In the English language, the word “not” is solely categorized as an Adverb.
- Adverb
The word “not” is considered as an adverb because it is used to modify adjectives, verbs, and other adverbs. For instance, in the sample sentence below:
They have been warned not to enter the room.
The word “not” is used to modify the verb “to enter.” Because it modifies a verb, it is then categorized as an adverb.
Definition:
a. used with an auxiliary verb or “be” to form the negative
- Example:
- She would not say.
b. used as a short substitute for a negative clause
- Example:
- Maybe we’ll have a test, but I hope not.
c. used to express the negative of other words
- Example:
- Not all old cars are considered classics.
Is «no» — a negative pronoun, adverb or something else?
There was no reply.
The song was no strain on her voice.
What do you think about this?
Negative sentences with introductory «there» are formed in the usual way for the verbs which are their predicates, that is, by means of
appropriate auxiliaries for all the verbs but to be. In the latter
case two negative constructions are possible:a) either with the negative pronoun no, as in:
There was no sign of him in the hall.
There is no knowing when he will
come…(http://doclecture.net/1-7538.html)
asked Nov 3, 2015 at 23:04
DaisyDaisy
3011 gold badge2 silver badges8 bronze badges
8
It’s not a pronoun because it doesn’t take the place of a noun — not by itself anyway. No one/nobody/nothing/nowhere would be some of the «pronoun forms» of no.
No generally modifies a noun so that makes it technically an adjective. When modifying a verb or adjective not is used.
No is also a typically a determiner — which can be considered a special type of adjective — because it can occupy the «spot» where an article or word like this/that/these/those would go.
answered Nov 4, 2015 at 2:58
LawrenceCLawrenceC
36.4k25 silver badges77 bronze badges
7
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged
.
It is a fact that almost every word of English has got the capacity to be employed as a different part of speech. At one place, a particular word may be used as a noun, at another as a verb, and yet at another place as an adjective.
These words enable the learners of the English language to understand the behavior of a particular word in various positions.
Importance of Parts of Speech in Communication
As you know, English sentences are used to communicate a complete thought. The importance of parts of speech lies in their proper utilization, which can help your understanding and confidence grow immensely.
Proper usage of parts of speech means that you can impart clear messages and understand them because you know the rules of the language.
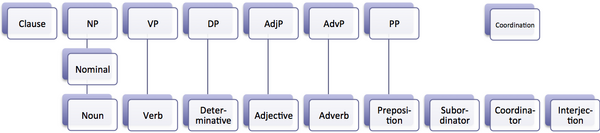
Each word in a sentence belongs to one of the eight parts of speech according to the work it is doing in that sentence. There are 8 parts of speech.
- Noun
- Verb
- Adjective
- Adverb
- Pronoun
- Prepositions
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
1 – Noun (Naming words)
The nouns stand for the names of people, places, animals, and things. The word noun means name. Look at these sentences.
“John lives in Chicago. He has two bikes. He is fond of riding bikes.”
In the above example, John is the name. We cannot use the same name again and again in different sentences. Here, we used “he” in the next two sentences instead of “John”. “He” is called the pronoun.
Types of nouns are
1.1 – Common Noun
It describes a person, place, and thing.
Examples: City, country, town, boy.
1.2 – Proper Noun
It includes a particular person, place, thing, or idea and begins with a capital letter.
Examples: Austria, Manchester, United Kingdom, etc.
1.3 – Abstract Noun
An abstract noun describes names, ideas, feelings, emotions or qualities, the subject of any paragraph comes under this category. It does not take “the”.
Examples: grief, loss, happiness, greatness.
1.4 – Concrete Noun
It describes material things, persons or places. The existence of that thing can be physically observed.
Examples: Book, table, car, etc.
1.5 – Countable and Uncountable Noun
Countable nouns can be singular or plural. It can be counted.
Examples: Ships, cars, buses, books, etc.
The uncountable noun is neither singular nor plural. It cannot be counted.
Examples: Water, milk, juice, butter, music, etc.
1.6 – Collective Noun
It includes the group and collection
people, things or ideas. It is in unit form and is considered as singular.
Examples: Staff of office, group of visitors.
However, people and police can be
considered both singular and plural.
1.7 – Possessive Noun
It shows ownership or relationship.
Examples: Jimmy’s pen.
Further Reading: 11 Types of Nouns with Examples
2 – Verb (Saying words)
These are used for saying something
about persons or things. The verb is concerned with doing or being.
Examples
- A hare runs (action) very fast.
- Aslam is a good student.
Types of verbs
2.1 – Actions verbs
(run, move, write etc)
2.2 – Linking verbs
(to be (is, am, are, was, were), seem, feel, look, understand)
2.3 – Auxiliary (helping) verbs
(have, do, be)
2.4 – Modal Verbs
(can, could, may, might, will/shall)
2.5 – Transitive verbs
It takes an object.
Example – He is reading a newspaper.
2.6 – Intransitive verbs
It does not take the object.
Example – He awakes.
Further Reading: What are the verbs in English?
3 – Adjectives (describing words)
These are joining to nouns to describe
them.
Examples
- A hungry wolf.
- A brown wolf.
- A lazy boy.
- A tall man.
It is used before a noun and after a linking verb.
Before noun example
A new brand has been launched.
After linking verb example
Imran is rich.
It is used to clarify nouns.
Example: smart boy, blind man
Types of adjectives
3.1 – Simple degree
He is intelligent.
3.2 – Comparative
Ali is intelligent than Imran.
3.3 – Superlative
Comparison of one person with class,
country or world. In this type “the” is used.
Example: Ali is the wisest boy.
3.4 – Demonstrative adjective
It points out a noun. These are four
in number.
This That These Those
3.5 – Indefinite adjectives
It points out nouns. They often tell
“how many” or “how much” of something.
Interrogative adjectives: it is used to ask questions
Examples
- Which book?
- What time?
- Whose car?
Further Reading: More About Adjectives
4 – Adverbs
Describing words that are added to verbs. Just as adjectives are added to describe them, adverbs are added to verbs to modify their meaning. The word “modify” means to enlarge the meaning of the adverbs.
Examples
- Emma sings beautifully. (used with verb)
- Cameron is extremely clever. (used with adjective)
- This motor car goes incredibly fast. (used with another adverb)
Types of adverb
4.1 – Adverb of manner
This type of adverb deals with the
action something
Example
- I walk quickly.
- He wrote slowly.
4.2 – Adverb of place
Happening of something or the place where it happens.
Examples:
There was somebody sitting nearby.
Here, these, upstairs, nowhere everywhere, outside, in, out, are called adverb of place.
4.3 – Adverb of time
It determines the time of the happening of something.
Examples
- She went there last night.
- Have you seen him before?
- He wrote a letter yesterday.
Tomorrow, today, now, then,
yesterday, already, ago.
4.4 – Linking adverbs (then, however)
It creates a connection between two clauses or sentences.
Example
There will be clouds in Lahore. However, the sun is expected in Multan.
Note: Besides modifying the meaning of a verb, adverbs also modify adjectives and other adverbs.
Examples
- It is a very large house.
- He is too weak to walk.
- He ran too fast.
Further Reading: 11 Types of Adverbs with Examples
5 – Pronouns
Words that are used instead of nouns to avoid tiresome repetition. Instead of using the word man in a composition, we often write he, him, himself. In place of the word “woman”, we write she, her, or herself. For both the nouns ‘men’ and ‘women’ we use, they, them, themselves.
Some of the most common pronouns are
Singular: I, he, she, it, me, him,
her
Plural: We, they, out, us, them.
Examples
Imran was hurt. He didn’t panic.
He checked the mobile. It still
worked.
Types of Pronouns
It stands instead of persons. They have different forms according to the person who is supposed to be speaking.
First person: I, we, me, us, mine, our, ourselves.
Second person: thou, you, there.
Third person: He, she, it, his, him
5.1 – Possessive pronouns
Such as mine, ours, yours, hers and theirs.
- This book is mine.
- My horse and yours are tired.
5.2 – Relative pronoun
Who, whom, which and they are called relative pronouns. They are called relative because they relate to some word in the main clause. The word to which pronoun relates is called the antecedent.
Example
I saw a boy who was going.
In this sentence, who is the relative pronoun and boy is its antecedent.
This is the girl who won the prize.
“which” is used for animals and things.
The dog which barks.
That is used instead of who or which in this case.
This is the best picture that I ever saw.
5.3 – Interrogative pronouns
It is used to introduce or create an asking position in a sentence. Who, whom, which, and whose are interrogative pronouns.
Examples
Who wrote this book? (for persons
only)
What is your name? (for things)
Which boy here is your friend?
5.4 – Demonstrative pronoun
It points out a person, thing, place
or idea. This, that, these and those are called demonstrative pronouns.
That is a circuit-breaker.
These are cups of a team.
5.5 – Reflexive pronoun
The type of pronoun that ends in self or selves is called a reflexive pronoun.
Examples: myself, ourselves, yourself, herself, himself, itself, themselves.
Use in sentence: They worked hard to
get out themselves from the debt.
Indefinite pronoun: An indefinite
pronoun does not refer to a specific person, place thing or idea.
Examples
Nothing lasts forever.
No one can make this design.
Further Reading: Different Types of Pronouns with 60+ Examples
6 – Prepositions
Words placed before a noun or pronoun
to show how the person or thing denoted stands in relation to some other person
or thing.
Examples: A house on a hill. Here, the word “on” is a preposition.
The noun and pronoun that follow the preposition are called its object. We can identify prepositions in the following examples.
In 2006, in March, in the garden,
On 14th August, on Friday, on the table
At 8:30 pm, at 9 o’clock, at the door, at noon, at night, at midnight
However, we use “in” for morning and evening.
Further Reading: Preposition Usage and Examples
7 – Conjunctions (joining words)
They join words or sentences.
Examples: Jimmy and Tom are good players.
In the above sentence, “and” is a conjunction.
Types of conjunctions
These are the types of conjunctions.
- Nor (used in later part of the negative sentence)
- But (when two different ideas are described in a sentence)
- Yet (when two contrast things are being described in a sentence)
- So (To explain the reason)
- For (it connects a reason to a result)
- Or (to adopt two equal choices)
- And (to join two things or work)
Further Reading: Conjunction Rules with Examples
8 – Interjections
Interjection words are not connected with other parts of a sentence. They are through into a sentence to express some feeling of a mind.
Examples: Hurrah! We won the match.
Alas, hurrah, wow, uh, oh-no, gush, shh are some words used to express the feeling.
It is important to note that placing a word in this or that part of speech is not fixed. It depends upon the work the words are doing in a particular sentence. Thus the same word may appear in three or four parts of speech.
Further Reading: More about Interjections
You can read a detailed article about parts of speech here.
Parts of Speech Exercise with Answers

Read also: 71 Idioms with Meaning and Sentences
The basic building blocks of any language are the words and sounds of that language. English is no exception. We will start with the categories into which we classify the words of English. It is quite likely that you will already know the names of some or all of the parts of speech. Nevertheless, this is where we must begin.
The parts of speech are as follows:
- Nouns
- Pronouns
- Adjectives
- Verbs
- Adverbs
- Articles
- Determiners
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
- Prepositions
These are also known as word classes. The terms are familiar to most people, and are in everyday use. However, many people would probably admit that their understanding of some of them is a little sketchy. We will now take each in turn and have a closer look.
Nouns
What are nouns? Very few people with a good knowledge of English would expect to experience any difficulty in picking the nouns out of the following list:
briefcase, open, disc, plate, London, knife, write, usually, and, however, football, sing
My guess is that you probably decided that the following were nouns:
- briefcase
- disc
- plate
- London
- knife
- football
Who knows? Perhaps you are right. Briefcase is certainly a noun and London as a place name must be, but what about knife? This is a more difficult decision. We have no context. What if we found this word in a sentence such as ‘He knifed me!’ — surely here it is a verb? And what about ‘plate’ — is this a noun? Suppose the context were ‘The window was plate glass.’ Or perhaps, ‘The frame had been plated with silver.’ So is ‘disc’ a noun? Not always, it depends on how it is used in a particular sentence. The lesson here is ‘Be careful!’ When a student asks you the meaning of a word, always check the context in which it appears before answering. Remember in the world of TEFL, as in the world in general, it is not what you don’t know that gives you the biggest problems, but what you think you know!
So how can we define the word class ‘noun’ then? One apparently acceptable definition might be that a noun is a word that represents one of the following:
|
a person |
David |
|
a place |
Paris |
|
a thing |
stapler |
|
an activity |
hockey |
|
a quality |
responsibility |
|
a state |
poverty |
|
an idea |
communism |
Does a noun have to be a single word? What about ‘disc jockey,’ or ‘post office’? Are these nouns? The answer is ‘Yes they are’. These are called compound nouns and are quite common in English. So the word class ‘noun’ is not restricted to single words. Can a noun consist of more than two words then? Once again the answer is ‘yes’. An example might be ‘football team coach’. These are often found in newspaper headlines, where space is at a premium, since they usually express quite complex ideas in very few words.
In a sentence nouns can be used as either the subject or the object of the main verb.
John (subject) kissed (verb) Maria (object).
Types of Nouns
The word class ‘Nouns’ can be sub-divided into the following four types:
|
Abstract |
The name of an action, an idea, a physical condition, quality or state of mind |
an attack, Communism, liveliness, modesty, insanity |
|
Collective |
A name for a collection or group of animals, people or things that are thought of as being one thing |
flock, gang, fleet |
|
Common |
A name that can be applied to all members of a large class of animals, people or things |
puppy, woman, banana |
|
Proper |
The name by which a particular animal, organisation, person, place or thing is known |
Fido, Microsoft, Julia, Liverpool, the Tower of London. Capital letters are used in order to distinguish between common nouns and proper nouns e.g., broom and Broom, where the former is an implement used for sweeping floors while the latter is a surname. |
There are some nouns that can be placed in more than one of these groups depending on how we are thinking at the time of usage. An example would be the noun ‘family’, which could be a collective if we are thinking of the family as a unit e.g. ‘My family is quite large.’ Or a common noun if we are thinking in terms of a collection of individuals e.g. Helen’s family are coming up next week.’ Many Americans may find this particular example unacceptable since in most parts of the US ‘family’ can never agree with the plural verb form ‘is’. In British English, however, this usage is perfectly correct.
Nouns can also be divided into two other groups: countable and uncountable. Water, flour and sand are examples of uncountable nouns. It would be very strange to use them with a number as in six flours or three sands. Countable nouns, on the other hand, can be used with numbers: seven men, two houses, etc. Countable nouns have a plural form. This is usually made by the addition of an ‘s’ or ‘es’ to the end of the singular form: guitars, books, ships, glasses etc. Some countable nouns, however, have an irregular plural form: men, children, wives, geese, etc. Plural countable nouns are always used with plural verb forms. So ‘Coconuts are nice.’ and not *’Coconuts is nice.’* Uncountable nouns have only one form and therefore can only be used with singular verbs. So ‘Water is used as a coolant.’ but never *’Water are used as a coolant.’*
Back to Top
Pronouns
In English, sentences such as ‘John ran up to the house, checked to see John wasn’t being watched and then John knocked on the door twice.’ would cause confusion. How many Johns are involved? Which of them knocked on the door? Probably the solution least likely to occur to a native speaker of English would be that there was only one John and that he carried out all three actions. Why is that? Well, it’s because English just doesn’t work like that! The sentence should be rendered thus ‘John ran up to the house, checked to see he wasn’t being watched and then knocked on the door twice.’ So what makes the difference? Obviously it must be the use of the word ‘he’ in place of John in the second instance. What is ‘he’ then? ‘He’ is a member of the word class Pronouns. These are words that stand in the place of nouns in order to avoid unnecessary repetition.
Kinds of pronoun:
|
Demonstrative |
this, that, these, those, the former, the latter ( ‘Have you seen this?’) |
|
Distributive |
each, either, neither ( ‘Give me either.’) |
|
Emphatic |
myself, yourself, his/herself, ourselves, etc. ( ‘Do it yourself.’) |
|
Indefinite |
one, some, any, some-body/one, any-body/one, every-body/one |
|
Interrogative |
what, which, who ( ‘Who was that?’) |
|
Personal |
I, you, he, she, it, we, you, they |
|
Possessive |
mine, yours hers, his, ours, theirs |
|
Reflexive |
myself, yourself, her/himself, ourselves, etc. ( ‘She cut herself, while slicing bread.’) |
|
Relative |
that, what, which, who (as in, ‘The car that hit him went that way.’) |
It should be noted that some of these words may also at times be deemed adjectives. It is a feature of the English language that many words have multiple uses and hence can be different parts of speech according to the context in which they are found.
Back to Top
Adjectives
Adjectives are words that describe/qualify nouns or pronouns:
- ‘She was a quiet woman.’
- ‘That’s an unusual one.’
Types of adjective
|
Demonstrative |
this, that, these, those (‘I like this picture.‘) |
|
Distributive |
either, neither, each, every (‘Either wine is fine by me.‘) |
|
Interrogative |
what? which? (‘Which wine would you like?‘) |
|
Numeral |
one, two, three, etc. |
|
Indefinite |
all, many, several |
|
Possessive |
my, your, his, her, our, their |
|
Qualitative |
French, wooden, nice |
Not surprisingly, most adjectives fit into the ‘Qualitative‘ category, as their basic function is to describe.
Some adjectives are made from nouns or verbs by the addition of a suffix:
- comfort — comfortable
- health — healthy
- success — successful
- consume — consumable
- consider — considerate
Many positive adjectives can be made negative by the addition of a prefix:
- comfortable — uncomfortable
- responsible — irresponsible
- respectful — disrespectful
- patient — impatient
- considerate — inconsiderate
Comparative and Superlative Adjectives
Some adjectives are used to compare and contrast things:
- big — bigger — biggest
- happy — happier — happiest
There is more information about this important use later.
Verbs
Verbs are words that indicate actions or physical and/or mental states.
|
Action |
Susan slapped Michael. |
|
Mental state |
Paul was exhausted. |
|
Physical state |
Stephen felt sad. |
It is a popular misconception that verbs are ‘doing-words‘. Unfortunately, this is too simple an explanation as only some verbs fit this description. An example of one that doesn’t might be ‘seem‘ as in, ‘ Sarah seemed puzzled‘. What is ‘done‘ in this case? Absolutely nothing! In fact, only verbs indicating actions can be called ‘doing-words‘.
Most verbs have three forms. The first form (present) also uses an inflection to indicate third person singular:
|
First form (present) |
Second form (past) |
Third form (past participle) |
|
do(es) |
did |
done |
|
give(s) |
gave |
given |
|
like(s) |
liked |
liked |
|
hit(s) |
hit |
hit |
As you can see sometimes the second and third forms coincide, and occasionally all three forms coincide as in ‘hit’. This is because verbs such as hit, give, take, do, have, etc. are irregular. That is to say that, unlike the vast majority of English verbs, they don’t use ‘-ed’ to make their second and third forms. There are only about two hundred irregular verbs in total, but since they tend to be the most common verbs it seems more. These can be quite a problem for EFL students as they simply have to be learnt and remembered.
Auxiliary and Modal Auxiliary Verbs
There is a category of verb known as ‘auxiliary verbs‘ or sometimes ‘helping verbs‘. This category includes to be, to do and to have. These three verbs are very important. ‘Be‘ is used in forming the ‘continuous aspect‘ — I am flying to France tomorrow.’ It is also used to form the ‘passive‘ — ‘I was arrested.’ ‘Do‘ is used in forming questions and for emphasis. ‘Have‘ is used to form the ‘perfect aspect‘ — ‘I have been here before.’ More about these later, when we look at the English tense system.
Also included in the category auxiliary verbs are nine very special verbs, which form a sub-category of their own called ‘modal auxiliary verbs‘ or ‘modal verbs‘ for short. This sub-category comprises the verbs can, could, may, might, shall, should, will, would and must. These nine verbs share some important characteristics:
- They can never be followed by ‘to‘: ‘I must to go.’ is a badly formed sentence in English.
- They cannot co-occur in the same verb phrase: ‘You must can go’ is also unacceptable.
- They have no ‘third person‘ inflection: ‘She likes reading.’ is fine, but ‘ She cans swim.’ is not.
In a verb phrase they always occupy the first position — ‘It must have been my aunt.’ Likewise, they do not have three forms.
So what exactly do these ‘modal verbs‘ do? An interesting question! The following table should give you some idea.
Modal verbs are used to express:
|
Degrees of certainty |
Certainty (positive/negative) |
We shall/shan’t come. |
|
Probability/Possibility |
She should arrive at about midday. |
|
|
Weak probability |
She might call — you never know! |
|
|
Theoretical/habitual possibility |
You may have a problem |
|
|
Conditional certainty/possibility |
If you had asked me, I would |
|
|
Obligation |
Strong obligation |
All employees must clock in and out. |
|
Prohibition |
Staff must not make personal calls. |
|
|
Weak obligation/recommendation |
When shall we leave? |
|
|
Willingness/Offering |
Can I help you? |
|
|
Permission |
Might I ask a favour? |
|
|
Ability |
Can you swim? |
|
|
Other uses |
Habitual behaviour |
When I was a boy, I would often go skiing. |
|
Irritation |
Must you do that? |
|
|
Requests |
Would you open the window please? |
Some linguists include verbs such as dare, need and ought in the modal verb sub-category. There is some justification for this, as they display the relevant characteristics some of the time. However, since they do not do so all the time it is better to leave them out of this group.
Back to Top
Adverbs
Adverbs describe or add to the meaning of verbs, prepositions, adjectives, other adverbs and even sentences. They answer questions such as ‘How’, ‘Where’ or ‘When’. Many, but by no means all, adverbs are made from adjectives by simply adding the suffix ‘ly’.
Types of adverb:
|
Adverbs of manner |
carefully, gently, quickly, willingly (She kissed him gently on the forehead.) |
|
Adverbs of place |
here, there, between, externally (He lived between a pub and a noisy factory.) |
|
Adverbs of time |
now, annually, tomorrow, recently (I only returned recently.) |
|
Adverbs of degree |
very, almost, nearly, too (She is very rich.) |
|
Adverbs of number |
|
|
Adverbs of certainty |
not, surely, maybe, certainly (Surely he’s not drunk again!) |
|
Interrogative |
How? What? When? Why? (What does it matter?) |
Adverbials
An adverbial is a general term for any word, phrase or clause that functions as an adverb. The definition is necessary because sometimes whole phrases and clauses act as adverbs:
- When I arrived she was watching TV. (adverbial time clause)
- We went to France to visit my brother. (adverbial clause of purpose)
- After breakfast, I went to work. (adverbial phrase)
An ordinary adverb is a single word adverbial.
The adverb/adverbial is quite a difficult area of the English language to get to grips with. It has been said that, when all the other words of English had been classified as nouns, verbs, prepositions, etc., those remaining were dumped into the adverb class because nobody knew what else to do with them. Even if this is not entirely historically accurate, it certainly describes the confused state of this word class.
Back to Top
Articles
The articles in English are the words ‘a‘, ‘an‘ and ‘the‘. They are used with nouns to distinguish between the definite and the indefinite. They are not really a word class in themselves but are actually a sub-group of the word class Determiners. However, EFL usually treats them as a class and so they are dealt with separately here.
The definite article is ‘the‘. Its most common uses are to show that the nouns it is used with refer to:
|
something known to both speaker and listener |
He is in the garage. |
|
something that has already been mentioned |
That woman keeps looking at you. |
|
something that is defined afterwards |
The house where my mother was born is somewhere near here. |
|
something as a specific group or class |
Can you play the piano? (But not ‘Can you play the instrument?’ — Unless which instrument is being referred to is understood by both speaker and listener.) |
The indefinite article is ‘a(n)». I write ‘is’ because ‘a’ and ‘an’ are really the same word: the ‘n’ is added to the article ‘a’ for ease of pronunciation when the following word begins with a vowel sound — an egg, an ostrich, an upwards motion but a unicorn, a united front (because unicorn and united begin with consonant sounds).
The most common uses of the indefinite article are to show that the nouns it is used with refer to:
|
one example of a group or class |
I’ll buy her an ornament for her birthday. |
|
a typical example of a group or class |
A reliable worker deserves a good boss. |
It should be noted that the indefinite implies ‘oneness’ and so cannot be used with plural or uncountable nouns.
Finally, there are some nouns (apart from plural and uncountable) with which articles are not usually used. Examples of these are the names of countries, towns and cities and of people, months, mealtimes (breakfast, lunch, etc.). Where no article is used this is often referred to as the ‘Zero article‘.
For the EFL student articles either present no difficulty at all, or are a major obstacle in their acquisition of English. The determining factor seems to be whether or not there are articles in the student’s first (native) language (L1). If it doesn’t have them, then the student will have additional problems to face when studying a second language (L2) that does. Even quite advanced students make frequent slips with articles. Compounding the problem is the fact that there are no good rules as far as articles are concerned. Many course books offer ‘rules’ but there are so many exceptions that they are difficult to apply and students have to fall back on learning them by heart. Fortunately,
In order to gain some understanding of the difficulty from a teaching perspective, how would you set about explaining to a student with absolutely no understanding of articles why the fourth of the following sentences is unacceptable in English? Then, having done that, how would you explain why the second is fine?
- ‘I stopped the car and got in.’
- ‘I stopped a car and got in.’
- ‘I stopped the car and got out.’
- *’I stopped a car and got out.’*
Or perhaps it is easier to explain why ‘the Moscow’ might be the river Moscow, the hotel Moscow or the restaurant Moscow but couldn’t possibly be the city of that name. Or why, in British English at least, if you are ‘going to the prison’, you are probably visiting someone or maybe you work there, whereas if you are just ‘going to prison’, you are going because you have been convicted of a crime.
By far the biggest problem with articles is not so much when to use ‘a’, ‘an’ or ‘the’ but when not to use an article at all!
Back to Top
Determiners
As has already been mentioned, the determiners are a word class that would normally include the articles, however, as is usual in TEFL, they have been listed above separately. Even so, it is important for the new teacher to understand that this distinction is false.
Determiners are words that restrict the meaning of the nouns they are used with. For example, ‘But I’m certain I put it in this cupboard. Where can it have got to?’ Even if we cannot see what is happening, we understand, from the speaker’s use of ‘this‘, that there must be more than one cupboard. Despite the obvious similarities, it should be clearly understood that determiners are not adjectives.
Types of determiner:
|
Articles |
a pen, the house |
|
Demonstratives |
this hat, these hats, that book, those books |
|
Possessives |
my dog, your sunglasses, her car, etc. |
|
Quantifiers |
many choices, some people, several hooligans, etc. |
|
Numerals |
the second option, seven possibilities, etc. |
Determiners can be grouped according to how they are used:
Group A includes the articles, demonstratives and possessives. The use of a Group A determiner allows us to understand whether or not the speaker believes the listener knows which one(s) is being referred to (e.g. a car, the car), or whether the speaker is talking about a specific example(s) or in general. It is not possible to put two group A determiners together in a phrase: so ‘the car‘ is fine but *’the her car‘* is not. If for some reason we want to do so, we have to use a structure using ‘of‘ (e.g. ‘this husband of yours‘).
Group B is composed mainly of quantifiers. It is possible to put two Group B determiners together where their individual meanings allow it. For example, ‘As a punishment for the city’s stubborn resistance, the invaders executed every third person.’
Most Group B determiners do not use ‘of‘ when placed before nouns (‘Do you have any cream?’ not *’Do you have any of cream?’*). However, when used in combination with a Group A determiner, ‘of‘ must be used (‘Several books were badly damaged in the fire.’, but ‘Several of the books were badly damaged in the fire.’). There are a few cases where a Group B determiner is used in combination with ‘of‘ when placed directly before a noun. These are mostly either place names (‘Most of London was destroyed in the great fire.’) or uncountable nouns that refer to entire subjects or activities (‘It is difficult to determine, with any great certainty, exactly what really happened in the past because much of recorded history was set down by interested parties.’).
Another important thing to be aware of, since many EFL students make this mistake, is that the ‘of‘ structure is not used after the Group B determiners ‘no‘ and ‘every‘. Instead ‘none‘ and ‘every one‘ are used (‘Every student was happy.’, but ‘Every one of her students were happy.’).
The correct use of ‘of‘ with determiners is a complex area and warrants more space than is available here. Those wishing to delve into this more deeply are again advised to refer to Michael Swan’s Practical English Usage.
Back to Top
Conjunctions
Conjunctions are words that join words, phrases or clauses together and show the relationships that exist between them. Examples of these are: but, and, or (these are known as co-ordinating conjunctions).
- ‘but» is most often used to join and emphasise contrasting ideas: ‘They were exhausted, but very happy.’
- ‘and‘ is simply used to join things without unduly emphasising any differences that may exist (which is not to say that ‘and» cannot be emphatic — with the right intonation obviously it can be.): ‘He put on his hat, coat and an air of indifference.’
Other conjunctions like ‘when‘, ‘because‘, ‘that‘ are known as subordinating conjunctions and unlike the co-ordinating conjunctions are a part of the clause they join.
- ‘when‘ is used to join a time clause to the rest of a sentence: ‘I was shocked when they announced they were giving the prize to me’.
- ‘because‘ joins a fact with its cause: ‘He lied because he thought the truth would hurt her.’
- ‘that‘ is used to join clauses that are acting as the object of a verb: He promised her that he would come if he could. (Compare the above with He(subject) promised(verb) her(indirect object) a new dress(object))
Conjunctions can consist of more than one word. Examples of these are: ‘such as‘, ‘in order to‘, etc.
Back to Top
Interjections
Interjections are words such as ‘Yuck!‘, ‘Ugh!‘, and ‘Ouch!‘ which indicate the emotions, like disgust, fear, shock, delight, etc., of the person who utters them.
Back to Top
Prepositions
Prepositions are words which are used to link nouns, pronouns and gerunds ( the ‘-ing‘ form of a verb which is being used as a noun e.g. ‘At high level Swimming is a very demanding sport.’) to other words. They are often short words like ‘on‘, ‘in‘, ‘up‘, ‘down‘, ‘about‘, etc. They can consist of more than one word: in front of, next to, etc.
In TEFL we talk a lot about prepositions of time, place and movement:
|
Time |
I’ll see you at six o’clock. |
|
I’ll be home by five. |
|
|
We’re having a party on Christmas eve. |
|
|
Let’s have a party at Christmas. |
|
|
Place |
I’m in London at the moment. |
|
He’s at work, I’m afraid. |
|
|
The bookshop is on the second floor. |
|
|
She always leaves a key under the doormat. |
|
|
Movement |
She went to post office. |
|
He flew here from Guyana. |
|
|
He leapt over the gate. |
|
|
An elderly man was slowly climbing up the hill. |
These of course are not the only prepositions. The biggest problem for EFL students and therefore for their teachers is that it is almost impossible to predict which preposition combines with which verb, noun or adjective in any particular case, or even whether one is necessary at all. Here are some examples to demonstrate this point:
- agree with somebody about a subject but on a decision and to a suggestion,
- angry with somebody about something (at could also be used in both cases), or angry with/at somebody for doing something
- get/be married to somebody but marry somebody (no preposition)
- ‘pay for the tickets’, but ‘pay a bill’.
To a native speaker of English these may at first sight seem obvious, but to an EFL student they are impossible to guess. After all what is really wrong with *’get married on somebody’*? This would be perfectly correct in a number of languages. Even native speakers fail to agree on the use of some prepositions: Americans can say ‘Congratulations for your exam results!’, or ‘In America football is different than soccer.’ but these feel very wrong to the British, who would prefer to say ‘Congratulations on your exam results .’, and ‘In America football is different from soccer.’ Interestingly, British English does allow ‘different than‘ if it is followed by a clause e.g. The situation is different than I expected.’ It should be said, however, that the impact of Hollywood on British English seems to be gradually causing these differences to disappear.
Another complication is that it is often very difficult to know whether a word is, in fact, an adverb particle or a preposition as many can be either depending on the particular context in which they are found. This creates a problem in distinguishing between phrasal verbs and prepositional verbs. In the sentence ‘She fell off her chair.’ Off is a preposition while in the sentence ‘She turned off the radio.’ it is an adverb particle. Why is this so important? Well, lets take a moment to consider these two examples.
1. She turned off the radio.
What happens to the word order in the above sentence if we replace ‘the radio’ with the pronoun ‘it’? We have to place ‘it’ between the verb and its adverb particle — ‘She turned it off.’ We cannot say *’She turned off it.’* We can, however, say ‘She turned the radio off.’
2. She fell off her chair.
What if we do the same to this sentence? We get ‘She fell off it (because she was laughing so much).’ In this case, we cannot insert ‘it’ into the middle of the prepositional verb. Nor can we say *’She fell the chair off.’*
No problem for a native speaker, of course, they ‘know’ what is right, but what about the poor EFL student, who doesn’t have this ‘knowledge’? And what about the poor EFL teacher, who has to find some way to help their students with this?
No matter what language is being studied prepositions are always a problem.
End of Section 1 Parts of Speech
Back to Top
Foundation TEFL methodology course
80 HOURS OF INPUT
- Engaging & interactive assignments
- Based on decades of combined experience
- Learn anywhere at any time
EXPLORE THE WORLD OF TEACHING! TEACH, INSPIRE & GROW
In grammar, a part of speech or part-of-speech (abbreviated as POS or PoS, also known as word class[1] or grammatical category[2]) is a category of words (or, more generally, of lexical items) that have similar grammatical properties. Words that are assigned to the same part of speech generally display similar syntactic behavior (they play similar roles within the grammatical structure of sentences), sometimes similar morphological behavior in that they undergo inflection for similar properties and even similar semantic behavior. Commonly listed English parts of speech are noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, interjection, numeral, article, and determiner.
Other terms than part of speech—particularly in modern linguistic classifications, which often make more precise distinctions than the traditional scheme does—include word class, lexical class, and lexical category. Some authors restrict the term lexical category to refer only to a particular type of syntactic category; for them the term excludes those parts of speech that are considered to be function words, such as pronouns. The term form class is also used, although this has various conflicting definitions.[3] Word classes may be classified as open or closed: open classes (typically including nouns, verbs and adjectives) acquire new members constantly, while closed classes (such as pronouns and conjunctions) acquire new members infrequently, if at all.
Almost all languages have the word classes noun and verb, but beyond these two there are significant variations among different languages.[4] For example:
- Japanese has as many as three classes of adjectives, where English has one.
- Chinese, Korean, Japanese and Vietnamese have a class of nominal classifiers.
- Many languages do not distinguish between adjectives and adverbs, or between adjectives and verbs (see stative verb).
Because of such variation in the number of categories and their identifying properties, analysis of parts of speech must be done for each individual language. Nevertheless, the labels for each category are assigned on the basis of universal criteria.[4]
History[edit]
The classification of words into lexical categories is found from the earliest moments in the history of linguistics.[5]
India[edit]
In the Nirukta, written in the 6th or 5th century BCE, the Sanskrit grammarian Yāska defined four main categories of words:[6]
- नाम nāma – noun (including adjective)
- आख्यात ākhyāta – verb
- उपसर्ग upasarga – pre-verb or prefix
- निपात nipāta – particle, invariant word (perhaps preposition)
These four were grouped into two larger classes: inflectable (nouns and verbs) and uninflectable (pre-verbs and particles).
The ancient work on the grammar of the Tamil language, Tolkāppiyam, argued to have been written around 2nd century CE,[7] classifies Tamil words as peyar (பெயர்; noun), vinai (வினை; verb), idai (part of speech which modifies the relationships between verbs and nouns), and uri (word that further qualifies a noun or verb).[8]
Western tradition[edit]
A century or two after the work of Yāska, the Greek scholar Plato wrote in his Cratylus dialogue, «sentences are, I conceive, a combination of verbs [rhêma] and nouns [ónoma]».[9] Aristotle added another class, «conjunction» [sýndesmos], which included not only the words known today as conjunctions, but also other parts (the interpretations differ; in one interpretation it is pronouns, prepositions, and the article).[10]
By the end of the 2nd century BCE, grammarians had expanded this classification scheme into eight categories, seen in the Art of Grammar, attributed to Dionysius Thrax:[11]
- ‘Name’ (ónoma) translated as «Noun«: a part of speech inflected for case, signifying a concrete or abstract entity. It includes various species like nouns, adjectives, proper nouns, appellatives, collectives, ordinals, numerals and more.[12]
- Verb (rhêma): a part of speech without case inflection, but inflected for tense, person and number, signifying an activity or process performed or undergone
- Participle (metokhḗ): a part of speech sharing features of the verb and the noun
- Article (árthron): a declinable part of speech, taken to include the definite article, but also the basic relative pronoun
- Pronoun (antōnymíā): a part of speech substitutable for a noun and marked for a person
- Preposition (próthesis): a part of speech placed before other words in composition and in syntax
- Adverb (epírrhēma): a part of speech without inflection, in modification of or in addition to a verb, adjective, clause, sentence, or other adverb
- Conjunction (sýndesmos): a part of speech binding together the discourse and filling gaps in its interpretation
It can be seen that these parts of speech are defined by morphological, syntactic and semantic criteria.
The Latin grammarian Priscian (fl. 500 CE) modified the above eightfold system, excluding «article» (since the Latin language, unlike Greek, does not have articles) but adding «interjection».[13][14]
The Latin names for the parts of speech, from which the corresponding modern English terms derive, were nomen, verbum, participium, pronomen, praepositio, adverbium, conjunctio and interjectio. The category nomen included substantives (nomen substantivum, corresponding to what are today called nouns in English), adjectives (nomen adjectivum) and numerals (nomen numerale). This is reflected in the older English terminology noun substantive, noun adjective and noun numeral. Later[15] the adjective became a separate class, as often did the numerals, and the English word noun came to be applied to substantives only.
Classification[edit]
Works of English grammar generally follow the pattern of the European tradition as described above, except that participles are now usually regarded as forms of verbs rather than as a separate part of speech, and numerals are often conflated with other parts of speech: nouns (cardinal numerals, e.g., «one», and collective numerals, e.g., «dozen»), adjectives (ordinal numerals, e.g., «first», and multiplier numerals, e.g., «single») and adverbs (multiplicative numerals, e.g., «once», and distributive numerals, e.g., «singly»). Eight or nine parts of speech are commonly listed:
- noun
- verb
- adjective
- adverb
- pronoun
- preposition
- conjunction
- interjection
- article* or (more recently) determiner
Additionally, there are other parts of speech including particles (yes, no)[a] and postpositions (ago, notwithstanding) although many fewer words are in these categories.
Some traditional classifications consider articles to be adjectives, yielding eight parts of speech rather than nine. And some modern classifications define further classes in addition to these. For discussion see the sections below.
The classification below, or slight expansions of it, is still followed in most dictionaries:
- Noun (names)
- a word or lexical item denoting any abstract (abstract noun: e.g. home) or concrete entity (concrete noun: e.g. house); a person (police officer, Michael), place (coastline, London), thing (necktie, television), idea (happiness), or quality (bravery). Nouns can also be classified as count nouns or non-count nouns; some can belong to either category. The most common part of speech; they are called naming words.
- Pronoun (replaces or places again)
- a substitute for a noun or noun phrase (them, he). Pronouns make sentences shorter and clearer since they replace nouns.
- Adjective (describes, limits)
- a modifier of a noun or pronoun (big, brave). Adjectives make the meaning of another word (noun) more precise.
- Verb (states action or being)
- a word denoting an action (walk), occurrence (happen), or state of being (be). Without a verb, a group of words cannot be a clause or sentence.
- Adverb (describes, limits)
- a modifier of an adjective, verb, or another adverb (very, quite). Adverbs make language more precise.
- Preposition (relates)
- a word that relates words to each other in a phrase or sentence and aids in syntactic context (in, of). Prepositions show the relationship between a noun or a pronoun with another word in the sentence.
- Conjunction (connects)
- a syntactic connector; links words, phrases, or clauses (and, but). Conjunctions connect words or group of words
- Interjection (expresses feelings and emotions)
- an emotional greeting or exclamation (Huzzah, Alas). Interjections express strong feelings and emotions.
- Article (describes, limits)
- a grammatical marker of definiteness (the) or indefiniteness (a, an). The article is not always listed among the parts of speech. It is considered by some grammarians to be a type of adjective[16] or sometimes the term ‘determiner’ (a broader class) is used.
English words are not generally marked as belonging to one part of speech or another; this contrasts with many other European languages, which use inflection more extensively, meaning that a given word form can often be identified as belonging to a particular part of speech and having certain additional grammatical properties. In English, most words are uninflected, while the inflected endings that exist are mostly ambiguous: -ed may mark a verbal past tense, a participle or a fully adjectival form; -s may mark a plural noun, a possessive noun, or a present-tense verb form; -ing may mark a participle, gerund, or pure adjective or noun. Although -ly is a frequent adverb marker, some adverbs (e.g. tomorrow, fast, very) do not have that ending, while many adjectives do have it (e.g. friendly, ugly, lovely), as do occasional words in other parts of speech (e.g. jelly, fly, rely).
Many English words can belong to more than one part of speech. Words like neigh, break, outlaw, laser, microwave, and telephone might all be either verbs or nouns. In certain circumstances, even words with primarily grammatical functions can be used as verbs or nouns, as in, «We must look to the hows and not just the whys.» The process whereby a word comes to be used as a different part of speech is called conversion or zero derivation.
Functional classification[edit]
Linguists recognize that the above list of eight or nine word classes is drastically simplified.[17] For example, «adverb» is to some extent a catch-all class that includes words with many different functions. Some have even argued that the most basic of category distinctions, that of nouns and verbs, is unfounded,[18] or not applicable to certain languages.[19][20] Modern linguists have proposed many different schemes whereby the words of English or other languages are placed into more specific categories and subcategories based on a more precise understanding of their grammatical functions.
Common lexical category set defined by function may include the following (not all of them will necessarily be applicable in a given language):
- Categories that will usually be open classes:
- adjectives
- adverbs
- nouns
- verbs (except auxiliary verbs)
- interjections
- Categories that will usually be closed classes:
- auxiliary verbs
- clitics
- coverbs
- conjunctions
- determiners (articles, quantifiers, demonstrative adjectives, and possessive adjectives)
- particles
- measure words or classifiers
- adpositions (prepositions, postpositions, and circumpositions)
- preverbs
- pronouns
- contractions
- cardinal numbers
Within a given category, subgroups of words may be identified based on more precise grammatical properties. For example, verbs may be specified according to the number and type of objects or other complements which they take. This is called subcategorization.
Many modern descriptions of grammar include not only lexical categories or word classes, but also phrasal categories, used to classify phrases, in the sense of groups of words that form units having specific grammatical functions. Phrasal categories may include noun phrases (NP), verb phrases (VP) and so on. Lexical and phrasal categories together are called syntactic categories.
Open and closed classes[edit]
Word classes may be either open or closed. An open class is one that commonly accepts the addition of new words, while a closed class is one to which new items are very rarely added. Open classes normally contain large numbers of words, while closed classes are much smaller. Typical open classes found in English and many other languages are nouns, verbs (excluding auxiliary verbs, if these are regarded as a separate class), adjectives, adverbs and interjections. Ideophones are often an open class, though less familiar to English speakers,[21][22][b] and are often open to nonce words. Typical closed classes are prepositions (or postpositions), determiners, conjunctions, and pronouns.[24]
The open–closed distinction is related to the distinction between lexical and functional categories, and to that between content words and function words, and some authors consider these identical, but the connection is not strict. Open classes are generally lexical categories in the stricter sense, containing words with greater semantic content,[25] while closed classes are normally functional categories, consisting of words that perform essentially grammatical functions. This is not universal: in many languages verbs and adjectives[26][27][28] are closed classes, usually consisting of few members, and in Japanese the formation of new pronouns from existing nouns is relatively common, though to what extent these form a distinct word class is debated.
Words are added to open classes through such processes as compounding, derivation, coining, and borrowing. When a new word is added through some such process, it can subsequently be used grammatically in sentences in the same ways as other words in its class.[29] A closed class may obtain new items through these same processes, but such changes are much rarer and take much more time. A closed class is normally seen as part of the core language and is not expected to change. In English, for example, new nouns, verbs, etc. are being added to the language constantly (including by the common process of verbing and other types of conversion, where an existing word comes to be used in a different part of speech). However, it is very unusual for a new pronoun, for example, to become accepted in the language, even in cases where there may be felt to be a need for one, as in the case of gender-neutral pronouns.
The open or closed status of word classes varies between languages, even assuming that corresponding word classes exist. Most conspicuously, in many languages verbs and adjectives form closed classes of content words. An extreme example is found in Jingulu, which has only three verbs, while even the modern Indo-European Persian has no more than a few hundred simple verbs, a great deal of which are archaic. (Some twenty Persian verbs are used as light verbs to form compounds; this lack of lexical verbs is shared with other Iranian languages.) Japanese is similar, having few lexical verbs.[30] Basque verbs are also a closed class, with the vast majority of verbal senses instead expressed periphrastically.
In Japanese, verbs and adjectives are closed classes,[31] though these are quite large, with about 700 adjectives,[32][33] and verbs have opened slightly in recent years. Japanese adjectives are closely related to verbs (they can predicate a sentence, for instance). New verbal meanings are nearly always expressed periphrastically by appending suru (する, to do) to a noun, as in undō suru (運動する, to (do) exercise), and new adjectival meanings are nearly always expressed by adjectival nouns, using the suffix -na (〜な) when an adjectival noun modifies a noun phrase, as in hen-na ojisan (変なおじさん, strange man). The closedness of verbs has weakened in recent years, and in a few cases new verbs are created by appending -ru (〜る) to a noun or using it to replace the end of a word. This is mostly in casual speech for borrowed words, with the most well-established example being sabo-ru (サボる, cut class; play hooky), from sabotāju (サボタージュ, sabotage).[34] This recent innovation aside, the huge contribution of Sino-Japanese vocabulary was almost entirely borrowed as nouns (often verbal nouns or adjectival nouns). Other languages where adjectives are closed class include Swahili,[28] Bemba, and Luganda.
By contrast, Japanese pronouns are an open class and nouns become used as pronouns with some frequency; a recent example is jibun (自分, self), now used by some young men as a first-person pronoun. The status of Japanese pronouns as a distinct class is disputed,[by whom?] however, with some considering it only a use of nouns, not a distinct class. The case is similar in languages of Southeast Asia, including Thai and Lao, in which, like Japanese, pronouns and terms of address vary significantly based on relative social standing and respect.[35]
Some word classes are universally closed, however, including demonstratives and interrogative words.[35]
See also[edit]
- Part-of-speech tagging
- Sliding window based part-of-speech tagging
Notes[edit]
- ^ Yes and no are sometimes classified as interjections.
- ^ Ideophones do not always form a single grammatical word class, and their classification varies between languages, sometimes being split across other word classes. Rather, they are a phonosemantic word class, based on derivation, but may be considered part of the category of «expressives»,[21] which thus often form an open class due to the productivity of ideophones. Further, «[i]n the vast majority of cases, however, ideophones perform an adverbial function and are closely linked with verbs.»[23]
References[edit]
- ^ Rijkhoff, Jan (2007). «Word Classes». Language and Linguistics Compass. Wiley. 1 (6): 709–726. doi:10.1111/j.1749-818x.2007.00030.x. ISSN 1749-818X. S2CID 5404720.
- ^ Payne, Thomas E. (1997). Describing morphosyntax: a guide for field linguists. Cambridge. ISBN 9780511805066.
- ^ John Lyons, Semantics, CUP 1977, p. 424.
- ^ a b Kroeger, Paul (2005). Analyzing Grammar: An Introduction. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 35. ISBN 978-0-521-01653-7.
- ^ Robins RH (1989). General Linguistics (4th ed.). London: Longman.
- ^
Bimal Krishna Matilal (1990). The word and the world: India’s contribution to the study of language (Chapter 3). - ^ Mahadevan, I. (2014). Early Tamil Epigraphy — From the Earliest Times to the Sixth century C.E., 2nd Edition. p. 271.
- ^
Ilakkuvanar S (1994). Tholkappiyam in English with critical studies (2nd ed.). Educational Publisher. - ^ Cratylus 431b
- ^ The Rhetoric, Poetic and Nicomachean Ethics of Aristotle, translated by Thomas Taylor, London 1811, p. 179.
- ^ Dionysius Thrax. τέχνη γραμματική (Art of Grammar), ια´ περὶ λέξεως (11. On the word):
- λέξις ἐστὶ μέρος ἐλάχιστον τοῦ κατὰ σύνταξιν λόγου.
λόγος δέ ἐστι πεζῆς λέξεως σύνθεσις διάνοιαν αὐτοτελῆ δηλοῦσα.
τοῦ δὲ λόγου μέρη ἐστὶν ὀκτώ· ὄνομα, ῥῆμα,
μετοχή, ἄρθρον, ἀντωνυμία, πρόθεσις, ἐπίρρημα, σύνδεσμος. ἡ γὰρ προσηγορία ὡς εἶδος τῶι ὀνόματι ὑποβέβληται. - A word is the smallest part of organized speech.
Speech is the putting together of an ordinary word to express a complete thought.
The class of word consists of eight categories: noun, verb,
participle, article, pronoun, preposition, adverb, conjunction. A common noun in form is classified as a noun.
- λέξις ἐστὶ μέρος ἐλάχιστον τοῦ κατὰ σύνταξιν λόγου.
- ^ The term ‘onoma’ at Dionysius Thrax, Τέχνη γραμματική (Art of Grammar), 14. Περὶ ὀνόματος translated by Thomas Davidson, On the noun
- καὶ αὐτὰ εἴδη προσαγορεύεται· κύριον, προσηγορικόν, ἐπίθετον, πρός τι ἔχον, ὡς πρός τι ἔχον, ὁμώνυμον, συνώνυμον, διώνυμον, ἐπώνυμον, ἐθνικόν, ἐρωτηματικόν, ἀόριστον, ἀναφορικὸν ὃ καὶ ὁμοιωματικὸν καὶ δεικτικὸν καὶ ἀνταποδοτικὸν καλεῖται, περιληπτικόν, ἐπιμεριζόμενον, περιεκτικόν, πεποιημένον, γενικόν, ἰδικόν, τακτικόν, ἀριθμητικόν, ἀπολελυμένον, μετουσιαστικόν.
- also called Species: proper, appellative, adjective, relative, quasi-relative, homonym, synonym, pheronym, dionym, eponym, national, interrogative, indefinite, anaphoric (also called assimilative, demonstrative, and retributive), collective, distributive, inclusive, onomatopoetic, general, special, ordinal, numeral, participative, independent.
- ^ [penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E/Roman/Texts/Quintilian/Institutio_Oratoria/1B*.html This translation of Quintilian’s Institutio Oratoria reads: «Our own language (Note: i.e. Latin) dispenses with the articles (Note: Latin doesn’t have articles), which are therefore distributed among the other parts of speech. But interjections must be added to those already mentioned.»]
- ^ «Quintilian: Institutio Oratoria I».
- ^ See for example Beauzée, Nicolas, Grammaire générale, ou exposition raisonnée des éléments nécessaires du langage (Paris, 1767), and earlier Jakob Redinger, Comeniana Grammatica Primae Classi Franckenthalensis Latinae Scholae destinata … (1659, in German and Latin).
- ^ The Oxford Dictionary of English Grammar by Bas Aarts, Sylvia Chalker & Edmund Weine. OUP Oxford 2014. Page 35.
- ^ Zwicky, Arnold (30 March 2006). «What part of speech is «the»«. Language Log. Retrieved 26 December 2009.
…the school tradition about parts of speech is so desperately impoverished
- ^ Hopper, P; Thompson, S (1985). «The Iconicity of the Universal Categories ‘Noun’ and ‘Verbs’«. In John Haiman (ed.). Typological Studies in Language: Iconicity and Syntax. Vol. 6. Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company. pp. 151–183.
- ^ Launey, Michel (1994). Une grammaire omniprédicative: essai sur la morphosyntaxe du nahuatl classique. Paris: CNRS Editions.
- ^ Broschart, Jürgen (1997). «Why Tongan does it differently: Categorial Distinctions in a Language without Nouns and Verbs». Linguistic Typology. 1 (2): 123–165. doi:10.1515/lity.1997.1.2.123. S2CID 121039930.
- ^ a b The Art of Grammar: A Practical Guide, Alexandra Y. Aikhenvald, p. 99
- ^ G. Tucker Childs, «African ideophones», in Sound Symbolism, p. 179
- ^ G. Tucker Childs, «African ideophones», in Sound Symbolism, p. 181
- ^ «Sample Entry: Function Words / Encyclopedia of Linguistics».
- ^ Carnie, Andrew (2012). Syntax: A Generative Introduction. New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 51–52. ISBN 978-0-470-65531-3.
- ^ Dixon, Robert M. W. (1977). «Where Have all the Adjectives Gone?». Studies in Language. 1: 19–80. doi:10.1075/sl.1.1.04dix.
- ^ Adjective classes: a cross-linguistic typology, Robert M. W. Dixon, Alexandra Y. Aikhenvald, OUP Oxford, 2006
- ^ a b The Art of Grammar: A Practical Guide, Alexandra Y. Aikhenvald, p. 97
- ^ Hoff, Erika (2014). Language Development. Belmont, CA: Cengage Learning. p. 171. ISBN 978-1-133-93909-2.
- ^ Categorial Features: A Generative Theory of Word Class Categories, «p. 54».
- ^ Dixon 1977, p. 48.
- ^ The Typology of Adjectival Predication, Harrie Wetzer, p. 311
- ^ The Art of Grammar: A Practical Guide, Alexandra Y. Aikhenvald, p. 96
- ^ Adam (2011-07-18). «Homage to る(ru), The Magical Verbifier».
- ^ a b The Art of Grammar: A Practical Guide, Alexandra Y. Aikhenvald, p. 98
External links[edit]
Media related to Parts of speech at Wikimedia Commons
- The parts of speech
- Guide to Grammar and Writing
- Martin Haspelmath. 2001. «Word Classes and Parts of Speech.» In: Baltes, Paul B. & Smelser, Neil J. (eds.) International Encyclopedia of the Social and Behavioral Sciences. Amsterdam: Pergamon, 16538–16545. (PDF)
A part of speech is a term used in traditional grammar for one of the nine main categories into which words are classified according to their functions in sentences, such as nouns or verbs. Also known as word classes, these are the building blocks of grammar.
Parts of Speech
- Word types can be divided into nine parts of speech:
- nouns
- pronouns
- verbs
- adjectives
- adverbs
- prepositions
- conjunctions
- articles/determiners
- interjections
- Some words can be considered more than one part of speech, depending on context and usage.
- Interjections can form complete sentences on their own.
Every sentence you write or speak in English includes words that fall into some of the nine parts of speech. These include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections. (Some sources include only eight parts of speech and leave interjections in their own category.)
Learning the names of the parts of speech probably won’t make you witty, healthy, wealthy, or wise. In fact, learning just the names of the parts of speech won’t even make you a better writer. However, you will gain a basic understanding of sentence structure and the English language by familiarizing yourself with these labels.
Open and Closed Word Classes
The parts of speech are commonly divided into open classes (nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs) and closed classes (pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections). The idea is that open classes can be altered and added to as language develops and closed classes are pretty much set in stone. For example, new nouns are created every day, but conjunctions never change.
In contemporary linguistics, the label part of speech has generally been discarded in favor of the term word class or syntactic category. These terms make words easier to qualify objectively based on word construction rather than context. Within word classes, there is the lexical or open class and the function or closed class.
Read about each part of speech below and get started practicing identifying each.
Noun
Nouns are a person, place, thing, or idea. They can take on a myriad of roles in a sentence, from the subject of it all to the object of an action. They are capitalized when they’re the official name of something or someone, called proper nouns in these cases. Examples: pirate, Caribbean, ship, freedom, Captain Jack Sparrow.
Pronoun
Pronouns stand in for nouns in a sentence. They are more generic versions of nouns that refer only to people. Examples: I, you, he, she, it, ours, them, who, which, anybody, ourselves.
Verb
Verbs are action words that tell what happens in a sentence. They can also show a sentence subject’s state of being (is, was). Verbs change form based on tense (present, past) and count distinction (singular or plural). Examples: sing, dance, believes, seemed, finish, eat, drink, be, became
Adjective
Adjectives describe nouns and pronouns. They specify which one, how much, what kind, and more. Adjectives allow readers and listeners to use their senses to imagine something more clearly. Examples: hot, lazy, funny, unique, bright, beautiful, poor, smooth.
Adverb
Adverbs describe verbs, adjectives, and even other adverbs. They specify when, where, how, and why something happened and to what extent or how often. Examples: softly, lazily, often, only, hopefully, softly, sometimes.
Preposition
Prepositions show spacial, temporal, and role relations between a noun or pronoun and the other words in a sentence. They come at the start of a prepositional phrase, which contains a preposition and its object. Examples: up, over, against, by, for, into, close to, out of, apart from.
Conjunction
Conjunctions join words, phrases, and clauses in a sentence. There are coordinating, subordinating, and correlative conjunctions. Examples: and, but, or, so, yet, with.
Articles and Determiners
Articles and determiners function like adjectives by modifying nouns, but they are different than adjectives in that they are necessary for a sentence to have proper syntax. Articles and determiners specify and identify nouns, and there are indefinite and definite articles. Examples: articles: a, an, the; determiners: these, that, those, enough, much, few, which, what.
Some traditional grammars have treated articles as a distinct part of speech. Modern grammars, however, more often include articles in the category of determiners, which identify or quantify a noun. Even though they modify nouns like adjectives, articles are different in that they are essential to the proper syntax of a sentence, just as determiners are necessary to convey the meaning of a sentence, while adjectives are optional.
Interjection
Interjections are expressions that can stand on their own or be contained within sentences. These words and phrases often carry strong emotions and convey reactions. Examples: ah, whoops, ouch, yabba dabba do!
How to Determine the Part of Speech
Only interjections (Hooray!) have a habit of standing alone; every other part of speech must be contained within a sentence and some are even required in sentences (nouns and verbs). Other parts of speech come in many varieties and may appear just about anywhere in a sentence.
To know for sure what part of speech a word falls into, look not only at the word itself but also at its meaning, position, and use in a sentence.
For example, in the first sentence below, work functions as a noun; in the second sentence, a verb; and in the third sentence, an adjective:
- Bosco showed up for work two hours late.
- The noun work is the thing Bosco shows up for.
- He will have to work until midnight.
- The verb work is the action he must perform.
- His work permit expires next month.
- The attributive noun [or converted adjective] work modifies the noun permit.
Learning the names and uses of the basic parts of speech is just one way to understand how sentences are constructed.
Dissecting Basic Sentences
To form a basic complete sentence, you only need two elements: a noun (or pronoun standing in for a noun) and a verb. The noun acts as a subject and the verb, by telling what action the subject is taking, acts as the predicate.
- Birds fly.
In the short sentence above, birds is the noun and fly is the verb. The sentence makes sense and gets the point across.
You can have a sentence with just one word without breaking any sentence formation rules. The short sentence below is complete because it’s a command to an understood «you».
- Go!
Here, the pronoun, standing in for a noun, is implied and acts as the subject. The sentence is really saying, «(You) go!»
Constructing More Complex Sentences
Use more parts of speech to add additional information about what’s happening in a sentence to make it more complex. Take the first sentence from above, for example, and incorporate more information about how and why birds fly.
- Birds fly when migrating before winter.
Birds and fly remain the noun and the verb, but now there is more description.
When is an adverb that modifies the verb fly. The word before is a little tricky because it can be either a conjunction, preposition, or adverb depending on the context. In this case, it’s a preposition because it’s followed by a noun. This preposition begins an adverbial phrase of time (before winter) that answers the question of when the birds migrate. Before is not a conjunction because it does not connect two clauses.