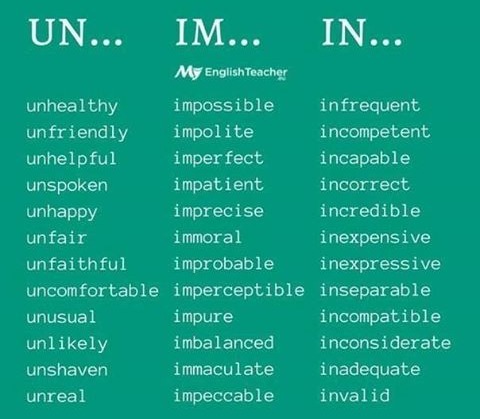
There are four main kinds of word formation: prefixes, suffixes, conversion and compounds.
Prefixes
We add prefixes before the base or stem of a word.
|
examples |
prefixes |
|
monorail, monolingual |
mono— means ‘one’ |
|
multipurpose, multicultural |
multi— means ‘many’ |
|
post-war, postgraduate |
post— means ‘after’ |
|
unusual, undemocratic |
un— means ‘not’ or ‘opposite to’ |
Suffixes
We add suffixes after the base or stem of a word. The main purpose of a suffix is to show what class of word it is (e.g. noun or adjective).
|
examples |
suffixes |
|
terrorism, sexism |
-ism and -dom are used to form nouns |
|
employer, actor |
-er and -or are used to form nouns to describe people who do things |
|
widen, simplify |
-en and -ify are used to form verbs |
|
reasonable, unprofitable |
-able is used to form adjectives |
|
unhappily, naturally |
-ly is a common suffix used to form adverbs |
Conversion
Conversion involves the change of a word from one word class to another. For example, the verbs to email and to microwave are formed from the nouns email and microwave:
Can you text her? (verb from noun text, meaning to send a text-message)
They are always jetting somewhere. (verb from noun jet)
If you’re not careful, some downloads can damage your computer. (noun from verb download)
OK, so the meeting’s on Tuesday. That’s a definite. (noun from adjective)
It’s a very big if and I’m not at all sure we can afford it. (noun from conjunction, meaning ‘it’s not at all certain’)
All companies have their ups and downs. (nouns from prepositions)
We also use conversion when we change a proper noun into a common noun:
Has anybody seen my Dickens? (copy of a book by Dickens)
Compounding
When we use compounding, we link together two or more bases to create a new word. Normally, the first item identifies a key feature of the second word. For example, the two bases back and ache can combine to form the compound noun backache, and the two bases post and card combine to form the compound noun postcard.
Compounds are found in all word classes. The most common types of compounds are: Nouns: car park, rock band
Adjectives: heartbreaking, sugar-free, airsick
Verbs: oven-bake, baby-sit, chain-smoke
Adverbs: good-naturedly, nevertheless
It is sometimes difficult to know where to put hyphens in words that are compound ed. It is also difficult to know whether to separate words (e.g. post box) or to join the words (e.g. postbox). In such cases, it is best to check in a good learner’s dictionary.
Abbreviation
Abbreviation involves shortening a word. We do this in three main ways: clipping, acronyms and blends.
We use clipping when we shorten or ‘clip’ one or more syllables from a word. We also commonly clip proper names for people:
ad: advertisement, advert
lab: laboratory
Matt: Matthew
Acronyms are a type of abbreviation formed when the initial letters of two or more words are combined in a way that produces consonant and vowel sequences found in words. Acronyms are normally pronounced as words:
RAM: random access memory (RAM is a term used to describe a computer’s memory.)
Initials are similar to acronyms but are pronounced as sets of letters, not as words:
WHO: World Health Organisation, pronounced W–H–O
CD: compact disc, pronounced C–D
We form blends when we combine parts of existing words to form a new word:
blog: blend of web and log
motel: blend of motor and hotel
smog: blend of smoke and fog
Back-formation
We form words with back-formation when we remove part of a word, usually something which we think is a suffix (or occasionally a prefix). We do this commonly when we form verbs from nouns.
For example: to liaise (back-formed from the noun liaison); to intuit (back-formed from the noun intuition), to enthuse (back-formed from the noun enthusiasm):
Can you liaise with Tim and agree a time for the meeting, please?
She’s always enthusing about her new teacher.
Loan words and new words
Loan words
Loan words are words that are borrowed from other languages. Some recent loan words for food taken from other languages include: sushi, tapas, chapatti, pizza. When we use loan words, we do not normally change them, though we do sometimes inflect them if they are singular countable nouns (pizzas, chapattis). We also sometimes pronounce them more like English words, instead of using their original pronunciation.
New words
Some prefixes are commonly used to create new words. In modern English the prefix e- is used to create new words that are connected with the Internet and the use of the Internet:
e-bank, e-cards, e-commerce, e-learning
Almost any noun may potentially combine with any other noun to form new noun compounds (e.g. computer virus, carbon footprint, quality time).
HOME > LOOK UP & LEARN
V2 Vocabulary Building Dictionary
Learn New Words and Remember Them Forever!
Welcome to the only dictionary that helps you to build and improve your vocabulary while looking up word definitions.
To get started, just type the word you want to learn into the box below, and V2 will take care of the rest!
Here you’ll find exactly when, where and how to use the over 2200 words most frequently looked up in dictionaries. Our comprehensive guide will not only help you learn new words and use them properly, but will help you assimilate them into your vocabulary — and remember them forever!
In Just Seven Days, You Can Discover
The Secrets To Building A Powerful
Vocabulary… For FREE
Want to develop a bigger vocabulary even faster?
While you are here, be sure to sign up for our FREE Seven Day Vocabulary Course.
In just Seven Days, you will discover the secret to building a powerful vocabulary absolutely FREE.
Sign Me Up! I want to enroll in your FREE online Verbal
Success course, and learn the same vocabulary building techniques that others
have paid over $200 to learn at the live Verbal Success Symposiums!
I understand there’s absolutely no cost or commitment — there’s nothing more to buy, and I can unsubscribe at any time!
Sample dictionary lookup: abet
Очень часто в английском языке слова, относящиеся к одной части речи, образуют слова, относящиеся к другой части речи. Чаще его это происходит путем присоединения суффиксов: to work работать, a worker —рабочий.
Возможен и другой способ, получивший название конверсия— переход слова из одной части речи в другую без изменения формы: towork работать—a work работа. Конверсия очень характерна для английского языка: ей способствуют отсутствие развитой системы окончаний и большое количество односложных слов. Наиболее часто конверсии подвергаются глаголы и существительные: a hand рука—to handвручить. Как правило, слова, имеющие одинаковое написание, и произносятся одинаково, но есть и исключения: в основном, различия заключаются в произношении звуков [s] и [z] или в переносе ударения: close [-s]близкий—to close [-z] закрывать, conduct[‘kOndAkt] поведение—to conduct [kOn’dAkt] вести. Обычно в существительных ударение падает на 1-й слог, у глаголов — на последний. Иногда с переносом ударения не только меняется часть речи, но и теряется видимая связь значений: to refuse [rI’fjHz] отказываться— refuse[‘refjHs] мусор. Конверсия затрагивает и оппозицию «существительное — прилагательное»: прилагательные часто субстантивируются, т. е. становятся существительными: brave смелый—the brave смельчак. То же можно наблюдать и в русском языке: больной (прил.) человек —больной (сущ.) выписан из больницы.
Словосложение — это способ словообразования путем соединения двух (или более) слов в одно, которое пишется слитно, или через дефис, а иногда раздельно: to pin-point уточнить, trailer-on-flat трейлер на платформе.
Сокращение — еще один способ образования новых слов: laser = light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation лазер (усиление света индуцированным испусканием излучения).
Путем использования префиксов: to doделать— to redo переделать.
|
НАИБОЛЕЕ УПОТРЕБИТЕЛЬНЫЕ СУФФИКСЫ ГЛАГОЛОВ |
||
|
СУФФИКС |
ЗНАЧЕНИЕ |
ПРИМЕР |
|
(сущ. +) -ize |
делать(ся) таким, как на то указывает основа |
summarize суммировать |
|
(прил. +) -en |
harden делать(ся) твердым |
|
|
(сущ. +) -ify, -fy |
превращать в, делать то, на что указывает основа |
gasifyпревращать(ся) в газ; electrifyэлектризовать |
|
(сущ. +) -ate |
подвергать воздействию, превращать в то, на что указывает основа |
vaccinateделать прививку; granulateгранулировать |
|
-er |
whisperшептать |
|
|
-ish |
establishустанавливать |
|
НАИБОЛЕЕ УПОТРЕБИТЕЛЬНЫЕ СУФФИКСЫ СУЩЕСТВИТЕЛЬНЫХ |
||
|
СУФФИКС |
ЗНАЧЕНИЕ |
ПРИМЕР |
|
(гл. +) -er, -or |
обозначение деятеля |
worker рабочий |
|
(гл. +) -ing |
действие в процессе |
boiling кипячение |
|
(прил. +) -ness |
свойство, качество |
whiteness белизна |
|
(прил. +) -ty, -ity |
состояние, условие, качество |
activityдеятельность |
|
(гл. +) -age |
акт или факт действия |
breakageполомка |
|
(сущ. +) -age |
содержание чего-либо (единиц измерения) |
percentage процентное содержание |
|
(гл. +) -ment |
отвлеченные понятия (абстрактные существительные) |
treatment лечение |
|
(гл. +) -ance, -ence |
resistance сопротивление |
|
|
(гл. +) -ancy, -ency |
expectancyнадежда |
|
|
(прил. +/сущ. +) -dom |
freedomсвобода |
|
|
(гл. +) -ion, -tion, -sion,-ssion |
revisionповторение |
|
|
-ure |
pressure давление |
|
|
-hood |
childhood детство |
|
|
-ship |
friendship дружба |
|
|
-th |
lengthдлина |
|
|
-an, -ian |
1) национальность; 2) профессия |
Americanамериканец, librarianбиблиотекарь |
|
-ism |
какое-либо течение (например, политическое) |
communismкоммунизм |
|
-ist |
1) принадлежность к какому-либо течению; 2) профессия |
communistкоммунист; artist художник |
|
НАИБОЛЕЕ УПОТРЕБИТЕЛЬНЫЕ СУФФИКСЫ НАРЕЧИЙ И ЧИСЛИТЕЛЬНЫХ |
|||||
|
СУФФИКСЫ НАРЕЧИЙ |
СУФФИКСЫ ЧИСЛИТЕЛЬНЫХ |
||||
|
СУФФИКС |
ЗНАЧЕНИЕ |
ПРИМЕР |
СУФФИКС |
ЗНАЧЕНИЕ |
ПРИМЕР |
|
(прил. +) -ly |
таким образом, способом |
entirely всецело |
-teen |
количественное числительное от 13 до 19 |
fifteenпятнадцать |
|
-ward(s) |
направление движения |
backwards назад |
-ty |
десятки |
seventy семьдесят |
|
-wise |
в таком направлении, таким способом |
clockwiseпо часовой стрелке |
-th |
порядковое числительное |
fourth четвертый |
|
НАИБОЛЕЕ УПОТРЕБИТЕЛЬНЫЕ СУФФИКСЫ ПРИЛАГАТЕЛЬНЫХ |
||
|
СУФФИКС |
ЗНАЧЕНИЕ |
ПРИМЕР |
|
(сущ. +) -al |
наличие признака, свойств и качеств, выраженных основой |
central центральный |
|
(сущ. +) -ic |
patrioticпатриотический |
|
|
(сущ. +) -ical |
geologicalгеологический |
|
|
(сущ. +) -ous |
famousизвестный |
|
|
(сущ. +) -ful |
usefulполезный |
|
|
(гл. +) -able, -ible |
expressible выразительный |
|
|
(гл. +) -ant, -ent |
dependentзависимый |
|
|
(гл. +) -ive |
active активный |
|
|
(сущ. +) -ly |
friendlyдружелюбный |
|
|
(сущ. +) -y |
grainy зернистый |
|
|
(гл. +) -ite |
favouriteлюбимый |
|
|
-ary |
pecuniaryденежный |
|
|
-ate |
fortunateудачный |
|
|
-ed |
cold-blooded хладнокровный |
|
|
-less |
отсутствие качества, признака |
uselessбесполезный |
|
-ish |
1) наличие признака в слабой степени; 2) принадлежность к национальности |
reddish красноватый; Polishпольский |
|
-ese |
принадлежность к национальности |
Japaneseяпонский |
|
-ian, -an |
Egyptian египетский |
|
|
-like |
сходство |
birdlikeптицеподобный |
|
-ern |
принадлежность к одной из сторон света |
northern северный |
|
НАИБОЛЕЕ УПОТРЕБИТЕЛЬНЫЕ ПРЕФИКСЫ И ИХ ЗНАЧЕНИЯ |
||||
|
ОТРИЦАТЕЛЬНЫЕ ПРЕФИКСЫ |
ДРУГИЕ ПРЕФИКСЫ |
|||
|
ПРЕФИКС |
ПРИМЕР |
ПРЕФИКС |
ЗНАЧЕНИЕ |
ПРИМЕР |
|
un- |
unable неспособный |
re- (+ гл.) |
вновь сделать то, на что указывает основа |
remake переделывать |
|
in- |
inactive бездеятельный |
|||
|
im- |
impossible невозможный |
en-, em- (+ гл.) |
придавать качество |
embody воплощать |
|
il- |
illegal незаконный |
|||
|
ir- |
irregular неправильный |
over- (+ гл.) |
избыточная степень качества или выполнения действия |
overproduce перепроизводить |
|
mis- |
misunderstand неправильно понять |
|||
|
dis- |
disapproval неодобрение |
under- (+ гл.) |
недостаточная степень качества или выполнения действия |
underestimate недооценивать |
Источник материала:http://study-english.info
Word formation — practice
- Exercise1.
- 10 exersises
- Practice wordbuilding — adjectives
Some Rules and Practice
1. Suffixes
|
Noun Suffixes |
||
|
Suffix |
Meaning |
Example |
|
-acy |
state or quality |
privacy |
|
-al |
act or process of |
refusal |
|
-ance, -ence |
state or quality of |
maintenance, eminence |
|
-dom |
place or state of being |
freedom, kingdom |
|
-er, -or |
one who |
trainer, protector |
|
-ism |
doctrine, belief |
communism |
|
-ist |
one who |
chemist |
|
-ity, -ty |
quality of |
veracity |
|
-ment |
condition of |
argument |
|
-ness |
state of being |
heaviness |
|
-ship |
position held |
fellowship |
|
-sion, -tion |
state of being |
concession, transition |
|
Verb Suffixes |
||
|
-ate |
become |
eradicate |
|
-en |
become |
enlighten |
|
-ify, -fy |
make or become |
terrify |
|
-ize, -ise |
become |
civilize |
|
Adjective Suffixes |
||
|
-able, -ible |
capable of being |
edible, presentable |
|
-al |
pertaining to |
regional |
|
-esque |
reminiscent of |
picturesque |
|
-ful |
notable for |
fanciful |
|
-ic, -ical |
pertaining to |
musical, mythic |
|
-ious, -ous |
characterized by |
nutritious, portentous |
|
-ish |
having the quality of |
fiendish |
|
-ive |
having the nature of |
creative |
|
-less |
without |
endless |
|
-y |
characterized by |
sleazy |
Prefixez
Negative Prefixes. Exercise1.
Negative Prefixes, Exercise2.
Negative Prefixes. Flash animation.
Noun suffixes. Exercise1
Video lesson on noun suffixes
( words plural & 3rd person present) ( wording present participle) ( worded past tense & past participle )
1 n-count A word is a single unit of language that can be represented in writing or speech. In English, a word has a space on either side of it when it is written.
The words stood out clearly on the page…, The word `ginseng’ comes from the Chinese word `Shen-seng’., …swear words…
2 n-plural Someone’s words are what they say or write.
oft with poss
I was devastated when her words came true…, The words of the young woman doctor echoed in his ears…
3 n-plural Thewords of a song consist of the text that is sung, in contrast to the music that is played.
usu the N
(=lyrics)
Can you hear the words on the album?
4 n-sing If you have a word with someone, you have a short conversation with them.
SPOKEN a N
I think it’s time you had a word with him…, James, could I have a quiet word?…
5 n-count If you offer someone aword of something such as warning, advice, or praise, you warn, advise, or praise them.
N of n
A word of warning. Don’t stick too precisely to what it says in the book…
6 n-sing If you say that someone does not hear, understand, or say a word, you are emphasizing that they hear, understand, or say nothing at all.
a N, with brd-neg (emphasis)
I can’t understand a word she says…, Not a word was spoken.
7 n-uncount If there is word of something, people receive news or information about it.
also the N
There is no word from the authorities on the reported attack…, Word has been spreading fast of the incidents on the streets…
8 n-sing If you give your word, you make a sincere promise to someone.
poss N
…an adult who gave his word the boy would be supervised…, He simply cannot be trusted to keep his word.
9 n-sing If someone gives the word to do something, they give an order to do it.
the N
I want nothing said about this until I give the word.
10 verb To word something in a particular way means to choose or use particular words to express it.
If I had written the letter, I might have worded it differently. V n adv/prep
♦
-worded comb in adj
…a strongly-worded statement., …a carefully-worded speech.
11
→
wording
→
code word
→
four-letter word
→
play on words
→
printed word
→
spoken word
→
written word
12 If you say that people consider something to be a dirty word, you mean that they disapprove of it.
♦
dirty word phrase usu v-link PHR
So many people think feminism is a dirty word.
13 If you do something from the word go, you do it from the very beginning of a period of time or situation.
♦
from the word go phrase PHR with cl
It’s essential you make the right decisions from the word go.
14 You can use in their words or in their own words to indicate that you are reporting what someone said using the exact words that they used.
♦
in sb’s words/in sb’s own words phrase PHR with cl
Even the Assistant Secretary of State had to admit that previous policy did not, in his words, produce results.
15 You use in a word to indicate that you are giving a summary of what you have just been saying, or are giving a reply, in as brief a way as possible.
♦
in a word phrase PHR with cl
(=in short)
`Shouldn’t he be given the leading role?’—`In a word<endash>No.’
16 If someone has the last word or the final word in a discussion, argument, or disagreement, they are the one who wins it or who makes the final decision.
♦
the last word/the final word phrase
She does like to have the last word in any discussion…, The final word will still come from the Secretary of State.
17 If you say that something is the last word in luxury, comfort, or some other quality, you are emphasizing that it has a great deal of this quality.
♦
the last word in sth phrase PHR n, usu v-link PHR (emphasis)
The spa is the last word in luxury and efficiency.
18 If you say that someone has said something, but not in so many words, you mean that they said it or expressed it, but in a very indirect way.
♦
in so many words phrase usu with brd-neg, usu PHR after v, PHR with cl
`And has she agreed to go with you?’—`Not in so many words. But I read her thoughts’.
19 If news or information passes by word of mouth, people tell it to each other rather than it being printed in written form.
♦
word of mouth phrase oft by/through PHR
The story has been passed down by word of mouth.
20 You say in other words in order to introduce a different, and usually simpler, explanation or interpretation of something that has just been said.
♦
in other words phrase PHR with cl
The mobile library services have been reorganised<endash>in other words, they visit fewer places.
21 If you say something in your own words, you express it in your own way, without copying or repeating someone else’s description.
♦
in one’s own words phrase PHR after v, PHR with cl
Now tell us in your own words about the events of Saturday.
22 If you say to someone `take my word for it’, you mean that they should believe you because you are telling the truth.
♦
take my word for it phrase V inflects
You’ll buy nothing but trouble if you buy that house, take my word for it.
23 If you repeat something word for word, you repeat it exactly as it was originally said or written.
♦
word for word phrase PHR after v
(=verbatim)
I don’t try to memorize speeches word for word.
24
→
not get a word in edgeways
→
edgeways
→
not mince your words
→
mince
→
the operative word
→
operative
→
war of words
→
war
code word ( code words plural ) , codeword, code-word A code word is a word or phrase that has a special meaning, different from its normal meaning, for the people who have agreed to use it in this way. n-count
…magnum, the code word for launching a radar attack.
four-letter word ( four-letter words plural ) A four-letter word is a short word that people consider to be rude or offensive, usually because it refers to sex or other bodily functions. n-count
(=swear word)
linking word ( linking words plural )
in BRIT, also use link word A linking word is a word which shows a connection between clauses or sentences. `However’ and `so’ are linking words. n-count
printed word
The printed word is the same as the written word. n-sing the N
spoken word
Thespoken word is used to refer to language expressed in speech, for example in contrast to written texts or music. n-sing usu the N
There is a potential educational benefit in allowing pictures to tell the story, rather than the spoken word.
swear word ( swear words plural ) , swearword A swear word is a word which is considered to be rude or offensive. Swear words are usually used when people are angry. n-count
-word ( -words plural ) You can use -word after a letter of the alphabet to refer politely or humorously to a word beginning with that letter which people find offensive or are embarrassed to use. comb in n-count
It was the first show to use the F-word and show nudity on stage…, Politicians began to use the dreaded R-word: recession.
word class ( word classes plural ) A word class is a group of words that have the same basic behaviour, for example nouns, adjectives, or verbs. n-count
word processing , word-processing
Word processing is the work or skill of producing printed documents using a computer. (COMPUTING) n-uncount oft N n
word processor ( word processors plural ) A word processor is a computer program or a computer which is used to produce printed documents. (COMPUTING) n-count
word wrapping
In computing, word wrapping is a process by which a word which comes at the end of a line is automatically moved onto a new line in order to keep the text within the margins. (COMPUTING) n-uncount
written word
You use the written word to refer to language expressed in writing, especially when contrasted with speech or with other forms of expression such as painting or film. n-sing usu the N
Even in the 18th century scholars continued to give primacy to the written word.

Англо-русский перевод WORD-BUILDING
transcription, транскрипция: [ ʹwɜ:d͵bıldıŋ ]
n лингв.
словообразование
New big English-Russian dictionary.
Большой новый Англо-Русский словарь.
2012