Select your language
Suggested languages for you:
Lerne mit deinen Freunden und bleibe auf dem richtigen Kurs mit deinen persönlichen Lernstatistiken
Jetzt kostenlos anmelden

Words don’t only mean something; they also do something. In the English language, words are grouped into word classes based on their function, i.e. what they do in a phrase or sentence. In total, there are nine word classes in English.
Word class meaning and example
All words can be categorised into classes within a language based on their function and purpose.
An example of various word classes is ‘The cat ate a cupcake quickly.’
-
The = a determiner
-
cat = a noun
-
ate = a verb
-
a = determiner
-
cupcake = noun
-
quickly = an adverb
Word class function
The function of a word class, also known as a part of speech, is to classify words according to their grammatical properties and the roles they play in sentences. By assigning words to different word classes, we can understand how they should be used in context and how they relate to other words in a sentence.
Each word class has its own unique set of characteristics and rules for usage, and understanding the function of word classes is essential for effective communication in English. Knowing our word classes allows us to create clear and grammatically correct sentences that convey our intended meaning.
Word classes in English
In English, there are four main word classes; nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs. These are considered lexical words, and they provide the main meaning of a phrase or sentence.
The other five word classes are; prepositions, pronouns, determiners, conjunctions, and interjections. These are considered functional words, and they provide structural and relational information in a sentence or phrase.
Don’t worry if it sounds a bit confusing right now. Read ahead and you’ll be a master of the different types of word classes in no time!
| All word classes | Definition | Examples of word classification |
| Noun | A word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea. | cat, house, plant |
| Pronoun | A word that is used in place of a noun to avoid repetition. | he, she, they, it |
| Verb | A word that expresses action, occurrence, or state of being. | run, sing, grow |
| Adjective | A word that describes or modifies a noun or pronoun. | blue, tall, happy |
| Adverb | A word that describes or modifies a verb, adjective, or other adverb. | quickly, very |
| Preposition | A word that shows the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence. | in, on, at |
| Conjunction | A word that connects words, phrases, or clauses. | and, or, but |
| Interjection | A word that expresses strong emotions or feelings. | wow, oh, ouch |
| Determiners | A word that clarifies information about the quantity, location, or ownership of the noun | Articles like ‘the’ and ‘an’, and quantifiers like ‘some’ and ‘all’. |
The four main word classes
In the English language, there are four main word classes: nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs. Let’s look at all the word classes in detail.
Nouns
Nouns are the words we use to describe people, places, objects, feelings, concepts, etc. Usually, nouns are tangible (touchable) things, such as a table, a person, or a building.
However, we also have abstract nouns, which are things we can feel and describe but can’t necessarily see or touch, such as love, honour, or excitement. Proper nouns are the names we give to specific and official people, places, or things, such as England, Claire, or Hoover.
Cat
House
School
Britain
Harry
Book
Hatred
‘My sister went to school.‘
Verbs
Verbs are words that show action, event, feeling, or state of being. This can be a physical action or event, or it can be a feeling that is experienced.
Lexical verbs are considered one of the four main word classes, and auxiliary verbs are not. Lexical verbs are the main verb in a sentence that shows action, event, feeling, or state of being, such as walk, ran, felt, and want, whereas an auxiliary verb helps the main verb and expresses grammatical meaning, such as has, is, and do.
Run
Walk
Swim
Curse
Wish
Help
Leave
‘She wished for a sunny day.’
Adjectives
Adjectives are words used to modify nouns, usually by describing them. Adjectives describe an attribute, quality, or state of being of the noun.
Long
Short
Friendly
Broken
Loud
Embarrassed
Dull
Boring
‘The friendly woman wore a beautiful dress.’

Adverbs
Adverbs are words that work alongside verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. They provide further descriptions of how, where, when, and how often something is done.
Quickly
Softly
Very
More
Too
Loudly
‘The music was too loud.’
All of the above examples are lexical word classes and carry most of the meaning in a sentence. They make up the majority of the words in the English language.
The other five word classes
The other five remaining word classes are; prepositions, pronouns, determiners, conjunctions, and interjections. These words are considered functional words and are used to explain grammatical and structural relationships between words.
For example, prepositions can be used to explain where one object is in relation to another.
Prepositions
Prepositions are used to show the relationship between words in terms of place, time, direction, and agency.
In
At
On
Towards
To
Through
Into
By
With
‘They went through the tunnel.’
Pronouns
Pronouns take the place of a noun or a noun phrase in a sentence. They often refer to a noun that has already been mentioned and are commonly used to avoid repetition.
Chloe (noun) → she (pronoun)
Chloe’s dog → her dog (possessive pronoun)
There are several different types of pronouns; let’s look at some examples of each.
- He, she, it, they — personal pronouns
- His, hers, its, theirs, mine, ours — possessive pronouns
- Himself, herself, myself, ourselves, themselves — reflexive pronouns
- This, that, those, these — demonstrative pronouns
- Anyone, somebody, everyone, anything, something — Indefinite pronouns
- Which, what, that, who, who — Relative pronouns
‘She sat on the chair which was broken.’
Determiners
Determiners work alongside nouns to clarify information about the quantity, location, or ownership of the noun. It ‘determines’ exactly what is being referred to. Much like pronouns, there are also several different types of determiners.
- The, a, an — articles
- This, that, those — you might recognise these for demonstrative pronouns are also determiners
- One, two, three etc. — cardinal numbers
- First, second, third etc. — ordinal numbers
- Some, most, all — quantifiers
- Other, another — difference words
‘The first restaurant is better than the other.’
Conjunctions
Conjunctions are words that connect other words, phrases, and clauses together within a sentence. There are three main types of conjunctions;
-
Coordinating conjunctions — these link independent clauses together.
-
Subordinating conjunctions — these link dependent clauses to independent clauses.
- Correlative conjunctions — words that work in pairs to join two parts of a sentence of equal importance.
For, and, nor, but, or, yet, so — coordinating conjunctions
After, as, because, when, while, before, if, even though — subordinating conjunctions
Either/or, neither/nor, both/and — correlative conjunctions
‘If it rains, I’m not going out.’
Interjections
Interjections are exclamatory words used to express an emotion or a reaction. They often stand alone from the rest of the sentence and are accompanied by an exclamation mark.
Oh
Oops!
Phew!
Ahh!
‘Oh, what a surprise!’
Word class: lexical classes and function classes
A helpful way to understand lexical word classes is to see them as the building blocks of sentences. If the lexical word classes are the blocks themselves, then the function word classes are the cement holding the words together and giving structure to the sentence.

In this diagram, the lexical classes are in blue and the function classes are in yellow. We can see that the words in blue provide the key information, and the words in yellow bring this information together in a structured way.
Word class examples
Sometimes it can be tricky to know exactly which word class a word belongs to. Some words can function as more than one word class depending on how they are used in a sentence. For this reason, we must look at words in context, i.e. how a word works within the sentence. Take a look at the following examples of word classes to see the importance of word class categorisation.
The dog will bark if you open the door.
The tree bark was dark and rugged.
Here we can see that the same word (bark) has a different meaning and different word class in each sentence. In the first example, ‘bark’ is used as a verb, and in the second as a noun (an object in this case).
I left my sunglasses on the beach.
The horse stood on Sarah’s left foot.
In the first sentence, the word ‘left’ is used as a verb (an action), and in the second, it is used to modify the noun (foot). In this case, it is an adjective.
I run every day
I went for a run
In this example, ‘run’ can be a verb or a noun.
Word Class — Key takeaways
-
We group words into word classes based on the function they perform in a sentence.
-
The four main word classes are nouns, adjectives, verbs, and adverbs. These are lexical classes that give meaning to a sentence.
-
The other five word classes are prepositions, pronouns, determiners, conjunctions, and interjections. These are function classes that are used to explain grammatical and structural relationships between words.
-
It is important to look at the context of a sentence in order to work out which word class a word belongs to.
Frequently Asked Questions about Word Class
A word class is a group of words that have similar properties and play a similar role in a sentence.
Some examples of how some words can function as more than one word class include the way ‘run’ can be a verb (‘I run every day’) or a noun (‘I went for a run’). Similarly, ‘well’ can be an adverb (‘He plays the guitar well’) or an adjective (‘She’s feeling well today’).
The nine word classes are; Nouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, prepositions, pronouns, determiners, conjunctions, interjections.
Categorising words into word classes helps us to understand the function the word is playing within a sentence.
Parts of speech is another term for word classes.
The different groups of word classes include lexical classes that act as the building blocks of a sentence e.g. nouns. The other word classes are function classes that act as the ‘glue’ and give grammatical information in a sentence e.g. prepositions.
The word classes for all, that, and the is:
‘All’ = determiner (quantifier)
‘That’ = pronoun and/or determiner (demonstrative pronoun)
‘The’ = determiner (article)
Final Word Class Quiz
Word Class Quiz — Teste dein Wissen
Question
A word can only belong to one type of noun. True or false?
Show answer
Answer
This is false. A word can belong to multiple categories of nouns and this may change according to the context of the word.
Show question
Question
Name the two principal categories of nouns.
Show answer
Answer
The two principal types of nouns are ‘common nouns’ and ‘proper nouns’.
Show question
Question
Which of the following is an example of a proper noun?
Show answer
Question
Name the 6 types of common nouns discussed in the text.
Show answer
Answer
Concrete nouns, abstract nouns, countable nouns, uncountable nouns, collective nouns, and compound nouns.
Show question
Question
What is the difference between a concrete noun and an abstract noun?
Show answer
Answer
A concrete noun is a thing that physically exists. We can usually touch this thing and measure its proportions. An abstract noun, however, does not physically exist. It is a concept, idea, or feeling that only exists within the mind.
Show question
Question
Pick out the concrete noun from the following:
Show answer
Question
Pick out the abstract noun from the following:
Show answer
Question
What is the difference between a countable and an uncountable noun? Can you think of an example for each?
Show answer
Answer
A countable noun is a thing that can be ‘counted’, i.e. it can exist in the plural. Some examples include ‘bottle’, ‘dog’ and ‘boy’. These are often concrete nouns.
An uncountable noun is something that can not be counted, so you often cannot place a number in front of it. Examples include ‘love’, ‘joy’, and ‘milk’.
Show question
Question
Pick out the collective noun from the following:
Show answer
Question
What is the collective noun for a group of sheep?
Show answer
Answer
The collective noun is a ‘flock’, as in ‘flock of sheep’.
Show question
Question
The word ‘greenhouse’ is a compound noun. True or false?
Show answer
Answer
This is true. The word ‘greenhouse’ is a compound noun as it is made up of two separate words ‘green’ and ‘house’. These come together to form a new word.
Show question
Question
What are the adjectives in this sentence?: ‘The little boy climbed up the big, green tree’
Show answer
Answer
The adjectives are ‘little’ and ‘big’, and ‘green’ as they describe features about the nouns.
Show question
Question
Place the adjectives in this sentence into the correct order: the wooden blue big ship sailed across the Indian vast scary ocean.
Show answer
Answer
The big, blue, wooden ship sailed across the vast, scary, Indian ocean.
Show question
Question
What are the 3 different positions in which an adjective can be placed?
Show answer
Answer
An adjective can be placed before a noun (pre-modification), after a noun (post-modification), or following a verb as a complement.
Show question
Question
In this sentence, does the adjective pre-modify or post-modify the noun? ‘The unicorn is angry’.
Show answer
Answer
The adjective ‘angry’ post-modifies the noun ‘unicorn’.
Show question
Question
In this sentence, does the adjective pre-modify or post-modify the noun? ‘It is a scary unicorn’.
Show answer
Answer
The adjective ‘scary’ pre-modifies the noun ‘unicorn’.
Show question
Question
What kind of adjectives are ‘purple’ and ‘shiny’?
Show answer
Answer
‘Purple’ and ‘Shiny’ are qualitative adjectives as they describe a quality or feature of a noun
Show question
Question
What kind of adjectives are ‘ugly’ and ‘easy’?
Show answer
Answer
The words ‘ugly’ and ‘easy’ are evaluative adjectives as they give a subjective opinion on the noun.
Show question
Question
Which of the following adjectives is an absolute adjective?
Show answer
Question
Which of these adjectives is a classifying adjective?
Show answer
Question
Convert the noun ‘quick’ to its comparative form.
Show answer
Answer
The comparative form of ‘quick’ is ‘quicker’.
Show question
Question
Convert the noun ‘slow’ to its superlative form.
Show answer
Answer
The comparative form of ‘slow’ is ‘slowest’.
Show question
Question
What is an adjective phrase?
Show answer
Answer
An adjective phrase is a group of words that is ‘built’ around the adjective (it takes centre stage in the sentence). For example, in the phrase ‘the dog is big’ the word ‘big’ is the most important information.
Show question
Question
Give 2 examples of suffixes that are typical of adjectives.
Show answer
Answer
Suffixes typical of adjectives include -able, -ible, -ful, -y, -less, -ous, -some, -ive, -ish, -al.
Show question
Question
What is the difference between a main verb and an auxiliary verb?
Show answer
Answer
A main verb is a verb that can stand on its own and carries most of the meaning in a verb phrase. For example, ‘run’, ‘find’. Auxiliary verbs cannot stand alone, instead, they work alongside a main verb and ‘help’ the verb to express more grammatical information e.g. tense, mood, possibility.
Show question
Question
What is the difference between a primary auxiliary verb and a modal auxiliary verb?
Show answer
Answer
Primary auxiliary verbs consist of the various forms of ‘to have’, ‘to be’, and ‘to do’ e.g. ‘had’, ‘was’, ‘done’. They help to express a verb’s tense, voice, or mood. Modal auxiliary verbs show possibility, ability, permission, or obligation. There are 9 auxiliary verbs including ‘could’, ‘will’, might’.
Show question
Question
Which of the following are primary auxiliary verbs?
-
Is
-
Play
-
Have
-
Run
-
Does
-
Could
Show answer
Answer
The primary auxiliary verbs in this list are ‘is’, ‘have’, and ‘does’. They are all forms of the main primary auxiliary verbs ‘to have’, ‘to be’, and ‘to do’. ‘Play’ and ‘run’ are main verbs and ‘could’ is a modal auxiliary verb.
Show question
Question
Name 6 out of the 9 modal auxiliary verbs.
Show answer
Answer
Answers include: Could, would, should, may, might, can, will, must, shall
Show question
Question
‘The fairies were asleep’. In this sentence, is the verb ‘were’ a linking verb or an auxiliary verb?
Show answer
Answer
The word ‘were’ is used as a linking verb as it stands alone in the sentence. It is used to link the subject (fairies) and the adjective (asleep).
Show question
Question
What is the difference between dynamic verbs and stative verbs?
Show answer
Answer
A dynamic verb describes an action or process done by a noun or subject. They are thought of as ‘action verbs’ e.g. ‘kick’, ‘run’, ‘eat’. Stative verbs describe the state of being of a person or thing. These are states that are not necessarily physical action e.g. ‘know’, ‘love’, ‘suppose’.
Show question
Question
Which of the following are dynamic verbs and which are stative verbs?
-
Drink
-
Prefer
-
Talk
-
Seem
-
Understand
-
Write
Show answer
Answer
The dynamic verbs are ‘drink’, ‘talk’, and ‘write’ as they all describe an action. The stative verbs are ‘prefer’, ‘seem’, and ‘understand’ as they all describe a state of being.
Show question
Question
What is an imperative verb?
Show answer
Answer
Imperative verbs are verbs used to give orders, give instructions, make a request or give warning. They tell someone to do something. For example, ‘clean your room!’.
Show question
Question
Inflections give information about tense, person, number, mood, or voice. True or false?
Show answer
Question
What information does the inflection ‘-ing’ give for a verb?
Show answer
Answer
The inflection ‘-ing’ is often used to show that an action or state is continuous and ongoing.
Show question
Question
How do you know if a verb is irregular?
Show answer
Answer
An irregular verb does not take the regular inflections, instead the whole word is spelt a different way. For example, begin becomes ‘began’ or ‘begun’. We can’t add the regular past tense inflection -ed as this would become ‘beginned’ which doesn’t make sense.
Show question
Question
Suffixes can never signal what word class a word belongs to. True or false?
Show answer
Answer
False. Suffixes can signal what word class a word belongs to. For example, ‘-ify’ is a common suffix for verbs (‘identity’, ‘simplify’)
Show question
Question
A verb phrase is built around a noun. True or false?
Show answer
Answer
False. A verb phrase is a group of words that has a main verb along with any other auxiliary verbs that ‘help’ the main verb. For example, ‘could eat’ is a verb phrase as it contains a main verb (‘could’) and an auxiliary verb (‘could’).
Show question
Question
Which of the following are multi-word verbs?
-
Shake
-
Rely on
-
Dancing
-
Look up to
Show answer
Answer
The verbs ‘rely on’ and ‘look up to’ are multi-word verbs as they consist of a verb that has one or more prepositions or particles linked to it.
Show question
Question
What is the difference between a transition verb and an intransitive verb?
Show answer
Answer
Transitive verbs are verbs that require an object in order to make sense. For example, the word ‘bring’ requires an object that is brought (‘I bring news’). Intransitive verbs do not require an object to complete the meaning of the sentence e.g. ‘exist’ (‘I exist’).
Show question
Answer
An adverb is a word that gives more information about a verb, adjective, another adverb, or a full clause.
Show question
Question
What are the 3 ways we can use adverbs?
Show answer
Answer
We can use adverbs to modify a word (modifying adverbs), to intensify a word (intensifying adverbs), or to connect two clauses (connecting adverbs).
Show question
Question
What are modifying adverbs?
Show answer
Answer
Modifying adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They add further information about the word.
Show question
Question
‘Additionally’, ‘likewise’, and ‘consequently’ are examples of connecting adverbs. True or false?
Show answer
Answer
True! Connecting adverbs are words used to connect two independent clauses.
Show question
Question
What are intensifying adverbs?
Show answer
Answer
Intensifying adverbs are words used to strengthen the meaning of an adjective, another adverb, or a verb. In other words, they ‘intensify’ another word.
Show question
Question
Which of the following are intensifying adverbs?
-
Calmly
-
Incredibly
-
Enough
-
Greatly
Show answer
Answer
The intensifying adverbs are ‘incredibly’ and ‘greatly’. These strengthen the meaning of a word.
Show question
Question
Name the main types of adverbs
Show answer
Answer
The main adverbs are; adverbs of place, adverbs of time, adverbs of manner, adverbs of frequency, adverbs of degree, adverbs of probability, and adverbs of purpose.
Show question
Question
What are adverbs of time?
Show answer
Answer
Adverbs of time are the ‘when?’ adverbs. They answer the question ‘when is the action done?’ e.g. ‘I’ll do it tomorrow’
Show question
Question
Which of the following are adverbs of frequency?
-
Usually
-
Patiently
-
Occasionally
-
Nowhere
Show answer
Answer
The adverbs of frequency are ‘usually’ and ‘occasionally’. They are the ‘how often?’ adverbs. They answer the question ‘how often is the action done?’.
Show question
Question
What are adverbs of place?
Show answer
Answer
Adverbs of place are the ‘where?’ adverbs. They answer the question ‘where is the action done?’. For example, ‘outside’ or ‘elsewhere’.
Show question
Question
Which of the following are adverbs of manner?
-
Never
-
Carelessly
-
Kindly
-
Inside
Show answer
Answer
The words ‘carelessly’ and ‘kindly’ are adverbs of manner. They are the ‘how?’ adverbs that answer the question ‘how is the action done?’.
Show question
Discover the right content for your subjects
No need to cheat if you have everything you need to succeed! Packed into one app!
Study Plan
Be perfectly prepared on time with an individual plan.
Quizzes
Test your knowledge with gamified quizzes.
Flashcards
Create and find flashcards in record time.
Notes
Create beautiful notes faster than ever before.
Study Sets
Have all your study materials in one place.
Documents
Upload unlimited documents and save them online.
Study Analytics
Identify your study strength and weaknesses.
Weekly Goals
Set individual study goals and earn points reaching them.
Smart Reminders
Stop procrastinating with our study reminders.
Rewards
Earn points, unlock badges and level up while studying.
Magic Marker
Create flashcards in notes completely automatically.
Smart Formatting
Create the most beautiful study materials using our templates.
Sign up to highlight and take notes. It’s 100% free.
This website uses cookies to improve your experience. We’ll assume you’re ok with this, but you can opt-out if you wish. Accept
Privacy & Cookies Policy
- Размер: 58 Кб
- Количество слайдов: 27



















1.
Definition and general characteristics of the word-group.
There
are a lot of definitions concerning the word-group. The most adequate
one seems to be the following: the word-group is a combination of at
least two notional words which do not constitute the sentence but are
syntactically connected. According to some other scholars (the
majority of Western scholars and professors B.Ilyish and V.Burlakova
– in Russia), a combination of a notional word with a function word
(on
the table)
may be treated as a word-group as well. The problem is disputable as
the role of function words is to show some abstract relations and
they are devoid of nominative power. On the other hand, such
combinations are syntactically bound and they should belong
somewhere.
General
characteristics of the word-group are:
1)
As a naming unit it differs from a compound word because the number
of constituents in a word-group corresponds to the number of
different denotates:
a
black bird – чорний
птах
(2), a blackbird – дрізд
(1);
a loud speaker (2), a loudspeaker (1).
2)
Each component of the word-group can undergo grammatical changes
without destroying the identity of the whole unit: to
see a house — to see houses.
3)
A word-group is a dependent syntactic unit, it is not a communicative
unit and has no intonation of its own.
2.
Classification of word-groups.
Word-groups
can be classified on the basis of several principles:
-
According
to the type of syntagmatic relations: coordinate
(you
and
me),
subordinate
(to
see a house, a nice dress),
predicative
(him
coming, for him to come), -
According
to the structure: simple
(all elements are obligatory), expanded
(to
read and translate the text
– expanded elements are equal in rank), extended
(a word takes a dependent element and this dependent element becomes
the head for another word: a
beautiful
flower
– a very beautiful flower).
3.
Subordinate word-groups.
Subordinate
word-groups are based on the relations of dependence between the
constituents. This presupposes the existence of a governing
Element
which is called the
head and
the dependent element which is called the
adjunct
(in noun-phrases) or the
complement
(in verb-phrases).
According
to the nature of their heads, subordinate word-groups fall into
noun-phrases
(NP) – a
cup of tea,
verb-phrases
(VP) – to
run fast,
to
see
a house,
adjective
phrases
(AP) – good
for you,
adverbial
phrases
(DP) – so
quickly,
pronoun
phrases
(IP) – something
strange, nothing to
do.
The
formation of the subordinate word-group depends on the valency of its
constituents. Valency
is
a potential ability of words to combine. Actual realization of
valency in speech is called combinability.
4.
The noun-phrase (NP).
Noun
word-groups are widely spread in English. This may be explained by a
potential ability of the noun to go into combinations with
practically all parts of speech. The NP consists of a noun-head and
an adjunct or adjuncts with relations of modification between them.
Three
types of modification are distinguished here:
-
Premodification
that comprises all the units placed before the head:
two
smart hard-working
students. Adjuncts
used in pre-head position are called pre-posed
adjuncts. -
Postmodification
that comprises all the units all the units placed after the head:
students
from
Boston.
Adjuncts used in post-head position are called post-posed
adjuncts. -
Mixed
modification
that comprises all the units in both pre-head and post-head
position: two
smart hard-working
students from
Boston.
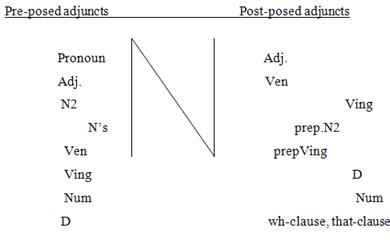
|
Pre-posed |
|
Post-posed |
|
Pronoun |
Adj. |
|
|
Adj. |
Ven |
|
|
N2 |
Ving |
|
|
N`s |
prep.N2 |
|
|
Ven |
prepVing |
|
|
Ving |
D |
|
|
Num |
Num |
|
|
D |
wh-clause, |
X
5.
Noun-phrases with pre-posed adjuncts.
In
noun-phrases with pre-posed modifiers we generally find adjectives,
pronouns, numerals, participles, gerunds, nouns, nouns in the
genitive case (see the table). According to their position all
pre-posed adjuncts may be divided into pre-adjectivals
and adjectiavals.
The position of adjectivals is usually right before the noun-head.
Pre-adjectivals occupy the position before adjectivals. They fall
into two groups: a) lim
iters (to
this
group belong mostly particles): just,
only, even, etc.
and b) determiners
(articles, possessive pronouns, quantifiers – the
first, the last).
Premodification
of nouns by nouns (N+N) is one of the most striking features about
the grammatical organization of English. It is one of devices to make
our speech both laconic and expressive at the same time. Noun-adjunct
groups result from different kinds of transformational shifts. NPs
with pre-posed adjuncts can signal a striking variety of meanings:
world
peace – peace all over the world
silver box – a box made of
silver
table lamp – lamp for tables
table legs – the legs
of the table
river sand – sand from the river
school child
– a child who goes to school
The
grammatical relations observed in NPs with pre-posed adjuncts may
convey the following meanings:
-
subject-predicate
relations: weather
change; -
object
relations: health
service, women hater; -
adverbial
relations:
a)
of time: morning
star,
b) place: world
peace, country house,
c) comparison: button
eyes,
d)
purpose: tooth
brush.
It
is important to remember that the noun-adjunct is usually marked by a
stronger stress than the head.
Of
special interest is a kind of ‘grammatical idiom’ where the
modifier is reinterpreted into the head: a
devil of a man, an angel of a girl.
6.
Noun-phrases with post-posed adjuncts.
NPs
with post-posed may be classified according to the way of connection
into prepositionless
and prepositional.
The basic prepositionless NPs with post-posed adjuncts are: Nadj. –
tea
strong,
NVen – the
shape unknown,
NVing – the
girl smiling,
ND – the
man
downstairs,
NVinf – a
book to read,
NNum – room
ten.
The
pattern of basic prepositional NPs is N1 prep. N2. The most common
preposition here is ‘of’ – a
cup of tea,
a
man of courage.
It may have quite different meanings: qualitative
—
a
woman of sense,
predicative
– the
pleasure of the company,
objective
– the
reading of the newspaper,
partitive
–
the
roof of the house.
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
Words are the building blocks in any sentence. They just don’t ‘mean’ something, they ‘do’ something in every sentence. Hence words are grouped into word classes based on what they do. A word class is a group of words that have certain common features. The term “word class” is analogous to the more conventional term, “part of speech.” It is also variously named grammatical category, lexical category, and syntactic category.
- Types of Word Classes
- Open and Closed Word Classes
- Open Word Classes
- Closed Word Classes
- How to identify the word classes in a sentence?
- How to classify a word class?
- What is the difference between a word class and part of speech?
Word classes can be divided into two families:
- Lexical Classes: Also known as open classes and form classes. The lexical classes include nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs.
- Function Classes: Also known as closed classes and structure classes. Includes: pronouns, determiners, conjunctions, prepositions, and interjections.
Open and Closed Word Classes
As previously mentioned some word classes are open, that is, the class can be expanded with the addition of new words. Take the example of the class of nouns, it is potentially infinite as the number of words in the class is increasing as new scientific and technological discoveries are made.
The latter half of the twentieth century witnessed developments in computer technology which have in turn given rise to many new nouns like the Internet, URL website, bitmap, email, etc.
On the other hand, the word classes of prepositions, determiners, or conjunctions are known as closed word classes. Words like of, the, and but come under these. They are named closed word classes because they consist of a definite set of words. These classes never expand even though the words included in the class may change their spelling.
Open Word Classes
1) Nouns
This class includes words that you frequently use in everyday life. Nouns are most commonly understood as “naming” words, that is, it performs the function of naming “people, places or things”.
- A person – Boy, Girl, John, etc
- A thing- House, Dog, etc
- A place- China, America, etc
However, the use of nouns is not restricted to just names of people, places, or things. Nouns also denote abstract and intangible concepts such as an idea, quality, or state. Example: Danger, Happiness, Love, etc.
2) Verbs
The words that you use to describe an action are known as verbs. Hence verbs are generally known as “action” words. Have a look at the given example: Rahul rides a scooter. The verb in the above sentence denotes an action that Rahul performs which is the action of riding a scooter.
However, the idea of verbs as “action” words is somewhat restricted. Many verbs don’t stand for action at all as in the given instance: Rahul seems desperate. We cannot say that the verb ‘seems ‘ refer to an action.
3) Adverbs
In English, an adverb describes a word that alters the meaning of a verb, adjective, or another adverb. Adverbs in a sentence give you more information about the sentence. They are used to express how an action is fulfilled. Adverbs can broadly be categorized into Simple Adverbs, IInterrogative adverbs, and Relative Adverbs.
Remember:
- Most adverbs end with the common ending – ly.
- An adverb that modifies an adjective or another adverb usually goes before it.
4) Adjectives
Adjectives describe the quality of a noun. For example They stay in a beautiful house
The word beautiful indicates or refers to one of the attributes of the house that is described. Hence beautiful becomes the adjective in the above sentence.
A point to keep in mind: Some adjectives can be identified by their ending. Typical adjective endings include: able, al, ful, ic, etc.
You can even try out our other articles on How to Improve Your Vocabulary as well to expand your knowledge base.
Closed Word Classes
1) Determiners
You might have often noticed that nouns are preceded by words like the, a, or an. These words are known as Determiners. They suggest the type of reference that the noun has.
- The determiner ‘the’ is called a Definite Article. It can be placed both before singular and plural nouns. For example The Taxi, The taxis
- The determiner a or an is known as the Indefinite Article. It is used along with a singular noun. Example: A taxi
Apart from these, many other determiners express quantity. These include ‘al’, ‘both’, ‘many’ etc.
2) Conjunctions
These are used to express connections between different words.
Example: John and David are friends. And is used as a conjunction in the given sentence.
The most familiar conjunctions in English are: and, but, and or.
Conjunctions are further divided into two:
- Coordinating Conjunctions: These conjunctions connect elements of equal syntactic structure. Example: Paul and David study together.
- Subordinating Conjunctions: Connects elements of unequal syntactic structure. Example: I left early because I had an interview the next day.
3) Prepositions
Prepositions indicate the relation between different words. They occur before a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase and indicate a direction, time, place, location, and spatial relationship. Common prepositions include across, after, at, before, by, during, from, in, into, of, on, to, under, with, without, etc.
4) Pronouns
If we did not have the pronoun word families we would have to repeat a whole lot of nouns. A word that takes the position of a noun is named as a pronoun. Pronouns can be employed as a substitute for a noun.
- Pronouns are divided into 5 categories:
- Personal Pronouns: I, you, she, etc
- Demonstrative Pronouns: This, these, etc
- Possessive Pronouns: Yours, His, etc
- Interrogative Pronouns: Which, What, etc
- Reflexive Pronouns: Herself, Himself, etc.
- Reciprocal Pronouns: Each other
- Indefinite Pronouns: Few, Nobody, etc.
- Relative Pronouns: Which, Whom, etc.
5) Interjections
Short exclamations like Oh!, Ah! etc are known as Interjections. Even though they have no grammatical value, we often use them in daily speech. Interjections are primarily used to express emotions such as anger, surprise, etc. Given below are a few examples.
Well! That hurts
Hey! Don’t be so clumsy
Remember, an interjection is always followed by an exclamation mark.
Read More:
- English Idioms
- Literary Devices
FAQs on Word Classes
1. How to identify the word classes in a sentence?
A word class is a group of words that have certain common features. To find out the word classes within a sentence it is important that you familiarise yourself with the most common word classes in English. These include nouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, prepositions, etc.
2. How to classify a word class?
Word classes in English belong to two major categories. These are Open word classes that include nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs. The second category is closed word classes that include: pronouns, determiners, interjections, etc.
3. What is the difference between a word class and part of speech?
The term “word class” is analogous to the more conventional term, “part of speech”. Both these terms refer to a group of words that have certain common features.
Conclusion
To understand the grammatical structures of sentences in a better way it’s best if you begin with word classes. Even though comprehending the different word classes may initially be a hectic task, once you master word classes, you will reach the exact meaning or message conveyed by a sentence.
Скачать материал

Скачать материал




- Сейчас обучается 268 человек из 64 регионов




Описание презентации по отдельным слайдам:
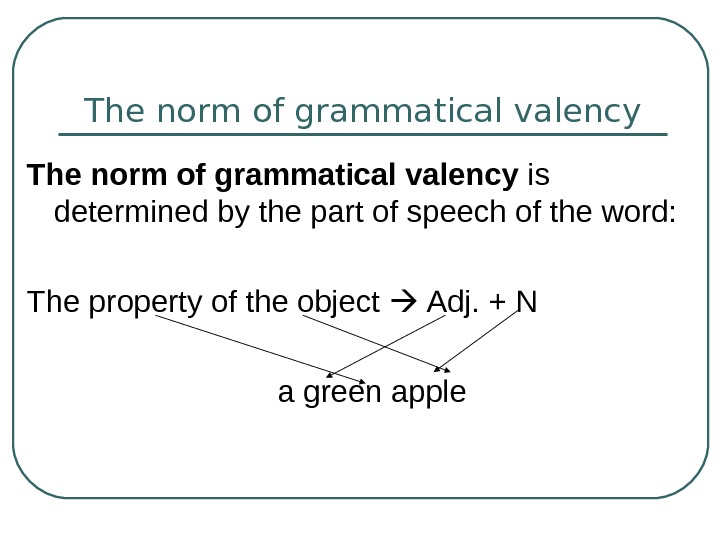
-
1 слайд
Word Groups and Phraseological Units
Words put together to form lexical units make up phrases or word-groups.
-
2 слайд
The main factors active in bringing words together are lexical and grammatical valency of the components of word-groups.
-
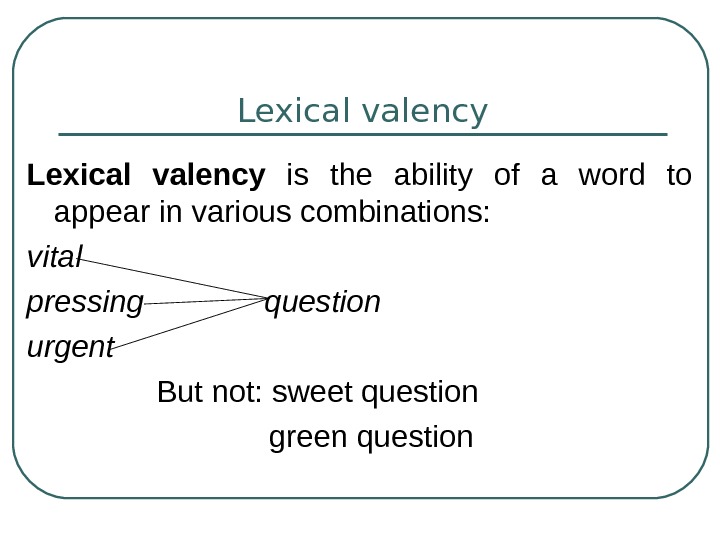
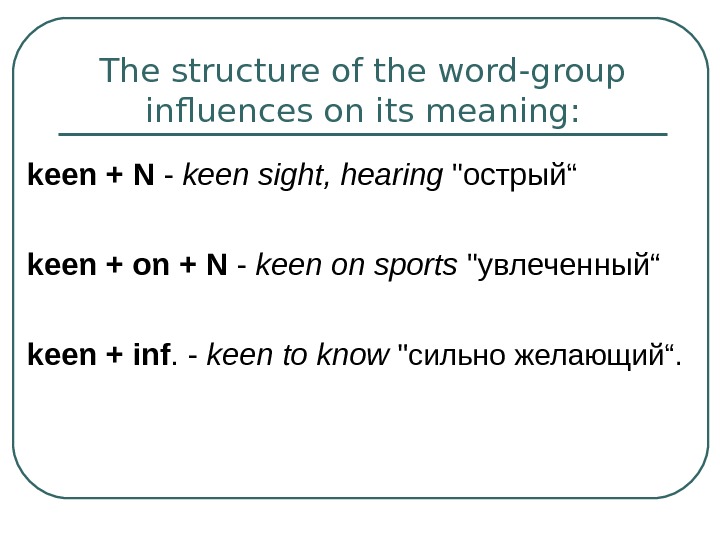
3 слайд
Lexical valency is the aptness of a word to appear in various collocations.
All the words of the language possess a certain norm of lexical valency.
-
4 слайд
Grammatical valency is the aptness of a word to appear in various grammatical structures.
Restrictions of grammatical valency are to be accounted for by the grammatical structure of the language.
-
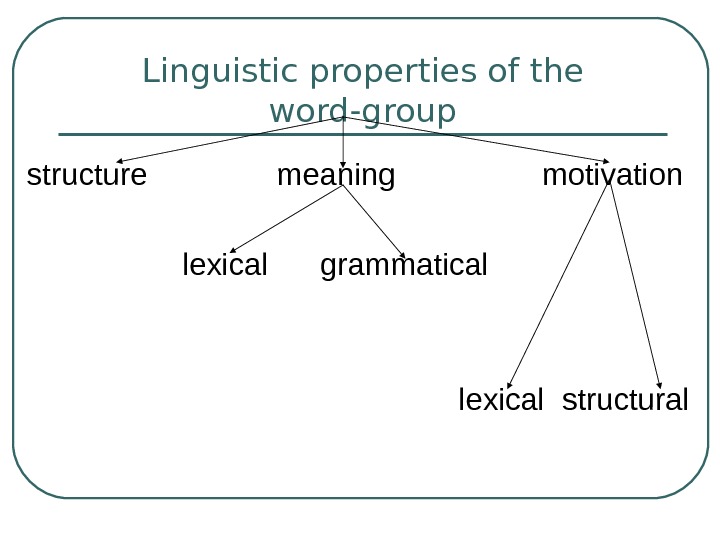
5 слайд
Semantically all word-groups may be classified into motivated and non-motivated. Non-motivated word-groups are usually described as phraseological units.
-
6 слайд
The same as words phraseological units express a single notion and are used in a sentence as one part of it.
American and British lexicographers call such units «idioms».
-
7 слайд
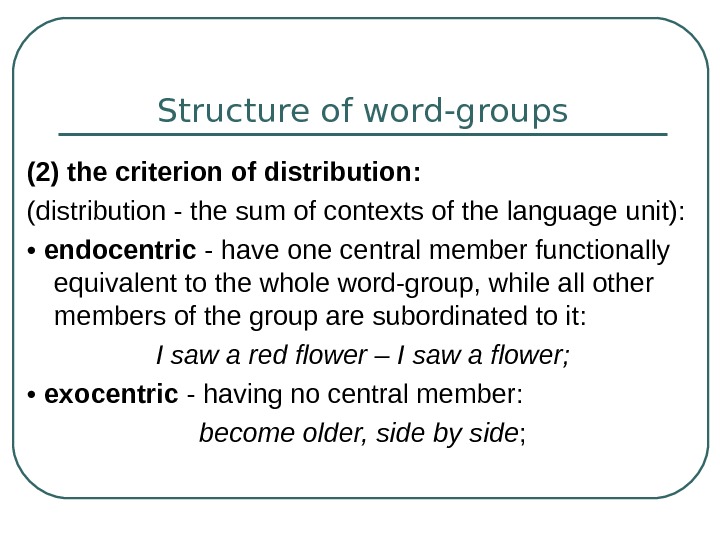
Phraseological Units
The border-line between free or variable word-groups and phraseological units is not clearly definedthe existing terms are: set-phrases, idioms, word-equivalents
-
8 слайд
Phraseological units are habitually defined as non-motivated word-groups that cannot be freely made up in speech but are reproduced as ready-made units
-
9 слайд
The main characteristic features of phraseological units are:
— stability of the lexical components
— lack of motivationCOMPARE: red flower and red tape
-
10 слайд
Phraseological units can be classified according to the ways they are formed, according to the degree of the motivation of their meaning, according to their structure and according to their part-of-speech meaning.
-
11 слайд
A.V. Koonin classified phraseological units according to the way they are formed.
He pointed out primary and secondary ways of forming phraseological units.
Primary ways of forming phraseological units are those when a unit is formed on the basis of a free word-group :
-
12 слайд
1) transferring the meaning of terminological word-groups:
«launching pad» in its terminological meaning is «стартовая площадка» , in its transferred meaning — «отправной пункт»,
«to link up» — «cтыковаться, стыковать космические корабли» in its tranformed meaning it means -«знакомиться»; -
13 слайд
2) from free word groups by transforming their meaning,
e.g. «granny farm» — «пансионат для престарелых»,
«Troyan horse» — «компьюторная программа, преднамеренно составленная для повреждения компьютера»; -
14 слайд
3) phraseological units can be formed by means of alliteration ,
e.g. «a sad sack» — «несчастный случай»,
«culture vulture» — «человек, интересующийся искусством»,
«fudge and nudge» — «уклончивость». -
15 слайд
4) they can be formed by means of distorting a word group,
e.g. «odds and ends» was formed from «odd ends», -
16 слайд
5) they can be formed when we use some unreal image,
e.g. «to have butterflies in the stomach» — «испытывать волнение»,
«to have green fingers» — »преуспевать как садовод-любитель -
17 слайд
Other ways:
when a phraseological unit is formed on the basis of another phraseological unit; they are:1) conversion, e.g. «to vote with one’s feet» was converted into «vote with one’s f eet»;
-
18 слайд
2) changing the grammar form, e.g. «Make hay while the sun shines» is transferred into a verbal phrase — «to make hay while the sun shines»
-
19 слайд
3)analogy,
e.g. «Curiosity killed the cat» was transferred into «Care killed the cat» -
20 слайд
4) contrast,
e.g. «cold surgery» — «a planned before operation» was formed by contrasting it with «acute surgery»,
«thin cat» — «a poor person» was formed by contrasting it with «fat cat»; -
21 слайд
6) shortening of proverbs or sayings
e.g. from the proverb «You can’t make a silk purse out of a sow’s ear» by means of clipping the middle of it the phraseological unit «to make a sow’s ear» was formed with the meaning «ошибаться -
22 слайд
7)borrowing phraseological units from other languages
e.g. « living space» (German), « to take the bull by the horns» ( Latin) -
23 слайд
Phraseological units sematically are classified according to V.V. Vinogradov :
-phraseological fusions (сращения) kick the bucket
phraseological unities (единства) e.g. the last straw, to ride the high horse
phraseological collocations (сочетания) e.g. to take smth for granted, to have a bite -
24 слайд
Structurally:
Verbal: to run for one’s life, to talk through one’s hat, to make a song and dance about smth.
Substantive: dog’s life, white lie, calf love.
Adjectival: high and mighty, brand new, safe and sound.
Adverbial: high and low, by hook or by crook
Interjectional: my God! Good Heavens!
Найдите материал к любому уроку, указав свой предмет (категорию), класс, учебник и тему:
6 210 144 материала в базе
- Выберите категорию:
- Выберите учебник и тему
- Выберите класс:
-
Тип материала:
-
Все материалы
-
Статьи
-
Научные работы
-
Видеоуроки
-
Презентации
-
Конспекты
-
Тесты
-
Рабочие программы
-
Другие методич. материалы
-
Найти материалы
Другие материалы
- 27.12.2020
- 4749
- 2
- 27.12.2020
- 4947
- 11
- 27.12.2020
- 5785
- 13
- 27.12.2020
- 5022
- 9
- 27.12.2020
- 4057
- 1
- 27.12.2020
- 3882
- 0
- 27.12.2020
- 3905
- 1
- 27.12.2020
- 3300
- 4
Вам будут интересны эти курсы:
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Основы туризма и гостеприимства»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Организация практики студентов в соответствии с требованиями ФГОС юридических направлений подготовки»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Организация деятельности помощника-референта руководителя со знанием иностранных языков»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Корпоративная культура как фактор эффективности современной организации»
-
Курс повышения квалификации «Актуальные вопросы банковской деятельности»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Уголовно-правовые дисциплины: теория и методика преподавания в образовательной организации»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Методика организации, руководства и координации музейной деятельности»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Гостиничный менеджмент: организация управления текущей деятельностью»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Технический контроль и техническая подготовка сварочного процесса»
-
Курс профессиональной переподготовки «Информационная поддержка бизнес-процессов в организации»
The word-group theory in Modern English
word-group
theory in Modern English
Content
Introduction
.
Definition and general characteristics of the
word-group
.
Classification of word-groups
.
Semantic features of word-groups
.
Motivated and non-motivated word-groups
.
Phraseological word-groups
Introduction
is a branch of linguistics — the
science of language. Lexicology as a branch of linguistics has its own aims and
methods of scientific research. Its basic task — being a study and systematic
description of vocabulary in respect to its origin, development and its current
use. Lexicology is concerned with words, variable word-groups, phraseological
units and morphemes which make up words.the object of the linguistic research
within the frameworks of the lexicological analysis, word-groups draw much
attention of different scientists at different stages of the research
history.linguists as Shveitser, Arnold, Nikitin, Akhmanova, Marchenko, and many
others devoted their research papers to the matter of the word-groups, their
classification, semantic features, and other specific characteristics. They
have contributed linguistic research with a number of works, connected with
this lexical units. The matter of the word-group thorough study is topical with
a glance at their specific features, some phraseological peculiarities and
semantic-grammatical structure.above-mentioned aspects have predetermined our
choice of the topic of the present report «The word-group theory in Modern
English».object of the investigation are word-groups of Modern
English.subject of the present report includes specific features and
characteristics of word-groups.purpose of the report writing is to investigate
word-groups functioning in the Modern English language.purporse of the report
has predetermined the following tasks of the investigation:
to define the notion of the
word-group and outline its general characteristics;
to suggest the classification of the
word-group;
to consider semantic features of
word-groups;
to characterize motivated and
non-motivated word-groups;
to specify peculiar features of
phraseological word-groups.practical value of the present report is performed
by the possibility of using its materials for the further thorough study of
this matter.
1. Definition and general
characteristics of the word-group
word group is the simplest
nonpredicative (as contrasted to the sentence) unit of speech. The word group
is formed on a syntactic pattern and based on a subordinating grammatical
relationship between two or more content words. This relationship may be one of
agreement, government, or subordination. The grammatically predominant word is
the main element of the word group, and the grammatically subordinated word the
dependent element.word group denotes a fragment of extralinguistic reality. The
word group combines formally syntactic and semantically syntactic features.
Such features reveal the compatibility of grammatical and lexical meanings with
the structure of the object-logical relations that these meanings
reflect.groups may be free or phraseological. Free word groups are formed in
accordance with regular and productive combinative principles; their meanings
may be deduced from those of the component words.are a lot of definitions
concerning the word-group. The most adequate one seems to be the following: the
word-group is a combination of at least two notional words which do not
constitute the sentence but are syntactically connected. According to some
other scholars (the majority of Western scholars and professors B.Ilyish and
V.Burlakova — in Russia), a combination of a notional word with a function word
(on the table) may be treated as a word-group as well. The problem is
disputable as the role of function words is to show some abstract relations and
they are devoid of nominative power. On the other hand, such combinations are
syntactically bound and they should belong somewhere.characteristics of the
word-group are:
) As a naming unit it differs from a
compound word because the number of constituents in a word-group corresponds to
the number of different denotates: a black bird — чорний птах (2), a blackbird
— дрізд (1);loud speaker (2), a loudspeaker (1).
) Each component of the word-group
can undergo grammatical changes without destroying the identity of the whole
unit: to see a house — to see houses.
) A word-group is a dependent
syntactic unit, it is not a communicative unit and has no intonation of its own
[4; p. 28].
groups can be classified on the
basis of several principles:
a)
According to the type of syntagmatic
relations: coordinate (you and me), subordinate (to see a house, a nice dress),
predicative (him coming, for him to come),
b)
According to the structure: simple
(all elements are obligatory), expanded (to read and translate the text —
expanded elements are equal in rank), extended (a word takes a dependent
element and this dependent element becomes the head for another word: a beautiful
flower — a very beautiful flower).
1) Subordinate
word-groups.word-groups are based on the relations of dependence between the
constituents. This presupposes the existence of a governingwhich is called the
head and the dependent element which is called the adjunct (in noun-phrases) or
the complement (in verb-phrases).to the nature of their heads, subordinate
word-groups fall into noun-phrases (NP) — a cup of tea, verb-phrases (VP) — to
run fast, to see a house, adjective phrases (AP) — good for you, adverbial
phrases (DP) — so quickly, pronoun phrases (IP) — something strange, nothing to
do.formation of the subordinate word-group depends on the valency of its
constituents. Valency is a potential ability of words to combine. Actual
realization of valency in speech is called combinability [6; p. 162-163].
) The noun-phrase (NP).word-groups
are widely spread in English. This may be explained by a potential ability of
the noun to go into combinations with practically all parts of speech. The NP
consists of a noun-head and an adjunct or adjuncts with relations of
modification between them. Three types of modification are distinguished here:
a)
Premodification that comprises all
the units placed before the head: two smart hard-working students. Adjuncts used
in pre-head position are called pre-posed adjuncts.
b)
Postmodification that comprises all
the units all the units placed after the head: students from Boston. Adjuncts
used in post-head position are called post-posed adjuncts.
c)
Mixed modification that comprises
all the units in both pre-head and post-head position: two smart hard-working
students from Boston.
) Noun-phrases with pre-posed
adjuncts.noun-phrases with pre-posed modifiers we generally find adjectives, pronouns,
numerals, participles, gerunds, nouns, nouns in the genitive case (see the
table) [8; p. 43]. According to their position all pre-posed adjuncts may be
divided into pre-adjectivals and adjectiavals. The position of adjectivals is
usually right before the noun-head. Pre-adjectivals occupy the position before
adjectivals. They fall into two groups: a) limiters (to this group belong
mostly particles): just, only, even, etc. and b) determiners (articles,
possessive pronouns, quantifiers — the first, the last).of nouns by nouns (N+N)
is one of the most striking features about the grammatical organization of
English. It is one of devices to make our speech both laconic and expressive at
the same time. Noun-adjunct groups result from different kinds of transformational
shifts. NPs with pre-posed adjuncts can signal a striking variety of
meanings:peace — peace all over the worldbox — a box made of silverlamp — lamp
for tableslegs — the legs of the tablesand — sand from the riverchild — a child
who goes to schoolgrammatical relations observed in NPs with pre-posed adjuncts
may convey the following meanings:
1)
subject-predicate relations: weather
change;
2)
object relations: health service,
women hater;
3)
adverbial relations: a) of time:
morning star,
b) place: world peace, country
house,) comparison: button eyes,) purpose: tooth brush.is important to remember
that the noun-adjunct is usually marked by a stronger stress than the
head.special interest is a kind of ‘grammatical idiom’ where the modifier is
reinterpreted into the head: a devil of a man, an angel of a girl.
) Noun-phrases with post-posed
adjuncts.with post-posed may be classified according to the way of connection
into prepositionless and prepositional. The basic prepositionless NPs with post-posed
adjuncts are: Nadj. — tea strong, NVen — the shape unknown, NVing — the girl
smiling, ND — the man downstairs, NVinf — a book to read, NNum — room
ten.pattern of basic prepositional NPs is N1 prep. N2. The most common
preposition here is ‘of’ — a cup of tea, a man of courage. It may have quite
different meanings: qualitative — a woman of sense, predicative — the pleasure
of the company, objective — the reading of the newspaper, partitive — the roof
of the house.
) The verb-phrase.VP is a definite
kind of the subordinate phrase with the verb as the head. The verb is
considered to be the semantic and structural centre not only of the VP but of
the whole sentence as the verb plays an important role in making up primary
predication that serves the basis for the sentence. VPs are more complex than
NPs as there are a lot of ways in which verbs may be combined in actual usage.
Valent properties of different verbs and their semantics make it possible to
divide all the verbs into several groups depending on the nature of their
complements [7; p. 91].of verb-phrases.can be classified according to the
nature of their complements — verb complements may be nominal (to see a house)
and adverbial (to behave well). Consequently, we distinguish nominal, adverbial
and mixed complementation.complementation takes place when one or more nominal
complements (nouns or pronouns) are obligatory for the realization of potential
valency of the verb: to give smth. to smb., to phone smb., to hear smth.(smb.),
etc.complementation occurs when the verb takes one or more adverbial elements
obligatory for the realization of its potential valency: He behaved well, I
live …in Kyiv (here).complementation — both nominal and adverbial elements are
obligatory: He put his hat on he table (nominal-adverbial).to the structure VPs
may be basic or simple (to take a book) — all elements are obligatory; expanded
(to read and translate the text, to read books and newspapers) and extended (to
read an English book).
) Predicative word-groups.word
combinations are distinguished on the basis of secondary predication. Like
sentences, predicative word-groups are binary in their structure but actually
differ essentially in their organization. The sentence is an independent
communicative unit based on primary predication while the predicative
word-group is a dependent syntactic unit that makes up a part of the sentence.
The predicative word-group consists of a nominal element (noun, pronoun) and a
non-finite form of the verb: N + Vnon-fin. There are Gerundial, Infinitive and
Participial word-groups (complexes) in the English language: his reading, for
me to know, the boy running, etc.)
. Semantic features of word-groups
word-group is the largest two-facet
lexical unit comprising more than one word but expressing one global
concept.lexical meaning of the word groups is the combined lexical meaning of
the component words. The meaning of the word groups is motivated by the
meanings of the component members and is supported by the structural pattern.
But it’s not a mere sum total of all these meanings! Polysemantic words are
used in word groups only in 1 of their meanings. These meanings of the
component words in such word groups are mutually interdependent and inseparable
(blind man — «a human being unable to see», blind type — «the
copy isn’t readable).groups possess not only the lexical meaning, but also the
meaning conveyed mainly by the pattern of arrangement of their constituents.
The structural pattern of word groups is the carrier of a certain semantic component
not necessarily dependent on the actual lexical meaning of its members (school
grammar — «grammar which is taught in school», grammar school —
«a type of school»). We have to distinguish between the structural
meaning of a given type of word groups as such and the lexical meaning of its
constituents [11; p. 62-64].is often argued that the meaning of word groups is
also dependent on some extra-linguistic factors — on the situation in which
word groups are habitually used by native speakers.put together to form lexical
units make phrases or word-groups. One must recall that lexicology deals with
words, word-forming morphemes and word-groups.degree of structural and semantic
cohesion of word-groups may vary. Some word-groups, e.g. at least, point of
view, by means, to take place, etc. seem to be functionally and semantically
inseparable. They are usually described as set phrases, word-equivalents or
phraseological units and are studied by the branch of lexicology which is known
as phraseology. In other word-groups such as to take lessons, kind to people, a
week ago, the component-members seem to possess greater semantic and structural
independence. Word-groups of this type are defined as free word-groups or
phrases and are studied in syntax.discussing phraseology it is necessary to
outline the features common to various word-groups irrespective of the degree
of structural and semantic cohesion of the component-words [18; p. 231].are two
factors which are important in uniting words into word-groups:
the lexical valency of words;
. Motivated and non-motivated
word-groups
word group semantic
motivated
The term motivation is used to
denote the relationship existing between the phonemic or morphemic composition
and structural pattern of the word on the one hand and its meaning on the
other.are three main types of motivation:
) phonetical
) morphological
) semantic
. Phonetical motivation is used when
there is a certain similarity between the sounds that make up the word. For
example: buzz, cuckoo, gigle. The sounds of a word are imitative of sounds in
nature, or smth that produces a characteristic sound. This type of motivation
is determined by the phonological system of each language.
. Morphological motivation — the
relationship between morphemic structure and meaning. The main criterion in
morphological motivation is the relationship between morphemes. One-morphemed
words are non-motivated. Ex — means «former» when we talk about humans
ex-wife, ex-president. Re — means «again»: rebuild, rewrite. In
borrowed words motivation is faded: «expect, export, recover (get
better)». Morphological motivation is especially obvious in newly coined
words, or in the words created in this century. In older words motivation is
established etymologically.structure-pattern of the word is very important too:
«finger-ring» and «ring-finger». Though combined lexical
meaning is the same. The difference of meaning can be explained by the arrangement
of the components.motivation has some irregularities: «smoker» — si
not «the one who smokes», it is «a railway car in which
passenger may smoke».degree of motivation can be different:
«endless» is completely
motivated
«cranberry» is partially
motivated: morpheme «cran-» has no lexical meaning.
. Semantic motivation is based on
the co-existence of direct and figurative meanings of the same word within the
same synchronous system. «Mouth» denotes a part of the human face and
at the same time it can be applied to any opening: «the mouth of a
river». «Ermine» is not only the anme of a small animal, but
also a fur. In their direct meaning «mouth» and «ermine»
are not motivated [13; p. 86].compound words it is morphological motivation
when the meaning of the whole word is based on direct meanings of its
components and semantic motivation is when combination of components is used
figuratively. For example «headache» is «pain in the head»
(morphological) and «smth. annoying» (sematic).the connection between
the meaning of the word and its form is conventional (there is no perceptible
reason for the word having this phonemic and morphemic composition) the word is
non-motivated (for the present state of language development). Words that seem
non-motivated now may have lost their motivation: «earn» is derived
from «earnian — to harvest», but now this word is non-motivated.to
compounds, their motivation is morphological if the meaning of the whole is
based on the direct meaning of the components, and semantic if the combination
is used figuratively: watchdog — a dog kept for watching property
(morphologically motivated); — a watchful human guardian (semantically
motivated) [5; p. 94-95].vocabulary is in a state of constant development.
Words that seem non-motivated at present may have lost their motivation [16; p.
34]. When some people recognize the motivation, whereas others do not,
motivation is said to be faded.all word-groups may be classified into motivated
and non-motivated. Non-motivated word-groups are usually described as phraseological
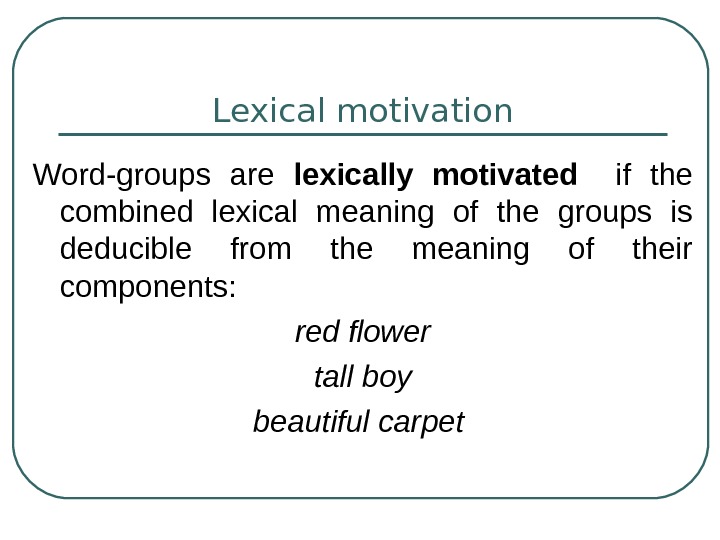
units or idioms.groups may be described as lexically motivated if the combined
lexical meaning of the groups is based on the meaning of their components. Thus
take lessons is motivated; take place — ‘occur’ is lexically
non-motivated.groups are said to be structurally motivated if the meaning of
the pattern is deduced from the order and arrangement of the member-words of
the group. Red flower is motivated as the meaning of the pattern quality —
substance can be deduced from the order and arrangement of the words red and
flower, whereas the seemingly identical pattern red tape (‘official
bureaucratic methods’) cannot be interpreted as quality — substance.identical
word-groups are sometimes found to be motivated or non-motivated depending on
their semantic interpretation. Thus apple sauce, e.g., is lexically and
structurally motivated when it means ‘a sauce made of apples’ but when used to
denote ‘nonsense’ it is clearly non-motivated [15; p. 90].groups like words may
be also analyzed from the point of view of their motivation. Word-groups may be
called as lexically motivated if the combined lexical meaning of the group is
deducible from the meaning of the components. All free phrases are completely
motivated.follows from the above discussion that word-groups may be also
classified into motivated and non-motivated units. Non-motivated word-groups
are habitually described as phraseological units or idioms.
. Phraseological word-groups
of English phraseology began not
long ago. English and American linguists as a rule are busy collecting
different words, word-groups and sentences which are interesting from the point
of view of their origin, style, usage or some other features. All these units
are habitually described as «idioms», but no attempt has been made to
describe these idioms as a separate class of linguistic units or a specific
class of word-groups.in terminology («set-phrases»,
«idioms» and «word-equivalents») reflects certain
differences in the main criteria used to distinguish types of phraseological
units and free word-groups. The term «set phrase» implies that the
basic criterion of differentiation is stability of the lexical components and
grammatical structure of word-groups.is a certain divergence of opinion as to
the essential features of phraseological units as distinguished from other
word-groups and the nature of phrases that can be properly termed
«phraseological units». The habitual terms «set-phrases»,
«idioms», «word-equivalents» are sometimes treated
differently by different linguists. However these terms reflect to certain
extend the main debatable points of phraseology which centre in the divergent
views concerning the nature and essential features of phraseological units as
distinguished from the so-called free word-groups.term «set
expression» implies that the basic criterion of differentiation is
stability of the lexical components and grammatical structure of
word-groups.term «word-equivalent» stresses not only semantic but
also functional inseparability of certain word-groups, their aptness to
function in speech as single words [10; p. 31].term «idioms»
generally implies that the essential feature of the linguistic units under
consideration is idiomaticity or lack of motivation. Uriel Weinreich expresses
his view that an idiom is a complex phrase, the meaning of which cannot be
derived from the meanings of its elements. He developed a more truthful
supposition, claiming that an idiom is a subset of a phraseological unit. Ray
Jackendoff and Charles Fillmore offered a fairly broad definition of the idiom,
which, in Fillmore’s words, reads as follows: «…an idiomatic expression or
construction is something a language user could fail to know while knowing
everything else in the language». Chafe also lists four features of idioms
that make them anomalies in the traditional language unit paradigm:
non-compositionality, transformational defectiveness, ungrammaticality and
frequency asymmetry.work in this field has been done by the outstanding Russian
linguist A. Shakhmatov in his work «Syntax». This work was continued
by Acad. V.V. Vinogradov. Great investigations of English phraseology were done
by Prof. A. Cunin, I. Arnold and others [1; p. 121].units are habitually
defined as non-motivated word-groups that cannot be freely made up in speech
but are reproduced as ready-made units; the other essential feature of
phraseological units is stability of the lexical components and grammatical
structure.components of free word-groups which may vary according to the needs
of communication, member-words of phraseological units are always reproduced as
single unchangeable collocations. E.g., in a red flower (a free phrase) the
adjective red may be substituted by another adjective denoting colour, and the
word-group will retain the meaning: «the flower of a certain colour»
[2; p. 54].the phraseological unit red tape (bürokratik
metodlar) no such substitution is possible, as a change of the adjective would
cause a complete change in the meaning of the group: it would then mean «tape
of a certain colour». It follows that the phraseological unit red tape is
semantically non-motivated, i.e. its meaning cannot be deduced from the meaning
of its components, and that it exists as a ready-made linguistic unit which
does not allow any change of its lexical components and its grammatical
structure [9; p. 45-46].structure of phraseological units is to a certain
degree also stable:tape — a phraseological unit;tapes — a free word-group;go to
bed — a phraseological unit;go to the bed — a free word-group.ways of forming
phraseological units are those when a unit is formed on the basis of a free
word-group 
phraseological units by means of transferring the meaning of terminological
word-groups, e.g. in cosmic technique we can point out the following phrases:
«launching pad» in its terminological meaning is «стартова
площадка», in its transferred meaning — «відправний пункт»,
«to link up» — «cтикуватися, стикувати космічні човни» in
its tranformed meaning it means -«знайомитися»;) a large group of
phraseological units was formed from free word groups by transforming their
meaning, e.g. «granny farm» — «пансионат для старих людей»,
«Troyan horse» — «компьютерна програма, яка навмиснестворена для
пвиведення з ладу компьютера»;) phraseological units can be formed by
means of alliteration, e.g. «a sad sack» — «нещасний
випадок», «culture vulture» — «людина, яка цікавиться
мистецтвом», «fudge and nudge» — «ухильність».) they
can be formed by means of expressiveness, especially it is characteristic for
forming interjections, e.g. «My aunt!», «Hear, hear !» etc)
they can be formed by means of distorting a word group, e.g. «odds and
ends» was formed from «odd ends»,) they can be formed by using
archaisms, e.g. «in brown study» means «in gloomy
meditation» where both components preserve their archaic meanings,) they
can be formed by using a sentence in a different sphere of life, e.g.
«that cock won’t fight» can be used as a free word-group when it is
used in sports (cock fighting ), it becomes a phraseological unit when it is
used in everyday life, because it is used metaphorically,) they can be formed
when we use some unreal image, e.g. «to have butterflies in the
stomach» — «відчувати хвилювання», «to have green
fingers» — «досягати успіхів як садовод-любитель» etc.) they can
be formed by using expressions of writers or polititions in everyday life, e.g.
«corridors of power» (Snow), «American dream» (Alby)
«locust years» (Churchil) , «the winds of change» (Mc
Millan).into consideration mainly the degree of idiomaticity phraseological
units may be classified into three big groups. This classification was first
suggested by Acad. V.V. Vinogradov. These groups are:
phraseological fusions,
phraseological unities,
phraseological collocations, or
habitual collocations.fusions are completely non-motivated word-groups.
Themeaning of the components has no connection at least synchronically with the
meaning of the whole group. Idiomaticity is combined with complete stability of
the lexical components and the grammatical structure of the fusion [19; p.
37].unities are partially non-motivated word-groups as their meaning can
usually be understood through (deduced from) the metaphoric meaning of the
whole phraseological unit [3; p. 84].unities are usually marked by a
comparatively high degree of stability of the lexical components and
grammatical structure. Phraseological unities can have homonymous free phrases,
used in direct meanings.
§ to skate on thin
ice — to skate on thin ice (to risk);
§ to wash one’s hands
off dirt — to wash one’s hands off (to withdraw from participance);
§ to play the first
role in the theatre — to play the first role (to dominate).must be not less
than two notional wordsin metaphorical meanings.collocations are partially
motivated but they are made up of words having special lexical valency which is
marked by a certain degree of stability in such word-groups. In phraseological
collocations variability of components is strictly limited. They differ from
phraseological unities by the fact that one of the components in them is used
in its direct meaning, the other — in indirect meaning, and the meaning of the
whole group dominates over the meaning of its components. As figurativeness is
expressed only in one component of the phrase it is hardly felt [14; p. 69].
§ to pay a visit,
tribute, attention, respect;
Conclusions
the course of the present report
writing we have specified the definition of the word-group and determined its
general characteristics. Specific attention has been drawn to the
classification of word-groups. We have thoroughly analyzed semantic features of
word-groups, their motivated and non-motivated types and their specific
subtype, i.e. phraseological word-groups.completed the report writing, we have
come to the following conclusions.word-group is a combination of at least two
notional words which do not constitute the sentence but are syntactically
connected.have concluded that according to the type of syntagmatic relations,
word-groups can be coordinate, subordinate and predicative, according to the
structure they are divided into simple, expanded and extended.lexical meaning
of the word groups is the combined lexical meaning of the component words. The
meaning of the word groups is motivated by the meanings of the component
members and is supported by the structural pattern.term motivation is used to
denote the relationship existing between the phonemic or morphemic composition
and structural pattern of the word on the one hand and its meaning on the
other.have come to the conclusion, that here are three main types of
motivation: 1) phonetical; 2) morphological; 3) semantic.have concluded,
phraseological units are created from free word-groups. But in the course of
time some words — constituents of phraseological units may drop out of the
language; the situation in which the phraseological unit was formed can be
forgotten, motivation can be lost and these phrases become phraseological
fusions.
Bibliography
1. Арнольд
И.В. Аспекты семантических исследований. — М., 1980.
2. Арнольд
И.В. Стилистика современного английского языка. — М., 1973.
. Кунин
А.В. Фразеология современного английского языка. — М., 1970
. Маковский
М.М. Английская этимология. — М., 1986
. Мешков
О.Д. Словообразование современного английского языка. -М., 1976
. Мостовий
М.I. Лексикологiя
англiйськоi
мови. — Харькiв, 1993
. Никитин
М.В. Лексическое значение слова (структура и комбинаторика). — М., 1983
Смирницкий А.И. Лексикология английского языка. — М., 1956
. Никитин
М.В. О предмете и понятиях комбинаторной семантики / Проблемы лексической и
грамматической семасиологии. Владимир, 1974 год выпуска
9. Смит
Л.П. Фразеология английского языка. — М., 1959
. Старикова
Е.Н.. Раевская Н.Н., Медведева Л.М. Лингвистические чтения. Проблемы
словообразования. Лингвистика текста. — К., 1985
11. Телия
В.Н. Типы языковых значений. Связанное значение слова в языке — М., 1981
Теоретические проблемы социальной лингвистики. — М., 1981
. Харитончик
З.А. Лексикология английского языка. — Минск, 1992
. Швейцер
А.Д. Очерк современного английского языка США. — М.. 1963
. Akhmanova
O. Lexicology. Theory and Method. — M., 1972 Ginsburg R.S. A Course in Modern
English Lexicology. M., 1979.
. Arnold
I.V. The English Word. — M., 1986
. Kuznetsova
V.S. Notes on English Lexicology.- K., 1968.
. L.P.
Smith, Semantics. An introduction to the science of meaning. Oxford University
Press, 1962.
. Vinogradov
V.V. Pixon P.G. Handbook of American Idioms and Idiomatic Usage, 1973.