There are so many words with spellings that just don’t appear to make sense in the English language. Many students have many worries when writing an essay or paper with so many hard words to spell. Although we live in an age where autocorrect is the new fad, the importance of spelling correctly can not be denied. It is always hard to spell words that do not appear the way they sound.
To aid school graders, college students, and adults alike, we have some of the hardest words to spell. This list of hard words to spell spans across words that are hard to spell for all categories of students and adults. Are you ready to go through our list of very hard words to spell? Here’s our list of top 100 hardest words to spell. Let’s explore!
Hardest Words To Spell Ever
The English language could be a real pest, even for native speakers. Sometimes, the spelling of some words seems to slip out of our heads the very times we need them, while sometimes, we just don’t know how to spell some words and make funny typos.
There are many hard English words to spell. A word may be difficult to spell for many reasons. It could be because it is from a language very different from the English language, e.g., Afrikaans, Sanskrit, etc., or because the pronunciation is very different from the spelling. A word can also be difficult if it has a silent letter or more or a peculiar double letter. Here’s a list of some super hard word to spell!
- Abacaxi
- Abgesang
- Aitch
- Autochthonous
- Chiaroscurist
- Coelacanth
- Kierkegaardian
Long Hard Words To Spell
- Antidisestablishmentarianism
- Floccinaucinihilipilification
- Pneumonoultramicroscopicsilicovolcanokoniosis
- Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism
- Psychoneuroendocrinological
- Hepaticocholangiogastrostomy
- Spectrophotofluorometrically
Easy Words That Are Hard To Spell
Surprisingly, some of the easiest words to spell in the English language often get misspelled. The words are usually so common and have been used so commonly that it’s unbelievable to know that many can’t spell it correctly – including you! So here’s a list of common words that are hard to spell.
- Misspell
- Pharaoh
- Weird
- Intelligence
- Pronunciation
- Handkerchief
- Logorrhea
Hard Words To Spell For 6th Graders
If you are looking for a nice spelling challenge for a 6th grader, you’re in the right place. Take a look at these hardest English words to spell for 6th graders.
- Noticeable
- Vacuum
- Recommend
- Chaos
- Accommodation
- Accidentally
- Strengthen
- Pneumonia
- Acknowledgment
- Occasion
- Descendant
- Liaison
Hard Words To Spell For 7th Graders
Looking for a 7th grade selling challenge, here are some really hard words to spell for 7th graders.
- Association
- Atmosphere
- Bicycle
- Corollary
- Confetti
- Defalcation
- Bizarre
- Braggadocio
- Echelon
- Gelatinous
- Panache
- Xylem
Hard Words To Spell For 8th Graders
- Condescend
- Discernible
- Concede
- Assuage
- Contemptuous
- Imprudent
- Conscience
- Bazaar
- Ferocious
- Pistachio
- Eloquent
- Lucrative
Hard Words To Spell For 9th Graders
- Stretch
- Substantial
- Superintendent
- Pageant
- Pamphlet
- Parachute
- Nuisance
- Omitted
- Tyranny
- Unanimous
- Vengeance
- Villain
Hard Words To Spell For 12th Graders
- Absolution
- Acerbic
- Adumbrate
- Dearth
- Encumber
- Expunge
- Insidious
- Penurious
- Resplendent
- Saccharine
- Scurrilous
Hard Words To Spell For College Students
- Arctic
- Australia
- Caribbean
- Euclidean
- Presbyterian
- Teutonic
- Abysmal
- Boulevard
- Bouillon
- Bourgeois
Hard Words To Spell For Adults
- Acquiesce
- Andragogy
- Criterion
- Holistic
- Incongruous
- Juxtaposition
- Malapropism
- Obfuscate
- Onomatopoeia
- Soliloquy
There are many spelling rules in the English language that often, it’s difficult to remember which applies. Learning how to spell hard words is a bane to students and adults alike. But don’t fret, we have some proven techniques that will make you conquer most words and spell them with ease.
It may be considered rather unfortunate that the old-fashioned rote memorization method remains the best way to learn how to spell the hardest words. However, memorization techniques have gotten better, making the learning process much more bearable.
There are several mnemonic training techniques and methods used by champion spellers worldwide, such as kinetic learning. This learning technique is the association of mental concepts with a series of movements which make learning much fun and retentive than mere repetition. So here are some tips for learning how to spell hard words!
- Trace the Letters
With one hand, track the letters on your palm as you pronounce them. This method is an easy way to apply kinetic learning. You use three learning pathways that reinforce the words in the memory. These are:
- The motion of your mouth and lips
- The movement of the fingers of one hand moving
- The feeling of the motion on the other palm
For a more active learning experience, you can engage the larger body. Also, movement makes more blood flow to the brain, making it more active and receptive.
- Vocalize the Letters
Another useful tool is to vocalize the letters of the words as you learn them. Repetition words by vocalization give those words a melodic feel, imprinting them more firmly on your mind, just like nursery rhymes. If used appropriately, this leaning method will help you recall words when other methods fail.
- Design Short Study Sessions
Short study sessions are usually more effective for long-term memorization. When you take breaks, the brain can refresh itself and get ready to take a new set of words without becoming overwhelmed.
- Use Repetitive Drills
It usually takes more than one repetition to get spelling correct consistently. Repeat the words you want to learn many times until it sinks into your mind and becomes melodic.
- Group The Words
This is another effective strategy for learning how to spell hard words. Grouping words imply that you put words that follow the same spelling pattern in a group. For example, words with “-ei-“combinations will follow the same pattern. Learning all similar words at the same time will help you build association and reinforce spellings. This method will help you to categorize words, which makes memorization much more manageable.
- Read, Read, Read
One of the best methods to learn how to spell words is to increase your reading. By merely reading and consuming a wide variety of books like wildfire, you’ll become a spelling champion without knowing it. Reading simply makes all the above rules much less confusing. You’ll also be able to build your intuition level and know just when a spelling looks wrong.
- Have Fun
Learning becomes easier if you can apply fun to it. Take the words you want to memorize and see how you can weave fun into it!
So here we are! 100 hard words to spell and how to learn to spell hard words. Wishing you luck in your spelling bee and life in general! If you need homework help, just contact our English assignment helpers.
-
#1
Hello everyone, I hope you are doing well. I just found this phrase :
Jane is the hardest-working student.
I thought the correct form would be:
Jane is the most hard-working student.
I researched and some people say both are correct, however when you use another compound adjective like WORLD-FAMOUS, what is the correct form? For example:
Certainly, Michael jackson is the most world-famous artist.
or
Certainly, Michael Jackson is the worldest-famous artist.
-
#2
I agree that both forms of the original sentence about Jane are acceptable.
«The worldest-famous» isn’t one of the possible options for the second sentence; the -est suffix would have to be applied to «-famous»: «the world-famousest.» But we would never say that either; it would have to be «the most world-famous artist.»
-
#3
Jane is the hardest-working student.
Jane is the most hard-working student.
Although both are grammatically correct, «hardest-working» is sort of a set term, so we would always use that to mean that she works harder than anyone else. The late singer James Brown was known as «the hardest-working man in show business.»
However, «the most» can also be used to mean just «very,» in which case the second one is better.
Ex.
Your son is the most thoughtful young man. (= very thoughtful)
They sent me the most touching letter. (= very touching)
-
#4
Although both are grammatically correct, «hardest-working» is sort of a set term, so we would always use that to mean that she works harder than anyone else. The late singer James Brown was known as «the hardest-working man in show business.»
However, «the most» can also be used to mean just «very,» in which case the second one is better.
Ex.
Your son is the most thoughtful young man. (= very thoughtful)
They sent me the most touching letter. (= very touching)
“You must get drunk,” wrote the decadent French poet Charles Baudelaire. “But on what? On wine, on poetry, or on virtue, your choice. But get drunk.”
This sentiment echoed through the findings of a 2016 study into the work and leisure habits of students at Queen’s University, Ontario. “[B]y far the strongest pairwise relationship was between attraction to accomplishment and attraction to leisure,” wrote the authors. In other words, those who work hard, play hard. Drunk on beer, drunk on studying – the common denominator for success is wholeheartedness.
Still, ground-level experience tells us that some students favour booze over books, or vice versa. Get enough of the first group together, and you’ve got yourself a party town. Enough of the bookish type, and a school can get an unwelcome reputation for seriousness!
Ivory Research knows you need to let off steam between study sessions, just as you need a sober environment to hit the books. We collected over 100,000 Instagram posts from around the world with the hashtags #worklife, #working, #partytime, or #partyhard. Then we analysed which countries, states, and cities focus more on work, and which ones prefer to party.
Key Findings
- Bolivia and Senegal are tied as the hardest-working countries, with 100% of their work or party-themed posts favouring work.
- North Dakota is America’s ‘hard work state’ with 90.9% work-themed posts.
- Vermont is America’s party state, with 72.2% of work/party-themed posts favouring leisure.
- Bedford and Sheffield are tied as the UK’s hardest-working cities, with an 85.7% work-rate.
- Colchester is the UK’s party city, with 86.7% of pertinent Instagram posts carrying a party-themed hashtag.
Workaholics vs. Party Animals: A World Map
Of the 121 countries with available data, 57 prefer to party, 60 are focussed on work, and the remaining four have a perfect 50-50 balance. Europe is clearly the ‘party meat’ in the work sandwich, with the stripe of orange through the centre of the map showing the countries with the most party-themed posts. The Americas and Asia are, for the most part, work-oriented Instagrammers.
However, it is Africa that has the most dramatic divide. The continent is home to three of the top four party nations (Congo, Ghana, and Kenya) as well as the joint top work-oriented country (Senegal – tied with Bolivia and Macao). The UK likes a bit of both and is midway down the list with a 54:46 work:party ratio.
One-third of Oxford Students Prefer to Party
Here’s a city-by-city look at the data. Click the tabs to switch between UK/US and workaholic/party cities.
Several American cities rate 100% for work ethic, but Newburgh takes the title with the highest total posts. This puts Newburgh 43% above the New York state average for workaholic-ism. At the other end of the scale, we found six US cities with a 100% party rate. Of these, Aurora and Syracuse come out on top with the highest number of posts.
Bedford and Sheffield share the title of the UK’s Workiest City. Both have an 85.7% work-rate. Sheffield’s Student Union is rated the top in the country, meaning you can party hard without wandering far from the seat of learning. Oh yeah, and Oxford? We found 66.7% of posts were work-related, against 33.3% party pics (although perhaps those are all from Oxford Brookes). All things in moderation, people!
North Dakota Knuckles Down
The US is a sober, hard-working nation, according to our research. Instagrammers in 41 states post more regularly about working than partying, while just 8 go the other way. Of course, it’s a sliding scale – so while North Dakota is the hardest-working state (90.9%), Virginia and Texas are almost evenly split, with 52% and 55% work-rates, respectively.
South Dakota strikes the perfect 50-50 balance between work and play. And one state stands out as the most party-oriented location: Vermont has the most party posts, with a staggering 11% lead over second-placed Nevada. The University of Vermont regularly appears near the top of lists of America’s party schools.
Success at university is all about balance. Knowing how to relax will help you study better – and new extra-curricular experiences can be just as valuable as your new qualifications. Party hard, work harder, Instagram in moderation, and don’t worry too much about what the student in the next dorm is getting up to!
METHODOLOGY & SOURCES
We selected the following Instagram hashtags:
- #worklife
- #working
- #partytime
- #partyhard
We collected posts on Instagram tagged with one of these hashtags (totalling 101,527 posts). Then we analysed the location of each post and assigned a status based on the balance of work and party hashtags in each city. Data collected in February 2021.
CHEATS
for
the teachers
of
the English Language
4.1,
4.2 and 4.3 modules
1. «According to
Webster’s Third New International Dictionary, methodology is…» *a) «“a
body of methods, procedures, working concepts, rules and postulates employed
[…] in the solution of a problem or in doing something”»
2. «Broughton
specifies the most typicalfeatures of the grammar-translation method, which
are…» *a) «rules, [its] examples, its paradigms […]
and related exercises»
3. «Give the
English equivalents for the following Russian/Uzbek words and use them in
sentences of your own» What is the focus of this task? ~ What skills are
targeted in this task? *a) Focuses on word-for-word translation of
isolated words and doesn’t not target any skills but simply tests the knowledge
of one meaning of each Uzbek/Russian word
4. «I always
repeat things aloud for myself. «What is the student’s dominant learning
style?
*a) Auditory
5. «I always use
colored pens to highlight my notes» What is the student’s dominant
learning style?
*a) Visual
6. «I like to
have something in my hand to squeeze or play with during a lesson. «What
is the student’s dominant learning style? *a) Tactile
7. «I would
rather start doing an activity instead of listening to instructions about how
to do it.» What is the student’s dominant learning style? *a) Kinesthetic
8. «In which
method students may create their own story and draw several sequential pictures
that describe story? *a) Story narrating through the pictures
9. «listening,
speaking, reading, and writing can be classified into which two groups?» *a)
receptive and productive
10. … a learning activity which
involves learners working together in pairs. *a) pair work
11. … are the guiding principles
(often moral or ethical in nature) that govern behaviour; they are typically
rooted in tradition, religion or in individual or shared philosophy and in
education they help to inform decisions at all levels, from national policy
right through to the classroom. *a) values
12. … is a teacher’s
detailed description of the course of instruction for one class. *a) A lesson plan
13. … is a teacher’s
detailed description of the course of instruction for one class. *a) A lesson plan
14. …is the most
abstract of all three concepts and refers to the linguistic, psycho-and
sociolinguistic principles. *a) approach
15. .…is teachers detailed description
of the course of instruction for one class. *a) A lesson plan
16. _____
discover the language and familiarize themselves with the sound of English. *a)
A1
17. _______ a group
activity in which learners have a free and relatively unstructured discussion
on an assigned topic as a way of generating ideas. *a) Brainstorming
18. ____________ has
become the most important tool for delivering distance education. *a) Internet
19. ____________ has
become the most important tool for delivering distance education. *a) Internet
20. ___________________
is that educational information and instruction is taught to learners who are
physically distant from the source of that information and instruction *a) Distance education
21. ___________________
is that educational information and instruction is taught to learners who are
physically distant from the source of that information and instruction *a) Distance education
22. “______
between two evils” *a) it’s not worth while choosing
23. “…. between two evils” *a) it
is not worth while choosing
24. “A word doesn’t depend on
dictionary”. About what approach is this definition correct? *a) Non-
traditional approach
25.
“Discuss
the situation with your partner!”,- what method is used in this instruction? *a)
In
pairs
26. “From practice to rules” is the
principle of ….*a) inductive learning
27. “From rule to practice” is the
principle of … *a) deductive learning
28.
“Make
up a dialogue with your neighbour”. *a) Pair work
29. “Rub” means *a) move
backwards and forwards
30. “The use of the
native language for explanation, retention and checking”. What approach is it
to foreign language teaching? *Traditional approach
31.
“Work
in threes or fours!” ,- this instruction belongs to… *a) Group work
32. … a word or phrase
used in an imaginative way to describe something else to show that the two
things have the same Qualities *a) metaphor
33.
…
is important because it shows what the teacher hopes to achieve in the lesson. *a)
Lesson
planning
34. … must be
comprehensive enough to be a help to the teacher and it must provide all the
recorder material. *Teachers’
books
35. … the system of
structures at word, sentence and text level in a Language *a) grammar
36. … the words that
come just before or after a word or phrase and help you to understand its
meaning. *a) context
37. … was widely used
in teaching the classics, namely Latin. *Grammar translation method
38. … which began to
be widely used in schools in the 1870’s. *The direct method
39. …. a group activity in which learners
have a free and relatively unstructured discussion on an assigned topic as a
way of generating ideas. *a) brainstorming
40. …. all the words a
person knows or uses *a) vocabulary
41. ……are statements of what is to be
achieved in a course or lesson. They are detailed descriptions of exactly what
a learner is expected to be able to do at the end of a period of learning. *a) Objectives
42. ……is used at the end of the term,
semester, or year in order to measure what has been achieved both by groups and
individuals
*a) Summative assessment
43. …..is the task of grouping a set of
objects in such a way that objects in the same group are more similar (in some
sense or another) to each other than to those in other groups *a) cluster
44. …..the study of teaching methods
and approaches. *a)
pedagogy
45. ….designed to show what level a
student has reached at any one time, and are used by employers and
universities, for example, who want a reliable measure of a student’s language
abilities.
*a) Proficiency test
46. ….enables the learners to interact
in a better way when giving ideas a) Communicative approach
47. ….is a day in honor of those
Americans who have given their lives to their country in all wars *a) Memorial
day
48.
……
are series of connected acts which have become automatic or semi-automatic as
the result of repetitions. a) Habits*
49. ………a group activity in which
learners have a free and relatively unstructured discussion on an assigned
topic as a way of generating ideas. *a) brainstorming
50. ……….. is intended
to enable students to give group presentations and assess their performance *b)
oral presentation
51.
……….are
combination of specific useful habits, serving a definite purpose and requiring
the application of definite knowledge *a) Skills
52. ………… assessment of
language allows teachers to see students using language in context, through
tasks that require performance of language. *c) direct
53. …………. are directly
related to the language courses taught to the examinees *b) Achievement tests
54. ………….. provides
valuable information regarding a number of core objectives related to students’
behavior. *b) observation of students
55. ……………… is
agreement between parts of the test *d) Consistency
56. ……………format means
that the examinees are given brief notes of a public address and the task is to
“unfold” these brief entries into full text *c)Contextual
57. …expose students
to real language as it is used in real life situations by native speakers? *a)
authentic
materials
58. …is a mini-lesson
that participants teach to each other *a) Microteaching
59. …is a teacher’s detailed
description of the course of instruction for one class *a) a
lesson plan
60. A ___ is a self-contained section
of the classroom in which students engage in independent and self-directed
leaning activities. Get information on learning centers and how to incorporate
them in to your instructional routine using this advice. *a) Learning
Centers
61. A _____is a
self-contained section of the classroom in which students engage in independent
and self-directed learning activities. Get information …. *a) Learning Centers
62. A bird in the hand ——— *a)
is worth two in the bush
63. A bird in the hand ……….. *a) is
worth two in the bush
64. A bird in the hand
*a) is
worth two in the bush
65. A chart to be filled in by learners
or teacher-participants, often used to summarise ideas or to focus reflection *a) grid
66. A common reference for describing
language learning, teaching. *a) CEFR
67. A common reference
for describing language learning, teaching. *a) CEFR
68. A conversation can consist of up to
………. words per minute *a) 220
69. A generalized set of classroom
specifications for accomplishing linguistic objectives. Primarily concerned
with teacher and student roles and behaviors and secondarily with such features
as linguistic and subject-matter objectives, sequencing, and materials. They
are almost always thought of as being broadly applicable to a variety of
audiences in a variety of contexts. *a) Method
70. A good reading lesson has … *а) pre, while
and post stages
71. A good reading
lesson has … *a) pre, while and post stages
72. A good reading
lesson has… *a) pre, while and post stages
73. A good reading
lesson has… *a) pre, while and post stages
74. A good writing
task should have _____, ________ and _________ stages *a) pre/ while / post
75. A group activity
in which learners have a free and relatively unstructured discussion on an
assigned topic as a way of generating ideas. *a) Brainstorming
76. A group of
activity in which learners have a free and relatively unstructured discussion
on an assigned topic as a way of generating ideas. *a) Brainstorming
77. A group of activity in which
learners have a free and relatively unstructured discussion on an assigned
topic as a way of generating ideas. *a) Brainstorming
78. A ——is a
self-contained section of the classroom in which students engage in independent
and self-directed learning ac…on learning centers and how to incorporate them
in to your instructional routine using this advice. *a) Learning Centers
79. A learning activity which involves
a small group of learners working together. The group may work on a single
task, or on different parts of a larger
task. Tasks for group members are often selected by the members of the group. *a) groupwork
80. A learning style …
*a) is
a specific way a person learns things.
81. A session plan is…
*a) A
compass
82. A silent period is
recommended until learners are ready to produce at their own pace in the target
language. *a) The
Natural Approach
83. A task which replicates or
resembles a real-life task, e.g. scanning an article for particular
information; this may be contrasted with a task which is specifically designed
for, and only relevant in, the classroom. *a) Authentic task
84. A teacher can make
listening using the following *Asking the questions
85. A teacher uses
talk to support vocabulary development by: *a) Establishing a
role play/drama area, developing Stop Rewind activities, asking pupils to
provide verbal feedback to written pieces and etc
86. A type of
co-operative activity in which each member of a group has a piece of
information needed to complete at reading work. *a) jig-saw activity
87. A type of co-operative activity in
which each member of a group has a piece of information needed to complete a
group task. *a)
jig-saw
activity
88. A type of co-operative activity in
which each member of a group has a piece of information needed to complete at
reading work. *a) jig-saw activity
89. A type of speed reading technique
which is used when the reader wants to locate a particular piece of information
without necessarily understanding the rest of a text or passage. For example,
the reader may read a chapter of a book as rapidly as possible in order to find
out information about a particular date, such as when someone was born. *a)
. Scanning
90. A type of speed reading technique
which is used when the reader wants to locate a particular piece of information
without necessarily understanding the rest of a text or passage *a) scanning
91. A type of speed reading
technique which is used when the reader wants to locate a particular piece of
information without necessarily understanding the rest of a text or passage.
For example, the reader may read a chapter of a book as rapidly as possible in
order to find out information about a particular date, such as when someone was
born. *a) Scanning
92. A typical
communicative activities involve … *a) Role-play,
info-gap activities, jigsaw, etc
93. A typical
communicative activities involve… *a) Role-play, info gap activities,
jigsaw, etc.
94. A typical feature
of association methods in vocabulary instruction is… a. Encouraging
learners to draw connections between what they do know and unfamiliar words
95. A word family/ a group of related
words is …. *a) Lexical set
96. A1 and A2 are…? *a)
Basic
user
97. A1….. *a) breakthrough
98. According to ….
authentic materials are a way to contextualize language learning. *a) Gephard
99. According to CEFR B2 level is
determined for *a) Vantage
100. According to CEFR
B2 level is determined for *a) Vantage
101. According
to CEFR C-2 level is determined for: ________. *a) Mastery
102. According to CEFR
C-2 level is determined for: ________. *a) Mastery
103. According to long
term observations early teaching of foreign languages. It gives an emphasis on
writing skills rather than ORAL *a) It opens a broad way to write
a better composition.
104. According to the
teachers point of view dictation activities work well in the classroom and such
kind of activities make better… *All answers correct
105. Activity – *a)
a short task which is a part of the lesson
106.
Activity *a)
A short task
which is a part of a lesson
107. Advantages of
using pair and group work – *a) all pupils are active
108. Affixes are ….*a)
prefixes and suffixes
109. All advertising
must …..the right product image. *a) boost
110. All the hotel in
the town was full up so we stayed in a ______village. *a) nearby
111. All the words that
someone knows, learns or uses… *a) Vocabulary
112. An activity in
which a pair or two groups of students hold different information , or where
one partner knows something that the other doesn’t. *a) Information gap
activity.
113. An activity in
which a pair or two groups of students hold different information, or where one
partner knows something that the other doesn’t. This gives a real purpose to a
communication activity. *a) Information gap activity
114. An activity in
which a pair or two groups of students hold different cards, where one partner
knows something that the other does not *a) Information gap
115. An activity in
which a pair or two groups of students hold different information, or where one
partner knows something that the other doesn’t. *a) Information
gap activity.
116. An activity to
make learners feel less nervous inhibited when they first meet. *Ice-breaker
117. An activity to
make learners feel less nervous inhibited when they first meet. *a) Ice-breaker
118. An activity which
involves re-ordering a mixed up text to find its correct order; it helps
learners see the connections between parts of a written text. *a) jigsaw
reading
119. An activity which
involves re-ordering a mixed up text to find its correct order; it helps
learners see the connections between parts of a written text. *a) jigsaw reading
120. An approach is a
way of looking at________________ *a) teaching and learning
121. An approach is a
way of looking at________________ *a) teaching and learning
122. An approach is a
way of looking at________________ *a) teaching and learning
123. An informal
interview may improve student`s____ skills *Speaking
124. Another reason for
using authentic materials is that……..*a) they represent an
unlimited source for planning and organizing teaching and learning activities;
125. Anticlockwise is
….*a) In
the opposite direction to the movement of the hands of a clock.
126. Any of
a wide variety of exercises, activities, or devices used in the language
classroom for realizing lesson objectives. *a) Technique
127. Any of a wide
variety of exercises, activities, or devices used in the language classroom for
realizing lesson objectives. *a) Technique
128. Any of
a wide variety of exercises, activities, or devices used in the language
classroom for realizing lesson objectives. *a) Technique
129. Apostrophe is
used….*a) all answers are correct
130.
Applied
linguistics… *a)
the study of
second and foreign language acquisition and learning the study of language and
linguistics in relation to practical problems, such as lexicography,
translation or speech pathology.
131. Approach is … *a)
Theoretical
positions and beliefs about the nature of the language, the nature of language
learning, and the applicability of both pedagogical settings
132. Approach is ….*a theoretical
positions and beliefs about the nature of the language, the nature language
learning and the applicability of both pedagogical settings
133. Approach is
defined…..*a) it is theoretical part of teaching foreign language
134. Are pair and group
work effective? *a) Yes
135. Are series of connected
acts which have become automatic or semi automatic as the result of…..
repetitions. *a) skills
136. Are speaking
activities successful? *a) Yes
137. Ask right questions
to get needed piece of information from others is … . *a) eliciting
138. Assesment is …… *a)
The
measurement of the ability of a person or the quality or success of a teaching
course, etc. Assessment may be by test, interview, questionnaire, observation
and so on.
139. Assessment is … *a the measurement
of the ability of a person or the quality or successes of a teaching course
140. Assessment is the
process of …..*a) gathering and evaluating information;
141.
Assessment….*a)
The measurement
of the ability of a person or the quality or success of a teaching course, etc.
Assessment may be by test, interview, questionnaire, observation and so on.
142. Association method
– *a) encouraging learners to draw connection between what do
they know and unfamiliar words
143. At the end of a
term, semester or year, we may want to do a final (sometimes called an exit
test) to see how well students have learnt everything. Their results on this
test may determine what class they are placed in next year (in some schools,
failing students have to repeat a year), or may be entered into some kind of
school-leaving certificate *a) Achievement test
144.
Attitudes….
*a) the way that a person thinks and
feels about somebody, something; the way that a person behaves towards
somebody, something that shows how he, she thinks and feels. In a classroom
this may show itself in a teacher‘s attitude to learners or in a learner‘s
attitude to a foreign language and the culture associated with it, for example.
145. Auditory learner
is … *a) They learn best through verbal lectures, discussions,
talking things through and listening to what others have to say. Auditory
learners interpret the underlying meanings of speech through listening to tone
of voice, pitch, speed and other tones.
146. Auditory learners *a)
those people who learn in information best by listening
147. Auditory learners *a)
those
people who learn in information best by listening
148. Auditory learners
prefer to learn by … *a) Listening or hearing
149. Auditory
learners: *a)
They learn best through verbal lectures, discussions, talking
things through and listening to what others have to say.
150. Auditory learners:
*a) They
learn best through verbal lectures, discussions, talking things through and
listening to what others have to say. Auditory learners interpret the
underlying meanings of speech through listening to tone of voice, pitch speed
and other tones.
151. Authentic material
can be used … *a) to promote motivation
152. Authentic
materials — nima *a) gazeta, jurnal materiallari, audio, video
materiallari, entsiklopediya materiallari, tarixiy faktlar va hakozolardir
153. Authentic
materials can involve the…………………… *a) students
to real language as it is used in real life situations by native speakers
154. Authentic
materials can
involve the…………………… *a) students to real language as it is used in
real life situations by native speakers
155. Authentic
materials….. *a) texts from real life sources
156. Authentic
materials….. *a) texts from real life sources
157. Authentic
materials…… *a) expose students to real language;
158. Authentic
materials…… *a) texts from real-life sources
159. Authentic task is…*a)
A
task which replicates or resembles a real-life task, e.g. scanning an article
for particular information; this may be contrasted with a task which is
specifically designed for, and only relevant in, the classroom.
160.
Authentic
task…. a) *A
task which replicates or resembles a real-life task, e.g. scanning an article
for particular information; this may be contrasted with a task which is
specifically designed for, and only relevant in, the classroom.
161.
Authentic
text *a) Texts which are taken from
newspapers, magazines, etc., and tapes of natural speech taken from ordinary radio
or television programmes, etc.
162. Authentic text
is…. *a) Texts
which are taken from newspapers, magazines, etc., and tapes of natural speech
taken from ordinary radio or television programmes, etc. When a teacher
prepares texts or tapes for use in the classroom, he/she often has to use
simplified texts as opposed to authentic texts.
163.
Authentivity
*a) The
degree to which language teaching materials have the qualities of natural
speech or writing.
164.
Autonomous
Learning *a)
The process of
learning without being controlled by anyone else.
165. Basic user …? *a) A1,A2
166. Beckon – *a)
to signal with your hand in order to tell that person to come closer
167.
Beliefs…..
*a) the
convictions that a teacher has about teaching or a learner about learning. When
beliefs become dogma, they may inhibit professional development in a teacher or
successful learning in a learner
168. Benefits of
dictations … *a) all answers are correct
169. Bilingual person
is … *a) able
to speak 2 languages equally well
170.
Blog *a)
A shared on-line
journal where people can post diary entries about their personal experiences
and hobbies
171. Bodily-kinesthetic
intelligence …
*a) expresses
itself in physical activities and movement: role-play, games, making posters
and doing projects.
172. Brainstorming …. *a)
encourages learners to produce the idea of solving practical and
scientific problems individually or in groups
173. Brainstorming …. *a)
encourages
learners to produce the idea of solving practical and scientific problems
individually or in groups
174. Brainstorming ….. *a)
collecting ideas very quickly
175. Brainstorming is…*a a group
activity in which learners have a free and relatively unstructured discussion
on an assigned topic as the way of generating ideas
176. Brainstorming
is……………. *a) a group activity in which learners have a free and
relatively unstructured discussion on an assigned topic, a way of generating
ideas without judging them
177. Brainstorming
is…………….. *a)
its technique for generating new ideas on
a topic
178. Brainstorming
is……………..*a) its technique for generating new ideas on a topic
179. Building friendly
classroom relationships with and between learners. *a) building rapport
180. Building Rapport- *a)
building friendly classroom relationship with and between learners
181. Building rapport
is…. *a) Building
friendly classroom relationships with and between learners.
182. CALL is…….. *a)
Computer
Assisted Language Learning
183. Can handle very
short social exchanges even though they don’t understand enough to keep the
conversation going themselves … . What level is it? *a) A2
184. Can handle very
short social exchanges even though they don’t understand enough to keep the
conversation going themselves…… What level is it? *c) A2
185. Case
study is……………………… *a) about a person, group, or situation that
has been studied over time.
186. CEFR is …… *d)
descriptive document
187. CEFR is not…. *b)
theoretical document
188. CEFR is not….. *a)
theoretical document
189.
CEFR is……………. *a) Common European Framework of
References
190. CEFRL is……. *a)
Common
European Framework of Reference for Languages
191. Choose an
appropriate definition to «technique» *a) technique is
just one single procedure to use in the classroom
192. Choose an
appropriate definition to “ technique” *a) Technique is just
one single procedure to use in the classroom
193. Choose an
appropriate definition to “technique” *a) technique is just one single
procedure to use in the classroom
194. Choose the amount
of lexical units the pupils must acquire in a foreign language after finishing
Grade 4. *a) 500
195. Choose the amount
of lexical units the pupils must acquire in a foreign language after finishing
Grade 4. *a) 500
196. Choose the
appropriate levels of CEFR *a) A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, C2
197. Choose the
appropriate levels of CEFR *a) A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, C2
198. Choose the best
answer to the following. …… draws upon some changes and innovations coming
mainly from applied linguistics, so I am going to give a summary of changes
about language nature and its knowledge. Language is considered a social
phenomenon by this approach, as it is a means of communication and interaction
between members of a *a) The communicative Approach
199. Choose the
classical method of teaching *a) Grammar translation method
200. Choose the
classical method of teaching *a) Grammar translational method
201. Choose the correct
useful English websites for teaching and learning English language *a) eslpartyland.com,
eslvideo.com, dictionary.com
202. Choose the inputs
of auditory children *a) songs, chants, poems, stories read aloud,
environment sounds (rains, cars, trucks, animals, vacuum cleaners, computer’s
printers, people walking)
203. Choose the inputs
of auditory children *a) songs, chants, poems, stories read aloud,
environment sounds (rains, cars, trucks, animals, vacuum cleaners, computer’s
printers, people walking)
204. Choose the inputs
of auditory children *a) Songs, chants, poems, stories read
aloud, environment sounds (rains, cars, trucks, animals, vacuum cleaner,
computer’s printers, people walking)
205. Choose the inputs
of auditory children. *a) like to learn new information by
hearing it
206. Choose the inputs
of tactile children *a) real life objects that children touch can
as well as toys and puppets (it is important to make sure that the child can
actually touch the objects and not merely look at them
207. Choose the inputs
of tactile children *a) real life objects that children touch can
as well as toys and puppets (it is important to make sure that the child can
actually touch the objects and not merely look at them
208. Choose the inputs
of visual children
*a) pictures such as drawings, sketches, photograph, paintings,
posters, murals, diagrams
209. Choose the inputs
of visual children
*a) pictures such as drawings, sketches, photograph, paintings,
posters, murals, diagrams
210. Choose the right
answer. We communicate orally in different ways… *Monologue,
dialogue
211. Choose the
strategy which matches the example. — I make notes about how native speakers
use English in films and TV shows. *a) paying attention to language use
212.
Choose which unit in a pronunciation resource book listed a-d,
a teacher could use to help her students with their pronunciation problems.
Students pronounce each word separately, so their speech doesn’t sound smooth. *a)
Practicing linking
213. Classroom
activities in which students take the roles of different participants in a
situation and act out what might typically happen in that situation. *a) role play
214.
Classroom
management *a) The
way a teacher organizes her classroom and learners (e.g. how the furniture is
organized, when to start and stop activities )
215. Classroom or
training activities which reproduce or simulate real situations and which often
involve learners/participants in playing roles and group discussion in order to
solve a problem or complete a given task. *a) simulation
216.
Clockwise *a) Moving around in
the same direction as the hands of a clock.
217. Cluster
is……………… *a) is the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way
that objects in the same group (called a cluster) are more similar (in some
sense or another) to each other than to those in other groups
218. Cluster is……………… *a)
is the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in
the same group (called a cluster) are more similar (in some sense or another)
to each other than to those in other groups
219. Cluster methods is
….? *a
a type of cooperative activity in which number of a group has a piece pf
information needed to complete a group task
220. Cluster Methods is
…? *a) the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way
that objects in the same group are more similar.
221. Comments or
information learners receive on the success of a learning task, either from the
teacher or from other learners. *a) feedback
222. Communicating
in English – nima *a) darsning ingliz tilida o’tilishiga
asoslanishdir
223. Communicative
language teaching makes use of ….. *a) real life situations that
necessitate communication
224. Communicative
language teaching makes use of… *a) .Role-play situation
225. Complete the
sentence. A good … task should have … purpose, relevant and interesting to
learners *a) Writing,
communicative
226. Complete the
sentence. A good writing task should have…., …. and …. stages. *a) Pre, while, post
227. Complete the
sentences. A GOOD…. task should have ….purpose, relevant and interesting to
learners *a) writing, communicative
228.
Comprehensible
Input *a) Input language which contains
linguistic items that are slightly beyond the learner‘s present linguistic
competence.
229. Concerning writing,
Donald H.Graves makes a notable point: writing is …*a) communication
230. Constructivist
teaching involves … *Negotiation
and scaffolding
231.
Context *a)
The ideas or
content which occurs before and/or after a word, a phrase or even a longer
utterance or text.
232. Controlled
writing.. *a) is used for teaching the mechanics of accuracy and
readiness for the further writing. It is completely controlled by the
teacher.(text , copying the text, working on handwriting, dictations)
233. Correction by a
learner of her/his own mistakes – usually possible only in the case of
post-systematic errors. *a) self-correction
234. Criteria of
successful speaking activities: *a) PW + GW STT > TTT
235. Demerits of
communicative approach_________________ *a) ignores grammar and
structures
236.
Demerits of communicative approach_________________ *a) ignores
grammar and structures
237. Demerits of
communicative approach_________________. *a) ignores grammar
and structures
238. Designs for
carrying a particular language program. Features include a primary concern with
the specification of linguistic and subject-mater objective, sequencing, and
materials to meet the needs of a designated group of learners in a defined
context *a)
Syllabus
239. Develop vocabulary
through the use of ICT by: *a) all answers are correct
240. Diagnostic tests –
*a) identify students’ strength and weaknesses
241. Dictation gives
pupils …. *a) all
answers are correct
242. Dictation makes
the pupils and the teacher aware of the pupils’ comprehension on ..… errors *a)
phonological and grammatical
243. Dictoglos dictation activity is … *It is such kind of dictation where listener listens twice
the text and writes some of notes.
244. Disadvantages of
using pair and group work *a the class is noisy
245. Discussion is … *a)
sharing ideas
246.
Discussion is …. *a) an active method of sharing
opinions on a specific problem individually and freely
247. Discussion is….. *a)
an active method of sharing opinions on a specific problem individually
and freely
248.
Distance
education a) *The
education of students who may not always be physically present at a school.
249.
Distance
education is _______________ the traditional education *a) different from
250. Do you know the
abbreviations TTT and STT mean? *a) Teacher Talking Time and Student
Talking Time
251. Dos of developing
listening skills are… *a) Use visual aids to support listening
comprehension, brainstorm learners` ideas on the topic
252. DUET, as one of
the intensive teaching training course of the English Language based on: *a)
two modules; face-to-face, distance module
253. Effective learning
of a foreign language depends on the pupils … *Memory
254. Effective, modern
methods of teaching listening skills encompass everything from interactive
exercises to ………………….. resources *a) multimedia
255.
EFL is…………. *a) English as Foreign Language
256.
Elicitation *a) Techniques or
procedures which a teacher uses to get learners to actively produce a response.
257. E-mail is …. *a)
electronic mail
258. E-mail is… *a) electronic mail
259. E-mail is… *a) electronic mail
260. ESL
is…………… *a) English as Second Language
261. everyday life.
262. Exam KET is……………. *a)
Key
English Test
263. Exam KET is……………. *a) Key English
Test
264.
Extracurricular
activities *a) Educational
activities not falling within the scope of the regular curriculum
265.
Facilitate
*a) To make a
learning process possible or easier; to work with a group in order to help them
to articulate ideas.
266.
Facilitator
*a) a person
who helps an individual or a whole group to learn and/or express themselves.
267. FCE is………. *a) First
Certificate in English
268. FCE is……….*a) First Certificate
in English
269.
Feedback *a)
(in teaching)
Comments or information learners receive on the success of a learning task,
either from the teacher or from other learners.
270. Feedback is …. *a)
Comments or information learners receive on the success of a learning
task, either from the teacher or from other learners
271. Feedback
is…………. *a) evaluative information derived from such a reaction
or response
272. Fill in the gaps? The case method
combines _____elements: the case itself and the discussion of that case. *a)
2
273. Fill the gap. …
has become the most important tool for delivering distance education. *a) internet
274. Fill the gap. …
has become the most important tool for delivering distance education. *a) internet
275. Fill the gap… has
become the most important tool for delivering distance education *a) Internet
276. Fill the gaps. A
good writing task should have _____, ________ and ________ stages. *a) pre, while and
post
277. Fill the gaps. A
good writing task should have _____, ________ and ________ stages. *a) pre, while and
post
278. Find a word which
has a prefix and suffix *a) disappearing
279. Find correct
definition for Question Dictation. *a) This fun ESL dictation is
ideal for reading comprehension practice. Stick numbered questions about your
target text in different places outside the classroom. Divide the students into
pairs.
280. Find correct definition
for Running Dictation *a) Here is one of the most popular types
of ESL dictation. Stick a text on a wall outside the classroom. Divide the
students into pairs. One student is the ‘reader’ and the other is the ‘writer’.
The readers run to the text, read a sentence or two, remember it, run back and
tell their writer.
281. Find correct
definition for Shouting Dictation *a) This ESL dictation helps
students with their communication and listening skills. Divide the students
into pairs (A and
282. Find correct definition
for Silent Dictation *a) In this amusing ESL dictation, students
dictate a text to a partner by whispering. Divide the students into pairs (A
and B). Put the chairs into two rows with the seats facing each other. Make the
space between the two rows quite large. The pairs sit opposite each other.
283. Find correct tip
for dictating. *a) It`s important to pause to make sense of a text
284.
Find
group work activity below. *a) Role play
285.
Find out real-situations where people listen the other people in
their native language. *a) Radio, telephone conversation,
interviews
286. Find out the name
of A1 level of CEFR *a) Basic User
287. Find out the name
of A1 level of CEFR *a) Basic User
288. Find out the name
of A1 level of CEFR *a) basic User
289. Find out the
objective of the while stage in listening *a) jigsaw listening
290. Find out the
objective of the while stage in reading *a) students scan the
text to find the name of the…
291. Find speaking
activity *a) find someone who
292. Find strategies of
reading *a) scanning and skimming
293.
Find
the advantages of the pair and group work below? *a) Group and pair
work involve learners to the learning process
294. Find the aspects
of speaking? *a) accuracy and fluency
295. Find the correct
criteria for successful speaking activities. *a) PW+GW STT>TTT
296. Find the correct
ways of teaching listening. *a) give questions about the passage, preteach
some unknown words
297.
Find
the disadvantages of the pair and group work below? *a) The class becomes
noisy
298. Find the
discription and the purpose of the “Cloze exercise” reading technique *a)
fill-in-the blank exercise, in which some words are ommited, designing
to measure how well the reader understands how a text is linked together
299. Find the
discription and the purpose of the “Outlining ” reading technique *a) note-taking
technique designed to help the reader to see overall organization of the text
300. Find the
discription and the purpose of the “Passage competition ” reading technique *a)
Finishing a reading passage (orally or in writing): involves predicting
a logical or suitable conclusion based on a through understanding of a text
301. Find the
discription and the purpose of the “Scrambled stories” reading technique *a)
The reader re-orders the mixed up pieces of a text to show he
understands how a text fits together
302. Find the effective
reading strategies *a) I look at titles, subtitles, pictures and
other visuals before reading
303. Find the
equivalent of aural-oral approach *a) ) Audio lingual approach
304. Find the
ineffective reading strategies. *a) I ask my teacher for help whenever
I meet a word I don`t know
305. Find the purpose
of the following listening activity: Listen to an announcement in the train
station and complete the formation about the trains leaving to Manchester. *a)
Listening
for specific information
306. Find the purpose
of the following listening activity: Listen to the story and write a title for
it. *a) Listening
for gist
307. Find the purpose
of the following listening activity: Listen to the description of a house and
draw it *a) Listening
for details
308. Find the readers’
statements with the ways of reading:“Looking at words around a word you don’t
understand can help guess its meaning” *a) deducing meaning from
the context
309. Find the stage of
the lesson: Students read very quickly in order to give answers to one or two
general questions. *a) -while stage
310. Find the stage of
the task. After
reading the first paragraph/sentence of the text students read several possible
continuations of the story and then predict which one the author used *a)
while
311. Find the stage of
the task. Before
reading the teacher introduces some new words. *a) pre
312. Find the stage of
the task. Students
complete a detailed True/False exercise. *a) while
313. Find the stage of
the task. Students
discuss topics related to the content of the text. *a) pre and
post
314. Find the stage of
the task. Students
draw or use pictures from magazines to create an illustration for the story. *a)
while and post
315. Find the stage of
the task. Students
infer the meaning of selected words and expressions from the context. *a)
while
316. Find the stage of
the task. Students
read very quickly in order to give answers to one or two general questions. *a)
while
317. Find the stage of
the task. Students
scan the text to find the name of the main character. *a) while
318. Find the stage of
the task. Students
write a paragraph, which could come immediately before the beginning of the
story. *a) Post
319. Find the stage of
the task. The
teacher draws attention to some of the grammar in the text. *a) while
320. Find the statement
for lesson objective. *a) Things that you want to achieve with an
activity, task, lesson or a session
321. Find the
strategies of reading. *a) Scanning and skimming
322. Find the
strategies of reading. *a) Scanning and skimming
323. Find the teachers’
comments with the aspects of listening. “ My students find it hard to recognize
the pronunciation of individual words and sounds when they hear people speak in
the street” *a)
working
with authentic texts
324. Find the teachers’
comments with the aspects of listening. “ The first listening task I give my
students is usually one in which they have to decide on the general meaning of
the text” *a) listening for gist
325. Find the teachers’
comments with the aspects of listening. “It’s nice if learners can just listen to
a story and enjoy it without doing a task on it.” *a) activating
students’ knowledge of the world
326. Find the types of
extracurricular activities below? *a) debates, sports, drama
327. Find the types of
learning style *a
tactile, visual, kinesthetic, auditory
328. Find the ways of
listening. “ When listening some important news we might want to make sense of
every word to find out what exactly happened and why.” *a) listening
extensively
329. Find the ways of
listening.- ” When listening to a train announcement for specific information
we might simply need to hear some times” *a) listening
intensively
330. Flash cards can be
used for…*a) telling a class a story
331.
Fluency *a)
In second and
foreign language teaching, fluency describes a level of proficiency in
communication, which includes:
332. For auditory
learners I recommend: *a) Ask your teacher for oral explanations if
you do not understand something; read aloud when you study at home; listen to
tapes.
333. For kinesthetic
learners I recommend: *a) draw something on your notes to remember
information better; move around your room while you are learning at home; take
frequent breaks.
334. For visual
learners I recommend: *a) look at pictures before you read a text;
look at a person who speaks with you.
335. For what it is
important to know the level of the students before planning the lesson? *a)
For identifying the role of each activity
336. For what purpose
is used brainstorming? *a) (in language teaching) a group activity in
which learners have a free and relatively unstructured discussion on an
assigned topic as a way of generating ideas.
337. Forms of formative
assessment *a) individual, pair and group work, homework tasks,
indirect(implicit)form using different questions or plays
338. Forms of formative
assessment. *a) test, matching, multiple choice
339. Forms of formative
assessment? *a) individual, pair and group work, homework tasks,
indirect (implicit) form using different questions or plays
340. From what is the
word “Dictation” origin from? *From Latin “dicto” to speak
341. Games can be
catagorized differently.
*a) For dividing large groups into small ones, introduction
games, grammar games, storytelling games, vocabulary games. They may also be
differentiated according 4 language skills.
342. Games can be found
to give practice in all__________ (reading, writing, listening and speaking *a)
the skills
343. Give the
definition of ‘ Group work “ *a) mode of doing a task or
activity in small groups
344. Give the
definition of “Group work” *a) mode of doing a task or activity in small
groups
345. Give the
definition of “Group work” *a) mode of doing a task or activity in small
groups
346. Give the
definition of “Pair work” *a) mode of doing a task or activity in pairs.
347. Give the
definition of “Pair work” *a) mode of doing a task or activity in pairs.
348.
Good operational command of the spoken language able to handle
communication in most situations. *a) C1
349. Graphic organizers
guide learners…… *a) thinking as they fill in and build upon a
visual map or diagram;
350. Has enough
language to get by, with sufficient vocabulary to express him/herself with some
hesitation and circumlocutions on topics such a family hobbies and interests,
work travel and current events, but lexical limitations cause repetition and
even difficulty with formulation at times. What level is it? *a) B1
351. How can we raise
our speaking skills? *a) all are true
352. How do auditory
learners learn best? *a
by hearing
353. How do visual learners
learn best? *a
by seeing
354. How do visual
learners learn best? *a) By seeing
355. How do visual
learners learn best? *a) By seeing
356. How is the
activity called? Give each group a box with buttons. Explain that each group
will get a picture. Groups
should describe the picture. Say that in groups participants should make up as
many sentences describing this picture as possible. Ask them not to pay
attention to possible mistakes. Ask to choose the most active person in a group
to be a secretary. The secretary does not make any sentences, but ticks each
new sentence of other members in a notebook without writing sentences down. Say
that a participant making up a sentence takes a button from the box, so at the
end of the activity the contribution of each member of the group is clear by a
number of buttons s/he has near her/him. It is important that all the
participants have an approximately equal number of buttons. Give them 4 minutes.
*a) Picture description.
357. How is the test
must be made on ……..? *a) the pervious theme which was learned
358. How long should
the text be for dictations? *a) A short text
359. How many aspects
in speaking? *a) 2
360. How many
challenges will be discussed along with solutions to help teachers using direct
assessment in language classrooms *a) 3
361. How many criteria
in the CEFR? *a) 5
362. How many criterias
are there in CEFR?
*a) 6
363.
How many
demerits of communicative approach do you know? *a) 4
364. How many distinct
words the “ Neurolinguistic programming “ can be broken down? *a) 3
365. How
many forms of speaking exist in a language? *a) 2
366. How many language
skills are in teaching English? *a) 4: speaking,reading, writing,
listening
367. How many levels
are there in CEFR? *a) 6
368. How many levels
are there in CEFR? *a) 6
369. How many levels of
CEFR are there? *a) 6
370. How many people
have taken TOEFL test since 1964? *a) 22 mln. People
371.
How
many stages does lesson planning have in storytelling lessons? *a) 3
372. How many steps of
listening activities? *a) 3
373. How many types of
feedback do you know? *a) 10
374. How many types of
learning styles? *a) 3
375. How many types of
reading are there? *a) 4
376. How many types of
reading do you know? *a) 2
377. How many types of
vocabulary are there? *a) active and passive
378. How the meanings
of words are given in monolingual dictionary? *a) English- English
379.
How’s called
an activity to make learners feel less nervous or inhibited when they first
meet? *a) icebreaker
380. I can write very
simple personal letters expressing thanks and apology. What level is it? *c) A2
381. I like to talk
when I write. *a
auditory
382. I wish he wouldn’t
keep clicking his pen. It’s getting _________________. *a) on my
nerves
383. Ice-breaker…. *a)
An
activity to make learners feel less nervous or inhibited when they first meet.
384. ICT core
competencies are………*a) searching, creating, teaching and
evaluating
385. Identify the
technique for presenting vocabulary *Real objects, Gestures and acting
opposite words
386. Identify this
sentence according to its types: “My family came to Germany when I was in grade
5, but I never learned to speak German well.” *a) compound-complex
387. Identify this
sentence according to its types: “While I was doing my homework and my mother
was cooking the dinner, my father was asleep in front of the television.” *d)
Compound-complex
388. IELTS is available
in two formats –___________________training *a)
Academic and General
389. IELTS is managed
by University of…… *a) Cambridge ;
390. IELTS is…….. *a) International
English Language Testing System
391. If a teachers
bring some real objects into the classroom, he … *a) uses realia
392. If the
PC is physical body of a man, then what is it’s mental body? *b) Software
393. Immersion – *a)
ESL students at school take all subjects in English. They take part in
class and school activities with native English students their own age
394. In dictations we
use: *a) Words
and pictures
395. In general, the
systematic gathering of information for purposes of decision making. It uses
quantitative methods (e.g. tests), qualitative methods (e.g. observations,
ratings) and value judgments *a) Evaluation
396. In inductive
presentation *a) Pupils work out grammar rules themselves with
the help of a teacher
397. In inductive
presentation *a) pupils work out grammar rules themselves with
the help of the teacher
398. In modern Method
grammar must be taught in… *a) context
399. In Modern Method
grammar must be taught in…. *a) context
400. In second and
foreign language teaching, it describes a level of proficiency in
communication, which includes: the ability to produce written and/or spoken
language with ease and without significant hesitation; *a) fluency
401. In teaching
grammar the teachers follow the … given in Teacher’s books *Recommendations
402. In testing or
teaching: a device in which the learner is presented with a question along with
four or five possible answers from which one must be selected *a) multiple-choice
403.
In the teaching learning process using TPR method, teacher plays
……… and ………….. *a) an active, direct role
404. In traditional
method teachers do not pay attention to *a) speaking and
pronunciation
405. In traditional
method teachers don’t pay attention to…. *a) Speaking and
pronunciation practice
406. In traditional way
of presenting grammar is called inductive when… *Pupils work out
grammar rules themselves with the help of teacher
407.
In traditional way of presenting grammar is called inductively
when… *a) pupils work out grammar rules themselves with the help
of teacher
408. In which
activities do pupils use given words for practicing vocabulary? *Classifying words
into lists, filling sentences gaps, filling tables with new words, crosswords
and puzzles
409. In which
activities do the pupils choose words themselves? *Chain drill,
Snowball, Birthday line
410. In which activity
students are encouraged to act out roles of people in different spheres of
society? *a) Role play
411. In which activity
students are encouraged to act out roles of people in different spheres of society
*a) role play-
412. In which method
Good habits are formed by having students produce correct sentences and
information. By memorizing dialogues and performing drills the chances for
making mistakes ….. *a) Traditional method
413. In which method
students write and re-tell the stories? *a) Traditional
414. In which method
teaching units are organized following these three methodological points:
Nothing will be spoken before it has been….. *a) the Audio
lingual method-
415. In which method well
known for its common use of small colored rods of varying length and color
coded word charts depicting pronunciation values, vocabulary and grammatical
paradigms( Fidel Chart, Word Chart, Sound Color Charts) and concentrates on
cognitive principles in language learning? *a) The Silent way
416. Incident
process…………………. *a) This teaching style involves a case study
format, but the process is not so rigid as a full case study training session.
The focus is on learning how to solve real problems that involve real people.
417. Independent user includes…….
……. *c) B1, B2
418. Inductive
presentation *a) pupils work out grammar rules themselves with
the help of the teacher
419. Inferring reading
is… *a) reading between lines(to understand things which are not
written in the text)
420. Information gap
activity – *a) an activity in which a pair or two groups of students
hold different 11 information, or where one partner knows something that the
other doesn’t. This gives a real purpose to a communication activity. An
information gap activity is an activity where learners are missing the
information they need to complete a task and need to talk to each other to find
it.
421. Information gap is
…. *a) An
activity in which a pair or two groups of students hold different information,
or where one partner knows something that the other doesn’t and it gives a real
purpose to a communication activity
422. Information gap or
info gap activities are…*a) They are activities in which a pupil knows
something that another pupil does not know, so they have to ask questions to
get the information.
423. Integrated skills
– *a) all the language skills together
424.
Integrated
skills *a) All
of the language skills (listening, reading, speaking, writing) together.
Integrated skills activities bring together different language skills (e.g.
learners discuss a writing assignment, thus practicing listening, speaking and
writing).
425. Integrated skills
….. *a) All of the language skills (listening, reading, speaking,
writing) together. Integrated skills activities bring together different
language skills (e.g. learners discuss a writing assignment, thus practicing
listening, speaking and writing).
426. Intensive methods
in teaching: *a) Games with situations, and imitations,
audiovisual methods, communicative, interactive communication
427. Intensive reading
– *a) reading for finding synonyms and antonyms
428. Interaction is….*a)
The leaners listened to a recording and wrote down the words he did not
know.
429.
Interaction
pattern *a) Mode
of work (individual work, pairwork, groupwork) used in learning or teaching
430.
Interlanguage
*a) A term
used to describe the state of a learner‘s language – somewhere between being a
complete beginner and native speaker standard.
431. Intrapersonal
intelligence is
…. *a) based
on silent individual work and self-reflection.
432. is a person who
helps an individual or a whole group to learn and/or express themselves. *a) Facilitator
433. Is it important to
know the aim of reading before you start to read? Why, why not? *a) It is important to
know the aim of reading because it influences how we read information.
434. Is it important to
use PW and GW? *a) Yes it is important
435. It is a strategy
of teaching students, where a teacher allows students to compare two different
historical perspectives to the same question. *a) true-false
activity
436. It is about a
person, group, or situation that has been studied over time. This method often
involves simply observing what happens to… *a) Case study
437. It’s on the top
shelf, out of _____. a) reach*
438.
It’s syllabus is organized structurally in sentence patterns,
gradually sequenced: vocabulary is considered a very important aspect of FLT;
the teacher is the model, creates the situation and reaches through questioning
and eliciting the learners’ answers: students are expected to deduce word
meaning from context, without translations or explanations in the mother tongue
are the characteristics which approach? *a) Audiolingual Method
439.
James
Asher worked in…………………….University *a) Jose State
440. Jigsaw – *a) a
type of co-operative activity in which each member of a group has a piece of
information needed to complete a group task
441. Jigsaw—— *a)
a type of co-operative activity in which each member of a group has
piece information………. needed to complete a group task
442.
KET is……………. *a) Key English Test
443. KET is…………….*a)
Key
English Test
444. Kid’s English 2
for which level is for? *a) A1
445. Kid’s English 2
for which level is for? *b) A1
446. Kinesthetic
learner is . . . . *a) Learn best through a hands-on approach,
actively exploring the physical world around them. They may find it hard to
seat still for long periods and may become distracted by
447. Kinesthetic
learner is….. *a) learn best through a hands-on approach,
actively exploring the physical world around them. They may find it hard to sit
still for long periods and may become distracted by their need for activity and
exploration.
448. Kinesthetic
learners *a) Those people who learn information best by doing
or moving
449. Kinesthetic
learners learn best…*a) By moving and doing
450. Kinesthetic
learners prefer to learn by … *a) Moving or doing
451.
Language
acquisition *a) Picking
up‘a language; not learning it consciously, but by being exposed to it in
natural situations
452. Language is
considered a social phenomenon because…….. *a) all the
individuals use it to construct interpersonal relations;
453. Language learning
skills- *a) A,B,C
454. Learner
responsibility – nima? *a) o’rganishga
mas’ullikdir
455. Learner to learner dictation is… *It is such kind of dictation where a pair could be reader
and writer and vice versa.
456. Learners at the
age of 7 are called…. *a) Young
457. Learners in the
modern language classroom often learn through techniques drawn from a variety
of methods/approaches in what has been labelled an … .*a) Eclectic approach
458.
Learners in TPR have the primary roles of ……….. and ……………. *a) listeners,
performers
459. Learning program
gives chance to study without …….. *a) Interfering
460. Lesson objective …
*a) To enable pupils to talk about timetables using simple
present.
461. Lesson plan gives
a Teacher … *a) confidence
462. Lessons move from
the presentation stage to the practice stage to the …stage *a) Production
463. LEVEL
…………Can interact in a simple way provided the other person talks slowly
and clearly and is prepared to help.*a) Level A1.
Breakthrough
464. Level……….Occasionally
produces inaccuracies and inappropriacies.*a) Level C1.
465. Lexis – *a) all
words and word forms in a language with meaning or function
466. Linguistic
intelligence is…. *a) revealed through specially designed
grammar and vocabulary exercises based on pair work in dialogues.
467. Listen to the
description of a house and draw it. *a) listening for details
468. Listening and
reading are ….. *a) receptive skills
469. Longitudinal
studies that show…………; *a) long-term effects or that isolate the
exercise of literacy,
470. Main principles of
CLT: *a) Interactive
mode of work, natural and spontaneous (free) use of language, meaningful
communication, and meaning has primacy over form,
471. Match the level A2
with explanation. *a) Wastage or elementary
472. Match the level A2
with explanation. *a) Wastage or elementary
473. Match
while-writing task with definition *a) draws on writing
itself
474. Match
while-writing task with definition *a) draws on writing
itself
475.
Method *a)
The procedures
and techniques characteristic of teaching
476. method is…- *a)
just the mediator between theory and classroom practice
477.
Mind map *a)
A diagram which
supposedly represents the brain or the mind: topics are clustered on the page
together as they are believed to be collected in the brain.
478. Mind map …. *a)
A diagram which supposedly represents the brain or the mind: topics are
clustered on the page together as they are believed to be collected in the
brain.
479. Mirror is mostly
used while teaching..*a) pronunciation
480. Mode of work
(individual work, pairwork, groupwork) used in learning or teaching *a) Interaction
pattern
481. Motivation is
defined as ―
*a) an interest and enthusiasm for the materials used in class;
482. Moving around in
the same direction as the hands of a clock. *a) clockwise
483. Multimedia is……………
*a) Multimedia is content that uses a combination of different
content forms such as text, audio, images, animations, video and interactive
content.
484.
Multiple-choice
*a) choice item will be a question or
incomplete sentence. This is known as the stem. The different possible answers
are known as alternatives. The alternatives typically include one correct
answer and several wrong answers or distractors.
485. Native Language
mostly used in…*a) Traditional Method
486. Non-verbal
communication is … *a) Body-language
487. Observation of a
teacher or trainee by a colleague of equal status. *a) peer observation
488. Offers freedom to
write the original content, using own language (essay, letters, narrations,
making up sentences, composition, essay, picture description) ……….. *a) free
writing
489. One way of
presenting grammar is called deductive when… *The teacher explains grammar rules
herself
490. Over the last …….
years, many countries have started implementing assessment exercises or
building on existing assessment systems. *a) 20
491. Pair work is … *a)
mode
of doing a task or activity in pairs
492.
Pair work________________________________________ *a) provides
opportunities for intensive listening and speaking practice
493.
Pairwork *a)
a learning
activity which involves learners working together in pairs.
494.
Pedagogy *a)
the study of
teaching methods and approaches.
495.
Peer
observation *a) Observation
of a teacher or trainee by a colleague of equal status.
496. Phonemic Chart can
be useful for….*a) improving pupils’ pronunciation
497. Phonetics deals
with *a) vowels, consonants, voiced and unvoiced sounds,
diphthongs
498. Planning lesson is
important for …… *a) for identifying the objectives identifying
outcomes of the lesson thinking of the essential aspects of the lesson
499. PPP stands for … *a)
Presentation,
Practice, Production
500. PPP stands for … *a)
Presentation,
Practice, Production
501. Pre listening…. *a)
Establish
that pre listening tasks help students to predict the content of the recording
and thus make it easier to understand it.
502. Pupils work out
grammar rules themselves with the help of the teacher. *a) Inductive
presentation of grammar
503. Put all the
language skills in correct order *a) listening, speaking,
reading, writing
504. Read the
instruction and find the type of the dictation. — Imagine I am a tape-recorder
(to draw on the board the buttons). I am dictating you the text, If you want me
to pause you say “pause”, if you want me to continue you say “play”, If you
want me to stop you say “stop”. *a) Tape-recorder dictation
505. Read the
instruction and find the type of the dictation. — You are listening to some
interesting sounds. First time you just listen While listening second time you
are writing some notes. Do not write whole sentences. Create a story in a group
*a) Sound-effects dictation
506. Read the
instruction and find the type of the dictation. -Listen once(the teacher is
dictating a story) and choose the best title for this story. Do not write anything.
-Listen twice and write only some notes. Do not write the whole sentences. *a)
dictoglos
507. Read the
instruction and find the type of the dictation. —Pointing to the board to tell
pupils that they are going to think of 7 words, № 1-the place ,where people
might live…….. *a) Wild dictation
508. Read the
instruction and find the type of the dictation. -You have got a passage with
gaps. Your partner has got the appropriate words. You read it loudly, your
partner listens to you carefully and helps you to fill the gaps. Then swap the
roles. *a) Shouting dictation
509. Read the listening
activities in column Activities. In column Purpose write: Listen to a radio
program and tell what it is about. *a) G if it is to
listen for the gist (general idea) . numbers).
510. Read the listening
activities in column Activities. In column Purpose write: Listen to a telephone
operator explaining how to find their office and follow the directions on the
map you have in front of you. *a) D if it is to listen for Detail
(e.g. turning right at a place, the shape of an object)
511. Read the listening
activities in column Activities. In column Purpose write: Listen to two friends
discussing how to solve the problem and decide whether you agree or disagree
with the solution. *a) MI if it is to listen for Main Ideas (e.g.
several things a person is describing)
512. Read the listening
activities in column Activities. In column Purpose write: Listen to your
partner describing a robot and draw it. *a) D if it is to
listen for Detail (e.g. turning right at a place, the shape of an object)
513. Read the listening
activities in column Activities. In column Purpose write: Listen to a crime
witness and select the picture of the burglar she is describing. *a) D if it is to
listen for Detail.
514. Read the listening
activities in column Activities. In column Purpose write: Listen to a person
telling about his favourite subjects at school and decide which of them are
true for you and which are not true. *a) MI if it is to
listen for Main Ideas (e.g. several things a person is describing)
515. Read the text and
choose a title for it. *a) skimming
516. Read the text and
find antonyms to the words in bold. *a) intensive reading
517. Read the text and
write the dates of birth of famous people in the table. *a) scanning
518. Reading a text for
getting specific information is…? *a) Scanning
519. Reading a text for
understanding its gist? *a) Skimming
520. Reading by paying
attention to wide range of details and ideas in the text. *a) extensive
reading
521. Reading is to the
mind… *a) what
exercise is to the body
522. Reading, listening,
speaking,writing are … *a) the four principal language skills
523. Reasons why they
are effective/ineffective in English lesson. I ask my teacher
for help whenever I meet a word I don’t know. *a) Ineffective ,because learner
becomes dependent on his/her Teacher.
524. Reasons why they
are effective/ineffective in English lesson. I look at titles,
subtitles, pictures and other visuals before reading. *a) Effective, it can help to
prepare a reader for reading.
525. Reasons why you
may need to use warm ups… *a) all answers are correct
526. Role play — *a)
classroom
activities in which students take the roles of different participants in a
situation and act out what might typically happen in that situation
527.
Second
Language Acquisition (SLa) *a) (in
applied linguistics) the processes by which people learn or acquire a
second or foreign language. These processes are often investigated with the
expectation that information about them may be useful in language teaching.
528.
Self-correction
*a) Correction
by a learner of her/his own mistakes – usually possible only in the case of post-systematic
errors.
529. Shouting dictation is … *It is
such kind of dictation where reader reads loudly and partner listens carefully
and fills the gaps.
530. Show the special
sign of e-mail. *a) @
531. Show the special
sign of e-mail. *a) @
532.
Simulation
*a) Classroom
or training activities which reproduce or simulate real situations and which
often involve learners/participants in playing roles and group discussion in
order to solve a problem or complete a given task.
533. Simulation is… *a) a role-play where
you play yourself in a given situation
534. Speaking and
writing are ….. *a) productive skills
535. Speaking has 2
aspects *a) accuracy,
an
ability to speak correctly, and fluency, an ability to speak confidently.
536. Speaking skill
is… *a) All
answers are correct
537. Speaking using
correct forms of grammar, vocabulary and pronunciation *a) accuracy
538. Stages of reading
lesson are… *a) pre reading, while-reading, post-reading
539. Students are not
passive in the assessment process but are engaged in developing the assessment,
determining what a good performance entails, and learning to score through
models provided by the teacher. Which key component of Assessment for Learning *b)
Student involved assessment
540. Students sing a
song “ Head and shoulders, knees and toes “. They touch the correct part of
their body as they sing the song. *a) Total Physical Response
541. Students work in
groups to make five questions about vocabulary from the previous unit. Then,
they exchange questions with another group and try to answer the questions. *a) Communicative
Language Teaching
542.
Study
Skills *a) Abilities,
techniques, and strategies which are used when reading, writing, or listening
for study purposes.
543. Tactile learners
like to learn by … *a) Touching or holding
544.
Tape
recorder, reading texts aloud; they are… *a) Auditory learners
545.
Teacher
development goes
beyond….*a) initial
training and deals with the on-going professional development of teachers,
particularly in in-service education programmes.
546.
Teacher
Education *a) The
field of activity which deals with the preparation and professional development
of teachers. Within the field of teacher education, a distinction is sometimes
made between teacher training and teacher development.
547.
Teacher
training deals
with…..*a) basic
teaching skills and techniques, typically for novice teachers in a pre-service
programme.
548. Teachers
are the main authority figure in this model. Students are viewed as “empty
vessels” whose primary role is to passively receive information (via lectures
and direct instruction) with an end goal of testing and assessment. It is the
primary role of teachers to pass knowledge and information onto their students.
In this model, teaching and assessment are viewed as two separate entities.
Student learning is measured through objectively scored tests and assessments.
What is it ? *c) Teacher-Centered Approach to Learning
549. Teaching a foreign
language means the formation and development of pupils … *Habits and skills
550. Teaching listening
should be … *a) close to the nature of listening in real life
551. Teaching practices
have a lasting………*a) effect on pupils ability and willingness
to read;
552. The ……..test
measures how well students use English, not just their knowledge of the
language. *a) TOEFL
553. The ability to act
and make decisions without being controlled by anyone else *a) Autonomy
554. The ability to
produce language confidently… *a) Fluency
555. The ability to
produce language in a correct way… *a) Accuracy
556.
the ability
to produce written and/or spoken language with ease and without significant
hesitation
557. The aim of
teaching foreign language at all levels of education of the Republic of
Uzbekistan is…. *a) to develop communicative competence (based on its
composites – linguistic, sociolinguistic, discourse, strategic, sociocultural
and social competences) of learners to be able to function in the multicultural
world in everyday, scientific and professional spheres.
558. The Audio Lingual
method of teaching… *It is based on the structural view of language
559. The Audiolingual
Approach to language teaching has a lot of _________________with the Direct
Method. *a) similarities
560. The CEFR aims are *a)
All answers correct
561. The
characteristics of auditory learners … *a) remember better when
they read something aloud or listen to a tape recorder
562. The
characteristics of kinesthetic learners …… *a) cannot sit still
for a long class
563. The communicative
approach aim to make all the _________ attain communicative competence *a)
learners
564. The development of
audiolingual skills first, i.e., listening comprehension and speaking are
called: … *Audiolingual
565. The dimensions of
CLIL are…….. *a) The Culture , the Environment, the Language, the
Content , the Learning
566. The Direct Method also
called……………….. *a) Natural Method
567. The Direct Method
also called………………..*a) Natural Method
568. The Direct Method
appeared as an answer to the shortcomings of the…………….. *a) Grammar
Translation Method
569. The direct method
highlighted the teaching of vocabulary while the audiolingual approach focus on
_________________. *a) grammar drills
570. The Direct Method
was established around …………. *a) 1900
571. The Direct Method
was established around ………….*a) 1900
572. The Direct Method
was established in ……………………… *a) Germany and France
573. The Direct Method
was established in ……………………… *a) Germany and France
574. The essential
methods of teaching EFL to young learners are based on … *All answers
correct
575. The
four main types of ……techniques are the following: Skimming, Scanning,
Intensive, Extensive*a) reading
576. The ideas or
content which occurs before and/or after a word, a phrase or even a longer
utterance or text. It often helps in understanding the particular meaning of
the word, phrase, etc. *a) context
577. The impact of
authentic materials on students‘ motivation and the results were ….*a) mixed
578. The language used
to analyze or describe a language is called … *a) Meta-language
579. The language you
first know as a child,your mother tongue. *a) L1
580. The language you
learn as a foreign language *a) L2
581. The main aim and
competence of CEFR is… *a) learning, teaching and assessment
582. The main aim and
competence of CEFR is… *a) learning, teaching and assessment
583. The main aim of Student Talking
Time is… *a) To
give pupils a chance to communicate in English. Pupils should speak more than a
teacher.
584. The main benefits
of using ICT in teaching English are……. *a) attract the learners
attention and elevates their interest in learning English language
585. The measurement of
the ability of a person or the quality or success of a teaching course, etc. It
may be by test, interview, questionnaire, observation and so on. *a) Assessment
586. The merits of
communicative approach based on______________. *a) the practical
utility
587. The merits of
communicative approach is to develop the________________ among the students. *a)
speech
ability
588. The merits of
communicative approach is to develop the________________ among the students *a)
speech ability
589. The merits of
communicative approach teaches___________________.*a) of different ways
of expression
590. The Method of
Discussion is…………………………………………………. *a) This type of interactive
method requires studying and teaching material on the theme before starting
discussion
591. The Method of Role
Playing is…………………………………………………. *a) It is also one of the activity
used in teaching innovative methods. They are made to improve the efficiency of
teaching. It involves the learners into active work by positively influencing
on their inner activity.
592. The process of
learning without being controlled by anyone else. *a) Autonomous
learning
593. The purpose of
feedback is …… *a) to give professional support
594. The purpose of the
feedback in teaching is … *a) to give and receive professional support
595. The purpose of the
feedback in teaching is … *a) to give and receive professional support
596. The role of
teachers in forming young generation’s attitudes to life… *a) is enormous, if we
say that we believe they can ‘fly high’ – they will
597. The teacher tells
a story about animals. Children make animal noises every time they hear the
name of the animal. *a) Total Physical Response
598. The third largest
country in the world with a population of more than 300 million people…*a) America
599. The useful methods
of teaching young learners are… *a) TPR, meaningful drilling, frequent
change of activities
600.
The way
which something is offered, shown or explained others. A formal monologue
presents ideas, opinions or a business proposal. *a) Presentation
601. The word dictation
comes from… *a) latin verb “dicto”
602. Theoretical
positions and beliefs about the nature of language, the nature of language
learning, and the applicability of both to pedagogical settings. *a) Approach
603. There are more
than……….. IELTS centers including Uzbekistan.*a) 500
604. They like to learn
new information by touching or holding things. The learners can be taught by
giving objects (a blue paper, a red paper, a shoe and a sock), writing
vocabulary words on a card for them to study, or giving them instructions
written on a card *a)
Tactile
learners
605. This teaching
style involves a case study format, but the process is not so rigid as a full
case study training session. What teaching style is it? *a) Incident Process
606. Those people who
learn information best by doing and moving it are called *a) kinaesthetic
learners
607. Those people who
learn information best by listening it are called. *a) auditory learners
608. Those people who
learn information best by seeing it are called. *a) visual learners
609. To make a learning
process possible or easier; to work with a group in order to help them to
articulate ideas. *a)
facilitate
610. To teach a foreign
language effectively the teacher needs … … and … … *Teaching aids and
teaching material
611. TOEFL iBT, what
does iBT mean?
*a) Internet-based test
612. TOEFL is………….. *a)
Test
of English as a Foreign Language
613. Topic sentence
is…..*a) this is a main idea of the paragraph the most general
sentence of paragraph
614. TPR built on
coordination of ……………………*a) speech and action
615. Traditional way of
presenting grammar when the teacher explains grammar rules herself/himself is
called…..
*a) Deductive presentation of grammar
616. True-false
activity — *a) It is a strategy of teaching students, where a teacher
allows students to compare two different historical perspectives to the same
question. It allows students to see differing opinions to the same problem and
go about doing history. It is designed to add inquiry into the teaching of
history.
617. Try to find
advantages of pair and group work. *a) All pupils are
active
618. TTT is … *a) teacher talking
time
619. Types of
brainstorming…..*a) making a list, free writing, mapping
620. Types of listening
sub-skills are……*a) listening for gist/global understanding,
specific information, detail or to infer attitude
621. United States cost
less than……. percent of per-pupil spending.*a) 0.25
622. Unstructured
discussion on an assigned topic as a way of generating ideas. *a) .Brainstorming
623. Uzbekistan. IELTS
is available in ….. formats.*a) two
624.
Values are ….*a) are the guiding principles (often
moral or ethical in nature) that govern behaviour; they are typically rooted in
tradition, religion or in individual or shared philosophy and in education they
help to inform decisions at all levels, from national policy right through to
the classroom.
625. Visual aids are … *a)
things
that learners can look at (e.g. a table, a map, a scheme) to help learners
understand something or remember information
626. Visual
intelligence is *a) developed when pupils do exercises supported
by pictures or flashcards
627. Visual learners
prefer to learn by … *a) Seeing or watching
628. Vocabulary is a
………………………. of words and phrases in language *a) collection
629. Warm up activity
is used to…*a) all answers are correct
630. Wat
does the MS Office Suite include? *b) Word, Excel, PowerPoint
631. We can make
presentations in … *a) PowerPoint
632. We can make
presentations in … *a) PowerPoint
633. We‘ve been ______
with that firm for many years. *a) dealing
634. What abilities
should have a teacher? *a) All answers are correct.
635. What activities can
be used as a warm up? *a) all answers are correct
636. What are Cases? a)
Cases
are narratives that contain information and invite analysis. Participants are
put in the position of making decisions or evaluations based on the information
available.
637. What are
extracurricular activities? *a) are those that fall outside the real of
the normal curriculum of school or university education, performed by students.
638. What are roles of
playing games during lessons? *a) To keep pupils’ motivation
639. What are roles of
playing games during lessons? *a) To keep pupils’ motivation
640. What
are the basic tools of «iSpring» PowerPoint add-on?*a) Composing
visual dialogues, creating interactive quizzes, embedding video or audio to
PowerPoint presentation
641. What are the
characteristics of the communicative approach? *a) Focuses on learner
and teacher is just a facilitator; lays less stress on grammar and emphasis on
language in use rather than language as structure. It stresses on the semantic
objective of the language, which means the meaning of language in real life
situation and contexts
642. What are the
components of concepts communicative language teaching? *a) Integration of
skills, info gap activities, authentic materials, groupwork, pairwork, learner
responsibility, teacher as a classroom manager,communicating in English.
643. What are the
inputs of authentic materials? *a) picture, video, cartoons
644. What are the main
aims of the lesson? *a) educational, developing, socio-cultural
or up bringing
645.
What
are the main principles in giving and receiving feedback? *a) All answers are
correct
646. What are the
merits of the dictation? *a) make the pupils and the teacher aware of
the pupils’ comprehension errors phonological, grammatical
647. What
are the multimedia components *d) Text, image, audio, animation, video,
interactivity
648. What are the
multimedia components? *a) text, image, audio, animation, video,
interactivity
649. What are the
people doing in all the conversations? *an exchanging information
650. What are the
problems of authentic materials? *a) usually long background noise might
interfere unknown vocabulary fast speech
651. What are the
problems of non authentic materials? *a) usually boring,
students might be deceived about the nature of the real life listening students
who are always exposed to nonauthentic listening texts, might find it difficult
to communicate in real life
652. What competence
did Dell Hymes consider as the main purpose of teaching language? *a) Communicative
competence
653. What
device is mostly used to process, edit and create information? *c) PC
654. What do PW and GW
stand for in the first formula? *a) Pair work and group work;
655. What does
«pre-writing» mean? *a) tasks prepare for writing, arouse
learners` interest
656. What does
«pre-writing» mean? *a) tasks prepare for writing, arouse
learners` interest
657. What does
“authentic” mean? *a) Real
658. What does “Group
work” stand for? Find the correct definition. *a) mode of doing a
task or activity in small groups
659. What does “Group
work” stand for? Find the correct definition. *a) mode of doing a
task or activity in small groups
660. What does
assessment include?
*a) It includes all methods, both formal and informal, used to
gather information about a pupils’ knowledge, ability, understanding, attitudes
and motivation
661. What does CEFR
stand for? *a) Common European Framework of References
662. What does EFL
mean? *English
as Foreign Language
663. What does ICT
stand for? *a) Information and Communication Technologies
664. What does ICT
stand for? *a) Information and Communication Technologies
665. What does ICT
stand for? *a) it’s an umbrella term for devices, software,
methods of storing, processing and sharing information
666. What
does ICT stands for? c) Its an umbrella term for devices, software, methods of storing,
processing and sharing information
667. What does IELTS
stand for? *a) International English language testing system
668. What does IELTS
stand for? *a) International English language testing system
669. What does IELTS
stand for? *a) International English language testing system
670. What does IELTS
stand for? *a) International English language testing system
671. What does it mean
pre-writing? *a) Tasks prepare for writing, arouse learners` interest
672. What does it mean
prewriting? *Tasks
prepare for writing, arouse learners` interest
673. What does it mean
pre-wrtitng? *a) Tasks prepare for writing, arouse learners` interest
674. What does PPP
stand for? *a) Presentation-Practice-Production
675. What does Scanning
stand for? *a) reading a text for getting specific information such
as dates, names, details, etc.
676. What does Skimming
stand for? *a) reading a text for understanding its gist.
677. What does the A1
level mean? a) * beginner
678. What does the A2
level mean? a) *elementary
679. What
does the acronym ICT mean? *a) Information-Communication Technologies
680. What does the B1
level mean? a) *pre-intermediate
681. What does the B2
level mean? a) *intermediate
682. What does the
C.E.F.R. stand for? *a) Common European Framework of Reference
683. What does the
C.E.F.R. stand for? *a) Common European Framework of Reference
684. What does the C1
level mean? a) * upper-intermediate
685. What does the C2
level mean? a) *advanced
686. What happens in a
Case Method classroom? *a) In classroom discussion, students analyze
the information in the case and use it to solve the problem set up by the case.
687. What helps to develop
listening skills? *a) all are correct
688. What helps to
develop listening skills? *a) all are correct
689. What is (NAEP)? *a)
The
National Assessment of Educational Progress;
690. What is ‘extensive
reading’? *a) reading
widely in order to improve reading comprehension, reading speed and vocabulary
691. What is ‘intensive
reading’? *a) reading
carefully for complete, detailed comprehension (e.g. main ideas, details,
vocabulary)
692. What is ‘making
inference’? *a) ‘reading between the lines’; the reader understands
what is meant but not stated in a passage.
693. What is
‘Paraphrasing’? *a) the ability to say or write ideas in other words;
measures the reader’s understanding of the main idea of the text
694.
What
is “learner- centered” lesson? *a) The pupils will be involved
actively in the lesson.
695. What is a cloze
activity? *a) fill-in-the-blanks exercise in which some words are
omitted designed to measure how well the pupils understand the text.
696. What is a
intensive technique for reading activity? *a) Reading a text for
finding synonyms, antonyms, some
697. What is a
microteaching? *a) a mini-lesson that participants teach to each other in
order to practice what they have learned
698. What is a
microteaching? *a) a mini-lesson that participants teach to each other in
order to practice what they have learned
699. What is a
pictogramm? *a) a drawing of a word which represents a word
700. What is a scanning
technique for reading activity? *a) Reading a text quickly to find
specific information
701. What is a scanning
technique for reading activity? *a) Reading a text quickly to find
specific information
702. What is a scanning
technique for reading activity? *Reading a text quickly to find specific
information
703. What is a skimming
technique for reading activity? *a) Reading a text quickly to get the
main idea
704. What is a skimming
technique for reading activity? *Reading a text quickly to get the main
idea
705. What is a STT? *a)
The
amount a learner or a student talk during a lesson
706. What is a STT? *a)
The
amount a learner or a student talk during a lesson
707. What is a suggestopedia?
*a) it is a type of method with using song or music
708. What is active
vocabulary? a) * words students can recognize, understand and
remember
709. What is an
information gap? *a
one person has information and the other does not, so there is a need to
communicate.
710. What is an
Information transfer technique for reading activity? *Changing
information into another form of information to check pupils understanding?
711. What is an
Information transfer technique for reading activity? *a) Changing
information into another form of information to check pupis` understanding?
712. What is an
intensive technique for reading activity? *Reading a text for finding
synonyms, antonyms, some
713. What is approach? *a)
An
approach is a way of looking at teaching and learning
714. What is approach? *An approach is a
way of looking at teaching and learning.
715. What is Bodily
kinesthetic intelligence? *It is an activity that expresses through physical
activities and movement: roleplay, games, making posters and doing projects.
716. What is
brainstorming? *a) a group activity in which learners have a free and
relatively unstructured discussion on an assigned topic as a way of generating
ideas.
717. What is Case
Study? *a) a
task that native speakers of a language would do in
718. What is CEFR? *a)
A
common reference for describing language learning, teaching, and assessment.
719. What is CEFR? *a)
A
common reference for describing language learning, teaching, and assessment.
720. What is Cloze
exercise? *a) fill
in the blank exercise, in which some words are omitted, designed to measure how
well the reader understands how a text is linked together
721. What is CLT? *a) An approach to
foreign or second language teaching which emphasizes that the goal of language
learning is communicative competence
722. What is CLT? *a)
communicative
language teaching
723. What is CLT? *a)
communicative
language teaching
724. What is
Competence-based approach? *a) This approach in the system of
higher is intended to increase attention to the effective and technological
formation of professional competences.
725. What is contextual
guessing? *a) making
guesses about the meaning of the words by looking at the surrounding words or
situation
726. What is different
about teaching young learners? *a) They learn things slowly but forget
easily.
727. What is different
about teaching young learners? *a) They learn things slowly but forget
easily.
728. What is direct
feedback? *a) teachers should be informed about their mistakes
and told what to do
729. What is Discussion
method? *a) It
demands that students come to class well prepared. Compelling them to think out
their arguments in advance and to answer their peers‘ questions and counter
arguments, it sharpens their powers of reason, analysis and articulation.
730. What is distance
education?*a) Distance
education is that educational information and instruction is taught to learners
who are physically distant from the source of that information and instruction.
731. What is effective
teacher feedback component of assessment for learning? *c) Students are not
passive in the assessment process but are engaged in developing the assessment,
determining what a good performance entails, and learning to score through
models provided by the teacher. Which key component of Assessment for Learning
732. What is ELL? *a) English
Language Learners
733. What is error
correction? *a) Error correction is the process of detecting errors in
transmitted messages and reconstructing the original error-free data. Error
correction ensures that corrected and error-free messages are obtained at the
receiver side.
734. What is ETS? *a)
Educational
Testing Service
735. What is ETS? *a)
Educational
Testing Service
736. What is feedback? *a)
Comments
or information learners receive on the success of a learning task, either from
the teacher or from other learners
737. What is fluency? *a)
the ability to produce the language easily, communicate quickly, but
not necessarily with grammatical correctness
738. What is Gist?
*a) b and c
739. What is grammar? *a)
the
system of structures at word, sentence and text level in a Language
740.
What
is important for teachers while doing group work? *a) Monitoring
741. What is important
while dictating a text? *a) The way how a teacher dictates a text
742. What is important
while dictating a text? *a) The way how a teacher dictates a text
743. What is
information gap? *a) an activity in which a pair or two groups
of students hold different 11 information, or where one partner knows something
that the other doesn’t. This gives a real purpose to a communication activity.
744. What is
information transfer? *a) change of information (e.g., a text) into
another form of information (e.g., a table) to check Ls’ understanding
745. What is intensive
reading? *a) Reading
by concentrating on specific details
746. What is intensive
reading? *a) reading
carefully for detailed understanding (e.g., main ideas, vocabulary, details)
747. What is intensive
reading? *a) reading
carefully for detailed understanding (e.g., main ideas, vocabulary, details)
748. What is
interaction? *a) patterns of communication (verbal and
non-verbal) between people
749. What is Jigsaw
activity? *a) A
type of co-operative activity in which each member of a group has a piece of
information needed to complete a group task.
750. What is Jigsaw
activity? *a) A
type of co-operative activity in which each member of a group has a piece of
information needed to complete a group task.
751. What is LAD? *a)
Language
Acquisition Device
752. What is learner
based approach? *a) It starts from the belief that the learner is
at the center of the learning process and not the syllabus and as such they are
self-directed equals in the learning process along with tutors, teachers
753. What is learning
style? *a
the way a person learns best, understands best and remembers best
754. What
is lesson integrity?*a) The accordance and relevance of lesson plan,
materials and activities
755. What is linguistic
competence? *a) A type of competence which refers to knowledge of
language areas (phonetics, vocabulary, grammar) and language skills (listening,
speaking, reading and writing) to the level sufficient for communication with
the target culture representatives.
756. What is Linguistic
intelligence? *It
is a specially designed grammar and vocabulary exercises based on pair work in
dialogues.
757. What is listening
for the specific detail? *a) Listen for specific information
758. What is listening
for the specific detail? *a) Listen for specific information
759. What is MOODLE? *a)
distance education
760. What is Multimedia
learning? *a) It is the combination of various media types as
text, audio and video materials by the help of which teacher presents
information to the learners.
761. What
is multimedia? *b) using more than one medium of expression or communication
762. What is one of the
first steps learners take in English *a) alphabet
763. What is passive
vocabulary? a) *words students can confidently use in speaking and
writing
764. What is post
writing? *a) Tasks
encourage learners to relate writing to their own life, gives opportunities to
express own ideas, or do something with the information they have got
765. What is post
writing? *a) Tasks
encourage learners to relate writing to their own life, gives opportunities to
express own ideas, or do something with the information they have got.
766. What is post
writing? *Tasks
encourage learners to relate writing to their own life, gives opportunities to
express own ideas, or do something with the information they have got
767. What is post-activity?
*a) what
is done after an activity, usually the next logical step
768. What is
post-activity? *a) what is done after an activity, usually the next
logical step
769. What is PPP? *a)
Presentation,
Practice and Production
770. What is
presentation? *a) The way which something is offered, shown or explained
others. A formal monologue presents ideas, opinions or a business proposal.
771. What is
punctuation? *a) A unit which teaches to use correctly marks in
writing46.
772. What is
recommended for auditory learners? *a) Participate in
discussions, read aloud when studying at home
773. What is
recommended for visual learners? *a) draw a picture in your head to
remember the info better, write things down, look at the picture before reading
774. What is
recommended for visual learners? *a) draw a picture in your head to
remember the info better, write things down, look at the picture before reading
775. What is
recommended for visual learners? *a) draw a picture in your head to
remember the info better, write things down, look at the picture before reading
776. What is role play?
*a) acting
and imitation of characters
777. What is running
dictation? *a) enables pupils to move a lot; .
778. What is scanning
technique for reading activity? *a) reading a text quickly to find
specific information (names, places, dates, numbers, etc.)
779. What is scanning
technique for reading activity? *a) reading a text quickly to find
specific information (names, places, dates, numbers, etc.)
780. What is scanning? *a)
reading
a passage quickly to find specific form
781. What is scanning? *a) reading a text for
getting specific information such as dates, names, details.
782. What is skimming? *a)
reading
a passage quickly to grasp the main idea
783. What is skimming? *a) reading a text for
understanding its gist (general idea)
784. What is some
advantage of distance education?*a) The flexibility it provides to
students;
785. What is speaking
consists of? *a) all answers are correct
786. What is State
Educational Standards of Continuous Education of Uzbekistan? *a) REQUIREMENTS
necessary for content and level of learners on foreign language
787. What is strategy? *a)
set of decisions to achieve an objective that results in plan.
788. What is Student
involved assessment component of assessment for learning? *a) Students
are not passive in the assessment process but are engaged in developing the
assessment, determining what a good performance entails, and learning to score
through models provided by the teacher
789. What is Task based
language learning? *a) it is a method of instruction which
focuses on the use of authentic language
790. What is teaching
approach? *a) Its one’s viewpoint toward teaching or refers to
what one believes in, regarding teaching, upon which are based on teaching
behaviors
791. What is Teaching
with the Case Method? *a) The case method combines two elements:
the case itself and the discussion of that case. A teaching case is a rich
narrative in which individuals or groups must make a decision or solve a
problem. Teaching cases provide information, but neither analysis nor
conclusions.
792. What is the
advantages of authentic materials? *a) exposure to
authentic conversation informal spoken language exposure to different accents
793. What is the
advantages of non authentic materials? *a) language is clear,
language structures are repeated (e.g. can), vocabulary can be taken from the
textbook good for revising vocabulary and grammar suitable for even elementary
students
794. What is the aim of
role plays? *a) to prepare the task and play
795. What
is the best example of multimedia? *b) Videogames
796. What is the
communicative approach? *a) The communicative approach is the
best-known current approach to language teaching.
797. What is the
communicative language? *a language spoken by members of a group or community
within a majority language context.
798.
What
is the definition of the word “feedback”? *a) Suggestion or
advice given to help someone improve weaknesses and emphasize strength and
support that person.
799.
What is
the difference between direct and audio lingual approach? *a) The direct method highlighted the
teaching of vocabulary while the audiolingual approach focus on grammar drills
800. What is the
difference of English lesson from other lessons? *a) it is practical
and directed to speaking
801. What is the
fluency in speaking? *a) To follow norms while speaking
802. What is the
fluency in speaking? *a) To follow norms while speaking
803. What is the goal
of CLT? *a) The goal of this teaching method is communication,
both in classroom and in real life. It encourages pupils to talk more on
communicative purposes. Teacher has a role of facilitator
804. What is the
importance of using didactic games in the lessons? *a) all are true
805. What is the lesson
plan? *a) The
map of lesson
806. What is the lesson
plan? *a) The
map of lesson
807. What is the level
of the 1-4th classes by SES in continuous education system of
Uzbekistan? *a) A1
808. What is the level
of the 1-4th classes by SES in continuous education system of
Uzbekistan? *a) A1
809. What is the level
of the 5-9th classes by SES in continuous education system of Uzbekistan? *a)
A2
810. What is the level
of the 5-9th classes by SES in continuous education system of Uzbekistan? *a)
A2
811. What is the main
aim of writing? *a) Communication
812. What
is the main reason for listening? *a) to get information
813. What is the
meaning of Anticlockwise? *a) the opposite direction to the movement of
the hands of a clock.
814. What is the
meaning of applied linguistics? *a) the study of second and foreign
language acquisition and learning the study of language and linguistics in
relation to practical problems, such as lexicography, translation or speech
pathology.
815. What
is the meaning of clockwise? *a) Moving around in the same direction as the
hands of a clock.
816. What is the
meaning of Incident process? *a) This teaching
style involves a case study format, but the process is not so rigid as a full
case study training session. The focus is on learning how to solve real
problems that involve real people. Small groups of participants are provided
details from actual incidents and then asked to develop a workable solution.
817. What is the
meaning of the word extracurricular activities? *a) outside the
regular program of courses
818. What
is the most common controls for multimedia content? *c)Play/Pause/Stop/
FFWD/REW (Next/Prev)
819. What is the most
important factors for learning words? *a) Context
820. What is the name
of CEFR level A2+ ? *a) Basic user enhanced level
821. What is the name
of CEFR level B2? *a) Independent user level
822. What is the name
of CEFR level C1? *a) Proficient initial user level
823. What is the
objective of the audiolingual method? *a) It is an accurate
pronunciation and grammar
824. What is the
objective of the audiolingual method? *a) It is an accurate
pronunciation and grammar
825. What is the proper
sequence of bringing knowledge nowadays? *a) Knowledge — ˃
Teacher — ˃ Student
826. What
is the proper sequence of bringing knowledge nowadays? *c)
Knowledge->Teacher->Student
827. What
is the purpose of «iSpring» PowerPoint add-on? *b) Creating
interactive lessons
828. What is the
purpose of Placement Test? *a) The purpose of the test is to find
out not only what students know, but also what they don’t know. As a result,
they can be placed in an appropriate class.
829. What is the
purpose of pre-reading activities? *a) to prepare pupils for
reading and understanding
830. What is the
purpose of pre-reading activities? *a) to prepare pupils
for reading and understanding
831. What
is the purpose of tablet? *b) To read, watch video, social networking, casual
gaming
832. What is the recent
and latest approach of teaching English? *a) Communicative
approach
833. What
is the software that is designed to teach languages called?*a) Computer
aided language learning (CALL)
834. What is the State
Educational standard? *a) Minimized educational standards
835. What is the State
Educational standard? *a) Minimized educational standards
836. What is the
structural view to language? *a) It is the view behind the audio-lingual
method
837. What is the topic
about? It is that educational information and instruction is taught to learners
who are physically distant from the source of that information and instruction *a)
distance
education
838. What is the topic
about? It is that educational information and instruction is taught to learners
who are physically distant from the source of that information and instruction *a)
distance
education
839. What is the word
building? *a) To
make a new word by combining words or adding some suffixation
840. What is the word
building? *a) To
make a new word by combining words or adding some suffixation
841. What
is torrent network?*a) Decentralized data sharing network
842. What is TPR? *a)
Total
Physical Response
843. What is TPR? *a)
Total
Physical Response
844. What is VAK? *a)
Learning
styles
845. What is VAK? *a)
visual,
auditory, kinaesthetic
846. What is Visual
intelligence? *It
is an activity that develops pupils learning process through exercises
supported by pictures or use flashcards.
847. What is while
reading? *a) Tasks
draw on writing itself, help to communicate a message
848. What is while
reading? *a) Tasks
draw on writing itself, help to communicate a message
849. What is while
reading? *Tasks
draw on writing itself, help to communicate a message
850. What is
while-activity? *a) what learners do while they are doing an activity
851. What is
while-activity? *a) what learners do while they are doing an activity
852. What kind of
activity Info-Gap activity? *a) It is an activity where learners are
missing the information they need to complete a task and need to talk to each
other to find it.
853. What kind of
activity Info-Gap activity? *a) It is an activity where learners are
missing the information they need to complete a task and need to talk to each
other to find it.
854.
What kind
of activity is jig saw activity? *a) A type of co-operative activity in which each member
of a group has a piece of information needed to complete a group task.
855.
What kind
of activity is true false activity? *a) It is a strategy of teaching
students, where a teacher allows students to compare two different historical
perspectives to the same question. It allows students to see differing opinions
to the same problem and go about doing history. It is designed to add inquiry
into the teaching of history.
856. What kind of
instructions are possible to give pupils? *a) short and simple
857.
What kind
of intelligence of Psychological and cognitive concepts of EFL learning do we
have? *a) all
are correct
858. What kind of
organizer is a “T”-charts? *a) analyzing
859. What
kind of specialists needed to develop a software designed to learn languages? *c)
Programmers, Designers, Photographers, Language specialists
860. What kind of texts
can be used for dictation? *a) all sorts of texts from single words at a
vocabulary list to sentences to full paragraph
861. What language is
used in grammar translation method? *a) Native language
862. What language
level was the “Keep Chain Story” activity? *a) pre-intermediate/
intermediate
863. What lessons
should we use pre-, while-, and post-activities for? *a) Reading, speaking,
writing and listening
864. What level is
called BREAKTHROUGH? *a) LEVEL A1
865. What level is
called BREAKTHROUGH? *a) LEVEL A1
866. What level is
called EFFECTIVE OPERATIONAL PROFICIENCY? *a) LEVEL C1
867. What level is
called EFFECTIVE OPERATIONAL PROFICIENCY? *a) LEVEL C1
868. What level is
called MASTERY? *a) LEVEL C2
869. What level is
called MASTERY? *a) LEVEL C2
870. What level is
called THRESHOLD? *a) LEVEL B1
871. What level is
called THRESHOLD? *a) LEVEL B1
872. What level is
called VANTAGE? *a) LEVEL B2
873. What level is
called VANTAGE? *a) LEVEL B2
874. What level is
called WAYSTAGE? *a) LEVEL A2
875. What level is
called WAYSTAGE? *a) LEVEL A2
876. What method is
cluster? *a) is
the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same
group (called a cluster) are more similar (in some sense or another) to each
other than to those in other groups
877. What
of the following is an mobile operating system? *d) Android, iOS, Symbian
878. What
of the following is physical network? *c) LAN, WAN
879. What opportunities
can students get through TOEFL? *a) to demonstrate their ability to
communicate in English;
880. What problems do
usually teachers have in the lessons when they teach listening to the pupils? *a)
pupils
don’t understand the passage
881. What role does the
facilitator play in the EFL classroom? *a) helper of the
student
882. What role does the
facilitator play in the EFL classroom? *a) helper of the
student
883. What should be a
listening task? *a) it should be close to the real life
884. What should be a
listening task? *a) it should be close to the real life
885. What should be
done to organize extracurricular activities? *a) to prepare the
plan and scenarios
886. What skill is
firstly taught in direct method? *a) Speaking
887. What skills are
called the active/productive skills? *a) speaking and writing
888. What skills are
called the passive/receptive skills? *a) reading and listening
889. What stages are
there in the listening lessons? *a) Pre-, while- and post listening
890. What stages are
there in the listening lessons? *a) Pre-, while- and post listening
891. What stages are
there in the reading lessons? *a) Pre-, while- and post reading
892. What stages are
there in the reading lessons? *a) Pre-, while- and post reading
893. What stages are
there in the writing lessons? *a) Pre-, while- and post writing
894. What stages are
there in the writing lessons? *a) Pre-, while- and post writing
895. What style is it? For these kinds of
learners, it is not enough to read or hear information to learn. They have to
do the information to remember. They learn best through different activities.
For these learners it may be difficult to sit still for a long class.*a) kinaesthetic
learners
896. What style is it? These learners
learn best through hearing information.They enjoy discussions and lectures.
They like to talk about things they learned. These learners remember better
when they read something aloud or listen to a tape recorder. *a) auditory learners
897. What style is it? These learners
need to see things to learn better. It helps if they see the teacher’s face and
body language during class. They may think in pictures, and learn best from
Handouts and videos. During a lesson, these learners like to take notes. *a) visual learners
898. What techniques
can be useful and efective for auditory learners? *a) Short lectures,
hearing the information in a song or asking students to repeat information
aloud help these learners remember new things
899. What types methods
of teaching and learning do we have? *b) methods, activities
900. What types of
assessment do we have? *b) formative and summative assessment
901. What types of
language acquisition do you know? *a) Oral and written
902. What usually
includes itself Principles of Constructive Approaches? *Cultural
Awareness
903. What VAK stand for
*a) visual,
auditory and kinaesthetic.
904. What was the
objective of the “Chain Story” activity? *a) to practise past
tenses, story telling
905. What was the
objective of the “Keep Talking” activity? *a) to develop fluency
906. What
word is used synonymously to the high quality pictures? *b) High-resolution
907. What`s CEFR? *a)
A
common reference for describing language learning, teaching and assessment
908. What’s
the word «app» stands for? *c) Application
909. When
are mistakes corrected in speaking activities? *a) after speaking
910. When is it
appropriate to ask pupils to read aloud in class? *a) When pupils do
exercises on pronunciation, intonation or when pupils role-play.
911. When is
microteaching used? *a) in training situation to concentrate on a
particular aspect of a teacher’s teaching skills
912. When the teachers
use to check on the progress of their students, to see how far they have
learnt, and then use this information to modify their future teaching plans. *a) Formative
assessment
913. When was adopted
the Resolution №1875 of the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan “On
measures to further improve foreign language learning system”? *a) December 10, 2012
914. When was adopted
the Resolution №1875 of the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan “On
measures to further improve foreign language learning system”? *a) December 10, 2012
915. Where the
conversation is? -Good
morning. — How can I help you? -Good morning. I’d like to cut my hair *a)
at the hairdresser
916. Where the
students’ progress is measured as it is happening, and where the measure of a
student’s achievement is the work done all through the learning period and not
just at the end
*a) Continuous Assessment
917. Which activities do
not develop interactive speaking skills? *a) substitution drills
918. Which activity dos
not focus on developing ideas? *a) jigsaw reading
919. Which answer can
be pros of communicative approach? *a) It develops the
speech ability among the students, teaches different ways of expression, it is
based on the practical effectiveness; it lays more stress on the functional
value of language; it enables the students to converse their ideas both inside
and outside the classroom
920. Which are
post-reading activity? *a) reflection summarizing
921. Which column
stands for vocabulary presenting technique? *a) All are correct
922. Which is correct
meaning of speaking? *a) express feelings orally
923. Which is not method
of teaching young learners a) short stories and essay*
924. Which of the
following is not considered a disadvantage of case study? *a) The
results are not able to be replicated
925. Which of the
international testing system has the formats «academic» and
«general»? *a) IELTS
926. Which of the
international testing system has the formats «academic» and
«general»? *a) IELTS
927. Which
of the listed features belong only to tablets?*a) Shooting photos,
videos, reading books, social networking
928. Which test type
can be used in the following situation — An English language course has been
completed? *b)
achievement
tests9
929. Which test type
can be used in the following situation — Students show signs of de-motivation
in the lessons *d) diagnostic tests
930. Which test type
can be used in the following situation An applicant is seeking admission to a
University in the UK. *a) Proficiency tests
931. Who are auditory
learners? *a) learners
who learn information best by listening to it
932. Who are auditory
learners? *a) learners
who learn information best by listening to it
933. Who corrects
dictations? *a) c, d
934. Who developed a
program to increase independent reading among middle school readers?*a) Morris and Kaplan;
935. Who is
actively involved in direct method? *a) learner
936. Who is auditory
learner? *a) Who
learn best by listening
937. Who learns best by
listening? *a) auditory learners
938. Who like to learn
new information by seeing it? *a) Visual learners
939. Who
was the visionary and the CEO of Apple Corp? *d) late Steve Jobs
940. Why CEFR was being
adapted in Europe? *d) all answers are correct
941. Why do people read
and accept their ideas? *a) For pleasure, to find necessary
information.
942. Why do we listen
for the first time? *a) To understand the gist
943. Why do we listen
for the second time? *a) To understand the details
944. Why is it
important to use pair work and group work in speaking activities? *a) It enables a
teacher to involve all pupils, to give pupils a certain freedom from teacher’s
control; as a result your pupils will feel more confident to speak English;
945. Why should we use
Icebreaker? *a) it is used to get to know each other
946. Why Teach with the
Case Method? *a) Case discussions bring energy and excitement to the
classroom, providing students with an opportunity to work with a range of
evidence, and improving their ability to apply the vocabulary, theory and
methods they have learned in the lesson
947. Word stress is *a)
saying a syllable in the word with a greater energy and higher
948. You can
demonstrate varying …. within a word by stretching rubber bands. *a) vowel
lengths
Week 1: Teach English Now! Foundational Principles Coursera Quiz Answers
Quiz 1: Welcome Guide
Q1. Who handles course content issues?
- ASU
- Coursera
Q2. Who handles technical issues?
- ASU
- Coursera
Q3. The deadlines are…
- to be followed exactly.
- simply a guide, except the last one at the end of the course.
- simply a guide.
Q4. To alert your peers to review an assignment, you should…
- do nothing.
- post a request with a shareable link in Discussions.
- post a request in Discussions.
Q5. In order to receive the 150 Hour TESOL certificate from ASU, you must…
- successfully finish the course you are taking right now.
- successfully complete Part 1.
- successfully complete Parts 1 and 2.
Quiz 2: Checkpoint 1
Q1. Students are constantly judging teacher performance and classroom
content. Which of the following statements explains how students can so
quickly judge a teacher’s performance?
- Students care about how exciting information is, and don’t care about how important that information might be.
- Students can quickly see teacher technique and ability, which speaks to the need for a teacher to help make meaning clear.
- Students need to be given motivation by being given cake.
- Students only pay attention to how a teacher dresses and speaks.
Q2. Motivation matters in the classroom. Identify the four major factors students need to be intrinsically motivated:
- Value, knowledge, support, and encouragement
- Enthusiasm, curiosity, passion, and energy
- Belonging, power, freedom and fun
- Autonomy, enthusiasm, mastery, and cheerfulness
Q3. A teacher who has taken courses on how to teach, but has no control over what they teach would fall into which of these four quadrants?
- Low technique, low content
- Low technique, high content
- High technique, low content
- High technique, high content
Quiz 3: Checkpoint 2
Q1. Part of motivation is a feeling of competence. Both Stephen Krashen and Lev Vygotsky believe students work best just a little above their performance level. Stephen Krashen calls it i + 1 . Leo Vygotsky calls it…
- zone + 1
- the zone of proximal development
- the language development zone
- the approximate learning zone
Q2. Vygotsky’s theory of the Zone of Proximal Development has students
working slightly above their level so they feel comfortable yet
challenged. To assist students in this
zone, teachers offer support – scaffolding – as they master a skill. Which of the following scenarios is an
example of scaffolding?
- Write an essay based on the science article discussed in class today. Use the model shown at the beginning of class to guide your writing. Also use the essay we created together for further support. Turn it in on Wednesday.
- Write an essay based on this science article. Look for relationships between it and the
video we watched in class. Turn it in on
Wednesday. - Write an essay after reading this article. Remember to use the form discussed in class. Turn it in on Wednesday.
- Write an essay using this science article. Use your notes from class to support your
opinion. Turn it in on Wednesday.
Q3. Dr. Dixon demonstrated the word “p’alante” in order to share how teachers can support language through the use of
- scaffolding
- body language
- teacher talk
- cake
Q4. Drs. Ambady and Rosenthal performed a study that demonstrated how quickly and proficiently students can determine the effectiveness of their teachers. One of the reasons that the study is so controversial is that
- students identified the “good” and “bad” teachers so quickly
- students weren’t paying attention to all the hard work the teachers put into the syllabus
- students demonstrated a lack of empathy for the difficulty teachers have in preparing lessons, and their judgment showed how callous learners have become.
- students weren’t really judging anything except superficial features, so the study’s validity is questionable.
Q5. Check all the characteristics of teacher talk:
- repetition
- elaboration
- clarification questions
- common cultural references
- confusing phrases
- reduced grammatical forms
- simplified vocabulary
- signpost expressions
- motivational words
Quiz 4: Module 1 Review Quiz
Q1. Part of motivation is a feeling of
competence. Both Stephen Krashen and Leo
Vygotsky believe students work best just a little above their performance
level. Stephen Krashen calls this…
- i + 1
- approximate learning zone
- zone of proximal development
- zone + 10
Q2. Vygotsky’s theory of the Zone of Proximal
Development has students working slightly above their level so they feel
comfortable yet challenged. To assist
students in this zone, teachers offer support – scaffolding – as they master a
skill. Which of the following
scenarios is an example of scaffolding?
- Write a paragraph about your favorite hero, using the writing frame we practiced together in class.
- Write a paragraph using six of the vocabulary words from the chapter.
- Read the excerpt on pg. 19 and answer the multiple choice questions at the end.
- Write a paragraph summarizing this reading excerpt. Remember to use the paragraph structure we discussed in class.
Q3. In order to scaffold correctly, a teacher needs to break down difficult concepts by…
- controlling: giving students information that is modified and simplified for their level
- adjusting: changing the input to match the students’ current understanding
- timed repetition: having students learn and process information bit by bit, not all at once
- guiding: showing students how to create a structure
- revising: giving students feedback based on their efforts
- practicing: allowing students to work on what they have done again so that they can get it right
- supporting: giving students time to process new information
- diverting: giving students information that is different from the original text
- converging: taking both the new information and the different information and placing them together to create something interesting
- modeling: showing both real examples and steps of a process
- guided practice: working through a process with students so that it is “controlled”
- independent practice: giving students a chance to do the process on their own
Q4. Three techniques to help make meaning clear are…
- elaboration, body language, and repetition
- the zone of proximal development, i + 1, and high technique/high content
- body language, teacher talk, and scaffolding
- high technique/low content, scaffolding, and teacher talk
Q5. Here is an example of effective teacher talk:
Before: “Construction on the Panama Canal was halted for a period of time due to engineering problems and high mortality rates from disease.”
- After: “Engineers stopped construction of the Panama Canal for a period of time because of engineering problems and a high number of worker deaths from disease.”
- This is an example of which teacher talk strategy?
- use of cultural references
- elaboration
- reduced grammatical forms
- repetition
Q6. According to Glasser, the four basic psychological needs of belonging, competence, freedom and fun are the foundation for…
- scaffolding
- extrinsic motivation
- language acquisition
- intrinsic motivation
Q7. A Harvard research study showed that students often judge a teacher in the first 6 seconds of class, based on…
- their content
- their use of technology
- their age
- their teaching technique
Q8. This illustration shows the importance of finding a balance between technique and content. Your goal should be to fit into which quadrant?
- High content, high technique
- Low content, high technique
- High content, low technique
- Low content, low technique
Q9. Which of the following sentences includes a cultural reference that English language learners might not understand?
- The young couple wanted to make sure they had their family’s approval before walking down the aisle.
- Language learning is fun!
- The President’s first priority will be fixing the economy.
- Mexican culture is known to be very family-oriented.
Q10. Showing students how to write a sentence in the passive voice is an example of…
- guided practice
- i + 1
- independent practice
- modeling
Week 2: Teach English Now! Foundational Principles Coursera Quiz Answers
Quiz 1: Checkpoint 1
Q1. Which are examples of
learning? (Check all that apply.)
- Using your new language in a
country that speaks it. - Filling in the blanks with the
proper form of a verb. - Studying vocabulary.
- Practicing a dialogue with a
partner.
Q2. When it comes to
studying a language, which is the BEST measure of your success at using the
language?
- Acquisition
- Learning
Q3. Which is an example of acquisition?
- Andrea is in a Japanese grocery store, shopping for supplies. She wants to buy salt, but she doesn’t know the Japanese word for it. She thinks she’s found a bag of salt, but it could be sugar too! She is not able to read the Japanese character for “salt”. She looks up the word for “salt” in her English-Japanese dictionary and asks a store clerk if what she has is indeed salt. It is!
- Ali studied English for four
years in high school and got good grades. One day, an English-speaking
tourist stops him on the street to ask for directions. He struggles to
find the words to explain.
Q4. How is language learning like a camera?
- Like a camera, language learning is about zooming in to focus on the details of a language’s structure as well as zooming out to learn to use language in a wider context.
- Like a camera, language
learning is delicate and easily broken. - Like a camera, language
learning is about a single moment in time.
Like a camera, language learning is complex and difficult to become an expert at.
Q5. Compare Brown’s and
Oakley’s metaphors. Choose the correct analogy.
- Brown’s zoom lens = Oakley’s focused mode
Brown’s wide-angle lens = Oakley’s diffuse mode - Brown’s zoom lens = Oakley’s diffuse mode
Brown’s wide-angle lens = Oakley’s focused mode
Q6. Which answer BEST defines your role as a language teacher?
- You are a photographer, sometimes helping students to focus on a specific language structure, other times providing opportunities for students to use the language and practice the new grammatical or sentence structures in a wider context.
- You are a telescope, able to bring distant concepts into view.
- You are a magnifying glass,
explaining small details about the language.
Quiz 2: Checkpoint 2
Q1. TRUE or FALSE: Michael Jordan can teach you to play basketball just like him by teaching you all the rules.
- TRUE
- FALSE
Q2. How is a language teacher like a coach? (Select the BEST answer.)
- A language teacher is like a coach because he or
she teaches the rules of the game, makes everyone practice a lot of drills, and
does a lot of yelling from the sidelines. - A language teacher is like a coach because he or she teaches the rules of the game, makes sure everyone gets plenty of opportunity to practice the game in many different ways, and encourages players to take risks and keep trying.
Q3. What is the 80/20 principle?
- A language teacher should spend 80 minutes lecturing about the language rules, and then students should spend 20 minutes practicing those rules.
- A language teacher should plan a lesson so that 20% of the time is used for focusing on the details of the language, and 80% of the time is used for students to practice the language.
- A language teacher should plan a lesson so that students will learn 80 new vocabulary words and 20 new grammatical structures a week.
Quiz 3: Module 2 Review Quiz
Q1. Learning is…
- the ability to apply concepts in real-world situations.
- the ability to pass a test.
- the ability to memorize concepts.
- the ability to comprehend and recall information.
Q2. Acquisition refers to…
- the ability to learn and apply principles in the real world.
- the ability to remember information for long periods of time
- the ability to speak another language perfectly
- the ability to understand another language
Q3. Which activity represents language learning in the wide-angle or diffuse mode?
- Practicing scripted telephone dialogues with a partner
- Role playing a doctor’s appointment
- Writing paragraphs using a new grammatical structure
- Using computer software to study vocabulary words
Q4. According to the 80/20 principle, 80% of class time should be spent on…
- instruction in the focused mode
- instruction in the diffuse mode
- instruction using spaced repetition
- vocabulary instruction
Q5. Using a website to study vocabulary and mark words that you still haven’t learned yet is an example of…
- synthesizing information.
- focused mode of instruction.
- the diffuse mode of instruction.
- a camera.
Q6. Brown’s zoom lens metaphor is similar to…
- spaced repetition.
- the Leitner System.
- Oakley’s diffuse mode.
- Oakley’s focused mode.
Q7. Spaced repetition refers to…
- studying the same information over and over again
- putting two unrelated ideas together to synthesize information
- spending a limited time studying material, then coming back to it later, increasing amounts of time between study sessions
- practicing items that you haven’t learned yet more frequently than those you have already memorized
Q8. Which is an example of an activity that helps advanced learners think critically and use language to express ideas.
- Compare and contrast wedding traditions from two different cultures.
- Identify key vocabulary words associated with wedding traditions.
- Use the future tense to write about a popular wedding tradition.
- Explain a wedding tradition in your culture.
Q9. Identify the learner that values accuracy over fluency.
- Gabriel is very open and gregarious and rather indifferent to language structures and cultural conventions. He will not hesitate to speak to people in his new language.
- Beatriz is very particular about speaking correctly. Before speaking, she spends several minutes quietly thinking to herself, checking her dictionary, and planning how she should best phrase her sentences.
- Andrea quickly considers what she is going to say, and then asks the nearest person for directions. She is only able to retain small chunks of information, so she must ask several people for help along the way.
Q10. Considering the descriptions above, which language learner do you think you would be the most like if you were learning a new language?
- Beatriz
- Gabriel
- Andrea
Week 3: Teach English Now! Foundational Principles Coursera Quiz Answers
Quiz 1: Checkpoint 1
Q1. How can self-awareness be a positive thing? Check all that apply.
- It helps you understand why you feel the way you do.
- It makes you nervous.
- You know how you look or feel.
- You have confidence because you know you look or feel good.
Q2. How can self-awareness be a negative thing? Check all that apply.
- You have confidence because you know you look or feel good.
- It can paralyze you because it makes you feel like everyone is judging what you are doing.
- In new situations, it causes you to over-think what you are doing and saying.
- You lose confidence because it feels like everything you do or say is wrong.
Q3. Which answer BEST describes how language learning is like being on stage?
- Like being on stage, learning a new language creates a heightened sense of self-awareness, where the learner is afraid to make mistakes and is almost paralyzed with tension.
- Like being on stage, language learning requires years of practice and effort to be good enough to use it.
- Like being on stage, language learning requires costumes, scripts, and a huge audience.
Q4. TRUE or FALSE: The affective filter is the complex set of emotions language learners experience as they try to process new information and produce language.
- TRUE
- FALSE
Q5. Which of these is NOT a good way to lower the affective filter in your students?
- Relate to your learners in ways that show you understand the challenges of learning a language.
- Be willing to look silly.
- Correct errors frequently and as soon as they happen.
- Use formative evaluation, by giving students practice opportunities where you can guide them with constructive feedback.
- Describe mistakes as normal part of the process.
Quiz 2: Checkpoint 2
Q1. After spending many days in his room studying vocabulary and grammar, why couldn’t Francois Gouin speak German? Check all that apply.
- He did not practice the language in real-world contexts.
- He couldn’t see the language with a “wide-angle lens”.
- He wasn’t using the best dictionaries and grammar books.
- He did not engage in activities in the diffuse mode.
Q2. What main point about language learning did the Francois Gouin story illustrate?
- Even smart men can make mistakes.
- Learning a language requires many hours of studying.
- Language learning requires practice and taking risks.
- Practice makes perfect.
Q3. Which strategy is NOT associated with successful language learning?
- Using imagery to remember new information
- Monitoring language output for accuracy in both form and meaning
- Predicting meaning from social and contextual clues.
- Memorizing thousands of words
Quiz 3: Module 3 Review Quiz
Q1. Which answer BEST describes how language learning is like being on stage?
- Like being on stage, language learning requires costumes, scripts, and a huge audience.
- Like being on stage, learning a new language creates a heightened sense of self-awareness, where the learner is afraid to make mistakes and is almost paralyzed with tension.
- Like being on stage, language learning requires years of practice and effort to be good enough to use it.
Q2. Which statement is NOT true about the concept of self-awareness.
- Self-awareness evolves over time.
- Self-awareness has nothing to do with language acquisition.
- Self-awareness has both positive and negative consequences.
- Self-awareness refers to one’s ability to see themselves as other people do.
Q3. TRUE or FALSE: A high affective filter leads to successful language acquisition.
- FALSE
- TRUE
Q4. TRUE or FALSE: An instructor describing mistakes as normal helps to lower the affective filter.
- True
- False
Q5. Which classroom environment would most likely lower the affective filter of language learners.
- The teacher shares stories about making mistakes when communicating in another language.
- The teacher is quick to correct learner mistakes and has them repeat the correct form.
Q6. Which of the following statements are true about formative assessments? Check all that apply.
- Formative assessments measure everything the student has learned during a unit of study.
- Formative assessments do not lower affective filters.
- Formative assessments give learners the opportunity to practice and prepare for future testing.
- Formative assessments are used to provide feedback to the learner.
Q7. Identify which activities would serve as a formative assessment. (Check all that apply.)
- The students take a final exam.
- The students present a final project.
- The students write about themselves, then conference with the teacher about how to improve their writing.
- The students study 10 vocabulary words and then play a game with those words.
Q8. After spending a year in Germany, why wasn’t Francois Gouin able to learn German? Check all that apply.
- He didn’t engage in meaningful practice.
- He didn’t spend enough time in the diffuse mode of language learning.
- He didn’t spend enough time in the focused mode of language learning.
- He didn’t study hard enough.
Q9. Identify the strategies used by good language learners. Check all that apply.
- They prepare in advance and take notes.
- They pay attention selectively to the most important information.
- They look everything up in a dictionary.
- They are not afraid to look ridiculous.
Q10. TRUE or FALSE: Students who play and experiment with language are typically good language learners.
- TRUE
- FALSE
Week 4: Teach English Now! Foundational Principles Coursera Quiz Answers
Quiz 1: Checkpoint 1
Q1. One of the major difficulties in teaching language is the problem of time. As explained in the videos, the problem of time means that…
- Students have to do extracurricular sports, student council, and many other tasks that get in the way of their language learning.
- Teachers struggle with time because they are given so many tasks to do, such as lesson planning and assessment.
- Most schools offer language instruction for one hour a day, meaning that students don’t have enough time to practice language.
- Parents do not give their children language support by spending time with them on their homework assignments.
Q2.What are some ways, explained in the video, to help support the learning of English OUTSIDE the classroom? Check all that apply.
- offer student exchanges
- select fun readings from a textbook
- invite students to write down a list of their language resources
- create English clubs
- make food from an English-speaking country and bring it to clas
Q3. As the story of Shane’s 5 years of Spanish suggested, some learners fail to learn language outside of the classroom, even when they have the resources to do it. What did the story suggest about why learners fail?
- Learners are too busy to learn a language. They are involved in the digital age, so they simply don’t see English as an important goal.
- Learners fail to see their resources as opportunities. They don’t connect their academic life to the world outside.
- Learners care about testing and getting grades, so they focus only on textbooks and fail to consider actually acquiring language.
- Most learners don’t care about learning a language. Learners these days are lazy and don’t think globally.
Quiz 2: Checkpoint 2
Q1. Identify the most common ways that students can learn language through the internet. Check all that apply.
- movies
- textbooks
- games
- music
Q2. The difference between language learning websites and websites that “happen to be in English” is that…
- language learning websites are designed for specific levels and needs of students, and websites that “happen to be in English” present real contexts and real information.
- Language learning websites are more appropriate because they contain modified input
- language learning websites are boring and unrealistic, and websites that are in real English help students to feel like they are really involved in language learning.
- websites that happen to be in English are more appropriate because they contain real English in real context.
Q3. Which of the following strategies might best encourage student autonomy? Check all that apply.
- empowering students to recognize language learning on the internet
- emphasizing test scores as the goal of language learning
- helping students understand the importance of the classroom
- helping students recognize their language resources
- inviting students to see themselves as part of a global community
Quiz 3: Module 4 Review Quiz
Q1. One of the major difficulties in teaching language is the problem of time. As explained in the videos, the problem of time means that…
- Teachers struggle with time because they are given so many tasks to do, such as lesson planning and assessment.
- Parents do not give their children language support by spending time with them on their homework assignments.
- Students have to do extracurricular sports, student council, and many other tasks that get in the way of their language learning.
- Most schools offer language instruction for one hour a day, meaning that students don’t have enough time to practice language.
Q2. Which is NOT a way to support language learners outside the classroom?
- invite students to write down a list of their language resources
- create English clubs
- make food from an English-speaking country and bring it to class
Q3. As the story of Shane’s 5 years of Spanish suggested, some learners fail to learn language outside of the classroom, even when they have the resources to do it. What did the story suggest about why learners fail?
- Learners are too busy to learn a language. They are involved in the digital age, so they simply don’t see English as an important goal.
- Most learners don’t care about learning a language. Learners these days are lazy and don’t think globally.
- Learners care about testing and getting grades, so they focus only on textbooks and fail to consider actually acquiring language.
- Learners fail to see their resources as opportunities. They don’t connect their academic life to the world outside.
Q4. Learners can acquire language through the internet in all of these places EXCEPT:
- songs
- textbooks
- television shows
- online games
Q5. Student autonomy means that
- students join with friends to form associations.
- students can learn for themselves without the help of another.
- students must be guided so that they can follow strong examples.
- students must obey their teachers or they will make too many errors.
Q6. The metaphor that language is outside a door means…
- that language learning can’t just happen within the walls of a classroom, but that outside of the classroom there are contexts and experiences that will help students acquire and love language.
- that language learning is learned through a series of stages. Language learning means that you walk through a lot of different doors in order to progress.
Q7. A student is an actor means that…
- students need to use body language and express themselves more than they need to learn vocabulary and grammar.
- a student is empowered to move about and participate in a global society.
- a student needs to join the theater.
Q8. In this module, we learned that language is a…
- fish…it helps us to see ourselves as part of a larger community, like a school of fish.
- hammer…it gives us power to share our way of thinking.
- passport…it gives us access to visit and understand many parts of the world.
Week 5: Teach English Now! Foundational Principles Coursera Quiz Answers
Quiz 1:Checkpoint 1
Q1. According to the lectures, why do language teachers experience high rates of teacher burnout?
- They care too much about their students.
- They utilize a learner-centered approach to teaching language, which requires a lot of preparation and a lot of skill.
- They teach too many hours each day.
- They have too many students in their classes.
Q2. What are the benefits of forming a network of teachers? Check all that apply.
- Take advantage of the expertise of other teachers
- Share ideas
- Avoid having to plan lessons
- Save time
Q3. In addition to forming networks at school, what are some other ways that teachers can network with other teachers? Check all that apply.
- Go to coffee shops and ask if there are any teachers there
- Join TESOL or other teacher organizations
- Search for teacher forums and communities on the internet
- Attend professional conferences
Quiz 2: Checkpoint 2
Q1. In Skinner and Edge’s book about self-determination, which two factors help people avoid burn-out?
- forming a network and having a sense of control
- sharing the workload and taking long vacations
- changing teaching assignments often and volunteering
- finding a support group to complain to and working less hours
Q2. What are some ways that teachers can maintain a sense of control? Check all that apply.
- Be an agent of change.
- Find balance between work and life.
- Cherish the rewards of teaching
- Focus on the things you can do, not the things you cannot.
Q3. What is meant by finding your core? Check all that apply.
- Be sincere. Don’t pretend to believe something you don’t.
- Know your own teaching philosophy.
- Find a core group of friends to spend time with.
- Find a cause or idea that you believe in.
Quiz 3: Module 5 Review quiz
Q1. What is the phenomenon known as teacher burnout?
- Teachers put so much time and energy into their teaching that they become exhausted and leave the teaching profession.
- Teachers feel bored by teaching the same things day after day, so they leave the profession.
- Teachers feel burned by low salaries and leave the teaching profession.
- Teachers feel overwhelmed by the responsibilities that come with teaching, so they leave to find an easier job.
Q2. What does the following statement mean? Teachers should be like actors, but not act.
- Teachers should not use their hands, face and body to communicate meaning.
- Teachers should not make their lessons more exciting or impactful by performing.
- Teachers should not act, or pretend to believe or feel something they don’t.
Q3. What are good ways to form a network? Check all that apply.
- Put out an advertisement.
- Consult online forums and blogs about ESL teaching.
- Join professional organizations.
- Find teachers and other ESL professionals at your school site that are willing to share ideas.
Q4. What are recommended strategies for maintaining self-control over your career? Check all that apply.
- Find a balance between work and life.
- Refuse to teach concepts that are uninteresting to you.
- Focus on the things you can do, and not the things you cannot.
- Find your core teaching beliefs.
Q5. In Skinner and Edge’s book about self-determination, they recommend which two strategies to avoid burnout?
- work shorter hours and travel
- volunteer more time and take long vacations
- form a network and maintain a sense of control
- don’t over-commit and change teaching assignments often
Week 6: Teach English Now! Foundational Principles Coursera Quiz Answers
Quiz 1: Final Assessment
Q1. In this course, it was stated that a principled teacher must find their core. What is meant by finding your core? Check all that apply.
- Find a cause or idea that you believe in.
- Be sincere. Don’t pretend to believe something you don’t.
- Know your own teaching philosophy.
- Tell stories about your experiences learning a language.
Q2. Much like the metaphor “language is cake,” a Harvard research study showed that students often judge a teacher in the first 6 seconds of class, based on…
- their teaching technique
- their use of technology
- their content
- their age
Q3. What does the following statement mean? Teachers should be like actors, but not act.
- Teachers should not use their hands, face and body to communicate meaning.
- Teachers should not make their lessons more exciting or impactful by performing.
- Teachers should not act, or pretend to believe or feel something they don’t.
Q4. According to Glasser, the four basic psychological needs of belonging, competence, freedom and fun are the foundation for…
- scaffolding
- intrinsic motivation
- language acquisition
- extrinsic motivation
Q5. Much like an actor, good teachers use which three techniques to help make meaning clear?
- body language, teacher talk, and scaffolding
- the zone of proximal development, i + 1, and high technique/high content
- elaboration, body language, and repetition
- high technique/low content, scaffolding, and teacher talk
Q6. Vygotsky’s theory of the Zone of Proximal Development has students working slightly above their level so they feel comfortable yet challenged. To assist students in this zone, teachers offer support, or scaffolding, as they master a skill. Which learning activity includes scaffolding?
- Read Chapter 4 and answer the chapter review questions on pg. 100.
- Write a paragraph summarizing Chapter 4. Remember to use the summarizing techniques I mentioned in class.
- Write a paragraph describing your favorite character from the story, using the writing frame we practiced together in class.
Write a paragraph using six of the vocabulary words from the chapter.
Q7. How is language learning like a camera?
- Like a camera, language learning is complex and difficult to become an expert at.
- Like a camera, language learning is delicate and easily broken.
- Like a camera, language learning is about a single moment in time.
- Like a camera, language learning is about zooming in to focus on the details of a language’s structure as well as zooming out to learn to use language in a wider context.
Q8. Which activity represents language learning in the wide-angle or diffuse mode?
- Role playing a job interview
- Using computer software to study vocabulary words
- Practicing scripted telephone dialogues with a partner
- Writing sentences using a new grammatical structure
Q9. How is a language teacher like a coach? (Select the BEST answer.)
- A language teacher is like a coach because he or she teaches the rules of the game, makes everyone practice a lot of drills, and does a lot of yelling from the sidelines.
- A language teacher is like a coach because he or she teaches the rules of the game, makes sure everyone gets plenty of opportunity to practice the game in many different ways, and encourages players to take risks and keep trying.
Q10. What is the 80/20 principle?
- A language teacher should plan a lesson so that 20% of the time is used for focusing on the details of the language, and 80% of the time is used for students to practice the language.
- A language teacher should plan a lesson so that students will learn 80 new vocabulary words and 20 new grammatical structures a week.
- A language teacher should spend 80 minutes lecturing about the language rules, and then students should spend 20 minutes practicing those rules.
Q11. Which answer BEST describes how language learning is like being on stage?
- Like being on stage, learning a new language creates a heightened sense of self-awareness, where the learner is afraid to make mistakes and is almost paralyzed with tension.
- Like being on stage, language learning requires costumes, scripts, and a huge audience.
- Like being on stage, language learning requires years of practice and effort to be good enough to use it.
Q12. In research studies, which strategies were good language learners found to use? Check all that apply.
- They are not afraid to look ridiculous.
- They prepare in advance and take notes.
- They pay attention selectively to the most important information.
- They find answers in multiple ways.
- They look everything up in a dictionary.
Q13. Like a mother bird encourages her baby bird to leave the nest, how can teachers encourage student autonomy? (Check all that apply)
- helping students recognize their language resources
- inviting students to see themselves as part of a global community
- empowering students to recognize language learning opportunities on the internet
- helping students understand the importance of the classroom
- emphasizing test scores as the goal of language learning
Q14. A student is an actor means that…
- a student needs to join the theater.
- students need to use body language and express themselves more than they need to learn vocabulary and grammar.
- a student is empowered to move about and participate in a global society.
Q15. Which metaphor explains the power that is gained by learning a language?
- Language is like a passport…it gives us access to visit and understand many parts of the world.
- Language is like a fish…it helps us to see ourselves as part of a larger community, like a school of fish.
- Language is like a hammer…it gives us power to establish our authority.
A. Complete using the correct form of the words in the box.
prefect • pupil • student
1 In our school, most classes have about 35 ………………… in them.
2 Every year, two new ………………… are chosen from the best students in each class.
3 The university accepts around 2000 new ………………… every year.
4 When he finally graduated, Victor felt he had ………………… everything he set out to do.
5 The work we’re doing now will make more sense when you ………………… the sixth.
6 Who ………………… you how to play the drums like that?
7 I would love to ………………… a new language I don’t know anything about, like Swedish.
high • primary • secondary
8 Children in England go to ………………… school from the ages of five to eleven.
9 In Britain, grammar schools, public schools and comprehensives are often referred to as ………………… schools.
10 Americans usually refer to their secondary school as a ………………… school, and there are often separate junior and senior schools.
degree • certificate • results
11 The exam ………………… come out today and I’m really nervous. I hope I’ve passed.
12 I was so proud when my exam ………………… finally arrived in the post.
13 I would prefer to go to university and do a ………………… in astronomy, rather than start work.
Answers
1 pupils 2 prefects 3 students 4 achieved
5 reach 6 taught 7 learn 8 primary
9 secondary 10 high 11 results 12 certificate
13 degree
B. Circle the correct word.
1 I made a few mistakes in the exam and I don’t think I passed / took it.
2 It’s not always easy to count / measure how intelligent someone is.
3 Did you know that our French teacher can speak / talk four languages?
4 My qualifications / qualities include a degree and an MA in chemistry.
5 Our headteacher had had her hair cut and I didn’t know / recognise her at first.
6 In design and technology, we were given the effort / task of designing a stadium.
7 You’ll find plenty of books on the subject / lesson of business studies in the library.
8 You have to read / study hard in order to do well at university.
9 Look at what we did in today’s lesson and we’ll have a quick exam / test tomorrow morning.
10 Our teacher asked us to choose one of our colleagues / classmates to be our partner for the next exercise.
Answers
1 passed 2 measure 3 speak 4 qualifications
5 recognise 6 task 7 subject 8 study
9 test 10 classmates
C. Write one word in each gap.
1 Just get ……………… with Exercise C and I’ll be back in a minute.
2 My teacher says that I should sail ……………… the exam, but I’m not so sure.
3 Dave didn’t understand what Miss Smith was getting ……………… so he asked her to explain it again.
4 We all tried to convince our teachers to change his mind about the school trip and he finally came ……………… .
5 If you make a mistake, just cross it ……………… with a single line.
6 Belinda missed a few months of school because of illness and found it difficult to keep ……………… with her classmates.
7 The other kids were making fun of me, but I didn’t catch ……………… until heard them laughing.
Answers
1 on 2 through 3 at 4 (a)round
5 out/through 6 up 7 on
D. Complete each second sentence using the word given, so that it has a similar meaning to the first sentence. Write between two and five words in each gap.
1 The ideas in your essay need to be organised better. set
You need to ……………………………… in your essay better.
2 Why don’t you consider the college’s offer for a few days and then call them? over
Why don’t you ……………………………… for a few days and then call them?
3 You’ll never pass the exam if you just stop trying like that. in
You’ll never pass the exam if you just ……………………………… like that.
4 When he was at university, Nick just couldn’t handle all the work. deal
Nick just couldn’t ……………………………… at university.
5 I suddenly realised that I had left my homework at home. dawned
It ……………………………… that I had left my homework at home.
6 Ed was very lonely at university and he left after only one month. out
Ed ……………………………… after only one month because he was very lonely.
Answers
1 set out the ideas
2 think the college’s offer over
3 give in
4 deal with all the work
5 suddenly dawned on me
6 dropped out of university
E. Choose the correct answer.
1 If you need to ………… the teacher’s attention, just put your hand up.
A pull B attract
C capture D draw
2 Make sure you ………… your homework before you go out.
A make B solve
C write D do
3 Could I ………… a suggestion? Why not have piano lessons?
A have B do
C put D make
4 I really don’t ………… the point of taking the exam when you’re not ready for it.
A take B see
C have D mind
5 I’ll meet you at the school gates during the lunch ………… .
A break B gap
C interval D pause
6 Do you think you could pass that book ………… to me, please?
A under B through
C over D in
7 Mrs Dawson said that we are ………… our lesson in the library next Monday.
A having B making
C reading D going
8 In English yesterday, we had a discussion ………… different cultures.
A around B about
C for D from
9 ………… my opinion, maths shouldn’t be a compulsory subject.
A From B To
C At D In
10 When you ………… the exam tomorrow, try to stay calm and relaxed.
A make B write
C take D answer
11 My dad wants me to go to university, but I’m in ………… minds about it.
A my B two
C some D different
12 I still have a lot ………… about the English language.
A learning B to learn
C for learning
D of learning
13 If the examiner can’t ………… sense of your writing, you’ll get a low mark.
A make B bring
C take D understand
14 I hadn’t studied, so when the teacher asked me I had ………… idea.
A none B no
C even D not
Answers
1 B 2 D 3 D 4 B 5 A 6 C
7 A 8 B 9 D 10 C 11 B 12 B
13 A 14 B
F. Each of the words in bold is incorrect. Rewrite them correctly.
1 I’ve always admired our music teacher from being so patient. …………………
2 My new school is quite similar with my old one. …………………
3 Mr Wilkins congratulated me for passing the exam. …………………
4 I’d better go home and study on tomorrow’s test. …………………
5 Ian is capable for doing very well this year if he works hard. …………………
6 This course is suitable to students who are considering a career in the media. …………………
7 If you don’t get into university, you’ll have to settle with art college. …………………
8 After six attempts, Bill finally succeeded with passing his driving test. …………………
Answers
1 for 2 to 3 on 4 for 5 of
6 for 7 for 8 in
G. Water has damaged part of this text form a diary. Read it and decide what you think each of the original words was. Write the words in the blank spaces.
Dear Diary
Well, my first day at the new school is over. I was able (1) ……………… make a few friends, although I hope (2) ……………… I meet more people tomorrow. I met one girl I didn’t like, who just boasted (3) ……………… her exam results and succeeded (4) ……………… annoying everyone. The teacher asked me what I’d been learning (5) ……………… at my other school and when I told her she said she failed (6) ……………… see how I would be able to catch up with the others. I’ll show her! I’m just as capable (7) ……………… doing the work as the others. I’m really going to study hard (8) ……………… the test.
Answers
1 to 2 that 3 about/of 4 in
5 about 6 to 7 of 8 for
H. Complete the sentences by changing the form of the word in capitals when this is necessary.
1 I wonder if you could tell me who was awarded the ………………… (SCHOLAR)?
2 Do you think that you pay enough ………………… (ATTEND) in class?
3 Could you tell me what the ………………… (SOLVE) to number seven is?
4 My dad said I’d better spend more time on my ………………… (STUDY).
5 I would like to know what qualifications ………………… (TEACH) require in your country.
6 Joshua was suspended from school for a week for bad ………………… (BEHAVE).
7 I did six hours of ………………… (REVISE) for the test, and I still failed!
8 Please send photocopies of all your ………………… (CERTIFY) to us at the address below.
Answers
1 scholarship 2 attention 3 solution 4 studies
6 teachers 7 revision 8 certificates
I. Complete the text by changing the form of the word in capitals.
Being unable to read
It seems (1) ………………… (THINK) today not to provide children with a decent (2) ………………… (EDUCATE). There is such an emphasis on (3) ………………… (ACADEMY) achievement these days that it’s easy to forget what a problem (4) ………………… (LITERATE) used to be. Being unable to read can be (5) ………………… (INTENSE) embarrassing and can make someone feel I like a complete (6) ………………… (FAIL). Someone who can’t read is often (7) ………………… (UNDERSTAND) afraid of certain situations. The problem can seem (8) ………………… (SOLVE). However, given the right teacher, a lot of hard work and a (9) ………………… (REASON) amount of time, anyone can learn. Being able to read can lead to an (10) ………………… (IMPROVE) quality of life.
Answers
1 unthinkable 2 education 3 academic 4 illiteracy
5 intensely 6 failure 7 understandably 8 unsolvable
9 reasonable 10 improved
Related Posts
- Practice English Vocabulary B2 Exercises – Vocabulary Test 2
- Practice English Vocabulary B2 Exercises – Vocabulary Test 1
- Practice English Vocabulary B2 Exercises – Vocabulary Review 14
- Practice English Vocabulary B2 Exercises – Vocabulary Review 13
- Practice English Vocabulary B2 Exercises – Vocabulary Review 12
- Practice English Vocabulary B2 Exercises – Vocabulary Review 11
Страница 8 из 53
TEST 4 A (Module 4)
*A. Fill in the correct word / phrase. Вставьте правильное слово / фразу.
• chat show • weather report • interview • documentary • cartoon • news
• ток−шоу • прогноз погоды • интервью • документальный • мультфильм • новости
Ответ:
TV GUIDE
Saturday, 4th November
Channel 1
16:30 African Animal Adventure
Interesting wildlife documentary about animals in Africa
17:00 Live at 5
International 1) news programme covering today’s events, business and sport, as well as a complete 2) weather report
17:30 OK!
A chance to hear all the gossip about your favourite pop stars, actors and celebrities. Find out the truth as you listen to an 3) interview with Jennifer Lopez
18:00 Oprah
4) Chat show with host Oprah Winfrey. Special guest today – Tom Cruise.
18:30 The Simpsons
5) Cartoon about the Simpson family.
Перевод:
ТЕЛЕПРОГРАММА
Суббота, 4 ноября
Канал 1
16:30 Приключения африканских животных
Интересная дикая природа, например документальный фильм о животных в Африке
17:00 Прямой эфир в 5
Международная программа 1) новостей, охватывающая сегодняшние события, бизнес и спорт, а также полный 2) прогноз погоды
17:30 ОК!
Возможность услышать все сплетни о любимых поп−звездах, актерах и знаменитостях. Узнай правду, слушая 3) интервью с Дженнифер Лопес
18:00 Опра
4) Ток−шоу с ведущей Опрой Уинфри. Специальный гость сегодня − Том Круз.
18:30 Симпсоны
5) Мультфильм о семье Симпсонов.
*B.Complete the sentences with the correct word. Дополните предложения правильным словом.
• gossip • fashion • music • text messages • horoscopes • article
• сплетни • мода • музыка • текстовые сообщения • гороскопы • статья
e.g. I read an interesting article about the media.
например, Я прочитал интересную статью о СМИ.
Ответ:
6. My sister buys a popular magazine to read gossip about famous people’s lives.
7. The music programme plays all the latest hits.
8. Horoscopes try to tell you what will happen in the future.
9. Polly likes to send text messages to her friends.
10. Jane buys Sugar magazine for its fashion advice.
Перевод:
6. Моя сестра покупает популярный журнал, чтобы читать сплетни о жизни известных людей.
7. В музыкальной программе звучат все последние хиты.
8. Гороскопы пытаются рассказать вам, что произойдет в будущем.
9. Полли любит отправлять текстовые сообщения своим друзьям.
10. Джейн покупает журнал Sugar за его советы по моде.
*C. Underline the correct word. Подчеркните правильное слово.
e.g. The fireman pulled the baby to safe / safety.
например, Пожарный вытащил ребенка в безопасное место.
Ответ:
11. John brave / bravely fought the bear.
12. The zebra ran off / went off before I could take a photograph.
13. I was surprised / surprising to hear I won the competition.
14. It can be difficult to come on / up with new ideas.
15. Mark was very exciting / excited when he won the writing award.
16. What does the weather article / report say?
17. Glossy magazines are attractive / popular* to teenagers.
18. I like the fashion and beauty advice / strips in this magazine.
19. In sports, it’s a great achievement to attend / break a world record.
20. This belt really goes with / on your shoes.
Перевод:
11. Джон храбро сражался с медведем.
12. Зебра убежала прежде, чем я успел сделать снимок.
13. Я был удивлен, узнав, что выиграл соревнование.
14. Придумывать новые идеи может быть непросто.
15. Марк был очень взволнован, когда выиграл писательскую премию.
16. Что говорится в прогнозе погоды?
17. Глянцевые журналы привлекательны для подростков.
18. Мне нравятся советы о моде и красоте в этом журнале.
19. В спорте побить мировой рекорд − это большое достижение.
20. Этот пояс отлично сочетается с вашей обувью.
*D. Put the verbs in brackets into the Past Continuous. Поставьте глаголы в скобках в Past Continuous.
e.g. Tony was walking (walk) home when it started raining.
например, Тони шел домой, когда пошел дождь.
Ответ:
21. We were planning (plan) to go to the zoo, but we stayed home instead.
22. Jackie was taking (take) notes during the lesson.
23. The students were working (work) hard because they wanted a good mark in the exam.
24. What were you doing (you/do) last night?
25. He was playing (play) with his nephew all day Saturday.
Перевод:
21. Мы планировали пойти в зоопарк, но остались дома.
22. Джеки делала заметки во время урока.
23. Студенты усердно работали, потому что хотели получить хорошую оценку на экзамене.
24. Что ты делал прошлой ночью?
25. В субботу он весь день играл со своим племянником.
*E. Put the verbs in brackets into the Past Simple or the Past Continuous. Поставьте глаголы в скобках в Past Simple или Past Continuous.
e.g. She left (leave) school when she was 16.
например, Она бросила (бросить) школу, когда ей было 16 лет.
Ответ:
26. Gary was riding (ride) his bicycle while Alan was skateboarding.
27. The policeman asked, “What were you doing (you/do) at the time of the robbery?”
28. I passed (pass) the exam without difficulty.
29. Mum cooked (cook) dinner before dad came home.
30. She was writing (write) a letter when the lights went out.
31. They went (go) on holiday in June.
32. A woman from Vancouver found (find) a bear in her kitchen.
33. When I was a teenager I played (play) in the school basketball team.
34. My aunt Jane was driving (drive) to Oxford when I phoned her.
35. Paul got dressed (get dressed), had breakfast and then went to school.
Перевод:
26. Гэри катался на велосипеде в то время, когда Алан катался на скейтборде.
27. Полицейский спросил: «Чем вы занимались во время ограбления?»
28. Я сдал экзамен без труда.
29. Мама приготовила ужин до того, как папа вернулся домой.
30. Она писала письмо, когда погас свет.
31. Они ездили в отпуск в июне.
32. Женщина из Ванкувера нашла медведя на своей кухне.
33. Когда я был подростком, я играл в школьной баскетбольной команде.
34. Моя тетя Джейн ехала в Оксфорд, когда я ей позвонил.
35. Пол оделся, позавтракал и пошел в школу.
*F. Choose the correct response. Подберите правильный ответ.
e.g. I passed all my exams! F A. How dreadful! Was she hurt?
36. You won’t believe this. I found a wallet in the street. B. What a story! How did they do that?
37. I broke my leg and can’t play in the match. C. Wow! How long did it take you?
38. Listen to this – Helen had a car accident! D. Oh dear! I hope you get well soon.
39. Did you hear about the chimpanzees that sailed across the Atlantic? E. Really? Did you take it to the police?
40. I climbed Mount Everest. F. That’s great news. Your parents will be pleased.
Перевод:
например, Я сдала все экзамены! F А. Как ужасно! Ей было больно?
36. Вы не поверите. Я нашел кошелек на улице. B. Какая история! Как они это сделали?
37. Я сломал ногу и не могу играть в матче. С. Вау! Сколько времени это заняло у вас?
38. Послушай это − Хелен попала в автомобильную аварию! D. О боже! Я надеюсь, что ты скоро поправишься.
39. Вы слышали о шимпанзе, которые переплыли Атлантический океан? E. В самом деле? Вы отнесли его в полицию?
40. Я поднялся на Эверест. F. Это отличные новости. Ваши родители будут довольны.
Ответ:
36 – E, 37 – D, 38 – A, 39 – B, 40 – C.
*G. Read the text and answer the questions. Прочитайте текст и ответьте на вопросы.
Sun Shines on Fun Run
On 12th June, a ‘Fun Run’ took place in the town of Sunnyfield. A group of sixteen−year−old students from the local high school came up with the idea and over 500 people of all ages took part.
Luckily, it was a sunny day. Everyone had fun running, walking or skate−boarding the 10−mile distance. Thanks to the event, £2,346 was raised for the charity ‘Cancer Care’.
Suzie Hamilton, one of the students who organised the run, said, “We wanted to do something useful for others and this seemed the most fun thing to do.”
The local headmaster was so proud, he decided to make the event part of the school’s yearly calendar.
Солнце светит на Веселых бегах
12 июня в Саннифилде прошли «Веселые бега». Идея пришла в голову группе шестнадцатилетних учеников местной средней школы, в которой приняли участие более 500 человек всех возрастов.
К счастью, день был солнечный. Всем было весело бежать, гулять или кататься на скейтборде на 10−мильную дистанцию. Благодаря мероприятию было собрано 2 346 фунтов стерлингов для благотворительной организации «Cancer Care».
Сьюзи Гамильтон, одна из учениц, организовавших забег, сказала: «Мы хотели сделать что−то полезное для других, и это казалось самым интересным занятием».
Местный директор был так горд, что решил сделать мероприятие частью годового календаря школы.
e.g. When did the event take place? On 12th June.
например, Когда прошло мероприятие? 12 июня.
41. Who planned the event?
42. How many people took part?
43. What was the weather like during the ‘run’?
44. How far did they have to go?
45. What happened as a result of the event?
41. Кто спланировал мероприятие?
42. Сколько человек приняли участие?
43. Какая была погода во время пробега?
44. Как далеко им нужно было идти?
45. Что произошло в результате события?
Ответ:
41. A group of sixteen−year−old students from the local high school.
42. Over 500.
43. It was a sunny day.
44. 10 miles.
45. £2,346 was raised for the charity ‘Cancer Care’ . The local headmaster decided to make it part of the school’s yearly calendar.
Перевод:
41. Группа шестнадцатилетних учеников местной средней школы.
42. Более 500.
43. Было солнечно.
44. 10 миль.
45. Было собрано 2 346 фунтов стерлингов для благотворительной организации «Cancer Care». Местный директор решил сделать его частью годового календаря школы.
*H. Listen to the reports. What are they about? Number them in the order you hear them. Послушайте отчеты. О чем они? Пронумеруйте их в том порядке, в котором вы их слышите.
e.g. new technology 1
например, новая технология
Аудио к заданию:
1. A new exhibition is opening today at Hillington Science Centre. Come and see the newest British robots. Open from 9 a.m. until 5 p.m., Monday to Saturday. For one week only!
2. World Number 1 tennis champion Roger Federer won his third title at the US Open in New York on Sunday. The Swiss player won 6−2, 4−6, 7−5, 6−1.
3. Cravendale Mall opened just three months ago and had become the most popular place for shopping and entertainment. It has helped the local community a lot because many people have found jobs there.
4. Eight puppies that someone left outside a local supermarket are now safe, thanks to the staff. The pups are around six weeks old and are looking for loving homes. If you can help, call Dogs Trust on 020 7837 006.
5. The government is planning a new programme worth £280 million to help change school children’s unhealthy eating habits. Children will have the chance to eat healthier foods in school canteens, such as salads and home−cooked meals, and there will be less junk food on offer.
6. A man in his 40s broke into the Natwest Bank today at 11.30 am and stole £500,000. Were you in Greg Street at this time? If you have any information, please contact your local Police station.
Перевод аудио:
1. Сегодня в научном центре Хиллингтона открывается новая выставка. Приходите посмотреть на новейших британских роботов. Открыта с 9:00 до 17:00, с понедельника по субботу. Всего на одну неделю!
2. Чемпион мира по теннису номер 1 Роджер Федерер выиграл свой третий титул на Открытом чемпионате США в Нью−Йорке в воскресенье. Швейцарский игрок выиграл 6−2, 4−6, 7−5, 6−1.
3. Торговый центр Cravendale Mall открылся всего три месяца назад и стал самым популярным местом для покупок и развлечений. Это очень помогло местному сообществу, потому что многие люди нашли там работу.
4. Восемь щенков, которых кто−то оставил у местного супермаркета, теперь в безопасности благодаря персоналу. Щенкам около шести недель, и они ищут любящий дом. Если вы можете помочь, позвоните в Dogs Trust по телефону 020 7837 006.
5. Правительство планирует новую программу стоимостью 280 миллионов фунтов стерлингов, чтобы помочь школьникам изменить нездоровые пищевые привычки. У детей будет возможность есть более здоровую пищу в школьных столовых, такую как салаты и домашние блюда, и в продаже будет меньше нездоровой пищи.
6. Сегодня в 11.30 человек в возрасте 40 лет ворвался в банк Natwest и украл 500 000 фунтов стерлингов. Вы были в это время на Грег−стрит? Если у вас есть какая−либо информация, обратитесь в местный полицейский участок.
Ответ:
46. a new shopping centre 3
47. a rescue 4
48. a bank robbery 6
49. school meals 5
50. a sports event 2
Перевод:
46. новый торговый центр 3
47. спасение 4
48. ограбление банка 6
49. школьное питание 5
50. спортивное мероприятие 2
поделиться знаниями или
запомнить страничку
- Все категории
-
экономические
43,633 -
гуманитарные
33,652 -
юридические
17,917 -
школьный раздел
611,709 -
разное
16,898
Популярное на сайте:
Как быстро выучить стихотворение наизусть? Запоминание стихов является стандартным заданием во многих школах.
Как научится читать по диагонали? Скорость чтения зависит от скорости восприятия каждого отдельного слова в тексте.
Как быстро и эффективно исправить почерк? Люди часто предполагают, что каллиграфия и почерк являются синонимами, но это не так.
Как научится говорить грамотно и правильно? Общение на хорошем, уверенном и естественном русском языке является достижимой целью.
When teaching a foreign language, one of the key things that we stumble upon is the introduction of new lexical patterns, new phrases and idiomatic expressions. Ensuring constant vocabulary enrichment with the learners is the key principle to achieve language fluency and coherence. Hence, helping the learners to acquire and grow their word stock in a stress free environment and have fun at the same time is a challenge all of us — educators deal with.
There are different theories and practices about what the best way of vocabulary presentation is. All of them come not merely from theory but from practice as well. Hence, there is no definite truth here. All we need to know is that if it works for the learner then WELL DONE!
Existing Theories
CELTA course gives us a very nice and structured way of vocabulary presentation — meaning, pronunciation, form (MPF). This is explained in the following way — teaching meaning is the first obligatory thing, as the learners should first understand what the word means and then deal with the form and polish its pronunciation. Pronunciation comes next as the word should be articulated properly to be understood by the interlocutors, and the form is the last one in the list, as seeing the word written might hijack its pronunciation, considering the students are not well versed in word stress and the pronunciation of certain letter combinations. This order, however, can be varied according to the language level of the learners, the material presented and the aim of the task. For instance, when working with B2 and higher level of learners we can have the presentation stages in the following order: form, pronunciation, meaning. At this level of language comprehension learners are less likely to make pronunciation mistakes and we can actually show the form and reinstate the pronunciation without working on the meaning first. This technique however, is risky with low level learners, as they might pronounce the word incorrectly or get lost in the form, thus, prolonging the assimilation stage.
Another theory suggests that having a context for vocabulary presentation is always a must, as a lesson should not be divided into different sections like vocabulary, grammar, listening, reading, writing, but it rather should be a unity where all language skill are intertwined with each other. This, being true, does not negate the fact that sometimes we hold mere vocabulary sessions where having all the aspects included is not a must.
As we know, there are different types of learners — visual, auditory, reading/writing, and kinesthetic. Though it is impossible to meet everyone’s needs all the time, we are trying to make sure each session contains material for each type of learner. It is worth mentioning here, that learners don’t have to be of a specific type, but can have certain aspects of each with one dominant type.
Let’s have a closer look at some practical points and choose the ones that will work well with the type of learners we are currently dealing with.
- Realia
Using realia in class when possible increases the chance of students remembering the targeted phrases with more ease and more vividly. This works better with lower level vocabulary where we are working with non abstract notions. Topics like ‘food, everyday objects, etc.’ go well with this method. We can go further and get more creative by using realia to revise/recycle vocabulary by asking the students to name the objects, or bring the objects they want to know how to call in English to class, and mingle. This can get very noisy, fun and educational.
- Picture
In case realia is hard to organize, pictures are always there to help thanks to the wide variety of Internet resources available nowadays. What I love pulling off during classes is trying to elicit an abstract phrase/idiom through a situational picture. It gives the students a chance to think longer, use their creativity and result in very interesting phrases.Below there is one of the idiomatic phrases I introduced during the class and students still remember it — Don’t cry over spilt milk.
First, the students brainstormed different phrases by looking at the picture. The only thing they knew was that it represents an idiomatic expression in English and they had to try to guess it. After the students mentioned the key words the phrase was revealed to them. After that, they started working with the meaning and finding synonymous idiomatic expressions in their L1.
Similarly, posters and flashcards can be very useful when working with visual learners. We can have a set of words to introduce with picture flash cards (either printed or using slides).
- Guessing the word from the context
This has been a great vocabulary introduction practice for quite a long time with different age groups, levels of target language comprehension and interests. One of the ways is to present a text to the students where the context leads to the understanding of the key word. Most textbooks use this technique. Another way, is to show the target word in different sentences to enable the students grasp the meaning. Checking whether the students have actually understood the meaning of the word or not is quite easy, by either asking them to make their own sentences using the target word or elicit the translation of the word if everyone shares the same L1.
For example:
“Audi is a luxurious car.”
“Gucci is a more luxurious brand than Guess.”
“They entered the elegant, newly decorated, and luxurious dining room.”
This technique works nice with reading/writing type of learners. It can also work with the auditory type if we decide to read the sentences out loud instead of presenting the learners with the written one.
- Definitions
This is another well-versed way of introducing new vocabulary. One challenge that we, teachers, might have with this, is making sure that the definition is actually comprehensible. Sometimes dictionaries provide definitions that include a lot of unknown words, hence confusing the learners even more. So, it is our job to choose/adapt the definitions according to the level of the learners to achieve a successful result.
An example of this I have come across when teaching B1 level students was the phrase “to cut down on something”:
To cut down on something — to start using something less extensive than previously
I adapted it like this — to start using something less than before
This technique can be quite nice for both reading/writing and auditory type of the learner depending on the way of its presentation.
- Personalization
It is a fact that learners remember things better when we give them strong associations. This can be examples from the real world around us (politics, celebrities, etc.), as well as personalized examples on students or the teacher.
Let’s say, you want to teach the phrase “to get on well with someone”. Something like this can definitely work:
“My sister and I understand each other very easily. We have the same interests, the same hobbies, the same opinion about different things and we never fight. We get on well with each other.”
We can either use the target phrase like it was in the example and ask the students to guess the meaning, or leave the space blank and let the students guess the phrase itself. The second way works better in revision sessions though.
- Find the word
This one is my personal favourite.
Let’s say we are going to introduce 4 words: reliable, arrogant, showy, trustworthy
We can create a grid with the words, cut them in half, and give to the students:
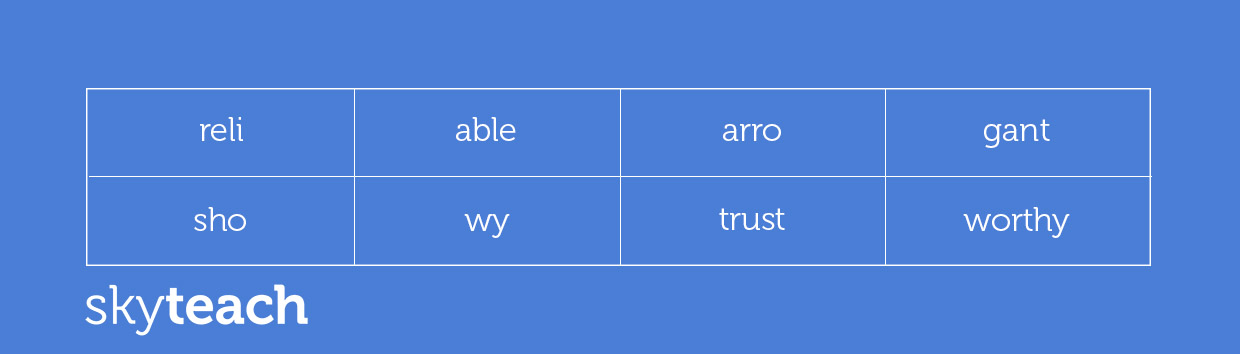
The students should try to find the correct beginnings and endings for the words knowing that there are only 4 words to compile.
This can be a little time consuming, but it gives the students a chance to compile the words on their own, hence, they work with word structure, exercise their background knowledge and having so much exposure to the target words enables them to remember them better.
- Graphs
This approach is a very nice way to help assimilate the target word/phrase easier and in a full package. Four categories are used to help the learner grasp the meaning of the word and its usage: synonym, antonym, example, non-example. The graph below represents it more clearly.
This is a full and exhaustive way of dealing with the word at hand. To make it more challenging, we can upgrade the students’ language and introduce the part of speech differences of the word as well.
Let’s say we are teaching the word ‘interesting’. The rank will go as follows
Noun — an interest (n.)
Verb — to interest (v.)
Adjective — interesting, interested (adj.)
Adverb — Interestingly (adv.)
At the same time, context and/or example sentences can be provided with these 4 words which will result in the students’ assimilating 4 words instead of 1.
- Ranking
This is another way of introducing sets of words. As we know, learning different shades of meaning is an effective way to enrich the students word-stock faster and help them understand the usage of each in a respective context. Though ranking is known to be a toll for vocabulary practice, it can also be used to challenge the students background knowledge and language feeling in general. Of course, here the level of the students is crucial, as we cannot demand A1 or A2 levels to have the that linguistic feeling.
Ranks work well with adjectives and adverbs quite nicely. Adverbs, however, can also be introduced with percentages as it is done in most textbooks (always — 100%, never — 0%).
Always-often-sometimes-occasionally-seldom/hardly ever-never

Happy-excited-delighted-ecstatic
- Classification
This is another way of introducing new language in Test-Teach-Test format. It can be as simple as asking the learners to classify the target words into respective columns (means of transport, food, clothes, etc.), to parts of speech.
This also requires a lot of exposure to the language where the students have a chance to look at the target words/phrases more than once, try to pronounce them correctly, use their background knowledge, their guy feeling. As mentioned, things which people achieve themselves and are not handed, stick in the long-term memory.
- Translation
Foreign language specialists, trainers, educators, instructors will agree that translation is not the best idea when working with a group of people trying to learn a target language. However, to me, it is not such a bad thing after all. Quite the opposite, when used moderately and to the point, it can be quite helpful in the teaching process.
Sometimes there are ideas and abstract notions which are hard to explain in a target language and near to impossible when dealing with low level learners. Here the L1 comes to help.
This being true, we should not forget, that translation is to be resorted only after we have tried all the possible ways to convey the meaning of the word and failed. It can be used to clarify the understanding rather than reveal it from the beginning.
Anyways, in general, it’s not a shame to have a good dictionary at hand and check the meaning of the words we, as teachers might not have come across yet. It creates a healthy learning environment if it’s done moderately and once again highlights the truth that learning is a lifelong process.
Alternatively, we can tell the students that we will check the word and get back to them. We should not be surprised that the students will take our word for it and wait for the clarification next class. So, it is important to keep our promises and get back to the students to answer their questions.
All of these said, it is worth pointing out that not all the techniques and methods will work with all types of groups and learners. Things that should be taken into account are age of the learners, interests, previous exposure to the language, background knowledge in general (this being a powerful tool when teaching in general, not just a language), their mother tongue, type of the learner and the means available at hand (technology, resources).
Let’s get creative and share more tools and techniques to facilitate vocabulary introduction. Looking forward to your comments!
Тесты для студентов всех факультетов и специальностей поступающих в магистратуру.
Тесты по английскому языку составлена для студентов курсов всех факультетов и специальностей, поступающих в магистратуру.
Тесты предназначены как для вступительных экзаменов в магистратуру, так и для аудиторной и самостоятельной работы студентов для контроля грамматических навыков и знаний студентов, и представляет собой сборник тестов, подобранных авторами из различных источников художественной и научной литературы, представляющих собой оригинальные предложения, составленные носителями языка, и организованных по степени возрастания сложности грамматического материала.
Методическая разработка имеет целью помочь студентам в освоении программных общеобразовательных тем, а также обеспечить контроль знаний студентов.
1. What is this? … is my exercise-book.
a. it
b. these
c. those
d. they
e. them
2. There is … pen on the table.
a. some
b. such
c. an
d. a
e. three
3. … car is this?
a. what
b. who’s
c. why
d. whom
e. whose
4. I’m cold. …open the window.
a. a not
b. don’t
c. no
d. none
e. –
5. He … to the University by tram.
a. is going
b. can
c. goes
d. go
e. are going
6. Nick … a book now.
a. is reading
b. are reading
c. read will read
d. had read
7. I like potatoes, but I … them everyday.
a. haven’t eat
b. not eat
c. doesn’t eat
d. don’t eat
e. isn’t eating
8. I … to see my friend tomorrow.
a. are going
b. have going
c. is going
d. were going
e. am going
9. She didn’t … breakfast yesterday.
a. had
b. has
c. have
d. having
e. haved
10. I can swim, but my friend …
a. is not
b. can’t
c. don’t
d. needn’t
e. aren’t
11. … I take your pen?
a. may
b. will be able
c. does
d. has
e. had
12. Must I wear these shoes? – No, you…
a. mustn’t
b. can’t
c. weren’t
d. isn’t
e. aren’t
13. My grandfather … to leave school when he was 15.
a. must
b. can
c. is
d. are
e. had to
14. I … speak French last year.
a. can’t
b. may not
c. must not
d. couldn’t
e. hasn’t
15. You will … speak English in 3 years.
a. can
b. has
c. had
d. be able to
e. were able to
16. When I called him, he … supper.
a. has having
b. was have
c. was having
d. is having
e. were having
17. They … up late yesterday.
a. get
b. got
c. has got
d. gets
e. getting
18. It is the … book I have ever read.
a. best
b. better
c. well
d. good
e. worse
19. Where … go? Let’s go to the cinema.
a. won’t we
b. is we
c. have we
d. shall we
e. are we
20. What has she … ?
a. doing
b. do
c. did
d. done
e. does
21. There … many students in the room now.
a. were
b. was
c. is
d. are
e. will
22. There … a university in the centre of the city.
a. is
b. are
c. be
d. shall
e. were
23. I can’t see … on my table.
a. nothing
b. nobody
c. anything
d. anywhere
e. somewhere
24. What … you going to do tonight?
a. was
b. will
c. were
d. is
e. are
25. There … any sugar in the tea.
a. weren’t
b. wasn’t
c. haven’t
d. hadn’t
e. won’t
26. We … in Moscow last year.
a. lives
b. is living
c. has living
d. live
e. lived
27. Where … she work?
a. do
b. done
c. doing
d. does
e. is
28. … speaks English well?
a. which
b. why
c. who
d. when
e. what
29. How many theatres … there in your city now?
a. were
b. are
c. have
d. is
e. was
30. What … you do tomorrow?
a. will
b. shall
c. will be
d. shall be
e. are
31. He said that he … at the plant last year.
a. are having
b. living
c. lives
d. had lived
e. lived
32. Let … tell his friends about his city.
a. his
b. him
c. he
d. her
e. she
33. My friend … breakfast when I called him.
a. were having
b. will having
c. are having
d. was having
e. is having
34. What … do you want to read?
a. another
b. yet
c. other
d. still
e. else
35. Which is the … river in our country?
a. long
b. longer
c. longest
d. large
e. larger
36. There was … in the room.
a. somebody
b. somewhere
c. anybody
d. anything
e. some
37. Who … you this story yesterday?
a. speak
b. tell
c. told
d. spoke
e. said
38. When we came in, the film … already begun.
a. are
b. is
c. were
d. was
e. had
39. The work … done well two days ago.
a. has done
b. was done
c. has been done
d. was do
e. did
40. Books by Dickens … many times.
a. is publishing
b. have published
c. are published
d. were published
e. is published
41. What … you do every day?
a. does
b. do
c. did
d. doing
e. done
42. This problem … tomorrow.
a. will be discussed
b. have been discussed
c. is discussing
d. will discuss
e. had discussed
43. I wonder, why there are so … people.
a. no
b. such
c. some
d. much
e. many
44. I am sorry… I come in?
a. could
b. might
c. may
d. must
e. need
45. I … do this work yesterday. I was busy.
a. mustn’t
b. can’t
c. couldn’t
d. aren’t
e. weren’t
46. What … you doing here?
a. are
b. is
c. will
d. be
e. can
47. He … going to translate this article.
a. do
b. have
c. may
d. is
e. are
48. These pictures … by a young painter last year.
a. are painted
b. were painted
c. is painted
d. will be painted
e. have been painted
49. I … know him.
a. doesn’t
b. haven’t
c. hasn’t
d. isn’t
e. don’t
50. … go to the library.
a. won’t
b. doesn’t
c. don’t
d. haven’t
e. isn’t
51. Do you often … English to your teacher?
a. spoken
b. spoke
c. speak
d. speaking
e. speaked
52. … of you likes to speak French?
a. which
b. who
c. why
d. what
e. whom
53. … of you lives in the centre of Moscow?
a. whom
b. whose
c. who
d. which
e. when
54. How long does your working day …?
a. has lasted
b. is lasting
c. lasted
d. last
e. lasting
55. My sister works …
a. many
b. much
c. some
d. not many
e. none
56. What … they discussing now?
a. are
b. were
c. will
d. is
e. was
57. Will you … at home tomorrow?
a. is
b. were
c. are
d. be
e. have
58. They … here an hour ago.
a. have
b. have been
c. was
d. were
e. are
59. I wrote him a letter …
a. since
b. today
c. last month
d. this month
e. tomorrow
60. … children don’t like to play football.
a. some
b. no
c. any
d. anybody
e. somebody
61. There … many children in the park yesterday.
a. hadn’t
b. aren’t
c. haven’t
d. wasn’t
e. weren’t
62. Where … we get these journals?
a. do
b. can
c. must
d. were
e. will
63. … I ask you a question? – Certainly.
a. am
b. must
c. may
d. was
e. will
64. He … come yet.
a. haven’t
b. didn’t
c. hasn’t
d. doesn’t
e. can’t
65. I was waiting … you at 5 o’clock yesterday.
a. with
b. at
c. for
d. in
e. –
66. Have you … the translation yet?
a. does
b. doing
c. do
d. did
e. done
67. Is … a library at your office?
a. where
b. there
c. anywhere
d. somewhere
e. nowhere
68. These books are too difficult .. me.
a. about
b. at
c. of
d. for
e. with
69. …you know about it yesterday?
a. hasn’t
b. haven’t
c. don’t
d. didn’t
e. doesn’t
70. You can help me, … you?
a. can’t
b. can
c. couldn’t
d. won’t
e. don’t
71. You didn’t see him last week, … you?
a. didn’t
b. did
c. does
d. doesn’t
e. won’t
72. … usually takes me half an hour to get to my office.
a. he
b. I
c. what
d. it
e. she
73. I’m hurrying … the University.
a. to
b. of
c. at
d. in
e. –
74. What is he afraid … ?
a. to
b. in
c. with
d. of
e. off
75. There … a lot of students at the lecture tomorrow.
a. will
b. will be
c. will have
d. will can
e. were
76. He won’t go to the cinema tomorrow, … he?
a. will
b. won’t
c. won’t be
d. didn’t
e. did
77. Here is the man … wanted to speak to you.
a. which of
b. which
c. who
d. whom
e. whose
78. He will come back … Simferopol in June.
a. –
b. of
c. at
d. in
e. to
79. I didn’t do my work …. I was busy.
a. that’s why
b. because
c. in order to
d. after
e. before
80. … you swim last year?
a. could
b. can
c. was able
d. will be able
e. could able
81. I … seen him this week.
a. hasn’t
b. haven’t
c. didn’t
d. don’t
e. doesn’t
82. You were waiting for me at 2 o’clock yesterday, … you?
a. aren’t
b. didn’t
c. wasn’t
d. weren’t
e. haven’t
83. Mr. Green won’t be able to come, .. he?
a. shall
b. will
c. can
d. has
e. does
84. He … a cup of coffee when the telephone rang.
a. drink
b. are drinking
c. is drinking
d. drank
e. was drinking
85. The company has so … money.
a. little
b. less
c. more
d. many
e. the least
86. I … going to invite you to my birthday party.
a. has
b. have
c. are
d. is
e. am
87. You … English before entering the University
a. has study
b. has studied
c. had studied
d. had study
e. studied
88. New York is the … city in the USA.
a. most large
b. larger
c. large
d. largest
e. much largest
89. Who is your … friend?
a. goodest
b. best
c. better
d. more better
e. most
90. He … always waited for.
a. being
b. been
c. has
d. are
e. is
91. Who … asked when you came in?
a. was
b. been
c. was being
d. were
e. were being
92. Many new houses … built in our city lately.
a. has been
b. had been
c. have been
d. have being
e. being
93. I … wait for him now. I am very busy.
a. can’t
b. couldn’t
c. wasn’t
d. hadn’t
e. hasn’t
94. He … many friends here.
a. have
b. haves
c. has
d. having
e. had had
95. Will you … to come tomorrow?
a. will able
b. had able
c. was able
d. able
e. be able
96. You must … to answer all my questions.
a. was ready
b. be ready
c. is ready
d. are ready
e. ready
97. … you learn English?
a. haven’t
b. aren’t
c. isn’t
d. don’t
e. doesn’t
98. How many lessons … you have every day?
a. do
b. does
c. have
d. has
e. are
99. You like to watch TV- programmes, … you?
a. do
b. don’t
c. doesn’t
d. does
e. did
100. What … your favourite subject at school?
a. did
b. has
c. are
d. were
e. was
1. a
2. d
3. e
4. b
5. c
6. a
7. d
8. e
9. c
100. e





