This page will improve your understanding and use of the different word forms of CONTEXT
CONTEXT: the situation or setting in which something takes place, which helps to explain the event
See the Macmillan Dictionary definition of CONTEXT here.
Example sentence:
I know what he said, but you need to think about the context in which he said it.
The different forms of the word CONTEXT are:
noun: context(s),
verb: contextualise
adjective: contextualised / uncontextualised / contextual
adverb: contextually
You can see a list of other word form exercises on this page here.
You can see my article about word form here.
- Top Definitions
- Synonyms
- Quiz
- Related Content
- More About Context
- Examples
- British
This shows grade level based on the word’s complexity.
[ kon-tekst ]
/ ˈkɒn tɛkst /
This shows grade level based on the word’s complexity.
noun
the parts of a written or spoken statement that precede or follow a specific word or passage, usually influencing its meaning or effect: You have misinterpreted my remark because you took it out of context.
the set of circumstances or facts that surround a particular event, situation, etc.
Mycology. the fleshy fibrous body of the pileus in mushrooms.
QUIZ
CAN YOU ANSWER THESE COMMON GRAMMAR DEBATES?
There are grammar debates that never die; and the ones highlighted in the questions in this quiz are sure to rile everyone up once again. Do you know how to answer the questions that cause some of the greatest grammar debates?
Which sentence is correct?
Origin of context
1375–1425; late Middle English <Latin contextus a joining together, scheme, structure, equivalent to contex(ere) to join by weaving (con-con- + texere to plait, weave) + -tus suffix of v. action; cf. text
OTHER WORDS FROM context
con·text·less, adjective
Words nearby context
contessa, contest, contestant, contestation, contested, context, context of situation, contextomy, contextual, contextual definition, contextualism
Dictionary.com Unabridged
Based on the Random House Unabridged Dictionary, © Random House, Inc. 2023
MORE ABOUT CONTEXT
What is context?
Context is a noun that means the parts of a statement that immediately precede or follow a specific section of the statement and help explain that section.
The context of a specific text clarifies the meaning of that text, as in When the politician was asked to apologize for lying, he claimed that he had been quoted out of context and that he wasn’t actually lying.
Context is also the conditions related to an event or situation that helps a person understand the event or situation. Conditions can include surroundings (where something took place), circumstances (what else was happening at the time), and background (such as events that happened before). For example, the context of a historical event, such as what else was happening at the time and how people understood their environment, can help us better understand the event itself.
One common expression that uses word context is context clues. Context clues are hints within a piece of writing that help us understand something unfamiliar, such as a word. For example, if you came across the word ethereal in a text, context clues could help you figure out that it means “delicate” and “beautiful.”
Another common expression that includes the word context is out of context. This expression is used to explain that the reason people understood a statement or text incorrectly was because the statement was removed from its surrounding text, which distorted its meaning.
Example: Understanding the historical and scientific contexts of the Romantic period are essential to understanding Mary Shelley’s “Frankenstein.”
Where does context come from?
The first records of the term context come from around the late 1300s to early 1400s. It comes from the Latin word contextus, meaning “a joining together, scheme, or structure.”
Did you know … ?
How is context used in real life?
The word context is a fairly common word used to refer to conditions or situations that give meaning to an event or behavior. It’s also commonly used to refer to the words surrounding a specific word or words in a text that give the text its meaning.
The best feeling in language learning is when you learn a new word, and then immediately see it again in an unrelated context. And you think, ‘I would have had no idea what this word meant if I had seen it last week, but now I do. I’m learning!’
— Fingtam Languages (@fingtamLangs) January 15, 2021
I think my favorite part about tweeting is that you don’t have to provide any context. You just say.
— C (@Frm79th) January 17, 2021
Please read this thread if you are considering tweeting offensive or otherwise problematic things you believe are self-evidently “irony” or “sarcasm”
It will not work. It will not land. It will not matter years later when people see those tweets “out of context.”
This is why.
— Catherynne M. Valente (@catvalente) January 5, 2021
Try using context!
True or False?
The context of a situation is what results from the situation.
Words related to context
background, situation, text, ambience, conditions, connection, lexicon, relation, substance, vocabulary, frame of reference
How to use context in a sentence
-
Learning is best when it is built around doing, and when the context is practical, allowing students to try their hand at solving problems even as they’re still learning.
-
It’s hard not to look at today’s announcement in the context of the overall challenges that Mozilla is going through.
-
Unicef now plans to run a series of pilot programs with various partner countries to observe how practical and effective their guidelines are in different contexts.
-
The video above also provides the missing context from the clips.
-
Now, the spirit of the Bauhaus has been invoked once more, in the context of Europe’s grand plan to go green.
-
In that context, Sotto Sotto was one of the all-out survivors.
-
Prevalence depends on context, and sometimes unique advantages outweigh the genetic costs.
-
I recognize my inability to truly understand these events in the same context or view these events through exactly the same prism.
-
Just wanted to place it in the context of slates needing picture choices that throw off revenue to make the numbers work.
-
Clearly the liberation of Gross took place in the context of what might be called a “grand bargain.”
-
She held it while the trooper bent over the strange scrawl, and ran his eyes along it to learn the context.
-
If the context makes an otherwise indefinite thing definite, it is sufficient.
-
The context in Chaucer does not seem to warrant the interpretation given by Tyrwhit.
-
I alter pleyneth in l. 2302 to pleyeth, to suit the context more closely.
-
The translator could think of no better word, because the context is jocular.
British Dictionary definitions for context
noun
the parts of a piece of writing, speech, etc, that precede and follow a word or passage and contribute to its full meaningit is unfair to quote out of context
the conditions and circumstances that are relevant to an event, fact, etc
Word Origin for context
C15: from Latin contextus a putting together, from contexere to interweave, from com- together + texere to weave, braid
Collins English Dictionary — Complete & Unabridged 2012 Digital Edition
© William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1979, 1986 © HarperCollins
Publishers 1998, 2000, 2003, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2012
контекст, связь, ситуация, обстановка, фон
существительное ↓
- контекст
out of context — в отрыве от контекста
- ситуация; среда, окружение
in this context — в данном случае; при этом условии; в этой связи
in the context of — в связи с; применительно к; с учётом; с точки зрения
in the context of today’s America — в условиях современной Америки
Мои примеры
Словосочетания
to cite a passage out of context — цитировать какой-л. фрагмент в отрыве от контекста 
historical context — исторический контекст 
context editor — контекстный редактор 
to lift a word from / out of context — вырывать слово из контекста 
context switch — контекстный переключатель (программы) 
context condition — контекстное условие 
association context — контекст соединения (абонентов сети) 
firm context — твердый контекст 
linear context — линейный контекст 
soft context — мягкий контекст 
Примеры с переводом
His comments, taken out of context, seem harsh. 
Его высказывания, вырванные из контекста, кажутся резкими.
This small battle is very important in the context of Scottish history. 
Это небольшое сражение было очень важным в контексте шотландской истории.
The statistics are not very meaningful when taken out of context. 
Статистические данные не очень осмысленны, когда они вырваны из контекста.
We need to consider these events in context. 
Мы должны рассматривать эти события в их историческом контексте.
Don’t distort her meaning by taking her words out of context. 
Не искажайте смысл её слов, вырывая их из контекста.
It is important to look at the novel in its historical context. 
Важно рассматривать этот роман в его историческом контексте.
This debate should be set in an international context. 
Эти дебаты должны быть проведены на международном уровне.
ещё 15 примеров свернуть
Примеры, ожидающие перевода
…the otherwise anodyne comments sounded quite inflammatory when taken out of context… 
The women have the opportunity to situate their own struggles in a wider historical context. 
…taking that statement completely out of context essentially falsifies it, whether that’s your intention or not… 
Для того чтобы добавить вариант перевода, кликните по иконке ☰, напротив примера.
Возможные однокоренные слова
contexture — сплетение, композиция, ткань
Формы слова
noun
ед. ч.(singular): context
мн. ч.(plural): contexts
We
distinguish btw lexical meaning of a w. in speech and its semantic
structure in the language. The meaning in speech is contextual. Any
actually usd w. has only one meaning (it is monosemantic in context),
but the bulk of english w-s is polysemantic, i.e. they posess more
than one meaning. The commoner the w., the more meanings it has.
Polysemy exists only in the language, not in speech. The meaning of a
w. form its semantic structure.
By
the semantic
structure of the w.
we mean the interdependance and interconnection of all the meanings
that the w. has. The sem. structure of a word is a fact of language
not of speech. It’s developed and fixed in the course of the
language history.
The
context shows as the real meaning of the word.
Polysemy
doesn’t interfere with the communicative function of the language
because in every particular case the situation and the context in
which the word occurs cancels all the meanings but one and make
speech clear, unequivocal. Polysemy is more characteristic of English
vocabulary as compared with Russian, due to the monosyllabic
character of English and the predominance of root words.
Every
time we have polysemy we have 2 types of ties/connection btw the
meanings of one and the same word. One of them is concatenation
– every next meaning is connected with the previous one (e.g.
board), and radiation
– we have one meaning. Every meaning is connected with the primary
meaning of a word (eye).
The
term context
is defined as the minuimum stretch of speech, necessary and
sufficient to determine which of the possible meanings of a
polysemantic word is used.
We have
2 main types of linguistic context, which are:
Lexical
c. and grammatical c.
Lexical
context
of a w. is the minimum environment of lexical units which is
sufficient to determine the individual lexical meaning of the word
(e.g. black – velvet, thoughts, days; heavy – book, rain,
artillery; take – book, train).
All
lexical contexts are subdivided into lex contexts of the first degree
and lexical contexts of the second degree. In the lex. c. of the
first degree there is a direct syntactical connection btw. the
indicator and the dependent: he took
the train
in 9:30. in lex. c. of the second degree there is no direct
syntactical connection btw a dependent and the indicator: I move
that
Mr N. addresses
the meeting.
The dependent move
(meaning suggest) is not directly connected to the indicating minimum
adresses
the meeting.
In
grammatical
context
it’s the grammatical structure (mainly the syntactic) of the
context that serves to determine various individual meanings of the
polysemantic word (make smb do sth = to cause; make a good wife).
20. Synonymic groupings of words. Types of synonyms. Sources of synonyms.
Words
are grouped according to their semantic similarity or polarity.
Semantic similarity is observed in synonyms and sem. polarity in
antonyms.
Lexical
synonyms
are words of the same part of speech which belong to the same range
of idea but are different in form. Words which are the same in the
plan of content but different in the plan of expression (beautifuln –
handsome, nice, good-looking, gorgeous).
There
are several groups
(types) of synonyms:
-
Absolute
synonyms
– which coincide in all their shades of meaning and in all their
stylistic charscteristics (preface, foreword). -
Most
synonyms differ in their material form. They are called ideographic
synonyms
– conveying the same concept but different in shades of meaning
(event, incedent, case). Each syn. Expresses a certain different
shade of meaning. -
Stylistic
synonyms
differ in their stylistic characteristics — connotational meaning,
degrees of emotional colouring or stylistic differences btw words
(try, attempt, strive, endeavour).
In
every group of ideographic and stylistic synonyms we can find the so
called synonymic
dominant
which usu expresses the most general shade of meaning.
Look –
stare, gaze, observe, glance. The word “look” is the synonymic
dominant, because it expresses the general meaning that is present in
all the other members of this synonymic group.
The
english word-stock is extremely rich in synonyms, which can be
largely explained by the abundance of borrowings
(begin – start (native), commence (french), initiate (latin)).
There
are no clear boarders btw ideographic and stylistic synonyms and
often in one and the same synonymic group we can find both
ideographic and stylistic synonyms (hearty- cordial).
The
important thing is that not only borrowings from the different
languages but other sources as well contributed to the stock of
English synonyms.
There
are, for instance, words that come from dialects
(lass (girl); whiskey /Irish/ (liquor)), and, in the last years, from
American English in particular (gimmick (USA) (trick), radio
(wireless), etc.
Synonyms
are also created by means of all word-forming
processes
productive in the language. The words already existing in the lang.
develop new meanings. New words may be formed by affixation
(effectivity – effectiveness) or loss of affixes (amongst –
among), by conversion (laughter – laugh (converted from to laugh),
compounding, shortening (mike –microphone; vegs (vegetables) and so
on.
In
polysemantic
words each meaning belongs to different synonymic groups (handsome –
beautiful, handsome –considerable (sum of money)).
There
is a special group of synonyms called euphemisms.
They
are synonimic substitutes for words which are considered vulgar,
indecent or rude, thus their function may be defined as making the
expression of a notion nobler, softer and refined.
We
distinguish btw religious and every day euphemisms.
Among
religious
euphamisms
we classify w-expressions that are used for religious notions and
notions of death (to die – to pass away, to join the majority, to
be no more; God – the Lord, the one above; devil – dickins,
deuce, father of lies).
Everyday
euphemisms
replace w-s which express notions about which it is considered
indecent to speak ( spit – expectorate; sweat – perspire;
pregnant – in a family way).
Sometimes
eu-s are used with political purposes to distort the real state of
things and to deceive the people (crisis – depression; uprising –
tention; starvation – undernourishment).
Thus
we can define synonyms
as words different in their sound form but similar in their
denotational or connotational meanings and interchangable in some
contexts.
21.
Productive types of word-building. The concept of word-building
model. Productive models of affixation.
Word –
formation – is the process of creating new words from the material
available in the language after certain structural and semantic
patterns.
We have
productive and unproductive types of word-formation.
Productive
types are affixation,
composition and conversion.
The
process of affixation
consists in coining a new word by adding an affix or several affixes
to some root ‘morpheme.
Composition
is a type of word-building in which new words are produced by
combining two or more stems.
Conversion
is a morphological (newly-coined w. has a new paradigme), syntactic
(syntactical position in the sent. is different) and semantic (the
word acquires a new meaning) word-building means.
Affixation
is subdivided into suffixation and prefixation.
Suffixes
are derivational affixes following the root morpheme (brotherhood,
kingdom).
Prefixes
are derivational affixes preceding the root (reread,
predominate).
The
difference btw these two kinds of affixes is that prefixes only modfy
the lexical meaning of a word without changing the part of speech to
which the word belongs. But suffixes not only modify the lexical
meaning of a word but form a word belonging to a different part of
speech.
We’ve
living(noun
forming: -ness, -dom, -hood, -age, -ment, -ship; adj forming: -en,
-ous, -ful, -y)
and dead affixes.
Affixes
which are used to form new w-s are called productive.
From
the etymological point of view affixes are classified into the same
large groups as words: native
and borrowed.
Words
that are made up of elements derived from 2 or more different
languages are called hybrids,
i.e. a word consisted of a native stem and a borrowed affix
(answerable) or vice versa (colourless, doubtless).
By
productive
affixes (-er, -ness, -ist, -ish, etc thinnish, baldish) we mean the
ones, which take part in deriving new words in this particular period
of language development. The best way to identify productive affixes
is to look for them among neologisms and so-called nonce-words, i.e.
w-s coined and used only for this particular occasion. We should not
confuse the productivity
of an affix with its frequency
(frequently-used –hood, -some, -en, -tion, -ant are
non-productive).
The
term word-building
pattern
is used to denote a meaningful combination of stems and affixes that
occur regularly enough to indicate the part of speech, the
lexico-semantic category and semantic peculiarities common to most
words with this particular arrangement of morphemes.
N + -ish
– when added to noun stems, it forms adj-s of the type ‘having
the nature of’ with slightly critical colouring (childish, boyish,
womanish).
With
adj. stems (Adj + -ish) the meaning is not derogatory, the adj
renders a moderate degree of the quality named (greenish, thinnish,
blackish).
It would
be also wrong to say that there exists a definite meaning associated
with this or that pattern, as they are often polysemantic, and the
affixex homonymous.
e.g.
a very productive opattern is out
+ V = V
the meaning is ‘to do sth faster, better than smb or sth’ (outdo,
out-grow, outnumber). When formed not on verbs but on names of
persons it means ‘to surpass this person in sth that is known as
his special property’ (to out-Herod Herod). On the other hand out
+ V=N
may occur with the locative out- and produce nouns (outbreak,
outburst). OUT- may be used with verbal stems and theis derivaties
(outstanding), with substantives (outfield), adj. (outbound),etc.
the more
productive an affix is the more probable the existence alongside the
usual pattern of some semantic variation.
-ee
is freely added to verbal stems to form nouns meaning ‘one who is
V-ed’ as employee, examinee, often paralleling agent nouns in –er,
as employer, examoner. However, sometimes it is added to intransitive
verbs; in this case the pattern V+-ee
means ‘one who V-s or one who has V-ed’ as in escapee.
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- Go to Preferences page and choose from different actions for taps or mouse clicks.
WordReference Random House Learner’s Dictionary of American English © 2023
con•text /ˈkɑntɛkst/USA pronunciation
n.
- the parts of a statement that come before or follow a word or passage and influence its meaning or effect: [countable]They tried to guess from the context what the message meant.[uncountable]What he said was taken out of context and was completely misunderstood.
- the facts that surround a particular event, etc.:[countable]We need to understand the whole context of the struggle in the Middle East.
con•text•u•al /kənˈtɛkstʃuəl/USA pronunciation adj.: contextual circumstances.
WordReference Random House Unabridged Dictionary of American English © 2023
con•text
(kon′tekst),USA pronunciation n.
- the parts of a written or spoken statement that precede or follow a specific word or passage, usually influencing its meaning or effect:You have misinterpreted my remark because you took it out of context.
- the set of circumstances or facts that surround a particular event, situation, etc.
- Fungi[Mycol.]the fleshy fibrous body of the pileus in mushrooms.
- Latin contextus a joining together, scheme, structure, equivalent. to contex(ere) to join by weaving (con- con— + texere to plait, weave) + -tus suffix of verb, verbal action; compare text
- late Middle English 1375–1425
con′text•less, adj.
- 2.See corresponding entry in Unabridged background, milieu, climate.
Collins Concise English Dictionary © HarperCollins Publishers::
context /ˈkɒntɛkst/ n
- the parts of a piece of writing, speech, etc, that precede and follow a word or passage and contribute to its full meaning: it is unfair to quote out of context
- the conditions and circumstances that are relevant to an event, fact, etc
Etymology: 15th Century: from Latin contextus a putting together, from contexere to interweave, from com- together + texere to weave, braid
‘context‘ also found in these entries (note: many are not synonyms or translations):
Context free words There are words with definite meanings which are retained in most contexts and are relatively contextfree.
n Context-free words are mainly found among proper and geographical names, titles of magazines and newspapers, names of various firms, organizations, ships and the like, as well as among technical terms used by experts in all fields of human endeavour.
Context-free words usually have permanent equivalents in target language n (TL), which in most cases, can be used in target text (TT). n
n The permanent equivalents of context -free words are often formed by transcription (with possible elements of transliteration) or loan translations.
Context-bound words n are words, the meaning of which largely depends on the context in which they are actualized
Context-bound words may be n n Polysemantic (words with several meanings) Monosemantic (words with only one meaning)
examples n n n «Few Europeans speak Mandarin“ «Few Europeans know the first thing about Mandarin» Mandarin – 1. Chinese language 2. Chinese imperial official 3. Chinese fruit.
n n The context has also a decisive role to play in the selection of TL equivalents to the words of equivalents the original. in most cases, the meaning of a SL word can be rendered in TL by a number of regular equivalents.
Variable equivalents can be found not only to the polysemantic words but also to the monosemantic words as well as to a semantic variant of a polysemantic word, n that is, to one of its meanings which can be actualized in the course of communication. n
n In such cases after the translator has ascertained what meaning the word has in the original text he still has to choose one of the regular equivalents which fits the context best of all, eg. :
n n «This issue of the paper devoted about half of its twenty news columns to the trial of a trial murderer». The context enables the translator to understand that the «issue“ refers here to a publication, the «paper» is a newspaper and the «column» is a department in that newspaper.
n But he has also to find additional information in the context which will allow him to choose an equivalent to «issue»among such RussianKazakh words (give equivalents) or to compare the use of the RussianKazakh words (give equivalents) as equivalents to
n No less important is the role of the context in translating the words with a wide range of reference whose equivalents are too numerous to be listed in any dictionary.
n For example, the English noun «record» is defined as «something that records» n or «the recorded facts about something or someone» and can refer to any document or any events, past or present.
n The context may modify the meaning of a word to such an extent that its regular equivalents will not fit TT, eg.
n n «History has dealt with Hitler; history will deal with all would-be Hitlers“ What is the meaning of the word “to deal” here?
The contextual modification may extend to the connotative meaning of the word. n The translator is greatly concerned about the adequate reproduction of this part of the word semantics since it has an impact upon the whole text. n
n n n Give your translation of the word “ambitious” in these examples «the UN ambitious program of providing food for the people of the earth» the «ambitious plans of South African racists»
n Even if the entry in his dictionary does not provide him with an equivalent that fits his context, the translator can use the dictionary data to facilitate the solution.
n n n The United States worked out a formula which a later came to be known as dollar diplomacy. as Look for the meanings of the word “formula” What equivalent can you give with the dictionary meaning hint?
HANDLING EQUIVALENTLACKING WORDS Equivalent lacking words are often found among SL names of specific national phenomena, n such as the English words «coroner, condominium, impeachment». n
n However, there are quite a number of «ordinary» words for which TL may have no equivalent lexical units: «bidder, conservationist» etc.
n n The absence of regular equivalents does not imply that the meaning of an equivalentan lacking SL unit cannot be rendered in translation or that its translation must be less accurate. The translator coming across an equivalentlacking word, resorts to occasional equivalents which can be created in one of the following ways:
n n 1. Using loan-words imitating in TL the form of SL word or word combination, word e. g. tribalism – , impeachment – , backbencher – brain-drain –. As often as not such occasional formations are adopted by the members of TL community and get the status of regular equivalents.
2. Using approximate substitutes that is TL words with similar meaning which is extended meaning to convey additional information (if necessary, with the help of foot notes) e. g. drugstore – , witchhunter – , afternoon n
n The Russian аптека (дәріхана) is not exactly a drugstore where they also sell such items as magazines, soft drinks, icecream, etс. , but in some cases this approximate equivalent can well be used.
3. Using all kinds of lexical (semantic) transformations modifying the meaning n of the SL word, e. g. «He died of exposure» may be rendered into TL as ……… n
4. Using an explanation to convey the meaning of the SL unit, e. g. n Landslide – n brinkmanship – n
This method is sometimes used in conjunction with the first one when the introduction of a introduction loan-word is followed by a foot-note explaining the meaning of the equivalentlacking word in ST. n After that the translator may freely employ the newly-coined subsitute. n
n The practising translator most often has to resort to such techniques when he comes across some new-coined words in the source text or deals with names of object or phenomena unknown to the TL community (the so-called «realia»).
n New words are coined in the language to give names to new objects, or phenomena which become known to the people.
n n n Such words may never get in common use and will not be registered by the dictionaries but they are well understood by the communicants since they are coined on the familiar structural and semantic models.
If someone is ever refferred to as a «Polandologist», the meaning will be readily understood against such terms n as «Kremlinologist» or «Sovietologist». n
If a politician is called «a nuclearist», the new coinage will obviously mean a supporter of nuclear arms race. n «A zerogrowther“ would be associated with some zero-growth theory or policy and so on. n
n n Therefore the translator coming across a new coinage has to interpret its meaning and to its choose the appropriate way of rendering it in his translation. Consider the following sentence: «In many European capitals central streets have been recently pedestrianized. »
n n As often as not a whole set of new words may enter in common use, all formed on the same all model. Thus, the anti-segregation movement in the United States in the 1960’s introduced a number of new terms to name various kinds of
public demonstrations formed from a verb + -in on the analogy of «sit-in». «ride-in» n (in segregated buses), «swim-in» (in segregated swimming pools), «pray-in» (in n segregated churches) and many others. n
n Quite a number of equivalent-lacking words of this type, however, still have no established no substitutes in Russian, and the translator has to look for an occasional equivalent each time he comes across such a word in the source text, eg. «filibustering», «baby-sitter», «tinkerer», «know-how», «ladykiller», and many others
n Special attention should be paid to English conjunction and prepositions which are often used differently from their apparent equivalents in Russian and are, in fact, equivalent-lacking.
n Such common conjunctions as «when, if, as, once, whichever» and some others are not infrequently the cause of errors in translation and should be most carefully studied.
n Similar pitfalls can be set for the translator by such productive English «semi-suffixes» as -minded, consciuos, -oriented, -manship, etc.
n In conclusion, let us recall that any word may become equivalent-lacking if the particular context makes it impossible to use its regular equivalent and forces the translator to resort to some semantic transformation.
Handling translator’s false friends International words are words in the source and target languages which are more or less similar in form. n The formal similarity is usually the result of the two words having the common origin, mainly derived from either Greek or Latin eg. Parliament, theorem, diameter, etc. n
Handling translator’s false friends n Give your examples of international words
Handling translator’s false friends n Words that are similar in form but different in meaning are called pseudointernational or translator’s false friends
n n Proper and geographical names are transcribed with TL letters, e. g. : Smith – John Fitzgerald Kennedy – Ontario – Downing Street –
n n The same is true about the titles of periodicals and the names of firms and corporations, e. g. : Life – General Motors Corporation – Harriman and Brothers –
n n Transcription is also used to reproduce in TL the names of ships, aircraft, missiles and pieces of military equipment: Queen Elizabeth – Spitfire – Hawk –
The rules of transcription have two minor exceptions n n First, it is sometimes supplemented by elements of transliteration when SL letters are reproduced in TT instead of sounds. This technique is used with mute and double consonants between vowels
or at the end of the word and with neutral vowels (Dorset, Bonners n Ferry-) as well as to preserve some elements of SL spelling so as to n make the TL equivalent resemble some familiar pattern (the Hercules missle Columbia-). n
n n n Second, there are some traditional exeptions in rendering the names of historical personalities and geographical names, e. g. : Charles I-, James II Edinborough-
Pseudointernational words n 1) — Are classified into 2 main groups: Words which are similar in form but completely different in meaning, eg. It lasted the whole decade. She has a very fine complexion. Well, he must be a lunatic.
Handling translator’s false friends n 2) There are many pseudointernational words which are not fully interchangeable though there are some common elements in their semantics.
Handling translator’s false friends n The translator should bear in mind that a number of factors can preclude the possibility of using the formally similar word as an equivalent:
1) Semantic factor The semantic factor resulting from the different subsequent development of the words borrowed by the two languages from the same source, eg. n Idiom – 1. идиом, 2. диалект (наречие), 3. стиль. n
n South Vietnam was a vast laboratory for the testing of weapons for counter-guerrilla warfare.
n n n 2) The stylistic factor resulting from the difference in the emotive or stylistic connotation of the correlated words, eg. “career” Davy took on Faraday as his assistant and thereby opened a scientific career for him.
n 3) The co-occurrence factor reflecting the difference in the lexical combinability rules in the two languages. The choice of an equivalent is often influenced by the usage preferring a standard combination of words to the formally similar substitute.
n n n So, a “defect” has a formal counterpart as «дефект» but “theoretical and organizational defects” will be rather “подсчеты/есептеулер“. A “gesture” may be rendered in another way: The reason for including only minor gestures of reforms in the program… (жалкое подобие реформ)
n 4) The pragmatic factor reflecting the difference in the background knowledge of the members of the two language communities which makes the translator reject the formal equivalent in favor of the more explicit or familiar variant.
n n The American Revolution was a close parallel to the wars of national liberation in the colonial and semi-colonial countries. The counter-revolutionary organization was set up to suppress the Negro-poor white alliance that sought to bring democracy in the South in the Reconstruction period.
n The senator knew Lincoln’s Emancipation Proclamation by heart.
COLLOCATIONAL ASPECTS OF TRANSLATION ATTRIBUTIVE GROUPS n there is a considerable dissimilarity in the semantic structure of attributive groups in English and in Russian. This dissimilarity gives rise to a number of translation problems.
n n The first group of problems stems from the broader semantic relationships between the attribute and the noun. the attribute may refer not only to some property of the object but also to its location, purpose, cause, etc.
n n As a result, the translator has to make a thorough analysis of the context to find out what the meaning of the group is in each particular case. He must be also aware of the relative freedom of bringing together such semantic elements within the attributive group in English that are distanced from each other by a number of intermediate ideas.
n Thus a resolution submitted by an executive body of an organization may be described as «the Executive resolution» and the majority of votes received by such a resolution will be «the Executive majority» .
n If a word-for-word translation of the name of the executive body (e. g. the «Executive Committee» — исполнительный комитет) may satisfy the translator, the other two attributive groups will have to be explicated in the Russian translation as (try to guess)
n n «резолюция, предложенная исполкомом» and «большинство голосов, поданных за резолюцию, которая была предложена исполкомом»
n The second group of problems results from the difficulties in handling multi-member attributive structures. The English-speaking people make wide use of «multi-storied» structures with complicated internal semantic relationships.
n n The tax paid for the right to take part in the election is described as «the poll tax». The states where this tax is collected are «the poll tax states» and the governors of these states are «the poll tax states governors». Now these governors may hold a conference which will be referred to as ‘the poll tax states governors conference» and so on.
The semantic relationships within a multimember group need not be linear. Consider the following sentence: “It was the period of the broad western hemisphere and world pre-war united people’s front struggle against fascism” (analyze the structure of the attr group) n
n Это был период широкой предвоенной борьбы против фашизма за единый народный фронт в Западном полушарии и во всем мире.
n n The same goes for attributive groups with latent predication where a whole sentence is used to qualify a noun as its attribute «He was being the boss again, using the its-my-money-now-do-as-you’retold voice».
n Here correspondences can also be described in an indirect way only by stating that the attribute is usually translated into Russian|Kazakh as a separate sentence and that this sentence should be joined to the noun by a short introductory element. Cf. :
n The Judge’s face wore his own I-knew-theywere-guilty-all-along expression.
n На лице судьи появилось обычное выражение, говорившее: «Я все время знал, что они виновны» .
n There was a man with a don’t-say-anythingto-me-or-I’ll-contradict-you face. (Ch. Dickens)
n Там был человек, на лице которого было написано: что бы вы мне ни говорили, я все равно буду вам противоречить.
n 3) An attributive group may be transformed into a similar group with the help of a suffix which is formally attached to the noun but is semantically related to the whole group. Thus «a sound sleeper» may be derived from «sound sleep» or the man belonging to the «Fifth column» may be described as «the Fifth columnist».
n As a rule, in the Russian translation the meanings of the original group and of the suffix would be rendered separately, e. g. : человек, обладающий здоровым (крепким) сном (крепко спящий человек), and человек, принадлежащий к пятой колонне (член пятой колонны).
4) As often as not, translating the meaning of an English attributive group into Russian may involve a complete restructuring of the sentence, e. g. : n To watch it happen, all within two and a half hours, was a thrilling sight. n Нельзя было не восхищаться, наблюдая, как все это происходило на протяжении каких-нибудь двух с половиной часов.
Translate the following attributive groups n n n 1. hearty eater; 2. practical joker; 3. conscientious objector; 4. sleeping partner; 5. stumbling block; 6. smoking concert;
Translate the following attributive groups
HANDLING PHRASEOLOGICAL UNITS n n n Plan of the lecture 1. Definition of phraseological units 2. Aspects of idioms’ meaning influencing the translation 3. Classification of idioms 4. Factors complicating the task of adequate translation Typical methods to handle a SL idiom in the translating
HANDLING PHRASEOLOGICAL UNITS n Phraseological units are figurative set expressions often described as «idioms».
Five aspects of idioms’ meaning that will influence the translator’s choice of an equivalent in the target language 1. the idiom’s figurative meaning, 2. its literal sense, 3. its emotive character, 4. stylistic register, 5. national colouring. n
n n The figurative meaning is the basic element of the idiom’s semantics: «red tape» means bureaucracy, «to kick the bucket» — to die, «to wash dirty linen in public» — to disclose one’s family troubles to outsiders.
n n The figurative meaning is inferred from the literal sense. «Red tape», «to kick the bucket», and «to wash dirty linen in public» also refer, respectively, to a coloured tape, an upset pail and a kind of laundering, though in most cases this aspect is subordinate and serves as a basis for the metaphorical use.
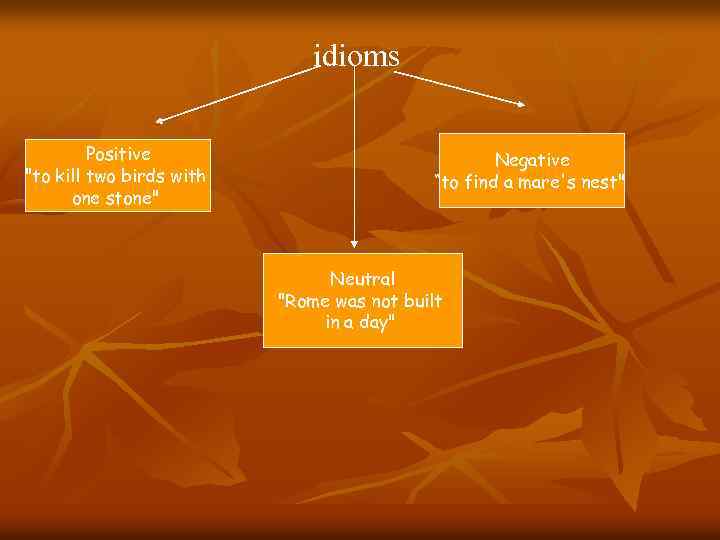
idioms Positive «to kill two birds with one stone» Negative “to find a mare’s nest» Neutral «Rome was not built in a day»
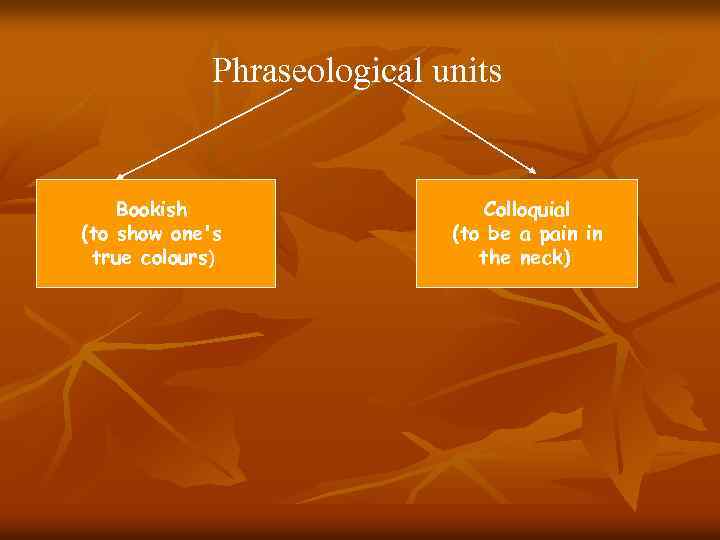
Phraseological units Bookish (to show one’s true colours) Colloquial (to be a pain in the neck)
Besides, an idiom can be nationally coloured, that is include some words which mark it as the product of a certain nation. n For instance, «to set the Thames on fire» and n «to carry coals to Newcastle» are unmistakably British. n
Factors which complicate the task of adequate identification, understanding and translation of idioms: — First, an idiom can be mistaken for a free word combination, especially if its literal sense is not «exotic» (to have butterflies in one’s stomach) but rather trivial (to measure one’s length, to let one’s hair down)
n Second, a SL idiom may be identical in form to a TL idiom but have a different figurative meaning. Thus, the English «to lead smb. by the nose» implies a total domination of one person by the other (cf. the Russian «водить за нос» ) and»to stretch one’s legs» means to take a stroll (cf. the Russian «протянуть ноги» )
n Third, a SL idiom can be wrongly interpreted due to its association with a similar, if not identical TL unit. For instance, «to pull the devil by the tail», that is to be in trouble, may be misunderstood by the translator under the influence of the Russian idioms «держать бога за бороду» or «поймать за хвост жар-птицу»
n Fourth, a wrong interpretation of a SL idiom may be caused by another SL idiom similar in form and different in meaning. Cf. «to make good time» and «to have a good time»
n n Fifth, a SL idiom may have a broader range of application than its TL counterpart apparently identical in form and meaning. For instance, the English «to get out of hand» is equivalent to the Russian «Oтбиться от рук» and the latter is often used to translate it:
n n n The children got out of hand while their parents were away. В отсутствии родителей дети совсем отбились от рук. But the English idiom can be used whenever somebody or something gets out of control while the Russian idiom has a more restricted usage: What caused the meeting to get out of hand? Почему собрание прошло так неорганизованно?
n n There are four typical methods to handle a SL idiom in the translating: First, the translator can make use of a TL idiom which is identical to the SL idiom in all five aspects of its semantics, e. g. «to pull chestnuts out of the fire for smb. » — таскать каштаны из огня для кого-либо.
n Second, the SL idiom can be translated by a TL idiom which has the same figurative meaning, preserves the same emotive and stylistic characteristics but is based on a different image, that is, has a different literal meaning, e. g. «make hay while the sun shines»
n n Third, the SL idiom can be translated by reproducing its form word-for-word in TL, e. g. «People who live in glass houses should not throw stones. » — Люди, живущие в стеклянных домах, не должны бросать камни.
n Fourth, instead of translating the SL idiom, the translator may try to explicate its figurative meaning, so as to preserve at least the main element of its semantics
GRAMMATICAL ASPECTS OF TRANSLATION n n HANDLING EQUIVALENT FORMS AND STRUCTURES Grammaticality is an important feature of speech units. Grammatical forms and structures, however, do not only provide for the correct arrangement of words in the text, they also convey some information which is part of its total contents.
They reveal the semantic relationships between the words, clauses and sentences in the text, n they can make prominent some part of the contents that is of particular significance for the communicants. n
n The syntactic structuring of the text is an important characteristics identifying either the genre of the text or its author’s style.
n In many cases, however, equivalence in translation can be best achieved if the translator does not try to mirror the grammatical forms in the source text.
n There are no permanent grammatical equivalents and the translator can choose between the parallel forms and various grammatical transformations. He may opt for the latter for there is never an absolute identity between the meaning and usage of the parallel forms in SL and TL.
n For instance, both English and RussianKazakh verbs have their infinitive forms. The analogy, however, does not preclude a number of formal and functional differences.
n We may recall that the English infinitive has perfect forms, both active and passive, indefinite and continuous, which are absent in the respective grammatical category in Russian and Kazakh.
n The idea of priority or non-performed action expressed by the Perfect Infinitive is not present in the meaning of the RussianKazakh Infinitive and has to be rendered in translation by some other means.
n Cf. ‘The train seems to arrive at 5. » — Поезд, видимо, приходит в 5. and ‘The train seems to have arrived at 5. » — Поезд, видимо, пришел в 5.
n A dissimilarity of the English and RussianKazakh Infinitives can be also found in the functions they perform in the sentence. Note should be taken, for example, of the Continuative Infinitive which in English denotes an action following that indicated by the Predicate:
n Parliament was dissolved, not to meet again for eleven years.
n Не came home to find his wife gone.
n n Парламент был распущен и не созывался в течение 11 лет. Он вернулся домой и обнаружил, что жена ушла.
n A similar difference can be observed if one compares the finite forms of the verb in English and in RussianKazakh. Theyh have active and passive forms, but in English the passive forms are more numerous and are more often used. As a result, the meaning of the passive verb in the source text is often rendered by an active verb in the translation:
n This port can be entered by big ships only during the tide.
n A most common example of dissimilarity between the parallel syntactic devices in the two languages is the role of the word order in English and in Russian. Both languages use a «direct» and an «inverted» word order. But the English word order obeys, in most cases, the established rule of sequence: the predicate is preceded by the subject and followed by the object.
n This order of words is often changed in the RussianKazakh translation since in Russian the word order is used to show the communicative load of different parts of the sentence, the elements conveying new information (the rheme) leaning towards the end of non-emphatic sentences.
n Thus if the English sentence «My son entered the room» is intended to inform us who entered the room, its Russian equivalent will be «В комнату вошел мой сын» but in case its purpose is to tell us what my son did, the word order will be preserved: «Мой сын вошел в комнату» .
n The predominantly fixed word order in the English sentence means that each case of its inversion (placing the object before the subject -predicate sequence) makes the object carry a great communicative load. This emphasis cannot be reproduced in translation by such a common device as the inverted word order in the Russian sentence and the translator has to use some additional words to express the same idea: Money he had none. Денег у него не было ни гроша.
n n I. Translate the following sentences with the special attention to the choice of RussianKazakh equivalents to render the meaning of the English infinitives. 1. The people of Roumania lived in a poverty difficult to imagine. 2. The Security Council is given the power to decide when a threat to peace exists without waiting for the war to break out. 3. The general was a good man to keep away from. 4. This is a nice place to live in. 5. He stopped the car for me to buy some cigarettes. 6. Jack London was the best short-story writer in his country to arise after Edgar Рое.
n n П. Note the way the meaning of the English passive forms is rendered in your translation of the following sentences. 1. The Prime-Minister was forced to admit in the House of Commons that Britain had rejected the Argentine offer to negotiate the Folklands’ crisis. 2. The amendment was rejected by the majority of the Security Council. 3. He rose to speak and was warmly greeted by the audience. 4. The treaty is reported to have been ratified by all participants.
HANDLING EQUIVALENTLACKING FORMS AND STRUCTURES n A lack of equivalence in the English and RussianKazakh systems of parts of speech can be exemplified by the article which is part of the English grammar and is absent in Russian||Kazakh.
n n As a rule, English articles are not translated into RussianKazakh for their meaning is expressed by various contextual elements and needn’t be reproduced separately. But in some cases there is a need to translate the meaning of the English article.
n Consider the following linguistic statement: ‘To put it in terms of linguistics: a sentence is a concrete fact, the result of an actual act of speech. The sentence is an abstraction. So a sentence is always a unit of speech; the sentence of a definite language is an element of that language. »
n It is obvious that an entity cannot be both a concrete fact and an abstraction. The difference between «a sentence» (любое отдельное предложение) and ‘the sentence» (предложение как понятие, тип предложения) should be definitely revealed in the Russian and Kazakh translations as well.
n n Even if some grammatical category is present both in SL and in TL, its subcategories may not be the same and, hence, equivalent-lacking. Both the English and the Russian verb have their aspect forms but there are no equivalent relationships between them. Generally speaking, the Continuous forms correspond to the Russian imperfective aspect, while the Perfect forms are often equivalent to the perfective aspect.
n As far as the Kazakh language is concerned we can observe more similarity with the English language: both of them have Continuous tense and perfect forms. (give your examples)
n However, there are many dissimilarities. Much depends on the verb semantics. The Present Perfect forms of non-terminative verbs, for instance, usually correspond to the Russian imperfeclive verbs in the present tense:
n n I have lived in Moscow since 2010. Я живу в Москве с 2010 г.
n The Past Indefinite forms may correspond either to the perfective or to the imperfective RussianKazakh forms and the choice is largely prompted by the context. Cf. :
n After supper he usually smoked in the garden. После ужина он обычно курил в саду.
n After supper he smoked a cigarette in the garden and went to bed. После ужина он выкурил в саду сигарету и пошел спать.
n The Past Pefect forms may also be indifferent to these aspective nuances, referring to an action prior to some other action or a past moment. Cf. :
n n I hoped he had read that book. (а) Я надеялся, что он читал эту книгу, (б) Я надеялся, что он (уже) прочитал эту книгу.
A special study should be made of the translation problems involved in handling the Absolute Participle constructions. n To begin with, an Absolute construction must be correctly identified by the translator. n
n The identification problem is particularly complicated in the case of the «with»-structures which may coincide in form with the simple prepositional groups.
n The phrase «How can you play with your brother lying sick in bed» can be understood in two different ways: as an Absolute construction and then its Russian equivalent will be «Как тебе не стыдно играть, когда твой брат лежит больной (в постели)» or as a prepositional group which should be translated as «Как тебе не стыдно играть с твоим больным братом» .
n Specific translation problems emerge when the translator has to handle a syntactical complex with a causative meaning introduced by the verb ‘to have» or «to get», such as: «I shall have him do it» or «I shall have him punished». First, the translator has to decide what TL causative verb should be used as a substitute for the English «have» or «get».
n Depending on the respective status of the persons involved, the phrase «I shall have him do it» may be rendered as «Я заставлю его (прикажу ему, велю ему, попрошу его и т. п. ) сделать это» or even «Я добьюсь (позабочусь о том, устрою так и т. п. ), чтобы он это сделал» .
n Second, the translator must be aware that such complexes are polysemantic and may be either causative or non-causative. The phrase ‘The general had his horse killed» may refer to two different situations.
n Either the horse was killed by the general’s order (Генерал приказал убить свою лошадь) or he was killed in combat and the general was not the initiator of the act but the sufferer (Под ним убили лошадь). An error in the translator’s judgement will result in a distorted translation variant.
n Many equivalent-lacking structures result from a noncausative verb used in the typical causative complex. Preserving its basic meaning the verb acquires an additional causative sense. Cf. : n They laughed merrily. n Они весело смеялись. n They laughed him out of the room. n Они так смеялись над ним, что он убежал из комнаты.
n n In such cases the translator has to choose among different ways of expressing causative relationships in TL. Cf. : The US Administration wanted to frighten the people into accepting the militarization of the country.
n n n Администрация США стремилась запугать народ, чтобы заставить его согласиться на милитаризацию страны. Не talked me into joining him. Он уговорил меня присоединиться к нему. It should be noted that such English structures are usually formed with the prepositions «into» and «out of as in the above examples
HANDLING MODAL FORMS
HANDLING STYLISTICALLYMARKED LANGUAGE UNITS The principal stylistic effect of the text is created, however, with the help of special stylistic devices) as well as by the interworking of the meanings of the words in a particular context. The speaker may qualify every object he mentions in his own way thus giving his utterance a specific stylistic turn.
n Some phrases become fixed through repeated use and they may have permanent equivalents in TL, e. g. true love — истинная любовь, dead silence — мертвая тишина, good old England — добрая старая Англия.
n In most cases, however, the translator has to look for an occasional substitute, which often requires an indepth study of the broad context, for example, J. Galsworthy in his «Forsyte Saga» refers to Irene as «that tender passive being, who would not stir a step for herself,
n the translator is faced with the problem of rendering the word «passive» into Russian so that its substitute would fit the character of that lady and all the circumstances of her life described in the novel.
n A common occurrence in English texts is the transferred qualifier syntactically joined to a word to which it does not belong logically, eg. «a corrupt alliance», «a sleepless bed» or «a thoughtful pipe».
n n ‘The sound of the solemn bells» will become «торжественное звучание колов» and «the smiling attention of the stranger» will be translated as «внимание улыбающегося незнакомца» .
n Note should also be taken of the inverted qualifier which syntactically is not the defining but the defined element. Such a qualifier precedes the qualified word which is joined to it by the preposition «of: «this devil of a woman», «the giant of a man», etc.
n The phrase can be transformed to obtain an ordinary combination (a devilish woman, a gigantic man) and then translated into Russian. The translation may involve an additional element: the devil of a woman — чертовски хитрая (умная, неотразимая и т. п. ) женщина.
n Another common type includes conventional indirect names of various objects or «paraphrases». A frequent use of paraphrases is a characteristic feature of the English language.
n Some of the paraphrases are borrowed from such classical sources as mythology or the Bible and usually have permanent equivalents in Russian (cf. Attic salt — аттическая соль, the three sisters — богини судьбы, the Prince of Darkness — принц тьмы).
n Others are purely English and are either transcribed or explained in translation: John Bull — Джон Буль, the three R’s — чтение, письмо и арифметика, the Iron Duke — герцог Веллингтон.
n n Complicated translation problems are caused by ST containing substandard language units used to produce a stylistic effect. The ST author may imitate his character’s speech by means of dialectal or contaminated forms.
n SL territorial dialects cannot be reproduced in TT, nor can they be replaced by TL dialectal forms. It would be inappropriate if a black American or a London cockney spoke in the Russian translation in the dialect, say, of the Northern regions of the country.
n n Fortunately, the English dialectal forms are mostly an indication of the speaker’s low social or educational status, and they can be rendered into Russian by a judicial employment of low-colloquial elements, e. g. : He do look quiet, don’t ‘e? D’e know ‘oo ‘e is, Sir? Вид-то у него спокойный, правда? Часом не знаете, сэр, кто он будет?
n Contaminated forms are used to imitate the speech of a foreigner. Sometimes, both SL and TL have developed accepted forms of representing the contaminated speech by persons of foreign origin.
n For example, the speech of a Chinese can be represented in English and in Russian in a conventional way, which facilitates the translator’s task, eg. Me blingee beer. Now you pay. n Моя плинесла пиво, твоя типель платить. n
n n n If no such tradition exists, the translator has to select some possible contaminated Russian forms to produce the desired effect, e. g. : When you see him quid’ then you quick see him ‘perm whale (the speech of a Kanaka). Когда твоя видел спрут, тогда твоя скоро-скоро видел кашалот.
Identify the referents of the following paraphrases. n 1. the Emerald Isle; 2. the Land of White Elephants; 3. the Land of the Shamrock; 4. the Land of the Thousand Lakes; 5. from John O’Groat’s to Land’s End; 6. the Mother State; 7. the Golden State; 8. the Evergreen State; 9. the City of Brotherly Love; 10. the City of Seven Hills;
n 11. the vale of misery; 12. John Barleycorn; 13. the Man of Destiny; 14. the Wise Men of the East; 15. a white elephant; 16. a white slave; 17. a white crow; 18. the Union Jack; 19. the Stars and Stripes; 20. John Doe
n n n 1. Ireland 2. Thailand 3. Ireland 4. Minnesota 5. the traversal of the whole length of the island of Great Britain between two extremities;
n n n n 6. Virginia 7. California 8. Washington 9. Philadelphia 10. Cincinnati 11. 12. Джон Ячменное Зерно
n n 13. Napoleon 14. (Three) Wise Men, (Three) Kings, or Kings from the East, were in Christian tradition, a group of distinguished foreigners who visited Jesus after his birth, bearing gifts of gold, frankincense and myrrh. They are regular figures in traditional accounts of the nativity celebrations of Christmas and are an important part of Christian tradition.
n n 15. is an idiom for a valuable but burdensome possession of which its owner cannot dispose and whose cost (particularly cost of upkeep) is out of proportion to its usefulness or worth. 16. a girl or woman forced or sold into prostitution
n n 18. Flag of the United Kingdom 20. устаревший термин, использовавшийся в ситуации, когда настоящий истецнеизвестен или анонимен (неизвестного ответчика называли Ричард Роу). Очень часто под этимпсевдонимом подразумевалось неопознанное тело. В случае, если тело принадлежало женщине, использовался термин Джейн Доу (англ. Jane Doe). Baby Doe — соответственно, дитя Доу. В случае, если в процессе фигурировало несколько неопознанных членов семьи, их именовали Джеймс Доу,
Examples from texts
The operational priorities will provide guidelines for a common framework to be used to pursue the objective of countering illicit drugs, crime and terrorism in the context of sustainable development.
Эти оперативные приоритеты будут служить руководящими положениями для общего фундамента в деятельности по борьбе с незаконными наркотиками, преступностью и терроризмом в контексте устойчивого развития.
© Организация Объединенных Наций, 2010 год
Change comes from releasing the appropriate resource, or activating the potential resource, for a particular context by enriching a person’s map of the world.
Изменения происходят при высвобождении или приведение в действие подходящих ресурсов в рамках конкретного контекста, благодаря обогащению карты мира данного человека.
Dilts, Robert / Strategies of Genius. Volume II: Albert EinsteinДилтс, Роберт / Стратегии гениев. Том 2. Альберт Эйнштейн
Стратегии гениев. Том 2. Альберт Эйнштейн
Дилтс, Роберт
Strategies of Genius. Volume II: Albert Einstein
Dilts, Robert
© Copyright 1994 by Meta Publications
In fact, it won’t, because the myObj.clickHandler function will get borrowed by the browser (just as our wayward dog borrowed a method from the tree object in the previous section) and invoked in the context of the element, not the Model object.
На самом деле этого не произойдет, так как функция myObj .clickHandler () заимствуется браузером (точно так же, как в предыдущем разделе собака заимствовала метод дерева), в результате чего она выполняется в контексте элемента, а не объекта модели.
Crane, Dave,Pascarello, Eric / Ajax in ActionКрейн, Дейв,Паскарелло, Эрик / Ajax в действии
Ajax в действии
Крейн, Дейв,Паскарелло, Эрик
© 2006 by Manning Publications Co.
© Издательский дом «Вильямс», 2006
Ajax in Action
Crane, Dave,Pascarello, Eric
© 2006 by Manning Publications Co.
This may be laid down as the meaning to be given to the term whenever nothing to the contrary is stated or implied by the context.
Это главное употребление и будет служить тем значением, какое вкладывается в термин, если в тексте не оговорено или не подразумевается иное.
Marshall, Alfred / Principles of EconomicsМаршалл, Альфред / Принципы экономической науки
Принципы экономической науки
Маршалл, Альфред
Principles of Economics
Marshall, Alfred
While some of the issues have been taken up occasionally by the treaty bodies, this has only been in the context of examining a single State’s report.
Хотя некоторые из этих вопросов иногда затрагивались договорными органами, это происходило лишь в контексте рассмотрения доклада того или иного государства.
© Организация Объединенных Наций, 2010 год
In this context, the Secretary- General’s annual report to the Council should serve as an important channel for conveying information gathered through the monitoring framework.
В связи с этим доклад Генерального секретаря, ежегодно представляемый Совету, должен служить важным инструментом передачи информации, собираемой в рамках механизма наблюдения.
© Организация Объединенных Наций, 2010 год
Investing in an international context is discussed in Chapter 25 (see the references list ed there) and in:
Инвестирование на международном уровне обсуждается в гл. 25 (см. примечания) и в работах:
Sharpe, William F. / InvestmentsШарп, Уильям Ф. / Инвестиции
Инвестиции
Шарп, Уильям Ф.
© 1995 by Prentice Hall, Inc.
© Перевод на русский язык. Издательский Дом «ИНФРА-М», 1997
© Оригинал-макет. Издательский Дом «ИНФРА-М», 1997
Investments
Sharpe, William F.
© 1999, 1995 by Prentice Hall, Inc.
Let’s describe it in the context of the electron two-slit experiment.
Рассмотрим ее в контексте экспериментов с электронами и двумя щелями.
Greene, Brian / The Elegant Universe: Superstrings, Hidden Dimensions, and the Quest for the Ultimate TheoryГрин, Брайан / Элегантная Вселенная. Суперструны, скрытые размерности и поиски окончательной теории
Элегантная Вселенная. Суперструны, скрытые размерности и поиски окончательной теории
Грин, Брайан
© 1999 by Brian R.Greene
© Перевод на русский язык: Едиториал УРСС, 2004
The Elegant Universe: Superstrings, Hidden Dimensions, and the Quest for the Ultimate Theory
Greene, Brian
© 1999, 2003 by Brian R. Greene
Each naming context hosted by the server is listed.
Показан каждый контекст именования, который хранится на выбранном сервере.
Boswell, William / Inside Windows Server 2003Бозуэлл, Уилльям / Внутренный мир Windows Server 2003, SP1 и R2
Внутренный мир Windows Server 2003, SP1 и R2
Бозуэлл, Уилльям
© Издательский дом «Вильямс», 2006
© Pearson Education, Inc., 2003
Inside Windows Server 2003
Boswell, William
© 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc.
In the context of the discussions of the Secretary-General’s reform agenda, the participants welcomed the steps taken by OHCHR to improve the servicing of the mandates and enhance their effectiveness.
В контексте обсуждения выдвинутой Генеральным секретарем программы реформы участники приветствовали принятые УВКПЧ шаги по улучшению обслуживания мандатов и повышению их эффективности.
© Организация Объединенных Наций, 2010 год
In 2001 quality change continued to be an important issue for discussion, but in the context of services.
В 2001 году изменение качества по-прежнему оставалось важным вопросом для обсуждения, но уже в контексте услуг.
© Организация Объединенных Наций, 2010 год
Of course, in many practical circumstances, you don’t need all these steps. There are reasonable defaults for the settings of the 2D graphics context. You only need to change the settings if you want to change the defaults.
Конечно, на практике обычно не нужно выполнять все эти действия, потому для многих параметров двумерного (2D) графического контекста предусмотрены значения по умолчанию, которые можно изменить в случае необходимости.
Horstmann, Cay S.,Cornell, Gary / Core Java™ 2. Volume II — Advanced FeaturesХорстманн, Кей С.,Корнелл, Гари / Java 2. Том II. Тонкости программирования
Java 2. Том II. Тонкости программирования
Хорстманн, Кей С.,Корнелл, Гари
© Издательский дом «Вильямc», 2002
© Prentice Hall, Inc., 2002
Core Java™ 2. Volume II — Advanced Features
Horstmann, Cay S.,Cornell, Gary
© 2002 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
This result is the four-dimensional generalization of the Gauss-Bonnet integral, widely known in the context of two-dimensional geometry:
Этот результат представляет собой обобщение на случай четырех измерений интеграла Гаусса — Бонне, хорошо известного в двумерной геометрии:
Misner, Charles W.,Thorne, Kip S.,Wheeler, John Archibald / GravitationМизнер, Ч.,Торн, К.,Уилер, Дж. / Гравитация
Гравитация
Мизнер, Ч.,Торн, К.,Уилер, Дж.
© 1973 by W. H. Freeman and Company
© Перевод на русский язык «Мир», 1977
Gravitation
Misner, Charles W.,Thorne, Kip S.,Wheeler, John Archibald
© 1970 and 1971 by Charles W. Misner, Kip S. Thorne, and John Archibald Wheeler.
© 1973 by W. H. Freeman and Company.
In the context of discussion there was an opinion that the demand for money will be supported by external financial aid and arrangement of the parliamentary election.
В контексте обсуждений было выражено мнение, что спрос на деньги в текущем году будет поддерживаться за счет поступления внешней финансовой помощи и проведения предвыборной парламентской кампании.
To put that number in context: for one-sixth of the cost of the war, the US could put its social security system on a sound footing for more than a half-century, without cutting benefits or raising contributions.
Если поместить эту цифру в контекст: за одну шестую военных расходов США могли бы поставить на твердую основу свою систему социального обеспечения и поддерживать ее в течение больше половины столетия, не сокращая пособий и не собирая пожертвований.
© Project Syndicate 1995 – 2011
© Project Syndicate 1995 – 2011
Add to my dictionary
context1/5
‘kɔntekstNounконтекстExamples
to cite a passage out of context — цитировать какой-л. фрагмент в отрыве от контекста
User translations
No translations for this text yet.
Be the first to translate it!
Collocations
association context
контекст соединения
bind context
контекст связывания
bounded context grammar
грамматика ограниченного контекста
browse context object
объект-контекст просмотра
context condition
контекстное условие
context control
управление контекстом
context editing
контекстное редактирование
context editing
редактирование по контексту
context editor
контекстный редактор
context grammar
контекстная грамматика
context help
контекстная справка
context identifier
контекстная ссылка
context identifier
контекстный идентификатор
context impression
контекстный показ
context name
контекстное имя