Путаете ли вы похожие английские слова? Не пугайтесь — с этой проблемой сталкиваются многие, но она решаема. На современных примерах из фильмов и сериалов покажем, как различать такие слова.
Мы уже рассказывали вам о похожих словах, которые часто путают в английском языке. Но их так много, что все в одну статью никак не поместились бы. Сегодня представим вам 20 новых пар так называемых commonly confused words. Узнайте, как не перепутать босса с поваром, персонал с материалом, цену с призом, кухню с двоюродным братом и политику со стратегией.
Если вы хотите расширить свой лексический запас, записывайтесь на бесплатный вводный урок.
1. Chief or chef?
| Характеристика | Слово | |
|---|---|---|
| chief /tʃiːf/ |
chef /ʃef/ |
|
| Перевод | существительное — лидер, руководитель
прилагательное — главный, самый важный; руководящий |
существительное — повар, шеф-повар |
| Синонимы | существительное — a boss, an employer, a head
прилагательное — main, supreme |
существительное — a cook |
| Пример употребления | I’d like to appoint Jeff chief loan officer. — Хочу назначить Джеффа ведущим кредитным специалистом.
The chief of the staff is responsible for taking serious decisions. — Руководитель персонала ответственен за принятие серьезных решений. |
Remi has always dreamt of becoming a chef at a Michelin-starred restaurant. — Реми всегда мечтал стать поваром ресторана, отмеченного звездами «Мишлен». |
2. Suit or suite?
| Характеристика | Слово | |
|---|---|---|
| suit BrE — /sjuːt/, AmE — /suːt/ |
suite /swiːt/ |
|
| Перевод | существительное — костюм, комплект одежды
глагол — подходить, устраивать, удовлетворять требованиям |
существительное — номер люкс; набор, комплект |
| Синонимы | существительное — a tuxedo
глагол — to satisfy, to match up, to measure up |
существительное — a deluxe room; a set |
| Пример употребления | Try on this suit, I guess it should fit you perfectly. — Примерь этот костюм, я думаю, он будет сидеть на тебе идеально.
The variety of beverages and appetizers at the party suited all tastes. — Разнообразие напитков и закусок на вечеринке удовлетворяло всем вкусам. |
I need a suite in your hotel. — Мне нужен номер люкс в вашем отеле.
We ordered a new four-piece suite for the kitchen. — Мы заказали новый комплект мебели из четырех предметов для кухни. |
3. Cousin or cuisine?
| Характеристика | Слово | |
|---|---|---|
| cousin /ˈkʌzn/ |
cuisine /kwɪˈziːn/ |
|
| Перевод | кузен, кузина; дальний родственник; единомышленник | кухня, кулинарное искусство |
| Синонимы | a distant relative; like-minded person | cookery, national food |
| Пример употребления | Honey, my cousin is going to stay with us for a couple of weeks. — Дорогая, мой двоюродный брат поживет у нас пару недель.
I’ve got plenty of cousins who support me. — У меня много единомышленников, которые поддерживают меня. |
Take me to some cafe where locals eat. I want to try their national cuisine. — Отведи меня в кафе, в котором едят местные. Хочу попробовать их национальную кухню. |
First cousin означает «двоюродный брат/сестра», а second cousin — «троюродный брат/сестра».
4. Deny or refuse?
| Характеристика | Слово | |
|---|---|---|
| deny /dɪˈnaɪ/ |
refuse /rɪˈfjuːz/ |
|
| Перевод | отрицать; мешать, препятствовать | отвергать, отклонять, отказывать |
| Синонимы | to disclaim; to prevent | to decline, to reject |
| Пример употребления | после глагола to deny употребляем существительное, местоимение that либо глагол с окончанием -ing:
The thief denied the theft of the car. — Вор отрицал, что он украл машину. |
The judge refused to sustain a claim. — Судья отказался удовлетворить иск. |
5. Ashamed or embarrassed?
| Характеристика | Слово | |
|---|---|---|
| ashamed /əˈʃeɪmd/ |
embarrassed /ɪmˈbærəst/ |
|
| Перевод | испытывающий чувство стыда | смущенный, сбитый с толку |
| Синонимы | sheepish, contrite, shameful | confused, abashed |
| Пример употребления | после прилагательного ashamed употребляем либо предлог of, либо местоимение that:
The accountant was ashamed of his awkward dancing at the corporate party. — Бухгалтер испытывал стыд после своих неловких танцев на корпоративной вечеринке. |
после прилагательного embarrassed употребляем предлог by или about:
I was embarrassed by her behavior. — Меня смутило ее поведение. I was too embarrassed about her words that I couldn’t do anything. — Я была настолько сбита с толку ее словами, что не смогла ничего сделать. |
6. Accept or agree?
| Характеристика | Слово | |
|---|---|---|
| accept /əkˈsept/ |
agree /əˈɡriː/ |
|
| Перевод | принимать (подарок, предложение, правду, идею), допускать | соглашаться, сходиться во взглядах; договариваться; соответствовать |
| Синонимы | to receive, to answer affirmatively, to admit | to consent |
| Пример употребления | Have you already accepted the invitation to their wedding? — Вы уже приняли приглашение на их свадьбу?
Her husband has passed away, but she still can’t accept the fact that he’s gone. — Ее муж умер, но она никак не может принять факт того, что его больше нет. |
после глагола to agree употребляем предлоги with, on/about, частицу to с глаголом или местоимение that:
We agreed to put off the meeting till Monday. — Мы условились отложить собрание до понедельника. We agree on many social and political issues. — Мы сходимся во взглядах по многим социальным и политическим вопросам. |
7. Tall or high?
| Характеристика | Слово | |
|---|---|---|
| tall /tɔːl/ |
high /haɪ/ |
|
| Перевод | определенного роста (о людях), высотный (о многоэтажных зданиях) | высокий (об объектах); высокопоставленный; отличный, превосходный |
| Синонимы | elevated, huge, vast | large, big |
| Пример употребления | How tall is your boy? — Насколько ваш мальчик высокий?
Tall skyscrapers almost reach the clouds. — Высотные небоскребы почти достают до облаков. |
It’s dangerous to swim today. The waves are extremely high. — Сегодня опасно плавать. Волны очень высокие.
Their goods are known for the high quality. — Их товары известны своим отличным качеством. |
8. Opportunity or possibility?
| Характеристика | Слово | |
|---|---|---|
| opportunity BrE — /ˌɒpəˈtjuːnəti/, AmE — /ˌɑːpərˈtuːnəti/ |
possibility BrE — /ˌpɒsəˈbɪləti/, AmE — /ˌpɑːsəˈbɪləti/ |
|
| Перевод | шанс, благоприятная возможность, удобный случай | вероятность, возможность |
| Синонимы | a chance | probability, likelihood |
| Пример употребления | после существительного an opportunity употребляем предлог for или конструкцию to do smth:
This private school is a great opportunity for your kids. — Эта частная школа — отличный шанс для ваших детей. I appreciate the opportunity to make a toast and thank you all. — Я ценю возможность произнести тост и поблагодарить вас всех. |
после существительного a possibility употребляем предлог of или местоимение that:
There is a possibility that the weather will be bad at the weekend. — Есть вероятность, что погода на выходных испортится. Is there a possibility of any injuries during the rock-climbing classes? — А какова вероятность получить травму во время занятий скалолазанием? |
9. Thankful or grateful?
| Характеристика | Слово | |
|---|---|---|
| thankful /ˈθæŋkfl/ |
grateful /ˈɡreɪtfl/ |
|
| Перевод | радостный оттого, что избежал опасности, радостный оттого, что что-то неприятное позади | благодарный за что-то хорошее |
| Синонимы | pleased | appreciative |
| Пример употребления | после прилагательного thankful употребляем предлог for, местоимение that или конструкцию to do smth:
Alice was thankful that she didn’t get in jail. — Элис была рада тому, что она не попала в тюрьму. I’m thankful to stay in one piece after the car crash. — Я рад, что остался жив после автомобильной аварии. |
после прилагательного grateful употребляем конструкцию to smb for smth (кому-то за что-либо) или местоимение that:
I’m grateful to my parents for my happy childhood. — Я благодарен своим родителям за счастливое детство. Nick was grateful that he had a shelter. — Ник был благодарен за то, что у него был приют. |
10. Foreigner or stranger?
| Характеристика | Слово | |
|---|---|---|
| foreigner BrE — /ˈfɒrənə(r)/, AmE — /ˈfɔːrənər/, /ˈfɑːrənər/ |
stranger BrE — /ˈstreɪndʒə(r)/, AmE — /ˈstreɪndʒər/ |
|
| Перевод | иностранец | незнакомец, посторонний; чужой в какой-то обстановке |
| Синонимы | someone is from abroad/overseas | an unknown person |
| Пример употребления | It’s not that easy for a foreigner to get a proper job. — Иностранцу не так легко получить должную работу. | I feel like a complete stranger in New York. — Я чувствую себя чужим в Нью-Йорке. |
11. Alternately or alternatively?
| Характеристика | Слово | |
|---|---|---|
| alternate(ly) BrE — /ɔːlˈtɜːnət/, AmE — /ˈɔːltərnət/ |
alternative(ly) BrE — /ɔːlˈtɜːnətɪv/, AmE — /ɔːlˈtɜːrnətɪv/ |
|
| Перевод | поочередный, чередующийся | альтернативный, другой вариант |
| Синонимы | in turns, consecutively | another option, instead, on the other hand |
| Пример употребления | Seasons change alternately in this region. — В этом регионе времена года меняются поочередно. | We were walking home on foot. Alternatively, we could take a taxi, but we didn’t have money. — Мы шли домой пешком. Как вариант, мы могли взять такси, но у нас не было денег. |
12. Staff or stuff?
| Характеристика | Слово | |
|---|---|---|
| staff BrE — /stɑːf/, AmE — /stæf/ |
stuff /stʌf/ |
|
| Перевод | существительное — служебный персонал
глагол — набирать персонал прилагательное — штатный |
существительное — штука, штуковина; материал, вещество; что-то неопределенное (идея, дело)
глагол — набивать, начинять |
| Синонимы | существительное — employees, personnel
глагол — to hire прилагательное — in-house |
существительное — a thing, an object, an item; a substance, material
глагол — to fill |
| Пример употребления | слово staff может употребляться как с глаголом во множественном числе, так и в единственном — подробнее об этом читайте в статье «Употребление существительных только во множественном и только в единственном числе»:
The staff are supposed to be hardworking. — Сотрудники должны быть трудолюбивыми. The staff has shown its readiness to work hard. — Персонал показал готовность работать усердно. |
I can’t meet you at the airport. I’ve got some stuff to do. — Я не могу встретить тебя в аэропорту. Мне надо сделать кое-какие дела.
Jim quickly stuffed his clothes into the suitcase and hurried to catch the train. — Джим быстро запихал вещи в чемодан и поторопился на поезд. |
13. Ache or pain?
| Характеристика | Слово | |
|---|---|---|
| ache /eɪk/ |
pain /peɪn/ |
|
| Перевод | существительное — боль (продолжительная, ноющая, доставляющая дискомфорт)
глагол — испытывать боль |
существительное — острая боль при травме или болезни; горе, страдание
глагол — причинять боль, болеть; мучить, огорчать |
| Пример употребления | Runner’s calves ached after the marathon. — Икры бегуна болели после марафона.
The kid felt a dull ache in the stomach after eating some cookies. — Ребенок почувствовал тупую боль в животе после того, как съел немного печенья. |
Let’s help this poor guy. He seems to be in pain. — Давай поможем этому бедолаге. Похоже, ему больно.
Mike felt sharp pain in his chest and we called an ambulance. — Майк почувствовал острую боль в груди, и мы вызвали скорую. |
14. Loudly or aloud?
| Характеристика | Слово | |
|---|---|---|
| loudly /ˈlaʊdli/ |
aloud /əˈlaʊd/ |
|
| Перевод | громко (о любом громком звуке) | вслух, во весь голос |
| Синонимы | in a loud voice | out loud |
| Пример употребления | The books fell loudly on the table. — Книги громко упали на стол. | Mary, please read your verse aloud for the whole class. — Мэри, пожалуйста, прочитай свое стихотворение вслух для всего класса. |
15. Price or prize?
| Характеристика | Слово | |
|---|---|---|
| price /praɪs/ |
prize /praɪz/ |
|
| Перевод | существительное — цена; жертва
глагол — устанавливать цену |
существительное — премия, награда; приз, выигрыш
глагол — высоко ценить, оценивать по достоинству |
| Синонимы | существительное — cost, charge, a fee; a sacrifice | существительное — an award, a trophy
глагол — to appreciate, to value |
| Пример употребления | Our wedding dresses range in price from 150 $ to 500 $. — Наши свадебные платья стоят от 150 до 500 долларов.
If you want to become rich, you have to pay a certain price. — Если ты хочешь быть богатым, придется чем-то пожертвовать. |
The main prize in the competition is a month for two in Italy. — Главный приз в соревнованиях — это поездка на двоих в Италию на месяц. |
16. Arise or rise?
| Характеристика | Слово | |
|---|---|---|
| arise /əˈraɪz/ |
rise /raɪz/ |
|
| Перевод | глагол — появляться, возникать; происходить, проистекать | глагол — восходить, подниматься; увеличиваться в объеме, расти
существительное — восход, рост, подъем; прибавка к зарплате |
| Синонимы | глагол — to start, to begin, to arrive | глагол — to go upwards, to lift, to increase |
| Пример употребления | If a crisis arises, we should come up with plan B. — Если возникнет кризис, мы должны придумать план Б.
People think that all their problems arise from the decisions of the government. — Люди считают, что все их проблемы проистекают из решений правительства. |
Accommodation prices will continue to rise during this year. — Цены на жилье продолжат расти в этом году.
Am I going to get a rise for the overtime work? — Я получу прибавку за переработки? |
17. City or town?
| Характеристика | Слово | |
|---|---|---|
| city /ˈsɪti/ |
town /taʊn/ |
|
| Перевод | BrE — большой значимый город, город с местным самоуправлением; жители города (с глаголом в единственном числе)
AmE — город любого размера, у которого определены границы и который наделен официальными полномочиями от правительства штата |
BrE — небольшой город; административный центр района, деловой центр; жители городка (с глаголом в единственном числе)
AmE — деревня |
| Пример употребления | Major Russian cities are Saint Petersburg and Moscow. — Главные русские города — Санкт-Петербург и Москва.
The city is waiting for a new election race. — Жители города ждут новой предвыборной гонки. |
My native town is very small. Its population is only 2 000 people. — Мой родной городок очень маленький. Его население всего лишь 2 000 человек.
Today I’m going to town for a brief business meeting. — Сегодня я еду в центр на короткую деловую встречу. |
18. Close or shut?
| Характеристика | Слово | |
|---|---|---|
| close BrE — /kləʊz/, AmE — /kloʊz/ |
shut /ʃʌt/ |
|
| Перевод | закрыть | захлопнуть, запереть на ключ |
| Синонимы | to end, to stop, to finish | to lock |
| Пример употребления | Close the door please when leaving. — Когда будете уходить, закройте, пожалуйста, дверь.
Calm down. Close your eyes and count to ten. — Расслабьтесь. Закройте глаза и посчитайте до десяти. |
Shut the door from the outside right now! — Сейчас же захлопни дверь с той стороны!
Switch off the light and shut the warehouse. — Выключи свет и запри склад. |
19. Politics or policy?
| Характеристика | Слово | |
|---|---|---|
| politics BrE — /ˈpɒlətɪks/, AmE — /ˈpɑːlətɪks/ |
policy BrE — /ˈpɒləsi/, AmE — /ˈpɑːləsi/ |
|
| Перевод | политика, политическая деятельность; политические убеждения и взгляды | линия поведения, стратегия; принципы, стандарты, нормы |
| Пример употребления | Many people say that they are not interested in politics, they want to discuss something entertaining. — Многие люди говорят, что их не интересует политика, и они хотят обсуждать что-то развлекательное. | I develop foreign policy of our company. — Я развиваю международную стратегию нашей компании. |
20. Hear or listen?
| Характеристика | Слово | |
|---|---|---|
| hear BrE — /hɪə(r)/, AmE — /hɪr/ |
listen /ˈlɪsn/ |
|
| Перевод | слышать, обладать слухом | слушать, внимательно и осознанно воспринимать информацию; Послушай! |
| Синонимы | to notice sound | to receive sonic information attentively, to pay attention to sounds |
| Пример употребления | I can hear them talking behind the door. — Я слышу, как они говорят за дверью.
I heard the rumours about closing our company for good. — Я слышала слухи о том, что нашу компанию хотят закрыть навсегда. |
Listen to him carefully and answer every question sincerely. — Слушай его внимательно и отвечай искренне на каждый вопрос.
While commuting, I listen to the music or audiobooks. — Добираясь до работы на транспорте, я слушаю музыку или аудиокниги. Listen! I want to talk to you. — Послушай! Я хочу поговорить с тобой. |
Знаете ли вы еще какие-то похожие английские слова? Пишите в комментариях.
© 2023 englex.ru, копирование материалов возможно только при указании прямой активной ссылки на первоисточник.
English is large and includes many a word that looks and/or sounds very much like another word. This list aims to help you keep such words straight.
Note that the definitions given here are simplified; for the full definition click on the word to be taken to its entry page.
-
Access is used as a noun referring to the ability to enter, as in «access to the building,» and as a verb meaning «to enter,» as in «access the stage from the rear.»
Excess functions as a noun or adjective that typically has to do with an amount that is more than usual or necessary, as in «an excess of salt» and «excess baggage.»
-
Addition and edition are both nouns. Addition refers to something added, as in «new additions to the museum’s collection» and «an addition to the house,» as well as to the process of adding, as in «the addition of cream to the soup» and «math problems involving addition and subtraction.» It’s also the word used in phrases with in: «cookies in addition to the pie and cake.»
Edition refers to a particular version of a book, product, newspaper, etc., as in «an illustrated edition,» or to something presented as one of a series, as in «tonight’s edition of the show.»
-
Allude is a verb that means «to speak of or mention something or someone in an indirect way,» as in «they alluded to difficulties at their former school.»
Elude is a verb that most often means «to avoid or escape someone or something by being quick, skillful, or clever,» as in «a criminal who has eluded capture.»
Check out this article for more about these two words
-
Allusion is a noun that means «a statement that refers to something without mentioning it directly,» as in «a colleague’s allusion to a former spouse.»
Illusion is a noun that refers to something that looks or seems different from what it is, as in «paint that creates the illusion of metal» and «an optical illusion.» It also refers to an idea that is based on something that is not true, as in «they were under the illusion that the car was brand new.»
-
Base is a noun, verb, and adjective. The noun has a variety of meanings, several of which refer to a literal or figurative foundation or bottom, as in «the lamp’s base,» «the base of a mountain,» «the company’s customer base,» and «base of operations.» It’s also used in various phrases like «touch base» and «on base.» The verb base means «to have a particular place as the main place where a person works or lives or where a business operates,» as in «a company based in Iowa.» It is also used in phrases with on and upon: «an economy based on tourism.» The adjective base means «not honest or good,» as in «base motives.»
Bass is a noun that refers to a low or deep sound or voice, or to a musical instrument. Another word bass rhymes with pass and refers to a kind of fish.
-
Bridal is an adjective that is used to describe things relating to a bride or wedding, as in «a bridal gown» and «bridal party.»
Bridle is a noun that refers to a device that fits on a horse’s head and that is used for guiding and controlling the horse. Bridle is also a verb with two meanings: one is «to put a bridle on a horse»; the other is «to react in an angry way,» as in «he bridled at their criticism of his methods.»
-
Climactic and climatic are both adjectives. Climactic is related to the word climax; it means «most exciting and important,» as in «the movie’s climactic chase scene.»
Climatic means «of or relating to climate,» as in «climatic conditions in the region that make it an ideal place to grow grapes.»
-
Collaborate and corroborate are both verbs. Collaborate means «to work with another person or group in order to achieve or do something,» as in «collaborating on a book about dogs.»
Corroborate means «to support or help prove a statement, theory, etc. by providing information or evidence,» as in «two witnesses corroborated her story» and «a theory corroborated by recent studies.»
-
Currant is a noun that refers to a small raisin or berry.
Current is a noun that refers to a continuous movement of water or air in the same direction, as in «ocean currents,» and also to a flow of electricity, as in «a strong/weak electrical current.» Current also functions as an adjective meaning «happening or existing now,» as in «the current month» and «the magazine’s current issue.»
-
Desert functions as a noun referring to an area of very dry land that is usually covered with sand and is very hot. Desert is also a verb that means «to leave a place,» as in «residents deserted the town,» or «to leave someone or withdraw support for someone,» as in «a promise to never desert them.» Desert is also the word in the phrase just deserts.
Dessert is sweet food that is eaten after a meal: «ice cream for dessert.»
-
Detract and distract are both verbs. Detract means «to reduce the strength, value, or importance of something,» as in «a minor error that does not detract from the overall quality of the report.»
Distract means «to cause someone to stop thinking about or paying attention to someone or something and to think about or pay attention to someone or something else instead,» as in «noises in the hallway that distracted the students.»
-
Device is a noun that most often refers to an object, machine, or piece of equipment that has been made for some special purpose, as in «electronic devices.»
Devise is a verb that means «to invent or plan something that is difficult or complicated,» as in «devising a new method for converting sunlight into electricity.»
-
Eminent and imminent are both adjectives. Eminent means «successful, well-known, and respected,» as in «an eminent physician.»
Imminent means «happening very soon,» as in «awaiting their imminent arrival» or «their arrival is imminent.»
-
Envelop is a verb that means «to completely enclose or surround someone or something,» as in «she enveloped the baby in the blanket» and «mist enveloping the mountains.»
Envelope is a noun that refers to an enclosing cover for a letter, card, etc. The word is also used in the phrase «push the envelope,» which means «to go beyond the usual or normal limits by doing something new, dangerous, etc.,» as in «a writer whose new novel pushes the envelope.»
-
Formally and formerly are both adverbs. Formally is used to describe things done in a serious and proper or official way, as in «guests were dressed formally» and «she has formally announced her candidacy.»
Formerly means «at an earlier time,» as in «a car formerly owned by my neighbor.»
-
Forth is an adverb used especially in literary contexts to mean «out into notice or view,» as in «spring’s blossoms bursting forth,» and «onward or forward in time or place,» as in «from this day forth.» It is also used in various phrases such as «and so forth,» «back and forth,» «bring forth,» and «set forth.»
Fourth is used as a noun, an adjective, and an adverb with meanings that relate to the number four. As a noun it can mean «number four in a series,» as in «arriving on the fourth of May,» and «one of four equal parts of something,» as in «cut the cake into fourths.» As an adjective it means «occupying the number four position in a series,» as in «the fourth day»; as an adverb it means «in the fourth place,» as in «he finished fourth in the race.»
-
Hoard is used as a noun to refer to a large amount of something valuable that is kept hidden, as in «a dragon’s hoard of treasure,» and as a verb to mean «to collect and hide a large amount of something valuable,» as in «a dragon hoarding treasure.»
Horde is a noun that refers to a large group of people, as in «a horde of shoppers crowded the store.»
Read this article for more on these two words.
-
Incredible and incredulous are both adjectives. Incredible means «difficult or impossible to believe,» as in «a movie telling an incredible story of survival,» and «extremely good, great, or large,» as in
«the musician’s incredible skill» and «a place of incredible beauty.»Incredulous means «not able or willing to believe something,» as in «people were incredulous that the child had achieved the feat.»
This article can give you more detail on these two words.
-
Liable is an adjective that can mean «legally responsible for something,» as in «determining who is liable for the damage»; or «likely to be affected or harmed by something,» as in «a condition that makes her liable to illness»; or «likely to do something,» as in «you’re liable to fall if you’re not more careful.»
Libel is a noun and a verb. As a noun it refers to the act of publishing a false statement that causes people to have a bad opinion of someone, as in «a newspaper found guilty of libel.» As a verb it means «to write and publish a false statement that causes people to have a bad opinion of someone,» as in «the jury found that the article libeled him.»
Read more on these two words here
-
Loose is most often used as an adjective with a variety of meanings that have to do, either literally or figuratively, with something not being tight or tightly fastened, attached, or held. Some examples are: «a loose tooth,» «a loose belt,» «loose rocks/papers,» «a loose coalition.» It is also used in various phrases like «break loose,» «cut loose,» and «let loose.» It is also a verb meaning «to release or untie an animal or person» and «to make something less tight.»
Lose is a verb with various meanings typically having to do with being unable to find, keep, or hold something, as in «I keep losing my keys,» «losing power,» «lose money,» «lost an advantage,» and with failing to win something, as in «losing a game/election.» It also appears in common phrases like «lose out,» «lose it,» «lose contact,» and «lose your way.»
-
Median and medium both function as both nouns and adjectives. As a noun, median can refer to a grassy or paved area that divides a highway (also called «a median strip»), or, in mathematics, to the middle value in a series of values arranged from smallest to largest. The adjective median is usually used in mathematics to mean «having a value that is in the middle of a series of values arranged from smallest to largest,» as in «the median price of homes in the area.»
Medium as an adjective means «in the middle of a range of possible sizes, amounts, etc.,» as in «a person of medium height» and «a medium blue.» The noun medium has several meanings, among them «something that is sold in a medium size,» as in «I wear a medium,» and «a particular form or system of communication (such as newspapers, radio, or television),» as in «an effective advertising medium.»
-
Moral is a noun and an adjective. The noun refers to a lesson that is learned from a story or an experience, as in «the moral of the story is to appreciate what you have,» and in its plural form morals to proper ideas and beliefs about how to behave in a way that is considered right and good by most people, as in «I don’t question her morals.» The adjective is used with a variety of meanings having to do with right or wrong behavior, as in «moral issues/standards» and «moral conduct.»
Morale is a noun referring to the feelings of enthusiasm and loyalty that a person or group has about a task or job, as in «employee morale was high in the wake of the project’s success.»
-
Peace is a noun that has several meanings relating to an end to war or fighting or to a state of calm, as in «a wish for world peace,» «looking for some peace and quiet,» and «peace of mind.» It is also used in phrases like «hold your peace» and «make peace with.»
Piece is a noun and a verb. As a noun piece has various meanings most of which have to do with a part, amount, or type of something, as in «a piece of pie,» «a large piece of land,» or «pieces of paper,» and «a piece of land.» It’s also used in various phrases including «to pieces» and «say your piece» more on this phrase The verb piece is typically used with together to express the idea of bringing parts together, as in «piecing together scraps for the quilt» and «we pieced the facts of the story together.»
-
Pedal is a noun that most often refers to a flat piece of metal, rubber, etc., that you push with your foot to make a machine move, work, or stop, as in «the bike’s pedals» and «the car’s brake pedal.» As a verb it typically means «to push the pedals of something, such as a bicycle,» as in «pedaling faster and faster.»
Peddle is a verb that is usually used to mean «to sell something usually in small amounts and often by traveling to different places,» as in «peddling fruits and vegetables from a roadside cart.»
-
Personal is an adjective often used to describe what belongs to or relates to a particular person, as in «personal property» and «my personal opinion,» or to a person’s private thoughts, feelings, etc., as in «a very personal question.»
Personnel is a noun most often used to refer to people who work for a particular company or organization.
Here is some more detail on how to keep these words apart.
-
Plain functions as an adjective, adverb, and noun. As an adjective, it often describes what lacks decoration, pattern, extra features, etc., as in «plain paper» or «a pair of plain shoes.» As an adverb, it means «truly, completely,» as in «it’s just plain wrong.» The noun plain refers to a large area of flat land without trees.
Plane most often functions as a noun referring to an airplane or to a flat surface. It also has verb and noun use with meanings relating to carpentry.
-
Pole is a noun. It can refer to a long, straight piece of wood, metal, etc., that is often placed in the ground so that it stands straight up. Additionally, pole refers to either end of the imaginary line around which something (such as the earth) turns, as in «the north/south pole»; to either one of the two ends of a magnet; to the positive point or the negative point on a battery; or to either one of two opposite positions, situations, etc., as in «opposite poles of an argument.»
Poll functions as both a noun and a verb. As a noun it refers to an activity in which several or many people are asked a question or a series of questions in order to get information about what most people think about something; this noun use has a related verb use: a magazine might «conduct a poll,» and a magazine might «poll its readers.» The noun poll in its plural form polls refers to the record of votes that were made by people in an election or to the places where those people vote.
-
Pore functions as a verb meaning «to read or study something very carefully,» as in «spent hours poring over the map.» As a noun it refers to a very small opening on the surface of your skin.
Poor is an adjective used to mean «having little money or few possessions,» as in «a poor person,» or to describe something of low quality («poor soil»), or someone of low skill («a poor player»).
Pour is a verb that means «to cause something to flow in a steady stream from or into a container or place,» as in «pour a cup of coffee.»
-
Pray is a verb that is used to mean «to speak to God especially in order to give thanks or to ask for something,» as in «praying for forgiveness,» as well as «to hope or wish very much for something to happen,» as in «praying they will succeed.»
Prey is used as a noun to refer to an animal that is hunted or killed by another animal for food, as in «the owl’s prey,» or to someone who is a victim. It also functions as a verb meaning «to hunt,» or «to hurt, cheat, or steal from someone,» as in «thieves who prey on the city’s tourists.»
-
Preposition and proposition are both nouns. Preposition refers to a word (such as in, on, or to) that is used with a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase to show direction, location, or time, or to introduce an object.
Proposition is a noun that most often refers to something, such as a plan or offer, that is presented to a person or group of people to consider, as in «a business proposition.»
Only one letter separates these words so be sure to read more
-
Quiet functions as an adjective, a verb, and a noun. As an adjective, it mostly describes things or people who make little noise, as in «a quiet engine» and «a quiet person,» or a situation or event in which there is little noise, as in «a quiet dinner for two.» As a verb, it means «to make or become calmer or less noisy,» as in «a lullaby to quiet the crying baby.» The noun quiet refers to the quality or state of being quiet or calm, as in «the quiet of the house at midnight.»
Quite is an adverb that most often means «very,» as in «quite tired»; «completely or entirely,» as in «we quite agree»; or «exactly or precisely,» as in «not quite what I said.»
-
Resume is a verb that is usually used to mean «to begin again after stopping,» as in «the musicians resumed playing.»
Résumé is a noun used especially to refer to a short document describing your education, work history, etc., that you give an employer when you are applying for a job.
-
Right functions as an adjective, adverb, noun, and verb. Some common adjective uses are «morally or socially correct or acceptable,» as in «the right thing to do,» and «accurate or correct,» as in «the right answer.» Adverbial uses include the directional «toward the right,» as in «turn right,» and «correctly,» as in «you guessed right.» Among meanings of the noun right are «behavior that is morally good or correct,» as in «knowing right from wrong,» and «something that a person is or should be morally or legally allowed to have, get, or do,» as in «human rights.» As a verb, right often means «to correct something wrong or unjust,» as in «trying to right a wrong.»
Rite is a noun that refers to an act that is part of a usually religious ceremony, as in «funeral rites.»
Write is a verb with various meaning including «to form letters or numbers on a surface with a pen, pencil, etc.,» as in «learning to write the alphabet,» and «to create a book, poem, story, etc.,» as in «writing a book about parrots.»
-
Role is a noun that to refers to the character played by an actor, or to a part or function that someone has in a group, situation, etc., as in «scientists who had a role in finding a cure to the disease.»
Roll functions as a verb and a noun. As a verb it has various meanings relating to movement, especially by turning over and over, as in «a ball rolling down a hill,» or in a smooth continuous movement, as in «clouds rolling past» and «a car rolling to a stop.» As a noun, roll often refers to a long piece of cloth, paper, film, tape, etc., that is rolled to form the shape of a tube or ring, as in «a roll of tape,» or to a round sweet cake («a cinnamon roll»), or to a deep continuous sound, as in «a roll of thunder.»
-
Stationary is an adjective meaning «not moving» or «not changing,» as in «a stationary target» and «a stationary population.»
Stationery is a noun that refers to materials (such as paper, pens, and ink) that are used for writing or typing, or specifically to paper that is used for writing letters and that usually has matching envelopes, as in «business stationery.»
Read this article for some tips to keep them apart.
-
Statue, stature, and statute are all nouns. Statue refers to a figure usually of a person or animal that is made from stone, metal, etc.
Stature refers to the level of respect that people have for a successful person, organization, etc., as in «a writer of her stature,» as well as to a person’s height, as in «a person of rather short stature.»
Statute refers to a written law that is formally created by a government, or to another kind of written rule or regulation.
-
Track functions as a noun and a verb. As a noun, it often refers to a mark left on the ground by a moving animal, person, or vehicle, as in «tire tracks,» or to
a pair of metal bars that a train, trolley, or subway car rides along, as in «train tracks.» The verb track often means «to follow and try to find an animal by looking for its tracks and other signs that show where it has gone,» as in «hunters tracking deer,» or «to follow and find someone or something especially by looking at evidence,» as in «tracking the suspect.»Tract is a noun that usually refers to a system of body parts or organs that has a particular purpose, as in «the digestive tract,» or to an area of land.
-
Waist is a noun that refers to the middle part of your body between the hips and chest or upper back, or to the part of a piece of clothing that fits around your waist.
Waste is a verb that means «to use something valuable in a way that is not necessary or effective,» as in «trying not to waste water/money/time.» As a noun, waste often refers to material that is left over or that is unwanted after something has been made, done, used, etc., as in «industrial waste.»
-
Wander is a verb used especially to mean «to move around or go to different places usually without having a particular purpose or direction,» as in «wandering through the meadow.»
Wonder functions as both a noun and a verb. As a noun it often means «a feeling caused by seeing something that is very surprising, beautiful, amazing, etc.,» as in «staring up at the monument in wonder.» As a verb it frequently means «to think about something with curiosity,» as in «wondering about the city’s history.»
Some words look the same, while others sound the same. Knowing the difference between these similar words can be very tricky. In this handout we have provided some of the most commonly confused word pairs, with definitions for each and sentences showing them in context. This is by no means a comprehensive list, but it should hopefully help you begin to recognize the particular differences between different words.
Here are what we consider to be the top ten most confusing word pairs, organized in alphabetical order:
Affect vs. Effect
Affect is a verb meaning to influence. Effect is a noun meaning result.
While the student didn’t see how studying affected his test-taking, the positive effects soon became clear.
Lie vs. Lay
Lie is a verb meaning to recline or rest on a surface. Lay is a verb meaning to put or place.
Kim lies down to take a nap every day at 3:30 p.m. Before falling asleep, Kim lays her bracelet on the table.
Lose vs. Loose
Lose is a verb meaning to misplace. Loose is an adjective meaning slack, moveable, or weak.
I always manage to lose my loose-fitting tank top.
One Word vs. Two Word combos
People often confuse similar words that appear as one word, or two words. They are used in separate contexts, however, and so learning when to use each will improve your writing’s quality. Examples of one word/two word pairs include altogether vs. all together; anyway vs. any way; and everyday vs. every day.
Here’s an example of the difference between them:
Anyway vs. Any way
Anyway is an adverb meaning regardless. Any way is a phrase meaning any manner or method.
I don’t want to go to the party, anyway. We could take any way we want to get to the party.
Than vs. Then
Than is a conjunction used to compare two things. Then is usually an adverb indicating time.
Do you think that Pepsi Cola is better than Coca Cola? We went to the store, and then to a movie.
That vs. Which
That is used when the phrase or clause that follows it is necessary in the sentence. Which is used when the phrase or clause that follows it is not necessary.
Students that fail to thoroughly proofread often miss unnecessary points. Procrastinated papers, which students write often, fail to lead to the desired grades for their classes.
Their vs. There vs. They’re
Their is a pronoun that is plural possessive. There is a word that means place. They’re is a contraction that means they are.
Their dog is over there digging through the trash. They’re not the most responsible pet owners.
To vs. Too vs. Two
To is a preposition indicating direction. Too is an adverb meaning in addition or also. Two is a number.
Too many times, students go to their adviser to set up their classes, but only have two of their five classes picked out.
Who vs. Whom
Who is a pronoun used as the subject of a sentence. Whom is a pronoun used as a direct object.
Who is responsible for the research on this group project? We assigned research to whom for this group project?
NOTE: As a general rule, if you can substitute “she” then “who” is the appropriate choice. If you can substitute “her” then “whom” is the appropriate choice.
Your vs. You’re
Your is a pronoun that is second person possessive. You’re is a contraction that means you are.
Your clothes will wrinkle if you’re not careful with the drying cycle you choose.
Other Confusing Word Pairs
Accept vs. Except
Allusion vs. Illusion
Appraise vs. Apprise
Capital vs. Capitol
Climactic vs. Climatic
Complement vs. Compliment
Compose vs. Comprise
Elicit vs. Illicit
Emigrate vs. Immigrate
Ensure vs. Insure
Farther vs. Further
Imitated vs. Intimated
Its vs. It’s
Passed vs. Past
Set vs. Sit
There are many other resources out there to find help with other commonly confusing word pairs. Check out what the internet has to offer to improve your grammar/mechanics and writing skills!
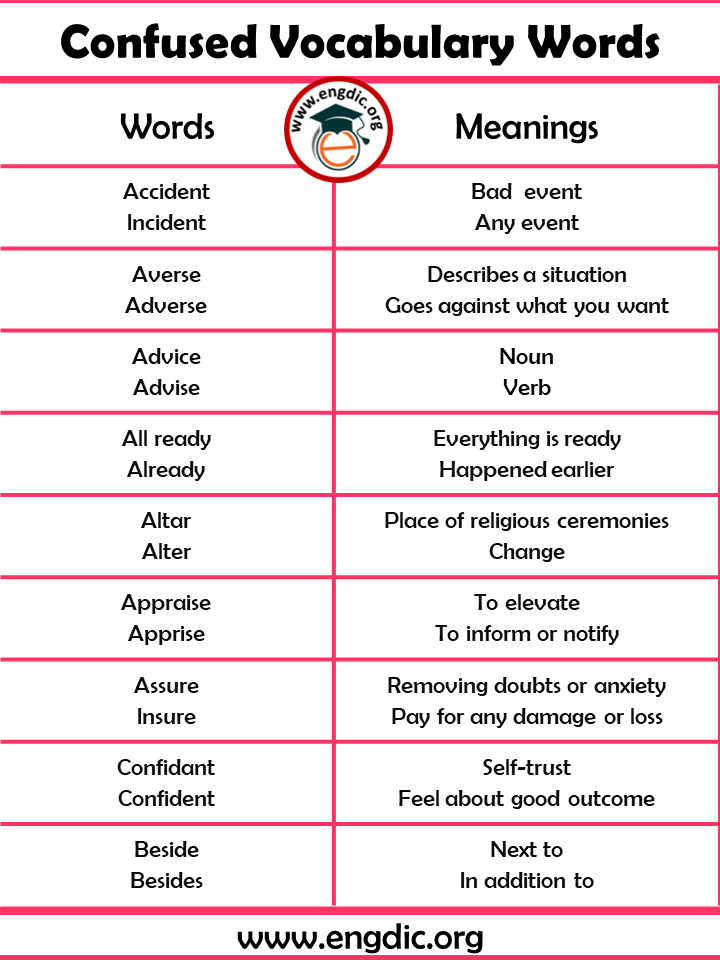
Most confused words in English with Meaning are listed here. These confused words are used in our daily conversation. You must know these confused words that makes your listening and understanding difficult.
What are the Confusing Words?
Confusing words are the words that we mistakenly use in the wrong place. These are the words with the most confusion. Confusing words is a very useful vocabulary lesson and a lot of English learners are looking for a compatible lesson of confusing words.
Important: Adverbs of Manner
Most confused words in English with Meaning
Here is the list of 100 words that are often confused with their correct meaning in English:
| Temperance
Temperament |
moderation
disposition |
| regret
Sorrow |
to grieve at
pain of mind |
| Flagrant
Fragrant |
glaring
sweet |
| Witch
Which |
Sorceress
What one |
| Accident
Incident |
Bad event
Any event |
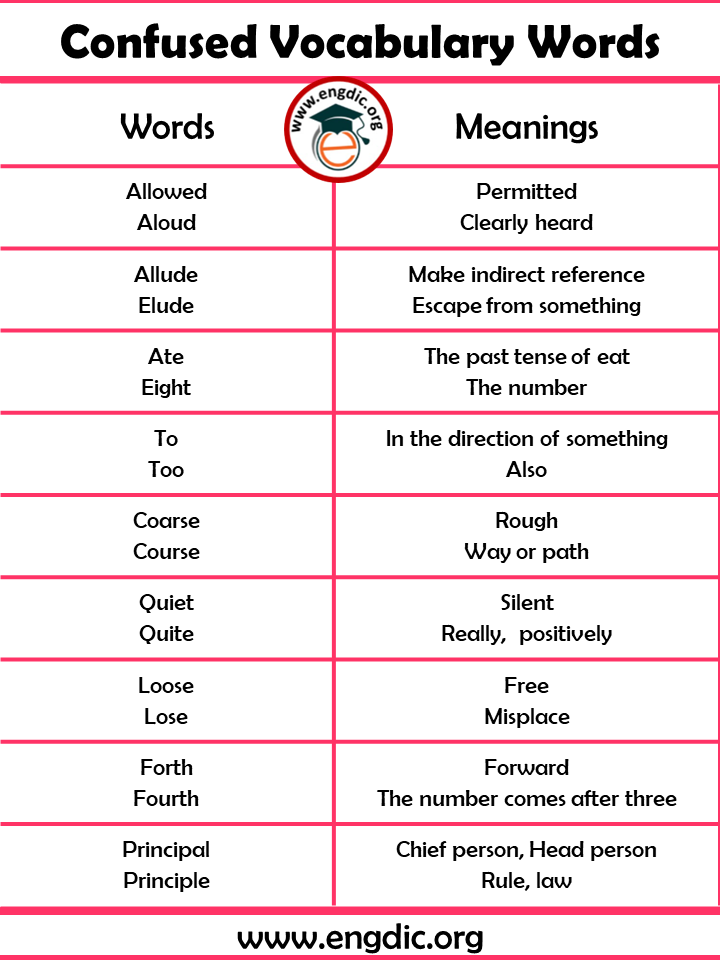
| Allowed
Aloud |
Permitted
Clearly heard |
| Statue
Statute |
an image
size |
| Last
Latest |
Final
Most recent |
| Confidant
Confident |
one who is entrusted with secrets
fully assured |
| Ascendant
Ascendancy |
rising
controlling influence |
| Simulate
Dissimulate |
to pretend to be what one is not
to hide what one is |
| Neglect
Negligence |
willful omission of duty
habitual omission of duty |
| Excite
Incite |
to stir up
to move the mind to action |
| Scenery
Sight |
a view of a landscape
a thing seen |
| Immunity
Impunity |
not liable to infection
freedom from punishment |
| Capable
Capacious |
having ability or skill to do
roomy |
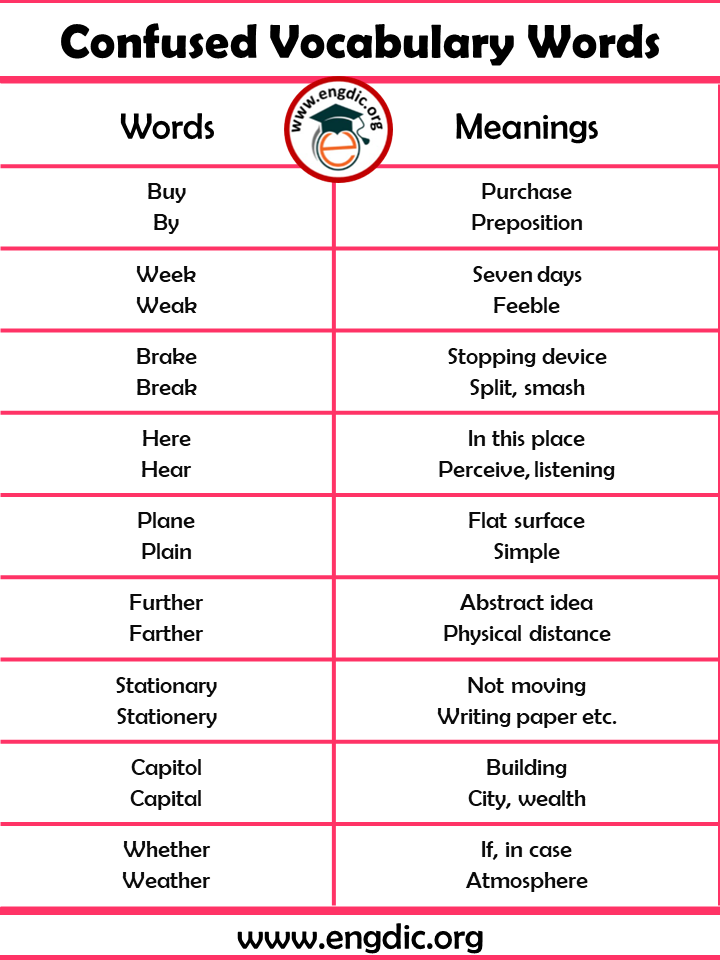
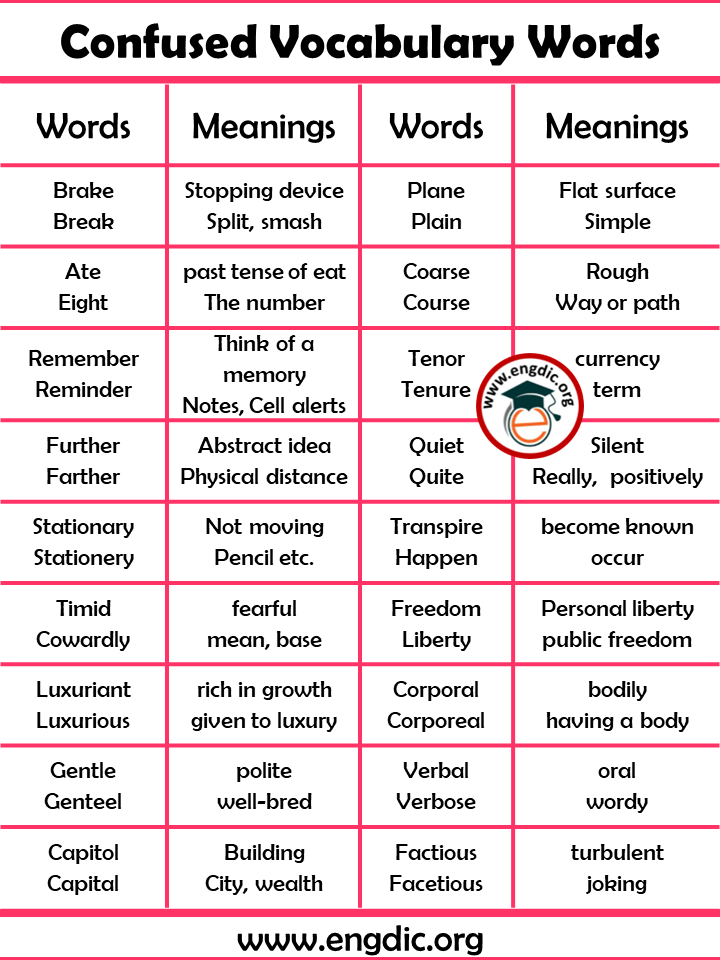
| Brake
Break |
Stopping device
Split, smash |
| Stimulant
Stimulus |
increasing or existing vital action
that which urge a man on |
| Ate
Eight |
The past tense of eat
The number |
| Honorary
Honorable |
intended merely to confer honor
worthy of Honor |
| Remember
Reminder |
Think of a memory
Notes, Cell alerts |
| Further
Farther |
Abstract idea
Physical distance |
| Stationary
Stationery |
Not moving
Writing paper etc. |
Confused Words List 2
| Timid
Cowardly |
fearful, wanting courage
mean, base |
| Luxuriant
Luxurious |
rich in growth
given to luxury |
| Collision
Collusion |
clash
a secret agreement to deceive |
| Gentle
Genteel |
polite
well-bred |
| Capitol
Capital |
Building
City, wealth |
| Altar
Alter |
Place of religious ceremonies
Change |
| Exceptionable
Exceptional |
to which exception can be taken
extraordinary |
| Take
Receive |
to take hold of thing ourselves
to accept delivery of a thing |
| Sell
Sale |
Verb
Noun |
| Forth
Fourth |
Forward
The number comes after three |
| Confidant
Confident |
Self-trust
Feel about good outcome |
| Good
Well |
Adjective
Adverb |
| Trifling
Trivial |
of small importance
a thing which is small in itself |
| Temporary
Temporal |
lasting for a time only
worldly |
| Hope
Expect |
to cherish pleasurable wishes
to look forward to as something about to happen |
| Wages
Fee |
money way to workmen
some paid to a professional man |
| Persecute
Prosecute |
to harass
to bring before a court |
| Lonely
Solitary |
forsaken
alone |
| See
Witness |
see is used for persons or things
witness is used for events or incidents |
| Healthful
Healthy |
conducive to health
possessing or enjoying health |
| Compliment
Complement |
Positive comment
Two things that go together |
| Scatter
Spread |
to throw things in different directions
to cover a certain area with something |
| Attenuate
Extenuate |
to make thin or lean
mitigate; to lessen the gravity of an act |
| Respectful | indicating respect |
| Union
Unity |
the stoke of different things being combined into one
oneness |
| Pair
Couple |
a set of two persons or things
two persons of different sexes bound to each other |
| Wave
Waive |
move
relinquish or forego |
| Practical
Practicable |
applying knowledge to some useful end and opposed to theoretical
capable of being performed |
| Testimony
Evidence |
oral or written statement
information tending to establish fast |
Confused Words List 3
| Compliment
Complement |
an expression to regard or praise
that which completes |
| Sensual
Sensuous |
one who indulges in animal appetites
pertaining to senses |
| Emigrate
Immigrate |
Leave your own country
Come and live in a country |
| Hate
Dislike |
to dislike intensely
to be displeased with |
| Plane
Plain |
Flat surface
Simple |
| Coarse
Course |
Rough
Way or path |
| Tenor
Tenure |
general run or currency
term |
| Quiet
Quite |
Silent
Really, positively |
| Transpire
Happen |
become known
occur |
| Freedom
Liberty |
personal and private liberty
public freedom |
| Corporal
Corporeal |
bodily
having a body or substance |
| Official
Officious |
pertaining to an office
too forward in offering services |
| Event
Accident |
An occurrence of some importance not necessarily unexpected
unexpected happening |
| Verbal
Verbose |
oral
wordy |
| Factious
Facetious |
turbulent
joking |
| Whether
Weather |
If, in case
Atmosphere |
| Probable
Possible |
that which is expected to happen
that which can happen |
| Part
Portion |
a section or a division
share giving when something is distributed |
| Farther
Further |
more far or distant
additional |
| Depreciate
Deprecate |
to low in value
to express disapproval of some |
| Polite
Politic |
courteous
well devised |
| Buy
By |
Purchase
Preposition |
| Spacious
Specious |
having ample room.
seeming right or true, but not really so |
| Avocation
Vocation |
subordinate occupation generally pursued for pleasure
occupation, career |
| Imaginary
Imaginative |
unreal
given to imagining |
| To
Too |
In the direction of something
Also |
| Quantity
Number |
the amount that can be measured
the amount that can be counted |
| Pray
Prey |
Asking God
An animal that is hunted |
Related: 100 Confusing Word in English
Confusing Words List 3
| Bring up
Grow up |
Parents bring up children
Children grow up |
| Ensure
Insure |
Guarantee
Financial liability |
| Suspense
Suspension |
state of indecision b
withholding |
| Willing
Willful |
disposed
obstinate |
| Sequel
Sequence |
result
order of succession |
| Shade
Shadow |
a spot sheltered from the sun
patch of shade projection by a body |
| Beside
Besides |
Next to
In addition to |
| Gone to
Been to |
You’ve traveled and not returned yet
You’ve traveled and have already returned |
| Poison
Venom |
If we inhale
Is injected |
| Effectual
Effective |
successful in producing the desired effect
having power to effect |
| Conscious
Conscientious |
aware of
one who acts according to the dictates of one’s conscience |
| Observance
Observation |
performance
act of recognizing and nothing |
| Averse
Adverse |
Describes a situation
Goes against what you want |
| Genius
Talent |
rare natural gifts
high mental ability or extraordinary capacity that is acquired |
| Loose
Lose |
Free
Misplace |
| Week
Weak |
Seven days
Feeble |
| Momentary
Momentous |
lasting only for a moment
of great importance |
| Decry
Descry |
to condemn
to discover by the eye |
| Peak
Pique |
Top
Provoke, Arouse |
| Literally
Actually |
whatever I say is literally true
he actually told a lie |
| Resources
Recourse |
means of raising money
a going to for aid or protection |
| Fetch
Bring |
to go and get
taking something with one |
| Deduce
Deduct |
to infer a truth or opinion from what precedes
to subtract |
| Here
Hear |
In this place
Perceive, listening |
| Salary
Income |
the money paid at regular intervals to officials, clerk, soldier
total money earned or received |
| Beneficial
Beneficent |
advantageous, useful
kind |
| Ugly
Awkward |
offensive to the eye
ungraceful |
| Deliverance
Delivery |
act of delivering from evil or fear
the act of speaking |
| Whom
Who |
Object
Subject |
Common Confused Words List 5
| House
Home |
Is still a house even if no one living inside it
Is a place where you live or the location |
| Accede
Concede |
to agree
to admit |
| Greed
Avarice |
desire for more than one needs
love for money for its own sake |
| Guarantee
Warranty |
Refers to promise
Used for products |
| Hardly
Scarcely |
with difficulty
hardly |
| Clumsy
Veracity |
ungainly
greed |
| Flee
Fly |
to run away
to move through the air on wings or in an aircraft |
| Then
Than |
At that time
Comparison |
| Piece
Peace |
Part, portion
Absence of war |
| House
Home |
building intended for habitation
the residence of family |
| Complacent
Complaisant |
pleased, satisfied
obliging |
| Hasten
Hurry |
to move with speed
to act with haste |
| Poor
Pore |
Have no money
Putting |
| Morale
Moral |
State of spirit
Lesson |
| Mitigate
Alleviate |
to make the burden mild punishment
to light the burden |
| Goal
Gaol |
destination
jail |
| Assure
Insure |
Removing doubts or anxiety
Pay for any damage or loss |
| Complete
Finish |
accomplish
to end |
| Advice
Advise |
Noun
Verb |
| Insight
Incite |
In depth
Provoke to action |
| recollect
remember |
that which we have difficulty in recalling
keep in mind |
Common Confused Words List 6
| Allude
Elude |
Make indirect reference
Escape from something |
| Appraise
Apprise |
To elevate
To inform or notify |
| Virtual
Virtuous |
for practical purposes
having model goodness |
| Wreck
Wreak |
ruin
take vengeance upon enemy |
| Principal
Principle |
Chief person, Head person
Rule, law |
| Popular
Populous |
pleasing to the people
full of people |
| All ready
Already |
Everything is ready
Happened earlier |
| Compensation
Remuneration |
reward for service
reward |
| Boldness
Courage |
courage of transient nature
the quality that enable men to meet danger without fear |
| Good
Goodly |
possessing desirable qualities
large; graceful |
| Cloth
Clothes |
Material cotton, wool
Items that we wear |
| Review
Revise |
To examine
Correction of errors |
Must Learn: Modal Verbs List
Infographics (Words often Confused with Meaning)
Download this lesson on Words often Confused with Meaning in PDF
Download PDF
What are the commonly confused words?
Here are Some Commonly Confused words with meaning:
| Confidant
Confident |
Self-trust
Feel about a good outcome |
| Beside
Besides |
Next to
In addition to |
| Averse
Adverse |
Describes a situation
Goes against what you want |
| Assure
Insure |
Removing doubts or anxiety
Pay for any damage or loss |
| Appraise
Apprise |
To elevate
To inform or notify |
| Altar
Alter |
Place of religious ceremonies
Change |
| All ready
Already |
Everything is ready
Happened earlier |
| Advice
Advise |
Noun
Verb |
| Accident
Incident |
Bad event
Any event |
What are the most confusing words in English?
Here is a list of 10 Most confusing Words in English:
| Whom
Who |
Object
Subject |
| Piece
Peace |
Part, portion
Absence of war |
| Morale
Moral |
State of spirit
Lesson |
| Last
Latest |
Final
Most recent |
| Insight
Incite |
In-depth
Provoke to action |
| House
Home |
Is still a house even if no one living inside it
Is a place where you live or the location |
| Guarantee
Warranty |
Refers to promise
Used for products |
| Good
Well |
Adjective
Adverb |
| Gone to
Been to |
You’ve traveled and not returned yet
You’ve traveled and have already returned |
| Ensure
Insure |
Guarantee
Financial liability |
| Emigrate
Immigrate |
Leave your own country
Come and live in a country |
About The Author
Let’s face it, English can be a confusing language at times. There are hundreds of confusing words in English: words that are separated by just one or two letters or words that sound exactly alike when you say them out loud but have completely different meanings.
That is why I have created this list of commonly confused words with detailed explanations on all of their uses and differences. I have done my best to make my explanations in everyday English, so that anyone and everyone reading these posts will be able to easily understand.
This list is by no means exhaustive and I am expanding it every day, so if you don’t see a set of words on here of which you would like an explanation, please send me an email at Jordan@writingexplained.org. I’d be happy to write an article.
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w
(A)
A hold versus Ahold
Ability versus Capability
Absorb versus Adsorb
Accept versus Except
Access versus Excess
Accent versus Ascent versus Assent
Accidentally versus Accidently
Accidently versus Accidentally
Acclimation versus Acclamation
Acknowledgment versus Acknowledgement
Acknowledgement versus Acknowledgment
Acumen versus Acuity versus Acuteness
Acute versus Chronic
Ad versus Add
Adapter versus Adaptor
Adaptor versus Adapter
Addenda versus Addendum
Addicting versus Addictive
Addictive versus Addicting
Adsorb versus Absorb
Adverse versus Averse
Advice versus Advise
Adviser versus Advisor
Advisor versus Adviser
Aerobic versus Anaerobic
Aeroplane versus Airplane
Affect versus Effect
Affect Change versus Effect Change
Affective versus Effective
Afflict versus Inflict
Afterward versus Afterwards
Afterwards versus Afterward
Ageing versus Aging
Aging versus Ageing
Ahold versus A hold
Aid versus Aide
Aide versus Aid
Airplane versus Aeroplane
Aisle versus Isle
Aka versus A.k.a.
All of a Sudden versus All of the Sudden
All ready versus Already
All right versus Alright
All together versus Altogether
Allowed versus Aloud
Allude versus Elude
Allusion versus Illusion
All ways versus Always
Alone versus Lonely
Altar versus Alter
Alter versus Altar
Aluminium versus Aluminum
Aluminum versus Aluminium
Always versus All ways
Aloud versus Allowed
Alot versus A lot
Aloud versus Out Loud
Already versus All ready
Alright versus All Right
Alumnus versus Alumni
Altogether versus All together
Ambiance versus Ambience
Ambience versus Ambiance
Amend versus Emend
Among versus Amongst
Among versus Between
Amoral versus Immoral
Amoral versus Unmoral
Amount versus Number
Anaerobic versus Aerobic
Analog versus Analogue
Analyse versus Analyze
Analysis versus Analyses
Analyses versus Analysis
Analyze versus Analyse
Anime versus Manga
Angel versus Angle
Angle versus Angel
Antagonist versus Protagonist
Anxious versus Eager
Any more versus Anymore
Any one versus Anyone
Any place versus Anyplace
Any way versus Anyway
Anymore versus Any more
Anyone versus Any one
Anyplace versus Any place
Anytime versus Any time
Anyway versus Any way
Anyway versus Anyways
Anyways versus Anyway
Any way versus Anyway
Apart versus A part
Apologise versus Apologize
Apologize versus Apologise
Are versus Is
Are versus Our
Armor versus Armour
Armour versus Armor
Artefact versus Artifact
Artifact versus Artefact
Assent versus Consent
Assume versus Presume
Assure versus Ensure versus Insure
Astrology versus Astronomy
Astronomy versus Astrology
Attain versus Obtain
Attorney versus Lawyer
Aural versus Oral
Autumn versus Fall
Avenge versus Revenge
Averse versus Adverse
Avocation versus Vocation
Awaiting versus Waiting
Award versus Reward
Awhile versus A While
Ax versus Axe
Axe versus Ax
(B)
Backup versus Back up
Backward versus Backwards
Backyard versus Back Yard
Bad Rap versus Bad Rep
Bad versus Badly
Badly versus Bad
Bail versus Bale
Bale versus Bail
Baptised versus Baptized
Baptized versus Baptised
Barbecue versus Barbeque
Barbeque versus Barbecue
Bare versus Bear
Bare with me versus Bear with Me
Baring versus Bearing
Base versus Bass
Bass versus Base
Bath versus Bathe
Bathe versus Bath
Bear versus Bare
Bear with me versus Bare with me
Bearing versus Baring
Because versus Since
Beck and Call versus Beckon Call
Bed post versus Bedpost
Bedpost versus Bed post
Began versus Begun
Begun versus Began
Behavior versus Behaviour
Behaviour versus Behavior
Beliefs versus Believes
Believes versus Beliefs
Bellow versus Below
Below versus Bellow
Bended versus Bent
Benefited versus Benefitted
Benefitted versus Benefited
Bent versus Bended
Beside versus Besides
Besides versus Beside
Between versus Among
Biannual versus Semiannual
Bi-weekly versus Semi-monthly
Bi-weekly versus Semi-weekly
Binded versus Bound
Bingeing versus Binging
Binging versus Bingeing
Bit versus Bitten
Bitten versus Bit
Blackmail versus Extortion
Blatant versus Flagrant
Blimp versus Zeppelin
Blond versus Blonde
Blonde versus Blond
Born versus Borne
Borne versus Born
Bought versus Brought
Bound versus Binded
Bourgeoisie versus Bourgeois
Breach versus Breech
Break versus Brake
Break down versus Breakdown
Breakdown versus Break down
Breath versus Breathe
Breathe versus Breath
Breech versus Breach
Brief versus Debrief
Brick and Mortar versus Brick and Morter
Bring versus Take
Broach versus Brooch
Brooch versus Broach
Broth versus Stock
Brought versus Bought
Brought versus Brung
Brung versus Brought
Buck Naked versus Butt Naked
Buildup versus Build up
Bunny versus Rabbit
Burned versus Burnt
Burnt versus Burned
Burst versus Bursted
Bursted versus Burst
Buses versus Busses
Busses versus Buses
Butt Naked versus Buck Naked
Buy versus Bye versus By
By Accident versus On Accident
Bye versus By versus Buy
(C)
Cacao versus Cocoa
Cactuses versus Cacti
Caddie versus Caddy
Calvary versus Cavalry
Calfs versus Calves
Calves versus Calfs
Camaraderie versus Comradery
Can versus May
Can not versus Cannot
Canceled versus Cancelled
Canon versus Cannon
Cannon versus Canon
Cannot versus Can not
Capability versus Ability
Capital versus Capitol
Cappuccino versus Latte
Caramel versus Carmel
Cardinal Numbers versus Ordinal Numbers
Caregiver versus Caretaker
Caretaker versus Caregiver
Carmel versus Caramel
Case and Point versus Case in Point
Cast versus Casted
Catalog versus Catalogue
Catalogue versus Catalog
Catsup versus Ketchup
Catty-Corner versus Kitty-Corner
Cavalry versus Calvary
Center versus Centre
Centre versus Center
Centrifugal versus Centripetal
Centripetal versus Centrifuga
Certificate versus Degree
Certificate versus Diploma
Charley Horse versus Charlie Horse
Charlie Horse versus Charley Horse
Check in versus Check-in
Check versus Cheque
Check up versus Checkup
Check-in versus Check in
Checkout versus Check out
Checkup versus Check up
Cheque versus Check
Childcare versus Child Care
Choir versus Chorus
Choose versus Chose
Chord versus Cord
Chorus versus Choir
Chose versus Choose
Chronic versus Acute
Client versus Customer
Collectable versus Collectible
Curricula versus Curriculum
Cite versus Site versus Sight
Cleanup versus Clean up
Climactic versus Climatic
Climatic versus Climactic
Clip versus Magazine
Cloth versus Clothes
Clothes versus Cloth
Co-operate versus Cooperate
Co-worker versus Coworker
Coarse versus Course
Coca versus Cocoa
Cocoa versus Cacao
Cocoa versus Coca
Cold versus Flu
Coldslaw versus Coleslaw
Coleslaw versus Coldslaw
College versus University
Coma versus Comma
Comma versus Coma
Compare To versus Compare With
Compare With versus Compare To
Competencies versus Skills
Complement versus Compliment
Compliment versus Complement
Comprise versus Compose
Concave versus Convex
Consent versus Assent
Conscience versus Conscious
Consignee versus Consignor
Consignor versus Consignee
Contagious versus Infectious
Contiguous versus Continuous
Continual versus Continuous
Continuous versus Contiguous
Continuous versus Continual
Continually versus Continuously
Continuously versus Continually
Convex versus Concave
Convince versus Persuade
Coliseum versus Colosseum
Collaborate versus Corroborate
Color versus Colour
Colour versus Color
Competence versus Competency
Comradery versus Camaraderie
Copyrighted versus Copywritten
Copywritten versus Copyrighted
Cord versus Chord
Corn Meal versus Corn Flour
Correspondance versus Correspondence
Correspondence versus Correspondance
Corroborate versus Collaborate
Cosy versus Cozy
Could Have versus Could Of
Could Of versus Could Have
Could versus Would
Council versus Counsel
Councilor versus Counselor
Counsel versus Council
Counselling versus Counseling
Counselor versus Councilor
Course versus Coarse
Coworker versus Co-worker
Cozy versus Cosy
Crawfish versus Crayfish
Crayfish versus Crawfish
Creek versus Crick
Criteria versus Criterion
Criterion versus Criteria
Criticise versus Criticize
Cue versus Queue
Currant versus Current
Current versus Currant
Customer versus Client
(D)
Dairy versus Diary
Dam versus Damn
Damn versus Dam
Debrief versus Brief
Deceased versus Diseased
Deduce versus Induce
Degree versus Diploma
Denounce versus Renounce
Defence versus Defense
Defendant versus Plaintiff
Defense versus Defence
Defuse versus Diffuse
Degree versus Certificate
Deep-Seated versus Deep-Seeded
Deep-Seeded versus Deep-Seated
Delusion versus Illusion
Dependant versus Dependent
Dependent versus Dependant
Depository versus Repository
Despite versus In Spite of
Device versus Devise
Devise versus Device
Diagnosis versus Prognosis
Dialog versus Dialogue
Dialogue versus Dialog
Diary versus Dairy
Dice versus Die
Die versus Dice
Dieing versus Dying
Different From versus Different Than
Different Than versus Different From
Diffuse versus Defuse
Diner versus Dinner
Dinner versus Diner
Dinner versus Supper
Diploma versus Certificate
Diploma versus Degree
Disburse versus Disperse
Diseased versus Deceased
Disc versus Disk
Discreet versus Discrete
Discrete versus Discreet
Disinterested versus Uninterested
Disk versus Disc
Disorganized versus Unorganized
Disperse versus Disburse
Dissatisfied versus Unsatisfied
Distrust versus Mistrust
Dived versus Dove
DNA versus RNA
Do versus Due
DO versus MD
Donut versus Doughnut
Doughnut versus Donut
Dove versus Dived
Draft versus Draught
Dragged versus Drug
Draught versus Draft
Dreamed versus Dreamt
Dreamt versus Dreamed
Drier versus Dryer
Drink versus Drunk
Drop off versus Drop off
Drug versus Dragged
Drunk versus Drink
Dryer versus Drier
Dual versus Duel
Due versus Do
Duel versus Dual
Duplicate versus Replicate
Dwarfs versus Dwarves
(E)
E-mail versus Email
Eager versus Anxious
Eatable versus Edible
Edible versus Eatable
Effect versus Affect
Effect Change versus Affect Change
Effective versus Affective
Effective versus Efficient
Effectiveness versus Efficiency
Efficacy versus Efficiency
Efficiency versus Effectiveness
Efficiency versus Efficacy
Efficient versus Effective
E.G. versus I.E.
Either versus Neither
Elder versus Older
Elegy versus Eulogy
Elfs versus Elves
Elicit versus Illicit
Elude versus Allude
Elves versus Elfs
Embed versus Imbed
Email versus E-mail
Emend versus Amend
Emigrate versus Immigrate
Eminent versus Imminent
Emoji versus Emoticon
Emoticon versus Emoji
Empathetic versus Empathic
Empathic versus Empathetic
Empathy versus Sympathy
Emphasise versus Emphasize
Emphasize versus Emphasise
En Route versus In Route
Endeavors versus Endeavours
Encase versus Incase
Enclosed versus Inclosed
Endeavours versus Endeavors
Endemic versus Epidemic
Endorsement versus Indorsement
Engrained versus Ingrained
Enquiry versus Inquiry
Enrollment versus Enrolment
Enrolment versus Enrollment
Ensure versus Insure versus Assure
Entitled versus Titled
Envelop versus Envelope
Envision versus Invision
Envy versus Jealousy
Epidemic versus Endemic
Equal versus Equitable
Equitable versus Equal
Espresso versus Expresso
Ethics versus Morals
Ethnicity versus Race
Eulogy versus Elegy
Everyday versus Every day
Everyone or Every One
Every thing versus Everything
Everything versus Every thing
Evoke versus Invoke
Except versus Accept
Excess versus Access
Excretion versus Secretion
Expiry versus Expiration
Explicit versus Implicit
Expresso versus Espresso
Extortion versus Blackmail
(F)
Fair versus Fare
Fall versus Autumn
Farther versus Further
Favor versus Favour
Favorite versus Favourite
Favour versus Favor
Favourite versus Favorite
Faze versus Phase
Fed versus Feed
Feed versus Fed
Fewer versus Less
Fiancé versus Fiancée
Fiancée versus Fiancé
Fiber versus Fibre
Fiction versus Nonfiction
Figuratively versus Literally
Fillet versus Filet
Firsthand versus First-hand
Fish versus Fishes
Fishes versus Fish
Fit versus Fitted
Flair versus Flare
Flagrant versus Blatant
Flammable versus Inflammable
Flautist versus Flutist
Flesh out versus Flush out
Flier versus Flyer
Flies versus Flys
Flounder versus Founder
Flu versus Cold
Flush out versus Flesh out
Flutist versus Flautist
Flys versus Flies
Follow up versus Followup
Followup versus Follow up
Foolproof versus Fullproof
Forego versus Forgo
Foreword versus Forward
Formulas versus Formulae
Forth versus Fourth
Forgo versus Forego
Former versus Latter
Forty versus Fourty
Foreword versus Forward
Foul versus Fowl
Founder versus Flounder
Fourth versus Forth
Fourty versus Forty
Fowl versus Foul
Free Reign versus Free Rein
Free Rein versus Free Reign
Freshman versus Freshmen
Freshmen versus Freshman
Fulfil versus Fulfill
Fulfill versus Fulfil
Fullproof versus Foolproof
Funner versus More Fun
Funnest versus Most Fun
(G)
Gage versus Gauge
Gaol versus Jail
Gases versus Gasses
Gasses versus Gases
Gauge versus Gage
Gist versus Jist
Glueing versus Gluing
Gluing versus Glueing
Got versus Gotten
Grammar versus Grammer
Grammer versus Grammar
Grateful versus Greatful
Greatful versus Grateful
Grey versus Gray
Grill versus Grille
Grille versus Grill
Grinded versus Ground
Gross versus Net
Ground versus Grinded
Guarantee versus Guaranty
Guaranty versus Guarantee
(H)
Hale versus Hail
Half-Mast versus Half-Staff
Half-Staff versus Half-Mast
Hands-on versus Hands on
Hangar versus Hanger
Hanged versus Hung
Hanger versus Hangar
Harbor versus Harbour
Harbour versus Harbor
Hardy versus Hearty
Hare versus Rabbit
Has versus Have
Have versus Has
Hayday versus Heyday
Heal versus Heel
Health Care versus Healthcare
Healthcare versus Health Care
Hear versus Here
Heard versus Herd
Hearty versus Hardy
Heel versus Heal
Height versus Heighth
Herd versus Heard
Here versus Hear
Her’s versus Hers
Hers versus Her’s
Heyday versus Hayday
Hillbilly versus Redneck
Himself versus Him self
Himself versus Hisself
Historic versus Historical
Historical versus Historic
Hoard versus Horde
Holistic versus Wholistic
Home in versus Hone in
Homogeneous versus Homogenous
Homogenous versus Homogeneous
Homonyms versus Homophones
Hone in versus Home in
Honor versus Honour
Honour versus Honor
Hoofs versus Hooves
Hooray versus Hurray
Hooves versus Hoofs
Hoping versus Hopping
Hopping versus Hoping
Horde versus Hoard
Humor versus Humour
Hurray versus Hooray
Hyper versus Hypo
Hypo versus Hyper
(I)
I versus Me
I.E. versus E.G.
Ignorant versus Stupid
Illegal versus Illicit
Illegal versus Unlawful
Illegible versus Unreadable
Illicit versus Illegal
Illicit versus Elicit
Illusion versus Allusion
Illusion versus Delusion
Imaginary versus Imaginative
Imaginative versus Imaginary
Imbed versus Embed
Immigrate versus Emigrate
Immanent versus Imminent
Imminent versus Eminent
Immoral versus Amoral
Immoral versus Unmoral
Implicit versus Explicit
Imply versus Infer
Impostor versus Imposter
In Case versus Incase
In Process versus In Progress
In Regard To versus In Regards To
In Route versus En Route
In Spite Of versus Despite
In tact versus Intact
Inalienable versus Unalienable
Incase versus Encase
Incase versus In Case
Incidence versus Incident
Incident versus Incidence
Inclosed versus Enclosed
Indexes versus Indices
Indices versus Indexes
Indorsement versus Endorsement
Induce versus Deduce
Inequality versus Inequity
Inequity versus Inequality
Infectious versus Contagious
Infer versus Imply
Inflammable versus Flammable
Inflict versus Afflict
Ingrained versus Engrained
Inquiry versus Enquiry
Installation versus Instillation
Instil versus Instill
Instill versus Instil
Instillation versus Installation
Insure versus Ensure versus Assure
Intact versus In tact
Inter- versus Intra-
Into versus In to
Invaluable versus Valuable
Invision versus Envision
Invoke versus Evoke
Is versus Are
Isle versus Aisle
Its versus It’s
(J)
Jail versus Gaol
Jealousy versus Envy
Jerry-rigged versus Jury-rigged
Jewelry versus Jewellery
Jibe versus Jive
Jist versus Gist
Jive versus Jibe
Judgement versus Judgment
Judgment versus Judgement
Jury-rigged versus Jerry-rigged
(K)
Ketchup versus Catsup
Kickoff versus Kick-off versus Kick off
Kitty-Corner versus Catty-Corner
Kneeled versus Knelt
Knelt versus Kneeled
Knew versus New
Knight versus Night
Knit versus Knitted
Knitted versus Knit
(L)
Labeled versus Labelled
Labelled versus Labeled
Labor versus Labour
Labour versus Labor
Ladder versus Latter
Laid out versus Layed out
Lasagna versus Lasagne
Later Than versus Later Then
Lath versus Lathe
Lathe versus Lath
Latitude versus Longitude
Latte versus Cappuccino
Latter versus Former
Latter versus Ladder
Lawyer versus Attorney
Layout versus Lay out
Layed out versus Laid out
Lead versus Led
Lead versus Lede
Leaned versus Leant
Leant versus Leaned
Leaped versus Leapt
Leapt versus Leaped
Learned versus Learnt
Learnt versus Learned
Leary versus Leery
Led versus Lead
Lede versus Lead
Leery versus Leary
Leftover versus Left over
Lend versus Loan
Lended versus Lent
Lens versus Lense
Lense versus Lens
Lent versus Lended
Less versus Fewer
Lessee versus Lessor
Lessor versus Lessee
Let’s versus Lets
Lets versus Let’s
Liar versus Lier
Lie versus Lye
Lier versus Liar
Libel versus Slander
Licence versus License
License versus Licence
Lighted versus Lit
Lifes versus Lives
Lifetime versus Life time
Light versus Lite
Lightening versus Lightning
Lightning versus Lightening
Likable versus Likeable
Linchpin versus Lynchpin
Liqueur versus Liquor
Liquor versus Liqueur
Lit versus Lighted
Lite versus Light
Liter versus Litre
Literally versus Figuratively
Lithograph versus Serigraph
Litre versus Liter
Lives versus Lifes
Loan versus Lend
Loathe versus Loath
Log in versus Login
Log in versus Log on
Login versus Log in
Lonely versus Alone
Longitude versus Latitude
Lose versus Loose versus Loosen
Loss versus Lost
Lost versus Loss
Lovable versus Loveable
Luge versus Skeleton
Lye versus Lie
Lynchpin versus Linchpin
(M)
Macro versus Micro
Magazine versus Clip
Maize versus Maze
Make Do versus Make Due
Makeup versus Make Up
Manga versus Anime
Mantel versus Mantle
Mantle versus Mantel
Many versus Much
Master versus Mister
Material versus Materiel
Materiel versus Material
Math versus Maths
Maths versus Math
May versus Can
May versus Might
May be versus Maybe
Maybe versus May be
Maze versus Maize
MD versus DO
Me versus I
Me versus Mine
Me versus Myself
Medal versus Metal
Metal versus Medal
Micro versus Macro
Mine versus Me
Minuscule versus Miniscule
Mischievous versus Mischievious
Miss versus Mrs.
Mister versus Master
Mistreatment versus Maltreatment
Mistrust versus Distrust
Mistrust versus Trust
Modeling versus Modelling
Mold versus Mould
Mom versus Mum
Moneys versus Monies
Monies versus Moneys
Monologue versus Soliloquy
Moot versus Mute
Moral versus Morale
Morale versus Moral
Morals versus Ethics
More Fun versus Funner
More Than versus More Then
More Then versus More Than
Moslem versus Muslim
Most Fun versus Funnest
Mould versus Mold
Moustache versus Mustache
Movable versus Moveable
Moveable versus Movable
Miss versus Mrs.
Mrs. versus Ms.
Ms. versus Mrs.
Much versus Many
Mucous vs. Mucus
Mucus versus Mucous
Mum versus Mom
Muslim versus Moslem
Mustache versus Moustache
Myself versus Me
(N)
Naught versus Nought
Nauseated versus Nauseous
Nauseous versus Nauseated
Nay versus Yay
Neighbors versus Neighbours
Neither versus Either
Nerve-racking versus Nerve-wracking
Nerve-wracking versus Nerve-racking
Net versus Gross
Never mind versus Nevermind
Nevermind versus Never mind
New versus Knew
Night versus Knight
Ninety versus Ninty
Ninty versus Ninety
No one versus Noone
Nobody versus No one
Nonfiction versus Fiction
Nonprofit versus Not-for-profit
Noone versus No one
No Later Than versus No Later Then
No one versus Nobody
Not Surprising versus Not Surprisingly
Not-for-profit versus Nonprofit
Nought versus Naught
Now a Days versus Nowadays
Nowadays versus Now a Days
Number versus Amount
(O)
Objective versus Subjective
Obligated versus Obliged
Obliged versus Obligated
Obtain versus Attain
Octopi versus Octopuses
Octopuses versus Octopi
Offence versus Offense
Offense versus Offence
Oftentimes versus Often times
Old-Fashion versus Old-Fashioned
Older versus Elder
Omelet versus Omelette
On Accident versus By Accident
Onboard versus On Board
One’s Self versus Oneself
Oneself versus One’s Self
Online versus On-Line
Onto versus On to
Opaque versus Translucent
Opossum versus Possum
Oral versus Aural
Oral versus Verbal
Ordinal Numbers versus Cardinal Numbers
Ordinance versus Ordnance
Organisation versus Organization
Organization versus Organisation
Orientated versus Oriented
Oriented versus Orientated
Orthopaedic versus Orthopedic
Orthopedic versus Orthopaedic
Our versus Are
Out Loud versus Aloud
Overnight versus Over Night
Over Time versus Overtime
Overtime versus Over Time
(P)
Pajamas versus Pyjamas
Patience versus Patients
Payed versus Paid
Pass time versus Pastime
Passed versus Past
Passersby versus Passerbys
Past time versus Pastime
Peace of Mind versus Piece of Mine
Peak versus Peek versus Pique
Peal versus Peel
Peel versus Peal
People versus Person
People versus Persons
Per cent versus Percent
Percent versus Per cent
Person versus People
Personal versus Personnel
Personnel versus Personal
Persons versus People
Perspective versus Prospective
Persuade versus Convince
Pet versus Petted
Phase versus Faze
Phenomena versus Phenomenon
Photo Shoot versus Photoshoot
Photoshoot versus Photo Shoot
Piece or Mine versus Peace of Mind
Pickup versus Pick Up
Plain versus Plane
Plaintiff versus Defendant
Plane versus Plain
Pleaded versus Pled
Pled versus Pleaded
Plough versus Plow
Poisonous versus Venomous
Polygamy versus Polygyny
Polygyny versus Polygamy
Port versus Starboard
Possum versus Opossum
Potatoes versus Potatos
Practice versus Practise
Practise versus Practice
Pray versus Prey
Precede versus Proceed
Precedence versus Precedent
Precedent versus Precedence
Premier versus Premiere
Premiere versus Premier
Prescribe versus Proscribe
Presence versus Presents
Presents versus Presence
Presume versus Assume
Pretence versus Pretense
Pretense versus Pretence
Preventative versus Preventive
Preventive versus Preventative
Previous versus Prior
Prey versus Pray
Principal versus Principle
Prior versus Previous
Proceed versus Precede
Prognosis versus Diagnosis
Program versus Programme
Programme versus Program
Prone versus Supine
Proof versus Prove
Proscribe versus Prescribe
Prospective versus Perspective
Protagonist versus Antagonist
Prove versus Proof
Proven versus Proved
Psychiatry versus Psychology
Psychology versus Psychiatry
Psychopath versus Sociopath
Purposefully versus Purposely
Purposely versus Purposefully
(Q)
Queue versus Cue
Quiet versus Quite
Quite versus Quiet
(R)
Rabbit versus Bunny
Rabbit versus Hare
Race versus Ethnicity
Racket versus Racquet
Racquet versus Racket
Rational versus Rationale
Read versus Read
Real versus Reel
Realise versus Realize
Realize versus Realise
Reckless versus Wreckless
Recognise versus Recognize
Recur versus Reoccur
Redneck versus Hillbilly
Reel versus Real
Regard to versus Regards to
Regard with versus Regards with
Regime versus Regimen
Regimen versus Regime
Regiment versus Regimen
Remuneration versus Renumeration
Renounce versus Denounce
Reoccur versus Recur
Replicate versus Duplicate
Repository versus Depository
Repression versus Suppression
Resiliency versus Resilience
Revenge versus Avenge
Reward versus Award
Rhyme versus Rime
Right versus Rite
Rime versus Rhyme
Rite versus Right
RNA versus DNA
Road versus Rode
Role versus Roll
Role Call versus Roll Call
Roll versus Role
Roll Call versus Role Call
Rollout versus Roll out
Roofs versus Rooves
Root versus Route
Rooves versus Roofs
Route versus Root
Run Amok versus Run Amuck
Run Amuck versus Run Amok
(S)
Sang versus Sung
Sank versus Sunk
Savior versus Saviour
Saw versus Seen
Scared versus Scarred
Scarfs versus Scarves
Scarves versus Scarfs
Scissor versus Scissors
Seam versus Seem
Secretion versus Excretion
Seen versus Saw
Seem versus Seam
Segue versus Segway
Segway versus Segue
Semiannual versus Biannual
Semi-monthly versus Bi-weekly
Semi-weekly versus Bi-weekly
Sensuous versus Sensual
Separate versus Seperate
Seperate versus Separate
Serigraph versus Lithograph
Set up versus Setup
Setup versus Set up
Sew versus Sow
Shelf versus Shelve
Sherbet versus Sherbert
Sherbert versus Sherbet
Shined versus Shone
Shoe-in versus Shoo-in
Shone versus Shined
Shoo-in versus Shoe-in
Shudder versus Shutter
Shutter versus Shudder
Sightseeing versus Site Seeing
Sign up versus Sign-up
Since versus Because
Site Seeing versus Sightseeing
Site versus Sight versus Cite
Sizable versus Sizeable
Sizeable versus Sizable
Skeleton versus Luge
Skill Set versus Skillset
Skills versus Competencies
Skillset versus Skill set
Slander versus Libel
Smartphone versus Smart phone
Smelled versus Smelt
Smelt versus Smelled
Smokey versus Smoky
Smoky versus Smokey
Smooth versus Smoothe
Sneaked versus Snuck
Snuck versus Sneaked
Soar versus Sore
Sociopath versus Psychopath
Sole versus Soul
Soliloquy versus Monologue
Some Day versus Someday
Some Thing versus Something
Some Time versus Sometime
Sometimes versus Some Times
Somebody versus Someone
Someday versus Some Day
Someone versus Somebody
Something versus Some Thing
Sometime versus Some Time
Sore versus Soar
Soul versus Sole
Sow versus Sew
Spatter versus Splatter
Specialty versus Speciality
Specter versus Spectre
Spelled versus Spelt
Spelt versus Spelled
Spilled versus Spilt
Spilt versus Spilled
Spoiled versus Spoilt
Splatter versus Spatter
Spread versus Spreaded
Staid versus Stayed
Stalactite versus Stalagmite
Stalagmite versus Stalactite
Stand-alone versus Stand alone
Stank versus Stunk
Starboard versus Port
State of the Art versus State-of-the-Art
Stationary versus Stationery
Stationery versus Stationary
Stayed versus Staid
Steal versus Steel
Stear Clear versus Steer Clear
Steel versus Steal
Steer Clear versus Stear Clear
Stent versus Stint
Stint versus Stent
Storey versus Story
Story versus Storey
Straight versus Strait
Strait versus Straight
Strived versus Strove
Stock versus Broth
Strove versus Strived
Stunk versus Stank
Stupid versus Ignorant
Subconscious versus Unconscious
Subjective versus Objective
Suite versus Suit
Suit versus Suite
Sulfur versus Sulphur
Sulphur versus Sulfur
Summary versus Summery
Sung versus Sang
Sunk versus Sank
Supercede versus Supersede
Supine versus Prone
Supper versus Dinner
Supposably versus Supposedly
Suppose versus Supposed
Supposed versus Suppose
Supposedly versus Supposably
Suppression versus Repression
Swept versus Sweeped
Sympathy versus Empathy
Systematic versus Systemic
Systemic versus Systematic
(T)
Take versus Bring
Talk to versus Talk with
Talk with versus Talk to
Tee shirt versus T-Shirt
Tenants versus Tenets
To versus Too versus Two
Than versus Then
That versus Which
Theater versus Theatre
Theatre versus Theater
Their versus There versus They’re
Theirselves versus Themselves
Them versus They
Themselves versus Theirselves
Then versus Than
Therefor versus Therefore
Therefore versus Therefor
They versus Them
Threw versus Through
Through versus Threw
Through versus Thru
Thru versus Through
Tied versus Tide
Tide versus Tied
Til versus Till
Till versus Til
Till versus Until
Titled versus Entitled
Tire versus Tyre
Tomatoes versus Tomatos
Ton versus Tonne
Tonne versus Ton
Too Hard versus To Hard
Too Long versus To Long
Too Much versus To Much
Too Much to Bear versus Too Much to Bare
Totaled versus Totalled
Totalled versus Totaled
Touch Base versus Touch Bases
Tough versus Tuff
Toward versus Towards
Trainer versus Trainor
Translucent versus Opaque
Translucent versus Transparent
Transparent versus Translucent
Traveling versus Travelling
Travelling versus Traveling
Trawling versus Trolling
Trolling versus Trawling
Truely versus Truly
Truly versus Truely
Trust versus Mistrust
T-shirt versus Tee shirt
Tuff versus Tough
Tyre versus Tire
(U)
Unalienable versus Inalienable
Unconscious versus Subconscious
Underway versus Under way
Uninterested versus Disinterested
University versus College
Unlawful versus Illegal
Unlawful versus Illicit
Unmoral versus Amoral
Unmoral versus Immoral
Unorganized versus Disorganized
Unreadable versus Illegible
Unsatisfied versus Dissatisfied
Until versus Till
Up-to-Date versus Up to Date
Upmost versus Utmost
Us versus We
Use to versus Used to
Used to versus Use to
Utmost versus Upmost
(V)
Vain versus Vein
Valentines Day versus Valentine’s Day
Valuable versus Invaluable
Vein versus Vain
Venomous versus Poisonous
Verbage versus Verbiage
Verbal versus Oral
Verbiage versus Verbage
Vocation versus Avocation
Voicemail versus Voice mail
(W)
Wack versus Whack
Waive versus Wave
Wander versus Wonder
Ware versus Wear
Was versus Were
Waste versus Waist
Waist versus Waste
Waiting versus Awaiting
Wary versus Weary
Wave versus Waive
We versus Us
Wear versus Ware
Weary versus Wary
Weather versus Whether
Waved versus Woven
Webpage versus Website
Website versus Web Site
Well-being versus Wellbeing
Wellbeing versus Well-being
Whack versus Wack
Where versus Were versus Wear
Whether versus Weather
Which versus That
Whiney versus Whiny
Whiny versus Whiney
Whiskey versus Whisky
Whisky versus Whiskey
Whoa is Me versus Woe is Me
Whoa versus Woah
Who versus Whom
Who’s versus Whose
Wholistic versus Holistic
Whose versus Who’s
While versus Whilst
Whilst versus While
Widow versus Widower
Will versus Would
With Regard to versus With Regards to
Woah versus Whoa
Woe is Me versus Whoa is Me
Wonder versus Wander
Workout versus Work out
Work in Progress versus Work in Process
Worse versus Worst
Worst versus Worse
Would versus Could
Would versus Will
Woven versus Weaved
Wreckless versus Reckless
(Y)
Ya’ll versus Y’all
Y’all versus Ya’ll
Yay versus Nay
Yea versus Yeah
Yeah versus Yea
Year old versus Year-old
Years old versus Year old
Yoghurt versus Yogurt
Yogurt versus Yoghurt
Yoke versus Yolk
Yolk versus Yoke
Your versus You’re
Your’s versus Yours
Yours versus Your’s
Youth versus Youths
(Z)
Zee versus Zed
Zeppelin versus Blimp
Zombi versus Zombie
Some words in English cause trouble for writers because these words share a similar pronunciation, meaning, or spelling with another word. These words are called commonly confused words. For example, read aloud the following sentences containing the commonly confused words new and knew:
I liked her new sweater.
I knew she would wear that sweater today.
These words may sound alike when spoken, but they carry entirely different usages and meanings. New is an adjective that describes the sweater, and knew is the past tense of the verb to know.
Recognizing Commonly Confused Words
New and knew are just two of the words that can be confusing because of their similarities. Familiarize yourself with the following list of commonly confused words. Recognizing these words in your own writing and in other pieces of writing can help you choose the correct word.
Commonly Confused Words
A, An, And
-
A (article). Used before a word that begins with a consonant.
a key, a mouse, a screen
-
An (article). Used before a word that begins with a vowel.
an airplane, an ocean, an igloo
-
And (conjunction). Connects two or more words together.
peanut butter and jelly, pen and pencil, jump and shout
Accept, Except
-
Accept (verb). Means to take or agree to something offered.
They accepted our proposal for the conference.
-
Except (conjunction). Means only or but.
We could fly there except the tickets cost too much.
Affect, Effect
-
Affect (verb). Means to create a change.
Hurricane winds affect the amount of rainfall.
-
Effect (noun). Means an outcome or result.
The heavy rains will have an effect on the crop growth.
Are, Our
-
Are (verb). A conjugated form of the verb to be.
My cousins are all tall and blonde.
-
Our (pronoun). Indicates possession, usually follows the pronoun we.
We will bring our cameras to take pictures.
By, Buy
-
By (preposition). Means next to.
My glasses are by the bed.
-
Buy (verb). Means to purchase.
I will buy new glasses after the doctor’s appointment.
Its, It’s
-
Its (pronoun). A form of it that shows possession.
The butterfly flapped its wings.
-
It’s (contraction). Joins the words it and is.
It’s the most beautiful butterfly I have ever seen.
Know, No
-
Know (verb). Means to understand or possess knowledge.
I know the male peacock sports the brilliant feathers.
-
No. Used to make a negative.
I have no time to visit the zoo this weekend.
Loose, Lose
-
Loose (adjective). Describes something that is not tight or is detached.
Without a belt, her pants are loose on her waist.
-
Lose (verb). Means to forget, to give up, or to fail to earn something.
She will lose even more weight after finishing the marathon training.
Of, Have
-
Of (preposition). Means from or about.
I studied maps of the city to know where to rent a new apartment.
-
Have (verb). Means to possess something.
I have many friends to help me move.
-
Have (linking verb). Used to connect verbs.
I should have helped her with that heavy box.
Quite, Quiet, Quit
-
Quite (adverb). Means really or truly.
My work will require quite a lot of concentration.
-
Quiet (adjective). Means not loud.
I need a quiet room to complete the assignments.
-
Quit (verb). Means to stop or to end.
I will quit when I am hungry for dinner.
Right, Write
-
Right (adjective). Means proper or correct.
When bowling, she practices the right form.
-
Right (adjective). Also means the opposite of left.
The ball curved to the right and hit the last pin.
-
Write (verb). Means to communicate on paper.
After the team members bowl, I will write down their scores.
Set, Sit
-
Set (verb). Means to put an item down.
She set the mug on the saucer.
-
Set (noun). Means a group of similar objects.
All the mugs and saucers belonged in a set.
-
Sit (verb). Means to lower oneself down on a chair or another place
I’ll sit on the sofa while she brews the tea.
Suppose, Supposed
-
Suppose (verb). Means to think or to consider
I suppose I will bake the bread, because no one else has the recipe.
-
Suppose (verb). Means to suggest.
Suppose we all split the cost of the dinner.
-
Supposed (verb). The past tense form of the verb suppose, meaning required or allowed.
She was supposed to create the menu.
Than, Then
-
Than (conjunction). Used to connect two or more items when comparing
Registered nurses require less schooling than doctors.
-
Then (adverb). Means next or at a specific time.
Doctors first complete medical school and then obtain a residency.
Their, They’re, There
-
Their (pronoun). A form of they that shows possession.
The dog walker feeds their dogs every day at two o’clock.
-
They’re (contraction). Joins the words they and are.
They’re the sweetest dogs in the neighborhood.
-
There (adverb). Indicates a particular place.
The dogs’ bowls are over there, next to the pantry.
-
There (pronoun). Indicates the presence of something
There are more treats if the dogs behave.
To, Two, Too
-
To (preposition). Indicates movement.
Let’s go to the circus.
-
To. A word that completes an infinitive verb.
to play, to ride, to watch.
-
Two. The number after one. It describes how many.
Two clowns squirted the elephants with water.
-
Too (adverb). Means also or very.
The tents were too loud, and we left.
Use, Used
-
Use (verb). Means to apply for some purpose.
We use a weed whacker to trim the hedges.
-
Used. The past tense form of the verb to use
He used the lawnmower last night before it rained.
-
Used to. Indicates something done in the past but not in the present
He used to hire a team to landscape, but now he landscapes alone.
Who’s, Whose
-
Who’s (contraction). Joins the words who and either is or has.
Who’s the new student? Who’s met him?
-
Whose (pronoun). A form of who that shows possession.
Whose schedule allows them to take the new student on a campus tour?
Your, You’re
-
Your (pronoun). A form of you that shows possession.
Your book bag is unzipped.
-
You’re (contraction). Joins the words you and are.
You’re the girl with the unzipped book bag.
Exercise 1
Complete the following sentences by selecting the correct word.
- My little cousin turns ________(to, too, two) years old tomorrow.
- The next-door neighbor’s dog is ________(quite, quiet, quit) loud. He barks constantly throughout the night.
- ________(Your, You’re) mother called this morning to talk about the party.
- I would rather eat a slice of chocolate cake ________(than, then) eat a chocolate muffin.
- Before the meeting, he drank a cup of coffee and ________(than, then) brushed his teeth.
- Do you have any ________(loose, lose) change to pay the parking meter?
- Father must ________(have, of) left his briefcase at the office.
- Before playing ice hockey, I was ________(suppose, supposed) to read the contract, but I only skimmed it and signed my name quickly, which may ________(affect, effect) my understanding of the rules.
- Tonight she will ________(set, sit) down and ________(right, write) a cover letter to accompany her résumé and job application.
- It must be fall, because the leaves ________(are, our) changing, and ________(it’s, its) getting darker earlier.
Strategies to Avoid Commonly Confused Words
When writing, you need to choose the correct word according to its spelling and meaning in the context. Not only does selecting the correct word improve your vocabulary and your writing, but it also makes a good impression on your readers. It also helps reduce confusion and improve clarity. The following strategies can help you avoid misusing confusing words.
- Use a dictionary. Keep a dictionary at your desk while you write. Look up words when you are uncertain of their meanings or spellings. Many dictionaries are also available online, and the Internet’s easy access will not slow you down. Check out your cell phone or smartphone to see if a dictionary app is available.
- Keep a list of words you commonly confuse. Be aware of the words that often confuse you. When you notice a pattern of confusing words, keep a list nearby, and consult the list as you write. Check the list again before you submit an assignment to your instructor.
- Study the list of commonly confused words. You may not yet know which words confuse you, but before you sit down to write, study the words on the list. Prepare your mind for working with words by reviewing the commonly confused words identified in this chapter.
Tip
Figure 4.1 A Commonly Misused Word on a Public Sign
Commonly confused words appear in many locations, not just at work or at school. Be on the lookout for misused words wherever you find yourself throughout the day. Make a mental note of the error and remember its correction for your own pieces of writing.
Writing at Work
All employers value effective communication. From an application to an interview to the first month on the job, employers pay attention to your vocabulary. You do not need a large vocabulary to succeed, but you do need to be able to express yourself clearly and avoid commonly misused words.
When giving an important presentation on the effect of inflation on profit margins, you must know the difference between effect and affect and choose the correct word. When writing an e-mail to confirm deliveries, you must know if the shipment will arrive in to days, too days, or two days. Confusion may arise if you choose the wrong word.
Consistently using the proper words will improve your communication and make a positive impression on your boss and colleagues.
Exercise 2
The following paragraph contains eleven errors. Find each misused word and correct it by adding the proper word.
The original United States Declaration of Independence sets in a case at the Rotunda for the Charters of Freedom as part of the National Archives in Washington, DC. Since 1952, over one million visitors each year of passed through the Rotunda too snap a photograph to capture they’re experience. Although signs state, “No Flash Photography,” forgetful tourists leave the flash on, an a bright light flickers for just a millisecond. This millisecond of light may not seem like enough to effect the precious document, but supposed how much light could be generated when all those milliseconds are added up. According to the National Archives administrators, its enough to significantly damage the historic document. So, now, the signs display quit a different message: “No Photography.” Visitors continue to travel to see the Declaration that began are country, but know longer can personal pictures serve as mementos. The administrators’ compromise, they say, is a visit to the gift shop for a pre-printed photograph.