In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use Python to count the number of words and word frequencies in both a string and a text file. Being able to count words and word frequencies is a useful skill. For example, knowing how to do this can be important in text classification machine learning algorithms.
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll have learned:
- How to count the number of words in a string
- How to count the number of words in a text file
- How to calculate word frequencies using Python
Reading a Text File in Python
The processes to count words and calculate word frequencies shown below are the same for whether you’re considering a string or an entire text file. Because of this, this section will briefly describe how to read a text file in Python.
If you want a more in-depth guide on how to read a text file in Python, check out this tutorial here. Here is a quick piece of code that you can use to load the contents of a text file into a Python string:
# Reading a Text File in Python
file_path = '/Users/datagy/Desktop/sample_text.txt'
with open(file_path) as file:
text = file.read()I encourage you to check out the tutorial to learn why and how this approach works. However, if you’re in a hurry, just know that the process opens the file, reads its contents, and then closes the file again.
Count Number of Words In Python Using split()
One of the simplest ways to count the number of words in a Python string is by using the split() function. The split function looks like this:
# Understanding the split() function
str.split(
sep=None # The delimiter to split on
maxsplit=-1 # The number of times to split
)By default, Python will consider runs of consecutive whitespace to be a single separator. This means that if our string had multiple spaces, they’d only be considered a single delimiter. Let’s see what this method returns:
# Splitting a string with .split()
text = 'Welcome to datagy! Here you will learn Python and data science.'
print(text.split())
# Returns: ['Welcome', 'to', 'datagy!', 'Here', 'you', 'will', 'learn', 'Python', 'and', 'data', 'science.']We can see that the method now returns a list of items. Because we can use the len() function to count the number of items in a list, we’re able to generate a word count. Let’s see what this looks like:
# Counting words with .split()
text = 'Welcome to datagy! Here you will learn Python and data science.'
print(len(text.split()))
# Returns: 11Count Number of Words In Python Using Regex
Another simple way to count the number of words in a Python string is to use the regular expressions library, re. The library comes with a function, findall(), which lets you search for different patterns of strings.
Because we can use regular expression to search for patterns, we must first define our pattern. In this case, we want patterns of alphanumeric characters that are separated by whitespace.
For this, we can use the pattern w+, where w represents any alphanumeric character and the + denotes one or more occurrences. Once the pattern encounters whitespace, such as a space, it will stop the pattern there.
Let’s see how we can use this method to generate a word count using the regular expressions library, re:
# Counting words with regular expressions
import re
text = 'Welcome to datagy! Here you will learn Python and data science.'
print(len(re.findall(r'w+', text)))
# Returns: 11Calculating Word Frequencies in Python
In order to calculate word frequencies, we can use either the defaultdict class or the Counter class. Word frequencies represent how often a given word appears in a piece of text.
Using defaultdict To Calculate Word Frequencies in Python
Let’s see how we can use defaultdict to calculate word frequencies in Python. The defaultdict extend on the regular Python dictionary by providing helpful functions to initialize missing keys.
Because of this, we can loop over a piece of text and count the occurrences of each word. Let’s see how we can use it to create word frequencies for a given string:
# Creating word frequencies with defaultdict
from collections import defaultdict
import re
text = 'welcome to datagy! datagy will teach data. data is fun. data data data!'
counts = defaultdict(int)
for word in re.findall('w+', text):
counts[word] += 1
print(counts)
# Returns:
# defaultdict(<class 'int'>, {'welcome': 1, 'to': 1, 'datagy': 2, 'will': 1, 'teach': 1, 'data': 5, 'is': 1, 'fun': 1})Let’s break down what we did here:
- We imported both the
defaultdictfunction and therelibrary - We loaded some text and instantiated a defaultdict using the
intfactory function - We then looped over each word in the word list and added one for each time it occurred
Using Counter to Create Word Frequencies in Python
Another way to do this is to use the Counter class. The benefit of this approach is that we can even easily identify the most frequent word. Let’s see how we can use this approach:
# Creating word frequencies with Counter
from collections import Counter
import re
text = 'welcome to datagy! datagy will teach data. data is fun. data data data!'
counts = Counter(re.findall('w+', text))
print(counts)
# Returns:
# Counter({'data': 5, 'datagy': 2, 'welcome': 1, 'to': 1, 'will': 1, 'teach': 1, 'is': 1, 'fun': 1})Let’s break down what we did here:
- We imported our required libraries and classes
- We passed the resulting list from the
findall()function into theCounterclass - We printed the result of this class
One of the perks of this is that we can easily find the most common word by using the .most_common() function. The function returns a sorted list of tuples, ordering the items from most common to least common. Because of this, we can simply access the 0th index to find the most common word:
# Finding the Most Common Word
from collections import Counter
import re
text = 'welcome to datagy! datagy will teach data. data is fun. data data data!'
counts = Counter(re.findall('w+', text))
print(counts.most_common()[0])
# Returns:
# ('data', 5)Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned how to generate word counts and word frequencies using Python. You learned a number of different ways to count words including using the .split() method and the re library. Then, you learned different ways to generate word frequencies using defaultdict and Counter. Using the Counter method, you were able to find the most frequent word in a string.
Additional Resources
To learn more about related topics, check out the tutorials below:
- Python
str.split()– Official Documentation - Python Defaultdict: Overview and Examples
- Python: Count Number of Occurrences in List (6 Ways)
- Python: Count Number of Occurrences in a String (4 Ways!)
Data preprocessing is an important task in text classification. With the emergence of Python in the field of data science, it is essential to have certain shorthands to have the upper hand among others. This article discusses ways to count words in a sentence, it starts with space-separated words but also includes ways to in presence of special characters as well. Let’s discuss certain ways to perform this.
Quick Ninja Methods: One line Code to find count words in a sentence with Static and Dynamic Inputs.
Python3
countOfWords = len("Geeksforgeeks is best Computer Science Portal".split())
print("Count of Words in the given Sentence:", countOfWords)
print(len("Geeksforgeeks is best Computer Science Portal".split()))
print(len(input("Enter Input:").split()))
Output:
Method #1: Using split() split function is quite useful and usually quite generic method to get words out of the list, but this approach fails once we introduce special characters in the list.
Python3
test_string = "Geeksforgeeks is best Computer Science Portal"
print ("The original string is : " + test_string)
res = len(test_string.split())
print ("The number of words in string are : " + str(res))
Output
The original string is : Geeksforgeeks is best Computer Science Portal The number of words in string are : 6
Method #2 : Using regex(findall()) Regular expressions have to be used in case we require to handle the cases of punctuation marks or special characters in the string. This is the most elegant way in which this task can be performed.
Example
Python3
import re
test_string = "Geeksforgeeks, is best @# Computer Science Portal.!!!"
print ("The original string is : " + test_string)
res = len(re.findall(r'w+', test_string))
print ("The number of words in string are : " + str(res))
Output
The original string is : Geeksforgeeks, is best @# Computer Science Portal.!!! The number of words in string are : 6
Method #3 : Using sum() + strip() + split() This method performs this particular task without using regex. In this method we first check all the words consisting of all the alphabets, if so they are added to sum and then returned.
Python3
import string
test_string = "Geeksforgeeks, is best @# Computer Science Portal.!!!"
print ("The original string is : " + test_string)
res = sum([i.strip(string.punctuation).isalpha() for i in test_string.split()])
print ("The number of words in string are : " + str(res))
Output
The original string is : Geeksforgeeks, is best @# Computer Science Portal.!!! The number of words in string are : 6
Method #4: Using count() method
Python3
test_string = "Geeksforgeeks is best Computer Science Portal"
print ("The original string is : " + test_string)
res = test_string.count(" ")+1
print ("The number of words in string are : " + str(res))
Output
The original string is : Geeksforgeeks is best Computer Science Portal The number of words in string are : 6
Method #5 : Using the shlex module:
Here is a new approach using the split() method in shlex module:
Python3
import shlex
test_string = "Geeksforgeeks is best Computer Science Portal"
words = shlex.split(test_string)
count = len(words)
print(count)
The shlex module provides a lexical analyzer for simple shell-like syntaxes. It can be used to split a string into a list of words while taking into account quotes, escapes, and other special characters. This makes it a good choice for counting words in a sentence that may contain such characters.
Note: The shlex.split function returns a list of words, so you can use the len function to count the number of words in the list. The count method can also be used on the list to achieve the same result.
Method #6: Using operator.countOf() method
Python3
import operator as op
test_string = "Geeksforgeeks is best Computer Science Portal"
print("The original string is : " + test_string)
res = op.countOf(test_string, " ")+1
print("The number of words in string are : " + str(res))
Output
The original string is : Geeksforgeeks is best Computer Science Portal The number of words in string are : 6
The time complexity of this approach is O(n), where n is the length of the input string.
The Auxiliary space is also O(n), as the shlex.split function creates a new list of words from the input string. This approach is efficient for small to medium-sized inputs, but may not be suitable for very large inputs due to the use of additional memory.
Method #7:Using reduce()
- Initialize a variable res to 1 to account for the first word in the string.
- For each character ch in the string, do the following:
a. If ch is a space, increment res by 1. - Return the value of res as the result.
Python3
from functools import reduce
test_string = "Geeksforgeeks is best Computer Science Portal"
print("The original string is : " + test_string)
res = reduce(lambda x, y: x + 1 if y == ' ' else x, test_string, 1)
print("The number of words in string are : " + str(res))
Output
The original string is : Geeksforgeeks is best Computer Science Portal The number of words in string are : 6
The time complexity of the algorithm for counting the number of words in a string using the count method or reduce function is O(n), where n is the length of the string. This is because we iterate over each character in the string once to count the number of spaces.
The auxiliary space of the algorithm is O(1), since we only need to store a few variables (res and ch) at any given time during the execution of the algorithm. The space required is independent of the length of the input string.
Method #8: Using numpy:
Algorithm:
- Initialize the input string ‘test_string’
- Print the original string
- Use the numpy ‘char.count()’ method to count the number of spaces in the string and add 1 to it to get the count of words.
- Print the count of words.
Python3
import numpy as np
test_string = "Geeksforgeeks is best Computer Science Portal"
print("The original string is : " + test_string)
res = np.char.count(test_string, ' ') + 1
print("The number of words in string are : " + str(res))
Output: The original string is : Geeksforgeeks is best Computer Science Portal The number of words in string are : 6
Time complexity: O(n)
The time complexity of the ‘char.count()’ method is O(n), where n is the length of the input string. The addition operation takes constant time. Therefore, the time complexity of the code is O(n).
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
The space complexity of the code is constant, as we are not using any additional data structures or variables that are dependent on the input size. Therefore, the space complexity of the code is O(1).
Strings are essential data types in any programming language, including python. We need to perform many different operations, also known as string preprocessing like removing the unnecessary spaces, counting the words in a string, making the string in the same cases (uppercase or lowercase). In this article, we will learn how to count words in a string in python.
We will learn how to count the number of words in a string. For example- We have a string-” Hello, this is a string.” It has five words. Also, we will learn how to count the frequency of a particular word in a string.
- Count Words Using For loop-
- Using split() to count words in a string
- Count frequency of words in a string using a dictionary
- Count frequency of words in string Using Count()
1. Count Words Using For loop-
Using for loop is the naïve approach to solve this problem. We count the number of spaces between the two characters.
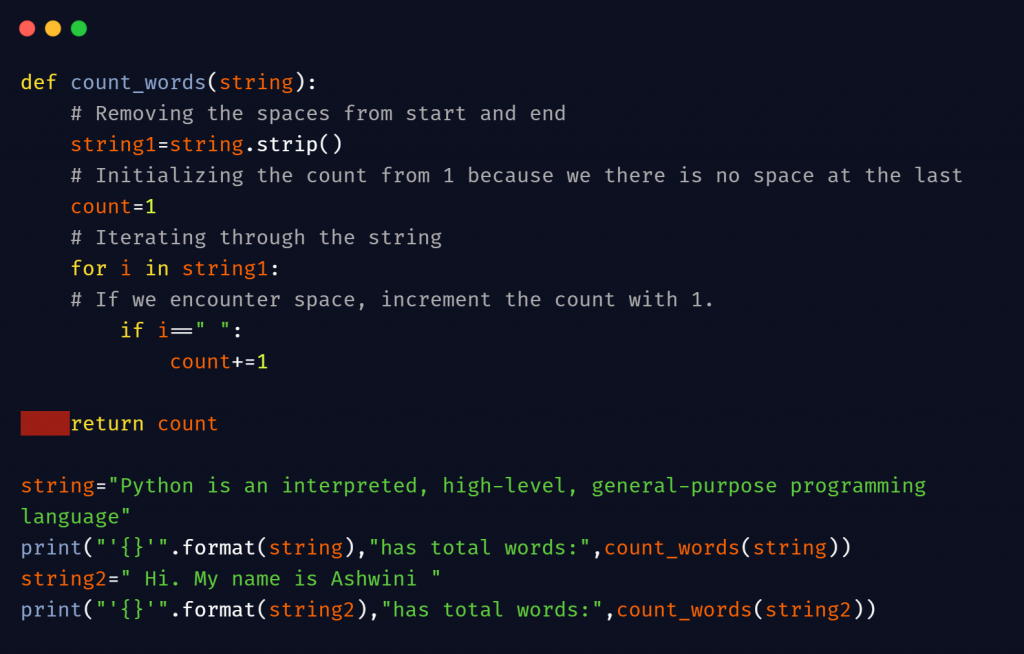
<pre class="wp-block-syntaxhighlighter-code">def count_words(string):
# Removing the spaces from start and end
string1=string.strip()
# Initializing the count from 1 because we there is no space at the last
count=1
# <a href="https://www.pythonpool.com/python-iterate-through-list/" target="_blank" rel="noreferrer noopener">Iterating</a> through the string
for i in string1:
# If we encounter space, increment the count with 1.
if i==" ":
count+=1
return count
string="Python is an interpreted, high-level, general-purpose programming language"
print("'{}'".format(string),"has total words:",count_words(string))
string2=" Hi. My name is Ashwini "
print("'{}'".format(string2),"has total words:",count_words(string2))</pre>
Output-
''Python is an interpreted, high-level, general-purpose programming language' has total words: 8'' Hi. My name is Ashwini ' has total words: 5
2. Using split() to count words in a string
We can use split() function to count words in string.
def word_count(string):
# Here we are removing the spaces from start and end,
# and breaking every word whenever we encounter a space
# and storing them in a list. The len of the list is the
# total count of words.
return(len(string.strip().split(" ")))
string="Python is an interpreted, high-level, general-purpose programming language"
print("'{}'".format(string),"has total words:",count_words(string))
string2=" Hi. My name is Ashwini "
print("'{}'".format(string2),"has total words:",word_count(string2))
Output-
''Python is an interpreted, high-level, general-purpose programming language' has total words: 8'' Hi. My name is Ashwini ' has total words: 5
3. Count the frequency of words in a String in Python using Dictionary
<pre class="wp-block-syntaxhighlighter-code">def wordFrequency(string):
# converting the string into lowercase
string=string.lower()
# Whenever we encounter a space, break the string
string=string.split(" ")
# Initializing a dictionary to store the frequency of words
word_frequency={}
# <a href="https://www.pythonpool.com/python-iterate-through-list/" target="_blank" rel="noreferrer noopener">Iterating</a> through the string
for i in string:
# If the word is already in the keys, increment its frequency
if i in word_frequency:
word_frequency[i]+=1
# It means that this is the first occurence of the word
else:
word_frequency[i]=1
return(word_frequency)
string="Woodchuck How much wood would a woodchuck chuck if a woodchuck could chuck wood ?"
print(wordFrequency(string)) </pre>
Output-
{'woodchuck': 3, 'how': 1, 'much': 1, 'wood': 2, 'would': 1, 'a': 2, 'chuck': 2, 'if': 1, 'could': 1, '?': 1}
4. Count frequency of words in string in Python Using Count()
Count() can be used to count the number of times a word occurs in a string or in other words it is used to tell the frequency of a word in a string. We just need to pass the word in the argument.
def return_count(string,word):
string=string.lower()
# In string, what is the count that word occurs
return string.count(word)
string2="Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers. How many pickled peppers did Peter Piper pick?"
return_count(string2,'piper')
Output-
2
If we want to know the number of times every word occurred, we can make a function for that.
set1=set()
string="Woodchuck How much wood would a woodchuck chuck if a woodchuck could chuck wood ?"
string=string.lower()
# splitting the string whenever we encounter a space
string=string.split(" ")
# iterate through list-string
for i in string:
# Storing the word and its frequency in the form of tuple in a set
# Set is used to avoid repetition
set1.add((i,string.count(i)))
print(set1)
Output-
{('how', 1), ('would', 1), ('woodchuck', 3), ('a', 2), ('chuck', 2), ('could', 1), ('if', 1), ('?', 1), ('wood', 2), ('much', 1)}
If we want to know how many times a particular word occur in a string in an interval, we can use start and end parameters of count().
For example-
string="Can you can a can as a canner can can a can?"
# if you want to take cases into account remove this line
string=string.lower()
# between index=8 and 17, how many times the word 'can' occurs
print(string.count("can",8,17))
Output-
2
Must Read
- How to Convert String to Lowercase in
- How to Calculate Square Root
- User Input | Input () Function | Keyboard Input
- Best Book to Learn Python
Conclusion
In the current era, data is very important. And as the world of Data Science is growing rapidly, and that too using python, data preprocessing is very important. We need to count words in a string in python to preprocess textual data and for that, the above-discussed methods are very important.
Try to run the programs on your side and let us know if you have any queries.
Happy Coding!
- Используйте методы
split()иlen()для подсчета слов в строке Python - Используйте модуль RegEx для подсчета слов в строке Python
- Используйте методы
sum(),strip()иsplit()для подсчета слов в строке Python - Используйте метод
count()для подсчета слов в Python String Python

Из этого туториала Вы узнаете, как считать слова в строковом Python.
Используйте методы split() и len() для подсчета слов в строке Python
split() — это встроенный в Python метод, который разделяет слова внутри строки с помощью определенного разделителя и возвращает массив строк. Этот метод принимает в качестве аргумента не более двух параметров:
separator(необязательно) — действует как разделитель (например, запятые, точка с запятой, кавычки или косая черта). Задает границу, на которой нужно разделить строку. По умолчаниюразделителемявляется любой пробел (пробел, новая строка, табуляция и т. Д.), Еслиseparatorне указан.maxsplit(необязательно) — определяет максимальное количество разделений. Значение по умолчаниюmaxsplit, если не определено, равно-1, что означает, что он не имеет ограничений и разбивает строку на несколько частей.
Синтаксис split():
str.split(separator, maxsplit)
len () также является встроенным методом Python, который возвращает количество строк в массиве или подсчитывает длину элементов в объекте. Этот метод принимает только один параметр: строку, байты, список, объект, набор или коллекцию. Он вызовет исключение TypeError, если аргумент отсутствует или недействителен.
Синтаксис len():
Посмотрим, как методы split() и len() подсчитывают количество слов в строке.
Пример 1: без параметров
# initialize string
text = 'The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog'
# default separator: space
result = len(text.split())
print("There are " + str(result) + " words.")
Выход:
Пример 2: С параметром separator
# initialize string
bucket_list = 'Japan, Singapore, Maldives, Europe, Italy, Korea'
# comma delimiter
result = len(bucket_list.split(','))
# Prints an array of strings
print(bucket_list.split(','))
print("There are " + str(result) + " words.")
Выход:
['Japan', ' Singapore', ' Maldives', ' Europe', ' Italy', ' Korea']
There are 6 words.
Метод split() вернет новый список строк, а len() считает строку внутри списка.
Пример 3: С параметрами separator и maxsplit
# initialize string
bucket_list = 'Japan, Singapore, Maldives, Europe, Italy, Korea'
# comma delimiter
result = len(bucket_list.split(',', 3))
# Prints an array of strings
print(bucket_list.split(',', 3))
print("There are " + str(result) + " words.")
Выход:
['Japan', ' Singapore', ' Maldives', ' Europe, Italy, Korea']
There are 4 words.
maxsplit разделяет только первые три запятые в bucket_list. Если вы установите maxsplit, в списке будет элементmaxsplit+1.
Выход:
['Japan', ' Singapore', ' Maldives, Europe, Italy, Korea']
There are 3 words.
Метод split() разбивает большие строки на более мелкие. Следовательно, подсчет слов в массиве строк будет основан не на словах, а на том, как определен разделитель.
Используйте модуль RegEx для подсчета слов в строке Python
Регулярное выражение, сокращенно regex или regexp, — очень мощный инструмент для поиска и управления текстовыми строками; это можно использовать для предварительной обработки данных, проверки, поиска шаблона в текстовой строке и т. д. Regex также может помочь в подсчете слов в текстовой строке в сценариях, где есть знаки препинания или специальные символы, которые не нужны. Regex — это встроенный в Python пакет, поэтому нам просто нужно импортировать пакет re, чтобы начать его использовать.
# import regex module
import re
# initialize string
text = 'Python !! is the be1st $$ programming language @'
# using regex findall()
result = len(re.findall(r'w+', text))
print("There are " + str(result) + " words.")
Выход:
Используйте методы sum(), strip() и split() для подсчета слов в строке Python
Этот подход считает слова без использования регулярного выражения. sum(), strip() и split() — все это встроенные методы в Python. Мы кратко обсудим каждый метод и его функции.
Метод sum() складывает элементы слева направо и возвращает сумму. Метод принимает два параметра:
iterable(обязательно) — строка, список, кортеж и т. Д. Для суммирования. Это должны быть числа.start(необязательно) — число, добавляемое к сумме или возвращаемому значению метода.
Синтаксис sum():
Следующим является метод strip(), который возвращает копию строки без начальных и конечных пробелов, если нет аргументов; в противном случае это удаляет строку, определенную в аргументе.
chars(необязательно) — указывает строку, которую нужно удалить из левой и правой частей текста.
Синтаксис string.strip():
Наконец, метод split() уже обсуждался до этого подхода.
Теперь давайте используем эти методы вместе для подсчета слов в строке. Во-первых, нам нужно импортировать строку, встроенный модуль Python, прежде чем использовать его функции.
import string
# initialize string
text = 'Python !! is the be1st $$ programming language @'
# using the sum(), strip(), split() methods
result = sum([i.strip(string.punctuation).isalpha() for i in text.split()])
print("There are " + str(result) + " words.")
Выход:
Используйте метод count() для подсчета слов в Python String Python
Метод count() — это встроенный в Python метод. Он принимает три параметра и возвращает количество вхождений на основе данной подстроки.
substring(обязательно) — ключевое слово для поиска в строкеstart(опция) — указатель начала поискаstop(опция) — указатель того, где заканчивается поиск
Примечание. В Python индекс начинается с 0.
Синтаксис count():
string.count(substring, start, end)
Этот метод отличается от предыдущего, поскольку он возвращает не общее количество слов, найденных в строке, а количество найденных вхождений для данной подстроки. Посмотрим, как работает этот метод, на примере ниже:
# initialize string
text = "Python: How to count words in string Python"
substring = "Python"
total_occurrences = text.count(substring)
print("There are " + str(total_occurrences) + " occurrences.")
Выход:
В этом методе не имеет значения, является ли подстрока целым словом, фразой, буквой или любой комбинацией символов или цифр.
Таким образом, вы можете выбрать любой из этих подходов в зависимости от вашего варианта использования. Для слов, разделенных пробелами, мы можем использовать простой подход: функции split() или len(). Для фильтрации текстовых строк для подсчета слов без специальных символов используйте модуль regex. Создайте шаблон, в котором подсчитываются слова, не содержащие определенных символов. Без использования regex используйте альтернативу, которая представляет собой комбинацию методов sum() + strip() + split(). Наконец, метод count() также может использоваться для подсчета конкретного слова, найденного в строке.
I have a string «Hello I am going to I with hello am«. I want to find how many times a word occur in the string. Example hello occurs 2 time. I tried this approach that only prints characters —
def countWord(input_string):
d = {}
for word in input_string:
try:
d[word] += 1
except:
d[word] = 1
for k in d.keys():
print "%s: %d" % (k, d[k])
print countWord("Hello I am going to I with Hello am")
I want to learn how to find the word count.
asked Jul 2, 2012 at 20:02
3
If you want to find the count of an individual word, just use count:
input_string.count("Hello")
Use collections.Counter and split() to tally up all the words:
from collections import Counter
words = input_string.split()
wordCount = Counter(words)
answered Jul 2, 2012 at 20:05
Joel CornettJoel Cornett
23.9k9 gold badges63 silver badges86 bronze badges
6
from collections import *
import re
Counter(re.findall(r"[w']+", text.lower()))
Using re.findall is more versatile than split, because otherwise you cannot take into account contractions such as «don’t» and «I’ll», etc.
Demo (using your example):
>>> countWords("Hello I am going to I with hello am")
Counter({'i': 2, 'am': 2, 'hello': 2, 'to': 1, 'going': 1, 'with': 1})
If you expect to be making many of these queries, this will only do O(N) work once, rather than O(N*#queries) work.
answered Jul 2, 2012 at 20:05
ninjageckoninjagecko
87.6k24 gold badges136 silver badges145 bronze badges
2
Counter from collections is your friend:
>>> from collections import Counter
>>> counts = Counter(sentence.lower().split())
answered Jul 2, 2012 at 20:05
Martijn Pieters♦Martijn Pieters
1.0m288 gold badges4004 silver badges3309 bronze badges
The vector of occurrence counts of words is called bag-of-words.
Scikit-learn provides a nice module to compute it, sklearn.feature_extraction.text.CountVectorizer. Example:
import numpy as np
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
vectorizer = CountVectorizer(analyzer = "word",
tokenizer = None,
preprocessor = None,
stop_words = None,
min_df = 0,
max_features = 50)
text = ["Hello I am going to I with hello am"]
# Count
train_data_features = vectorizer.fit_transform(text)
vocab = vectorizer.get_feature_names()
# Sum up the counts of each vocabulary word
dist = np.sum(train_data_features.toarray(), axis=0)
# For each, print the vocabulary word and the number of times it
# appears in the training set
for tag, count in zip(vocab, dist):
print count, tag
Output:
2 am
1 going
2 hello
1 to
1 with
Part of the code was taken from this Kaggle tutorial on bag-of-words.
FYI: How to use sklearn’s CountVectorizerand() to get ngrams that include any punctuation as separate tokens?
answered Aug 11, 2015 at 23:40
Considering Hello and hello as same words, irrespective of their cases:
>>> from collections import Counter
>>> strs="Hello I am going to I with hello am"
>>> Counter(map(str.lower,strs.split()))
Counter({'i': 2, 'am': 2, 'hello': 2, 'to': 1, 'going': 1, 'with': 1})
answered Jul 2, 2012 at 20:14
Ashwini ChaudharyAshwini Chaudhary
242k58 gold badges456 silver badges502 bronze badges
3
Here is an alternative, case-insensitive, approach
sum(1 for w in s.lower().split() if w == 'Hello'.lower())
2
It matches by converting the string and target into lower-case.
ps: Takes care of the "am ham".count("am") == 2 problem with str.count() pointed out by @DSM below too 
answered Jul 2, 2012 at 20:05
LevonLevon
136k33 gold badges199 silver badges188 bronze badges
2
You can divide the string into elements and calculate their number
count = len(my_string.split())
answered Jan 23, 2020 at 10:02
BooharinBooharin
73510 silver badges9 bronze badges
0
You can use the Python regex library re to find all matches in the substring and return the array.
import re
input_string = "Hello I am going to I with Hello am"
print(len(re.findall('hello', input_string.lower())))
Prints:
2
answered Sep 9, 2016 at 20:06
ode2kode2k
2,64513 silver badges20 bronze badges
def countSub(pat,string):
result = 0
for i in range(len(string)-len(pat)+1):
for j in range(len(pat)):
if string[i+j] != pat[j]:
break
else:
result+=1
return result
answered Nov 1, 2018 at 19:45
1