From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
WordPerfect, a word processor first released for minicomputers in 1979 and later ported to microcomputers, running on Windows XP
A word processor (WP)[1][2] is a device or computer program that provides for input, editing, formatting, and output of text, often with some additional features.
Early word processors were stand-alone devices dedicated to the function, but current word processors are word processor programs running on general purpose computers.
The functions of a word processor program fall somewhere between those of a simple text editor and a fully functioned desktop publishing program. However, the distinctions between these three have changed over time and were unclear after 2010.[3][4]
Background[edit]
Word processors did not develop out of computer technology. Rather, they evolved from mechanical machines and only later did they merge with the computer field.[5] The history of word processing is the story of the gradual automation of the physical aspects of writing and editing, and then to the refinement of the technology to make it available to corporations and Individuals.
The term word processing appeared in American offices in early 1970s centered on the idea of streamlining the work to typists, but the meaning soon shifted toward the automation of the whole editing cycle.
At first, the designers of word processing systems combined existing technologies with emerging ones to develop stand-alone equipment, creating a new business distinct from the emerging world of the personal computer. The concept of word processing arose from the more general data processing, which since the 1950s had been the application of computers to business administration.[6]
Through history, there have been three types of word processors: mechanical, electronic and software.
Mechanical word processing[edit]
The first word processing device (a «Machine for Transcribing Letters» that appears to have been similar to a typewriter) was patented by Henry Mill for a machine that was capable of «writing so clearly and accurately you could not distinguish it from a printing press».[7] More than a century later, another patent appeared in the name of William Austin Burt for the typographer. In the late 19th century, Christopher Latham Sholes[8] created the first recognizable typewriter although it was a large size, which was described as a «literary piano».[9]
The only «word processing» these mechanical systems could perform was to change where letters appeared on the page, to fill in spaces that were previously left on the page, or to skip over lines. It was not until decades later that the introduction of electricity and electronics into typewriters began to help the writer with the mechanical part. The term “word processing” (translated from the German word Textverarbeitung) itself was created in the 1950s by Ulrich Steinhilper, a German IBM typewriter sales executive. However, it did not make its appearance in 1960s office management or computing literature (an example of grey literature), though many of the ideas, products, and technologies to which it would later be applied were already well known. Nonetheless, by 1971 the term was recognized by the New York Times[10] as a business «buzz word». Word processing paralleled the more general «data processing», or the application of computers to business administration.
Thus by 1972 discussion of word processing was common in publications devoted to business office management and technology, and by the mid-1970s the term would have been familiar to any office manager who consulted business periodicals.
Electromechanical and electronic word processing[edit]
By the late 1960s, IBM had developed the IBM MT/ST (Magnetic Tape/Selectric Typewriter). This was a model of the IBM Selectric typewriter from the earlier part of this decade, but it came built into its own desk, integrated with magnetic tape recording and playback facilities along with controls and a bank of electrical relays. The MT/ST automated word wrap, but it had no screen. This device allowed a user to rewrite text that had been written on another tape, and it also allowed limited collaboration in the sense that a user could send the tape to another person to let them edit the document or make a copy. It was a revolution for the word processing industry. In 1969, the tapes were replaced by magnetic cards. These memory cards were inserted into an extra device that accompanied the MT/ST, able to read and record users’ work.
In the early 1970s, word processing began to slowly shift from glorified typewriters augmented with electronic features to become fully computer-based (although only with single-purpose hardware) with the development of several innovations. Just before the arrival of the personal computer (PC), IBM developed the floppy disk. In the early 1970s, the first word-processing systems appeared which allowed display and editing of documents on CRT screens.
During this era, these early stand-alone word processing systems were designed, built, and marketed by several pioneering companies. Linolex Systems was founded in 1970 by James Lincoln and Robert Oleksiak. Linolex based its technology on microprocessors, floppy drives and software. It was a computer-based system for application in the word processing businesses and it sold systems through its own sales force. With a base of installed systems in over 500 sites, Linolex Systems sold 3 million units in 1975 — a year before the Apple computer was released.[11]
At that time, the Lexitron Corporation also produced a series of dedicated word-processing microcomputers. Lexitron was the first to use a full-sized video display screen (CRT) in its models by 1978. Lexitron also used 51⁄4 inch floppy diskettes, which became the standard in the personal computer field. The program disk was inserted in one drive, and the system booted up. The data diskette was then put in the second drive. The operating system and the word processing program were combined in one file.[12]
Another of the early word processing adopters was Vydec, which created in 1973 the first modern text processor, the «Vydec Word Processing System». It had built-in multiple functions like the ability to share content by diskette and print it.[further explanation needed] The Vydec Word Processing System sold for $12,000 at the time, (about $60,000 adjusted for inflation).[13]
The Redactron Corporation (organized by Evelyn Berezin in 1969) designed and manufactured editing systems, including correcting/editing typewriters, cassette and card units, and eventually a word processor called the Data Secretary. The Burroughs Corporation acquired Redactron in 1976.[14]
A CRT-based system by Wang Laboratories became one of the most popular systems of the 1970s and early 1980s. The Wang system displayed text on a CRT screen, and incorporated virtually every fundamental characteristic of word processors as they are known today. While early computerized word processor system were often expensive and hard to use (that is, like the computer mainframes of the 1960s), the Wang system was a true office machine, affordable to organizations such as medium-sized law firms, and easily mastered and operated by secretarial staff.
The phrase «word processor» rapidly came to refer to CRT-based machines similar to Wang’s. Numerous machines of this kind emerged, typically marketed by traditional office-equipment companies such as IBM, Lanier (AES Data machines — re-badged), CPT, and NBI. All were specialized, dedicated, proprietary systems, with prices in the $10,000 range. Cheap general-purpose personal computers were still the domain of hobbyists.
Japanese word processor devices[edit]
In Japan, even though typewriters with Japanese writing system had widely been used for businesses and governments, they were limited to specialists who required special skills due to the wide variety of letters, until computer-based devices came onto the market. In 1977, Sharp showcased a prototype of a computer-based word processing dedicated device with Japanese writing system in Business Show in Tokyo.[15][16]
Toshiba released the first Japanese word processor JW-10 in February 1979.[17] The price was 6,300,000 JPY, equivalent to US$45,000. This is selected as one of the milestones of IEEE.[18]
Toshiba Rupo JW-P22(K)(March 1986) and an optional micro floppy disk drive unit JW-F201
The Japanese writing system uses a large number of kanji (logographic Chinese characters) which require 2 bytes to store, so having one key per each symbol is infeasible. Japanese word processing became possible with the development of the Japanese input method (a sequence of keypresses, with visual feedback, which selects a character) — now widely used in personal computers. Oki launched OKI WORD EDITOR-200 in March 1979 with this kana-based keyboard input system. In 1980 several electronics and office equipment brands entered this rapidly growing market with more compact and affordable devices. While the average unit price in 1980 was 2,000,000 JPY (US$14,300), it was dropped to 164,000 JPY (US$1,200) in 1985.[19] Even after personal computers became widely available, Japanese word processors remained popular as they tended to be more portable (an «office computer» was initially too large to carry around), and become necessities in business and academics, even for private individuals in the second half of the 1980s.[20] The phrase «word processor» has been abbreviated as «Wa-pro» or «wapuro» in Japanese.
Word processing software[edit]
The final step in word processing came with the advent of the personal computer in the late 1970s and 1980s and with the subsequent creation of word processing software. Word processing software that would create much more complex and capable output was developed and prices began to fall, making them more accessible to the public. By the late 1970s, computerized word processors were still primarily used by employees composing documents for large and midsized businesses (e.g., law firms and newspapers). Within a few years, the falling prices of PCs made word processing available for the first time to all writers in the convenience of their homes.
The first word processing program for personal computers (microcomputers) was Electric Pencil, from Michael Shrayer Software, which went on sale in December 1976. In 1978 WordStar appeared and because of its many new features soon dominated the market. However, WordStar was written for the early CP/M (Control Program–Micro) operating system, and by the time it was rewritten for the newer MS-DOS (Microsoft Disk Operating System), it was obsolete. Suddenly, WordPerfect dominated the word processing programs during the DOS era, while there was a large variety of less successful programs.
Early word processing software was not as intuitive as word processor devices. Most early word processing software required users to memorize semi-mnemonic key combinations rather than pressing keys such as «copy» or «bold». Moreover, CP/M lacked cursor keys; for example WordStar used the E-S-D-X-centered «diamond» for cursor navigation. However, the price differences between dedicated word processors and general-purpose PCs, and the value added to the latter by software such as “killer app” spreadsheet applications, e.g. VisiCalc and Lotus 1-2-3, were so compelling that personal computers and word processing software became serious competition for the dedicated machines and soon dominated the market.
Then in the late 1980s innovations such as the advent of laser printers, a «typographic» approach to word processing (WYSIWYG — What You See Is What You Get), using bitmap displays with multiple fonts (pioneered by the Xerox Alto computer and Bravo word processing program), and graphical user interfaces such as “copy and paste” (another Xerox PARC innovation, with the Gypsy word processor). These were popularized by MacWrite on the Apple Macintosh in 1983, and Microsoft Word on the IBM PC in 1984. These were probably the first true WYSIWYG word processors to become known to many people.
Of particular interest also is the standardization of TrueType fonts used in both Macintosh and Windows PCs. While the publishers of the operating systems provide TrueType typefaces, they are largely gathered from traditional typefaces converted by smaller font publishing houses to replicate standard fonts. Demand for new and interesting fonts, which can be found free of copyright restrictions, or commissioned from font designers, occurred.
The growing popularity of the Windows operating system in the 1990s later took Microsoft Word along with it. Originally called «Microsoft Multi-Tool Word», this program quickly became a synonym for “word processor”.
From early in the 21st century Google Docs popularized the transition to online or offline web browser based word processing, this was enabled by the widespread adoption of suitable internet connectivity in businesses and domestic households and later the popularity of smartphones. Google Docs enabled word processing from within any vendor’s web browser, which could run on any vendor’s operating system on any physical device type including tablets and smartphones, although offline editing is limited to a few Chromium based web browsers. Google Docs also enabled the significant growth of use of information technology such as remote access to files and collaborative real-time editing, both becoming simple to do with little or no need for costly software and specialist IT support.
See also[edit]
- List of word processors
- Formatted text
References[edit]
- ^ Enterprise, I. D. G. (1 January 1981). «Computerworld». IDG Enterprise. Archived from the original on 2 January 2019. Retrieved 1 January 2019 – via Google Books.
- ^ Waterhouse, Shirley A. (1 January 1979). Word processing fundamentals. Canfield Press. ISBN 9780064537223. Archived from the original on 2 January 2019. Retrieved 1 January 2019 – via Google Books.
- ^ Amanda Presley (28 January 2010). «What Distinguishes Desktop Publishing From Word Processing?». Brighthub.com. Archived from the original on 1 April 2019. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
- ^ «How to Use Microsoft Word as a Desktop Publishing Tool». PCWorld. 28 May 2012. Archived from the original on 19 August 2017. Retrieved 3 May 2018.
- ^ Price, Jonathan, and Urban, Linda Pin. The Definitive Word-Processing Book. New York: Viking Penguin Inc., 1984, page xxiii.
- ^ W.A. Kleinschrod, «The ‘Gal Friday’ is a Typing Specialist Now,» Administrative Management vol. 32, no. 6, 1971, pp. 20-27
- ^ Hinojosa, Santiago (June 2016). «The History of Word Processors». The Tech Ninja’s Dojo. The Tech Ninja. Archived from the original on 6 May 2018. Retrieved 6 May 2018.
- ^ See also Samuel W. Soule and Carlos Glidden.
- ^ The Scientific American, The Type Writer, New York (August 10, 1872)
- ^ W.D. Smith, “Lag Persists for Business Equipment,” New York Times, 26 Oct. 1971, pp. 59-60.
- ^ Linolex Systems, Internal Communications & Disclosure in 3M acquisition, The Petritz Collection, 1975.
- ^ «Lexitron VT1200 — RICM». Ricomputermuseum.org. Archived from the original on 3 January 2019. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
- ^ Hinojosa, Santiago (1 June 2016). «The History of Word Processors». The Tech Ninja’s Dojo. Archived from the original on 24 December 2018. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
- ^ «Redactron Corporation. @ SNAC». Snaccooperative.org. Archived from the original on 15 December 2018. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
- ^ «日本語ワードプロセッサ». IPSJコンピュータ博物館. Retrieved 2017-07-05.
- ^ «【シャープ】 日本語ワープロの試作機». IPSJコンピュータ博物館. Retrieved 2017-07-05.
- ^ 原忠正 (1997). «日本人による日本人のためのワープロ». The Journal of the Institute of Electrical Engineers of Japan. 117 (3): 175–178. Bibcode:1997JIEEJ.117..175.. doi:10.1541/ieejjournal.117.175.
- ^ «プレスリリース;当社の日本語ワードプロセッサが「IEEEマイルストーン」に認定». 東芝. 2008-11-04. Retrieved 2017-07-05.
- ^
«【富士通】 OASYS 100G». IPSJコンピュータ博物館. Retrieved 2017-07-05. - ^ 情報処理学会 歴史特別委員会『日本のコンピュータ史』ISBN 4274209334 p135-136
Hello Learners, Today we will learn What are Examples of Word Processor Software?
In this post, I will explain the various types of word processor software.
This Article is the Best on the whole internet.
If you read this article carefully you will understand all about the examples of word processors and the features of a word processor.
I Guarantee you, after reading this article you will not need to read any other Articles. In fact, our readers are satisfied with this blog post.
What Is Word Processor?
Word processor is a type of application software, which is being widely used in different fields at present. With the help of a word processor, you can create any type of document. Microsoft word is a very popular word processor software.
Word processors software creates many types of word files extensions like — text files (.txt), rich text files (.rtf), HTML files (.htm & .html), and Word files (.doc & .docx).
I hope you understand this.
There are various examples of word processor software, which names are given below.
- Microsoft Word
- Google Docs
- iWork Pages
- OpenOffice Writer
- WordPerfect
- FocusWriter
- LibreOffice Writer
- AbiWord
- WPS Word
- Polaris Docs
- Writemonkey
- Dropbox Paper
- Scribus
- Zoho Docs Writer
1. Microsoft Word
Picture of Microsoft Word Logo
Microsoft Word ( MS) is a word processing software developed by Microsoft company. It was first released on October 25, 1983, as a replacement for the Microsoft Basic program.
As of 2021, it is the most popular word processing application in the world, with over 240 million active users.
Word is used for a variety of purposes, including composing text, creating documents, formatting text, and creating tables and diagrams.
It also supports a wide range of fonts and colors, as well as advanced formatting features such as headings, subheadings, lists, and tables.
2. Google Docs
Google Docs — Examples of Word Processor
Google Docs is a free online application that lets you create, edit, and share documents with others.
It includes features such as an easy-to-use interface, collaboration features, and automatic updates.
Documents can be edited in any web browser, and they are stored in the Google Docs cloud.
Google Docs is a great tool for businesses of all sizes. It’s perfect for creating and sharing documents with colleagues, clients, or customers.
It also makes it easy to keep track of changes and updates to your documents.
3. iWork Pages
iWork Page is a cloud-based platform that allows users to create and manage their own websites and online portfolios.
It includes features such as a drag-and-drop website builder, unlimited storage space, and the ability to add custom domains.
iWork Pages also offers a variety of marketing tools, including social media integration, email marketing, and AdWords campaigns.
4. OpenOffice Writer
OpenOffice Writer is a free and open-source office suite that includes a word processor, a spreadsheet application, and a presentation program.
It is available for all major operating systems, and it has been downloaded more than 100 million times.
OpenOffice Writer is perfect for anyone who wants to create professional-grade documents easily and quickly.
It has all the features you would expect in a top-of-the-line word processor, including support for spell checking, grammar checking, and syntax highlighting.
It also has a wide range of features for working with documents, including support for embedding images and videos, creating tables and charts, and more.
5. WordPerfect
Examples of Word Processor — WordPerfect
WordPerfect is a software suite that was first released in 1987 and is still used by millions of people today.
It includes a word processor, a spreadsheet program, a presentation program, and a graphics program.
It is popular for its ease of use and its ability to handle long documents with ease.
WordPerfect is versatile and reliable, and it can be used by both small businesses and professionals who need a high-quality word processing solution.
If you’re looking for affordable, reliable software that’s been around for years, WordPerfect is definitely worth considering.
6. FocusWriter
The FocusWriter platform provides users with detailed writing instructions, as well as a range of helpful tools and resources that make it easy to create high-quality content.
In addition, the platform offers a variety of customization options that allow users to create content that is specific to their needs and interests.
FocusWriter is perfect for anyone who wants to improve their writing skills, increase their online presence, or boost the effectiveness of their marketing campaigns.
It’s also a great resource for individuals who want to learn more about various business topics.
7. LibreOffice Writer
LibreOffice Writer is a free, open-source office productivity software that enables users to create, edit, and format documents using a variety of standard text and graphics editors.
It includes a word processor, spreadsheet application, presentation software, and more.
LibreOffice Writer is available for Windows, macOS, Android, and iOS operating systems.
8. AbiWord
AbiWord is a word processing program that can be used to create documents in a variety of languages, including English.
It offers a variety of features, such as support for spell checking, grammar checking, and hyphenation.
It is also able to generate PDF and EPUB files from your documents.
AbiWord is free to download and use, and it is available on most major platforms, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
9. WPS Word
WPS Word is an all-in-one word processing and office suite that provides a user with everything they need to create and edit professional documents.
It includes a word processor, a spreadsheet application, a presentation tool, and a password manager.
WPS Word is available as a free download on the Microsoft Windows platform.
10. Polaris Docs
Polaris Docs is a cloud-based document management service that helps small businesses and freelancers to easily manage and share their PDF files, documents, and presentations.
It offers a wide range of features such as password protection, tracking, versioning, and collaboration.
Polaris Docs is also HIPAA compliant and can be used for a variety of purposes such as legal filings, marketing materials, and more.
11. Writemonkey
Writemonkey is a popular online word processor that’s been around since 2001.
It’s a great choice for anyone looking for a simple, yet powerful tool to help them write and edit text.
Some of the features that make Writemonkey stand out include A wide variety of formatting options, including text formatting, table formatting, and image formatting.
The ability to add links, graphics, and tables directly into your document.
A user-friendly interface that makes editing easy. Support for multiple languages, including English, Spanish, French, German, Italian, Japanese, and Chinese
12. Dropbox Paper
Dropbox Paper is a new way to save and share your work with coworkers, clients, or friends.
It’s an online platform that lets you add documents, images, and videos to a library and share them with others. You can also comment on and rate each item.
Dropbox Paper is perfect for Help Desk workers who need to share workarounds, solutions, or screenshots with other team members.
It can also be helpful for clients who need quick access to product documentation or customer service responses.
13. Scribus
Scribus is a free, open-source document production system designed for the professional desktop publishing market.
It is a cross-platform application that runs on Windows, Mac OS X, and various UNIX platforms.
It can be used for tasks such as content creation, layout, design, printing, and exporting to various formats.
14. Zoho Docs Writer
Zoho Docs Writer is a simple, fast, and affordable online document editor that lets you easily create, edit, and share documents with others.
It’s perfect for creating and editing documents such as resumes, cover letters, business proposals, and more.
You can also use it to create PDFs and DOCs files that can be shared with others.
Zoho Docs Writer is available free of charge to everyone who registers for a Zoho account. It’s easy to use and requires no special skills or knowledge.
Features of Word Processor Software
There are various features of word processor software, which features are given below.
- Text formatting
- Text Copy
- Text Cut
- Text Paste
- Multimedia
- Spelling and Grammar
- Adjust the layout
- Find Feature
- Search and Replace
- Indentation and lists
- Insert table
- Word wrap
- Header and footer
- Thesaurus
- Multiple windows
- AutoCorrect
- Mailers and labels
- Import data
- Merge
- Macros
- Collaboration
What are the Types of Word Processor?
There are various types of word processor software, which are given below.
These all are types of word processor software.
Conclusion
Although Microsoft Word is a very popular word processor software around the world. But like Microsoft Word, there are many processor software that you can use.
Today there are many options of word processor software in front of you, but you have to choose which word processor software is right for you, although what we have told about the word processor, all the word processor software is very good.
Today, due to the presence of many word processors, you must be a little worried, about which word processor will be best for me, although the interface of all word processor software is different, you have to choose which word processor software is good for you.
FAQ Related to Word Processor
What are the 5 examples of word processor?
5 examples of word processor, which are given below.
- WordPad
- Notepad
- WordPerfect
- Microsoft Word
- Lotus word Pro
What are the 7 examples of word processor?
- Microsoft Word
- Google Docs
- iWork Pages
- OpenOffice Writer
- WordPerfect
- FocusWriter
- LibreOffice Writer
What is the most popular word processor?
Microsoft Word is the most popular word processor software worldwide.
Is Google Docs a word processor?
Yes, Google Docs is a online word processor.
Last Updated: February 19, 2022 | Author: Jack Purkey
What is the 3 types of word processors?
Through history, there have been three types of word processors: mechanical, electronic and software.
Free Word Processor for Windows, Mac & Linux: Top Picks
| Name | Platform | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Word | Windows, Mac, Android, iOS | Learn More |
| Google Doc | Web, iOS, and Android, and Mac | Learn More |
| Writer | Web, iOS, and Android | Learn More |
| Grammarly | Web and browser extension | Learn More |
•
Dec 31, 2021
What is word processor and examples?
A word processor, or word processing program, does exactly what the name implies. It processes words. It also processes paragraphs, pages, and entire papers. Some examples of word processing programs include Microsoft Word, WordPerfect (Windows only), AppleWorks (Mac only), and OpenOffice.org.
What are the four word processing?
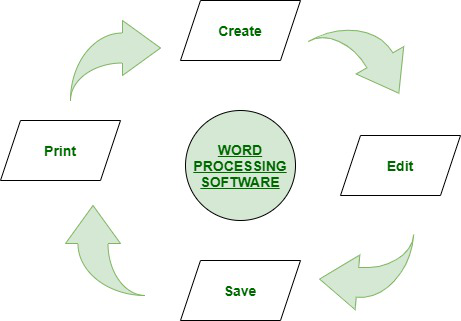
There are four primary functions of word processors: composing, editing, saving and printing.
What is word processor class 10?
Answer: A Software or a computer that enables users to build, edit, and print documents is a word processor. It helps users to write text, save it electronically, show it on a computer, edit it by entering keyboard commands and characters, and print it out.
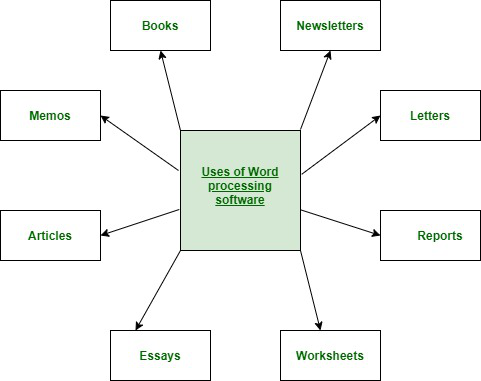
What are uses of word processor?
word processor, computer program used to write and revise documents, compose the layout of the text, and preview on a computer monitor how the printed copy will appear.
What are popular word processors?
Microsoft Word and Google Docs are two of the most common word processing software applications.
Is Microsoft Word a word processor?
Microsoft Word – Word Processing Software | Office.
What is Microsoft Word processor?
Sometimes abbreviated as WP, a word processor is a software program capable of creating, storing, and printing typed documents. Today, the word processor is one of the most frequently used software programs on a computer, with Microsoft Word being the most popular word processor.
What is the difference between word processor and Microsoft Word?
The difference between Microsoft Word and word processing is that word processing is a generic term that refers to any program that allows you to edit and format text. Microsoft Word is a popular brand of word processing software.
What is the difference between a word processor and word processing?
Word processing is the production, storage, and manipulation of text on a computer or word processor, while word processor is a program or machine for storing, manipulating, and formatting text entered from a keyboard and providing a printout.
Is Excel a word processor?
Microsoft Word, OpenOffice Writer and WordPerfect are examples of word processing programs. … Microsoft Excel, OpenOffice Calc and Lotus 1-2-3 are examples of spreadsheet programs. Like the word processing applications, each spreadsheet program can open files created in another application.
Is Notepad a word processor?
Notepad is a word processing program, which allows changing of text in a computer file. … It is a text editor, a very simple word processor. It has been a part of Microsoft Windows since 1985. The program has options such as changing the font, the font size, and the font style.
How many versions of Microsoft Word are there?
Release history
| Year released | Name | Version |
|---|---|---|
| 2006 | Microsoft Word 2007 | 12.0 |
| 2010 | Word 2010 | 14.0 |
| 2013 | Word 2013 | 15.0 |
| 2016 | Word 2016 | 16.0 |
What are the 5 views in Microsoft Word?
Word can display your document in one of five views, which can help you better understand the layout, margins, and page breaks in your document:
- Print Layout: …
- Full Screen Reading: …
- Web Layout: …
- Outline (also called Master Document Tools): …
- Draft:
How many types of MS Office are there?
Microsoft also rebranded most of their standard Office 365 editions into Microsoft 365 to emphasize their current inclusion of products and services.
…
Microsoft Office.
| Microsoft Office 2021 for Mac apps from top left to bottom right: Word, Excel, PowerPoint and Outlook | |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
| show List of languages | |
| Type | Office suite |
Basically these word processors They can be seen as the modern version of typewriters, but in a more digital way with many more functions. These began to reach our world for several years being the year 1970, where the experimental tests with them began and today it is even possible to use these word processors from our cell phones.
What is a text processor?
These processors are nothing more than different software or computer programs, which are intended to create, edit, modify and process documents with different text formats, either due to the type or size of its typography, shapes, colors as well as other more really necessary details.
All the texts that we manage to process in these software are stored on our computers as the files named documents. Of course there is also the option to save them on other devices such as pen drives or other mobile devices, they also allow you to print these documents.
What function do these word processors have?
The truth is that their functions are varied and definitely important nowadays, since most of us have used them like this only once.
You may also be interested in:
From these software, we can have the ability to edit texts, change the font, or its size. It will also be possible to place outstanding features, such as the «bold font « or «italics«.
Of course, from these processors we can align texts in terms of paragraphs, as well as inserting images, hyperlinks, and all kinds of details such as indexes, footers and even headers.
They have made so much progress that it is even possible to detect all kinds of spelling errors in what is being written, it also allows adding tables and lists. In addition to insert graphics made in other programs such as spreadsheets.
What are the existing types?
There are a wide variety of processors, which you have special features in each of them, among the most common, we can mention the following.
memo pad
This is one of the simplest word processors of all, because in addition to that it has very few tools, thus limiting it to a really basic use. One of the characteristics of this is that it only saves the texts in plain text TXT, although it is possible to change the font and the letter time that is being used.
OpenOffice Writer
This is a word processor which basically comes from the Open Office suite and developed by Sun System. It is one of the alternatives, similar to Microsoft Word itself, and basically it could be said that this together with Microsoft Word, are one of the most used worldwide.
Wordpad
Again we stumble upon a really basic word processor, similar to notepad, but unlike this one, it has a little more tools that apart from changing the size and type of the letter, will allow you to save the generated texts in more than one format.
Pages
This is part of the iWork products coming from apple, and as expected it runs on macOS operating systems, the truth is very easy and simple to use, allowing you to create text documents as if you were a professional. This also brings different forms such as those of a curriculum or diagrams, in order to facilitate things.
Microsoft Word
He is part of a package that goes by the name Microsoft Office, which basically could be said to be one of the most used word processors by most users, as it has a wide variety of tools that will definitely help to generate texts like a true professional.
AbiWord
This is one of the processors that really has little to envy processors like Microsoft Word or Pages, since it really has several functions and in addition to that, it is completely free.
One of its advantages, in addition to its non-existent price, is that it is actually lighter than the two mentioned above, and its installation is really easy.
Another important aspect is that it can be used both in Linux, Mac OS X, and Microsoft Windows operating systems, making it one of the most versatile of all, ideal for obsolete equipment.
Summary
- A Word processor can be used to create, edit, format, save and print documents.
- With online word processing platforms, you can share and collaborate with teams.
- Word processing app for android makes it easy to create documents with android devices.
- A huge difference between text editors and word processing apps is their inability to format texts and layout documents.
- There are two major types of word processors: mechanical and software-based.
- Four types of software-based word processors were identified: proprietary, standalone, open office, and online.
- Some identified examples of word processing applications include:
- Microsoft 365
- WordPerfect
- AbiWord
- Apache OpenOffice
- Applix Word
- Adobe InCopy
- StarOffice Writer
- Apple Pages
- LibreOffice Writer
- Google Docs
- Zoho Writer
- SkyDesk Docs, etc
A word processor, like word processing, is a computer application used to create, edit, format, save and print documents. Usually, a word processor has inbuilt features that assist users to create and format texts in standardized document formats.
Text editors can process texts but they do not have features to format texts and documents. Hence, they are usually used in coding or to preserve texts. Examples of text editors include Notepad, TextEdit, Sublime, Vim, Atom, Visual Studio Code, etc.
Text editors have text processing capability in that they provide room for input, editing, and out of texts. But texts processed with text editor remain as was inputted. To create a standard document for business and presentation, a word processor is required.
Word processors have the capability of producing standardized documents such as a memo, letter, newsletter, resume, books, etc. This is why they are one of the most used applications in business, education, and industry.
Types of a word processor
Technically, there are 2 major types of word processors, namely mechanical and software word processors.
Mechanical word processors, whether manual or electronic are devices that can be used to create text documents. A typical example is a typewriter. Software-based word processors are computer programs used to create text-based professional business documents.
We can classify the software-based word processors into four as follow:
1. Proprietary word processors:
These are word processors that represent the trademark of the company that produces them. E.g. Apple, Corel, etc. Moreover, in this article, we define proprietary word processors as word applications that usually come with the operating system. Proprietary word processors are shipped together with the operating system; they, therefore, represent their operating system brands.
Examples are:
a. Microsoft WordPad: it comes with Windows operating system.
b. Pages: it comes with Mac operating system and is part of the iWorks office suite.
c. OpenOffice writer/ AbiWord: OpenOffice is installed with most Linux distribution, e.g. Redhat, but Redhat 7.1 comes with AbiWord.
d. Microsoft word: Windows OS usually comes with MS Word starter version preinstalled, however, it expires after 60 days.
2. Standalone word processors:
These are word processors that could be installed in any operating system. They may be shipped with an operating system, however, they can be installed or uninstalled. They may be designed for different Operating Systems, say, Mac, Linux, or Windows. But the owner can decide to install or uninstall such application at will. Unlike proprietary that can only be removed with the operating system.
Examples are:
a. Microsoft word: part of Microsoft 365 suite, a product of Microsoft inc.
b. Starwriter: part of StarOffice suite, a product of Sun Microsystem inc.
c. WordPerfect: part of WordPerfect Office productivity software developed by Corel.
d. Apple Pages
e. Applix word, a product of VistaSource inc.
f. Atlantis Word, a light-weight word processing program created for Windows operating system.
g. Adobe InCopy: a word processing application developed by Adobe Inc. used to create professional documents.
3. Open source word processors:
These are word processing applications that are publicly accessible. Being public means that anyone, including users, has access to the source code. Therefore, anyone with coding knowledge can inspect, modify and enhance such code. Most open-source software is free for the public to use.
Hence, open-source word processors are word processors that are available for the public to download, install and use.
Examples are:
a. Apache OpenOffice Writer: Apache OpenOffice is an office productivity software suite with a word processor, spreadsheet application, etc. It is a cross-platform application that has versions for Windows, Mac, and Linus operating systems.
b. LibreOffice Writer: LibreOffice is also based on openOffice.org and is a cross-platform office application. It has the writer (word processor), Calc (spreadsheet), Impress (presentation), Draw (graphics), Base (database), and Math (formula editing). A great advantage of LibreOffice is its support for Microsoft Office document formats such as .doc, .docx, .xls, etc.
c. AbiWord: AbiWord is a free word processor licensed under the GNU General Public Licence (GPL). It is small and fast and has support for Linux operating systems.
d. GNU TeXmacs: TeXmacs is free application software used to create well-structured text and scientific documents. With TeXmacs you can create the following types of content: text, mathematics, graphics, interactive content, slides, etc. The software is available for Linux, Mac, and Windows operating systems.
e. Calligra Words: Calligra words is part of the Calligra Suite, a word processor. Calligra office has applications to handle most desktop publishing services such as word processing, spreadsheet, presentation, database, etc, It has versions for Linux, Mac, and Windows operating systems.
4. Online word processor:
Online word processors are applications that allow you to create and edit documents from anywhere and with any device. Most of them will allow users to share and collaborate with others in real-time as well as track changes made.
Some of the leading proprietary and standalone word processors have their online versions. With the advent of mobile devices, different word processing app for android and ios have been developed.
One advantage of online word processors for students and small businesses is that one can use them for free. Also, there is a free word processor app for mobile devices. These apps can be used by anyone who installed them or uses the online word processor version.
Examples of word processors – Online word processors
The following are examples of online word processors. Some are free while some require a subscription to have access to the full functionality.
Microsoft 365
Formerly called Office 365 is a superb cloud-based office productivity tool for education and business. You can collaborate with friends and colleagues using the word, excel, PowerPoint, and OneNote.
Key features

- Bring out your best
- Protect what’s important
- Free and subscription plan available
- Work across your devices
- Organize your time
- Accomplish more together
Google Docs
An online-based Google word processor is used to access, create and edit documents on the go.

Key features
- Get a head start with templates
- Create more than letters and words
- Get to your documents anywhere, anytime
- Do more together: share, edit, chat and comment in real-time
- Work with Microsoft Word
- Never hit save again
Pages
Pages are Apple’s word processor that lets one create stunning documents. It usually comes included with most Apple devices. With real-time collaboration, you can work together from anywhere using Mac, iPad, iPhone, or a PC.
To get started with Pages on a PC, you will need an Apple ID.
Key features

- Start with beautiful templates
- Turn handwriting into text, magically
- Write reports easier with the report wizard
- Skim through your document without accidental editing
- Play video in your document
- Create gorgeous charts
SkyDesk Docs
With SkyDesk Docs, you will get started creating documents with 1 GB of free space for storage. You can access all your files anywhere, anytime, and from any device.
Key features

- Store and manage documents
- Organize your files
- Share files securely
- Password-protected file sharing
- Available for word, spreadsheet and presentation
Zoho Writer
A free cloud-based online word processor for creating elegant documents and collaborating with team-mates in real-time.
Key features

- Create beautiful documents easily
- Don’t worry about constantly saving your work
- Lock or mask sensitive information
- Improve your writing with Zia, the smart writing assistant
- Start with an extensive collection of templates
- Work better together: chat with collaborators
Examples of word processors – Word processing app for android
With massive apps being developed for android devices across the world, users have a wide range of choices to make. Word processing app for android is one of the numerous free competitive apps made available for users to choose from.
With a word processing app for android, you can create, edit, format, and share documents. Note that online word processors can be used on any device, hence, they can be used in android devices. Some of the popularly used word processors for android are:
- Microsoft word
- Google docs
- Zoho writer
- WPS Office
- Documents to Go
- SmartOffice
- Polaris Office
- OfficeSuite
Each of the above word processors can be downloaded from the Google Play Store on any android device.
Basic Features of a Word Processor
Modern word processing applications are designed to help users create standardized and professional documents with ease. As a result, such applications are packed with similar features. Such features allow users to create standard layouts and formats for different purposes.
For example, creating a resume, newsletter, blog post, or report requires different layouts. Such layouts are made possible because of the rich-features that come with the different word processing applications.
Also, different documents have different sizes depending on their purpose and use. For example, a memo may be printed on an executive or A5 paper size. Similarly, a letter may be printed on a letter or A4 paper size. The need for differing sizes of papers is taken into account by this application software.
Below are the common features that can be seen in most word processing software in the market today.
1. Templates
These days leading word processing apps are competing with each other with the provision of already made documents. These documents are already designed and customised to assist people in creating similar documents.
With templates, creating a document is easy and fast. You don’t need to start from the scratch to create a memo, letter or report. You will simply select a template of choice and change its contents with your own. This is one of the power of a modern word processor.
2. Layouts
In an office setting, there are different paper sizes for different documentation purposes. Some documentation requires the legal paper type while others require the A4 size.
Page layout allows you to create different layouts for your document. Here you set the orientation, margins, and determine to use columns or add page borders. In general, the shape, size and overall outlook of your document is made possible with the layout feature.
3. Formatting
One of the basic features of every word processor is the availability of formatting commands. These commands are used to format texts in a document in order to make them readable. Such format commands include text color, bold, italics, font, font size, underline, bullets & numbers, and alignment.
The formatting feature differentiates a text editor and a simple word processing app like Grammarly or WordPad.
4. Images & charts
With word processing software you can insert images, clipart, shapes and charts to a document. This functionality makes it easy for one to create a blog post of newsletter using word processing apps. With modern word processing applications, you can insert, crop, resize and position different sizes of pictures in a document.
In fact, in Microsoft Word, you can even edit a shape using edit shape command in the Format tab. This has made word applications useful in mini graphics designing, though not as powerful as graphic applications. But with a standard word processing app, you can create a document that graphics and charts.
5. Proof reading
Word processing applications usually come with inbuilt dictionary that contains basic English words. As a user inputs text in a document, the application compares words entered with the ones in the dictionary. Words that do not match are usually flagged for error with a red underline.
Different underline colors mean different things to a word processing software e.g. spelling or grammatical error. We usually use the Spelling & Grammar command tool for proofreading in MS Word.
6. Review
In recent time, review is a key feature of word processing applications because it helps to keep track of changes. Most, if not all online word processing platforms, include this functionality to maintain different versions of a document.
In Microsoft Word, the review tab is loaded with features that help users to track changes made to a document. You can save each revised document as a version of the document.
7. Autocomplete
Autocomplete is an AI capability that assists you in writing. This feature automatically suggests words and tenses to a user while he/she is still typing. You can immediately select the word or phrase from the suggested list. With this feature typing is made easier and faster.
However, this feature is not available by default in all word processing applications.
Conclusion
Though Microsoft Word is the most used word processing application, other word processors exist. If you do not have access to the desktop software, you can make do with the online word processing apps.
Asked by: Armani Ernser
Score: 4.1/5
(48 votes)
A word processor is software or a device that allows users to create, edit, and print documents. It enables you to write text, store it electronically, display it on a screen, modify it by entering commands and characters from the keyboard, and print it. Of all computer applications, word processing is the most common.
What is word processor and examples?
Word Processing refers to the act of using a computer to create, edit, save and print documents. … One example of a Word Processor is Microsoft Word, but other word processing applications are also widely used. Examples include: Microsoft Works Word Processor, Open Office Writer, Word Perfect and Google Drive Document..
What is a word processor in MS Word?
A word processor (WP) is a device or computer program that provides for input, editing, formatting, and output of text, often with some additional features. … The functions of a word processor program fall somewhere between those of a simple text editor and a fully functioned desktop publishing program.
Which of the following is a word processor?
WordPerfect, Wordpad and MS Word are word processing software.
Is Microsoft Word a word processor?
Microsoft Word — Word Processing Software | Office.
44 related questions found
What are 10 features of Microsoft Word?
What are 10 features of Microsoft Word?
- Changing case.
- Create a custom tab.
- Quick parts.
- Add placeholder text.
- Edit wrap points when wrapping text.
- Convert a list to a table.
- Convert a bulleted list to SmartArt.
- Quick selection methods.
Can I just download Microsoft Word?
If you wish to use only Word and do not want to install the suite’s other components, then your best option would be just to purchase and install Word outright and not worry about getting the office suite at all. Word can be obtained online for a one-time installation fee of $129.
Is Apple pages a word processor?
Pages is a powerful word processor that lets you create stunning documents, and comes included with most Apple devices. And with real-time collaboration, your team can work together from anywhere, whether they’re on Mac, iPad, iPhone or a PC.
Is word processor software answers?
A word processor is software or a device that allows users to create, edit, and print documents. It enables you to write text, store it electronically, display it on a screen, modify it by entering commands and characters from the keyboard, and print it.
Is Google Docs a word processor?
Google Docs is an online word processor that lets you create and format documents and work with other people.
What are the types of word processor?
Word processors are of 3 types which are electronic, mechanical, and software.
…
Examples or Applications of a Word Processing Software :
- Wordpad.
- Microsoft Word.
- Lotus word pro.
- Notepad.
- WordPerfect (Windows only),
- AppleWorks (Mac only),
- Work pages.
- OpenOffice Writer.
What are the advantages of word processor?
What are the advantages of word processing?
- It is faster and easier than writing by hand.
- You can store documents on your computer, which you cannot do on a typewriter.
- There are more formatting choices with a word processor (the spelling, grammar and language tools).
- You can print copies of your documents.
What is the purpose of word processors?
Word processor, computer program used to write and revise documents, compose the layout of the text, and preview on a computer monitor how the printed copy will appear. The last capability is known as “what you see is what you get” (WYSIWYG; pronounced wi-zē-wig).
What are the 5 examples of word processor?
Examples of word processor programs
- Abiword.
- Apple iWork — Pages.
- Apple TextEdit — Apple macOS included word processor.
- Corel WordPerfect.
- Dropbox Paper (online and free).
- Google Docs (online and free).
- LibreOffice -> Writer (free).
- Microsoft Office -> Microsoft Word.
What is an example of Microsoft Word?
The correct answer is Application Software. MS Word is an example of application software developed by the company Microsoft. It allows users to type and save documents.
Is Notepad a word processor?
Notepad is a text editor, meant for basic plain text entry, while WordPad is a word processor, meant for formatting and printing documents—like Microsoft Word, but not quite as advanced. They aren’t the only programs in their respective categories, either.
What is a word processor class 9?
Answer: A Software or a computer that enables users to build, edit, and print documents is a word processor. It helps users to write text, save it electronically, show it on a computer, edit it by entering keyboard commands and characters, and print it out. … People can type words faster than writing in a pen.
What is word processing job?
A word processor, or typist, generally works in an office setting. As a word processor, your job duties involve preparing reports, correspondence, and other written documents using a computer and word processing software. They also use fax machines, scanners, copiers, and other equipment on a regular basis.
Is Pages better than word?
Word has a good selection of templates, but for our money the selection in Pages is better. Pages has 65 templates compared to Word’s 18 (a lot of Pages templates are slight variations, however). As with most things Apple, the design of its templates are just marginally better looking in all respects.
Can I open a Pages document in word?
Opening a Pages Format File from Mac in Microsoft Windows
Right-click on the . pages file and choose “Rename” … zip file to be able to open and access the Pages format content within Microsoft Word, Office, or WordPad.
Do Macs come with word?
You can use Word, Excel, and Powerpoint on a MacBook, just like on any other laptop. You just have to buy this 365 software separately, because it’s not included with a MacBook by default. … The most often used applications such as Word, Excel, and Powerpoint, are always included.
Does Windows 10 come with Word?
Windows 10 includes online versions of OneNote, Word, Excel and PowerPoint from Microsoft Office. The online programs often have their own apps as well, including apps for Android and Apple smartphones and tablets.
How do I install Microsoft Word?
Sign in to download and install Office
- Go to www.office.com and if you’re not already signed in, select Sign in. …
- Sign in with the account you associated with this version of Office. …
- After signing in, follow the steps that match the type of account you signed in with. …
- This completes the download of Office to your device.
Improve Article
Save Article
Like Article
Improve Article
Save Article
Like Article
Word Processing Software :
The word “word processor” means it processes words with pages and paragraphs. Word processors are of 3 types which are electronic, mechanical, and software.
The word processing software is used to apply the basic editing and design and also helps in manipulating the text to your pages whereas the word processor, is a device that provides editing, input, formatting, and output of the given text with some additional features.
It is a type of computer software application or an electronic device. In today’s generation, the word processor has become the word processing software or programs that are running on general-purpose computers.
Examples or Applications of a Word Processing Software :
- Wordpad
- Microsoft Word
- Lotus word pro
- Notepad
- WordPerfect (Windows only),
- AppleWorks (Mac only),
- Work pages
- OpenOffice Writer
Features :
- They are stand-alone devices that are dedicated to the function.
- Their programs are running on general-purpose computers
- It is easy to use
- Helps in changing the shape and style of the characters of the paragraphs
- Basic editing like headers & footers, bullets, numbering is being performed by it.
- It has a facility for mail merge and preview.
Functions :
- It helps in Correcting grammar and spelling of sentences
- It helps in storing and creating typed documents in a new way.
- It provides the function of Creating the documents with basic editing, saving, and printing of it or same.
- It helps in Copy the text along with moving deleting and pasting the text within a given document.
- It helps in Formatting text like bold, underlining, font type, etc.
- It provides the function of creating and editing the formats of tables.
- It helps in Inserting the various elements from some other types of software.
Advantages :
- It benefits the environment by helping in reducing the amount of paperwork.
- The cost of paper and postage waste is being reduced.
- It is used to manipulate the document text like a report
- It provides various tools like copying, deleting and formatting, etc.
- It helps in recognizing the user interface feature
- It applies the basic design to your pages
- It makes it easier for you to perform repetitive tasks
- It is a fully functioned desktop publishing program
- It is time-saving.
- It is dynamic in nature for exchanging the data.
- It produces error-free documents.
- Provide security to our documents.
Disadvantages :
- It does not give you complete control over the look and feel of your document.
- It did not develop out of computer technology.
Like Article
Save Article
Word Processing
Andrew Prestage, in Encyclopedia of Information Systems, 2003
V. Types of Word Processors
Word processors are either character based or contain a GUI. Character-based word processors do not display documents exactly as they will appear on the printed page. Some character-based word processors, however, include a “preview” capability, allowing the user to preview documents as they will appear on the printed page. This useful feature allows the user to verify that the appearance of the document matches the desired expectations.
The arrival of popular GUIs such as the Macintosh and Windows operating systems led to a change in the way word processors handled fonts. Word processors offering a GUI allow the user to see the document on the computer’s display screen exactly as it will appear after it is printed. In other words, with a GUI word processor what you see is what you get (known as the acronym WYSIWYG).
Word processor types range from simple text editors to full-featured applications. As the name implies, a simple text editor contains very limited capabilities such as the ability to enter, store for later retrieval, modify, and print text. In addition to these basic capabilities, a full-featured word processor permits users to use sophisticated text enhancement tools, check spelling and grammar, incorporate drawing tools, and perform sorting and mail merge operations. The following subsections explore examples of each of these types of word processors.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B0122272404001982
End-User Computing Tools
Jose Stigliano, Marco Bruni, in Encyclopedia of Information Systems, 2003
III.A. Word Processors
Word processors are tools specifically designed to process textual information, that is, information consisting primarily of words in arbitrary arrangements called documents. Word processors typically read input entered by the user through the keyboard, process the text according to the commands given by the user, and create a file containing the user’s application such as a letter, office memo, or report. Word processors support the task of writing, letting end users create, edit, store, search, and retrieve documents containing formatted text and graphics. This text, which has been produced with a word processor, provides an example of the formatting capabilities of the tool.
A variety of tasks can be automated using standard built-in functions: replacing a string of text throughout the document, generating a table of contents, or merging the text of a letter with a list of addressees for mailing purposes. These functions perform the relevant task in response to commands issued by the user. However, for tasks that need to be repeated often, issuing a command each time can be too time consuming; macros help automate the execution of repetitive tasks.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B0122272404000575
Positive Technology, Computing, and Design: Shaping a Future in Which Technology Promotes Psychological Well-Being
Andrea Gaggioli, … Rafael A. Calvo, in Emotions and Affect in Human Factors and Human-Computer Interaction, 2017
Active Integration
Currently, consumers buy particular word processors and email systems, not because they will support any aspect of their well-being, but because these systems help achieve their goals, complete their tasks and work.
Calvo and Peters (2014) have argued that consumers will seek future technologies that support health and well-being. This is likely to occur in the same way they currently seek healthy foods not just for sustenance or even pleasure, but as a way to live healthy and meaningful lives.
Well-being can be actively integrated into technology by designing to actively support components of well-being in an application that has a different overall goal. We need techniques that allow designers to assess the impact that different choices have on the determinant factors of well-being. A number of fields within computing can contribute to measuring this impact. For example, affective computing, the discipline that studies how computers can detect and process human emotions is increasingly part of design considerations in health and education (Riva et al., 2015a). Currently, most approaches to measure psychological well-being require interrupting users to ask about their state of mind. These interruptions are needed for the sake of measuring but themselves can be disengaging and obtrusive. Affective computing techniques can be used to reduce the amount of questioning and self-reporting by automating some of the emotion detection. Furthermore, being able to detect emotions will allow computer interfaces to better adapt to users’ states of mind and better engage, since emotional states are a most important aspect of psychological well-being.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128018514000185
Four Easy Data Hiding Exercises
Michael Raggo, Chet Hosmer, in Data Hiding, 2013
Hiding Data in Microsoft Word
Microsoft Word remains the predominant word processor standard. In fact, many people using a Mac also use Microsoft Word as their word processor. Therefore it serves us well to begin our exploration by investigating the many ways in which data can be hidden within your standard Microsoft Word document.
Microsoft Word, Excel, and PowerPoint 2007 and 2010 provide a variety of ways to hide data within the document. These include comments, personal information, watermarks, invisible content, hidden content, and custom XML data. Using the Hidden Text font options provides an easy yet amazingly effective way to hide data. First, type a standard document, and additionally input the data you’d like to hide (see Figure 2.1).
Figure 2.1. Inputting Data into a Microsoft Word Document to be Hidden
Then highlight the content you’d like to hide, and right-click and choose Font. You will notice in newer version of Microsoft Word a new checkbox labeled “Hidden.” By selecting Hidden and then Save, you will notice that the highlighted text will be hidden from normal viewing (see Figures 2.2 and 2.3).
Figure 2.2. Using the Hidden Option in Microsoft Word
Figure 2.3. Microsoft Word Document after Hiding the Second Sentence
By default, hidden text is also not printed when printing the document. In order for an average user to know if there is hidden text they would need to go to File, Options, and select Display. Selecting the “Hidden Text” checkbox will enable formatting marks to alert a user to hidden text, and “Print Hidden Text” to determine if there is any hidden text (see Figure 2.4).
Figure 2.4. Microsoft Word Display Options for Identifying Hidden Text
Another way to identify hidden text is to use the Inspect Document option in File => Info => Check for Issues => Inspect Document. The Inspect Document is actually a great way to identify a variety of metadata hidden within the document such as authors, comments, and possibly other personal identifiable information (PII). In addition it can be used to identify hidden text (see Figure 2.5).
Figure 2.5. Using Document Inspector to Find Hidden Text and Other Metadata
Select Inspect to have the Document Inspector identify the metadata and create a report of results. In this example, the Document Inspector correctly identifies the Hidden Text and allows the user to remove it if they desire. The interesting thing here is that most people never check for the existence of Hidden Text and therefore have no idea it’s there (see Figure 2.6).
Figure 2.6. Document Inspector Identified Hidden Text in the Document
It is important to note that the only Hidden Text identified is text hidden using the Font dialog box. For example, if text is hidden from viewing using the white text on the white background, the Document Inspector will not identify this hidden text.
The ability to hide data in the document is practical if you want to print two versions of the same document, one with the hidden data and one without. This is common for PowerPoint presentations when an individual may print the slides for the audience and print the slides with notes for the presenter.
There are a variety of other things that can be hidden within Microsoft Word 2010 Properties section, including tags, author’s name, comment, etc. (see Figure 2.7).
Figure 2.7. Microsoft Word Properties and Metadata
In addition, the Properties drop-down allows access to the Advanced Properties where customs fields may be added as well (see Figure 2.8).
Figure 2.8. Custom Tab in Microsoft Word Advanced Properties
It’s important to note that these are not displayed in the main Properties view, and therefore must be viewed by manually opening the Custom Tab in the Advanced Properties window.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B978159749743500002X
UX Design Guidelines
Rex Hartson, Partha S. Pyla, in The UX Book, 2012
22.8.3 Automation Issues
Automation, in the sense we are using the term here, means moving functions and control from the user to the internal system functionality. This can result in not letting users do something the designers think they should not do or something that the designers did not think about at all. In many such cases, however, users will encounter exceptions where they really need to do it.
As an analogy, think of a word processor that will not let you save a document if it has anything marked as a spelling or grammatical error. The rationale is easy: “The user will not want to save a document that contains errors. They will want to get it right before they save it away.” You know the story, and cases almost always arise in which such a rationale proves to be wrong. Because automation and user control can be tricky, we phrase the next guideline about this kind of automation guardedly.
Avoid loss of user control from too much automation
The following examples show very small-scale cases of automation, taking control from the user. Small though they may be, they can still be frustrating to users who encounter them.
-
Example: Does the IRS know about this?
The problem in this example no longer exists in Windows Explorer, but an early version of Windows Explorer would not let you name a new folder with all uppercase letters. In particular, suppose you needed a folder for tax documents and tried to name it “IRS.” With that version of Windows, after you pressed Enter, the name would be changed to “Irs.”
So, in slight confusion, you try again but no deal. This had to be a deliberate “feature,” probably made by a software person to protect users from what appeared to be a typographic error, but that ended up being a high-handed grasping of user control.
-
Example: The John Hancock problem
Figure 22-62 shows part of a letter being composed in an early version of Microsoft Word and exhibiting another example of automation that takes away user control.
Figure 22-62. The H. John Hancock problem.
Let us just say that a user named H. John Hancock was observed typing a business letter, intending to sign it at the end as:
-
H. John Hancock
-
Sr. Vice President
Instead he got:
-
H. John Hancock
-
I.
Mr. Hancock was confused about the “I” so he backed up and typed the name again but, when he pressed Enter again, he got the same result. At first he did not know what was happening, why the “I” appeared, or how to finish the letter without getting the “I” there. At least for a few moments, the task was blocked and Mr. Hancock was frustrated.
Being a somewhat experienced user of Word, his composition of text going back to some famous early American documents, he eventually determined that the cause of the problem was that the Automatic Numbered List option was turned on as a kind of mode. At least for this occasion and this user, the Automatic numbered list option imposed too much automation and not enough user control.
That the user had difficulty understanding what was happening is due to the fact that, for this user, there was no indication of the Automatic numbered list mode. In fact, however, the system did provide quite a helpful feedback message in response to the automated action it had taken, via the “status” message of Figure 22-63, displayed at the top of the window.
Figure 22-63. If only Mr. Hancock had seen this
(screen image courtesy of Tobias Frans-Jan Theebe).
However, Mr. Hancock did not notice this feedback message because it violated the assessment guideline to “Locate feedback within the user’s focus of attention, perhaps in a pop-up dialogue box but not in a message or status line at the top or bottom of the screen.”
Help the user by automating where there is an obvious need
This section is about automation issues, but not all about avoiding automation. In some cases, automation can be helpful. The following example is about one such case.
-
Example: Sorry, off route; you lose!
No matter how good your GPS system is, as a human driver you can still make mistakes and drive off course, deviating from the route planned by the system. The Garmin GPS units are very good at helping the driver recover and get back on route. It recalculates the route from the current position immediately and automatically, without missing a beat. Recovery is so smooth and easy that it hardly seems like an error.
Before this kind of GPS, in the early days of GPS map systems for travel navigation, there was another system developed by Microsoft, called Streets and Trips. It used a GPS receiver antenna plugged into a USB port in a laptop. The unit had one extremely bad trait. When the driver got off track, the screen displayed the error message, Off Route! in a large bright red font.
Somehow you just had to know that you had to press one of the F, or function, keys to request recalculation of the route in order to recover. When you are busy contending with traffic and road signs, that is the time you would gladly have the system take control and share more of the responsibility, but you did not get that help. To be fair, this option probably was available in one of the preference settings or other menu choices, but the default behavior was not very usable and this option was not discovered very easily.
Designers of the Microsoft system may have decided to follow the design guideline to “keep the locus of control with the user.” While user control is often the best thing, there are times when it is critical for the system to take charge and do what is needed. The work context of this UX problem includes:
- ▪
-
The user is busy with other tasks that cannot be automated.
- ▪
-
It is dangerous to distract the user/driver with additional workload.
- ▪
-
Getting off track can be stressful, detracting further from the focus.
- ▪
-
Having to intervene and tell the system to recalculate the route interferes with the user’s most important task, that of driving.
Another way to interpret these twin guidelines about automation is to keep the user in control at higher task levels, where the user has done the initial planning and is driving to get somewhere. But take control from the user when the need is obvious and the user is busy.
This interpretation of the two guidelines means that, on one hand, the system does not insist on staying on this route regardless of driver actions, but quietly allows the driver to make impromptu detours. This interpretation also means that, on the other hand, the system should be expected to continue to recalculate the route to help the driver eventually reach his or her destination.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123852410000221
Analysis of quantitative and qualitative data
Kirsty Williamson, Amanda Bow, in Research Methods for Students, Academics and Professionals (Second Edition), 2002
1 Transcribe the data
This simply means to type the notes or interview tapes into a word processor making the information much more accessible and easier to analyse. In some cases, researchers have been known to analyse straight from the tapes. However, this is not recommended as it makes it very difficult to re-check easily what was said, and to categorise the data. Transcribing the data into a word processor also means that researchers can easily use computer software programs such as NVivo. If you are using NVivo or another analysis package, you would put your data into NVivo and print it out after you have finished transcribing it.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9781876938420500277
CPUs
Marilyn Wolf, in High-Performance Embedded Computing (Second Edition), 2014
2.4.2 Superscalar processors
Superscalar processors issue more than one instruction per clock cycle. Unlike VLIW processors, they check for resource conflicts on the fly to determine what combinations of instructions can be issued at each step. Superscalar architectures dominate desktop and server architectures. Superscalar processors are not as common in the embedded world as in the desktop/server world. Embedded computing architectures are more likely to be judged by metrics such as operations per watt rather than raw performance.
A surprising number of embedded processors do, however, make use of superscalar instruction issue, though not as aggressively as do high-end servers. The embedded Pentium processor is a two-issue, in-order processor. It has two pipes: one for any integer operation and another for simple integer operations. We saw in Section 2.3.1 that other embedded processors also use superscalar techniques.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780124105119000022
Introduction
William J. Buchanan BSc, CEng, PhD, in Software Development for Engineers, 1997
29.7 File types
Most files created have a certain purpose; for example documents from a word processor, spread-sheets, text files. The filename extension adds extra information about what type of file it is. Common filename extensions are given in Table 29.5.
Table 29.5. Example file extensions
| File extension | File type | File extension | File type |
|---|---|---|---|
| .ASC | ASCII Text | .PAS | Pascal file |
| .BAK | Backup File | .PCX | Picture file |
| .BAT | DOS Batch File | .PRN | Print File |
| .C | C language File | .SYS | System File |
| .COM | DOS Program File | .TXT | Text File |
| .EXE | DOS Executable program | .WK1 | 123 Ver 1/2 File |
| .HLP | Help File | .WK3 | 1–2–3 Ver 3 File |
| .OVL | Overlay File used by program | .TMP | Temporary File |
Test run 29.10 shows a sample DOS listing. Notice that this directory contains System Files (.SYS), DOS Commands (.COM and .EXE), Text Files (.TXT) and Help Files (.HLP). The other typical files include Basic Language Files (.BAS), Initialization Files (.INI) and Listings (.LST). Programs with the .COM, .EXE or .BAT extension can be executed.
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780340700143500748
Brainstorming
Chauncey Wilson, in User Experience Re-Mastered, 2010
Analysis Techniques
Listing Ideas
All the ideas from a brainstorming session can be listed in a spreadsheet, word processor, or specialized tools like PathMaker® or Inspiration. If you have numbered the items sequentially as they were generated, your list would be chronological. To facilitate recall days, weeks, or even months later when you look through this list, you can annotate the list with clarifications and brief explanation of any unusual terms or abbreviations.
Grouping Ideas from Brainstorming
Affinity diagramming, a method for organizing data by similarity, can be used to reveal groups of related items. The number of groups that emerge from an affinity diagramming is sometimes used as a measure in brainstorming research.
Voting on Brainstorming Ideas
A group can vote on which brainstorming items should be considered further by placing adhesive dots or ink marks on the items, by removing the items from the master list, or voting online using tools like Excel, Google Spreadsheet, or SurveyMonkey.
Criteria-Based Evaluation
Criteria-based evaluation uses a decision matrix to choose the top ideas from brainstorming. The people charged with choosing which ideas will be considered further rate or rank each idea against a list of criteria like cost, ease of programming, novelty, and generality. The ratings/rankings for each idea are averaged, the ideas are sorted by the average value, and the top rated/ranked ideas are chosen for consideration (see Table 4.3). Criteria-based evaluation can be done with online survey tools if you want to expand the process of choosing the top ideas beyond the brainstorming participants.
Table 4.3. A Decision Matrix for a Criterion-Based Approach to Choosing the Best Ideas from Brainstorming
| Criterion 1 | Criterion 2 | Criterion 3 | … | Criterion N | Sum | Mean Rating/Ranking | Top Ideas | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Idea 1 | ||||||||
| Idea 2 | ||||||||
| Idea 3 | ||||||||
| Idea 4 | ||||||||
| Idea …. | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | |
| Idea N |
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123751140000074
Brainwriting
Chauncey Wilson, in Brainstorming and Beyond, 2013
2.6.2 Analysis Techniques
2.6.2.1 Listing Ideas
All the ideas from a brainstorming session can be listed in a spreadsheet, word processor, or specialized tools like PathMaker® or Inspiration. If you have numbered the items sequentially as they were generated, your list would be chronological. To facilitate recall, days, weeks, or even months later when you look through this list, you can annotate the list with clarifications and brief explanations of any unusual terms or abbreviations.
2.6.2.2 Grouping Ideas from Brainwriting
Affinity diagramming can be used to organize ideas into related groups. See Chapter 1 for some details on affinity diagramming.
2.6.2.3 Rating or Ranking Brainwriting Ideas
The process of brainwriting focuses on generating ideas. For some purposes, you may want to prioritize ideas against specific criteria. One simple approach you can use for prioritizing data is to apply a simple criterion (or a few criteria) to each idea and eliminate the ideas that don’t meet the criterion. A criterion would include the word “should”, for example, “the idea should be compatible with the existing user interface,” “the idea should not extend the schedule,” “the idea should be easily learned,” and “the idea should minimize errors.” You might do something like rate each idea on a 0-to-5 scale where 0 means “does not meet the criterion at all” and 5 is “meets the criterion quite well.” Once the brainwriting team has chosen items to be investigated further, individuals or team could be assigned to examine the costs and benefits of chosen items or assigned to evaluate them on specific dimensions (costs, benefits to the users, time to implement, and so on).
The nominal group rating technique described in Chapter 1 on brainstorming is sometimes used after a brainwriting session as a method for prioritizing the ideas that emerged. The facilitator would ask each member of the brainwriting team to rate privately all the ideas as a 1 (low), 2 (medium), or 3 (high). The ideas with the highest average rating would get the highest priority.
2.6.2.4 Decision Matrix
A decision matrix (sometimes called a “prioritization matrix”) uses the ideas from brainwriting and a set of criteria for rating the ideas. Some software products include a “decision matrix” where the ideas are listed on one axis and the criteria on another axis (Table 2.4). Participants would rate each item according to how well the item meets the criteria. This assumes that you are reasonably sure of the criteria for deciding which ideas to carry forward. Criteria that you might use in this table include:
Table 2.4. Layout of a Prioritization Matrix
| Idea/Criteria | Criterion 1 | Criterion 2 | Criterion 3 | Criterion … | Criterion N | Sum | Mean Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Idea 1 | |||||||
| Idea 2 | |||||||
| Idea 3 | |||||||
| Idea 4 | |||||||
| Idea … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
| Idea n |
- •
-
Cost
- •
-
Skill required to implement the idea (you might have a great idea, but now the personnel to implement the idea)
- •
-
Technical feasibility
- •
-
Consistency with existing products
- •
-
Time to code
Read full chapter
URL:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780124071575000026
- List of word processors
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
-
Comparison of word processors — Contents 1 General information 2 Characteristics 3 Operating System Compatibility 4 Import or Open capabilities … Wikipedia
-
Comparison of early word processors — This article compares early word processing software. Operating System Compatibility This table gives a comparison of what operating systems are compatible with each word processor in 1985. Word Processor Operating System Compatibility Word… … Wikipedia
-
Word processor — OpenOffice.org Writer in Version 3.2 … Wikipedia
-
List of text editors — The following is a list of text editors. For a list of outliners, see that article s external links. Graphical and Text User Interface The following editors can either be used with a Graphical user interface or a Text user interface. System… … Wikipedia
-
List of software that supports Office Open XML — Office Open XML Office Open XML file formats Open Packaging Conventions Open Specification Promise Vector Markup Language Office Open XML software Comparison of Office Open XML software Office Open XML standardization This is an overview of… … Wikipedia
-
List of software products — This is a list of software by genre, operating system, and type of licensing. Contents 1 Office 1.1 Office suites 1.2 Word processors 1.3 Database management systems … Wikipedia
-
word processor — 1. a computer program or computer system designed for word processing. 2. a person who performs word processing. [1975 80] * * * ▪ computing computer program used to write and revise documents, compose the layout of the text, and preview on … Universalium
-
List of HTML editors — The following is a list of HTML editors with articles in Wikipedia.Text editorsPlain text editors may be used to produce webpages. The following are some commonly used text editors:*EditPlus *Emacs *gedit *jEdit *Kate *Microsoft Script Editor… … Wikipedia
-
Microsoft Word Viewer — Word Viewer Word Viewer Developer(s) Microsoft Corporation Stable release 2010 / June 15, 2010; 16 months ago ( … Wikipedia
-
List of Apple II application software — Following is a List of Apple II applications.A* ADTPro Telecom * Apple Works Integrated Word Processor, Spreadsheet, and Data Base Suite (II GS) * Apple Writer Word Processor * ASCII Express TelecomB* Bank Street Writer Word ProcessorC* Contiki 8 … Wikipedia