Setting the background color of a web page or an element on the page can enable you to create unique layouts.
Take the homepage of Delish as an example. The background image of its header section is a colorful soup. To ensure readers can still see the name of the recipe, the background color of the text box is set to white. The effect is striking and easy to read.
In the past, you could use the background color attribute to change the background color of a page or element.
Say you wanted to change the background color of a web page to maroon. You would have simply added the bgcolor attribute in the opening body tag and set it to the hex color code #800000, as shown below.
<body bgcolor=”#800000">
However, this attribute has been deprecated in the latest version of HTML and replaced by a much better alternative, the CSS background-color property. Using this property, you can add and change background colors on your website.
Let’s go through how you can change background color in HTML. We’ll cover:
- Adding a background color in HTML
- Changing the background color in HTML
- Changing the background color of a div
- Choosing how to write your HTML color codes
- Adding transparency to a background color
- Creating a gradient background color
- Frequently asked questions
To add background color in HTML, use the CSS background-color property. Set it to the color name or code you want and place it inside a style attribute. Then add this style attribute to an HTML element, like a table, heading, div, or span tag.
Adding a background color can help a certain element stand out on the page, making it more readable.
We’ll walk through this process step-by-step. For this tutorial, we’ll make a table in HTML as an example.
1. Identify the HTML element you’d like to add a background to or create one.
Scan your HTML code to pinpoint which element you’d like to change. If it’s the header, look for the <header> opening tag. If it’s a div, look for the <div> tag.
In this example, we’re creating a table with the <table> tag.
2. Choose an HTML background color.
You have plenty of HTML color codes to choose from. For this example, we’ll make the color #33475b.
3. Add a style attribute to the opening tag.
Next, add the style attribute to the opening tag of your element. For this tutorial, only the background color of this specific table will change. The change will not affect any other element on the page.
Here’s the HTML with inline CSS:
<table style="background-color:#33475b">
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Job Title</th>
<th>Email address</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Anna Fitzgerald</td>
<td>Staff Writer</td>
<td>example@company.com</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>John Smith</td>
<td>Marketing Manager</td>
<td>example2@company.com</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Zendaya Grace</td>
<td>CEO</td>
<td>example2@company.com</td>
</tr>
</table>
That’s simple. Now let’s look at what to do if you want to set the background color of multiple elements on a page.
How to Change Background Color in HTML
Let’s say you set the background color of your entire web page to one color and want to change the background color of a specific element to another color. The good news is the process for changing the background color of an element is nearly identical to the process for adding it.
You can use inline CSS to do this, but we’ll use multiple styles of CSS in the example below. Let’s walk through this process step-by-step.
1. Find the “body” CSS selector.
Rather than add this CSS in the body tag of the HTML file, we’ll add it using the body CSS selector. Find it in your website’s CSS code.
2. Change the background color of the body.
Next, we’ll change the background color of the entire web page using the background-color property.
Here’s the CSS:
body {
background-color: #DBF9FC;
}
Here’s the result:
If this was the only CSS, then everything on the page would have the same light blue background. Next, we’ll add inline CSS to change the background color of the table.
3. Add inline CSS to change the background color of specific elements.
If we want to change the background color of the table, we can use inline CSS to target that single element.
Here’s the opening tag with inline CSS:
<table style="background-color:#33475b">
Here’s the result:
How to Change a Div Background Color
A div is a container element that’s commonly used to designate different sections of a webpage.
Changing the background color of a div is identical to changing the background color of your web page’s body.
Usually, a web page will have many divs. In this tutorial, we’ll teach you how to change one div only.
Let’s go through the process step-by-step.
1. Add a CSS class to the div you’d like to change.
First, find the div in your HTML code and add a class to the opening tag. Adding a class to an element will allow you to change that element only.
Here’s what that looks like:
<div class=”example”>This is a div on a webpage. </div>
2. Add the new class selector to your CSS code.
Next, head over to your CSS code and add your new class selector. Within the brackets, include the background-color property.
Here’s what that looks like:
.example {background-color: ; }
3. Choose a new background color.
Next, choose a CSS background color for your background-color property. We chose rgb(255, 122, 89).
Here’s what that code looks like:
.example { background-color: rgb(255, 122, 89); }
Here’s the result:
All done! You’ve changed the background of a div on your web page.
Learn More: The Beginner’s Guide to HTML & CSS
Want to learn more about HTML? Download our free guide for best practices for getting started with HTML.
Background Color HTML Codes
In this post, we’ve been using color codes (more specifically, hex color codes) to add colors to the backgrounds of our page elements. But, there are actually a few ways to specify your background colors. Next, let’s review the different ways you can write colors in CSS.
Background Color Hex Codes
Hex codes are the most popular format for adding color to page elements in HTML. A hex code is a hexadecimal (base 16) number preceded by a hash symbol (#).
Every hex code contains six characters, and each pair of characters determines the intensity of the three primary colors (red, green, and blue in that order) from 00 (lowest intensity) to FF (highest intensity).
For example, the color white is the highest intensity of all three colors, so its hex code is #FFFFFF. Black is the opposite — the lowest intensity of all colors, or #000000. For the color green, we crank up the intensity for green and lower it for red and blue, giving us the hex code #00FF00. HubSpot’s signature shade of orange, Solaris, has the hex code #FF5C35.
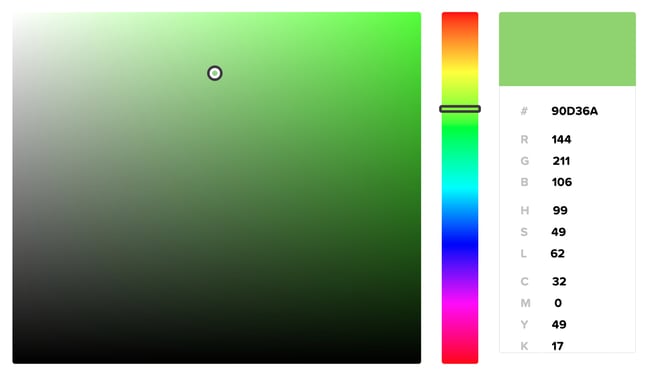
If you do the math, this comes out to 16,777,216 possible hex codes. Fortunately, you don’t need to guess which color works best for your background. You can use an HTML color picker like this one to select a color from a spectrum, then simply copy the hex code it gives you.
Image Source
Background Color Names
Hex values aren’t too difficult to understand, but there’s an even simpler way to add color in HTML: simply use the name of a color.
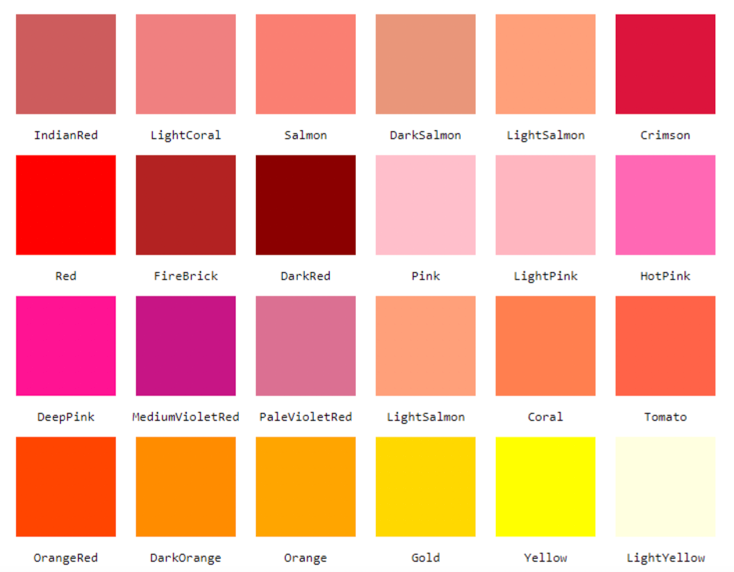
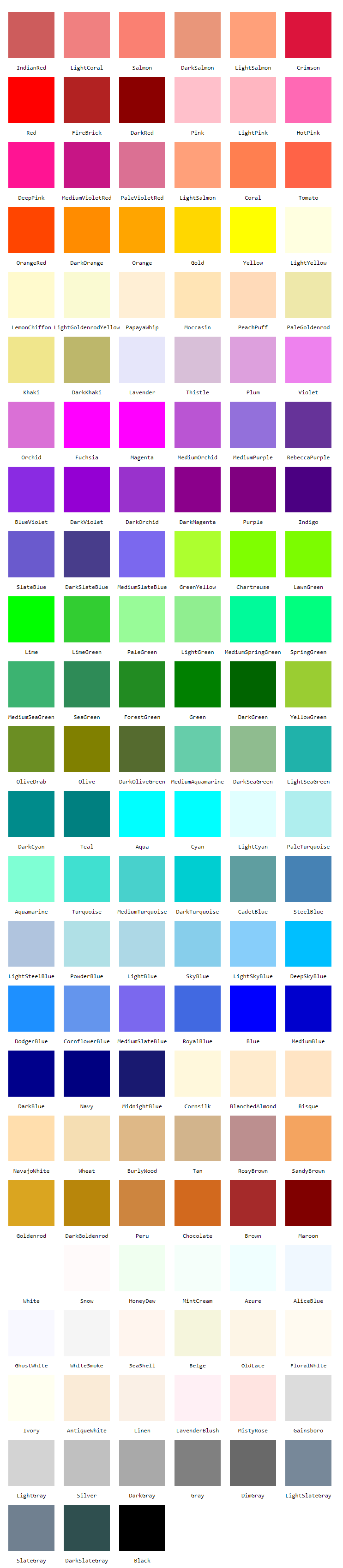
Modern browsers support 140 standardized HTML color names, including simple ones like Red, Green, Blue, Yellow, Orange, etc. There are also more precise hues like DarkRed, SpringGreen, SkyBlue, Khaki, and Coral.
Check out a color reference like this one for a list of all HTML color names and their corresponding hex and RGB codes. When you find a color value you like, use it as the value of your background-color property (no # symbol necessary).
body {
background-color: SpringGreen;
}
Background Color RGB Codes
We can also create HTML color values with RGB (red green blue) notation. Like hex codes, RGB values allow us to target a color value by specifying its red, green, and blue intensity.
To add color with RGB, we use the rgb() CSS function. This function takes three values inside the parentheses, each specifying the intensity of red, green, and blue in the color. Each value is a number from 0 to 255, with 0 being the least intense and 255 being the most intense.
For example, the RGB function for Solaris orange in CSS is rgb(255, 92, 53):
body {
background-color: rgb(255, 92, 53);
}
HTML color pickers will also provide RGB values along with hex codes, so this is the easiest way to find the RGB code you need. There are also plenty of hex-to-RGB converters online, like this one.
Alternatively, you can set an opacity level of your color with the CSS function rgba(). The “a” stands for alpha channel, which represents the level of transparency in a color. This function takes one extra value from 0 to 1, where 0 is completely transparent and 1 is completely opaque.
So, if I wanted to use Solaris with 75% transparency, I’d write the following:
body {
background-color: rgba(255, 92, 53, 0.75);
}
Background color HSL Values
Finally, you can use HSL values to set your colors in CSS. HSL, which stands for hue, saturation, and lightness, is written with the hsl() function. The syntax is similar to RGB, except you use percentages to indicate the saturation and lightness of the hue you pick.
To create Solaris with HSL, for example, use the function hsl(12, 100%, 60%).
body {
hsl(12, 100%, 60%);
}
You can also specify an alpha channel value with the function hsl(), which accepts an additional value from 0 to 1 and sets the transparency of the color.
How to Add Transparency to Your HTML Background Color
When changing background color in HTML, you aren’t limited to solid colors. You can change the opacity and transparency to create interesting visual effects.
To do that, you’d use the opacity property in CSS.
What’s the CSS opacity property?
The CSS opacity property is added to an HTML element (such as a div or a table) or a CSS attribute (such as a class) to make those elements partially or fully transparent. Values for this property range from 0 to 1, with 0 being completely transparent and 1 being completely opaque.
For this tutorial, we’ll use two buttons as an example. Let’s walk through the process of adding transparency step-by-step.
1. Identify the HTML elements you’d like to make transparent.
If you already know what you want to change, go ahead and find it in your HTML code.
In this tutorial, we have two Bootstrap buttons side by side. We want visitors to click one — the submit button — and not click the other — the “no thanks” option.
Here’s the HTML:
<button class="btn" type="submit">Submit</button>
<button class="btn" type="submit">No thanks</button>
We want to decrease the opacity of the latter to make it seem deactivated and drive fewer clicks.
To achieve this result, we’ll use the CSS opacity property after adding a class to the button we’ll change.
2. Add a class to the element you’d like to change.
Next, we’ll assign an additional CSS class to the second button to distinguish it from the first.
We’ll add the class btn-secondary to the button we want to deemphasize.
Here’s what that looks like:
<button class="btn" type="submit">Submit</button>
<button class="btn btn-secondary" type="submit">No thanks</button>
3. Add the class selector to your CSS code and apply the opacity property.
Now that you’ve created a new class, it’s time to add it to your CSS code.
To make the second button 40% see-through, we’ll use the .btn-secondary class selector to apply the opacity property. Then, we’ll set the opacity level to 0.4.
Here’s the CSS:
.btn-secondary {
opacity: 0.4;
}
Here’s the result:
You may have noticed we did not need to use the CSS background-color property because we used Bootstrap’s default modifier classes.
Learn more about Bootstrap in The Ultimate Guide to Bootstrap CSS.
How to Create an HTML Background Color Gradient
For even more style options, you can create a gradient background. This is a special type of image that most commonly shows one color gradually changing to another color in a certain direction like top to bottom, left to right, or diagonally.
These are known as linear gradients. To create a linear gradient, you have to specify at least two color stops.
Let’s look at four quick examples below.
Linear Gradient Tutorial — Top to Bottom
Say you want your background color to transition from white at the top of the screen to blue at the bottom.
Using the body CSS selector, you’ll apply unique style properties to the body of the web page. Here’s what that looks like from beginning to end.
- Step 1: Find the body selector in your CSS code.
- Step 2: Your body might already have a background-color property. Delete that. Rather than use the background-color property, you’ll use the background-image property.
- Step 3: Set the property to “linear-gradient” and specify two color stops in parentheses. Here’s the syntax:
body { background-image: linear-gradient(color, color); }
- Step 4: Next, you want to set the HTML element’s height to 100% to ensure this image takes up the entire screen.
All together, here’s the CSS:
html {
height: 100%;
}
body {
background-image: linear-gradient(#FFFFFF, rgb(255, 122, 89));
}
Here’s the HTML (including the body tags):
<body>
<h1>Linear Gradient</h1>
<p>This linear gradient starts as white at the top and transitions to orange at the bottom.</p>
</body>
Here’s the result:
Linear Gradient — Left to Right
No direction was specified for the linear gradient above. That’s because top to bottom is the default direction.
If you’d like to specify another direction, then you’ll add it in the parentheses, before the color stops.
Here’s the CSS for the example above, rewritten so the gradient is left to right.
html {
height: 100%;
}
body {
background-image: linear-gradient(to right, #FFFFFF, rgb(255, 122, 89));
}
Here’s the HTML:
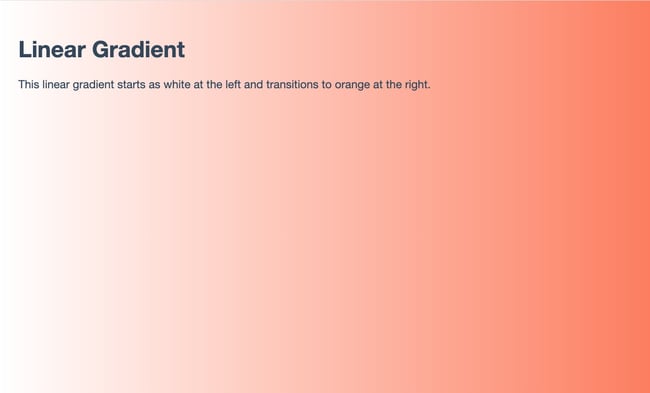
<body>
<h1>Linear Gradient</h1>
<p>This linear gradient starts as white at the left and transitions to orange at the right.</p>
</body>
Here’s the result:
Linear Gradient — 45° Angle
If I wanted the gradient to go diagonally, then I could use the keywords “to bottom right,” “to bottom left,” “to top right,” or “to top left.” If you’d like more control over the direction of your gradient, then you could use angles rather than keywords.
Note that a value of 0 degrees is equivalent to the keyword «to top,” 90 degrees is equivalent to «to right,” and 180 degrees is equivalent to «to bottom.”
If I wanted the gradient to go to the top right, for example, then I could set the direction to 45deg.
Here’s the CSS:
html {
height: 100%;
}
body {
background-image: linear-gradient(45deg, #FFFFFF, rgb(255, 122, 89));
}
Here’s the HTML:
<body>
<h1>Linear Gradient</h1>
<p>This linear gradient starts as white at the bottom left and transitions to orange at the top right.</p>
</body>
Here’s the result:
Linear Gradient — Multiple Color Stops
To create a linear gradient, you need a minimum of two color stops. But there’s no maximum, which means you can use as many as you want. Below is an example with four color stops.
Here’s the CSS:
html {
height: 100%;
}
body {
background-image: linear-gradient(to bottom right, #33475b, #0033CC, #FF77CC, rgb(255, 122, 89));
}
Here’s the HTML:
<body>
<h1>Linear Gradient</h1>
<p>This linear gradient starts as dark blue at the top left and transitions from pink to orange at the bottom right.</p>
</body>
Here’s the result:
FAQs: Changing Background Color in HTML
Still have questions? We have answers for you.
How do you change text background color in HTML?
You can change the background color of text in HTML by adding a background-color property to a paragraph (p) or heading (H1, H2, H3… ) element.
Add this property either via inline CSS or on your website’s CSS code.
What is the default background color in HTML?
The default background color in HTML is transparent.
How do I make a background color transparent?
You can make a background color fully or partially transparent by using an RGBA color code to define the background-color property.
Here’s what that looks like in CSS:
background-color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0);
The last value determines transparency. Be sure that it’s set to 0 if you want the color to be completely invisible.
How do I remove background color in HTML?
You can fully remove background color by setting the background-color property to “transparent.”
Here’s what that looks like in CSS:
background-color: transparent;
Changing Your Background Color with HTML & CSS
Using HTML and CSS, you can add background color to your web page or different elements on the page. This background color can be solid, transparent, or gradient depending on the style that you like. This basic web design knowledge can enable you to customize your website and make your content more readable and engaging.
Editor’s note: This post was originally published in September 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.
Download Article
An easy-to-follow guide for coding with CSS and HTML to add the background colors of a page
Download Article
- Setting a Solid Background Color
- Creating a Gradient Background
- Creating a Changing Background
- Q&A
- Tips
- Warnings
|
|
|
|
|
Did you want to change the background color of that page using HTML? Unfortunately, with HTML 5, this is no longer possible in just HTML coding. Instead, you’ll need to use both HTML and CSS coding, which works even better. This wikiHow teaches you how to change the background color of a web page by editing its HTML and CSS.
Things You Should Know
- Although the attribute for HTML to manage background color is gone, you can still use HTML with CSS to change your background color easily.
- You’ll need a numeric code for the color you want if you want a specific color. If you don’t need a specific color, you can use words like «orange» or «light blue.»
- When editing a web page with HTML and CSS, you can create a solid background, gradient, or changing background.
-
1
Find your document’s «html» header. It should be near the top of the document.
-
2
Add the «background-color» property to the «body» element. Type
background-color:between the body brackets. You should now have the following «body» element:- In this context, only one spelling of «color» will work; you can’t use «colour» here.
body { background-color: }
Advertisement
-
3
Add your desired background color to the «background-color» property. Type your selected color’s numeric code followed by a semicolon next to the «background-color:» element to do so. For example, to set your page’s background to pink, you would have the following:
body { background-color: #d24dff; }
-
4
Review your «style» information. At this point, your HTML document’s header should resemble the following:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> body { background-color: #d24dff } </style> </head> </html>
-
5
Use «background-color» to apply background colors to other elements. Just as you set it in the body element, you can use «background-color» to define the backgrounds of other elements such as headers, paragraphs, and so on. For example, to apply a background color to a main header (<h1>) or a paragraph (<p>), you would have something resembling the following code:[1]
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> body { background-color: #93B874; } h1 { background-color: #00b33c; } p { background-color: #FFFFFF); } </style> </head> <body> <h1>Header with Green Background</h1> <p>Paragraph with white background</p> </body> </html>
Advertisement
-
1
Find your document’s «html» header. It should be near the top of the document.
-
2
Understand the basic syntax of this process. When making a gradient, there are two pieces of information you’ll need: the starting point/angle, and the colors that the gradient will transition between. You can select multiple colors to have the gradient move between all of them, and you can set a direction or angle for the gradient.[2]
background: linear-gradient(direction/angle, color1, color2, color3, etc);
}}
-
3
Make a vertical gradient. If you don’t specify the direction, the gradient will go from top to bottom. To create your gradient, add the following code between the
<style></style>tags:- Different browsers have different implementations of the gradient function, so you’ll have to include several versions of the code.
html { min-height: 100%; } body { background: -webkit-linear-gradient(#93B874, #C9DCB9); background: -o-linear-gradient(#93B874, #C9DCB9); background: -moz-linear-gradient(#93B874, #C9DCB9); background: linear-gradient(#93B874, #C9DCB9); background-color: #93B874; }
-
4
Make a directional gradient. If you’d rather create a gradient that isn’t strictly vertical, you can add direction to the gradient in order to change the way the color shift appears. Do so by typing the following in between the
<style></style>tags:[3]
- You can play around with the «left» and «right» tags to experiment with different directions for your gradient.
html { min-height: 100%;} body { background: -webkit-linear-gradient(left, #93B874, #C9DCB9); background: -o-linear-gradient(right, #93B874, #C9DCB9); background: -moz-linear-gradient(right, #93B874, #C9DCB9); background: linear-gradient(to right, #93B874, #C9DCB9); background-color: #93B874; }
-
5
Use other properties to adjust the gradient. There’s a lot more that you can do with gradients.
- For example, not only can you add more than two colors, you can also put a percentage after each one. This will allow you to set how much spacing you want each color segment to have. Here’s a sample gradient that uses this principle:
background: linear-gradient(#93B874 10%, #C9DCB9 70%, #000000 90%);
- For example, not only can you add more than two colors, you can also put a percentage after each one. This will allow you to set how much spacing you want each color segment to have. Here’s a sample gradient that uses this principle:
-
6
Add transparency to your colors. This will make the color fade. Use the same color to fade from the color to nothing. You’ll need to use the rgba() function to define the color. The ending value determines the transparency: 0 for solid and 1 for transparent.
background: linear-gradient(to right, rgba(147,184,116,0), rgba(147,184,116,1));
-
7
Review your completed code. The code to create a color gradient as your website’s background will look something like this:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> html { min-height: 100%; } body { background: -webkit-linear-gradient(left, #93B874, #C9DCB9); background: -o-linear-gradient(right, #93B874, #C9DCB9); background: -moz-linear-gradient(right, #93B874, #C9DCB9); background: linear-gradient(to right, #93B874, #C9DCB9); background-color: #93B874; } </style> </head> <body> </body> </html>
Advertisement
-
1
Find your document’s «html» header. It should be near the top of the document.
-
2
Add the animation property to the «body» element. Type the following into the space below the «body {» bracket and above the closing bracket:[4]
- The top line of text is for Chromium-based browsers while the bottom line of text is for other browsers.
-webkit-animation: colorchange 60s infinite; animation: colorchange 60s infinite;
-
3
Add your colors to the animation. Now you’ll use the @keyframes rule to set the background colors through which you’ll cycle, as well as the length of time each color will appear on the page. Again, you’ll need separate entries for the different sets of browsers. Enter the following lines of code below the closed «body» bracket:[5]
- Note that the two rules (@-webkit-keyframes and @keyframes have the same background colors and percentages. You’ll want these to stay uniform so the experience is the same on all browsers.
- The percentages (0%, 25%, etc) are of the total animation length (60s). When the page loads, the background will be the color set at 0% (#33FFF3). Once the animation has played for 25% of of 60 seconds, the background will turn to #7821F, and so on.
- You can modify the times and colors to fit your desired outcome.
@-webkit-keyframes colorchange { 0% {background: #33FFF3;} 25% {background: #78281F;} 50% {background: #117A65;} 75% {background: #DC7633;} 100% {background: #9B59B6;} } @keyframes colorchange { 0% {background: #33FFF3;} 25% {background: #78281F;} 50% {background: #117A65;} 75% {background: #DC7633;} 100% {background: #9B59B6;} }
-
4
Review your code. Your entire code for the changing background color should resemble the following:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> body { -webkit-animation: colorchange 60s infinite; animation: colorchange 60s infinite; } @-webkit-keyframes colorchange { 0% {background: #33FFF3;} 25% {background: #78281F;} 50% {background: #117A65;} 75% {background: #DC7633;} 100% {background: #9B59B6;} } @keyframes colorchange { 0% {background: #33FFF3;} 25% {background: #78281F;} 50% {background: #117A65;} 75% {background: #DC7633;} 100% {background: #9B59B6;} } </style> </head> <body> </body> </html>
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
How do I set a background color for a specific width?
Use the background-size property inside of the «body» element. For example, «background-size: 300px 150px» makes the background 300 pixels wide and 150 pixels high.
-
Question
It does not work. What can I do?
UsernameHere11
Community Answer
To make it black, try:
body {
background-color: #190707} -
Question
What is the correct HTML for adding a background color?
My text goes here!
Replace the html code above with your text and selected your preferred color.
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
-
Use online HTML pickers if you want a very specific color for your background. If, for example, you want the background to be the same color as your walls, you can match HTML colors with paint splotches at certain sites.
-
If you want to use basic colors within your HTML code, you can type the colors’ names without the pound sign (#) instead of using an HTML color code. For example: to create an orange background, you would type in
background-color: orange;here.
Show More Tips
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
Advertisement
-
Make sure you test any changes to your website before publishing them online.
Advertisement
References
About This Article
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 1,497,602 times.
Is this article up to date?
First thing you should know is that there are different types of HTML colors, such as Hex color codes, HTML color names, RGB and RGBa values, HSL colors, etc. To choose your preferred color use our Color Tools.
In this snippet, you can find many different ways of adding a background color. Let’s start from the easiest one.
Add the style attribute to the <body> element
You can set a background color for an HTML document by adding style="background-color:" to the <body> element.
Example of setting a background color with the style attribute:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title of the document</title>
</head>
<body style="background-color:#1c87c9;">
<h1>Some heading</h1>
<p>Some paragraph for example.</p>
</body>
</html>Result
Some heading
Some paragraph for example.
Add the CSS background-color property to the <body> element
The background-color property is used to change the background color. Inserting it to the <body> element you will have a full colored cover of the page.
Example of setting a background color with the CSS background-color property:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title of the document </title>
<style>
body {
background-color: #1c87c9;
}
</style>
</head>
<body></body>
</html>You can also add a background color to specific elements in your document. For example, let’s see how to change the color of the heading and paragraphs.
Example of adding a background color to specific elements:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title of the document</title>
<style>
body {
background-color: #e6ebef;
}
h2 {
background-color: #8ebf42;
}
p {
background-color: #1c87c9;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Some heading with green background.</h2>
<p>Some paragraph with blue background.</p>
</body>
</html>Let’s see another example, where we add a background color with a color name value to the <h1> element. We specify a RGB value for the <h2>, HSL for the <p>, and RGBa value for the <span> element.
Example of setting background colors with different color types:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title of the document</title>
<style>
h1 {
background-color: lightblue;
}
h2 {
background-color: rgb(142, 191, 66);
}
p {
background-color: hsl(300, 100%, 25%);
}
span {
background-color: rgba(255, 127, 80, 0.58);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Example</h1>
<h2>Some heading with green background.</h2>
<p>Some paragraph with blue background.</p>
<span>Some paragraph for</span>
</body>
</html>Gradient backgrounds let you create smooth transitions between two or more specified colors.
There are two types of gradient backgrounds: linear-gradient and radial-gradient.
In linear-gradient backgrounds, you can set a starting point for the colors. If you don’t mention a starting point, it will automatically set «top to bottom» by default.
Example of setting a linear-gradient background:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title of the document</title>
<style>
#grad {
height: 500px;
background-color: blue;/* For browsers that do not support gradients */
background-image: linear-gradient(to right, #1c87c9, #8ebf42);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Right to Left Linear Gradient background</h1>
<div id="grad"></div>
</body>
</html>The given example shows a linear gradient that starts from the left. It starts from blue, transitioning to green. Change it according to your requirements.
In radial gradient backgrounds, the starting point is defined by its center.
Example of setting a radial-gradient background:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title of the document</title>
<style>
#grad {
height: 500px;
background-color: grey;/* For browsers that do not support gradients */
background-image: radial-gradient(#e6ebef, #1c87c9, #8ebf42);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Radial Gradient Background</h1>
<div id="grad"></div>
</body>
</html>You can also adjust percentages of your colors like this: (color1 30%, color2 50%, color3 20%).
You can create a background which will change its colors in the mentioned time. For that, add the animation property to the <body> element. Use the @keyframes rule to set the background colors through which you’ll flow, as well as the length of time each color will appear on the page.
Example of creating a changing background:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title of the document</title>
<style>
body {
-webkit-animation: colorchange 20s infinite;
animation: colorchange 20s infinite;
}
@-webkit-keyframes colorchange {
0% {
background: #8ebf42;
}
25% {
background: #e6ebef;
}
50% {
background: #1c87c9;
}
75% {
background: #095484;
}
100% {
background: #d0e2bc;
}
}
@keyframes colorchange {
0% {
background: #8ebf42;
}
25% {
background: #e6ebef;
}
50% {
background: #1c87c9;
}
75% {
background: #095484;
}
100% {
background: #d0e2bc;
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Changing Background</h1>
</body>
</html>The percentages specify the animation length mentioned in «colorchange» (e.g. 20s).
You can change the time and colors to achieve your preferred result.
You have started creating your HTML page, and you want to give it some color – maybe change the color of the text or set a nice background. So how do you do that?
In this article I’ll show you how you can change the background color of a page in a few different ways.
You can change the background color of an HTML element using the background-color CSS property and giving it a value of a color.
p {
background-color: pink;
}For example, this code will make all paragraph elements in your HTML file have a pink background because the background-color property has a value of pink.
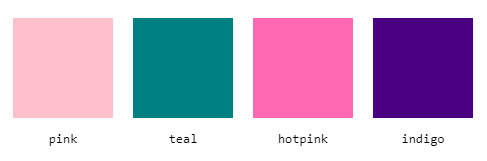
There are about 140 color names that you can use, like teal, hotpink, indigo and many others.
Note: if you give a background-color to an element and don’t see it change, it can be a syntax error, or it can also be that the element does not have a width or height. Try to put some content in it, or give it a width and an height using the CSS properties width and height.
There are actually almost 16.8 million colors that you can use. You can use all these colors using RGB values. There are also HSL colors where you have about 3.7 million colors to choose from. In the next section you will learn about all these different ways of creating colors.
Different Color Notations
The background-color property accepts colors as possible values. Here you will see four different notations for color values.
The first will be color names, and there are around 140 keywords that you can use. This is the easiest way to choose a color as it doesn’t require understanding special notations – but it has a limited range of options.
The second and third ways to name or choose colors are RGB values and hexadecimal values. In these notations, colors are identified by the amount of red, green, and blue that they contain.
This comes from how a screen produces color. A screen is made of pixels, and each pixel is lighted by LEDs of three different colors, green, blue and red, that can shine at different intensities.
The fourth notation is HSL colors, or Hue-Saturation-Lightness. This notation comes from Graphic Design, as it reflects a more natural way for humans to think about color: a pure color (hue), of which saturation and lightness can be varied.
You can use any of these color notations to give a color to the background, but let’s see them in more details, so you can choose the one you prefer.
HTML Color Names
There are 16 basic colors recognised in the first version of HTML. Now there are 140+ named colors you can use.
body {
background-color: black;
}body is given a black background
body being given a background-color of blackYou can see all the named colors in the appendix at the end of the article.
RGB Colors
RGB stands for Red-Green-Blue. The colors in this format are written rgb(0,0,0), where each value is a number between 0 and 255 representing the amount of red, green, and blue used to make each color, respectively.
For example, if you have rgb(0,0,0) you get black.
To get red, you write rgb(255,0,0), where there is as much red as possible with 255, 0 for blue, and 0 for green.
You can get other variations of red with small amounts of green and/or blue, and a bit less red. For example you can get an orange red with rgb(255,69,0) or a dark red with rgb(139,0,0).
div {
background-color: rgb(139,0,0);
}div elements are given a dark red background.
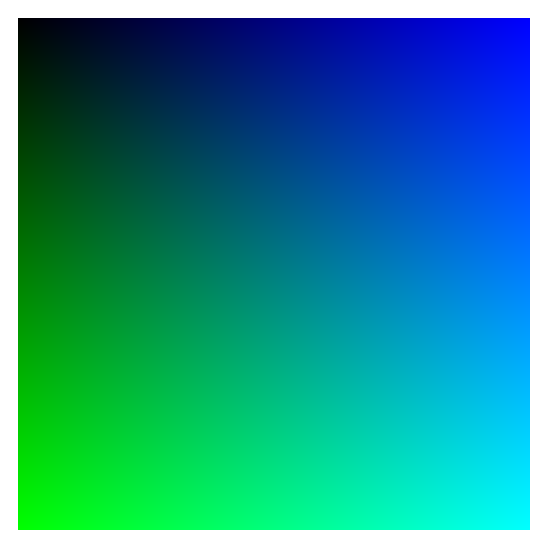
div element being given a background-color of rgb(139,0,0)Below an example of how the color changes when you adjust two of the RGB values: the top left corner of the colored square is equal to rgb(0,0,0), the top right is equal to rgb(0,0,255), the bottom left corner to rgb(0,255,0) and the bottom right corner to rgb(0,255,255).
Fortunately, you don’t need to guess the numbers to get the color you want. You can find various color pickers online that let you choose the color with sliders (or other methods) and give you the RGB color value you want to use.
Hexadecimal Colors
Hexadecimal colors are a different way to write RGB colors. With hexadecimals you also have three numbers, one for each color, with 256 possible values.
In this case, though, each color has two digits that go from 0 to F (that is, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, and A, B, C, D, E, F). One single digit has 16 possible values, and two digits have 256 possible values, from 00, to FF (255).
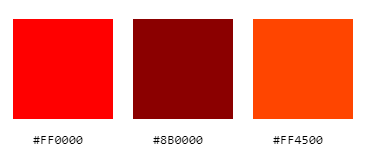
Hexadecimal colors are written with a # in front of the value. Red is written as #FF0000, dark red as #8B0000, and orange red as #FF4500, for example.
h1 {
background-color: #FF4500;
}h1 elements are given a background of orange red.
h1 element being given a background-color of #FF4500You can also use color pickers to generate hexadecimal values.
Hexadecimal shorthand
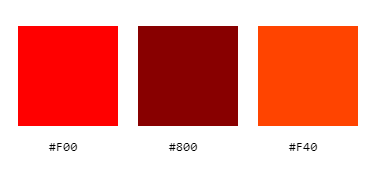
You can write hexadecimal numbers in shorthand form, using only three digits instead of six. For example, you can write red like #F00. This reduces the number of possible colors to just above 4,000, but it is shorter to write, and sometimes that is what is important.
Each digit is in place of two identical digits, so we can’t write #8B0000 in shorthand form, as 8 and B are not identical. But we can write #800 which is equal to #880000, pretty similar to the other dark red. And orange red can be #F40 (equal to #FF4400).
HSL Colors
HSL means Hue-Saturation-Lightness, and it is a completely different way of writing colors than what we have seen so far.
HSL colors are represented with three numbers: the hue goes from 0 to 360, and saturation and lightness from 0 to 100.
The hue determines the base color, and its value is an angle, a degree on the color wheel. In this case, red is 0, green is 120, blue is 240, and 360 is again red.
Saturation goes from 0, which makes the color gray, to 100, which shows the full color.
Lightness is the amount of black or white added to the color. 0 is black, 50 is the color itself, and 100 is white.
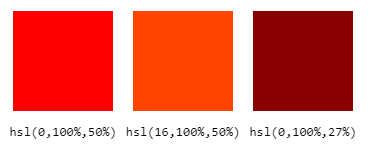
For example, you’d write red as hsl(0,100%,50%), orange red as hsl(16,100%,50%), and dark red as hsl(0,100%,27%).
It can be easier to find similar colors using HSL than with the other color schemes. With red and its variations you have seen that to get a darker red you can just change the lightness percentage, and mixing red with an other color is enough to change its hue value a bit.
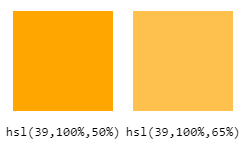
Let’s see it in action with a mixed color in hexadecimal, like orange (#FFA500 or rgb(255,166,0)), written in HSL as hsl(39,100%,50%). You can get a lighter orange just by increasing the lightness.
So for example you can write hsl(39,100%,65%) to get this lighter orange. With the other notations you would have needed to write rgb(255,193,77) or #FFC14D.
main element being given a background-color of hsl(39, 100%, 65%)
You can also find color pickers online for HSL colors.
Property name short-hand
You can also set the background color using the short-hand background property.
p {
background: pink;
}
body {
background: black;
}
div {
background: rgb(139,0,0);
}
h1 {
background: #FF4500;
}
main {
background: hsl(39,100%,65%);
}background shorthand property.
This is a more versatile property, as it is shorthand for various background properties, like background-image and background-position. When you use it with a color value it works exactly the same as background-color.
Conclusion
You have learned how to give a background color to your HTML elements using the background-color property and its shorthand background, and using different color notations.
Now you have all the tools you need to add whatever colors you want to your web pages. Enjoy!
Appendix
All 140+ named colors
Spelling Variations
The color names containing the word «Gray» can also be written with the spelling «Grey» as shown below.
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
| Internet Explorer | Chrome | Opera | Safari | Firefox | Android | iOS | |
| 6.0+ | 8.0+ | 1.0+ | 3.5+ | 1.0+ | 1.0+ | 1.0+ | 1.0+ |
Краткая информация
| Значение по умолчанию | transparent |
|---|---|
| Наследуется | Нет |
| Применяется | Ко всем элементам |
| Процентная запись | Неприменима |
| Ссылка на спецификацию | http://www.w3.org/TR/CSS21/colors.html#propdef-background-color |
Версии CSS
| CSS 1 | CSS 2 | CSS 2.1 | CSS 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
Описание
Определяет цвет фона элемента. Хотя это свойство не наследует свойства
своего родителя, из-за того, что начальное значение устанавливается
прозрачным, цвет фона дочерних элементов совпадает с цветом фона родительского элемента.
Синтаксис
background-color: <цвет> | transparent | inherit
Значения
См. цвет
- transparent
- Устанавливает прозрачный фон.
- inherit
- Наследует значение родителя.
Пример
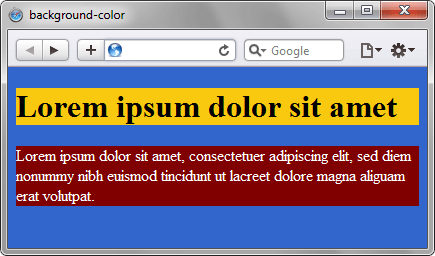
HTML5CSS2.1IECrOpSaFx
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>background-color</title>
<style>
body{
background-color: #3366CC; /* Цвет фона веб-страницы */
}
h1 {
background-color: RGB(249, 201, 16); /* Цвет фона под заголовком */
}
p {
background-color: maroon; /* Цвет фона под текстом параграфа */
color: white; /* Цвет текста */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet</h1>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit, sed diem
nonummy nibh euismod tincidunt ut lacreet dolore magna aliguam erat volutpat.</p>
</body>
</html>В данном примере для элементов веб-страницы применяется три различных способа задания фонового цвета. Результат примера показан на рис. 1.
Рис. 1. Применение background-color
Объектная модель
[window.]document.getElementById(«elementID«).style.backgroundColor
Браузеры
Internet Explorer до версии 7.0 включительно не поддерживает значение inherit.

![Download Now: 25 HTML & CSS Hacks [Free Guide]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/848be230-f06a-420e-9a24-82b45fe61632.png)





.png?width=269&name=Image%20Hackathon%20%E2%80%93%20Vertical%20(41).png)