We make use of the word ‘could’ to express ability or past possibility, whereas ‘would’ can be used to show willingness or when we imagine a situation.
…
Comparison Chart.
| Basis for Comparison | Could | Would |
|---|---|---|
| Examples | Maybe she could meet Piya when she go to Amsterdam. | I would meet you, but I was little busy. |
•
29 oct. 2019
Also What are conditional and define it with examples?
The definition of a conditional is a grammar term that means a sentence structure that expresses a particular situation or circumstance and its consequences. An example of a conditional is a sentence telling someone that you will be mad at them if they are late.
Subsequently, Where we use could and would? Could is used to say that an action or event is possible. Would is used to talk about a possible or imagined situation, and is often used when that possible situation is not going to happen.
What is the difference between could and would? Could expresses possibility, while would expresses certainty and intent. A good way to remember the differences between these two words is simply to bring each word back to its root verb. Could is the past tense of can. Would is the past tense of will.
Related Contents
- 1 Could in a sentence example?
- 2 What do you mean by conditional mean?
- 3 What are the two types of conditional and explain each?
- 4 What are conditionals in English grammar?
- 5 Would and could in a sentence?
- 6 Where we use would?
- 7 Could or would you please?
- 8 Could you please vs Would you please?
- 9 When we can use would?
- 10 Could VS would in questions?
- 11 When to use the word could in a sentence?
- 12 Could or can in a sentence?
- 13 When Could is used?
- 14 What means conditional statement?
- 15 What is conditional mean and variance?
- 16 What are the two types of conditionals?
- 17 What are the two types of conditional clauses?
- 18 What is a Type 2 conditional?
- 19 What are the 3 types of conditional?
- 20 What are the types of conditional statements?
- 21 What are conditional statements?
Could in a sentence example?
Could sentence example. I had let so much gas out of my balloon that I could not rise again, and in a few minutes the earth closed over my head. The doctor thought I could not live. I could not help it.
What do you mean by conditional mean?
1 : subject to, implying, or dependent upon a condition a conditional promise. 2 : expressing, containing, or implying a supposition the conditional clause if he speaks. 3a : true only for certain values of the variables or symbols involved conditional equations.
What are the two types of conditional and explain each?
5 Types of Conditional Sentences
| Conditional sentence type | When to use |
|---|---|
| Type 1 | A possible situation and the result |
| Type 2 | A hypothetical condition and its possible result |
| Type 3 | An impossible past situation and its result in the past |
| Mixed Conditionals | An impossible past situation and its result in the present |
•
26 août 2021
What are conditionals in English grammar?
What are conditionals in English grammar? Sometimes we call them ‘if clauses’. They describe the result of something that might happen (in the present or future) or might have happened but didn’t (in the past) . They are made using different English verb tenses.
Would and could in a sentence?
“Would” to Show Certainty
While “could” shows ability or possibility, “would” shows certainty in a past or hypothetical situation. If you think about “would” being the past tense of “will,” then it completely makes sense. For example: When I was younger, I would ride my bike home in 10 minutes.
Where we use would?
We use would as the past of will, to describe past beliefs about the future: I thought we would be late, so we would have to take the train.
Could or would you please?
But I would suppose that “would” is more polite, because it expresses the idea of probability, and of willingness, and of the desire that something be done, whereas “could” is more in the realm of ability (yes I can). And according to the American Heritage Dictionary, “would” is used to make a polite request.
Could you please vs Would you please?
But I would suppose that “would” is more polite, because it expresses the idea of probability, and of willingness, and of the desire that something be done, whereas “could” is more in the realm of ability (yes I can). And according to the American Heritage Dictionary, “would” is used to make a polite request.
When we can use would?
‘will’ and ‘would’
- We use will:
- would is the past tense form of will. …
- We use will to express beliefs about the present or future:
- We use would as the past of will, to describe past beliefs about the future:
- We use would as the past tense of will:
- We use I will or We will to make promises and offers:
Could VS would in questions?
When making general polite suggestions or asking a question, both could and can are possible (“Excuse me, can/could you tell me what time it is?”). … Would can also be used to ask polite questions (“Would you mind if I had another cup of tea?”), or to wish for something (“I wish she would write a book.”).
When to use the word could in a sentence?
In the sentence “We could have as many as ten people come to dinner tonight,” could is used to say that it is possible that ten people will come to the speaker’s home for dinner (“I think that it is possible we will have as many as ten people for dinner tonight.”).
Could or can in a sentence?
The modal verbs can and could represent the ability of a person or thing in doing something. However, there is a difference in their usage, as ‘can‘ is used in present situation, whereas we can use ‘could’ for talking about a past ability. Both are followed by a base form of the verb.
When Could is used?
“Could” is a modal verb used to express possibility or past ability as well as to make suggestions and requests. “Could” is also commonly used in conditional sentences as the conditional form of “can.” Examples: Extreme rain could cause the river to flood the city.
What means conditional statement?
Definition. A conditional statement is a statement that can be written in the form “If P then Q,” where P and Q are sentences. For this conditional statement, P is called the hypothesis and Q is called the conclusion. Intuitively, “If P then Q” means that Q must be true whenever P is true.
What is conditional mean and variance?
In probability theory and statistics, a conditional variance is the variance of a random variable given the value(s) of one or more other variables. Particularly in econometrics, the conditional variance is also known as the scedastic function or skedastic function.
What are the two types of conditionals?
Conditional
| Conditional sentence type | Usage | If clause verb tense |
|---|---|---|
| Zero | General truths | Simple present |
| Type 1 | A possible condition and its probable result | Simple present |
| Type 2 | A hypothetical condition and its probable result | Simple past |
| Type 3 | An unreal past condition and its probable result in the past | Past perfect |
What are the two types of conditional clauses?
The 4 Types of Conditionals. Conditional sentences have two clauses: a condition (if…) and a result. The verb tenses used in each clause depends on whether the speaker thinks the result is probable (real) or only exists in the imagination (unreal).
What is a Type 2 conditional?
The type 2 conditional refers to an unlikely or hypothetical condition and its probable result. … In type 2 conditional sentences, the time is now or any time and the situation is hypothetical.
What are the 3 types of conditional?
Conditional
| Conditional sentence type | Usage | If clause verb tense |
|---|---|---|
| Zero | General truths | Simple present |
| Type 1 | A possible condition and its probable result | Simple present |
| Type 2 | A hypothetical condition and its probable result | Simple past |
| Type 3 | An unreal past condition and its probable result in the past | Past perfect |
What are the types of conditional statements?
Conditional Statements : if, else, switch
- If statement.
- If-Else statement.
- Nested If-else statement.
- If-Else If ladder.
- Switch statement.
What are conditional statements?
Conditional Statements
Use if to specify a block of code to be executed, if a specified condition is true. Use else to specify a block of code to be executed, if the same condition is false. Use else if to specify a new condition to test, if the first condition is false.
Asked by: Mr. Roderick Pouros DVM
Score: 4.4/5
(36 votes)
Could sentence example. I had let so much gas out of my balloon that I could not rise again, and in a few minutes the earth closed over my head. The doctor thought I could not live. I could not help it.
Could used in a sentence?
In the sentence «We could have as many as ten people come to dinner tonight,» could is used to say that it is possible that ten people will come to the speaker’s home for dinner («I think that it is possible we will have as many as ten people for dinner tonight.»).
Where could is used?
Could: “Could” is used to express possibility. Something that could happen is not necessarily something that must happen. Could does not express desire or opinion. It is simply used to state one or more things that are possible (even if they are unlikely) or were possible in the past (even if they didn’t happen).
Could meaning and examples?
The definition of could is often used in the place of «can» to show a little doubt. An example of could is someone asking if they can help someone. An example of could is saying that something is able to happen if someone does something. Used to indicate ability or permission in the past.
How do you use the word could?
Could, would, and should are all used to talk about possible events or situations, but each one tells us something different. Could is used to say that an action or event is possible. Would is used to talk about a possible or imagined situation, and is often used when that possible situation is not going to happen.
21 related questions found
Can and could sentence examples?
Examples: She can speak Italian very well. I could swim, but I couldn’t ride a bike when I was nine years old. You can play with Amy after you do your homework.
Could you VS would you?
‘Could You’ is considered to be an informal way of asking something, contrary, ‘Would You’ is a formal way of requesting someone to do something.
Can be or could be?
The modal verbs can and could represent the ability of a person or thing in doing something. However, there is a difference in their usage, as ‘can‘ is used in present situation, whereas we can use ‘could’ for talking about a past ability. Both are followed by a base form of the verb.
Is could present tense?
Could is used for past and future instances, or sometimes in the present tense (although in the present tense it is normally describing a possibility or is part of a question).
Could in a sentence easy?
Could sentence example. I had let so much gas out of my balloon that I could not rise again, and in a few minutes the earth closed over my head. The doctor thought I could not live. I could not help it.
Could is used for future?
We often use could to express possibility in the present and the future.
Can I or could I?
«Can I» is best for semi-formal situations. «Could I» is best for semi-formal situations.
Could it be more polite than can?
‘Can’ is used when there is nothing that would stop the thing from happening. When asking someone to do something, either word can be used, but ‘could’ is considered to be more polite.
Why we use would?
Would is an auxiliary verb — a modal auxiliary verb. We use would mainly to: talk about the past. talk about the future in the past.
What is would grammar?
‘Would’ has quite a lot of different uses. It’s often a kind of past tense version of ‘will’. Remember that both ‘had’ and ‘would’ can be shorted to ‘d. But only ‘would’ is followed by an infinitive without ‘to’. ‘Had’ is followed by a past participle or by ‘to + infinitive’.
What does could be mean?
adjective. attributive. Able to be or become; possible.
Is CAN past or present tense?
The verb “can” in its present form is perfect to ask for permission or to give permission to someone. Also, its negative form, can’t, can be used to refuse permission. Its past form, could, can be used to ask for permission in a more polite way.
Can or could you please?
1 Answer. If taken literally, «Can you» is equivalent to asking the person if they’re capable of doing something. «Could you», on the other hand, implies that the action can be completed under some circumstances by the person. The usage of can you is idiomatic, and hence, is more popular used phrase of the two.
Could be sentences in English?
«Could» is a modal verb used to express possibility or past ability as well as to make suggestions and requests.
…
Using «Could» in Present, Past, and Future
- John could be the one who stole the money.
- John could have been the one who stole the money.
- John could go to jail for stealing the money.
Can could be able to grammar?
We sometimes use be able to instead of «can» or «could» for ability. Be able to is possible in all tenses — but «can» is possible only in the present and «could» is possible only in the past for ability. … So we use be able to when we want to use other tenses or the infinitive.
Is could you please rude?
-> They both are impolite. They both sound like a command/order.
Is could respectful?
4 Answers. So yeah, politeness isn’t the issue at all. This is probably why, even if you’re not aware of the nuanced meaning, could is more polite. It’s not insulting the target by questioning their ability to perform something.
Can you tell me or could you tell me?
2 Answers. “Could you” is more polite than “can you”. Regarding the rest of the wording, something about “tell me my next work” rings wrong to my ears. Probably, because you don’t “tell a work”.
Examples of how to use the word “could” in a sentence. How to connect “could” with other words to make correct English sentences.
could (modal, v): used as a more polite form of “can” when asking for permission; past simple of “can”, used to talk about what someone or something was able or allowed to do
Use “could” in a sentence
| You could have called me for help. |
| She could swim. |
| Could I use your knife, please?
Back to “3000 Most Common Words in English” |
0 Shares

Глагол could — это форма прошедшего времени глагола can, его мы также рассмотрим в этой статье.
Содержание:
- Таблица: модальный глагол Can в утвердительной, отрицательной, вопросительной форме.
- Употребление модального глагола Can.
- Оборот could have + Past Participle.
- Модальный глагол Can и оборот to be able to.
Как и другие модальные глаголы, глагол can употребляется не по общим правилам:
- В утвердительной и отрицательной форме между can и глаголом не ставится частица to. То есть нельзя сказать: I can to swim — Я могу плавать, нужно: I can swim.
- Глагол can не образует форму будущего времени с помощью вспомогательного глагола will. Нельзя сказать: I will can help you tomorrow — Я смогу помочь тебе завтра. Как выразить возможность в будущем, читайте ниже.
- В форме третьего лица единственного числа глагол can не изменяется. Мы говорим: He swims, She sings, но He can swim, She can sing.
- По особой схеме строятся вопрос и утверждение (см. таблицу).
| Схема | Пример | |
| Утверждение | Подлежащее + can/could + глагол | I can/could fly |
| Отрицание | Подлежащее + can’t/couldn’t + глагол | I can’t/couldn’t fly |
| Вопрос | Can/could + подлежащее + глагол | Can/could I fly? |
В отрицательной форме можно использовать как cannot / could not, так и can’t / couldn’t, но в разговорной речи практически всегда используется сокращенная форма. Форму can’t, кстати, британцы и американцы произносят по разному:
- Британский вариант: [kɑːnt]
- Американский вариант: [kænt]
Употребление модального глагола Can (Could)
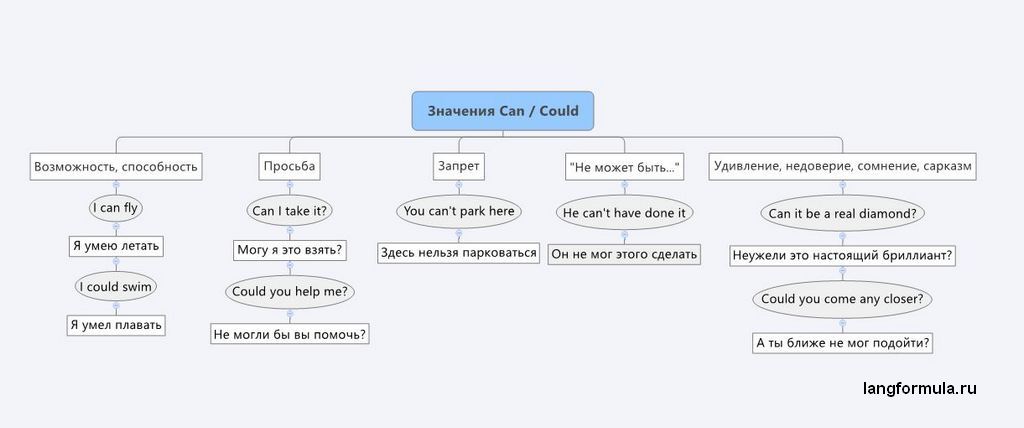
Особенность модальных глаголов в том, что с их помощью можно выразить много разных оттенков мысли, отношения к действию. Сводка значение глаголов can/could представлена на изображении. Более подробно читайте ниже.
Модальный глагол can/could используется:
1. Для выражения физической (умственной) возможности, способности что-то сделать
Can используется с глаголом в неопределенной форме (инфинитивом) без частицы to. Could имеет то же самое значение, но по отношению к прошлому.
Примеры с глаголом can:
I can hold my breath for two minutes. — Я могу задержать дыхание на две минуты.
My sister can make pancakes. — Моя сестра умеет печь блинчики.
Joe can swim but he can’t ride a bike. — Джо умеет плавать, но не умеет ездить на велосипеде.
It can’t be. — Этого не может быть.
Can you walk on a wire? — Вы умеете ходить по канату?
Can I trust you? — Я могу тебе доверять?
Примеры с глаголом could:
She could sing like an angel when she was younger. — Она могла петь как ангел, когда была младше.
My neighbors couldn’t find their dog. — Мои соседи не могли найти свою собаку.
Could you swim when you were a teenager? — Ты умел плавать, когда был подростком?
Примечание: глагол CAN в будущем времени
Обратите внимание, что can, как и «может», «можете» и др. в русском языке, может относиться не только к настоящему, но и к будущему времени:
You can solve your problems later. — Ты можешь решить свои проблемы позже.
We can watch this movie next time. — Мы можем посмотреть этот фильм в следующий раз.
Также вместо глагола can для обозначения возможности в будущем можно использоваться оборот will be able to, подробнее об этом читайте ниже.
2. Для выражения просьбы
Используются can и could в вопросительной форме. Просьба с could звучит несколько вежливее, она используется в предложениях, обращенных к другому лицу (то есть не с местоимением I).
Can I take your pen? — Могу я взять вашу ручку?
Can I suggest you another option? — Могу я предложить вам другой вариант?
Can you give me a hand? — Не можешь ли ты мне помочь? (to give a hand — букв.: дать руку, перен.: помочь)
Could you tell me where the library is? — Не подскажете ли вы, где находится библиотека?
Could you do me a favour, please? — Не могли бы вы сделать мне одолжение?
3. Для выражения запрета
Глагол can’t часто употребляется, чтобы выразить запрет, то есть сказать не «вы не можете», а «вам нельзя».
You can’t smoke here, there are kids playing. — Здесь нельзя курить, здесь играют дети.
You can’t park here. It’s a private territory. — Вам нельзя здесь парковаться, это частная территория.
4. Для выражения удивления, сомнения, недоверия
Здесь есть много нюансов, многое зависит от контекста.
Сомнение с оттенком недоверия чаще выражается в отрицательных предложениях с глаголом в неопределенной форме:
He can’t swim across Lake Tahoe. — Да не может он переплыть озеро Тахо (недоверие, сомнение).
Удивление с оттенком сомнения, недоверия обычно выражено в вопросительных предложения с глаголом в неопределенной форме. В переводе часто используют слово «неужели», чтобы был понятнее смысл.
Can this unicorn be real? — Неужели этот единорог настоящий?
Если в таком же вопросе использовать could смысл немного изменится. Получится что-то вроде:
Could this unicorn be real? — Разве мог бы этот единорог быть настоящим?
Часто таки предложения с can/could используются иронически, с сарказмом, например:
Could you buy more milk? — А ты еще больше молока не мог купить?
Could you wake up any later? — А ты еще позже не мог проснуться?
Но в этом случае большое значение имеет интонация и контекст. Один из героев сериала «Друзья», Чендлер, подобные фразочки с «Could it be» так часто использовал, что его даже иногда передразнивали. К сожалению, эта особенность речи Чендлера почти не отобразилась в переводе.
5. Для выражения сомнения в случившемся
То есть я не верю в то, что нечто произошло. Схема: cannot + have + Past Participle (утвердительная или вопросительная форма).
Оборот обычно переводят с помощью «не может быть» или другого подходящего выражения.
He is my best friend, he cannot have betrayed me. — Он мой друг, не может быть, чтобы он меня предал.
Billy doesn’t have much money. He can’t have bought this car. — У Билли не много денег. Не мог он эту машину купить.
Can she have forgotten to pick up the kids from house? — Неужели она могла забыть забрать детей из дома?
Читайте также: «Времена в английском языке«
Оборот COULD HAVE + Past Participle
Отдельно следует рассмотреть оборот could have + Past Participle (причастие прошедшего времени, третья форма глагола). Он может значить:
1. Действие, которое кто-то мог сделать, но не сделал
She could have married him but she didn’t want to. — Она могла выйти за него замуж, но не захотела.
They could have bought a house here 20 years ago but chose not to. — Они могли купить здесь дом 20 лет назад, но решили не делать этого.
Часто при этом присутствует оттенок упрека.
You could have helped me instead of just sitting there. — Ты мог бы помочь мне вместо того, чтобы сидеть здесь.
I could have done more to help you. Sorry. — Я мог бы сделать больше, чтобы помочь тебе. Извини.
2. Предположение, догадка о чем-то, произошедшем в прошлом
В этом случае, с несколько иным значением, могут быть использованы may have или might have, см. «Глагол May (Might)«.
Simon could have told her the truth. — Возможно, Саймон рассказал ей правду.
They could have overheard what we said. — Они могли услышать то, что мы сказали.
В отрицании и вопросе можно использовать can have + Past Participle, тогда получится оборот типа «Неужели…?» или «Не может быть…», рассмотренный выше (п. 5 «Для выражения сомнения в случившемся»)
Can she have forgotten about our meeting? — Разве могла она забыть о нашей встрече?
He can’t have seen us. — Не может быть, чтобы он нас видел.
3. Предположение о чем-то, что в реальности не произошло
Этот случай относится к одному из типов условных предложений, подробнее о них читайте в этой статье.
I could have done well in my exam if I had worked harder. — Я мог бы справиться лучше с экзаменом, если бы лучше готовился.
Модальный глагол CAN и оборот TO BE ABLE TO
Глагол can в значении «быть способным сделать что-то» может быть заменен синонимичным оборотом to be able to + глагол (быть способным сделать что-то). Но между этими двумя способами выражения возможности есть разница.
Can / to be able to в будущем времени
Обычно говорят, что оборот to be able to удобно применять, когда нужно сказать о возможности сделать что-то в будущем, потому что у глагола can нет формы будущего времени (нельзя сказать will can).
Но тут важно помнить такой нюанс.
Сам по себе глагол can может относиться к будущему. Например:
You can rest later. Now we have to work. — Ты сможешь (можешь) отдохнуть позже. Сейчас мы должны работать.
We can read this book tomorrow, let’s play videogames. — Мы сможем (можем) почитать эту книгу завтра, давай поиграем в видеоигры.
В будущем времени оборот to be able to используется, когда мы говорим о возможности, способности, навыке, которого нет сейчас, но он появится в будущем. Глагол can НЕ может использоваться для выражения возможности, способности, которая появится только в будущем.
Правильно: I will be able to walk properly after the surgery. — Я смогу нормально ходить после операции.
Неправильно: I can walk properly after the surgery.
Еще пример:
Правильно: When I complete this training course, I will be able to work as a sailor. — Когда я закончу эти курсы, я смогу работать матросом.
Неправильно: When I complete this training course, I can work as a sailor.
Оба варианта, can или to be able to, можно использовать, говоря о решениях или договоренностях, относящихся к будущему:
The doctor can / will be able to see you later today. — Доктор сможет принять вас сегодня попозже.
I can / will be able to help you with your homework later. — Я смогу помочь тебе с домашним заданием позже.
I can / will be able to give you a lift home tonight. — Я смогу подвезти тебя домой сегодня вечером.[/su_list]
Can / to be able to в настоящем времени
В настоящем времени to be able to звучит более формально, даже странновато. Все равно, что по-русски сказать не «я могу играть на гитаре», а «я способен играть на гитаре».
I can play a guitar. — Я могу играть на гитаре.
I am able to play a guitar. — Я способен играть на гитаре.
Michelle can bake delicious cakes. — Мишель умеет печь вкусные пироги.
Michelle is able to bake delicious cakes. — Мишель способна печь вкусные пироги.
Варианты с can используются намного чаще.
Can / to be able to в прошедшем времени
Когда речь идет о способности или возможности, существовавшей в прошлом, можно использовать оба варианта:
When I was younger, I could remember everything so well. — Когда я был моложе, я мог помнить все лучше.
When I was younger, I was able to remember everything so well. — Когда я был моложе, я мог помнить все лучше.
Обратите внимание, что в прошедшем времени could обычно значит (в утвердительных предложениях) способность делать что-то вообще и не используется, когда говорится о каком-то разовом действии в определенный момент. Другими словами, если вы хотите сказать «смог» в значении «умудрился», «получилось», а не в значении «был способен», то используйте to be able to.
- Правильно: We were able to visit Mary on Monday, because she wasn’t busy. — Мы смогли (сумели, у нас получилось) навестить Мэри в понедельник, потому что она не была занята.
- Неправильно: We could visit Mary on Monday, because she wasn’t busy.
«We could visit Mary» значит «Мы могли посетить Мэри», то есть у нас была возможность. «We were able to visit Mary» значит «Мы смогли (сумели, умудрились и проч.) посетить Мэри».
В отрицательных предложениях как couldn’t, так и wasn’t/weren’t able to могут использоваться и для длительных действий, и для разовых.
I couldn’t / wasn’t able to finish all my homework yesterday. — Я не мог закончить домашнюю работу вчера.
I couldn’t / wasn’t able to see the band at all from where I was standing. — Мне совсем не было видно (не мог видеть) музыкантов с того места, где я стоял.
I couldn’t / wasn’t able to drive when I was younger. — Я не умел водить машину, когда был моложе.
Здравствуйте! Меня зовут Сергей Ним, я автор этого сайта, а также книг, курсов, видеоуроков по английскому языку.
Подпишитесь на мой Телеграм-канал, чтобы узнавать о новых видео, материалах по английскому языку.
У меня также есть канал на YouTube, где я регулярно публикую свои видео.
Modal verb can
›Grammar
What is modality and why is it needed at all when learning English?
At their core, modal verbs are not ordinary actions like run (run) or look (look), they allow you to make different shades of these very actions, for example, I must run (I must run), I can run (I can run) or I have to run (I have to run).
The difference in meanings is obvious, which is why so much attention is paid to modal verbs in English.
But in this article we will talk just about the modal verb can. It is found most often and it is it that schoolchildren begin to study it already in elementary school. This refers to the simplest sentences like “I can swim”, “I can count to 10” and so on. However, can has its own peculiarities. Let’s figure it out.
The modal verb can in the affirmative in the present tense
In affirmative sentences, you can very simply express your thought, you just have to remember about the structure of the sentence, namely: in order to say that you know how to do something, it is enough to use can with any action. Moreover, after can we use only the verb WITHOUT the TO particle, that is, the so-called bare infinitive or, in other words, “bare infinitive”. That is, for affirmative sentences, the small formula is applicable can+Vwhere V is the action.
For example, the
- I can ride a bike really well.
- Masha and her friends can sing popular songs so professionally (Masha and her friends can sing popular songs professionally).
It is important to note that the modal verb can does not change depending on the number and person of the noun and pronoun, that is, we should not add any forms or endings either to it or to the action itself. Actions, in turn, refer to either the present or the immediate future.
For example, the
- She can write interesting texts, she is a cool copywriter (She can write interesting texts, she is a cool copywriter).
- Maria can make professional sketches, she is an artist (Maria can create professional sketches, she is an artist).
The modal verb can in negative present tense
As for negatives, here we just have to add a negative NOT particle to our modal verb, and schematically it will look like this: can + not + v, where V is a semantic verb.
Moreover, the full negative form of two words is written into one, that is, can not, in colloquial speech, we, as in other cases, can use an abbreviation that looks like this can’t.
Moreover, it is worth paying attention to the pronunciation: cannot read [‘kænɔt], can’t as [kɔ: nt].
For example, the
- People can’t fly birds, but they use special equipment to do it (People can’t fly like birds, but they use special equipment to do it).
- My sister cannot drive, that’s why she is studying at the driver training center to have a driving license.
The modal verb can in the interrogative form in the present tense
Speaking about interrogative sentences, it is worth remembering that the modal verb can does not require any special auxiliary verbs, it itself performs their role, therefore, in order to ask the question of whether someone knows how to do something, it is worth putting can at the beginning of the sentence.
For example, the
- Can I help you with your baggage? (Can I help you with your luggage?)
- Can you wake me up at 6 am? My train leaves the station at 7 am (Can you wake me up at 6 am? My train leaves the station at 7 am).
To create a small emotional shade in colloquial speech, you can use the question-negative form, that is, you need to put « can’t » at the beginning of the sentence, in which case, in Russian, these sentences will begin with the words «Really?»
For example, the
- Can’t you call me back in 3 minutes? I’m really busy now and I can’t talk with you, sorry. (Can’t you call back in 3 minutes? I’m very busy right now and can’t talk to you, sorry).
- Can’t you bake gingerbread men? Hmm, I must have eaten them made by you. (Don’t you know how to bake gingerbread men? Hmm .. I already ate them in your performance).
Modal verb can in the past tense
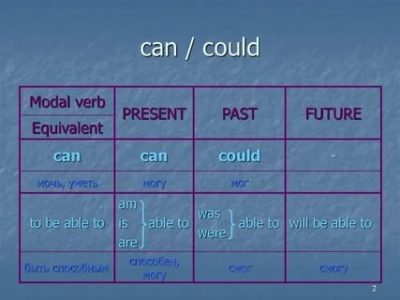
In general, based on the official grammatical data, in English there are 3 forms of the modal verb can:
Present tensePresent Simple
Source: https://englishfun.ru/grammatika/modalnyj-glagol-can
The verb can in English: its meanings, forms and examples of use
27.06.2019
The modal verb can and its past form could is by far the most commonly used modal. It is found in literature, and in the media, and in colloquial speech.
If you compare the frequency of use of can and could, it becomes clear that can is much more common.
This is due to the fact that in colloquial speech and literature, events occur mainly in the present tense, which means that can will be used in the meaning of physical ability. Let’s consider the grammatical features of these modal verbs and the peculiarities of their use.
What verbs are called modal?
Unlike ordinary verbs of the English language, modal verbs do not denote any processes or states, but only indicate the attitude of the actor to the action itself. For this reason, they are not used independently, but are always part of a predicate composed of verbs. For example: I can write it in a song (I can write / describe it in a song).
There are relatively few words of this kind in the English language. The most common of them are the modal verbs can (could), may (might), must.
Unique properties of modal verbs
- Words of this type belong to defective verbs (insufficient) because they do not have all the properties of ordinary verbs. For example, of the three above, modal verbs have an individual form in the past tense: can (could), may (might). Most other similar terms are devoid of such properties as the time of the future, perfect forms and a passive voice, an extended form (for example: need, ought to and dare, must). In most cases, the corresponding equivalent words are used instead.
- Modal verbs do not have impersonal forms (infinitive, gerund and participle).
- Modal words never act as an independent member of a sentence — only together with another verb in the infinitive form, but without the usual to (except for need to, ought to). For example: I believe I can fly, but: I need to feel loved.
- Unlike other verbs, which in Present Simple (present tense) in the III person singular get the ending -s, modals do not have this feature. For example: She can read very well, but: My sister reads tales.
Rules for modal verbs Can, Could
Dog translated into Russian as «to be able, to be able, to have the ability to do something.» This verb fulfills all 3 conditions of modal verbs, with the exception of one: it changes in tenses, namely, it has the form of the past tense — Could.
The American economy emerged from the crisis thanks to the Second World War. Front-line needs spurred industrialization, the country even faced a shortage of labor resources.
Wartime advertising campaigns urged people to be thrifty, to provide each other with all possible help.
Many women at this time also began to work at the machine: the slogan on one of the most famous posters of this period sounded «We can do it!» — «We can do this!» (1942).
This verb has 2 main uses.
- In the meaning of «to be able, to be able, to have the physical ability to do something.»
- Terry can swim. — Terry can swim.
- Can Terry swim? — Yes, he can./ No, he can’t. — Terry can swim,
- Terry could swim when he was a child. — Terry knew how to swim as a child.
- Could Terry swim when he was a child? — Yes, he could./ No, he couldn’t. — Did Terry know how to swim as a child?
- To ask permission in an interrogative form + tail please. Although you can not use this ponytail.
- Can I open the window, please? — Yes, you can./ No, you can’t. — May I open the window?
- Could I open the window, please? — Yes, you could./ No, you couldn’t. — May I open the window?
- In this case, the difference in value or time between can и Could no. Just Could Is a more polite form from can .
How to build a sentence with can (could)
In the table, we will clearly show how to use can in different types of sentences.
Can I help you. — I can help you? Could they ride a bike. — Did they know how to ride a bike?
Let’s take a look at a few of the uses of can.
- Can (could) is always between subject and predicate.
- To ask questions, we’ll just move can and could to the first place, nothing else needs to be added.
- In negation, the particle not joins can (could) to form cannot (could not). In colloquial speech, we usually abbreviate to can’t (couldn’t).
Using can / could in different situations
As mentioned above, can, as a general rule, denotes a physical or mental ability to do something. That is, this is what a person can do based on their own strengths and skills. This rule is best illustrated by the cases for the designation of physical ability:
- I can swim well, don’t be afraid — I can swim, don’t worry.
The second case is a general possibility or likelihood, something that is easy to guess from the available facts.
- She can be there, it’s quite her style — to vanish in some hidden nook for a couple of days — She can be there, it’s like her — disappear for a couple of days and sit in some secluded corner.
The third is not a concrete but a theoretical possibility. Sentences of this type are familiar to everyone from the school curriculum:
- You can see a lot of pictures in the museum — You can see a lot of pictures in the museum.
Often can is used in asking questions. By the way, in denials that mean refusal, only can is used, which can be seen from the following example:
- Can I come in? — No, you can’t, I am too busy. — May I come in? — No, you can’t, I’m very busy.
Can has an equivalent, may. But even to a question that begins with may, the answer will still be can’t. This question is more formal and polite than the can option.
- May I take this cake? — No, you can’t. It’s for guests. — Can I have a cake? — No, you can’t, this is for guests.
Could, unlike can, is used either as a more polite option or to express past action. Could + have + V3 is used to denote a reproach:
- Look what you did! You could have been more careful! — Look what you’ve done! You could be more careful!
Examples of using the modal verb can
The modal verb can corresponds to the Russian to be able, to be able, to be able to be used in appropriate cases:
- I can write and I can read. (I can write and I can read.)
- I can ski but I can’t skate. (I can (can) ski, but I cannot (cannot) skate.)
- I can’t tell you that. (I can’t tell you this.)
- I can’t do it anymore. (I cannot (cannot) do this anymore.)
Source: https://tutorblog.ru/drugoe/glagol-can-v-anglijskom-yazyke-ego-znacheniya-formy-i-primery-upotrebleniya.html
When is can. can and could — rules of use
Modal verb can (I can) and its shape Could (could) is the most commonly used modal verb in English. We use it to show that we can, are able, capable of doing something. In this article, we will get acquainted with all the features of the modal verb. can (Could).
The first thing to remember is after can or Could another verb must go. After all by itself can does not inform about the action, but only shows our attitude towards it: «I can do some action.» And after that «can I» must be added «can I do what?»: can dance (I can dance) can sing (I can sing) etc.
And the second thing to remember, after can we do not put to: can speak English… We are used to the fact that two verbs in English should be related to each other using to: decide to drink coffee (decide to have a coffee) or offer to go for a walk (suggest going for a walk). But modal can works without to.
We noted that this modal verb has two forms: can и Could… We use these forms with any subject, both singular and plural.
My friend can speak Japanese. — My friend can speak Japanese.
My friends can dance salsa. — My friends can dance salsa.
What’s the difference between can и Could? Dog used when someone is currently able to do something, and Could — when someone knew how to do something in the past, now, most likely, they no longer know how.
He can swim. — He knows how to swim.
He Could swim. — He was able to swim.
How to build a sentence with can (could)
In the table we will clearly show how to use can in different types of sentences.
Approval SubjectDog/CouldAction Example Negation
| IYouHeSheItWeThey | cancould | verb | I can help you… — I can help you.They could ride a bike… “They knew how to ride a bike. |
| IYouHeSheItWeThey | can not (can’t)could not (couldn’t) | verb | I cannot help you… — I can not help you.They couldn’t ride a bike… “They didn’t know how to ride a bike. |
And in the question, as expected, the word order will be slightly different.
QuestionDog/CouldSubject Action Example
| Can Sould | Iyouhesheitwethey | verb | Can I help you? — I can help you?Could they ride a bike? — Did they know how to ride a bike? |
Let’s dwell on a few features of use can:
- Dog (Could) is always between the subject and the predicate.
- To ask questions, we will simply postpone can и Could in the first place, nothing else needs to be added.
- In negation, the particle Note joins can (Could), forming the form can not (could not). In colloquial speech, we usually can not reduce to can’t (couldn’t) By the way can not — this is the only modal that merges with the particle Note when writing. Do you know how to pronounce correctly can’t: /kɑːnt/ or /kænt/? There is a British pronunciation — / /. And teacher Ronnie will teach you the American pronunciation in his video.
What does the modal verb can (could) mean?
The easiest way to understand the meaning can (Could) by examples. We express with can:
- The mental or physical ability to do something.
In this case, can (Could) is usually translated as «to be able», «to be able».
I can’t speak to you now but I can call you in the evening. — I can’t talk to you now, but I can call you tonight.
He could speak French. — He could speak French.
Can you drive a car? — Can you drive a car?
- Generally accepted statements
- Permission, request, prohibition.
There are several patterns here: a request is usually conveyed through a question, permission through an assertion, and a prohibition through denial. If we see a request or permission in a proposal, then we translate can the verb «to be able», the prohibition is most often translated by the word «no».
— Can I take your car for the weekend? — Can I take your car for the weekend? (request) — Yes, you can. — Yes you can. (permission)
— But you can’t exceed the speed limit. — But you can’t exceed the speed. (ban)
We use canwhen we want to show that some statement is correct in most cases. Here we translate can how to «be able».
The vacuum can frighten your cat. — The vacuum cleaner can scare your cat. (as a rule, cats are afraid of vacuum cleaners, but not all)
In New York it can be difficult to rent an apartment. — It can be difficult to rent an apartment in New York.
Flowers can grow faster if they get a lot of sunshine. — Flowers can grow faster if they receive a lot of sunlight.
It should be noted that we are not using the form Could to express this value.
We can express a request with can и Could… Both options are often used in speech, only such requests differ in the degree of politeness. Let’s take a look at some examples:
Can you tell me where the nearest bus station is? — Can you tell me where the nearest bus stop is? (such treatment is more typical if you communicate with a person of your same age)
Could you tell me where the nearest bus stop is? — Could you tell me where the nearest bus stop is? (this is a more polite question, more often the British will use this option in order to be as polite and courteous as possible in a conversation)
With help can we can not only ask permission, but also propose something ourselves. For this we use a question form.
Can I offer you a cup of tea? — May I offer you a cup of tea?
Can I help you choose a dress for the party? — Can I help you choose a dress for the party?
Watch an interesting video from the teacher Alex, in which he, to the already known to us can и Could, added a verb may.
- And you can also learn about the features of the modal verb may in the article «».
This function also has its own patterns: doubt and distrust are usually found in negative sentences, and surprise — in interrogative ones. The verb is translated can (Could) in such cases, the words «really», «cannot be», «hardly», «do not believe», «possibly», «probably».
Can these shoes cost so much money? — Do these shoes really cost that much? (astonishment)
He can’t work all day round. — It can’t be that he works around the clock. (mistrust)
Do you know that Could Is the form of the past tense can… But if we want to express doubt in the past, then we use the form can’t have.
He can’t have fallen asleep at the meeting. — It cannot be that he fell asleep during the meeting.
They can’t have missed the last bus. “I can’t believe they missed the last bus.
If someone violated the prohibition or did not follow the advice, then you can reproach him for this using the same verb can… There is, however, one peculiarity: such proposals are constructed in the form of a negative question.
Can’t you just stop telling silly jokes to the guests? — Can you just stop telling stupid jokes to the guests?
Can’t you get along with her friends? — Can’t you communicate normally with her friends?
Expressions with the verb can (could)
Dog (Could) occurs in some well-established expressions. Here are some of the most common ones:
- Сan’t (couldn’t) but do something — there was nothing left but how.
I couldn’t but agree with him. — I had no choice but to agree with him.
- Couldn’t help doing something — could not resist to; could not help but.
I couldn’t help laughing. — I could not help laughing.
- Сan’t stand something / somebody — I hate something / someone.
I can’t stand him. — I can’t stand him.
To make sure the modal verb can (Could) you remember well, take the test and keep our handy plate for yourself.
(* .pdf, 259 Kb)
Test
Using the modal verb can (could)
Today we will start exploring the category of modality. It includes verbs that are not actions, but allow to indicate the shades of the main events. With their help, the desire, opportunity, prohibition or permission of the specified action is expressed.
In today’s lesson, we will analyze what and when the modal verb can is intended to denote in English. This is the most ambiguous and frequently encountered in conversations representative of this group.
Let’s consider its construction, application and other grammatical nuances.
In general, it is not difficult to apply this verb, therefore, even textbooks for toddlers contain the principle of forming phrases with can. Of course, only the simplest designs are selected for children, but complicated combinations are not difficult for older people.
Currently,
In an affirmative sentence, the compound predicate has the form «can + infinitive«. It is important to note that in this case, infinitives are always used without to.
- Nick can run solid — Nick can run fast.
- My sister can cook a cake —Mysisterknows howCookcake.
The conjugation of the verb can in the present tense is the same for all persons of nouns and pronouns: it never changes its form and does not attach any endings. By meaning, this form of the verb can express events of the present or future (nearest).
- My relatives can meet me at the railway station tomorrow —Morelativeswill be able totomorrowmeetmeontrain station.
- She can call Them today — She can call them today.
Modal verbs do not require the participation of auxiliary words, since in fact they themselves are. Therefore, they create interrogative and negative contexts on their own.
In questions, the compound predicate is broken up, and can moves to the beginning of the sentence. If there are special interrogative words in the phrase, then they always precede the modal word.
- Dog you bring the book? — Can you bring this book?
- When can they arrive to us? —When can they come to us?
To negate the main verb, can appends the particle not, forming the combination cannot, or abbreviated can’t. Pay attention to the continuous spelling of the official form.
- My wife can not drive a car — My wife doesn’t know how to drive a car.
- I can‘t cook lamb
Source: https://msutt.ru/v-kakih-sluchayah-pishetsya-can-can-i-could-pravila-upotrebleniya/
Using the to particle after modal verbs
I am glad to welcome you, friends! When you remember all the rules you have learned at school in English lessons, what you have heard dozens of times becomes clear in your memory:
«After modal verbs, the -to particle is not used, except for the following exceptions.»
After the word “exclusion,” the thread of memory is interrupted. I believe that a similar situation is observed among many school leavers, and in general, it will be useful for beginners to learn about this rule. Let’s put things right by putting in place the words that are exceptions and those that aren’t.
The to particle after the modal verb
The general rule is that a modal verb is always followed by an infinitive verb
It is well known that the grammatical feature of a verb in the infinitive is nothing more than the particle –to. A continuation of the above rule is a very important point that the verb is placed in the infinitive, but without the -to particle, indicating the infinitive.
When the to particle is not used
After the next series of modal verbs, the use of the infinitive indicator –to is not allowed:
| Do not need an infinitive | ||
| Verb | Example | Transfer |
| Dog | My uncle can solve any mathematical equation. | My uncle can solve any mathematical equation. |
| May | You may go if you want. | You can go if you want. |
| Must | I must forget about my personal dis if I am a good doctor. | I must forget about my personal animosity if I am a good doctor. |
| Hall | Is it too warm here, shall we leave this place? | It’s very hot in here, maybe we’d better get out of here? |
| Should | We should send this letter. | We must send this letter. |
| Will | We will visit this church when we come back to Moscow. | We will go to this church when we come back to Moscow. |
| Would | He told her that you would invite her. | He told her that you would invite her. |
Modal verbs that combine with the to particle
As mentioned, there are a few modal verbs that are exceptions when used in conjunction with –to.
| Used from -to parts | ||
| Verb | Example | Transfer |
| Right to | You ought to say this thing to him. | You need to tell him that. |
| Have (got) to | You have to go with him, if you are free. He has got to be at work by 7:45 am. | You should go with him if you’re free. He should be at work at 7:45 AM. |
| Be to | The bus is to leave in 8 minutes.When are we to return? | The bus leaves in 8 minutes, when do we need to get back? |
Using to with the verbs need and dare
In addition to the first and second groups of verbs, there are several modal verbs in English, which in some cases require the use of the -to particle after themselves, in some its use ceases to be necessary, these include:
-Need has not only one shape, but two — sufficient (or correct) and insufficient.
Insufficient form is used most often when specifying a one-time action. Observed only in negative and interrogative types of sentences in the present tense and used without -to to indicate the need for action
- Need we go now? — Do we really need to go now?
But the sufficient form –need is used to indicate repetitive actions in the meaning of «need», «required». Has the form of present and past tenses and can be used in all three types of sentences.
- Do you need to help them every day? — Do you need to help them every day?
- Do we need to go there every Sunday? — Should we go there every Sunday?
-Dare is a semi-modal verb due to the fact that it stands on the border between full-valued and modal
The modal –dare means “to have arrogance / courage”, has the forms of the present and the past, after which the infinitive is not used.
- How dare she tell him this thing? — How dare she say that to him?
The full-valued –dare has all the properties and characteristics of an ordinary verb, which is why it is followed by a verb in the infinitive with –to after it, as after an ordinary one.
- John dares to lie to him. — John dares to lie to him.
- He did not dare to lay a hand on her. “He dared not touch her.
Features of the modal verb used to
Another verb that should be mentioned in this article is -used to, always used with -to. Until now, its belonging to the category of modal words remains controversial, some linguists attribute it to the usual — full-valued. However, I am inclined to believe that its essence is closer to modal.
Its main difference from other modal words is that it has only one temporary form — the past.
- John used to be so serious when we knew him. “John was so serious when we knew him.
The auxiliary verb -do can be used to form negations and questions with -used to.
- I did not use to think of computer as a common thing when I was your age. “I didn’t treat the computer as a completely ordinary thing when I was your age.
- Did she use to visit them? — Did she visit them?
It is possible to construct these types of sentences without -do, which is another feature of this word.
- I used not to worry about my clothes when I was 10 years old. — I didn’t pay attention to my clothes when I was 10.
- Used you to play the piano? — Did you play the piano?
Hopefully you’ve figured out how to use –to after English modal verbs.
Good Luck!
Modal verbs in English
Source: https://englishfull.ru/grammatika/to-posle-modalnih-glagolov.html
Modal verbs can, could, be able to: rules and examples
Modal verbs in English differ from other verbs in that they are not used independently and do not denote a specific action or state, they reflect its modality, that is, the speaker’s attitude towards it. Below we will consider the similarities and differences of the important pair of verbs can could be able to.
The can verb in English
In English, there are two phenomena that express «Skill», «ability» to do something is the modal can and the be able to construct.
The modal verb can is found already at an early stage of learning, so we, without hesitation, use it in speech, since we have been familiar with it for a long time. In the same article, we will focus on what is the difference between using can and be able to.
Modal verb can / kæn / (the past tense form could / kʊd /) is the most common of the modal verbs. Used with a verb without particle to (can swim, can run, can read).
Can is the only modal verb with which the negative particle not is written together — cannot / ˈKænɒt / (short form can’t / kаnt /).
The verb can (could) has the following meaning: to have a physical or mental ability, the ability to perform an action expressed by the verb with which can (could) is combined.
The verb can combined with verbs in the active voice (I can’t) is translated into Russian «to be able», «to be able» (I can, I can do). If can comes before the verb in the passive voice (It can be done), then it translates as «can be done», «can be done.» Let’s consider in detail with examples:
- He can speak English. — He can speak English. (active voice)
- He could run fast when he was 20. — He could run fast when he was 20. (active voice)
- What can be done to help you? — What can be done to help you? (passive voice)
- The house can be built here. — A building can be built here. (passive voice)
Past and present can verb
Affirmative form
В affirmative sentences can is also used with the following meanings:
Permissions to take action.
- You can go home. — You can go home.
- You can use this phone. — You can use this phone.
Expressions of regretthat any action has not been performed in the past, the opportunity has not been realized.
In doing so, we use Could + Perfect Infinitive (have done).
- He could have done it himself. — He could do it himself. (but didn’t)
- You could have told me about it long ago… “You could have told me about this long ago. (but didn’t say)
negative form
In a negative sentence cannot (can’t and couldn’t) translates to “cannot” or “cannot be” and is used in the following cases:
For prohibition expressions.
- I’m sorry you can’t park here. “I’m sorry, but you can’t park here.
- It cannot be done. — It cannot be done (it cannot be done).
For expressions of doubt, surprise, mistrust and will be translated as «it cannot be that», «incredible.» If we use infinitives of verbs in the present tense (do — Simple, be doing — Continuous), then we mean the present tense.
- She can’t be at home now. “It’s unbelievable that she’s home now.”
- You cannot be telling the truth! — It cannot be that you are telling the truth!
If we express doubt or surprise in the past, then you need to use can / could + have done (Perfect Infinitive).
- He can’t have done it. “It can’t be that he did it.
- She can’t / couldn’t have said this. “It can’t be that she said that.
Combination cannot but + verb translates as «I can not not», «I can not help.»
- I cannot but agree with you. — It is impossible not to agree with you (I cannot but agree with you).
- One cannot but admit — It is impossible not to admit
Interrogative form
Let’s take a look at the use of can / could in interrogative sentences:
In questions, can / could comes first.
- Can you drive a car? — Can you drive a car?
- Can you speak any foreign language? — Can you speak any foreign language?
Also, can in questions can express doubt, surprise, and then the verb can is translated as «really» (if we use could, then we express a greater degree of doubt).
If the action refers to the past tense, then can / could + have done (Perfect) is used.
- Can he be still working? — Is he still working?
- Can you dis the book — Don’t you like this book?
- Can / could they have left yesterday? — Did they leave yesterday?
The verb can in questions can express a request. In a more polite form, could is used.
- Can / could I take your dictionary? — Can I get your dictionary?
- Could / can you answer my questions? — Could you answer my questions?
Use of turnover to BE ABLE TO
What is the use of can could be able to? It is no coincidence that these words were in the same row. All of them express the ability of a person to perform any action. The only difference is in the use. But first things first.
- CAN — expresses the ability of a person to do something in the present tense
- COULD — the CAN verb in the past tense, expresses the ability to perform an action in the past
- TO BE ABLE TO — a substitute for CAN in the future tense; can be applied at all other times.
The verb can has the equivalent be able / ˈeɪb (ə) l /, which is used with the particle to.
The modal verb can in English officially cannot be used in the future tense, i.e. you cannot add will to it.
Yes, it can be used to designate the shades of the future, as in Present Simple, but nothing more.
We can use can to indicate opportunities that we already have, but we plan to take advantage of them in the future. If, however, we are talking about something that will only be mastered or obtained by us, then it is necessary to replace can with its equivalent to be able to.
Source: https://englandlearn.com/grammatika/can-could-be-able-to-pravila
Modal verb CAN (COULD): rules of use and example sentences
In order not to miss new useful materials, subscribe to site updates
The modal verb can (I can) and its form could (could) is the most common modal verb in English. We use it to show that we can, are able, capable of doing something. In this article, we will get acquainted with all the features of the modal verb can (could).
The first thing to remember is that there must be another verb after can or could. After all, can by itself does not report an action, but only shows our attitude towards it: «I can do some action.» And after that, «can I» must be added «can I do what?»: Can dance (I can dance), can sing (I can sing), etc.
And the second thing to remember is that after can we don’t put to: can speak English. We are used to the fact that two verbs in English should be related to: decide to drink coffee (decide to drink coffee) or offer to go for a walk (offer to go for a walk). But the modal can works without the to.
We noted that this modal verb has two forms: can and could. We use these forms with any subject, both singular and plural.
My friend can speak Japanese. — My friend can speak Japanese.
My friends can dance salsa. — My friends can dance salsa.
What is the difference between can and could? Can is used when someone is able to do something at the present time, and could — when someone knew how to do something in the past, now, most likely, they no longer know how.
He can swim. — He knows how to swim.
He Could swim. — He was able to swim.
Using the modal verbs Can (Could) and May (Might), be able to
What is a modal verb ?!
Modal verbs in English differ from other verbs in that they are not used independently and do not indicate a specific action or
states, they reflect his modality, that is, the attitude of the speaker towards him. Together, the modal verb and the infinitive of the significant verb form a composite modal predicate.
I can swim. I can swim.
The speaker can assess the action as possible, necessary, permitted, requested, prohibited, ordered, unlikely, very likely, etc.
Can or May?
The use of the verbs can and may in modern English is often difficult. Once upon the strict rules of English grammar
can expressed physical or mental capacity,
may — permission and approval… It was considered wrong to use can in the resolution value.
Today, the rules of the language are not so definite. Already from the second half of the 19th century
can used in informal speech to express permission. V
formal and formal communication situations, the verb should be used may to request permission.
For example, in a conversation with a restaurant waiter, it will sound more profitable
May I have more salt, please?
As for prohibition / denial, then the use mayn’t extremely NOT recommended. This applies to all styles.
The use of may in such cases, although formal and permissible, sounds unnatural. Educated people would rather say
«Can’t I?», Not «Mayn’t I?» or «May I not?» And even according to the strict rules of English grammar, the question «Why mayn’t I go to the disco?» sounds
incorrect, one can say “not
in English».
CAN is used:
1. When expressing abilities or capabilities
do anything. (Indefinite Infinitive)
I can swim. You can play. / I can swim. You can play.
2. In the case of denial of opportunity or ability to do anything.
I cannot swim. He cannot see / I cannot swim. He cannot see.
3. When the possibility is denied that the action could
come true in reality. (Perfect Infinitive)
You cannot have done it. / It cannot be that you did it.
COULD is used:
1. When expression capabilities or abilities
taking any action in the past… (Indefinite Infinitive)
They could swim. / They couldn’t swim.
2. When expression denial of opportunity or ability
taking any action in the past.
She couldn’t swim. / She couldn’t swim.
3. When consumed indirect speechdepending from the verb in the past tense… (Indefinite Infinitive and Perfect Infinitive)
I said that you couldn’t have done that. / I said you couldn’t do it.
4. In the main part of conditional sentences.
In conditional sentences of the second type and the third type (Indefinite Infinitive and Perfect Infinitive).
If he tried, he could do it. / If he tried, he could do it.
If he had tried, he could have done it. / If he tried, he could do it.
MAY is used:
1. To express permission for any action (Indefinite Infinitive)
You may go home now. / Now you can go home.
2. To express an assumption: related to the present and the future (Indefinite Infinitive) or to the past (Perfect Infinitive)
It may rain today. / It may rain today.
She may have returned to Moscow. / She may have returned to Moscow.
MIGHT is used:
1. When using indirect speech, depending on the verb in the past tense.
for expressing permission (Indefinite Infinitive) or expressing an assumption (Indefinite Infinitive and Perfect Infinitive)
She said that he might take her cellphone. / She said he could take her phone.
He said that she might know their address. / He said that she might know their address.
2. In the main part of conditional sentences: in conditional sentences of the second (Indefinite Infinitive) and third type (Perfect Infinitive)
If you tried, you might get her phone number. / If you tried, you could get hold of this book.
If he had been here, he might have helped us. / If he was here, he could help us.
It must be remembered
— With all personal pronouns, the modal verb does not change.
I, WE, YOU, THEY, HE, SHE, IT — can (cannot / can’t), could (couldn’t) — the verb «abilities» (do, play, see, come ..)
— Between the modal verb and the verb «ability»
noTO!
Statement of a question
In an interrogative sentence, the first place is
1. An interrogative word, followed by 2. A modal verb, then 3. Acting person and finally 4. An action verb.
(1) When (2) can (3) you (4) get home? / When can you come home?
Will you be able to give me your book? — Can you give me your book? (As you can see, in the case of be able to, the question remains the same as with a regular verb.)
Source: https://engrammar.ru/grammar/upotreblenie-modalnyx-glagolov-can-could-i-may-might-be-able-to/
Can or May? What is the difference between these verbs
The question is which verb to use can or may may arise because in Russian we use words such as “can”, “can” where in English we meet and dog, и may, for example:
May I ask you something? — Can I ask you something?
Dog you wait for a while? — You can wait a little?
In this article, we’ll look at when to speak can, and when may and what is the difference between them.
Can or May? The main difference
In short, the main difference is that can usually implies the physical ability to do something, and may — permission, permission. In other words, “I can” is like “I can”, and “I may” is like “I can”.
I can lift a car. — I AM I can lift the car (I can physically).
I may eat all the cookies. — To me can eat all the cookies (I was allowed).
But there are other nuances, let’s consider them in more detail.
When do we say Can?
First, let’s look at the cases when we say can.
- The physical ability to do something.
I can breath underwater. — I can breathe underwater.
Tomas can sleep four hours a day and feel well. — Thomas can sleep four hours a day and feel good.
I can’t help you. — I cannot help you (I have no opportunity).
This implies not just physical ability, but the availability of skills.
Dog you ride a horse? — Do you know how to ride?
I can’t play basketball. — I can not play basketball.
- A question about physical ability or skill.
When you ask a question, you are asking not whether, for example, an airplane is allowed to fly in space, but whether it is physically capable of it.
Dog an airplane fly in the space? — Can a plane fly in space?
Dog you play the piano? — Can you play the piano?
- Expressions of surprise, doubt, disbelief
For more information on this function of the can verb, see the article “The modal verb Can, Could”.
Dog it be the truth? — Can it be true?
No way, you can’t have done it! — It can’t be, you couldn’t do that!
When do we say May?
- Assumption of some probability, possible action.
In this case, along with may used frequently might with a slight difference in meaning (if might, then the possibility seems a little less likely).
Take an umbrella, It may / might rain tonight. — Take an umbrella, it may rain in the evening.
The table is reserved but there might be another option. — This table has been booked, but perhaps there is another option.
- Permission and prohibition (old school English).
In Strictly Correct Old School English, permission and prohibition are expressed by may
May I suggest another decision? — May I suggest another solution?
you mayNote play in the garden. — You can’t play in the garden.
However, in modern English in these cases, they use and canand may.
When can you say both Can and May?
- Asking or giving permission
dad, can / may I take your car? — Dad, can I take your car?
Oh, you finished painting the fence! Well done! you can / may go now. — Oh, you’ve already painted the fence! Well done! You can go.
As I mentioned above, it used to be the norm to use mayto ask or give permission. Strictly speaking, the question with can implies physical ability, and the question with may — permission. There is a well-known joke: a student raises his hand and asks “Can I go to the bathroom?” (can I go to the toilet?) and the teacher says “I don’t know, can you?” (I don’t know, can you?)
However, in modern English, almost no one adheres to these differences, on the contrary, sentences with can in the «permissive» meaning are even more common (this is discussed in this article on Merriam-Webster). I once came across an interesting discussion on the Duolingo app where it was mentioned that the “May I” generation finally gave way to the “Can I” generation:
“I think the last time I saw ‘May I’ was in the 1962 movie ‘Music Man’, where a piano teacher tried to get his student to say that. I’m afraid the “May I” generation lost to the “Can I” generation. (screenshot from Duolingo app)
In English, a prohibition can be expressed in different ways, the harshest way is must not. If we say, “You must not cross this line” — this is something like “You are not allowed to cross this line,” that is, we are talking about a strict, categorical prohibition. Inhibit expressions with can not и may softer, but between them there is a small, not always significant difference in meaning.
Prohibition with can’t means some kind of abstract neutral “forbidden”.
I’m sorry but you can’t park here. — Sorry, but you can’t park here.
you can’t smoke in the park. — No smoking in the park.
Ban with may not can be perceived as a more personal prohibition with a touch of edification, instruction. Something like “you are not allowed”, “you are not allowed”, “you are not allowed”.
you may not play with Bobby, he is a bully! — You can’t play with Bobby, he’s a bully!
you may not go the party, you are grounded. — You are not allowed (I do not allow) to go to the party, you are punished
Note: to ground — punish the child with “house arrest”.
Source: https://langformula.ru/english-grammar/can-may/
Difference between can and could — which is better
Can, could, be able to Is like employees of one organization called Opportunity. Dog — the president, be able to is his deputy, a Could Is a lady accountant of venerable age.
Be able to, the use of which helps to form the future, the past and convey the subtle shades of meaning — this is, in fact, a synonym for the verb can… And a very useful synonym, because in itself can does not have enough flexibility to change in different tenses and grammatical aspects.
Modal verbs are generally not very likely to change their form, and they often need helpers. For example, must often outsourcing their functions to the verb have to.
By the way, we have already touched upon the inexhaustible topic of modality before. For example, here in this article we explored the difference between can from may.
A little about why modal verbs are needed
I play the flute.I play the flute.
I can play the flute. I can play the flute.
How are these two phrases different? Of course, the fact that the second has a modal verb can.
Modal verbs Are words that modify, that is, change the meaning of the semantic verb. More often than not, they help express ideas of opportunity, intention, commitment, and need.
- The verb can gives other words a characterization feasibility, feasibility or skills.
- Adding can in the sentence «I play the flute «, we get the value «the ability to play the flute«,»flute skills».
- Simply put, I can = I can, I can.
- Moreover, this “I can«Can be as an innate, natural skill, ability or property given by nature:
Birds can fly.Birds can fly.
Humans can make mistakes.People can make mistakes.
Oil can be very sweet.Olya can be very nice.
and a skill that develops with training, like a learned language or the ability to play the guitar:
I can speak Japanese, I’ve been learning this language for 10 years.I speak Japanese, I studied this language for ten years.
I can’t play the flute well enough. I don’t play the flute well enough.
Olja is in the first grade, she can read and write.Olya is in first grade, she can read and write.
- Can is added to the schema sentence:
- In it, S is the subject (the one who performs the action), M is the modal verb, and V is the semantic verb.
- In a sentence «Mary can sing «(Mary can sing), Mary — subject, can Is a modal verb, and sing — semantic.
- Armed with this pattern, you can form a wide variety of sentences with modal verbs.
Teachers can teach.Teachers can (can) teach.
Cats can catch mice.Cats can (can) catch mice.
I can watch TV for hours.I can watch TV for hours.
Can also be used in the following cases:
- When we ask someone for something in an informal setting:
Dog you lend me ten dollars?Can you lend me ten dollars?
- When we talk about plans for the near future:
We can go out to the new Italian restaurant for dinner. We can dine at the new Italian restaurant.
We have already said that modal verbs are quite clumsy people. Here is a list of what canAs modal verb, cannot do:
- Can’t bend over faces.
I must say that in general, when verbs are declined in English, this is expressed only in one thing — they add s in the third person singular:
I sing. (I sing).She sings.(She sings).
Everything. Different faces in English verbs do not cause any more transformations.
So, modal verbs don’t change at all. These are conservative verbs. Dog will remain in any person can:
I can dance.I can dance.
She can dance.She can dance.
Mistake: She can dance.
- Can cannot be used with other auxiliary verbs.
For example, you cannot use the verb to ask a question do:
Do you play the flute? — wrong.
It should be said simply:
Can you play the flute?Can you play the flute?
- Can not append an ending —ing.
Consequently, the aspect of duration is inaccessible to him. To describe the duration of an action, you need some other verb.
- Aspect perfect action is also unavailable.
- Can does not exist in perfect. Therefore, one cannot say:
- «I have canned»,
- And you need:
- «I have been able» (I was able).
- У can there are no past and future tense forms.
- This verb simply does not cope alone with all tenses, therefore it resorts to the help of its «employees» — could and be able to.
- Let’s dwell on them in more detail.
Can, could, be able to: regulations use
Let’s see how this small team of professionals handles a wide variety of grammatical tasks.
Mold
- Is a specialist in the past tense (do you remember that can does not understand anything in the past tense).
Imagine Mold in the form of an old woman who constantly remembers how everything was before. We can say that she lives her past:
I Could sleep less when I was young.I could sleep less when I was young.
I Could walk for miles and miles.I could walk for miles and miles.
Source: https://sosh16zernograd.ru/prochee/raznitsa-mezhdu-glagolami-can-i-could.html
Modal verbs — CAN, MUST, MAY and others!
Why do we need modal verbs in English? Which modal verbs should and shouldn’t be memorized? How to build phrases with modal verbs correctly? You will find answers and many examples of English sentences with modal verbs in this article.
Modal verbs are unusual in that they are never used on their own. A modal verb is always used in conjunction with another — a semantic verb. It is the semantic verb that shows what action is being discussed. And the role of the modal verb is to show the speaker’s attitude to this action.
The easiest way to understand the purpose of modal verbs is with examples. Take a look at the proposal:
I play football.
I’m play soccer.
Now, let’s add the modal verbs can, must, may to this sentence and watch how the meaning changes:
I can play football.
I can play football.
I must play football.
I have to play football.
I may play football.
I am allowed to play football.
All three sentences have the same semantic verb — play (to play). But look how different in meaning we got the sentences using different modal verbs.
Thus, modal verbs should be used when it comes to:
- possibility / impossibility to perform an action;
- presence / absence of the need to perform an action;
- advice / order / recommendation to take action;
- assessing the likelihood of performing an action.
This is not a complete list of what modal verbs are used for in English. Next, we will take a closer look at 10 basic English modal verbs, what meanings they have and how to apply them correctly. Let’s start with the three most common modal verbs.
Modal verbs in English: rules of use
Modal verbs in English behave differently from most ordinary verbs. To correctly build sentences with modal verbs, you need to know a few rules. Here are the basic rules for using modal verbs:
1. As already mentioned, a modal verb is always paired with a semantic verb.
Moreover, the semantic verb is always taken in an indefinite form and the particle to is not placed in front of it. The combination of a modal and a semantic verb is called a modal predicate. In an affirmative sentence, the modal predicate is put in the place of the usual predicate, that is, immediately after the subject.
Correctly:
I can speak Spanish.
I can speak Spanish.
You must help me.
You have to help me.
Wrong:
I can speak Spanish. You must help me.
2. Modal verbs do not change by person. The ending «-s» in the third person is not appended to them.
Correctly:
Source: http://pcards.hreminder.com/24-spravochnye-materialy/79-modalnye-glagoly-v-anglijskom-yazyke.html
Modal verb Can in English
No can climb any tree.
He can climb any tree.
After combining be able followed by an infinitive with a particle to.
He is able to climb any tree.
He can (he can) climb any tree.
Forms:
CAN is used in all persons in the present tense in the form can + Indefinite Infinitive and relates the action to the present or future.
COULD is used in the past tense in the form could + Indefinite Infinitive and in conditional sentences.
Negative form: cannot (can’t), could not (couldn’t). (The negation of not with the verb can is written together.)
Interrogative: can I ?, could I? etc.
Interrogative negative: can I not (can’t I) ?, could I not (couldn’t I)? etc.
To be able (to) — equivalent to Can
Negative: I am not able (I’m not able), he is not able (he’s not able), etc.
Interrogative form: Am I able? Is he able? Are you able? etc.
Interrogative negative: Am I not able? Aren’t I able? (ain’t I able — colloquial) Is he not able? (isn’t he able?) etc.
Using can and its equivalent be able (to)
1. Dog и be able (to) used to express a physical ability or ability to perform an action.
NOTE, however, that the modal verb can means the possibility of performing an action in general, usually constantly, a to be able (to) — the possibility of performing an action for a single, specific case. For example:
Dog you skate?
Do you skate? (Can you (generally) skate?)
Are you able to skate?
Are you able to skate (i.e. skate after a fall, injury, etc.)?
I can swim across this river.
I can swim across this river (generally).
I am able to swim across this river.
I am able to swim across this river (now when necessary).
Mold you speak English last year?
Could you speak English last year?
He wasn’t able to come yesterday because he had no time.
He could not come yesterday because he did not have time.
Dog used to express a possibility due to something (the state of something, circumstances, etc.).
you can ski on the hills. (There is enough snow.) You can ski (walk) on the slides. (There is a lot of snow already.)
We couldn’t bathe there. (The river was very deep.)
We couldn’t swim there. (The river was very deep.)
Notice:
Combination of an indefinite pronoun one с can
Source: https://catchenglish.ru/grammatika/can-i-be-able-to.html
Though as a couple of best known modal verbs in the English language can and could are recognized by many users it is necessary to remember that there exists a difference between can and could. These are auxiliary verbs that are used with the main verb, whose uses in grammar are often confused with. Can is in the present tense while could is in the past tense. In other words, could is the past tense of can. Therefore, basically they carry similar meanings. However, these two, can and could, are used in many ways. A small difference between can and could be pointed as can having a meaning as a noun too while could only has a use as a verb.
What does Can mean?
Can in the present tense is used to state a fact and declare ability. When used in a sentence, the word can state the fact that someone has the ability, or he knows how to do a thing and that he has the skill to do it. Can is also used to express possibility and things that can be done potentially. Can is also used to request someone to do something. Look at the following examples.
She can run fast. (Ability)
They can take the dog with them if they want. (Express possibility)
Can you call me in the afternoon? (Request)
What does Could mean?
Could is used as a past tense of can to state an ability in the past or the things one was able to do in past but not anymore. In addition to that, could express possibility as well but the time is just stated in the past. The word could is also used to state condition as is the following sentence.
If I had money, I could buy you a car.
Could is also used in making suggestions and polite requests.
Could you pass me the salt, please?
What is the difference between Can and Could?
Both can and could are used in imperative expressions usually in question form. They are used to make requests or permissions, but the use of could suggests a more polite mood. Example of this usage is this sentence following sentence.
Can I leave now? Could you get me a glass of water?
Moreover, the use of could suggests a level of doubt and uncertainty. This means that when the word could is used in a sentence the meaning may suggest that the information being expressed is maybe true or not. Can may express that a person is able to do, while could about 50% possibility that it will be done.
Can and could sometimes are very confusing, however, given the pointers above, you can get passed the confusion because simply you can.
Summary:
Can vs Could
• Can is used to state a fact, ability, potential, and possibility.
• Could is used to state a past ability, condition, and possibility.
• Can and could are used to ask for permissions, make requests or commands.
• Could suggests a polite manner when making a request and it suggests a level of doubt or certainty.
Images Courtesy:
- A Smile Is The Prettiest Thing You Can Wear by seaternity (CC BY-SA 2.0)