1). In Excel, this is a prerecorded formula that provides a shortcut for complex calculations __
— View Answer |
||||
2). The following computer’s memory is characterised by low cost per bit stored _______
— View Answer |
||||
3). A supercomputer Param has been developed and designed in India by:
— View Answer |
||||
4). The smallest unit of computer data is
— View Answer |
||||
5). The Michele Anjelo Virus is:
— View Answer |
||||
6). Which one of the following is applicable to all the computers?
— View Answer |
||||
7). What happens when we try to delete the files on the floppy?
— View Answer |
||||
8). In word, replace option is available on ______.
— View Answer |
||||
9). To reverse the effect of your-last action in word, _____.
— View Answer |
||||
10). The time for the actual data transfer after receiving the request for data from secondary storage is referred to as the disk’s _____.
— View Answer |
|
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
|
AVEDEV function |
Returns the average of the absolute deviations of data points from their mean |
|
AVERAGE function |
Returns the average of its arguments |
|
AVERAGEA function |
Returns the average of its arguments, including numbers, text, and logical values |
|
AVERAGEIF function |
Returns the average (arithmetic mean) of all the cells in a range that meet a given criteria |
|
AVERAGEIFS function |
Returns the average (arithmetic mean) of all cells that meet multiple criteria |
|
BETA.DIST function |
Returns the beta cumulative distribution function |
|
BETA.INV function |
Returns the inverse of the cumulative distribution function for a specified beta distribution |
|
BINOM.DIST function |
Returns the individual term binomial distribution probability |
|
BINOM.DIST.RANGE function |
Returns the probability of a trial result using a binomial distribution |
|
BINOM.INV function |
Returns the smallest value for which the cumulative binomial distribution is less than or equal to a criterion value |
|
CHISQ.DIST function |
Returns the cumulative beta probability density function |
|
CHISQ.DIST.RT function |
Returns the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution |
|
CHISQ.INV function |
Returns the cumulative beta probability density function |
|
CHISQ.INV.RT function |
Returns the inverse of the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution |
|
CHISQ.TEST function |
Returns the test for independence |
|
CONFIDENCE.NORM function |
Returns the confidence interval for a population mean |
|
CONFIDENCE.T function |
Returns the confidence interval for a population mean, using a Student’s t distribution |
|
CORREL function |
Returns the correlation coefficient between two data sets |
|
COUNT function |
Counts how many numbers are in the list of arguments |
|
COUNTA function |
Counts how many values are in the list of arguments |
|
COUNTBLANK function |
Counts the number of blank cells within a range |
|
COUNTIF function |
Counts the number of cells within a range that meet the given criteria |
|
COUNTIFS function |
Counts the number of cells within a range that meet multiple criteria |
|
COVARIANCE.P function |
Returns covariance, the average of the products of paired deviations |
|
COVARIANCE.S function |
Returns the sample covariance, the average of the products deviations for each data point pair in two data sets |
|
DEVSQ function |
Returns the sum of squares of deviations |
|
EXPON.DIST function |
Returns the exponential distribution |
|
F.DIST function |
Returns the F probability distribution |
|
F.DIST.RT function |
Returns the F probability distribution |
|
F.INV function |
Returns the inverse of the F probability distribution |
|
F.INV.RT function |
Returns the inverse of the F probability distribution |
|
F.TEST function |
Returns the result of an F-test |
|
FISHER function |
Returns the Fisher transformation |
|
FISHERINV function |
Returns the inverse of the Fisher transformation |
|
FORECAST function |
Returns a value along a linear trend Note: In Excel 2016, this function is replaced with FORECAST.LINEAR as part of the new Forecasting functions, but it’s still available for compatibility with earlier versions. |
|
FORECAST.ETS function |
Returns a future value based on existing (historical) values by using the AAA version of the Exponential Smoothing (ETS) algorithm |
|
FORECAST.ETS.CONFINT function |
Returns a confidence interval for the forecast value at the specified target date |
|
FORECAST.ETS.SEASONALITY function |
Returns the length of the repetitive pattern Excel detects for the specified time series |
|
FORECAST.ETS.STAT function |
Returns a statistical value as a result of time series forecasting |
|
FORECAST.LINEAR function |
Returns a future value based on existing values |
|
FREQUENCY function |
Returns a frequency distribution as a vertical array |
|
GAMMA function |
Returns the Gamma function value |
|
GAMMA.DIST function |
Returns the gamma distribution |
|
GAMMA.INV function |
Returns the inverse of the gamma cumulative distribution |
|
GAMMALN function |
Returns the natural logarithm of the gamma function, Γ(x) |
|
GAMMALN.PRECISE function |
Returns the natural logarithm of the gamma function, Γ(x) |
|
GAUSS function |
Returns 0.5 less than the standard normal cumulative distribution |
|
GEOMEAN function |
Returns the geometric mean |
|
GROWTH function |
Returns values along an exponential trend |
|
HARMEAN function |
Returns the harmonic mean |
|
HYPGEOM.DIST function |
Returns the hypergeometric distribution |
|
INTERCEPT function |
Returns the intercept of the linear regression line |
|
KURT function |
Returns the kurtosis of a data set |
|
LARGE function |
Returns the k-th largest value in a data set |
|
LINEST function |
Returns the parameters of a linear trend |
|
LOGEST function |
Returns the parameters of an exponential trend |
|
LOGNORM.DIST function |
Returns the cumulative lognormal distribution |
|
LOGNORM.INV function |
Returns the inverse of the lognormal cumulative distribution |
|
MAX function |
Returns the maximum value in a list of arguments |
|
MAXA function |
Returns the maximum value in a list of arguments, including numbers, text, and logical values |
|
MAXIFS function |
Returns the maximum value among cells specified by a given set of conditions or criteria |
|
MEDIAN function |
Returns the median of the given numbers |
|
MIN function |
Returns the minimum value in a list of arguments |
|
MINA function |
Returns the smallest value in a list of arguments, including numbers, text, and logical values |
|
MINIFS function |
Returns the minimum value among cells specified by a given set of conditions or criteria. |
|
MODE.MULT function |
Returns a vertical array of the most frequently occurring, or repetitive values in an array or range of data |
|
MODE.SNGL function |
Returns the most common value in a data set |
|
NEGBINOM.DIST function |
Returns the negative binomial distribution |
|
NORM.DIST function |
Returns the normal cumulative distribution |
|
NORM.INV function |
Returns the inverse of the normal cumulative distribution |
|
NORM.S.DIST function |
Returns the standard normal cumulative distribution |
|
NORM.S.INV function |
Returns the inverse of the standard normal cumulative distribution |
|
PEARSON function |
Returns the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient |
|
PERCENTILE.EXC function |
Returns the k-th percentile of values in a range, where k is in the range 0..1, exclusive |
|
PERCENTILE.INC function |
Returns the k-th percentile of values in a range |
|
PERCENTRANK.EXC function |
Returns the rank of a value in a data set as a percentage (0..1, exclusive) of the data set |
|
PERCENTRANK.INC function |
Returns the percentage rank of a value in a data set |
|
PERMUT function |
Returns the number of permutations for a given number of objects |
|
PERMUTATIONA function |
Returns the number of permutations for a given number of objects (with repetitions) that can be selected from the total objects |
|
PHI function |
Returns the value of the density function for a standard normal distribution |
|
POISSON.DIST function |
Returns the Poisson distribution |
|
PROB function |
Returns the probability that values in a range are between two limits |
|
QUARTILE.EXC function |
Returns the quartile of the data set, based on percentile values from 0..1, exclusive |
|
QUARTILE.INC function |
Returns the quartile of a data set |
|
RANK.AVG function |
Returns the rank of a number in a list of numbers |
|
RANK.EQ function |
Returns the rank of a number in a list of numbers |
|
RSQ function |
Returns the square of the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient |
|
SKEW function |
Returns the skewness of a distribution |
|
SKEW.P function |
Returns the skewness of a distribution based on a population: a characterization of the degree of asymmetry of a distribution around its mean |
|
SLOPE function |
Returns the slope of the linear regression line |
|
SMALL function |
Returns the k-th smallest value in a data set |
|
STANDARDIZE function |
Returns a normalized value |
|
STDEV.P function |
Calculates standard deviation based on the entire population |
|
STDEV.S function |
Estimates standard deviation based on a sample |
|
STDEVA function |
Estimates standard deviation based on a sample, including numbers, text, and logical values |
|
STDEVPA function |
Calculates standard deviation based on the entire population, including numbers, text, and logical values |
|
STEYX function |
Returns the standard error of the predicted y-value for each x in the regression |
|
T.DIST function |
Returns the Percentage Points (probability) for the Student t-distribution |
|
T.DIST.2T function |
Returns the Percentage Points (probability) for the Student t-distribution |
|
T.DIST.RT function |
Returns the Student’s t-distribution |
|
T.INV function |
Returns the t-value of the Student’s t-distribution as a function of the probability and the degrees of freedom |
|
T.INV.2T function |
Returns the inverse of the Student’s t-distribution |
|
T.TEST function |
Returns the probability associated with a Student’s t-test |
|
TREND function |
Returns values along a linear trend |
|
TRIMMEAN function |
Returns the mean of the interior of a data set |
|
VAR.P function |
Calculates variance based on the entire population |
|
VAR.S function |
Estimates variance based on a sample |
|
VARA function |
Estimates variance based on a sample, including numbers, text, and logical values |
|
VARPA function |
Calculates variance based on the entire population, including numbers, text, and logical values |
|
WEIBULL.DIST function |
Returns the Weibull distribution |
|
Z.TEST function |
Returns the one-tailed probability-value of a z-test |
► MCQ Exam ON : Educational Computer MCQ
This is not a function category in Excel —
| 1) |
Logical |
|
| 2) |
Data Series |
|
| 3) |
Financial |
|
| 4) |
Text |
|
| 5) | NULL |
(Complaint Here As Incorrect)

Trishna Mahanta
5 years ago
Which is not a function in Microsoft excel?
A. sum
B. Max
C. Avg
D. None of these
Answer: Option C
Solution(By Examveda Team)
Average is function
Join The Discussion
Comment*
Comments ( 2 )
-
Ashu Jhaa :
4 years ago
What is the reason??
-
Binod Kumar :
4 years ago
Reason batao sir….how average is not a function of ms Excel
Related User Ask Questions
Which of the following is not a primary function of a Bank?
A. Granting Loans
B. Collecting Cheques/Drafts customers
C. Facilitating import of goods
D. Issuing Bank Drafts
View Answer
View Answer
Though ULIPs (Unit Linked Insurance Plan) are considered to be a better investment vehicle it has failed to capture the imagination of the retail investors in India because of which of the following reasons?
A. Regulatory jurisdictional fight between SEBI and IRDA
B. They don’t offer better tax benefits
C. They offer lesser returns compared to traditional insurance policies
D. All of the above
View Answer
View Answer
The Chameli Devi Jain Award is given for an outstanding woman ____?
A. Scientist
B. Reporter
C. Player
D. Teacher
View Answer
View Answer
HDFC bank has been named among 50 most valuable banks in 2014. It has got 45th rank. Wells Fargo & Co. has got first rank in this list. This bank belongs to which country?
A. UK
B. France
C. European Union
D. USA
View Answer
View Answer
View all User Ask Questions
Read More: MCQ Type Questions and Answers
- Arithmetic Ability
- Competitive Reasoning
- Competitive English
- Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- State GK
- History
- Geography
- Current Affairs
- Banking Awareness
- Computer Fundamentals
- Networking
- C Program
- Java Program
- SQL
- Database
- HTML
- CSS
- Javascript
- PHP
- Computer Science
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Mechanical Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Chemical Engineering
- Commerce
- Management
- Law
- Agriculture
- Sociology
- Political Science
- Pharmacy
Excel Functions Test – Excel 2010 – Formulas & Functions in Excel – Free Online Microsoft Excel Test
a) The Financial category.
b) The Text category.
c) The Conditional Formatting category.
d) The Engineering category.
a) It is used to search for specific functions using keywords and descriptions.
b) It is used to insert a specific function by clicking on its name in the Insert Function list.
c) It is used to display information about the arguments needed to build a function.
d) All of the above options are correct.
a) There are four arguments: IF, Logical_test, Value_if_true and Value_if_false.
b) There are three arguments: Logical_test, Value_if_true and Value_if_false.
c) There are two arguments: Logical and Value.
d) There are five arguments: IF, Logical_test, Value_if_true and Value_if_false and Logical_test.
a) It will return: above average
b) It will return: below average
c) It will return the value: 12.
d) It will return an error.
a) It is: 0.
b) It is: ISBLANK.
c) It is: A1.
d) It is: 10.
a) Double click the cell containing the function and make amendments to the function within the cell.
b) Click the cell containing the function and then click in the Formula Bar to make amendments to the function.
c) Click the cell containing the function and then click on the fx symbol to the left of the Formula Bar to launch the Function Arguments dialogue box where amendments can be made.
d) All of the above options are correct.
a) If he clicks on the Home tab in Excel, he can use the Find & Select function to look for a function that counts items.
b) If he presses Ctrl+F on his keyboard, he can use the Find dialogue box to look for a function that counts items.
c) If he presses Shift+F3 he can use the Insert Function dialogue box to look for a function that counts items.
d) All of the above options are correct.
a) In the Insert Function dialogue box, click on the function name to get a short description of what the function is used for.
b) Open Excel Help from the Backstage View and search for the function in the Help Library.
c) Insert the function in a cell and right-click the cell for an explanation.
d) All of the above options are correct.
a) Under the Insert tab on the Ribbon.
b) Under the Formulas tab.
c) Under the Home tab on the Ribbon.
d) All of the above options are correct.
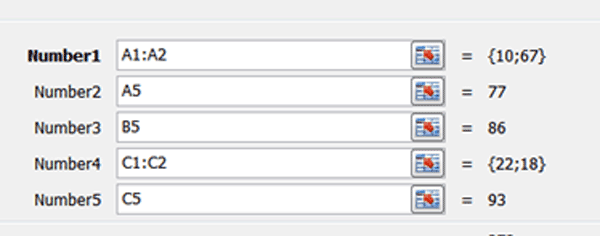
a) No, the references entered into Number1 and Number4 are incorrect.
b) No, the cells are not from the same range, for example A5 and B5 is not even the same column reference.
c) Yes, the cells contain valid arguments referring to various non-adjacent cell references.
d) The arguments above do not represent the SUM function.