and the ones highlighted in the questions in this quiz are sure to rile everyone up once again. Do you know how to answer the questions that cause some of the greatest grammar debates?
Which sentence is correct?
Origin of many
First recorded before 900; Middle English mani, meni,Old English manig, menig; akin to Old Saxon, Old High German manag, menig,Danish mange,Gothic manags
synonym study for many
1. Many, innumerable, manifold, numerous imply the presence or succession of a large number of units. Many is a popular and common word for this idea: many times. Numerous, a more formal word, refers to a great number or to very many units: letters too numerous to mention. Innumerable denotes a number that is beyond count or, more loosely, that is extremely difficult to count: the innumerable stars in the sky. Manifold implies not only that the number is large but also that there is variety or complexity.
OTHER WORDS FROM many
o·ver·man·y, adjective
Words nearby many
manwise, Manx, manx cat, Manxman, Manx shearwater, many, many a, Many are called but few are chosen, man-year, manyfold, Many hands make light work
Dictionary.com Unabridged
Based on the Random House Unabridged Dictionary, © Random House, Inc. 2023
Words related to many
abounding, alive with, bounteous, bountiful, copious, countless, crowded, divers, frequent, innumerable, legion, lousy with, manifold, multifarious, multifold, multiplied, multitudinous, myriad, numberless, numerous
How to use many in a sentence
-
Like many trans users, Transartist often gets used as a source of information more than anything else.
-
But he, like many people using dating apps whatever their sexual identity, remains stoutly positive.
-
Like many Americans—but few Republican presidential candidates—the former Florida governor has evolved on the issue.
-
In an email exchange a friend said many had repeated this same succinct review but they could never elaborate.
-
For many years afterward it was a never-ending topic of conversation, and is more or less talked of even to this day.
-
And she would be wearing some of the jewels with the white dress—just a few, not many, of course.
-
Many of them were delicious in the role; one of them was the embodiment of every womanly grace and charm.
-
Only in the carnage of the head, the tilt of the chin, was the insolence expressed that had made her many enemies.
-
As there are still many varieties of the plant grown in America, so there doubtless was when cultivated by the Indians.
-
Babylas raised his pale face; he knew what was coming; it had come so many times before.
British Dictionary definitions for many
determiner
(sometimes preceded by a great or a good)
- a large number ofmany coaches; many times
- (as pronoun; functioning as plural)many are seated already
(foll by a, an, or another, and a singular noun) each of a considerable number ofmany a man
(preceded by as, too, that, etc)
- a great number ofas many apples as you like; too many clouds to see
- (as pronoun; functioning as plural)I have as many as you
noun
the many the majority of mankind, esp the common peoplethe many are kept in ignorance while the few prosper Compare few (def. 7)
Word Origin for many
Old English manig; related to Old Frisian manich, Middle Dutch menech, Old High German manag
Collins English Dictionary — Complete & Unabridged 2012 Digital Edition
© William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1979, 1986 © HarperCollins
Publishers 1998, 2000, 2003, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2012
Other Idioms and Phrases with many
In addition to the idioms beginning with many
- many a
- many hands make light work
- many happy returns
- many is the
also see:
- as many
- good (great) many
- in so many words
- irons in the fire, too many
- so many
- too many cooks spoil the broth
The American Heritage® Idioms Dictionary
Copyright © 2002, 2001, 1995 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company.
Word Meaning Lecture # 6 Grigoryeva M.
Word Meaning Approaches to word meaning Meaning and Notion (понятие) Types of word meaning Types of morpheme meaning Motivation
Each word has two aspects: the outer aspect ( its sound form) cat the inner aspect (its meaning) long-legged, fury animal with sharp teeth and claws
Sound and meaning do not always constitute a constant unit even in the same language EX a temple a part of a human head a large church
Semantics (Semasiology) Is a branch of lexicology which studies the meaning of words and word equivalents
Approaches to Word Meaning The Referential (analytical) approach The Functional (contextual) approach Operational (information-oriented) approach
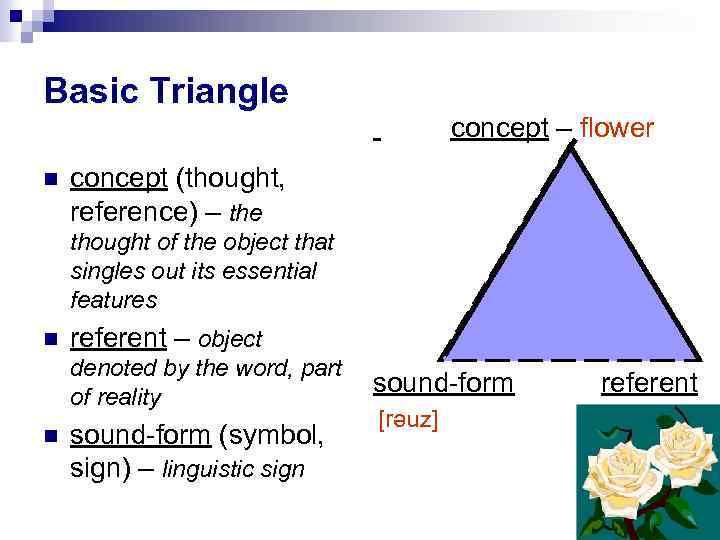
The Referential (analytical) approach formulates the essence of meaning by establishing the interdependence between words and things or concepts they denote distinguishes between three components closely connected with meaning: the sound-form of the linguistic sign, the concept the actual referent
Basic Triangle concept – flower concept (thought, reference) – the thought of the object that singles out its essential features referent – object denoted by the word, part of reality sound-form (symbol, sign) – linguistic sign sound-form [rәuz] referent
In what way does meaning correlate with each element of the triangle ? • In what relation does meaning stand to each of them? •
Meaning and Sound-form are not identical different EX. dove — [dΛv] English [golub’] Russian [taube] German sound-forms BUT the same meaning
Meaning and Sound-form nearly identical sound-forms have different meanings in different languages EX. [kot] Russian – a male cat [kot] English – a small bed for a child identical sound-forms have different meanings (‘homonyms) EX. knight [nait]
Meaning and Sound-form even considerable changes in sound-form do not affect the meaning EX Old English lufian [luvian] – love [l Λ v]
Meaning and Concept concept is a category of human cognition concept is abstract and reflects the most common and typical features of different objects and phenomena in the world meanings of words are different in different languages
Meaning and Concept identical concepts may have different semantic structures in different languages EX. concept “a building for human habitation” – English Russian HOUSE ДОМ + in Russian ДОМ “fixed residence of family or household” In English HOME
Meaning and Referent one and the same object (referent) may be denoted by more than one word of a different meaning cat pussy animal tiger
Meaning is not identical with any of the three points of the triangle – the sound form, the concept the referent BUT is closely connected with them.
Functional Approach studies the functions of a word in speech meaning of a word is studied through relations of it with other linguistic units EX. to move (we move, move a chair) movement (movement of smth, slow movement) The distriution ( the position of the word in relation to others) of the verb to move and a noun movement is different as they belong to different classes of words and their meanings are different
Operational approach is centered on defining meaning through its role in the process of communication EX John came at 6 Beside the direct meaning the sentence may imply that: He was late He failed to keep his promise He was punctual as usual He came but he didn’t want to The implication depends on the concrete situation
Lexical Meaning and Notion denotes the Lexical meaning is reflection in the realization of a mind of real objects notion by means of a definite language system Notion is a unit of Word is a language thinking unit
Lexical Meaning and Notions are Meanings are internationally limited especially with the nations of the same EX GO (E) —- ИДТИ(R) cultural level “To move” BUT !!! To GO by bus (E) ЕХАТЬ (R) EX Man -мужчина, человек Она – хороший человек (R) She is a good person (E)
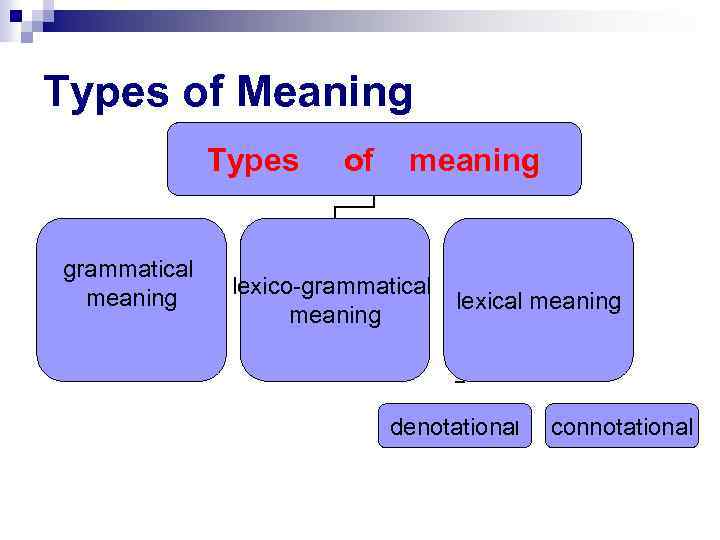
Types of Meaning Types grammatical meaning of meaning lexico-grammatical meaning lexical meaning denotational connotational
Grammatical Meaning component of meaning recurrent in identical sets of individual forms of different words EX. girls, winters, toys, tables – grammatical meaning of plurality asked, thought, walked – meaning of past tense
Lexico-grammatical meaning (part –of- speech meaning) is revealed in the classification of lexical items into: major word classes (N, V, Adj, Adv) minor ones (artc, prep, conj) words of one lexico-grammatical class have the same paradigm
Lexical Meaning is the meaning proper to the given linguistic unit in all its forms and distributions EX. Go – goes — went lexical meaning – process of movement
PRACTICE Group the words into 3 column according to the grammatical, lexical or part-of –speech meaning • • Boy’s, nearest, at, beautiful, think, man, drift, wrote, tremendous, ship’s, the most beautiful, table, near, for, went, friend’s, handsome, thinking, boy, nearer, thought, boys, lamp, go, during.
• Grammatical 1. The case of nouns: boy’s, ship’s, friend’s 2. The degree of comparison of adj: nearest, the most beautiful 3. The tense of verbs: wrote, went, thought • Lexical 1. Think, thinking, thought 2. Went, go 3. Boy’s, boys 4. Nearest, nearer 5. At, for, during (“time”) 6. Beautiful, the most beautiful • Part-of-speech Nouns—verbs—adj—-prep
Aspects of Lexical meaning The denotational aspect The connotational aspect The pragmatic aspect
Denotational Meaning “denote” – to be a sign of, stand as a symbol for” establishes the correlation between the name and the object makes communication possible EX booklet “a small thin book that gives info about smth”
PRACTICE Explain denotational meaning • • A lion-hunter To have a heart like a lion To feel like a lion To roar like a lion To be thrown to the lions The lion’s share To put your head in lion’s mouth
PRACTICE • A lion-hunter A host that seeks out celebrities to impress guests • To have a heart like a lion To have great courage • To feel like a lion To be in the best of health • To roar like a lion To shout very loudly • To be thrown to the lions To be criticized strongly or treated badly • The lion’s share Much more than one’s share • To put your head in lion’s mouth
Connotational Meaning reflects the attitude of the speaker towards what he speaks about it is optional – a word either has it or not Connotation gives additional information and includes: The emotive charge EX Daddy (for father) Intensity EX to adore (for to love) Imagery EX to wade through a book “ to walk with an effort”
PRACTICE Give possible interpretation of the sentences • She failed to buy it and felt a strange pang. • Don’t be afraid of that woman! It’s just barking! • He got up from his chair moving slowly, like an old man. • The girl went to her father and pulled his sleeve. • He was longing to begin to be generous. • She was a woman with shiny red hands and workswollen finger knuckles.
PRACTICE Give possible interpretation of the sentences • She failed to buy it and felt a strange pang. (pain—dissatisfaction that makes her suffer) • Don’t be afraid of that woman! It’s just barking! (make loud sharp sound—-the behavior that implies that the person is frightened) • He got up from his chair moving slowly, like an old man. (to go at slow speed—was suffering or was ill) • The girl went to her father and pulled his sleeve. (to move smth towards oneself— to try to attract smb’s attention) • He was longing to begin to be generous. (to start doing— hadn’t been generous before) • She was a woman with shiny red hands and work-swollen finger knuckles. (colour— a labourer involved into physical work , constant contact with water)
The pragmatic aspect of lexical meaning the situation in which the word is uttered, the social circumstances (formal, informal, etc. ), social relationships between the interlocutors (polite, rough, etc. ), the type and purpose of communication (poetic, official, etc. ) EX horse (neutral) steed (poetic) nag (slang) gee-gee (baby language)
PRACTICE State what image underline the meaning • I heard what she said but it didn’t sink into my mind. • You should be ashamed of yourself, crawling to the director like that. • They seized on the idea. • Bill, chasing some skirt again? • I saw him dive into a small pub. • Why are you trying to pin the blame on me? • He only married her for her dough.
PRACTICE State what image underline the meaning • I heard what she said but it didn’t sink into my mind. • (to understand completely) • You should be ashamed of yourself, crawling to the director like that. (to behave humbly in order to win favour) • They seized on the idea. (to be eager to take and use) • Bill, chasing some skirt again? (a girl) • I saw him dive into a small pub. (to enter suddenly) • Why are you trying to pin the blame on me? (to blame smb unfairly) • He only married her for her dough. (money)
Types of Morpheme Meaning lexical differential functional distributional
Lexical Meaning in Morphemes root-morphemes that are homonymous to words possess lexical meaning EX. boy – boyhood – boyish affixes have lexical meaning of a more generalized character EX. –er “agent, doer of an action”
Lexical Meaning in Morphemes has denotational and connotational components EX. –ly, -like, -ish – denotational meaning of similiarity womanly , womanish connotational component – -ly (positive evaluation), -ish (deragotary) женственный женоподобный
Differential Meaning a semantic component that serves to distinguish one word from all others containing identical morphemes EX. cranberry, blackberry, gooseberry
Functional Meaning found only in derivational affixes a semantic component which serves to refer the word to the certain part of speech EX. just, adj. – justice, n.
Distributional Meaning the meaning of the order and the arrangement of morphemes making up the word found in words containing more than one morpheme different arrangement of the same morphemes would make the word meaningless EX. sing- + -er =singer, -er + sing- = ?
Motivation denotes the relationship between the phonetic or morphemic composition and structural pattern of the word on the one hand, and its meaning on the other can be phonetical morphological semantic
Phonetical Motivation when there is a certain similarity between the sounds that make up the word and those produced by animals, objects, etc. EX. sizzle, boom, splash, cuckoo
Morphological Motivation when there is a direct connection between the structure of a word and its meaning EX. finger-ring – ring-finger, A direct connection between the lexical meaning of the component morphemes EX think –rethink “thinking again”
Semantic Motivation based on co-existence of direct and figurative meanings of the same word EX a watchdog – ”a dog kept for watching property” a watchdog – “a watchful human guardian” (semantic motivation)
• PRACTICE
Analyze the meaning of the words. Define the type of motivation a) morphologically motivated b) semantically motivated • Driver • Leg • Horse • Wall • Hand-made • Careless • piggish
Analyze the meaning of the words. Define the type of motivation a) morphologically motivated b) semantically motivated • Driver Someone who drives a vehicle morphologically motivated • Leg The part of a piece of furniture such as a table semantically motivated • Horse A piece of equipment shaped like a box, used in gymnastics semantically motivated
• Wall Emotions or behavior preventing people from feeling close semantically motivated • Hand-made Made by hand, not machine morphologically motivated • Careless Not taking enough care morphologically motivated • Piggish Selfish semantically motivated
what she said but it didn’t sink in my mind “do down to the bottom” ‘to be accepted by mind” semantic motivation I heard Why are you trying to pin the blame on me? “fasten smth somewhere using a pin” – ”to blame smb” semantic motivation I was following the man when he dived into a pub. “jump into deep water” – ”to enter into suddenly” semantic motivation You should be ashamed of yourself, crawling to the director like that “to move along on hands and knees close to the ground” – “to behave very humbly in order to win favor” semantic motivation











![Meaning and Sound-form are not identical different EX. dove - [dΛv] English [golub’] Russian Meaning and Sound-form are not identical different EX. dove - [dΛv] English [golub’] Russian](https://present5.com/presentation/54919015_285694613/image-10.jpg)
![Meaning and Sound-form nearly identical sound-forms have different meanings in different languages EX. [kot] Meaning and Sound-form nearly identical sound-forms have different meanings in different languages EX. [kot]](https://present5.com/presentation/54919015_285694613/image-11.jpg)