You can perform calculations and logical comparisons in a table by using formulas. The Formula command is found on the Table Tools, Layout tab, in the Data group.
A formula in Word automatically updates when you open the document that contains the formula. You can also update a formula result manually. For more information, see the section Update formula results.
Note: Formulas in Word or Outlook tables are a type of field code. For more information about field codes, see the See Also section.
In this article
-
Insert a formula in a table cell
-
Update formula results
-
Update the result of specific formulas
-
Update all the formula results in a table
-
Update all the formulas in a document
-
-
Examples: Sum numbers in a table by using positional arguments
-
Available functions
-
Use bookmarknames or cell references in a formula
-
RnCn references
-
A1 references
-
Insert a formula in a table cell
-
Select the table cell where you want your result. If the cell is not empty, delete its contents.
-
On the Table Tools, Layout tab, in the Data group, click Formula.
-
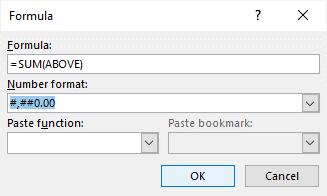
Use the Formula dialog box to create your formula. You can type in the Formula box, select a number format from the Number Format list, and paste in functions and bookmarks using the Paste Function and Paste Bookmark lists.
Update formula results
In Word, the result of a formula is calculated when it is inserted, and when the document containing the formula opens. In Outlook, the result of a formula is only calculated when it is inserted and won’t be available for the recipient of the email to edit.
You can also manually update:
-
The result of one or more specific formulas
-
The results of all formulas in a specific table
-
All the field codes in a document, including formulas
Update the result of specific formulas
-
Select the formulas that you want to update. You can select multiple formulas by holding down the CTRL key while you make selections.
-
Do one of the following:
-
Right-click the formula, then click Update field.
-
Press F9.
-
Update all the formula results in a table
-
Select the table that contains formula results that you want to update, and then press F9.
Update all the formulas in a document
Important: This procedure updates all the field codes in a document, not just formulas.
-
Press CTRL+A.
-
Press F9.
Examples: Sum numbers in a table by using positional arguments
You can use positional arguments (LEFT, RIGHT, ABOVE, BELOW) with these functions:
-
AVERAGE
-
COUNT
-
MAX
-
MIN
-
PRODUCT
-
SUM
As an example, consider the following procedure for adding numbers by using the SUM function and positional arguments.
Important: To avoid an error while summing in a table by using positional arguments, type a zero (0) in any empty cell that will be included in the calculation.
-
Select the table cell where you want your result. If the cell is not empty, delete its contents.
-
On the Table Tools, Layout tab, in the Data group, click Formula.
-
In the Formula dialog box, do one of the following:
|
To add the numbers… |
Type this in the Formula box |
|---|---|
|
Above the cell |
=SUM(ABOVE) |
|
Below the cell |
=SUM(BELOW) |
|
Above and below the cell |
=SUM(ABOVE,BELOW) |
|
Left of the cell |
=SUM(LEFT) |
|
Right of the cell |
=SUM(RIGHT) |
|
Left and right of the cell |
=SUM(LEFT,RIGHT) |
|
Left of and above the cell |
=SUM(LEFT,ABOVE) |
|
Right of and above the cell |
=SUM(RIGHT,ABOVE) |
|
Left of and below the cell |
=SUM(LEFT,BELOW) |
|
Right of and below the cell |
=SUM(RIGHT,BELOW) |
-
Click OK.
Available functions
Note: Formulas that use positional arguments (e.g., LEFT) do not include values in header rows.
The following functions are available for use in Word and Outlook table formulas:
|
Function |
What it does |
Example |
Returns |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ABS() |
Calculates the absolute value of the value inside the parentheses |
=ABS(-22) |
22 |
|
AND() |
Evaluates whether the arguments inside the parentheses are all TRUE. |
=AND(SUM(LEFT)<10,SUM(ABOVE)>=5) |
1, if the sum of the values to the left of the formula (in the same row) is less than 10 and the sum of the values above the formula (in the same column, excluding any header cell) is greater than or equal to 5; 0 otherwise. |
|
AVERAGE() |
Calculates the average of items identified inside the parentheses. |
=AVERAGE(RIGHT) |
The average of all values to the right of the formula cell, in the same row. |
|
COUNT() |
Calculates the count of items identified inside the parentheses. |
=COUNT(LEFT) |
The number of values to the left of the formula cell, in the same row. |
|
DEFINED() |
Evaluates whether the argument inside the parentheses is defined. Returns 1 if the argument has been defined and evaluates without error, 0 if the argument has not been defined or returns an error. |
=DEFINED(gross_income) |
1, if gross_income has been defined and evaluates without error; 0 otherwise. |
|
FALSE |
Takes no arguments. Always returns 0. |
=FALSE |
0 |
|
IF() |
Evaluates the first argument. Returns the second argument if the first argument is true; returns the third argument if the first argument is false. Note: Requires exactly three arguments. |
=IF(SUM(LEFT)>=10,10,0) |
10, if the sum of values to the left of the formula is at least 10; 0 otherwise. |
|
INT() |
Rounds the value inside the parentheses down to the nearest integer. |
=INT(5.67) |
5 |
|
MAX() |
Returns the maximum value of the items identified inside the parentheses. |
=MAX(ABOVE) |
The maximum value found in the cells above the formula (excluding any header rows). |
|
MIN() |
Returns the minimum value of the items identified inside the parentheses. |
=MIN(ABOVE) |
The minimum value found in the cells above the formula (excluding any header rows). |
|
MOD() |
Takes two arguments (must be numbers or evaluate to numbers). Returns the remainder after the second argument is divided by the first. If the remainder is 0 (zero), returns 0.0 |
=MOD(4,2) |
0.0 |
|
NOT() |
Takes one argument. Evaluates whether the argument is true. Returns 0 if the argument is true, 1 if the argument is false. Mostly used inside an IF formula. |
=NOT(1=1) |
0 |
|
OR() |
Takes two arguments. If either is true, returns 1. If both are false, returns 0. Mostly used inside an IF formula. |
=OR(1=1,1=5) |
1 |
|
PRODUCT() |
Calculates the product of items identified inside the parentheses. |
=PRODUCT(LEFT) |
The product of multiplying all the values found in the cells to the left of the formula. |
|
ROUND() |
Takes two arguments (first argument must be a number or evaluate to a number; second argument must be an integer or evaluate to an integer). Rounds the first argument to the number of digits specified by the second argument. If the second argument is greater than zero (0), first argument is rounded down to the specified number of digits. If second argument is zero (0), first argument is rounded down to the nearest integer. If second argument is negative, first argument is rounded down to the left of the decimal. |
=ROUND(123.456, 2) =ROUND(123.456, 0) =ROUND(123.456, -2) |
123.46 123 100 |
|
SIGN() |
Takes one argument that must either be a number or evaluate to a number. Evaluates whether the item identified inside the parentheses if greater than, equal to, or less than zero (0). Returns 1 if greater than zero, 0 if zero, -1 if less than zero. |
=SIGN(-11) |
-1 |
|
SUM() |
Calculates the sum of items identified inside the parentheses. |
=SUM(RIGHT) |
The sum of the values of the cells to the right of the formula. |
|
TRUE() |
Takes one argument. Evaluates whether the argument is true. Returns 1 if the argument is true, 0 if the argument is false. Mostly used inside an IF formula. |
=TRUE(1=0) |
0 |
Use bookmarknames or cell references in a formula
You can refer to a bookmarked cell by using its bookmarkname in a formula. For example, if you have bookmarked a cell that contains or evaluates to a number with the bookmarkname gross_income, the formula =ROUND(gross_income,0) rounds the value of that cell down to the nearest integer.
You can also use column and row references in a formula. There are two reference styles: RnCn and A1.
Note: The cell that contains the formula is not included in a calculation that uses a reference. If the cell is part of the reference, it is ignored.
RnCn references
You can refer to a table row, column, or cell in a formula by using the RnCn reference convention. In this convention, Rn refers to the nth row, and Cn refers to the nth column. For example, R1C2 refers to the cell that is in first row and the second column. The following table contains examples of this reference style.
|
To refer to… |
…use this reference style |
|---|---|
|
An entire column |
Cn |
|
An entire row |
Rn |
|
A specific cell |
RnCn |
|
The row that contains the formula |
R |
|
The column that contains the formula |
C |
|
All the cells between two specified cells |
RnCn:RnCn |
|
A cell in a bookmarked table |
Bookmarkname RnCn |
|
A range of cells in a bookmarked table |
Bookmarkname RnCn:RnCn |
A1 references
You can refer to a cell, a set of cells, or a range of cells by using the A1 reference convention. In this convention, the letter refers to the cell’s column and the number refers to the cell’s row. The first column in a table is column A; the first row is row 1. The following table contains examples of this reference style.
|
To refer to… |
…use this reference |
|---|---|
|
The cell in the first column and the second row |
A2 |
|
The first two cells in the first row |
A1,B1 |
|
All the cells in the first column and the first two cells in the second column |
A1:B2 |
Last updated 2015-8-29
See Also
Field codes in Word and Outlook
Word provides some simple formulas and functions without need to embed Excel tables. It is easy
to insert and use formulas:
- In a Word table:
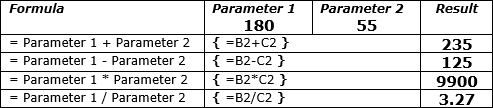
- In a document body:
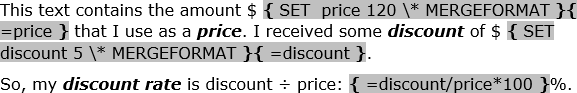
You can use simple formulas in Microsoft Word, such as addition (+), subtraction (-),
multiplication (*), or division (/). Also, you can calculate a power of (^):
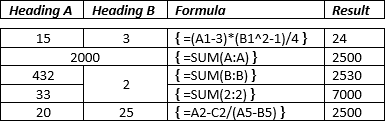
See
How to reference a cell of a Word
table
for more details.
All functions you can see in the Paste function drop-down list of the
Formula dialog box:
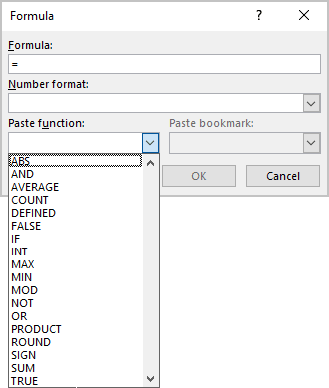
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| ABS () | Calculates the absolute value of the value inside the parentheses. |
| AND () | Evaluates whether the arguments inside the parentheses are all TRUE. |
| AVERAGE () | Calculates the average of the elements identified inside the parentheses. |
| COUNT () | Calculates the number of elements identified inside the parentheses. |
| DEFINED () | Evaluates whether the argument inside parentheses is defined. Returns 1 if the argument has been defined and evaluates without error, 0 if the argument has not been defined or returns an error. |
| FALSE | Always returns 0 |
| IF () | Evaluates the first argument. Returns the second argument if the first argument is true; returns the third argument if the first argument is false. Note: Requires exactly three arguments. |
| INT () | Rounds the value inside the parentheses down to the nearest integer. |
| MAX () | Returns the maximum value of the items identified inside the parentheses. |
| MIN () | Returns the minimum value of the items identified inside the parentheses. |
| MOD () | Takes two arguments (must be numbers or evaluate to numbers). Returns the remainder after the second argument is divided by the first. If the remainder is 0 (zero), returns 0.0. |
| NOT | Evaluates whether the argument is true. Returns 0 if the argument is true, 1 if the argument is false. Mostly used inside an IF formula. |
| OR () | Takes two arguments. If both are false, returns 0, else returns 1. Mostly used inside an IF formula. |
| PRODUCT () | Calculates the product of items identified inside the parentheses. |
| ROUND () | Rounds the first argument to the number of digits specified by the second argument. If the second argument is greater than zero (0), first argument is rounded down to the specified number of digits. If second argument is zero (0), first argument is rounded down to the nearest integer. If second argument is negative, first argument is rounded down to the left of the decimal. |
| SIGN () | Takes one argument that must either be a number or evaluate to a number. Evaluates whether the item identified inside the parentheses if greater than, equal to, or less than zero (0). Returns 1 if greater than zero, 0 if zero, -1 if less than zero. |
| SUM () | Calculates the sum of items identified inside the parentheses. |
| TRUE | Always returns 1. |
The arguments can be:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| ABOVE | Cells above the current. For example, =SUM(ABOVE) |
| BELOW | Cells below the current. For example, =SUM(BELOW) |
| LEFT | Cells on left of the current. For example, =SUM(LEFT) |
| RIGHT | Cells on right of the current. For example, =SUM(RIGHT) |
See also this tip in French:
Fonctions et formules dans Word.
Please, disable AdBlock and reload the page to continue
Today, 30% of our visitors use Ad-Block to block ads.We understand your pain with ads, but without ads, we won’t be able to provide you with free content soon. If you need our content for work or study, please support our efforts and disable AdBlock for our site. As you will see, we have a lot of helpful information to share.
Create Calculations in Word Tables Using Formulas
by Avantix Learning Team | Updated October 9, 2021
Applies to: Microsoft® Word® 2013, 2016, 2019 or 365 (Windows)
You can insert formulas in Word tables to perform calculations. These formulas can include functions such as SUM or AVERAGE or basic operators. When you insert formulas in Word tables, you are really inserting fields so the fields will need to be updated if the data in the table changes. For more complex calculations, it’s usually best to create formulas in Excel where they will update automatically.
Formulas and functions in Word tables only work with numbers. You can’t perform text calculations or output text.
Recommended article: 3 Simple Ways to Copy or Import Excel Data into Word (Linked or Unlinked)
Note: Buttons and Ribbon tabs may display in a different way (with or without text) depending on your version of Word, the size of your screen and your Control Panel settings. For Word 365 users, Ribbon tabs may appear with different names. For example, the Table Tools Design tab may appear as Table Design.
To insert a formula in a cell in a Word table, you’ll need to use the Function command on the Table Tools Layout or Table Layout tab in the Ribbon:
Do you want to learn more about Microsoft Word? Check out our virtual classroom or live classroom Word courses >
Understanding formula syntax
When you insert a table in Word, each column and row are identified like cells in Excel worksheets and each cell is assigned a cell reference. In a Word table, the first column would be column A and the first row would be row 1 so the first cell would be identified as A1. Therefore, you can create calculations that refer to cells (such as =A1+A2).
In Word and Excel, you can use the same basic operators:
- addition (+)
- subtraction (-)
- multiplication (*)
- division (/)
Typically, formulas in Word tables are created using common functions such as SUM, AVERAGE, MIN, MAX or COUNT and refer to a range. They must start with an equal sign (=).
You can refer to ranges of cells using ABOVE, LEFT, RIGHT or BELOW as the arguments for functions. If you’re trying to sum the cells at the bottom of a column, the formula would be =SUM(ABOVE). You can also combine these arguments. For example, you could enter a formula =SUM(ABOVE,LEFT) and it would sum all cells that are above and to the left of that cell. Functions can also refer to cell references such as =SUM(C1:C10). You can also refer to individual cells such =SUM(B1,C1,D5).
Word tables can also perform more complex calculations using the IF function with the syntax =IF(test,true,false). For example, =IF(A5>=1000,0,50) could be used to calculate a shipping cost of 50 if orders are less than 1000. You can also use the AND and OR functions with the IF function.
Inserting a formula in a table
To insert a formula in a table:
- Click in the cell where you want to enter a formula.
- Click the Table Tools Layout or Table Layout tab in the Ribbon.
- Select Function (fx) in the Data group. A dialog box appears. Word will typically insert a function and arguments in the Formula box.
- If you want to accept the suggested formula, click OK. If you want to change the formula, click in the Formula box and enter a formula (starting with =). You can also choose other functions from the Paste Function drop-down menu.
- If necessary, select a format from the Format drop-down menu.
- Click OK. Word inserts the formula as a field and displays the results.
The Function dialog box appears as follows with a formula and a format selected:
Updating a formula
If the original data changes, you can right-click the Formula field and select Update from the drop-down menu or press F9. If you want to update all formulas in a table, select all of the cells in the table and press F9. To select the entire table, click the four arrows on the top left of the table.
Changing a formula
To change a formula in a table:
- Right-click the formula or error. A drop-down menu appears.
- Select Edit field.
- Make the desired changes.
- Click OK.
Updating all fields
To update all fields in all tables:
- Press Ctrl + A to select all.
- Press F9.
Formula fields are just one type of field you can use in Word. There are many other fields that can insert variable information in Word documents.
Subscribe to get more articles like this one
Did you find this article helpful? If you would like to receive new articles, join our email list.
More resources
4 Ways to Create a Table in Word
How to Insert Fields in Word (Built-in or Custom)
5 Ways to Insert the Division Symbol in Word (Type or Insert ÷)
How to Insert Reusable Text Snippets in Word with Quick Parts
10 Microsoft Word Tips, Tricks and Shortcuts for Selecting in Tables
Related courses
Microsoft Word: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft Excel: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft PowerPoint: Intermediate / Advanced
Microsoft Word: Long Documents Master Class
Microsoft Word: Styles, Templates and Tables of Contents
Microsoft Word: Designing Dynamic Word Documents Using Fields
VIEW MORE COURSES >
Our instructor-led courses are delivered in virtual classroom format or at our downtown Toronto location at 18 King Street East, Suite 1400, Toronto, Ontario, Canada (some in-person classroom courses may also be delivered at an alternate downtown Toronto location). Contact us at info@avantixlearning.ca if you’d like to arrange custom instructor-led virtual classroom or onsite training on a date that’s convenient for you.
Copyright 2023 Avantix® Learning
Microsoft, the Microsoft logo, Microsoft Office and related Microsoft applications and logos are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in Canada, US and other countries. All other trademarks are the property of the registered owners.
Avantix Learning |18 King Street East, Suite 1400, Toronto, Ontario, Canada M5C 1C4 | Contact us at info@avantixlearning.ca
Просмотров 38.5к. Обновлено 4 ноября 2020
Обычно в Word создаются таблицы, которые содержат числовую информацию, такую как простые выписки или прайс-листы. Если бы потребовалось применить простые операции расчета, эти формулы можно решить в программе Word без необходимости использования электронной таблицы Excel. В этом разделе обсуждается использование основных математических операторов и функций для разработки простых операций вычисления в таблицах Word.
Возможно вы искали статью на тему Как написать математическую формулу в ворд
Содержание
- Сумма в ворде
- Word: диалоговое окно «Формула»
- Обновить формулы в ворде
- Функции расчета доступны в Word
- Видео инструкция
Сумма в ворде
Для настройки операции суммирования необходимо использовать поле формулы, действуя следующим образом:
1 — Поместите точку вставки в ячейку, где должен быть получен результат.
2 — На вкладке «Макет» группы кнопок «данные» нажмите кнопку Формула FX
После того, как вы нажали кнопку «Формула» на вкладке «Макет», откроется диалоговое окно «Формула», в котором в качестве параметра предлагается ввести функцию суммы = SUM (ВЫШЕ)
Word: диалоговое окно «Формула»
В окне Формула по умолчанию предлагается операция суммирования ( SUM ).
Названия функций расчета, применимых в Word, в последних версиях программы, больше не переводятся.
Предлагаемых операторов 18 и в их синтаксисе в скобках необходимо указывать направление расчета. Например, выше ( ABOVE ), ниже (BELOW) , слева ( LEFT ), справа RIGHT )
Функции AVERAGE (), COUNT (), MAX (), MIN (), PRODUCT () и SUM () также могут принимать ссылки на ячейки таблицы в качестве аргументов. ссылочные координаты в режиме Excel или в первом столбце таблицы будут называться A, затем B, C, D …. и первая строка 1, а затем 2,3,4 ….
Пример: чтобы добавить значения в столбец 2 вместо = SUM (ABOVE), можно написать = B2 + B3 + B4, учитывая, что подразумеваются альфа-заголовки (как если бы мы были в листе Excel) –числа столбцов и строк.
В этом режиме выражения формулы можно организовать еще более сложные расчеты, например, расчет НДС (см. Изображение ниже).
При построении этих формул следует учитывать, что они будут выполняться слева направо. Как и в математических уравнениях, операторы * (умножение) и / (деление) будут иметь приоритет при расчете сумм и вычитаний.
Если были суммы или вычитания, которые можно было выполнить перед умножением или делением, они будут заключены в скобки (). Пример = (А1 + А2) * А5
Обновить формулы в ворде
Формулы в Word автоматически обновляются при открытии документа. Вы можете вручную обновить результат формулы. Просто выделите результат и щелкните правой кнопкой мыши по нему и выберите опцию «Обновить поле».
Все функции, рассмотренные в Word, перечислены ниже.
ABS Возвращает положительное значение числа формулы, независимо от того, является ли его значение положительным или отрицательным.
AND Возвращает значение 1, если все выраженные логические выражения являются истинными, или значение 0 (ноль), если хотя бы одно из выражений является ложным.
AVERAGE Рассчитывает среднее значение ряда значений.
COUNT Подсчитывает количество элементов в списке.
DEFINED Возвращает значение 1 или 0 в зависимости от того, является ли выражение допустимым или не может быть вычислено.
FALSE Возвращает нулевое значение.
IF Вычисляет первый аргумент. Если первый аргумент является истинным, возвращает второй аргумент; если ложным — третий. Пример (=IF(SUM(ABOVE)>10;да;нет))
INT Возвращает только целочисленные значения, исключая десятичные дроби без аппроксимации.
MIN Возвращает наименьшее значение числового ряда.
MAX Возвращает наибольшее значение числового ряда.
MOD Возвращает остаток, полученный в результате деления значения x на значение y несколько раз.
NOT Возвращает значение 0 (false), если логическое выражение x истинно, или значение 1 (true), если выражение ложно. ИЛИ Возвращает значение 1 (истина), если одно или оба из логических выражений x и y являются истиной, или значение 0 (ложь), если оба выражения ложны.
OR Имеет два аргумента. Если хотя бы один из них является истинным, возвращает значение 1. Если оба аргумента являются ложными, возвращает значение 0. В основном используется в функции IF.
PRODUCT Рассчитать произведение элементов, указанных в скобках.
ROUND. Вернуть округленное значение для указанного числа десятичных знаков.
SIGN Возвращает значение 1, если ссылочная ячейка x имеет положительное значение, -1 и отрицательное.
SUM Рассчитать сумму заданного диапазона ячеек TRUE Возвращает значение 1.
TRUE Если аргумент является истинным, возвращает значение 1, если ложным — 0. В основном используется в функции IF.
В статье использовался Microsoft word 2016 купить который вы можете на сайта softtools.ru
Видео инструкция
-
Работа с формулами в Ворде, кому и зачем это надо
-
Как писать формулы в Ворд (вставлять)
-
Как поменять шрифт в Ворде в формулах
-
Как в Ворде вставлять формулы с дробями
-
Как перемещать формулу в Ворде
-
Заключение
Как писать формулы в Ворд, на этот вопрос будет дан подробный ответ в статье. Многие новички, которые работают с этим редактором, пишут формулы в Ворде вручную, что не удобно. В Word есть редактор готовых формул в виде заготовок, которые мы можем использовать для написания различных документов.
Работа с формулами в Ворде, кому и зачем это надо

Например, Вам нужно написать контрольную (научную, дипломную) работу по алгебре, геометрии, химии, физике, работу по другим предметам. В этих работах часто пишут формулы. Вам придется писать формулы в программе Ворд, если Вы делаете курсовую или дипломную работу на заказ.
Работа с формулами в Ворде нужна в основном студентам, школьникам и тем, кто зарабатывает через Интернет с помощью Word. Иногда формулы встречаются в статьях на сайтах и блогах. Как писать формулы в Ворд быстро? На данный вопрос стоит ответить, поскольку это надо знать студентам, школьникам и тем, кто зарабатывает через Интернет с помощью Ворда. По инструкции, Вы сможете написать любую формулу, без особых затруднений.
к оглавлению ↑
Как писать формулы в Ворд (вставлять)
Есть несколько способов вставки формул в документ Ворда:
- через функцию «П»;
- с помощью функции «Объект».
Рассмотрим оба варианта. Первое, что нам нужно сделать, это открыть документ Word на компьютере и кликнуть мышкой на то место в документе где будет установлена формула. Далее, нажимаем вверху этого же документа раздел «Вставка» и кликаем мышкой по функции «П» «Формула» (Скрин 1).
Отобразятся различного вида формулы. Нажимаем левой кнопкой мыши на любую из них.
После этого в документ вставиться готовый редактор формулы, которым Вы сможете полноценно управлять (Скрин 2).
В самом верху панели документа, можно увидеть объекты, которые вставляются в формулу:
- дроби;
- индексы;
- радикалы;
- интегралы и так далее.
После работы над формулой, её можно сохранить. Нажимаете с правой стороны редактора формулы – «Параметры формул» (Скрин 3).
Затем, выбираете из списка «Сохранить, как новую формулу».
Итак, как писать формулы в Ворд вторым способом? Здесь, всё просто. Нажимаем, снова на «Вставка» далее «Объект» из раздела выбираем «Microsoft Equation 3.0» и сохраняемся с помощью кнопки «ОК» (Скрин 4).
Появится панель управления с формулами, и сам редактор, в котором можно прописать любую формулу через эту панель (Скрин 5).
Просто выбирайте готовые значения формул левой кнопкой мыши и устанавливаете их в редакторе.
к оглавлению ↑
Как поменять шрифт в Ворде в формулах
В формулах можно поменять шрифт. Для этого мы нажимаем по вставленной формуле и правой кнопкой мыши из меню выбираем шрифт (Скрин 6).
Откроется панель со списком разных шрифтов. Выбираете любой из них, и сохраняете все изменения кнопкой «ОК». После этого, шрифт Вашей формулы должен изменится на другой.
к оглавлению ↑
Как в Ворде вставлять формулы с дробями
Теперь, мы попробуем вставить в Ворде формулы с дробями. Это делается очень легко. Выделяете формулу в редакторе, и наверху в панели управления формулами, нужно нажать кнопку «Дробь». Там можно выбрать формулы с дробями (Скрин 7).
И заменить основную формулу на другую.
к оглавлению ↑
Как перемещать формулу в Ворде
Перемещать формулу в Word Вам помогут обычные горячие клавиши. Для этого выделяем формулу с помощью таких клавиш, как CTRL+A, (нужно нажать их одновременно). Далее, нажимаем ещё клавиши CTRL+C копировать.
Затем, следует кликнуть на кнопку «Enter», чтобы выбрать расположение для формулы в Ворде и нажать на CTRL+V вставить. Таким образом, Ваша формула переместится в определённое место документа.
к оглавлению ↑
Заключение
Мы рассмотрели в этой статье, как писать формулы в Ворд. Вы можете вставлять формулы автоматически, через панель редактора формул, который предоставляет пользователям редактор Word. Важно отметить, что в таких операционных системах, как Windows 8,10 есть панель математического ввода. С помощью которой, можно также легко создавать формулы. Удачи Вам и всего хорошего!
С уважением, Иван Кунпан.
Просмотров: 122457