In English texts and everyday communication, the word “like” serves a variety of purposes. It can act as an adjective, a preposition, an adverb, a conjunction, a noun, or a verb.
- Adjective
This word is classified under adjectives if it is used to modify a noun or a pronoun by indicating similarities in qualities or characteristics. For example, in the sentence below:
You’re not talking about like things when you compare football and golf.
The word “like” is used as an adjective that describes the noun “things.”
Definition:
a. having the same or similar qualities
- Example:
- I responded in like manner.
- Preposition
Another common function of the word “like” is as a preposition that also means “for example” or “similar to.” In the sample sentence below:
Their house is like a barn.
The word “like” is used as a preposition that indicates that the “house” is similar to a “barn.”
Definition:
a. having the same characteristics or qualities as
- Example:
- There were other suits like mine in the shop.
b. used to draw attention to the nature of an action or event
- Example:
- We apologize for coming over unannounced like this.
c. such as; for example
- Example:
- They discussed books like 1984 and Animal Farm.
- Adverb
The word ”like” can also be categorized as an adverb if it is used to modify a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. Take for example, the sentence below:
The distance is more like 750 miles.
In this sentence, the word modifies the adjective “750,” and is therefore considered as an adverb.
Definition:
a. nearly; approximately
- Example:
- It was like 8 feet deep.
b. used in speech as a meaningless filler or to signify the speaker’s uncertainty about an expression just used
- Example:
- There was this funny smell—sort of dusty like.
- Conjunction
There are also some cases wherein the word “like” is used as a conjunction that connects two clauses to form one sentence. For instance, in the sample sentence below:
I hate girls who change boyfriends like they change clothes.
The word “like” serves as a conjunction that links together the clauses “I hate girls who change boyfriends” and “they change clothes.”
Definition:
a. in the same way that; as
- Example:
- They raven down scenery like children do sweetmeats.
b. as though; as if
- Example:
- I felt like I’d been kicked by a horse.
- Noun
Other times, the word “like” is considered as a noun, which refers to something of the same kind. In the example:
Did you ever hear the like?
The word “like” is used as a noun that is used to indicate a thing of the same kind.
Definition:
a. a thing or things of the same kind
- Example:
- We will never see anyone of her like again.
- Verb
The word “like” is also typically used as a verb that indicates a state of being. Take for example, the sentence:
He likes baseball more than anything.
In this sentence, the word suggests the state of being of the pronoun “he,” and is therefore considered as a verb.
Definition:
a. to enjoy (something); to get pleasure from (something)
- Example:
- I like all Dan Brown’s books.
b. wish for; want
- Example:
- Would you like a cup of tea?
Table of Contents
- Is likes Past or present?
- What type of tense is likes?
- Is liked a regular verb?
- What are examples of likes?
- What does liking mean?
- How do you spell likes?
- Where can I use likes?
- What does light mean?
- What but means?
- What part of grammar is but?
- What can I write instead of but?
- How do you avoid the word but?
- What is another word for still?
- What is a synonym for but?
- Can I use However instead of but?
- How do you spell butt?
- Does but mean bum?
- Why do we have butts?
- How do you shave your bum hair?
- Do guys like hair down there?
- Is it normal to have hair in your vag?
- Is it normal to have hair in your bum for a girl?
- Should I shave my pubic hair?
The word “like” is also typically used as a verb that indicates a state of being. Take for example, the sentence: He likes baseball more than anything. In this sentence, the word suggests the state of being of the pronoun “he,” and is therefore considered as a verb.
Is likes Past or present?
The past tense of like is liked. The third-person singular simple present indicative form of like is likes. The present participle of like is liking.
Past Tense of Like
| Present Tense: | Like |
|---|---|
| Past Tense: | Liked |
| Past Participle: | Liked |
| Present Participle: | Liking |
Is liked a regular verb?
In English, for example, verbs such as play, enter, and like are regular since they form their inflected parts by adding the typical endings -s, -ing and -ed to give forms such as plays, entering, and liked.
What are examples of likes?
If you love something
- “I love eating ice-cream.”
- “I adore sun-bathing.”
- “She’s mad about that new boy band.”
- “He’s crazy about that girl.”
- “She’s fond of chocolate.”
- “I like swimming very much.”
- “He really likes that new golf course.” (Remember to stress “really” in this sentence.)
- “He quite likes going to the cinema.”
What does liking mean?
noun. preference, inclination, or favor: to show a liking for privacy. pleasure or taste: much to his liking. the state or feeling of a person who likes.
How do you spell likes?
Correct spelling for the English word “likes” is [lˈa͡ɪks], [lˈaɪks], [l_ˈaɪ_k_s] (IPA phonetic alphabet)….Similar spelling words for LIKES
- LINEs,
- dikes,
- Liakos,
- likewise,
- liked,
- bikes,
- pikes,
- Lijewski,
Where can I use likes?
Liked sentence example
- As he’d said earlier, he liked dogs.
- Alex liked being in control, and he had none in this situation.
- Everyone liked the idea, so they returned to their rooms and cleaned up.
- I thought you liked it here.
- Mary liked him, and the feelings were obviously mutual.
What does light mean?
Light is a source of illumination, whether a natural one (like the sun) or an artificial one (like your lamp). Like light itself, the word can take a lot of different forms — it can be a noun, an adjective, or a verb, and it can mean “bright” or “not heavy”.
What but means?
—used to introduce a statement that adds something to a previous statement and usually contrasts with it in some way. : other than. —used in speech at the beginning of a sentence that expresses surprise, shock, etc. but.
What part of grammar is but?
In the English language, the word “but” is also used for multiple purposes. It can serve as a conjunction, a preposition, an adverb, or a noun in sentences. This word is commonly categorized under conjunctions because it can connect two clauses together and form a single sentence.
What can I write instead of but?
other words for but
- although.
- however.
- nevertheless.
- on the other hand.
- still.
- though.
- yet.
How do you avoid the word but?
“Yet” can often replace “but” in a sentence without changing anything else, as both are coordinating conjunctions that can introduce a contrast. Alternatively, you could use one of these subordinating conjunctions: Although (e.g., I like Brian May, although I find his hair ridiculous.)
What is another word for still?
What is another word for still?
| calm | peaceful |
|---|---|
| serene | tranquil |
| placid | smooth |
| stilly | undisturbed |
| halcyon | pacific |
What is a synonym for but?
SYNONYMS. yet. nevertheless, nonetheless, even so, however, still, notwithstanding, despite that, in spite of that, for all that, all the same, just the same, at the same time, be that as it may. though, although.
Can I use However instead of but?
No, we can not use “However” instead of “But” in each sentence, because both ‘But’ and ‘However’ are two words in English language that have to be understood with precision so that they can be used correctly either in spoken or written English.
How do you spell butt?
Your butt is your buttocks, your tush, your rear end. Saying butt is more childish than offensive. Butt is a four-letter word, though using it won’t get you in much trouble — It’s much less offensive than ass.
Does but mean bum?
Butt and but are easily confused words. It means the bottom, the posterior, or the end portion of something. In slang, as a noun, it means the two fleshy cheeks and the anus on the backside of the human body. In slang, as a noun, it means the discarded remainder of a cigarette after its been smoked.
Why do we have butts?
On humans, the gluteus maximus attaches to the upper part of the pelvis, the ilium. This placement allows for trunk stability and helps keep us balanced. Most researchers believe that we have big butts because it helps us stay upright, and helps balance us when walking and running.
How do you shave your bum hair?
Shaving
- Wash the area using mild soap and water.
- Lather the area with all-natural shaving cream or gel.
- Prop one leg up on the side of the tub.
- Use one hand to pull your cheeks apart and hold the skin taut.
- Shave the area very slowly and carefully using small strokes.
- Rinse well and pat dry.
Do guys like hair down there?
The data revealed that a huge 46 per cent of men prefer women to go completely bare, 30 per cent like it neatly trimmed and 12 per cent favour a landing strip. Predictably, only six per cent prefer a natural look.
Is it normal to have hair in your vag?
Yes, having hair on your vulva is completely healthy and normal. Both guys and girls grow hair — pubic hair — around their genitals during puberty. Some people have a lot of pubic hair, and some have less. Some people choose to remove their pubic hair for cosmetic reasons.
Is it normal to have hair in your bum for a girl?
It is normal for both girls and guys to have hair around their anus. Some people have very little hair in this area while others have more. There are no health benefits to removing the hair in this area and doing so may cause a rash and irritation, and possibly infection.
Should I shave my pubic hair?
Shaving, whether it’s your legs, armpits, or pubic area, is a personal choice. You certainly don’t have to shave before sex if you don’t want to. Shaving pubic hair (or not) is a cosmetic preference, and it does not mean you are “cleaner” if you shave. Instead, shave the day before to give the area time to calm down.
“Like” is one of the most commonly used words in English – and when you’re new to learning the language, it can be a bit of a confusing one, as it has so many different meanings!
In fact – did you know that there are actually five different ways to use the word “like”? Phew! Sounds like hard work.
You might hear it a lot in everyday spoken English – especially as it has become very popular to use colloquially. But if you’re not sure on how to use this word correctly, then read on to find out.
Like – to enjoy
One of the most common ways that you’ll hear the word “like” is as a verb – “to like”.
This is a verb used to express the fact that you enjoy something, and it can be used just like many other verbs in English.
For example: “I like walking to work, but she liked to drive instead.”
Nice and simple!
Would like – to request something
“Like” can also be used as an alternative to the verb, “to want”, in a form that is considered less aggressive and demanding, and more polite. You would use the word with the modal verb, “would”, and you always need to use the full phrase “would like”.
For example: “She would like to place her order now.”
Be like – to describe the characteristics of something
This is when the uses of “like” start to get a bit more complex. In this use, the word is used to describe the personality, character or particular traits of something.
In this case it is used with the verb “to be”. If you are using it in the past tense, only the main part of the verb “to be” is changed, and the word “like” stays the same.
For example: “What was he really like?”
Like – as a simile
Developing from the previous use of the word, “like” is often used as a simile – or a comparison with something else, in order to describe something.
Sounds confusing? Let’s take a look at an example!
“The bedroom was like a disaster zone.”
In a simile, you still need to use the verb “to be” with the word “like”, but instead of describing the actual characteristics, you can use something else – which might be drastically different.
For example: “She was nervous and shaky, like a mouse.”
This is a great way of adding a bit more personality into your spoken English, but you would not use similes very often in written English, unless you are writing creatively.
Look like – describing appearances
The last common use of the word “like” is to describe experiences. This is done through the verb “to look like”. You can use this just as in the previous examples when you used the form “to be like”. In this case, the part of the phrase that changes according to tense and subject is “look”, while the word “like” stays the same.
For example: “I look like a really messy person, while she looks like a celebrity!”
Your turn
Understanding how the word “like” is used in different contexts and forms is a really helpful way to build on your English skills – make sure you practice each of the five uses as much as you can!
Expressing likes and dislikes is a part of life. From a young age, most children start recognizing the things they enjoy and the ones they don’t, and as their speech develops kids become eager to share this information with family and friends. The verb “like” is the one used for this purpose, and it’s also one of the most common verbs in English.
Is “like” a verb?
Well, yes and no! The answer is not that simple. “Like” is, in fact, a verb. As a verb, it has a meaning, a conjugation, and can be used in different tenses in English. However, “like” can also be used as a preposition, conjunction, and a suffix.
What’s the meaning of the verb “like”?
In English, the meaning of the verb “like” is similar to the verb “love” but the feeling is not as strong, it implies that the person enjoys something or that he or she has a positive feeling about it.
For example, “I like my new shoes.”, this implies that the subject enjoys the new shoes and feels positive about them. On the contrary, when it’s a negative sentence with the verb like, for example: “I don’t like summer”, it means that person doesn’t feel positive about summer but it’s not a strong feeling of dislike.
Conjugation of the verb “like” in English
The verb “like” is a regular verb, this means that it doesn’t change as much when used in different tenses. Also, it’s important to remember that the verb “like” always requires an object.
In order to make a sentence with “like” the correct structure is to put the subject first, then the verb like, and then the thing that he or she likes (subject + like + what the subject likes). For example: “I like water”, “I have a pen. I like it”.
Present tense: like/likes
I like – I don’t like
you like – you don’t like
he/she/it likes – he/she/it doesn’t like
you like – you don’t like
we like – we don’t like
they like – they don’t like
The present tense of the verb “like” in affirmative is very easy to make. Since it’s a regular verb, it doesn’t change much for the different pronouns in English, just for the third person where there’s an “s” added to the word “like”. The negative sentences with the verb “like” in Present Simple are formed adding don’t or doesn’t -depending on the subject- before the word “like”.
Examples with the verb “like” in Present Simple:
Elliot likes strawberry ice cream.
Cowy and I like our art class a lot.
Baby Bot is studying English, he likes to learn languages.
Elliot, Billy and I are traveling to Canada soon. We like cold weather!
Oh! Billy doesn’t like his new bed!.
We don’t like to eat alone, so we always eat together.
Past tense of the verb “like”: liked
I liked – I didn’t like
you liked – you didn’t like
he/she/it liked – he/she/it didn’t like
you liked – you didn’t like
we liked – we didn’t like
they liked – they didn’t like
Given that the verb “like” is regular, its past is formed by adding the letter “-d” at the end of the word “like”. This applies to all pronouns. The negative of the verb “like” in Past Simple is formed by adding the word didn’t (verb “to do” in the past tense) before the word “like”.
Examples with the verb “like” in Past:
I liked your gift, it was amazing!.
Billy liked to go out on Sundays, but now he doesn’t.
I received your card, I liked it a lot! Thanks!.
When Cowy was little, she liked coconut candy.
Lisa didn’t like her shirt, so she changed it.
Cowy didn’t like the beach, so she prefers to go to the mountains.
Future tense of the verb “like”: will like
I will like – I won’t like
you will like – you won’t like
he/she/it will like – he/she/it won’t like
you will like – you won’t like
we will like – we won’t like
they will like – they won’t like
As usual in English, the future tense of the verb “like” is formed by adding the word “will” just before the verb “like” for affirmative sentences, and the word “won’t” for negative sentences.
Examples with the verb “like” in Future:
We are going on a road trip next Sunday! The Lingokids will like it!.
Are you sure the movie is funny? Otherwise, I don’t know if I will like it.
I will like to go to your house tomorrow, Billy!.
There’s a new game coming out. I’m sure Cowy will like to play it.
It’s going to be really cold today, I probably won’t like walking home.
Don’t but Lisa a big watch, she won’t like it.
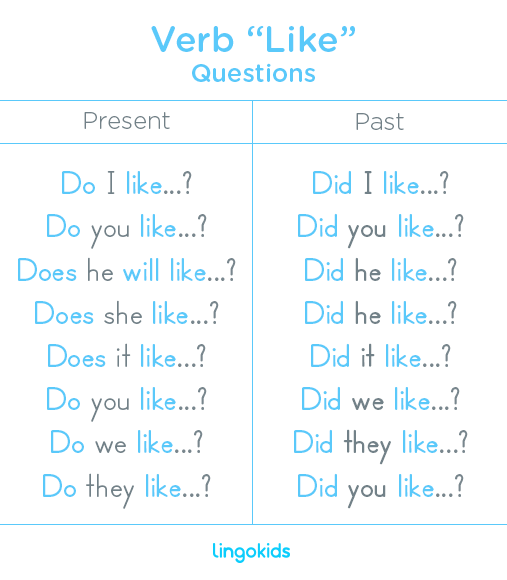
Questions with the verb “like”
Do I like…? – Did I like…?
Do you like…? – Did you like…?
Does he/she/it like…? – Did he/she/it like…?
Do we like…? – Did we like…?
Do you like…? – Did you like…?
Do they like…? – Did they like…?
Just as it happens with the majority of verbs in English, the questions with the verb “like” are constructed using the verb “to do” in English, with the words “do ” or “does ” for questions in present tenses or the word “did ” for questions in past.
Examples of questions with the verb “like”:
Does Cowy like her new guitar? Yes, she likes it a lot.
I got you a present, did you like it? Yes, thanks!.
Billy and Baby Bot are coming later, do they like peach tea?.
Rafael is getting new shoes, does he like the blue ones or the green ones?
Other uses of “like” in English
“Like” is not only a verb, it can also be used as a preposition, as a suffix, and in some cases, it can even be used as a conjunction.
When “like” is used as a preposition, it means ‘similar to”, and in this case, it usually goes with verbs related to the senses, such as look, sound, or feel. For example, “The cookie tastes like mint.” When “like” is used as a suffix, it has the same meaning as a preposition, but it goes at the end of a noun. For example: “She is doing some sports-like activities.”
The use of like as a conjunction is common, although is not considered grammatically correct in some cases, and it’s considered informal speeches. In this case, it’s used as a substitute for the word “as”. For example: “Nobody knows this school like I do.” which will be “Nobody knows this school as I do.”
Playlearn with Lingokids!
With the Lingokids app, your kids will learn the use of the verb “like” easily while playing through fun activities like games and songs! Join today!
A Grammatical Analysis for Children
The word like serves as seven of the parts of speech. The only function it doesn’t serve? It isn’t a pronoun. But it does cover the other seven.
Like as a Verb
If your children ask about the correct meaning of like, point out that it serves as a verb, all by itself. Your children can say, “I like waffles” or “I would like another serving.”
Like as a Preposition
Point out that it also serves as a preposition and in that capacity hooks nouns to sentences. Your children can say, “He runs like the wind.”
Indeed, go ahead and point out that to be can join like if they truly want to show what something or somebody was like.
Thus the commercial “I want to be like Mike” has its grammar in order.
So does “He was like a father to me.”
But virtually everyone addicted to the like word uses it to show not what something is like but what something actually is. They use it to show identity (is), not similarity (like): He’s like tall. Well, is he or isn’t he?
Like as a Noun
You can also point out that like serves as a noun, as in likes and dislikes.
Like as an Adjective
The word spans almost all parts of speech and can serve as an adjective (she mastered lacrosse, field hockey, and like sports).
Like as an Adverb
Informally, like can serve as an adverb (the tree is more like 100 than 50 feet).
Like as a Conjunction
Here we stir up a hornet’s nest. According to some sources, the word like can also act as a subordinating conjunction.
Charles Darwin wrote in 1866: “Unfortunately few have observed like you have done.” New Fowler, p. 458.
Consider the words of Random House:
Like as a conjunction meaning “as, in the same way as” (Many shoppers study the food ads like brokers study market reports) or “as if” (It looks like it will rain) has been used for nearly 500 years and by many distinguished literary and intellectual figures. Since the mid-19th century there have been objections, often vehement, to these uses. Nevertheless, such uses are almost universal today in all but the most formal speech and writing. In extremely careful speech and in much formal writing, as, as if, and as though are more commonly used than like: The commanding general accepted full responsibility for the incident, as any professional soldier would. Many of the Greenwich Village bohemians lived as if (or as though) there were no tomorrow. Random House, p. 1114.
Other sources fervently disagree with this loose approach. Mr. Fowler himself minced no words:
Every illiterate person uses this construction daily . . . . New Fowler, p. 458.
The Oxford English Dictionary notes that examples of the use of like as a conjunction do appear in the works of “many recent writers of standing” but also points out that such use is “generally condemned as vulgar or slovenly . . . .” Quoted in New Fowler, p. 458.
Click page 2 below ….
Like as a Conjunction: Four Uses
New Fowler examined the works of leading writers in England, America, and other countries, and identified four situations where they use like as a conjunction:
1. The If you knew Susie Exception: Repeat the Verb
In the subordinate clause, writers often repeat the verb appearing in the main clause. They introduce the subordinate clause with like:
I need a new car like I need a hole in the head. —E. Good, 2001.
If you knew Susie like I know Susie . . . .
New Fowler’s Comment: “[This construction] must surely escape further censure or reproach.”
The following examples and comments appear in New Fowler, p. 458.
2. To Replace As If or As Though
It looks like it’s still a fox. —New Yorker, 1986.
3. The Like I said Exception
Substitutes for as in “fixed, somewhat jocular, phrases of saying and telling . . . .”
Like you say, you’re a dead woman. —M. Wesley, 1983.
4. To Make Comparisons
Used in the same way as “in the manner (that)” or “in the way (that).”
How was I to know she’d turn out like she did? —C. Burns, 1985.
As a budding grammarian, you should know of this battle. At Bubba’s you can easily get away with like as a conjunction. But in formal settings—the faculty lounge, scholarly writing (and talking), your master’s thesis—you should use the traditional conjunctions as, as if, and as though. In the words of New Fowler:
It would appear that in many kinds of written and spoken English like as a conjunction is struggling towards acceptable standard or neutral ground. It is not there yet. But the distributional patterns suggest that the long-standing resistance to this omnipresent little word is beginning to crumble. New Fowler, p. 459.