Definite and Indefinite Articles (a, an, the)
TIP Sheet
DEFINITE AND INDEFINITE ARTICLES
In English there are three articles: a, an, and the. Articles are used before nouns or noun equivalents and are a type of adjective. The definite article (the) is used before a noun to indicate that the identity of the noun is known to the reader. The indefinite article (a, an) is used before a noun that is general or when its identity is not known. There are certain situations in which a noun takes no article.
As a guide, the following definitions and table summarize the basic use of articles. Continue reading for a more detailed explanation of the rules and for examples of how and when to apply them.
Definite article
the (before a singular or plural noun)
Indefinite article
a (before a singular noun beginning with a consonant sound)
an (before a singular noun beginning with a vowel sound)
Count nouns — refers to items that can be counted and are either singular or plural
Non-count nouns — refers to items that are not counted and are always singular
| COUNT NOUNS | NON-COUNT NOUNS | |
| Rule #1 Specific identity not known |
a, an | (no article) |
| Rule #2 Specific identity known |
the | the |
| Rule #3 All things or things in general |
(no article) | (no article) |
For the purposes of understanding how articles are used, it is important to know that nouns can be either count (can be counted) or noncount (indefinite in quantity and cannot be counted). In addition, count nouns are either singular (one) or plural (more than one). Noncount nouns are always in singular form.
For example, if we are speaking of water that has been spilled on the table, there can be one drop (singular) or two or more drops (plural) of water on the table. The word drop in this example is a count noun because we can count the number of drops. Therefore, according to the rules applying to count nouns, the word drop would use the articles a or the.
However, if we are speaking of water in general spilled on the table, it would not be appropriate to count one water or two waters — there would simply be water on the table. Water is a noncount noun. Therefore, according to the rules applying to noncount nouns, the word water would use no article or the, but not a.
Following are the three specific rules which explain the use of definite and indefinite articles.
Rule #1 — Specific identity not known: Use the indefinite article a or an only with a singular count noun whose specific identity is not known to the reader. Use a before nouns that begin with a consonant sound, and use an before nouns that begin with a vowel sound.
- Use the article a or an to indicate any non-specified member of a group or category.
I think an animal is in the garage
That man is a scoundrel.
We are looking for an apartment.
- Use the article a or an to indicate one in number (as opposed to more than one).
I own a cat and two dogs.
- Use the article a before a consonant sound, and use an before a vowel sound.
a boy, an apple
◊ Sometimes an adjective comes between the article and noun:
an unhappy boy, a red apple
- The plural form of a or an is some. Use some to indicate an unspecified, limited amount (but more than one).
an apple, some apples
Rule #2 — Specific identity known: Use the definite article the with any noun (whether singular or plural, count or noncount) when the specific identity of the noun is known to the reader, as in the following situations:
- Use the article the when a particular noun has already been mentioned previously.
I ate an apple yesterday. The apple was juicy and delicious.
- Use the article the when an adjective, phrase, or clause describing the noun clarifies or restricts its identity.
The boy sitting next to me raised his hand.
Thank you for the advice you gave me.
- Use the article the when the noun refers to something or someone that is unique.
the theory of relativity
the 2003 federal budget
Rule #3 — All things or things in general: Use no article with plural count nouns or any noncount nouns used to mean all or in general.
Trees are beautiful in the fall. (All trees are beautiful in the fall.)
He was asking for advice. (He was asking for advice in general.)
I do not like coffee. (I do not like all coffee in general.)
Additional Information Regarding the Use of Articles
- When indicating an unspecified, limited amount of a count or noncount noun, use some.
My cousin was seeking some advice from a counselor (not advice in general or advice about everything, but a limited amount of advice).
I would love some coffee right now (not coffee in general, but a limited amount of coffee).
We might get rain tomorrow. Some rain would be good for the crops (a certain amount of rain, as opposed to rain in general).
There are some drops of water on the table (a limited number, but more than one drop).
- Noncount nouns are those which usually cannot be counted. Following are some common examples:
◊ Certain food and drink items: bacon, beef, bread, broccoli, butter, cabbage, candy, cauliflower, celery, cereal, cheese, chicken, chocolate, coffee, corn, cream, fish, flour, fruit, ice cream, lettuce, meat, milk, oil, pasta, rice, salt, spinach, sugar, tea, water, wine, yogurt
◊ Certain nonfood substances: air, cement, coal, dirt, gasoline, gold, paper, petroleum, plastic, rain, silver, snow, soap, steel, wood, wool
◊ Most abstract nouns: advice, anger, beauty, confidence, courage, employment, fun, happiness, health, honesty, information, intelligence, knowledge, love, poverty, satisfaction, truth, wealth
◊ Areas of study: history, math, biology, etc.
◊ Sports: soccer, football, baseball, hockey, etc.
◊ Languages: Chinese, Spanish, Russian, English, etc.
◊ Other: clothing, equipment, furniture, homework, jewelry, luggage, lumber, machinery, mail, money, news, poetry, pollution, research, scenery, traffic, transportation, violence, weather, work
- Geographical names are confusing because some require the and some do not.
◊ Use the with: united countries, large regions, deserts, peninsulas, oceans, seas, gulfs, canals, rivers, mountain ranges, groups of islands
the Gobi Desert
the United Arab Emirates
the Sacramento River
the Aleutians
◊ Do not use the with: streets, parks, cities, states, counties, most countries, continents, bays, single lakes, single mountains, islands
Japan
Chico
Mt. Everest
San Francisco Bay
Examples of the Use of Articles
I do not want a gun in my house (any gun).
The gun is in his closet (implies there is a specific gun).
I am afraid of guns (all guns in general).
She sent me a postcard from Italy (an unspecific postcard — not a letter, not an e-mail).
It’s the postcard that I have in my office (one specific postcard).
Getting postcards makes me want to travel (any postcard in general).
I have a dog (one dog).
The dog is very friendly (the dog that I have already mentioned).
Dogs make great pets (dogs in general).
Greta needs furniture in her apartment (furniture is a noncount noun).
She is going to select the furniture that she needs (the specific furniture that she needs).
She hopes to find some furniture this weekend (an unspecified, limited amount of furniture).
We are going to see the Statue of Liberty this weekend (the only Statue of Liberty).
How to Use Articles in English? Articles are used to introduce a noun. There are two main types of articles in English. In which, “a, an” is an indefinite article; “the” is a definite article.
Here, let’s learn how to use these articles with English tivi right now.
You might also like: ALL the English Grammar Basics You Need
How to Use Indefinite Articles “A” and “An”
1. Use “a” or “an” before a singular countable noun. They mean one. They are used in sentences that are general or refer to a subject that has not been mentioned before.
- A ball is round. (General, generic, all balls)
- I saw a boy in the street. (We don’t know which boy, not mentioned before)
2. The article “an” is used before words that begin with a vowel sound (in pronunciation, not in writing). Consists of:
- Words that start with the vowels “a, e, i, o”:
Example: an aircraft, an empty glass, an object
- Some words that start with “u”:
Example: an uncle, an umbrella
- Some words that start with a silent “h”:
Example: an heir, half an hour
- Words that begin with an abbreviation:
Example: an S.O.S/ an M.P
3. Use “a” first:
- Words that start with a consonant. These include the rest of the letters and some cases start with “u, y, h“.
Example: a house, a university, a home party, a heavy load, a uniform, a union, a year income, etc.
- Before a noun that begins with “uni…” and “eu”
Example: a university/ a uniform/ universal/ union, Europe, eulogy, euphemism, eucalyptus
- Used in idioms indicating a certain quantity such as: a lot of/a great deal of/a couple of/a dozen of.
- Use before certain numbers, usually thousands, hundreds like: a/one hundred – a/one thousand.
- Use before “half” when it follows a whole unit: a kilo or a half, or when it is combined with another noun to indicate a half (when written with a hyphen): a half – share, a half – holiday.
- Used with fractional units such as: 1/3 (a/one-third), 1/5 (a/one -fifth).
- Used in idioms indicating price, speed, rate: a dollar, a kilometer, an hour, 4 times a day.
You might also like: Modal Verbs: Definition, Usage Examples and Exercises
How to Use the Definite Article “The”
1. Use “the” in front of a noun that has been specifically identified in terms of its properties, characteristics, position, or has been mentioned before, or common, well-known concepts.
- The boy in the corner is my friend.
- The earth is round.
2. With uncountable nouns, use “the” if referring to a specific thing, not “the” if speaking in general.
- Sugar is sweet.
- The sugar on the table is from Cuba.
3. With plural countable nouns, when they mean to represent a class of things of the same type, do not use “the”.
- Oranges are green until they ripen.
- Athletes should follow a well-balanced diet.
4. Some common cases of using “The” according to the above rule:
- The + noun + preposition + noun:
– The girl in blue, the Gulf of Mexico.
- Use before superlative or only comparative adjectives:
– The only way, the best day.
- Used for specified time periods:
– In the 1990s
- The + noun + relative pronoun + subordinate clause:
– The man to whom you have just spoken is the chairman.
- The + singular noun represents a group of animals or things:
– The whale = whales, the deep-freeze
- For “man” when it means “human” absolutely do not use “the”:
– Since man lived on the earth…
- Used before a singular noun to refer to a certain group or class of people in society:
– The small shopkeeper, The top official.
- The + adj: Symbolizes a group of people, they are never allowed in the plural but are considered plural nouns. Therefore, verbs and pronouns that go with them must be in the 3rd person plural:
– The old = The old people (The old are often very hard in their moving)
- The + name of the choir/classical orchestra/popular band:
– The Back Choir/The Philharmonique Philadelphia Orchestra/The Beatles.
- The + names of newspapers (not magazines) / ships / hot air balloons:
– The Times/ The Titanic/ The Hindenberg
- The + family surname in the plural = home family:
– The Smiths = Mr. Smith, Mrs. Smith, and their children
- Usually do not use “the” before a given name unless there are many people or things with the same name and the speaker wants to refer to a particular person among them.
– There are three Sunsan Parkers in the telephone directory. The Sunsan Parker that I know lives on the First Avenue.
- Similarly, do not use “the” before meals: breakfast, lunch, dinner
– We ate breakfast at 8a.m this morning.
- Unless to refer to a specific meal:
– The dinner that you invited me last week was delicious.
- Do not use “the” before some nouns such as: home, bed, church, court, jail, prison, hospital, school, class, college, university etc… when it goes with verbs and prepositions of motion indicating only go there for the main purpose or get out there for the main purpose:
– Students go to school everyday.
– The patient was released from hospital.
- But if going there or leaving is not for the main purpose, use “the”
– Students go to the school for a class party.
– The doctor left the hospital for lunch.
5. The table uses “the” and does not use “the” in some typical cases
| Use “The” | Not Use “The” |
|
1. Used before names of oceans, rivers, seas, bays and lake clusters (plural) – The Red Sea, the Atlantic Ocean, the Persian Gufl, the Great Lakes 2. Before the name of the mountain range: – The Rocky Mountains 3. Before the names of only objects in the universe or in the world: – The earth, the moon 4. The schools, colleges, universities + of + proper noun – The University of Florida 5. The + ordinal + noun – The third chapter. 6. Before the names of regional wars, provided that the name of the region must be magnetized – The Korean War, The Vietnamese economy 7. Before names of countries with two or more words (except Great Britain) – The United States, The Central African Republic 8. Before the names of countries that are considered an archipelago or an archipelago – The Philippines, The Virgin Islands, The Hawaii 9. Before the names of historical documents or events – The Constitution, The Magna Carta – The Indians – The violin is difficult to play. – Who is that on the piano? |
1. Before the name of a lake – Lake Geneva 2. Before the name of a mountain – Mount Vesuvius 3. Before the names of planets or constellations – Venus, Mars 4. Before these field names if preceded by a proper name – Stetson University 5. Before nouns with a count – Chapter three, Word War One 6. Before the names of countries, there is only one word: – China, France, Venezuela, Vietnam 7. Before names of countries that begin with New, a directional adjective: – New Zealand, North Korean, North Africa 8. Before the names of continents, provinces, states, cities, counties, districts: – Europe, Florida 9. Before the name of any sport – baseball, basketball 10. Before abstract nouns (except for some special cases): – freedom, happiness 11. Before the names of subjects in general – Mathematics 12. Before the names of holidays and New Year – Christmas, Thanksgiving 13. Before the names of musical instruments in specific musical forms (Jazz, Rock, classical music…) – To perform jazz on trumpet and piano |
You might also like: What is a Noun? Nouns in English with Example
Articles A, An, The Exercises
1: ……………….. umbrella.
- A
- An
2: ……………….. European.
- A
- An
3: I read……………….. great book today.
- a
- an
4:……………….. ant is……………….. insect.
- A/ an
- An/ an
- The/ an
- ø
5: The Nile is……………….. river.
- a
- an
- the
- ø
6: Can you tell me how to get to……………….. bank from here?
- a
- an
- the
- ø
7: I can’t believe I failed……………….. yesterday’s test!
- a
- an
- the
- ø
8: ……………….. apple a day keeps……………….. doctor away.
- A / the
- An / the
- The/ a
9: You should evaluate……………….. equipment and make sure fitness machines are modern and in working order.
- a
- an
- the
10: Harold is……………….. most obnoxious person I know.
- the
- an
- a
11: Diana is……………….. very nice person.
- the
- a
- an
12: I’d like to invite him to……………….. dinner next week, if that’s OK with you.
- the
- a
- an
- ø
13: I saw……………….. man going into the office. I don’t know who……………….. man was.
- the/a
- a/the
- a/a
Question 14: The greatest invention of the 20th century is……………….. computer.
- the
- a
- an
15: A volcano has erupted in……………….. Philippines recently.
- a
- the
- an
16: ……………….. city museum is closed today.
- A
- An
- The
- ø
17: I’ve noticed that……………….. Spanish eat a lot of vegetables.
- an
- a
- the
18: When you come out the lift, you’ll see two doors,……………….. red one and
……………….. blue one. My door is……………….. red one.
- the/the/a
- a/a/the
- a/a/a
- the/the/the
19: Could you close……………….. door, please? It’s really cold.
- an
- a
- the
20: She has been playing……………….. flute for ten years.
- a
- an
- the
- ø
Read more: English Grammar
Articles A, An, The Exercises with Answers
1: ……………….. umbrella.
- A
- An
2: ……………….. European.
- A
- An
3: I read……………….. great book today.
- a
- an
4:……………….. ant is……………….. insect.
- A/ an
- An/ an
- The/ an
- ø
5: The Nile is……………….. river.
- a
- an
- the
- ø
6: Can you tell me how to get to……………….. bank from here?
- a
- an
- the
- ø
7: I can’t believe I failed……………….. yesterday’s test!
- a
- an
- the
- ø
8: ……………….. apple a day keeps……………….. doctor away.
- A / the
- An / the
- The/ a
9: You should evaluate……………….. equipment and make sure fitness machines are modern and in working order.
- a
- an
- the
10: Harold is……………….. most obnoxious person I know.
- the
- an
- a
11: Diana is……………….. very nice person.
- the
- a
- an
12: I’d like to invite him to……………….. dinner next week, if that’s OK with you.
- the
- a
- an
- ø
13: I saw……………….. man going into the office. I don’t know who……………….. man was.
- the/a
- a/the
- a/a
Question 14: The greatest invention of the 20th century is……………….. computer.
- the
- a
- an
15: A volcano has erupted in……………….. Philippines recently.
- a
- the
- an
16: ……………….. city museum is closed today.
- A
- An
- The
- ø
17: I’ve noticed that……………….. Spanish eat a lot of vegetables.
- an
- a
- the
18: When you come out the lift, you’ll see two doors,……………….. red one and
……………….. blue one. My door is……………….. red one.
- the/the/a
- a/a/the
- a/a/a
- the/the/the
19: Could you close……………….. door, please? It’s really cold.
- an
- a
- the
20: She has been playing……………….. flute for ten years.
- a
- an
- the
- ø
Download File: Articles A, An, The Exercises PDF
Conclusion
You have learned all about articles in English grammar. Be proactive in doing exercises to get the best results.
Subscribe to the English TV channel on Youtube to improve your English skills!
Post Views: 4,592
Definite and Indefinite Articles ( A, An, The)
What is an Article?
The word A, An/The says Article. According to Modern English Grammar, Article comes/called Determiners, which are used before Nouns. If an adjective comes before Noun then use the Article before the adjective.
If Noun comes before an Adjective and an Adjective comes before Adverb then we use the article before the Adverb.
These are some Examples
Sita is a girl.
Sita is a very good girl.
Sita is an ideal girl.
Sita is an intelligent girl.
This is the horse.
This is the strongest horse.
In many situations Articles come after such as All, Both, Such, Double, Half, Rather, etc.
These are some Examples
All the boys.
Such a woman.
half an hour.
Double the amount.
If the Adjective comes before Noun and How/so/too/as comes before the Adjective, then the article comes middle of the adjective & Noun. Such as How/so/too/as + adjective + a/an + noun are these serial.
These are some Examples
How fine a day.
too proud a girl
It is so fine a day!
How brave a warrior was he!
Definite and Indefinite Articles.
There are two types of Articles:-
1. Definite Articles- The
2. Indefinite Articles- A/An
What are Definite Articles?
Definite Articles says “The”. The definite article (the) is used before a noun to indicate that personal, certain, or former acquaintance; which has already been discussed and well-acquainted speaker and audience. In other words, The uses were to denote certain metals/persons/animals. The is used with countable Nouns (Singular noun & Plural noun) and uncountable nouns.
Uses of Definite Article
1. Before a Noun
We use ” The ” when we talk about something that has already been referred to in the prior sentence, we use “The”.
Example:
A cat got in honor of our dog today. The dog wins the battle.
2. Already Noun Knows to the User
When the user already knows the thing you are talking about, at such places use “The”. Instead of describing that thing since it is known to the user.
Example:
“Mr. Micheal is wearing a suit at the party.” In this example, a person already knows about the party to which the other person is referring in this sentence, and thus used “the” to refer to the party.
3.Before Unique Nouns
“The” will always refer to Universal things Like The Sun, The Moon, The Arabian Ocean, The Bermuda Triangle, The Eiffel Tower, The Himalayas, etc. All these Universal things or Places are certain and would not change. So you use “The” to refer to such things.
4.Superlative Adjectives
Superlative adjective is used for Definite Nouns and to describe some special and unique.
Example:
My mother cooks the Best North Indian Food in Society.
At 3307 ft. Height, Burj Khalifa Tower is The Tallest tower in the world.
Here “Best” and “Tallest” are the superlative adjectives, and thus we used “The” before them.
5.Before Adjectives are Used as Nouns
When you are talking about some advice or duty, we also use “The” in such places.
Example:
The government should do something for the jobless people.
Here Jobless People are used both as a noun and adjective, that’s why we used “The” before it.
6.Proper Nouns
With Proper Nouns such as Nation’s Name, Plural names of nations, some titles, some associations, some structures, papers, masterpieces, explicit family names, mountains, waterways, oceans, gatherings of islands, and deserts, that use “the”.
Example:
The Indian sea, The Bay of Bengal, The Netherlands, The Caspian, The United States of America, The Taj Mahal, The Times of India, The Suez Canal, The Bay of Bengal, and The Guptas.
7. With Nationalities
When we talk about any nationality, we must use “the” before it to emphasize that word.
Example:
The Mughals and The British controlled India for a long time.
Regardless of whether nationality is in the plural. Like:
The Indians.
The Chinese.
The Americans.
8. Mentions of Services and Systems
Switch on the television to watch the newest show.
We must go to the police station to report the crime.
You should take this to the buyer’s court.
9.Comparative Proclamations
When we compare two things with each other motivational advice or something else, must be used “in such a sentence.
Example:
The more he works, the more he will be successful.
The more we travel, the more we shall fall in love with Nature.
General Rules / Tricks to use “The” Definite Article
• Use them for things that have been mentioned already.
• Use when there is something unique, even if not mentioned already.
• Use them when we are expressing a statement for a particular person or object.
What are Indefinite Articles?
The indefinite article says “A/An”. Because it does not refer to a particular person or thing, but rather to an indefinite person or thing.
Uses of Indefinite Article-
1. Before Singular Countable Noun (Common noun & Collective noun)
2. If the adjective or adverb +adjective comes before Noun then A/An is used according to comes closest word.
Example:
She is a girl.
She is an extremely beautiful girl.
3. If word sounds start with vowel sounds, then use “An”. If a word sound starts with a consonant sound then use “A”.
4. Some words are starting with vowel letters but it is not necessary its sound starts with a vowel sound.
5. “A/An” is used in the sense of one or anyone.
Example:
I saw a Boy.
A farmer had three sons.
6. “A/An” using before rate, weight, and speed indicators.
Example:
Grain sells for eight rupees a kilo.
The car runs sixty kilometres an hour.
7. “A/An” comes before count pointers.
Example:
A couple, A dozen, A hundred, A thousand, etc.
I have a hundred rupees.
He has a dozen bananas.
Definite and Indefinite Articles Examples
Definite Articles Examples:
- The dog is a faithful pet.
- The pen is Japanese.
- Govind is the tallest boy in the class.
- Who invented the radio?
- Mahendra will play the violin.
- Ramesh missed the last train for his hometown.
- Where is the headmaster?
- The Congress party is the national party.
- Mr Narendra Modi is the prime minister.
- Rakesh goes to the office at 10.
Indefinite Articles Examples:
- A lion killed a deer.
- An apple grows on a tree.
- Mr Ramshanker Katherina is an M.P.
- They filled an F.I.R.
- You are a Shakespeare.
- He is a Sachin Tendulkar.
- We walk Five kilometres an hour.
- Radha ran without an ambarella.
- Mr Shanky is a doctor.
- An Elephant killed a man.
Difference Between Definite and Indefinite Articles
Serial No. |
Definite Articles |
Indefinite Articles |
|
1 |
Definite Articles are used to indicate something specific | Indefinite Articles are used to indicate something nonspecific |
|
2 |
Can be used after introducing the noun or noun phrase | Can be used to introduce the noun or noun phrase |
|
3 |
Can be used with singular and plural nouns and can | Can be used with plural nouns |
|
4 |
Used to discuss something that is already known by the reader or listener can not can not | Cannot be used to discuss something that is already known by the reader or listener |
|
5 |
Used with a countable and uncountable noun | Cannot be used with a countable and uncountable noun |
Definite and Indefinite Articles Exercise
Fill in the blanks with the appropriate articles in the following sentences:
1. I am …… honest boy.
Ans: An
2. …… milk was very tasty.
Ans: The
3. ……. milk of this cow is very sweet.
Ans: The
4. ……. Coffee was hot.
Ans: The
5. This is ……. interesting story.
Ans: An
6. You are ….. Indian.
Ans: A
7. …….. Hour is enough to finish my work.
Ans: An
8. Have you ….. two rupee notes?
Ans: A
9. It was ….. one-sided game.
Ans: A
10. He is ….. university professor.
Ans: A
11. Ramu is ….. one-eyed boy.
Ans: A
12. You are ….. B.A.
Ans: A
13. He is ….. M.A.
Ans: An
14. It was ….. unique sight.
Ans: A
15. Are you …… I.A.S.?
Ans: An
16. He is ….. F.O.
Ans: An
17. Are you …… forest officer?
Ans: A
18. …… girl I meet yesterday has come today.
Ans: The
19. ……. gold of India is not very yellow.
Ans: The
20. ……. water of this well is pure.
Ans: The
21. ……. watch was old.
Ans: The
22. I have ….. watch.
Ans: A
23. I lost ……. watch you gave me.
Ans: The
24. ……. Ram of ….. Ramayan is …… ideal personality.
Ans: The, The, An
25. …….. horse is …… useful ….. animal.
Ans: A/The, An
26. ……. Indian Nation was …..important daily.
Ans: The, An
27. …… TajMahal is …. historical building.
Ans: The, A
28. …… man you met yesterday is ….. very bad man.
Ans: The, A
29. ……. coffee was very good.
Ans: The
30. …… Ramayan is ….. religious book of …… Hindus.
Ans: The, A, The
FAQ’s
Que 1. What are the 4 definite articles?
Ans. In English grammar there, are three articles: a, an, and the. The definite article (the) is used before a noun to indicate that the identity of the noun is known to the reader/listener. In Spanish, we have to choose between four definite articles: el, la, Los, and las. Which one we choose depends on the noun which follows. All nouns (including words for things) are either masculine or feminine: this is called their gender and they can also be either singular or plural.
Que 2. What are the 2 types of articles?
Ans. There are two types of Articles:-
1. Definite Articles- The
2. Indefinite Articles- A/An
Que 3. What is the difference between definite and indefinite tenses?
Ans. We use indefinitely to mean non-specific. Indefinite is general. We use definitely to mean specific.
Que 4. What are the 3 indefinite articles?
Ans. There are three indefinite articles in English – two for the singular form (a, an) and one for the plural form (some).
Использование артиклей вызывает существенные трудности у всех, кто пытается освоить английский язык, ведь в русском языке артиклей нет, а в английском они не имеют самостоятельного значения, в их применении слишком много правил и исключений.
Неопределенный артикль — The indefinite article
В английском языке существуют две формы неопределенного артикля (indefinite article) a and an. То какой артикль использовать, зависит от первой буквы слова, которое следует за артиклем. Если слово начинается с согласной буквы, а также u и eu (если они произносятся с использованием согласного звука / j /), то используется артикль а. Если слово начинается с гласной буквы (a,e,i,o,u) или с немой буквы h, то используется артикль an.
E.g.,
A dog
A table
An arm
An engineer
An old man
An ugly woman
A European (согласный звук /j /)
A union (согласный звук /j /)
An hour (немая буква h)
A house
Неопределенный артикль используется только с исчисляемыми существительными в единственном числе, если речь идет об одном человеке или предмете, еще неизвестном читателю или собеседнику, если человек или предмет упоминается впервые:
He bought a book yesterday.
There is a telephone in the room.
Неопределенный артикль употребляется, если мы хотим показать, что человек или предмет принадлежит к определенному классу или группе, перед названиями профессий и титулов, национальностей и религий.
My brother is an engineer.
This is a dictionary.
Ricardo is an Italian footballer.
Mary is a buddhist.
Неопределенный артикль употребляется, если речь идет о всяком, любом представителе определенного класса людей или предметов.
A child can understand it (=All children)
A triangle has three sides (=All triangles)
Неопределенный артикль употребляется в восклицательных предложениях перед исчисляемыми существительными в единственном числе, стоящим после «what» and «such»:
What a shame !
She is such a clever girl!
What a lovely day!
Неопределенный артикль не используется в таких же предложениях с существительными во множественном числе и неисчисляемыми существительными:
These are such interesting books. (= plural noun)
Have you ever seen such weather? (= uncount noun)
Неопределенный артикль используется в значении «один» и относится к единичному лицу, предмету или единице измерения:
I’ll come in an hour.
He didn’t say a word.
He bought one kilogram of sugar.
You can’t run a mile in 5 minutes.
He has won a thousand pounds.
Неопределенный артикль используется в следующих фразах и выражениях:
We use the indefinite article in the following phrases and expressions:
A lot of
A great deal of
A great number of
A few
A little
To have a cold/headache
To have a good time
To be in a hurry
For a short (long) time
Определенный артикль — The definite article
Слово»the» — самое частоупотребимое слово в английском языке. Определенный артикль произошел от указательного местоимения «that».
Определенный артикль «the» используется, если оба собеседника знают, о ком или о чем идет речь, или если предмет разговора уже был упомянут ранее.
Please close the window.
When I entered the room, I saw a man. The man was very old.
Определенный артикль используется, если человек или предмет являются единственными в своем роде или единственными в данной ситуации:
Show me the letter which was received yesterday.
The earth is millions of miles from the sun.
Dad, can I borrow the car?
Look at the girl over there.
The president will be speaking on TV tonight.
Определенный артикль используется перед прилагательными в превосходной степени, порядковыми числительными и названиями десятилетий:
He is the tallest boy in the class.
This is the third time I have visited him.
He was born in the seventies.
This is the best wine I have ever drunk.
Определенный артикль используется с названиями морей, рек, горных цепей и групп островов, с названиями стран во множественном числе или если название включает в себя слова «Республика», «Королевство», «Штаты», «Федерация», «Эмираты»:
I have never been to the Netherlands.
He is from the Republic of Ireland.
I will go on a cruise down the Pacific Ocean.
They are travelling in the Sahara Desert
Определенный артикль используется с существительными в единственном и множественном числе, если речь идет о целом классе объектов (например, богатые, бедные, пожилые, безработные, члены одной семьи):
The pineapple grows in southern countries.
Life can be very hard for the poor.
The Browns have left Paris.
Определенный артикль используется с существительными во множественном числе, если речь идет о всех представителях данного класса.
Give me a list of the members.
Определенный артикль используется в определениях со словами same, very, last, following, next, only:
He is the very person I need.
This is the only book I have.
Определенный артикль используется с собственными именами существительными (названиями зданий, музеев, произведений искусства, памятников, газет, гостиниц и ресторанов):
He works for the New York Times.
They would like to visit the Eiffel Tower.
We ate at the Royal Oak.
Определенный артикль используется в следующих фразах и выражениях:
In the morning/in the evening/in the afternoon/in the night
The day before yesterday/the after tomorrow
To tell the truth
On the other hand
On the right (left)
Нулевой артикль — The zero article
Артикль не используется (или используется в нулевой артикль) в большинстве названий стран (кроме перечисленных выше), с названиях языков, имен людей и титулов, если они стоят вместе с именем.
My father’s name is John.
He lives in China.
She was born in Germany
I speak French.
Prince Charles is Queen Elizabeth’s son.
Артикль не используется с большинством названий городов, улиц, магазинов, вокзалов, аэропортов, отдельных гор, озер и островов:
They’re flying into Gatwick.
New Street Station is in the centre of Birmingham.
Can you go to Asda for me?
Артикль не используется со словами school, college, hospital, university, and government, class, prison and camp, если они имеют значения института, а не конкретного здания:
She was taken to hospital.
Нулевой артикль используется с существительными во множественном числе или если речь идет о предметах именно данного класса:
Boys like to play football.
They packed the goods in bags and boxes.
Нулевой артикль используется с неисчисляемыми существительными, с названиями «завтрак», «обед» или «ужин».
Did you have breakfast this morning?
Milk is often added to tea in England.
Нулевой артикль используется с названиями видов спорта, игр, видов деятельности и профессий:
I love swimming.
I’ll probably study engineering.
Нулевой артикль используется с датами:
I was born in 1985.
Нулевой артикль используется с названиями дней недели, месяцев, времен года, праздников, времени суток:
on Monday
in March
in summer
at Christmas
at noon
at night
at midnight
Нулевой артикль используется в следующих выражениях и фразах:
At work
At home
At school
At first sight
By train, bus,plane etc
By sea, by land, by air
By mistake
By chance
By heart
Узнайте свой уровень английского языка, пройдя бесплатный онлайн тест на нашем сайте.
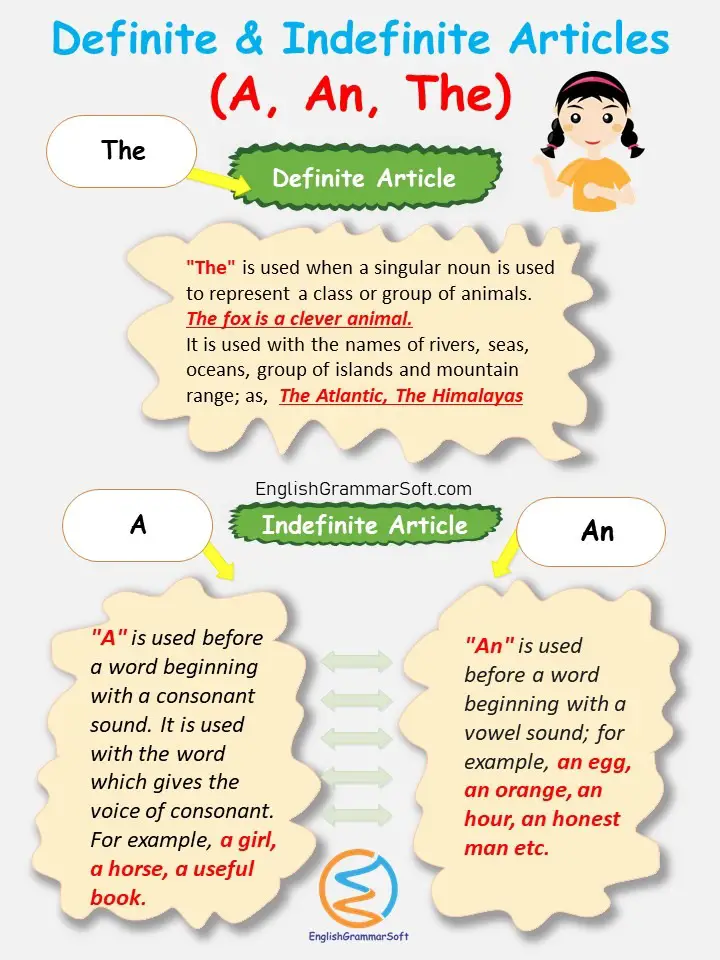
‘A’, ‘An’, and ‘The’ are called articles. They are really demonstrative. It means they are adjectives used to point to something.
There are two kinds of articles
- Indefinite Articles
- Definite Article
Indefinite Articles
“A” and “An” are called indefinite articles because they only generalize a noun; as, a student; that means any student.
Use of “a” and “an”
“A” is used before a word that begins with a consonant sound, but “an” is generally used before a word that begins with a vowel sound.
Examples:
- I am going to a party this evening. (Notice that the first letter of party begins with a consonant sound.)
- An umbrella is useful in rainy weather. (Notice that the first letter of umbrella begins with a vowel sound.)
The choice between “a” and “an” is determined by a sound of a singular countable noun.
“A” is used before a word beginning with a consonant sound. It is used with the word which gives the voice of consonant. For example, a girl, a horse, a useful book.
“An” is used before a word beginning with a vowel sound; for example, an egg, an orange, an hour, an honest man, etc.
In some cases, an indefinite article gives sense of “one” or “any”.
For example,
- I saw a man in the street.
It is used to make a common noun of a proper noun; as,
- He is a newton of our country.
Definite Article
Uses of “The”
“The” is used when a singular noun is used to represent a class or group of animals.
- The fox is a clever animal.
- The horse is a useful animal.
It is used with the names of rivers, seas, oceans, group of islands and mountain range; as,
- The Atlantic
- The Ravi
- The Arabian Sea
- The West Indies
- The Netherlands
- The Himalayas
It is used before the names of certain book newspapers, journals; as The Holy Quran is our sacred book.
The Nation is a famous newspaper.
It is used before superlatives and first, second and only etc, used as adjectives or pronouns. For example,
- The first week
- The best day
- The only way
She is the most beautiful girl in the class.
It is used with historical events.
The partition of India is a historical event.
It is used with names of unique objects; as,
the earth, the sea, the sky.
It is used before a noun mentioned second time; as,
I saw a man in the street, the man was carrying a sack.
We use it before an adverb with comparatives.
- The more we get, the more we desire.
- The higher we go, the cooler it is.
The omission of the article
1 – “A” and “An” are not used before the plural nouns.
2 – Uncountable nouns are always singular but we do not use “a” or “an” with them. These nouns are often preceded by some, any, no, a little, etc. or by nouns such as bit, piece, slice. See these examples
- I don’t want (any) advice.
- I don’t need a piece of advice.
3 – We do not use “a” or “an” before the names of meals except when these are preceded by an adjective.
For example,
We have breakfast at 8 a.m.
4 – “The” is not used before proper nouns, material nouns, and abstract nouns; as,
- Afzal will go to Lahore tomorrow.
- Gold is a precious metal.
- Honesty is the best policy.
5 – “The” is not used before names of languages and skills.
- She can speak Arabic frequently.
- He is weak in French.
- He is a doctor by profession.
Read also: 27 Figures of Speech with Examples

.png)