способность,
inability
неспособность;
disability
нетрудоспособность
способный, умелый
unable
неспособный
disabled
искалеченный; инвалид
дать возможность
disable
делать неспособным, калечить
умело, искусно
абсурдность
абсурдный
приемлемость
приемлемый
unacceptable
неприемлемый
принимать, соглашаться
доступ
accessibility
доступность
доступный
доступно
случай, случайность
случайный
нечаянно, случайно
действие
actor
актер
actress
актриса
activity
активность
activities
деятельность
acting
представление
активный
acting
действующий, работающей
действовать
активно
достижение
достигать
привычка, приверженность, увлеченность
addict
увлеченный человек, имеющий стойкую привычку
способный вызывать привычку
увлекаться, предаваться
восхищение
восхитительный
восхищаться
восхитительно
совет
рекомендуемый
советовать
притворство, искусственность
affection
привязанность, любовь
притворный
affectionate
любящий
affective
эмоциональный
воздействовать, влиять; притворяться
соглашение, согласие
disagreement
разногласие, несогласие
соответствующий, приятный
соглашаться
disagree
не соглашаться
соответственно
агрессия
aggressor
агрессору зачинщик
агрессивный
нападать
агрессивно
цель
бесцельный
целиться, намереваться
бесцельно
то, что может быть позволено
unaffordable
то, что невозможно себе позволить
позволять себе
развлечение
приятно изумленный
amusing
забавный
развлекать, забавлять
изумленно
внешность; появление
disappearance
исчезновение
появляться
disappear
исчезать
назначение; деловая встреча
disappointment
разочарование, досада
назначенный
disappointed
огорченный
disappointing
разочаровывающий
назначать
disappoint
разочаровывать
одобрение
одобренный
approving
одобрительный
одобрять
одобрительно
соглашение; расположение
приведенный в порядок
приводить в порядок, организовывать
аргумент, довод
argumentation
аргументация
доказуемый (в споре)
argumentative
спорный, конфликтный
утверждать, спорить, ссориться
доказательно
присвоение; ассигнование
подходящий, соответствующий
inappropriate
несоответствущий, неуместный
присваивать, предназначать
соответственно, подходяще
прибытие
прибывать, приезжать
притяжение, привлекательность
привлеченный
attractive
привлекательный
привлекать
привлекательно
избежание, отмена
то, чего можно избежать
unavoidable
неизбежный
избегать
неизбежно
красота; красавица
красивый
украшать
красиво
роды
сносный, допустимый
unbearable
невыносимый
носить; терпеть
невыносимо
вера
вероятный, правдоподобный
unbelievable
невероятный
верить
выгода
выгодный
получать выгоду
зануда
boredom
скука
испытывающий скуку
boring
скучный, надоедливый
надоедать
скучно
дыхание, дуновение
breathing
дыхание
breather
короткая передышка
дышащий
breathless
бездыханный
дышать
затаив дыхание
дело
businessman
деловой мужчина
businesswoman
деловая женщина
занятой
businesslike
деловой, практичный
занимать делом
деловито, по-деловому
забота, уход
заботливый
careless
небрежный
заботиться, любить
заботливо
carelessly
небрежно
празднование
celebrity
знаменитость
знаменитый, прославленный
праздновать, прославлять
определенность
uncertainty
неопределенность, неуверенность
определенный
uncertain
неопределенный
определенно, уверенно
изменение; мелочь, сдача
изменчивый
changed
изменившийся
changeless
неизменный
unchanged
не изменившийся
менять; обменивать(ся)
неизменно
характер
характерный, типичный
характеризовать
выбор
разборчивый
выбирать
ребенок
children
дети
детский; ребяческий
очистка; устранение препятствий
четкий, ясный
очищать, расчищать
четко, ясно
облако
облачный
cloudless
безоблачный
собрание; коллекция
collector
сборщик
коллективный, совокупный
собирать; коллекционировать
колония
колониальный
колонизировать
цвет
цветной
colourless
бесцветный
multi-coloured
разноцветный
раскрашивать
комфорт; утешение
discomfort
беспокойство; неудобство
удобный, комфортабельный
uncomfortable
неудобный
утешать, успокаивать
удобно
uncomfortably
неудобно
община, общество
общественный, коллективный
сообщение
communicator
коммуникатор, переговорщик
использующийся в общении; коммуникативный
сообщать; общаться
сравнение
сравниваемый
comparative
сравнительный
сравнивать
сравнительно, относительно
соревнование; конкуренция
competitor
конкурент, соперник
соревновательный
соревноваться, конкурировать
в форме соревнования, конкуренции
завершение, окончание
законченный
complete
полный, завершенный
incomplete
неполный, назавершенный
заканчивать, завершать
полностью
поздравление
поздравлять
соединение, объединение
связанный, соединенный
соединять
disconnect
разъединять
внимание; рассмотрение, обсуждение
значительный
considerate
внимательный, деликатный, тактичный
inconsiderate
неосмотрительный; невнимательный к другим
считать, полагать; рассматривать
значительно
совесть
совестливый, добросовестный
conscientiousless
бессовестный
добросовестно
сознание
осознающий
unconscious
без сознания
сознательно, осознанно
консультация
consultant
консультант
консультирующий
консультировать
вместилище, контейнер
содержащий
содержать, вмещать
непрерывность
продолжающийся, длящийся
продолжать
непрерывно
управление, руководство
поддающийся управлению
uncontrollable
неподдающийся управлению
controlled
управляемый
uncontrolled
неуправляемый
управлять, регулировать
бесконтрольно
убеждение
убедительный
convinced
убежденный
убеждать
убедительно
повар
cooker
плита, духовка
переваренный
under-cooked
недоваренный
готовить еду
исправление
corrector
корректор
правильный
incorrect
неправильный
исправлять
правильно
прилавок
discount
скидка
accountant
бухгалтер
исчисляемый
uncountable
неисчисляемый
считать
немеряно, без счета
храбрость
храбрый
encouraged
воодушевленный
encouraging
подбадривающий
discouraged
обескураженный
приободрять, поддерживать
discourage
отговаривать, обескураживать
смело, храбро
создание
creativity
творчество
creator
творец, создатель
creature
творение; живое существо
творческий
создавать, творить
творчески
вера, доверие
вероятный, заслуживающий доверия
incredible
невероятный
вероятно
incredibly
невероятно
критик
criticism
критика
критический; переломный; рискованный
критиковать
критично, критически
культивация, обработка
культивированный, обработанный
обрабатывать
культура
культурный, воспитанный
cultural
культурный (как часть культуры)
культурно
лекарство; лечение
излечимый
incurable
неизлечимый
вылечивать, исцелять
неизлечимо
опасность
опасный
угрожать
опасно
день
ежедневный
ежедневно
обман, заблуждение
обманчивый
deceitful
обманчивый, лживый
обманывать
обманчиво, предательски
решение
определенный, явный
undecided
нерешительный, неясный
decisive
решительный, убежденный, убедительный
решать, принимать решение
решительно, определенно
определение
четкий, определенный
indefinite
неопределенный
определять, давать определение
определенно, ясно
indefinitely
нечетко, неопределенно
восторг, наслаждение
восхитительный
delighted
польщенный
восхищаться
с восторгом
доставка, поставка
доставленный
доставлять
зависимость
independence
независимость
зависимый
independent
независимый
зависеть
независимо
депрессия, подавленность
депрессивный, вызывающий депрессию
depressed
подавленный
подавлять
описание
описательный, наглядный
описывать
проект, дизайн
designer
дизайнер, проектировщик
проектировать
желание, стремление
желательный, желаемый
undesirable
нежелательный
желать, стремиться
желательно
разрушение
разрушенный
разрушать, уничтожать
решительность; определение
решительный
решать, определять
развитие
developer
разработчик
развитой
developing
развивающийся
undeveloped
неразвитый
развивать(ся)
умирающий
умирать
разница, различие
indifference
безразличие
другой, отличающийся
indifferent
безразличный
отличаться
по-другому
indifferently
с безразличием
тревога, беспокойство; нарушение тишины, порядка
обеспокоенный
disturbing
беспокоящий
беспокоить, мешать
сомнение
сомнительный
doubtless
несомненный
undoubted
бесспорный
сомневаться
с сомнением
doubtlessly
не сомневаясь
undoubtedly
без сомнения
легкость, свобода
disease
болезнь
легкий
uneasy
неловкий, тревожный
облегчать, ослаблять
легко
uneasily
неловко
хозяйство
экономический
economical
экономный
экономить
экономически; экономно
воспитатель, педагог
education
образование
образованный
uneducated
необразованный
educative
образовательный
воспитывать, давать образование
следствие, результат
effectiveness
эффективность
эффективный, действующий
производить, выполнять
эффективно, действенно
электричество
electrician
электрик
электрический
электрифицировать
империя
empiror
император
имперский
empiric / empirical
исходящий из опыта, эмпирический
служба, работа
unemployment
безработица
employer
наниматель, работодатель
employee
работающий по найму
нанятый, занятый
unemployed
безработный
нанимать
конец, окончание
бесконечный
unending
нескончаемый
конец, окончание
бесконечно
окружающая среда
природный
развлечение
развлекательный
развлекать
энтузиазм, восторг
enthusiast
энтузиаст, восторженный человек
восторженный
с восторгом
оборудование
снаряженный, оборудованный
снаряжать
сущность
главный, основной
главным образом
экзамен; медосмотр
проэкзаменованный; осмотренный врачом
экзаменовать; осматривать
возбуждение, волнение
возбуждающий
excitable
возбудимый
excited
возбужденный, взволнованный
возбуждать, волновать
взволнованно, возбужденно
ожидание, предчувствие
ожидаемый
unexpected
неожиданный
ожидать, предчувствовать
расход(ы), затраты
дорогой
inexpensive
недорогой
тратить, расходовать
дорого
опыт, опытность
inexperience
неопытность
experiment
эксперимент
опытный
inexperienced
неопытный
experimental
эспериментальный
испытывать
взрыв
explosive
взрывчатое вещество
взрывчатый
взрываться
выражение
выразительный
выражать
выразительно
пространство, степень
длительный,обширный
extensive
обширный
простираться, тянуться
обширно, протяженно
крайняя степень, крайность
крайний, чрезвычайный
крайне
очарование, обаяние
чарующий
fascinated
очарованный
очаровывать
справедливость; порядочность
порядочный, справедливый
unfair
несправедливый
справедливо, честно; довольно-таки
финансы
финансовый
финансировать
финансово
твердость
твердый
утверждать
твердо
физическая форма, физическое состояние
находящийся в хорошей форме; подходящий
unfit
неподходящий
подгонять, подстраивать
следующий
следовать
глупыш, дурак
глупый
обманывать
глупо
забываемый
unforgettable
незабываемый
forgetful
забывчивый
forgotten
забытый
забывать
прощение
прощающий
forgivable
простительный
unforgivable
непростительный
прощать
с прощением
судьба, счастье; богатство, состояние
счастливый
unfortunate
несчастный
к счастью
unfortunately
к сожалению
свобода
свободный; бесплатный
свободно
частота
частый
часто посещать
часто
друг
friendship
дружба
friendliness
дружелюбие
дружеский, дружелюбный
unfriendly
недружеский
дружелюбно
страх, испуг
страшный
frightened
испуганный
frightening
пугающий
пугать, устрашать
страшно; испуганно
щедрость
щедрый
щедро
джентльмен
мягкий, нежный
мягко, нежно
привидение, призрак
похожий на привидение
трава
травяной
привычка, обычай
habitant
обитатель
habitat
естественная среда
habitation
жилище, обиталище
привычный
приучать
обычно
рука; рабочий
handful
горсть
удобный (для использования)
handmade
изготовленный вручную
вручать
счастье
unhappiness
несчастье
счастливый
unhappy
несчастный
счастливо
unhappily
несчастливо
вред
вредный
harmless
безвредный
повредить, навредить
вредно
здоровье
здоровый
unhealthy
нездоровый
дом, жилище
бездомный
честь
почетный
почитать, чтить
почетно
надежда
hopefulness
оптимизм, надежда
надеющийся
hopeless
безнадежный
надеяться
с надеждой
человечество
человеческий
humane
гуманный
inhuman
бесчеловечный
humanitarian
гуманитарный
юмор
юмористический
с юмором
спешка
торопливый, спешащий
hurried
торопливый
торопиться
торопливо
лед
ледяной
важность
важный
unimportant
незначительный
важно
впечатление
впечатленный
impressive
впечатляющий
unimpressed
безучастный
производить впечатление
впечатляюще
улучшение
улучшенный
улучшать
толчок, побуждение
импульсивный
импульсивно
несчастный случай; конфликт, инцидент
случайный
случайно
рост, увеличение
растущий
увеличивать(ся)
с ростом
промышленность
промышленный
industrious
трудолюбивый. усердный
индустриализовать
в промышленном отношении
сообщение, информация
informant
осведомитель
formality
формальность
осведомленный
well-informed
знающий, хорошо информированный
misinformed
неверно информированный
formal
формальный, официальный
informal
неофициальный
информировать
misinform
неверно сообщать; дезинформировать
информационно
интенсивность
интенсивный
интенсифицировать
интенсивно
интерес
заинтересованный
interesting
интересный
интересовать
изобретатель
invention
изобретение
изобретательный
изобретать
изобретательно
приглашение
приглашенный
приглашать
вдохновение
вдохновленный
inspiring
вдохновляющий
вдохновлять
знание
acknowledgement
признание; расписка
признанный
признавать, подтверждать
законность, легальность
юридический, законный
illegal
незаконный, подпольный
легализовать
законно
illegally
незаконно
сходство, подобие
приятный
unlike
непохожий
like
аналогичный
относиться хорошо
dislike
относиться отрицательно
вероятно
unlikely
невероятно
unlike
в отличие
жизнь
living
жизнь
оживленный, веселый
live
актуальный, реальный
жить
оживленно
литература
буквальный
literary
литературный
literate
грамотный
illiterate
неграмотный
буквально
место, поселение
местный
размещать
в определенном месте
одиночество
одинокий; один
удача
удачливый
unlucky
неудачливый, неудачный
к счастью
роскошь
шикарный
большинство
главный, основной
управляющий, руководитель
управленческий
управлять; справляться
женитьба
женатый / замужняя
unmarried
неженатый / незамужняя
жениться
встреча; собрание
встречать, знакомиться
память
memorial
мемориал
памятный
заучивать наизусть
нищета
нищенский, ничтожный
месяц
ежемесячный
ежемесячно
движение
неподвижный
показывать жестом
тайна, загадка
таинственный, загадочный
таинственно, загадочно
необходимость
необходимый
unnecessary
ненужный
необходимо
нерв
нервный
нервировать
нервно
число; количество
многочисленный
numerate
умеющий считать
innumerate
неумеющий считать
обозначать цифрами
объект, предмет
objective
цель; возражение
объективный
возражать
объективно
упрямый
упрямо
случай, происшествие
происходить
операция; оперирование, приведение в действие
управлять, действовать
возможность
opportunist
оппортунист
своевременный, подходящий
оппозиция, противостояние
opponent
оппонент, противник
напротив
opposed
противоположный
противопосталять
владелец, хозяин
собственный
владеть
боль
болезненный
painless
безболезненный
болезненно
painlessly
безболезненно
терпение
impatience
нетерпение
patient
пациент
терпеливый
impatient
нетерпеливый
терпеливо
impatiently
нетерпеливо
участник
participation
участие
участвующий
принимать участие
подробности
особенный
особенно
совершенство
совершенный, идеальный
imperfect
несовершенный
совершенствовать, улучшать
отлично, безупречно
период, срок
периодический
периодически
представление; исполнение
performer
исполнитель
исполнять, выполнять, совершать
мир, спокойствие
мирный
мирно
разрешение
permissiveness
вседозволенность
permit
пропуск
позволяющий
позволять
с позволением
удовольствие
приятный
pleased
довольный
displeased
недовольный
доставлять удовольствие
приятно
точка; пункт
остроконечный, нацеленный
pointful
уместный, удачный
pointless
бесцельный
указывать, направлять
остро, по существу
вежливость
вежливый
impolite
невежливый
вежливо
популярность
популярный
unpopular
непопулярный
популяризировать
владение, собственность
possessor
обладатель, владелец
собственнический
владеть, обладать
вероятность, возможность
возможный
impossible
невозможный
возможно
сила, мощь
мощный
powerless
бессильный
уполномочивать
предпочтение
предпочтительный
preferential
пользующийся препочтением
предпочитать
предпочтительно
подготовка
подготовленный
unprepared
неподготовленный
подготовить
с готовностью
престиж
престижный
престижно
профессия
профессиональный
профессионально
выгода
выгодный
unprofitable
не приносящий выгоды
получать выгоду
выгодно
прогресс, продвижение
прогрессивный
продвигаться вперед
постепенно, продвигаясь вперед
предложение
предложенный
делать предложение
процветание
процветающий
процветать
процветающе
общественность
общественный
разглашать
открыто, публично
быстрота
быстрый
убыстрять
быстро
реальность
realization
реализация, осуществление
реальный, настоящий
unreal
нереальный
реализовать, осуществлять
действительно, в самом деле
признание, узнавание
признанный
узнавать; признавать
снижение, понижение
уменьшенный; сниженный
снижать; сбавлять
отдых, расслабление
расслабленный
relaxing
отдыхающий; расслабляющий
отдыхать, расслабляться
расслабленно
надежность
надежный
unreliable
ненадежный
доверять, полагаться
надежно
религия
религиозный
нежелание, неохота
неохотный
неохотно
регулярность
irregularity
нерегулярность
регулярный, правильный
irregular
неправильный; нестандартный
регулировать
регулярно
замечание
замечательный
замечать, отмечать
замечательно
представление
representative
представитель
представительный
представлять
упрек
безупречный
упрекать
с упреком
репутация
имеющий хорошую репутацию, почтенный
disreputable
имеющий плохую репутацию
давать репутацию
disrepute
компрометироватъ
сопротивление
ударопрочный;
irresistible
неотразимый
resistant
прочный
сопротивляться
неотразимо
уважение
уважительный
уважать
с уважением
отдых
беспокойный
отдыхать
беспокойно
награда
стоящий награды
unrewarded
невознагражденный
награждать
богатства
richness
богатство
богатый
обогащать
богато
риск
рискованный
рисковать
грусть
грустный
огорчать
грустно
сейф
safety
безопасность
безопасный
unsafe
опасный
спасать; экономить
безопасно
удовлетворение
dissatisfaction
неудовлетворенность; недовольство
довольный
dissatisfied
недовольный
satisfactory
удовлетворительный
unsatisfactory
неудовлетворительный
удовлетворять
dissatisfy
разочаровывать; огорчать
исследование
искать, осуществлять поиск
безопасность
безопасный
insecure
находящийся в опасности
охранять, гарантировать
безопасно
серьезность
серьезный
серьезно
наука
scientist
ученый
научный
научно
чувство
insensibility
отсутствие чувствительности
чувствительный
insensitive
несочувствующий
sensible
разумный
insensible
нечувствительный, неосознающий
ощущать
чувствительно
sensibly
разумно
услуга, обслуживание
servant
слуга
обслуженный; поданный на стол
служить, обслуживать, подавать на стол
значительный
insignificant
незначительный
иметь значение
значительно
сходство, похожесть
похожий, подобный
похоже, подобно
искренность
искренний
insincere
неискренний
искренне
шорты
короткий
укорачивать
кратко
сон
sleeper
спящий; спальный вагон
спящий
sleepless
бессонный
спать
без сна
решение; раствор
решенный; растворенный
решать; находить выход; растворять
специальность; фирменное блюдо
specialty
особенность
особенный; специальный
specific
специфический
точно определять
specialize
специализировать(ся)
специально
specifically
специфично
сила
сильный
укреплять
сильно
стресс
стрессовый
ударять, ставить ударение
в состоянии стресса
успех
успешный
unsuccessful
безуспешный
преуспевать
успешно
достаточность
insufñcience
недостаточность
достаточный
insufficient
недостаточный
быть достаточным
достаточно
подходящий
unsuitable
неподходящий
подходить, устраивать
предложение
предлагать
подозреваемый
подозрительный
подозревать
подозрительно
пловец
swimming
плавание
плавающий, плавательный
плавать
сочувствие, понимание
сочувствующий
сочувствовать
с пониманием; сочувственно
уверенность
уверенный
unsure
неуверенный
assured
обеспеченный; уверенный
self-assured
уверенный в себе
обеспечивать; гарантировать
assure
уверять, обеспечивать
конечно; уверенно
assuredly
с уверенностью
окружение
окруженный
окружать
беседа, разговор
разговорчивый
беседовать
вкус
distaste
отсуствие вкуса
сделанный со вкусом; обладающий вкусом
tasteless
безвкусный
пробовать
со вкусом
tastelessly
без вкуса
террор
terrorist
террорист
ужасный
terrific
потрясающий
terrifying
ужасающий
terrified
напуганный
ужасать
ужасно
terrifically
потрясающе
жажда
испытывать жажду
колготки
плотный, тесный
сжимать, натягивать
тесно, плотно
мысль
задумчивый
thoughtless
бездумный
думать, иметь мнение
задумчиво
трагедия
трагичный
tragical
трагический
трагично
путешествие
traveller
путешественник
путешествующий
путешествовать
правда
untruth
неправда
правильный; настоящий
untrue
неверный, не соответствующий действительности
truthful
правдивый
по-настоящему, искренне
truthfully
правдиво
ценность
ценимый
valuable
ценный
ценить, оценивать
разнообразие
variability
изменчивость, непостоянство
изменяемый
invariable
неизменный
менять, разнообразить
неизменно
год
ежегодный
ежегодно
понимание
misunderstanding
непонимание; недоразумение
понятный
понимать
польза
misuse
неправильное использование;
usage
использование
полезный
useless
бесполезный
used
использованный
unused
неиспользованный
использовать, пользоваться
полезно
uselessly
бесполезно
неделя
еженедельный
еженедельно
ширина
широкий
расширять
широко
воля, желание; завещание
жаждущий, желающий
unwilling
не желающий
проявлять волю, желать
охотно, с удовольствием
unwillingly
неохотно
ветер
ветренный
windless
безветренный
мудрость
мудрый
unwise
неблагоразумный
мудро
unwisely
неблагоразумно
стоимость, ценность
достойный
worthless
не имеющий ценности
При изучении английского один из важных аспектов — новые слова. Как правило, студенты пишут их в тетрадь/приложение, с примерами и переводом. Стараются запомнить новую лексику. Но одной зубрежкой здесь не обойтись. Предлагаю научиться пользоваться словообразованием, то есть изменять уже знакомые слова.
Словообразование (word formation) — это способы, при которых из одного слова можно сделать новые. Путем добавления суффикса, приставки, сокращения или конверсии. Овладев словообразованием вы будете гораздо свободнее чувствовать себя в английской лексике.
Содержание:
- 1 4 способа словообразования в английском
- 2 Приставки как способ словообразования в английском
- 3 Суффиксы как способ словообразования в английском
- 4 Как образуются глаголы в английском
- 5 Как образуются наречия в английском
- 6 Таблица словообразования по частям речи
- 7 Объединение суффиксов и приставок: преобразование слов в английском языке
- 8 Конверсия в английском
- 9 Сокращение в английском
4 способа словообразования в английском
Английский язык известен своим способом формирования и использования слов и предложений. Образование новых слов из существующего корневого слова путем прибавления слога или другого слова — общий процесс; однако есть несколько способов, которыми это можно сделать.
Образование слов классифицируется на четыре типа в зависимости от того, как осуществляется процесс образования.
- Добавляя префиксы
- Добавляя суффиксы
- Преобразование из одного класса слов в другой
- Образовать сложные слова
Начать практиковать английский вы можете уже сегодня. В Telegram-канале вы найдете интересные тексты, разборы фраз, а также много другой полезной информации.
Добавление префиксов
Приставка (prefix)– это буква или группа букв, которые добавляются к началу слова (at the beginning of the word) с целью образовать новое слово. Наиболее часто используемые префиксы включают «in-», «un-», «dis-», «im-», «ir-» и т. д.
Примеры словообразования путем добавления приставки:
| Discipline – indiscipline | Дисциплина — недисциплинированность |
| Just – unjust | Справедливый — несправедливый |
| Tidy – untidy | Аккуратный — неаккуратный |
| Respect – disrespect | Уважение — неуважение |
| Understand – misunderstand | Понять — неправильно понять |
| Comfortable – uncomfortable | Удобный — неудобный |
| Comfort – discomfort | Комфорт – дискомфорт |
| Responsible – irresponsible | Ответственный — безответственный |
| Honest – dishonest | Честный — нечестный |
| Happy – unhappy | Счастливый – несчастный |
| Polite – impolite | Вежливый — невежливый |
| Experience – inexperience | Опыт — неопытность |
| Practical – impractical | Практичный – непрактичный |
| Important – unimportant | Важно — неважно |
| Legal – illegal | Легальный — незаконный |
| Ethical – unethical | Этично — неэтично |
| Potent – impotent | Мощный — бессильный |

Добавление суффиксов
Суффикс – это короткий слог, добавляемый в конце основного слова. Добавление суффиксов обычно изменяет класс конкретного слова. Наиболее распространенные суффиксы включают «-ment», «-ness», «-ity», «-ous», «-tion», «-sion», «-al», «-able», «-ible», ‘-ive’, ‘-ly’, ‘-ate’, ‘-er’, ‘-or’ и т. д.
Примеры словообразования путем добавления суффикса:
| Comprehend (verb) – comprehension (noun) – comprehensible (adjective) | Постигать (глагол) – понимать (существительное) – понимать (прилагательное) |
| Inform (verb) – information (noun) – informative (adjective) | Информировать (глагол) – информация (существительное) – информативно (прилагательное) |
| Invest (verb) – Investment (noun) – Investor (noun) | Инвестировать (глагол) – Инвестировать (существительное) – Инвестор (существительное) |
| Write (verb) – writer (noun) | Писать (глагол) – писатель (существительное) |
| Authorise (verb) – authorisation (noun) | Authorize (глагол) – авторизация (существительное) |
| Move (verb) – movement (noun) | Move (глагол) – движение (существительное) |
| Add (verb) – addition (noun) | Добавить (глагол) – добавить (существительное) |
| Happy (adjective) – happiness (noun) | Happy (прилагательное) – счастье (существительное) |
| Conserve (verb) – conservation (noun) | Консервировать (глагол) – консервировать (существительное) |
| Wide (Adjective) – widen (verb) | Широкий (прилагательное) – расширять (глагол) |
| Manage (verb) – manageable (adjective) – manager (noun) | Управлять (глагол) – управляемый (прилагательное) – менеджер (существительное) |
| Courage (noun) – courageous (adjective) | Мужество (существительное) – мужественный (прилагательное) |
| Brave (adjective) – bravery (noun) | Храбрый (прилагательное) – храбрость (существительное) |
| Quick (adjective) – quickly (adverb) | Быстрый (прилагательное) – быстро (наречие) |
| Sad (adjective) – sadness (noun) | Грустный (прилагательное) – печаль (существительное) |
Преобразование
Процесс преобразования фокусируется исключительно на изменении класса конкретного слова. Обратите внимание, как некоторые существительные используются для выполнения роли глагола или прилагательного, действующего как существительное, просто добавляя другое слово или слегка изменяя написание фактического слова.
- The rich should help the poor. / Богатые должны помогать бедным.
Прилагательные, такие как «богатый» и «бедный», используются как существительные с артиклем «the».
- Everyone is talented. / Все талантливы.
«Талантливый» — причастие прошедшего времени используется в качестве прилагательного. Слово образовано добавлением суффикса «ed» к концу существительного «талант».

- There will definitely be a lot of ups and downs in life. / В жизни определенно будет много взлетов и падений.
Предлоги «вверх» и «вниз» используются как существительные с добавлением «s» в конце.
- He texted me about the meeting only at the last minute. / Он написал мне о встрече только в последнюю минуту.
Существительное «текст», используемое для обозначения текстового сообщения, отправленного по телефону, используется в качестве глагола в предложении путем добавления «ed» в конце слова.
- The financial aid had to be approved before we could make a decision. / Финансовая помощь должна была быть одобрена, прежде чем мы смогли принять решение.
Существительное «финансы» используется как прилагательное, добавляя к нему «ial» в конце, а глагол «решать» используется как существительное, удаляя «de» и добавляя к слову «sion».
Формирование сложных слов
Сложные слова образуются путем соединения одной части речи с другой, образуя определенный класс слов. Существует множество способов образования сложных слов. Глаголы соединяются с прилагательными, образуя составные глаголы, причастие настоящего времени сочетается с существительным, образуя составное существительное, два существительных соединяются, образуя составное существительное, прилагательное и существительное соединяются, образуя составное существительное, наречие в сочетании с существительным образуют составное существительное, прилагательное в сочетании с причастием прошедшего времени образует составное прилагательное и так далее.
| Over (adverb) + load (noun) – Overload | Сверх (наречие) + нагрузка (существительное) — Перегрузка |
| White (adjective) + wash (verb) – Whitewash | Белый (прилагательное) + мыть (глагол) – Белить |
| Black (adjective) + board (noun) – Blackboard | Черный (прилагательное) + доска (существительное) — Школьная доска |
| Cup (noun) + board (noun) – Cupboard | Чашка (существительное) + доска (существительное) – Буфет/Кухонный шкаф |
| Swimming (present participle) + pool (noun) – Swimming pool | Плавание (причастие настоящего времени) + бассейн (существительное) – Плавательный бассейн |
| Three (adjective) + legged (past participle) – Three-legged | Третий (прилагательное) + длинноногий (причастие прошедшего времени) — Трехногий |
| Break (verb) + Down (preposition) – Breakdown | Перерыв (глагол) + вниз (Предлог) — упадок |
| Up (preposition) + town (noun) – Uptown | Вверх (предлог) + город (существительное) — жилые кварталы |
| Copy (verb) + writer (noun) – Copywriter | Копировать (глагол) + писатель (существительное) – Копирайтер |
| Sun (noun) + rise (verb) – Sunrise | Солнце (существительное) + восход (глагол) – Восход солнца |
| Flash (verb) + mob (noun) – Flash mob | Вспышка (глагол) + толпа (существительное) – Flash mob /Массовая акция |
| Master (noun) + piece (noun) – Masterpiece | Мастер (существительное) + произведение (существительное) – Шедевр |
Далее предлагаю более подробно разобрать словообразование в каждой части речи.

Приставки как способ словообразования в английском
Приставки в английском языке являются одним из самых сложных грамматических аспектов для изучения. Приставки типа im-, in-, un- могут изменить весь смысл предложения. Приставки можно разделить на две группы: отрицательные и все остальные. Наиболее употребительные отрицательные приставки: un-, in-, dis-.
Отрицательные приставки в английском языке
Отрицательные приставки
| de | deactivate — деактивировать |
| un | unhappy — несчастный |
| in | indirect — непрямой |
| aab | amoral — аморальный |
| anti | antivirus — антивирус |
| counter | counter-clockwise — против часовой стрелки |
| dis | dislike — не нравиться |
Приставка un-
| comfortable — удобный | uncomfortable — неудобный |
| equal — равный | unequal — неравный |
| expected — ожидаемый | unexpected — неожиданный |
| happy — счастливый | unhappy — несчастный |
| important — важный | unimportant — неважный |
| known — известный | unknown — неизвестный |
| limited — ограниченный | unlimited — неограниченный |
| pleasant — приятный | unpleasant — неприятный |
Также un- присоединяется к глаголам, чтобы выразить противоположное действие.
| to dress — одеваться | to undress — раздеваться |
| to lock — запирать | to unlock — отпирать |
| to pack — упаковывать | to unpack — распаковывать |
Приставка in-
Нет правил, регулирующих, когда используется un-, а когда in-, хотя по смыслу эти приставки не отличаются. Важная разница в том, что in- НЕ используется в глаголах.
| ability — способность | inability — неспособность |
| adequate — достаточный | inadequate — недостаточный |
| capable — способный | incapable — неспособный |
| comparable — сравнимый | incomparable — несравнимый |
| complete — полный | incomplete — неполный |
| direct — прямой | indirect — непрямой |
| experienced — опытный | inexperienced — неопытный |
Приставка in — видоизменяется в некоторых случаях:
- перед l превращается в il-
- перед r превращается в ir-
- перед m и p превращается в im-
| legal — законный | illegal — незаконный |
| logical — логичный | illogical — нелогичный |
| regular — регулярный | irregular — нерегулярный |
| responsible — ответственный | irresponsible — безответственный |
| patient — терпеливый | impatient — нетерпеливый |
| possible — возможный | impossible — невозможный |

Приставка dis-
Dis- может выражать отрицание или противоположное действие.
Отрицание:
| honest — честный | dishonest — бесчестный |
| to approve — одобрять | disapprove — не одобрять |
| to like — любить (I like — мне нравится) | to dislike — не любить (I dislike — мне не нравится) |
Противоположное действие:
| to appear — появляться | to disappear — исчезать |
| to arm — вооружать | to disarm — разоружать |
| to connect — соединять | to disconnect — разъединять |
Простой шаг для изучения английского — Telegram-канале. Здесь вы найдете интересные тексты, разборы фраз, а также много другой полезной информации.
Другие отрицательные приставки
Среди прочих отрицательных приставок много международных, латинского и греческого происхождения, встречающихся и в русском языке.
- aab— (без-, не-, а-): abnormal — ненормальный, amoral — аморальный.
- anti- (анти-, противо-): antivirus — антивирус, antibiotic — антибиотик.
- counter- (контр-, противо-): counterstrike — контрудар, counter-clockwise — против часовой стрелки.
- de- (лишать, удалять): decode — раскодировать, deformation — расформирование.
- non- (отрицание, отсутствие): non-stop — безостановочный, non-alcoholic — безалкогольный.
Приставки с разными значениями
| en | encircle — окружать (делать круг) |
| ultra | ultra-violet — ультрафиолетовый |
| sub | submarine — подводный |
| ex | ex-husband — бывший муж |
| inter | intertown — междугородний |
| re | to reread — перечитать |
| mis | to misquote — неправильно цитировать |
| over under | to overpay — переплатить |
| pre/ post | post-war — послевоенный |
| co | co-author — соавтор |
| Приставка re- (снова, заново, вновь) | |
| to appear — появиться | to reappear — снова появиться |
| to construct — построить | to reconstruct — перестроить |
| to read — прочитать | to reread — перечитать |
| to sell — продать | to resell — перепродать |
| Приставка mis- (неправильно, неверно) | |
| to hear — услышать | to mishear — ослышаться, неправильно услышать |
| to lead — вести | to mislead — ввести в заблуждение |
| to quote — цитировать | to misquote — неправильно цитировать |
| to understand — понимать | to misunderstand — неправильно понимать |
| Приставки over- (сверх, чрезмерно) и under- (недо-, недостаточно) | |
| to estimate — оценивать | to overestimate — переоцениватьTo underestimate — недооценивать |
| to pay — платить | to overpay — переплатитьto underpay — недоплатить |
| Приставки pre- (перед, ранее) и post- (пост-, после), часто пишутся через дефис | |
| revolutionary — революционный | pre-revolutionary — дореволюционныйpost-revolutionary — послереволюционный |
| war — война | pre-war — довоенныйpost-war — послевоенный |
| Приставка co- (сотрудничество, общность действия), часто пишется через дефис | |
| author — автор | co-author — соавтор |
| existence — существование | co-existence — сосуществование |
| operation — операция | co-operation — кооперация, содействие |
| Приставка inter- (между, среди, взаимно) | |
| national — национальный | international — международный |
| action — действие | interaction — взаимодействие |
| town — город | intertown — междугородний |
| Приставка ex- (экс-, бывший), пишется через дефис | |
| husband — муж | ex-husband — бывший муж |
| president — президент | ex-president — экс-президент |
| Приставка sub- (суб-, под-) | |
| marine — морской | submarine — подводный |
| section — секция | subsection — подсекция |
| Приставка ultra- (ультра-, сверх-), пишется через дефис | |
| microscopic — микроскопический | ultramicroscopic — ультрамикроскопический |
| violet — фиолетовый | ultra-violet — ультрафиолетовый |
| Приставка en- (делать что-то) | |
| circle — круг | encircle — окружать (делать круг) |
| large — большой | enlarge — увеличивать (делать больше) |
| slave — раб | enslave — порабощать (делать рабом) |
- В современном английском языке есть слова с неотделяемыми приставками, в них входят приставки, перечисленные в таблице выше, но, отделив их, мы не получим самостоятельного слова. Например: reduce (сокращать), discuss (обсуждать), prepare (готовить). На самом деле эти приставки — уже и не приставки вовсе. Когда-то давно они приросли к корням слов, ныне уже неупотребительным и видоизмененным, и постепенно сами вошли в состав корня слова. К примеру, в слове prepare (готовить) pre — это уже не приставка, а часть корня слова.
- В разговорной речи в ходу слово «ex» — оно в точности соответствует нашему «бывший, бывшая» и имеет значение «бывший мужпарень, бывшая женадевушка»: My ex texted me — Мой бывший написал мне СМС.
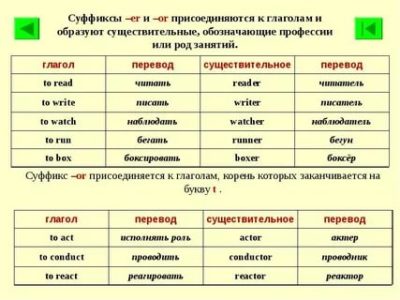
Суффиксы как способ словообразования в английском
Суффикс — это буква или группа букв, присоединяемые к концу слова для образования нового слова или для изменения грамматической функции (или части речи) слова. Например, глагол read превращается в прилагательное readable добавлением суффикса -able.
Понимание значений общих суффиксов может помочь вам понять значения новых слов, с которыми вы сталкиваетесь. В некоторых случаях написание корня или основы слова изменяется при добавлении суффикса. Например, в словах, оканчивающихся на y , которым предшествует согласная (например, существительное beauty и прилагательное ugly), y может измениться на i при добавлении суффикса (как в прилагательном beautiful и существительном ugliness).
Подробная статья о суффиксах в английском языке — «СУФФИКСЫ ПРИЛАГАТЕЛЬНЫХ В АНГЛИЙСКОМ — ПРОСТЫМ ЯЗЫКОМ». В статье не только суффиксы прилагательных, но и словообразование существительных и глаголов с помощью суффиксов.
Как образуются глаголы в английском
Глаголы в английском языке образуются с помощью суффиксов (обособленных, неотделяемых), префиксов и с помощью конверсии.
Префиксы для образования глаголов
| Prefix | Пример |
| re- | restructure, revisit, reappear, rebuild, refinance / реструктурировать, пересмотреть, появиться вновь, перестроить, рефинансировать |
| dis- | disappear, disallow, disarm, disconnect, discontinue / исчезнуть, запретить, разоружить, отсоединить, прекратить |
| over- | overbook, oversleep, overwork / переутомление, проспать, переутомиться |
| un- | unbend, uncouple, unfasten / разгибать, расцеплять, отстегивать |
| mis- | mislead, misinform, misidentify / вводить в заблуждение, дезинформировать, неверно идентифицировать |
| out- | outperform, outbid / превзойти, перекупить |
| co- | co-exist, co-operate, co-own / сосуществовать, сотрудничать, совместно владеть |
| de- | devalue, deselect / обесценить, отменить выбор |
| fore- | foreclose, foresee / лишать права выкупа, предвидеть |
| inter- | interact, intermix, interface / взаимодействовать, перемешивать, сопрягать |
| pre- | pre-expose, prejudge, pretest / предварительное разоблачение, предвосхищение, предварительное тестирование |
| sub- | subcontract, subdivide / заключать субподряд, подразделять |
| trans- | transform, transcribe, transplant / трансформировать, транскрибировать, трансплантировать |
| under- | underfund, undersell, undervalue, underdevelop / недостаточное финансирование, недопродажа, недооценка, недоразвитость |

Суффиксы для образования глаголов
Суффиксы помогают преобразовывать одну часть речи в другую. Например, The butter is very soft because of the heat. – The butter softens when it is hot. / Масло очень мягкое из-за тепла. — Масло размягчается, когда оно горячее.
Другой пример — «-ize », который превращает существительные в глаголы. We should try to synthesize all of this information so that it is easier to understand. / Мы должны попытаться синтезировать всю эту информацию, чтобы ее было легче понять.
Наиболее распространенные глагольные суффиксы и их значение:
| -en | Soften, darken, widen, weaken, strengthen / Смягчать, затемнять, расширять, ослаблять, укреплять |
| -ise/-ize | Sympathise, empathise, synthesize / Сочувствовать, сопереживать, синтезировать |
| -ate | Activate, collaborate, create / Активируйте, сотрудничайте, создавайте |
| -ify, -fy | Justify, magnify, amplify, satisfy / Активируйте, сотрудничайте, создавайте |
Как образуются наречия в английском
Наречие — это слово, которое изменяет глагол, прилагательное или другое наречие. Другими словами, наречия описывают действия или другие описательные слова.
В большинстве случаев наречие образуется путем добавления «ly» к прилагательному.
| quick / быстрый | quickly / быстро |
| slow /межденный | slowly / медленно |
| beautiful / красивый | beautifully / красиво |
| firm / твердый | firmly / твердо |
| delicate / нежный | delicately / нежно |
| abrupt / резкий | abruptly / резко |
| careful / осторожный | carefully / осторожно |
| harsh / суровый | harshly / сурово |
| cheerful / веселый | cheerfully / весело |
| sad / грустный | sadly / грустно |
Иногда прилагательное оканчивается на «у». В этих случаях замените «y» на «i» и добавьте «ly».
| easy / простой | easily / легко |
| lucky / удачливый | luckily /к счастью |
| happy / счастливый | happily / счастливо |
| angry / сердитый | angrily / сердито |
| hungry / голодный | hungrily / нетерпеливо |
С использованием суффиксов -wise, -ward, -like и пр.
Очень важно, чтобы слова образовывались правильно: помимо суффикса -ly, наречия могут образоваться и при помощи иных суффиксов: -wise, -ward, -like.
| war / война | warlike / воинственно |
| sea / море | seaward / по направлению к морю |
Некоторые слова относятся и к наречию, и к прилагательному.
far/near — далеко/близко;
early/late — рано/поздно;
high/low — высоко/низко;
little/much — мало/много.

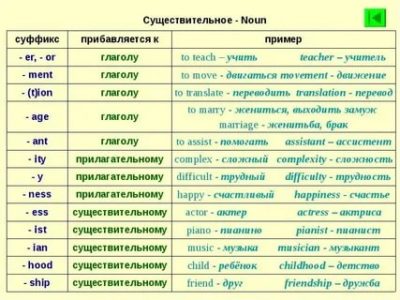
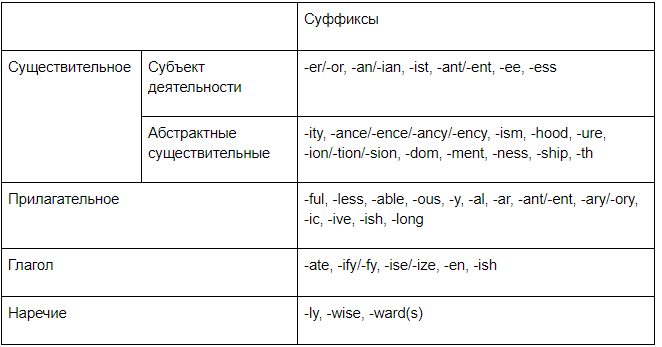
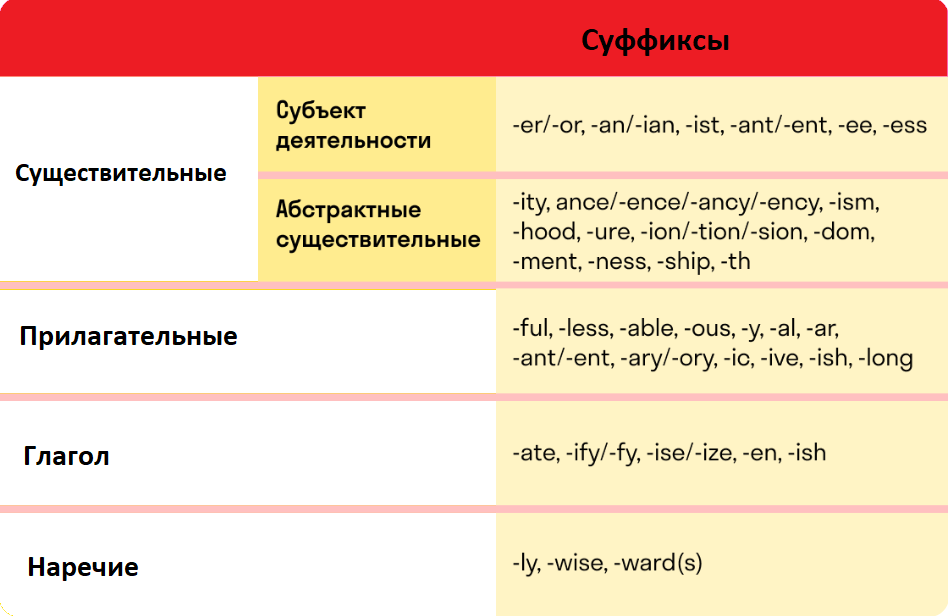
Таблица словообразования по частям речи
Для того чтобы разобраться в множестве вариантов и лучше усвоить образование слов в английском языке, я подготовила таблицу.
Объединение суффиксов и приставок: преобразование слов в английском языке
Важнейшим элементом в процессе преобразования является смысл. Слово, которое не претерпевает структурных изменений, но изменяет грамматические категории (и, следовательно, в некоторой степени значение), претерпело преобразование.
Ключевая характеристика словообразования – это его продуктивность. От одного корня можно образовать целую группу слов, добавляя разные приставки и суффиксы. Приведем несколько примеров.
- Для possible словообразование может выглядеть следующим образом: possible (возможный) — possibility (возможность) — impossibility (невозможность).
- Цепочка переходов для слова occasion: occasion (случай) — occasional (случайный) — occasionally (случайно).
- Для слова agree словообразование можно выстроить в цепочки с приставкой и без приставки: agree (соглашаться) — agreeable (приемлемый / приятный) — agreeably (приятно) — agreement (соглашение, согласие).
agree (соглашаться) — disagree (противоречить, расходиться в мнениях) — disagreeable (неприятный) — disagreeably (неприятно) — disagreement (разногласие).
Конверсия в английском
Конверсия – это процесс словообразования, при котором слово одной грамматической формы становится словом другой грамматической формы без изменения в написании или произношении.
Например, существительное email появилось в английском задолго до глагола. Еще десятилетие назад единственным возможным вариантом было сказать: send an email (отправить имейл. Здесь email — существительное), в то время как сейчас мы можем просто email people («имейлить» людям. Здесь email является глаголом).
| access /доступ | to access /получить доступ |
| to google /гуглить/ искать в Google | |
| host / хозяин | to host /для размещения |
| spear /копье | to spear /протыкать |
| torch /факел | to torch /зажечь |
| verb / глагол | to verb the truth / глаголить (говорить) истину |
Сокращение в английском
Часто аббревиатуры можно встретить в интернет переписках и в различных мессенджерах. Ими заменяют часто используемые выражения, которые слишком долго писать целыми. Например, сокращения btw — by the way, idk — I don’t know. Более подробно эту тему я разбирала в статье «АНГЛИЙСКИЙ МОЛОДЕЖНЫЙ СЛЕНГ — 100 САМЫХ ПОПУЛЯРНЫХ ФРАЗ»
Словообразование важный аспект при изучении английского языка. Он относится к процессам, посредством которых создаются новые слова. Глубоко понять английский невозможно без погружения в эту тему.
PROGRESS English School поможет вам освоить новые английские слова и выражения. Мы разработали курс «Интенсив», который всего за 1-3 месяца улучшит ваш английский на 1-3 уровня.
Very often we form many words from one and the same root, e.g. friend, friendship, friendly, unfriendly, friendless, friendliness, and befriend. A study of the formation of words is, therefore, not only interesting but also fruitful. Here is list of Noun words, Verb words and Adjective words to learn, how to form Nouns from Verbs, Verbs from Noun, Nouns from Adjectives, Adjectives from Nouns, Verbs from Adjectives, Adjectives from Verbs, Abstract Nouns from Concrete Nouns:
Formation of Nouns from Verb Words
| Verb Words | Noun Words |
|---|---|
| Abide | Abode |
| Abound | Abundance |
| Accuse | Accusation |
| Achieve | Achievement |
| Acquaint | Acquaintance |
| Add | Addition |
| Admire | Admiration |
| Admit | Admission |
| Agree | Agreement |
| Allot | Allotment |
| Amuse | Amusement |
| Apply | Application |
| Appoint | Appointment |
| Approve | Approval |
| Arrive | Arrival |
| Ascend | Ascent |
| Assure | Assurance |
| Attend | Attention |
| Attract | Attraction |
| Bear | Birth |
| Behave | Behavior |
| Believe | Belief |
| Belong | Belonging |
| Bite | Bite, bit |
| Bless | Blessings |
| Break | Breakage |
| Bury | Burial |
| Carry | Carriage |
| Choose | Choice |
| Civilizes | Civilization |
| Collect | Collection |
| Compare | Comparison |
| Compel | Compulsion |
| Compete | Competition |
| Complete | Completion |
| Conceal | Concealment |
| Confer | Conference |
| Confine | Confinement |
| Confirm | Confirmation |
| Consider | Consideration |
| Convert | Conversion |
| Cooperative | Cooperation |
| Create | Creation |
| Criticize | Criticism |
| Decide | Decision |
| Defend | Defence |
| Define | Definition |
| Deliver | Delivery |
| Deny | Denial |
| Depart | Departure |
| Describe | Description |
| Destroy | Destruction |
| Determine | Determination |
| Die | Death |
| Digest | Digestion |
| Direct | Ditch |
| Discover | Direction |
| Disturb | Disturbance |
| Divide | Division |
| Do | Deed |
| Drive | Driver |
| Educate | Education |
| Enjoy | Enjoyment |
| Enter | Entry |
| Entreat | Entreaty |
| Envelop | Envelope |
| Erect | Erection |
| Examine | Examination |
| Exceed | Excess |
| Exist | Existence |
| Expand | Expansion |
| Expect | Expectation |
| Expel | Expulsion |
| Expire | Expiry |
| Explain | Explanation |
| Express | Expression |
| Extent | Extension |
| Fail | Failure |
| Feed | Food |
| Flow | Flood, |
| Fly | Flight |
| Forgive | Forgiveness |
| Furnish | Furniture |
| Give | Gift |
| Govern | Government |
| Grieve | Grief |
| Grow | Growth |
| Hate | Hatred |
| Hold | Hilt, Hold |
| Imagine | Imagination |
| Increase | Increment |
| Inherit | Inheritance |
| Injure | Injury |
| Inquire | Inquiry |
| Inspect | Inspection |
| Inspire | Inspiration |
| Intend | Intention |
| Introduce | Introduction |
| Investigate | Investigation |
| Invite | Invitation |
| Irrigate | Irrigation |
| Join | Joint |
| Judge | Judge, Justice |
| Know | Knowledge |
| Laugh | Laughter |
| Learn | Learning |
| Lend | Loan |
| Lose | Loss |
| Mix | Mixture |
| Move | Movement |
| Multiply | Multiplication |
| Obey | Obedience |
| Object | Objection |
| Oblige | Obligation |
| Occupy | Occupation |
| Offend | Offence |
| Omit | Omission |
| Oppose | Opposition |
| Pass | Passage |
| Pay | Payment |
| Perform | Performance |
| Please | Pleasure |
| Populate | Population |
| Pray | Prayer |
| Prefer | Preference |
| Prepare | Preparation |
| Preserve | Preservation |
| Press | Pressure |
| Proclaim | Proclamation |
| Produce | Production |
| Project | Protection |
| Prophesy | Prophecy |
| Propose | Proposal |
| Prosper | Prosperity |
| Prove | Proof |
| Provide | Provision |
| Qualify | Qualification |
| Rebel | Rebellion |
| Receive | Receipt |
| Recite | Recitation |
| Recommend | Recommendation |
| Recover | Recovery |
| Reduce | Reduction |
| Refer | Reference |
| Refresh | Refreshment |
| Refuse | Refusal |
| Relieve | Relief |
| Remain | Remainder |
| Remove | Removal |
| Repeat | Repetition |
| Repent | Repentance |
| Revolve | Revolution |
| Satisfy | Satisfaction |
| See | Sight |
| Sell | Sale |
| Serve | Service |
| Settle | Settlement |
| Sew | Shock |
| Shake | Seed |
| Sing | Song |
| Sit | Tale |
| Slay | Seat |
| Solve | Slaughter |
| Speak | Solution |
| Spell | Speech, Speaker |
| Steal | Spelling |
| Strike | Stealth |
| Subtract | Stroke |
| Succeed | Subtraction |
| Supervise | Success |
| Tell | Supervision |
| Thieve | Theft |
| Think | Thought |
| Translate | Translation |
| Treat | Treatment |
| Try | Trial |
| Unite | Unity, Union |
| Vacate | Vacancy |
| Vary | Variety |
| Wed | Wedding |
| Weigh | Weight |
| Withdraw | Withdraw |
Formation of Verbs from Noun Words
| Noun Words | Verb Words |
|---|---|
| Advice | Advise |
| Beauty | Beautify |
| Blood | Bleed |
| Circle | Encircle |
| Class | Classify |
| Colony | Colonies |
| Courage | Encourager |
| Custom | Accustom |
| Danger | Endanger |
| Depth | Deepen |
| Difference | Differ |
| Fame | Defame |
| Force | Enforce |
| Freight | Frighten |
| Friend | Befriend |
| Glass | Glaze |
| Glory | Glorify |
| Gold | Gild |
| Grass | Graze |
| Hand | Handle |
| Haste | Hasten |
| Height | Heighten |
| Heir | Inherit |
| Horror | Horrify |
| Joy | Enjoy |
| Knot | Knit |
| Length | Lengthen |
| Life | Live |
| Magnet | Magnetise |
| Memory | Momorise |
| Nation | Nationalize |
| Necessity | Necessitate |
| Office | Officiate |
| Peril | Imperil |
| Power | Empower |
| Practice | Practise |
| Publicity | Publish |
| Radio | Radiate |
| Slave | Enslave |
| Society | Associate |
| Spark | Sparkle |
| Strength | Strengthen |
| Sympathy | Sympathise |
| System | Systematize |
| Table | Tabulate |
| Television | Televise |
| Terror | Terrify |
| Vapour | Evaporate |
| Vigour | Invigorate |
Formation of Nouns from Adjective Words
| Adjective Words | Noun Words |
|---|---|
| Able | Ability |
| Absent | Absence |
| Accurate | Accuracy |
| Active | Activity |
| Brave | Bravery |
| Brutal | Brutality |
| Busy | Business |
| Civil | Civility |
| Coward | Cowardice |
| Decent | Decency |
| Difficult | Difficulty |
| Diligent | Diligence |
| Dry | Drought |
| Durable | Durability |
| Efficient | Efficiency |
| Foolish | Folly |
| Frank | Frankness |
| Free | Freedom |
| Lame | Lameness |
| Lazy | Laziness |
| Loyal | Loyalty |
| Merry | Merriment |
| Moist | Moisture |
| Moral | Morality |
| Mortal | Mortality |
| Noble | Nobility |
| Neutral | Neutrality |
| Novel | Novelty |
| One | Oneness |
| Patient | Patience |
| Perfect | Perfection |
| Pious | Piety |
| Polite | Politeness |
| Popular | Popularity |
| Poor | Poverty |
| Possible | Possibility |
| Present | Presence |
| Prior | Priority |
| Private | Privacy |
| Proud | Pride |
| Prudent | Prudence |
| Punctual | Punctuality |
| Frugal | Frugality |
| Gallant | Gallantry |
| Gay | Gaiety |
| Generous | Generosity |
| Great | Greatness |
| Happy | Happiness |
| Holy | Holiness |
| Honest | Honesty |
| Hospitable | Hospitality |
| Hot | Heat |
| Human | Humanity |
| Important | Importance |
| Inferior | Inferiority |
| Innocent | Innocence |
| Insane | Insanity |
| Jealous | Jealousy |
| Pure | Purity |
| Quick | Quickness |
| Rapid | Rapidity |
| Rival | Rivalry |
| Sacred | Sacredness |
| Safe | Safety |
| Scarce | Scarcity |
| Secret | Secrecy |
| Senior | Seniority |
| Sever | Severity |
| Short | Shortage |
| Silent | Silence |
| Slow | Slowness |
| Solitary | Solitude |
| Special | Specialty |
| Splendid | Splendor |
| Supreme | Supremacy |
| Sure | Surety |
| TRUE | Truth |
| Uniform | Uniformity |
| Vain | Vanity |
| Weak | Weakness |
| Wise | Wisdom |
| Young | Youth |
Formation of Adjective Words from Noun Words
| Noun Words | Adjective Words |
|---|---|
| Accident | Accidental |
| Advantage | Advantageous |
| Adventure | Adventurous |
| Advice | Advisable |
| Affection | Affectionate |
| Air | Airy |
| America | American |
| Angel | Angelic |
| Anger | Angry |
| Arabia | Arabian |
| Asia | Asiatic |
| Atmosphere | Atmospheric |
| Autumn | Autumnal |
| Beauty | Beautiful |
| Blood | Bloody |
| Body | Bodily |
| Book | Bookish |
| Boy | Boyish |
| Brass | Brazen |
| Brother | Brotherly |
| Brute | Brutal |
| Center | Central |
| Ceremony | Ceremonial |
| Cheer | Cheerful |
| Child | Childish |
| China | Chinese |
| Circle | Circular |
| Clay | Clayey |
| Colony | Colonial |
| Comfort | Comfortable |
| Contempt | Contemptible |
| Crime | Criminal |
| Custom | Customary |
| Danger | Dangerous |
| Day | Daily |
| Earth | Earthen |
| Ease | Easy |
| East | Eastern |
| Economy | Economical |
| Emperor | Imperial |
| Enemy | Inimical |
| England | English |
| Essence | Essential |
| Example | Exemplary |
| Expense | Expensive |
| Fable | Fabulous |
| Faith | Faithful |
| Fame | Famous |
| Fate | Fateful |
| Father | Fatherly |
| Fault | Faulty |
| Favour | Faveourable |
| Fever | Feverish |
| Fiction | Fictitious |
| Fire | Fiery |
| Flower | Flowery |
| Fog | Foggy |
| Fool | Foolish |
| Force | Forceful |
| France | French |
| Friend | Friendly |
| Frost | Frosty |
| Fruit | Fruitful |
| Fury | Furious |
| Gas | Gaseous |
| Germany | German |
| Ghost | Ghostly |
| Gift | Gifted |
| Glass | Classy |
| Gloom | Gloomy |
| Glory | Glorious |
| God | Godly |
| Gold | Golden |
| Grass | Grassy |
| Greed | Greedy |
| Habit | Habitual |
| Hair | Hairy |
| Hand | Handy |
| Harm | Harmful |
| Harmony | Harmonious |
| Haste | Hasty |
| Haze | Hazy |
| Heart | Hearty |
| Heaven | Heavenly |
| Heredity | Hereditary |
| Hero | Heroic |
| Hill | Hilly |
| Holland | Dutch |
| Home | Homely |
| Honour | Honourable |
| Horror | Horrible |
| Hour | Hourly |
| Hunger | Hungry |
| Ice | Icy |
| Ignorance | Ignorant |
| India | Indian |
| Industry | Industrial |
| Japan | Japanese |
| Joke | Jocular |
| Joy | Joyful |
| King | Kingly |
| Labour | Laborious |
| Land | Landed |
| Language | Linguistic |
| Law | Lawful |
| Life | Lifelike |
| Limit | Limited |
| Lord | Lordly |
| Love | Lovely |
| Machine | Mechanical |
| Man | Manly |
| Medicine | Medicinal |
| Memory | Memorable |
| Merchant | Mercantile |
| Mercy | Merciful |
| Merit | Meritorious |
| Might | Mighty |
| Military | Martial |
| Milk | Milky |
| Miracle | Miraculous |
| Moment | Momentary |
| Money | Monetary |
| Month | Monthly |
| Mother | Motherly |
| Mystery | Mysterious |
| Nation | National |
| Nature | Natural |
| Navy | Naval |
| Need | Needy |
| Neighbor | Nieghbouring |
| Notice | Noticeable |
| Number | Numeral |
| Ocean | Oceanic |
| Office | Official |
| Oil | Oily |
| Origin | Original |
| Ornament | Ornamental |
| Pakistan | Pakistani |
| Palace | Palatial |
| Passion | Passionate |
| Peace | Peaceful |
| Persia | Persian |
| Picture | Pictorial |
| Play | Playful |
| Population | Populous |
| Practice | Practical |
| Price | Percious |
| Pride | Proud |
| Profit | Profitable |
| Quarrel | Quarrelsome |
| Question | Questionable |
| Red | Reddish |
| Ruin | Ruinous |
| Russia | Russian |
| Sand | Sandy |
| Science | Scientific |
| Sense | Sensible |
| Silk | Silken |
| Silver | Silvery |
| Slave | Slavish |
| Smoke | Smoky |
| Society | Social |
| Space | Spacious |
| Spain | Spanish |
| Spark | Sparking |
| Sponge | Spongy |
| Star | Starry |
| Stone | Stony |
| Storm | Stormy |
| Study | Studious |
| Success | Successful |
| Sun | Sunny |
| Sympathy | Sympathetic |
| System | Systematic |
| Talk | Talkative |
| Taste | Tasty |
| Terror | Terrible |
| Thirst | Thirsty |
| Thought | Thoughtful |
| Tribe | Tribal |
| Trouble | Troublesome |
| Turkey | Turkish |
| Type | Typical |
| Use | Useful |
| Value | Valuable |
| Velvet | Velvety |
| Vice | Vicious |
| Vigour | Vigorous |
| Virtue | Virtuous |
| Voice | Vocal |
| War | Warlike |
| Water | Watery |
| Will | Willing |
| Wind | Wincy |
| Winter | Wintry |
| Woman | Womanly |
| Wood | Wooden |
| Wool | Woolen |
| World | Worldly |
| Worth | Worthy |
| Wretch | Wretched |
| Year | Yearly |
| Youth | Youthful |
| Zeal | Zealous |
Formation of Verbs from Adjective Words
| Adjective Words | Verb Words |
|---|---|
| Able | Enable |
| Base | Debase |
| Bitter | Embitter |
| Black | Blacken |
| Board | Broaden |
| Brief | Abbreviate |
| Certain | Ascertain |
| Cheap | Cheapen |
| Civil | Civilizes |
| Clean | Cleanse |
| Clear | Clarify |
| Dark | Darken |
| Dear | Endear |
| Deep | Deepen |
| Dense | Condense |
| Different | Differentiate |
| Double | Duplicate |
| Equal | Equalize |
| False | Falsify |
| Familiar | Familiarize |
| Fast | Fasten |
| Fertile | Fertilise |
| Fine | Refine |
| Flat | Flatten |
| General | Generalize |
| Glad | Gladden |
| Hard | Harden |
| Humble | Humiliate |
| Just | Justify |
| Large | Enlarge |
| Little | Belittle |
| Local | Localize |
| Long | Lengthen |
| Low | Lower |
| Mad | Madden |
| Moist | Moisten |
| New | Renew |
| Noble | Ennoble |
| Poor | Impoverish |
| Popular | Popularize |
| Public | Publish |
| Pure | Purify |
| Quick | Quicken |
| Real | Realize |
| Red | Redden |
| Rich | Enrich |
| Right | Rectify |
| Sad | Sadden |
| Safe | Save |
| Satisfactory | Satisfy |
| Sharp | Sharpen |
| Short | Shorten |
| Sick | Sicken |
| Soft | Soften |
| Special | Specialize |
| Specific | Specify |
| Stable | Stabilize |
| Strong | Strengthen |
| Sure | Assure |
| Sweet | Sweeten |
| Thick | Thicken |
| Weak | Weaken |
| White | Whiten |
| wide | Widen |
Formation of Adjective Words from Verbs
| Verb Words | Adjective Words |
|---|---|
| Abound | Abundant |
| Accomplish | Accomplished |
| Act | Active |
| Admit | Admissible |
| Advise | Advisable |
| Affect | Effective |
| Apologise | Apologetic |
| Authorize | Authoritative |
| Beautify | Beautiful |
| Believe | Believable |
| Bless | Blessed |
| Break | Breakable |
| Compel | Compulsory |
| Decide | Decisive |
| Die | Deadly |
| Exceed | Excessive |
| Excel | Excellent |
| Favour | Favourable |
| Fill | Full |
| Furnish | Furnished |
| Grieve | Grievous |
| Heal | Healthy |
| Ignore | Ignorant |
| Labour | Laboriorus |
| Learn | Learned |
| Limp | Lame |
| Love | Lovely |
| Marry | Marriageable |
| Move | Movable |
| Need | Needy |
| Note | Notable |
| Obey | Obedient |
| Object | Objectionable |
| Offend | Offensive |
| Oppose | Opposite |
| Please | Pleasing |
| Project | Protective |
| Quarrel | Quarrelsome |
| Rely | Reliable |
| Rot | Rotten |
| Ruin | Ruinous |
| Serve | Serviceable |
| Shake | Shaky |
| Steal | Stealthy |
| Strike | Striking |
| Study | Studious |
| Trace | Traceable |
| Urge | Urgent |
| Use | Useful |
| Vacate | Vacant |
| Vary | Various |
| weigh | Weighty |
Formation of Abstract Nouns from Concrete Nouns
| Concrete Nouns | Abstract Nouns |
|---|---|
| Agent | Agency |
| Baby | Babyhood |
| Boy | Boyhood |
| Broker | Brokerage |
| Brother | Brotherhood |
| Cart | Cartage |
| Chairman | Chairmanship |
| Chemist | Chemistry |
| Child | Childhood |
| Christian | Christianity |
| Coin | Coinage |
| Collector | Collection |
| Cook | Cookery |
| Coward | Cowardice |
| Creature | Creation |
| Dictator | Dictatorship |
| Enemy | Enmity |
| Father | Fatherhood |
| Favourite | Favouritism |
| Friend | Friendship |
| Hero | Heroism |
| Infant | Infancy |
| Judge | Justice |
| King | Kingship |
| Man | Manhood |
| Martyr | Martyrdom |
| Member | Membership |
| Monarch | Monarchy |
| Mother | Motherhood |
| Neighbor | Neighborhood |
| Owner | Ownership |
| Patriot | Patriotism |
| Patron | Patronage |
| Pilgrim | Pilgrimage |
| Regent | Regency |
| Servant | Service |
| Slave | Slavery |
| Speaker | Speech |
| Stateman | Statesmanship |
| Young | Youth |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Word formation. Noun suffixes in English (grade 9)
This is a lesson from the cycle «Word formation in English» and in it we will consider the common noun suffixes: -er / or, -tion, -ing, -ness, -ence / ance (5). Exercises on word formation of a noun will help you understand how nouns are formed in English using suffixes, as well as prepare for English exams in the form of the OGE and USE.
for posting on other Internet resources is prohibited. EnglishInn.ru.
Basic noun suffixes in English (grade 9)
Remember 5 main noun suffixes.
- er / or (worker)
- tion (informaproduction)
- ing (reading)
- ness (happyness)
- ence / ance (difference)
Next, let’s dwell in more detail on each of them.
1. Suffixes of nouns formed from a verb
- -er / or (doer suffix) dance — dancer work — workercollect — collector
invent — inventor
- -tion (process suffix) collect — collection
invent — invention
- -ingsuffer — suffering warn — warning
mean — meaning
Remember three suffixes -er (-or), -tion, -ing, with the help of which nouns are formed from the verb.
2. Suffixes of nouns formed from an adjective
- -nessill — illness
kind — kindness
- -ance / -ence (corresponding adjectives have suffixes: -ant / -ent) important — importance
different — difference
Remember two suffixes: -ness, -ence (ance), with the help of which nouns are formed from an adjective.
Suffixes of nouns in English. Exercises
Suffixes -ness & -tion Are the most common noun suffixes.
Exercise 1. Suffix -ness. Translate these nouns and indicate the adjectives from which they are derived.
foolishness, happiness, seriousness, illness, readiness, richness, strangeness, carelessness, whiteness, cleverness, greatness, brightness
Note.
Source: http://englishinn.ru/slovoobrazovanie-suffiksyi-sushhestvitelnyih-v-angliy.html
Formation of verbs in English
Download this online tutorial in PDF
Verbs in English are formed using suffixes (detached, non-separable), prefixes and using conversion.
Formation of verbs using separate suffixes
New verbs are often formed from existing ones using separate suffixes. The most common single suffixes are: back, away, down, in, off, on, out, up, over… Separated suffixes are usually added to monosyllabic verb stems. Matching in form with adverbs, individual suffixes in some cases retain spatial shades of meaning, slightly changing the meaning of the original stem:
to go (to go) — to go away (to leave),
to come (to come) — to come back (to return),
to look (look) — to look up (look up)
In other cases, adding a separate suffix creates a verb with a completely new meaning:
to give (to give) — to give up (to give up some activity), to get (to receive) — to get off (get off the vehicle), to go (to go) — to go on (to continue doing something).
Examples of verbs with separate suffixes:
away: to go away to leave; to run away escape; to throw away to throw; to do away with smth. destroy, liquidate something; to take away
back: to come / go back — return
down: to sit down to sit down; to settle down to settle; to come down to go down; to climb down to get down, get off; to slow down to slow down (The vehicle slowed down at the next turn) to write down to write
in: to come in to enter (Come in, please!) to get in to enter the transport; to hand in hand in, hand over (Hand in your papers!) to run in to run in; to drop in visit
off: to bite off bite off; to cut off cut off, chop off; to take off take off (Take off your cap and boots) to switch off off (Switch off the lights, it isn’t dark.) to get off off the vehicle (This is where I usually get off).
on: to call on to attend (He often called on Helen when she was ill.) to go on to continue (Go on writing!) to carry on to continue some work; to put on put on, put on; to switch on turn on, turn on the light (Switch on the lights, it’s getting dark.) to get on live (How is Mike getting on?)
out: to get out to go out (Get out! Go away!) to run out to run out; to take out take out; to find out find out; to carry out execute (We should carry out our research.) to cut out cut; to make out understand, understand (I can’t make anything out).
over: to come over to come (Hey, Kate, come over to my place!) to talk over to discuss; to think over to think (We should think it over).
up: to come up to come; to drive up to drive up by car; to cheer up to cheer up, to cheer up (Cheer up, Jack! Don’t be sad, Jack!) to get up to get out of bed; to look up to look up; to shut up to shut up (Shut up, Terry!) to make up invent, compose; to wake up wake up
Formation of verbs using inseparable suffixes
Of the suffixes of the usual type for the formation of verbs, the suffix -ize is often used, which forms verbs with an abstract meaning: to realize, to privatize, to mobilize, to organize.
There are also verbs formed from adjectives using the -en suffix: broad (wide) — to broaden (expand) to lengthen, to widen, to redden, to darken.
Forming verbs using prefixes
With the help of prefixes, verbs are usually formed from the verbs themselves. Frequent verb prefixes are as follows:
The prefix ge-, which means repeated action:
reread
rebuild
rewrite (write again, rewrite)
Verbs with other meanings also have this prefix: to remember, to respect, to recover, etc.
The prefix dis-, which means an action opposite to that expressed by the derivative verb stem:
to disagree, to disappear, to disapprove, to discover, to dis.
The prefix mis-, which means an action performed by an error: to misunderstand (misunderstand), to mispronounce (mispronounce), to misbehave (misbehave), to mistake (make a mistake, mistakenly consider someone else).
Formation of verbs using conversion
Thus, verbs are formed mainly from nouns:
dust — to dust
a bomb (bomb) — to bomb (bomb)
water — to water
a hand (hand) — to hand (hand)
a head — to head
a finger (finger) — to finger (press with a finger)
winter (winter) — to winter (winter)
The number of verbs formed from nouns by conversion is very large.
Source: http://englishgu.ru/obrazovanie-glagolov-v-angliyskom-yazyike/
Suffixes in English: 40 Most Common
Hey.
Source: https://corp.lingualeo.com/ru/2016/11/16/suffiksyi-v-angliyskom-yazyike/
Methods of forming nouns in English
How to replenish vocabulary more than 3 times without memorizing? Adopt this method and — voila! Vocabulary enlarged before our eyes.
This method is word formation. How does this work for nouns?
Briefly — about the main thing Usually the topic is studied indefinitely. There is a more effective method: covering the entire «puzzle» at a time. Seeing a clear picture, you can easily refine the little things without negativity.
So, the formation of nouns in English assumes skills:
- convert a noun from a verb and vice versa;
- use affixes;
- put a different emphasis;
- replace the consonant at the root;
- form compound words.
Many do not assume how many words they ALREADY know. They simply do not know how to use this wealth competently.
Having learned 5 skills, you can refer to the dictionary just to check it.
1. Conversion
Nouns in English are related to verbs in an interesting way: they can be the same word. This method is called conversion… This is the first skill. Using it, it is easy to guess about the translation of 60% of English words. Moreover, verbs can be converted not only into nouns, but also into adjectives.
The examples below will help you understand the phenomenon of conversion.
Example: love = to love / love.
Verb convergent word noun
| dream, dream | dream | dream |
| call | name | name, title |
| lift up | lift | lift, lift |
| to send | ||
| milk | milk | milk |
| pour | water | water |
| mind | mind | mind, opinion |
Many are embarrassed that in translation into Russian, both words are not the same root. But the language is different.
It’s funny, but the British created it for themselves! For native speakers, these are absolutely identical words: to milk — milk (milk), to name — name (name — name).
2. Affixation
This «scary» word means suffixes plus prefixes. All prefixes are of two types: negative and significant.
Acquaintance with negative ones has already taken place through borrowing: dysfunction, antispam, deflation. Significant — different in meaning, but amenable to logic.
Prefixes
2 groups of prefixes will allow you to find the meaning of a word by context without a dictionary. If you learn the meaning of each prefix separately, the brain starts to panic, it looks for the right algorithm. It takes time, and speech slows down.
And most importantly, the desire to study the language at all disappears.
Example: everyone knows the prefixes «dis-«, «de-«, «anti-«. But for some reason they do not notice them in English!
An important detail: most negative prefixes of nouns work with verbs.
Negative prefixes
| Console | Examples |
| anti- | Antistress, antipode, antispam. |
| dis- | Disharmony, disqualification. |
| de- | Depiction, departure. |
| mis- | Misfortune, misunderstanding. |
| as- | Sedition, separation. |
| not- | Nonconformist, nonstop. |
Significant prefixes
Most are present in their native language, in borrowings.
You can check the skill of forming nouns in English using a dictionary, but after an independent attempt.
For example, form words: disqualification, pseudoscience, professional, extraordinary, hyperactive, and others. Such training is enjoyable and helps to understand the language.
| Attachment type | Examples of prefixes |
| involvement | Anti-, co-, con-, contra-, vice-. |
| censures |
Source: https://www.study.ru/courses/elementary/obrazovanie-sushchestvitelnyh
Suffixes in English — Learn All
There can be confusion between suffixes and endings in English (both are often called word endings), besides, English terminology in this matter is slightly different from Russian. Therefore, let’s start with the basic concepts.
The ending is an inflectional morpheme. It changes the form of a word, but not its meaning, and at the same time carries a grammatical load:
- pencil — pencils (ending indicates plural)
- work — worked (the ending indicates the elapsed time)
The suffix, in turn, is a derivational morpheme. Suffixes in English create new words, either by changing the meaning of the original one, or by converting one part of speech to another:
- red — reddish (red — reddish)
- teach — teacher (teach — teacher)
There are very few endings in English — these are -s (-es), -ed and -ing. There are a lot of suffixes in English. In this article, we will consider only the most common ones.
Profession and occupation suffixes (-er, -ent, -ess)
The -er suffix is perhaps the most common and productive for «doers.» With it, you can form a noun from almost any verb.
- write> writer — write> writer
- bake> baker — oven> baker
- paint> painter — paint> painter
Most modern words denoting the performer of an action are formed precisely with his help. This also applies to inanimate objects.
- printer — printer
- scanner — scanner
Many words that come from French and Latin have the -or suffix:
- doctor — doctor
- tailor — tailor
- actor — actor
The English suffix -ist often denotes an activity related to science and medicine:
- scientist — scientist
- dentist — dentist
- biologist — biologist
It also denotes an adherent of any views and beliefs:
- pacifist — pacifist
- communist — communist
- realist — realist
Other suffixes in English of words of Latin and Greek origin:
Suffix -ian:
- musician — musician
- librarian — librarian
- mathematician — mathematician
Suffix -ent:
- student — student
- resident — resident, resident
- agent — agent
Suffix -ant:
- informant — informant
- assistant — assistant
- confidant — confidant
The -ess suffix is one of the few «feminine» suffixes in English:
- waitress — waitress
- actress — actress
- princess — princess
Process, action, phenomenon suffixes (-ment, -ion, -ism)
The suffix in English -ment is needed when forming verbal nouns and means an action or its result:
- movement — movement
- entertainment — entertainment
- concealment — concealment
The -ion suffix also denotes an action, process, or result of that process:
- revolution — revolution
- isolation — isolation
- restriction — restriction
The suffix -ism denotes a system of views, beliefs:
- racism — racism
- communism — communism
- pacifism — pacifism
State, quality, property suffixes (-ance / -ence, -dom, -hood, -ity, -ness, -ship, -th)
The -ance / -ence suffix in a noun usually matches the -ant / -ent suffix in an adjective:
- different — difference
- important — importance (important — importance)
- independent — independence
The suffixes in English -hood and -ship mean a person’s condition associated with his age, social relations, and sometimes activity; or a group of people united by this state.
- childhood — childhood
- motherhood — motherhood
- priesthood — clergy
- friendship — friendship
- internship — internship, internship
The suffix -dom means states and properties of a broader meaning:
- freedom — freedom
- wisdom — wisdom
- martyrdom — Martyrdom
The suffix in English -ness means possession of some quality and serves to form nouns from adjectives:
- kindness — kindness
- usefulness — usefulness
- vastness — vastness
The -th suffix more often means physical properties:
- strength — strength
- length — length
- warmth — warm
The suffix -ity means property, quality, and is common for words of Latin origin:
- brevity — brevity
- velocity — speed
- purity — purity
Adjective suffixes
The suffix -ful in English means possession of quality (and is related to the adjective full — «full»):
- beautiful — beautiful
- useful — useful
The -less suffix is opposite in meaning to the previous one and means lack of quality:
- careless — carefree
- harmless — harmless
The suffix -able, -ible characterizes the property or accessibility for any action:
- edible — edible
- portable — portable, portable
- admirable — admirable
The suffixes -ic and -al mean «related, related»:
- heroic — heroic
- mythic — mythical
- cultural — cultural
- musical — musical
The -ous suffix also carries a characteristic:
- dangerous — dangerous
- nutritious — nutritious
The English suffix -ish has several meanings:
expresses similarity (in terms of appearance, behavior)
- girlish — girlish
- childich — childish, childish
- foolish — stupid
weakens the meaning of an adjective
- reddish — reddish
- narrowish — narrowish
means nationality, language or country
- English — English
- Swedish — Swedish
The suffix -ive means possession of a property, the ability:
- attractive — attractive
- sedative — sedative
The English suffix -y is used to form many simple adjectives:
- rainy — rainy
- dirty — dirty
- sunny — sunny
Vertex suffixes
Verb suffixes are not so diverse and almost all have the meaning of «doing something» or «becoming something.»
Suffix -ate
- motivate — to motivate
- activate — activate
Suffix -en
- lengthen — lengthen
- strengthen — strengthen
Suffix -ify
- verify — confirm
- clarify — to clarify
Suffix -ize, -ise
- visualize — render
- neutralize — neutralize
Adverb suffix
Adverbs are formed with just one suffix in English -ly:
- loudly — loudly
- beautifully — beautifully
- politely — politely
We read further:
10 ways to tell an adjective from an adverb in English
What are the types of sentences in English
5 simple rules for word order in English
Adverb, know your place!
Source: https://skyeng.ru/articles/chto-vy-ne-znali-o-suffiksah-v-anglijskom
Plural in English — online lessons for beginners
Read the entire lesson and do a short, easy listening exercise (a translation is shown after each assignment). In the second block of the exercise, you will be asked to write the same phrases under dictation, so listen and read carefully the phrases that you compose in the first block.
Start exercise
In most cases, the plural in English is formed very simply — the ending “-s» or «-Is«, which read differently depending on the consonant in front of it — voiced or voiceless:
For words ending in «s, ss, ch, tch, x» (hissing or whistling sounds), the ending «-Is«, Which reads loudly [of].
In a side-by-side exercise (see the main exercise below), an English noun is shown; to see it in the plural, just click on the word.
In the lesson exercise, beginners will be able to compose phrases on their own — click on the English words to translate the phrase proposed in Russian. A few words that we will meet in the exercise:
- to want [that uOnt] — to want (the verb following the verb «to want» requires the use of a particle «to«- I want to help you — I want to help you) to have [tu hEv] — to have one [uan] — one
Features of the use of plural nouns
Grammatical addition: in English, the plural can be in «countable nouns«. There are a number of nouns that are used only in the singular (we emphasize, in English; the use of words in Russian and English can both coincide and diverge, but we need to get out of the habit of making comparisons with the native language, and plunge into the logic of English):
- money [mani] — money hair [hea] — hair advice [adv] — advice
A number of other nouns are used only in the plural form:
- glasses [glAsiz] — glassesgoods [goodz] — goods trousers [trauzez] — trousers people [people] — people (singular, but implies the plural)
A number of English nouns form the plural in a special way:
- man — men [men] — [men] — man / men, people woman — women [umen] — [wiming] — woman / women (we prepare the organs of speech for pronouncing [y], but immediately pronounce the next sound) child — children [child] — [chIldren] — child / children
A separate lesson will be devoted to these features of the plural in English; now it is important for beginners to remember the basic rule for the formation of the plural.
Plural adjectives
Adjectives in english do not change in the plural and do not change by gender:
- good guy [good boy] — good boy good boys [good boys] — good boys good girl [good girl] — good girl good girls [good girls] — good girls
A noun before another noun can act as an adjective; in this case, it is not used in the plural:
- life situations — life situations
▲ Start online exercise
Next: Articles A, AN, THE and a bit of TO. • Tutor: preparation for the exam and exam, passing international exams.
• «My day» / «Working day» / «My day off»
• TEST elementary / intermediate
Source: http://english.prolingvo.info/beginner/plural.php
Formation of adjectives in English
The formation of adjectives in English is a rather important and interesting topic. Of course, you can speak English at a fairly high level without going into such details, but such information will not be superfluous.
As in Russian, English adjectives can be derived from other parts of speech. These are usually verbs and nouns. Adjectives are formed using suffixes and prefixes. So, first things first.
Formation of English adjectives using prefixes
Prefixes, or prefixes, are added at the beginning of a word and change its meaning. Usually they change the meaning of the adjective to the opposite, negative. A few examples:
- un— (unlucky)
- in— (invisible)
- dis— (discontent)
- il— (illegal)
- ir— (irrational)
- im— (immovable)
There are several prefixes that change the meaning of a word, but without a negative meaning:
- pre— (pre-emptive)
- hyper— (hypertensive, hyperactive)
Formation of English adjectives using suffixes
There are a lot of varieties of English adjectives formed in the suffix way. As an example, there is a picture with the main suffixes, as well as a few examples of words.
- ful (wonderful, graceful)
- less (pointless, careless)
- able (vulnerable, tolerable)
- ible (terrible, permissible)
- ant (pleasant, hesitant)
- ent (different, patient)
- ic (scientific, iconic)
- ive (active, impressive)
- y (angry, dirty)
- ing (interesting, worrying)
- ed (confused, excited)
- al (general, typical)
- (i) an (Victorian, American)
- You reprise the theme of the (gorgeous, famous)
- ish (childish, Irish)
There is also a classification of English adjectives according to the parts of speech from which they are derived. Adjectives can be formed from nouns, verbs, as well as from other adjectives using various suffixes and prefixes, examples of which have already been considered. The very form of the word may also change. For example, the adjective long is formed from the noun length with a change at the root of the word.
Source: https://english-bird.ru/forming-adjectives/
Formation of nouns in English: suffixes, prefixes, etc.
To do it right assignments 26 — 31 from section «Grammar and Vocabulary» on the Unified State Exam in English, You need to know the most used prefixes and suffixes of nouns.
I want to say right away that the article will be long, so be patient and read it to the end.
Helpful advice:
Be sure to learn all the words from this article, as they are selected from real assignments of past years, which were proposed for implementation on the exam in English.
Work separately with each block, spelling out the words, even if they seem familiar to you.
Remember that in assignments 26 — 31 along with your ability to form new words using various affixes, your spelling skills are assessed!
Education model: Verb + er = Noun
When adding a suffix — er to a verb or noun, a noun is formed, denoting a profession, occupation of a person, as well as the names of some objects:
To write — writer, to sing — singer, to drive — driver, to teach — teacher, to examine — examiner, to learn — learner, to build — builder, to loaf — loafer (quitter)
Trumpet — trumpeter (trumpeter), bank — banker (banker), finance — financier (financier)
To contain — container (container), to dust — duster (duster), to grate — grater (grater), to mix — mixer (mixer), to shake — shaker (shaker), to blend — blender (blender), to open — opener (can-opener)
Mince (minced meat) — mincer (meat grinder)
Exception: to lie (lie) — LIAR (liar / liar)
Education model:Verb + or = noun
When adding a suffix — or a noun denoting a profession, occupation of a person is formed to the verb (these are mainly nouns of Latin and French origin):
To act — actor (actor), to advise — advisor / —er (advisor, consultant), to animate — animator (animator), to conduct — conductor (conductor), to create — creator (creator), to decorate — decorator (decorator, painter, wallpaper passer), to direct — director (director, director), to educate — educator (teacher), to illustrate — illustrator (illustrator), to invent — inventor (inventor), to invest — investor (investor, contributor), to instruct — instructor (instructor), to translate — translator (translator), to sail — sailor (sailor), to visit — visitor (visitor), to conquer — coqueror (conqueror)
Here are some more nouns with the suffix —or, to remember:
doctor, professionalor, sculptureor, sponsor, ancestor (ancestor), tutor, mentor (mentor)
Education model: Noun + ist = Noun
When adding a suffix -ist a noun is formed to the noun, denoting a profession, occupation of a person:
art — art (artist), cello — cell (cellist), chemistry — chem (chemist, pharmacist), drama — dramat (playwright), ecology — ecolog (ecologist), economics — econom (economist), geology — geolog (geologist), genetics — genetic (geneticist), guitar — guitar (guitarist), journal — journal (journalist), medal — medal (medalist), meteorology — meteorolog (meteorologist), optimism — optim
Source: https://crownenglishclub.ru/dlya-nachinayushhih/obrazovanie-sushhestvitelnyh-v-anglijskom-yazyke-suffiksy-pristavki-i-dr.html
Formation of words in English in examples
As in our native Russian, in other languages, words are also added, for example, with suffixes, as a result of which a new word is obtained. Knowledge of how words are formed in English opens up quite a lot to the student. Having mastered some simple rules and looking at a few examples, you will soon learn to intuitively “create” new phrases as you speak. Fortunately, this is easier in English than in Russian.
Nouns are the basis for word formation. It is from them that, as a rule, comes the formation of verbs, adjectives, as well as their various degrees. It is worth noting that English words are not inflected for cases, only prepositions are used for this.
There are many types of word formation. However, they are not difficult to learn. For a start, it’s a good idea to know how they are created.
Conversion: we create a new one without changing anything
It is common in the English language such a change when nothing changes, except for the part of speech. Such is the pun, however, it is. Most often, a noun is transformed, becoming a verb. In this case, the spelling and pronunciation remain the same. This is called conversion.
Attention! This is not a rule, that is, you cannot just take any noun and use it instead of a verb. It’s just that a lot of words are created in English that way. There are many examples:
- a look — look
- to look at — look
- present — a gift
- to present — to be present; present
- present — present
It should be separately noted here that the word «present» in English is one of the many forms of the verb. It is included here to illustrate how multifaceted the use of the same word is in this case.
There are also words where the spelling remains the same, but the stress changes. A change in stress occurs along with a change in part of speech:
Conversion words are not worth experimenting with. Especially if you are with native speakers or if you are communicating with those who know it better than you. This type and the moments when it can be applied are studied in the process, as if by themselves.
Composition
Composition is a simple «mathematics of words». In this case, 2 words just add up into one. This is akin to our «plumbing» and the like. It’s the same in English.
New words are formed in this way simply — there are practically no additional letters for connection, most often the original words are simply written together or with a hyphen:
- Schoolday — school day (in Russian it is advisable to replace it with «school day»).
- Air-base — air base.
Changing parts of speech using suffixes
There are several suffixes in English that allow you to conveniently change the part of speech. In this case, most often the «connecting part» does not change.
In Russian it is more difficult: beauty is beautiful. That is, to transform it into an adjective, you also need to change the ending of the original «beauty». In English, a suffix is simply added, and occasionally you only have to change one letter.
Here only the letter «y» has changed. In many cases, this is not required either.
How to write adjective comparison forms
Comparison of adjectives is about the same as in Russian. Let’s remember: high — higher — highest (highest).
In English, suffixes are used for this:
— er for comparison;
— the + word + suffix est for superlative.
- tall (high) — taller — the tallest.
This is how all comparisons are formed; no more than a dozen exceptions. It should be remembered that if the original variant ends in «y», then before the suffix it will be replaced with «i». Also, in all cases when the word ends with «e», instead of «er» will be simply «r», instead of «est» — «st». The second «e» is, as it were, eaten.
This addition rule is valid for any suffixes, not just comparative degrees. Exceptions are very rare.
«-Ful» and «-less» for adjectives
There are not so many adjectives that exist on their own, which have not been affected in any way by the word formation of English words. More than half of all adjectives are formed with various suffixes. Among them «-ful» and «-less» — they require separate consideration.
Literally, they can be translated as «a lot, full» and «little, not enough», respectively.
- Success is success.
- Successful — «full of success», or rather successful.
This is how many adjectives are formed. In this case, as in all others, it must be borne in mind that not every method and not every word is suitable. Big experiments are not worth carrying out. But knowing all the suffixes will make translation from English several times easier. Just knowing the translation of one noun, reading a book or listening to another person, you can instantly draw a conclusion about what this or that adjective means.
- help — help
- helpless — helpless
If you come across words familiar to you with the addition of the suffixes «-ful» and «-less», you can first translate them verbatim and immediately recall a simpler and more frequently used translation.
Formation of adjectives from verbs
There is another way to «make» an adjective from a verb. There are the following suffixes used for this purpose:
- — able;
- — en;
- — al;
- — ible;
- — ant;
- — ent.
It should be noted that these are far from all, but the most used suffixes. As you learn English, you will most likely soon learn to guess what this or that suffix means if you didn’t know it before:
- Eat — eatable
- Effect — effective
How to make a noun out of a noun?
Also, with the help of simple suffixes -or and -er, the names of professions, statuses and the like are created. Sometimes from nouns, and sometimes from other parts of speech, verbs, for example.
- Bike — biker
- Teach — teacher
- Work — worker
This rule is quite common. Basically, this is how the occupation is indicated in English: by adding a suffix, as a rule, to a noun or to a verb, you get a new noun that characterizes a person by his activities or hobbies. Sometimes such a word can also mean the object with which the action is performed:
- To mix — mixer
Other endings are also used for the same purpose: -ment, -ent, -ant:
- to study — student
How do you know which ending to use? Most often, short endings are added to short words, and long endings to long ones. Also, if you don’t know how to do it correctly, try to orient yourself by ear: substitute what sounds better. The rules were invented for a reason, they are quite intuitive.
«-Ly» and «-en»: Formation of adverbs and adjectives
To make an adjective or adverb out of a noun, the suffix «-ly» or «y» is often added:
- Friend — friendly
- Luck — lucky
With the help of all the same «-ly» and «-y», adverbs can be formed from adjectives:
- Sad — sadly
- Bad — badly
There is also a suffix «-en», with the help of which an object is converted into a property:
- Wood — wooden
- Gold — golden
Word formation using prefixes
In addition to suffixes, there are also so-called prefixes in English. In a sense, they are analogous to Russian prefixes and prepositions, many of them can even be translated.
Among the common ones are «un-«, as well as «ir-«, analogs of the particle «not»:
- Irregular — irregular
- Unknown — unknown
For the same purpose, the following prefixes are used:
- of;
- im;
- il;
- mis;
- non;
- say;
- anti.
There are also prefixes that mean «over», «over», «overly»:
- about;
- super;
- ultra;
- extra.
The list of the listed forms of word formation in English, given above, is not complete. This topic is very extensive, it requires more in-depth study. However, the main methods of word formation are shown, those that are used most often.
It will be difficult to just learn and apply them, but you can easily recognize new words in the language, just remembering this set of rules. It should be noted that it is very difficult to predict which particular suffix or prefix will be used. But in the process of studying you will often meet with them and gradually you will be able to remember their meaning automatically.
Article recommended by an expert: Maria Solomatina
Source: https://1hello.ru/grammatika/obrazovanie-slov-v-anglijskom-yazyke-v-primerax.html
Nouns in English (The Nouns): gender, classification, method of formation, 100 popular nouns
In this article we will talk about nouns in English, about their structure, classification, method of formation and use cases. And also you will find out which nouns are the most popular today.
A noun (the noun) is a word that is the name of something, for example, a person, object, place, quality, concept, etc. Answers the questions what is this? (what is this?) and who is this? (who is this?). The noun comes from the Latin word nomen (name).
Gender of nouns in English
In some languages, the noun has gender. This means that it «forces» other words, such as an adjective, to change their spelling according to certain rules. In Russian: a beautiful girl, an interesting film, etc. The gender category in grammar has nothing to do with the gender (gender) category in biology.
In English grammar, nouns have no gender category. But, on the other hand, the concept of the biological sex of a person or an object has a definite impact on some areas of English grammar.
The choice of a particular noun in English depends on where the personal or possessive pronoun occupies in the sentence. But such a difference in gender is noticeable only with nouns in the singular.
For example, the
— He didn’t appreciate his help. — He did not appreciate his help
— He didn’t appreciate it. — He didn’t appreciate it.
Despite the fact that before the word help is the possessive pronoun his, it does not become masculine, however, there is a certain «echo».
But with all this, according to some groups of nouns in English that name people, it is possible to determine whether it is masculine or feminine.
man — woman
husband — wife
The genus of some animals can be distinguished by their name.
Male (male) A cock — cock
A bull — bull
Female A hen — chicken
A cow — cow
Below is a table of masculine / feminine nouns.
As for the neuter gender, it can only be determined by the pronouns it and its.
— The truth will emerge. It always does. — The truth will be revealed. It always opens up.
Nouns denoting inanimate objects and abstract concepts are also neuter: government, summer, brochure, etc.
With some nouns of a general gender (i.e. when the word can be both masculine and feminine), you can determine the gender if you have the necessary information. But if there is no such knowledge, then choosing a suitable pronoun becomes problematic. For example,
— a driverhe / she (driver) — the cookhe / she (cook)
— doctorhe / she (doctor)
In the informal colloquial version of the English language, a solution was found — the pronoun their is most often used instead of his / her, even despite the singular number. Many believe that this is grammatically incorrect, however, this option has taken root and is widely used.
— Someone has left their coat in my room. “Someone left their coat in my office.
— Today, I picked up a few things at the store, and then I picked up my childs at school. Just a regular day in my lifes, many other daies! — Today I bought a few things in the store, then I took the children from school. Just an ordinary day in my life, just like every other day!
At first glance, quite normal sentences with several nouns. But this is only for the first time. In fact, several errors can be found here. Pay attention to the following words — childs, lifes, daies. The plural is incorrectly formed in these words.
Using the example of this sentence, it becomes clear that it is important to pay attention, it is necessary to use the noun in the singular or in the plural, and, accordingly, to know the rules for the formation of plural.
There are several basic rules for the formation of plural nouns in English.
- 1. Most nouns in English require the addition of an ending —s. For example,
Source: https://englishmix.ru/grammatika/nouns/sushhestvitelnye-v-angliyskom-the-noun
Word formation in English
High USE results in English are a real opportunity for school graduates to enter universities for specialties that require proficiency in English. According to the official data, the section «Grammar and Vocabulary», where the language competence of graduates is checked, the examinees perform worse than the sections «Listening» and «Reading», so preparation for it requires serious attention. But word formation tasks seem to be especially difficult for graduates.
In different textbooks, word formation exercises are found, but there is no proper systematization in any of them. In this regard, it became necessary to create a system of exercises together with the generalization and systematization of students’ knowledge on the topic «Word formation».
At first glance, it may seem that there are many such exercises in any collection. But the structure of this collection is such that the systematization is carried out from simple to complex with increasing and expanding information.
First, students practice word formation using affixes of only nouns, then only adjectives, then nouns and adjectives, after which verbs, adverbs and numbers are added. There are exercises to recognize the suffixes of various parts of speech, to determine the composition of words.
The selection of exercises ends with a test, which includes all types of exercises.
This system of exercises can be used in preparation for the exam by repeating the topic «Word formation with the help of affixes».
Word formation using affixes
Many new words in English are formed by affixing, when the prefixes en-joy, dis-, re-read or the suffixes develop-ment, self-ish are added to the beginning or end of a word (root). Affixes are prefixes and suffixes. Prefixes are at the beginning of a word, and suffixes are at the end. Prefixes, as a rule, change the meaning of a word, but do not change its belonging to one or another part of speech:
order (noun) order — disorder (noun) disorder.
Suffixes are used to form one part of speech from another:
beauty (noun) beautiful (adjective) beautiful.
Negative prefixes
Negative prefixes — un-, in-, dis-, non-.
Un- comfortable — uncomfortable, limited — unlimited. The prefix un- is sometimes attached to verbs to express the opposite action: to load — to unload, to lock — to unlock,
in-
ability — inability, complete — incomplete. Before l, the prefix in- turns into il-, before r — into ir-, and before m and p — into im-: legal — illegal, regular — irregular,
patient — impatient.
Dis- This prefix expresses negation or opposite action: negation opposite action to — to dis, to appear — to disappear, honest — dishonest, to arm — to disarm. Non- Words prefixed with non- are most often hyphenated:
conductor — non-conductor.
Prefixes with different meanings
| Prefix | Value | Compliance with the Russian prefix | Examples |
| anti- | negation | anti anti | fascist — antifascist |
| co- | between, mutually | co- | existence — co-existence |
| counter- | counter- | attack — counterattack | |
| ex- | former | the ex- | champion — ex-champion |
| one- | делать | rich — enrich | |
| inter- | between, among, mutually | national — international | |
| mis- | wrong, wrong | to understand — to myunderstand | |
| over- | over, overly | re- | to load — to overload |
Source: http://www.englishege.ru/grammar/150-slovoobrazovanie-v-anglijskom-yazyke.html
The participle in English (The Participle)
According to the impersonal forms of the verb, we only have the English participle for dessert. And here I have 2 news for you. I’ll start with the good one: a participle in English can correspond to a Russian participle. Bad news: the English participle can also correspond to the Russian participle. And bonus news: the English participle can be easily confused with a gerund. And in a whisper: the English participle has several forms.
Now, don’t panic! Once you probably confused the letters «G» and «J» in the English alphabet, but this is already a distant past. We’ll figure it out, put it on the shelves and go to practice.
What is an English participle
This is another impersonal form of the verb that combines the following properties:
— verb (denotes action)
broken heart — broken heart;
— adjective (can answer the question «which»)
working machine — a working mechanism;
— adverbs (can answer the question «how?», «Where?», «Where?», «When?», «Why?», «For what purpose?», «To what extent?»)
He was rather furious asking Ann about the school marks — He was pretty angry asking Anya about her grades. (Was angry when? Asking for grades)
Forms of the English participle
There are two main types:
1. participle I (Participle I), or present participle (Present Participle):
1.1. Present Participle Simple
This is an imperfect analogue of our Russian participle or gerunds.
Walking Look at that walking man. Look at that man walking.
I can’t be serious walking with you in the street. I can’t be serious walking down the street with you.
1.2. Present participle perfect
This is a perfect analogue of the Russian gerunds.
Having done
Having done the work she went home. After completing the work, she went home.
Source: https://iloveenglish.ru/theory/anglijskaya_grammatika/prichastie_v_anglijskom_yazike
English nouns (The Noun)
›Grammar and rules› Nouns ›English nouns (The Noun): structure, education, role in a sentence
The bitter truth when learning English is that it will not be very easy to immediately form beautiful sentences with introductory words and participial phrases. The fact is that, as in Russian, you first need to gain an active and passive vocabulary.
At the initial stage, it is not necessary to memorize some high-flown and fanciful adjectives in order to amaze the native speakers. Even if you achieve this goal, the conversation will not work out for you, because conversations in everyday life are usually about everyday trifles.
That is why let’s look at English nouns, touch on their differences, ways of education and compose the top 100 most common English words of this part of speech.
First, let’s figure out what English nouns are.
The Noun ([naun]) or noun in English is an independent part of speech that denotes an object / person / phenomena / abstract concepts and answers the questions what is this? (what is this?) and who is this? (who is this?).
Depending on their structure, meaning and method of formation, nouns can be divided into several groups.
English nouns: structure
English nouns are formed by:
- Rhoda (gender)
- Case
- Number
Gender of nouns
The gender of nouns in English is masculine, feminine and neuter. There is no grammatical ending for separating genders in English, so they do not change by gender, they do not obey any grammar rule, which greatly facilitates the use of nouns. However, when replacing nouns with pronouns, it should be borne in mind that:
- The pronouns he (he) and she (she) are used when talking about people:
| Mom’s cooking.
(Mom loves to cook.) |
She’s cooking.
(She loves to cook.) |
| The student is smart.
(This student is smart.) |
He is smart.
(He is smart.) |
| Liz hasn’t found beautiful dresses.
(Liz couldn’t find any pretty dresses.) |
She hasn’t found beautiful dresses.
(She couldn’t find any pretty dresses.) |
- The pronoun it (it) is used when talking about the neuter gender, that is, about inanimate objects and animals.
| The dog was lying next to me.
(The dog was lying next to me.) |
It was lying next to me.
(She was lying next to me.) |
| The book was written in 1996.
(The book was written in 1996.) |
It was written in 1996.
(It was written in 1996.) |
Now pet owners often use pronouns she / he in relation to them when they know their gender, so this English form of noun replacement is also possible.
Cases of nouns
The grammar of the English language has two cases in its arsenal:
- The general case is the case that absolutely all nouns have. In this form, they are given in dictionaries and textbooks. The noun has no ending in this case.
| nature | nature |
| England | England |
| grammar | grammar |
- Possessive case — a case that is usually characteristic of animate objects. Such a case shows that some object or feature belongs to a particular person. The form is formed by adding an apostrophe to the noun and the ending –s. Let’s take a look at some of the features of using this form on tables:
- If the noun is in singular, an apostrophe and the ending -s are added to it:
| Jane’s family | Jane’s family |
| sister’s book | sister’s book |
- If the noun is plural and ends in -s, then only an apostrophe is added to it:
| brothers’ presents | brothers gifts |
| singers’ concerts | concerts of singers |
- If a singular noun ends in -s, you can use two options:
| Hopkins’s role | Role of Hopkins |
| Hopkins’ role |
- If a subject or sign refers to several nouns at once, then the apostrophe and the ending are used only with the last one:
| Tito and mia’s project | Tito and Mia’s project |
| Helen and george’s ideas | Helen and George’s ideas |
- If a subject or sign refers to several nouns separately, then an apostrophe and an ending are used with each:
Source: https://speakenglishwell.ru/anglijskie-sushhestvitelnye-the-noun/
Для знания иностранного языка богатство словарного запаса ничуть не менее важно, чем понимание грамматики. Чем большим количеством слов владеет человек, тем свободнее он себя чувствует в иноязычной среде.
Многообразие лексики во многом определяется богатством словообразования в английском языке. Построение новых слов основано на общих принципах. И тот, кто знает эти принципы, чувствует себя среди незнакомой лексики гораздо увереннее.
Структура слова и ее изменение
Новые слова усваиваются постепенно. Чаще всего, сначала мы только понимаем их в текстах или чужой речи, а уже потом начинаем активно использовать в своей. Поэтому освоение новой лексики – процесс длительный и требует от ученика терпения, активной практики чтения, слушания и работы со словарем.
Один из методов быстро расширить свой словарный запас – освоить способы словообразования в английском языке. Поняв принципы, по которым строятся слова, можно из уже известного слова вывести значения его однокоренных слов.
Строительный материал для каждого слова – это корень, приставки и суффиксы. Корень – это та часть слова, которая несет основной смысл. Слово без корня не может существовать. Тогда как приставки и суффиксы – необязательная часть, однако прибавляясь к корню, именно они помогают образовать новые слова. Поэтому, описывая словообразование в английском, мы будем разделять приставочные и суффиксальные способы.
Все приставки и суффиксы обладают собственным значением. Обычно оно довольно размыто и служит для изменения основного значения слова. Когда к корню добавляется приставка или суффикс (или же оба элемента), то их значение прибавляется к значению корня. Так получается новое слово.
Образование новых слов может приводить не только к изменению значения, но и менять части речи. В этой функции чаще выступают суффиксы. Прибавляясь к корню, они переводят слово из одной части речи в другую, например, делают прилагательное из глагола или глагол из существительного.
Так, от одного корня может образоваться целая группа, все элементы которой связаны между собой. Поэтому словообразование помогает изучающим английский видеть смысловые отношения между словами и лучше ориентироваться в многообразии лексики.
Получить новое слово можно не только за счет приставок и суффиксов. Еще один способ – это словосложение, при котором в одно слово объединяются два корня, образуя новый смысл. Кроме того, к словообразованию относится сокращение слов и создание аббревиатур.
Приставки как способ словообразования в английском
Приставка (также употребляется термин «префикс») – элемент слова, который ставится перед корнем. Приставочное словообразование английский язык редко использует для смены частей речи (в качестве исключения можно назвать префикс «en-» / «em-» для образования глаголов). Зато приставки активно используются для изменения значения слова. Сами префиксы могут иметь различные значения, но среди них выделяется большая группа приставок со схожей функцией: менять смысл слова на противоположный.
1. Приставки с отрицательным значением:
- un-: unpredictable (непредсказуемый), unable (неспособный)
- dis-: disapproval (неодобрение), disconnection (отделение от)
- im-, in-, il -,ir-: inactive (неактивный), impossible (невозможный), irregular (нерегулярный), illogical (нелогичный). То, какая из этих приставок будет присоединяться к слову, зависит от следующего за ней звука. «Im-» ставится только перед согласными «b», «p», «m» (impatient — нетерпеливый). «Il-» возможно только перед буквой «l» (illegal — незаконный), «ir-» – только перед «r» (irresponsible — безответственный). Во всех остальных случаях употребляется приставка «in-» (inconvenient – неудобный, стесняющий).
- mis-: misfortune (несчастье, беда). Приставка «mis-» может использоваться не только для образования прямых антонимов, но и иметь более общее значение отрицательного воздействия (misinform — дезинформировать, вводить в заблуждение, misunderstand — неправильно понять).
2. Другие приставочные значения
- re-: rebuild (отстроить заново, реконструировать). Приставка описывает повторные действия (rethink — переосмыслить) или указывает на обратное направление (return — возвращаться).
- co-: cooperate (сотрудничать). Описывает совместную деятельность (co-author – соавтор).
- over-: oversleep (проспать). Значение префикса — избыточность, излишнее наполнение (overweight — избыточный вес) или прохождение определенной черты (overcome — преодолеть).
- under-: underact (недоигрывать). Приставку можно назвать антонимом к приставке «over-», она указывает на недостаточную степень действия (underestimate — недооценивать). Кроме того, приставка используется и в изначальном значении слова «under» — «под» (underwear — нижнее белье, underground — подземка, метро).
- pre-: prehistoric (доисторический). Приставка несет в себе идею предшествования (pre-production — предварительная стадия производства).
- post-: post-modern (постмодернизм). В отличие от предыдущего случая, приставка указывает на следование действия (postnatal – послеродовой).
- en-, em-: encode (кодировать). Префикс служит для образования глагола и имеет значение воплощения определенного качества или состояния (enclose — окружать). Перед звуками «b», «p», «m» приставка имеет вид «em-» (empoison — подмешивать яд), в остальных случаях – «en-» (encourage — ободрять).
- ex-: ex-champion (бывший чемпион). Используется для обозначения бывшего статуса или должности (ex-minister — бывший министр).
Образование новых слов при помощи суффиксов
Суффиксы занимают позицию после корня. За ними может также следовать окончание (например, показатель множественного числа «-s»). Но в отличие от суффикса окончание не образует слова с новым значением, а только меняет его грамматическую форму (boy – мальчик, boys – мальчики).
По суффиксу часто можно определить, к какой части речи принадлежит слово. Среди суффиксов существуют и такие, которые выступают только как средство образования другой части речи (например, «-ly» для образования наречий). Поэтому рассматривать эти элементы слова мы будем в зависимости от того, какую часть речи они характеризуют.
Словообразование существительных в английском языке
Среди суффиксов существительных можно выделить группу, обозначающую субъектов деятельности и группу абстрактных значений.
1. Субъект деятельности
- -er, -or: performer (исполнитель). Такие суффиксы описывают род занятий (doctor — доктор, farmer — фермер) или временные роли (speaker — оратор, visitor — посетитель). Могут использоваться и в качестве характеристики человека (doer — человек дела, dreamer — мечтатель).
- -an, -ian: magician (волшебник). Суффикс может участвовать в образовании названия профессии (musician — музыкант) или указывать на национальность (Belgian — бельгийский / бельгиец).
- -ist: pacifist (пацифист). Этот суффикс описывает принадлежность к определенному роду деятельности (alpinist – альпинист) или к социальному течению, направлению в искусстве (realist — реалист).
- -ant, -ent: accountant (бухгалтер), student (студент).
- -ee: employee (служащий), conferee (участник конференции).
- -ess : princess (принцесса). Суффикс используется для обозначения женского рода (waitress – официантка).
2. Абстрактные существительные
Основа этой группы значений – обозначение качества или состояния. Дополнительным значением может выступать объединение группы людей и обозначение определенной совокупности.
- -ity: activity (деятельность), lability (изменчивость).
- -ance, -ence, -ancy, -ency: importance (важность), dependence (зависимость), brilliancy (великолепие), efficiency (эффективность).
- -ion, -tion, -sion: revision (пересмотр, исправление), exception (исключение), admission (допущение), information (информация).
- -ism: realism (реализм). В отличие от суффикса «-ist» обозначает не представителя некоторого течения, а само течение (modernism — модернизм) или род занятий (alpinism — альпинизм).
- -hood: childhood (детство). Может относиться не только к состоянию, но и описывать группу людей, форму отношений: brotherhood (братство).
- -ure: pleasure (удовольствие), pressure (давление).
- -dom: wisdom (мудрость). Также используется при обозначении группы людей, объединения по некоторому признаку: kingdom (королевство).
- -ment: announcement (объявление), improvement (улучшение).
- -ness: darkness (темнота), kindness (доброта).
- -ship: friendship (дружба). К дополнительным значениям относится указание на титул (lordship — светлость), умение (airmanship — лётное мастерство) или на объединение круга людей определенными отношениями (membership — круг членов, partnership — партнерство).
- -th: truth (правда), length (длина).
Словообразование прилагательных в английском языке
- -ful: helpful (полезный). Указывает на обладание определенным качеством (joyful — радостный, beautiful — красивый).
- -less: countless (бессчетный). Значение суффикса близко к отрицанию и характеризует отсутствие определенного качества, свойства (careless — беззаботный). Этот суффикс можно определить как антоним для «-ful» (hopeless — безнадежный, а hopeful — надеющийся).
- -able: comfortable (комфортный). «Able» (способный) существует и как самостоятельное прилагательное. Оно определяет значение суффикса – возможный для выполнения, доступный к осуществлению (acceptable – приемлемый, допустимый, detectable – тот, который можно обнаружить).
- -ous: famous (знаменитый), dangerous (опасный).
- -y: windy (ветреный), rusty (ржавый).
- -al: accidental (случайный), additional (добавочный).
- -ar: molecular (молекулярный), vernacular (народный).
- -ant, -ent: defiant (дерзкий), evident (очевидный).
- -ary, -ory: secondary (второстепенный), obligatory (обязательный).
- -ic: democratic (демократический), historic (исторический).
- -ive: creative (творческий), impressive (впечатляющий).
- -ish: childish (детский, ребяческий). Суффикс описывает характерный признак с негативной оценкой (liquorish – развратный) или с ослабленной степенью качества (reddish — красноватый). Кроме того, суффикс может отсылать к национальности (Danish — датский).
- -long: livelong (целый, вечный). Такой суффикс обозначает длительность (lifelong — пожизненный) или направление (sidelong — косой, вкось) и может принадлежать не только прилагательному, но и наречию.
Словообразование глаголов
Для глагольных суффиксов сложно определить конкретные значения. Основная функция таких суффиксов — перевод в другую часть речи, то есть само образование глагола.
- -ate: activate (активизировать), decorate (украшать).
- -ify, -fy: notify (уведомлять), verify (проверять).
- -ise, -ize: summarize (суммировать), hypnotize (гипнотизировать).
- -en: weaken (ослабевать), lengthen (удлинять).
- -ish: demolish (разрушать), embellish (украшать).
Словообразование наречий
- -ly: occasionally (случайно).
- -wise: otherwise (иначе). Обозначает способ действия (archwise — дугообразно).
- -ward(s): skyward/skywards (к небу). Обозначает направление движения (northward — на север, shoreward — по направлению к берегу).
Суффиксы: таблица словообразования по частям речи
Приведенный список суффиксов – это далеко не все возможности английского языка. Мы описали наиболее распространенные и интересные случаи. Для того чтобы разобраться в этом множестве вариантов и лучше усвоить образование слов в английском языке, таблица резюмирует, для каких частей речи какие суффиксы характерны.
Поскольку суффиксальное преобразование слов в английском языке различается по частям речи, таблица разбита на соответствующие группы. Одни и те же суффиксы могут добавляться к разным частям речи, но в результате они определяют, к какой части речи принадлежит новое слово.
Объединение суффиксов и приставок
Важная характеристика словообразования – это его продуктивность. От одного корня можно образовать целую группу слов, добавляя разные приставки и суффиксы. Приведем несколько примеров.
- Для possible словообразование может выглядеть следующим образом: possible (возможный) — possibility (возможность) — impossibility (невозможность).
- Цепочка переходов для слова occasion: occasion (случай) — occasional (случайный) — occasionally (случайно).
- Для слова agree словообразование можно выстроить в цепочки с приставкой и без приставки: agree (соглашаться) — agreeable (приемлемый / приятный) — agreeably (приятно) — agreement (соглашение, согласие).
agree (соглашаться) — disagree (противоречить, расходиться в мнениях) — disagreeable (неприятный) — disagreeably (неприятно) — disagreement (разногласие).
Словосложение и сокращение слов
Словосложение — еще один способ образовать новое слово, хотя и менее распространенный. Он основан на соединении двух корней (toothbrush — зубная щетка, well-educated — хорошо образованный). В русском языке такое словообразование тоже встречается, например, «кресло-качалка».
Если корень активно используется в словосложении, то он может перейти в категорию суффиксов. В таком случае сложно определить, к какому типу – суффиксам или словосложению – отнести некоторые примеры:
- -man: fireman (пожарный), spiderman (человек-паук)
- -free: sugar-free (без сахара), alcohol-free (безалкогольный)
- -proof: fireproof (огнестойкий), soundproof (звукоизолирующий)
Помимо объединения нескольких корней, возможно также сокращение слов и создание аббревиатур: science fiction — sci-fi (научная фантастика), United States of America – USA (Соединенные Штаты Америки, США).
Новые слова без внешних изменений
К особенности словообразования в английском языке относится и то, что слова могут выступать в разных частях речи без изменения внешнего вида. Это явление называется конверсией:
I hope you won’t be angry with me — Надеюсь, ты не будешь на меня злиться (hope – глагол «надеяться»).
I always had a hope to return to that city — У меня всегда оставалась надежда вернуться в этот город (hope – существительное «надежда»).
The sea is so calm today — Море так спокойно сегодня (calm – прилагательное «спокойный»).
With a calm she realized that her life was probably at its end — Со спокойствием она осознала, что ее жизнь, вероятно, подходила к концу (calm – существительное «спокойствие, невозмутимость»).
I beg you to calm down — Я умоляю тебя успокоиться (calm – глагол «успокоиться»).
В английском языке, как и в других, словообразование является инструментом обогащения речи.
В этом материале рассмотрены наиболее распространенные способы, с помощью которых образуются новые слова:
- префиксы (prefixes);
- суффиксы (suffixes);
- конверсия (conversion);
- словосложение (compounding);
- сокращение (abbreviation).
Краткий обзор понятий и принципов словообразования облегчит понимание языка. Знание основ образования новых слов значительно ускорит процесс изучения английского.
Таблица 1. Префиксация
Префикс – часть слова, которая ставится перед корнем. С помощью префикса слово принимает новое значение. В большинстве случаев слово не переходит в другую часть речи, но бывают исключения.
Префикс + Корень = Новое слово
Примеры
- re + build (строить) = rebuild (перестроить по новой)
- mis + conduct (поведение) = misconduct (плохое поведение)
В таблице рассмотрены префиксы, которые встречаются наиболее часто.
|
Приставки и их значения |
Примеры |
|
un- , dis- , in- , non- , il- , im- , ir- : указывают на отрицание, делают слово противоположным по значению |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| mis- : меняет смысл слова на «неверный», «ложный» |
|
| re- : «снова», «вновь»; сделать что-либо повторно |
|
| co-: аналог приставки в русском языке «со» |
|
Таблица 2. Суффиксация
Суффикс – часть слова, которая ставится после корня. Суффикс придает слову новое значение и обычно преобразовывает его в другую часть речи.
Корень + Суффикс = Новое слово
Примеры
- teach + er = teacher (учитель)
- child + hood = childhood (детство)
В таблице рассмотрены суффиксы, которые встречаются наиболее часто.
|
Суффикс и его значения |
Примеры |
|
Образование существительного |
|
| -er, -or, -ar: из глагола переходит существительное в значении «исполнитель действия» |
|
| -ment, -age, -ure, -dom, -tion, -sion: глагол > существительное |
|
| -hood, -ship: образуют существительные от других существительных |
|
| -ist: используется для указания принадлежности к профессии или политическому званию |
|
| -ian: указывают на национальность, реже профессию |
|
| -ness: преобразовывает прилагательное в существительное |
|
|
Образование прилагательного |
|
| -ful: образует прилагательные от существительных и означает наличие качества |
|
| -able, -ible: образуют прилагательные от глаголов и выражают возможность подвергнуться действию, выраженному соответствующим глаголом |
|
| -less: образует прилагательные от существительных и означает отсутствие качества |
|
| -ish: национальная принадлежность; качество |
|
| -y: образует прилагательные от существительных |
|
|
Образование глагола |
|
| -en: образует глаголы от прилагательных и существительных |
|
| -fy, -ify: обычно образует глаголы от прилагательных |
|
| -ise, -ize: обычно образует глаголы от существительных |
|
Таблица 3. Конверсия
Конверсия – переход слова в другую часть речи, без изменения его структуры.
|
Глагол > существительное |
|
| to call (кричать, звонить) | call (крик, телефонный звонок) |
| to hope (надеяться) | hope (надежда) |
| to attack (атаковать) | attack (атака) |
|
Глагол > существительное (с изменением ударения и произношения) |
|
| to ac’cent (акцентировать) | ‘accent (акцент) |
| to use (использовать): буква s читается как русская з | use (использование): буква s читается как русская с |
| to excuse (извиняться): буква s читается как русская з | excuse (извинение): буква s читается как русская с |
| to pre’sent (дарить) | ‘present (подарок) |
|
Существительное > глагол |
|
| love (любовь) | to love (любить) |
| trip (путешествие) | to trip (отправляться в путешествие) |
| film (фильм) | to film (снимать фильм) |
|
Прилагательное > существительное |
|
| calm (спокойный) | calm (спокойствие) |
| black (чёрный) | black (чёрный цвет) |
| dead (мёртвый) | dead (мертвец) |
Таблица 4. Словосложение
Словосложение – соединение двух слов и более в сложное слово. Такие слова пишутся как через дефис, так и слитно.
|
Сложные существительные |
|
| toothpaste (зубная паста) | существительное (tooth) + существительное (paste) |
| highway (большая дорога, шоссе) | прилагательное (high) + существительное (way) |
| underworld (преисподняя) | предлог (under) + существительное (world) |
| haircut (стрижка, причёска) | существительное (hair) + глагол (cut) |
|
Сложные глаголы |
|
| to babysit (присматривать за ребенком) | существительное (baby) + глагол (sit) |
| to window-shop (рассматривать витрины) | существительное (window) + существительное (shop) |
| to downgrade (понижать) | наречие (down) + существительное (grade) |
| to blackwash (клеветать) | прилагательное (black) + существительное (wash) |
|
Сложные прилагательные |
|
| smoke-free (бездымный) | существительное (smoke) + прилагательное (free) |
| part-time (занимающий меньше стандартного времени) | существительное (part) + существительное (part) |
| short-sighted (близорукий) | прилагательное (short) + глагол (sighted) |
|
Сложные наречия |
|
| outside (снаружи) | предлог (out) + существительное (side) |
| everywhere (везде, всюду) | прилагательное (every) + наречие (where) |
Таблица 5. Сокращение
|
Усеченные слова |
||
| laboratory | lab | лаборатория |
| refrigerator | fridge | холодильник |
| cinematograph | cinema | кинематограф |
|
Аббревиатуры и сокращения |
||
| electronic mail | электронная почта | |
| between | betw. | между, в промежутке |
| United Nations Organization | U.N.O. | Организация Объединённых Наций (ООН) |
|
Слова-гибриды (образование нового слова путем сочетания частей нескольких слов) |
||
| documentary + drama | docudrama | документальная драма |
| science + fiction | sci-fi | научная фантастика |
| smoke + fog | smog | густой туман с дымом и копотью; смог |
Другие полезные материалы
1. Упражнение на словообразование (с ответами)