Need to write or read in a different language? Follow these tips
Updated on October 15, 2022
What to Know
- In Windows: Choose the desired Display and Help Languages in File > Options > Word Options > Language.
- Then, select Choose Editing Options in the same section to change the editing language.
- All but the proofing language in Office for Mac are the same as those for the operating system. To change it in Word: Tools > Language.
This article explains how to change display and/or editing languages in Word for Office 365, Word 2019, Word 2016, Word 2013, Word 2010, Word Online, and Word for Mac. In Windows—but not in macOS—you can choose them independently of the language installed for your operating system.
How to Change the Display Language
The display language in Word governs the ribbon, buttons, tabs, and other controls. To force a display language in Word that’s different from that of your operating system:
-
Select File > Options.
-
In the Word Options dialog box, select Language.
-
In the Choose Display Language section, choose the Display Language and Help Language you want to use. Languages installed in Windows 10 are listed.
-
If a specific language is not listed, select Get more display and help languages from Office.com. If necessary, install a Language Accessory Pack, then close and re-launch Word. You may need to reboot your computer, as well. After a language pack loads, go to the Word Options menu and choose that pack in the Display Language and Help Language lists.
-
Select Set as Default for both the Display Language and the Help Language lists.
-
Select OK to save your changes.
How to Change the Editing Language in Word
The editing language—which governs spelling, grammar, and word sorting—can be changed in the Word Options screen. Go to the Choose Editing Languages section, and select a language from the list. If the language isn’t listed, select the Add additional editing languages drop-down arrow and choose a language.
To proofread in the selected language, highlight the text, then go to the Review tab and select Language > Set proofing language. Choose a language from the list. Word will consider the highlighted selection to be the non-default, selected language and will check the spelling and grammar accordingly.
How to Change Language in Word Online
Language options for Office Online are similar to those in desktop versions of Office. In Office Online, highlight the text for proofing in the non-default language. Select Review > Spelling and Grammar > Set Proofing Language, then choose your alternative language. All proofing in that selected block will be governed by the rules of the alternative language.
How to Change Language in Word for Mac
The display and keyboard layout languages used in Office for Mac are the same as the ones for the operating system. You cannot use separate languages for the OS and Office applications. However, you can specify a different proofing language for Office for Mac.
To change the proofing language in Office for Mac, select Tools > Language in Word or another Office application. To change the proofing language for new documents, select Default.
If you select OK instead of Default, the proofing language you chose will only apply to the current file.
Normally, Word defaults to the language of the operating system. As a rule, you should use Windows to install language files rather than rely on an application like Word to do it for you.
FAQ
-
How do you delete a page in Word?
To delete a page in Word, select View, then go to the Show section and select Navigation Pane. In the left pane, select Pages, choose the page you want to delete and tap the delete or backspace key.
-
How do I check the word count in Word?
To check the word count in Microsoft Word, look at the status bar. If you don’t see the number of words, right-click the status bar and choose Word Count.
-
How do I insert a signature in Word?
To insert a signature in Microsoft Word, scan and insert a signature image into a new Word document and type your information beneath the signature. Then, select the signature block and go to Insert > Quick Parts > Save Selection to Quick Part Gallery. Name the signature > AutoText > OK.
Thanks for letting us know!
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Subscribe
Excel for Microsoft 365 Word for Microsoft 365 Outlook for Microsoft 365 PowerPoint for Microsoft 365 Access for Microsoft 365 OneNote for Microsoft 365 Project Online Desktop Client Publisher for Microsoft 365 Visio Plan 2 Excel 2021 Word 2021 Outlook 2021 PowerPoint 2021 Access 2021 Project Professional 2021 Project Standard 2021 Publisher 2021 Visio Professional 2021 Visio Standard 2021 OneNote 2021 Excel 2019 Word 2019 Outlook 2019 PowerPoint 2019 Access 2019 Project Professional 2019 Project Standard 2019 Publisher 2019 Visio Professional 2019 Visio Standard 2019 Excel 2016 Word 2016 Outlook 2016 PowerPoint 2016 Access 2016 OneNote 2016 Project Professional 2016 Project Standard 2016 Publisher 2016 Visio Professional 2016 Visio Standard 2016 Excel 2013 Word 2013 Outlook 2013 PowerPoint 2013 Access 2013 OneNote 2013 Project Professional 2013 Project Standard 2013 Publisher 2013 Visio Professional 2013 Visio 2013 Excel 2010 Word 2010 Outlook 2010 PowerPoint 2010 Access 2010 OneNote 2010 Project 2010 Project Standard 2010 Publisher 2010 Visio Premium 2010 Visio 2010 Visio Standard 2010 Excel Starter 2010 Language Preferences Language Preferences 2010 Language Preferences 2013 Language Preferences 2016 More…Less
You can use the Office language options to add a language, to choose the UI display language, and to set the authoring and proofing language.
The language options are in the Set the Office Language Preferences section of the Office Options dialog box, which you can access by going to File > Options > Language. The display and authoring languages can be set independently. For example, you could have everything match the language of your operating system, or you could use a combination of languages for your operating system, authoring, and Office UI display.
The available languages depend on the language version of Office and any additional language pack, language interface pack, or ScreenTip languages that are installed on your computer.
Add a language
You can add a display language or an authoring language. A display language determines the language Office uses in the UI — ribbon, buttons, dialog boxes, etc. An authoring language influences text direction and layout for vertical, right-to-left, and mixed text. Authoring languages also include proofing tools such as dictionaries for spelling and grammar checking. (The preferred authoring language appears at the top of the list in bold. You can change this by choosing the language you want and selecting Set as Preferred.)
To add a display language:
-
Open an Office program, such as Word.
-
Select File > Options > Language.
-
Under Office display language, on the Set the Office Language Preferences, select Install additional display languages from Office.com.
-
Choose the desired language in the Add an authoring language dialog and then select Add. A browser page opens where you can download the installation file.
-
On the browser page, select Download and run the downloaded pack to complete installation.
-
The added language appears in the list of Office display languages.
To add an authoring language:
-
Open an Office program, such as Word.
-
Select File >Options >Language.
-
On the Set the Office Language Preferences, under Office authoring languages and proofing, select Add a Language….
-
Choose the desired language in the Add an authoring language dialog and then select Add. A browser page opens where you can download the installation file.
-
On the browser page, select Download and run the downloaded pack to complete installation.
-
The added language appears in the list of Office authoring languages.
If Proofing available appears next to the language name, you can obtain a language pack with proofing tools for your language. If Proofing not available is next to the language name, then proofing tools are not available for that language. If Proofing installed appears next to the language name, you’re all set.
-
To go online and get the language pack you need, select the Proofing available link.
Both kinds of Office languages (display and authoring) have a preferred language that you can set independently.
The preferred language appears in bold at the top of each language list. The order of the languages in the list is the order in which languages are used by Office. For example, if your display language order is Spanish <preferred>, German, and Japanese, and the Spanish language resources are removed from your computer, German becomes your preferred display language.
To set the preferred language:
-
Open an Office program, such as Word.
-
Select File > Options > Language.
-
Under Set the Office Language Preferences, do one or both of the following:
-
Under Office display language, choose the language you want from the list and then select Set as Preferred.
-
Under Office authoring languages and proofing, choose the language you want from the list and then select Set as Preferred.
-
You can use the Office language options to add a language or to choose the language in which the Help and ScreenTips display.
The language options are in the Set the Office Language Preferences dialog box, which you can access by going to File > Options > Language. The display and help languages can be set independently. For example, you could have everything match the language of your operating system, or you could use a combination of languages for your operating system, editing, display, and Help.
The available languages depend on the language version of Office and any additional language pack, language interface pack, or ScreenTip languages that are installed on your computer.
Add a language
You can add a language to Office programs by adding an editing language. An editing language consists of the type direction and proofing tools for that language. The proofing tools include language-specific features, such as dictionaries for spelling and grammar checking. (The default editing language appears at the top of the list in bold. You can change this by choosing the language you want and selecting Set as Default.)
-
Open an Office program, such as Word.
-
Select File > Options > Language.
-
In the Set the Office Language Preferences dialog box, under Choose Editing Languages, choose the editing language that you want to add from the Add additional editing languages list, and then select Add.
The added language appears in the list of editing languages.
If Not enabled appears in the Keyboard Layout column, do the following:
-
Select the Not enabled link.
-
Windows settings will open to the Language page. In the Add Languages dialog box of Windows settings, select Add a language, choose your language in the list, and then select Add.
-
Close the Add Languages dialog box in Windows settings. In the Office dialog box, your language should display as Enabled under Keyboard Layout in the Choose Editing Languages section.
If Not Installed appears in the Proofing column, you might need to obtain a language pack or language interface pack to obtain the proofing tools for your language.
-
To go online and get the language pack you need, select the Not installed link.
The display and Help languages are the languages used in Office for display elements, such as menu items, commands, and tabs, in addition to the Help file display language.
The default language appears in bold at the top of the list. The order of the languages in the display and Help lists is the order in which languages are used by Office. For example, if your display language order is Spanish <default>, German, and Japanese, and the Spanish language tools are removed from your computer, German becomes your default display language.
To set the default language:
-
Open an Office program, such as Word.
-
Click File > Options > Language.
-
In the Set the Office Language Preferences dialog box, under Choose Display and Help Languages, choose the language that you want to use, and then select Set as Default.
Which display language is being used for which Office program?
If you use multiple languages and have customized Office so that it fits the way that you want to work, you can review all of the Office programs to see which language is the default display language for each.
-
In the Set the Office Language Preferences dialog box, under Choose Display and Help languages, select View display languages installed for each Microsoft Office program.
Note: This feature is available only for the following Office programs: Excel, OneNote, Outlook, PowerPoint, Publisher, Visio, and Word. It is not available for Office 2016 programs.
ScreenTips are small pop-up windows that provide brief, context-sensitive help when you rest the pointer on a display element, such as a button, tab, dialog box control, or menu. Setting the ScreenTip language in one Office program sets it for all of the Office programs that you have installed.
-
Open an Office program, such as Word.
-
Select File > Options > Language.
-
In the Set the Office Language Preferences dialog box, under Choose ScreenTip Language, choose your ScreenTip language.
Notes:
-
This feature is not available in Office 2016.
-
If the language that you want is not listed, you might need to add more language services. Select How do I get more ScreenTip languages from Office.com, and then follow the download and installation instructions.
-
After you install a new ScreenTip language, it becomes your default ScreenTip language.
-
For more information about ScreenTips, see Show or hide ScreenTips.
See also
Enable or change the keyboard layout language
Check spelling and grammar in a different language
Turn on automatic language detection
Need more help?
For users in the US, Word automatically displays the ribbon and commands in English and makes English the default language for spell-checking text and suggesting corrections. However, if you often work with documents in other languages, you can change the language in Word. This will make your work much easier. There are actually two different language settings in Word:
The display language is the language in which user controls and menus are displayed. The editing language is the language of the document. This language is important for checking spelling and suggesting corrections. For example, if spell check is not working, Word could be set to the wrong editing language. However, you can easily change the spell check language in Word.
Contents
- Changing the display language in Word
- Changing the editing language
- Changing the display language in Word Online
- Changing the editing language in Word Online
- How to change Word language on a Mac
Changing the display language in Word
To change the display language in Word, click “File” on the ribbon and then “Options”. In the next dialog box, select “Language” in the sidebar on the left. The display language and help language are now displayed at the bottom of the dialog box. By default, Word uses the language of the Windows operating system as the display language. However, you can select a different language at any time and click “Set as Default” to make it your default for future documents. This setting isn’t applied until you restart Word. The user interface is then displayed in the new language.
Select a help language in the list box on the right. By default, the help language is the same as the display language. This is the language in which help is displayed in Word. You can also change this language: For example, if you normally use Word in English but have a different native language, you can display help in your native language without changing the language of the user interface in Word. After making your changes, click “OK” at the bottom of the window and restart Word.
Changing the editing language
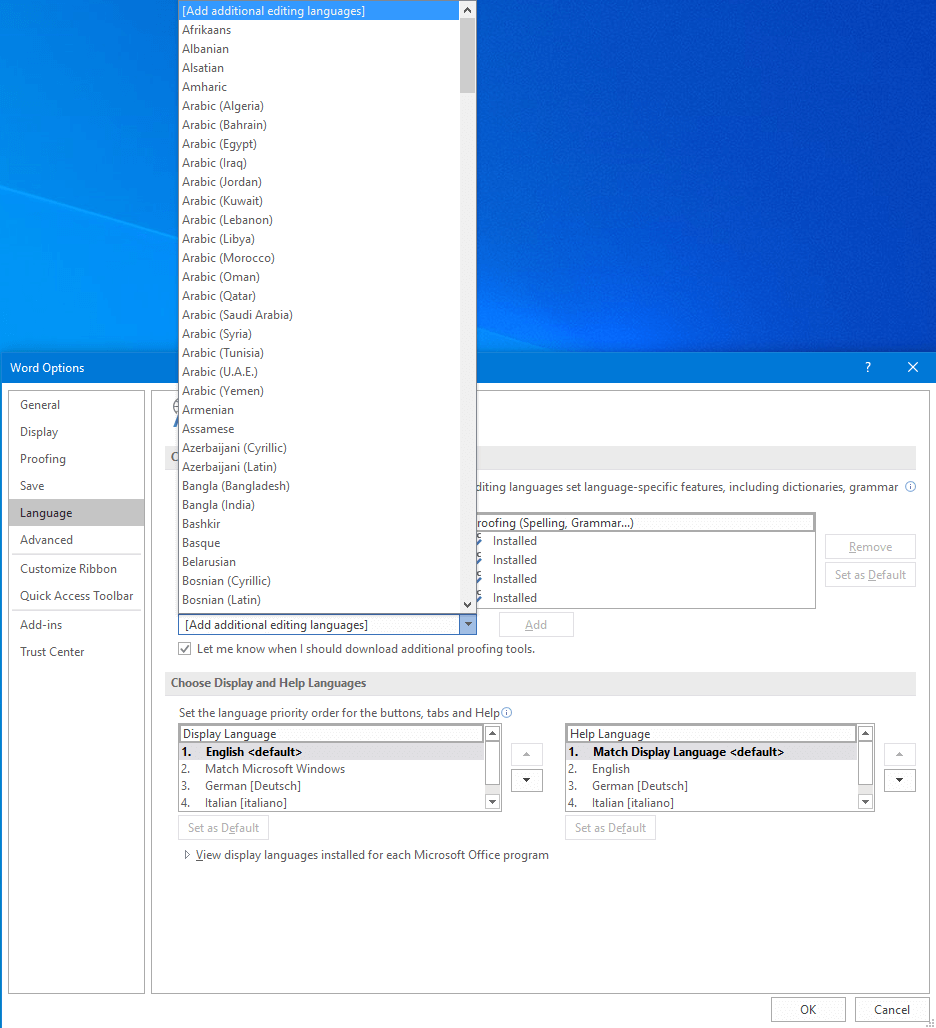
You can also change the editing language in the same dialog box under “File” -> “Options”. In the “Language” section, all installed editing languages are displayed at the top of this dialog box. To enable a language, click one of the languages marked “Not enabled”. You can add additional editing languages in the list box below the list of editing languages. Word allows you to choose from over 100 languages and dialects. Select the desired language and enable it. In some cases, you may have to download additional proofing tools, e.g. if a language is written from right to left.
Once you’ve enabled the language you want, click “Set as Default” to use this editing language for all new documents. Save your changes by choosing “OK”.
Changing the display language in Word Online
Word Online edits documents in OneDrive and uses the same display language as OneDrive.
1. Go to onedrive.live.com, click the settings icon in the upper right corner of your browser and then click the language currently displayed.
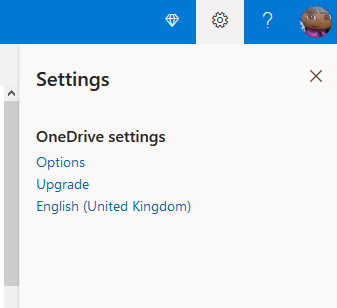
2. Now you can select a different display language for OneDrive from the list.
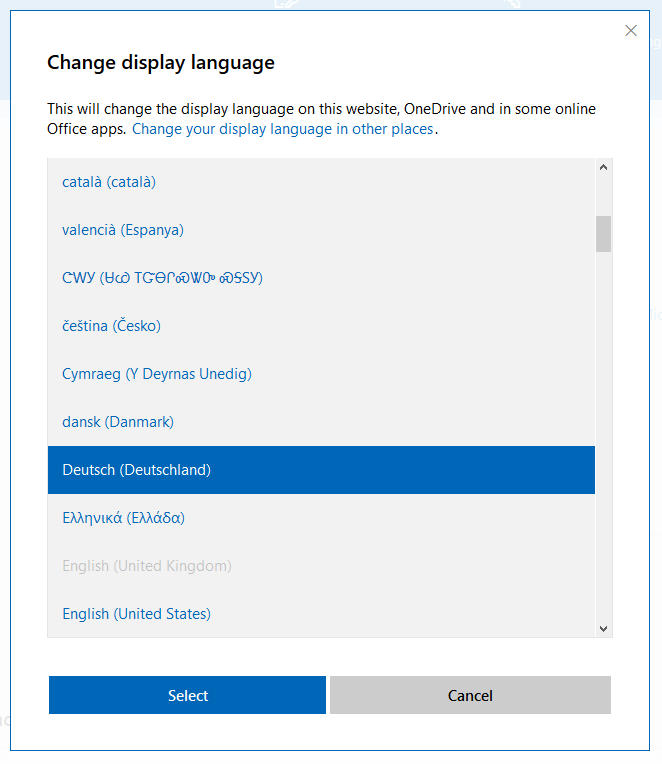
3. Save your changes by choosing “OK”. The OneDrive interface is then displayed in your browser in the new language.
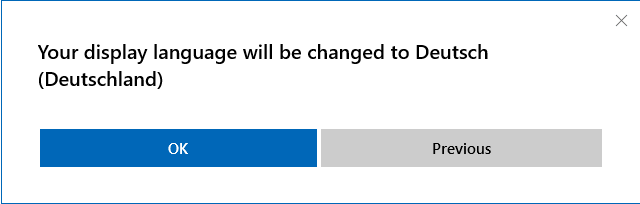
4. You have to confirm a second time to verify that you can read the new language.

5. The user interface of Word Online will appear in the new language once you have confirmed a second time.
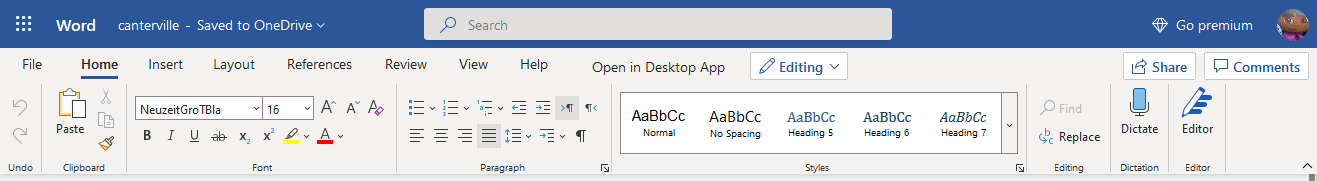

Tip
Microsoft 365 is a server-based office solution that includes the popular Office applications Word, Excel and PowerPoint and is ideal for home users and small businesses. Automatic updates ensure that you always have the latest version.
Changing the editing language in Word Online
In Word Online, the editing language is set individually for each document. Open a document, select all text using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + A or select several paragraphs. Right-click within the selected area. A toolbar and a context menu will appear. In the context menu, select “Set Proofing Language”. A list of available languages will appear. Select the language you want to use and click “OK”.
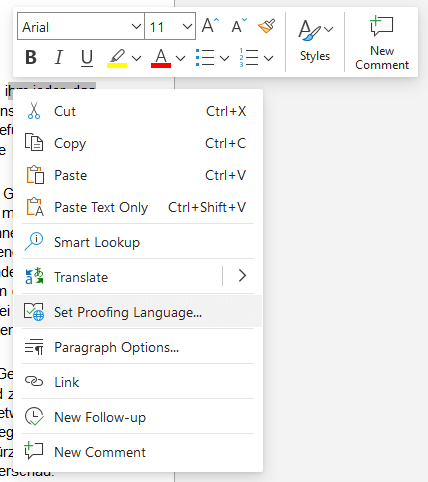
The procedure for setting the language is slightly different in the macOS version of Microsoft Word. To change the editing language on a Mac, go to “Tools” -> “Language” and select the desired language. If you want to use this editing language as the default language for all new documents, click the “Default” button.
The display language for Word cannot be changed independently of the operating system language in macOS. Word always uses the system setting on a Mac. If you want to change the display language for the user interface, you have to change the language for the operating system. You can find this setting in the Apple menu under “System Preferences” -> “Language & Region”.

Word table: Creating a table in Microsoft Word
In Word, tables prove useful in the most diverse situations, and you have several options for creating them. You can either use the table templates provided by the Microsoft tool, or you can design your own. This enables you to improve your reports, invoices or the performance of household tasks. Even data from Excel can be integrated as a table into a Word file.
Word table: Creating a table in Microsoft Word

Word Shortcuts: an overview of the best ones
Word shortcuts make working with the popular word processing program quicker and easier. Whether you are copying text, printing a document or changing the formatting – many commands do not need a mouse click to be activated. Thanks to shortcuts, you can work faster and more effectively. Here is a list of the most common Word shortcuts.
Word Shortcuts: an overview of the best ones

Inserting footnotes and endnotes in Word
When you insert footnotes and endnotes in Microsoft Word, you’re able to provide supplemental context by explaining technical terms, commenting on paragraphs or adding citations to sources. These comments don’t disrupt the flow of the text because they are separate sections within a document. At the same time, they allow the reader to look up a respective passage where necessary. We’ll show you…
Inserting footnotes and endnotes in Word

Microsoft Word: Find and Replace made simple
Microsoft Word’s Find and Replace function is an extremely useful tool if you have to adapt particular terms in a text. From changing a name to correcting a common spelling mistake, the function helps you in a wide range of situations. But it also has its peculiarities. This guide will help you use the Find and Replace function in Word correctly and avoid pitfalls.
Microsoft Word: Find and Replace made simple

Password-protect a Word document
By password-protecting a Word document, you are encrypting important data from unauthorized access or unlawful modification. Your Microsoft Word or Office program file can only be opened if a valid password is entered. Password-protecting a Word document is also possible in older versions of Word.
Password-protect a Word document
Microsoft Word is one of the most popular and widely used programs for documentation purposes around the world. If you hail from a non-English speaking country, then you may want to use MS Word in your own language or any other language of your choice.
Sometimes, you may want to access accent marks or include special characters from a different language in your writing – this would require you to change the MS Word language itself. Fortunately, Microsoft Word allows you to change the editing language, proofing tools, and the user interface language (display language) and set a different display language while applying another language in editing and proofing documents.
In this article, we’ll show you how to change the display language as well as the editing and proofing language in Microsoft Word. Throughout the post, we’ll be using Microsoft 365 but most of the options are similar to the offline versions (2019, 2016, 2013, or 2010) and Office 365. So irrespective of the version you’re using, this article can surely help change or switch up the language(s) on your Microsoft Word.
Changing the Display and Help Languages
When you install Microsoft Office, it usually has English as its default language or the local/regional language of the location that powered the MS Word purchase. If you want to change this language(s) to any other, you would have to manually install it/them first.
A display language is the one that’s visible on all tabs, menus, buttons, preferences, dialog boxes and other controls on your Word application. If you want to use a different language instead of the default, follow these steps:
Open Microsoft Word and click the ‘File’ tab.
In the backstage view, click ‘Options’.
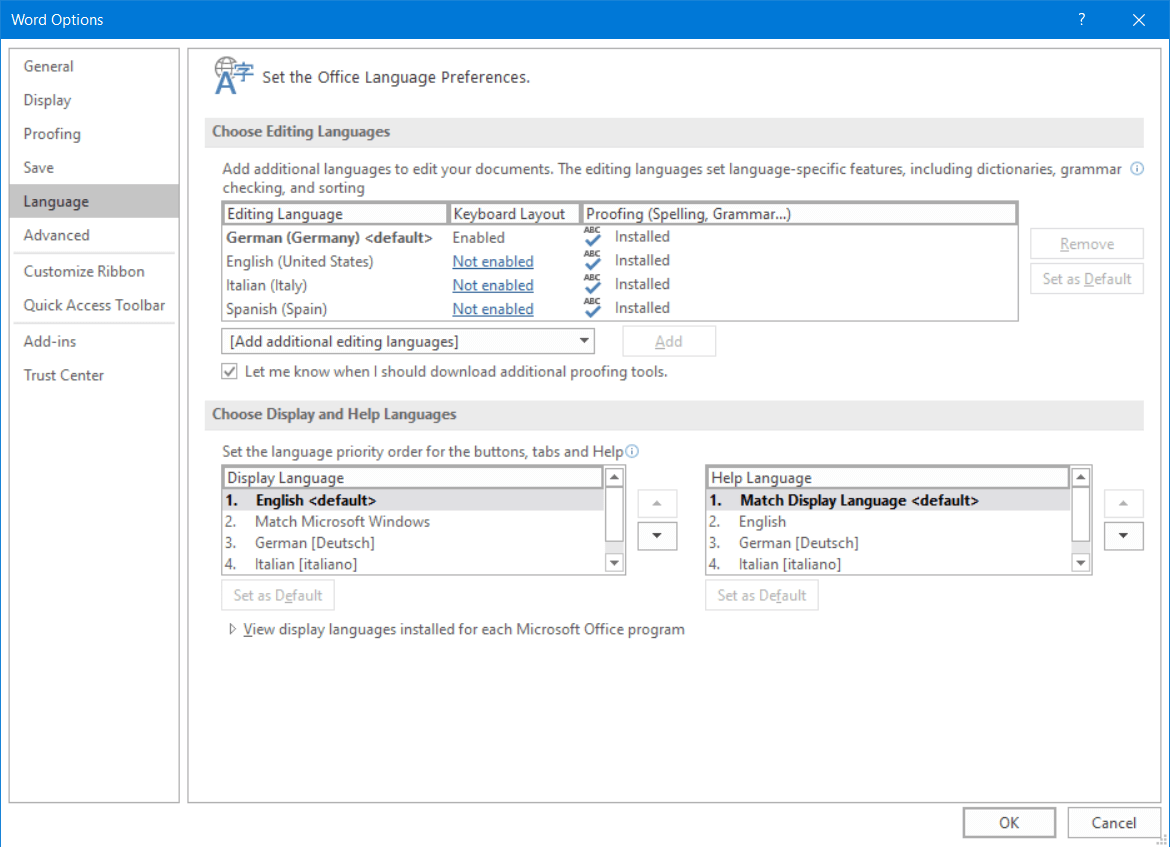
A Word Options dialog window will appear. Here, select the ‘Language’ tab. In the Language tab, you will see two sections – ‘Office display language’ and ‘Office authoring languages and proofing’.
If you are using Office 2019, 2016, 2013, or 2010, you will see ‘Choose Editing Languages’ and ‘Choose Display Languages’
‘Office display language’ or ‘Choose Display Languages’ section is where you can set the MS Word display (UI) language. You’ll see a list of installed languages under this section. If the language you’re looking for is not in the box, you would have to manually download and install that particular language pack.
Adding Language Packs on Office
If a specific language is not listed here, click the ‘Install additional display languages from Office.com’ link below the box (as shown below).
This will show you a ‘Install a display language’ dialog. Here, choose your language and click ‘Install’.
This will take you to the Microsoft website where you can download the language pack for the selected language as shown below. Here, click the ‘Download’ button.
Run the downloaded setup file to install it.
Wait for the installation to complete, then close and re-launch Word. Sometimes, you may need to reboot your computer for smoother functioning.
Then, open the MS Word app again and go to File > Options > Language. As you can see, the ‘Office display language’ box lists the installed language. Now, select your desired language and click the ‘Set as Preferred’ or ‘Set as Default’ option (for Office 2019 and older versions).
After you select the ‘Set as preferred’ or ‘Set as Default’ button, your selected language should show ‘<preferred>’ at the end as shown below. Then, click ‘OK’.
Adding Language Packs from Office Webpage
Alternatively, you can directly visit the MS Office’s Language pack for Office page, where you can download the language you wish to use. Microsoft Office offers over 100 additional language accessory packs which you can download and install for free.
Once you’re on Office’s language accessory pack webpage, scroll to see a section called ‘Step 1: Install the language accessory pack’. Under this section, select your Office version tab.
Then, choose your language from the ‘Which language do you need?’ drop-down.
Once you select the language, you’ll notice the ’32-bit’ and ’64-bit’ download links. If your operating system is of 32-bit architecture, click ‘Download (32-bit)’. Or if your system uses 64-bit OS, then, select the ‘Download (64)’ bit.
After the file is downloaded, install the setup file, close, and re-open the Word app. Then, go to the Word Options menu, choose the language pack you installed under the ‘Office display language’ box and select ‘Set as Preferred or ‘Set as default’. Then, click ‘OK’.
Restart Word and you’ll see that the UI language is changed for MS Word.
Changing the Editing and Proofing Language
The editing/authoring language is the language in which you write and edit documents. This language also controls the text direction and arrangement for vertical, right-to-left, and mixed text. The Proofing tool checks for spelling and grammatical errors. If the editing/input and proofing language is already installed on your computer, you can easily change it. If not, you need to first manually install the language and then change it.
Open the Word application, click the ‘File’ tab and select ‘Options’ to open Word Options. You can also open the Word Options window by switching to the ‘Review’ tab in the Ribbon and clicking the ‘Language’ button and then selecting the ‘Language Preference’ option.
In the Word Options, select the ‘Language’ tab. You’ll see the ‘Office authoring languages and proofing’ or ‘Choose Editing language’ section where you can add and set the language for editing. When you install MS Word, the app will automatically be configured to use the default system language.
The ‘Office authoring languages and proofing’ box lists all installed system and Office languages. If the language you want to change is on the list, select the language and click ‘Set as Preferred’ or ‘Set as Default’.
Installing Additional Input Languages for Word
Follow these installation steps if a specific language is on the ‘Office authoring languages and proofing’ box.
To add an authoring language, click the ‘Add a Language..’ button.
Select the language you want to add and click ‘Add’.
Most of the time, even if you add the language, you still have to manually install the language or additional proofing tools on your Windows OS.
To install additional input/editing language on your computer, click the ‘Install additional keyboards from Windows Settings’ link below the Office authoring languages and proofing box.
This will open the Windows Settings page where you can install languages on your system. Click the ‘Add a language’ button (if you have Windows 10 or 11).
In the ‘Choose a language to install’ dialog box, choose a language and select ‘Next’.
On the next page, select ‘Install’.
Once done, you’ll see the installed language in the list of languages.
Usually, when you type on your computer, the system will use the default input language (first in this list) to input characters. So, you should change the input language to the recently installed language to actively use the latter. You can do this via the settings application or from the taskbar.
Via Settings App
To change the input keyboard layout, select the ‘Time & language’ settings, and click the ‘Typing’ option.
Then, select ‘Advanced keyboard settings’.
Now, choose your input method to use as a default.
Via Taskbar
OR, you can easily switch between the input method from the taskbar.
After you installed the language, go back to File > Options > Language. In the Word Options, you’ll notice the installed language in the ‘Office authoring and proofing language’ box.
To remove an editing language, first, select the language and then hit ‘Remove’.
Installing Proofing Tools
Sometimes, proofing tools may not be installed on Office even after installing the input language. If you’re using Microsoft 365, you would see three proofing tool statuses next to each language, namely – ‘Proofing available, Proofing not available, Proofing installed’. For other Office suites (like Office 2019, 2016, etc.), the status will be shown as ‘Enabled’ or ‘Not enabled’ under the Keyboard layout column.
‘Proofing not available’ means the proofing tools are not available for that particular language. ‘Proofing available’ suggests you download and install the language pack with proofing tools for that language. And ‘Proofing installed’ means the proofing tools are installed for that specific language and you are free to use them.
If Proofing tools are available but not installed, click the ‘Proofing available’ link next to the language you want to use to download the language pack.
This will direct you to the Language pack download page on the Microsoft Office website. Here, click the ‘Download’ button.
After the download is complete, install the ‘OfficeSetup.exe’ file, wait for the installation to complete, then close and re-launch the Word app.
After re-launching the app, go to Word Options. You’ll now see ‘Proofing installed’ next to the chosen language. Now, select the language and click ‘Set as Preferred’.
Word will show you a warning message to let you know that the authoring language you just chose will take effect the next time you launch Office. It also warns you of changes that may occur to custom settings (like your preferred default font). If you want to continue, click ‘Yes’. Then, click ‘OK’ to close the Word Options.
Now, restart your Microsoft Word, again, to change the editing and proofing language.
Once the Word editing language is changed, you would have to change your keyboard layout to type text in the changed language. Usually, the keyboard layout language matches the characters of a different language as the keys on your keyboard would automatically translate to the chosen different language on your screen. Essentially, the keyboard layout language controls and changes display characters when manually typed.
Switching Between Keyboard Layouts
When you install a new language on your OS, it comes with a keyboard for language-specific key layouts and input options. After you install more than one keyboard layout for different languages, you can easily switch between those keyboard languages using the language bar.
When you change/switch the keyboard language, the keyboard layout shifts to the keyboard for that particular language. For instance, if you are writing something in English and if you want to include content in a different language, you can quickly switch between keyboard layouts to write in different languages.
Here’s what you need to do to change the keyboard layout to a different language.
When you have more than one layout installed, the Language bar (language abbreviation) automatically appears in the ‘System Tray’ or ‘Notification Area’. To change the keyboard layout, click the language icon (ENG stands for English keyboard) and select the language you want to use from the list of available keyboards.
If you have Windows 10 or 11, you can press Windows+Spacebar to switch layouts. The language abbreviation represents the active keyboard layout of the system.
Now, you can easily write and edit Word documents using a different language.
Proofreading in Different Languages
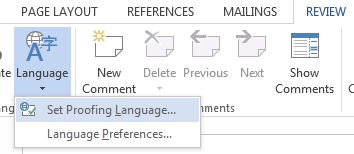
MS Word also allows you to write or edit in one language and proofread text in another. To proofread in a different language, go to the ‘Review’ tab, select ‘Language’, and click the ‘Set Proofing Languages..’ option.
Then, select the language from the Language dialog box and click ‘OK’. Here, you also have options to ignore spelling/grammar errors, detect language automatically or set the default language.
For instance, if you want to include a word or phrase in a different language without showing grammatical errors, you should only change the proofing language for the particular word or phrase.
To do this, first, select the word or phrase, then go to the ‘Review’ tab, select ‘Language’ and click the ‘Set Proofing Languages..’ option. Then, choose a language from the list and click ‘OK’. Word will ignore spelling and grammar on the highlighted selection.
That’s it, folks! You can now easily change both the display and editing and proofreading languages on your MS Word to any language(s) of your choice.
The automatic spellchecker in Microsoft Word is far from perfect, but it can be useful for spotting mistakes in your written work. First, though, you’ll need to know how to change the language settings.
This is vital because even regional variations of English can differ in spelling, which means the automatic spellchecker will miss mistakes if the wrong settings are used. Luckily, changing the language in Microsoft Word is a quick and simple process.
Changing Language Settings
There are two main ways to set the language of a new document in Microsoft Word. The first is to use the “Review” tab on the main ribbon:
- Go to the “Review” tab and find the “Language” section
- Click on “Language” and select “Set Proofing Language…”
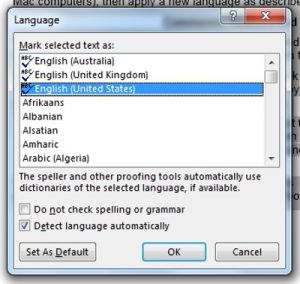
- Choose the language required in your document from the new window and click “OK”
The second option is possibly even simpler:
- Click on the language section of the blue bar at the bottom of your document (this will display the current language settings by default)
- In the new window, select your chosen language and click “OK”
Either approach will ensure the spellchecker looks for spellings specific to your region. For American English, the correct option is “English (United States).” If you click “Set as Default,” the same settings will be applied to all new documents.
Applying a New Language to Existing Text
If you’re applying new language settings to an existing document rather than starting from scratch, you’ll need to select the text you want to modify first.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
You can do this by selecting the passages you want to check and using the steps outlined above to pick a new proofing language. This also allows you to use different language settings in different parts of the same document, if required.
Alternatively, you can quickly select all of the text in a document using “Ctrl + A” (or “Cmd + A” on Mac computers), then apply a new language as described above.
Comments, Headers and Footnotes
For reasons beyond the comprehension of mortal minds, Microsoft treats the language options for comments, headers and footnotes as separate from the main text in your document.
If you’re using any of these features, you’ll need to check that the language settings are consistent with the rest of your document. You can do this either by selecting the relevant text and using the process described above, or by following these steps:
- Go to “Styles” and right click the style you want to update (e.g., “Header”)
- In the dropdown menu, click “Modify…” to open a new window
- In this menu, click “Format” in the bottom left and select “Language”
- Pick the language required and click “OK”
This will ensure consistency between different parts of the document in question, which is especially important if your paper includes extensive footnotes.