Synonymy relates to the topic of semantics, which concerns the study of meaning in language. The term synonymy originates from the Greek words sún and onoma, which mean with and name.
Synonymy in semantics
Synonymy in semantics refers to a word with the same (or nearly the same) meaning as another word.
Let’s see if you’ve grasped the concept of synonymy by finding two synonymous words in these sentences:
- Today’s weather is awful.
- Today’s weather is terrible.
The first sentence uses awful to describe the weather and the second uses terrible. Although both sentences use different words, they have the same meaning: bad. In other words, awful and terrible are synonyms of bad.
Important note: Be careful of the slight differences between the synonyms. Not every synonymous word fits in all situations, eg small isn’t exactly the same as tiny. You have to consider some factors, including the context, the relationship between words, register, and regional variation, among others. Take a look at the ‘types of synonymy’ section for more details.
To test whether two words are synonyms (or synonymous), we can use a substitution method: if one word can be replaced by another without changing the meaning/sense of the sentence, the two words are synonyms. The opposite of synonymy is antonymy. Synonymy can be found across all parts of speech: in nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, etc.
A ≈ B
Synonym examples
Here are some examples of synonyms:
-
big-large
-
small — little
-
easy — effortless
-
difficult — hard
Let’s put the synonyms into a sentence and use the substitution method:
1a. You have a big house.
1b. You have a large house.
By substituting big with large, we can keep the sentence’s meaning (the description of the house) in a similar degree/sense as the original sentence.
2a. He had a difficult decision to make.
2b. He had a hard decision to make.
The same as before, the substitution of difficult with hard does not change the sentence’s meaning (the description of the decision).
Synonymy in literature
Synonymy is one of the literary devices in which a word is replaced with another word with a similar meaning, to avoid repetition.
Here are some examples of synonymy in literature:
If there’s just one kind of folks, why can’t they get along with each other? If they’re all alike, why do they go out of their way to despise each other? Scout, I think I’m beginning to understand something. I think I’m beginning to understand why Boo Radley’s stayed shut up in the house all this time. It’s because he wants to stay inside.
— Harper Lee, To Kill a Mockingbird, 1960.
Instead of repeating the word one kind, Lee chooses its synonym: alike, to relay a similar meaning to ‘very similar’. The same thing happens in the case of stayed shut up in the house and stay inside. Using synonymy, Lee enriches the prose by avoiding repetition while keeping the meaning similar in both cases.
For thee I watch, whilst thou dost wake elsewhere.
— William Shakespeare, Sonnet 61, 1609.
Wake is a synonym of watch. Here, wake means ‘to stay awake to watch or tend’ (Oxford English Dictionary). Notice the slightly richer sense of see in watch compared to wake, yet the two words carry a similar meaning. By adopting synonymy, Shakespeare enhances the quality of the words he uses.
I love your daughter fondly, dearly, disinterestedly, devotedly. If ever there were love in the world, I love her.
— Charles Dickens, A Tale of Two Cities, 1859.
Fondly and devotedly are synonyms that describe ‘a way to show great love for somebody/something’ (Oxford Learner’s Dictionary). Using two different words with a similar meaning, Dickens describes how strong the character’s feelings are (how I love your daughter) without repeating the word.
Types of synonyms
Now that we’ve looked at the concept, let’s examine the two types of synonymy:
-
Absolute synonyms
-
Partial synonyms
Absolute synonyms
With absolute synonyms, the meaning and function of the synonymous words are exactly the same. If you have a pair of absolutely synonymous words, you can substitute the words in every possible context (semantic, grammatical, sociolinguistic, etc.) with its synonym. This condition is very rare because, usually, two words that refer to the same meaning/object can’t co-exist. An example of an absolute synonym is airport and aerodrome. The former is what we commonly use nowadays, whereas the latter is an old-fashioned word.
Partial synonyms
Partial synonyms, on the other hand, occur when words have very closely related meanings. The meanings are not exactly the same, only partially, but close enough to relay the same message. Partial synonyms can differ in their collocation, register, and regional/social variation.
Have a look at these examples of partial synonyms:
| 1. We have a big problem. | Although gigantic is synonymous with big, the word combination of gigantic problem (1c) doesn’t sound natural. This is what’s called a collocation (a pairing of words with a high level of frequency). |
| a. We have a large problem. | |
| b. We have a huge problem. | |
| c. We have a gigantic problem. |
| 2a. The tickets can only be bought online. | Generally, buy and purchase mean ‘to obtain something by paying money for it’ (Oxford Learner’s Dictionary). However, the two words differ in their register. Buy is considered a general term, whereas purchase is often used in a more formal context. |
| 2 B. The tickets can only be purchased online. |
| 3a. It’s been a very chilly autumn this year. |
Both autumn and fall mean ‘the season of the year between summer and winter.’ But, autumn is Commonly used in British English, while fall is used in American English. They differ in regional/social variety. |
| 3b. It’s been a very chilly fall this year. |
Synonymy and homonymy — what’s the difference?
Synonymous words are words that carry similar meanings (meaning 1 is similar to meaning 2 and meaning 3). Homonymous words (homonymy) are words that are pronounced the same or spelt the same (or both), but their meanings are dissimilar.
Important to note: Homonym is a broader term for homophone (words that sound the same but have different meanings) and homograph (words that are spelt the same but have different meanings).
Synonymy and polysemy — what’s the difference?
When a set of different words carries a similar meaning it is called synonymy. When a single word has several meanings (word form 1 has meaning 1 and meaning 2), it is called polysemy.
Synonymy — similar meanings: wing — extension & section.
- They are building a new wing for the maternity department.
- They are building a new extension for the maternity department.
Even though the word wing is replaced with extension, we still get the same information about ‘a new section of the hospital is currently being constructed and it is for the maternity department’. The meaning of extension isn’t exactly the same as wing , but similar.
- My room is on the west wing.
- My room is on the west section (of the building).
The same explanation can also be found here. We still get the same information about where my room is: on the west side of the building.
Polysemy — multiple meanings: wing — animal parts for flying & a section of a building.
-
They are building a new wing for the maternity department.
The meaning of wing in this sentence refers to ‘a section of building’ and not ‘animal parts for flying’.
-
The bird’s wing is broken.
Here, the meaning of wing is about the ‘animal parts for flying’ and not ‘a section of a building’.
Synonymy vs. Polysemy
- In synonymy, you can substitute a word with its similar meaning and the sense/meaning of the sentence doesn’t change. A is similar to B .
- Synonyms are usually used as a means of avoiding word repetition. However, be careful of the slightly different meanings of synonymous words. Always be mindful of the context and valency of the sentence.
- Polysemy isn’t about word substitution. Because a single polysemic word has many meanings (A means B and C) , it can cause ambiguity. It is often used for wordplay or for creating “hidden” meanings.
Synonymy — Key takeaways
- Synonymy is a linguistic term for words with similar meanings.
- If you replace one word with its synonym, the meaning/sense of the sentence doesn’t change. You can test synonymy by using the substitution method.
- There are two types of synonymy: Absolute synonyms, when the meaning and function of the words is exactly the same, and partial synonyms, when the meaning and function of the words is only partially the same. This may depend on the collocation, register, and regional/social variety of the words.
- Synonymy features words with similar meanings, while homonymy has words with different meaning but have the same pronunciation or spelling or both.
- Synonymy involves words with similar meanings, while polysemy is words with multiple meanings did create wordplay.
You can learn the difference between similar-sounding words in English, the context in which these words are used, along with the relevant examples.
Identical words are quite complex. They almost look alike but they differ in their meanings and contexts. We can also say that some English words have twins. When you learn English vocabulary, you come across different words that are identical, but in reality, they are very different from one another.
Synonyms are words that have very similar meanings but slightly different functions or applications. Instead of simply saying the pasta you had last night was delicious, you could spice things up by using synonyms like tasty, yummy, or even mouthwatering.
In addition to synonyms, there are words with the same spelling and pronunciation but different meanings (homonyms), words that sound the same but are spelled and used differently (homophones), and words with the same spelling but different pronunciations and meanings (homographs).
All these similar words in English are quite confusing and sometimes frustrating as well. We will explore some tips to distinguish these similar words.
1. Use a dictionary regularly
The dictionary is your best language-learning guide. If you are not sure what a word means, look it up in an English-language dictionary.
Keep in mind that a single word can have numerous meanings and applications. A good dictionary or dictionary app will list them all, with context examples. A thesaurus (which lists synonyms for any word) can also aid in the identification of words with similar meanings.
2. Create your own clues about the word
Similar English words can be very complicated, but you can create special cues and images to help you to remember which one is which.
Make an image of something familiar (a person, a thing, or an event) and connect it to the word. When you see the word again, that clue will automatically come to mind, and you will easily remember the difference.
3. Use flashcards to make notes
There are numerous ways to use flashcards as learning tools. Use the flashcard to test yourself by writing the word on one side and its meaning on the other. Flashcards are portable, enabling you to review them when you have free time. Even better, you can create and study with flashcards online.
4. Focus on learning words based on their context
If you only try to remember English words and their definitions, you will quickly become confused. There are several words that are used interchangeably. For example, the words ‘rob’ and ‘steal’ are used interchangeably but their definitions may vary in the dictionary.
The definitions of ‘rob’ and ‘steal’ in the dictionary are:
Rob: “to take personal property from someone by violence or danger”
Steal: “to take the property of another illegally”
Now the two definitions look identical but they vary in their context. To understand the contextual difference, you would need to hear native speakers in real situations. You can also learn the contextual use of English words with italki. Enroll yourself to learn English online with the best and most professional online English tutors who will improve your understanding of similar words in English.
Find Your Perfect Teacher
At italki, you can find your English tutor from all qualified and experienced teachers. Now experience the excellent language learning journey!
Book a trial lesson

The instructors will help you generate your notes for English vocabulary, parts of speech, conjunction, prepositions, and homophones in English with relevant examples and exercises.
Words having similar spellings but different meanings
Coarse/Course
Coarse: (adjective) a rough, not smooth texture.
Example: Is the upper you are wearing smooth or coarse in texture?
Course: (noun) a series of classes taken to learn about a specific subject.
Example: Are you taking any courses to improve your writing skills?
Race/Raise
Race: (verb) compete in a speed contest, such as running or cycling.
Example: My kids enjoy racing each other in school.
Raise: (verb) lift up something like your hand.
Example: If you want chocolate, raise your hand.
Desert/Dessert
Desert: (noun) a hot, dry land with few plants and people (for example, the Sahara)
Example: If you plan to visit the Sahara desert, how much water would you require?
Dessert: (noun) a sweet dish served at the end of a meal (for example, cake)
Example: Maybe we should have dessert at the end of the meal.
Bear/Bare
Bear: (verb) produce outcomes or fruit
Example: This tree will bear fruits this summer.
Bare: (verb) expose or display
Example: When we opened the gate, John’s dog ran up and started to bare its teeth at us.
Break/Brake
Break: (verb) divide something into pieces or cause it to stop working, usually after dropping or misusing it.
Example: Please do not break this expensive glass.
Brake: (verb) slow down or come to an end
Example: You should press the brake of your car at the signal.
Price/Prize
Price: (noun) the amount of money you pay for something.
Example: I did not buy the dress because its price was very high.
Prize: (noun) something offered to conquerors of a competition or contest.
Example: If you want to get first prize, you must work hard.
Lose/Loose
Lose: (verb) suffer a loss or fail to keep something in your ownership.
Example: Please do not lose these papers or you won’t be able to host the meeting.
Loose: (adjective) not tightly or properly fixed.
Example: She is very thin, and this jacket is loose for her.
Plain/Plane/Plan
Plain: (adjective) average, not decorated
Example: This top is too plain. I am not wearing it.
Plane: (noun) short form of airplane
Example: I am traveling to the USA by plane.
Plan: (noun) a thorough program of action.
Example: My plan is to travel to all the nearby places in a month.
Words in English with Similar Meanings
Rob/Steal
Rob: (verb) take something away from someone forcefully.
Example: someone tried to rob John this afternoon.
Steal: (verb) take something away illegally or without consent.
Example: if I leave my bag in the park, someone will definitely steal it.
Cut/Chop
Cut: (verb) divide something into pieces with a knife or any sharp tool.
Example: Please cut the onion into small pieces.
Chop: (verb) cut into many small pieces with recurrent strokes of a knife.
Example: You must chop the garlic before putting it into the pan.
Lend/Borrow
Lend: (verb) give someone short-term use of something in exchange for it being returned later.
Example: Do not worry if you don’t have money, I can lend you some.
Borrow: (verb) accept or demand temporary use of something in exchange for its return later.
Example: I have a Mathematics test tomorrow, can I borrow your calculator?
Hear/Listen
Hear: (verb) become conscious of a sound.
Example: Did you hear the phone ring?
Listen: (verb) pay attention or be aware of a sound.
Example: I like to listen to music when I am sad.
Ice/Snow
Ice: (noun) frozen water
Example: It is so cold that the car is covered with a layer of ice.
Snow: (noun) tiny white frozen droplets of water that fall from the sky.
Example: Snow is expected tonight.
Amount/Number
Amount: (noun) the total number or quantity, used for innumerable things.
Example: you must use this amount of baking powder in the cake.
Number: (noun) the total quantity of units, used for countable things.
Example: The number of passes sold this month is twice the previous month’s passes.
See/Watch/Look
See: (verb) identify by eye or sight
Example: Did you see him taking the book from the shelf?
Watch: (verb) observe responsively.
Example: we are all set to watch a cricket match tonight.
Look: (verb) cast your eye on
Example: Please look at this object before you start sketching.
So, these were some words that look similar and can be very confusing. We hope that the differences are clear to you now. Sometimes, we get confused while using similar words. Such as, a majority of people get confused about whether to use to or too. It requires deep observation and plenty of practice to get a command of these words.
Conclusion
If you are learning English, you must make flashcards for yourself. Practice them on daily basis in your conversations with friends and family. You can also read English books and watch English movies or web series to understand the difference between similar words in English.
Most importantly, keenly observe native speakers while they utter such words. It will help you understand the use of different words based on their context.
Want to learn a language at italki?
Here are the best resources for you!
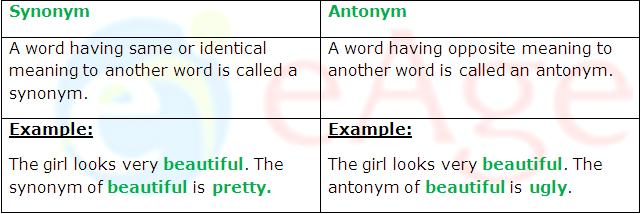
What are Synonyms and Antonyms:
Synonyms are words that have similar meaning Two different words that mean the same are said to be synonymous and the quality of being synonymous is known as synonymy. The term synonym has been derived from a Greek word called syn which means ‘with’ and onoma which means ‘name’. Antonyms are words that have opposite meaning to another word. Two words that mean the opposite are said to be antonymous. Antonym has been derived from a Greek word called anti which means ‘opposite’ and onoma which means ‘name’.
Example of Synonym:
The girl is very thin. The skinny man runs fast.
In the above mentioned sentences, thin and skinny mean the same. Both of the words (thin and skinny) are used to describe a person who is very lean.
Example of Antonym:
He has become very thin. Look at that fat man!
In the above mentioned sentences, thin and fat are opposites and hence they are regarded as antonyms.
Difference between Synonym and Antonym
Few More Examples of Synonyms and Antonyms
Below mentioned are the examples of synonyms and antonyms.
Synonym:
Brave
I am very brave. The synonym of brave is courageous.
Naughty
The boy is very naughty. The synonym of naughty is mischievous.
Big
The house is too big. The synonym of big is huge.
Antonym
Timid/Shy
The boy is very timid. The antonym of brave is timid.
Courteous
That man is very courteous. The antonym of naughty is courteous.
Small
My grandmother lives in a small hut. The antonym of big is small.
Synonym and Parts of Speech
There are eight parts of speech in English. A synonym can be any part of speech. It can be a verb, adjective, adverb, preposition but both the words should be the same part of speech.
Example:
• Verb
Manage-handle
• Adjective
Happy-glad
• Adverb
Nevertheless-still
• Preposition
Below-under
Difference Between Synonym, Antonym and Homonym
A word having similar meaning to another word is known as synonym. A word having opposite meaning to another word is known as antonym. Words that have same spelling and pronunciation, but different meanings are known as homonyms.
Example:
Synonym
The tiny man came near us. Little is a synonym of tiny.
Antonym
You are doing a good job! Bad is an antonym of good.
Homonym
Rock (a large mass of stone), rock (a kind of music)
Want to know more about “Synonym and Antonym?” Click here to schedule live online session with e Tutor!
About eAge Tutoring:
eAgeTutor.com is the premier online tutoring provider. eAge’s world class faculty and ace communication experts from around the globe help you to improve in an all round manner. Assignments and tasks based on a well researched content developed by subject matter and industry experts can certainly fetch the most desired results for improving spoken English skills. Overcoming limitations is just a click of mouse away in this age of effective and advance communication technology. For further information on online English speaking course or to experience the wonders of virtual classroom fix a demonstration session with our tutor. Please visit www.eagetutor.com.
Contact us today to know more about our spoken English program and experience the exciting world of e-learning.
Reference Links:
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Synonym
- http://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Synonym
- http://www.brainpop.com/english/grammar/antonymssynonymsandhomonyms/preview.weml

By
Last updated:
January 27, 2022
15+ Similar Words in English and How to Tell Them Apart
Are there any twins in your family?
Do you have friends who are identical twins?
Or maybe you’re even a twin yourself!
Twins are two siblings who are born at the same time.
They may look almost exactly alike, but their personalities can still be completely different.
I guess that must be how their parents and friends tell them apart.
Then there are twins who don’t look like each other but share similar personalities and tastes.
Interesting, isn’t it?
What’s more interesting is that even in the English language, some words have twins.
Synonyms, for example, are words with very close meanings but slightly different functions or usages. So instead of simply saying the pizza you had last night was delicious, you could use synonyms like tasty, yummy or even mouthwatering to spice things up.
Besides synonyms, there are also words with the same spelling and pronunciation but different meanings (homonyms), words that sound the same but are spelled and used differently (homophones) and words that share the same spelling but have different pronunciations and meanings (homographs).
With all these similar words bouncing around, things can get pretty confusing!
The question is, how can you learn to tell these similar words apart and use them correctly in any context?
Let’s find out.
Download:
This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you
can take anywhere.
Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Which Is Which? Quick Tips to Tell Similar English Words Apart
Make it a habit to use the dictionary and thesaurus.
In language learning, the dictionary and thesaurus are your best friends. Whenever you’re unsure of a word’s meaning, look it up in an English-language dictionary.
Remember, one word can have many different meanings and usages. A quality dictionary or dictionary app will list them all with examples for context. A thesaurus (which lists synonyms for any word) will also help you identify words with similar meanings.
Better yet, check out Visual Thesaurus, which creates interactive word maps to help you learn and distinguish similar English words.
The farther away two words are on the map, the more different they are. This visual element makes words and their synonyms much more memorable. You can even search and display similar words in multiple languages!
Create your own clues about the word.
Similar English words can often be very confusing, but you can create clues and images in your mind to help you remember which word is which.
Create an image of something familiar (a person, thing or event, whatever works!) and relate it to the word. Then when you see the word again, that clue will automatically pop up in your mind and you’ll easily recall the difference.
In our list of similar English words below, we’ll give you examples of this type of clue.
Use flashcards to learn and test yourself.
There are lots of ways you can use flashcards as memory aids, too. Write the word on one side of the flashcard and its meaning on the other side and use it to test yourself.
Flashcards are easy to carry around with you so you can review them whenever you have free time. Better yet, you can even create and study with flashcards online. To get started, check out these 10 helpful English flashcard apps you can download right now.
Focus on learning new words in context.
If you just memorize English words and their definitions things will get confusing fast.
For example, here are the dictionary definitions for the similar words rob and steal (which we’ll cover in depth later in this post):
Rob: “to take personal property from [someone] by violence or threat”
Steal: “to take the property of another wrongfully”
Okay… those definitions look practically identical! To learn how native English speakers use those words, you’d near to hear them in real sentences and situations (but hopefully not when someone actually robs you).
Words that look and sound similar can be very confusing, don’t you agree? But don’t worry! Once you understand their differences and with lots of practice, you’ll soon build up the confidence to use them.
For some of the words below, I’ve included my clues to help you remember which word is which. As for the others, here’s a challenge for you—create your own clues!
Words with Similar Spellings/Pronunciations but Different Meanings
1. Coarse/Course
Coarse: (adjective) texture that feels rough, not smooth
Is the texture of the jacket you’re wearing smooth or coarse?
Course: (noun) a series of classes you take to learn about a certain subject
Tip to tell them apart:
Think of the letter “u” as in a course “you” are taking.
Are you currently taking a course to improve your English?
2. Race/Raise
Race: (verb) compete in a contest of speed, like running or cycling
My neighbor’s children love to race each other home from school.
This word can also be used as a noun to refer to a contest of speed.
Which runner won the race this afternoon?
Raise: (verb) lift up something like your hand or a flag
Tip to tell them apart:
Picture the letter “i” here as someone raising their hand.
If you want some ice cream, raise your hand now before I finish the whole tub!
3. Bear/Bare
Bear: (verb) produce results or fruit
I hope this tree will bear more apples next year.
Bare: (verb) expose or show
When I opened the door, his dog ran up and started to bare its teeth at me.
4. Desert/Dessert
Desert: (noun) a hot, dry land with little rain and few plants or people (for example, the Sahara)
If you had to go to the desert for three days, how much water would you bring?
Dessert: (noun) a sweet dish served at the end of a meal (for example, cake or ice cream)
Maybe we should have chocolate ice cream for dessert.
Tip to tell them apart:
Think of the two s’s as an abbreviation (short form) for sweet serving.
5. Break/Brake
Break: (verb) separate something into pieces or cause it to stop working—usually after dropping or misusing it
Please don’t break those expensive Italian vases.
Brake: (verb) slow down or come to a stop
You should brake your car when you see someone crossing the street.
6. Price/Prize
Price: (noun) the money you pay for something
I didn’t buy it because the price was too high.
Prize: (noun) something offered to winners of a contest or competition
If you want to win the first prize, you must practice harder.
7. Lose/Loose
Lose: (verb) suffer a loss or fail to keep something in your possession
Please don’t lose these keys or you won’t be able to get into the apartment.
Loose: (adjective) not tightly fitted
She’s much thinner now and her clothes have become far too loose for her.
Tip to tell them apart:
People often use the word lose when they mean loose, especially when writing. To use the right word, think of the two o’s in loose as representing extra space—meaning it’s not tight but baggy.
8. Plain/Plane/Plan
Plain: (adjective) ordinary, not decorated
This dress is too plain. I prefer something with a floral print.
Plane: (noun) short for airplane
How long will the journey take by plane?
Plan: (noun) a detailed program of action
My plan is to stay longer in places that are less often visited by tourists.
Words with Similar Meanings
9. Cut/Chop
Cut: (verb) divide something into pieces with a knife or scissors
Let’s not cut the cake until everyone gets here.
Chop: (verb) cut into many small pieces with repeated strokes of a knife
You have to chop the garlic finely before you add it to the pan.
10. Rob/Steal
Rob: (verb) take something away from someone by force
Someone tried to rob him while he was walking home late last night.
Steal: (verb) take something away illegally or without permission
If I accidentally leave my phone in the park, will someone steal it?
Tip to tell them apart:
As noted earlier, these words’ definitions are very similar. However, English speakers do use them differently.
Rob typically refers to a single incident, often a violent one. For example, if someone surprised you on the street, pointed a weapon at you and demanded your wallet, they would be robbing you.
Steal, by contrast, often refers to theft that’s unseen and sometimes prolonged. If a coworker secretly took money out of your wallet every time you went to the bathroom, they would be stealing from you.
However, note that a native English speaker won’t be confused if you use these words interchangeably.
11. Lend/Borrow
Lend: (verb) give someone temporary use of something on the condition that it’s returned later
You left your wallet at home? That’s okay, I can lend you some money.
Borrow: (verb) receive or ask for temporary use of something on the condition that it’s returned later
I have a history test tomorrow. Could I borrow your book to study?
12. Hear/Listen
Hear: (verb) become aware of a sound
Did you hear the doorbell ring?
Listen: (verb) pay attention or be alert to a sound
I like to listen to music while I’m driving.
Tip to tell them apart:
Both of these words have to do with the concept of hearing. The difference is in the intent.
When you listen, there’s intent. For example, at a concert, you listen to the music—you’re focusing on the melody and enjoying every note.
But to hear something, you don’t have to be consciously paying attention. When someone shouts your name from across the street, you would hear it, even if you weren’t listening for it.
13. Ice/Snow
Ice: (noun) frozen water
It was so cold last night that my car’s windows were covered in a layer of ice this morning.
Snow: (noun) small white frozen drops of water that fall from the sky
The weatherman says that light snow is expected today.
Tip to tell them apart:
Snow is soft.
Ice is hard and clear. Ice can coat a surface or it can be in a cube, like ice cubes in your drink.
14. Amount/Number
Amount: (noun) the total number or quantity, used for uncountable items
You must use this amount of baking powder for the cake to rise.
Number: (noun) the total sum of units, used for countable items
The number of tickets sold this year has increased by 20 percent.
Tip to tell them apart:
Many people say the amount of when they mean the number of. Remember that you can count numbers, so the number of should be used for countable items.
15. See/Watch/Look
See: (verb) detect by eye or sight
Did you see him throw the ball at the window?
Watch: (verb) observe attentively
We’re all set to watch the football game on TV tonight.
Look: (verb) cast your eye on
Please look at this picture before you start drawing.
Tip to tell them apart:
All three of these words have to do with the concept of sight, but the difference is in the intent.
Often, you see something without actually intending to. You could be walking your dog and happen to see someone throwing a ball that hits the window.
When you watch TV or a football game, you’re doing it with an intent to purposefully see what happens on the TV show or who wins the game.
When you look, you’re paying attention to what you’re seeing. So again, there’s a purpose here. However, looking is generally quick and focused on a static object, while watching takes place over a period of time. That’s why we watch movies but look at pictures.
So there we have it: words that look similar and can be very confusing. I hope their differences are clearer to you now and you’ll be more confident in choosing the right word to use. You can always print out a copy of this article and refer to it when in doubt. Happy learning!
Download:
This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you
can take anywhere.
Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Similar words meaning examples, Popular books are in use at our schools give long list of pairs of words between which they and fanciful distinctions, whereas the distinctions do not exist and the words so distinguished are used interchangeably in modern English.
Here you get a list of 38 commonly confused words similar in meaning, whatever the original difference, such as abandon and forsake, abstain and refrain, assent and consent, avenge and revenge, allow and permit, etc. are now used interchangeably.
I have italicized and underlined the main word, which will be easy for you to understand.
The following distinctions may, however, be noted:
👉Accident and Incident
Accident means mishap; while Incident means a minor occurrence; as,
Example:
A bus accident took place near Delhi.
No noteworthy incident took place in the examination hall.
👉Alter and Change
To Alter means to change in parts, make some difference by adding and reducing. To Change means to substitute one thing for another; as,
He made many alterations in my plan.
He changed his ideas and came back.
👉Banish and Exile
To Banish means to send a person out of a country, whether a native or a foreigner. To Exile means to send a man out of the country of his birth; as,
Rama was sent into exile for fourteen years.
The duke was banished from the country.
👉Battle and War
A Battle means a single engagement of troops; a War means a whole series of battles from the beginning of hostilities to the restoration of peace; as,
A severe battle was fought between Babar and Ibrahim Lodhi at Panipat.
The Indo-Pak war of 1971 lasted for fourteen days.
👉Beat and Strike
Strike means to hit repeatedly and Beat means to strike; as,
He beat the hot iron on the anvil with a hammer.
The blow he struck made on his opponent fall down like a log of wood.
👉Bring and Fetch
Bring means to take a thing from one place to another. Fetch means to go and bring it; as,
Bring me a tumbler of water, please.
Fetch some water from the well.
👉Cheat and Deceive
To Cheat means to obtain something by deceiving, while to Deceive means to give one a false idea and to make one believe what is not true; as,
Sohan cheated me of ten rupees.
Sharif deceived his father by telling him lie.
👉Compare and Contrast
To Compare is to find points of likeness, to Contrast is to bring out points of dissimilarities; as,
You may compare one wise man with another; but between a fool and philosopher there is nothing but contrast.
Compare and Contrast Akbar and Aurangzeb.
👉Confess and Admit
Confess means to acknowledge guilt (used in bad sense); while Admit means to accept (used in good sense); as,
The thief confessed his guilt.
I admit that he is an intelligent student.
👉Contagious and Infectious
Contagious means communication of diseases from one person to another by touch. Infectious means communication through water or atmosphere; as,
Small-pox is a contagious disease.
Cholera is an infectious disease.
👉Contented and Satisfied
We are Satisfied when our desires are fulfilled, but we may be Contented even our desires remain unfulfilled; as,
A contented mind is a great blessing.
I was satisfied when my due share was given to me.
👉Cost, Value and Price
Cost is the money spent upon the purchase or production of a thing; Price is the money demanded by the seller and Value means worth or utility of a thing; as,
The cost of the book is one rupee. Its price is two rupees and I value it more than a heap of gold.
👉Crime, Vice and Sin
Crime means a violation of the law of the country, Vice means violations of law the society; and Sin means a violation of religious laws; as,
Stealing is a crime.
Gambling and drinking are vices.
It is a sin to tell a lie.
👉Deny, Refuse and Decline
Deny means to rebut a change;Refuse means to give a negative reply to an offer; Decline means to refuse to accept an invitation; as,
He denied the charge.
He refused to lend me the book.
He declined the invitation.
👉Defend and Protect
To Defend means to save from a present danger; to Protect means to save from what may happen at any time; as,
Chand bibi defended the fort when it was besieged by Prince Murad.
The high wall protected the city against sudden attacks.
👉Desert and Leave
We Leave a place with the intention of returning; we Desert a person or a place for good; as,
He left his work incomplete.
He has deserted his friends.
We found the place deserted.
👉Devoted and Addicted
The former is used in good sense and the latter in bad sense; as,
I am devoted to my studies.
He is addicted to gambling.
👉Election and Selection
Election means by choosing by votes; Selection means a choice of excellence; as,
Kailash stood for election to the Parliament.
Let us make a selection of some useful books.
👉Freedom and Liberty
Freedom means non-slavery; Liberty means a right to do as one pleases; as,
Indian has won freedom.
You have a liberty to do whatever you like.
👉Hope and Expect
Expect denotes that an occurrence is probable, whether it is desired or not; while the Hope denotes pleasurable expectation or wish; as,
I expect there will soon be outbreak of war between India and Pakistan.
I hope he will send you a present on your birthday.
👉Hear and Listen
To Listen implies attention, while Hearing may be accidental; as,
I listen to his story very carefully.
I have heard the case and shall pronounce judgement tomorrow.
👉Habit and Custom
A Habit generally concerns and individual while Custom denotes what is commonly practised in a society or a country; as,
Smoking is a bad habit.
In some parts of India, it is still a custom for the brides to hide their faces from their fathers-in-law.
👉Invent and Discover
We Discover what exists already, and we Invent when we make something new; as,
Columbus discovered America.
Galileo invented the telescope.
👉Look and See
We say Look when we intend to draw attention to a particular spot or object, while Seeing has a general sense; as,
Look at the bird sitting on that mango tree.
I saw the gentleman today.
👉Probable and Possible
Probable means likely to be or happen, Possible means that something can happen; as,
It is possible he may come (and just as possible that he may not)
It is probable (it is likely) that the valley may have a snowfall someday this week.
👉Receive and Takes
To Take means to obtain a thing by effort, while to Receive means to be given by another; as,
The thieves took away whatever they could lay their hands upon.
I received a letter from Sanjay yesterday.
👉Remember and recollect
The former means to have in mind, and latter to call to mind; as,
I remember the days gone by.
I cannot recollect your name at present.
👉Roof and Ceiling
Ceiling means the inner roof, whereas the Roof means the entire covering; as,
The ceiling of the roof was of plaster.
The roof of this room leaks now and then.
👉Say, Tell and Speak
Say is used to make a statement or declaration; as,
I say you are a thief.
Tell is used to give orders, narrate a story, or make a communication; as,
Tell him to bring me some water.
Speak means to make a speech; as
He spoke aloud. He spoke on Politics.
👉Rent and Hire
Rent is a tenant’s payment to the landlord for use of house etc., while Hire is wages for use of a thing for personal services; as,
I got a house at a rent of Rs. 10000 per month.
I hired a tonga. I hired a taxi.
👉Scatter and Spread
Scatter means to through or place a number of things in different directions, and to Spread means to cover a certain area with a given thing or substance; as,
He spread butter on the toast.
The wind scattered the leaves.
👉Shade and Shadow
We sit in the shade of a tree.
The tree casts its shadow on the ground.
👉Sink and Drown
Drown is used for living beings only, while Sink is used for lifeless things; as,
The boy was drowned.
The ship sank in the sea.
👉Swim and Float
Swim is for living beings, and Float for lifeless things; as,
A boy is swimming in the tank.
A piece of wood is floating in the river.
👉Tedious and Irksome
A work is Tedious when it is difficult, long and unpleasant; it is Irksome when we have not taste for it; as,
This is a tedious piece of work.
It is very irksome to me to go and talk to him.
👉Tomorrow and on the morrow
Tomorrow means the day after today, on the morrow means the day following that day; as,
I shall reach here tomorrow.
He left the island on the morrow.
👉Transitory and Fleeting
The former is used for the life the world and its pleasures, and latter for the time; as,
Worldly pleasures and joys are transitory.
Time is fleeting.
👉Wear and put on
To Put on denotes single action, and to Wear denotes a continuous action or a habit; as,
He wears a long coat and a white hat.
He put on his hat and went out.