Понятие настоящего времени в английском языке не всегда совпадает с нашим. Одним из самых ярких примеров такого различия как раз является Present Perfect.
В этой статье мы разберемся, что такое Present Perfect, как оно образуется, в каких случаях употребляется, каким правилам подчиняется и закрепим знания на реальных примерах предложений с переводом.
Что такое Present Perfect Tense?
Present Perfect Tense (Present Perfect) — это настоящее совершенное время в английском языке. Оно обозначает действие, которое завершилось в настоящий момент времени.
В этом и состоит основная сложность времени Present Perfect для изучающих. В русском языке нет времени аналогичного Present Perfect. Для нас если что-то происходит сейчас — это и есть настоящее, а если совершилось — это уже прошлое.
Но не для англичан. Они воспринимают время немного по-другому. По логике носителей языка, действие вполне может закончиться и в настоящем или близко к настоящему моменту. Для выражения такой связи прошлого с настоящим и существует Present Perfect.
Из-за этих особенностей в понимании действий и времени — на русский язык Present Perfect обычно переводится глаголом в прошедшем времени.
I have already done my homework — Я уже сделал домашнее задание
В этом примере используется время Present Perfect (have done), потому что речь идет о том, что действие (работа над домашним заданием) закончилось совсем недавно.
Но на русский язык мы переводим предложение используя прошедшее время (уже сделал).
Как образуется Present Perfect?
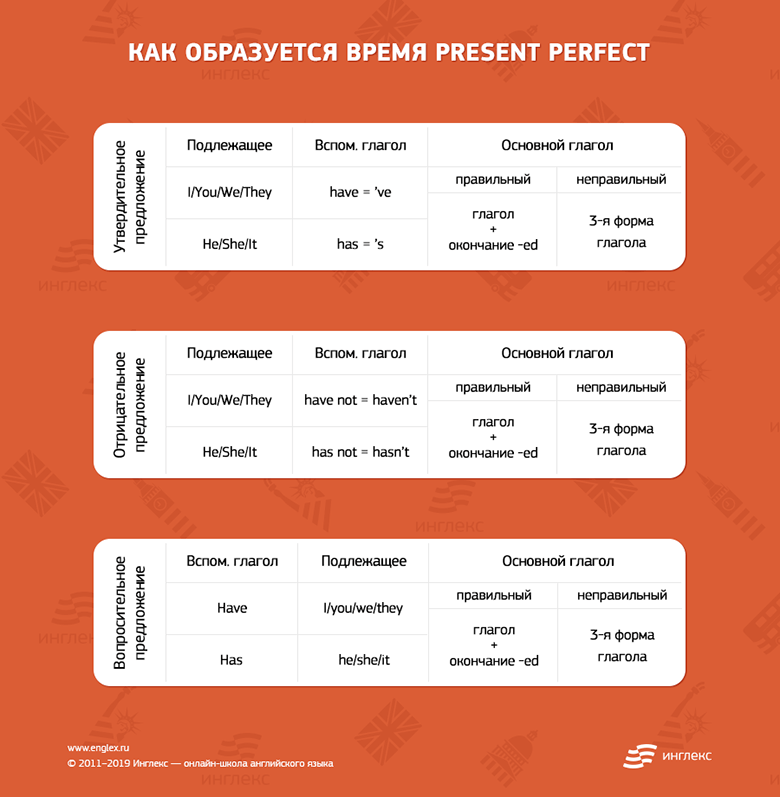
Время Present Perfect образуется при помощи вспомогательного глагола have / has и Past Participle (третьей формы смыслового глагола: V3).
Вспомогательный глагол меняется в зависимости от подлежащего:
- I / You / We / They → have (для 1-го, 2-го лица и форм множественного числа)
- She / He / It → has (для 3-го лица единственного числа)
Завершает конструкцию времени Present Perfect смысловой глагол в третьей форме (V3).
Если смысловой глагол правильной формы — то его третья форма (V3) образуется при помощи окончания -ed.
Если смысловой глагол неправильный — то его третью форму (V3) берем из таблицы неправильных глаголов.
Например:
- to try → tried (пытаться)
to cook → cooked (готовить)
to finish → finished (заканчивать) - to get → got (получать)
to keep → kept (хранить)
to see → seen (видеть)
Утверждение:
Утвердительное предложение в Present Perfect образуется при помощи вспомогательного глагола have / has и смыслового глагола с окончанием -ed для правильных глаголов или третьей формы неправильного глагола (V3) по формуле:
- I / You / We / They + have + Ved (V3)
- She / He / It + has + Ved (V3)
I have decided — Я решил
You have played — Ты играл
He has done — Он сделал
It has turned on — Оно включилось
В предложениях и повседневной речи часто можно встретить сокращенную форму вспомогательных глаголов have / has. Она образуется при помощи добавления к подлежащему ‘ve (для have) или ‘s (для has):
- I have = I’ve
- You have = You’ve
- We have = We’ve
- They have = They’ve
- She has = She’s
- He has = He’s
- It has = It’s
I’ve done my tasks — Я выполнил свои задачи
He’s washed the dishes — Он вымыл посуду
Отрицание:
Отрицательные предложения в Present Perfect образуется при помощи добавления частицы not после вспомогательного глагола have / has, но перед основным смысловым глаголом. Формула выглядит следующим образом:
- I / You / We / They + have not + Ved (V3)
- She / He / It + has not + Ved (V3)
I have not done my homework — Я не сделал домашнюю работу
They have not come — Они не пришли
She has not finished her tasks — Она не выполнила свои задачи
It has not turned on — Оно не включилось
В отрицании частицу not можно сократить путем присоединения ее к вспомогательному глаголу have / has:
- Have not = haven’t
- Has not = hasn’t
I haven’t washed my hair — Я не помыл волосы
She hasn’t been to London yet — Она еще не была в Лондоне
Вопрос:
Вопросительное предложение в Present Perfect образуется путем постановки вспомогательного глагола have / has в начало предложения. Формула будет такой:
- Have + I / You / We / They + Ved (V3)
- Has + She / He / It + Ved (V3)
Have I bought all the presents? — Я купил все подарки?
Have you finished the classes? — Ты закончил занятия?
Has she just arrived home? — Она только что приехала домой?
Has it turned on? — Оно включилось?
Специальные вопросы образуются при помощи question words (вопросительных слов). Таких, как when (когда), how (как), what (что), where (где) и других. Далее идет такой же порядок слов, как и в вопросе.
- QW + have + I / You / We / They + Ved (V3)
- QW + has + She / He / It + Ved (V3)
What has he just said? — Что он только что сказал?
How long have you knocked on the door? — Как давно ты стучал в дверь?
Когда употребляется Present Perfect?
А сейчас рассмотрим самые распространенные случаи употребления и использования времени Present Perfect в речи:
- Завершенное действие в настоящем
В таком случае акцент ставится на результат завершенного действия. Другими словами, когда результат действия виден в настоящем.
I have cooked a good dinner — Я приготовил хороший ужин (действие завершилось, результат — хороший ужин)
I know Nina. We have already met — Я знаю Нину. Мы уже встречались (встреча произошла в прошлом, но нас интересует результат в настоящем)
- Незавершенное действие в настоящем
Время Present Perfect используется в случае, когда мы описываем действие, которое началось в прошлом, еще не закончилось в настоящем, но результат очевиден.
I’ve written five pages of the new book this morning — Я написал пять страниц новой книги этим утром (утро еще не закончилось, он может написать еще несколько страниц)
She has finished watching “Harry Potter” this week — Она закончила смотреть «Гарри Поттера» на этой неделе (неделя еще идет, но она уже закончила смотреть фильм)
- Факт действия / личный опыт
Если говорящему важно подчеркнуть факт какого-то свершившегося события без точного указания времени — на помощь также приходит Present Perfect. Часто это время используется, когда мы говорим о своем прошлом опыте или же, спрашиваем об этом своего собеседника.
I have been to Bratislava — Я был (бывал) в Братиславе
В вопросе, когда мы интересуемся фактом из чьей-то жизни — используем также Present Perfect:
Have you ever been to France? — Ты когда-нибудь был (бывал) во Франции?
Маркеры времени Present Perfect
Present Perfect употребляется с неточными выражениями и словами, которые указывают на еще не закончившийся период времени
- never (никогда)
- ever (когда-либо)
- already (уже)
- yet (еще) / not yet (еще нет)
- often (часто)
- lately (в последнее время)
- just (только что)
- once (однажды)
- recently (недавно)
- before (раньше)
- today (сегодня)
- this week (на этой неделе)
- this year (в этом году)
- for an hour (в течение часа)
- for a long time (долгое время)
- since two o’clock – с двух часов
- ince December – с Декабря
Примеры предложений Present Perfect с переводом
Утвердительные:
I’ve studied English since my childhood — Я учил английский язык с детства
She has visited this beauty shop recently — Она недавно заходила в этот магазин косметики
People have walked on the Moon — Люди ходили по Луне.
We’ve just eaten, so we don’t want to go to the cafe — Мы только что поели, так что не хотим идти в кафе
I have just cut my finger — Я только что порезал свой палец
Отрицательные:
He has not returned from school yet — Он еще не вернулся из школы
I haven’t bought the new car. This is my old one — Я не купил новую машину. Это старая
Jane hasn’t been to Asia yet — Джейн еще не была в Азии
I have not been at university this week because of the flu — Я не был на этой неделе в университете из-за гриппа
I haven’t replaced the batteries in the doorbell — Я не заменил батарейки в дверном звонке
Вопросительные:
Have you seen this film about space? — Ты видел этот фильм о космосе?
Has Jimmy bought the tickets yet? — Джимми уже купил билеты?
How many deals has she made at the moment? — Сколько сделок она заключила на текущий момент?
How much coffee have you drunk today? — Сколько кофе ты сегодня выпил?
How long have you known Mary? — Как давно ты знаешь Мэри?
Introduction:
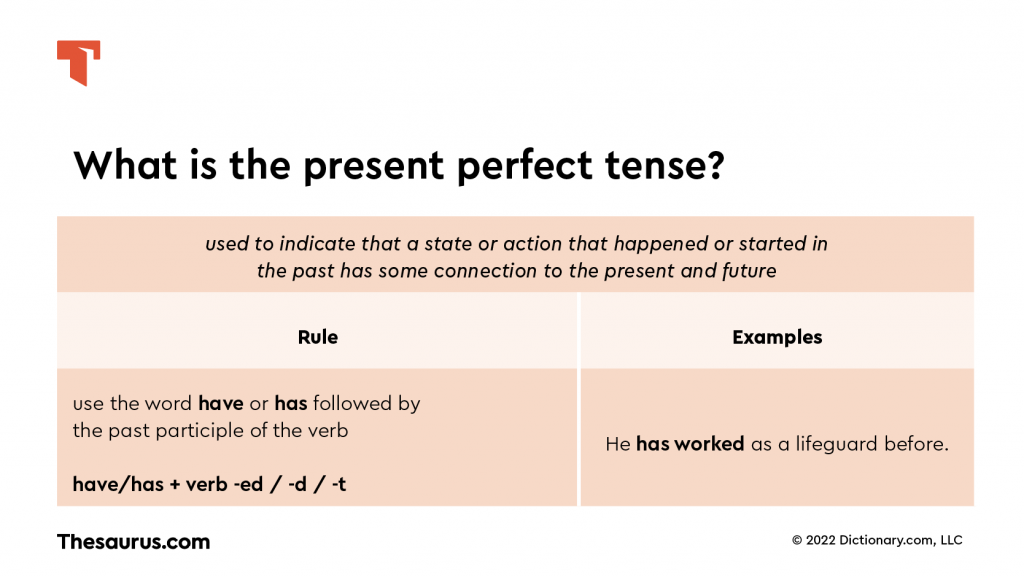
The present perfect tense is used to describe actions that started in the past, but still have effect on the present.
The focus in the present perfect tense is the result of the action.
Generally, the time at which the action started (or stopped) is not important.
Every sentence in this tense has a verb to have as an auxiliary verb in addition to a past participle form of the main verb.
Let’s have a look at the different forms of sentences in the present perfect.
Forms

Affirmative Sentences
Subject + have or has + past participle verb (verb 3)
- I have sent invitation emails.
- They have completed the task.
- She has run out of money.
Negative Sentences
Subject + have or has + not + past participle verb (verb 3)
- I have not explained my point of view yet.
- We haven’t contacted the guests speaker yet.
- The boy has not finished his food yet.
Questions
Have or Has + subject + past participle verb (verb 3) …?
- Have you called the doctor?
- Have they checked the employee lists?
- Has your mother arrived?
(Check a list of regular and irregular verbs here.)
Uses
Present Perfect verbs are used to describe the following:
Finished actions, seen results
We use the present perfect tense to describe actions that happened and finished in the past but their results are still obvious in the present.
The time when they actions happened is not important. The focus here is on the result.
Examples:
- He has washed the car. It looks gorgeous now.
- The children have cleaned up their room.
- My mother has baked a fruit cake. The smell is so good.
- Somebody has eaten my pizza.
Recently finished actions
Present perfect verbs also describe actions that have just finished.
The adverb just is used with the verb.
Examples:
- She has just had her lunch. She needs to brush her teeth.
- The students have just finished their test.
- I have just arrived home. I’m going to check on the children.
- Terry feels tired. He has just completed the project.
Unfinished actions
These actions usually take a long time. They started in the past but have not finished yet.
Examples:
- We have lived in this house for 10 years.
- She has worked for this company since 2018.
- They have stayed at this hotel for four days.
- I have known my best friend since I was fourteen.
Life experiences
Experiences that we have or have not lived can be expressed by the present perfect tense.
The adverbs never, ever, already, and yet can be used here.
We ask about life experiences with Have you ever …?
Examples:
- I have never climbed a mountain.
- Have you ever driven an electric car?
- They have tried sushi at this restaurant.
- We haven’t played squash.
Repeated actions
In addition, present perfect verbs are used to describe actions repeated a number of times between the past and the present, and they may happen again.
Examples:
- She has taken a number of language courses.
- My father has published five books so far.
- We have eaten at this restaurant many times.
- The teacher has given us three assignments this month.
Signal words/phrases used with the present perfect
- ever
- never
- just
- already
- yet
- for
- since
- so far
- lately/recently
- always (I have always wanted to be a doctor.)
- How long…?
- this week, month, etc.
Hi there! Сегодня поговорим о главной тайне английского языка — Present Perfect и его наречия. В этой статье мы напомним том, как строится и когда используется Present Perfect, какие маркеры с ним можно применить и расскажем о нюансах их употребления.
Содержание статьи:
- Present Perfect — прошлое или настоящее?
- Слова-маркеры Present Perfect
- Куда ставить маркеры в предложении?
- Что выбрать: Past Simple или Present Perfect?
- Заключение
Present Perfect — прошлое или настоящее?
В английском языке прошедшее время может быть представлено в разных вариациях, смотря на чем автор делает акцент (на результате действия, времени или длительности).
Present Perfect — настоящее совершенное время. Оно не имеет аналога в русском языке и переводится глаголом совершенного вида в прошедшем времени (I have found it. – Я нашел это.)
Чтобы построить Present Perfect, возьмем have/has как вспомогательный глагол, а основной будет всегда в третьей форме (окончание «-ed» или третья колонка в таблице). И в отрицании и в вопросе глагол сохранит третью форму.
I have finished my project. – Я закончил свой проект.
I haven’t finished my project. – Я не закончил свой проект.
Have you finished your project? – Ты закончил свой проект?
Используя Present Perfect, мы подразумеваем прошлые действия, которые связаны с настоящим. Как они могут быть связаны?
- Действие началось в прошлом и все еще продолжается.
I have learnt English since childhood. – Я учил английский с детства (и все еще учу).
- В настоящем есть результат прошлого действия.
I have broken my leg and I am at hospital now. – Я сломал ногу и сейчас в больнице.
- Дело сделано, а время еще не закончилось.
I have made all the tasks this week. – Я сделал все задания на этой неделе (а неделя все еще идет).
Подробнее о Present Perfect можно прочесть в соответствующей статье.
На простых примерах все легко. А когда вы столкнетесь с нетипичными контекстами и будете испытывать сомнения и муки выбора между Present Perfect и другими временами, то на помощь придут специальные маркеры.
Читай также
Сочинение My summer holidays на английском с переводом
Слова-маркеры Present Perfect
Обычно маркеры Present Perfect представлены наречиями, которые крайне размыто сообщают нам о времени действия. Например, «уже» (already) – когда именно? Сегодня? Вчера?
Чтобы не путаться и не сомневаться, достаточно выучить такие наречия и всегда использовать с ними Present Perfect:
ever – когда-либо, когда бы то ни было, когда-нибудь;
never – никогда;
just – как раз, точно, едва, только что, всего лишь, совсем, только-только, лишь, сейчас;
already – уже, ранее, даже;
not … yet – все еще нет, нет еще, еще не, нет, еще нет;
before – раньше, прежде, пока не, уже, перед тем как;
lately – давно, в последнее время, недавно, за последнее время;
of late – с недавних пор, за последнее время, недавно;
so far – уже, к настоящему времени, на этот час, пока, до сих пор, вплоть до этого момента;
recently – недавно, на днях, в последнее время, только что, не так давно;
by now – на настоящий момент;
up to now – до сих пор, до настоящего времени;
since – с (с какого-то момента);
still – все еще.
Куда ставить маркеры в предложении?
Некоторые наречия Present Perfect имеют особенности употребления.
- Самые частые маркеры Present Perfect «already» и «just» употребляются перед смысловым глаголом и после «have/has».
I have already bought a gift. – Я уже купил подарок.
He has just started this task. – Он только начал это задание.
Есть случаи, когда мы поставим «already» в конце для того, чтобы выразить удивление.
You have come already! – Ты пришел уже!
- «Never» — слово, которое уже содержит отрицание, поэтому с его участием глагол будет только в утвердительной форме.
I have never seen him. – Я никогда его не видел (обратите внимание, в русском варианте двойное отрицание — «никогда + не», в английском «я видел его никогда»).
- «Already», «lately», «recently», «of late» обычно стоят в середине предложения (перед смысловым глаголом), однако их можно поставить и в конец.
He has lately read many books. – Он недавно прочитал много книг.
She has made good progress recently. – Она добилась прогресса в последнее время.
They have not spoken of late. – Последнее время они не разговаривали.
I have already been here. – Я уже здесь был.
- «Before» и «yet», как правило, ставятся в конце предложения.
I have seen this film before. – Я видел этот фильм раньше.
They haven’t finished their project yet. – Они еще не закончили свой проект.
- «Yet» — для отрицаний и вопросов. «Ever» — только для вопросов.
I haven’t had lunch yet. – Я еще не обедал.
Have you ever been to New York? – Ты когда—нибудь был в Нью-Йорке?
Have you cooked dinner yet? – Вы уже приготовили ужин?
В вопросах «yet» используют, чтобы узнать что-либо, получить информацию. Часто «not yet» используют для короткого ответа — «Еще нет»:
— Have you congratulated Bill? — Not yet. I’ll call him right now. – Ты поздравил Билла? — Еще нет. Я позвоню ему прямо сейчас.
- «So far», «up to now», «by now» чаще всего находятся в конце, но можно поставить и в начало, и перед смысловым глаголом.
She has read all his books by now. – К настоящему моменту она прочитала все его книги.
He has so far written ten letters to her. – К этому времени он уже написал ей десять писем.
Up to now I haven’t found my keys. – До сих пор я не нашел мои ключи.
- «Still» указывает на то, что ситуация остается неизменной; процесс затянулся и еще не завершился.
I still haven’t finished writing my composition. – Я все никак не закончу писать сочинение.
He still hasn’t found a new job! – Он все никак не найдет работу!
Что выбрать: Past Simple или Present Perfect?
В американском английском маркеры «just», «already», «yet» сопутствуют как и Present Perfect, так и Past Simple. Не удивляйтесь, если встретите:
The mail just came. – Почта только пришла (американский вариант).
The mail has just come (британский вариант).
I already heard the news. – Я уже слышал эту новость (амер.).
I’ve already heard the news (брит.).
Сочетание «just now» используется исключительно с простым прошедшим временем Past Simple.
She was here just now. – Она только что была здесь.
У маркера recently есть 2 значения: «не так давно» и «за последнее время».
В значении «не так давно» будем употреблять Past Simple.
I started playing the piano only recently. – Я начал играть на фортепиано не так давно.
В значении «в последнее время» используем Present Perfect.
I haven’t heard from her recently. – Я не слышал о ней в последнее время.
Читай также
Как учить английский для детей 5-6 лет: полезные советы родителям
Заключение
And that’s all for today! Не так страшен Present Perfect, как о нем пишут. Надеемся, что наши секреты помогли вам понять это слегка коварное время.
May your English be perfect! And don’t forget, there’s always a better You living inside!
Большая и дружная семья EnglishDom
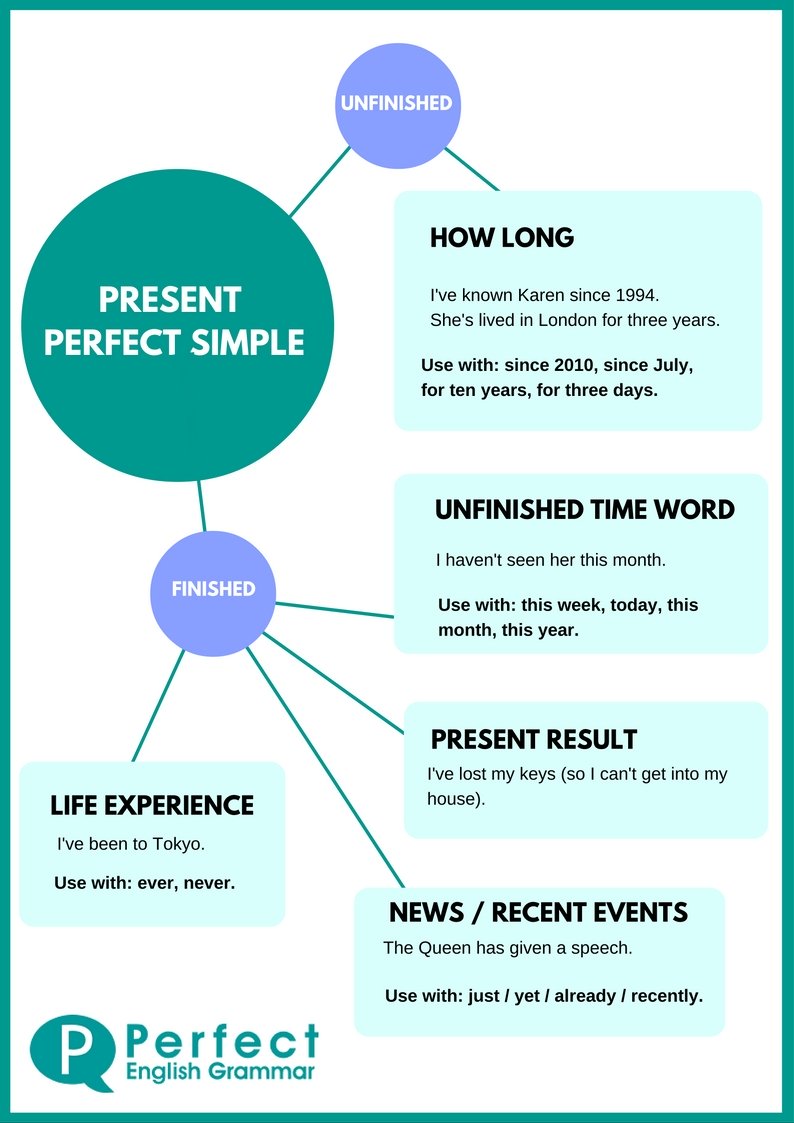
We use this tense for unfinished and finished actions.
Unfinished Actions
1: We use this tense when we want to talk about unfinished actions or states or habits that started in the past and continue to the present. Usually we use it to say ‘how long’ and we need ‘since’ or ‘for’. We often use stative verbs.
- I’ve known Karen since 1994.
- She’s lived in London for three years.
- I’ve worked here for six months.
‘Since’ and ‘For’
We use ‘since’ with a fixed time in the past (2004, April 23rd, last year). The fixed time can be another action, which is in the past simple (since I was at school, since I arrived).
- I’ve known Sam since 1992.
- I’ve liked chocolate since I was a child.
- She’s been here since 2pm.
We use ‘for’ with a period of time (2 hours, three years, six months).
- I’ve known Julie for ten years.
- I’ve been hungry for hours.
- She’s had a cold for a week.
Finished Actions
2: Life experience. These are actions or events that happened sometime during a person’s life. We don’t say when the experience happened, and the person needs to be alive now. We often use the words ‘ever’ and ‘never’ here.
- I have been to Tokyo.
- They have visited Paris three times.
- We have never seen that film.
3: With an unfinished time word (this month, this week, today). The period of time is still continuing.
- I haven’t seen her this month.
- She’s drunk three cups of coffee today.
- I’ve already moved house twice this year!
We CAN’T use the present perfect with a finished time word.
- NOT:I’ve seen him yesterday.
4: A finished action with a result in the present (focus on result). We often use the present perfect to talk about something that happened in the recent past, but that is still true or important now. Sometimes we can use the past simple here, especially in US English.
- I’ve lost my keys (so I can’t get into my house).
- She’s hurt her leg (so she can’t play tennis today).
- They’ve missed the bus (so they will be late).
5: We can also use the present perfect to talk about something that happened recently, even if there isn’t a clear result in the present. This is common when we want to introduce news and we often use the words ‘just / yet / already / recently’. However, the past simple is also correct in these cases, especially in US English.
- The Queen has given a speech.
- I’ve just seen Lucy.
- The Mayor has announced a new plan for the railways.
Been and Gone
In this tense, we use both ‘been’ and ‘gone’ as the past participle of ‘go’, but in slightly different circumstances.
We use ‘been’ (often when we talk about life experience) to mean that the person we’re talking about visited the place and came back.
- I’ve been to Paris (in my life, but now I’m in London, where I live).
- She has been to school today (but now she’s back at home).
- They have never been to California.
We use ‘gone’ (often when we are talking about an action with a result in the present) to mean that the person went to the place and is at the place now.
- Where’s John? He’s gone to the shops (he’s at the shops now).
- Julie has gone to Mexico (now she’s in Mexico).
- They’ve gone to Japan for three weeks (now they’re in Japan).
Read more about the difference between the present perfect and the past simple here.
Read more about the difference between the present perfect simple and the present perfect continuous here.
Try some present perfect exercises here.
Как образуется Present Perfect и когда употребляется? Какие у Present Perfect слова-маркеры? Какая разница между Past Simple и Present Perfect? Найдем ответы на все эти вопросы в сегодняшней статье.
Содержание:
- 1. Как образуется Present Perfect
- 2. Когда употребляется Present Perfect
- 3. Слова-маркеры Present Perfect
- 4. Разница между Past Simple и Present Perfect
- 5. Have been или have gone?
Как образуется Present Perfect
Давайте посмотрим на образование Present Perfect.
Примеры утвердительных предложений в Present Perfect:
I have bought a new car! — Я купил новую машину!
He has lied to me. — Он мне солгал.
We’ve agreed! — Мы пришли к согласию!
Sue’s come home. — Сью пришла домой.
Примеры отрицательных предложений в Present Perfect:
They have not done their work properly. — Они не выполнили свою работу должным образом.
Rachel has not met David yet. — Рэйчел еще не знакома с Дэвидом.
They haven’t seen this film. — Они не видели этот фильм.
My teacher hasn’t checked the tests. — Мой учитель не проверил тесты.
Примеры вопросительных предложений в Present Perfect:
Have we paid the bills this month? — Мы оплачивали счета в этом месяце?
Has Gloria delivered the package on time? — Глория доставила посылку вовремя?
Когда употребляется Present Perfect
Давайте рассмотрим случаи употребления Present Perfect:
- Завершенные действия, у которых есть результат в настоящем
Если действие произошло в прошлом, но у него есть связь с настоящим, используем Present Perfect.
I can’t go to the mountains with you, I’ve broken my arm. — Я не могу пойти с тобой в горы, я сломала руку! (результат в настоящем — не могу пойти в горы)
I’m so upset. You haven’t done your homework again! — Я так расстроена. Ты снова не выполнил домашнюю работу! (результат в настоящем — я расстроена) - Новости
Чтобы поделиться недавними новостями, мы употребляем Present Perfect.
I’ve won in the lottery! — Я выиграл в лотерею!
John and Lily have broken up. — Джон и Лили расстались.Обращаем ваше внимание на то, что о дальнейших деталях новости обычно рассказывают в Past Simple:
I’ve passed my English exam! (новость) I scored 90%! (детали) — Я сдал свой экзамен по английскому! Я набрал 90% !
— Mark’s come back from Italy!
— How long was he there? Where did he stay?
— Марк вернулся из Италии!
— Сколько он там пробыл? Где он жил? - Действия, которые многократно повторялись до настоящего момента
I’ve called you three times, where have you been? — Я звонила тебе три раза, где ты был?
- Действия, которые начались в прошлом и все еще продолжаются
Обычно в этой функции используется Present Perfect Continuous, но с глаголами состояния употребляем Present Perfect.
Mrs Baker has been being has been a teacher since 1995. — Миссис Бейкер работает учителем с 1995.
I have been knowing have known the Smiths family for about a decade. — Я знаю семью Смитов уже около десяти лет.С глаголами to work, to live, to study, to play и некоторыми другими можно использовать как Present Perfect Continuous, так и Present Perfect. При переводе на русский язык обычно употребляем глаголы в настоящем времени.
I have lived / have been living in this house since my childhood. — Я живу в этом доме с самого детства.
Susan has played / has been playing tennis for 10 years. — Сьюзан играет в теннис 10 лет. - Опыт
Чтобы рассказать, что с нами случалось или не случалось в прошлом, также используем Present Perfect. В такой ситуации нам совершенно не важно, когда этот опыт был получен, важен лишь факт его наличия.
I’ve ridden an elephant! — Я каталась на слоне!
Mike has read the Harry Potter book series. — Майк читал серию книг о Гарри Поттере.
We’ve never gone skiing! — Мы никогда не катались на лыжах.
Если вы хотите попрактиковаться в употреблении Present Perfect на примерах из жизни, записывайтесь на курс практической грамматики.
Слова-маркеры Present Perfect
Рассмотрим слова, которые укажут нам на время Present Perfect:
- Already — уже
Обычно ставится между вспомогательным и основным глаголом и используется в утверждениях.
I’ve already seen this episode! — Я уже видел эту серию!
My employees have already completed their task. — Мои подчиненные уже завершили свои задачи. - Just — только что
Обычно ставится между вспомогательным и основным глаголом.
I’ve just finished working. — Я только что закончила работать.
Wait, that’s it? We’ve just started! — Погоди, и все? Мы же только начали! - Yet — уже, еще
Используется в отрицательных и вопросительных предложениях, обычно ставится в конце предложения.
I haven’t finished my homework yet. — Я еще не закончил свою домашнюю работу.
Have you made the bed yet? — Ты уже застелил кровать? - Still — все еще
В отличие от yet, still обычно ставится перед вспомогательным глаголом.
You still haven’t washed the towels, have you? — Ты все еще не постирал полотенца, да?
- Ever — когда-либо
Используйте, чтобы спросить об опыте вашего собеседника, обычно ставится перед основным глаголом.
Have you ever tried Japanese food? — Ты когда-либо пробовал японскую еду?
Has Rosa ever cheated in the exam? — Роза когда-либо списывала на экзамене? - Never — никогда
Ставится перед смысловым глаголом. Хотим напомнить, что в английском языке слово never употребляется с глаголами в положительной форме, без частицы not.
I have never been here. — Я здесь никогда не был.
I have never played any musical instrument. — Я никогда не играл ни на каком музыкальном инструменте. - Before — до этого, раньше
I have met John before. — Я встречал Джона до этого.
Lucy hasn’t tried ice-cream before. — Люси раньше не пробовала мороженое. - Recently, lately — в последнее время, недавно
We have missed too many opportunities lately. — Мы упустили слишком много возможностей в последнее время.
It’s the best film I’ve seen recently. — Это лучший фильм, что я видел за последнее время. - Since — с какого-то момента
I haven’t seen a comedy since last year. — Я не смотрел комедии с прошлого года.
We have been together since 2014. — Мы вместе с 2014 года. - For — на протяжении
I’ve worked here for 5 years. — Я здесь проработал 5 лет.
We haven’t seen each other for months, it seems. — Похоже, мы не виделись несколько месяцев.
Разница между Past Simple и Present Perfect
Для многих изучающих английский язык разница между этими двумя временами остается загадкой и по сей день. Разберемся, когда употребляется Present Perfect, а в каких случаях — Past Simple.
- Говорим или не говорим, когда что-то произошло
В Present Perfect важен факт совершения действия и не имеет значения, когда именно оно произошло. В Past Simple обычно указывается, когда именно произошло действие. Примеры слов-маркеров в Past Simple: yesterday (вчера), in 2015 (в 2015), ago (тому назад), when I was younger (когда я был моложе) и другие.
I have ridden a horse! — Я ездил верхом! (неважно, когда это было)
I rode a horse yesterday morning! — Вчера утром я ездил верхом! (конкретный момент в прошлом) - Законченный период времени или текущий
Если мы говорим о периоде времени, который все еще продолжается, употребляем Present Perfect. Часто на текущий период указывают такие слова-маркеры, как today (сегодня), this week (на этой неделе), this month (в этом месяце) и this year (в этом году). Если период закончен, используем Past Simple, на него указывают следующие слова-маркеры: last week (на прошлой неделе), last month (в прошлом месяце), last year (в прошлом году).
I haven’t seen you in the office this week. — Я не видел тебя в офисе на этой неделе. (неделя не закончилась)
I didn’t see Sofie at work last week. — Я не видел Софи на работе на прошлой неделе. (прошлая неделя закончилась) - Связь с настоящим и факт из прошлого
У Present Perfect всегда есть какая-то привязка к настоящему, тогда как при помощи Past Simple можно просто изложить факты о прошлом.
We’re so happy! We have learnt English! — Мы так счастливы! Мы выучили английский! (мы счастливы сейчас — привязка к настоящему)
Ivan learned English at school. — Иван учил английский в школе. (факт из прошлого)
Чтобы вы могли с легкостью ориентироваться в разнице между Past Simple и Present Perfect, мы подготовили следующую таблицу:
| Present Perfect | Past Simple |
|---|---|
| Не говорим, когда действие произошло
We’ve travelled around the world! — Мы объехали весь мир! |
Говорим, когда действие произошло
We travelled to the South last summer. — Прошлым летом мы поехали на юг. |
| Текущий период времени
I haven’t eaten any meat this month. — В этом месяце я не ела мяса. |
Законченный период времени
John didn’t eat any meat last summer. — Джон не ел мяса прошлым летом. |
| Есть связь с настоящим
That’s great! I have done my homework! — Как здорово! Я сделала домашнюю работу! |
Нет связи с настоящим
I didn’t do my homework yesterday. — Я не сделала домашнюю работу вчера. |
Have been или have gone?
Студенты иногда путаю конструкции have been и have gone. Давайте рассмотрим их значения:
- Have been — побывал, съездил/сходил и вернулся
I have been to Spain. — Я был в Испании.
Have you been to the lecture? — Ты ходил на лекцию? - Have gone — уехал/ушел и еще не вернулся
Sue has gone to London. — Сью уехала в Лондон.
My neighbours have gone to Turkey for summer. — Мои соседи уехали в Турцию на лето.
А теперь предлагаем пройти тест по Present Perfect.
Тест по теме «Present Perfect — правила и примеры»
© 2023 englex.ru, копирование материалов возможно только при указании прямой активной ссылки на первоисточник.
The present perfect tense is used a lot in English, so it’s important to get it right. In fact, as soon as you arrive in an English-speaking country people will use this tense when they ask you, “How long have you been here?”
How would you answer this? If you are not sure, today’s lesson will help.
This lesson will help you use the present perfect tense to answer this kind of question and so much more in English.
There are many situations that need the present perfect. You’ll learn each one and get examples to understand it clearly.
There are also some words you SHOULD use with present perfect and some you definitely SHOULDN’T. So let’s go make sure you know those too.
Learn to use the present perfect correctly — every time.
What Is the Present Perfect?
It’s a way of using verbs that makes it clear that an action has a connection between the past and now.
For example, we use the present perfect tense if something started in the past and is still true or still describes the current situation.
- I have lived here for 3 years. (I started living here 3 years ago in the past and I still live here now. The total time of me living here is 3 years till now. This started in the past and is not finished)
- I have loved chocolate since I was 3 years old. (I started to love chocolate when I was 3 years old and I still love it now. This is still true now.)
These examples have a couple of the words we use a lot with present perfect — for and since. If you use ‘for’ or ‘since’ with present perfect then you are definitely getting it right.
One word we should NOT use with present perfect is ‘ago.’
If we use ‘ago’ we are saying something happened in the past, there is no connection with now, so it definitely should not be used with the present perfect.
And for Questions Like, “How’s your day going?”
We also use present perfect when a period of time has not finished, it is still going on, like today, this week, this month, none of these have finished yet.
For example:
- I have been so busy today! (today is still going, this is still the present moment)
- You have been so grumpy this week! (you started being grumpy in the past, earlier this week. The week has not ended and you are still in a bad mood!)
Don’t Forget — Something that JUST Happened
The present perfect is also used when something just happened, like:
- Ouch! I’ve just cut my finger.
- They’ve just gone home. (they left a short time earlier)
Do you notice a pattern in these sentences? ‘Just’ is a word we use a lot with present perfect.
- OMG! I’ve just passed my exam!
- She’s just broken up with her boyfriend.
- He’s just become a father.
Use the Present Perfect to Talk about Your Experience
Another way we use it is when we are talking about something we have or have not done in our lives, so our life experiences:
- I’ve been to 6 countries.
- You haven’t been to Disneyland?
- She’s completed 3 university degrees.
- He’s eaten scorpion and eel, he’s a very adventurous eater!
How to Correctly Form the Present Perfect
To correctly form this tense, we need 2 things, ‘have’ or ‘has’ + the past participle of the verb. The past participle is also know as the third form of the verb.
Remember learning drink, drank, drunk? Or write, wrote, written? Drunk and written are the third forms.
Regular Verb Forms for the Present Perfect
Verb
Ask
Call
Help
Liked
Move
Look
Subject
I
You
We
They
She
He
Perfect Form
have asked
have called
have helped
have liked
has moved
has looked
Example Sentence
I’ve asked her to come tomorrow.
You’ve called him too many times!
We’ve helped her a lot this month.
They’ve liked this band for years!
She’s moved into a new apartment.
He hasn’t looked everywhere!
Irregular Verb Forms for the Present Perfect
Verb
Be
Go
Go
Come
Find
Leave
Make
Put
Take
Forget
Have
Subject
I
You
They
We
She
He
It
I
You
She
It
Perfect Form
have been
have been
have gone
have come
has found
has left
has made
have put
have taken
has forgotten
has had
Example Sentence
I’ve been a teacher for 10 years.
You’ve been to Fiji?
They haven’t gone home already.
We’ve come to help you.
She’s found the perfect job!
He’s left his bag behind.
It’s made me so happy!
I’ve put the files on your desk.
You’ve taken my favorite pen!
She’s forgotten to take out the trash!
It’s had a terrible effect!
An easy trick you can use to know when to use the present perfect AND when NOT to use it.
There are some tricks that can help you remember when to use present perfect.
For example, we use it a lot with the words: ever, never, always.
- I’ve never tried bungee jumping.
- Have you ever been to Japan? → When someone starts a question with, “Have you ever…” that’s a quick clue that you should use the present perfect in your answer.
- She’s always loved jazz.
But, when you talk about a specific time in the past that has already finished you shouldn’t use it.
For example, you SHOULD NOT say:
- X I have done it yesterday. (you should use past simple: I did it yesterday)
- X I’ve seen it last year. (you should use past simple: I saw it last year)
- X I’ve been there in 2018. (you should use past simple: I went there in 2018)
- X It has arrived on May 1st. (you should use past simple: It arrived on May 1st)
Now THIS was a serious lesson!
But the good news is, you are ready to use present perfect perfectly!
Now it is fresh in your mind, it’s a great chance to practice. We would love to hear your answers to one of these questions, using present perfect (I have…/I’ve…), so please share below. If you prefer you can write about someone else using she has (she’s) or he has (he’s):
- What are some amazing and memorable things you have done in your life?
- What brave things you have done?
- What are some amazing or unusual foods you have tried?
The best place to share, get feedback, and learn from others in the Confident English Community is in the comments below.
Have a fantastic Confident English Wednesday!
~ Annemarie
P.S. ❤️this lesson? Check out: 5 Common Grammar Mistakes with Easy Fixes
You’ll also get my Confident English lessons delivered by email every Wednesday and occasional information about available courses. You can unsubscribe any time.
Meet Sam. Here are some neat facts about Sam: Sam has performed in a rock band. Sam has met two American presidents. Sam’s mother has won the lottery twice. Not only are all these facts pretty cool, but they all use a special bit of grammar to connect the past with the present. All of these sentences use verbs in the present perfect tense. Let’s stop living in the past and take a moment to learn more about this interesting aspect of grammar right now. And enough about Sam!
What is present perfect tense?
We use verbs, to put it simply, to refer to actions or states of being. In English, we use a variety of different verb tenses in sentences. Generally speaking, the tense of a verb tells you about when in time something happened. Today, we will look at the present perfect tense. The present perfect tense may strike some as a bit of a misnomer, because it doesn’t seem to be referring to the present at all at first glance. You can see this in the following sentence that uses the present perfect tense:
- I have gone to the store three times today.
This sentence describes an action that happened in the past, as it says that I have made three trips to the store prior to the current moment when I am saying this sentence. At first look, this sentence seems to suggest that the present perfect tense does the same job as the simple past tense: I went to the store three times today. While simple past and present perfect can sometimes be effectively used interchangeably to get the same meanings (as with our inefficient trips to the store example), there can be slight but important differences in these two verb tenses. Look at the following two sentences:
- Simple past tense: She owned two Dalmatians for 10 years.
- Present perfect tense: She has owned two Dalmatians for 10 years.
Do you notice the difference? The first sentence states that she owned Dalmatians for a period of 10 years in the past but she doesn’t own them now. The action is finished and completed. The second sentence, however, implies that she still owns these dogs now. The action is still happening in the present. That is the key difference between these two similar verb tenses.
We have a simple explanation for all your questions about the simple past tense, right here.
When do you use present perfect tense?
One of the main reasons we use the present perfect tense is to indicate that a state or action that happened or started in the past has some connection to the present and future. Typically, we use the present perfect tense to indicate something happened in the past but continues to occur. For example:
- I have waited for two hours. (I started waiting two hours ago and I am still waiting now.)
- They have lived here all their lives. (They started living here a long time ago and still live here now.)
The present perfect tense can also connect present events to those that happened in the past. For example, the sentence Josh is acting as our tour guide through Boston because he has been here before says that Josh traveled to Boston sometime in the past. This sentence also implies that we are all in Boston right now because it also uses the present continuous tense.
Often, we are faced with the tough decision of whether we should use the present perfect tense or the simple past tense in a sentence. If a past action has no connection to the present, it may be more appropriate to use the simple past tense:
- I have lost my wallet! (You recently lost your wallet in the past and you really want to find it right now.)
- I lost my wallet. (You lost your wallet in the past but it has no impact on the current time. You either found it or it remained lost forever and you gave up looking for it.)
That said, in everyday speech, both utterances do effectively mean the same thing. Thanks, grammar.
Notably, we don’t use the present perfect tense when we talk about specific times or time periods that began and completely ended in the past:
❌ Incorrect: I have cleaned the house at 9 am this morning.
✅ Correct: I cleaned the house at 9 am this morning.
❌ Incorrect: He has studied Spanish last year.
✅ Correct: He studied Spanish last year.
How to form present perfect tense
In order to form the present perfect tense, we use the word have or has followed by the past participle of the verb. For regular verbs, the past participle is a form of the verb that ends in -ed, -d, or -t. For example, the past participle of cook is cooked and so the present perfect tense would be have/has cooked. Some verbs use a –t variant in the past participle and end in a –t rather than -ed. For example, the past participle of bend is bent and the past participle of sleep is slept.
Has and have make a lot of difference in English grammar. See what else they have going on here.
Keep in mind, though, that there are many irregular verbs that don’t follow this general rule. Here are the past participles of just a few irregular verbs:
- go → gone
- fly → flown
- catch → caught
- be → been
- rise → risen
- ride → ridden
- break → broken
We use the word have in the present perfect tense except when the subject is in the third person singular, in which case we use the word has. For example:
- I have worked as a lifeguard before.
- The cats have eaten twice already.
- She has given me lots of good advice.
- I think Brian has seen my house once before.
When using the present perfect tense, we can also shorten our sentences with contractions:
- I’ve worked as a lifeguard before.
- They’ve eaten twice already.
- She’s given me lots of good advice.
- I think he’s seen my house once before.
How to make present perfect tense negative
To make the present perfect tense negative, all you need to do is put the word not after have/has. The contractions haven’t and hasn’t can also be used. Here are examples of sentences that use the present perfect tense in the negative:
- I have not talked to Ashley yet.
- I haven’t talked to Ashley yet.
- Vince has not finished his sandwich.
- Vince hasn’t finished his sandwich.
- We haven’t met the new neighbor.
- We have not met the new neighbor.
- Our teacher has not graded our exams yet.
- Our teacher hasn’t graded our exams yet.
What else is perfect? Your writing
You won’t mistake your verb tenses again when you check your writing on Thesaurus.com’s Grammar Coach™. This tool uses machine learning technology uniquely designed to catch grammar and spelling errors. Its Synonym Swap will find the best nouns, adjectives, and more to help say what you really mean, guiding you toward clearer, stronger, writing.
Whether you’re writing about the past, present, or future, start writing smarter today!