You will encounter both large and small sets; therefore, you should learn how to describe these sets.
Before we embark on describing sets, it important to learn how to define and write a set.
In this article, we will learn:
- How to define, write, and describe a set.
- The key properties of sets.
Remember, we have provided a practice test and an answer key at the end of this article. Don’t forget to test your understanding.
Let’s start by defining a set.
What is a set in math?
A set is a collection of well-defined objects. We refer to these objects as members or elements of the set.
Like in ordinary language, we usually talk of sets of cutleries or sets of chairs, etc. In mathematics, we can also talk of sets of numbers, sets of equations, or sets of variables.
For example, the set of natural numbers contains all the natural numbers. Therefore, each natural number is an element or member of that set.
We usually apply the concept of a set as a prerequisite to understanding several branches of mathematics, such as algebra, mathematical analysis, and probability theory.
How do we write a set in math?
Writing a set in math is pretty simple. We just:
- list the elements in the set,
- separate each element in the set using a comma,
- enclose the elements in the set using curly braces, {}.
For example, the numbers 5,6 and 7 are members of the set {5,6,7}
By convention, we should use an uppercase letter to denote a set and lowercase letters to denote a set’s elements. Also, we should always put an equality sign after the uppercase letter just before writing the elements of the set.
Let’s say we want to write down set A with the elements a, b, and c. So, we will write it as follows:
A={a,b,c}
We can also write down set B that has elements 1,2,3, 4, and 5 as follows:
We can also write sets within a set. For example, sets D and E below.
D={p,q,{p,q,r}}
E={1,2,{3,5},6}
Set D contains the set {p,q,r}, and set E contains the set {3,5}.
Set Membership
We use the symbol ∈ to show that an object is a member of a set. The symbol is read as ‘is an element of’ or ‘is a member of.’
1 is an element of set B above, so we write 1 ∈ B.
We use the symbol ∉ to show that an object is not a member of a set. The symbol is read as ‘is not an element of’ or ‘is not a member of.’
7 is not an element of set B above, so we write 7 ∉ B.
In some cases, we will encounter very large sets or even infinite sets in mathematics. This makes it impossible to list all the elements in the set. In such cases, we:
- write down a few elements of the set to establish the pattern, say, 4 or 5 elements.
- put an ellipsis sign or three dots to show that the set has elements that continue in the same pattern.
We can put the ellipsis sign between the listed elements to show that there are other elements between the listed elements or after the listed elements to show other elements after the ones we have listed. Sets A and N illustrate this.
We write the set A of all the odd numbers between 30 and 70 as:
A={31,33,35,…,67,69}
We also write the set N of all the natural numbers as:
N={1,2,3,4,…}
Properties of sets
We consider these properties when writing down sets.
- A set must be well defined.
This eliminates the chances of ambiguity. For example, ‘the set of all short people’ is not well defined, but ‘the set of all people with a height less than 5.5 feet’ is well defined.
- The elements of a given set must be distinct.
Elements in a set should not be repeated. For example, we should write the set {1,3,5,3,7,9,7} as {1,3,5,7,9}.
The order in which the elements are written in a set does not matter. For example, the set {1,2,3,4} can be written as {4,3,2,1}, or {2,4,3,1}. All these sets are the same.
Now, we can comfortably learn how to describe sets.
How do we describe a set?
When we specify elements of a set, we are simply describing the set. The most common methods used to describe sets are:
- The verbal description method
- The roster notation or listing method
- The set-builder notation
Let us go into the details.
The verbal description method
When using this method, we describe the set in words using a verbal statement. We have to ensure that the statement is well-defined.
Examples of sets written using the verbal description method:
- The set of colors on the American flag.
- The set of all the natural numbers less than 10.
- The set of all even numbers.
- The set of all integers between -10 and -15.
The roster notation or listing method
This method is also called the tabulation method. When using this method, we list the elements of the set in a row between curly braces.
We refer to this method as the roster notation because a roster is a list of elements in the set.
This method is also known as the enumeration method because we usually list the elements, one after the other.
We should always separate the elements using commas.
This method is convenient when describing small sets.
Limitations of the roster notation
The roster notation is a straightforward method of describing sets but not convenient when describing large sets. Imagine using the roster method to describe the set of all the natural numbers less than 100!
Examples of sets written using the roster notation:
Now, let’s convert the sets above from the verbal description method to roster notation.
A={white,red,blue}
B={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}
C={2,4,6,8,….}
D={-11,-12,-13,-14}
The set-builder notation
When using this method, we:
- set a variable to represent any element in the set.
- add a brief description of a specific property that is common to all members of that set.
We have to ensure that the property we are using to describe the elements of the set should be common to all the elements in that set. This helps us to tell clearly which objects belong to the set and which ones do not.
We can describe set K, using the set-builder notation as shown below.
K={x| x has the property M} or
K={x: x has the property M}, where x is the set variable
We read this as ‘set K is the set of all elements x, such that x has the property M.’
The vertical bar (|) or the colon (:) can be used interchangeably to replace the phrase ‘such that’ or ‘for which’ when describing sets. We use either the vertical bar or the colon to separate the variable we have set from the property we are using to describe the elements of the set.
The advantage of the set-builder notation
The set-builder notation is more suitable than the roster notation because it can be used to describe both large and small sets.
Let’s use the set-builder notation to describe the set T of all integers greater than 5.
We select y as our set variable and identify a suitable property that describes the set. In this case, y must be an integer greater than 5.
We describe set T as shown below:
T={y| y is an integer,y>5}
Let’s convert the examples above into the set-builder notation.
Examples of sets written using the set-builder notation
A={x| x is a color of the American flag }
B={y:y is a natural number less than 10}
C={x:x is an even number}
D={m|m is an integer between -10 and -15 }
We can also use the set-builder notation to describe intervals of real numbers, as shown in the table below.
| Interval | Description |
| [a,b] | {x| a≤x≤b} (closed interval) |
| (a,b] | {x| a<x≤b} (half-open interval) |
| [a,b) | {x| a≤x<b} (half-open interval) |
| (a,b) | {x| a<x<b} (open interval) |
Different Methods of Describing Sets
| Verbal description | Set-builder notation | Roster notation |
| The set of all odd positive numbers less than or equal to 5 | {x:x is an odd number and 0<x≤5} | {1,2,3,4,5} |
Descriptions of Sets of Numbers in Mathematics
The table below shows some of the sets of numbers you may encounter in the course of studying mathematics.
| Set name | Symbol | Description |
| Natural numbers | N | N={1,2,3,…} N={x| x is a natural number} |
| Whole numbers | W | W={0,1,2,3,…} W={x| x is a whole number} |
| Integers | Z | Z={…,-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3,…} Z={x| x is an integer} |
| Rational numbers | Q | Q={x| x is a rational number} Q={x| x can be written in the form p/q where q≠0} |
| Real numbers | R | R={x| x is a real number} |
| Complex numbers | C | C={x: x is a complex number} C={x+yi| a,b∈R and i is an imaginary unit } |
Thus far, we have had so much fun describing sets. Now, it’s time to try out a few questions.
Practice Questions
- Describe set A containing all natural numbers less than 10 using:
(a) The set-builder notation
(b) The roster notation - Describe the set M below using the verbal description method.
M={x| x∈R,0<x<1} - Describe the set N using the set-builder notation.
N={1,3,5,7,9} - Write down the set E of positive even numbers less than 10 using the roster notation.
- Describe the set P of all prime numbers greater than 100 using the set-builder notation.
Answer key
- (a) A={x| x is a natural number less than 10}/ A={x| x∈N,x<10}/A={x| x is a natural number and x<10} (b) A={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}
- The set M is the set of all real numbers between 0 and 1.
- N={x|x is a positive odd number less than 10}/N={x|x is a positive odd number and x<10}
- E={2,4,6,8}
- P={x|x is a prime number greater than 100}/P={x|x is a prime number and x>100}
Previous Lesson | Main Page | Next Lesson
| Sets | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ways to Describe Sets | Subsets | Venn Diagrams |
What is a set?
A set is a collection of objects, things or symbols which are
clearly defined. The individual objects in a set are called the
members or elements of the set.
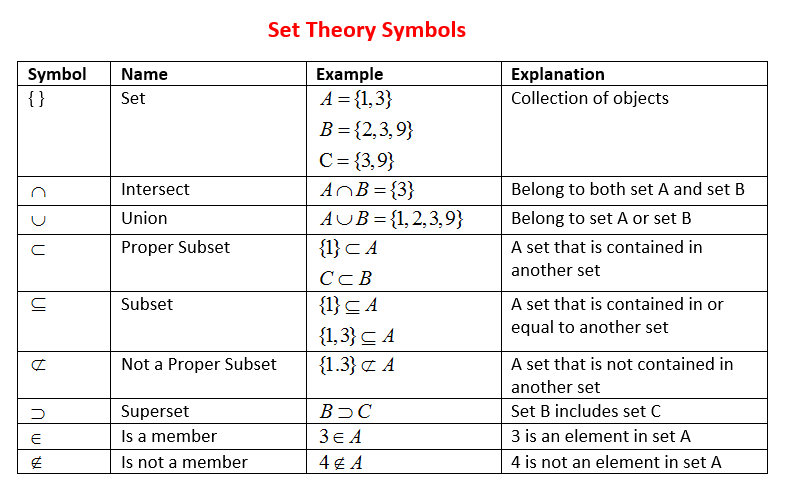
The following table shows some Set Theory Symbols. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions
of how to use the symbols.
A set must be properly defined so that we can find out whether an object is a member of the set.
Ways to Describe a Set
1. Listing The Elements (Roster Method)
The set can be defined by listing all its elements, separated by commas and enclosed within braces.
This is called the roster method.
Examples:
V = {a, e, i, o, u}
B = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10}
X = {a, b, c, d, e}
However, in some instances, it may not be possible to list all the elements of a set. In such cases,
we could define the set by methods 2 or 3.
2. Describing The Elements
The set can be defined, where possible, by describing the elements clearly in words.
Examples:
R is the set of multiples of 5.
V is the set of vowels in the English alphabet.
M is the set of months of a year.
3. Description By Set Builder Notation
The set can be defined by describing the elements using mathematical statements. This is called the
set-builder notation.
Examples:
C = {x : x is an integer, x > –3 }
This is read as: “C is the set of elements x such that x is an integer greater than –3.”
D = {x: x is the capital city of a state in the USA}
We should describe a certain property which all the elements x, in a set, have in common so that we
can know whether a particular thing belongs to the set.
We relate a member and a set using the symbol ∈. If an object x is an element of set A, we
write x ∈ A. If an object z is not an element of set A, we write z ∉ A.
∈ denotes “is an element of’ or “is a member of” or “belongs to”
∉ denotes “is not an element of” or “is not a member of” or “does not belong to”
Example:
If A = {1, 3, 5} then 1 ∈ A and 2 ∉ A
Basic Vocabulary Used In Set Theory
A set is a collection of distinct objects. The objects can be called elements or members of the set.
A set does not list an element more than once since an element is either a member of the set or it is not.
There are three main ways to identify a set:
- A written description,
- List or Roster method,
- Set builder Notation,
The empty set or null set is the set that has no elements.
The cardinality or cardinal number of a set is the number of elements in a set.
Two sets are equivalent if they contain the same number of elements.
Two sets are equal if they contain the exact same elements although their order can be different.
- Show Video Lesson
Definition And Notation Used For Subsets And Proper Subsets
If every member of set A is also a member of set B, then A is a subset of B, we write A ⊆ B. We can
also say A is contained in B.
If A is a subset of B, but A is not equal B then A is a proper subset of B, we write A ⊂ B.
The empty set is a subset of any set.
If a set A has n elements that it has 2n subsets.
- Show Video Lesson
How To Use Venn Diagrams To Show Relationship Between Sets And Set Operations?
A Venn diagram is a visual diagram that shows the relationship of sets with one another. The set of all
elements being considered is called the universal set (U) and is represented by a rectangle. Subsets of
the universal set are represented by ovals within the rectangle.
The complement of A, A’, is the set of elements in U that is not in A.
Sets are disjoint if they do not share any elements.
The intersection of A and B is the set of elements in both set A and set B.
The union of A and B is the set of elements in either set A or set B or both.
- Show Video Lesson
Examples Of Basic Venn Diagrams And Set Operations
- Show Video Lesson
Try the free Mathway calculator and
problem solver below to practice various math topics. Try the given examples, or type in your own
problem and check your answer with the step-by-step explanations.
We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.
Скачай 1) Word description 2) Set-builder form 3 и еще Конспекты лекций в формате PDF Высшая математика только на Docsity! Section 1.2: Introduction to sets — Continued. There are three ways to define a set: 1) Word description 2) Set-builder form 3) Roster form Word Description: Simply using words to describe the elements of a set. There may be more than one correct way to define a set using a word description. It will be helpful if we remember the definition of Natural numbers when we complete the next few examples. The set of Natural numbers is a set you should be familiar with. The set of Natural numbers is often assigned the letter N, and it contains integers greater than 0. N = set of Natural numbers = {1,2,3,4,5…} Example: Write a word description of the set: A = {1,2,3,4,5} Answer 1: A is the set of Natural numbers between 1 and 5 inclusive. Answer 2: A is the set of Natural numbers less than 6. Both word descriptions are equal to the set A = {1,2,3,4,5} There are many correct answers. When asked for a word description we only need to give one of many possible correct answers. Example: Write a word description of the set: A = {4,5,6,7…} Answer 1: A is the set of Natural numbers greater than or equal to 4. Answer 2: A is the set of Natural numbers greater than 3. Both word descriptions produce the set A = {4,5,6,7…} Homework #1 – 8. Write a word description of each set 1) D = {2, 3, 4, …} 2) B = {4,5,6 …} 3) A = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7} 4) E = {5,6,7,8,9,10} 5) D = {Bashful, Doc, Dopey, Grumpy, Happy, Sleepy, Sneezy} 6) B = {California, Oregon, Washington} 7) V = {a, e, i, o, u} 
One way to specify a set is to give a verbal description of its elements. This is known as the Descriptive form of specification.
The description must allow a concise determination of which elements belong to the set and which elements do not.
Let us look into some examples to understand how to write the given set in descriptive form.
Example 1 :
Write the following set in descriptive form.
A = {a, e, i, o, u}
Solution :
The given set contains vowels. So, we can represent the above set in descriptive form as follows.
A is the set of all vowels in the English alphabet
Example 2 :
Write the following set in descriptive form.
B = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11}
Solution :
The given set contains odd numbers. But it ends with 11. So, we can represent the above set in descriptive form as follows.
B is the set of all odd natural numbers less than or equal to 11
Example 3 :
Write the following set in descriptive form.
C = {1, 4, 9, 16, 25}
Solution :
The given set contains the square of natural numbers. But it ends with 25. So, we can represent the above set in descriptive form as follows.
C is the set of all square numbers less than 26.
Example 4 :
Write the following set in descriptive form.
P = {x : x is a letter in the word ‘set theory’}
Solution :
The given set is in set builder form. It contains the letters of the word «set theory».
P is the set of all letters in the word ‘set theory’
Example 5 :
Write the following set in descriptive form.
Q = {x : x is a prime number between 10 and 20}
Solution :
The given set is in set builder form. It contains the prime numbers between 10 and 20.
Q is the set of all prime numbers between 10 and 20
Example 6 :
Write the following set in descriptive form.
Q = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
Solution :
The given set contains the set of natural numbers. But it ends with 6. So, we can represent the above set in descriptive form as follows.
Q is the set of natural numbers less than 7.
Example 7 :
Write the following set in descriptive form.
R = {2, 4, 6, 8, ……………….}
Solution :
The given set contains the set of even numbers. . So, we can represent the above set in descriptive form as follows.
R is the set of even numbers.
Example 8 :
Write the following set in descriptive form.
S = {3, 6, 9, 12, ……………….}
Solution :
The given set contains multiples of 3. So, we can represent the above set in descriptive form as follows.
S is the multiples of 3.
Apart from the stuff given above, if you need any other stuff in math, please use our google custom search here.
Kindly mail your feedback to v4formath@gmail.com
We always appreciate your feedback.
©All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
На основании Вашего запроса эти примеры могут содержать грубую лексику.
На основании Вашего запроса эти примеры могут содержать разговорную лексику.
описание набора
описание ряда
In step 240 description of a set of vehicle functions, for which the user is authorized, compare with the first set of vehicle functions that are potentially possible to implement in the vehicle (i.e. maxnye functionality of the vehicle).
На этапе 240 описание набора функций транспортного средства, для которых пользователь является авторизованным, сопоставляют с первым набором функций транспортного средства, которые потенциально возможны для выполнения в транспортном средстве (то есть максимальные функциональные возможности транспортного средства).
In the process of converting a bitmap image, only the description of a set of pixels is the initial data, so there is the problem of replacing a smaller number of pixels by a larger (increasing) or larger by a smaller (with decreasing)
При преобразовании растровой картинки исходными данными является только описание набора пикселей, поэтому возникает проблема замены меньшего числа пикселей на большее (при увеличении, или большего на меньшее (при уменьшении).
A use case is a generalized description of a set of interactions between the system and one or more actors, where an actor is either a user or another system.
Сценарий описывается как «обобщенное описание ряда взаимодействий между системой и одним или более агентами, где агент — пользователь или другая система».
A use case has been described as «a generalized description of a set of interactions between the system and one or more actors, where an actor is either a user or another system.»
Сценарий описывается как «обобщенное описание ряда взаимодействий между системой и одним или более агентами, где агент — пользователь или другая система».
Description of a set of entities which share common characteristics, relations, attributes, and semantics.
Описание набора сущностей, которые имеют общие характеристики, отношения, атрибуты и семантику.
A description of a set of objects that share the same attributes, operations, methods, relationships, and semantics.
Описание набора объектов, характеризующихся одинаковыми атрибутами, операциями, методами, взаимоотношениями и семантикой.
A description of a set of data elements usually associated with a single data set
Описание набора элементов данных, обычно увязываемых с единственным набором данных
This article is devoted to the description of a set of ideas aimed at developing personal and professional selfdetermination and the skill of conscious choice in adolescence and early adolescence, united in the «System Choice» program of Smart Course’s.
Статья посвящена описанию комплекса идей, направленных на развитие личностно-профессионального самоопределения и навыка осознанного выбора в подростковом и раннем юношеском возрасте, объединенных в программе «Система Выбор» компании Смарт Курс.
Chapter Two, «Orientalist Structures and Restructures,» attempts to trace the development of modern Orientalism by a broadly chronological description, and also by the description of a set of devices common to the work of important poets, artists, and scholars.
Глава 2 «Ориентализм строит и перестраивает» посвящена пытке проследить развитие современного ориентализма в виде широкого хронологического описания, а также через описания множества приемов, присущих работам крупнейших поэтов, художников и ученых.
populate the database containing the description of a set of controlled active network equipment and management systems, active network equipment, including the identification parameters of the equipment: IP addresses and network names
заполнение базы данных, содержащей описание множества контролируемого активного сетевого оборудования и систем управления активным сетевым оборудованием, включая в него идентификационные параметры данного оборудования: IP-адреса и сетевые имена
Simply put, an object is a thing, generally drawn from the vocabulary of the problem space or the solution space; a class is a description of a set of common objects.
В самом общем смысле объект — это сущность, обычно извлекаемая из словаря предметной области или решения, а класс является описанием множества однотипных объектов.
Результатов: 11. Точных совпадений: 11. Затраченное время: 56 мс
Documents
Корпоративные решения
Спряжение
Синонимы
Корректор
Справка и о нас
Индекс слова: 1-300, 301-600, 601-900
Индекс выражения: 1-400, 401-800, 801-1200
Индекс фразы: 1-400, 401-800, 801-1200