-
The object of semasiology.
Two approaches to the study of meaning. -
Types of meaning.
-
Meaning and motivation.
3.1.
The branch of lexicology which studies meaning is called
«semasiology«.
Sometimes the term «semantics»
is used as a synonym to semasiology, but it is ambiguous as it can
stand as well for (1)
the expressive aspect of language in general and (2)
the meaning of one particular word.
Meaning
is certainly the most important property of the word but what is
«meaning»?
Meaning
is one of the most controversial terms in lexicology. At present
there is no generally accepted definition of meaning. Prof.
Smirnitsky defines meaning as «a certain reflection in the mind
of objects, phenomena or relations that makes part of the linguistic
sign, its so-called inner facet, whereas the sound form functions as
its outer facet». Generally speaking, meaning can be described
as a component of the word through which a concept is communicated,
enabling the word to denote objects in the real world.
There are
two
approaches
to the study of meaning: the
referential approach
and the
functional approach.
The former tries to define meaning in terms of relations between the
word (sound form), concept (notion, thought) and referent (object
which the word denotes). They are closely connected and the
relationship between them is represented by «the semiotic
triangle» ( = the basic triangle) of Ogden and Richards (in the
book «The Meaning of Meaning» (1923) by O.K. Ogden and I.A.
Richards).

symbol
referent
(sound form)
This view denies a direct link
between words and things, arguing that the relationship can be made
only through the use of our minds. Meaning is related to a sound
form, concept and referent but not identical with them: meaning is a
linguistic phenomenon while neither concept nor referent is.
The
main criticism of this approach is the difficulty of identifying
«concepts»: they are mental phenomena and purely
subjective, existing
in the minds of individuals. The strongest point of this approach is
that it connects meaning and the process of nomination.
The functional approach to
meaning is less concerned with what meaning is than with how it
works. It is argued, to say that «words have meanings»
means only that they are used in a certain way in a sentence. There
is no meaning beyond that. Ludwig Wittgenstein (1889-1951), in
particular, stressed the importance of this approach in his dictum:
«The meaning of the word is its use in the language». So
meaning is studied by making detailed analyses of the way words are
used in contexts, through their relations to other words in speech,
and not through their relations to concepts or referents.
Actually,
the functional approach is basically confined to the analysis of
sameness or difference of meaning. For example, we can say that in
«take
the bottle»
and «take
to the
bottle»
take
has different meaning as it is used differently, but it does not
explain what the meaning of the verb is. So the functional approach
should
be used not as the theoretical basis for the study of meaning, but
only as complementary to the referential approach.
3.2.
Word meaning is made up of different components, commonly known
as types
of meaning.
The two main types of meaning are grammatical
meaning and
lexical meaning.
Grammatical
meaning
belongs to sets of word-forms and is common to
all words of the given part of speech,
e.g.
girls,
boys, classes, children, mice
express the meaning of
«plurality».
Lexical
meaning
belongs to an individual word in all its forms. It
comprises several components. The two main ones are the
denotational
component and
the connotational component.
The
denotational (
=
denotative)
component,
also called «referential
meaning» or «cognitive meaning», expresses the
conceptual (notional)
content of a word; broadly, it is some information, or knowledge,
of the real-world object that the word denotes.
Basically, this is the component that makes communication possible.
e.g.
notorious
«widely-known»,
celebrated «known
widely».
The
connotational (connotative) component
expresses the attitude of
the speaker to what he is saying, to the object denoted by the word.
This component consists of emotive
connotation and
evaluative connotation.
1) Emotive
connotation
( = «affective meaning», or an emotive charge),
e.g.
In «a
single tree»
single states that there is only one tree,
but
«a
lonely tree»
besides giving the same information, also renders
(conveys) the feeling of sadness.
We
shouldn’t confuse emotive connotations and emotive denotative
meanings
in which some emotion is named, e.g. horror,
love, fear, etc.
2) Evaluative
connotation
labels
the referent as «good» or «bad»,
e.g.
notorious
has a negative evaluative connotation, while
celebrated
a positive one. Cf.: a
notorious criminal/liar/ coward,
etc.
and a
celebrated singer/ scholar/ artist, etc.
It
should be noted that emotive and evaluative connotations are not
individual, they are common to all speakers of the language. But
emotive implications are individual (or common to a group of
speakers),
subjective, depend on personal experience.
e.g.
The word «hospital»
may evoke all kinds of emotions in
different
people (an
architect, a doctor, an invalid, etc.)
Stylistic
connotation,
or stylistic reference, another component of word meaning, stands
somewhat apart from emotive and evaluative connotations. Indeed, it
does not characterize a referent, but rather states how a word should
be used by referring it to a certain functional style of the language
peculiar to a specific sphere of communication. It shows in what
social context, in what communicative situations the word can be
used.
Stylistically,
words can be roughly classified into literary,
or formal
(e.g.
commence, discharge, parent),
neutral
(e.g.
father, begin, dismiss)
and non-literary,
or informal
(e.g.
dad, sack, set off).
3.3.
The term «motivation»
is used to denote the relationship between the
form of the word, i.e. its sound form, morphemic composition and
structural pattern, and its meaning.
There
are three
main types of motivation:
phonetic,
morphological
and
semantic.
1)
Phonetic
motivation
is a direct connection between the sound form
of a word and its meaning. There are two types of phonetic
motivation: sound
imitation and
sound symbolism.
a) Sound
imitation, or
onomatopoeia:
phonetically motivated words are
a direct imitation of the sounds they denote (or the sounds produced
by actions or objects they denote),
e.g.
buzz,
swish, bang, thud, cuckoo.
b) Sound
symbolism.
It’s argued by some linguists that the sounds that make up a word may
reflect or symbolise the properties of the object which the word
refers
to, i.e. they may suggest size, shape, speed, colour, etc.
e.g.
back
vowels
suggest big size, heavy weight, dark colour, front
vowels
suggest lightness, smallness, etc.
Many
words beginning with sl-
are slippery in some way: slide,
slip, slither, sludge,
etc.
or pejorative: slut,
slattern, sly, sloppy, slovenly;
words that end in -ump
almost
all refer to some kind of roundish mass: plump,
chump,
rump, hump, stump.
Certainly, not every word with
these phonetic characteristics will have the meaning suggested. This
is, perhaps, one of the reasons why sound symbolism is not
universally recognized in linguistics.
2) Morphological
motivation
is
a direct connection between the lexical meaning of the component
morphemes, the pattern of their arrangement and the meaning of the
word.
Morphologically motivated
words are those whose meaning is determined by the meaning of their
components,
e.g.
re-write
«write
again»,
ex-wife «former
wife».
The degree
of morphological motivation may be different. Words may be
fully
motivated
(then they are transparent), partially
motivated
and
non-motivated
(idiomatic, or opaque).
a)
If the meaning of the word is determined by the meaning of the
components
and the structural pattern, it is fully
motivated:
e.g. hatless.
b)
If the connection between the morphemic composition of a word and
its meaning is arbitrary, the word is non-motivated,
e.g. buttercup
«yellow-flowered plant».
c)
In hammer
-er
shows that it is an instrument, but what is «hamming«?
«Ham»
has no lexical meaning in this word, thus the word is partially
motivated.
Cf. also cranberry.
Motivation may be lost in the
course of time,
e.g.
in OE wīfman
was
motivated morphologically: wīf
+ man «wife
of a man»; now it is opaque;
its motivation is said to be faded (woman).
3) Semantic
motivation
is based on co-existence of direct and figurative
meanings of the same word,
e.g.
butterfly
–
1) insect; 2) showy and
frivolous person.( = metaphorical extension of the direct meaning).
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
Скачать материал

Скачать материал




- Сейчас обучается 396 человек из 63 регионов




Описание презентации по отдельным слайдам:
-
1 слайд
Word Meaning
Lecture # 6
Grigoryeva M. -
2 слайд
Word Meaning
Approaches to word meaning
Meaning and Notion (понятие)
Types of word meaning
Types of morpheme meaning
Motivation
-
3 слайд
Each word has two aspects:
the outer aspect
( its sound form)
catthe inner aspect
(its meaning)
long-legged, fury animal with sharp teeth
and claws -
4 слайд
Sound and meaning do not always constitute a constant unit even in the same language
EX a temple
a part of a human head
a large church -
5 слайд
Semantics (Semasiology)
Is a branch of lexicology which studies the
meaning of words and word equivalents -
6 слайд
Approaches to Word Meaning
The Referential (analytical) approachThe Functional (contextual) approach
Operational (information-oriented) approach
-
7 слайд
The Referential (analytical) approach
formulates the essence of meaning by establishing the interdependence between words and things or concepts they denotedistinguishes between three components closely connected with meaning:
the sound-form of the linguistic sign,
the concept
the actual referent -
8 слайд
Basic Triangle
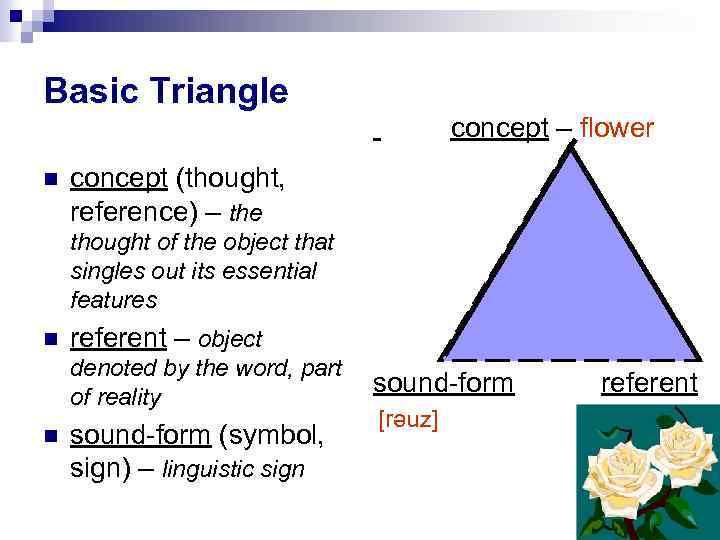
concept (thought, reference) – the thought of the object that singles out its essential features
referent – object denoted by the word, part of reality
sound-form (symbol, sign) – linguistic sign
concept – flowersound-form referent
[rәuz] -
9 слайд
In what way does meaning correlate with
each element of the triangle ?In what relation does meaning stand to
each of them? -
10 слайд
Meaning and Sound-form
are not identical
different
EX. dove — [dΛv] English sound-forms
[golub’] Russian BUT
[taube] German
the same meaning -
11 слайд
Meaning and Sound-form
nearly identical sound-forms have different meanings in different languages
EX. [kot] Russian – a male cat
[kot] English – a small bed for a childidentical sound-forms have different meanings (‘homonyms)
EX. knight [nait]
night [nait] -
12 слайд
Meaning and Sound-form
even considerable changes in sound-form do not affect the meaningEX Old English lufian [luvian] – love [l Λ v]
-
13 слайд
Meaning and Concept
concept is a category of human cognitionconcept is abstract and reflects the most common and typical features of different objects and phenomena in the world
meanings of words are different in different languages
-
14 слайд
Meaning and Concept
identical concepts may have different semantic structures in different languagesEX. concept “a building for human habitation” –
English Russian
HOUSE ДОМ+ in Russian ДОМ
“fixed residence of family or household”
In English HOME -
15 слайд
Meaning and Referent
one and the same object (referent) may be denoted by more than one word of a different meaning
cat
pussy
animal
tiger -
16 слайд
Meaning
is not identical with any of the three points of the triangle –
the sound form,
the concept
the referentBUT
is closely connected with them. -
17 слайд
Functional Approach
studies the functions of a word in speech
meaning of a word is studied through relations of it with other linguistic units
EX. to move (we move, move a chair)
movement (movement of smth, slow movement)The distriution ( the position of the word in relation to
others) of the verb to move and a noun movement is
different as they belong to different classes of words and
their meanings are different -
18 слайд
Operational approach
is centered on defining meaning through its role in
the process of communicationEX John came at 6
Beside the direct meaning the sentence may imply that:
He was late
He failed to keep his promise
He was punctual as usual
He came but he didn’t want toThe implication depends on the concrete situation
-
19 слайд
Lexical Meaning and Notion
Notion denotes the reflection in the mind of real objectsNotion is a unit of thinking
Lexical meaning is the realization of a notion by means of a definite language system
Word is a language unit -
20 слайд
Lexical Meaning and Notion
Notions are international especially with the nations of the same cultural levelMeanings are nationally limited
EX GO (E) —- ИДТИ(R)
“To move”
BUT !!!
To GO by bus (E)
ЕХАТЬ (R)EX Man -мужчина, человек
Она – хороший человек (R)
She is a good person (E) -
21 слайд
Types of Meaning
Types of meaninggrammatical
meaninglexico-grammatical
meaning
lexical meaning
denotational
connotational -
22 слайд
Grammatical Meaning
component of meaning recurrent in identical sets of individual forms of different wordsEX. girls, winters, toys, tables –
grammatical meaning of pluralityasked, thought, walked –
meaning of past tense -
23 слайд
Lexico-grammatical meaning
(part –of- speech meaning)
is revealed in the classification of lexical items into:
major word classes (N, V, Adj, Adv)
minor ones (artc, prep, conj)words of one lexico-grammatical class have the same paradigm
-
24 слайд
Lexical Meaning
is the meaning proper to the given linguistic unit in all its forms and distributionsEX . Go – goes — went
lexical meaning – process of movement -
25 слайд
PRACTICE
Group the words into 3 column according to the grammatical, lexical or part-of –speech meaning
Boy’s, nearest, at, beautiful,
think, man, drift, wrote,
tremendous, ship’s, the most beautiful,
table, near, for, went, friend’s,
handsome, thinking, boy,
nearer, thought, boys,
lamp, go, during. -
26 слайд
Grammatical
The case of nouns: boy’s, ship’s, friend’s
The degree of comparison of adj: nearest, the most beautiful
The tense of verbs: wrote, went, thoughtLexical
Think, thinking, thought
Went, go
Boy’s, boy, boys
Nearest, near, nearer
At, for, during (“time”)
Beautiful, the most beautifulPart-of-speech
Nouns—verbs—adj—-prep -
27 слайд
Aspects of Lexical meaning
The denotational aspectThe connotational aspect
The pragmatic aspect
-
28 слайд
Denotational Meaning
“denote” – to be a sign of, stand as a symbol for”establishes the correlation between the name and the object
makes communication possibleEX booklet
“a small thin book that gives info about smth” -
29 слайд
PRACTICE
Explain denotational meaningA lion-hunter
To have a heart like a lion
To feel like a lion
To roar like a lion
To be thrown to the lions
The lion’s share
To put your head in lion’s mouth -
30 слайд
PRACTICE
A lion-hunter
A host that seeks out celebrities to impress guests
To have a heart like a lion
To have great courage
To feel like a lion
To be in the best of health
To roar like a lion
To shout very loudly
To be thrown to the lions
To be criticized strongly or treated badly
The lion’s share
Much more than one’s share
To put your head in lion’s mouth -
31 слайд
Connotational Meaning
reflects the attitude of the speaker towards what he speaks about
it is optional – a word either has it or notConnotation gives additional information and includes:
The emotive charge EX Daddy (for father)
Intensity EX to adore (for to love)
Imagery EX to wade through a book
“ to walk with an effort” -
32 слайд
PRACTICE
Give possible interpretation of the sentencesShe failed to buy it and felt a strange pang.
Don’t be afraid of that woman! It’s just barking!
He got up from his chair moving slowly, like an old man.
The girl went to her father and pulled his sleeve.
He was longing to begin to be generous.
She was a woman with shiny red hands and work-swollen finger knuckles. -
33 слайд
PRACTICE
Give possible interpretation of the sentences
She failed to buy it and felt a strange pang.
(pain—dissatisfaction that makes her suffer)
Don’t be afraid of that woman! It’s just barking!
(make loud sharp sound—-the behavior that implies that the person is frightened)
He got up from his chair moving slowly, like an old man.
(to go at slow speed—was suffering or was ill)
The girl went to her father and pulled his sleeve.
(to move smth towards oneself— to try to attract smb’s attention)
He was longing to begin to be generous.
(to start doing— hadn’t been generous before)
She was a woman with shiny red hands and work-swollen finger knuckles.
(colour— a labourer involved into physical work ,constant contact with water) -
34 слайд
The pragmatic aspect of lexical meaning
the situation in which the word is uttered,
the social circumstances (formal, informal, etc.),
social relationships between the interlocutors (polite, rough, etc.),
the type and purpose of communication (poetic, official, etc.)EX horse (neutral)
steed (poetic)
nag (slang)
gee-gee (baby language) -
35 слайд
PRACTICE
State what image underline the meaningI heard what she said but it didn’t sink into my mind.
You should be ashamed of yourself, crawling to the director like that.
They seized on the idea.
Bill, chasing some skirt again?
I saw him dive into a small pub.
Why are you trying to pin the blame on me?
He only married her for her dough. -
36 слайд
PRACTICE
State what image underline the meaning
I heard what she said but it didn’t sink into my mind.
(to understand completely)
You should be ashamed of yourself, crawling to the director like that.
(to behave humbly in order to win favour)
They seized on the idea.
(to be eager to take and use)
Bill, chasing some skirt again?
(a girl)
I saw him dive into a small pub.
(to enter suddenly)
Why are you trying to pin the blame on me?
(to blame smb unfairly)
He only married her for her dough.
(money) -
37 слайд
Types of Morpheme Meaning
lexical
differential
functional
distributional -
38 слайд
Lexical Meaning in Morphemes
root-morphemes that are homonymous to words possess lexical meaning
EX. boy – boyhood – boyishaffixes have lexical meaning of a more generalized character
EX. –er “agent, doer of an action” -
39 слайд
Lexical Meaning in Morphemes
has denotational and connotational components
EX. –ly, -like, -ish –
denotational meaning of similiarity
womanly , womanishconnotational component –
-ly (positive evaluation), -ish (deragotary) женственный — женоподобный -
40 слайд
Differential Meaning
a semantic component that serves to distinguish one word from all others containing identical morphemesEX. cranberry, blackberry, gooseberry
-
41 слайд
Functional Meaning
found only in derivational affixes
a semantic component which serves to
refer the word to the certain part of speechEX. just, adj. – justice, n.
-
42 слайд
Distributional Meaning
the meaning of the order and the arrangement of morphemes making up the word
found in words containing more than one morpheme
different arrangement of the same morphemes would make the word meaningless
EX. sing- + -er =singer,
-er + sing- = ? -
43 слайд
Motivation
denotes the relationship between the phonetic or morphemic composition and structural pattern of the word on the one hand, and its meaning on the othercan be phonetical
morphological
semantic -
44 слайд
Phonetical Motivation
when there is a certain similarity between the sounds that make up the word and those produced by animals, objects, etc.EX. sizzle, boom, splash, cuckoo
-
45 слайд
Morphological Motivation
when there is a direct connection between the structure of a word and its meaning
EX. finger-ring – ring-finger,A direct connection between the lexical meaning of the component morphemes
EX think –rethink “thinking again” -
46 слайд
Semantic Motivation
based on co-existence of direct and figurative meanings of the same wordEX a watchdog –
”a dog kept for watching property”a watchdog –
“a watchful human guardian” (semantic motivation) -
-
48 слайд
Analyze the meaning of the words.
Define the type of motivation
a) morphologically motivated
b) semantically motivatedDriver
Leg
Horse
Wall
Hand-made
Careless
piggish -
49 слайд
Analyze the meaning of the words.
Define the type of motivation
a) morphologically motivated
b) semantically motivated
Driver
Someone who drives a vehicle
morphologically motivated
Leg
The part of a piece of furniture such as a table
semantically motivated
Horse
A piece of equipment shaped like a box, used in gymnastics
semantically motivated -
50 слайд
Wall
Emotions or behavior preventing people from feeling close
semantically motivated
Hand-made
Made by hand, not machine
morphologically motivated
Careless
Not taking enough care
morphologically motivated
Piggish
Selfish
semantically motivated -
51 слайд
I heard what she said but it didn’t sink in my mind
“do down to the bottom”
‘to be accepted by mind” semantic motivationWhy are you trying to pin the blame on me?
“fasten smth somewhere using a pin” –
”to blame smb” semantic motivationI was following the man when he dived into a pub.
“jump into deep water” –
”to enter into suddenly” semantic motivationYou should be ashamed of yourself, crawling to the director like that
“to move along on hands and knees close to the ground” –
“to behave very humbly in order to win favor” semantic motivation
Найдите материал к любому уроку, указав свой предмет (категорию), класс, учебник и тему:
6 210 150 материалов в базе
- Выберите категорию:
- Выберите учебник и тему
- Выберите класс:
-
Тип материала:
-
Все материалы
-
Статьи
-
Научные работы
-
Видеоуроки
-
Презентации
-
Конспекты
-
Тесты
-
Рабочие программы
-
Другие методич. материалы
-
Найти материалы
Другие материалы
- 22.10.2020
- 141
- 0
- 21.09.2020
- 530
- 1
- 18.09.2020
- 256
- 0
- 11.09.2020
- 191
- 1
- 21.08.2020
- 197
- 0
- 18.08.2020
- 123
- 0
- 03.07.2020
- 94
- 0
- 06.06.2020
- 73
- 0
Вам будут интересны эти курсы:
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Формирование компетенций межкультурной коммуникации в условиях реализации ФГОС»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Клиническая психология: теория и методика преподавания в образовательной организации»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Введение в сетевые технологии»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «История и философия науки в условиях реализации ФГОС ВО»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Основы построения коммуникаций в организации»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Организация практики студентов в соответствии с требованиями ФГОС медицинских направлений подготовки»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Правовое регулирование рекламной и PR-деятельности»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Организация маркетинга в туризме»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Источники финансов»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Техническая диагностика и контроль технического состояния автотранспортных средств»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Осуществление и координация продаж»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Технический контроль и техническая подготовка сварочного процесса»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Управление качеством»
Word Meaning Lecture # 6 Grigoryeva M.
Word Meaning Approaches to word meaning Meaning and Notion (понятие) Types of word meaning Types of morpheme meaning Motivation
Each word has two aspects: the outer aspect ( its sound form) cat the inner aspect (its meaning) long-legged, fury animal with sharp teeth and claws
Sound and meaning do not always constitute a constant unit even in the same language EX a temple a part of a human head a large church
Semantics (Semasiology) Is a branch of lexicology which studies the meaning of words and word equivalents
Approaches to Word Meaning The Referential (analytical) approach The Functional (contextual) approach Operational (information-oriented) approach
The Referential (analytical) approach formulates the essence of meaning by establishing the interdependence between words and things or concepts they denote distinguishes between three components closely connected with meaning: the sound-form of the linguistic sign, the concept the actual referent
Basic Triangle concept – flower concept (thought, reference) – the thought of the object that singles out its essential features referent – object denoted by the word, part of reality sound-form (symbol, sign) – linguistic sign sound-form [rәuz] referent
In what way does meaning correlate with each element of the triangle ? • In what relation does meaning stand to each of them? •
Meaning and Sound-form are not identical different EX. dove — [dΛv] English [golub’] Russian [taube] German sound-forms BUT the same meaning
Meaning and Sound-form nearly identical sound-forms have different meanings in different languages EX. [kot] Russian – a male cat [kot] English – a small bed for a child identical sound-forms have different meanings (‘homonyms) EX. knight [nait]
Meaning and Sound-form even considerable changes in sound-form do not affect the meaning EX Old English lufian [luvian] – love [l Λ v]
Meaning and Concept concept is a category of human cognition concept is abstract and reflects the most common and typical features of different objects and phenomena in the world meanings of words are different in different languages
Meaning and Concept identical concepts may have different semantic structures in different languages EX. concept “a building for human habitation” – English Russian HOUSE ДОМ + in Russian ДОМ “fixed residence of family or household” In English HOME
Meaning and Referent one and the same object (referent) may be denoted by more than one word of a different meaning cat pussy animal tiger
Meaning is not identical with any of the three points of the triangle – the sound form, the concept the referent BUT is closely connected with them.
Functional Approach studies the functions of a word in speech meaning of a word is studied through relations of it with other linguistic units EX. to move (we move, move a chair) movement (movement of smth, slow movement) The distriution ( the position of the word in relation to others) of the verb to move and a noun movement is different as they belong to different classes of words and their meanings are different
Operational approach is centered on defining meaning through its role in the process of communication EX John came at 6 Beside the direct meaning the sentence may imply that: He was late He failed to keep his promise He was punctual as usual He came but he didn’t want to The implication depends on the concrete situation
Lexical Meaning and Notion denotes the Lexical meaning is reflection in the realization of a mind of real objects notion by means of a definite language system Notion is a unit of Word is a language thinking unit
Lexical Meaning and Notions are Meanings are internationally limited especially with the nations of the same EX GO (E) —- ИДТИ(R) cultural level “To move” BUT !!! To GO by bus (E) ЕХАТЬ (R) EX Man -мужчина, человек Она – хороший человек (R) She is a good person (E)
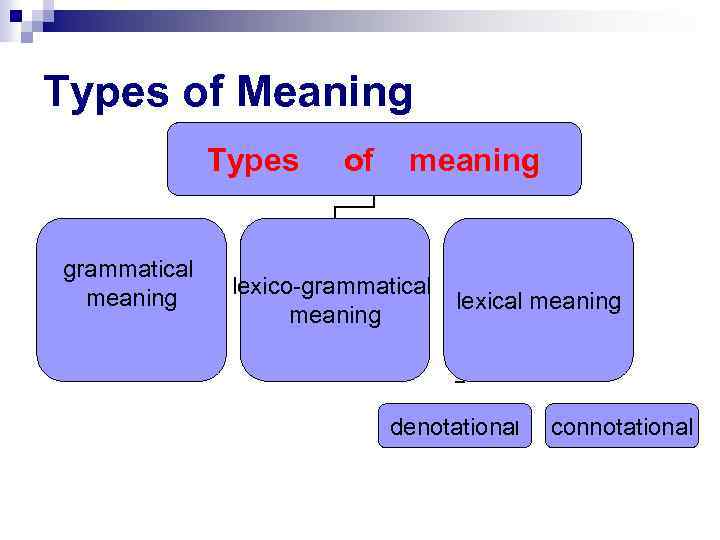
Types of Meaning Types grammatical meaning of meaning lexico-grammatical meaning lexical meaning denotational connotational
Grammatical Meaning component of meaning recurrent in identical sets of individual forms of different words EX. girls, winters, toys, tables – grammatical meaning of plurality asked, thought, walked – meaning of past tense
Lexico-grammatical meaning (part –of- speech meaning) is revealed in the classification of lexical items into: major word classes (N, V, Adj, Adv) minor ones (artc, prep, conj) words of one lexico-grammatical class have the same paradigm
Lexical Meaning is the meaning proper to the given linguistic unit in all its forms and distributions EX. Go – goes — went lexical meaning – process of movement
PRACTICE Group the words into 3 column according to the grammatical, lexical or part-of –speech meaning • • Boy’s, nearest, at, beautiful, think, man, drift, wrote, tremendous, ship’s, the most beautiful, table, near, for, went, friend’s, handsome, thinking, boy, nearer, thought, boys, lamp, go, during.
• Grammatical 1. The case of nouns: boy’s, ship’s, friend’s 2. The degree of comparison of adj: nearest, the most beautiful 3. The tense of verbs: wrote, went, thought • Lexical 1. Think, thinking, thought 2. Went, go 3. Boy’s, boys 4. Nearest, nearer 5. At, for, during (“time”) 6. Beautiful, the most beautiful • Part-of-speech Nouns—verbs—adj—-prep
Aspects of Lexical meaning The denotational aspect The connotational aspect The pragmatic aspect
Denotational Meaning “denote” – to be a sign of, stand as a symbol for” establishes the correlation between the name and the object makes communication possible EX booklet “a small thin book that gives info about smth”
PRACTICE Explain denotational meaning • • A lion-hunter To have a heart like a lion To feel like a lion To roar like a lion To be thrown to the lions The lion’s share To put your head in lion’s mouth
PRACTICE • A lion-hunter A host that seeks out celebrities to impress guests • To have a heart like a lion To have great courage • To feel like a lion To be in the best of health • To roar like a lion To shout very loudly • To be thrown to the lions To be criticized strongly or treated badly • The lion’s share Much more than one’s share • To put your head in lion’s mouth
Connotational Meaning reflects the attitude of the speaker towards what he speaks about it is optional – a word either has it or not Connotation gives additional information and includes: The emotive charge EX Daddy (for father) Intensity EX to adore (for to love) Imagery EX to wade through a book “ to walk with an effort”
PRACTICE Give possible interpretation of the sentences • She failed to buy it and felt a strange pang. • Don’t be afraid of that woman! It’s just barking! • He got up from his chair moving slowly, like an old man. • The girl went to her father and pulled his sleeve. • He was longing to begin to be generous. • She was a woman with shiny red hands and workswollen finger knuckles.
PRACTICE Give possible interpretation of the sentences • She failed to buy it and felt a strange pang. (pain—dissatisfaction that makes her suffer) • Don’t be afraid of that woman! It’s just barking! (make loud sharp sound—-the behavior that implies that the person is frightened) • He got up from his chair moving slowly, like an old man. (to go at slow speed—was suffering or was ill) • The girl went to her father and pulled his sleeve. (to move smth towards oneself— to try to attract smb’s attention) • He was longing to begin to be generous. (to start doing— hadn’t been generous before) • She was a woman with shiny red hands and work-swollen finger knuckles. (colour— a labourer involved into physical work , constant contact with water)
The pragmatic aspect of lexical meaning the situation in which the word is uttered, the social circumstances (formal, informal, etc. ), social relationships between the interlocutors (polite, rough, etc. ), the type and purpose of communication (poetic, official, etc. ) EX horse (neutral) steed (poetic) nag (slang) gee-gee (baby language)
PRACTICE State what image underline the meaning • I heard what she said but it didn’t sink into my mind. • You should be ashamed of yourself, crawling to the director like that. • They seized on the idea. • Bill, chasing some skirt again? • I saw him dive into a small pub. • Why are you trying to pin the blame on me? • He only married her for her dough.
PRACTICE State what image underline the meaning • I heard what she said but it didn’t sink into my mind. • (to understand completely) • You should be ashamed of yourself, crawling to the director like that. (to behave humbly in order to win favour) • They seized on the idea. (to be eager to take and use) • Bill, chasing some skirt again? (a girl) • I saw him dive into a small pub. (to enter suddenly) • Why are you trying to pin the blame on me? (to blame smb unfairly) • He only married her for her dough. (money)
Types of Morpheme Meaning lexical differential functional distributional
Lexical Meaning in Morphemes root-morphemes that are homonymous to words possess lexical meaning EX. boy – boyhood – boyish affixes have lexical meaning of a more generalized character EX. –er “agent, doer of an action”
Lexical Meaning in Morphemes has denotational and connotational components EX. –ly, -like, -ish – denotational meaning of similiarity womanly , womanish connotational component – -ly (positive evaluation), -ish (deragotary) женственный женоподобный
Differential Meaning a semantic component that serves to distinguish one word from all others containing identical morphemes EX. cranberry, blackberry, gooseberry
Functional Meaning found only in derivational affixes a semantic component which serves to refer the word to the certain part of speech EX. just, adj. – justice, n.
Distributional Meaning the meaning of the order and the arrangement of morphemes making up the word found in words containing more than one morpheme different arrangement of the same morphemes would make the word meaningless EX. sing- + -er =singer, -er + sing- = ?
Motivation denotes the relationship between the phonetic or morphemic composition and structural pattern of the word on the one hand, and its meaning on the other can be phonetical morphological semantic
Phonetical Motivation when there is a certain similarity between the sounds that make up the word and those produced by animals, objects, etc. EX. sizzle, boom, splash, cuckoo
Morphological Motivation when there is a direct connection between the structure of a word and its meaning EX. finger-ring – ring-finger, A direct connection between the lexical meaning of the component morphemes EX think –rethink “thinking again”
Semantic Motivation based on co-existence of direct and figurative meanings of the same word EX a watchdog – ”a dog kept for watching property” a watchdog – “a watchful human guardian” (semantic motivation)
• PRACTICE
Analyze the meaning of the words. Define the type of motivation a) morphologically motivated b) semantically motivated • Driver • Leg • Horse • Wall • Hand-made • Careless • piggish
Analyze the meaning of the words. Define the type of motivation a) morphologically motivated b) semantically motivated • Driver Someone who drives a vehicle morphologically motivated • Leg The part of a piece of furniture such as a table semantically motivated • Horse A piece of equipment shaped like a box, used in gymnastics semantically motivated
• Wall Emotions or behavior preventing people from feeling close semantically motivated • Hand-made Made by hand, not machine morphologically motivated • Careless Not taking enough care morphologically motivated • Piggish Selfish semantically motivated
what she said but it didn’t sink in my mind “do down to the bottom” ‘to be accepted by mind” semantic motivation I heard Why are you trying to pin the blame on me? “fasten smth somewhere using a pin” – ”to blame smb” semantic motivation I was following the man when he dived into a pub. “jump into deep water” – ”to enter into suddenly” semantic motivation You should be ashamed of yourself, crawling to the director like that “to move along on hands and knees close to the ground” – “to behave very humbly in order to win favor” semantic motivation
3.1. The object of semasiology. Two approaches to the study of meaning.
3.2. Types of meaning.
3.3. Meaning and motivation.
3.1. The branch of lexicology which studies meaning is called » semasiology «. Sometimes the term » semantics » is used as a synonym to semasiology, but it is ambiguous as it can stand as well for (1) the expressive aspect of language in general and (2) the meaning of one particular word.
Meaning is certainly the most important property of the word but what is » meaning»?
Meaning is one of the most controversial terms in lexicology. At present there is no generally accepted definition of meaning. Prof. Smirnitsky defines meaning as » a certain reflection in the mind of objects, phenomena or relations that makes part of the linguistic sign, its so-called inner facet, whereas the sound form functions as its outer facet». Generally speaking, meaning can be described as a component of the word through which a concept is communicated, enabling the word to denote objects in the real world.
There are two approaches to the study of meaning: the referential approach and the functional approach. The former tries to define meaning in terms of relations between the word (sound form), concept (notion, thought) and referent (object which the word denotes). They are closely connected and the relationship between them is represented by » the semiotic triangle» (= the basic triangle) of Ogden and Richards (in the book » The Meaning of Meaning» (1923) by O.K. Ogden and I.A. Richards).


 |
symbol referent
(sound form)
This view denies a direct link between words and things, arguing that the relationship can be made only through the use of our minds. Meaning is related to a sound form, concept and referent but not identical with them: meaning is a linguistic phenomenon while neither concept nor referent is.
The main criticism of this approach is the difficulty of identifying » concepts»: they are mental phenomena and purely subjective, existing in the minds of individuals. The strongest point of this approach is that it connects meaning and the process of nomination.
The functional approach to meaning is less concerned with what meaning is than with how it works. It is argued, to say that » words have meanings» means only that they are used in a certain way in a sentence. There is no meaning beyond that. Ludwig Wittgenstein (1889-1951), in particular, stressed the importance of this approach in his dictum: » The meaning of the word is its use in the language». So meaning is studied by making detailed analyses of the way words are used in contexts, through their relations to other words in speech, and not through their relations to concepts or referents.
Actually, the functional approach is basically confined to the analysis of sameness or difference of meaning. For example, we can say that in » take the bottle » and » take to the bottle » take has different meaning as it is used differently, but it does not explain what the meaning of the verb is. So the functional approach should be used not as the theoretical basis for the study of meaning, but only as complementary to the referential approach.
3.2. Word meaning is made up of different components, commonly known as types of meaning. The two main types of meaning are grammatical meaning and lexical meaning.
Grammatical meaning belongs to sets of word-forms and is common to all words of the given part of speech,
e.g. girls, boys, classes, children, mice express the meaning of » plurality».
Lexical meaning belongs to an individual word in all its forms. It comprises several components. The two main ones are the denotational component and the connotational component.
The denotational (= denotative) component, also called » referential meaning» or » cognitive meaning», expresses the conceptual (notional) content of a word; broadly, it is some information, or knowledge, of the real-world object that the word denotes. Basically, this is the component that makes communication possible.
e.g. notorious » widely-known», celebrated » known widely».
The connotational (connotative) component expresses the attitude of the speaker to what he is saying, to the object denoted by the word. This component consists of emotive connotation and evaluative connotation.
1) Emotive connotation (= » affective meaning», or an emotive charge),
e.g. In » a single tree » single states that there is only one tree, but » a lonely tree » besides giving the same information, also renders (conveys) the feeling of sadness.
We shouldn’t confuse emotive connotations and emotive denotative meanings in which some emotion is named, e.g. horror, love, fear, etc.
2) Evaluative connotation labels the referent as » good» or » bad»,
e.g. notorious has a negative evaluative connotation, while celebrated a positive one. Cf.: a notorious criminal/liar/ coward, etc. and a celebrated singer/ scholar/ artist, etc.
It should be noted that emotive and evaluative connotations are not individual, they are common to all speakers of the language. But emotive implications are individual (or common to a group of speakers), subjective, depend on personal experience.
e.g. The word » hospital » may evoke all kinds of emotions in different people (an architect, a doctor, an invalid, etc.)
Stylistic connotation, or stylistic reference, another component of word meaning, stands somewhat apart from emotive and evaluative connotations. Indeed, it does not characterize a referent, but rather states how a word should be used by referring it to a certain functional style of the language peculiar to a specific sphere of communication. It shows in what social context, in what communicative situations the word can be used.
Stylistically, words can be roughly classified into literary, or formal (e.g. commence, discharge, parent), neutral (e.g. father, begin, dismiss) and non-literary, or informal (e.g. dad, sack, set off).
3.3. The term » motivation » is used to denote the relationship between the form of the word, i.e. its sound form, morphemic composition and structural pattern, and its meaning.
There are three main types of motivation: phonetic, morphological and semantic.
1) Phonetic motivation is a direct connection between the sound form of a word and its meaning. There are two types of phonetic motivation: sound imitation and sound symbolism.
a) Sound imitation, or onomatopoeia: phonetically motivated words are a direct imitation of the sounds they denote (or the sounds produced by actions or objects they denote),
e.g. buzz, swish, bang, thud, cuckoo.
b) Sound symbolism. It’s argued by some linguists that the sounds that make up a word may reflect or symbolise the properties of the object which the word refers to, i.e. they may suggest size, shape, speed, colour, etc.
e.g. back vowels suggest big size, heavy weight, dark colour, front vowels suggest lightness, smallness, etc.
Many words beginning with sl- are slippery in some way: slide, slip, slither, sludge, etc. or pejorative: slut, slattern, sly, sloppy, slovenly; words that end in -ump almost all refer to some kind of roundish mass: plump, chump, rump, hump, stump.
Certainly, not every word with these phonetic characteristics will have the meaning suggested. This is, perhaps, one of the reasons why sound symbolism is not universally recognized in linguistics.
2) Morphological motivation is a direct connection between the lexical meaning of the component morphemes, the pattern of their arrangement and the meaning of the word.
Morphologically motivated words are those whose meaning is determined by the meaning of their components,
e.g. re-write » write again», ex-wife » former wife».
The degree of morphological motivation may be different. Words may be fully motivated (then they are transparent), partially motivated and non-motivated (idiomatic, or opaque).
a) If the meaning of the word is determined by the meaning of the components and the structural pattern, it is fully motivated: e.g. hatless.
b) If the connection between the morphemic composition of a word and its meaning is arbitrary, the word is non-motivated, e.g. buttercup » yellow-flowered plant».
c) In hammer -er shows that it is an instrument, but what is » hamming «? » Ham » has no lexical meaning in this word, thus the word is partially motivated. Cf. also cranberry.
Motivation may be lost in the course of time,
e.g. in OE wī fman was motivated morphologically: wī f + man » wife of a man»; now it is opaque; its motivation is said to be faded (woman).
3) Semantic motivation is based on co-existence of direct and figurative meanings of the same word,
e.g. butterfly – 1) insect; 2) showy and frivolous person.(= metaphorical extension of the direct meaning).
|
Практические расчеты на срез и смятие При изучении темы обратите внимание на основные расчетные предпосылки и условности расчета… |
Функция спроса населения на данный товар Функция спроса населения на данный товар: Qd=7-Р. Функция предложения: Qs= -5+2Р,где… |
Аальтернативная стоимость. Кривая производственных возможностей В экономике Буридании есть 100 ед. труда с производительностью 4 м ткани или 2 кг мяса… |
Вычисление основной дактилоскопической формулы Вычислением основной дактоформулы обычно занимается следователь. Для этого все десять пальцев разбиваются на пять пар… |











![Meaning and Sound-formare not identical
different
EX. dove - [dΛv]... Meaning and Sound-formare not identical
different
EX. dove - [dΛv]...](https://documents.infourok.ru/2d0c9b9d-1c12-4da2-8c1e-80496902c301/slide_10.jpg)

















































![Meaning and Sound-form are not identical different EX. dove - [dΛv] English [golub’] Russian Meaning and Sound-form are not identical different EX. dove - [dΛv] English [golub’] Russian](https://present5.com/presentation/54919015_285694613/image-10.jpg)
![Meaning and Sound-form nearly identical sound-forms have different meanings in different languages EX. [kot] Meaning and Sound-form nearly identical sound-forms have different meanings in different languages EX. [kot]](https://present5.com/presentation/54919015_285694613/image-11.jpg)