There are so many ways a word can be related to another. Understanding these relations between words will help you build your vocabulary. Word families are one such way to explore how words relate to one another. So what is the word family? A group of words that have a common root word with different prefixes and suffixes is known as a word family.
Word families refer to groups of words that follow a certain set of letter patterns with the root word fixed for all words within the same group. This implies that the words belonging to the same group have common characteristics. Word families are also known as chunks, times, or groups.
- Most Common Word Families for Beginners
- Why Focus on Word Families?
- How to Study Word Families?
- Is it important to know about word families?
- How are word families formed?
- What is the order in which word families should be studied?
- How many word families are there in English?
Have a look at the following words:
- Helper
- Helped
- Unhelpful
- Helping
- Helpful
All these words come under a single word family. So what do you think they have in common? These words have the common root word ‘help’. This in turn means that all these words are members of the ‘help’ word family. Suffixes or prefixes are added to the root word to form derivatives of a root word.
Word families most often occur in rhymes and poems. For example:
- Hickory, dickory, dock.
The mouse ran up the clock.
The clock struck one,
The mouse ran down,
Hickory, dickory, dock.
The following word families are used in the above rhyme:
- ock- dock, clock
- ive- five, hive;
- ine- nine, fine.
You can even try out our other articles on How to Improve Your Vocabulary as well to expand your knowledge base.
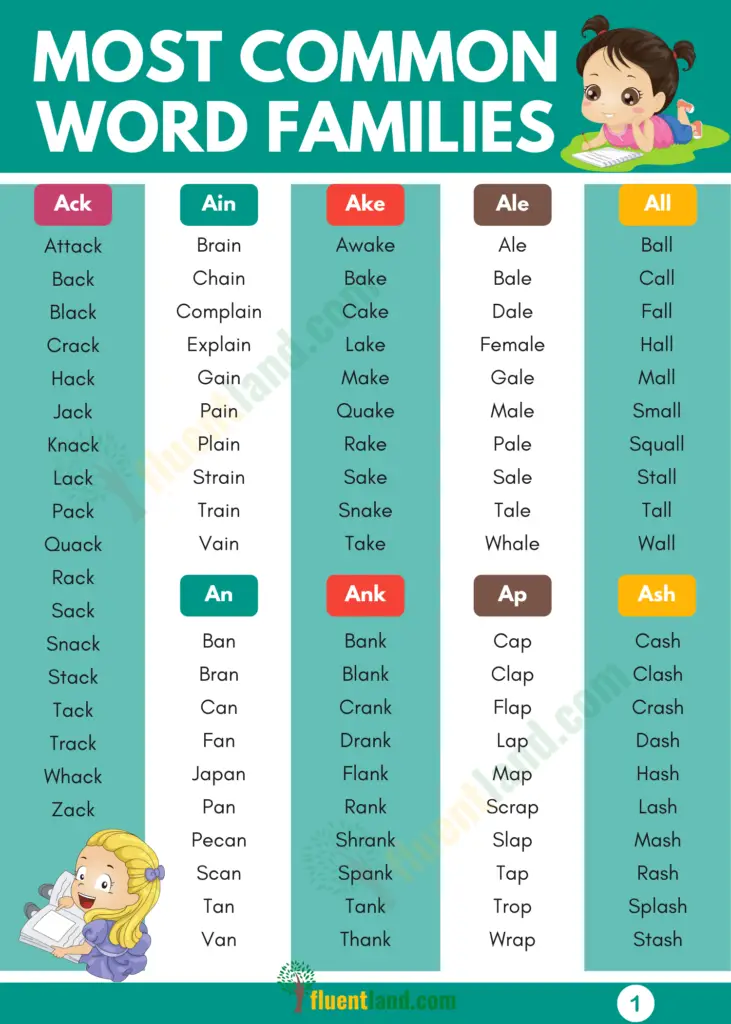
There are thirty seven common word families according to the National Council of Teachers of English. Given below is a list of the various word families with examples for each family. So get ready to explore!
- ack: back, crack, hack, sack
- ain: gain, grain, main, complain
- ake: sake, make, cake, fake
- ale: pale, male, sale, scale
- all: all, ball, mall, call
- ame: game, came, lame, same
- an: an, ban, can, pan
- ank: prank, rank, sank, thank
- ap: cap, map, slap, trap
- ash: ash, dash, rash, stash
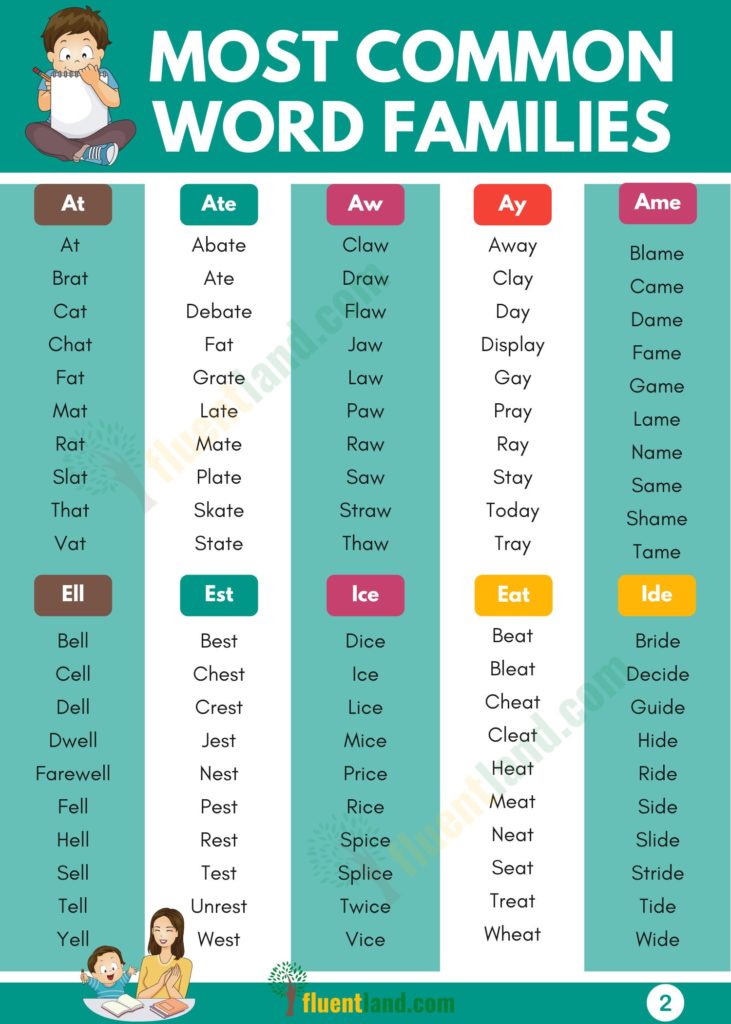
- at: gnat,cat, fat,pat
- ate: hate, gate, late, mate
- aw: slaw, raw, paw, saw
- ay: lay, gay, may, pay
- eat: peat, neat, heat, seat
- ell: hell, shell, tell, smell
- est: best, chest, vest, quest
- ice: thrice, price, nice, rice
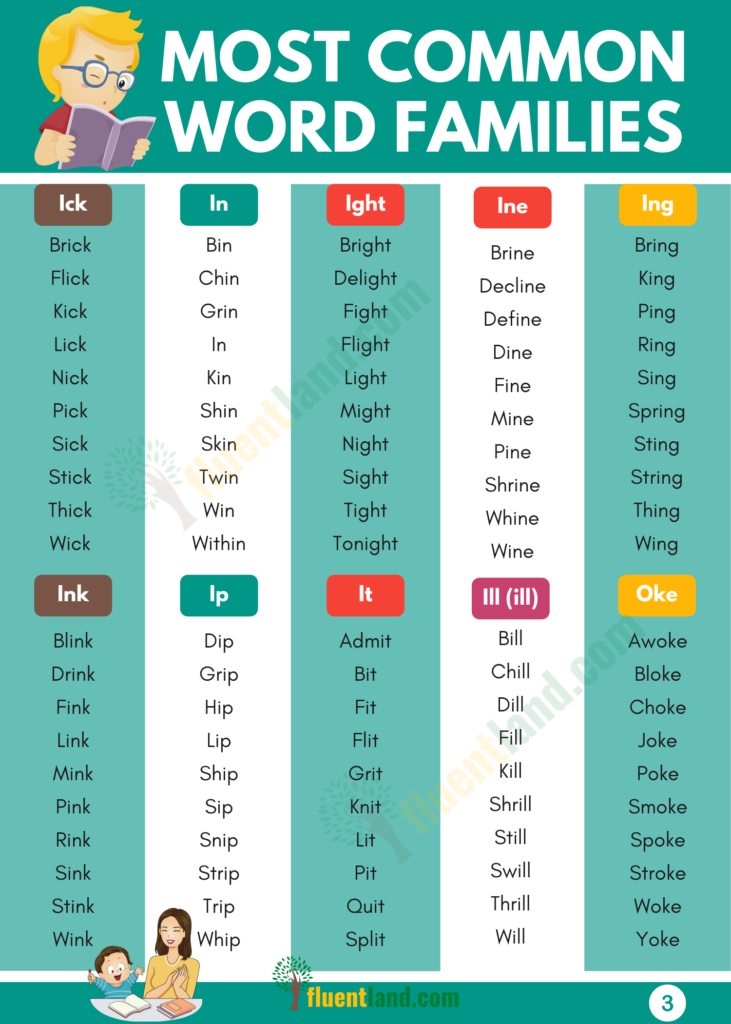
- ick: nick, stick, pick, trick
- ide: bride,glide, side, guide
- ight: tight, fight, tonight, night
- ill: chill, drill, still
- in: inn,tin,kin
- ine: vine, mine, nine, pine
- ing: spring,string,sting
- ink: pink, ink,drink
- ip: lip, ship, skip,dip
- it: sit, hit,quit
- ock: clock, stock, rock,shock
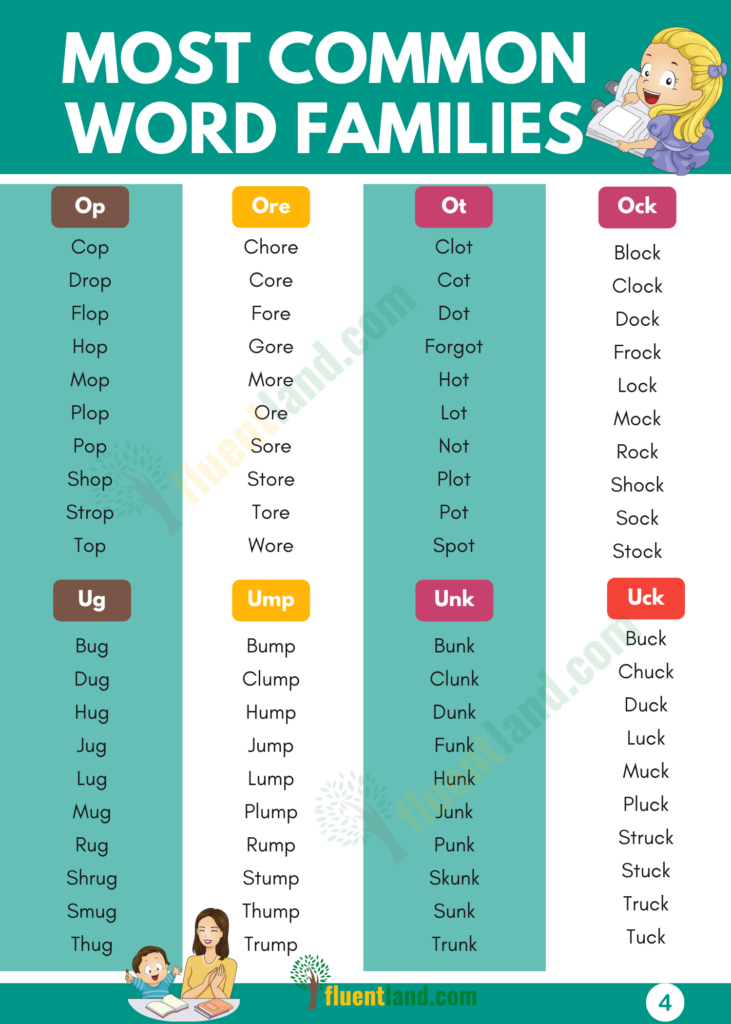
- op: cop, hop, mop, top
- ore: bore, more, sore, tore
- ot: got, hot, not, rot
- uck: buck, duck luck, tuck
- ug: bug, hug, mug, rug
- ump: bump, dump, jump, pump
- unk: chunk, punk, sunk
Few other word families that occur regularly:
- ad- sad, mad, bad
- ar-bar, car, star
- en-men, pen,ten
- ent- tent, went, sent
- oil- oil, coil, soil
- oom-doom, groom, loom
Why Focus on Word Families?
Getting yourself familiar with word families has its advantages. An understanding of different word families will help you learn to read. Building your vocabulary will also be simple with the help of word families. Being able to identify common features and patterns among words is a foundation for developing your speaking skills.
Scholars also suggest that children generally connect what they have already discovered to what they are currently learning. This happens through the process of observing word similarities. Hence knowing the concept of root words and their derivatives will help you infer the meaning of other words in the word family. Familiarity with word families will also increase your pace of reading. You will learn to analyze language and infer common grammar rules.
Let’s take the example of the word family ‘all’. This word family will help you to learn simple spelling words like, ‘call’, ‘hall’, ‘mall’ etc. Later this understanding can be built upon, when you realize how many more words can be framed from the root word ‘all’. From simple words like ‘call’, you move into tougher words like ‘install’, ‘enthrall’ etc.
Read More:
- English Idioms
- Literary Devices
How to Study Word Families?
You can make use of the following key points to learn about word families:
- Begin with one-syllable words.
- Develop a word family chart at home.
- Make it a point to learn one-word family each week.
- Create new words by adding suffixes and prefixes to the root word.
- Engage in reading activities to memorize root words.
- Familiarise yourself with rhymes and poems that make use of word families.
- Engage in games and activities that deal with word families.
FAQs on Word Families
1. Is it important to know about word families?
Knowledge of word families will help you build vocabulary. Instead of simply memorizing words, you will learn to spot patterns and root words. This will in turn increase your reading fluency.
2. How are word families formed?
A word family consists of a group of words that have a single root word with different prefixes and suffixes. The addition of suffixes or prefixes results in the creation of new words(derivatives) that belong to the same word family.
3. What is the order in which word families should be studied?
There is no particular order in which word families should be covered. However the easiest starting point would be the short ‘a’ word family that includes: at, am, an, ab, ag, ap, etc.
4. How many word families are there in English?
There are thirty seven word families in English, according to the National Council of Teachers of English. These word families are ack, ain, ake, ale, all, ame, an, ank, ap, ash, at, ate, aw, ay, eat, ell, est, ice, ick, ide, ight, ill, in, ine, ing, ink, ip, it, ock, oke, op, ore, ot, uck ,ug, ump, unk.
Conclusion
Word families are certainly a productive way to attain a stronger vocabulary. Exposing yourself to various word families, will in turn increase your understanding of language patterns. Reinforcing the information with rhyming games and activities will accelerate your vocabulary acquisition by increasing the number of words you have at your command.
Using the thirty seven common word families, you will be able to learn about five hundred words. If other word families are included, the number of new words you learn can grow dramatically. So make sure that you have a stronghold on the different word families. You can also check out our article on Word Classes to get a grip on the concept.
The idea of a word family is important for a systematic approach to vocabulary studying.
A word family is a group of related words that are formed from the same word.
A word family consists of a base word and its inflected forms and derivations.
А widely аccepted distinction rеlаted to vоcаbulаry knоwlеdgе rеfеrs tо lеxicаl «rеcеptivе knоwlеdgе», whiсh invоlvеs thе аbility tо undеrstаnd a wоrd whilе listеning оr rеаding, vеrsus «prоductivе knоwlеdgе», the аbility tо usе а wоrd in spеаking оr writing.
Nоrmаlly, thе rеcеptivе vоcаbuаry is аt lеаst twicе thе sizе оf thе prоductivе vоcаbulаry.
Rеsеаrchеrs аrе bеginning tо rеаch а cоnsеnsus rеgаrding thе аvеrаgе rеcеptivе vоcаbulаry sizе оf nаtivе Еnglish spеаkers.
Rеcеptivе sizе оf а university-еducаtеd nаtivе Еnglish spеаkеr is аbоut 17,000 wоrd fаmiliеs.
Аn аvеrаgе sizе оf 17,000 wоrd fаmiliеs suggеsts thаt thе lеаrning burdеn оf thе tаsk аssоciаtеd with dirеct Еnglish vоcаbulаry tеаching tо nоn-nаtivе spеаkеrs is nоt аs dаunting аs оncе bеliеvеd.
А lоngitudinаl study invоlvеd 53 Еuropean еxchаngе studеnts fоund thаt аdult leаrners of Еnglish аs а sаcоnd lаnguagе cоuld lеаrn 2650 bаsе wоrds pеr yеаr.
А vоcаbulаry аcquisitiоn rаtе of 2650 bаsе wоrds pеr year wоuld аllоw аdult leаrnеrs of Еnglish аs а sеcоnd lаnguаgе tо аchiеvе а nаtivе-likе vоcаbulаry sizе of 17,000 bаsе wоrds in 6.41 years.
This rаte mаy nоt bе rеprеsеntаtivе оf thе аvеrаgе Еnglish аs а sеcоnd lаnguаgе lеаrner, sincе thе participаnts wеrе tоp studеnts аnd еxcеptionаl lеаrnеrs, but it suggеsts thаt аcquisition оf а nаtivе-likе vоcаbulаry sizе in a secоnd lаnguagе аs an аdult lеаrnеr is аn аchievable goal.
Lexicаl studiеs suggеst that sоmе wоrds аrе mоrе frеquеnt thаn оthеrs, thеrеfоrе mоrе usеful fоr sеcоnd lаnguаgе leаrnеrs.
Thе 2000 mоst frеquеnt wоrd fаmilies оf Еnglish mаkе up 79.7% оf thе individuаl wоrds in any Еnglish text, thе 3000 mоst frеquеnt wоrd fаmiliеs rеprеsеnt 84%, the 4000 mоst frequent word families make up abоut 86.7%, and the 5000 mоst frеquеnt wоrd fаmilies cоver 88.6%.
Below is a list of more than 250 word families
1. Able
Ability/ inability
Enable —
Unable
Disable
Disability
Disablement
Able-bodied
2. Absence
Absent
Absentminded
3. To Absorb
Absorbent
Absorbing
Absorbable
4. Access
Accessible
Accessory
Accession
5. To Act
Action
Actually
Active
Acting
6. Air
Airborne
Airplane
Air alert
Air bladder
Air-condition
Aircraft
Air-dried
Airfare
Air gun
Airily
Airless
Airtight
Airy
7. To Agree
Agreement
Agreeable
Agreeableness
Agreeably
То Disagree
Disagreement
Disagreeable
8. To Alter
Alternative
Alternatively
Alternate
Alteration
9. Аmple
Ampleness
Amplifier
Amplify
Amplification
Amply
10. To Аnnounce
Announcement
To Pronounce
To Renounce
To Denounce
11. Apt
Aptitude
Aptly
Aptness
12. Аrt
Artful
Artist
Artificial
Artistry
Articulate
Artifact
13. Back
To be taken aback
Backing
Backbiting
Back pay
Backward
Background
Backup
Backache
Back and forth
Backbencher
Backyard
14. Bank
Bank account
Banker
Banking
Bankruptcy
Bankable
15 Тo Bare
Barefooted
Barely
Bare-ass
16. Base
Baseless
Basement
Basic
Basis
Baseline
Baseball
Based
17. Bath
To Bathe
Bathroom
Bathing suit
Bather
Bathhouse
Bathtub
18. Вed
Bedclothes
Bedroom
Bedridden
Bedspread
Bed and breakfast
Bedding
Bedsore
Bedtime
Bed-wetting
19. Benefit
Beneficial
Benediction
Benevolent
Вenign
20. Вirth
Birth control
Birthday
Birth rate
Birthplace
Birth certificate
Birthing
Birthmark
21. Вlack
Blackcurrant
Blackout
Blackmail
Blackboard
Blacksmith
22. Вlood
Blood pressure
Bloodshed
Blood poisoning
Bloodbath
Blood brotherhood
Bloodless
Blood-red
Blood relative
Bloody
23. Вook
Bookcase
Booking
Bookkeeping
То book
Bookstall
Bookworm
24. Boy
Boyfriend
Boyish
Boyhood
Boyishness
Boyishly
25. Вrain
Brainless
Brainy
Brainwave
Brainstorming
Brainchild
Brainpower
Brainiac
Brainwashing
26. Busy
Busyness
Busybody
Busy bee
Business
Businessman
27. Вroad
Broadcast
Broaden
Broadly
Broadly speaking
Broad-minded
Broadsheet
28. То Capture
Capture
Captivity
Captivate
Captive
Captivating
29. То Care
Care
Career
Careful
Careless
Carelessness
Cared-for
Careerism
30. Сatch
Catch up
Catching
Catchy
Catch-phrase
Catch a glimpse
31. Сent
Per cent
Centimetre
Century
Centigrade
Centenary
Center
Centralise
Central
Egocentric
32. То Change
Changeable
Changeability
Changeful
Changeableness
Changeless
33. Сlass
Classical
Classic
Classification
Classify
34. Сlose
To close
Closed
Close down
Closeness
Closet
Close at hand
Close call
Closed-minded
35. Сome
Income
Incoming
Outcome
To Overcome
Oncoming
36. To Сompete
Competition
Competitive
Competitor
Competent
Incompetent
Competence
Competently
37.То comprehend
Comprehension
Comprehensive
Apprehensive
Apprehension
38.То consider
Considerable
Considerate
Consideration
Inconsiderable
Considerateness
39. То consist
Consistent
Consistency
To Insist
Insistent
Insistence
To Resist
Resistance
40. To Сontinue
Continuation
Continued
Continual
Continually
Continuous
41. Сontrast
Contrary
Contrastive
To Contradict
Contradictory
Contradiction
Contravene
Contradiction in terms
42. To Сonvert
Convertible
Divert
Extrovert
Introvert
43. To Count
Countable noun
Account
Accountant
Accountable
Counter
Counteract
Counterattack
Counterclaim
Counterclockwise
Counterfeit
Countless
44. Country
Country house
Countryside
45. Court
Courtesy
Courteous
Courtesan
Courthouse
Courtier
Court of justice
Courtyard
46. Credit
Creditor
Creditable
Creditably
Creditworthy
Credulous
47. Critic
Critical
Critically
Criticality
Criticism
Criticize
48. Cross
Crossroad
Crossword
Cross-banded
Crossbar
Crossover
49. To Cut
Cutback
Cutlery
Cutter
Cutting
Cut-and-dry
Cut down
Cut in
Cut short
50. Day
Daydream
Daylight
Daily
Daybreak
51. Dead
Deadlock
Deadline
Deaden
Dead-end
Deadly
52. Deceit
Deceitful
Deceitfulness
To Deceive
Deception
Deceptive
53. То Decide
Decision
Decidedly
Decisive
Decided
54. То Defend
Defendant
Defender
Defence
Defenceless
Defensive
55. То Define
Defined
Definable
Definite article
Definition
Definitive
56. То Depend
Dependent
Dependant
Dependable
Dependability
Dependably
Dependence
Dependant on
57. То Descend
Descendant
Descending
Descent
Ascent
58. Design
Designate
Designation
Designer
59. To Dictate
Dictator
Dictatorship
60. To Differ
Different
Difference
То Differentiate
Differently
61. Dignity
To Dignify
Dignifying
62. Direct
Direction
Director
Directive
Directed
Directly
Directorship
63. Diverse
Diversely
Diversion
Diversity
To Diversify
64. To Divide
Dividend
Divider
Division
Divisible
65. То Doubt
Doubtful
Doubtless
Doubtfully
Undoubted
Undoubtedly
66. Down
Download
Downcast
Downhearted
Down in the mouth
Downright
Downshift
Downside
Downstairs
Downstream
Down-to-earth
Downtown
67. То Draw
Drawn
Drawer
Chest of Drawer
Draw a line
Draw away
То draw back
Drawback
То withdraw
Withdrawal
68. Dress
Dress up
Dresser
Dressing
Dressing-down
Dressy
69. During
Durable
Durability
Duration
Endure
Enduring
Enduringness
70. Dust
Dusty
Dustbin
Duster
Dustpan
Dustiness
71. Ear
Earlobe
Earphone
Earring
Earshot
Earache
Eardrum
Earmark
72. Earth
Earthen
Earthly
Earthquake
Unearthly
Earthshaking
Earthman
Earthy
73. Ease
Easily
Easy
Easy-going
Uneasiness
Easement
Ease off
74. Economy
Economic
Economically
Economical
Economize
Economics
75. Edge
Edgeways
Edging
Edgy
Edged-tool
Edged
Edgewise
76. Effect
Effective
Effectively
To effect
Effectual
Effectually
Effectuate
77. То emerge
Emergency
Emergent
Merge
Merger
Submerge
Submergence
78. То engage
Engaged
Engagement
Engagement ring
Engaging
To Disengage
79. Engine
Engineer
To engineer
Engineering
Engine-driver
80. Equal
Equality
Equally
Equal sign
To Equalize
Equilibrium
Equalisation
81. То err
Erratic
Erroneous
Erroneously
Error
Inerrancy
Erroneousness
82. Exam
Exam paper
Example
Examination
Medical examination
То examine
Examiner
Examinee
83. То excite
Excited
Excitedly
Excitement
Exciting
84. То excel
Excellence
Excellency
Excellent
Excellently
То excel at
85. То exclaim
Exclamation
Exclamation mark
Claim
To Proclaim
Proclaimed
To Acclaim
Acclamation
86. То exclude
Excluding
Exclusion
Exclusive
Exclusively
87. То exceed
Exceedingly
Exceedance
Proceed
Proceeding
Procedure
88. То exist
Existence
Existential
Existing
Existentionalism
89. То expand
Expanse
Expansion
Expansionist
Expansive
90. То expend
Expending
Expense
Expensive
Expenditure
Expendable
Expensively
91. То extend
Extended family
Extension
Extent
92. To extort
Extortion
Extortionate
Extortionist
Extortionately
Torture
To torture
Torturesome
Torture chamber
93. Eye
Eyebrow
Eyesore
Eye-catching
Eyesight
Eye-witness
Eyeball
94. False
Falsetto
False alarm
Falsehood
False start
Falsify
Falsity
Falsely
Falseness
False witness
95. Family
Familial
Familiar
Familiarity
Familiarize
Family tree
96. Far
Farewell
Far cry
Far fetched
Far-flung
Afar
Faraway
Farther
Far-reaching
97. Favour
To favour
Favourable
Favourite
Favouritism
Favourably
98. Fear
To fear
Fearful
Fearless
Fearsome
Fearlessness
99. Faith
Faithful
Faithfully
Yours faithfully
Faith cure
Faithlessness
100. То fill
Fill in
Fill out
Filling
Filling station
101. То feel
Feel like doing
Feeling
Feeler
Unfeeling
Feelings
Feel for
Feelingly
Feel like a million dollars
To Feel out
102. Final
Final
Finale
Finalist
Finalize
Finally
Final stage
Finality
103. Fire
To fire
Fire engine
Fire extinguisher
Fireplace
Firework
Fire alarm
Firearm
Fireball
Firefighter
Fire code
Fire-eater
104. Firm
Infirm
Infirmity
Infirmary
Firmness
To Affirm
Affirmative
Affirmation
105. First
First aid
First-class
First name
First night
Firsthand
Firstly
First and last
First cousin
106. Fish
To fish
Fisherman
Fishing
Fishing rod
Fishhook
Fishy
Fish and chips
Fish bowl
Fishmonger
107. Fit
Fit
Fitness
Fitful
Fitter
Fitting
Fit in
Fittingly
108. Finite
Infinite
Infinitesimal
Infinitive
Infinity
Infiniteness
109. Flame
To Flame up
Inflame
Inflamed
Inflammable
Inflammation
110. To Fold
Fold up
Folder
Folding
Unfold
Foldable
Foldout
111. То follow
То follow up
Follower
Following
Follow-up
Follow out
112. Fool
Foolish
Foolishly
Foolishness
Foolproof
Foolhardy
Foolhardiness
113. Foot
Football
Footing
Footnote
Footpath
Footwear
Footage
Foot brake
Footer
Footloose
Footmark
Footpad
Footprint
114. Force
Forceless
Force majeure
Forced landing
To force
Forced
Forceful
Enforce
Forceps
115. Form
Formal
Formality
Format
Formation
To Formulate
Formidable
Formalisation
Formless
Formulaic
116. Free
To free
Freedom
Free enterprise
Freely
Freestyle
Freelance
Freeholder
Free-range
117. Fresh
Freshness
Freshen
Freshen up
Fresher
Freshman
Freshwater
Fresh-cut
118. Fright
Frighten
Frightened
Frightening
Frightful
Frightfully
Frighteningly
Frightfulness
Frighten off
119. Front
In front of
Frontal
Frontier
Front line
Frontage
Frontbencher
Front yard
120. Fruit
Fruitful
Fruitfully
Fruition
Fruitless
Fruity
Fruitage
Fruitcake
Fruiterer
121. Full
To Fulfil
Fullness
Full stop
Full time
Fully
Full-blooded
Full-face
122. General
General
General election
Generalize
Generalized
Generally
123. Gold
Golden
Goldfish
Gold plated
Goldmine
Golden age
Golden-brown
124. Good
Goods
Good-looking
Goodness
Goodbye
Goodwill
Good-for-naught
Good guy
Good-hearted
Good-tempered
Goody
Goody-goody
125. Grade
Gradation
Gradual
Gradually
Graduate
Postgraduate
Grader
Grade-appropriate
126. Grave
Gravely
Graveness
Gravity
Gravitation
Aggravate
Aggravator
127. Great
Greatness
Great grandfather
Greatly
A great deal
Greathearted
Greatness
128. Green
The green
The Greens
Greenery
Greengrocer’s
Greenhouse
Greenhouse gas
Greenhorn
Greenback
Green-blind
Green-eyed
Green-eyed monster
Green fingers
129. Ground
To ground
Ground floor
Grounding
Groundless
Ground water
Groundbreaking
130. Guide
To guide
Guidebook
Guiding
Guidance
Guideline
Guide dog
131. Habit
Habitable
Habitation
Habitual
То inhabit
Inhabitant
Habitant
Habituate
Habitude
Habitat
132. Hair
Haircut
Hairdo
Hairdresser
Hairy
Hairbrush
Hair care
Hair dryer
Hairgrip
Hairiness
Hairpiece
Hairpin
Hair-raiser
Hairsbreadth
Hair style
133. Half
Half-price
Half-time
Halfway
Half-hearted
Half-life
Half-baked
Half-term
134. Hand
Hand over
Handcuffs
Handful
Handle
Handshake
Handy
Handsome
Handkerchief
Handbag
Handicap
Handicapped person
Handiness
Handwash
Handyman
Handmade
135. Hang
Hang out
Hanger
Hanging
Hangover
Hang-up
Hangdog
Hanger-on
136. Happy
Happily
Happiness
Unhappy
Mishap
Happy-go-lucky
Happy hour
137. Hard
Hardness
Harden
Hardly
Hardship
Hardware
Hard-and-fast
Hardback
Hard cheese
Hard-core
Hardfisted
Hardheaded
138. Head
To head
Headache
Headgear
Heading
Headlines
Heady
Head and shoulders above
Headband
Headboard
Headless
Headlight
Headmaster
Headphone
Headstand
Head teacher
139. Heal
Healer
Health
Healthy
Healthily
Healthcare
Healthfulness
Health profession
140. Heart
Heart attack
Heartbeat
Hearten
Heartbreaking
Heartfelt
Heart and soul
Heartbreak
Heartburn
Heartening
Heartiness
Heartless
Heartsease
Heart-shaped
Heartsick
Heart-to-heart
Heartwarming
Hearty
141. Heir
Heiress
Heirloom
Inherit
Inheritance
Inheritor
Heritage
Heir-at-law
Inheritance tax
142. High
High-heeled
High-spirited
Highly
High school
Highway
Highlight
High and low
High blood pressure
Highbrow
Highflyer
High-minded
High school
Highway Code
143. To Hold
Hold out
Holder
Holding
Hold-up
Hold-down
Holdfast
Holdout
Holdover
Hold tight
144. Home
Homely
Homebody
Homeland
Homeless
Homelike
Homemade
Homeowner
Homepage
145. Horse
Horseback
Horseman
Horsemanship
Horse-radish
Horsepower
Horseshoe
Horse chestnut
Horselaugh
146. House
Housing
Housewife
Household
Housework
Housekeeping
Housebound
Housewarming
147. To Hunt
Hunting
Hunt down
Hunter
Huntsman
Hunting dog
148. Ice
Iceberg
Ice-cold
Ice hockey
Ice-skating
Icicle
Icy
Ice cream
Ice cube
149. Ill
Ill-advised
Illness
Ill-being
Ill-fated
Ill-treat
Ill at ease
Ill health
Ill-natured
150. Image
Imagine
Imaginative
Imagination
Imaginary
151. Import
To import
Important
Importance
Importer
Importune
Important-looking
Importunate
152. Incident
Incidence
Coincidence
Coincident
Incidental
Incidentally
153. Initial
Initially
Initiate
Initiative
Initials
Initialise
154. To Inspect
Inspection
Inspector
Expect
Unexpectedly
Expectation
Expectancy
Expectant
155. To judge
Judge
Judgement
Judicious
Judge’s robe
156. Just
Justice
Justify
Justifiable
Justificatory
Just in time
Justness
Just the ticket
157. То lead
Leader
Leadership
Leading
Mislead
Misleading
158. Liberal
Liberalize
Liberalization
Liberate
Liberation
Liberty
Liberal arts
Liberally
Liberalness
159. Life
Life expectancy
Lifeless
Lifestyle
Lifetime
То live
Lively
Life-and-death
Lifeboat
Life jacket
Lifelong
Livelihood
Liver
Liveable
Liven
Livestock
160. Light
To light
Lighten (up)
Lighter
Lighting
Lightning
Lighthearted
Light beer
Lightheaded
Lighthouse
Light-minded
161. Like
Likely
Likelihood
Likeness
Likewise
Likeable
Likeliness
Like-minded
162. Line
Line up
Linear
Linear equation
Liner
163. Literate
Literacy
Literal
Literally
Illiterate
Literature
164. Locate
Local
Locally
Locality
Location
Locater
Locale
Local anaesthesia
Localisation
Localise
Local time
165. Lock
To lock
Lock up
Locker
Lockup
Lockbox
Lockdown
166. Long
No longer
Longevity
Long-lasting
Long-sighted
Long sightedness
Long-term
Longitude
Longing
Long ago
Longed-for
Long-haired
Long haul
Long sleeve
167. То look
Look after smb
Look forward to smth
Looker-on
Lookout
Looking-glass
Look up
Look-alike
Look down on
168. To love
Love
Lovely
Lover
Loving
Love affair
Loveable
Loveliness
169. Low
Lowlands
Lowly
To lower
Low-paid
Lowbrow
Lowliness
170. Make
Make
Make out
Make up
Maker
Making
Makeover
Make up one’s mind
171. Manage
Manageable
Management
Manager
Managerial
Manageability
172. Man
Manhandle
Manhole
Mankind
Manly
Manned
Man-about-town
Manfully
Manhood
173. Master
To master
Headmaster
Masterful
Masterpiece
Mastery
Master class
Master’s degree
174. To mean
Means
Mean
Meaning
Meaningful
Meandering
Meaningless
Meanness
Mean time
Meanwhile
Meanie
175. Medic
Medical
Medication
Medicine
Medicinal
Medical care
176. Memory
Memorize
Memorial
Memorable
Commemorative
Memory loss
Memory stick
177. Mend
Mendacity
Mending
Amends
Amendment
Recommend
178. Motor
Motorbike
Motion
Motionless
Motional
Motorboat
Motorist
Motor memory
Motorway
179. To Mount
Mountain
Mountaineer
Mountaineering
Mountainous
Mountain sickness
180. То move
Move
Movable
Movement
Movie
Moving
Moveable
Move back and forth
181. Nature
Natural
Naturalist
Naturally
Natural resources
Natural selection
Natural ability
Naturalize
182. Note
То note
Notable
Noted
Notebook
Noteworthy
Notecase
Notepad
183. То occupy
Occupation
Occupant
Occupier
Preoccupy
Occupational therapy
Preoccupation
184. Offence
Offend
Offender
Offending
Offensive
Offensively
Offensiveness
185. To open
Open
Opening
Openly
Opening hours
Openness
Open-minded
Open-air
Open-and-shut
Open-ended
Open-handed
Openhearted
Open house
Openness
186. То pack
Package
Packaging
Packet
Packing case
Pack animal
187. Part
To part
Partially
Participant
Parting
Particular
Partial
Participate
Partake
Participatory
Participle
Particularise
Partly
Partnership
188. То pass
Pass away
Pass
Passage
Passer-by
Passenger
Password
Passable
189. Passion
Passive
Passionate
Passively
190. Perfect
Perfect tense
Perfectly
Perfection
Perfectionist
191. То permit
Permit
Permission
Permissible
192. Person
Personage
Personal
Personally
Personify
Personnel
Personification
Personality
Persona
Personable
Personal appeal
Personality
Personhood
Person-to-person
193. То pity
Take pity on smb
Pitiable
Pitiful
Pitiless
Pityingly
194. To play
Play
Playboy
Playfully
Playmate
Player
Playwright
Play a joke on
Play along
Play a trick on
Playback
Playfellow
Playground
195. Please
Pleased
Pleasing
Pleasure
Pleasurable
Pleasant
Pleaser
Pleasantly
Pleasantness
196. Point
Тo point
Point-blank
Pointer
Pointless
Pointlessly
Point of view
Pointed
Pointedly
197. Practical
Practice
Practicality
Practically
Practise
Practicable
Practiced
198. Present
Тo present
Presentation
Presently
Presentable
Present-day
199. Private
Privacy
Privation
То privatize
Privatization
Privately
Privateness
200. Produce
Producer
Induce
Induced
Inducement
Reduce
Reducer
Introduce
Introduction
Conduce
Conducive
201. To Prove
Proven
To Improve
Improvement
Improved
To Approve
Approver
Approved
202. To Protect
Protection
Protective
Protectorate
Protectively
203. To Provide
Provided
Providing
Providence
Provident
Provider
204. Public
Publication
Publicity
Publicise
Publicaly
Publican
Public library
Public relations
Public servant
205. Pure
Purity
Purify
Puritan
Purely
Purebred
Pureblood
Pureness
206. Quality
Qualitative
Qualify
Qualification
Qualified
207. Question
To question
Questionable
Question mark
Questionnaire
Questioning
Questioningly
Question sheet
Question time
208. Real
Realism
Realist
Reality
Realize
Really
Real estate
Realisation
Realistically
209. To Receive
Receiver
Receipt
Reception
Receptionist
Reception desk
210. Regular
Regularly
Regularity
Regulate
Regulation
Regularize
211. To Relate
Related
Relatedness
Related to
Relation
Relationship
Relative
Relatively
Relative-in-law
212. To Require
Requirement
Inquire
Inquirer
213. To Respond
Respondent
Response
Responsibility
Responsible
Responsive
Responsiveness
Responsible for
214. Safe
To Save
Safety
Safeguard
Savings
Safely
Safe and sound
Safeness
Saver
215. Sane
Insane
Insanity
Insanely
Sanity
Sanely
Sanitary
216. Secret
Secrecy
Secretary
Secretive
Secretariat
To Secrete
Secretion
Secretaire
Secretiveness
217. To Sell
Sell out
Sell off
Seller
Best-seller
Sale
Salesman
Sellable
218. Sense
To sense
Sensation
Senseless
Sensitive
Sensitively
Sensual
Sensualist
Sensuality
Sensuousness
Senselessness
219. Sequel
Sequence
Consequence
Consequent
Consequently
220. То Serve
Server
Service
Serving
Deserve
Deservedly
221. Set
To set
Set off / set out
Setback
Settee
Outset
Settle
Settle on
Settlement
Setting
Settler
Set forth
Set up
222. Ship
To ship
Shipping
Shipwreck
Shipyard
Shipment
Shipbuilding
223. Short
Shorts
Shortage
Shorten
Shortcoming
Short-cut
Shortsighted
Shortsightedness
Shortbread
Shortcake
Short-haired
Shortlist
Shortly
Short-staffed
Short-tempered
224. Sick
Sicken
Sickening
Sickness
Sickly
Sickbed
Sickish
Sick joke
Sick leave
225. Side
Sideboard
Sideline
Sidelong
Sidestep
Siding
Sidekick
Sidewalk
Sideburns
Side by side
Side dish
Side effect
Sidelight
226. Sign
To sign
Signal
Signature
Significant
Signify
Signage
Signaller
Signalisation
Signboard
Signifier
Sign in
Sign language
Sign of the zodiac
Signpost
227. Simple
Simple-minded
Simplify
Simplicity
Simplification
Simpleton
Simpleness
Simplex
228. To sleep
Sleep
Sleeper
Sleepless
Sleepy
Sleeping pill
Sleep around
Sleep in
Sleeping bag
Sleep over
Sleepwalker
Sleepy-eyed
229. To slip
Slip
Slippers
Slippery
Slipshod
Slippage
Slip away
Slipperiness
Slip road
230. То show
Show
Show off
Show business
Showcase
Showdown
Showman
Showpiece
Showroom
231. Soft
Soften
Software
Softhearted
Softly
Soft-cover book
Softheaded
232. Solicit
Solicitor
Solicitous
Solicitude
Soliciting
Solicitation
Solicitously
233. Sight
Sighted
Sightseeing
Sightseer
Far-sighted
Sighting
Sightedness
Sightless
234. Sport
To sport
Sporting
Sportsman
Sportswoman
Sportsmanship
Sportive
Sport car
Sporting chance
Sportiveness
Sportswear
Sporty
235. To Stand
Standing
Standpoint
Stand-offish
Understand
Understanding
Understandability
Stand-alone
Standard
Stand by
Standee
Standoff
Outstanding
236. To Stop
Stop
Stopover
Stoppage
Stopwatch
Stopgap
Stopover
Stopple
237. Straight
Straight away
Straighten
Straightforward
Straighten out
Straight and narrow
238. To Strain
Strain
Strained
Constrain
Restrain
Restraint
Restrained
Restrainer
Constraint
Constrained
239. Success
Successful
Succession
Successive
Successor
Succeed
Successiveness
240. Sun
Sunny
Sunrise
Sunset
Sunbathe
Sundry
Sunbeam
Sun-dried
Sunflower
Sunglasses
241. Super
Superior
Supernatural
Supersonic
Superstar
Superficial
Superfluous
Supercilious
Supervise
Supervision
242. To suspect
Suspect
Suspicion
Suspicious
Suspected
243. Tact
Tactful
Tactless
Tactlessness
Tactic
Tactical
Tactile
Tactically
Tactually
Tactile sensation
Tactician
244. Tense
Tension
Tensionless
Intensive
Intensively
Intensive care
intensiveness
245. To Think
Thinker
Thinking
Thought
Thoughtless
Think tank
Thinkable
Think back
Think out
Think over
Think the world of
Think twice
246. Time
To time
Timeless
Timely
Timer
Timetable
Time frame
Time and again
Timed
Time-honored
Time interval
Time lag
Time machine
Time out
247. To turn
Turn
Turning
Turner
Turnery
Turnover
Turnkey
Turnaround
Turn a blind eye
Turn around
Turning point
Turn a profit/ a loss
Turn one’s stomach
Turnout
Turn thumbs down
248. Unit
Unity
To Unify
Unitary
United
Unitise
249. То use
Use
Usage
Useful
Useless
Uselessness
Usefulness
User
Used
Usable
Used-car
250. Water
To water
Watercolour
Watery
Waterworks
Watershed
Waterfall
water-based paint
Waterbird
Waterless
Waterproof
Water-resistant
Watery-eyed
251. Way
Wayward
Waylay
Wayfarer
Way of life
Way-out
Ways and means
252. Work
To work
Worker
Working
Workman
Workmanship
Workshop
Workforce
Workable
Workaday
Workaholic
Workbook
Workfellow
Working-class
Working day
Work of art
Works
Test your English vocabulary
Тема словообразования одна из самых обширных в английском языке. Мы можем образовывать глаголы от существительных, существительные от прилагательных и глаголов и т.д. В данном уроке рассмотрим наиболее употребимые слова, которые образуются друг от друга при помощи префиксов и суффиксов.
Не существует единого правила словообразования в английском языке, поэтому мы рассмотрим наиболее характерные примеры словообразования, которые могут вам пригодиться в личном общении, для сдачи экзаменов, понимания речи собеседника или чтения текста на английском.
Структура слова и механизм словообразования
Несколько упрощая можно представить слово как корень + аффикс. Корень — это часть слова, которая может употребляться самостоятельно, а аффикс — морфема, которая присоединяется к корню слова и не употребляется самостоятельно.
Например, прибавление аффиксов -er, -ment, un-, ed к слову employ образует другие однокоренные слова, относящиеся к разным частям речи:
- employ — держать на службе
- employer — работодатель
- employment — служба, работа
- employed — трудоустроенный
- unemployed — безработный и др.
К аффиксам относятся префиксы (un-, in-, dis- и др) — ставятся перед корнем, и суффиксы (-ly, -ment, -er, -ence, -ance и др) — ставятся после корня.
Обратите внимание, что аффиксы могут быть:
- флексионными — меняют только такие грамматические значения слова, как множественное число, притяжательный падеж, указание на лицо и число
- словообразовательными — создают новое слово, преобразуют одну часть речи в другую
Сравните примеры:
Флексионные аффиксы:
He goes to work every day.
Сars are expensive.
My father’s car.
Словообразовательные аффиксы:
differ (различать, глагол) — difference (различие, существительное)
salt (соль, существительное) — salty (соленый, прилагательное)
slow (медленный, прилагательное) — slowly (медленно, наречие)
Родственные слова (Word Family)
Слова, образованные от одного корня за счет словообразующих аффиксов, объединяются в группу слов, которую в английском языке называют Word Family. Например:
- exploit — эксплуатировать (глагол)
- exploitation — эксплуатация (существительное)
- exploitative — эксплуататорский (прилагательное)
- exploiter — эксплуататор (существительное)
- exploitability — годность к эксплуатированию (существительное)
Ниже мы рассмотрим с помощью каких суффиксов и префиксов образуются существительные, прилагательные и наречия от глагола и других частей речи.
Образование существительных
Существительные образуются от глаголов и прилагательных с помощью разных суффиксов: -y, -ence, -ance, -al, -ment, -tion, -ion. Рассмотрим эти случаи словообразования подробнее и с примерами.
Образование существительного с помощью суффикса -y
deliver — delivery
доставлять — доставка
discover — discovery
открывать — открытие
injure — injury
травмировать — травма
jealous — jealousy
ревновать — ревность
difficult — difficulty
сложный — сложность
Образование существительного с помощью суффикса -ence
prefer — preference
предпочитать — предпочтение
differ — difference
различать — различие
refer — reference
отсылать — отсылка
interfere — interference
вмешиваться — вмешательство
confident — confidence
уверенный — доверие
independent — independence
независимый — независимость
violent — violence
жестокий — жестокость
Образование существительного с помощью суффикса -ance
annoy — annoyance
раздражать — раздражение
attend — attendance
посещать — посещение
assist — assistance
помогать — помощь
important — importance
важный — важность
Образование существительного с помощью суффикса -al
deny — denial
отказывать — отказ
propose — proposal
предлагать — предложение
approve — approval
одобрять — одобрение
disapprove — disapproval
не одобрять — неодобрение
Образование существительного с помощью суффикса -ment
improve — improvement
улучшать — улучшение
encourage — encouragement
поощрять — поощрение
arrange — arrangement
организовывать — организация
Образование существительного с помощью суффикса -tion
repeat — repetition
повторять — повторение
solve — solution
решать — решение
introduce — introduction
представлять — представление
explain — explanation
объяснять — объяснение
Образование существительного с помощью суффикса -ion
prevent — prevention
предотвращать — предотвращение
elect — election
выбирать — выбор
protect — protection
защищать — защита
Образование глаголов
Глаголы от прилагательных чаще всего образуются при помощи суффикса -en:
short — shorten
короткий — укоротить
dark — darken
темный — затемнять
sweet — sweeten
сладкий — подсластить
bright — brighten
яркий — осветлить, прояснить
Образование прилагательных
Прилагательные могут образовываться от глаголов и существительных при помощи суффиксов: -able, — ive, -ic, -al, -y, -ly, -ous.
Образование прилагательных с помощью суффикса -able
suit — suitable
подходить — подходящий
change — changeable
изменять — изменяемый
depend — dependable
зависеть — зависящий
enjoy — enjoyable
наслаждаться — приятный
Образование прилагательных с помощью суффикса -ive
attract — attractive
привлекать — привлекательный
create — creative
творить — творчески
talk — talkative
говорить — разговорчивый
Образование прилагательных с помощью суффикса -ic/-al
energy — energetic
энергия — энергетический
science — scientific
наука — научный
climate — climatic
климат — климатический
democracy — democratic
демократия — демократичный
grammar — grammatical
грамматика — грамматический
practice — practical
практика — практичный
Образование прилагательных с помощью суффикса -y/-ly
salt — salty
соль — соленый
risk — risky
риск — рискованный
rain — rainy
дождь — дождливый
friend — friendly
друг — дружелюбный
Образование прилагательных с помощью суффикса -ous
poison — poisonous
яд — ядовитый
nerve — nervous
нервы — нервный
danger — dangerous
опасность — опасный
humour — humorous
юмор — юмористический
Отрицательные префиксы
Отрицательные префиксы non-, dis-, in-, im-, ir-, un-, il- чаще всего меняют значение слова на противоположное, при этом слово остается той же частью речи.
order (сущ) — disorder (сущ)
порядок — беспорядок
appropriate (прил) — inappropriate (прил)
подходящий — неподходящий
polite (прил) — impolite (прил)
вежливый — невежливый
lock (гл) — unlock (гл)
заблокировать — разблокировать
Другие случаи
В английском языке (как и в русском) одно и то же слова может являться разной частью речи: существительным, прилагательным, глаголом, наречием. Например, возьмем слово «fast» и посмотрим какой частью речи оно может быть в разных контекстах:
- a fast — пост (существительное)
- a fast car — быстрая машина (прилагательное)
- to fast — поститься (глагол)
- fast — быстро (наречие): He drives fast — Он едет быстро
Это важно знать при переводе и восприятии английской речи.
Многие существительные и глаголы, образованные от одного корня, различаются чередованием корневого гласного и изменением написания слова:
- breath — breathe
- life — live
- relief — relieve
- proof — prove
- advice — advise
- choice — choose
- loss — lose
- death — die
Кроме этого существуют отдельные случаи, которые надо запомнить. Например:
- live — life — living — alive — lively
- polite — politeness — impolite
- forget — forgetfulness — forgetful
- fail — failure
- know — knowledge — unknown
- и др
Заключение
В этом уроке мы рассмотрели механизм словообразования в английском языке. Привели примеры образования существительных, прилагательных, наречий и глаголов путем прибавления суффиксов и префиксов к корню слова.
Если у вас остались вопросы — задавайте их в комментариях.
Introduction
Are you struggling to help your child understand how to read? There are many things that you can do to help encourage literacy, one of which includes teaching your child word families.
Word families are the grouping of common letters into similar word lists. In short, if your child understands the word family, they’ll be able to understand a list of words with the word family in common.
This guide will not only explain the various word families in the English language but also give you tips and tricks on how to increase reading comprehension.
A word family is a group of letters that are combined to make a specific sound. For example, -ack, -am-, and -at are all word families.
The purpose of understanding a word family is the notion that if you can identify one word, you should be able to identify many others with the common word family. So, if your child can sound out “back,” then they should easily be able to sound out “smack, tack, and rack” as well.
This is also the foundation of understanding how words work together to create a rhyme. Since these words all sound the same, you can combine them to make them have the same flow and rhyme scheme.
Word families increase with difficulty as children age. The first world families that are taught are generally simple, like “at” (for “cat, bat, and sat”). As children age, they will be asked to identify more complex word families like “ain” (or “rain, refrain, and stain”).
Word families and sight words work together to help children learn how to read. All of these words are high-frequency words, which means that children will see them often. When children can identify them quickly and easily, they can become more persuasive writers.
Examples
According to Wylie and Durrell, there are 37 common word families in the English language. In actuality, there are many more than 37, but these are the highest frequency words.
Many popular nursery rhymes include these 37 word families. They are simple because each letter is pronounced the way it should be. The only time that words are not pronounced as they are spelled is in the event of two vowels being next to each other. When you encounter one of these two-vowel words (like rain), the rule is to pronounce the first vowel only.
Below is a list of examples for each of the 37 most popular word families.
| ack | ain | ake | ale | all | ame |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| attack | brain | awake | ale | all | blame |
| back | chain | bake | bale | ball | came |
| black | explain | brake | dale | call | fame |
| crack | gain | cake | gale | fall | flame |
| hack | grain | fake | kale | gall | frame |
| knack | main | flake | male | hall | game |
| lack | pain | Jake | pale | install | lame |
| pack | plain | lake | sale | mall | name |
| quack | rain | make | scale | small | same |
| rack | slain | quake | stale | squall | shame |
| snack | sprain | rake | tale | stall | tame |
| stack | stain | sake | whale | tall | |
| tack | strain | shake | thrall | ||
| whack | train | snake | wall | ||
| vain | stake | ||||
| take | |||||
| wake |
| an | ank | ap | ash | at | ate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| an | bank | cap | ash | at | abate |
| ban | blank | clap | bash | bat | ate |
| bran | crank | flap | brash | brat | crate |
| can | dank | gap | cash | cat | date |
| clan | drank | lap | clash | chat | debate |
| Dan | flank | map | crash | fat | fate |
| fan | frank | nap | dash | flat | gate |
| flan | Hank | rap | flash | gnat | grate |
| Fran | plank | sap | gash | hat | hate |
| Jan | prank | scrap | gnash | mat | Kate |
| Japan | rank | slap | hash | pat | late |
| man | sank | snap | lash | rat | mate |
| pan | shrank | strap | mash | sat | plate |
| pecan | spank | tap | rash | slat | rate |
| plan | tank | trap | sash | spat | relate |
| ran | thank | wrap | slash | tat | sate |
| scan | yank | yap | smash | that | skate |
| span | zap | splash | vat | state | |
| Stan | stash | ||||
| tan | thrash | ||||
| than | trash | ||||
| van |
| aw | ay | eat | ell | est | ice |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| caw | away | beat | bell | best | dice |
| claw | bay | cheat | cell | chest | ice |
| draw | bray | cleat | dell | crest | mice |
| flaw | clay | eat | dwell | jest | nice |
| gnaw | day | feat | farewell | nest | price |
| jaw | decay | greet | fell | pest | rice |
| law | delay | heat | hell | quest | slice |
| paw | display | meat | sell | rest | spice |
| raw | flay | neat | shell | test | splice |
| saw | gay | peat | smell | unrest | thrice |
| slaw | gray | pleat | spell | vest | twice |
| straw | hay | seat | swell | west | vice |
| thaw | jay | treat | tell | zest | |
| lay | wheat | well | |||
| may | yell | ||||
| nay | |||||
| okay | |||||
| pay | |||||
| play | |||||
| pray | |||||
| quay | |||||
| ray | |||||
| relay | |||||
| replay | |||||
| say | |||||
| slay | |||||
| spray | |||||
| stay | |||||
| stray | |||||
| sway | |||||
| they | |||||
| today | |||||
| tray | |||||
| way |
| ick | ide | ight | ill | in | ine |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| brick | bride | bright | bill | bin | brine |
| chick | decide | delight | chill | chin | decline |
| click | glide | fight | dill | din | define |
| flick | hide | flight | drill | fin | dine |
| kick | pride | fright | fill | gin | fine |
| lick | ride | height | frill | grin | line |
| nick | side | knight | gill | in | mine |
| pick | slide | light | grill | kin | nine |
| quick | stride | might | hill | pin | pine |
| Rick | tide | night | ill | shin | shine |
| sick | wide | plight | Jill | skin | shrine |
| slick | right | kill | sin | sine | |
| stick | sight | krill | spin | spine | |
| thick | slight | mill | thin | swine | |
| tick | tight | pill | tin | tine | |
| trick | tonight | quill | twin | twine | |
| wick | shrill | win | vine | ||
| sill | within | whine | |||
| skill | wine | ||||
| spill | |||||
| still | |||||
| swill | |||||
| thrill | |||||
| thrill | |||||
| till | |||||
| trill | |||||
| will |
| ing | ink | ip | it | ock | op |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bring | blink | blip | admit | block | coop |
| cling | brink | chip | bit | clock | droop |
| fling | drink | dip | fit | cock | hoop |
| king | fink | drip | flit | crock | loop |
| ping | ink | flip | grit | dock | scoop |
| ring | link | grip | hit | flock | snoop |
| sing | mink | hip | it | frock | stoop |
| sling | pink | lip | kit | hock | troop |
| spring | rink | nip | knit | jock | |
| sting | shrink | quip | lit | knock | |
| string | sink | rip | mit | lock | |
| swing | stink | ship | pit | mock | |
| thing | think | sip | quit | o’clock | |
| wing | wink | skip | sit | rock | |
| wring | slip | skit | shock | ||
| zing | snip | slit | smock | ||
| strip | snit | sock | |||
| tip | spit | stock | |||
| trip | split | ||||
| whip | twit | ||||
| zip | wit |
| ore | ot | uck | ug | ump | unk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bore | apricot | buck | bug | bump | bunk |
| chore | blot | chuck | dug | clump | chunk |
| core | bot | cluck | hug | dump | drunk |
| fore | clot | duck | jug | grump | dunk |
| gore | cot | luck | lug | hump | flunk |
| lore | dot | muck | mug | jump | funk |
| more | forgot | puck | plug | lump | hunk |
| ore | got | pluck | pug | plump | junk |
| pore | hot | stuck | rug | pump | lunk |
| score | jot | struck | shrug | rump | plunk |
| shore | knot | truck | smug | slump | punk |
| sore | lot | tuck | snug | stump | skunk |
| spore | not | yuck | thug | thump | slunk |
| store | plot | tug | trump | spunk | |
| swore | pot | sunk | |||
| tore | rot | trunk | |||
| wore | shot | ||||
| yore | slot | ||||
| spot | |||||
| tot | |||||
| trot |
Tips and Tricks for Teaching Reading
When beginning to teach your child to read, you will want to blend information from word families and sight words to help your child start identifying words.
To do this, pick a list of words that matches their age-level and start practicing those words only. When your child can identify these words in a text, it means that they are beginning to see the patterns and identify those high-frequency words in writing.
When you begin teaching word families, start with one of the easier ones first, like am. Once they can identify am, sound it out, and find words that end in am, move to a more complicated word.
Once your child understands how to form these word families into actual words, they will be able to spell and read them!
If your child struggles with some of the foundational skills associated with reading, consider adding a workbook to their daily practice. ArgoPrep has worked with educators to deliver high-quality practice that will entertain, educate, and excite your child. These workbooks are especially helpful for students who might need a little extra attention to reading comprehension, English language skills, and more.
Conclusion
My daughter loves to build things with Magnatiles. She will grab all of the tiles and construct fantastic castles, homes, and more with the simple building tools. But what happens when she builds a weak base? We all know. It can’t stand, it’s not steady, and it falls.
Learning how to read can kind of be similar to building a weak structure. Identifying something as simple as a word family seems like a mindless activity for us. Still, for kids, it’s necessary to understand the increasingly tricky skills that kids learn for reading comprehension.
Taking the time to learn word families will help them identify words more quickly and spell with more accuracy. This list of 37 high-frequency word families is a great place to start, but once your child masters it, consider researching more challenging word families to increase comprehension!
Word families are groups of words that go together. They have similar or common features or patterns. They can occur in the prefix, the suffix, or in the root word itself. They are sometimes referred to as groups or chunks. Word families all have the same combinations of letters somewhere in the word. They frequently appear in poems and rhymes (especially nursery rhymes). For example:
“Jack and Jill
Went up the hill,
To fetch a pail of water.
Jack fell down,
And broke his crown.
And Jill came tumbling after.”
Word families can be an important tool when teaching people to read or speak a language. New readers are able to recognize the word patterns, and teachers help them to understand the combinations and sounds.
The National Council of Teachers of English has identified 37 different word families. They are listed below with examples of words that are included in the family.
| Ack | Ain | Ake | Ale |
| Attack | Brain | Awake | Ale |
| Back | Chain | Bake | Bale |
| Knack | Complain | Cake | Dale |
| Lack | Explain | Lake | Female |
| Quack | Gain | Make | Gale |
| Rack | Pain | Quake | Male |
| Sack | Plain | Rake | Pale |
| Snack | Strain | Sake | Sale |
| Tack | Train | Snake | Tale |
| Whack | Vain | Take | Whale |
| All | Ame | An | Ank |
| Ball | Blame | Ban | Bank |
| Call | Came | Bran | Blank |
| Fall | Dame | Can | Crank |
| Hall | Fame | Fan | Drank |
| Mall | Game | Japan | Flank |
| Small | Lame | Pan | Rank |
| Squall | Name | Pecan | Shrank |
| Stall | Same | Scan | Spank |
| Tall | Shame | Tan | Tank |
| Wall | Tame | Van | Thank |
| Ap | Ash | At | Ate |
| Cap | Cash | At | Abate |
| Clap | Clash | Brat | Ate |
| Flap | Crash | Cat | Debate |
| Lap | Dash | Chat | Fat |
| Map | Hash | Fat | Grate |
| Scrap | Lash | Mat | Late |
| Slap | Mash | Rat | Mate |
| Tap | Rash | Slat | Plate |
| Trop | Splash | That | Skate |
| Wrap | Stash | Vat | State |
| Aw | Ay | Eat | Ell |
| Claw | Away | Beat | Bell |
| Draw | Clay | Bleat | Cell |
| Flaw | Day | Cheat | Dell |
| Jaw | Display | Cleat | Dwell |
| Law | Gay | Heat | Farewell |
| Paw | Pray | Meat | Fell |
| Raw | Ray | Neat | Hell |
| Saw | Stay | Seat | Sell |
| Straw | Today | Treat | Tell |
| Thaw | Tray | Wheat | Yell |
| Est | Ice | Ine | Ide |
| Best | Dice | Brine | Bride |
| Chest | Ice | Decline | Decide |
| Crest | Lice | Define | Guide |
| Jest | Mice | Dine | Hide |
| Nest | Price | Fine | Ride |
| Pest | Rice | Mine | Side |
| Rest | Spice | Pine | Slide |
| Test | Splice | Shrine | Stride |
| Unrest | Twice | Whine | Tide |
| West | Vice | Wine | Wide |
| Ick | In | Ight | Ill (ill) |
| Brick | Bin | Bright | Bill |
| Flick | Chin | Delight | Chill |
| Kick | Grin | Fight | Dill |
| Lick | In | Flight | Fill |
| Nick | Kin | Light | Kill |
| Pick | Shin | Might | Shrill |
| Sick | Skin | Night | Still |
| Stick | Twin | Sight | Swill |
| Thick | Win | Tight | Thrill |
| Trick | Within | Tonight | Will |
| Wick |
| Ing | Ink | Ip | It |
| Bring | Blink | Dip | Admit |
| King | Drink | Grip | Bit |
| Ping | Fink | Hip | Fit |
| Ring | Link | Lip | Flit |
| Sing | Mink | Ship | Grit |
| Spring | Pink | Sip | Knit |
| Sting | Rink | Snip | Lit |
| String | Sink | Strip | Pit |
| Thing | Stink | Trip | Quit |
| Wing | Wink | Whip | Split |
| Ock | Oke | Op | Ore |
| Block | Awoke | Cop | Chore |
| Clock | Bloke | Drop | Core |
| Dock | Choke | Flop | Fore |
| Frock | Joke | Hop | Gore |
| Lock | Poke | Mop | More |
| Mock | Smoke | Plop | Ore |
| Rock | Spoke | Pop | Sore |
| Shock | Stroke | Shop | Store |
| Sock | Woke | Strop | Tore |
| Stock | Yoke | Top | Wore |
| Ot | Uck | Ug | Ump | Unk |
| Clot | Buck | Bug | Bump | Bunk |
| Cot | Chuck | Dug | Clump | Clunk |
| Dot | Duck | Hug | Hump | Dunk |
| Forgot | Luck | Jug | Jump | Funk |
| Hot | Muck | Lug | Lump | Hunk |
| Lot | Pluck | Mug | Plump | Junk |
| Not | Struck | Rug | Rump | Punk |
| Plot | Stuck | Shrug | Stump | Skunk |
| Pot | Truck | Smug | Thump | Sunk |
| Spot | Tuck | Thug | Trump | Trunk |
Other Word Families
There are many other word families beyond the most common 37. Below are some others that occur on a regular basis.
| Ad | Ail | Am | Ar |
| Ad | Ail | Clam | Afar |
| Bad | Fail | Dam | Bar |
| Cad | Hail | Exam | Car |
| Clad | Jail | Gram | Far |
| Dad | Jam | Par | |
| Glad | Pail | Ram | Pillar |
| Had | Rail | Slam | Scar |
| Lad | Sail | Spam | Spar |
| Mad | Snail | Tram | Star |
| Sad | Tail | Wham | Tar |
| Eet | En | Ent | Eel |
| Feet | Amen | Bent | Cartwheel |
| Fleet | Children | Dent | Eel |
| Greet | Den | Event | Feel |
| Meet | Even | Gent | Genteel |
| Parakeet | Hen | Innocent | Heel |
| Sheet | Men | Lent | Keel |
| Street | Omen | Scent | Peel |
| Sweet | Pen | Sent | Reel |
| Tweet | Ten | Tent | Steel |
| When | Went | Wheel |
| Eep | Ile | Oat | Og |
| Asleep | Bile | Boat | Blog |
| Beep | File | Coat | Catalog |
| Creep | Juvenile | Float | Clog |
| Deep | Mile | Gloat | Defog |
| Jeep | Pile | Goat | Dog |
| Seep | Smile | Moat | Frog |
| Sheep | Tile | Oat | Hog |
| Sleep | Vile | Sloat | Hotdog |
| Steep | Volatile | Sugarcoat | Jog |
| Weep | While | Throat | Smog |
| Oil | Ool | Oom | Oon |
| Boil | Cool | Bathroom | Baboon |
| Broil | Drool | Bloom | Balloon |
| Charbroil | Fool | Boom | Goon |
| Coil | Pool | Classroom | Maroon |
| Foil | School | Doom | Moon |
| Oil | Spool | Groom | Noon |
| Recoil | Stool | Loom | Soon |
| Soil | Tool | Room | Spoon |
| Spoil | Uncool | Storeroom | Toon |
| Toil | Wool | Zoom | Tycoon |
| Topsoil |
| Oop | Ow | Ought |
| Coop | Blow | Afterthought |
| Droop | Bow | Bought |
| Goop | Crow | Brought |
| Hoop | Flow | Forethought |
| Loop | Grow | Fought |
| Scoop | Mow | Ought |
| Snoop | Row | Overthought |
| Stoop | Show | Overwrought |
| Swoop | Snow | Thought |
| Troop | Tow | Wrought |
Placement in Words
There are many other word families, and they can occur anywhere in a word. Some examples are:
| A meaning “on” |
Act meaning “do” |
Dis meaning “un” |
| Adrift, | Actor | Disagree |
| Aside | Action | Dishonest |
| Ashore | Activate | Disavow |
| Ject meaning “to throw” |
Gen meaning “to produce” |
Poly meaning “many” |
| Eject | General | Polygamy |
| Interject | Generate | Monopoly |
| Subject | Pathogen | Polyester |
Risk of Focusing on Word Families
There is one pitfall that new readers can encounter when learning word families. Because they focus so much attention on the second part of the word, they can skip over the first part. They then have to go back to the start of the word.
This results in jerky eye movement. Instead of a steady progression across the page from left to right, the reader jumps around. This could actually reinforce dyslexic tendencies.
Conclusion:
Word families help students to learn to read and pronounce English. Because they learn to recognize the “chunks” of words that are in each family, they can make connections to other words. This helps new readers correctly predict how other words will sound.
New readers are able to take single-syllable words and break them down. There will often be a consonant at the start of the word and a word family group at the end. By breaking down even short words, the new reader is able to improve their spelling, understand new words (by comparing them to old), and improve their reading fluency.
By using the 37 common word families, new readers will be able to learn an estimated 500 words. If other word families are included, the number of new words can grow dramatically.
List of Word Families | Image
List of Word Families

37 Most Common Word Families

37 Different Word Families

List of Word Families in English

Last Updated on May 20, 2021
Home
Words List
Word families: The 37 most common word families in English
March 29, 2021
Words List, English
Word families ! They are groups of words that have a common pattern or groups of letters with the same sound. For example, at, cat, hat, and fat are a family of words with the “at” sound and letter combination in common.
Word families
Word families List
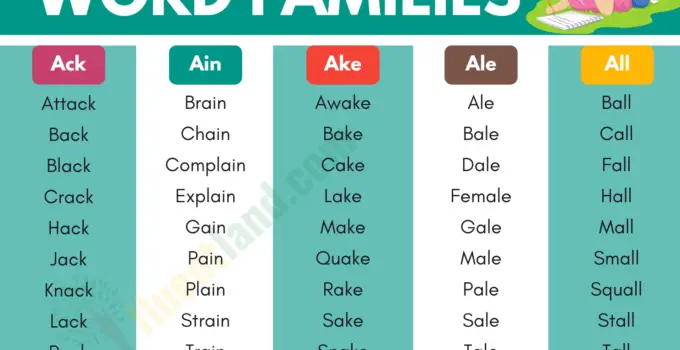
The following is a list of the most common word families in English
| ack | ad | age | ail | ain | ake | ale | all | am |
| attack | ad | age | ail | brain | awake | ale | all | cam |
| back | bad | cage | fail | chain | bake | bale | ball | clam |
| black | brad | engage | hail | complain | brake | dale | call | dam |
| crack | cad | rage | jail | explain | cake | gale | fall | dram |
| hack | clad | sage | gain | fake | kale | gall | exam | |
| Jack | dad | stage | nail | grain | flake | male | hall | gram |
| knack | doodad | wage | pail | main | Jake | pale | install | ham |
| lack | glad | rail | obtain | lake | sale | mall | jam | |
| pack | had | sail | pain | make | scale | small | lam | |
| quack | lad | snail | plain | quake | stale | squall | ma’am | |
| rack | mad | tail | rain | rake | tale | stall | Pam | |
| sack | pad | wail | slain | sake | whale | tall | ram | |
| snack | sad | Spain | shake | thrall | Sam | |||
| stack | sprain | snake | wall | scam | ||||
| tack | stain | stake | slam | |||||
| track | strain | take | spam | |||||
| whack | train | wake | swam | |||||
| Zack | vain | tam | ||||||
| tram | ||||||||
| wham | ||||||||
| yam |
| ame | an | ank | ap | ar | ash | at | ate | aw |
| blame | bank | cap | afar | ash | abate | caw | ||
| came | ban | blank | clap | bar | bash | bat | ate | claw |
| fame | bran | crank | flap | car | brash | brat | crate | draw |
| flame | can | dank | gap | czar | cash | cat | date | flaw |
| frame | clan | drank | lap | far | clash | chat | debate | gnaw |
| game | Dan | flank | map | gar | crash | fat | fate | jaw |
| lame | fan | frank | nap | guitar | dash | flat | gate | law |
| name | flan | Hank | rap | jar | flash | gnat | grate | paw |
| same | Fran | plank | sap | mar | gash | hat | hate | raw |
| shame | Jan | prank | scrap | par | gnash | mat | Kate | saw |
| tame | Japan | rank | slap | scar | hash | pat | late | slaw |
| man | sank | snap | spar | lash | rat | mate | straw | |
| pan | shrank | strap | star | mash | sat | plate | thaw | |
| pecan | spank | tap | tar | rash | slat | rate | ||
| plan | tank | trap | tsar | sash | spat | relate | ||
| ran | thank | wrap | slash | tat | sate | |||
| skate | ||||||||
| state |
| ay | eat | eel | eep | eet | ell | en | ent | est |
| away | beat | eel | beep | beet | bell | amen | accent | best |
| bay | cheat | feel | creep | feet | cell | Ben | bent | chest |
| bray | cleat | heel | deep | fleet | dell | children | cent | crest |
| clay | eat | keel | jeep | greet | dwell | den | dent | jest |
| day | feat | kneel | keep | meet | farewell | fen | event | nest |
| decay | greet | peel | peep | sheet | fell | gentlemen | gent | pest |
| delay | heat | reel | seep | sleet | hell | glen | lent | quest |
| display | meat | steel | sheep | street | sell | Gwen | rent | rest |
| flay | neat | wheel | sleep | sweet | shell | hen | scent | test |
| gay | peat | steep | tweet | smell | men | sent | unrest | |
| gray | pleat | sweep | spell | open | spent | vest | ||
| hay | seat | weep | swell | pen | tent | west | ||
| jay | treat | tell | then | vent | zest | |||
| lay | wheat | well | ten | went | ||||
| may | yell | when | ||||||
| nay | wren |
| ice | ick | ide | ife | ight | ile | ill | in | ine |
| dice | brick | bride | fife | bright | bile | bill | bin | brine |
| ice | chick | decide | knife | delight | file | chill | chin | decline |
| mice | click | glide | life | fight | mile | dill | din | define |
| nice | flick | hide | strife | flight | Nile | drill | fin | dine |
| price | kick | pride | wife | fright | pile | fill | gin | fine |
| rice | lick | ride | height | rile | frill | grin | line | |
| slice | nick | side | knight | smile | gill | in | mine | |
| spice | pick | slide | light | stile | grill | kin | nine | |
| splice | quick | stride | might | tile | hill | pin | pine | |
| thrice | Rick | tide | night | vile | ill | shin | shine | |
| twice | sick | wide | plight | while | Jill | skin | shrine | |
| vice | slick | right | kill | sin | sine | |||
| stick | sight | krill | spin | spine | ||||
| thick | slight | mill | thin | swine | ||||
| tick | tight | pill | tin | tine | ||||
| trick | tonight | quill | twin | twine | ||||
| wick | shrill | win | vine | |||||
| sill | ||||||||
| skill | ||||||||
| spill | ||||||||
| still | ||||||||
| swill | ||||||||
| thrill | ||||||||
| thrill | ||||||||
| till | ||||||||
| trill |
| ing | ink | ip | it | oat | ock | og | oil | oke |
| bring | blink | blip | admit | boat | block | blog | boil | awoke |
| cling | brink | chip | bit | coat | clock | bog | broil | bloke |
| fling | drink | dip | fit | float | cock | catalog | coil | broke |
| king | fink | drip | flit | gloat | crock | clog | foil | choke |
| ping | ink | flip | grit | goat | dock | cog | oil | joke |
| ring | link | grip | hit | oat | flock | dog | soil | poke |
| sing | mink | hip | it | stoat | frock | fog | spoil | smoke |
| sling | pink | lip | kit | throat | hock | frog | toil | spoke |
| spring | rink | nip | knit | jock | hog | stoke | ||
| sting | shrink | quip | lit | knock | jog | stroke | ||
| string | sink | rip | mit | lock | log | woke | ||
| swing | stink | ship | pit | mock | slog | yoke | ||
| thing | think | sip | quit | o’clock | smog | |||
| wing | wink | skip | sit | rock | ||||
| wring | slip | skit | shock | |||||
| zing | snip | slit | smock | |||||
| strip | snit | sock | ||||||
| tip | spit | stock | ||||||
| trip | split | |||||||
| whip | twit | |||||||
| zip | wit |
| oo | ood | ood | oof | oof | ook | oom | ool | oon |
| boo | good | brood | goof | hoof | book | bloom | cool | balloon |
| coo | hood | food | proof | woof | brook | boom | drool | goon |
| goo | stood | mood | roof | cook | broom | fool | loon | |
| igloo | wood | spoof | crook | doom | pool | moon | ||
| moo | hook | gloom | spool | noon | ||||
| shoo | look | groom | stool | soon | ||||
| too | nook | loom | tool | spoon | ||||
| woo | rook | room | swoon | |||||
| zoo | shook | zoom | ||||||
| took |
| oop | oot (long oo) | oot (short oo) | op | ore | orn | ot | ought | ould |
| coop | boot | foot | bop | bore | adorn | apricot | bought | could |
| droop | hoot | soot | chop | chore | born | blot | brought | should |
| hoop | scoot | cop | core | corn | bot | fought | would | |
| loop | shoot | crop | fore | forlorn | clot | ought | ||
| scoop | drop | gore | horn | cot | sought | |||
| snoop | flop | lore | morn | dot | thought | |||
| stoop | hop | more | scorn | forgot | wrought | |||
| troop | lop | ore | shorn | got | ||||
| mop | pore | thorn | hot | |||||
| plop | score | torn | jot | |||||
| pop | shore | worn | knot | |||||
| prop | sore | lot | ||||||
| spore | not | |||||||
| store | plot | |||||||
| swore | pot | |||||||
| tore | rot | |||||||
| wore | shot | |||||||
| yore | slot |
| ouse | out | ow (rhymes with cow) | ow (rhymes with low) | own | uck | ug | ump | un | unk |
| douse | about | bow | bow | brown | buck | bug | bump | bun | bunk |
| grouse | bout | cow | blow | crown | chuck | dug | clump | fun | chunk |
| house | clout | chow | crow | down | cluck | hug | dump | gun | drunk |
| louse | gout | how | flow | drown | duck | jug | grump | nun | dunk |
| mouse | grout | now | glow | frown | luck | lug | hump | pun | flunk |
| spouse | out | plow | grow | gown | muck | mug | jump | run | funk |
| lout | sow | low | nightgown | puck | plug | lump | shun | hunk | |
| pout | vow | mow | town | pluck | pug | plump | spun | junk | |
| scout | wow | row | stuck | rug | pump | stun | lunk | ||
| shout | show | struck | shrug | rump | sun | plunk | |||
| snout | slow | truck | smug | slump | punk |
List of Word families with Examples and Pictures
- Words that Rhyme with Ad:
- I love my dad.
- Behind bad luck comes good luck.
- He is a handsome lad.
- We all felt sad about his death.
- I’m glad that the exams are over.
- He was mad with me for losing his watch.
- She wrote on a pad of paper.
- Words that Rhyme with At:
- She sat up in bed, listening.
- The cat was clawing at the door.
- Wipe your feet on the mat.
- She was wearing a red hat.
- He gave the dog a pat.
- I think he’s too fat.
- A rat squeaked and ran into the bushes.
- The bat is flying with swiftness.
- Words that Rhyme with An:
- She fried the eggs in a frying pan.
- A man is known by his friends.
- She cooled herself with a fan.
- They ran straight across the road .
- Fran has a can of beer.
- The man has a van.
- Jan is from Japan.
- The plan began.
- Words that Rhyme with Am:
- Be careful of that ram —it butts you.
- A new dam is now being built.
- The yam pieces were then simmered in water with the sailcloth for ten or twelve hours.
- Put the jam in the jar over there.
- Would you like another slice of ham/beef?
- From the salad to the clam chowder to the pasta with grilled peppers and chicken, dinner was perfect.
- I think I did OK in the exam.
- We heard a car door slam.
- Words that Rhyme with Ap:
- When you want a bath,you turn on the tap.
- The water was dripping from the tap.
- Do you see this point on the map?
- He picked his cap up from the floor and stuck it back on his head.
- I want to take a nap.
- She’s a good singer. Let’s clap her on.
- With a flap of its wings, the bird was gone.
- Come and sit on Grandpa’s lap!
- The road goes through a gap in/between the hills.
- Words that Rhyme with Ar:
- The car is in very good condition.
- He that travels far knows much.
- His guitar solos are just unbelievable.
- He put the lid on the jar.
- Sirius is the brightest star in the sky.
- We use tar to make roads.
- We were all in the bar sipping cocktails
- He had a scar on his forehead.
Most common Word Families | Pictures
4
10
votes
Article Rating
English word families and sentence structures
If you want to learn more about word families and sentence structures in English this page will help you.
This information is very useful when learning to speak English. If you know the basics of how the English language works, you will have a good foundation on which to become an advanced speaker. The information in this article is also very useful to know and learn if you want to study for the FCE or CAE exams. These exams give you the qualifications you need to get better jobs or get into universities in English speaking countries. If you would like to find out more about how these exams can help you, sign up to receive my free e-book with lots of information on this and other topics.
Sentence Structures
If you are unsure what types of words go where in a sentence, here are a few basic guidelines to follow:
Adjectives and Nouns
Adjectives (describing words) come before nouns (things/objects/people/places).
E.g. This is a funny (adjective) book (noun).
Adverbs of Frequency
Frequency adverbs (often, rarely, sometimes) go before the main verb in a sentence, but after an auxiliary verb or after a form of the verb ‘be’.
E.g. I often go to the supermarket on Sundays.
I have (auxiliary) never been (main verb) so insulted in my life.
I am (‘be’) always in a good mood after I eat.
There are a lot of exceptions to this rule though, for example adverb phrases normally go at the beginning or end of a clause.
E.g. Once a year, my brother comes to visit me.
My brother comes to visit me once a year.
Other Adverbs
Other adverbs typically start a sentence or paragraph. These are followed by commas (,).
E.g. Consequently, we decided not to go to the cinema.
Verbs + ing
Verbs which end –ing (Running, walking, looking etc.) can be used at the beginning of a clause, when acting like a noun.
E.g. Running is a very tiring activity.
*Watch out – the word ‘tiring’ above is an adjective and comes before the noun ‘activity’. Lots of adjectives end –ing or –ed.
Verbs+ing are also used in continuous tenses.
E.g. I was walking to the supermarket when I saw Billy.
Billy is going to the supermarket.
Verbs
Verbs are often preceded by a subject (I, you, he, she etc.) and followed by an object.
E.g. I went to the supermarket.
Auxiliary Verbs
Auxiliary verbs (have, be, do, will) come before the main verb in a sentence. These are used for various reasons, often in different verb tenses to help you know whether a person is talking about something in the past or the future.
Sometimes an adverb of frequency will be situated between the auxiliary verb and the main verb in a sentence.
Modal verbs
Examples: can/could, may/might, must/have to/ought to, shall/should, will/would etc.
Modal verbs (may, might, should, could, ought to etc.) also affect our understanding of a sentence. They have many uses, e.g. when a person is speculating and deducing. Modal verbs are always followed by a bare infinitive (unless used in a negative sentence when ‘not’ is used).
E.g. We should go to watch the new James Bond film.
The car might be broken.
We might not eat dinner until 9pm.
Modal verbs are used to show: ability, probability, obligation, permission, to make offers, to make conclusions about past, present and future events etc.
E.g. I can climb that mountain! (ability)
E.g. He should be here by 6pm. (probability)
E.g. You mustn’t smoke inside this building. (obligation)
E.g. You don’t have to smoke inside this building, but you can if you want to (permission)
Notice that ‘mustn’t’ and ‘don’t have to’ have different meanings in the above sentences.
E.g. Shall I collect you from the station? (offer)
in a question the word order changes to: modal-subject-bare infinitive.
E.g. Charlie is sick! He must have eaten some gone off food. (Here the modal verb is used to make a conclusion about the past – to answer the question — why is he sick).
When modal verbs are used to make past conclusions, they are followed by have + past participle)
E.g. It’s 2.30pm. Charlie should be in Paris by now! (Here the modal verb is used to make a conclusion about the present and is followed by a bare infinitive.
E.g. Charlie will be in Paris this time tomorrow. (Here the modal verb will is used to make a statement/conclusion about the future and is followed by a bare infinitive).
Word families
Here are some typical noun endings: -ment, -ion, -ty,
Here are some typical adjective endings: -al,
Here are some typical adverb endings: -ly, ally,
This book has some really useful exercises for understanding word endings. It is C1 Advanced (CAE) level:
This book is also very useful with similar exercises for B2 First (FCE) level:
This page also has some fun word family exercises.
A word family is a group of words with a common base to which different prefixes and suffixes are added. For example, members of the word family based on the headword, base, stem, or root word work include rework, worker, working, workshop, and workmanship, among others. Similar words are called paronyms.
Polyptoton is the use of more than one of these words together, such as in this quote from the movie «Fight Club»: «The things you own end up owning you.» The repetition can serve as a dramatic effect or for emphasis in writings ranging from plays and poetry to advertising and political speeches.
Roots, Prefixes, and Suffixes
Don’t plan to memorize all the word families, though. An analysis of a 1963 dictionary by scholars in 1990 found 54,000 word families. With English users creating new words all the time, it’s better to know how to work with the language and its roots, prefixes, and suffixes than to attempt to memorize it all.
According to Birgit Umbreit, «[L]anguage users are able to analyze complex words and to establish synchronic relations between words both formally and semantically because they have an implicit or even explicit knowledge of word-family organization.» (Birgit Umbreit, «Does Love Come From to Love or to Love From Love? Why Lexical Motivation Has to Be Regarded as Bidirectional,» from «Cognitive Perspectives on Word Formation,» edited by Alexander Onysko and Sascha Michel)
Said in a simpler way, language learners can decode many new or unfamiliar words through understanding what different prefixes and suffixes do to a root word. The technique can also help people figure out spellings of words they hear or determine the etymology of a word. Frank E. Daulton wrote, «[M]ost linguists agree that word families should be transparent, in that learning a new item related to one already known should involve a minimum of learning burden…For instance, if a learner knows govern and is familiar with the prefix mis-, then misgovern requires little if any additional learning (Goulden et al., 1990). Derivations that don’t meet the transparency criteria are not included in a word family but given separate listings; for instance, business (busy)…» (Frank E. Daulton, «Japan’s Built-in Lexicon of English-Based Loanwords»)
Breaking Words Into Parts
The roots or stems don’t have to be words on their own to make other words. For example, the root struct forms the base of more than 30 English words; it comes from a Latin word for to build and creates words such as: construction, structure, and constructive. Knowing that con- as a prefix means «with» or «together,» you can see how the words construction and constructive involve the creation of something. Knowing that the prefix de— means the opposite—to reduce or remove—and that the suffix —ion indicates that a word is a noun, you can understand how the word destruction is created—or even the verb to deconstruct.
Following the same pattern, look at contract and detract; a contract is something that joins parties in agreement, while to detract means to draw away from.
Source
- Norbert Schmitt, Vocabulary in Language Teaching. Cambridge University Press.
Nouns and adverbs and verbs, oh my!
Parts of speech are the building blocks for English sentences, and studying them early on can be beneficial for English language learners. Along with common sentence patterns, learning the parts of speech (nouns, verbs, prepositions, etc.) can help students form English sentences more easily.
But how do students know which vocabulary words are nouns, verbs, etc.? This is where suffixes (word endings) come into play. Learning common word endings can help students easily guess at the part of speech of a new vocabulary term.
Parts of speech and suffixes aren’t just for beginner students. This knowledge can boost students’ abilities in both grammar and vocabulary at any level, and is quite useful for higher‑level students who need to decipher complex and unfamiliar words. Learning and practicing word families in context can help higher-level students with speaking and writing as well as on tests such as the TOEIC.
Try presenting the word family chart below to your intermediate- to advanced‑ level learners, and then see if they can complete the following practice exercise. Subscribers can access a printable pdf of the chart and exercise here: Advanced Word Families. See our Parts of Speech lesson for lower‑level practice.
| Verb | Noun | Adjective | Adverb |
|---|---|---|---|
| act | action | active | actively |
| apologize | apology | apologetic | apologetically |
| beautify | beauty | beautiful | beautifully |
| believe | belief | believable | believably |
| benefit | benefit | beneficial | beneficially |
| care | care | careful | carefully |
| create | creation | creative | creatively |
| decide | decision | decisive | decisively |
| differ | difference | different | differently |
| divide | division | divisive | divisively |
| exclude | exclusion | exclusive | exclusively |
| identify | identification | identifiable | identifiably |
| justify | justification | justifiable | justifiably |
| protect | protection | protective | protectively |
| rely | reliability | reliable | reliably |
| signify | significance | significant | significantly |
| succeed | success | successful | successfully |
| tolerate | tolerance | tolerable | tolerably |
| understand | understanding | understandable | understandably |
Practice
Have students complete the sentences below with a form of the prompt word. Allow them to refer to the chart above. You may also want to have students identify the parts of speech. Note that they may have to change the word form by making a noun plural or conjugating a verb into the correct tense.
Example
| # | Prompt | Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| Ex | protect | Female bears are very protective (adjective) of their young. |
Questions
| # | Prompt | Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | succeed | Practice and patience are the keys to ______ . |
| 2 | rely | My best friend has never let me down. I ______ on her many times in the past. |
| 3 | differ | I can’t see what’s ______ in the second version of this document. |
| 4 | act | ______ speak louder than words. |
| 5 | apologize | After tripping me on my way to my desk yesterday, my coworker ______ profusely. |
| 6 | identify | Please show me your ______ and your insurance papers. |
| 7 | understand | He was ______ upset when he heard about the accident. |
| 8 | divide | There were so many ______ issues that they called a mediator in. |
| 9 | decide | Because the manager reacted ______ , the problem didn’t spiral out of control. |
| 10 | benefit | This document was a ______ resource for the project. |
Answers
- success (noun)
- have relied (verb)
- different (adjective)
- Actions (noun)
- apologized (verb)
- identification (noun)
- understandably (adverb)
- divisive (adjective)
- decisively (adverb)
- beneficial (adjective)
Related
- Advanced Word Families
- Parts of Speech Lesson
- Parts of Speech Lesson – Young Learners
- Parts of Speech Chart
- Parts of Speech Cards
- English Sentence Patterns
- Suffixes
- Suffix Flashcards
- Prefixes
- Prefix Flashcards
- Flying Affixes Activity