Word Association 1
.
Missing links
.
Each of the sets of four words below can be linked by one other word. All the words are to do with legal matters. What are the five missing link words? Write them in the center of the charts. More than one answer may be correct, though you will find a suggested answer bellow.
.
CIVIL…………………………….. COMMERCIAL
.
………………..1.__________
.
CRIMINAL …………………….CONSTITUTIONAL
.
.
OPEN…………………………….. ACTION
.
………………..2.__________
.
CASE……………………………… CONTEMPT
.
.
MEMBERS………………………. FOREMAN
.
………………..3.___________
.
VERDICT………………………… MAJORITY
.
.
EVASION………………………… EXEMPTION
.
………………..4.__________
.
ALLOWANCE………………….. AVOIDANCE
.
.
CONCURRENT………………… CONSECUTIVE
.
………………..5.__________
.
CUSTODIAL…………………….. SUSPENDED
.
.
Answers: 1. LAW – 2.COURT – 3. JURY – 4. TAX – 5. SENTENCE
18.SAD: Seasonal Affective Disorder
19.SIDS: Sudden Infant Death Syndrome
20.STI: Sexually Transmitted Infection
21.TB: Tuberculosis
22.TBI: Total Body Irradiation
23.UV: Ultraviolet
24.VDH: Valvular Disease of the Heart
25.WHO: World Health Organization
Symptoms & common illnesses 1 (p. 31)
|
1. |
influenza |
2. rubella |
3. coryza |
4. varicella |
|
5. |
rubeola |
6. infectious |
parotitis |
7. pertussis |
|
8. |
allergic rhinitis |
Symptoms & common illnesses 2 (p. 32)
Exercise 1.
1.Chickenpox is the same as varicella
2.A cold is the same as coryza
3.The flu is the same as influenza
4.German measles is the same as rubella
5.Hay fever is the same as allergic rhinitis
6.Measles is the same as rubeola
7.Mumps is the same as infectious parotitis
8.Whooping cough is the same as pertussis
|
Exercise 2. |
|||||||
|
1. hay fever |
2. German measles 3. whooping cough |
||||||
|
4. flu |
5. mumps |
6. chickenpox |
|||||
|
Diagnosis (p. 33) |
|||||||
|
1. epilepsy 2. gangrene |
3. cataracts |
4. Parkinson’s |
|||||
|
disease |
5. tuberculosis |
6. cystic fibrosis |
7. cirrhosis |
||||
|
8. diphtheria |
9. cerebral palsy |
10. gastroenteritis |
|||||
|
How it works (p.34) |
|||||||
|
1. d) |
10. h) |
||||||
|
2. k) |
11. p) |
||||||
|
3. g) |
12. q) |
||||||
|
4. m) |
13. c) |
||||||
|
5. r) |
14. o) |
||||||
|
6. a) |
15. l) |
||||||
|
7. b) |
16. j) |
||||||
|
8. f) |
17. i) |
||||||
|
9. n) |
18. e) |
||||||
|
Instruments and equipment (p. 35) |
|||||||
|
1. wheelchair |
2. scalpel |
3. probe |
4. forceps |
||||
|
5. curette |
6. pipette |
7. tourniquet |
8. hook |
||||
|
9. drain |
10. gag |
11. syringe |
12. catheter |
||||
|
13. bandage |
14. sling |
15. stretcher |
16. splint |
||||
|
17. stethoscope |
18. thermometer |
Chemistry (p. 36)
1.Na, sodium, (e) the basic substance in salt
2.Ca, calcium, (p) metallic element which is the major component of bones and teeth
3.Pb, lead, (l) heavy soft metallic element which is poisonous in compounds
4.Ti, titanium, (n) light metallic element which does not corrode
5.Ba, barium, (d) used as a contrast when taking X-ray photographs of soft tissue
6.Zn, zinc, (s) white metallic trace element
7.Fe, iron, (j) an essential part of the red pigment in blood cells, found in liver and eggs
8.Co, cobalt, (f) metallic element which is the basis of a radioactive isotope used to treat cancer
9.Cl, chlorine, (q) powerful greenish gas, used to sterilise water
10.He, helium, (m) very light gas used in combination with oxygen, especially to relieve asthma or sickness caused by decompression
11.S, sulphur, (t) yellow non-metallic element found in some amino acids
12.Au, gold, (r) soft yellow-coloured precious metal, used as a compound in various drugs, and sometimes as a filling for teeth
13.O, oxygen, (h) colourless gas which is present in air and essential to human life
14.H, hydrogen, (k) gas which combines with oxygen to form water
15.HCI, hydrochloric acid, (a) acid found in the gastric juices which helps to break apart the food
16.N, nitrogen, (o) gas which is the main component of air and an essential part of protein
17.HCN, hydrocyanic acid, (b) acid which forms cyanide
18.C, carbon, (i) one of the common non-metallic elements which is an essential component of living matter and organic chemical compounds
19.N2O, nitrous oxide, (g) colourless gas with a sweet smell, used in combination with other gases as an anaesthetic in dentistry and surgery
20.C10H14N2, nicotine, (c) main alkaloid substance found in tobacco
Word association 1: missing links
Each of the sets of four words below can be linked by another word. All the words are related to military matters. What are the missing words? Write them in the centre of the charts. The first one has been done for you as an example.
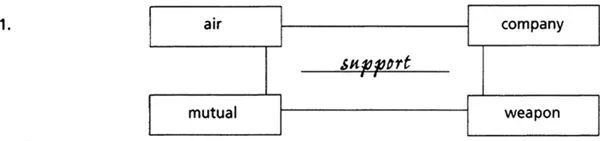
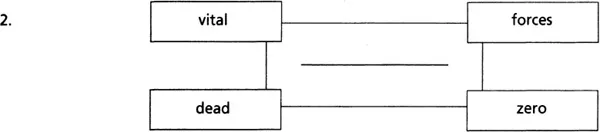
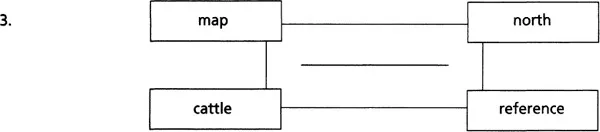
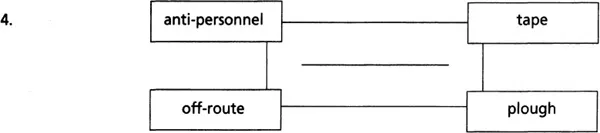
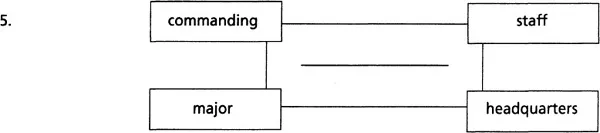
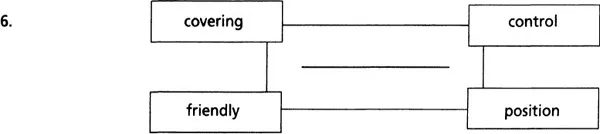
Two-word expressions
Make 14 two-word expressions connected with military matters by combining words from the two boxes: A and B. Then match each expression with the appropriate phrase. Use each word once. The first one has been done for you as an example.
Box A.
compassionate • voice • exclusion • supply • harrassing • home • shock manoeuvre • field • pincer • distress • observation • static • flight
Box B.
zone • gun • defence • signal • leave • post • action • dump path • procedure • line • fire • warfare • movement
1. Defence of a State’s own territory in the event of war.
2. Area or region, which the armed forces or shipping of another State are not allowed to enter.
3. Holiday granted to a service man who has problems at home.
4. Standard words and expressions which are used when talking on the radio.
5. Sign or message signifying that a person, ship or aircraft is in danger.
6. Covert position from which an area of ground may be watched.
7. Temporary store of ammunition, food, fuel, etc., in the field.
8. Method used to open a parachute as the parachutist jumps out the aircraft.
9. Tactical manouevre, in which two groupings attack an enemy force at the same time, but from different directi…
Citation styles for Check Your Vocabulary for Military EnglishHow to cite Check Your Vocabulary for Military English for your reference list or bibliography: select your referencing style from the list below and hit ‘copy’ to generate a citation. If your style isn’t in the list, you can start a free trial to access over 20 additional styles from the Perlego eReader.
APA 6 Citation
Bloomsbury. (2015). Check Your Vocabulary for Military English (1st ed.). Bloomsbury Publishing. Retrieved from https://www.perlego.com/book/391861/check-your-vocabulary-for-military-english-a-workbook-for-users-pdf (Original work published 2015)
Chicago Citation
Bloomsbury. (2015) 2015. Check Your Vocabulary for Military English. 1st ed. Bloomsbury Publishing. https://www.perlego.com/book/391861/check-your-vocabulary-for-military-english-a-workbook-for-users-pdf.
Harvard Citation
Bloomsbury (2015) Check Your Vocabulary for Military English. 1st edn. Bloomsbury Publishing. Available at: https://www.perlego.com/book/391861/check-your-vocabulary-for-military-english-a-workbook-for-users-pdf (Accessed: 14 October 2022).
MLA 7 Citation
Bloomsbury. Check Your Vocabulary for Military English. 1st ed. Bloomsbury Publishing, 2015. Web. 14 Oct. 2022.
Word association 1: missing Unit 0000 links Each of the sets of four words below can be linked by one other word. All the words are related to medical matters. What are the missing words Write them in the centre of the charts. 1. ciliary temperature <strong>for</strong>eign fat 2. throbbing relief abdominal threshold 3. metacarpal graft cancellous marrow 4. cardiac fatigue skeletal spasm 5. black bath glass drops 6. blood membrane beta body For reference see A & C Black Dictionary of Medical Terms (0 7136 7603 5). 1
Unit Word 0000 <strong>for</strong>mation: nouns A fast way to expand your vocabulary is to make sure you know the different <strong>for</strong>ms of the words you learn. Exercise 1. The words in this list are all verbs. What are the noun <strong>for</strong>ms Write them in the second column. The first one has been done <strong>for</strong> you as an example. 1. diagnose diagnosis 2. examine ______________ 3. prescribe ______________ 4. suffer ______________ 5. operate ______________ 6. cure ______________ 7. recover ______________ 8. analyse ______________ 9. infect ______________ 10. carry ______________ 11. replace ______________ 12. degenerate ______________ 13. refer ______________ 14. paralyse ______________ 15. obstruct ______________ Exercise 2. First, check your answers to Exercise 1 in the key. Then rewrite the sentences below, changing the verbs (which are in bold) to nouns. Do not change the meaning of the sentences, but be prepared to make grammatical changes if necessary. The first one has been done <strong>for</strong> you as an example. 1. I diagnosed that the patient had a heart condition. My diagnosis was that the patient had a heart condition. 2. I examined the patient fully. I made a full 9. We found that the tissue was infected. We found an 10. Ten per cent of the population are thought to carry the bacteria. Ten per cent of the population are thought to be 3. I prescribed a course of antibiotics. I wrote a 11. We replaced the patient’s hip. The patient was given a hip 4. He suffered very little. He experienced very little 12. His condition has degenerated. There has been a 5. We operated immediately. The 13. The patient was referred to a specialist. The patient was given a 6. This disease cannot be cured. There is no 14. His arm was paralysed after the stroke. He suffered 7. He has recovered fully. He has made a full 15. The artery was obstructed by a blood clot. The blood clot was <strong>for</strong>ming an 8. The lab analysed the blood sample. The lab made an 2 For reference see A & C Black Dictionary of Medical Terms (0 7136 7603 5).
- Page 2 and 3: CHECK YOUR ENGLISH VOCABULARY FOR M
- Page 4 and 5: Introduction The worksheets in this
- Page 6 and 7: Page VOCABULARY IN CONTEXT 25 Good
- Page 10 and 11: Two-word expressions Unit 0000 Make
- Page 12 and 13: Word formation: adjectives Unit 000
- Page 14 and 15: Opposites 1: Unit prefixes 0000 Exe
- Page 16 and 17: Word association 3: mind Unit maps
- Page 18 and 19: Adjectives Unit 00001 Complete the
- Page 20 and 21: Unit Verbs 0000 1 The sentences in
- Page 22 and 23: Verbs: past tense ~ regular Unit ve
- Page 24 and 25: Phrasal Unit verbs 0000 Natural Eng
- Page 26 and 27: The sentences below do not read cor
- Page 28 and 29: Word Unit stress 0000 1 One of the
- Page 30 and 31: Verbs in the present tense add an ‘
- Page 32 and 33: Good Unit advice 0000 These sentenc
- Page 34 and 35: In each set of words one is the odd
- Page 36 and 37: Opposites 2 Exercise 1. Match the w
- Page 38 and 39: Symptoms & common illnesses 1 These
- Page 40 and 41: Diagnosis Read the eleven descripti
- Page 42 and 43: Instruments and equipment Match eac
- Page 44 and 45: Anagrams 1 Solve the anagrams by re
- Page 46 and 47: Communicative crossword 1 sheet A T
- Page 48 and 49: Anagrams 2 Solve the anagrams by re
- Page 50 and 51: Communicative crossword 2 sheet A T
- Page 52 and 53: Parts of the body crossword 2 All t
- Page 54 and 55: Communicative crossword 3 sheet A T
- Page 56 and 57: Quiz How many of these questions ca
- Page 58 and 59:
Word-building Word association 1: m
- Page 60 and 61:
5. The injured person was comforted
- Page 62 and 63:
18. SAD: Seasonal Affective Disorde
- Page 64 and 65:
Anagrams 2 (p. 41) 1. Cerebrum 2. A
show all
CHECK YOUR ENGLISH VOCABULARY FOR
MEDICINE
third edition
A & C Black
폷 London
www.acblack.com
First published in Great Britain 1995
Second edition published 2000
Third edition published 2006
A & C Black Publishers Ltd
38 Soho Square, London W1D 3HB
© Peter Collin Publishing 1995, 2000
© A & C Black Publishers Ltd 2006
All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced in
any form without the permission of the publishers.
A CIP entry for this book is available from the British Library
ISBN-10: 0 7136 7590 X
ISBN-13: 978 0 7136 7590 0
eISBN-13: 978-1-4081-0238-1
Text typeset by A & C Black
Printed in Italy by Legoprint
A & C Black uses paper produced with elemental chlorine-free pulp,
harvested from managed sustainable forests.
Introduction
The worksheets in this workbook contain a variety of exercises appropriate for students
requiring a working knowledge of English medical terminology. The worksheets can be used
either for self-study or in the classroom and can be completed in any order. Several have
‘extensions’: short classroom exercises based on the language in the main exercise. All the
questions within this workbook are based on the A & C Black Dictionary of Medical Terms,
fourth edition (ISBN 0 7136 7603 5).
This workbook is aimed at students with at least an intermediate level of English. However,
many people who work in medicine have to read in English on a regular basis; students with
a more basic level of English may therefore already have the passive vocabulary to handle
many of the exercises.
Specialist vocabulary
It is important to appreciate that ‘knowing’ specialist vocabulary involves more than simply
recognising it.
You can understand the meaning of a word when reading or listening and yet be
unable to remember that same word when speaking or writing.
You may remember the word, but use it incorrectly. This can be a grammatical
problem, like knowing that ‘fracture’ can be used both as a noun and as a verb. Or
it may be a question of collocation: a surgeon makes an incision during an operation,
but when he wants a piece of bread he simply cuts it.
Then there is the question of the sound of the word. Can you pronounce it? And do
you recognise it when you hear it pronounced?
For these reasons — memory, use and sound — it is important that students practise specialist
vocabulary so that they can learn to use it more confidently and effectively. The exercises in
this workbook will help students to expand their knowledge and use of medical vocabulary.
Using the Dictionary of Medical Terms
All of the vocabulary taught or practised in this workbook is in the A & C Black Dictionary of
Medical Terms. The Dictionary of Medical Terms gives definitions in simple English which
students can read and understand. Many of the examples and definitions in the workbook
are taken directly from the dictionary. Students should have a copy of the Dictionary of
Medical Terms for referring to when completing the exercises; using the dictionary is an
essential part of successful language learning.
Structure of a Dictionary of Medical Terms entry
Each entry within the dictionary includes key elements that help a student understand the
definition of the term and how to use it in context. Each term has a clear example, and part
of speech. This is followed by example sentences and quotations from newspapers and
magazines that show how the term is used in real life. These elements of the dictionary are
used to create the questions within this workbook.
Vocabulary Record Sheet
At the back of the book is a Vocabulary Record Sheet. Recording useful vocabulary in a
methodical way plays a key role in language learning and could be done, for example, at the
end of each lesson. The Dictionary of Medical Terms is a useful tool for ensuring that the
personal vocabulary record is accurate and is a good source for example sentences to show
how words are used, as well as for notes about meaning and pronunciation, etc.
Workbook contents
WORD-BUILDING
Word association 1:
missing links
Linking each set of four words with one other word
Word formation:
nouns
Forming nouns from list of verbs; rewriting sentences
using noun forms instead of verbs
Two-word expressions Combining words from two lists to make two-word
expressions that fit the definitions
Plural formation
Multiple choice: choosing correct plural forms of singular
nouns
Word formation:
adjectives
Rewriting sentences using adjective forms instead of
nouns
6
Self-study
Word association 2:
partnerships
Linking each verb with a noun to make a ‘partnership’;
using the ‘partnerships’ to complete sentences
Opposites 1: prefixes
Selecting the correct prefix for each adjective to create an
opposite; using the adjectives to complete sentences
Extension: working with a partner to test one another
Word formation: verbs Making verb forms from list of nouns; writing sentences
using the verbs
Word association 3:
mind maps
Finding words in a mind map that fit definitions;
designing mind maps
PARTS OF SPEECH
Nouns
Sentence completion
11
Self-study
Adjectives 1
Sentence completion
Adjectives 2
Sentence completion
Verbs 1
Matching verbs with their correct definitions
Verbs 2
Matching verbs with their correct definitions
15
Self-study
Verbs: past tense ~
regular verbs
Sentence completion
Verbs: mixed tenses
Sentence completion
Phrasal verbs
Sentence completion
Extension: working with a partner to write a dialogue
using phrasal verbs
Verbs: active/passive
Changing sentences from active to passive tense
Adverbs
Identifying adverbs in sentences and swapping adverbs
around so that each sentence makes sense
Prepositions
Correcting sentences with deliberate mistakes in
the prepositions
PRONUNCIATION
Pair work
Word stress 1
Identifying three-syllable words and classifying by their
pronunciation
Extension: practising the dialogues with a partner
Word stress 2
Completing sentences using four-syllable words;
classifying four-syllable words by their pronunciation
Present simple
Identifying present tense verbs and classifying by their
pronunciation
Extension: working with a partner to identify plural
nouns in each pronunciation category
Past tense
Identifying past tense verbs and classifying by their
pronunciation
Page
Mode
Title
Description
VOCABULARY IN CONTEXT
Pair work
Good advice
Matching half-sentences together to make complete
sentences
Extension: writing pieces of medical advice with a
partner
26
Self-study
Multiple meanings
Classifying meanings
Odd one out
Identifying word that is different to others in each set
Body parts — categories Deciding which category each body part belongs to
Opposites 2
Matching words with opposite meanings; inserting
correct opposites in sentences
Extension: working with a partner to test one another
Pair work
Abbreviations
Stating what abbreviations stand for
Extension: working with a partner to test one another
Symptoms & common
illnesses 1
Checking meanings of words; matching descriptions to
names of illnesses
Symptoms & common
illnesses 2
Matching formal and informal names of illnesses;
completing conversations by using informal names of
illnesses
Extension: practising conversations with a partner
Pair work
Diagnosis
Identifying each disease or illness from its description
Extension: writing a description of a disease or illness
and testing a partner
How it works
Matching half-sentences together to make complete
sentences
Instruments and
equipment
Matching each instrument and item of equipment with
its correct description
Extension: working with a partner to test one another
Pair work
Chemistry
Matching symbols of chemical elements and compounds
with correct names and descriptions
Extension: working with a partner to test one another
PUZZLES & QUIZZES
51
Answer key
Answers to all worksheets
Anagrams 1
Solving anagrams by reading clues and putting letters
in order
Parts of the body
crossword 1
Solving crossword
39-
40
Pair work
Communicative
crossword 1
Completing crossword by working with partner and
defining words
Anagrams 2
Solving anagrams by reading clues and putting letters
in order
Word search
Finding words hidden in letters using clues listed
43-
Communicative
crossword 2
Completing crossword by working with partner and
defining words
Parts of the body
crossword 2
Solving crossword
Gap fill crossword
Completing crossword with missing words from
sentences
47-
Communicative
crossword 3
Completing crossword by working with partner and
defining words
Quiz
Answering questions
Extension: writing a quiz with a partner
Vocabulary Record
Sheet
Recording new vocabulary, definitions and terms
Page
Mode
Title
Description
Most students find it easier to assimilate new vocabulary if the words are learned in related groups, rather
than in isolation. For example, words frequently occur in the same context as their opposites and, as such, it
makes sense to learn the pairs of opposites together (see worksheets on pages 7 and 29). Similarly, mind
maps encourage students to look for connections between words (see worksheet on page 9). The exercises
and activities in this workbook have all been grouped into sections. These sections practise different elements
of medical vocabulary, enabling the student to gain a fuller understanding of the words learnt.
The first section, Word-building (pages 1-9), encourages the student to identify links between words and to
learn words that are morphologically related (for example, verbs and nouns which have the same stems).
Within the Parts of Speech (pages 10-20) section, the emphasis is on understanding meanings and how to
use terms in their correct grammatical forms. The worksheets in the third section practise the Pronunciation
of medical vocabulary (pages 21-24). The section Vocabulary in Context (pages 25-36) includes topic-
specific exercises such as identifying diseases and illnesses from their descriptions. The activities in the last
section, Puzzles & Quizzes (pages 37-49), expand students’ knowledge and use of vocabulary in a fun way.
Communicative crosswords
Included in the last section are three communicative crosswords. These are speaking exercises where students
complete a half-finished crossword by exchanging clues with a partner. There are two versions of the
crossword: A & B. The words which are missing from A are in B, and vice versa. No clues are provided: the
students’ task is to invent them. This is an excellent exercise for developing linguistic resourcefulness; in
having to define words themselves, students practise both their medical vocabulary and the important skill of
paraphrasing something when they do not know the word for it.
Using Communicative crosswords in the classroom
Stage 1 — Set-up. Divide the class into two groups — A and B — with up to four students in each group. Give
out the crossword: sheet A to group A, sheet B to group B together with a copy of the Dictionary of Medical
Terms. Go through the rules with them. Some answers may consist of more than one word.
Stage 2 — Preparation. The students discuss the words in their groups, exchanging information about the
words they know and checking words they do not know in the Dictionary of Medical Terms. Circulate,
helping with any problems. This is an important stage: some of the vocabulary in the crosswords is quite
difficult.
Stage 3 — Activity. Put the students in pairs — one from group A and one from group B. The students help
each other to complete the crosswords by giving each other clues.
Make sure students are aware that the idea is to help each other complete the crossword, rather than to
produce obscure and difficult clues.
—
What’s one down?
—
It’s a person who works in a hospital.
—
A doctor?
—
A sort of doctor. He does operations.
—
A surgeon?
—
Yes, that’s right.
Alternatively, students can work in small groups, each group consisting of two As and two Bs and using the
following strategies:
i)
defining the word
ii)
describing what the item looks like
iii)
stating what the item is used for
iv)
describing the person’s role
v)
stating what the opposite of the word is
vi) giving
examples
vii)
leaving a gap in a sentence for the word
viii)
stating what the word sounds like.
Unit 0000
For reference see A & C Black Dictionary of Medical Terms (0 7136 7603 5).
Using the workbook
Students work in groups,
checking vocabulary
A A
A A
B B
B B
Students work in pairs,
co-operating to solve
their crosswords
A B
A B
A B
A B
Each of the sets of four words below can be linked by one other word. All the words are
related to medical matters. What are the missing words? Write them in the centre of the
charts.
Unit 0000
1
For reference see A & C Black Dictionary of Medical Terms (0 7136 7603 5).
Word association 1: missing links
ciliary
foreign
throbbing
abdominal
metacarpal
cancellous
cardiac
skeletal
black
glass
blood
beta
temperature
fat
relief
threshold
graft
marrow
fatigue
spasm
bath
drops
membrane
body
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
A fast way to expand your vocabulary is to make sure you know the different forms of the
words you learn.
Exercise 1. The words in this list are all verbs. What are the noun forms? Write them in the
second column. The first one has been done for you as an example.
Exercise 2. First, check your answers to Exercise 1 in the key. Then rewrite the sentences
below, changing the verbs (which are in bold) to nouns. Do not change the meaning of the
sentences, but be prepared to make grammatical changes if necessary. The first one has
been done for you as an example.
2
Unit 0000
For reference see A & C Black Dictionary of Medical Terms (0 7136 7603 5).
Word formation: nouns
1.
diagnose
diagnosis
2.
examine
______________
3.
prescribe
______________
4.
suffer
______________
5.
operate
______________
6.
cure
______________
7.
recover
______________
8.
analyse
______________
9.
infect
______________
10.
carry
______________
11.
replace
______________
12.
degenerate
______________
13.
refer
______________
14.
paralyse
______________
15.
obstruct
______________
1. I diagnosed that the patient had a heart
condition.
My
diagnosis was that the patient had a heart
condition.
2. I examined the patient fully.
I made a full
3. I prescribed a course of antibiotics.
I wrote a
4. He suffered very little.
He experienced very little
5. We operated immediately.
The
6. This disease cannot be cured.
There is no
7. He has recovered fully.
He has made a full
8. The lab analysed the blood sample.
The lab made an
9. We found that the tissue was infected.
We found an
10. Ten per cent of the population are thought to
carry the bacteria.
Ten per cent of the population are thought to be
11. We replaced the patient’s hip.
The patient was given a hip
12. His condition has degenerated.
There has been a
13. The patient was referred to a specialist.
The patient was given a
14. His arm was paralysed after the stroke.
He suffered
15. The artery was obstructed by a blood clot.
The blood clot was forming an
Make 15 two-word expressions connected with medicine by combining words from the
two lists: A and B. Match each expression with the appropriate phrase. Use each word
once. The first one has been done for you as an example.
Unit 0000
3
For reference see A & C Black Dictionary of Medical Terms (0 7136 7603 5).
Two-word expressions
A
allergic
balanced
bedside
biological
bone
brain
clinical
digestive
general
general
heart
malignant
plastic
primary
surgical
B
anaesthetic
attack
clock
death
diet
intervention
manner
marrow
practitioner
reaction
surgery
system
tooth
trial
tumour
1.
A condition in which the heart has a
reduced blood supply because one of the
arteries becomes blocked by a blood clot,
causing myocardial ischaemia and
myocardial infarction
heart attack
2.
A substance given to make someone lose
consciousness so that a major surgical
operation can be carried out
3.
Soft tissue in cancellous bone.
4.
The treatment of disease or other condition
by surgery.
5.
Any one of the first twenty teeth which
develop in children between about six
months and two-and-a-half years of age,
and are replaced by the permanent teeth at
around the age of six.
6.
Surgery to repair damaged or malformed
parts of the body.
7.
A condition in which the nerves in the brain
stem have died, and the person can be
certified as dead, although the heart may
not have stopped beating.
8.
The way in which a doctor behaves towards
a patient, especially a patient who is in bed.
9.
An effect produced by a substance to which
a person has an allergy, such as sneezing or
a skin rash.
10.
A trial carried out in a medical laboratory on
a person or on tissue from a person.
11.
A tumour which is cancerous and can grow
again or spread into other parts of the
body, even if removed surgically.
12.
A doctor who provides first-line medical
care for all types of illness to people who
live locally, refers them to hospital if
necessary and encourages health
promotion.
13.
The rhythm of daily activities and bodily
processes such as eating, defecating or
sleeping, frequently controlled by
hormones, which repeats every twenty-four
hours.
14.
The set of organs such as the stomach, liver
and pancreas which are associated with the
digestion of food.
15.
A diet that provides all the nutrients needed
in the correct proportions.
In Column A of this table there are 25 nouns relating to medicine. For each of the nouns
decide whether the correct plural form is in Column B or Column C and then circle it.
The first question has been done for you as an example.
4
Unit 0000
For reference see A & C Black Dictionary of Medical Terms (0 7136 7603 5).
Plural formation
1.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
stratum
foot
fibula
glomerulus
abscess
joint
bulla
testis
septum
oesophagus
diagnosis
humerus
syringe
acetabulum
larva
chorda
varix
fungus
ganglion
villus
atrium
pons
ovum
bout
cortex
stratums
foots
fibulae
glomerulae
abscesses
jointes
bullae
testises
septa
oesophaguses
diagnoses
humeruses
syringes
acetabula
larvae
chordas
varices
fungi
ganglions
villi
atria
pontes
ovums
bouts
cortexes
strata
feet
fibulas
glomeruli
abscessi
joints
bullas
testes
septums
oesophagi
diagnosises
humeri
syringae
acetabulums
larvi
chordae
varixi
funguses
ganglia
villae
atriums
ponses
ova
boutae
cortices
Column A
Column B
Column C
The italicised words in the sentences in Column A are all nouns. What are the adjective
forms? Complete the sentences in Column B using the correct adjective forms.
Unit 0000
5
For reference see A & C Black Dictionary of Medical Terms (0 7136 7603 5).
Word formation: adjectives
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
The surgeons operated to repair the
defect on the patient’s heart valve.
His diet has a calcium deficiency.
She has a physical dependence on
amphetamines.
The doctor noted an excess of bile in
the patient’s blood.
An attack of hypoglycaemia can be
prevented by eating glucose or a lump
of sugar when feeling faint.
The vaccine should give immunity to
tuberculosis.
They have periods of complete
inactivity.
The pain in his foot is so great that he
can hardly walk.
I injured my spine in the crash.
She complained of stiffness in the
joints.
The surgeons operated to repair the
patient’s …
His diet is calcium-…
She is physically …
The doctor noted an …
A …
The vaccine should make you …
They have periods when they are
completely …
His foot is so …
I suffered …
She complained of …
Column A
Column B
Exercise 1.
Link each verb on the left with a noun on the right to make 10 ‘partnerships’. The first
one has been done for you as an example.
Exercise 2.
Complete these sentences using the partnerships from Exercise 1. You may have to make
some changes to fit the grammar of the sentences. The first one has been done for you
as an example.
6
Unit 0000
For reference see A & C Black Dictionary of Medical Terms (0 7136 7603 5).
Word association 2: partnerships
1.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
administer
analyse
arrange
burp
catch
detect
discontinue
ease
resist
prescribe
an improvement
a baby
antibiotics
the treatment
some infections
an appointment
a sample
the pain
a drug
a cold
Verbs
Nouns
1.
The doctor will
Do’stlaringiz bilan baham:
CHECK YOUR ENGLISH VOCABULARY FOR
MEDICINE
third edition
A & C Black London
Introduction
####### The worksheets in this workbook contain a variety of exercises appropriate for students
####### requiring a working knowledge of English medical terminology. The worksheets can be used
####### either for self-study or in the classroom and can be completed in any order. Several have
####### ‘extensions’: short classroom exercises based on the language in the main exercise. All the
####### questions within this workbook are based on the A & C Black Dictionary of Medical Terms ,
####### fourth edition (ISBN 0 7136 7603 5).
####### This workbook is aimed at students with at least an intermediate level of English. However,
####### many people who work in medicine have to read in English on a regular basis; students with
####### a more basic level of English may therefore already have the passive vocabulary to handle
####### many of the exercises.
####### Specialist vocabulary
####### It is important to appreciate that ‘knowing’ specialist vocabulary involves more than simply
####### recognising it.
####### You can understand the meaning of a word when reading or listening and yet be
####### unable to remember that same word when speaking or writing.
####### You may remember the word, but use it incorrectly. This can be a grammatical
####### problem, like knowing that ‘fracture’ can be used both as a noun and as a verb. Or
####### it may be a question of collocation: a surgeon makes an incision during an operation,
####### but when he wants a piece of bread he simply cuts it.
####### Then there is the question of the sound of the word. Can you pronounce it? And do
####### you recognise it when you hear it pronounced?
####### For these reasons — memory, use and sound — it is important that students practise specialist
####### vocabulary so that they can learn to use it more confidently and effectively. The exercises in
####### this workbook will help students to expand their knowledge and use of medical vocabulary.
####### Using the Dictionary of Medical Terms
####### All of the vocabulary taught or practised in this workbook is in the A & C Black Dictionary of
####### Medical Terms. The Dictionary of Medical Terms gives definitions in simple English which
####### students can read and understand. Many of the examples and definitions in the workbook
####### are taken directly from the dictionary. Students should have a copy of the Dictionary of
####### Medical Terms for referring to when completing the exercises; using the dictionary is an
####### essential part of successful language learning.
####### Structure of a Dictionary of Medical Terms entry
####### Each entry within the dictionary includes key elements that help a student understand the
####### definition of the term and how to use it in context. Each term has a clear example, and part
####### of speech. This is followed by example sentences and quotations from newspapers and
####### magazines that show how the term is used in real life. These elements of the dictionary are
####### used to create the questions within this workbook.
####### Vocabulary Record Sheet
####### At the back of the book is a Vocabulary Record Sheet. Recording useful vocabulary in a
####### methodical way plays a key role in language learning and could be done, for example, at the
####### end of each lesson. The Dictionary of Medical Terms is a useful tool for ensuring that the
####### personal vocabulary record is accurate and is a good source for example sentences to show
####### how words are used, as well as for notes about meaning and pronunciation, etc.
Workbook contents
WORD-BUILDING
1 Word association 1: Self-study
missing links
Linking each set of four words with one other word
2 Word formation: Self-study
nouns
Forming nouns from list of verbs; rewriting sentences
using noun forms instead of verbs
3 Two-word expressions Combining words from two lists to make two-word Self-study
expressions that fit the definitions
4 Plural formation Multiple choice: choosing correct plural forms of singular Self-study
nouns
5 Word formation: Self-study
adjectives
Rewriting sentences using adjective forms instead of
nouns
6 Word association 2: Self-study
partnerships
Linking each verb with a noun to make a ‘partnership’;
using the ‘partnerships’ to complete sentences
7 Opposites 1: prefixes Selecting the correct prefix for each adjective to create an Self-study
opposite; using the adjectives to complete sentences
Extension : working with a partner to test one another
8 Word formation: verbs Making verb forms from list of nouns; writing sentences Self-study
using the verbs
9 Word association 3: Self-study
mind maps
Finding words in a mind map that fit definitions;
designing mind maps
PARTS OF SPEECH
10 Nouns Sentence completion Self-study
11 Adjectives 1 Sentence completion Self-study
12 Adjectives 2 Sentence completion Self-study
13 Verbs 1 Matching verbs with their correct definitions Self-study
14 Verbs 2 Matching verbs with their correct definitions Self-study
15 Verbs: past tense ~ Self-study
regular verbs
Sentence completion
16 Verbs: mixed tenses Sentence completion Self-study
17 Phrasal verbs Sentence completion Self-study
Extension : working with a partner to write a dialogue
using phrasal verbs
18 Verbs: active/passive Changing sentences from active to passive tense Self-study
19 Adverbs Identifying adverbs in sentences and swapping adverbs Self-study
around so that each sentence makes sense
20 Prepositions Correcting sentences with deliberate mistakes in Self-study
the prepositions
PRONUNCIATION
21 Self-study
Pair work
Word stress 1 Identifying three-syllable words and classifying by their
pronunciation
Extension : practising the dialogues with a partner
22 Word stress 2 Completing sentences using four-syllable words; Self-study
classifying four-syllable words by their pronunciation
23 Present simple Identifying present tense verbs and classifying by their Pair work
pronunciation
Extension : working with a partner to identify plural
nouns in each pronunciation category
24 Past tense Identifying past tense verbs and classifying by their Self-study
pronunciation
Page Title Description Mode
Most students find it easier to assimilate new vocabulary if the words are learned in related groups, rather
than in isolation. For example, words frequently occur in the same context as their opposites and, as such, it
makes sense to learn the pairs of opposites together ( see worksheets on pages 7 and 29 ). Similarly, mind
maps encourage students to look for connections between words ( see worksheet on page 9 ). The exercises
and activities in this workbook have all been grouped into sections. These sections practise different elements
of medical vocabulary, enabling the student to gain a fuller understanding of the words learnt.
The first section, Word-building ( pages 1-9 ), encourages the student to identify links between words and to
learn words that are morphologically related (for example, verbs and nouns which have the same stems).
Within the Parts of Speech ( pages 10-20 ) section, the emphasis is on understanding meanings and how to
use terms in their correct grammatical forms. The worksheets in the third section practise the Pronunciation
of medical vocabulary ( pages 21-24 ). The section Vocabulary in Context ( pages 25-36 ) includes topic-
specific exercises such as identifying diseases and illnesses from their descriptions. The activities in the last
section, Puzzles & Quizzes ( pages 37-49 ), expand students’ knowledge and use of vocabulary in a fun way.
Communicative crosswords
Included in the last section are three communicative crosswords. These are speaking exercises where students
complete a half-finished crossword by exchanging clues with a partner. There are two versions of the
crossword: A & B. The words which are missing from A are in B, and vice versa. No clues are provided: the
students’ task is to invent them. This is an excellent exercise for developing linguistic resourcefulness; in
having to define words themselves, students practise both their medical vocabulary and the important skill of
paraphrasing something when they do not know the word for it.
Using Communicative crosswords in the classroom
Stage 1 — Set-up. Divide the class into two groups — A and B — with up to four students in each group. Give
out the crossword: sheet A to group A, sheet B to group B together with a copy of the Dictionary of Medical
Terms. Go through the rules with them. Some answers may consist of more than one word.
Stage 2 — Preparation. The students discuss the words in their groups, exchanging information about the
words they know and checking words they do not know in the Dictionary of Medical Terms. Circulate,
helping with any problems. This is an important stage: some of the vocabulary in the crosswords is quite
difficult.
Stage 3 — Activity. Put the students in pairs — one from group A and one from group B. The students help
each other to complete the crosswords by giving each other clues.
Make sure students are aware that the idea is to help each other complete the crossword, rather than to
produce obscure and difficult clues.
- What’s one down?
— It’s a person who works in a hospital. - A doctor?
— A sort of doctor. He does operations. - A surgeon?
— Yes, that’s right.
Alternatively, students can work in small groups, each group consisting of two As and two Bs and using the
following strategies:
i) defining the word
ii) describing what the item looks like
iii) stating what the item is used for
iv) describing the person’s role
v) stating what the opposite of the word is
vi) giving examples
vii) leaving a gap in a sentence for the word
viii) stating what the word sounds like.
Unit 0000
Using the workbook
Students work in groups,
checking vocabulary
A A
A A
B B
B B
Students work in pairs,
co-operating to solve
their crosswords
A B A B
A B A B
####### Each of the sets of four words below can be linked by one other word. All the words are
####### related to medical matters. What are the missing words? Write them in the centre of the
####### charts.
Unit 0000
1
Word association 1: missing links
####### ciliary
####### foreign
####### throbbing
####### abdominal
####### metacarpal
####### cancellous
####### cardiac
####### skeletal
####### black
####### glass
####### blood
####### beta
####### temperature
####### fat
####### relief
####### threshold
####### graft
####### marrow
####### fatigue
####### spasm
####### bath
####### drops
####### membrane
####### body
####### Make 15 two-word expressions connected with medicine by combining words from the
####### two lists: A and B. Match each expression with the appropriate phrase. Use each word
####### once. The first one has been done for you as an example.
Unit 0000
3
Two-word expressions
A
allergic
balanced
bedside
biological
bone
brain
clinical
digestive
general
general
heart
malignant
plastic
primary
surgical
B
anaesthetic
attack
clock
death
diet
intervention
manner
marrow
practitioner
reaction
surgery
system
tooth
trial
tumour
-
A condition in which the heart has a
reduced blood supply because one of the
arteries becomes blocked by a blood clot,
causing myocardial ischaemia and
myocardial infarction
heart attack -
A substance given to make someone lose
consciousness so that a major surgical
operation can be carried out -
Soft tissue in cancellous bone.
-
The treatment of disease or other condition
by surgery. -
Any one of the first twenty teeth which
develop in children between about six
months and two-and-a-half years of age,
and are replaced by the permanent teeth at
around the age of six. -
Surgery to repair damaged or malformed
parts of the body. -
A condition in which the nerves in the brain
stem have died, and the person can be
certified as dead, although the heart may
not have stopped beating. -
The way in which a doctor behaves towards
a patient, especially a patient who is in bed. -
An effect produced by a substance to which
a person has an allergy, such as sneezing or
a skin rash. -
A trial carried out in a medical laboratory on
a person or on tissue from a person. -
A tumour which is cancerous and can grow
again or spread into other parts of the
body, even if removed surgically. -
A doctor who provides first-line medical
care for all types of illness to people who
live locally, refers them to hospital if
necessary and encourages health
promotion. -
The rhythm of daily activities and bodily
processes such as eating, defecating or
sleeping, frequently controlled by
hormones, which repeats every twenty-four
hours. -
The set of organs such as the stomach, liver
and pancreas which are associated with the
digestion of food. -
A diet that provides all the nutrients needed
in the correct proportions.
####### In Column A of this table there are 25 nouns relating to medicine. For each of the nouns
####### decide whether the correct plural form is in Column B or Column C and then circle it.
####### The first question has been done for you as an example.
4
Unit 0000
Plural formation
stratum
foot
fibula
glomerulus
abscess
joint
bulla
testis
septum
oesophagus
diagnosis
humerus
syringe
acetabulum
larva
chorda
varix
fungus
ganglion
villus
atrium
pons
ovum
bout
cortex
stratums
foots
fibulae
glomerulae
abscesses
jointes
bullae
testises
septa
oesophaguses
diagnoses
humeruses
syringes
acetabula
larvae
chordas
varices
fungi
ganglions
villi
atria
pontes
ovums
bouts
cortexes
strata
feet
fibulas
glomeruli
abscessi
joints
bullas
testes
septums
oesophagi
diagnosises
humeri
syringae
acetabulums
larvi
chordae
varixi
funguses
ganglia
villae
atriums
ponses
ova
boutae
cortices
Column A Column B Column C
####### Exercise 1.
####### Link each verb on the left with a noun on the right to make 10 ‘partnerships’. The first
####### one has been done for you as an example.
####### Exercise 2.
####### Complete these sentences using the partnerships from Exercise 1. You may have to make
####### some changes to fit the grammar of the sentences. The first one has been done for you
####### as an example.
6
Unit 0000
Word association 2: partnerships
administer
analyse
arrange
burp
catch
detect
discontinue
ease
resist
prescribe
an improvement
a baby
antibiotics
the treatment
some infections
an appointment
a sample
the pain
a drug
a cold
Verbs Nouns
-
The doctor will administer a drug to the patient.
-
She was ____________________.
-
As soon as the patient reported severe side-effects, the doctor ___________________.
-
I’ve ____________________ from one of my colleagues at work.
-
The laboratory ____________________ of the food and found traces of bacteria.
-
A healthy body can ____________________.
-
I would like to ____________________ with the dental hygienist for 10 tomorrow.
-
She had an injection to ____________________ in her leg.
-
The health visitor advised the new parents to ____________________ after feeding.
-
The nurses _____________________ in the patient’s condition.
####### Exercise 1.
####### English often uses prefixes to create opposites. There are several different prefixes that are
####### used. Choose the right prefix for each of the adjectives below and write them into the
####### table. The first one has been done for you:
####### Exercise 2.
####### Use ten of the adjectives in the table to complete these sentences. The first one has been
####### done for you as an example.
####### Extension. Work with a partner and test each other. One partner closes the book, while
####### the other asks questions such as » What’s the opposite of conscious? «.
Unit 0000
7
Opposites 1: prefixes
active adequate coherent compatible complete
conscious controllable dependent digested direct fertile fit healthy
hygienic legal movable operable palpable pure qualified reducible
regular sanitary soluble stable well
-
-
inactive
il- im- in- ir- un-
-
He was found unconscious in the street.
-
He felt ________________ and had to go home.
-
The serum makes the poison ________________.
-
The children have a very _______________ diet.
-
The nurse noted that the patient had developed an ________________ pulse.
-
She used to play a lot of tennis, but she became ________________ in the winter.
-
The surgeon decided that the cancer was ________________.
-
Cholera spread rapidly because of the ________________ conditions in the town.
-
The patient was showing signs of an ________________ mental condition.
-
She has an ________________ desire to drink alcohol.
####### A mind map is a way of organising vocabulary to show the connections between words.
####### This mind map is based on the word ‘surgery’.
####### Exercise 1.
####### Find words and expressions in the mind map that fit the following definitions.
####### Exercise 2.
####### Design a mind map for one or more of the following:
####### health
####### hospital
####### patient
Unit 0000
9
Word association 3: mind maps
general anaesthetic
heart surgery local anaesthetic
major surgery
anaesthetist
exploratory surgery
heart surgeon
surgeon
surgery
scrub up
consultant
A & E department
ambulance
accident
operate
operation
operating table
operating theatre
theatre nurse
incision
scalpel
surgical instruments
surgical gloves
- A special room in a hospital, where surgical operations are carried out ………………..
- A nurse who is specially trained to assist a surgeon during an operation ………………..
- The part of a hospital which deals with people who need urgent treatment because they have had
accidents or are in sudden serious pain ……………….. - Surgical operations involving important organs in the body ………………..
- A doctor who specialises in surgery ………………..
- An anaesthetic which removes the feeling in a single part of the body only ………………..
- A senior specialised doctor in a hospital ………………..
- A surgical operation to remedy a condition of the heart ………………..
- To clean the hands and arms thoroughly before performing surgery ………………..
- The treatment of diseases or disorders by procedures which require an operation to cut into, to
remove or to manipulate tissue, organs or parts ………………..
####### There are 20 nouns connected with medicine in the box below. Use them to complete the
####### sentences — in some cases you will need to make them plural. The first one has been done
####### for you as an example.
10
Unit 0000
Nouns
accident allergy ambulance biopsy consent course examination excess
exercise injection intake overdose paroxysm progress rash recurrence
surgery tendency treatment vaccination
-
He developed an allergy to penicillin.
-
He suffered _______________ of coughing in the night.
-
She went into a coma after an _______________ of heroin.
-
The patient will need plastic _______________ to remove the scars he received in the accident.
-
She took a _______________ of steroid treatment.
-
He had a _______________ of a fever which he had caught in the tropics.
-
There is a _______________ to obesity in her family.
-
From the _______________ of the X-ray photographs, it seems that the tumour has not spread.
-
The doctor gave him an _______________ to relieve the pain.
-
He doesn’t take enough _______________: that’s why he’s fat.
-
The injured man was taken away in an _______________.
-
She was advised to reduce her _______________ of sugar.
-
The _______________ of the tissue from the growth showed that it was benign.
-
The parents gave their _______________ for their son’s heart to be used in the transplant
operation. -
The doctors seem pleased that she has made such good _______________ since her operation.
-
This is a new _______________ for heart disease.
-
Her body could not cope with an _______________ of blood sugar.
-
Three people were injured in the _______________ on the motorway.
-
_______________ is mainly given against cholera, diphtheria, rabies, smallpox, tuberculosis and
typhoid. -
She had a high temperature and then broke out in a _______________.
####### Complete the sentences using the adjectives in the box. Use each adjective once only. The
####### first one has been done for you as an example.
12
Unit 0000
Adjectives 2
acute bedridden critical deaf depressed excessive harmful infirm
inflamed latent lethal mobile obsessive painful persistent premature
severed subjective tender viable
-
These fumes are lethal if inhaled.
-
The report was _______________ of the state of aftercare provision.
-
She had a _______________ cough.
-
The psychiatrist gave a _______________ opinion on the patient’s problem.
-
My grandfather is quite _______________ now.
-
The skin has become _______________ around the sore.
-
It is important for elderly patients to remain _______________.
-
His foot is so _______________ he can hardly walk.
-
A fetus is _______________ by about the 28th week of the pregnancy.
-
You have to speak slowly and clearly when you speak to Mr Jones because he’s quite ________.
-
The baby was born five weeks _______________.
-
The patient was passing _______________ quantities of urine.
-
He felt _______________ chest pains.
-
He is _______________ and has to be looked after by a nurse.
-
The children were tested for _______________ viral infection.
-
He has an _______________ desire to steal small objects.
-
Her shoulders are still _______________ where she got sunburnt.
-
Surgeons tried to sew the _______________ finger back onto the patient’s hand.
-
She was _______________ for weeks after the death of her husband.
-
Bright light can be _______________ to your eyes.
####### The sentences in Column A contain examples of useful verbs in medicine. In Column B
####### there are definitions of the verbs. Read the examples and match the verbs (in italics ) with
####### the definitions. Then write the infinitive forms into the spaces in the definitions in Column
####### B. The first one has been done for you as an example.
Unit 0000
13
Verbs 1
Column A: Examples Column B: Definitions
-
After the accident the passengers
were treated in hospital for cuts. -
Nurses dressed the wounds of the
accident victims. -
He specialises in children with
breathing problems. -
She suffers from headaches.
-
She was vaccinated against smallpox
as a child. -
Some forms of cancer cannot be
cured. -
The calamine lotion will soothe the
rash. -
The doctor diagnosed appendicitis.
-
The doctor prescribed a course of
antibiotics. -
The drug suppresses the body’s
natural instinct to reject the
transplanted tissue. -
The operation may endanger the life
of the patient. -
The surgeons decided to operate as
the only way of saving the baby’s
life.
a) diagnose means to identify a
condition or illness, by examining the
person and noting symptoms
b) _________ means to to use medical
methods to cure a disease or help a
sick or injured person to recover
c) _________ means to make someone
healthy
d) _________ means to put someone or
something at risk
e) _________ means to give instructions
for a person to get a specific dosage
of a drug or a specific form of
therapeutic treatment
f) _________ means to study or treat
one particular disease or one
particular type of patient
g) _________ means to have an illness
for a long period of time
h) _________ means to treat a person
for a condition by cutting open the
body and removing a part which is
diseased or repairing a part which is
not functioning correctly
i) _________ means to introduce
vaccine into a person’s body in order
to make the body create its own
antibodies, so making the person
immune to the disease
j) _________ means to relieve pain
k) _________ means to clean a wound
and put a covering over it
l) _________ means to reduce the
action of something completely, e.
to remove a symptom or to stop the
release of a hormone
CHECK YOUR ENGLISH VOCABULARY FOR
MEDICINE
third edition
A & C Black 폷 London
www.acblack.com
First published in Great Britain 1995
Second edition published 2000
Third edition published 2006
A & C Black Publishers Ltd
38 Soho Square, London W1D 3HB
© Peter Collin Publishing 1995, 2000
© A & C Black Publishers Ltd 2006
All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced in
any form without the permission of the publishers.
A CIP entry for this book is available from the British Library
ISBN-10: 0 7136 7590 X
ISBN-13: 978 0 7136 7590 0
eISBN-13: 978-1-4081-0238-1
Text typeset by A & C Black
Printed in Italy by Legoprint
A & C Black uses paper produced with elemental chlorine-free pulp,
harvested from managed sustainable forests.
Introduction
The worksheets in this workbook contain a variety of exercises appropriate for students
requiring a working knowledge of English medical terminology. The worksheets can be used
either for self-study or in the classroom and can be completed in any order. Several have
‘extensions’: short classroom exercises based on the language in the main exercise. All the
questions within this workbook are based on the A & C Black Dictionary of Medical Terms,
fourth edition (ISBN 0 7136 7603 5).
This workbook is aimed at students with at least an intermediate level of English. However,
many people who work in medicine have to read in English on a regular basis; students with
a more basic level of English may therefore already have the passive vocabulary to handle
many of the exercises.
Specialist vocabulary
It is important to appreciate that ‘knowing’ specialist vocabulary involves more than simply
recognising it.
You can understand the meaning of a word when reading or listening and yet be
unable to remember that same word when speaking or writing.
You may remember the word, but use it incorrectly. This can be a grammatical
problem, like knowing that ‘fracture’ can be used both as a noun and as a verb. Or
it may be a question of collocation: a surgeon makes an incision during an operation,
but when he wants a piece of bread he simply cuts it.
Then there is the question of the sound of the word. Can you pronounce it? And do
you recognise it when you hear it pronounced?
For these reasons — memory, use and sound — it is important that students practise specialist
vocabulary so that they can learn to use it more confidently and effectively. The exercises in
this workbook will help students to expand their knowledge and use of medical vocabulary.
Using the Dictionary of Medical Terms
All of the vocabulary taught or practised in this workbook is in the A & C Black Dictionary of
Medical Terms. The Dictionary of Medical Terms gives definitions in simple English which
students can read and understand. Many of the examples and definitions in the workbook
are taken directly from the dictionary. Students should have a copy of the Dictionary of
Medical Terms for referring to when completing the exercises; using the dictionary is an
essential part of successful language learning.
Structure of a Dictionary of Medical Terms entry
Each entry within the dictionary includes key elements that help a student understand the
definition of the term and how to use it in context. Each term has a clear example, and part
of speech. This is followed by example sentences and quotations from newspapers and
magazines that show how the term is used in real life. These elements of the dictionary are
used to create the questions within this workbook.
Vocabulary Record Sheet
At the back of the book is a Vocabulary Record Sheet. Recording useful vocabulary in a
methodical way plays a key role in language learning and could be done, for example, at the
end of each lesson. The Dictionary of Medical Terms is a useful tool for ensuring that the
personal vocabulary record is accurate and is a good source for example sentences to show
how words are used, as well as for notes about meaning and pronunciation, etc.
Workbook contents
WORD-BUILDING
1 Self-studyWord association 1:
missing links
Linking each set of four words with one other word
2
Self-study
Word formation:
nouns
Forming nouns from list of verbs; rewriting sentences
using noun forms instead of verbs
3
Self-study
Two-word expressions Combining words from two lists to make two-word
expressions that fit the definitions
4
Self-study
Plural formation Multiple choice: choosing correct plural forms of singular
nouns
5 Self-studyWord formation:
adjectives
Rewriting sentences using adjective forms instead of
nouns
6 Self-studyWord association 2:
partnerships
Linking each verb with a noun to make a ‘partnership’;
using the ‘partnerships’ to complete sentences
7 Self-studyOpposites 1: prefixes Selecting the correct prefix for each adjective to create an
opposite; using the adjectives to complete sentences
Extension: working with a partner to test one another
8
Self-study
Word formation: verbs
Making verb forms from list of nouns; writing sentences
using the verbs
9 Self-studyWord association 3:
mind maps
Finding words in a mind map that fit definitions;
designing mind maps
PARTS OF SPEECH
10 Self-studyNouns Sentence completion
11 Self-studyAdjectives 1 Sentence completion
12 Self-studyAdjectives 2 Sentence completion
13 Self-studyVerbs 1 Matching verbs with their correct definitions
14 Self-studyVerbs 2 Matching verbs with their correct definitions
15 Self-studyVerbs: past tense ~
regular verbs
Sentence completion
16 Self-studyVerbs: mixed tenses Sentence completion
17 Self-studyPhrasal verbs Sentence completion
Extension: working with a partner to write a dialogue
using phrasal verbs
18 Self-studyVerbs: active/passive Changing sentences from active to passive tense
19 Self-studyAdverbs Identifying adverbs in sentences and swapping adverbs
around so that each sentence makes sense
20 Self-studyPrepositions Correcting sentences with deliberate mistakes in
the prepositions
PRONUNCIATION
21 Self-study
Pair work
Word stress 1 Identifying three-syllable words and classifying by their
pronunciation
Extension: practising the dialogues with a partner
22
Self-study
Word stress 2 Completing sentences using four-syllable words;
classifying four-syllable words by their pronunciation
23 Pair workPresent simple Identifying present tense verbs and classifying by their
pronunciation
Extension: working with a partner to identify plural
nouns in each pronunciation category
24 Self-studyPast tense Identifying past tense verbs and classifying by their
pronunciation
Page ModeTitle
Description
VOCABULARY IN CONTEXT
25 Self-study
Pair work
Good advice Matching half-sentences together to make complete
sentences
Extension: writing pieces of medical advice with a
partner
26 Self-studyMultiple meanings Classifying meanings
27 Self-studyOdd one out Identifying word that is different to others in each set
28 Self-studyBody parts — categories Deciding which category each body part belongs to
29 Self-study
Pair work
Opposites 2 Matching words with opposite meanings; inserting
correct opposites in sentences
Extension: working with a partner to test one another
30 Self-study
Pair work
Abbreviations Stating what abbreviations stand for
Extension: working with a partner to test one another
31 Self-studySymptoms & common
illnesses 1
Checking meanings of words; matching descriptions to
names of illnesses
32
Self-study
Pair work
Symptoms & common
illnesses 2
Matching formal and informal names of illnesses;
completing conversations by using informal names of
illnesses
Extension: practising conversations with a partner
33 Self-study
Pair work
Diagnosis Identifying each disease or illness from its description
Extension: writing a description of a disease or illness
and testing a partner
34 Self-studyHow it works Matching half-sentences together to make complete
sentences
35 Self-study
Pair work
Instruments and
equipment
Matching each instrument and item of equipment with
its correct description
Extension: working with a partner to test one another
36
Self-study
Pair work
Chemistry Matching symbols of chemical elements and compounds
with correct names and descriptions
Extension: working with a partner to test one another
PUZZLES & QUIZZES
51 Answer key Answers to all worksheets
37 Self-studyAnagrams 1 Solving anagrams by reading clues and putting letters
in order
38
Self-study
Parts of the body
crossword 1
Solving crossword
39-
40
Pair work Communicative
crossword 1
Completing crossword by working with partner and
defining words
41 Self-studyAnagrams 2 Solving anagrams by reading clues and putting letters
in order
42 Self-studyWord search Finding words hidden in letters using clues listed
43-
44
Pair work
Communicative
crossword 2
Completing crossword by working with partner and
defining words
45
Self-study
Parts of the body
crossword 2
Solving crossword
46 Self-studyGap fill crossword Completing crossword with missing words from
sentences
47-
48
Pair work Communicative
crossword 3
Completing crossword by working with partner and
defining words
49 Self-study
Pair work
Quiz Answering questions
Extension: writing a quiz with a partner
50
Self-study
Vocabulary Record
Sheet
Recording new vocabulary, definitions and terms
Page ModeTitle
Description
Most students find it easier to assimilate new vocabulary if the words are learned in related groups, rather
than in isolation. For example, words frequently occur in the same context as their opposites and, as such, it
makes sense to learn the pairs of opposites together (see worksheets on pages 7 and 29). Similarly, mind
maps encourage students to look for connections between words (see worksheet on page 9). The exercises
and activities in this workbook have all been grouped into sections. These sections practise different elements
of medical vocabulary, enabling the student to gain a fuller understanding of the words learnt.
The first section, Word-building (pages 1-9), encourages the student to identify links between words and to
learn words that are morphologically related (for example, verbs and nouns which have the same stems).
Within the Parts of Speech (pages 10-20) section, the emphasis is on understanding meanings and how to
use terms in their correct grammatical forms. The worksheets in the third section practise the Pronunciation
of medical vocabulary (pages 21-24). The section Vocabulary in Context (pages 25-36) includes topic-
specific exercises such as identifying diseases and illnesses from their descriptions. The activities in the last
section, Puzzles & Quizzes (pages 37-49), expand students’ knowledge and use of vocabulary in a fun way.
Communicative crosswords
Included in the last section are three communicative crosswords. These are speaking exercises where students
complete a half-finished crossword by exchanging clues with a partner. There are two versions of the
crossword: A & B. The words which are missing from A are in B, and vice versa. No clues are provided: the
students’ task is to invent them. This is an excellent exercise for developing linguistic resourcefulness; in
having to define words themselves, students practise both their medical vocabulary and the important skill of
paraphrasing something when they do not know the word for it.
Using Communicative crosswords in the classroom
Stage 1 — Set-up. Divide the class into two groups — A and B — with up to four students in each group. Give
out the crossword: sheet A to group A, sheet B to group B together with a copy of the Dictionary of Medical
Terms. Go through the rules with them. Some answers may consist of more than one word.
Stage 2 — Preparation. The students discuss the words in their groups, exchanging information about the
words they know and checking words they do not know in the Dictionary of Medical Terms. Circulate,
helping with any problems. This is an important stage: some of the vocabulary in the crosswords is quite
difficult.
Stage 3 — Activity. Put the students in pairs — one from group A and one from group B. The students help
each other to complete the crosswords by giving each other clues.
Make sure students are aware that the idea is to help each other complete the crossword, rather than to
produce obscure and difficult clues.
— What’s one down?
— It’s a person who works in a hospital.
— A doctor?
— A sort of doctor. He does operations.
— A surgeon?
— Yes, that’s right.
Alternatively, students can work in small groups, each group consisting of two As and two Bs and using the
following strategies:
i) defining the word
ii) describing what the item looks like
iii) stating what the item is used for
iv) describing the person’s role
v) stating what the opposite of the word is
vi) giving examples
vii) leaving a gap in a sentence for the word
viii) stating what the word sounds like.
Unit 0000
For reference see A & C Black Dictionary of Medical Terms (0 7136 7603 5).
Using the workbook
Students work in groups,
checking vocabulary
A A
A A
B B
B B
Students work in pairs,
co-operating to solve
their crosswords
A B A B
A B A B
Each of the sets of four words below can be linked by one other word. All the words are
related to medical matters. What are the missing words? Write them in the centre of the
charts.
Unit 0000
1
For reference see A & C Black Dictionary of Medical Terms (0 7136 7603 5).
Word association 1: missing links
ciliary
foreign
throbbing
abdominal
metacarpal
cancellous
cardiac
skeletal
black
glass
blood
beta
temperature
fat
relief
threshold
graft
marrow
fatigue
spasm
bath
drops
membrane
body
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
A fast way to expand your vocabulary is to make sure you know the different forms of the
words you learn.
Exercise 1. The words in this list are all verbs. What are the noun forms? Write them in the
second column. The first one has been done for you as an example.
Exercise 2. First, check your answers to Exercise 1 in the key. Then rewrite the sentences
below, changing the verbs (which are in bold) to nouns. Do not change the meaning of the
sentences, but be prepared to make grammatical changes if necessary. The first one has
been done for you as an example.
2
Unit 0000
For reference see A & C Black Dictionary of Medical Terms (0 7136 7603 5).
Word formation: nouns
1. diagnose diagnosis
2. examine ______________
3. prescribe ______________
4. suffer ______________
5. operate ______________
6. cure ______________
7. recover ______________
8. analyse ______________
9. infect ______________
10. carry ______________
11. replace ______________
12. degenerate ______________
13. refer ______________
14. paralyse ______________
15. obstruct ______________
1. I diagnosed that the patient had a heart
condition.
My diagnosis was that the patient had a heart
condition.
2. I examined the patient fully.
I made a full
3. I prescribed a course of antibiotics.
I wrote a
4. He suffered very little.
He experienced very little
5. We operated immediately.
The
6. This disease cannot be cured.
There is no
7. He has recovered fully.
He has made a full
8. The lab analysed the blood sample.
The lab made an
9. We found that the tissue was infected.
We found an
10. Ten per cent of the population are thought to
carry the bacteria.
Ten per cent of the population are thought to be
11. We replaced the patient’s hip.
The patient was given a hip
12. His condition has degenerated.
There has been a
13. The patient was referred to a specialist.
The patient was given a
14. His arm was paralysed after the stroke.
He suffered
15. The artery was obstructed by a blood clot.
The blood clot was forming an
Make 15 two-word expressions connected with medicine by combining words from the
two lists: A and B. Match each expression with the appropriate phrase. Use each word
once. The first one has been done for you as an example.
Unit 0000
3
For reference see A & C Black Dictionary of Medical Terms (0 7136 7603 5).
Two-word expressions
A
allergic
balanced
bedside
biological
bone
brain
clinical
digestive
general
general
heart
malignant
plastic
primary
surgical
B
anaesthetic
attack
clock
death
diet
intervention
manner
marrow
practitioner
reaction
surgery
system
tooth
trial
tumour
1. A condition in which the heart has a
reduced blood supply because one of the
arteries becomes blocked by a blood clot,
causing myocardial ischaemia and
myocardial infarction
heart attack
2. A substance given to make someone lose
consciousness so that a major surgical
operation can be carried out
3. Soft tissue in cancellous bone.
4. The treatment of disease or other condition
by surgery.
5. Any one of the first twenty teeth which
develop in children between about six
months and two-and-a-half years of age,
and are replaced by the permanent teeth at
around the age of six.
6. Surgery to repair damaged or malformed
parts of the body.
7. A condition in which the nerves in the brain
stem have died, and the person can be
certified as dead, although the heart may
not have stopped beating.
8. The way in which a doctor behaves towards
a patient, especially a patient who is in bed.
9. An effect produced by a substance to which
a person has an allergy, such as sneezing or
a skin rash.
10. A trial carried out in a medical laboratory on
a person or on tissue from a person.
11. A tumour which is cancerous and can grow
again or spread into other parts of the
body, even if removed surgically.
12. A doctor who provides first-line medical
care for all types of illness to people who
live locally, refers them to hospital if
necessary and encourages health
promotion.
13. The rhythm of daily activities and bodily
processes such as eating, defecating or
sleeping, frequently controlled by
hormones, which repeats every twenty-four
hours.
14. The set of organs such as the stomach, liver
and pancreas which are associated with the
digestion of food.
15. A diet that provides all the nutrients needed
in the correct proportions.
In Column A of this table there are 25 nouns relating to medicine. For each of the nouns
decide whether the correct plural form is in Column B or Column C and then circle it.
The first question has been done for you as an example.
4
Unit 0000
For reference see A & C Black Dictionary of Medical Terms (0 7136 7603 5).
Plural formation
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
stratum
foot
fibula
glomerulus
abscess
joint
bulla
testis
septum
oesophagus
diagnosis
humerus
syringe
acetabulum
larva
chorda
varix
fungus
ganglion
villus
atrium
pons
ovum
bout
cortex
stratums
foots
fibulae
glomerulae
abscesses
jointes
bullae
testises
septa
oesophaguses
diagnoses
humeruses
syringes
acetabula
larvae
chordas
varices
fungi
ganglions
villi
atria
pontes
ovums
bouts
cortexes
strata
feet
fibulas
glomeruli
abscessi
joints
bullas
testes
septums
oesophagi
diagnosises
humeri
syringae
acetabulums
larvi
chordae
varixi
funguses
ganglia
villae
atriums
ponses
ova
boutae
cortices
Column A Column B Column C
The italicised words in the sentences in Column A are all nouns. What are the adjective
forms? Complete the sentences in Column B using the correct adjective forms.
Unit 0000
5
For reference see A & C Black Dictionary of Medical Terms (0 7136 7603 5).
Word formation: adjectives
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
The surgeons operated to repair the
defect on the patient’s heart valve.
His diet has a calcium deficiency.
She has a physical dependence on
amphetamines.
The doctor noted an excess of bile in
the patient’s blood.
An attack of hypoglycaemia can be
prevented by eating glucose or a lump
of sugar when feeling faint.
The vaccine should give immunity to
tuberculosis.
They have periods of complete
inactivity.
The pain in his foot is so great that he
can hardly walk.
I injured my spine in the crash.
She complained of stiffness in the
joints.
The surgeons operated to repair the
patient’s …
His diet is calcium-…
She is physically …
The doctor noted an …
A …
The vaccine should make you …
They have periods when they are
completely …
His foot is so …
I suffered …
She complained of …
Column A Column B
Exercise 1.
Link each verb on the left with a noun on the right to make 10 ‘partnerships’. The first
one has been done for you as an example.
Exer
cise 2.
Complete these sentences using the partnerships from Exercise 1. You may have to make
some changes to fit the grammar of the sentences. The first one has been done for you
as an example.
6
Unit 0000
For reference see A & C Black Dictionary of Medical Terms (0 7136 7603 5).
Word association 2: partnerships
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
administer
analyse
arrange
burp
catch
detect
discontinue
ease
resist
prescribe
an improvement
a baby
antibiotics
the treatment
some infections
an appointment
a sample
the pain
a drug
a cold
Verbs Nouns
1. The doctor will administer a drug to the patient.
2. She was ____________________ .
3. As soon as the patient reported severe side-effects, the doctor ___________________ .
4. I’ve ____________________ from one of my colleagues at work.
5. The laboratory ____________________ of the food and found traces of bacteria.
6. A healthy body can ____________________ .
7. I would like to ____________________ with the dental hygienist for 10.00am tomorrow.
8. She had an injection to ____________________ in her leg.
9. The health visitor advised the new parents to ____________________ after feeding.
10. The nurses _____________________ in the patient’s condition.
Exercise 1.
English often uses prefixes to create opposites. There are several different prefixes that are
used. Choose the right prefix for each of the adjectives below and write them into the
table. The first one has been done for you:
Exer
cise 2.
Use ten of the adjectives in the table to complete these sentences. The first one has been
done for you as an example.
Extension. Work with a partner and test each other. One partner closes the book, while
the other asks questions such as «What’s the opposite of conscious?«.
Unit 0000
7
For reference see A & C Black Dictionary of Medical Terms (0 7136 7603 5).
Opposites 1: prefixes
active adequate coherent compatible complete
conscious controllable dependent digested direct fertile fit healthy
hygienic legal movable operable palpable pure qualified reducible
regular sanitary soluble stable well
1. 1.
2.
3.
1. inactive
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
1.
2.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
il- im- in- ir- un-
1. He was found unconscious in the street.
2. He felt ________________ and had to go home.
3. The serum makes the poison ________________.
4. The children have a very _______________ diet.
5. The nurse noted that the patient had developed an ________________ pulse.
6. She used to play a lot of tennis, but she became ________________ in the winter.
7. The surgeon decided that the cancer was ________________.
8. Cholera spread rapidly because of the ________________ conditions in the town.
9. The patient was showing signs of an ________________ mental condition.
10. She has an ________________ desire to drink alcohol.
Exercise 1.
The words listed in the table below are nouns. What are the verb forms of these nouns?
The first question has been done for you as an example.
Exer
cise 2.
Choose ten verbs from Exercise 1 and write a sentence below for each one. Write the
correct form of each verb in the column on the right and leave gaps for the verbs in the
sentences. Cover up the right-hand column and give the sentences to another student as
a test. For example:
8
Unit 0000
For reference see A & C Black Dictionary of Medical Terms (0 7136 7603 5).
Word formation: verbs
1. abuse abuse
2. admission
3. bandage
4. blood
5. breath
6. coagulation
7. consultation
8. convalescence
9. fertilisation
10. identification
11. immunisation
12. implant
13. maceration
14. management
15. occurrence
16. perspiration
17. preparation
18. provision
19. reabsorption
20. regeneration
21. registration
22. regurgitation
23. rehabilitation
24. reproduction
25. resuscitation
26. sedation
27. stammer
28. stitch
29. suppression
30. sweat
She ……………. with her local GP. registered
1. ………………………………………………………………………
2. ………………………………………………………………………
3. ………………………………………………………………………
4. ………………………………………………………………………
5. ………………………………………………………………………
6. ………………………………………………………………………
7. ………………………………………………………………………
8. ………………………………………………………………………
9. ………………………………………………………………………
10. ………………………………………………………………………














