The alma mater, meaning «nourishing mother» in Latin, is one of the most enduring symbols of the university. The phrase was first used to describe the University of Bologna, Italy, founded in 1088.
A university (from Latin universitas ‘a whole’) is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school.
The word university is derived from the Latin universitas magistrorum et scholarium, which roughly means «community of teachers and scholars».[1]
The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic Church monks.[2][3][4][5][6] The University of Bologna (Università di Bologna), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of:
- Being a high degree-awarding institute.
- Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy.
- Using the word universitas (which was coined at its foundation).
- Issuing secular and non-secular degrees: grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.[7][8][9][10][11]
History[edit]
Definition[edit]
The original Latin word universitas refers in general to «a number of persons associated into one body, a society, company, community, guild, corporation, etc».[12] At the time of the emergence of urban town life and medieval guilds, specialized «associations of students and teachers with collective legal rights usually guaranteed by charters issued by princes, prelates, or the towns in which they were located» came to be denominated by this general term. Like other guilds, they were self-regulating and determined the qualifications of their members.[13]
In modern usage the word has come to mean «An institution of higher education offering tuition in mainly non-vocational subjects and typically having the power to confer degrees,»[14] with the earlier emphasis on its corporate organization considered as applying historically to Medieval universities.[15]
The original Latin word referred to degree-awarding institutions of learning in Western and Central Europe, where this form of legal organisation was prevalent and from where the institution spread around the world.[citation needed]
Academic freedom[edit]
An important idea in the definition of a university is the notion of academic freedom. The first documentary evidence of this comes from early in the life of the University of Bologna, which adopted an academic charter, the Constitutio Habita,[16] in 1155 or 1158,[17] which guaranteed the right of a traveling scholar to unhindered passage in the interests of education. Today this is claimed as the origin of «academic freedom».[18] This is now widely recognised internationally – on 18 September 1988, 430 university rectors signed the Magna Charta Universitatum,[19] marking the 900th anniversary of Bologna’s foundation. The number of universities signing the Magna Charta Universitatum continues to grow, drawing from all parts of the world.
Antecedents[edit]
Moroccan higher-learning institution Al-Qarawiyin (founded in 859 A.D.) was transformed into a university under the supervision of the ministry of education in 1963.[20]
An early institution often called a university is the Harran University, founded in the late 8th century.[21] Scholars occasionally call the University of al-Qarawiyyin (name given in 1963), founded as a mosque by Fatima al-Fihri in 859, a university,[22][23][24][25] although Jacques Verger writes that this is done out of scholarly convenience.[26] Several scholars consider that al-Qarawiyyin was founded[27][28] and run[20][29][30][31][32] as a madrasa until after World War II. They date the transformation of the madrasa of al-Qarawiyyin into a university to its modern reorganization in 1963.[33][34][20] In the wake of these reforms, al-Qarawiyyin was officially renamed «University of Al Quaraouiyine» two years later.[33]
Some scholars, including George Makdisi, have argued that early medieval universities were influenced by the madrasas in Al-Andalus, the Emirate of Sicily, and the Middle East during the Crusades.[35][36][37] Norman Daniel, however, views this argument as overstated.[38] Roy Lowe and Yoshihito Yasuhara have recently drawn on the well-documented influences of scholarship from the Islamic world on the universities of Western Europe to call for a reconsideration of the development of higher education, turning away from a concern with local institutional structures to a broader consideration within a global context.[39]
Medieval Europe[edit]
The modern university is generally regarded as a formal institution that has its origin in the Medieval Christian tradition.[40][41]
European higher education took place for hundreds of years in cathedral schools or monastic schools (scholae monasticae), in which monks and nuns taught classes; evidence of these immediate forerunners of the later university at many places dates back to the 6th century.[42]
In Europe, young men proceeded to university when they had completed their study of the trivium – the preparatory arts of grammar, rhetoric and dialectic or logic–and the quadrivium: arithmetic, geometry, music, and astronomy.
The earliest universities were developed under the aegis of the Latin Church by papal bull as studia generalia and perhaps from cathedral schools. It is possible, however, that the development of cathedral schools into universities was quite rare, with the University of Paris being an exception.[43] Later they were also founded by kings (University of Naples Federico II, Charles University in Prague, Jagiellonian University in Kraków) or municipal administrations (University of Cologne, University of Erfurt). In the early medieval period, most new universities were founded from pre-existing schools, usually when these schools were deemed to have become primarily sites of higher education. Many historians state that universities and cathedral schools were a continuation of the interest in learning promoted by The residence of a religious community.[44] Pope Gregory VII was critical in promoting and regulating the concept of modern university as his 1079 Papal Decree ordered the regulated establishment of cathedral schools that transformed themselves into the first European universities.[45]
The first universities in Europe with a form of corporate/guild structure were the University of Bologna (1088), the University of Paris (c. 1150, later associated with the Sorbonne), and the University of Oxford (1167).
The University of Bologna began as a law school teaching the ius gentium or Roman law of peoples which was in demand across Europe for those defending the right of incipient nations against empire and church. Bologna’s special claim to Alma Mater Studiorum[clarification needed] is based on its autonomy, its awarding of degrees, and other structural arrangements, making it the oldest continuously operating institution[17] independent of kings, emperors or any kind of direct religious authority.[46][47]
The conventional date of 1088, or 1087 according to some,[48] records when Irnerius commences teaching Emperor Justinian’s 6th-century codification of Roman law, the Corpus Iuris Civilis, recently discovered at Pisa. Lay students arrived in the city from many lands entering into a contract to gain this knowledge, organising themselves into ‘Nationes’, divided between that of the Cismontanes and that of the Ultramontanes. The students «had all the power … and dominated the masters».[49][50]
All over Europe rulers and city governments began to create universities to satisfy a European thirst for knowledge, and the belief that society would benefit from the scholarly expertise generated from these institutions. Princes and leaders of city governments perceived the potential benefits of having a scholarly expertise develop with the ability to address difficult problems and achieve desired ends. The emergence of humanism was essential to this understanding of the possible utility of universities as well as the revival of interest in knowledge gained from ancient Greek texts.[51]
The recovery of Aristotle’s works – more than 3000 pages of it would eventually be translated – fuelled a spirit of inquiry into natural processes that had already begun to emerge in the 12th century. Some scholars believe that these works represented one of the most important document discoveries in Western intellectual history.[52] Richard Dales, for instance, calls the discovery of Aristotle’s works «a turning point in the history of Western thought.»[53] After Aristotle re-emerged, a community of scholars, primarily communicating in Latin, accelerated the process and practice of attempting to reconcile the thoughts of Greek antiquity, and especially ideas related to understanding the natural world, with those of the church. The efforts of this «scholasticism» were focused on applying Aristotelian logic and thoughts about natural processes to biblical passages and attempting to prove the viability of those passages through reason. This became the primary mission of lecturers, and the expectation of students.
The university culture developed differently in northern Europe than it did in the south, although the northern (primarily Germany, France and Great Britain) and southern universities (primarily Italy) did have many elements in common. Latin was the language of the university, used for all texts, lectures, disputations and examinations. Professors lectured on the books of Aristotle for logic, natural philosophy, and metaphysics; while Hippocrates, Galen, and Avicenna were used for medicine. Outside of these commonalities, great differences separated north and south, primarily in subject matter. Italian universities focused on law and medicine, while the northern universities focused on the arts and theology. There were distinct differences in the quality of instruction in these areas which were congruent with their focus, so scholars would travel north or south based on their interests and means. There was also a difference in the types of degrees awarded at these universities. English, French and German universities usually awarded bachelor’s degrees, with the exception of degrees in theology, for which the doctorate was more common. Italian universities awarded primarily doctorates. The distinction can be attributed to the intent of the degree holder after graduation – in the north the focus tended to be on acquiring teaching positions, while in the south students often went on to professional positions.[54] The structure of northern universities tended to be modeled after the system of faculty governance developed at the University of Paris. Southern universities tended to be patterned after the student-controlled model begun at the University of Bologna.[55] Among the southern universities, a further distinction has been noted between those of northern Italy, which followed the pattern of Bologna as a «self-regulating, independent corporation of scholars» and those of southern Italy and Iberia, which were «founded by royal and imperial charter to serve the needs of government.»[56]
Early modern universities[edit]
During the Early Modern period (approximately late 15th century to 1800), the universities of Europe would see a tremendous amount of growth, productivity and innovative research. At the end of the Middle Ages, about 400 years after the first European university was founded, there were 29 universities spread throughout Europe. In the 15th century, 28 new ones were created, with another 18 added between 1500 and 1625.[59] This pace continued until by the end of the 18th century there were approximately 143 universities in Europe, with the highest concentrations in the German Empire (34), Italian countries (26), France (25), and Spain (23) – this was close to a 500% increase over the number of universities toward the end of the Middle Ages. This number does not include the numerous universities that disappeared, or institutions that merged with other universities during this time.[60] The identification of a university was not necessarily obvious during the Early Modern period, as the term is applied to a burgeoning number of institutions. In fact, the term «university» was not always used to designate a higher education institution. In Mediterranean countries, the term studium generale was still often used, while «Academy» was common in Northern European countries.[61]
The propagation of universities was not necessarily a steady progression, as the 17th century was rife with events that adversely affected university expansion. Many wars, and especially the Thirty Years’ War, disrupted the university landscape throughout Europe at different times. War, plague, famine, regicide, and changes in religious power and structure often adversely affected the societies that provided support for universities. Internal strife within the universities themselves, such as student brawling and absentee professors, acted to destabilize these institutions as well. Universities were also reluctant to give up older curricula, and the continued reliance on the works of Aristotle defied contemporary advancements in science and the arts.[62] This era was also affected by the rise of the nation-state. As universities increasingly came under state control, or formed under the auspices of the state, the faculty governance model (begun by the University of Paris) became more and more prominent. Although the older student-controlled universities still existed, they slowly started to move toward this structural organization. Control of universities still tended to be independent, although university leadership was increasingly appointed by the state.[63]
Although the structural model provided by the University of Paris, where student members are controlled by faculty «masters», provided a standard for universities, the application of this model took at least three different forms. There were universities that had a system of faculties whose teaching addressed a very specific curriculum; this model tended to train specialists. There was a collegiate or tutorial model based on the system at University of Oxford where teaching and organization was decentralized and knowledge was more of a generalist nature. There were also universities that combined these models, using the collegiate model but having a centralized organization.[64]
Early Modern universities initially continued the curriculum and research of the Middle Ages: natural philosophy, logic, medicine, theology, mathematics, astronomy, astrology, law, grammar and rhetoric. Aristotle was prevalent throughout the curriculum, while medicine also depended on Galen and Arabic scholarship. The importance of humanism for changing this state-of-affairs cannot be underestimated.[65] Once humanist professors joined the university faculty, they began to transform the study of grammar and rhetoric through the studia humanitatis. Humanist professors focused on the ability of students to write and speak with distinction, to translate and interpret classical texts, and to live honorable lives.[66] Other scholars within the university were affected by the humanist approaches to learning and their linguistic expertise in relation to ancient texts, as well as the ideology that advocated the ultimate importance of those texts.[67] Professors of medicine such as Niccolò Leoniceno, Thomas Linacre and William Cop were often trained in and taught from a humanist perspective as well as translated important ancient medical texts. The critical mindset imparted by humanism was imperative for changes in universities and scholarship. For instance, Andreas Vesalius was educated in a humanist fashion before producing a translation of Galen, whose ideas he verified through his own dissections. In law, Andreas Alciatus infused the Corpus Juris with a humanist perspective, while Jacques Cujas humanist writings were paramount to his reputation as a jurist. Philipp Melanchthon cited the works of Erasmus as a highly influential guide for connecting theology back to original texts, which was important for the reform at Protestant universities.[68] Galileo Galilei, who taught at the Universities of Pisa and Padua, and Martin Luther, who taught at the University of Wittenberg (as did Melanchthon), also had humanist training. The task of the humanists was to slowly permeate the university; to increase the humanist presence in professorships and chairs, syllabi and textbooks so that published works would demonstrate the humanistic ideal of science and scholarship.[69]
Although the initial focus of the humanist scholars in the university was the discovery, exposition and insertion of ancient texts and languages into the university, and the ideas of those texts into society generally, their influence was ultimately quite progressive. The emergence of classical texts brought new ideas and led to a more creative university climate (as the notable list of scholars above attests to). A focus on knowledge coming from self, from the human, has a direct implication for new forms of scholarship and instruction, and was the foundation for what is commonly known as the humanities. This disposition toward knowledge manifested in not simply the translation and propagation of ancient texts, but also their adaptation and expansion. For instance, Vesalius was imperative for advocating the use of Galen, but he also invigorated this text with experimentation, disagreements and further research.[70] The propagation of these texts, especially within the universities, was greatly aided by the emergence of the printing press and the beginning of the use of the vernacular, which allowed for the printing of relatively large texts at reasonable prices.[71]
Examining the influence of humanism on scholars in medicine, mathematics, astronomy and physics may suggest that humanism and universities were a strong impetus for the scientific revolution. Although the connection between humanism and the scientific discovery may very well have begun within the confines of the university, the connection has been commonly perceived as having been severed by the changing nature of science during the Scientific Revolution. Historians such as Richard S. Westfall have argued that the overt traditionalism of universities inhibited attempts to re-conceptualize nature and knowledge and caused an indelible tension between universities and scientists.[72] This resistance to changes in science may have been a significant factor in driving many scientists away from the university and toward private benefactors, usually in princely courts, and associations with newly forming scientific societies.[73]
Other historians find incongruity in the proposition that the very place where the vast number of the scholars that influenced the scientific revolution received their education should also be the place that inhibits their research and the advancement of science. In fact, more than 80% of the European scientists between 1450 and 1650 included in the Dictionary of Scientific Biography were university trained, of which approximately 45% held university posts.[74] It was the case that the academic foundations remaining from the Middle Ages were stable, and they did provide for an environment that fostered considerable growth and development. There was considerable reluctance on the part of universities to relinquish the symmetry and comprehensiveness provided by the Aristotelian system, which was effective as a coherent system for understanding and interpreting the world. However, university professors still have some autonomy, at least in the sciences, to choose epistemological foundations and methods. For instance, Melanchthon and his disciples at University of Wittenberg were instrumental for integrating Copernican mathematical constructs into astronomical debate and instruction.[75] Another example was the short-lived but fairly rapid adoption of Cartesian epistemology and methodology in European universities, and the debates surrounding that adoption, which led to more mechanistic approaches to scientific problems as well as demonstrated an openness to change. There are many examples which belie the commonly perceived intransigence of universities.[76] Although universities may have been slow to accept new sciences and methodologies as they emerged, when they did accept new ideas it helped to convey legitimacy and respectability, and supported the scientific changes through providing a stable environment for instruction and material resources.[77]
Regardless of the way the tension between universities, individual scientists, and the scientific revolution itself is perceived, there was a discernible impact on the way that university education was constructed. Aristotelian epistemology provided a coherent framework not simply for knowledge and knowledge construction, but also for the training of scholars within the higher education setting. The creation of new scientific constructs during the scientific revolution, and the epistemological challenges that were inherent within this creation, initiated the idea of both the autonomy of science and the hierarchy of the disciplines. Instead of entering higher education to become a «general scholar» immersed in becoming proficient in the entire curriculum, there emerged a type of scholar that put science first and viewed it as a vocation in itself. The divergence between those focused on science and those still entrenched in the idea of a general scholar exacerbated the epistemological tensions that were already beginning to emerge.[78]
The epistemological tensions between scientists and universities were also heightened by the economic realities of research during this time, as individual scientists, associations and universities were vying for limited resources. There was also competition from the formation of new colleges funded by private benefactors and designed to provide free education to the public, or established by local governments to provide a knowledge-hungry populace with an alternative to traditional universities.[79] Even when universities supported new scientific endeavors, and the university provided foundational training and authority for the research and conclusions, they could not compete with the resources available through private benefactors.[80]
By the end of the early modern period, the structure and orientation of higher education had changed in ways that are eminently recognizable for the modern context. Aristotle was no longer a force providing the epistemological and methodological focus for universities and a more mechanistic orientation was emerging. The hierarchical place of theological knowledge had for the most part been displaced and the humanities had become a fixture, and a new openness was beginning to take hold in the construction and dissemination of knowledge that were to become imperative for the formation of the modern state.
Modern universities[edit]
Modern universities constitute a guild or quasi-guild system. This facet of the university system did not change due to its peripheral standing in an industrialized economy; as commerce developed between towns in Europe during the Middle Ages, though other guilds stood in the way of developing commerce and therefore were eventually abolished, the scholars guild did not. According to historian Elliot Krause, «The university and scholars’ guilds held onto their power over membership, training, and workplace because early capitalism was not interested in it.»[81]
By the 18th century, universities published their own research journals and by the 19th century, the German and the French university models had arisen. The German, or Humboldtian model, was conceived by Wilhelm von Humboldt and based on Friedrich Schleiermacher’s liberal ideas pertaining to the importance of freedom, seminars, and laboratories in universities.[citation needed] The French university model involved strict discipline and control over every aspect of the university.
Until the 19th century, religion played a significant role in university curriculum; however, the role of religion in research universities decreased during that century. By the end of the 19th century, the German university model had spread around the world. Universities concentrated on science in the 19th and 20th centuries and became increasingly accessible to the masses. In the United States, the Johns Hopkins University was the first to adopt the (German) research university model and pioneered the adoption of that model by most American universities. When Johns Hopkins was founded in 1876, «nearly the entire faculty had studied in Germany.»[82] In Britain, the move from Industrial Revolution to modernity saw the arrival of new civic universities with an emphasis on science and engineering, a movement initiated in 1960 by Sir Keith Murray (chairman of the University Grants Committee) and Sir Samuel Curran, with the formation of the University of Strathclyde.[83] The British also established universities worldwide, and higher education became available to the masses not only in Europe.
In 1963, the Robbins Report on universities in the United Kingdom concluded that such institutions should have four main «objectives essential to any properly balanced system: instruction in skills; the promotion of the general powers of the mind so as to produce not mere specialists but rather cultivated men and women; to maintain research in balance with teaching, since teaching should not be separated from the advancement of learning and the search for truth; and to transmit a common culture and common standards of citizenship.»[84]
In the early 21st century, concerns were raised over the increasing managerialisation and standardisation of universities worldwide. Neo-liberal management models have in this sense been critiqued for creating «corporate universities (where) power is transferred from faculty to managers, economic justifications dominate, and the familiar ‘bottom line’ eclipses pedagogical or intellectual concerns».[85] Academics’ understanding of time, pedagogical pleasure, vocation, and collegiality have been cited as possible ways of alleviating such problems.[86]
National universities[edit]
A national university is generally a university created or run by a national state but at the same time represents a state autonomic institution which functions as a completely independent body inside of the same state. Some national universities are closely associated with national cultural, religious or political aspirations, for instance the National University of Ireland, which formed partly from the Catholic University of Ireland which was created almost immediately and specifically in answer to the non-denominational universities which had been set up in Ireland in 1850. In the years leading up to the Easter Rising, and in no small part a result of the Gaelic Romantic revivalists, the NUI collected a large amount of information on the Irish language and Irish culture.[citation needed] Reforms in Argentina were the result of the University Revolution of 1918 and its posterior reforms by incorporating values that sought for a more equal and laic[further explanation needed] higher education system.
Intergovernmental universities[edit]
Universities created by bilateral or multilateral treaties between states are intergovernmental. An example is the Academy of European Law, which offers training in European law to lawyers, judges, barristers, solicitors, in-house counsel and academics. EUCLID (Pôle Universitaire Euclide, Euclid University) is chartered as a university and umbrella organization dedicated to sustainable development in signatory countries, and the United Nations University engages in efforts to resolve the pressing global problems that are of concern to the United Nations, its peoples and member states. The European University Institute, a post-graduate university specialized in the social sciences, is officially an intergovernmental organization, set up by the member states of the European Union.
Organization[edit]
Although each institution is organized differently, nearly all universities have a board of trustees; a president, chancellor, or rector; at least one vice president, vice-chancellor, or vice-rector; and deans of various divisions. Universities are generally divided into a number of academic departments, schools or faculties. Public university systems are ruled over by government-run higher education boards[citation needed]. They review financial requests and budget proposals and then allocate funds for each university in the system. They also approve new programs of instruction and cancel or make changes in existing programs. In addition, they plan for the further coordinated growth and development of the various institutions of higher education in the state or country. However, many public universities in the world have a considerable degree of financial, research and pedagogical autonomy. Private universities are privately funded and generally have broader independence from state policies. However, they may have less independence from business corporations depending on the source of their finances.
Around the world[edit]
The funding and organization of universities varies widely between different countries around the world. In some countries universities are predominantly funded by the state, while in others funding may come from donors or from fees which students attending the university must pay. In some countries the vast majority of students attend university in their local town, while in other countries universities attract students from all over the world, and may provide university accommodation for their students.[87]
Classification[edit]
The definition of a university varies widely, even within some countries. Where there is clarification, it is usually set by a government agency. For example:
In Australia, the Tertiary Education Quality and Standards Agency (TEQSA) is Australia’s independent national regulator of the higher education sector. Students rights within university are also protected by the Education Services for Overseas Students Act (ESOS).
In the United States there is no nationally standardized definition for the term university, although the term has traditionally been used to designate research institutions and was once reserved for doctorate-granting research institutions. Some states, such as Massachusetts, will only grant a school «university status» if it grants at least two doctoral degrees.[88]
In the United Kingdom, the Privy Council is responsible for approving the use of the word university in the name of an institution, under the terms of the Further and Higher Education Act 1992.[89]
In India, a new designation deemed universities has been created for institutions of higher education that are not universities, but work at a very high standard in a specific area of study («An Institution of Higher Education, other than universities, working at a very high standard in specific area of study, can be declared by the Central Government on the advice of the University Grants Commission as an Institution (Deemed-to-be-university). Institutions that are ‘deemed-to-be-university’ enjoy the academic status and the privileges of a university.[90] Through this provision many schools that are commercial in nature and have been established just to exploit the demand for higher education have sprung up.[91]
In Canada, college generally refers to a two-year, non-degree-granting institution, while university connotes a four-year, degree-granting institution. Universities may be sub-classified (as in the Macleans rankings) into large research universities with many PhD-granting programs and medical schools (for example, McGill University); «comprehensive» universities that have some PhDs but are not geared toward research (such as Waterloo); and smaller, primarily undergraduate universities (such as St. Francis Xavier).
In Germany, universities are institutions of higher education which have the power to confer bachelor, master and PhD degrees. They are explicitly recognised as such by law and cannot be founded without government approval. The term Universität (i.e. the German term for university) is protected by law and any use without official approval is a criminal offense. Most of them are public institutions, though a few private universities exist. Such universities are always research universities. Apart from these universities, Germany has other institutions of higher education (Hochschule, Fachhochschule). Fachhochschule means a higher education institution which is similar to the former polytechnics in the British education system, the English term used for these German institutions is usually ‘university of applied sciences’. They can confer master’s degrees but no PhDs. They are similar to the model of teaching universities with less research and the research undertaken being highly practical. Hochschule can refer to various kinds of institutions, often specialised in a certain field (e.g. music, fine arts, business). They might or might not have the power to award PhD degrees, depending on the respective government legislation. If they award PhD degrees, their rank is considered equivalent to that of universities proper (Universität), if not, their rank is equivalent to universities of applied sciences.
Colloquial usage[edit]
Colloquially, the term university may be used to describe a phase in one’s life: «When I was at university…» (in the United States and Ireland, college is often used instead: «When I was in college…»). In Ireland, Australia, New Zealand, Canada, the United Kingdom, Nigeria, the Netherlands, Spain and the German-speaking countries, university is often contracted to uni. In Ghana, New Zealand, Bangladesh and in South Africa it is sometimes called «varsity» (although this has become uncommon in New Zealand in recent years). «Varsity» was also common usage in the UK in the 19th century.[citation needed]
Cost[edit]
In many countries, students are required to pay tuition fees.
Many students look to get ‘student grants’ to cover the cost of university. In 2016, the average outstanding student loan balance per borrower in the United States was US$30,000.[92] In many U.S. states, costs are anticipated to rise for students as a result of decreased state funding given to public universities.[93] Many universities in the United States offer students the opportunity to apply for financial scholarships to help pay for tuition based on academic achievement.
There are several major exceptions on tuition fees. In many European countries, it is possible to study without tuition fees. Public universities in Nordic countries were entirely without tuition fees until around 2005. Denmark, Sweden and Finland then moved to put in place tuition fees for foreign students. Citizens of EU and EEA member states and citizens from Switzerland remain exempted from tuition fees, and the amounts of public grants granted to promising foreign students were increased to offset some of the impact.[94] The situation in Germany is similar; public universities usually do not charge tuition fees apart from a small administrative fee. For degrees of a postgraduate professional level sometimes tuition fees are levied. Private universities, however, almost always charge tuition fees.
See also[edit]
- Alternative university
- Alumni
- Ancient higher-learning institutions
- Catholic university
- College and university rankings
- Corporate university
- International university
- Land-grant university
- Liberal arts college
- List of academic disciplines
- Lists of universities and colleges
- Pontifical university
- Research university
- School and university in literature
- Science tourism
- UnCollege
- University student retention
- University system
- Urban university
References[edit]
- ^ «Universities» . Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). 1911.
- ^ Den Heijer, Alexandra (2011). Managing the University Campus: Information to Support Real Estate Decisions. Academische Uitgeverij Eburon. ISBN 9789059724877.
Many of the medieval universities in Western Europe were born under the aegis of the Catholic Church, usually as cathedral schools or by papal bull as Studia Generali.
- ^ A. Lamport, Mark (2015). Encyclopedia of Christian Education. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 484. ISBN 9780810884939.
All the great European universities-Oxford, to Paris, to Cologne, to Prague, to Bologna—were established with close ties to the Church.
- ^ B M. Leonard, Thomas (2013). Encyclopedia of the Developing World. Routledge. p. 1369. ISBN 9781135205157.
Europe established schools in association with their cathedrals to educate priests, and from these emerged eventually the first universities of Europe, which began forming in the eleventh and twelfth centuries.
- ^ Gavroglu, Kostas (2015). Sciences in the Universities of Europe, Nineteenth and Twentieth Centuries: Academic Landscapes. Springer. p. 302. ISBN 9789401796361.
- ^ GA. Dawson, Patricia (2015). First Peoples of the Americas and the European Age of Exploration. Cavendish Square Publishing. p. 103. ISBN 9781502606853.
- ^ «The University from the 12th to the 20th century — University of Bologna». www.unibo.it. Archived from the original on 5 April 2021. Retrieved 23 March 2021.
- ^ Top Universities Archived 17 January 2009 at the Wayback Machine World University Rankings Retrieved 6 January 2010
- ^ Paul L. Gaston (2010). The Challenge of Bologna. p. 18. ISBN 978-1-57922-366-3. Archived from the original on 10 March 2021. Retrieved 7 July 2016.
- ^ Hunt Janin: «The university in medieval life, 1179–1499», McFarland, 2008, ISBN 0-7864-3462-7, p. 55f.
- ^ de Ridder-Symoens, Hilde: A History of the University in Europe: Volume 1, Universities in the Middle Ages Archived 13 December 2021 at the Wayback Machine, Cambridge University Press, 1992, ISBN 0-521-36105-2, pp. 47–55
- ^ Lewis, Charlton T.; Short, Charles (1966) [1879], A Latin Dictionary, Oxford: Clarendon Press
- ^ Marcia L. Colish, Medieval Foundations of the Western Intellectual Tradition, 400-1400, (New Haven: Yale Univ. Pr., 1997), p. 267.
- ^ «university, n.», OED Online (3rd ed.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2010, archived from the original on 30 April 2021, retrieved 27 August 2013
- ^ «university, n.», OED Online (3rd ed.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2010, archived from the original on 30 April 2021, retrieved 27 August 2013,
…In the Middle Ages: a body of teachers and students engaged in giving and receiving instruction in the higher branches of study … and regarded as a scholastic guild or corporation.
Compare «University», Oxford English Dictionary (2nd ed.), Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1989,The whole body of teachers and scholars engaged, at a particular place, in giving and receiving instruction in the higher branches of learning; such persons associated together as a society or corporate body, with definite organization and acknowledged powers and privileges (esp. that of conferring degrees), and forming an institution for the promotion of education in the higher or more important branches of learning….
- ^ Malagola, C. (1888), Statuti delle Università e dei Collegi dello Studio Bolognese. Bologna: Zanichelli.
- ^ a b Rüegg, W. (2003). «Chapter 1: Themes». In De Ridder-Symoens, H. (ed.). A History of the University in Europe. Vol. 1. Cambridge University Press. pp. 4–34. ISBN 0-521-54113-1.
- ^ Watson, P. (2005), Ideas. London: Weidenfeld and Nicolson, page 373
- ^ «Magna Charta delle Università Europee». .unibo.it. Archived from the original on 15 November 2010. Retrieved 28 May 2010.
- ^ a b c Belhachmi, Zakia: «Gender, Education, and Feminist Knowledge in al-Maghrib (North Africa) – 1950–70», Journal of Middle Eastern and North African Intellectual and Cultural Studies, Vol. 2–3, 2003, pp. 55–82 (65):
The Adjustments of Original Institutions of the Higher Learning: the Madrasah. Significantly, the institutional adjustments of the madrasahs affected both the structure and the content of these institutions. In terms of structure, the adjustments were twofold: the reorganization of the available original madaris and the creation of new institutions. This resulted in two different types of Islamic teaching institutions in al-Maghrib. The first type was derived from the fusion of old madaris with new universities. For example, Morocco transformed Al-Qarawiyin (859 A.D.) into a university under the supervision of the ministry of education in 1963.
- ^ Frew, Donald (1999). «Harran: Last Refuge of Classical Paganism». The Pomegranate: The International Journal of Pagan Studies. 13 (9): 17–29. doi:10.1558/pome.v13i9.17.
- ^ Verger, Jacques: «Patterns», in: Ridder-Symoens, Hilde de (ed.): A History of the University in Europe. Vol. I: Universities in the Middle Ages, Cambridge University Press, 2003, ISBN 978-0-521-54113-8, pp. 35–76 (35)
- ^ Esposito, John (2003). The Oxford Dictionary of Islam. Oxford University Press. p. 328. ISBN 978-0-1951-2559-7.
- ^ Joseph, S, and Najmabadi, A. Encyclopedia of Women & Islamic Cultures: Economics, education, mobility, and space. Brill, 2003, p. 314.
- ^ Swartley, Keith. Encountering the World of Islam. Authentic, 2005, p. 74.
- ^ A History of the University in Europe. Vol. I: Universities in the Middle Ages. Cambridge University Press, 2003, 35
- ^ Petersen, Andrew: Dictionary of Islamic Architecture, Routledge, 1996, ISBN 978-0-415-06084-4, p. 87 (entry «Fez»):
The Quaraouiyine Mosque, founded in 859, is the most famous mosque of Morocco and attracted continuous investment by Muslim rulers.
- ^ Lulat, Y. G.-M.: A History Of African Higher Education From Antiquity To The Present: A Critical Synthesis Studies in Higher Education, Greenwood Publishing Group, 2005, ISBN 978-0-313-32061-3, p. 70:
As for the nature of its curriculum, it was typical of other major madrasahs such as al-Azhar and Al Quaraouiyine, though many of the texts used at the institution came from Muslim Spain…Al Quaraouiyine began its life as a small mosque constructed in 859 C.E. by means of an endowment bequeathed by a wealthy woman of much piety, Fatima bint Muhammed al-Fahri.
- ^ Shillington, Kevin: Encyclopedia of African History, Vol. 2, Fitzroy Dearborn, 2005, ISBN 978-1-57958-245-6, p. 1025:
Higher education has always been an integral part of Morocco, going back to the ninth century when the Karaouine Mosque was established. The madrasa, known today as Al Qayrawaniyan University, became part of the state university system in 1947.
They consider institutions like al-Qarawiyyin to be higher education colleges of Islamic law where other subjects were only of secondary importance.
- ^ Pedersen, J.; Rahman, Munibur; Hillenbrand, R.: «Madrasa», in Encyclopaedia of Islam, 2nd edition, Brill, 2010:
Madrasa, in modern usage, the name of an institution of learning where the Islamic sciences are taught, i.e. a college for higher studies, as opposed to an elementary school of traditional type (kuttab); in medieval usage, essentially a college of law in which the other Islamic sciences, including literary and philosophical ones, were ancillary subjects only.
- ^ Meri, Josef W. (ed.): Medieval Islamic Civilization: An Encyclopedia, Vol. 1, A–K, Routledge, ISBN 978-0-415-96691-7, p. 457 (entry «madrasa»):
A madrasa is a college of Islamic law. The madrasa was an educational institution in which Islamic law (fiqh) was taught according to one or more Sunni rites: Maliki, Shafi’i, Hanafi, or Hanbali. It was supported by an endowment or charitable trust (waqf) that provided for at least one chair for one professor of law, income for other faculty or staff, scholarships for students, and funds for the maintenance of the building. Madrasas contained lodgings for the professor and some of his students. Subjects other than law were frequently taught in madrasas, and even Sufi seances were held in them, but there could be no madrasa without law as technically the major subject.
- ^ Makdisi, George: «Madrasa and University in the Middle Ages», Studia Islamica, No. 32 (1970), pp. 255–264 (255f.):
In studying an institution which is foreign and remote in point of time, as is the case of the medieval madrasa, one runs the double risk of attributing to it characteristics borrowed from one’s own institutions and one’s own times. Thus gratuitous transfers may be made from one culture to the other, and the time factor may be ignored or dismissed as being without significance. One cannot therefore be too careful in attempting a comparative study of these two institutions: the madrasa and the university. But in spite of the pitfalls inherent in such a study, albeit sketchy, the results which may be obtained are well worth the risks involved. In any case, one cannot avoid making comparisons when certain unwarranted statements have already been made and seem to be currently accepted without question. The most unwarranted of these statements is the one which makes of the «madrasa» a «university».
- ^ a b Lulat, Y. G.-M.: A History Of African Higher Education From Antiquity To The Present: A Critical Synthesis, Greenwood Publishing Group, 2005, ISBN 978-0-313-32061-3, pp. 154–157
- ^ Park, Thomas K.; Boum, Aomar: Historical Dictionary of Morocco, 2nd ed., Scarecrow Press, 2006, ISBN 978-0-8108-5341-6, p. 348
al-qarawiyin is the oldest university in Morocco. It was founded as a mosque in Fès in the middle of the ninth century. It has been a destination for students and scholars of Islamic sciences and Arabic studies throughout the history of Morocco. There were also other religious schools like the madras of ibn yusuf and other schools in the sus. This system of basic education called al-ta’lim al-aSil was funded by the sultans of Morocco and many famous traditional families. After independence, al-qarawiyin maintained its reputation, but it seemed important to transform it into a university that would prepare graduates for a modern country while maintaining an emphasis on Islamic studies. Hence, al-qarawiyin university was founded in February 1963 and, while the dean’s residence was kept in Fès, the new university initially had four colleges located in major regions of the country known for their religious influences and madrasas. These colleges were kuliyat al-shari’s in Fès, kuliyat uSul al-din in Tétouan, kuliyat al-lugha al-‘arabiya in Marrakech (all founded in 1963), and kuliyat al-shari’a in Ait Melloul near Agadir, which was founded in 1979.
- ^ Nuria Sanz, Sjur Bergan (1 January 2006). The heritage of European universities, Volume 548. Council of Europe. p. 28. ISBN 9789287161215. Archived from the original on 5 September 2015.
- ^ Makdisi, George (April–June 1989). «Scholasticism and Humanism in Classical Islam and the Christian West». Journal of the American Oriental Society. 109 (2): 175–182 [175–77]. doi:10.2307/604423. JSTOR 604423.; Makdisi, John A. (June 1999). «The Islamic Origins of the Common Law». North Carolina Law Review. 77 (5): 1635–1739.
- ^ Goddard, Hugh (2000). A History of Christian-Muslim Relations. Edinburgh University Press. p. 99. ISBN 978-0-7486-1009-9.
- ^ Daniel, Norman (1984). «Review of «The Rise of Colleges. Institutions of Learning in Islam and the West by George Makdisi»«. Journal of the American Oriental Society. 104 (3): 586–8. doi:10.2307/601679. JSTOR 601679.
Professor Makdisi argues that there is a missing link in the development of Western scholasticism, and that Arab influences explain the «dramatically abrupt» appearance of the «sic et non» method. Many medievalists will think the case overstated, and doubt that there is much to explain.
- ^ Lowe, Roy; Yasuhara, Yoshihito (2013), «The origins of higher learning: time for a new historiography?», in Feingold, Mordecai (ed.), History of Universities, vol. 27, Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp. 1–19, ISBN 9780199685844, archived from the original on 5 September 2015
- ^ Rüegg, Walter: «Foreword. The University as a European Institution», in: A History of the University in Europe. Vol. 1: Universities in the Middle Ages, Cambridge University Press, 1992, ISBN 0-521-36105-2, pp. XIX–XX
- ^ Verger, Jacques. “The Universities and Scholasticism,” in The New Cambridge Medieval History: Volume V c. 1198–c. 1300. Cambridge University Press, 2007, 257.
- ^ Riché, Pierre (1978): «Education and Culture in the Barbarian West: From the Sixth through the Eighth Century», Columbia: University of South Carolina Press, ISBN 0-87249-376-8, pp. 126-7, 282-98
- ^ Gordon Leff, Paris and Oxford Universities in the Thirteenth and Fourteenth Centuries. An Institutional and Intellectual History, Wiley, 1968.
- ^ Johnson, P. (2000). The Renaissance : a short history. Modern Library chronicles (Modern Library ed.). New York: Modern Library, p. 9.
- ^ Thomas Oestreich (1913). «Pope St. Gregory VII». In Herbermann, Charles. Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
- ^ Makdisi, G. (1981), Rise of Colleges: Institutions of Learning in Islam and the West. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press.
- ^ Daun, H. and Arjmand, R. (2005), Islamic Education, pp 377-388 in J. Zajda, editor, International Handbook of Globalisation, Education and Policy Research. Netherlands: Springer.
- ^ Huff, T. (2003), The Rise of Early Modern Science. Cambridge University Press, p. 122
- ^ Kerr, Clark (2001). The Uses of the University. Harvard University Press. pp. 16 and 145. ISBN 978-0674005327.
- ^ Rüegg, W. (2003), Mythologies and Historiography of the Beginnings, pp 4-34 in H. De Ridder-Symoens, editor, A History of the University in Europe; Vol 1, Cambridge University Press.p. 12
- ^ Grendler, P. F. (2004). «The universities of the Renaissance and Reformation». Renaissance Quarterly, 57, pp. 2.
- ^ Rubenstein, R. E. (2003). Aristotle’s children: how Christians, Muslims, and Jews rediscovered ancient wisdom and illuminated the dark ages (1st ed.). Orlando, Florida: Harcourt, pp. 16-17.
- ^ Dales, R. C. (1990). Medieval discussions of the eternity of the world (Vol. 18). Brill Archive, p. 144.
- ^ Grendler, P. F. (2004). «The universities of the Renaissance and Reformation». Renaissance Quarterly, 57, pp. 2-8.
- ^ Scott, J. C. (2006). «The mission of the university: Medieval to Postmodern transformations». Journal of Higher Education. 77 (1): 6. doi:10.1353/jhe.2006.0007. S2CID 144337137.
- ^ Pryds, Darleen (2000), «Studia as Royal Offices: Mediterranean Universities of Medieval Europe», in Courtenay, William J.; Miethke, Jürgen; Priest, David B. (eds.), Universities and Schooling in Medieval Society, Education and Society in the Middle Ages and Renaissance, vol. 10, Leiden: Brill, pp. 84–85, ISBN 9004113517
- ^ «University League Tables 2021». www.thecompleteuniversityguide.co.uk. Archived from the original on 25 June 2011. Retrieved 2 May 2021.
- ^ «The best UK universities 2021 – rankings». the Guardian. Archived from the original on 4 May 2021. Retrieved 2 May 2021.
- ^ Grendler, P. F. (2004). The universities of the Renaissance and Reformation. Renaissance Quarterly, 57, pp. 1-3.
- ^ Frijhoff, W. (1996). Patterns. In H. D. Ridder-Symoens (Ed.), Universities in early modern Europe, 1500-1800, A history of the university in Europe. Cambridge [England]: Cambridge University Press, p. 75.
- ^ Frijhoff, W. (1996). Patterns. In H. D. Ridder-Symoens (Ed.), Universities in early modern Europe, 1500-1800, A history of the university in Europe. Cambridge [England]: Cambridge University Press, p. 47.
- ^ Grendler, P. F. (2004). The universities of the Renaissance and Reformation. Renaissance Quarterly, 57, p. 23.
- ^ Scott, J. C. (2006). «The mission of the university: Medieval to Postmodern transformations». Journal of Higher Education. 77 (1): 10–13. doi:10.1353/jhe.2006.0007. S2CID 144337137.
- ^ Frijhoff, W. (1996). Patterns. In H. D. Ridder-Symoens (Ed.), Universities in early modern Europe, 1500-1800, A history of the university in Europe. Cambridge [England]: Cambridge University Press, p. 65.
- ^ Ruegg, W. (1992). Epilogue: the rise of humanism. In H. D. Ridder-Symoens (Ed.), Universities in the Middle Ages, A history of the university in Europe. Cambridge [England]: Cambridge University Press.
- ^ Grendler, P. F. (2002). The universities of the Italian renaissance. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, p. 223.
- ^ Grendler, P. F. (2002). The universities of the Italian renaissance. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, p. 197.
- ^ Ruegg, W. (1996). Themes. In H. D. Ridder-Symoens (Ed.), Universities in Early Modern Europe, 1500-1800, A history of the university in Europe. Cambridge [England]: Cambridge University Press, pp. 33-39.
- ^ Grendler, P. F. (2004). The universities of the Renaissance and Reformation. Renaissance Quarterly, 57, pp. 12-13.
- ^ Bylebyl, J. J. (2009). Disputation and description in the renaissance pulse controversy. In A. Wear, R. K. French, & I. M. Lonie (Eds.), The medical renaissance of the sixteenth century (1st ed., pp. 223-245). Cambridge University Press.
- ^ Füssel, S. (2005). Gutenberg and the Impact of Printing (English ed.). Aldershot, Hampshire: Ashgate Pub., p. 145.
- ^ Westfall, R. S. (1977). The construction of modern science: mechanisms and mechanics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, p. 105.
- ^ Ornstein, M. (1928). The role of scientific societies in the seventeenth century. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- ^ Gascoigne, J. (1990). A reappraisal of the role of the universities in the Scientific Revolution. In D. C. Lindberg & R. S. Westman (Eds.), Reappraisals of the Scientific Revolution, pp. 208-209.
- ^ Westman, R. S. (1975). «The Melanchthon circle:, rheticus, and the Wittenberg interpretation of the Copernicantheory». Isis. 66 (2): 164–193. doi:10.1086/351431. S2CID 144116078.
- ^ Gascoigne, J. (1990). A reappraisal of the role of the universities in the Scientific Revolution. In D. C. Lindberg & R. S. Westman (Eds.), Reappraisals of the Scientific Revolution, pp. 210-229.
- ^ Gascoigne, J. (1990). A reappraisal of the role of the universities in the Scientific Revolution. In D. C. Lindberg & R. S. Westman (Eds.), Reappraisals of the Scientific Revolution, pp. 245-248.
- ^ Feingold, M. (1991). Tradition vs novelty: universities and scientific societies in the early modern period. In P. Barker & R. Ariew (Eds.), Revolution and continuity: essays in the history and philosophy of early modern science, Studies in philosophy and the history of philosophy. Washington, D.C: Catholic University of America Press, pp. 53-54.
- ^ Feingold, M. (1991). Tradition vs novelty: universities and scientific societies in the early modern period. In P. Barker & R. Ariew (Eds.), Revolution and continuity: essays in the history and philosophy of early modern science, Studies in philosophy and the history of philosophy. Washington, D.C: Catholic University of America Press, pp. 46-50.
- ^ See; Baldwin, M (1995). «The snakestone experiments: an early modern medical debate». Isis. 86 (3): 394–418. doi:10.1086/357237. PMID 7591659. S2CID 6122500.
- ^ Krause, Elliot (1996). Death of Guilds:Professions, States, and The Advance of Capitalism, 1930 to The Present}. Yale University Press, New Haven and London.
- ^ Menand, Louis; Reitter, Paul; Wellmon, Chad (2017). «General Introduction». The Rise of the Research University: A Sourcebook. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. pp. 2–3. ISBN 9780226414850. Archived from the original on 15 February 2017. Retrieved 25 January 2017.
- ^ «Oxford Dictionary of National Biography». Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (online ed.). Oxford University Press. 2004. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/69524. Archived from the original on 6 March 2016. Retrieved 28 May 2010. (Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
- ^ Anderson, Robert (March 2010). «The ‘Idea of a University’ today». History & Policy. United Kingdom: History & Policy. Archived from the original on 27 November 2010. Retrieved 9 December 2010.
- ^ Maggie Berg & Barbara Seeber. The Slow Professor: Challenging the Culture of Speed in the Academy, p. x. Toronto: Toronto University Press. 2016.
- ^ Maggie Berg & Barbara Seeber. The Slow Professor: Challenging the Culture of Speed in the Academy. Toronto: Toronto University Press. 2016. (passim)
- ^ «Basic Classification Technical Details». Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching. Archived from the original on 13 June 2007. Retrieved 20 March 2007.
- ^ «Massachusetts Board of Education: Degree-granting regulations for independent institutions of higher education» (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 May 2010. Retrieved 28 May 2010.
- ^ «Higher Education». Privy Council Office. Archived from the original on 23 February 2009. Retrieved 6 December 2007.
- ^ «Deemed University». mhrd.gov.in. MHRD. Archived from the original on 7 December 2015.
- ^ — Peter Drucker. «‘Deemed’ status distributed freely during Arjun Singh’s tenure — LearnHub News». Learnhub.com. Archived from the original on 7 July 2010. Retrieved 29 July 2010.
- ^ «Students are graduating with $30,000 in loans». 18 October 2016. Archived from the original on 21 September 2017. Retrieved 21 September 2017.
- ^ «Students at Public Universities, Colleges Will Bear the Burden of Reduced Funding for Higher Education». Time. 25 January 2012. Archived from the original on 9 March 2013. Retrieved 14 January 2013.
- ^ «Studieavgifter i högskolan» Archived 15 May 2013 at the Wayback Machine SOU 2006:7 (in Swedish)
Further reading[edit]
- Aronowitz, Stanley (2000). The Knowledge Factory: Dismantling the Corporate University and Creating True Higher Learning. Boston: Beacon Press. ISBN 978-0-8070-3122-3.
- Barrow, Clyde W. (1990). Universities and the Capitalist State: Corporate Liberalism and the Reconstruction of American Higher Education, 1894–1928. Madison, Wis: University of Wisconsin Press. ISBN 978-0-299-12400-7.
- Diamond, Sigmund (1992). Compromised Campus: The Collaboration of Universities with the Intelligence Community, 1945–1955. New York, NY: Oxford Univ. Press. ISBN 978-0-19-505382-1.
- Pedersen, Olaf (1997). The First Universities: Studium Generale and the Origins of University Education in Europe. Cambridge: Cambridge Univ. Press. ISBN 978-0-521-59431-8.
- Ridder-Symoens, Hilde de, ed. (1992). A History of the University in Europe. Vol. 1: Universities in the Middle Ages. Rüegg, Walter (general ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-36105-7.
- Ridder-Symoens, Hilde de, ed. (1996). A History of the University in Europe. Vol. 2: Universities in Early Modern Europe (1500–1800). Rüegg, Walter (general ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-36106-4.
- Rüegg, Walter, ed. (2004). A History of the University in Europe. Vol. 3: Universities in the Nineteenth and Early Twentieth Centuries (1800–1945). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-36107-1.
- Segre, Michael (2015). Higher Education and the Growth of Knowledge: A Historical Outline of Aims and Tensions. New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-73566-7.
External links[edit]
Wikiversity has learning resources about University
- «Universities» . Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). 1911.
- University at Curlie
| Schools |
|---|
|
|
| Education |
| History of education |
| Pedagogy |
| Teaching |
| Homeschooling |
| Preschool education |
| Child care center |
| Kindergarten |
| Primary education |
| Elementary school |
| Secondary education |
| Middle school |
| Comprehensive school |
| Grammar school |
| Gymnasium |
| High school |
| Preparatory school |
| Public school |
| Tertiary education |
| College |
| Community college |
| Liberal arts college |
| University |
A university is an institution of higher education and research, which grants academic degrees at all levels (bachelor, master, and doctorate) in a variety of subjects. A university provides both tertiary and quaternary education. The word university is derived from the Latin universitas magistrorum et scholarium, roughly meaning «community of teachers and scholars.»
Universities are seen as a place of great personal development, but have the reputation of isolation or independence from regular society due to the often erudite nature of subjects studied therein. Regardless of their exact nature, universities fall within the purview of education, in particular higher education after the level considered necessary to function effectively as an adult citizen—that offered by elementary and high schools. As such, colleges teach more specialized mastery of particular skills, greater depth in academic knowledge, or otherwise advance the individual interests and talents of their students. This aspect of education is built on, and requires, the foundation of earlier education, which includes not only academic knowledge but the emotional development and social skills that are acquired in earlier childhood.
Overview
The word university means «institution of higher learning» or «body of persons constituting a university.» The word comes from the Latin universitatum, meaning corporation or society.[1]
University is one type of tertiary education. Other forms include vocational schools and community colleges. Vocational schools are more narrow in their focus and often have some immediate professional goal in mind such as a training for a career as a paralegal or auto-mechanic. Community colleges offer continuing adult education for those interested in taking classes for personal enjoyment or interest. They also serve as preparatory schools for four year university undergraduate programs or as alternatives to those who cannot afford to enroll in a traditional four year program. In the United States, university is used to refer to schools offering graduate education while colleges offer undergraduate education.
History
Degree ceremony at the University of Oxford. The Pro-Vice-Chancellor in MA gown and hood, Proctor in official dress and new Doctors of Philosophy in scarlet full dress. Behind them, a bedel, another Doctor and Bachelors of Arts and Medicine.
The first universities were not actually degree-granting institutions. The original Latin word universitas, first used in time of renewed interest in Classical Greek and Roman tradition, tried to reflect this feature of the Academy of Plato. The choice for the oldest institution of higher learning is usually among Nalanda, Constantinople, Al Karaouine or Al-Azhar. Nalanda University, founded in Bihar, India around the fifth century B.C.E. conferred academic degree titles to its graduates, while also offering post-graduate courses. Another Indian university whose ruins were only recently excavated was Ratnagiri University in Orissa. Chinese institutions of higher learning were the semi-legendary Shang Hsiang, and later Taixue and Guozijian serve as the highest level of educational establishment while academies became very popular as non-governmental establishments teaching Confucianism and Chinese literature among other things. Also the acdemy of Gundishapour is one of the oldest universities in the world, made around the fourth century C.E. in Iran.
Al-Azhar University, founded in Cairo, Egypt in the tenth century, offered a variety of post-graduate degrees, and is often regarded as the first full-fledged university. The University of Constantinople, founded in 849, by the regent Bardas of emperor Michael III, is generally considered the first institution of higher learning with the characteristics we associate today with a university (research and teaching, auto-administration, academic independence, et cetera). The Guinness Book of World Records recognizes the University of Al Karaouine in Fez, Morocco as the oldest university in the world with its founding in 859.
Byzantine university
Byzantine university refers to higher education during the era of the Byzantine empire.
The medieval Greek world had no autonomous and continuing institutions of higher learning comparable to the universities of the later Middle Ages in Western Europe, but higher education was provided by private teachers, professional groups and state appointed teachers.
In the early period Rome, Athens, and Alexandria were the main centers of learning, but were overtaken in the fifth century by the Queen of cities, Constantinople. After the closing of the Academy in Athens in 529 due to its pagan teachings, and the conquest of Alexandria and Beirut by the Arabs in the mid seventh century, the focus of all higher learning moved to Constantinople.
After the foundation of Constantinople in 330 teachers were drawn to the new city and various steps were taken for official state support and supervision, however nothing lastingly formal in the way of state funded education emerged. However in 425 Theodosius II established a clear distinction between teachers who were private, and those who were public and paid from imperial funds. These official teachers enjoyed privilege and prestige. There were a total of 31 teachers: ten each for Greek and Latin grammar; five for Greek rhetoric; three for Latin rhetoric; two for law; one for philosophy. This system lasted with various degrees of official support until the seventh century.
University of Salamanca (Spain) founded in 1218
In the seventh and eighth centuries Byzantine life went through a difficult period (sometimes called the Byzantine Dark Age). Continued Arab pressure from the south and the Slavs, Avars and Bulgars to the north led to dramatic economic decline and transformation of Byzantine life. However during this period higher education continued to receive some official funding, the details of which are not well known to scholars, but it is assumed the quality of the education was probably low.
With improving stability in the ninth century came measures to improve the quality of higher education. In 863 chairs of grammar, rhetoric and philosophy (includes mathematics, astronomy, and music) were founded and given a permanent location in the imperial palace. These chairs continued to receive official state support for the next century-and-a-half, after which the leading role in the provision of higher education was taken up the Church. During the twelfth century the Patriarchal School was the leading center of education which included men of letters such as Theodore Prodromos and Eustathius of Thessalonica.
The tower of the University of Coimbra, the oldest Portuguese university.
The capture of Constantinople in 1204 by Crusaders during the Fourth Crusade ended all support for higher education, although the government in exile in Nicaea gave some support to individual private teachers. After the restoration in 1261 attempts were made to restore the old system, but it never fully recovered and most teaching fell to private teachers and professions. Some of these private teachers include the diplomat and monk Maximos Planudes (1260-1310), the historian Nikephoros Gregoras (1291-1360), and the man of letters Manuel Chrysoloras, who taught in Florence and influence the early Italian humanists on Greek studies. In the fifteenth century many more teachers from Constantinople would follow in Chrysoloras’ footsteps.
Medieval European universities
The first European medieval institutions generally considered to be universities were established in Italy, France, and England in the late eleventh and the twelfth centuries for the study of arts, law, medicine, and theology. These universities evolved from much older schools and monasteries, and it is difficult to define the date at which they became true universities, although the lists of studia generalia for higher education in Europe held by the Vatican are a useful guide. A different case is the university of Constantinople, which was founded in the ninth century as a secular institute of higher learning, to support the state administration.
Representation of a university class, (1350s).
With the increasing professionalization of society during the twelfth and thirteenth centuries, a similar demand grew for professional clergy. Before the twelfth century, the intellectual life of Europe had been relegated to monasteries, which were mostly concerned with the study of the liturgy and prayer; very few monasteries could boast true intellectuals. Following the Gregorian Reform’s emphasis on canon law and the study of the sacraments, bishops formed cathedral schools to train the clergy in Canon law, but also in the more secular aspects of church administration, including logic and disputation for use in preaching and theological discussion, and accounting to more effectively control finances.
Learning became essential to advancing in the ecclesiastical hierarchy, and teachers also gained prestige. However, demand quickly outstripped the capacity of cathedral schools, each of which was essentially run by one teacher. In addition, tensions rose between the students of cathedral schools and burghers in smaller towns. So, cathedral schools migrated to large cities, like Paris and Bologna.
The predecessor of the modern university found its roots in Paris, especially under the guidance of Peter Abelard, who wrote Sic et Non («Yes and No»), which collected texts for university study. Dissatisfied with tensions between burghers and students and the censorship of leading intellectuals by the Church, Abelard and others formed the Universitas, modeled on the medieval guild, a large-scale, self-regulating, permanent institution of higher education.
By the thirteenth century, almost half of the highest offices in the Church were occupied by degreed masters (abbots, archbishops, cardinals), and over one-third of the second-highest offices were occupied by masters. In addition, some of the greatest theologians of the High Middle Ages, Thomas Aquinas and Robert Grosseteste, were products of the medieval university.
The development of the medieval university coincided with the widespread reintroduction of Aristotle from Byzantine and Arab scholars and the decline in popularity of Platonism and Neoplatonism in favor of Aristotelian thought.
Initially medieval universities did not have a campus. Classes were taught wherever space was available such as churches and homes, a university was not a physical space but a collection of individuals banded together as a universitas (the corporation). Soon, however, some universities (such as Cambridge) began to buy or rent rooms specifically for the purposes of teaching.
Universities were generally structured along three types, depending on who paid the teachers. The first type was in Bologna, where students hired and paid for the teachers. The second type was in Paris, where teachers were paid by the church. Oxford and Cambridge were predominantly supported by the crown and the state, a fact which helped them survive the Dissolution of the Monasteries in 1538 and the subsequent removal of all the principal Catholic institutions in England. These structural differences created other characteristics. At the Bologna university the students ran everything—a fact that often put teachers under great pressure and disadvantage. In Paris, teachers ran the school; thus Paris became the premiere spot for teachers from all over Europe. Also, in Paris the main subject matter was theology, so control of the qualifications awarded was in the hands of an external authority—the Chancellor of the diocese. In Bologna, where students chose more secular studies, the main subject was law.
University studies took six years for a Bachelor’s degree and up to 12 additional years for a master’s degree and doctorate. The first six years were organized by the faculty of arts, where the seven liberal arts were taught: arithmetic, geometry, astronomy, music theory, grammar, logic, and rhetoric. The primary emphasis was on logic.
Once a Bachelor of Arts degree had been conferred, the student could leave the university or pursue further studies, in one of the three other faculties—law, medicine, or theology—in which to pursue the master’s degree and doctorate degree. Theology was the most prestigious area of study, and the most difficult.
Courses were offered according to books, not by subject or theme. For example a course might be on a book by Aristotle, or a book from the Bible. Courses were not elective: the course offerings were set, and everyone had to take the same courses. There were, however, occasional choices as to which teacher to use.
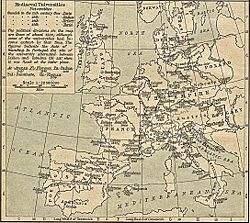
Map of Mediaeval Universities
Students entered the University at 14 to 15 years of age. Classes usually started at 5:00 a.m. or 6:00 a.m.. Students were afforded the legal protection of the clergy. In this way no one was allowed to physically harm them; they could only be tried for crimes in a church court, and were thus immune from any corporal punishment. This gave students free rein in urban environments to break secular laws with impunity, a fact which produced many abuses: theft, rape, and murder were not uncommon among students who did not face serious consequences. This led to uneasy tensions with secular authorities. Students would sometimes «strike» by leaving a city and not returning for years. This happened at the University of Paris strike of 1229 after a riot (started by the students) left a number of students dead; the University went on strike and they did not return for two years. As the students had the legal status of clerics which, according to the Canon Law, could not be held by women, women were not admitted into universities.
A popular textbook for university study was called the Sentences (Quattuor libri sententiarum) of Peter Lombard; theology students and masters were required to write extensive commentaries on this text as part of their curriculum. Much of medieval thought in philosophy and theology can be found in scholastic textual commentary because scholasticism was such a popular method of teaching.
Most universities of international excellence in Europe were registered by the Holy Roman Empire as a Studium Generale. Members of these institutions were encouraged to disseminate their knowledge across Europe, often giving lecture courses at a different Studium Generale.
Medieval Asian universities
Outside of Europe, there were many notable institutions of learning throughout history. In China, there was the famous Hanlin Academy, established during the Tang Dynasty (618-907 C.E.), and was once headed by the Chancellor Shen Kuo (1031-1095), a famous Chinese scientist, inventor, mathematician, and statesman.
Medieval universities did not exist in Asia in the strict sense of the phrase. However, there were important centers of learning that can be compared to the universities of Europe. It must be noted that unlike the European universities, non-western institutions of higher learning were never known to issue degrees to their graduates and therefore do not meet what many hold to be the technical definition of university. This does not, however, bar their importance to the history of non-western cultures.
One of the most important Asian centers of learning was Nalanda, which had been established by the fifth century B.C.E., in Bihar, India. The second century Buddhist philosopher Nagarjuna was based there.
Nanjing University was founded in 258 in China. There were several other universities, called Guozijian, in ancient China.
In Persia, one notable institution was the Academy of Gundishapur.
In the Near East, such as the Islamic Al-Azhar University in Cairo, founded in 988.
In Vietnam, the Quoc Tu Giam (國子監, literally «National University»), functioned for more than 700 years, from 1076 to 1779.
Emergence of modern universities
Indoor tennis courts are part of extensive sports facilities at the University of Bath, England.
The end of the medieval period marked the beginning of the transformation of universities that would eventually result in the modern research university. Many external influences, such as eras of humanism, Enlightenment, Reformation, and revolution, shaped research universities during their development, and the discovery of the New World in 1492 added human rights and international law to the university curriculum.
By the eighteenth century, universities published their own research journals, and by the nineteenth century, the German and the French university models had arisen. The German, or Humboldtian model, was conceived by Wilhelm von Humboldt and based on Friedrich Schleiermacher’s liberal ideas pertaining to the importance of freedom, seminars, and laboratories in universities. The French university model involved strict discipline and control over every aspect of the university.
Universities concentrated on science in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, and they started to become accessible to the masses after 1914. Until the nineteenth century, religion played a significant role in university curriculum; however, the role of religion in research universities decreased in the nineteenth century, and by the end of the nineteenth century, the German university model had spread around the world. The British also established universities worldwide, and higher education became available to the masses not only in Europe. In a general sense, the basic structure and aims of universities have remained constant over the years.
Nazi universities
Universities changed drastically in Nazi Germany. Books from university libraries, written by anti-Nazi or Jewish authors, were burned in places (in Berlin for example) in 1933, and the curricula were subsequently modified. Jewish professors and students were expelled according to the racial policy of Nazi Germany. University of Poznań was closed by the Nazi Occupation in 1939, its faculty replaced with German substitutes. University of Strasbourg was transferred to Clermont-Ferrand and Reichsuniversität Straßburg existed 1941–1944. Nazi-run universities ended with the fall of Nazi Germany in 1945.
Soviet universities
Soviet type universities existed in the Soviet Union and in other countries of the Eastern Bloc.
Medical, technical, economical, technological and arts faculties were frequently separated from universities. Soviet ideology was taught divided into three disciplines: Scientific Communism, Marxism-Leninism, and Communist Political Economy) and was introduced as part of many courses, such as teaching Karl Marx’ or Vladimir Lenin’s views on energy or history. Sciences were generally tolerated, but humanities curbed. In 1922, the Bolshevik government expelled some 160 prominent intellectuals on the Philosophers’ ship, later some professors and students were killed or worked in Gulag camps. Communist economy was preferred, liberal ideas criticized or ignored. Genetics was reduced to Lysenkoism from the middle of the 1930s to the middle of the 1960s. Communist parties controlled or influenced universities. The leading university was the Moscow State University. After Joseph Stalin’s death, universities in some Communist countries obtained more freedom. The Patrice Lumumba Peoples’ Friendship University provided higher education as well as a KGB training ground for young communists from developing countries. The system failed during the years 1989-1991. In some countries a number of communists and political police informers were expelled from universities, political universities resolved or reorganized.
Organization
Brooks Hall, home of the Terry College of Business at the University of Georgia in Athens, Georgia, United States
Although each institution is differently organized, nearly all modern universities have a board of trustees, a president, chancellor or rector, at least one vice president, vice-chancellor or vice-rector, and deans of various divisions. Universities are generally divided into a number of academic departments, schools or faculties. Public university systems are ruled over by government-run higher education boards. They review financial requests and budget proposals and then allocate funds for each university in the system. They also approve new programs of instruction and cancel or make changes in existing programs. In addition, they plan for the further coordinated growth and development of the various institutions of higher education in the state or country. However, many public universities in the world have a considerable degree of financial, research and pedagogical autonomy. Private universities are privately funded having generally a broader independence from state policies.
Despite the variable policies, or cultural and economic standards available in different geographical locations create a tremendous disparity between universities around the world and even inside a country, the universities are usually among the foremost research and advanced training providers in every society. Most universities not only offer courses in subjects ranging from the natural sciences, engineering, architecture or medicine, to sports sciences, social sciences, law or humanities, they also offer many amenities to their student population including a variety of places to eat, banks, bookshops, print shops, job centers, and bars. In addition, universities have a range of facilities like libraries, sports centers, students’ unions, computer labs, and research laboratories. In a number of countries, major classic universities usually have their own botanical gardens, astronomical observatories, business incubators, and university hospitals.
Criticism
In his study of the American university since World War II, The Knowledge Factory, Stanley Aronowitz argued that the American university has been besieged by growing unemployment issues, the pressures of big business on the land grant university, as well as the political passivity and «ivory tower» naivete of American academics. A part of these pressures results in debates over academic freedom in which professors, students, and administrators are coerced into working on or prevented from working on certain topics that may be controversial.
In a somewhat more theoretical vein, the late Bill Readings contended in his 1995 study The University in Ruins that the university around the world has been hopelessly commodified by globalization and the bureaucratic non-value of «excellence.» His view is that the university will continue to linger on as an increasingly consumerist, ruined institution until or unless we are able to conceive of advanced education in transnational ways that can move beyond both the national subject and the corporate enterprise.
In some countries, in some political systems, universities are controlled by political and/or religious authorities, who forbid certain fields and/or impose certain other fields. Sometimes national or racial limitations exist—for students, staff, and research.
Notes
- ↑ University Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved March 27, 2020.
References
ISBN links support NWE through referral fees
- Aronowitz, Stanley. The Knowledge Factory, Boston, MA: Beacon, 2000. ISBN 0807031224
- Barrow, Clyde W. Universities and the Capitalist State: Corporate Liberalism and the Reconstruction of American Higher Education, 1894–1928. University of Wisconsin Press, 1990. ISBN 0299124045
- Browning, Robert. «The patriarchal school at Constantinople in the twelfth century,» Byzantion Volume 32 (1962):167-202
- Browning, Robert. «Universities, Byzantine» in Dictionary of the Middle Ages. (12) (1989): 300.
- Cobban, Alan B. English University Life in the Middle Ages. Columbus, OH: Ohio State University Press, 1999. ISBN 0814208266
- Diamond, Sigmund. Compromised Campus: The Collaboration of Universities with the Intelligence Community, 1945–1955. Oxford University Press, 1992. ISBN 0195053826
- Ferruolo, Stephen. The Origins of the University: The Schools of Paris and their Critics, 1100-1215. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press, 1998. ISBN 0804712662
- Haskins, Charles Homer. The Rise of Universities. Ithaca, New York: Cornell University Press, 1972. ISBN 0879683791
- Rait, Robert S. Life in the Medieval University Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1931. ISBN 0527736503
- Rashdall, Hastings, rev. by F. M. Powicke, and A. B. Emden. The Universities of Europe in the Middle Ages. 3 vols. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1987. ISBN 0198214316
- Readings, Bill. The University in Ruins. Harvard University Press, 1996. ISBN 0674929535
- Ruegg, Walter (ed.). A History of the University in Europe. Cambridge University Press, (3 vols), 2004. ISBN 0521361079
- Seybolt, Robert Francis, (trans.). The Manuale Scholarium: An Original Account of Life in the Mediaeval University. Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 1921.
- Thorndike, Lynn, (trans. and ed.). University Records and Life in the Middle Ages, New York, NY: Columbia University Press, 1975. ISBN 039309216X
- Wilson, N. G. Scholars of Byzantium. London:Duckworth, 1983. ISBN 0715617052
External links
All links retrieved April 16, 2020.
- From Manuscript to Print: Evolution of the Mediaeval Book.
- Life of the Students at Paris.
- Cambridge, A Brief History: The Mediaeval University.
- Mediaeval Science, the Church, and Universities
Credits
New World Encyclopedia writers and editors rewrote and completed the Wikipedia article
in accordance with New World Encyclopedia standards. This article abides by terms of the Creative Commons CC-by-sa 3.0 License (CC-by-sa), which may be used and disseminated with proper attribution. Credit is due under the terms of this license that can reference both the New World Encyclopedia contributors and the selfless volunteer contributors of the Wikimedia Foundation. To cite this article click here for a list of acceptable citing formats.The history of earlier contributions by wikipedians is accessible to researchers here:
- University history
- Medieval_university history
- Medieval_university_(Asia) history
- Byzantine_university history
The history of this article since it was imported to New World Encyclopedia:
- History of «University»
Note: Some restrictions may apply to use of individual images which are separately licensed.
The word university is derived from the Latin universitas magistrorum et scholarium, which roughly means “community of teachers and scholars”.
What is the full meaning of university?
university Add to list Share. Just like the word universe (“the whole world”), university comes from the Latin word universus, meaning “whole, entire.” So think of a university as being sort of a world of its own — an institute of higher education where you live and study.
What is the root word of uni?
The prefix uni- which means “one” is an important prefix in the English language. For instance, the prefix uni- gave rise to the words unicycle, uniform, and unison. Perhaps the easiest way to remember that uni- means “one” is through the word unicorn, or mythological horse that had “one” horn.
What makes a university a university?
Universities are public or private institutions that offer both undergraduate and graduate degrees and are known for their lively, diverse campuses. Universities are also generally more devoted to research, featuring an impressive array of facilities and labs to support these efforts.
At what age do you go to university?
The minimum age to study a degree programme at the university is normally at least 17 years old by the 20 September in the year the course begins. There is no upper age limit. The University will continue to review the minimum age requirement in light of recent changes to national legislation.
Is university better than college?
Many students ask if a university is better than a college. For example, if a student wants to attend a school with a variety of programs and classes, then a university may be a better choice. If a student values small class sizes and a closer relationship with professors, then a college might be the best option.
Is Uni more fun than high school?
University life is more fun than high school if and only if you are ready to let go of yourself completely. University life is more fun than high school if and only if you are ready to let go of yourself completely.
What is the difference between high school and university?
The biggest difference between high school and university is that you’re treated as an adult. That means you get to take greater control of how you spend your time and what you study. During school hours, students are expected to stay on school grounds.
Is Uni easier than IB?
Material wise, “college” is only slightly more difficult in terms of depth and complexity. In terms of worldoad, as /u/tony18rox said, IB is definitely harder. In terms of difficulty, I was told in school that IB would be harder than first year uni in any programme apart from medicine and engineering.
Is college or high school easier?
Is college easier than high school? In many ways, yes. College is easier than high school because you will know exactly what’s expected of you. At the start of the semester, your professors will give you a syllabus outlining all of the reading assignments, exam dates and paper due dates for that class.
Can GoGuardian see you through your camera?
While CPS spokeswoman Emily Bolton said GoGuardian did not directly give anyone remote control of or access to a camera or microphone, she acknowledged the preview function essentially allowed just that. CPS has since changed the settings that defaulted to cameras and microphones automatically turning on.
English[edit]
Western Illinois University
Etymology[edit]
From Middle English universite (“institution of higher learning, body of persons constituting a university”) from Anglo-Norman université, from Old French universitei, from Medieval Latin stem of universitas, in juridical and Late Latin «A number of persons associated into one body, a society, company, community, guild, corporation, etc»; in Latin, «the whole, aggregate,» from universus (“whole, entire”).
Pronunciation[edit]
- (Received Pronunciation) IPA(key): /juːnɪˈvɜːsəti/
- (General American) IPA(key): /junɪˈvɝsəti/, /junɪˈvɝsɪti/
- Hyphenation: uni‧ver‧si‧ty
Noun[edit]
university (plural universities)
- Institution of higher education (typically accepting students from the age of about 17 or 18, depending on country, but in some exceptional cases able to take younger students) where subjects are studied and researched in depth and degrees are offered.
-
The only reason why I haven’t gone to university is because I can’t afford it.
- 1661, John Fell, The Life of the most learned, reverend and pious Dr. H. Hammond
- During the whole time of his abode in the university he generally spent thirteen hours of the day in study; by which assiduity besides an exact dispatch of the whole course of philosophy, he read over in a manner all classic authors that are extant […]
-
2013 July 20, “The attack of the MOOCs”, in The Economist, volume 408, number 8845:
-
Since the launch early last year of […] two Silicon Valley start-ups offering free education through MOOCs, massive open online courses, the ivory towers of academia have been shaken to their foundations. University brands built in some cases over centuries have been forced to contemplate the possibility that information technology will rapidly make their existing business model obsolete.
-
-
Usage notes[edit]
- In western Europe, and later the United States, universities were typically founded by executive act (e.g. royal charter) and were generally relatively large (compared to colleges), offering postgraduate degrees in addition to undergraduate degrees. In other countries, this distinction is not made and any degree-granting institution is called a university.
- In the United States, Ireland, and the Philippines, students will sometimes say that they go to «the university» or to «a university», but they are far more likely to say they are going «to college», even if the institution they attend is a university. In the UK, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and most other English-speaking countries, students go «to university (or uni)», without the article, if they are attending a school that grants bachelor’s or postgraduate degrees.
Synonyms[edit]
- academy
- college
- institute
- uni
- varsity
Hypernyms[edit]
- institution
- school
Hyponyms[edit]
- plate-glass university
- technical university
- technological university
- university of technology
Derived terms[edit]
- varsity
[edit]
- universal
- universe
Descendants[edit]
- → Tokelauan: Iunivehite
Translations[edit]
institution of higher education
- Afrikaans: universiteit (af)
- Albanian: fakulltet m, universitet (sq) m
- Amharic: ዩኒቨርሲቲ (yunivärsiti)
- Arabic: جَامِعَة (ar) f (jāmiʕa)
- Egyptian Arabic: جامعة f (gamʿa)
- Gulf Arabic: جامعة (jam3ə)
- Aragonese: universidat f
- Armenian: համալսարան (hy) (hamalsaran)
- Aromanian: univirsitati f
- Assamese: বিশ্ববিদ্যালয় (bissobiiddaloy)
- Asturian: universidá f
- Azerbaijani: universitet, danişgah (South Azerbaijani), darülfünun (archaic)
- Basque: unibertsitate (eu)
- Belarusian: універсітэ́т m (univjersitét), унівэрсытэ́т m (universytét) (Taraškievica)
- Bengali: বিশ্ববিদ্যালয় (bn) (biśśobiddaloẏ), জামেয়া (bn) (jameẏa)
- Breton: skol-veur f
- Bulgarian: университе́т m (universitét)
- Burmese: တက္ကသိုလ် (my) (takka.suil)
- Catalan: universitat (ca) f
- Chamorro: unibetsedåt
- Chechen: университет (universitet), говзарт (gowzart) (archaic)
- Chinese:
- Cantonese: 大學/大学 (yue) (daai6 hok6)
- Dungan: дащүә (daxüə)
- Hakka: 大學/大学 (thai-ho̍k)
- Mandarin: 大學/大学 (zh) (dàxué)
- Min Nan: 大學/大学 (zh-min-nan) (tāi-ha̍k)
- Cornish: pennskol f, universita m
- Corsican: università (co) f
- Czech: univerzita (cs) f, vysoká škola (cs) f, vysoké učení n
- Danish: universitet (da) n
- Dutch: universiteit (nl) f, (used attributively) universitair (nl), unief (nl) f
- Esperanto: universitato (eo)
- Estonian: ülikool (et)
- Faroese: fróðskaparsetur n, universitet n
- Finnish: yliopisto (fi)
- French: université (fr) f, fac (fr) f, univ (fr) f
- Friulian: please add this translation if you can
- Fula:
-
- Adlam: 𞤶𞤢𞥄𞤩𞤭 𞤸𞤢𞥄𞤪𞤼𞤭𞤣𞤫,
- Latin: jaaɓi haartide
- Galician: universidade (gl) f
- Georgian: უნივერსიტეტი (ka) (universiṭeṭi)
- German: Universität (de) f, Hochschule (de) f, Uni (de) f
- Gilaki: دانشگا (dânišgâ)
- Greek: πανεπιστήμιο (el) n (panepistímio)
- Ancient: please add this translation if you can
- Greenlandic: ilisimatusarfik, universiteti
- Guaraní: mbo’ehao guasu
- Gujarati: યુનિવર્સિટી (yunivarsiṭī)
- Haitian Creole: inivèsite
- Hausa: jami’a
- Hebrew: אוּנִיבֶרְסִיטָה (he) f (univérsita)
- Hindi: विश्वविद्यालय (hi) m (viśvavidyālay), यूनिवर्सिटी (hi) f (yūnivarsiṭī), महाविद्यालय (hi) m (mahāvidyālay), विद्यापीठ m (vidyāpīṭh), वीद्यापीठ (hi) m (vīdyāpīṭh), जामिया m (jāmiyā), कालिज (hi) m (kālij), विश्वविद्यानिलय m (viśvavidyānilay)
- Hungarian: egyetem (hu), tudományegyetem
- Icelandic: háskóli (is) m
- Ido: universitato (io)
- Indonesian: universitas (id), universitet (id) (archaic)
- Interlingua: universitate
- Irish: ollscoil (ga)
- Italian: università (it) f, accademia (it) f, istituto (it) m, politecnico (it) m, collegio (it) m, ateneo (it) m
- Japanese: 大学 (ja) (だいがく daigaku), 大学校 (ja)
- Kalmyk: ик сурһуль (ik surğulĭ)
- Kannada: ವಿಶ್ವವಿದ್ಯಾನಿಲಯ (kn) (viśvavidyānilaya), ಕಲಿವೀಡು (kn) (kalivīḍu)
- Kazakh: университет (kk) (universitet)
- Khmer: សាកលវិទ្យាល័យ (km) (saakɑl vɨttyiəlay), មហាវិទ្យាល័យ (km) (mɔhaavityiəlay)
- Korean: (College) 대학(大學) (ko) (daehak), (University) 대학교(大學校) (ko) (daehakgyo)
- Kurdish:
- Central Kurdish: زانکۆ (ckb) (zanko), زانْستگە (zanistge), زانْستگا (zanistga), دانْشگا (danişga), جامْعە (ckb) (cami’e)
- Northern Kurdish: zanko (ku) f, zanîngeh (ku) f
- Kyrgyz: университет (ky) (universitet)
- Ladino: universita
- Lao: ມະຫາວິທະຍາໄລ (lo) (ma hā wi tha nyā lai)
- Latin: universitas f, studium generale n
- Latvian: universitāte f, augstskola f
- Lithuanian: universitetas (lt) m
- Luxembourgish: Universitéit (lb) f
- Lü: please add this translation if you can
- Macedonian: универзите́т m (univerzitét)
- Malay: universiti (ms), menara gading, madrasah jamiah
- Malayalam: സർവ്വകലാശാല (ml) (saṟvvakalāśāla), യൂനിവേഴ്സിറ്റി (yūnivēḻsiṟṟi), യൂണിവേഴ്സിറ്റി (yūṇivēḻsiṟṟi)
- Maltese: università (mt) f
- Manchu: ᠠᠮᠪᠠ
ᡨᠠᠴᡳᡴᡡ (amba tacikū) - Manx: please add this translation if you can
- Marathi: विद्यापीठ (vidyāpīṭh), युनिव्हर्सिटी f (yunivharsiṭī)
- Mongolian: их сургууль (ix surguulʹ)
- Norman: euniversitaé f (Guernsey), unnivèrsité f (Jersey)
- Northern Sami: universitehtta
- Northern Thai: please add this translation if you can
- Norwegian:
- Bokmål: universitet (no) n
- Nynorsk: universitet n
- Occitan: universitat (oc) f
- Pashto: پوهنتون (ps) m (pohantun)
- Persian: دانشگاه (fa) (dânešgâh)
- Polish: uniwersytet (pl) m, wszechnica (pl) f
- Portuguese: universidade (pt) f
- Punjabi: ਯੂਨੀਵਰਸਿਟੀ (pa) (yūnīvrasiṭī)
- Quechua: jatun yachay wasi
- Romanian: universitate (ro) f
- Romansch: please add this translation if you can
- Russian: университе́т (ru) m (universitét)
- Rwanda-Rundi: kaminuza class 9/10
- Scots: varsitie
- Scottish Gaelic: oilthigh m
- Serbo-Croatian:
- Cyrillic: универзѝте̄т m, свеу̀чилӣште n
- Roman: univerzìtēt (sh) m, sveùčilīšte (sh) n
- Shan: ႁူင်းႁဵၼ်းၸၼ်ႉၸွမ် (húung háen tsâ̰n tsǎum), ၸၼ်ႉၸွမ် (tsâ̰n tsǎum), တၵ်ႈၵသူဝ်ႇ (tāk kǎ sò), တၵ်ႉၵသူဝ်ႇ (tâ̰k kǎ sò)
- Sicilian: univirsitati (scn) f, univirsità (scn) f
- Sindhi: ڪاليج
- Sinhalese: විශ්ව විද්යාලය (wiśwa widyālaya), විශ්වවිද්යාල (wiśwawidyāla)
- Slovak: univerzita (sk) f
- Slovene: univerza (sl) f
- Sorbian:
- Lower Sorbian: uniwersita f
- Upper Sorbian: uniwersita f
- Spanish: universidad (es) f
- Swabian: Universidäd
- Swahili: chuo kikuu (sw)
- Swedish: universitet (sv) n, högskola (sv)
- Tagalog: pamantasan (tl), unibersidad (tl)
- Tajik: донишгоҳ (tg) (donišgoh)
- Tamil: பல்கலைக்கழகம் (ta) (palkalaikkaḻakam)
- Tatar: университет (uniwersitet)
- Telugu: విశ్వవిద్యాలయము (te) (viśvavidyālayamu)
- Thai: มหาวิทยาลัย (th) (má-hǎa-wít-tá-yaa-lai)
- Tibetan: སློབ་གྲྭ་ཆེན་མོ (slob grwa chen mo)
- Tok Pisin: yunivesiti
- Turkish: üniversite (tr), darülfünun (tr)
- Turkmen: uniwersitet
- Ukrainian: університе́т (uk) m (universytét)
- Urdu: جامعہ (jāmi’a), دانش گاہ f (dânish-gâh)
- Uyghur: ئۇنىۋېرسىتېت (uniwërsitët), داشۆ (dashö), ئالىي مەكتەپ (aliy mektep)
- Uzbek: universitet (uz)
- Vietnamese: trường đại học (vi), đại học (vi) (大學)
- Volapük: niver (vo)
- Walloon: please add this translation if you can
- Warray: yunibersidad, unibersidad
- Welsh: prifysgol (cy) f
- West Frisian: universiteit c
- Western Panjabi: یونیورسٹی (pnb)
- Yiddish: אוניווערסיטעט f (universitet)
- Zhuang: dayoz
See also[edit]
- Wikiversity
References[edit]
university on Wikipedia.Wikipedia
Scots[edit]
Alternative forms[edit]
- varsity
Etymology[edit]
From Middle English universite, from Medieval Latin [Term?].
Pronunciation[edit]
- IPA(key): [ˈjunəvɛrsəti]
Noun[edit]
university (plural universities)
- university


- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Geography & Travel
- Health & Medicine
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Literature
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- Science
- Sports & Recreation
- Technology
- Visual Arts
- World History
- On This Day in History
- Quizzes
- Podcasts
- Dictionary
- Biographies
- Summaries
- Top Questions
- Infographics
- Demystified
- Lists
- #WTFact
- Companions
- Image Galleries
- Spotlight
- The Forum
- One Good Fact
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Geography & Travel
- Health & Medicine
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Literature
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- Science
- Sports & Recreation
- Technology
- Visual Arts
- World History
- Britannica Explains
In these videos, Britannica explains a variety of topics and answers frequently asked questions. - Britannica Classics
Check out these retro videos from Encyclopedia Britannica’s archives. - Demystified Videos
In Demystified, Britannica has all the answers to your burning questions. - #WTFact Videos
In #WTFact Britannica shares some of the most bizarre facts we can find. - This Time in History
In these videos, find out what happened this month (or any month!) in history.
- Student Portal
Britannica is the ultimate student resource for key school subjects like history, government, literature, and more. - COVID-19 Portal
While this global health crisis continues to evolve, it can be useful to look to past pandemics to better understand how to respond today. - 100 Women
Britannica celebrates the centennial of the Nineteenth Amendment, highlighting suffragists and history-making politicians. - Saving Earth
Britannica Presents Earth’s To-Do List for the 21st Century. Learn about the major environmental problems facing our planet and what can be done about them! - SpaceNext50
Britannica presents SpaceNext50, From the race to the Moon to space stewardship, we explore a wide range of subjects that feed our curiosity about space!