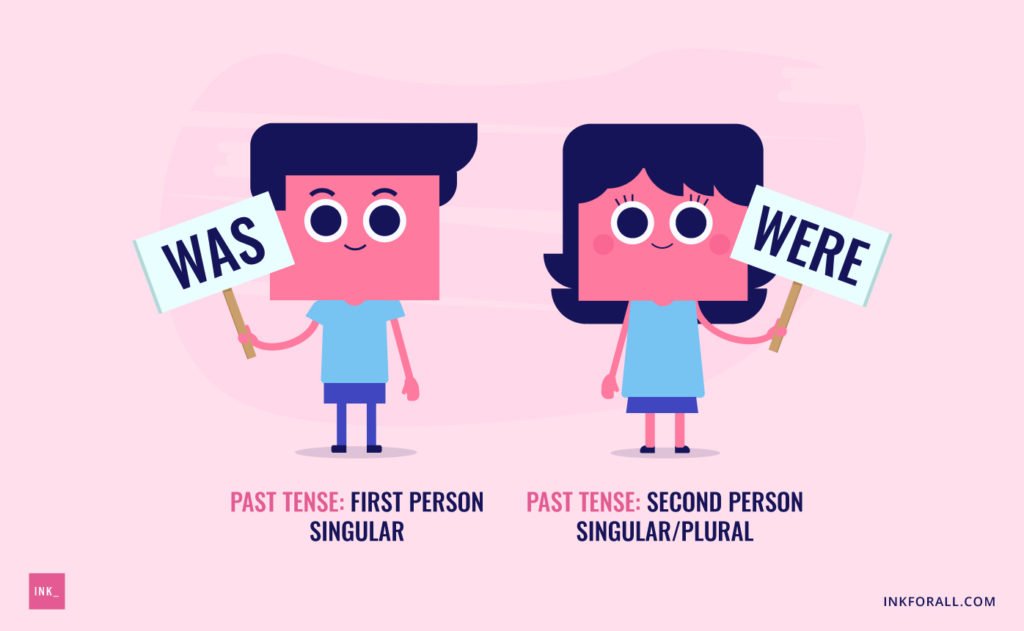
Both was and were are correct forms of the verb “to be.” However, when to use was vs. were depends on whether you’re talking about something imaginary or something real.
Hypothetical situations need the subjunctive mood, so you should use were regardless of the speaker’s point of view. However, situations that actually happened in the past need the indicative mood. This means subject-verb agreement comes into play, so you should use was with I/he/she (She was here) but were with you/we/they (You/we/they were here).
When to Use Was vs. Were at a Glance:
Should you use was or were? This is a grammar question that even native English speakers struggle to answer correctly. Let’s look at the easiest way to know the difference between was and were. What’s more, you’ll see was vs. were example sentences and learn how to correctly use this irregular verb.
| Indicative Mood: Past tense of the verb “to be” | I was | you were | he was | she was | it was | we were | you were | they were |
| Subjunctive Mood: Hypothetical situations with the verb “to be” | I were | you were | he were | she were | it were | we were | you were | they were |
In this way, the difference between was and were comes down to describing something that actually happened in the past vs. an imaginary situation that never happened at all. Moreover, it also depends on who is speaking. Finally, subject-verb agreement also comes into play.
3 Easy Steps That Tell you When to use Was vs. Were
1. Ask yourself these questions:
- Did it really occur in the past?
- Or, are we talking about an imaginary situation that can’t be real?
2. If it actually occurred in the past:
Use was with the first and third person singular points of view:
- I was
- She was
- He was
- It was
- You were
But, use were with the second person (you) or third person (they) plural points of view. This helps ensure correct subject-verb agreement.
- You were
- They were
3. If the situation is imaginary and can’t be real:
Were is the only correct option. As such, use were for every point of view.
Why Second Conditional Uses Were?
A second conditional, or type 2 conditional sentence, describes hypothetical or imaginary situations, like dreams and wishes. In some instances, those situations could happen in the future, but they most likely won’t.
Below is the structure for a second conditional statement:
If + verb to be + condition
In the statement above, we used “were” instead of “was.” That’s even if the latter is considered the proper past simple form of the verb to be to go with the pronoun “I.”
We do this because we’re talking about an imaginary situation. No one can reverse time and be a child again, right? That’s just impossible. By saying “If I were,” we’re changing the mood of the verb to be from indicative to subjunctive.
The indicative mood describes real situations or facts. On the other hand, the subjunctive mood describes situations that are hypothetical or are not real. For second conditional statements, we always use were.
“Was” Usually Refers to the Past
When you see the word “was,” we’re most likely talking about something that previously occurred.
Specifically, was indicates that the first and third singular person points of view acted in the past. For this reason, we use was with the indicative mood.
In other words, the rule for was/were typically comes down to singular vs. plural when using the past tense of the verb “to be.”
However, as with most grammatical rules in English, there is an exception here.
Which is Correct: “If I Was” or “If I Were”
Most statements that include if are subjunctive. In these cases, we use were. Notwithstanding, there is one exception for the first person point of view: I.
On one side, we have was in the indicative mood to indicate reality.
On the other, we have were in the subjunctive mood to refer to imaginary or hypothetical situations.
But, there is also a third option in the middle: what should you use when you aren’t sure if something is real or imaginary?
In this case, “If I was” is the grammatically correct choice. In other words, when it’s not clear if something is real or hypothetical, “I was” is correct.
In the above example, the speaker isn’t sure if they made a mistake or not. This situation might be imaginary, but it might also be real. As a result, the speaker can’t use were since this option is for purely imaginary situations.
Therefore, we use “If I was” to show this doubt grammatically.
Now, let’s compare the “If I was vs. were” in action:
The above example expresses a purely imaginary situation: I don’t live in Los Angeles, so I don’t drive to work. I show that the scenario isn’t real by using the verb “to be” with the subjunctive mood were.
Conversely, the above example expresses doubt. For instance, I did live in Los Angeles in the past, but I don’t anymore. Additionally, I used to drive, but I don’t anymore.
If I don’t remember exactly when I moved or when I stopped driving, I should use the if I was construction to express this doubt to my audience.
When “Were” is Past Tense and When it’s Subjunctive
Was tends to hang out exclusively with the past tense in the indicative mood. However, were can express the real past tense in the indicative mood or an imaginary situation in the subjunctive mood. How do you tell the difference?
Were and Past Tense
The trick here is to associate were and the past tense with subject-verb agreement. In other words, whether you should use was vs. were depends on who is speaking.
For example, use was with these points of view:
- First person singular = I was
- Third person singular = he/she/it was
However, use were with these points of view:
- Second person singular = you were
- Second person plural = you (all) were
- First person plural = wewere
- Third person plural = theywere
Should I use Was or Were with There?
Whether to use was or were with therehas to do with subject-verb agreement. When a sentence starts with the word there, the words following the verb are typically the subject. For example, in the sentence “There are oranges on the table,” the subject is oranges. If the subject is singular, then you should use the verb was (“There was an orange…“). Yet, if the subject is plural, then the correct verb to use is were (“There were oranges…“).
📝 Whether to use was or were depends on several factors, including:
- Subject-verb agreement
- Whether you’re using the subjunctive mood
- Point of view
Were and the Subjunctive Mood
Subjunctive what? Unless you’re a diehard grammarian or advanced polyglot, you’ve probably never heard of subjunctive mood. In simple terms, the phrase describes a verb tense we associate with unreal statements or questions.
Essentially, whereas most statements reveal something that is currently happening or has previously happened, a subjunctive sentence refers to something that hasn’t actually happened. That may be a want, a wish, or a suggestion.
📝 We use the subjunctive mood to express:
- Demands
- Proposals
- Desires
- Wishfulness
- Hypothetical situations
- Possibilities
In both written and spoken English, subjunctive mood usually appears by an indicative verb such aswant, wish, desire, suggest, or recommend. What’s more, sentences that express possibilities often include the word if.
When creating a subjunctive mood, the traditional singular/plural rules for was/were don’t apply. In fact, when it comes to the subjunctive mood, there’s an easy rule for choosing was or were: always choose were.
📝 Phrases used to express subjunctive mood include:
- I were
- You were
- He/she were
- It were
- They were
- This were
- That were
You’ll note that none of these examples describes a current reality. Instead, they all describe hypothetical, desired, or imaginary situations. Therefore, we use were regardless of whether the subject is singular or plural to make this departure from reality clear.
Which is Correct Grammatically: If I Was or If I Were?
Both of the phrases if I was and if I were are grammatically correct, but they mean very different things. Therefore, the difference between if I was and if I weredepends on what you are trying to say. First, use if I was for something that might be real, or to express doubt when you’re not sure if something is true (If I was late responding to you, I apologize). Second, use if I were to express something unreal, imaginary, or hypothetical (If I were a dragon…”
Often, the word if introduces subjunctive mood. When a sentence includes the phrase if I was orif I were, grammatists tend to label this subjunctive mood. That means the sentence refers to something that goes against, or is contrary to, the current truth. In other words, the sentence may express a desire, wish, possibility, or hypothetical situation. For subjunctive statements or questions, the grammatically correct phrase is “If I were“.
Was and Were Sentence Examples
Here are examples of was vs. were in a sentence:
Can you say if I Were?
You can say if I were. In fact, were is typically the correct conjugation of the verb to be in this context. Because this phrase begins with the word if, it’s subjunctive mood. That’s another way of saying it describes a hypothetical or unreal situation. In subjunctive sentences, the correct form of to be is always were.
Is If I Were a Boy Grammatically Correct?
If I were a boy is grammatically correct. This construction is correct because it reflects subjunctive mood. In other words, the phrase refers to a hypothetical or unreal situation. In this particular hypothetical, the writer is speculating about what might happen if her gender were different. When you write a sentence using subjunctive mood, you should always conjugate the the verb “to be” as were— regardless of the speaker’s point of view.
Were vs. Was: a Matter of Style?
It’s also worth noting that more and more writers are opting to use was instead of were in subjunctive sentences. This is particularly true in informal prose. It’s led some grammarians to speculate about the subjunctive were eventually becoming obsolete.
A Brief Was/Were Recap
By following a few basic rules, understanding when to use was and were doesn’t have to leave you with a headache.
- When conjugating the verb to be in the past tense, use was when writing in first or third person singular. Use were when writing in second person singular or plural or first-person or third-person plural.
- Use were when crafting sentences that involve hypothetical situations, speculation, or wishes. This is known as subjunctive mood and is often identified by the inclusion of the word if.
- If a sentence starts with the word there, use was if the subject is singular. Use were if the subject is plural.
Main Was vs. Were Takeaways:
- Was and were are past tense versions of the verb to be. They are both correct, depending on the context.
- When you want to talk about an imaginary, hypothetical, or unreal situation, use the subjunctive mood were across the board (If I were a dinosaur…).
- When you want to talk about reality, follow the normal conjugation for the verb “to be” in the past tense. Use the indicative mood was for I/he/she (She was here) but were with you/we/they (You/we/they were here).
Practice Your Grammar Skills With These Was and Were Exercises
Was and Were Question #1
A. Verbs
B. Adjectives
C. Adverbs
D. Nouns
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is A. “Was” and “were” are past tense versions of the verb “to be.”
Use or When Question #2
A. Point of view
B. Use of subjunctive mood
C. Subject-verb agreement
D. All of the above
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is D. All the factors outlined above can determine whether to use “was” or “when”.
Was vs. Were Question #3
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is WAS. “Was” is the correct choice when writing in first person or third person (he, she, it) singular.
Were vs. Was Question #4
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is WERE. “Were” is correct when writing in the second-person singular, second-person plural, and first and third-person plural.
Was and Were Question #5
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is WERE. Hypothetical situations need the subjunctive mood. So “were” is appropriate.
Was vs. Were Question #6
A. Demands
B. Wishfulness
C. Past events
D. Hypothetical situations
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is C. A subjunctive sentence refers to something that hasn’t happened.
Were vs. Was Question #7
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is C. Either can be appropriate, depending on the subject-verb agreement.
Was or Were Question #8
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is WAS. The situation occurred in the past, and it’s in first-person singular.
Were or Was Question #9
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is WERE. The situation occurred in the past, and it’s in third-person plural.
Was vs. Were Question #10
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is WERE. The situation is imaginary.
Were vs. Was Question #11
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is WAS. The situation occurred in the past, and it’s in third-person singular.
Was vs. Were Question #12
Correct!
Wrong!
The answer is WERE. The situation occurred in the past, and it’s in third-person plural.
Was vs. Were Quiz Result
Expert!
Not bad!
Almost got it! Review the article and try again.
Read More: 🛣️ Toward Vs. Towards: An Easy Guide On When To Use Which
Download Article
Download Article
The words “was” and “were” are both past-tense conjugations of the word “to be,” meaning they describe how something was in the past. But it’s not always easy to decide when to use one word over the other. First, decide if you’re talking in the indicative or subjunctive mood. Then, decide if the subject of the action is singular or plural. We’ll help you sort out which mood is which, then give you a simple guide on when to use “was” versus “were,” with plenty of examples along the way.
Things You Should Know
- Use “was” to describe factual statements in the first or third-person singular.
- Use “were” to describe factual statements in the second person or first- and third-person plural.
- Use “were” to describe hypothetical statements or statements contrary to fact.
-
«Was» and «were» are past tense forms of the verb “to be,” but they’re used at different times. Deciding which word is grammatically correct in a specific sentence can be a little confusing, but you only need to need to know 2 main things to figure it out:
- The point of view (first-, second-, or third-person point of view)
- If the verb needs to be in the past indicative or past subjunctive tense
Advertisement
-
1
Use “were” with plural subjects. When your subject includes more than one person or thing, like “they” or “we,” use “were” to describe the action. For example, “They were at the store,” or “We were riding in the car.”[1]
-
2
Use “were” when talking about the second person. The second person is any time you use the word “you” as the subject of the verb, like when you’re talking directly to somebody else. In this case, use “were” to describe the action.[2]
- “You were absent that day.”
- “I remember when you were little.”
-
3
Use “were” when speaking in hypothetical situations. Any time you’re describing a hypothetical about the past or something that goes against fact, use “were.” This includes conditional phrases where the situation described is impossible, like, “If he were a duck, he’d probably quack.”[3]
- When you’re not talking about something that actually happened, you’re speaking in the “subjunctive mood.” This includes talking about things that might happen but which haven’t happened yet, things you wish would happen, or when you’re talking about things that are contrary to fact.[4]
- “I wish I were there when it happened.”
- “If you were Lady Gaga, you’d have a good voice.”
- When you’re not talking about something that actually happened, you’re speaking in the “subjunctive mood.” This includes talking about things that might happen but which haven’t happened yet, things you wish would happen, or when you’re talking about things that are contrary to fact.[4]
Advertisement
-
1
Use “was” when talking about the singular, first-person indicative. Singular first-person is any time you use the word “I” as a subject, like “I was at the store.” When you’re describing something that actually happened (indicative) to you (first person), go with “was.”
- “I was there when he fell.”
- “I was eating ice cream.”
-
2
Use “was” to describe a situation that could have happened. Here’s where things can get confusing. When a hypothetical or conditional statement (a statement using the word “if”) is possible or could be true, use “was” to describe it.[5]
However, stick to “were” if the situation is impossible.- “If I was wrong, I’ll eat my hat.” In this sentence, the speaker is admitting that the hypothetical situation (being wrong) could in fact be true (as opposed to an impossible hypothetical), and so the speaker uses “was.”
Advertisement
-
1
“If I was” describes a situation that could have happened. The situation described after this phrase is either true, or it might be true, and so we use “was.” [6]
- “I’m sorry if I was wrong.”
- “If she wasn’t busy, she could go on the trip.”
-
2
“If I were” is used when describing a situation that isn’t true. These situations can never happen and call for the subjunctive mood, so we use “were.”[7]
- “If I were incorrect, I’d apologize.”
- “If I were a fish, I’d breathe underwater.”
Advertisement
-
1
Use “there was” to describe single objects. When the subject described in the sentence is singular, we use “was.”[8]
- “There was a dog in the tree.”
- “When I woke up, I realized there was no blanket on the bed.”
-
2
Use “there were” to describe plural objects. When the subject described in the sentence is plural, we use “were.”[9]
- “There were dogs in the tree.”
- “When I woke up, I realized there were no pillows on the bed.”
Advertisement
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
Tip
- Don’t sweat the grammar too much! Unless your teacher or employer indicates that they want you to use the correct form of the past tense “to be,” you probably shouldn’t get too hung up on it. It can be handy to know, but language rules are always changing, and even now the rules on “was” versus “were” are becoming looser. Plenty of notable authors mix them up or use them in ways contrary to grammar rules.[10]
- Looking for homework help or textbook rentals? Check out our coupon site for Chegg.
References
About This Article
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 928 times.
Did this article help you?
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
Subscribe
You’re all set!
Was and were are both past tenses of the verb to be. The verb be is a tricky one because it is an irregular verb and one that we find ourselves using with great frequency, so it is that much more important that we choose the correct verb for our sentences.
In this post, I want to go over the grammar behind was vs. were, when it’s correct to use which one, and give you a few tips to keep track of them both. After reading this post, you shouldn’t have any trouble correctly choosing between was or were in your future writing.
Forms of Was and Were

Was is used in the first person singular (I) and the third person singular (he, she, it).
Were is used in the second person singular and plural (you, your, yours) and first and third person plural (we, they).
The forms that was and were will take in your sentence are summarized in the chart below,
Singular = I was, You were, He was, She was, It was
Plural = We were, You were, They were
- I was driving to the park.
- You were drinking some water.
- He was about to eat dinner.
- She was at the roller rink.
- It was a great time.
- We were in the right spot.
- They were nowhere to be seen.
If I was vs. If I were
While some people get mixed up on what we’ve covered above, most of the confusion with these two words centers on the use of the subjunctive mood and specifically the two phrases if I was vs. if I were. For example, which of the following two choices is correct?
- If I was a better cook, I could entertain more.
-or-
- If I were a better cook, I could entertain more.
You hear people say both each and every day, so it’s hard to know which is correct. The answer, however, has to do with the subjunctive mood.
Subjunctive Mood

- I wish I weren’t so shy.
- I wish it were warmer outside.
- If I were taller, I could dunk a basketball.
- If John were a rich man, he could drive a fancy car.
- He acts as if he were the one in charge.
- John spends money as if he were a millionaire.
All of the above sentences use the verb were because they aren’t true; they do not describe reality.
In the first two sentences, I am talking about things I wish would happen.
In the third and fourth sentences, I am talking about situations that would happen if I were taller and if John were rich, speaking hypothetically.
And the fifth and sixth sentences are examples of unreal statements.
When to Use Were
Another good example of the subjunctive mood can be found in the musical Fiddler on the Roof. In the song, “If I were a rich man,” the character Tevye sings about how different his life would be and all the things he would do if he were rich.
If I were a rich man, I’d build a big tall house…
If I were a rich man, I’d have the time that I lack.
If I were a wealthy man, I wouldn’t have to work hard.
In these lines, Tevye is fantasizing about life as a wealthy man. He isn’t rich now; he’s just imagining it, so we need to use the subjective “If I were,” not “If I was.”
The correct answer for the example above, therefore, is, “If I were a better cook, I could entertain more.”
Tricks to Remember
Two good clues for the subjunctive mood are the words if and wish. If you see either of these words, there is a good chance you will need to use the subjunctive.
When to Use Was
Since were is used for statements that do not describe reality, was is just the opposite. Was is used for statements of fact. For example,
- Last night, I was watching TV until midnight.
- When I was younger, I wanted to be a singer.
- Your brother was my college roommate.
Summary
These words are used differently in sentences, so it’s important to know when to use were vs. was.
Was is used in the first and third person singular past. It is used for statements of fact.
Were is used in the second person singular and plural and first and third person plural. It is used in the subjunctive mood to indicate unreal or hypothetical statements. The words if and wish usually indicate the subjunctive mood.
< Where versus Were versus Wear
Was versus Were >
Contents
- 1 Forms of Was and Were
- 2 If I was vs. If I were
- 3 Subjunctive Mood
- 4 When to Use Were
- 5 Tricks to Remember
- 6 When to Use Was
- 7 Summary
If you sometimes struggle knowing when to use was and were, you aren’t alone. Many people are confused as to when to use the verb was and when to use the verb were. But the rules for using these terms are clear when you know what to look for.
Were and was are past tenses of the irregular verb to be. The verb to be is an irregular verb, which is a verb that does not follow any pattern or rules in its conjugation.
The verb to be is probably one of the most commonly used and confusing verbs in the English language. It can be particularly hard to understand whether to use were or was in certain situations if you don’t first determine the point of view the subject of the sentence provides.
What Is the Difference Between Was and Were?
Was and were are past tenses of the verb to be. The subject’s point of view determines whether you use was or were.
First Person Point of View: I, Me, My, Mine, Myself, We, Us, Our, Ours
Second Person Point of View: You, Your, Yours, Yourself
Third Person Point of View: He, Him, himself, She, Her, Hers, Herself, It, They, Them, Their, Theirs, Themselves
Was is the first person singular past tense form of the verb to be.
- I was walking to the grocery store.
Was is also the third person singular past tense form of the verb to be.
- She was not friendly when introduced to my sister.
Were is the second person singular and second person plural past tense form of the verb to be.
- You were heading in the wrong direction.
- You all were supposed to meet me after school yesterday.
Were is also the first and third person plural past tense form of the verb to be.
- We were going to the park when you drove by.
- They were heading to the game after school.
Be serves as an irregular verb and an irregular auxiliary verb. But what does being an irregular or irregular auxiliary verb have to do with it? First, let’s look at how to be is conjugated, so you understand how irregular verbs differ from other verbs.
Conjugating To Be
To be conjugates into five different forms:
What Is an Irregular Auxiliary Verb?
As you can see above, to be never used -ed in the past tense. Irregular verbs are defined as verbs that don’t use -ed in the past tense.
Irregular verbs rely on the auxiliary verb (or helping verb) to indicate the future, present, or past tense.
The past tense of to be can be used as a verb and as an auxiliary verb. When used as an auxiliary, it is followed by the verb to describe the tense.
For example:
- She was playing soccer.
- We were playing basketball.
It can also serve as a verb. For example,
- She was fifteen years old.
- They were high school graduates.
When to Use Was in a Sentence
Was is the first person singular past tense form of the verb to be and the third person singular past tense form of the verb to be.
For example:
- I was home last night.
- He was in bed at ten o’clock.
- She was at the restaurant until eleven.
- It was not a late night.
When to Use Were in a Sentence
Were is the second person singular and plural past tense form of the verb to be and the first and third person plural past tense form of the verb to be.
For example:
- We were going to the beach.
- You were home last night.
- The boys were in bed by ten o’clock.
- They were asleep by eleven.
There Were or There Was?
The use of were vs. was can get a little murky in a few situations. The first situation is when using the phrases there were or there was.
To use these terms correctly, you must identify the subject of the sentence and ensure the subject and verb are in agreement. Ensuring that a subject and verb are in agreement means making sure that they are either both plural or singular.
A good rule to remember is when a sentence begins with there, the subject is found after the verb. Once the subject has been identified, use the following rules:
- Use was if the subject is singular.
- Use were if the subject is plural.
Remember this rule when trying to decide whether to use was, were, or some other form of the verb to be.
For example:
- There was a dog on the road. (The subject is “dog,” a singular noun.)
- There were three people trying to lure the dog away from the road. (The subject is “people,” a plural noun.)
Hypothetical Situations
Using the word if or wish is a reliable indicator of using the subjective mood.
A subjunctive mood expresses a hypothetical situation that has not come to pass but might come to pass. It may be conditional, or it may simply be imaginary.
Subjunctive moods are almost always expressed using an if or I wish phrase.
A subjunctive mood always uses the past tense verb were. The verb were is the correct choice, regardless of whether the subject is singular or plural, when speaking of a conditional or hypothetical situation.
For example:
- If I were to ask her out, it’s possible she might tell me no.
- I wish I were there instead of sitting in class.
Using the word if is a reliable indicator of using subjective mood. Now you know that when faced with a choice between the phrases if I were or if I was, the phrase if I were is always correct.
Let’s Review
First Person Singular = Was
Third Person Singular = Was
Second Person Singular = Were
First Person Plural = Were
Second Person Plural = Were
Third Person Plural = Were
If the sentence is a hypothetical statement, always use were no matter whether the subject is singular or plural.
Правильное употребление глагола to be — камень преткновения в изучении английского языка. В частности, затруднения возникают при выборе прошедших форм глагола «быть» — was и were. Они используются и как самостоятельные глаголы, и в составе разных конструкций. Разберем все возможные случаи употребления was и were и узнаем, как выбрать нужную форму.
Was и were как прошедшая форма глагола быть (to be)
Was и were в качестве прошедших форм глагола to be для Past Simple используются в значении «был», «находился». В этом разделе мы рассмотрим, когда и как нужно употреблять эти формы.
Когда was, а когда — were?
Чтобы понять, какую форму выбрать в конкретном случае, необходимо посмотреть на подлежащее. Если оно выражено существительным в единственном числе или местоимениями I, he, she или it, то was — верная форма. А если подлежащее стоит во множественном числе или представляет собой местоимения you, we или they, то выбрать нужно were.
Стоит отметить одну особенность английского языка: местоимение you согласуется с глаголами только в форме множественного числа. Это значит, что в настоящем времени глагол to be превращается в are, а в прошедшем, соответственно, в were:
- You are an engineer. — Ты инженер.
- You were an engineer. — Ты был инженером.
Случаи употребления was и were
Самые частые случаи употребления was и were — описание качеств, профессий, местонахождения в прошедшем времени:
- That evening was amazing. — Тот вечер был замечательным.
- His sister was a singer. — Его сестра была певицей.
- My books were on the table. — Мои книги были на столе.
Was и were в отрицательных предложениях
Для отрицания нужно просто добавить частицу not после глагола:
- Jane’s father was not in the office. — Отец Джейн не был в офисе.
- The animals were not sick. — Животные не были больны.
Часто используют сокращенную форму глагола, соединяя его с частицей not апострофом (надстрочной запятой):
- I wasn’t hungry. — Я не был голоден.
- My friends weren’t at the party three days ago. — Мои друзья были на вечеринке 3 дня назад.
Was и were в вопросительных предложениях и коротких ответах
Образование вопросов с was и were отличается от стандартных предложений в Past Simple. Обычно вопросительное предложение в этом времени выглядит так:
- Did you go to school yesterday? — Ты ходил в школу вчера?
Вспомогательный глагол did стоит на первом месте. Однако если нужно составить вопрос с to be в прошедшей форме, то was или were играют роль вспомогательного глагола и выносятся в начало предложения:
- Were you at school yesterday? — Ты был вчера в школе?
Короткий ответ на такой вопрос строится по схеме: Yes (no), subject (подлежащее) + was/were (not). Рассмотрим на примере:
- Were they in Moscow last year? — Были ли они в Москве в прошлом году?
- Yes, they were. — Да, были.
- No, they were not (weren’t) — Нет, не были.
Was и were в устойчивых выражениях с глаголом to be
Существует множество устойчивых выражений с глаголом to be. Чаще всего используются:
- to be interested in — интересоваться;
- to be good at–быть способным к чему-либо;
- to be glad– радоваться;
- to be in a hurry — спешить;
- to be famous for — известный чем-либо;
- to be fond of — любить;
- to be familiar with — хорошо знать что-либо;
- to be afraid of — бояться чего-либо;
- to be busy with — быть занятым чем-либо;
- to be upset about — быть расстроенным чем-либо.
Для образования предложений с этими словосочетаниями в прошедшем времени глагол to be превращается в was или were. Форма зависит от лица и числа подлежащего:
- All my students were good at foreign languages. — Все мои студенты были способны к иностранным языкам.
- I wasn’t afraid of darkness in my childhood. — В детстве я не боялся темноты.
- What was this city famous for? — Чем был известен этот город?


Английский для детей
Групповые и индивидуальные онлайн-уроки английского для детей с носителем языка. Попробуйте бесплатно!
попробовать
Формы there was / there were
Грамматический оборот there was / there were используется в тех же случаях, что и there is / there are, только в прошедшем времени. Мы употребляем эту конструкцию для описания места, указания факта существования чего-либо:
- There were 2 apples and 5 oranges on the table. — На столе было 2 яблока и 5 апельсинов.
- There was a beautiful picture on the wall. — На стене была красивая картина.
There was используется, если следующее за ним существительное — неисчисляемое (water, sugar, bread) или стоит в единственном числе, а there were — если существительное во множественном числе.
В вопросительных предложения слова конструкции меняются местами:
- Were there any carpets in the flat? — В квартире были ковры?
Также можно добавлять вопросительные слова how much / how many, what:
- How many carpets were there in the flat? — Сколько было ковров в квартире?
- What was there in the cupboard? — Что было в шкафу?
Was / were как вспомогательный глагол в Past Continuous
Past Continuous обозначает событие или процесс, которое длилось в определенный момент в прошлом. Для образования этого времени понадобятся was (для единственного числа) или were (для множественного числа) и причастие с окончанием -ing. Рассмотрим на примерах утвердительное, отрицательное и вопросительное предложения:
- You were cooking spaghetti at 5 o’clock yesterday. — Ты готовил спагетти вчера в 5 часов.
- You weren’t cooking spaghetti at 5 o’clock yesterday. — Ты не готовил спагетти вчера в 5 часов.
- Were you cooking spaghetti at 5 o’clock yesterday? — Ты готовил вчера спагетти в 5 часов?
Was / were и пассивный залог
Существует 2 вида залога — активный (active voice) и пассивный (passive voice). Различие между ними заключается в том, как происходит действие. В первом случае подлежащее выполняет действие:
- They visited the library. — Они посетили библиотеку.
Во втором случае — в пассивном залоге — действие осуществляется над подлежащим:
- The library was visited. — Библиотеку посетили.
Пассивная конструкция образуется так: was / were + причастие прошедшего времени (Participle II). Форма глагола to be зависит от лица и числа подлежащего:
- The pupils were asked to bring new exercise-books. — Учеников попросили принести новые тетради.
- I wasn’t invited to the party. — Меня не пригласили на вечеринку.
- When was the castle built? — Когда замок был построен?
Модальный глагол to be to в прошедшем времени
Модальный глагол to be to выражает обязанность или необходимость. На русский язык эта конструкция может переводиться как «должен», «обязан», «договорились». А форма was/were + to + Simple Infinitive говорит о том, что что-то должно было произойти, но мы не знаем, произошло ли на самом деле. Рассмотрим на примере:
- They were to prepare the documents. — Они должны были подготовить документы.
Также эта конструкция может выражать строгий запрет:
- Kate was not to go there. — Кейт не должна была туда идти.
Употребление was/were в условных предложениях
Прошедшая форма глагола to be используется во втором типе условных предложений (Second Conditional). Они описывают нереальные или воображаемые ситуации в настоящем или будущем времени. В условной части такого предложения (после if) ставится глагол в Past Simple, а во второй части, где указывается следствие, используются would и инфинитив смыслового глагола:
- If I were you, I would call her. — На твоем месте я бы ей позвонил.
- If Olga were not offended, she would visit us. — Если бы Ольга не была обижена, она бы пришла к нам.
Здесь важно отметить, что в условии глагол to be принимает только форму were, независимо от того, в каком числе и лице стоит подлежащее.
В конструкции «I wish…»
Грамматическая конструкция wish + were переводится как «жаль, что../» или «хотел бы../».
- I wish my company were more successful. — Я хотел бы, чтобы моя компания была более успешной.
- I wish I were 16 years old. — Жаль, что мне не 16 лет.
В этой конструкции всегда ставится форма were, даже если подлежащее представлено единственным числом.
С местоимениями each/none и неисчисляемыми существительными
Все существительные делятся на исчисляемые (countable) и неисчисляемые (uncountable). Различать их просто: к исчисляемым относятся объекты, которые можно посчитать (ручка — ручки, книга — книги, дерево — деревья), тогда как неисчисляемые существительные не поддаются счету (вода, мука, воздух).
С неисчисляемыми существительными используется was:
- The water was very warm. — Вода была очень теплой.
- Sugar was in the box. — Сахар был коробке.
Что касается местоимений each и none, с ними также употребляется форма was:
- Each of the participants was ready to read a report. — Каждый из участников был готов прочитать доклад.
- None of us was happy to hear that. — Никто из нас не был рад услышать это.
Важно: в предложениях с none не нужно ставить дополнительно частицу not после глагола, так как это местоимение уже обозначает отрицание.
Выбор верной прошедшей формы глагола to be зависит от конкретного предложения. В большинстве случаев глагол согласуется с подлежащим: для единственного числа употребляется was, для множественного — were.
What is the difference between was vs were?
The words “was” and “were” are past tense forms of the verb “to be,” a word English speakers use more often than they realize. Whenever we use the terms are, is, am, was, were, be being, or been–– we are using the verb ‘be’ (to be).
The verb ‘to be’ contains several forms because it’s an auxiliary verb, which means it assists or modifies another verb. Similar auxiliary verbs include do (did, does, doing) or have (had, has, having), and it’s common to see these verbs paired with ‘be,’ as well.
‘To be’ is also an irregular verb, so it doesn’t function the way other verbs do in the English Language. For instance, regular verbs contain past tense forms with the letter “d” or “-ed” at the end (e.g., answered, forced, hunted, etc.).
In the case of ‘to be,’ the irregular verb is broken down in the following eight tenses:
- Present tense: am, are, is.
- Simple past tense: was, were.
- Present continuous: am being, are being, is being.
- Present perfect: have been, has been.
- Future: will be.
- Future perfect: will have been.
- Past continuous: was being, were being, was being.
- Past perfect: had been.
What does ‘to be’ mean?
English speakers use the verb ‘to be’ to describe a variety of actions, but the overall meaning is to ‘exist’ or ‘occur’ as something in time and space. Let’s take a look at five general ways to define and write ‘to be’ in a sentence:
To be equal to something, the same, or to symbolize something. For example,
“Life is good.”
“If y is 20, let x be 16.”
To belong to a class or a category of something.
“That building is a local high school.”
“Learning is your job.”
“You are a student.”
To exist in reality, to live, or remain undisturbed.
“I was born.”
“I am alive.”
“Let me be.”
To occur or exist in a specific location.
“The coffee is on the table.”
“He is at the park.”
“They were in the car.”
“The event was on Monday.”
To say (informal).
“They were like, ‘you can’t do that.’”
“He was like, ‘no way!’”
Synonyms
Breathe, dwell, exist, happen, inhabit, live, occur, remain, reside, sit, stand, stay, subsist.
Antonyms
Cease, depart, die, discontinue, expire, halt, pass, perish, stop, succumb.
How to use was vs. were in a sentence?
To write was and were in a sentence correctly, we must use them for the simple past tense and pay attention to narrative mood, perspective, and noun count.
The simple past tense for was vs. were
The simple past tense is the only past tense form we use for were and was because “was” and “were” are the preterite forms of the verb ‘to be.’ There are two other past-tense verb forms, the present perfect and past perfect tenses, but they incorporate the verb’s past participle “been,” instead. For example,
Present perfect: have been, has been.
Past perfect: had been.
We use the simple past tense to describe past events in a historical manner. Sentences that use the simple past tense contain an adverb or adverb phrase that pertains to time (e.g., yesterday, on Monday, last month, etc.).
For the simple past tense, we use the verbs was and were in the following ways:
- I was …
- You were …
- She/he/it was …
- We were …
- They were …
The simple past tense also contains two forms in itself: the progressive tense and the continuous form. The progressive verb tense describes longer, ongoing actions that progress in some fashion before a shorter, interruptive activity. The continuous tense indicates how an action proceeded without interruption or is ongoing.
All progressive tenses use “-ing” at the end of a verb. In fact, this verb tense typically uses the verb ‘to be’ in front of another verb’s infinitive form with “-ing.” For example,
“They were sleeping.”
“He was talking.”
For the past continuous or progressive forms, we use the verbs was or were in the following manner:
- I was being …
- You were being …
- She/he/it was being …
- We were being …
- They were being …
Narrative perspectives: was vs. were
Do you recall how we used the past tense forms of “were” and “was” differently for I, she, we, or they pronouns? That’s because the verbs are affected by the narrative (i.e., the perspective of the storyteller).
English narrative perspectives:
- The first person (I, we): “I ran a mile.”
- The second person (you): “Did you want to talk about it?”
- The third person (She, he, it, they): “She doesn’t like emojis.”
The use of “was” and “were” depends on the narrative’s point of view. The first person perspective (I, we) uses “was,” while the second person perspective (you) uses “were.” The third-person perspective (she, he, it, they) only uses “were.”
Narrative mood: was vs. were
The verbs “were” and “was” are additionally affected by the narrative’s mood (i.e., indicative vs. subjunctive). The indicative mood conveys ‘what is’ or ‘is not,’ but the subjunctive mood expresses a hypothetical situation or fantasized reality.
Subjunctive phrases often include “if I were …” or “if I was …,” but this mood has different grammar rules than the indicative mood “I was …” or “you were …” For the subjunctive mood, avoid using “was” and only use “were” instead.
Subjunctive mood examples for was vs. were
Correct: “If I were a rich man.”
Incorrect: “If I was a rich man.”
Correct: “I wish I were taller.”
Incorrect: “I wish I was taller.”
Indicative mood examples for was vs. were
Correct: “He was at the store.”
Incorrect: “He were at the store.”
Correct: “They were great last night.”
Incorrect: “They was great last night.”
Correct: “I was like, ‘no way!”
Incorrect: “I were like, ‘no way!”
Singular and plural nouns: was vs. were
Verb forms also depend on the number of nouns that they act upon. In other words, how many nouns involve the act of “being”? If there is one noun, the verb is singular, but if there are more than two nouns, the verb is plural.
“Was” is a singular verb form and “were” is a plural verb form. This is why we exercise narrative rules for each verb form. “They” or “we” implies multiple nouns (were), while “I” or “you” conveys one noun (was).
Cheat sheet for remembering was vs. were
We know it seems as though there are a million rules for using was vs. were, but learning how to write the verb correctly becomes easier with practice. Using the grammar rules above, we can summarize the verb’s grammatical rules based on the indicative vs. subjunctive mood tenses:
Was vs. were for the indicative mood
Only use the verb was with the indicative mood and for the following verb forms:
- The first person singular past tense (I was).
- The third-person singular past tense (he was, she was, it was).
Use the verb were for:
- The second person singular past tense (you were).
- The second person plural past tense (I were, we were).
- The third person plural past tense (they were).
Simple past tense forms of was and were for the indicative mood:
- I/she/he/it was ….
- I/she/he/it was being ….
- You/we/they were …
- You/we/they were being …
Was vs. were for the subjunctive mood
For the subjunctive mood, use the verb were for:
- The first person singular subjunctive tense (I were).
- The second person singular subjunctive tense (you were).
- The third-person singular subjunctive tense (he were, she were, it were).
- The first person plural subjunctive tense (I were, we were).
- The second person plural subjunctive tense (you were).
- The third person plural subjunctive tense (they were).
Simple past tense forms of was and were for the subjunctive mood:
- If (pronoun) were …
- (Pronoun) wish (pronoun) were … (e.g., “I wish we were …”)
FAQ: Related to were vs was
If I use were or was, am I writing in passive voice?
The verbs ‘was’ or ‘were’ do not indicate passive voice by themselves, but we construct passive sentences by pairing a conjugation of ‘to be’ with a past participle of a different verb. For example,
‘To be’ + the past participle of transitive verbs:
“He was found.”
“The child is being found.”
‘To be’ + the present participle in progressive tenses:
“She is sleeping.”
“I have been sleeping.”
‘To be’ + the past participle of certain intransitive verbs (for archaic perfect tenses):
“He is risen.”
‘To be’ + the infinitive and ‘to’ to convey a future arrangement or obligation:
“I am to tend to the garden.”
“She was to become a great gardener.”
It’s worth noting that while most people believe the passive voice is a grammatical error, the passive voice isn’t technically incorrect. Most grammarians simply prefer the active voice because it emphasizes the sentence subject instead of the object that receives a verb.
What is the present perfect tense?
The present perfect tense connects the present to the past with an action that began in the past at an unspecified time. We can identify the present perfect tense through the use of “has been” or “have been.”
What is the past perfect tense?
The past perfect tense describes completed actions that occurred before a different, past event. We can identify past perfect tense through the use of “had been.”
Are verbs like was or were homophones?
A homophone is a set of words that sound alike but have different meanings and spellings. The verbs ‘was’ and ‘were’ are not homophones because we pronounce them differently, they are spelled separately, and they share the same verb and meaning.
Test Yourself!
Think you’re ready to use the verb ‘be’ like a pro? Challenge your grammar know-how with the following multiple-choice questions for was vs. were.
- Which verb tense is not a form of the verb ‘to be’?
a. Are
b. Was
c. Have
d. Being - True or false: the verb ‘was’ is the correct choice for the subjunctive mood?
a. True
b. False - True or false: The indicative mood changes the word choice for was vs. were?
a. True
b. False - Singular nouns correspond to which verb form of ‘to be’?
a. Was
b. Were
c. Been
d. Being - Past tenses of the verb ‘to be’ do not include ________?
a. Were
b. Was
c. Was being
d. None of the above
Answers
- D
- B
- A
- A
- D
Sources
- “Be.” Lexico, Oxford University Press, 2020.
- “Be.” The Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary, Merriam-Webster Inc., 2020.
- “Grammar Handbook: Regular and Irregular Verbs.” Center for Writing Studies, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 2013.
- “Passive Voice.” USC Rossier, University of Southern California, n.d.
- “To be.” Reverso Conjugation, Reverso-Softissimo, 2020.
- “What’s the Difference between progressive and continuous tenses?” Insights To English, TESOL International Association, 7 Aug 2018.
There are plenty of questions associated with the verb to be. “To be or not to be,” for one. On a less existential note, there’s the question of how to use to be in the grammatically correct way. I am, you are, he was, they were—the forms of the verb to be, among many other things, are messy in English.
You might find yourself puzzling out a sentence such as: If she was unhappy, she should have said so. Is this sentence correct? Or should If she was switch to the phrase If she were?
Was vs. were, what’s the difference?
Much of the confusion lies in when to use was versus were, which are the past tense forms of to be. The answer all depends on two factors: 1) is your verb using first, second, or third person? And, 2) is your verb in past indicative or past subjunctive tense? Past indicative is used for ordinary objective statements or questions, and past subjunctive is used for imaginary or hypothetical statements or questions.
Were is always correct in the past subjunctive:
- I were
- You were
- He/she/it were
- We were
- You were
- They were
If this looks a little odd, remember that these constructions are often accompanied by a word like if, as if, and though. You might say, “If I were a rich man …”
Don’t we all wish we were rich … so would you say “wish I was” or “wish I were”?
To conjugate to be in the past indicative, however, using was or were depends on the subject:
- I was
- You were
- He/she/it was
- We were
- You were
- They were
It’s possible to get mixed up even with this straight conjugation in mind. But there are some tips and tricks to remember to make sure you use the correct verb form every time.
When to use was
Was is a past tense indicative form of be, meaning “to exist or live,” and is used in the first person singular (I) and the third person singular (he/she/it).
You use the past indicative when you’re talking about reality and known facts. If you went to the store, for example, then you would say, “I was at the store” because it is something that definitely happened. The same is true if you’re talking about someone else in the third person (or if you make the choice to talk about yourself in the third person). You would say, “Sarah was at the store,” for example, or “She was at the store.”
Another way to use was is as an auxiliary verb with a singular subject in the past continuous tense. An auxiliary verb is used with another verb that follows it in the sentence to express different tenses, aspects, moods, etc., and the past continuous tense refers to something that was ongoing in the past.
If you were to modify the previous example (I was at the store) with an auxiliary verb, you would say, “I was searching for spices at the store.” Was is the auxiliary verb (or helping verb) used to talk about what you were doing in the past (searching).
Examples of was in a sentence
So to recap, if you’re talking about something real that happened in the past, use the past tense indicative: I was or he/she/it was. (Were is used with the other pronouns.) Here are some example sentences:
- I was sick last night.
- He had an amazing imagination when he was a child.
- We turned down the music because it was too loud.
When to use were
Whereas was is the singular past tense of to be, were is used for both the third person plural past tense (they and we) and the second person past tense (you).
In the past indicative, were acts similar to was. “They were at the store,” you could say, for example. It also acts similar as an auxiliary verb, as in “They were searching for spices at the store.”
Things get a little more complicated with were, though, and it’s all thanks to this thing called the subjunctive mood.
The subjunctive mood is the opposite of indicative, and it’s all about things that are unreal or conditional. When you’re talking about your hopes and dreams, you’re using the subjunctive mood. The same goes for talking about something you intend or want to do, as well as for things you know will never be true or are no longer true.
A telltale sign that you’re working with the subjunctive mood is the word if, because this suggests a hypothetical. “If I were to go shopping, I could search for spices,” for example. It doesn’t matter if the subject is singular or plural, or if it’s first, second, or third person. If you’re using the subjunctive mood, the grammatically correct past tense of to be is were.
Speech is always evolving, and the subjunctive mood is used far less extensively than it was in the past. And what’s more, much of the way we talk and write in everyday English isn’t what our old schoolteachers would wag the ruler at us as “grammatically correct.” But if you want to conform with those standards, use were when it comes to the past tense of to be.
Examples of were in a sentence
If you’re discussing things that are unreal or conditional, then use were: I were and he/she/it were. Here are some example sentences:
- If I were in better shape, I would run in the race.
- She took over the meeting as if she were the boss.
- His father talked to him as though he were a child.
When to use was vs. were
To sum it all up, always use was for the past indicative first and third person singular. That goes for whether it’s a simple verb or auxiliary. “I was ready to watch the Auburn Tigers win the game,” and “He was watching number two score the winning touchdown.”
Write smarter with our thesaurus-powered Grammar Coach™! Get spelling help, synonyms suggestions, grammar check and more! Sign up now!
For the past indicative second person and all plural forms, use were. “They were in the stadium,” and “You were standing the whole game.” Also use were for the hypothetical or fantastical subjunctive mood for both singular and plural forms, as in “If they were to bring back popcorn, I would eat it.”
There was vs. there were
Was and were are also used in some instances with the pronoun there. This pronoun introduces a sentence or clause in which the verb comes before its subject (or those instances where the verb has no complement). When the subject that follows is singular, use was: When I opened the fridge, I found there was no more milk left. When the subject that follows is plural, use were: When I opened the fridge, I found there were no more eggs left.
In the end, yes, you were technically correct when you noted that the class lyric “I wish I was a little bit taller” should have been “I wish I were a little bit taller.” But don’t fret if you get it technically wrong at times. Were may be formally correct, but because the subjunctive mood has largely fallen out of common use, was may slip into yours and others’ speech at times.
English can be difficult, especially when it comes to words that can be easily confused. A couple of examples would be who vs whom and further vs farther. Another combo that can get confusing is was vs were.
There are several reasons why you might be struggling to decide whether you should be using “was” or “were” in a sentence. The simplest of these is the conjugation of the singular and plural forms of the past tense of “to be.” While this can cause minor problems to those learning English as a second language as they study, first language English speakers usually have few problems with this. The most common cause of debate and confusion is the use of “were” instead of “was” in the subjunctive mood (We’ll explain that below if you aren’t sure what subjunctive mood is.). We’ll cover both past and subjunctive mood topics in this article, and you’ll soon see just how simple it all is.
Singular and Plural
As we’ve observed, this is the easiest of the choices you need to make, but it also gives rise to the problems that so many people have when they begin to use the subjunctive mood.
Singular: I was, he was, she was, it was – BUT you were. (Just to make things more fun!)
Plural: It’s always ‘were’, regardless of whether we’re talking about “they,” “we” or “you.” So far, so easy! But now we’ll examine how this relates to one of the most common errors in spoken or written English: the choice of “was” instead of “were” in the subjunctive mood.
If I were / was a rich man – the famous subjunctive mood
The subjunctive mood is used to describe or speculate on a hypothetical situation, and you’ll hear people using both ‘”was” and “were” in this context. But only one of these is correct. Whenever we’re talking about something that isn’t a reality at the moment, we discard “was” and choose “were” instead. It doesn’t matter whether we are referring to a single person or a group of people. As soon as we cross the border between reality and speculation, “were” is the only word to choose. For example
- I was rich and I owned a house at the seaside.
- If I were rich, I would have owned a house at the seaside.
- He was the captain of the team and he chose a different strategy.
- If he were captain of the team, he would have chosen a different strategy.
In each of the pairs of sentences above, the first one refers to something that actually happened in the past, and the word “was” is the correct choice. The second sentence is a wish or a speculation – it refers to an event that did not actually happen, and “were” is the correct choice.
- They were the winning team, so they celebrated their victory.
- If they were the winning team, they would celebrate their victory.
As we can see, the subjunctive mood doesn’t result in any change in word choice in this example. No matter how many people you are referring to, the subjunctive mood calls for the word “were.” If you’ve been prone to saying the incorrect “I wish I was,” “If he was” or “I wish she was” instead of the correct ‘I wish I were,” “If he were” or “I wish she were,” it will be easy to make the necessary adaptation and correct your grammar.
Look out for the subjunctive mood. As soon as something is a wish or a hypothetical (if) situation, you will always choose “were” over “was.”
It’s a common grammar mistake. In spoken as well as written English, you’ll find that just about everyone from plumbers to presidents is guilty of this mistake. Of course, when presidents make this error, those who know better will laugh at them, so if you’re hoping that what you say will be taken seriously, it’s worth learning when to use “were” instead of “was.” After all, once you understand the basic rules, it’s quite easy.
Speak English fluently using was and were
The post is about How to use was and were information but also try to cover the following subject:
– How to make WH-Questions?
– Basic English grammar
– Past Continuous Tense
Today we will learn the use of was and were. If you want to speak English, you have to learn the use of was and were very well. Then you can speak English fluently. Today I will teach you how to use them very easily. I hope after today it will never be wrong to use them again.
Was and were used in Past Tense. Or ‘was, were’ is used to explain past events.
Was – is used with I, he, she, it, John (any name)
Were –used with we, they, you, (Plural subject)
You – ‘Were’ always sits with ‘you’. Although ‘You’ is Singular Number.
In a word, they are called Be Verb. It is also called Helping Verb. Was were used as a helping verb. Sometimes they are used as Main Verb.
If ‘Was were’ is used in a sentence, then the sentence should be taken as Past Indefinite Tense. And if ‘ing‘ is added to the verb which means Was / were + Verb + ing then it will be Past Continuous Tense.
How to use was and were correctly?
S + Was/were + O
For example –
He was sick.
If I say –
He was not sick.
Using ‘not’ here makes this sentence a Negative Sentence. If you want to make a Negative Sentence then the sentence structure will be-
S + Was/were + not + O
This means you have to put ‘not’ after Was / were.
For example –
They were not happy.
Daily use Sentences with Was and were
- I was tired.
- I was wrong.
- He was alone.
- He was brave.
- It was night.
- I was at home.
- He was patient.
- I was a teacher.
- He was very happy.
- We were all tired.
- There were two cakes.
- All of us were silent.
- They were very excited.
- Forty people were present.
- There were ten eggs in all.
- We were very busy last week.
- All our efforts were in vain.
Questions with was and were
How to make Interrogative Sentence?
When we make an Interrogative Sentence, we will place the Be Verb before the subject and the Interrogative sign at the end.
Was/were + S + O + ?
For example –
Was I wrong?
Let’s see more examples –
- Was the movie good?
- Was the book interesting?
- Was he at home yesterday?
- Was there a lot of traffic?
- Were you busy yesterday?
- Were you out last night?
- Were you at home yesterday?
- Were you at school at that time?
- Were you playing cricket yesterday?
WH-Questions with was and were
If you have to use Wh-Word in a sentence, then the sentence structure will be like this:
Wh-Word + was/were + S + O + ?
For example –
- How was your day?
- When was she born?
- Where was John born?
- How was your summer?
- What was that noise?
- How was today’s game?
- How was your weekend?
- How was the math test?
- How was your afternoon?
- Who was the book written by?
- What was served at the party?
- When was the last time we met?
- What was it that you gave him?
- Where were you going?
- Why were you absent yesterday?
- What were you doing there?
- Why were you late this morning?
- Why were you absent from school yesterday?
Was and Were in Past Continuous Tense
Past continuous Tense is used when something was happening or was going on for a while in the past.
Sentence Structure: Subject is followed by was or were according to person and number and ‘ing’ is added at the end of the main verb.
Subject + was/were + main verb + ing + O
- He was standing.
- She was making tea.
- It was getting dark.
- He was cleaning his room.
- He was playing the piano.
- I was eating dinner then.
- He was listening to music.
- He was sitting on a bench.
- It was really interesting.
- He was reading a newspaper.
- The dog was digging a hole.
- He was standing at the door.
- They were lying on the grass.
- They were fighting on the street.
- You were talking in your sleep last night.
- They were watching television.
- Where were you going?
- Why were you late this morning?