Contents
- Tools, Calculators and Simulations
- Dashboards and Reports with Charts
- Automate Jobs with VBA macros
- Solver Add-in & Statistical Analysis
- Data Entry and Lists
- Games in Excel!
- Educational use with Interactive features
- Create Cheatsheets with Excel
- Diagrams, Mockups, Gantt Charts
- Fetch live data from web
- Excel as a Database
Excel is one of the most used software in today’s digital world. Most people quickly open up an Excel file when they need to write or calculate anything. It is like “paper”. (remember those graph notebooks from school times..)
Actually, this is not only specific to Microsoft’s Excel but most of the spreadsheet software like open office or google sheets. However, we will focus on Excel and what can you do with it today, as it offers huge flexibility you will discover below.
Let’s start with the main usage areas of Excel. As we all know, spreadsheets are designed to make calculations easier. So they contain “formulas”. They allow us to make basic math like summing, multiplying, finding average as well as advanced calculations like regression analysis, conversions, and so on.
When we combine these powerful math features with some tables, lists, or other UI elements, we can come up with a calculator. And most of the time they will be dynamic (meaning that when you change a parameter all the rest of the calculations will adapt accordingly)
Below see an example from our past studies as Someka:
We have built this calculator for an app development company executive. He was changing the parameters he wants and sees the outcomes immediately.
This is great especially when you try to make big “models” in excel. Financial Modeling is one of the most used application areas of these big models. If we tried to do this with pen-paper (which used to be the way once upon a time) it would be horrible I guess:
Financial modeling is also being used to test the excel skills of experts. They even make a competition for it: ModelOff
We also have a tool for startups to make a feasibility study playing with their own variables:
This is a comprehensive Feasibility Study Excel Template for app startups with download projections, costs, financial calculations, charts, dashboard, and more.
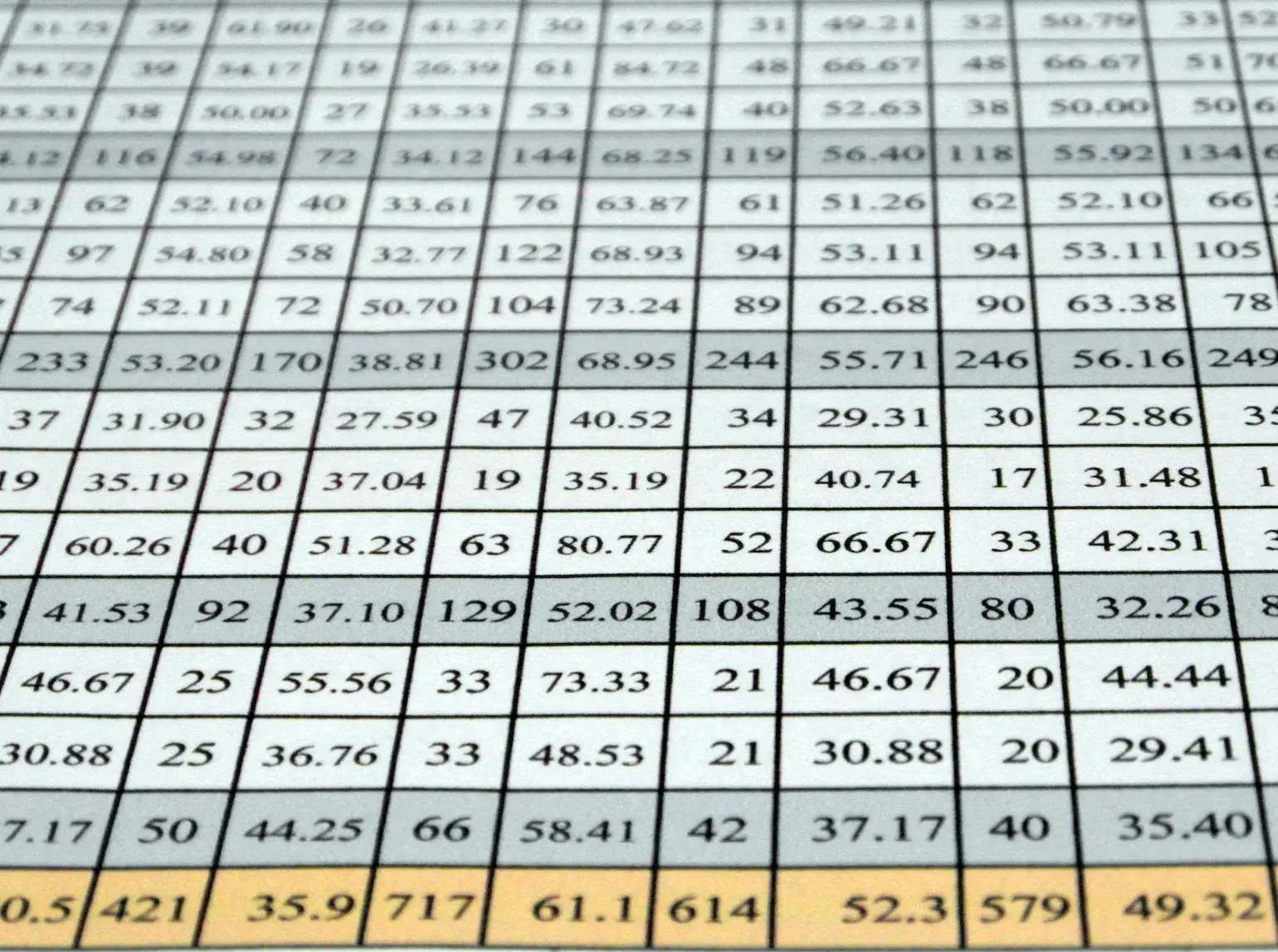
The business world is demanding. It is not enough just to make the calculations, set up your tables, and write the text. You have to create pie charts, trends, line graphs, and many more. Whether you are getting prepared for your pitch or make a presentation in your company, you can use Excel’s chart features.
Pivot Tables
One of the greatest features which Excel offers is Pivot tables. This is an advanced Excel tool that helps you create dynamic summary reports from raw data very easily. After you create your table you can play with parameters easily with a drag and drop interface.
It looks like this:
Dashboards
Complex excel models do have lots of variables, calculations, and settings. And instead of managing all variables one by one on different sheets, different places it is a very good idea to put them together like a “control panel”.
You can think dashboards as cockpits of planes.
Recently dashboards became very popular. There are lots of training videos about how to build and design control panels for our excel models. Actually, they are not so different from the rest of the calculations.
But the main idea is: if there is something you may want to change, later on, don’t write it directly in the formula but bind it to a variable.
Let’s say you are building a sales report for your manager. He asks you to make the file changeable so that he can see the results in US dollars or Euros according to the situation. Instead of writing an Fx rate into the calculations, you should bind this to a cell that you can play with later on.
Like this:
This may seem so obvious to some of you. But this is the basic approach of all dashboards in excel files. Of course, you can improve it with more complex formulas, buttons, cool charts, and even VBA but the main idea stands still.
Here is an example of a complete set of the dashboard:
Or a dashboard for a livestock feasibility study:
If you are interested in Sales Dashboards, you may want to check out our Excel template:
This is an interactive Sales Report Template in Excel. Features a dashboard with profitability, sales analysis and charts.
Other than that, Marketing ROI Calculator would be very helpful to prioritize your marketing campaigns in Excel:
It will provide essential metrics and help you to manage all your marketing campaign channels in one place.
Most of the users who use Excel extensively are already coding. But if you ask them whether they know how to code most probably they will say no. Of course, writing formulas is a very small part of the things you can do with VBA. It is a strong programming language that lets you create small scripts (macros), user forms, user-defined functions, add-ins, and even games! (which we will touch below separately)
I will not dive into VBA here since it is a detailed area. But there are some basic things that will be beneficial to know for those who use Excel often:
- You can record macros for repeating jobs: You don’t need to code from scratch. Just click on the record macro button and it will write the code for you in the background. (If you want, you can modify later on)
- It extends the borders of Excel world. If you feel like you are limited somehow in Excel, you are more like an advanced user. It is time to get a little bit into VBA.
- You can create user forms with VBA only. If you see something like this, know that it is using VBA:
VBA is quite powerful and if you work with Excel extensively you won’t regret learning a bit. For example wouldn’t it be nice if you could send bulk emails from an Excel spreadsheat with a button click?
It is not surprising for spreadsheet software like Excel to offer advanced math techniques to make more complicated studies. (To be honest, I am not a statistics expert but with an engineering background, I will try to do my best to explain the basics. Feel free to correct me if I’m wrong)
Data analysis is a trending concept for recent years with the development of powerful computers and improved software. We are collecting and recording much much more data compared to the past. Take a look at this chart to understand what I mean:
Especially this part:
“more data has been created in the past two years than in the entire previous history of the human race”
It is a bit frightening, isn’t it? Ok, we are not going to dive into the “Big Data” world. Let’s get back to our humble excel world.
As we collect this much data, some people will want to analyze it. Otherwise, it makes no sense to spend billions of dollars on those data centers. Excel has built-in functions for basic descriptive statistics methods like Mean, Median, Mode, Standard Deviation, Variance etc.
But if we want to go a bit further I will mention two Excel features (actually add-ins) at this step: Solver and Regression Analysis
Solver
Have you ever heard of “optimization”? When we have more than one parameters that affect the outcome, we can only have a most optimized solution rather than a maximum solution. This may sound weird but it is very valid in our daily lives.
One of the simplest and popular examples is: Farmer Fence Optimization Problem
“A farmer owns 500 meters of the fence and wants to enclose the largest possible rectangular area. How should he use his fence?”
This is a very simple example to explain what a solver does. But actually, you can run much more complicated data sets with Solver.
Regression Analysis
Since this is a bit advanced topic for this blog post, I will only touch the surface.
In most simple terms, regression analysis helps you find the correlation between the variables. For example, you may want to know what is the relation between the number of birds flown over your head and the money you earned today. (sorry for the silly example. No, I am not curious about it 
It seems something like this:
You put your data:
Run the regression from Analysis Toolpak:
And get results something like this:
Of course, there is much more sophisticated software to run data analysis. However, there is a joke in business intelligence communities:
- What is the most used feature of any business intelligence solution?
- It is “Export to Excel”
Looks like we won’t stop using Excel anytime soon.
Coming back from boring data analysis world, let’s mention the simplest and most handy usage area of excel: Make Lists!
It is already self-explaining so I won’t bother with the details. When you want to list down some simple data, take notes, create to-do lists, or anything. Just open the excel and write it down. Did we mention that “paper alternative” thing? Oh yes, we did.
A lead list example:
You can also convert PDF files into Excel files in order to make it easier to work on. This can be done automatically with some software. But some pdf files cannot be processed automatically (like handwritten documents, scanned invoices, etc). You will need to do it manually.
When you want to play with the data on a web page, you can easily copy-paste it into an excel file and then you can sort, filter or do anything you want:
For example, Fortune 500 US List:
Everybody loves to-do lists. And we have created useful to-do list in Excel for business or personal uses. Check it out, it is free:
To-Do List Excel Template
We already mentioned this in the VBA section above. But it is worth to talk a bit more.
Visual Basic allows you to code complex things like games as well. But of course, don’t expect a GTA or FIFA. Things like chess, sudoku, or Monopoly is OK. But, a few people have gone far and created more complicated things, like an RPG game. Take a look at this:
This game has been created by an accountant, Cary Walkin. I know it doesn’t look great but it is in Excel! (you can play it at the office 
Another example:
A flight simulator in Excel?? Is it the same thing we use to sum up the sales figures? Lol yeah.
You can also embed flash games into Excel (like Super Mario, Angry Birds or whatever) But I count them off as they are not built with VBA.
As we mentioned in the Financial Modeling section, Excel is quite good for creating dynamic results according to the inputs. We get the benefit of this to create interactive tools.
One example that comes to my mind is this spreadsheet, guys from San Francisco have prepared:
I haven’t tried it myself but an Excel tutorial in Excel. Liked the idea!
Another similar interactive Excel learning tool is from Keyskillset:
Actually, this is not completely in Excel and works as separate software but I liked how they combine the Excel training with gamification features.
Quizzes are good tools for interactive learning and you can prepare in Excel as well. A quizmaster template from indzara.com:
A student lesson plan template in excel which we have prepared recently:
You can learn Excel in Excel!
As said: Practice Makes Perfect!
You can test your Excel skills in Excel with Excel Formulas Trainer:
This is actually an Excel template prepared with VBA macros and basically works as a practice worksheet. It has 30 sections and around 100 questions. You can learn VLOOKUP, IF and much more excel formulas by doing. If you like the idea of “learning by doing”, then it is worth to check.
Also, this online course from GoSkills is for everyone as well, covering beginner, intermediate and advanced lessons.
By cheat sheets, we don’t refer to the piece of paper with information written down on it that an unethical person might create if they weren’t prepared for a test. What we mean is a reference tool that provides simple, brief instructions for accomplishing a specific task. We use this term because it is highly popular recently.
For example, this is a cheat sheet:
This compacted and summarized info is very useful in many aspects. When you try to memorize things, lookup, reference, etc. And can be easily created with Excel. Let’s make a Google search for a cheat sheet made in Excel.
This one is from Dave Child (cheatography.com) and I was also using this one I first learned HTML:
The last example is an Excel Cheatsheet made for Excel shortcuts:
Of course, if you are looking for stylish infographics and cheat sheets, you should check out design software.
I know Excel is maybe not the best tool to do these. There are great programs or websites to make mockups, diagrams, brainstorming, mind-mapping, or project scheduling. But there are habits as well. Even though I am very open to try and use these kinds of brand-new tools, I find myself using excel for a mockup or a mind map. (select shapes, put notes, put arrows, change colors etc. Omg it is tedious)
Gantt charts can be a bit old-school as agile project management methods are increasing in popularity, they are still being used widely. There are several Gantt chart excel templates on the web.
A Gantt chart example from vertex42.com:
I just found out a reporting structure mockup I have prepared in Excel once upon a time:
By the way, did you see our Automatic Organization Chart Generator?
This is an Excel template that lets you create organization charts from Excel lists with a click of a button. It can be useful for small business owners and Human Resources departments.
These type of charts are directly related to Excel as most of the companies already keep their data in spreadsheets. But I also know people who even build their website mockups in Excel (with links to other sections, placement of buttons, sliders etc.).
Sometimes you may need your excel files to be updated automatically from a live data source. For example, if you are making a stock market analysis and want the latest data of some stock prices at NYSE, you can connect your Excel file to a data feed and let it take the latest info automatically (unless you want to input them one by one!)
As this is a comprehensive topic I will leave it for another post. But here is a few things you can fetch into excel:
- Stock prices
- Match results of soccer, NBA, NFL or any sports games (from live score sites)
- Fx rates
- Real-time flight data of airports
- Any info in a shared database (whether it is your company intranet or public)
This topic is getting more and more important as most data is kept on cloud systems. We don’t download info bits to our computers as we used to do in the past. So, Microsoft is working hard to improve the web integration of Excel.
Recommended Reading: Can Excel Extract Data From Website?
Yes, it is not the best idea to use Excel as a database. Because it is not designed for this purpose. Queries will take a long time especially when data gets bigger. It can be unreliable sometimes and not very secure. It is all accepted. However, we are not always after a complete set of the database systems and it can serve us as a mini-warehouse for our little data.
For example, if you keep records of your invoice data and want to make some sales analysis, it can be a good starting point. If later, you want to see more details, want to record more breakdowns you will need to move to a “real database”. It can be Access, SQL or anything. Just keep an eye on your Excel file because it has a maximum of 1 million rows.
Some of you may say “hey, it is more than enough, isn’t it?”
Generally yes. But you cannot believe how data increase in size when you want to see details. I remember when I was working as an analyst in a game development company, we were holding records of 1+ billion rows of data.
Precisely because of that, we have built some of our Excel templates (which is the favorite feature of all the users) with a database section. You may check our Invoice Generators and see how invoice recording would be super easy in Excel!
Conclusion
As the internet gets more available for everybody people started to use collaboration platforms more than before. In this aspect, online spreadsheet applications, like Google Sheets, increase in popularity and stands as a competitor to Microsoft’s Excel. Other free alternatives like open office or libre office are also popular. But if you need the advanced functionalities of Excel there is still no substitute.
Microsoft is improving the software actively. PowerPivot, Power BI, and Excel Online are all brand new features they developed recently. We will wait and see how things evolve in the following years. (investintech.com has made interviews with Excel experts about the future of Excel)
I tried to cover most of the things that can be done with Excel. If I have missed anything or if you find any errors, let me know by commenting down or sending an email.
Also, don’t forget to check our Excel Templates Collection. You may find something useful for yourself:
Excel Templates and Spreadsheets – Someka
Complete List of Things You Can Do With Excel
- Tools, Calculators and Simulations.
- Dashboards and Reports with Charts.
- Automate Jobs with VBA macros.
- Solver Add-in & Statistical Analysis.
- Data Entry and Lists.
- Games in Excel!
- Educational use with Interactive features.
- Create Cheatsheets with Excel.
Contents
- 1 What are 7 things you can use Excel for?
- 2 What cool things can excel do?
- 3 What are the 10 uses of Microsoft Excel?
- 4 What are the 9 Uses of Excel?
- 5 What are the 3 common uses for Excel?
- 6 How can excel be used in everyday life?
- 7 How do I make Excel fun?
- 8 What is the most important thing in Excel?
- 9 What is the hardest thing to do in Excel?
- 10 What are the five uses of spreadsheet?
- 11 How can excel help students?
- 12 What is the main function of Excel?
- 13 How do you do Tetris on Excel?
- 14 How do I make cute in Excel?
- 15 Are there games in Excel?
- 16 What are the things to be learned in Excel?
- 17 What are the basic things to learn in Excel?
- 18 What is the most powerful tool in Excel to you?
- 19 What is Vlookup in Excel?
- 20 What Excel skills are employers looking for?
What are 7 things you can use Excel for?
More Than a Spreadsheet: 7 Things You Can Do with Microsoft Excel
- Accounting. Excel has long been a trusted accounting tool.
- Data Entry, Storage, and Verification. At its core, Excel is data-entry software.
- Data Visualisation.
- Data Forecasting.
- Inventory Tracking.
- Project Management.
- Creating Forms.
What cool things can excel do?
20 Excel Tricks That Can Make Anyone An Excel Expert
- One Click to Select All.
- Open Excel Files in Bulk.
- Shift Between Different Excel Files.
- Create a New Shortcut Menu.
- Add a Diagonal Line to a Cell.
- Add More Than One New Row or Column.
- Speedily Move and Copy Data in Cells.
- Speedily Delete Blank Cells.
What are the 10 uses of Microsoft Excel?
Top 10 Uses of Microsoft Excel in Business
- Business Analysis. The number 1 use of MS Excel in the workplace is to do business analysis.
- People Management.
- Managing Operations.
- Performance Reporting.
- Office Administration.
- Strategic Analysis.
- Project Management.
- Managing Programs.
What are the 9 Uses of Excel?
Uses of MS Excel
- Get Quick Totals.
- Data Analysis and Interpretation.
- Plenty of Formulas to Work with Data.
- Data Organising and Restructuring.
- Data Filtering.
- Goal Seek Analysis.
- Flexible and User-Friendly.
- Online Access.
What are the 3 common uses for Excel?
The three most common general uses for spreadsheet software are to create budgets, produce graphs and charts, and for storing and sorting data. Within business spreadsheet software is used to forecast future performance, calculate tax, completing basic payroll, producing charts and calculating revenues.
How can excel be used in everyday life?
Whether it is family-based planning for a weekly, monthly or yearly calendar or a personal appointment daily planner or a schedule for managing bill payments, homework, favorite sports team’s games, and many more, excel can make it easy to compile, filter, search, organize and simplify large amounts of data.
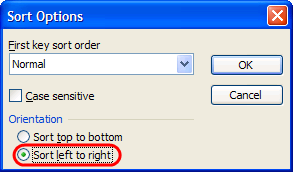
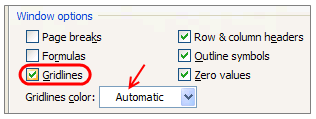
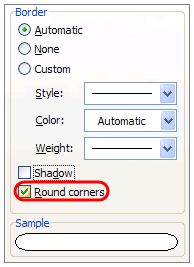
How do I make Excel fun?
Excel can be Exciting – 15 fun things you can do with your spreadsheet in less than 5 seconds
- Change the shape / color of cell comments.
- Filter unique items from a list.
- Sort from Left to Right.
- Hide the grid lines from your sheets.
- Add rounded border to your charts, make them look smooth.
What is the most important thing in Excel?
Conditional Formatting
Making sense of our data-rich, noisy world is hard but vital. Used well, Conditional Formatting brings out the patterns of the universe, as captured by your spreadsheet. That’s why Excel experts and Excel users alike vote this the #1 most important feature.
What is the hardest thing to do in Excel?
Top 10 things we struggle to do in Excel & awesome remedies for…
- VBA, Macros & Automation. VBA is the most struggling area of Excel.
- Writing Formulas. Excel has hundreds of functions.
- Making Charts.
- Pivot Tables.
- Conditional formatting.
- Array Formulas.
- Dashboards.
- Working with data.
What are the five uses of spreadsheet?
What Is the Purpose of Using a Spreadsheet?
- Business Data Storage. A spreadsheet is an easy way to store all different kinds of data.
- Accounting and Calculation Uses.
- Budgeting and Spending Help.
- Assisting with Data Exports.
- Data Sifting and Cleanup.
- Generating Reports and Charts.
- Business Administrative Tasks.
How can excel help students?
Excel reduces the difficulty of plotting data and allows students a means for interpreting the data. You can also reverse the traditional process of analyzing data by giving students a completed chart and see if they can reconstruct the underlying worksheet.
What is the main function of Excel?
A function in Excel is a preset formula, that helps perform mathematical, statistical and logical operations. Once you are familiar with the function you want to use, all you have to do is enter an equal sign (=) in the cell, followed by the name of the function and the cell range it applies to.
How do you do Tetris on Excel?
Tetris on Excel
- Step 1: Enable Macros. Open the excel file then enable the macros following steps:
- Step 2: Controls. The controls are based on keyboards and already set-up.
- Step 3: Scoring. Scores are based on lines completed.
- Step 4: All Done! Whenever game is over, a message box will prompt.
How do I make cute in Excel?
13 Ways to Make your Excel Formatting Look More Pro
- Don’t use column A or row 1.
- Use charts, but avoid 3D charts.
- Images are important.
- Resize rows and columns.
- Don’t use many colors.
- Turn off gridlines and headers, and chart borders.
- Avoid using more than 2 fonts.
- Table of contents.
Are there games in Excel?
Excel Games Roundup
Almost all games use a combination of VBA and handcrafted macros to deliver the fun, but Excel can also play host to many flash games. Be warned: the flash games are much harder to hide from other people!
What are the things to be learned in Excel?
10 essential things you should learn about Microsoft Excel
- How to create a Pivot Table in Excel.
- How to enter basic formulas and calculations in Excel.
- Use the SUM function to add up a column or row of cells in Excel.
- Absolute and relative references in Excel.
- Rounding numbers in Excel.
What are the basic things to learn in Excel?
Basic Skills for Excel Users
- Sum or Count cells, based on one criterion or multiple criteria.
- Build a Pivot Table to summarize date.
- Write a formula with absolute and relative references.
- Create a drop down list of options in a cell, for easier data entry.
- Sort a list of text and/or numbers without messing up the data.
What is the most powerful tool in Excel to you?
More specifically, PivotTables — arguably Excel’s most powerful data analysis tool. PivotTables allow you to instantly organize, filter, summarize, and analyze your raw information through a flexible and user-friendly interface, exposing patterns and insights that may have otherwise been lost in the noise.
What is Vlookup in Excel?
VLOOKUP stands for ‘Vertical Lookup’. It is a function that makes Excel search for a certain value in a column (the so called ‘table array’), in order to return a value from a different column in the same row.
What Excel skills are employers looking for?
Below is the list of Microsoft Excel skills that you need to look for while hiring the entry-level hires:
- SUMIF/SUMIFS.
- COUNTIF / COUNTIFS.
- Data Filters.
- Data Sorting.
- Pivot Tables.
- Cell Formatting.
- Data validation.
- Excel shortcut keys.
Sometimes, Excel seems too good to be true. All I have to do is enter a formula, and pretty much anything I’d ever need to do manually can be done automatically.
Need to merge two sheets with similar data? Excel can do it.
Need to do simple math? Excel can do it.
Need to combine information in multiple cells? Excel can do it.
In this post, I’ll go over the best tips, tricks, and shortcuts you can use right now to take your Excel game to the next level. No advanced Excel knowledge required.
-
What is Excel?
-
Excel Basics
-
How to Use Excel
-
Excel Tips
-
Excel Keyboard Shortcuts
What is Excel?
Microsoft Excel is powerful data visualization and analysis software, which uses spreadsheets to store, organize, and track data sets with formulas and functions. Excel is used by marketers, accountants, data analysts, and other professionals. It’s part of the Microsoft Office suite of products. Alternatives include Google Sheets and Numbers.
Find more Excel alternatives here.
What is Excel used for?
Excel is used to store, analyze, and report on large amounts of data. It is often used by accounting teams for financial analysis, but can be used by any professional to manage long and unwieldy datasets. Examples of Excel applications include balance sheets, budgets, or editorial calendars.
Excel is primarily used for creating financial documents because of its strong computational powers. You’ll often find the software in accounting offices and teams because it allows accountants to automatically see sums, averages, and totals. With Excel, they can easily make sense of their business’ data.
While Excel is primarily known as an accounting tool, professionals in any field can use its features and formulas — especially marketers — because it can be used for tracking any type of data. It removes the need to spend hours and hours counting cells or copying and pasting performance numbers. Excel typically has a shortcut or quick fix that speeds up the process.
You can also download Excel templates below for all of your marketing needs.
After you download the templates, it’s time to start using the software. Let’s cover the basics first.
Excel Basics
If you’re just starting out with Excel, there are a few basic commands that we suggest you become familiar with. These are things like:
- Creating a new spreadsheet from scratch.
- Executing basic computations like adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing.
- Writing and formatting column text and titles.
- Using Excel’s auto-fill features.
- Adding or deleting single columns, rows, and spreadsheets. (Below, we’ll get into how to add things like multiple columns and rows.)
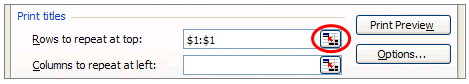
- Keeping column and row titles visible as you scroll past them in a spreadsheet, so that you know what data you’re filling as you move further down the document.
- Sorting your data in alphabetical order.
Let’s explore a few of these more in-depth.
For instance, why does auto-fill matter?
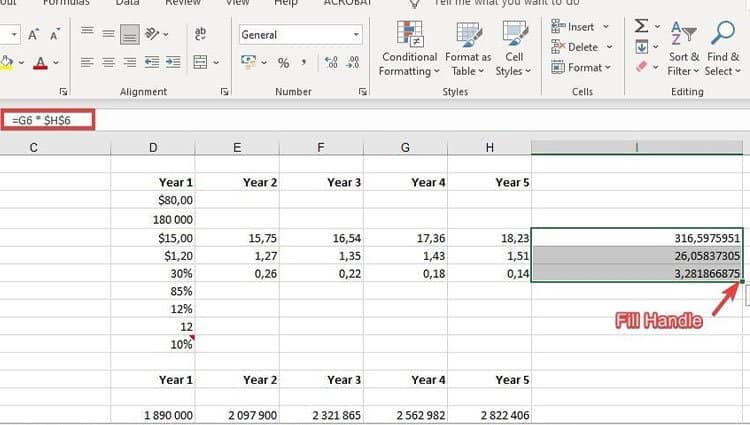
If you have any basic Excel knowledge, it’s likely you already know this quick trick. But to cover our bases, allow me to show you the glory of autofill. This lets you quickly fill adjacent cells with several types of data, including values, series, and formulas.
There are multiple ways to deploy this feature, but the fill handle is among the easiest. Select the cells you want to be the source, locate the fill handle in the lower-right corner of the cell, and either drag the fill handle to cover cells you want to fill or just double click:
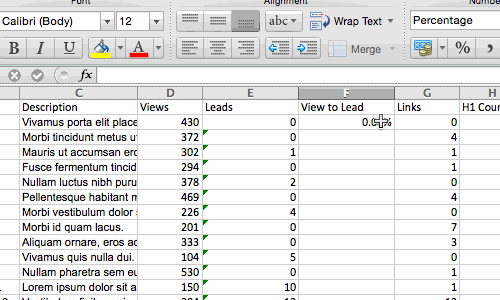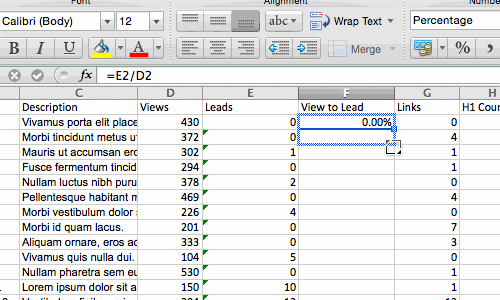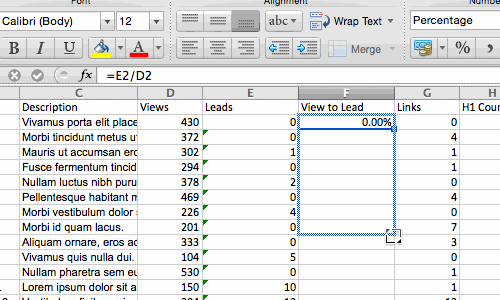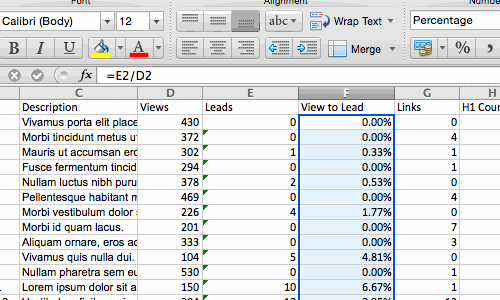
Sometimes you may have a list of data that has no organization whatsoever. Maybe you exported a list of your marketing contacts or blog posts. Whatever the case may be, Excel’s sort feature will help you alphabetize any list.
Click on the data in the column you want to sort. Then click on the «Data» tab in your toolbar and look for the «Sort» option on the left. If the «A» is on top of the «Z,» you can just click on that button once. If the «Z» is on top of the «A,» click on the button twice. When the «A» is on top of the «Z,» that means your list will be sorted in alphabetical order. However, when the «Z» is on top of the «A,» that means your list will be sorted in reverse alphabetical order.
Let’s explore more of the basics of Excel (along with advanced features) next.
To use Excel, you only need to input the data into the rows and columns. And then you’ll use formulas and functions to turn that data into insights.
We’re going to go over the best formulas and functions you need to know. But first, let’s take a look at the types of documents you can create using the software. That way, you have an overarching understanding of how you can use Excel in your day-to-day.
Documents You Can Create in Excel
Not sure how you can actually use Excel in your team? Here is a list of documents you can create:
- Income Statements: You can use an Excel spreadsheet to track a company’s sales activity and financial health.
- Balance Sheets: Balance sheets are among the most common types of documents you can create with Excel. It allows you to get a holistic view of a company’s financial standing.
- Calendar: You can easily create a spreadsheet monthly calendar to track events or other date-sensitive information.
Here are some documents you can create specifically for marketers.
- Marketing Budgets: Excel is a strong budget-keeping tool. You can create and track marketing budgets, as well as spend, using Excel. If you don’t want to create a document from scratch, download our marketing budget templates for free.
- Marketing Reports: If you don’t use a marketing tool such as Marketing Hub, you might find yourself in need of a dashboard with all of your reports. Excel is an excellent tool to create marketing reports. Download free Excel marketing reporting templates here.
- Editorial Calendars: You can create editorial calendars in Excel. The tab format makes it extremely easy to track your content creation efforts for custom time ranges. Download a free editorial content calendar template here.
- Traffic and Leads Calculator: Because of its strong computational powers, Excel is an excellent tool to create all sorts of calculators — including one for tracking leads and traffic. Click here to download a free premade lead goal calculator.
This is only a small sampling of the types of marketing and business documents you can create in Excel. We’ve created an extensive list of Excel templates you can use right now for marketing, invoicing, project management, budgeting, and more.
In the spirit of working more efficiently and avoiding tedious, manual work, here are a few Excel formulas and functions you’ll need to know.
Excel Formulas
It’s easy to get overwhelmed by the wide range of Excel formulas that you can use to make sense out of your data. If you’re just getting started using Excel, you can rely on the following formulas to carry out some complex functions — without adding to the complexity of your learning path.
- Equal sign: Before creating any formula, you’ll need to write an equal sign (=) in the cell where you want the result to appear.
- Addition: To add the values of two or more cells, use the + sign. Example: =C5+D3.
- Subtraction: To subtract the values of two or more cells, use the — sign. Example: =C5-D3.
- Multiplication: To multiply the values of two or more cells, use the * sign. Example: =C5*D3.
- Division: To divide the values of two or more cells, use the / sign. Example: =C5/D3.
Putting all of these together, you can create a formula that adds, subtracts, multiplies, and divides all in one cell. Example: =(C5-D3)/((A5+B6)*3).
For more complex formulas, you’ll need to use parentheses around the expressions to avoid accidentally using the PEMDAS order of operations. Keep in mind that you can use plain numbers in your formulas.
Excel Functions
Excel functions automate some of the tasks you would use in a typical formula. For instance, instead of using the + sign to add up a range of cells, you’d use the SUM function. Let’s look at a few more functions that will help automate calculations and tasks.
- SUM: The SUM function automatically adds up a range of cells or numbers. To complete a sum, you would input the starting cell and the final cell with a colon in between. Here’s what that looks like: SUM(Cell1:Cell2). Example: =SUM(C5:C30).
- AVERAGE: The AVERAGE function averages out the values of a range of cells. The syntax is the same as the SUM function: AVERAGE(Cell1:Cell2). Example: =AVERAGE(C5:C30).
- IF: The IF function allows you to return values based on a logical test. The syntax is as follows: IF(logical_test, value_if_true, [value_if_false]). Example: =IF(A2>B2,»Over Budget»,»OK»).
- VLOOKUP: The VLOOKUP function helps you search for anything on your sheet’s rows. The syntax is: VLOOKUP(lookup value, table array, column number, Approximate match (TRUE) or Exact match (FALSE)). Example: =VLOOKUP([@Attorney],tbl_Attorneys,4,FALSE).
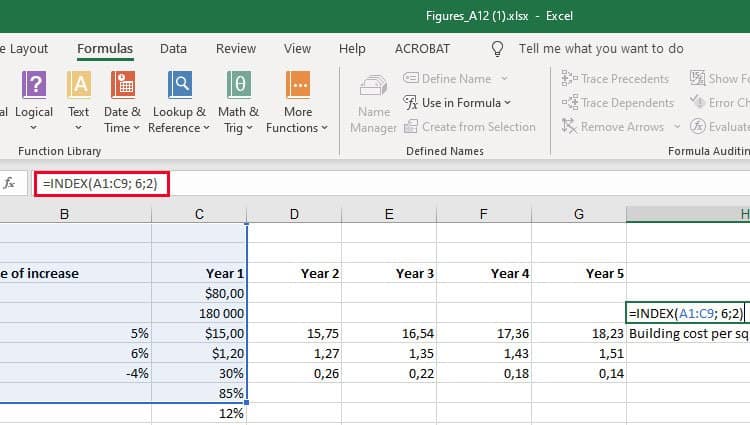
- INDEX: The INDEX function returns a value from within a range. The syntax is as follows: INDEX(array, row_num, [column_num]).
- MATCH: The MATCH function looks for a certain item in a range of cells and returns the position of that item. It can be used in tandem with the INDEX function. The syntax is: MATCH(lookup_value, lookup_array, [match_type]).
- COUNTIF: The COUNTIF function returns the number of cells that meet a certain criteria or have a certain value. The syntax is: COUNTIF(range, criteria). Example: =COUNTIF(A2:A5,»London»).
Okay, ready to get into the nitty-gritty? Let’s get to it. (And to all the Harry Potter fans out there … you’re welcome in advance.)
Excel Tips
- Use Pivot tables to recognize and make sense of data.
- Add more than one row or column.
- Use filters to simplify your data.
- Remove duplicate data points or sets.
- Transpose rows into columns.
- Split up text information between columns.
- Use these formulas for simple calculations.
- Get the average of numbers in your cells.
- Use conditional formatting to make cells automatically change color based on data.
- Use IF Excel formula to automate certain Excel functions.
- Use dollar signs to keep one cell’s formula the same regardless of where it moves.
- Use the VLOOKUP function to pull data from one area of a sheet to another.
- Use INDEX and MATCH formulas to pull data from horizontal columns.
- Use the COUNTIF function to make Excel count words or numbers in any range of cells.
- Combine cells using ampersand.
- Add checkboxes.
- Hyperlink a cell to a website.
- Add drop-down menus.
- Use the format painter.
Note: The GIFs and visuals are from a previous version of Excel. When applicable, the copy has been updated to provide instruction for users of both newer and older Excel versions.
1. Use Pivot tables to recognize and make sense of data.
Pivot tables are used to reorganize data in a spreadsheet. They won’t change the data that you have, but they can sum up values and compare different information in your spreadsheet, depending on what you’d like them to do.
Let’s take a look at an example. Let’s say I want to take a look at how many people are in each house at Hogwarts. You may be thinking that I don’t have too much data, but for longer data sets, this will come in handy.
To create the Pivot Table, I go to Data > Pivot Table. If you’re using the most recent version of Excel, you’d go to Insert > Pivot Table. Excel will automatically populate your Pivot Table, but you can always change around the order of the data. Then, you have four options to choose from.
- Report Filter: This allows you to only look at certain rows in your dataset. For example, if I wanted to create a filter by house, I could choose to only include students in Gryffindor instead of all students.
- Column Labels: These would be your headers in the dataset.
- Row Labels: These could be your rows in the dataset. Both Row and Column labels can contain data from your columns (e.g. First Name can be dragged to either the Row or Column label — it just depends on how you want to see the data.)
- Value: This section allows you to look at your data differently. Instead of just pulling in any numeric value, you can sum, count, average, max, min, count numbers, or do a few other manipulations with your data. In fact, by default, when you drag a field to Value, it always does a count.
Since I want to count the number of students in each house, I’ll go to the Pivot table builder and drag the House column to both the Row Labels and the Values. This will sum up the number of students associated with each house.
2. Add more than one row or column.
As you play around with your data, you might find you’re constantly needing to add more rows and columns. Sometimes, you may even need to add hundreds of rows. Doing this one-by-one would be super tedious. Luckily, there’s always an easier way.
To add multiple rows or columns in a spreadsheet, highlight the same number of preexisting rows or columns that you want to add. Then, right-click and select «Insert.»
In the example below, I want to add an additional three rows. By highlighting three rows and then clicking insert, I’m able to add an additional three blank rows into my spreadsheet quickly and easily.
3. Use filters to simplify your data.
When you’re looking at very large data sets, you don’t usually need to be looking at every single row at the same time. Sometimes, you only want to look at data that fit into certain criteria.
That’s where filters come in.
Filters allow you to pare down your data to only look at certain rows at one time. In Excel, a filter can be added to each column in your data — and from there, you can then choose which cells you want to view at once.
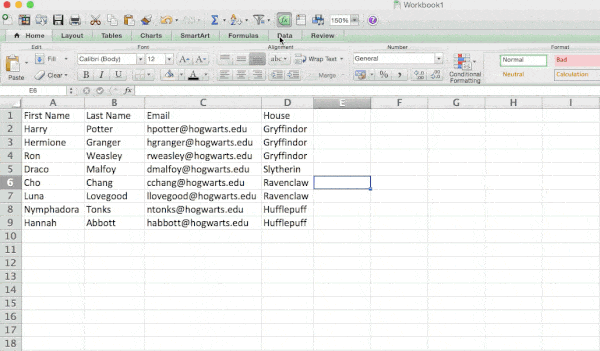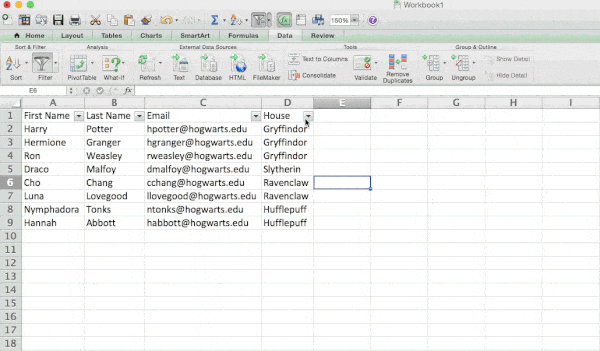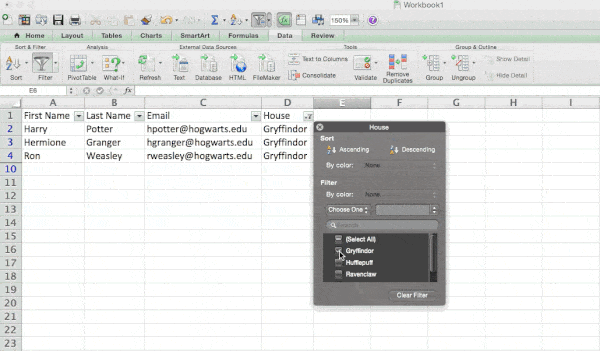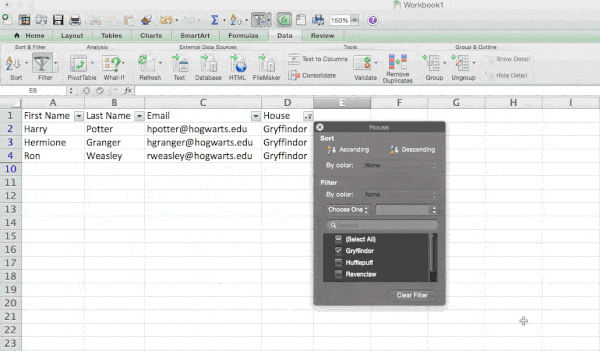
Let’s take a look at the example below. Add a filter by clicking the Data tab and selecting «Filter.» Clicking the arrow next to the column headers and you’ll be able to choose whether you want your data to be organized in ascending or descending order, as well as which specific rows you want to show.
In my Harry Potter example, let’s say I only want to see the students in Gryffindor. By selecting the Gryffindor filter, the other rows disappear.
4. Remove duplicate data points or sets.
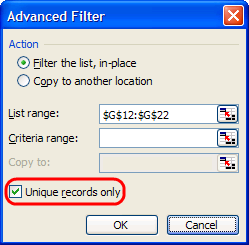
Larger data sets tend to have duplicate content. You may have a list of multiple contacts in a company and only want to see the number of companies you have. In situations like this, removing the duplicates comes in quite handy.
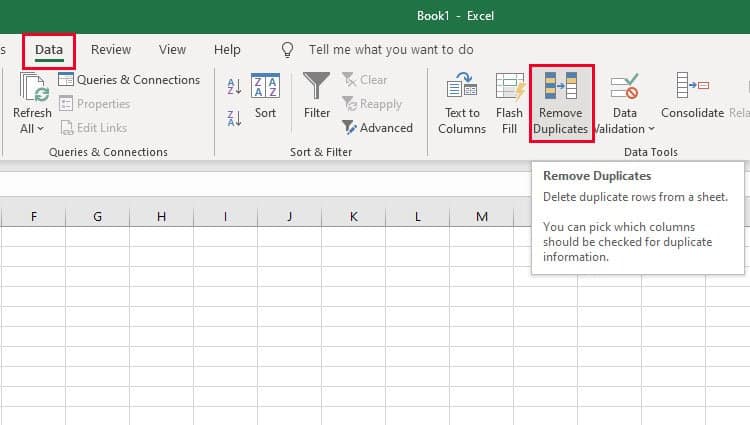
To remove your duplicates, highlight the row or column that you want to remove duplicates of. Then, go to the Data tab and select «Remove Duplicates» (which is under the Tools subheader in the older version of Excel). A pop-up will appear to confirm which data you want to work with. Select «Remove Duplicates,» and you’re good to go.
You can also use this feature to remove an entire row based on a duplicate column value. So if you have three rows with Harry Potter’s information and you only need to see one, then you can select the whole dataset and then remove duplicates based on email. Your resulting list will have only unique names without any duplicates.
5. Transpose rows into columns.
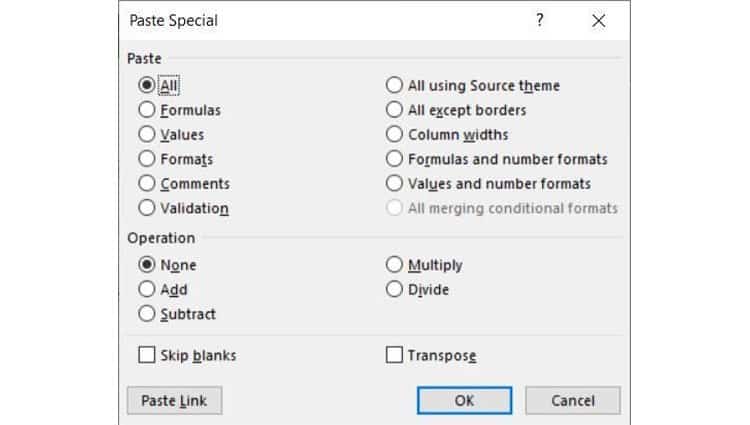
When you have rows of data in your spreadsheet, you might decide you actually want to transform the items in one of those rows into columns (or vice versa). It would take a lot of time to copy and paste each individual header — but what the transpose feature allows you to do is simply move your row data into columns, or the other way around.
Start by highlighting the column that you want to transpose into rows. Right-click it, and then select «Copy.» Next, select the cells on your spreadsheet where you want your first row or column to begin. Right-click on the cell, and then select «Paste Special.» A module will appear — at the bottom, you’ll see an option to transpose. Check that box and select OK. Your column will now be transferred to a row or vice-versa.
On newer versions of Excel, a drop-down will appear instead of a pop-up.
6. Split up text information between columns.
What if you want to split out information that’s in one cell into two different cells? For example, maybe you want to pull out someone’s company name through their email address. Or perhaps you want to separate someone’s full name into a first and last name for your email marketing templates.
Thanks to Excel, both are possible. First, highlight the column that you want to split up. Next, go to the Data tab and select «Text to Columns.» A module will appear with additional information.
First, you need to select either «Delimited» or «Fixed Width.»
- «Delimited» means you want to break up the column based on characters such as commas, spaces, or tabs.
- «Fixed Width» means you want to select the exact location on all the columns that you want the split to occur.
In the example case below, let’s select «Delimited» so we can separate the full name into first name and last name.
Then, it’s time to choose the Delimiters. This could be a tab, semi-colon, comma, space, or something else. («Something else» could be the «@» sign used in an email address, for example.) In our example, let’s choose the space. Excel will then show you a preview of what your new columns will look like.
When you’re happy with the preview, press «Next.» This page will allow you to select Advanced Formats if you choose to. When you’re done, click «Finish.»
7. Use formulas for simple calculations.
In addition to doing pretty complex calculations, Excel can help you do simple arithmetic like adding, subtracting, multiplying, or dividing any of your data.
- To add, use the + sign.
- To subtract, use the — sign.
- To multiply, use the * sign.
- To divide, use the / sign.
You can also use parentheses to ensure certain calculations are done first. In the example below (10+10*10), the second and third 10 were multiplied together before adding the additional 10. However, if we made it (10+10)*10, the first and second 10 would be added together first.
8. Get the average of numbers in your cells.
If you want the average of a set of numbers, you can use the formula =AVERAGE(Cell1:Cell2). If you want to sum up a column of numbers, you can use the formula =SUM(Cell1:Cell2).
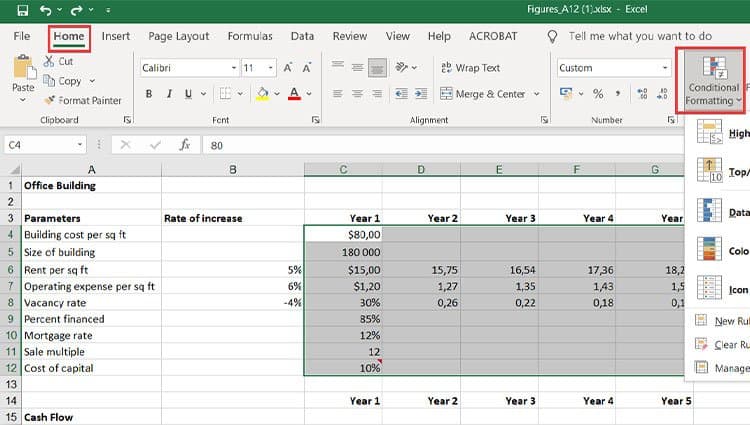
9. Use conditional formatting to make cells automatically change color based on data.
Conditional formatting allows you to change a cell’s color based on the information within the cell. For example, if you want to flag certain numbers that are above average or in the top 10% of the data in your spreadsheet, you can do that. If you want to color code commonalities between different rows in Excel, you can do that. This will help you quickly see information that is important to you.
To get started, highlight the group of cells you want to use conditional formatting on. Then, choose «Conditional Formatting» from the Home menu and select your logic from the dropdown. (You can also create your own rule if you want something different.) A window will pop up that prompts you to provide more information about your formatting rule. Select «OK» when you’re done, and you should see your results automatically appear.
10. Use the IF Excel formula to automate certain Excel functions.
Sometimes, we don’t want to count the number of times a value appears. Instead, we want to input different information into a cell if there is a corresponding cell with that information.
For example, in the situation below, I want to award ten points to everyone who belongs in the Gryffindor house. Instead of manually typing in 10’s next to each Gryffindor student’s name, I can use the IF Excel formula to say that if the student is in Gryffindor, then they should get ten points.
The formula is: IF(logical_test, value_if_true, [value_if_false])
Example Shown Below: =IF(D2=»Gryffindor»,»10″,»0″)
In general terms, the formula would be IF(Logical Test, value of true, value of false). Let’s dig into each of these variables.
- Logical_Test: The logical test is the «IF» part of the statement. In this case, the logic is D2=»Gryffindor» because we want to make sure that the cell corresponding with the student says «Gryffindor.» Make sure to put Gryffindor in quotation marks here.
- Value_if_True: This is what we want the cell to show if the value is true. In this case, we want the cell to show «10» to indicate that the student was awarded the 10 points. Only use quotation marks if you want the result to be text instead of a number.
- Value_if_False: This is what we want the cell to show if the value is false. In this case, for any student not in Gryffindor, we want the cell to show «0». Only use quotation marks if you want the result to be text instead of a number.
Note: In the example above, I awarded 10 points to everyone in Gryffindor. If I later wanted to sum the total number of points, I wouldn’t be able to because the 10’s are in quotes, thus making them text and not a number that Excel can sum.
The real power of the IF function comes when you string multiple IF statements together, or nest them. This allows you to set multiple conditions, get more specific results, and ultimately organize your data into more manageable chunks.
Ranges are one way to segment your data for better analysis. For example, you can categorize data into values that are less than 10, 11 to 50, or 51 to 100. Here’s how that looks in practice:
=IF(B3<11,“10 or less”,IF(B3<51,“11 to 50”,IF(B3<100,“51 to 100”)))
It can take some trial-and-error, but once you have the hang of it, IF formulas will become your new Excel best friend.
11. Use dollar signs to keep one cell’s formula the same regardless of where it moves.
Have you ever seen a dollar sign in an Excel formula? When used in a formula, it isn’t representing an American dollar; instead, it makes sure that the exact column and row are held the same even if you copy the same formula in adjacent rows.
You see, a cell reference — when you refer to cell A5 from cell C5, for example — is relative by default. In that case, you’re actually referring to a cell that’s five columns to the left (C minus A) and in the same row (5). This is called a relative formula. When you copy a relative formula from one cell to another, it’ll adjust the values in the formula based on where it’s moved. But sometimes, we want those values to stay the same no matter whether they’re moved around or not — and we can do that by turning the formula into an absolute formula.
To change the relative formula (=A5+C5) into an absolute formula, we’d precede the row and column values by dollar signs, like this: (=$A$5+$C$5). (Learn more on Microsoft Office’s support page here.)
12. Use the VLOOKUP function to pull data from one area of a sheet to another.
Have you ever had two sets of data on two different spreadsheets that you want to combine into a single spreadsheet?
For example, you might have a list of people’s names next to their email addresses in one spreadsheet, and a list of those same people’s email addresses next to their company names in the other — but you want the names, email addresses, and company names of those people to appear in one place.
I have to combine data sets like this a lot — and when I do, the VLOOKUP is my go-to formula.
Before you use the formula, though, be absolutely sure that you have at least one column that appears identically in both places. Scour your data sets to make sure the column of data you’re using to combine your information is exactly the same, including no extra spaces.
The formula: =VLOOKUP(lookup value, table array, column number, Approximate match (TRUE) or Exact match (FALSE))
The formula with variables from our example below: =VLOOKUP(C2,Sheet2!A:B,2,FALSE)
In this formula, there are several variables. The following is true when you want to combine information in Sheet 1 and Sheet 2 onto Sheet 1.
- Lookup Value: This is the identical value you have in both spreadsheets. Choose the first value in your first spreadsheet. In the example that follows, this means the first email address on the list, or cell 2 (C2).
- Table Array: The table array is the range of columns on Sheet 2 you’re going to pull your data from, including the column of data identical to your lookup value (in our example, email addresses) in Sheet 1 as well as the column of data you’re trying to copy to Sheet 1. In our example, this is «Sheet2!A:B.» «A» means Column A in Sheet 2, which is the column in Sheet 2 where the data identical to our lookup value (email) in Sheet 1 is listed. The «B» means Column B, which contains the information that’s only available in Sheet 2 that you want to translate to Sheet 1.
- Column Number: This tells Excel which column the new data you want to copy to Sheet 1 is located in. In our example, this would be the column that «House» is located in. «House» is the second column in our range of columns (table array), so our column number is 2. [Note: Your range can be more than two columns. For example, if there are three columns on Sheet 2 — Email, Age, and House — and you still want to bring House onto Sheet 1, you can still use a VLOOKUP. You just need to change the «2» to a «3» so it pulls back the value in the third column: =VLOOKUP(C2:Sheet2!A:C,3,false).]
- Approximate Match (TRUE) or Exact Match (FALSE): Use FALSE to ensure you pull in only exact value matches. If you use TRUE, the function will pull in approximate matches.
In the example below, Sheet 1 and Sheet 2 contain lists describing different information about the same people, and the common thread between the two is their email addresses. Let’s say we want to combine both datasets so that all the house information from Sheet 2 translates over to Sheet 1.
So when we type in the formula =VLOOKUP(C2,Sheet2!A:B,2,FALSE), we bring all the house data into Sheet 1.
Keep in mind that VLOOKUP will only pull back values from the second sheet that are to the right of the column containing your identical data. This can lead to some limitations, which is why some people prefer to use the INDEX and MATCH functions instead.
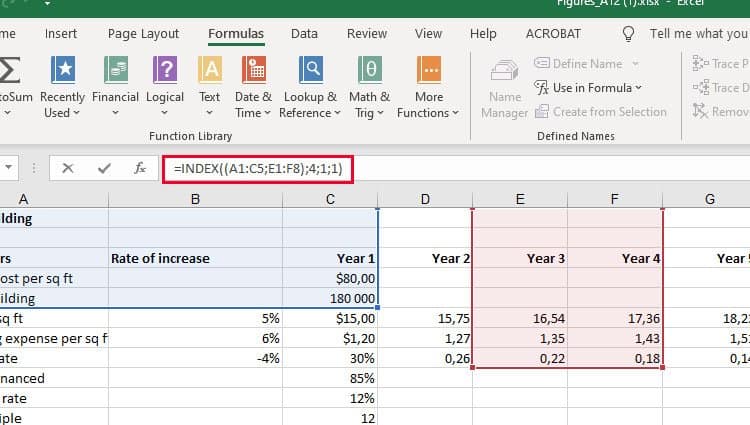
13. Use INDEX and MATCH formulas to pull data from horizontal columns.
Like VLOOKUP, the INDEX and MATCH functions pull in data from another dataset into one central location. Here are the main differences:
- VLOOKUP is a much simpler formula. If you’re working with large data sets that would require thousands of lookups, using the INDEX and MATCH function will significantly decrease load time in Excel.
- The INDEX and MATCH formulas work right-to-left, whereas VLOOKUP formulas only work as a left-to-right lookup. In other words, if you need to do a lookup that has a lookup column to the right of the results column, then you’d have to rearrange those columns in order to do a VLOOKUP. This can be tedious with large datasets and/or lead to errors.
So if I want to combine information in Sheet 1 and Sheet 2 onto Sheet 1, but the column values in Sheets 1 and 2 aren’t the same, then to do a VLOOKUP, I would need to switch around my columns. In this case, I’d choose to do an INDEX and MATCH instead.
Let’s look at an example. Let’s say Sheet 1 contains a list of people’s names and their Hogwarts email addresses, and Sheet 2 contains a list of people’s email addresses and the Patronus that each student has. (For the non-Harry Potter fans out there, every witch or wizard has an animal guardian called a «Patronus» associated with him or her.) The information that lives in both sheets is the column containing email addresses, but this email address column is in different column numbers on each sheet. I’d use the INDEX and MATCH formulas instead of VLOOKUP so I wouldn’t have to switch any columns around.
So what’s the formula, then? The formula is actually the MATCH formula nested inside the INDEX formula. You’ll see I differentiated the MATCH formula using a different color here.
The formula: =INDEX(table array, MATCH formula)
This becomes: =INDEX(table array, MATCH (lookup_value, lookup_array))
The formula with variables from our example below: =INDEX(Sheet2!A:A,(MATCH(Sheet1!C:C,Sheet2!C:C,0)))
Here are the variables:
- Table Array: The range of columns on Sheet 2 containing the new data you want to bring over to Sheet 1. In our example, «A» means Column A, which contains the «Patronus» information for each person.
- Lookup Value: This is the column in Sheet 1 that contains identical values in both spreadsheets. In the example that follows, this means the «email» column on Sheet 1, which is Column C. So: Sheet1!C:C.
- Lookup Array: This is the column in Sheet 2 that contains identical values in both spreadsheets. In the example that follows, this refers to the «email» column on Sheet 2, which happens to also be Column C. So: Sheet2!C:C.
Once you have your variables straight, type in the INDEX and MATCH formulas in the top-most cell of the blank Patronus column on Sheet 1, where you want the combined information to live.
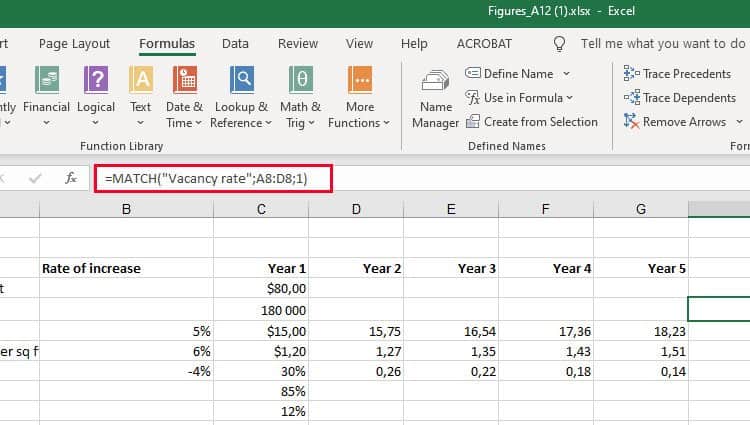
14. Use the COUNTIF function to make Excel count words or numbers in any range of cells.
Instead of manually counting how often a certain value or number appears, let Excel do the work for you. With the COUNTIF function, Excel can count the number of times a word or number appears in any range of cells.
For example, let’s say I want to count the number of times the word «Gryffindor» appears in my data set.
The formula: =COUNTIF(range, criteria)
The formula with variables from our example below: =COUNTIF(D:D,»Gryffindor»)
In this formula, there are several variables:
- Range: The range that we want the formula to cover. In this case, since we’re only focusing on one column, we use «D:D» to indicate that the first and last column are both D. If I were looking at columns C and D, I would use «C:D.»
- Criteria: Whatever number or piece of text you want Excel to count. Only use quotation marks if you want the result to be text instead of a number. In our example, the criteria is «Gryffindor.»
Simply typing in the COUNTIF formula in any cell and pressing «Enter» will show me how many times the word «Gryffindor» appears in the dataset.
15. Combine cells using &.
Databases tend to split out data to make it as exact as possible. For example, instead of having a column that shows a person’s full name, a database might have the data as a first name and then a last name in separate columns. Or, it may have a person’s location separated by city, state, and zip code. In Excel, you can combine cells with different data into one cell by using the «&» sign in your function.
The formula with variables from our example below: =A2&» «&B2
Let’s go through the formula together using an example. Pretend we want to combine first names and last names into full names in a single column. To do this, we’d first put our cursor in the blank cell where we want the full name to appear. Next, we’d highlight one cell that contains a first name, type in an «&» sign, and then highlight a cell with the corresponding last name.
But you’re not finished — if all you type in is =A2&B2, then there will not be a space between the person’s first name and last name. To add that necessary space, use the function =A2&» «&B2. The quotation marks around the space tell Excel to put a space in between the first and last name.
To make this true for multiple rows, simply drag the corner of that first cell downward as shown in the example.
16. Add checkboxes.
If you’re using an Excel sheet to track customer data and want to oversee something that isn’t quantifiable, you could insert checkboxes into a column.
For example, if you’re using an Excel sheet to manage your sales prospects and want to track whether you called them in the last quarter, you could have a «Called this quarter?» column and check off the cells in it when you’ve called the respective client.
Here’s how to do it.
Highlight a cell you’d like to add checkboxes to in your spreadsheet. Then, click DEVELOPER. Then, under FORM CONTROLS, click the checkbox or the selection circle highlighted in the image below.
Once the box appears in the cell, copy it, highlight the cells you also want it to appear in, and then paste it.
17. Hyperlink a cell to a website.
If you’re using your sheet to track social media or website metrics, it can be helpful to have a reference column with the links each row is tracking. If you add a URL directly into Excel, it should automatically be clickable. But, if you have to hyperlink words, such as a page title or the headline of a post you’re tracking, here’s how.
Highlight the words you want to hyperlink, then press Shift K. From there a box will pop up allowing you to place the hyperlink URL. Copy and paste the URL into this box and hit or click Enter.
If the key shortcut isn’t working for any reason, you can also do this manually by highlighting the cell and clicking Insert > Hyperlink.
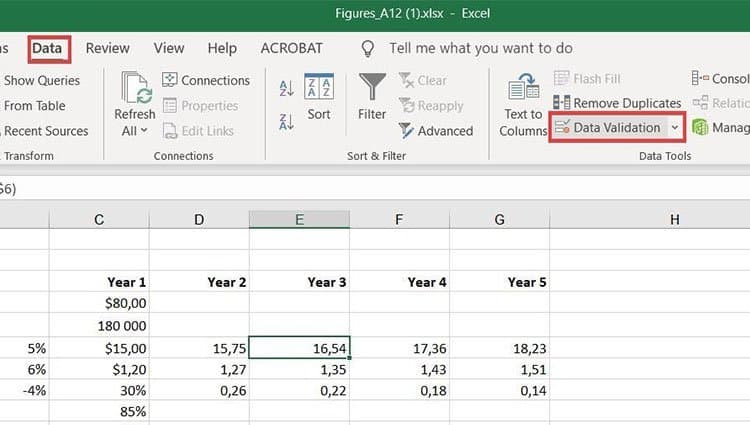
18. Add drop-down menus.
Sometimes, you’ll be using your spreadsheet to track processes or other qualitative things. Rather than writing words into your sheet repetitively, such as «Yes», «No», «Customer Stage», «Sales Lead», or «Prospect», you can use dropdown menus to quickly mark descriptive things about your contacts or whatever you’re tracking.
Here’s how to add drop-downs to your cells.
Highlight the cells you want the drop-downs to be in, then click the Data menu in the top navigation and press Validation.
From there, you’ll see a Data Validation Settings box open. Look at the Allow options, then click Lists and select Drop-down List. Check the In-Cell dropdown button, then press OK.
19. Use the format painter.
As you’ve probably noticed, Excel has a lot of features to make crunching numbers and analyzing your data quick and easy. But if you ever spent some time formatting a sheet to your liking, you know it can get a bit tedious.
Don’t waste time repeating the same formatting commands over and over again. Use the format painter to easily copy the formatting from one area of the worksheet to another. To do so, choose the cell you’d like to replicate, then select the format painter option (paintbrush icon) from the top toolbar.
Excel Keyboard Shortcuts
Creating reports in Excel is time-consuming enough. How can we spend less time navigating, formatting, and selecting items in our spreadsheet? Glad you asked. There are a ton of Excel shortcuts out there, including some of our favorites listed below.
Create a New Workbook
PC: Ctrl-N | Mac: Command-N
Select Entire Row
PC: Shift-Space | Mac: Shift-Space
Select Entire Column
PC: Ctrl-Space | Mac: Control-Space
Select Rest of Column
PC: Ctrl-Shift-Down/Up | Mac: Command-Shift-Down/Up
Select Rest of Row
PC: Ctrl-Shift-Right/Left | Mac: Command-Shift-Right/Left
Add Hyperlink
PC: Ctrl-K | Mac: Command-K
Open Format Cells Window
PC: Ctrl-1 | Mac: Command-1
Autosum Selected Cells
PC: Alt-= | Mac: Command-Shift-T
Other Excel Help Resources
- How to Make a Chart or Graph in Excel [With Video Tutorial]
- Design Tips to Create Beautiful Excel Charts and Graphs
- Totally Free Microsoft Excel Templates That Make Marketing Easier
- How to Learn Excel Online: Free and Paid Resources for Excel Training
Use Excel to Automate Processes in Your Team
Even if you’re not an accountant, you can still use Excel to automate tasks and processes in your team. With the tips and tricks we shared in this post, you’ll be sure to use Excel to its fullest extent and get the most out of the software to grow your business.
Editor’s Note: This post was originally published in August 2017 but has been updated for comprehensiveness.
Excel for Microsoft 365 Excel 2021 Excel 2019 Excel 2016 Excel 2013 Excel 2010 More…Less
Excel is an incredibly powerful tool for getting meaning out of vast amounts of data. But it also works really well for simple calculations and tracking almost any kind of information. The key for unlocking all that potential is the grid of cells. Cells can contain numbers, text, or formulas. You put data in your cells and group them in rows and columns. That allows you to add up your data, sort and filter it, put it in tables, and build great-looking charts. Let’s go through the basic steps to get you started.
Excel documents are called workbooks. Each workbook has sheets, typically called spreadsheets. You can add as many sheets as you want to a workbook, or you can create new workbooks to keep your data separate.
-
Click File, and then click New.
-
Under New, click the Blank workbook.
-
Click an empty cell.
For example, cell A1 on a new sheet. Cells are referenced by their location in the row and column on the sheet, so cell A1 is in the first row of column A.
-
Type text or a number in the cell.
-
Press Enter or Tab to move to the next cell.
-
Select the cell or range of cells that you want to add a border to.
-
On the Home tab, in the Font group, click the arrow next to Borders, and then click the border style that you want.
For more information, see Apply or remove cell borders on a worksheet .
-
Select the cell or range of cells that you want to apply cell shading to.
-
On the Home tab, in the Font group, choose the arrow next to Fill Color
, and then under Theme Colors or Standard Colors, select the color that you want.
For more information about how to apply formatting to a worksheet, see Format a worksheet.
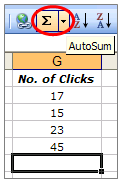
When you’ve entered numbers in your sheet, you might want to add them up. A fast way to do that is by using AutoSum.
-
Select the cell to the right or below the numbers you want to add.
-
Click the Home tab, and then click AutoSum in the Editing group.
AutoSum adds up the numbers and shows the result in the cell you selected.
For more information, see Use AutoSum to sum numbers
Adding numbers is just one of the things you can do, but Excel can do other math as well. Try some simple formulas to add, subtract, multiply, or divide your numbers.
-
Pick a cell, and then type an equal sign (=).
That tells Excel that this cell will contain a formula.
-
Type a combination of numbers and calculation operators, like the plus sign (+) for addition, the minus sign (-) for subtraction, the asterisk (*) for multiplication, or the forward slash (/) for division.
For example, enter =2+4, =4-2, =2*4, or =4/2.
-
Press Enter.
This runs the calculation.
You can also press Ctrl+Enter if you want the cursor to stay on the active cell.
For more information, see Create a simple formula.
To distinguish between different types of numbers, add a format, like currency, percentages, or dates.
-
Select the cells that have numbers you want to format.
-
Click the Home tab, and then click the arrow in the General box.
-
Pick a number format.
If you don’t see the number format you’re looking for, click More Number Formats. For more information, see Available number formats.
A simple way to access Excel’s power is to put your data in a table. That lets you quickly filter or sort your data.
-
Select your data by clicking the first cell and dragging to the last cell in your data.
To use the keyboard, hold down Shift while you press the arrow keys to select your data.
-
Click the Quick Analysis button
in the bottom-right corner of the selection.
-
Click Tables, move your cursor to the Table button to preview your data, and then click the Table button.
-
Click the arrow
in the table header of a column.
-
To filter the data, clear the Select All check box, and then select the data you want to show in your table.
-
To sort the data, click Sort A to Z or Sort Z to A.
-
Click OK.
For more information, see Create or delete an Excel table
The Quick Analysis tool (available in Excel 2016 and Excel 2013 only) let you total your numbers quickly. Whether it’s a sum, average, or count you want, Excel shows the calculation results right below or next to your numbers.
-
Select the cells that contain numbers you want to add or count.
-
Click the Quick Analysis button
in the bottom-right corner of the selection.
-
Click Totals, move your cursor across the buttons to see the calculation results for your data, and then click the button to apply the totals.
Conditional formatting or sparklines can highlight your most important data or show data trends. Use the Quick Analysis tool (available in Excel 2016 and Excel 2013 only) for a Live Preview to try it out.
-
Select the data you want to examine more closely.
-
Click the Quick Analysis button
in the bottom-right corner of the selection.
-
Explore the options on the Formatting and Sparklines tabs to see how they affect your data.
For example, pick a color scale in the Formatting gallery to differentiate high, medium, and low temperatures.
-
When you like what you see, click that option.
Learn more about how to analyze trends in data using sparklines.
The Quick Analysis tool (available in Excel 2016 and Excel 2013 only) recommends the right chart for your data and gives you a visual presentation in just a few clicks.
-
Select the cells that contain the data you want to show in a chart.
-
Click the Quick Analysis button
in the bottom-right corner of the selection.
-
Click the Charts tab, move across the recommended charts to see which one looks best for your data, and then click the one that you want.
Note: Excel shows different charts in this gallery, depending on what’s recommended for your data.
Learn about other ways to create a chart.
To quickly sort your data
-
Select a range of data, such as A1:L5 (multiple rows and columns) or C1:C80 (a single column). The range can include titles that you created to identify columns or rows.
-
Select a single cell in the column on which you want to sort.
-
Click
to perform an ascending sort (A to Z or smallest number to largest).
-
Click
to perform a descending sort (Z to A or largest number to smallest).
To sort by specific criteria
-
Select a single cell anywhere in the range that you want to sort.
-
On the Data tab, in the Sort & Filter group, choose Sort.
-
The Sort dialog box appears.
-
In the Sort by list, select the first column on which you want to sort.
-
In the Sort On list, select either Values, Cell Color, Font Color, or Cell Icon.
-
In the Order list, select the order that you want to apply to the sort operation — alphabetically or numerically ascending or descending (that is, A to Z or Z to A for text or lower to higher or higher to lower for numbers).
For more information about how to sort data, see Sort data in a range or table .
-
Select the data that you want to filter.
-
On the Data tab, in the Sort & Filter group, click Filter.
-
Click the arrow
in the column header to display a list in which you can make filter choices.
-
To select by values, in the list, clear the (Select All) check box. This removes the check marks from all the check boxes. Then, select only the values you want to see, and click OK to see the results.
For more information about how to filter data, see Filter data in a range or table.
-
Click the Save button on the Quick Access Toolbar, or press Ctrl+S.
If you’ve saved your work before, you’re done.
-
If this is the first time you’ve save this file:
-
Under Save As, pick where to save your workbook, and then browse to a folder.
-
In the File name box, enter a name for your workbook.
-
Click Save.
-
-
Click File, and then click Print, or press Ctrl+P.
-
Preview the pages by clicking the Next Page and Previous Page arrows.
The preview window displays the pages in black and white or in color, depending on your printer settings.
If you don’t like how your pages will be printed, you can change page margins or add page breaks.
-
Click Print.
-
On the File tab, choose Options, and then choose the Add-Ins category.
-
Near the bottom of the Excel Options dialog box, make sure that Excel Add-ins is selected in the Manage box, and then click Go.
-
In the Add-Ins dialog box, select the check boxes the add-ins that you want to use, and then click OK.
If Excel displays a message that states it can’t run this add-in and prompts you to install it, click Yes to install the add-ins.
For more information about how to use add-ins, see Add or remove add-ins.
Excel allows you to apply built-in templates, to apply your own custom templates, and to search from a variety of templates on Office.com. Office.com provides a wide selection of popular Excel templates, including budgets.
For more information about how to find and apply templates, see Download free, pre-built templates.
Need more help?
If you’re a long-time denizen of the internet, you’ve probably encountered memes about how hard Excel is to master. Some may not get the joke. For most people, Excel is just a collection of tables and spreadsheets. However, underneath the hood, you have access to a wide variety of automation tools, formulas, graphs, pivot tables, etc.
Knowing how to access and exploit these features can be invaluable to your career and business. However, in addition to making your resume more enticing, it can also save you time and help you organize your life. Thus, in the following guide, we will explore twenty things to do in Excel that will make you an expert.
This guide will be a mixed bag of advanced and intermediate usage tips and tricks. We’ll cover operations such as pivot tables, functions, keyboard shortcuts, and more. Without further ado, here are the most useful tips, tricks, and hacks in Microsoft Excel.
1. Pivot Tables
Pivot tables summarize your data for you. They are particularly useful when you’re working with large tables of data. They can save you from creating lots of summary calculations. The easiest way to create a pivot table using Microsoft Excel is:
- Make sure that the table or spreadsheet you want to create the pivot table for is selected
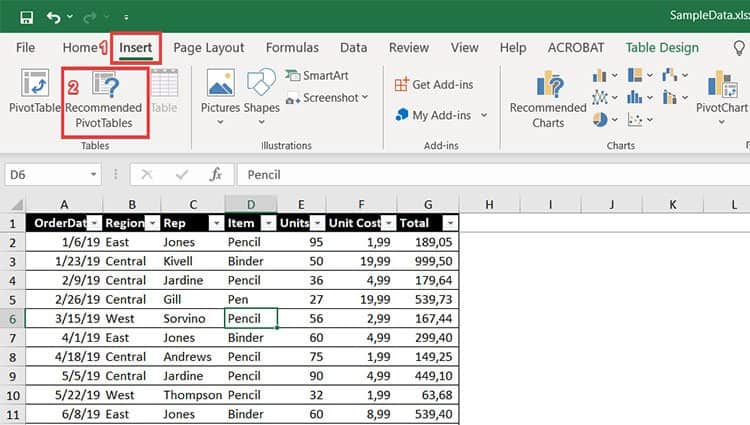
- Click on the Insert tab
- Select Recommended Pivot Tables
From there, you’ll be able to select a few different options of how you might like to summarize your data. Selecting one of the recommended pivot tables will create a new spreadsheet with the pivot table inserted inside.
If you plan to teach yourself how to use pivot tables, this is an excellent place to start. Once you understand how recommended pivot tables function, you can create your very own blank table.
They also have content showing you how to arrange, slice and filter your pivot tables. If that isn’t enough, there is a wide variety of videos, books, and articles that can help you learn the intricacies of pivot tables.
2. Managing Duplicates
If you’re working with large sets of data, running into duplicate data is not uncommon. Fortunately, there are a couple of ways of eliminating duplicate data in Excel. You can either filter, use the Remove Duplicate data tool, or quick format for it.
These are great alternatives to painstakingly and manually searching for duplicates yourself. Knowing how to manage duplicate data in Excel will make you look like a real expert.
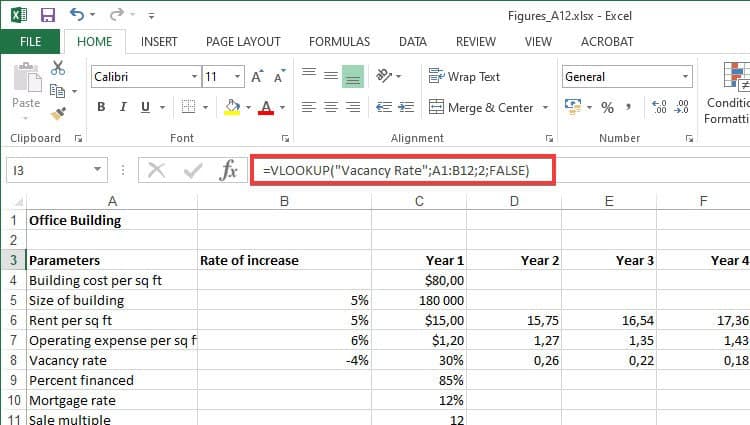
3. Using VLOOKUP (Vertical Lookup)
VLOOKUP is considered one of Excel’s most useful functions. If your data is organized into vertical columns, you can use the VLOOKUP function to search for a value in the first column of a sectioned data table. VLOOKUP will use the search value to return a corresponding value from another column.
The VLOOKUP function takes four parameters:
- Value: The search value
- Column_Range: The table or range of data columns you’re searching through
- Column_Number: The column number from which the corresponding value must be returned.
- Approximate_Match: A Boolean argument that instructs the function to either search for the exact match (0 or FALSE) or the approximate match (1 or TRUE). It’s an optional argument that is TRUE by default.
So the final function structure will look like this: VLOOKUP(Value; Column_Range; Column_Number; Approximate_Match)
Again, VLOOKUP is particularly useful when you’re working with large sets of data. It can help you summarize or emphasize important figures in your spreadsheets. It’s even more accessible than ever.
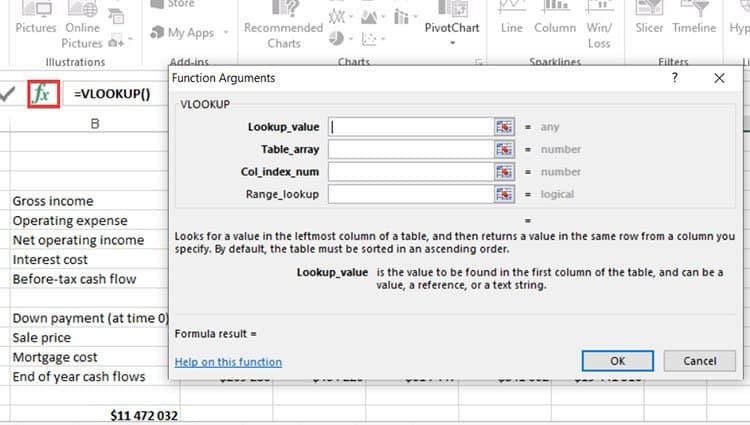
The latest versions of Excel provide you with a wizard to help you construct functions like VLOOKUP. All you need to do is click on the formulas button (fx) and select the VLOOKUP from the list.
The wizard gives you an in-depth explanation of each required parameter. While typing out the function from scratch can make you look like a real Excel expert, using the Insert Function wizard is way easier.
While this function is simple enough to understand and master, you can learn more about it from Microsoft’s official VLOOKUP tutorial.
*Note: The international version of Microsoft Excel uses semicolons to separate arguments in a function (list separator). Contrastingly, the American version uses commas (,) to separate arguments.
4. Working with Multiple Excel Files
You can simultaneously open multiple Excel files in different Excel instances by selecting the files in your file explorer and pressing Enter on your keyboard. To quickly switch between Excel instances/files, simply press CTRL + TAB on your keyboard.
This dazzling display of skill can make you look like some sort of Excel sorcerer to neophytes. Additionally, it can significantly increase your productivity.
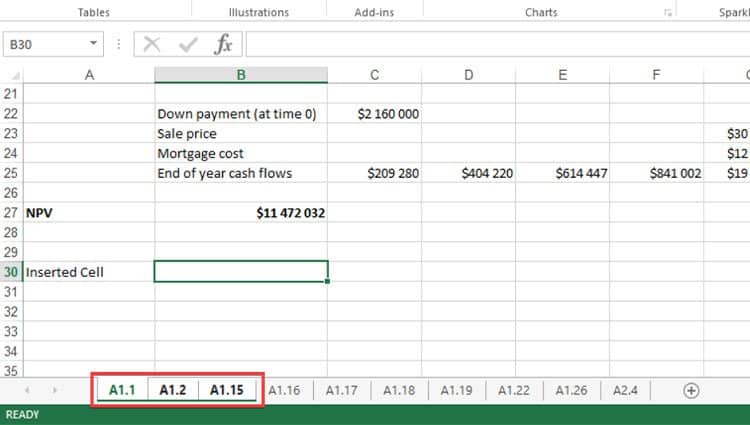
5. Grouping and Ungrouping Worksheets
Grouping worksheets allows you to simultaneously edit multiple worksheets. To group your spreadsheets, do the following:
- Hold the Ctrl button on your keyboard
- Select all the spreadsheets you want to group
- Release the Ctrl button
If you insert a value into any cell of any of the grouped spreadsheets, Excel will update all the spreadsheets with that value in the same cell.
For instance, if you have three spreadsheets in a group and you update cell A30 of your first spreadsheet with the value “Insert Cell”, it will update cell A30 in the other spreadsheets in the group too.
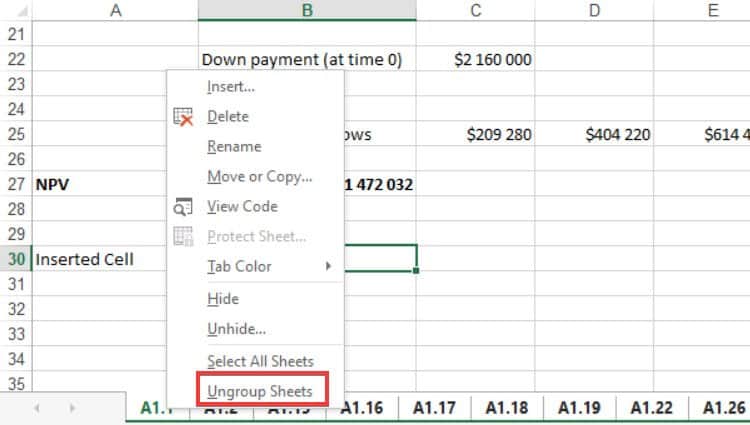
Grouping your worksheets is great for bulk editing. If you want to ungroup your spreadsheets, all you need to do is right-click on one of the spreadsheet tabs and select Ungroup Sheets from the context menu.
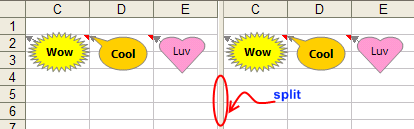
6. Using Freeze Panes
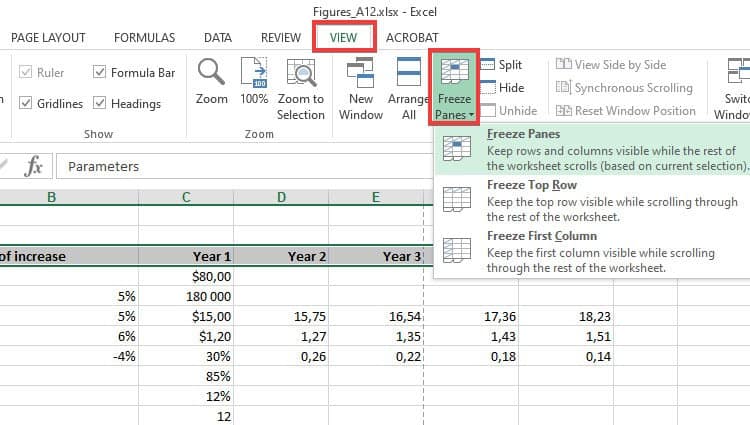
Excel has a freeze pane feature that allows you to freeze columns and rows. This makes it easier to compare and reference data. To access Freeze Panes:
- Select cell/row underneath the row(s) you want to freeze
- Click on the VIEW tab
- Click on the Freeze Panes option
- Select Freeze Panes from the context menu
The row above your selected cell/row will be frozen as you scroll through your spreadsheet. Alternatively, you can select Freeze Top Row or Freeze First Column from the Freeze Panes menu. Freeze Top Row will freeze the first row for vertical scrolling, while Freeze First Column will freeze your first column for horizontal scrolling.
To unfreeze your Panes, click on the Unfreeze Panes option from the Freeze Panes menu.
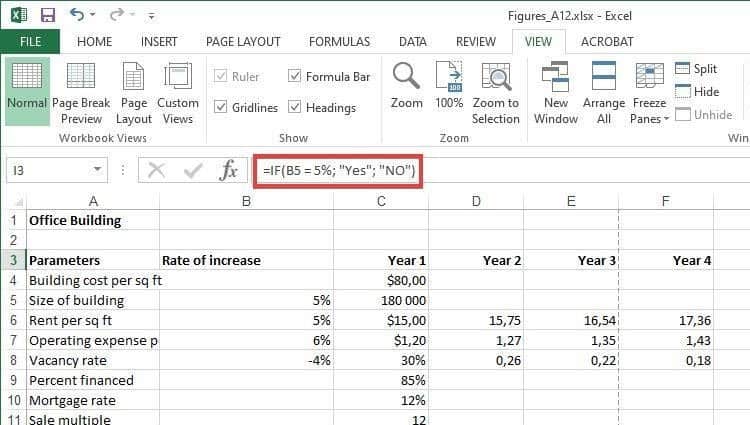
7. IF Function
Excel’s IF function can make your data more dynamic. It’s a function that tells Excel to input or return a value if it meets a certain condition. It takes three parameters:
- Logical_test: A test condition that can be validated as either true or false
- Value_if_true: The value that Excel should use if the logical test is true
- Vaue_if_false: The value that Excel should use if the logical test is false
The logical test compares two values or cells using the equals (=), greater than (>), or the lesser than (<) symbols, e.g., = IF (C2>C3; “Yes”, “No”).
*Note: Text or strings of characters need to be surrounded by quotation marks (“”).
8. Using The Sum Function
Excel allows you to perform a wide range of mathematical operations using one of its many functions. While you can perform advanced mathematical operations such as finding the cosine of an angle, it’s the simpler operations you may find useful.
For instance, one of the most widely used math functions is the sum function. We use it to add numbers together. You can use cell indexes and/or actual numbers. The latest versions of Excel have an argument limit of 255 numbers. This means that you can have 255 terms.
The syntax of the Sum function can look like this:
- =Sum(1;2): Adds two simple numbers. The output will be 3.
- =Sum(A1;CB): Adds the contents of two cells together.
- =Sum(A1;2): Adds contents of a cell to a number.
- =Sum(A1:CB): Adds all the numbers in between (and including) these two indexes.
- =Sum(A1:CB;5): Adds all the numbers in a range of cells and adds an additional specified number to the sum.
- =Sum(A1:CB; G7:G1): Add all the numbers in two different cell index ranges.
These are only just a few of the variations. It’s a remarkably flexible function.
If you want to appear even more impressive, you can use the SUMIF function, which combines the SUM function with the IF function.
9. Using The INDEX Function
The INDEX function will return a value at the specified index within a table or a table section. It allows you to search for specific values in your spreadsheet. It comes in two forms:
- Array Form – Takes an array for its first argument. The second argument is the row number, while the third is the column number. The array is constructed using the range of cells you want to search in your spreadsheet, i.e., A1:C20. The syntax of the function looks like this:
=INDEX(array;row_num;col_num)
=INDEX(A1:C20; 2; 3)
- Reference Form – This takes a reference as its first argument. A reference allows you to input more than one range or a set of arrays. The second argument is the row number, and the third is the column number. The fourth allows you to select which array to search in. The syntax of the function looks like this:
=INDEX((reference); row_num; col_num;area_num)
e.g.
=INDEX((A1:C9;D1:F8);2;3;1)
While the INDEX function is suited to simple searches, it can be used for advanced dynamic operations.
10. Using the MATCH Function
The MATCH function is another search function used to find the index of a value in a one-dimensional array/list (a table made up of one column or row). It consists of three arguments:
- Search_Value: The value whose index you’re looking for
- Array_Range: The array or range of cells you want to search through – must consist of one column or row to work, i.e., A1:A9 or A1:E1
- Match_Type: An optional parameter that specifies if the function should find the exact match for the search value. It takes one of the following values:
- -1: Looks for the largest value that is less than or equal to the search value
- 0: Looks for the exact match of the search value
- 1: Looks for the smallest value that is greater than or equal to the search value
The syntax for the function looks like this:
=MATCH(Search_Value; Array_Range;Match_Type)
e.g.
=MATCH(1; A1:A5;0)
11. Conditional Formatting
Much like charts, conditional formatting offers a way to visualize your data using color-coding that’s based on a cell’s value. To use conditional formatting, do the following:
- Select all the cells you want formatted
- Click on the Home tab
- Click on Conditional Formatting
From there, you’ll be able to select which rules you’d like to instate for conditional formatting. You can even create your own custom rules.
12. Using Data Validation
Data validation allows you to verify and ensure that your data is logical and fits certain parameters. If you’re working with text, it allows you to check if the text is spelled correctly. Excel’s Data Validation feature can be accessed by doing the following:
- Select the cell or group of cells you want to perform data validation on
- Click on the Data tab
- Click on Data Validation
A dialog should pop up. It will allow you to set what type of values a cell allows. Additionally, it will allow you to set a range of acceptable values. You can also set an input message that displays itself when a cell is selected.
The last tab in the data validation screen allows you to display an error alert when incorrect data is inserted into a cell.
13. Using The Fill Handle to Copy Formulas
Excel allows you to fill in calculations across multiple cells. For instance, if you perform a calculation using cells from two different columns (but the same row), you can use the fill handle to copy the operation across multiple cells in the same column.
To illustrate, if I perform a calculation in cell C1 where I multiply the contents of cell A1 by the contents of B1 (=A1*B1) and drag the fill handle to cell C2, it will multiply the contents of cell A2 by B2 (=A2*B2).
While it’s a simple enough tool, knowing when or how to use it effectively can make you look like a real Excel expert.
14. Switching Between Relative, Absolute, and Mixed Cell References
In the previous entry, we spoke about using Excel’s fill handle. By default, the fill handle uses relative references. In other words, Excel will use the original calculation as a template and then infer its relative operands by looking at the position in the spreadsheet and looking at the original calculation’s operands.
However, if you want more control over how Excel copies calculations across, you can use absolute cell references. This allows you to dictate some of the operands that get copied across. Thus, it enables you to copy a dynamic variable against a fixed value. For instance, you may want all the cells in column A to be multiplied by the contents of B1 (and only B1).
To accomplish this, you’ll need to use a dollar sign ($) to lock the cell. Where you’re multiplying each cell in the A column by B1, the syntax of your calculation will look like this (=A1*B$1). When you drag the fill handle, every affected cell in the column will multiply its contents by B1 (=A2*B$1, =A3*B$1, etc.)
Mastering this will bring you closer to becoming a real spreadsheet maestro.
*Note: If you place the dollar sign in front of the column letter, it will lock and copy the cell across columns($B1). If you place it after the column letter (in front of the row number), it will lock the cell across rows(B$1). If you place a dollar sign in front and after the column letter, it will lock the cell across both columns and rows($B$1).
15. Using Paste Special
Excel allows you to control how you copy and paste data using its paste special feature. It allows you to copy and paste formatting, formulas, and values between cells. You can even use the paste special feature to perform a simple mathematical operation on copied data.
To access the past special feature, do the following:
- Copy your data
- Right-click on the cell(s) you want to paste the data into
- Select Paste Special from the context menu
If you initiate the above steps correctly, you should be greeted by this dialog:
16. Transposing data in Excel
Microsoft Excel gives you a plethora of options to reposition or transpose data. You can transpose vertical (row) data into horizontal (column) data or vice versa using one of the following methods:
- The Transpose function
- The Transpose Paste Special option
The easiest way would be to use the transpose paste option. However, it may seem far more impressive to master the Transpose function.
17. Using The TRIM Function
The TRIM function allows you to remove unwanted trailing and leading white spaces from Excel data. The Trim function only requires one argument (text). It will copy and input transposed data into a cell.
The syntax of the trim function looks like this:
=TRIM(Text)
e.g.
=TRIM(A1)
=TRIM(“ hello world”)
It’s a very simple function; however, if you work with a lot of text-based data, you may find it useful.
18. Using Macros
If you want to truly become an Excel expert, you’ll need to master Macros. Macros allow you to automate repetitive tasks in Excel by adding programming elements through Visual Basic code. You can even use Macros to extend some of Excel’s functionality.
However, you don’t need programming experience to create basic Macros. Excel allows you to record repetitive actions, and it will write the code for you in the background.
Covering Macros would take an entire article to explain in detail. Fortunately for you, there is a slew of content on the internet that will help you achieve a basic understanding of Macros.
*Note: Before you can use Macros, you’ll have to display the Developer tab in Excel’s ribbon menu.
19. Combining Functions
Excel allows you to combine multiple functions or formulas to expand their capabilities. For instance, while INDEX and MATCH are great search tools, they have limitations. To get around these limitations and initiate more advanced and dynamic searches, you can combine the two.
For instance, you can use the MATCH function as the INDEX function’s row or column number i.e.
=INDEX(Array_Range; MATCH(Search_Value; Array_Range;Match_Type);Column_Number)
=INDEX(A1:C12;MATCH(“Size of building”;A1:A6);1)
Once you learn how to master your most-used functions and formulas in Excel, you’ll get more comfortable with combining them. This is sure to make you look like an expert.
20. Keyboard Shortcuts
Using keyboard shortcuts in Excel is sure to make you look like an expert. However, not only does it make you look cool, it can save you time.
We recommend you study and memorize an Excel keyboard shortcut cheat sheet. You can learn how to shift between tools, change your font, create a new spreadsheet, etc. All without having to use your mouse.
Conclusion
Microsoft Excel is a powerful business tool. One could say that it has the whole world’s financial system propped upon its shoulders. Becoming well-versed in Excel isn’t just a skill that will decorate your resume, but you can also use it to organize your life.
In the above text, we explored 20 things you can do in Excel that will make you an expert. Do you have any tips or tricks of your own? Leave them down in the comment section below. As always, thank you for reading.
20 Excel Tricks That Can Make Anyone An Excel Expert
- One Click to Select All.
- Open Excel Files in Bulk.
- Shift Between Different Excel Files.
- Create a New Shortcut Menu.
- Add a Diagonal Line to a Cell.
- Add More Than One New Row or Column.
- Speedily Move and Copy Data in Cells.
- Speedily Delete Blank Cells.
•
Contents
- 1 Whats the coolest thing you can do in Excel?
- 2 What are 7 things you can use Excel for?
- 3 What are some things you can do with Excel?
- 4 How do I make Excel fun?
- 5 What is the hardest thing to do in Excel?
- 6 What are the best features of Excel?
- 7 What are the 10 uses of Microsoft Excel?
- 8 What are the 3 common uses for Excel?
- 9 What are the 5 functions in Excel?
- 10 What are some basic Excel skills?
- 11 What are the main things to learn in Excel?
- 12 How do you use Excel in life?
- 13 How do you play a game in Excel?
- 14 Is there a game hidden in Excel?
- 15 How do I create a unique code in Excel?
Whats the coolest thing you can do in Excel?
The 10 most useful things you can do in Excel
- Conditional Formatting. Utility: 100. Difficulty: 3.
- PivotTables. Utility: 95. Difficulty: 3.
- Paste Special. Utility: 88.
- Add Multiple Rows. Utility: 87.
- Absolute References. Utility: 85.
- Print Optimisation. Utility: 84.
- Extend formula across/down. Utility: 84.
- Flash Fill. Utility: 84.
What are 7 things you can use Excel for?
More Than a Spreadsheet: 7 Things You Can Do with Microsoft Excel
- Accounting. Excel has long been a trusted accounting tool.
- Data Entry, Storage, and Verification. At its core, Excel is data-entry software.
- Data Visualisation.
- Data Forecasting.
- Inventory Tracking.
- Project Management.
- Creating Forms.
What are some things you can do with Excel?
These are things like:
- Creating a new spreadsheet from scratch.
- Executing basic computations like adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing.
- Writing and formatting column text and titles.
- Using Excel’s auto-fill features.
- Adding or deleting single columns, rows, and spreadsheets.
How do I make Excel fun?
Excel can be Exciting – 15 fun things you can do with your spreadsheet in less than 5 seconds
- Change the shape / color of cell comments.
- Filter unique items from a list.
- Sort from Left to Right.
- Hide the grid lines from your sheets.
- Add rounded border to your charts, make them look smooth.
What is the hardest thing to do in Excel?
Top 10 things we struggle to do in Excel & awesome remedies for
- VBA, Macros & Automation. VBA is the most struggling area of Excel.
- Writing Formulas. Excel has hundreds of functions.
- Making Charts.
- Pivot Tables.
- Conditional formatting.
- Array Formulas.
- Dashboards.
- Working with data.
What are the best features of Excel?
The Top 10 Excel Features
- Conditional Formatting. Utility: 100 | Difficulty: 3 | Learn in 180 mins.
- PivotTables. Utility: 95 | Difficulty: 3 | Learn in 240 mins.
- Paste Special. Utility: 88 | Difficulty: 3 | Learn in 10 mins.
- Absolute References.
- Print Optimisation.
- Extend formula across/down.
- Flash Fill.
- INDEX-MATCH.
What are the 10 uses of Microsoft Excel?
Top 10 Uses of Microsoft Excel in Business
- Business Analysis. The number 1 use of MS Excel in the workplace is to do business analysis.
- People Management.
- Managing Operations.
- Performance Reporting.
- Office Administration.
- Strategic Analysis.
- Project Management.
- Managing Programs.
What are the 3 common uses for Excel?
The three most common general uses for spreadsheet software are to create budgets, produce graphs and charts, and for storing and sorting data. Within business spreadsheet software is used to forecast future performance, calculate tax, completing basic payroll, producing charts and calculating revenues.
What are the 5 functions in Excel?
5 Functions of Excel/Sheets That Every Professional Should Know
- VLookup Formula.
- Concatenate Formula.
- Text to Columns.
- Remove Duplicates.
- Pivot Tables.
What are some basic Excel skills?
Basic Excel Skills
- Saving and Opening a Workbook. Saving and opening an Excel workbook is just like as you do in any other application.
- Managing Worksheets.
- Formatting Cells.
- Printing.
- Excel Functions (Basic)
- Charts.
- Sorting Data.
- Find and Replace Option.
What are the main things to learn in Excel?
10 essential things you should learn about Microsoft Excel
- How to create a Pivot Table in Excel.
- How to enter basic formulas and calculations in Excel.
- Use the SUM function to add up a column or row of cells in Excel.
- Absolute and relative references in Excel.
- Rounding numbers in Excel.
How do you use Excel in life?
10 Life Tips For How to Excel In Life (2020 Edition)
- #1: Redefine Success.
- #2: Understand Your Internal Biases (and How to Change Them)
- #3: Re-Frame (To Change Your Reality)
- #4: Learn To Be Vulnerable.
- #5: Challenge The Voice Inside.
- #6: Live With Purpose (For Meaning and Fulfillment)
- #7: Let Go of Busy.
How do you play a game in Excel?
Fun and Games with Microsoft Excel Download Microsoft excel games. These games get download in few seconds. Extract the and open excel file and to play games in Excel, you need to enable Macro. Don’t worry its very easy, when you open the game file, a dialog box automatically appear and ask you to enable macros.
Is there a game hidden in Excel?
Microsoft Excel contained a hidden Doom-like mini-game called “The Hall of Tortured Souls”, a series of rooms featuring the names and faces of the developers.
How do I create a unique code in Excel?
Copy (Ctrl+C) the same first cell of the range (A2). Paste (Ctrl+V) into all cells in the range (A2:A10). Observe each cell now has the formula that generates a unique ID and its own unique ID value. Copy (Ctrl+C) all the same cells in the range (A2:A10).
Loading…
One of the FASTEST ways to Learn Excel is to learn some of the Excel TIPS and TRICKS, period and if you learn a single Excel tip a day you can learn 30 new things in a month.
But you must have a list that you can refer to every day instead of searching here and there. Well, I’m super PROUD to say that this is the most comprehensive list with all the basic and advanced tips that you can find on the INTERNET.
In this LIST, I have covered 300+ Excel TIPS and TRICKS which you can learn to Level Up your Excel Skills.
1. Add Serial Numbers
If you work with large data then it’s better to add a serial number column to it. For me, the best way to do this is to apply the table (Control + T) to the data and then add 1 in the above serial number, just like below.

To do this, you simply need to add 1 to the first cell of the column and then create a formula to add 1 to the above cell’s value. As you are using a table, whenever you create a new entry in the table, Excel will automatically drop down the formula and you will get the serial number.
2. Insert Current Date and Time
The best way to insert the current date and time is to use the NOW function which takes the date and time from the system and returns it.

The only problem with this function is it’s volatile, and whenever you recalculate something it updates its value. And if you don’t want to do this, the best way is to convert it to hard value. You can also use the below VBA code.
Sub timestamp()
Dim ts As Date
With Selection
.Value = Now
.NumberFormat = "m/d/yyyy h:mm:ss AM/PM"
End With
End SubOr these methods to insert a timestamp in a cell.
3. Select Non-Continues Cells
Normally we all do it this way, hold the control key, and select cells one by one. But I have found that there is a far better way for this. All you have to do is, select the first cell and then press SHIFT + F8.
This gives you add or remove selection mode in which you can select cells just by selecting them.
4. Sort Buttons
If you deal with data that needs to sort frequently then it’s better to add a button to the quick access toolbar (if it’s not there already).

All you need to do is click on the down arrow on the quick access toolbar and then select “Sort Ascending” and “Sort Descending”. It adds both buttons to the QAT.
5. Move Data
I’m sure you think about copy-paste but you can also use drag-drop for this.
Simply select the range where you have data and then click on the border of the selection. By holding it move to the place where you need to put it.
6. Status Bar
The status bar is always there but we hardly use it to the full. If you right-click on it, you can see there are a lot of options you can add.
7. Clipboard
There is a problem with normal copy-paste that you can only use a single value at a time.
But here is the kicker: When you copy a value, it goes to the clipboard and if you open the clipboard you can paste all the values which you have copied. To open a clipboard, click on the go to Home Tab ➜ Editing and then click on the down arrow.

It will open the clipboard on the left side, and you can paste values from there.

8. Bullet Points
The easiest way to insert bullet points in Excel is by using custom formatting and here are the steps for this:
- Press Ctrl + 1 and you will get the “Format Cell” dialogue box.
- Under the number tab, select custom.
- In the input bar, enter the following formatting.
- ● General;● General;● General;● General
- In the end, click OK.

Now, whenever you enter a value in the cell Excel will add a bullet before that.
9. Worksheet Copy
To create a copy of a worksheet in the same workbook drag and drop in the best way.
You just need to click and hold the mouse on the sheet’s name tab and then drag and drop it, to the left or right, where you want to create a copy.
10. Undo-Redo
Just like sort buttons you can also add undo and redo buttons to the QAT. The best part about those buttons is you can use them to undo a particular activity without pressing the shortcut key again and again.

More Basic Tips: Delta Symbol | Degree Symbol | Formula to Value | Concatenate a Range of Cells | Insert a Check Mark Symbol in Excel | Convert Negative Number into Positive | Highlight Blank Cells in Excel
11. AutoFormat
If you deal with financial data, then auto format can be one of your best tools. It simply applies the format to small as well as large data sets (especially when data is in tabular form).

- First of all, you need to add it to the quick access toolbar (here are the steps).
- After that, whenever you need to apply the format, just select the data where you want to apply it and click on the AUTO FORMAT button from the quick access toolbar.
- It will show you a window to select the formatting type and after selecting that click OK.
The AUTOFORMAT is a combination of six different formattings and you have the option to disable any of them while applying it.
12. Format Painter
The simple idea with the format painter is to copy and paste formatting from one section to another. Let’s say you have specific formatting (Font Style and Color, Background Color to a Cell, Bold, Border, etc.) in the range B2:D7, and with format painter, you can copy that formatting to range B9: D14 with a click.
- First of all, select the range B2:D7.
- After that, go to the Home Tab ➜ Clipboard and then click on “Format Painter”.
- Now, select cell C1 and it will automatically apply the formatting on B9: D14.
The format painter is fast and makes it easy to apply to format from one section to another.
Related: Format Painter Shortcut
13. Cell Message
Let’s say you need to add a specific message to a cell, like “Don’t delete the value”, “enter your name” or something like that.
In this case, you can add a cell message for that particular cell. When the user will select that cell, it will show the message you have specified. Here are the steps to do this:

- First, select the cell to which you want to add a message.
- After that, go to the Data Tab ➜ Data Tools ➜ Data Validation ➜ Data Validation.
- In the data validation window, go to the Input Message tab.
- Enter the title, and message, and make sure to tick mark “Show input message when the cell is selected”.
- In the end, click OK.

Once the message is shown you can drag and drop it to change its position.
14. Strikethrough
Unlike Word, in Excel, there is no option on the ribbon to apply strikethrough. But I have figured out that there are 5 ways to do it and the easiest of all of them is a keyboard shortcut.
All you need to do is select the cell where you want to apply the strikethrough and use the below keyboard shortcut.
Ctrl + 5
And if you are using MAC then:
⌘ + ⇧ + X
Quick Note: You can use the same shortcut keys if you need to do this for partial text.
15. Add Barcode
It is one of those secret tips that most Excel users are unaware of. To create a bar-code in Excel all you need to do is install this bar-code font from ID-AUTOMATIC.
Once you install this font, you will have to type the number in a cell for which you want to create a bar code and then apply the font style.

learn more about this tip
16. Month Name
Alright, let’s say you have a date in a cell, and you want that date to show as a month or a year. For this, you can apply custom formatting.

- First, select the cell with a date and open formatting options (use Ctrl + 1).
- Select the “Custom” option and add “MMM” or “MMMMMM” for the month or “YYYY” for the year format.
- In the end, click OK.
Custom formatting just changes the formatting of the cell from date to year/month, but the value remains the same.
17. Highlight Blank Cells
When you work with large data sheets it’s hard to identify the blank cells. So, the best way is to highlight them by applying a cell color.
- First, select all the data from the worksheet using the shortcut key Ctrl + A.

- After that, go to Home Tab ➜ Editing ➜ Find & Select ➜ Go to Special.

- From Go to Special dialog box, select Blank and click OK.

- At this point, you have all the blank cells selected and now apply a cell color using font settings.

…but you can also use conditional formatting for this
18. Font Color with Custom Formatting
In Excel, we can apply custom formatting and in custom formatting, there is an option to use font colors (limited but useful).
For example, if you want to use the Green color for positive numbers and the red color for negative numbers then you need to use the custom format.
[Green]#,###;[Red]-#,###;0;

- First, select the cells where you want to apply this format.
- After that open the format option using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + 1 and go to the “Custom” category and the custom format in the input dialogue box.
- In the end, click OK.
19. Theme Color
We all have some favorite fonts and colors which we use in Excel. Let’s say you received a file from your colleague and now you want to change the font and colors for the worksheet from that file. The point is, you need to do this one by one for each worksheet and that takes time.
But if you create a custom theme with your favorite colors and fonts then you can change the style of the worksheet with a single click. For this, all you have to do is apply your favorite designs to the tables, colors to the shapes and charts, and font style, and then save it as a custom theme.

- Go to the Page Layout Tab ➜ Themes ➜ Save Current Theme. It opens a “Save As” dialogue box, names your theme, and saves it.
- And now, every time you need just one click to change any worksheet style to your custom style.
20. Clear Formatting
This is a simple keyboard shortcut that you can use to clear formatting from a cell or range of cells.
Alt ➜ H ➜ E ➜ F
Or, otherwise, you can also use the clear formatting option from the Home Tab (Home Tab ➜ Editing ➜ Clear ➜ Formats).

21. Sentence Case
In Excel, we have three different functions (LOWER, UPPER, and PROPER) to convert text into different cases. But there is no option to convert a text into a sentence case. Here is the formula which you can use:
=UPPER(LEFT(A1,1))&LOWER(RIGHT(A1,LEN(A1)-1))

This formula converts the first letter of a sentence into capital and the rest all in small (learn how this formula works).
22. Random Numbers
In Excel, there are two specific functions that you can use to generate random numbers. First is RAND which generates random numbers between 0 and 1.

And second is RANDBETWEEN which generates random numbers within the range of two specific numbers.

ALERT: These functions are volatile so whenever you re-calculate your worksheet or hit enter, they update their values so make sure to use them with caution. You can also use RANDBETWEEN to generate random letters and random dates.
23. Count Words
In Excel, there is no specific function to count words. You can count characters with LEN but not words. But, you can use the following formula which can help you to count words from a cell.
=LEN(A1)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(A1,” “,”))+1

This formula counts the number of spaces from a cell and adds 1 to it after that which equals the total number of words in a cell.
24. Calculate the Age
The best way to calculate a person’s age is by using the DATEDIF. This mysterious function is specifically made to get the difference between a date range.
And the formula will be:
=”Your age is “& DATEDIF(Date-of-Birth,Today(),”y”) &” Year(s), “& DATEDIF(Date-of-Birth,TODAY(),”ym”)& ” MONTH(s) & “& DATEDIF(Date-of-Birth,TODAY(),”md”)& ” Day(s).”
25. Calculate the Ratio
I have figured out that there are four different ways to calculate the ratio in Excel but using a simple divide method is the easiest one. All you need to do is divide the larger number into the smaller ones and concatenate it with a colon and one and here’s the formula you need to use:
=Larger-Number/Smaller-Number&”:”&”1″

This formula divides the larger number by the smaller one so that you can take the smaller number as a base (1).
26. Root of Number
To calculate the square root, cube root, or any root of a number the best way is to use the exponent formula. In the exponent formula, you can specify the Nth number for which you want to calculate the root.
=number^(1/n)
For example, if you want to calculate a square root of 625 then the formula will be:
=625^(1/2)

28. Month’s Last Date
To simply get the last date of a month you can use the following dynamic formula.
=DATE(YEAR(TODAY()),MONTH(TODAY())+1,0)

29. Reverse VLOOKUP
As we all know there is no way to look up to left for a value using VLOOKUP. But if you switch to INDEX MATCH you can look up in any direction.

30. SUMPRODUCT IF
You can use the below formula to create a conditional SUMPRODUCT and product values using a condition.
=SUMPRODUCT(–(C7:C19=C2),E7:E19,F7:F19)
31. Smooth Line
If you love to use a line chart, then you are awesome but it would be more awesome if you use a smooth line in the chart. This will give a smart look to your chart.
- Select the data line in your chart and right-click on it.
- Select “Format Data Series”.
- Go to Fill & Line ➜ Line ➜ Tick mark “Smoothed Line”.

33. Hide Axis Labels
This charting tip is simple but still quite functional. If you don’t want to show axis label values in your chart you can delete them. But the better way is to hide them instead of deleting them. Here are the steps:
- Select the Horizontal/Vertical axis in the chart.
- Go to “Format Axis” Labels.
- In the label position, select “None”.

And again, if you want to show it then just select “Next to axis”.
34. Display Units
If you are dealing with large numbers in your chart, you can change the units for axis values.

- Select the chart axis of your chart and open the format “Format Axis” options.
- In axis options, go to “Display Units” where you can select a unit for your axis values.
35. Round Corner
I often use Excel charts with rounded corners and if you like to use round corners too, here are the simple steps.
- Select your chart and open formatting options.
- Go to Fill and Line ➜ Borders.
- In borders sections, tick mark rounded corners.
36. Hide Gap
Let’s say you have a chart with monthly sales in which June has no amount and the cell is empty. You can use the following options for that empty cell.

- Show the gap for the empty cell.
- Use zero.
- Connect data points with the line.
Here are the steps to use these options.
- Right, click on your chart & select “Select Data”.
- In the select data window, click on “Hidden and Empty Cell”.
- Select your desired option from “Show Empty Cell as”.

Make sure to use “Connect data points with the line” (recommended).
38. Chart Template
Let’s say you have a favorite chart formatting you want to apply every time you create a new chart. You can create a chart template to use anytime in the future and the steps are as follow.
- Once you have done with your favorite formatting, right-click on it & select “Save As Template”.

- Using the save as dialog box, save it in the template folder.
- To insert a new one with your favorite template, select it from templates in the insert chart dialog.

39. Default Chart
You can use a shortcut key to insert a chart, but the problem is, it will only insert the default chart, and in Excel, the default chart type is “Column Chart”. So if your favorite chart is a line chart, then the shortcut is useless for you. But let’s conquer this problem. Here are the steps to fix this:
- Go to Insert Tab ➜ Charts.
- Click on the arrow at the bottom right corner.
- Then in your insert chart window, go to “All Charts” and then select the chart category.
- Right, click on the chart style you want to make your default Select “Set as Default Chart”.
- Click OK.

40. Hidden Cells
When you hide a cell from the data range of a chart, it will hide that data point from the chart as well. To fix this, just follow these steps.

- Select your chart and right-click on it.
- Go to ➜ Select Data ➜ Hidden and empty cells.
- From the pop-up window, tick the mark “Show data in hidden rows and columns”.
41. Print Titles
Let’s say you have headings on your table, and you want to print those headings on every page you print. In this case, you can fix “Print Titles” to print those headings on each page.
- Go to “Page Layout Tab” ➜ Page Set Up ➜ Click on Print Titles.
- Now in the page setup window go to the sheet tab and specify the following things.

- Print Area: Select the entire data which you want to print.
- Rows to repeat at the top: Heading row(s) which you want to repeat on every page.
- Columns to repeat at the left: Column(s) which you want to repeat at the left side of every page (if any).

42. Page Order
Specifying the page order is quite useful when you want to print large data.
- Go to File Tab ➜ Print ➜ Print Setup ➜ Sheets Tab.
- Now here, you have two options:
- The First Option: To print your pages using a vertical order.
- The Second Option: To print your pages using a horizontal order.

If you add comments to your reports then you can print them as well. At the end of all printed pages, you can get a list of all the comments.
- Go to File Tab ➜ Print ➜ Print Setup ➜ Sheets Tab.
- In the print section, select “At the end of the sheet” using the comment dropdown.
- Click OK.
44. Scale to Fit
Sometimes we struggle to print entire data on a single page. In this situation, you can use the “Scale to Fit” option to adjust the entire data into a single page.
- Go to File Tab ➜ Print ➜ Print Setup ➜ Page Tab.
- Next, you need to adjust two options:
- Adjust % of normal size.
- Specify the number of pages in which you want to adjust your entire data using width and length.

Instead of using the page number in the header and footer, you can also use a custom header and footer.
- Go to File Tab ➜ Print ➜ Print Setup ➜ Header/Footer.
- Click on the custom header or footer button.

- Here you can select the alignment of the header/footer.

- And the following options can be used:
- Page Number
- Page Number with total pages.
- Date
- Time
- File Path
- File Name
- Sheet Name
- Image
46. Center on Page
Imagine you have less data to print on a page. In this case, you can align it at the center of the page while printing.
- Go to File Tab ➜ Print ➜ Print Setup ➜ Margins.
- In “Center on Page” you have two options to select.
- Horizontally: Aligns data to the center of the page.
- Vertically: Aligns data to the middle of the page.
Before printing a page make sure to see the changes in the print preview.
47. Print Area
The simple way to print a range is to select that range and use the option “print selection”. But what if you need to print that range frequently, in that case, you can specify the printing area and print it without selecting it every time.

Go to the Page Layout Tab, click on the Print Area drop-down, and after that, click on the Set Print Area option.
48. Custom Margin
- Go to File Tab ➜ Print.
- Once you click on print, you’ll get an instant print preview.
- Now from the bottom right side of the window, click on the “Show Margins” button.

It will show all the margins applied and you can change them just by dragging and dropping.
49. Error Values
You can replace all the error values while printing with a specific value (three other values to use as a replacement).
- Go to File Tab ➜ Print ➜ Print Setup ➜ Sheet.
- Select the replacement value from the “Cell error as” dropdown.
- You have three options to use as a replacement.
- Blank
- Double minus sign.
- “#N/A” error for all the errors.

- After selecting the replacement value, click OK.
I believe using a “Double minus sign” is the best way to present errors in a report while printing it on a page.
Related: Ignore All the Errors
50. Custom Start Page Number
If you want to start the page number from a custom number let’s say 5. You can specify that number and the rest of the pages will follow that sequence.
- Go to File Tab ➜ Print ➜ Print Setup ➜ Page.
- In the input box “First page Number”, enter the number from where you want to start the page number.

- In the end, click OK.
This option will only work if you have applied the header/footer in your worksheet.
51. Tracking Important Cells
Sometimes we need to track some important cells in a workbook and for this, the best way is to use the watch window. In the watch window, you add those important cells and then get some specific information about them in one place (without navigating to each cell).
- First, go to Formula Tab ➜ Formula Auditing ➜ Watch Window.

- Now in the “Watch Window” dialog box, click on “Add Watch”.

- After that select the cell or range of cells that you want to add and click OK.
Once you hit OK, you’ll get some specific information about the cell(s) in the watch window.
52. Flash Fill
Flash fill is one of my favorite options to use in Excel. It’s like a copycat, perform the task which you have performed. Let me give you an example.
Here are the steps to use it: You have dates in the range A1: A10 and now, you want to get the month from the dates in the B column.
All you need to do is to type the month of the first date in cell B1 and then come down to cell B2 and press the shortcut key CTRL + E. Once you do this it will extract the month from the rest of the dates, just like below.
53. Combine Worksheets
I’m sure somewhere in the past you have received a file from your colleague where you have 12 different worksheets for 12 months of data. In this case, the best solution is to combine all of those worksheets using the “Consolidate” option, and here are the steps for this.
- First, add a new worksheet and then go to Data Tab ➜ Data Tools ➜ Consolidate.

- Now in the “Consolidate” window, click on the upper arrow to add the range from the first worksheet and then click on the “Add” button.
- Next, you need to add references from all the worksheets using the above step.

- In the end, click OK.
54. Protect a Workbook
Adding a password to a workbook is quite simple, here are the steps.
- While saving a file when you open a “Save As” dialog box go to Tools General Options.

- Add a password to “Password to Open” and click OK.

- Re-enter the password and click OK again.
- In the end, save the file.
Now, whenever you re-open this file it will ask you to enter the password to open it.
55. Live Image
In Excel, using a live image of a table can help you resize it according to space, and to create a live image there are two different ways in which you can use it.
One is camera tools and the second is the paste special option. Here are the steps to use the camera tool and for paste special use the below steps.
- Select the range you want to paste as an image and copy it.
- Go to the cell and right-click, where you want to paste it.
- Go to Paste Special ➜ Other Paste ➜ Options Linked Picture.

56. Userform
A few of the Excel users know that there is a default data entry form is there which we can use. And the best part is there is no need to write a single line of code for this.

Here’s how to use it:
- First of all, make sure you have a table with headings where you want to enter the data.
- After that select any of the cells from that table and use the shortcut key Alt + D + O + O to open the user form.
57. Custom Tab
We all have some favorite options or some options which we use frequently. To access all those options in one place you create a tab and add them to it.

- First, go to File Tab ➜ Options ➜ Customize Ribbon.
- Now click on “New Tab” (this will add a new tab).
- After that right-click on it and name it and then name the group.
- Finally, we need to add options to the tab and for this go to “Choose Commands From” and add them to the tab one by one.
- In the end, click OK.
59. Text to Speech
This is an option where you can make Excel speak the text you have entered into a cell or a range of cells.
60. Named Range
To create a named range the easiest method is to select the range and create it using the “Create from Selection” option. Here are the steps to do this:
- Select the column/row for which you want to create a named range.
- Right-click and click on “Define name…”.

- Select the option to add the name for the named range and click OK.

That’s it.
61. Trim
TRIM can help you to remove extra spaces from a text string. Just refer to the cell from where you want to remove the spaces and it will return the trimmed value in the result.

62. Remove Duplicates
One of the most common things we face while working with large data is “Duplicate Values”. In Excel, removing these duplicate values is quite simple. Here’s how to do this.

- First, select any of the cells from the data or select the entire data.
- After that, go to Data ➜ Data Tools ➜ Remove Duplicates.
- At this point, you have the “Remove Duplicates” window, and from this window, select/de-select the columns which you want to consider/not consider while removing duplicate values.
- In the end, click OK.
Once you click OK, Excel will remove all the rows from the selected data where values are duplicates and show a message with the number of values removed and unique values left.

64. Remove Specific Character
In the range, A1: A5 and you want to concatenate all of them in a single cell. Here’s how to do this with fill justify.

- All you need to do is select that column and open the find and replace dialog box.
- After that click on the “Replace” tab.
- Now here, in “Find What” enter the character you want to replace and make sure to leave “Replace with” blank.
- Now click on “Replace All”.
The moment you click on “Replace All” Excel will remove that particular character from the entire column.
Related: Remove First Character from a Cell in Excel
65. Combine Text
So, you have text in multiple cells, and you want to combine all the text into one cell. No, this time not with fill justify. We are doing it with TEXT JOIN. If you use Office 365, there is a new function TEXTJOIN which is a game-changer when it comes to the concatenation of text.

Here’s the syntax:
TEXTJOIN(delimiter, ignore_empty, text1, [text2], …)
All you need to do is to add a delimiter (if any), and TRUE if you want to ignore empty cells, and in the end, refer to the range.
66. Unpivot Data
Look at the below table, you can use it as a report but you can’t use it further as raw data. No, you can’t. But if you convert this table to something like the one below you can use it easily anywhere.

But if you convert this table into something like the one below you can use it easily anywhere. So how to do this?
here are the simple steps you need to follow.
67. Delete Error Cells
Mostly while working with large data it is obvious to have error values but it’s not good to keep them. The easiest way to deal with these error values is to select them and delete them and these are the simple steps.
- First of all, go to Home Tab ➜ Editing ➜ Find & Replace ➜ Go To Special.
- In the Go To dialog box, select formula, and tick mark errors.

- In the end, click OK.
Once you click OK it will select all the errors and then you can simply delete all by using the “Delete” button.
68. Arrange Columns
Let’s say you want to arrange columns from the data using custom order. The normal way is to cut and paste them one by one.
But we also have an out-of-the-box way. In Excel, you can sort columns just like you sort rows and by using the same methods you can arrange them in a custom order.

⇢ Complete Tip
69. Convert to Date
Sometimes you have dates that are stored as text and you can use them in a calculation and further analysis. To simply convert them back to valid dates you can use the DATEVALUE function.

Other ways to convert text to date
71. Format Painter
Before I started to use format painter for applying cell formatting, I was using paste special with the shortcut key.
- Select the cell or a range from where you want to copy cell formatting.
- Go to ➜ the Home Tab ➜ Clipboard.
- Make double-click on the “Format Painter” button.
- As soon as you do this, your cursor will convert into a paintbrush.
- You can apply that formatting anywhere in your worksheet, in another worksheet, or, even in another workbook.
72. Rename a Worksheet
I always found it quicker than using a shortcut key to change the name of a worksheet. All you have to do is just double-click on the sheet tab and enter a new name.
Let me tell you why this method is faster than using a shortcut. Suppose if want to rename more than one worksheet using a shortcut key.
Before you change the name of a worksheet, you need to activate it. But if you use the mouse it will automatically activate that worksheet and edit the name with only two clicks.
73. Fill Handle
I am sure shortcut addicts always use a shortcut key to drag formulas and values in downward cells. But using a fill handle is more impressive than using a shortcut key.
- Select the cell in which you have a formula or a value that you want to drag.
- Make a double click on the small square box at the right bottom of the cell selection border.
This method only works if you have values in the corresponding column and it works only in the vertical direction.
74. Hide Ribbon
If you want to work in a distraction-free mode, you can do this by collapsing your Excel ribbon.
Just make double-click on the active tab in your ribbon and it will collapse the ribbon. And if you want to expand it back just double-click on it again.
75. Edit a Shape
You often use shapes in our worksheets to present some messages and you have to insert some text into those shapes. Besides the typical method, you can use a double click to edit a shape and insert the text into it.
You can also use this method to edit and enter text in a text box or into a chart title.
76. Column Width
Whenever you have to adjust the column width you can double-click on the right edge of the column header. It auto-sets the column width according to the column data.
The same method can be used to auto-adjust row width.
77. Go to the Last Cell
This trick can be useful if you are working with a large dataset. By using a double click, you can go to the last cell in the range which has data.
You have to click on the right edge of the active cell to go to the right side and on the left edge if you want to go to the left side.
78. Chart Formatting
If you use Control + 1 to open formatting options to format a chart, then I bet you’ll love this trick. All you have to do is just make double-click on the border of the graph to open the formatting option.
79. Pivot Table Double Click
Let’s say someone sent you a pivot table without the source data. As you already know Excel stores data in a pivot cache before creating a pivot table.
You can extract data from a pivot table by double-clicking on data values. As soon as you do this Excel will insert a new worksheet with the data which has been used in the pivot table.
There is a right-click drop-down menu in Excel that few users know about. To use this menu all you need to do is select a cell or a range of the cell and then right-click and while holding it, drop the selection to somewhere else.
81. Default File Saving Location
Normally while working on Excel I create more than 15 Excel files every day. And, if I save each of these files to my desktop it looks nasty. To solve this problem, I have changed my default folder for saving a workbook, and here’s you can do this.
- First, go to the File tab and open Excel options.
- In Excel options, go to the “Save” category.
- Now, there is an input bar where you can change the default local file location.
- From this input bar, change the location address and in the end, click OK.

From now onward, when you open the “Save As” dialog box Excel will show you the location you have specified.
82. Disable Start Screen
I’m sure just like me you hate when you open Microsoft Excel (or any other Office app) and you see the start pop-up screen. It takes time depending on your system’s speed and the add-ins you have installed. Here are the steps to disable the start-up screen in Microsoft Office.

- First, go to the File tab and open Excel options.
- In Excel options, go to the “General” category.
- From the option, drill down to the “Start-Up” options and un-tick the “Show the Start screen when this application starts”.
- In the end, click OK.
From now onward, whenever you start Excel it will directly open the workbook without showing the start-up screen.
83. Developer Tab
Before you start writing VBA codes the first thing you need to do is to enable the “Developer Tab”. When you first install Microsoft Excel, a developer wouldn’t be there. So, you need to enable it from the settings.

- First, go to the File tab and click on the “Customize Ribbon” category.
- Now from the tab list, tick marks the developer tab and click OK.
Now when you come back to your Excel window, you’ll have a developer tab on the ribbon.
84. Enable Macros
When you open a macro-enabled file, you need to enable macro options to run VBA codes. Follow these simple steps:

- First, go to the File tab and click on the “Trust Center” category.
- From here click on “Trust Center Settings”.
- Now in “Trust Center Settings”, click on macro settings.
- After that, click on “Enable all macros with Notifications”.
- In the end, click OK.
85. AutoCorrect Option
If you do a lot of data entry in Excel, then this option can be a game-changer for you. With the auto-correct option, you can tell Excel to change a text string into another when you type it.
Let me tell you an example:
My name is “Puneet” but sometimes people write it like “Punit” but the correct spelling is the first one. So, what I can do is, use autocorrect and tell Excel to change “Punit” into “Puneet”. Follow these simple steps:

- First, go to the File tab and go to options and click on the “Proofing” category.
- After that, click on “AutoCorrect Option” and this will open the auto-correct window.
- Here in this window, you have two input bars to specify the text to replace and text to replace with.
- Enter both values and then click OK.
86. Custom List
Just think like this, you have a list of 10 products that you sell. Whenever you need to insert those product names you can insert them using a custom list. Let me tell you how to do this:
- First, go to the File tab and go to options and click on the “Advanced” category.
- Now, drill down and go to the “General” section and click on “Edit Custom List…”.
- Now in this window, you can enter the list, or you can also import it from a range of cells.
In the end, click OK.
Now, to enter the custom list you have just created, enter the first entry of the list in the cell and then drill down that cell using the fill handle.
87. Apply Table
If you use pivot tables a lot then it’s important to apply the table to the raw data. With a table, there is no need to update the pivot table’s data source, and it drag-down formulas automatically when you add a new entry.

To apply the table to the data just use Ctrl + T keyboard shortcut key and click OK.
88. Gridline Color
If you are not happy with the default color of cell gridlines then you can simply change it with a few clicks and follow these simple steps for this:
- First, go to the File tab and click on the “Advanced” category.
- Now, go to the “Display options for this workbook” section and select the color you want to apply.

- In the end, click OK.
Related – Print Gridlines
89. Pin to Taskbar
This is one of my favorite one-time sets up to save time in the long run. The thing is instead of going to the start menu to open Microsoft Excel, the best way is to point it to the taskbar.

This way you can open it by clicking on the icon from the taskbar.
90. Macro to QAT
If you have a macro code that you need to use frequently. Well, the easiest way to run a macro code is to add it to the Quick Access Toolbar.

- First, go to the File tab and click on the “Quick Access Toolbar” category.
- After that, from “Choose Command from”, select Macros.
- Now select the macro (you want to add to QAT) and click on add.
- From here click on “Modify” and select an icon for the macro button.
- In the end, click OK.
Now you have a button on QAT that you can use to run the macro code you have just specified.
Related – How to Record a Macro in Excel
91. Select Formula Cells
Let’s say you want to convert all the formulas into values and the cells where you have formulas are non-adjacent. So instead of selecting each cell one by one, you can select all the cells where you have a formula. Here are the steps:
- First, go to Home Tab ➜ Editing ➜ Find & Select ➜ Go To Special.
- In the “Go To Special” dialog box, select formulas and click OK.

92. Multiply using Paste Special
To do some one-time calculations you can use the paste special option and save yourself from writing formulas.
93. Highlight Duplicate Values
Well, you can use a VBA code to highlight values but the easiest way is to use conditional formatting. Here are the steps you need to follow:

- First of all, select the range where you want to highlight the duplicate values.
- After that, go to Home Tab ➜ Styles ➜ Highlight Cells Rule ➜ Duplicate Values.
- Now from the dialog box, select the color to use and click OK.
Once you click OK, all the duplicate values will get highlighted.
94. Quick Analysis Tool
If you ever noticed that when you select a range of cells in Excel, a small icon at the bottom of the selection appears? This icon is called the “Quick Analysis Tool”.

When you click on this icon you can see some of the options which are there on the ribbon which you can directly use from here to save time.
95. RUN Command
Yes, you can also open your Excel application using the RUN command.

- For this, all you have to do is open RUN (Window Key + R) and then type “excel” into it.
- In the end, hit enter.
96. Open Specific File
I’m sure like me you also have a few or maybe one of those kinds of workbooks that you open every day when you start working on Excel. There is an option in Excel which you can use to open a specific file(s) whenever you start Excel in your system. Here are the steps.

- Go to File ➜ Options ➜ Advanced ➜ General.
- In general, enter the location (yes, you have to type) of the folder where you have those file(s) in “At startup open all the files in”.
97. Open Excel Automatically
Whenever I “Turn ON” my laptop the first thing I do is open Excel and I’m sure you do the same thing. Well, I’ve got a better idea here, you can add Excel to your system’s startup folder.

- First, open “File Explorer” by using the Windows key + E.
- Now, enter the below address into the address bar to open the folder (change the username with your actual username).
- C:UsersUserAppDataRoamingMicrosoftWindowsStart MenuProgramsStartup
- After that, open the Start Screen, right-click on the Excel App, and click Open file location.
- From the location (Excel App Folder), copy the Excel App icon and paste it into the “Startup” folder.
Now whenever you open your system, Excel will automatically start.
98. Smart Look Up
In Excel, there is an option called “Smart Lookup” and with this option, you can look up a text on the internet. All you have to do is, select a cell or a text from a cell, and go to Review ➜ Insights ➜ Smart Lookup.

Once you click on it, it opens a side pane where you’ll have information about that particular text which you have selected. The idea behind this option is to get information by seeing definitions, and images for the topic (text) from different online sources.
99. Screen Clipping
Sometimes you need to add screenshots to your spreadsheet. And for this, Excel has an option that can capture the screen instantly, and then you can paste it into the worksheet. For this go to ➜ Insert ➜ Illustrations ➜ Screen Clipping.

Related – Excel Camera
100. Locate a Keyboard Shortcut
If you use Excel 2007 to Excel 2016, then you can locate a keyboard shortcut by pressing the ALT key. Once you press it, it shows the keys for the options which are there on the ribbon, just like below.

Let’s say, you want to press the “Wrap Text” button, and the key will be ALT H W. In the same way you can reach all the options using the shortcut keys.
Related – Insert Row
101-300
- Add and Delete a Worksheet in Excel
- Add and Remove Hyperlinks in Excel
- Add Watermark in Excel
- Apply Accounting Number Format in Excel
- Delete Hidden Rows in Excel
- Deselect Cells in Excel
- Draw a Line in Excel
- Formula Bar in Excel
- Add a Button in Excel
- Add a Column in Excel
- Apply Comma Style in Excel
- Group Worksheets in the Excel
- Make Negative Numbers Red in Excel
- Merge – Unmerge Cells in Excel
- Show Ruler in Excel
- Spell Check in Excel
- Fill Handle in Excel
- View Two Sheets Side by Side in Excel
- Increase and Decrease Indent in Excel
- Insert an Arrow in a Cell in Excel
- Remove Pagebreak in Excel
- Rotate Text in Excel (Text Orientation)
- Row Vs Column in Excel (Difference)
- Delete Blank Rows in Excel
- Sort By Date, Date, and Time & Reverse Date Sort in Excel
- Find and Replace in Excel
- Make a Paragraph in a Cell in Excel
- Cell Style (Title, Calculation, Total, Headings…) in Excel
- Hide and Unhide a Workbook in Excel
- Change Date Format in Excel
- Center a Worksheet Horizontally and Vertically in Excel
- Make a Copy of the Excel Workbook (File)
- Write (Type) Vertically in Excel
- Add or Remove Grand Total in a Pivot Table in Excel
- Add Running Total in a Pivot Table in Excel
- Add Calculated Field and Item (Formulas in a Pivot Table)
- Count Unique Values in a Pivot Table in Excel
- Delete a Pivot Table in Excel
- Filter a Pivot Table in Excel
- Add Ranks in Pivot Table in Excel
- Apply Conditional Formatting to a Pivot Table
- Pivot Table using Multiple Files in Excel
- Group Dates in a Pivot Table
- Link a Single Slicer with Multiple Pivot Tables
- Move a Pivot Table
- Pivot Table Formatting
- Pivot Table Keyboard Shortcuts
- Pivot Table Timeline in Excel
- Refresh a Pivot Table
- Refresh All Pivot Tables at Once in Excel
- Sort a Pivot Table in Excel
- Apply Print Titles in Excel (Set Row 1 to Print on Every Page)
- Apply Multiple Filters to Columns
- Create a Data Validation with Date Range
- Create a Yes – No Drop Down in Excel
- Merge Cells in Excel without Losing Data in Excel
- Remove Drop Down List (Data validation) in Excel
- Formulas in Conditional Formatting
- Print a Graph Paper in Excel (Square Grid Template)
- Recover Unsaved Excel Files When Excel Crashed
- Save Excel File (Workbook) as CSV (XLSX TO CSV)
- Create a Pivot Table from Multiple Worksheets
- Create Pivot Chart in Excel
- Activate a Sheet using VBA
- Create WAFFLE CHART in Excel
- Excel Funnel Chart (Template + Steps to Create)
- Excel Gantt Chart Template
- Add a Horizontal Line in a Chart in Excel
- Add a Vertical Line in a Chart in Excel
- Create a Bullet Chart in Excel
- Create a Dynamic Chart Range in Excel
- Create a HEAT MAP in Excel (Simple Steps) + Template
- Create a Milestone Chart in Excel
- Create a Population Pyramid Chart in Excel
- Create a Step Chart in Excel
- Create a Tornado Chart in Excel
- Create Interactive Charts in Excel
- Insert a People Graph in Excel
- Top 10 ADVANCED Excel Charts and Graphs (Free Templates Download)
- Add Secondary Axis in Excel Charts
- Create a HISTOGRAM in Excel – Step by Step
- SPEEDOMETER Chart in Excel
- Thermometer Chart in Excel
- Merge [Combine] Multiple Excel FILES into ONE WORKBOOK
- Perform VLOOKUP in Power Query in Excel
- Calculate the Coefficient of Variation (CV) in Excel
- Does Not Equal Operator in Excel
- MAX IF in Excel
- Round a Number to Nearest 1000, 100, and 10 in Excel
- Round to Nearest .5, 5. 50 (Down-Up) in Excel
- Square a Number in Excel
- #DIV/0
- #SPILL!
- #Value
- 3D Reference in Excel
- Wildcard Characters in Excel
- Hide Formula in Excel
- R1C1 Reference Style in Excel
- VLOOKUP with Multiple Criteria in Excel
- Wildcards with VLOOKUP in Excel
- Average TOP 5 Values in Excel
- Calculate Compound Interest in Excel
- Calculate Cube Root in Excel
- Calculate Percentage Variance (Difference) in Excel
- Calculate Simple Interest in Excel
- Calculate the Weighted Average in Excel
- Absolute Reference (Excel Shortcut)
- Add Column (Excel Shortcut)
- Add Indent (Excel Shortcut)
- Add New Sheet (Excel Shortcut)
- Align Center (Excel Shortcut)
- Apply Border (Excel Shortcut)
- Apply and Remove Filter (Excel Shortcut)
- Auto Fit (Excel Shortcut)
- AutoSum (Excel Shortcut)
- Check Mark (Excel Shortcut)
- Clear Contents (Excel Shortcut)
- Close (Excel Shortcut)
- Currency Format (Excel Shortcut)
- Delete Cell (Excel Shortcut)
- Delete Row(s) (Excel Shortcut)
- Delete Sheet (Excel Shortcut)
- Edit Cell (Excel Shortcut)
- Fill Color (Excel Shortcut)
- Freeze Pane (Excel Shortcut)
- Full Screen (Excel Shortcut)
- Group (Excel Shortcut)
- Hyperlink (Excel Shortcut)
- Insert Cell (Excel Shortcut)
- Lock Cells (Excel Shortcut)
- Merge-Unmerge Cells (Excel Shortcut)
- Paste Values (Excel Shortcut)
- Percentage Format (Excel Shortcut)
- Select Row (Excel Shortcut)
- Show Formulas (Excel Shortcut)
- Subscript (Excel Shortcut)
- Superscript (Excel Shortcut)
- Switch Tabs (Excel Shortcut)
- Transpose (Excel Shortcut)
- Shortcut for Unhide Columns (Excel Shortcut)
- Zoom-In (Excel Shortcut)
- Pivot Table Keyboard Shortcuts
- Apply Date Format (Excel Shortcut)
- Apply Time Format (Excel Shortcut)
- Delete (Excel Shortcut)
- Open Go To Option (Excel Shortcut)
- Add Month to a Date in Excel
- Add Years to Date in Excel
- Add-Subtract Week from a Date in Excel
- Compare Two Dates in Excel
- Convert Date to Number in Excel
- Count Years Between Two Dates in Excel
- Custom Date Formats in Excel
- Get Day Name from a Date in Excel
- Get Day Number of Year in Excel
- Get First Day of the Month in Excel (Beginning of the Month)
- Get Quarter from a Date [Fiscal + Calendar] in Excel
- Get Years of Service in Excel
- Highlight Dates Between Two Dates in Excel
- Number of Months Between Two Dates in Excel
- Quickly Concatenate Two Dates in Excel
- Years Between Dates in Excel
- Add Hours to Time in Excel
- Add Minutes to Time in Excel
- Calculate Time Difference Between Two Times in Excel
- Change Time Format in Excel
- Military Time (Get and Subtract) in Excel
- Separate Date and Time in Excel
- Count Between Two Numbers (COUNTIFS) in Excel
- Count Blank (Empty) Cells using COUNTIF in Excel
- Count Cells Less than a Particular Value (COUNTIF) in Excel
- Count Cells Not Equal To in Excel (COUNTIF)
- Count Cells That Are Not Blank in Excel
- Count Cells with Text in Excel
- Count Greater Than 0 (COUNTIF) in Excel
- Count Specific Characters in Excel
- Count the Total Number of Cells from a Range in Excel
- COUNT Vs. COUNTA
- OR Logic in COUNTIF/COUNIFS in Excel
- Sum an Entire Column or a Row in Excel
- Sum Greater Than Values using SUMIF
- Sum Not Equal Values (SUMIFS) in Excel
- Sum Only Visible Cells in Excel
- Sum Random Cells in Excel
- SUMIF / SUMIFS with an OR Logic in Excel
- SUMIF with Wildcard Characters in Excel
- SUMIFS Date Range (Sum Values Between Two Dates Array)
- Add New Line in a Cell in Excel (Line Break)
- Add Leading Zeros in Excel
- Capitalize First Letter in Excel
- Change Column to Row (Vice Versa) in Excel
- Concatenate with a Line Break in Excel
- Create a Horizontal Filter in Excel
- Create a Star Rating Template in Excel
- Get the File Name in Excel
- Get Sheet Name in Excel
- Randomize a List (Random Sort) in Excel
- Separate names in Excel – (First & Last Name)
- Check IF 0 (Zero) Then Blank in Excel
- Check IF a Value Exists in a Range in Excel
- Combine IF and AND Functions in Excel
- Combine IF and OR Functions in Excel
- Compare Two Cells in Excel
- Conditional Ranking in Excel using SUMPRODUCT Function [RANKIF]
- IF Cell is Blank (Empty) using IF + ISBLANK in Excel
- IF Negative Then Zero (0) in Excel
- SUMPRODUCT IF to Create a Conditional Formula in Excel
- IFERROR with VLOOKUP in Excel to Replace #N/A in Excel
- Perform Two Way Lookup in Excel
- VLOOKUP MATCH Combination in Excel
Download Article
Download Article
Are you new to Microsoft Excel and need to work on a spreadsheet? Excel is so overrun with useful and complicated features that it might seem impossible for a beginner to learn. But don’t worry—once you learn a few basic tricks, you’ll be entering, manipulating, calculating, and graphing data in no time! This wikiHow tutorial will introduce you to the most important features and functions you’ll need to know when starting out with Excel, from entering and sorting basic data to writing your first formulas.
Things You Should Know
- Use Quick Analysis in Excel to perform quick calculations and create helpful graphs without any prior Excel knowledge.
- Adding your data to a table makes it easy to sort and filter data by your preferred criteria.
- Even if you’re not a math person, you can use basic Excel math functions to add, subtract, find averages and more in seconds.
-
1
Create or open a workbook. When people refer to «Excel files,» they are referring to workbooks, which are files that contain one or more sheets of data on individual tabs. Each tab is called a worksheet or spreadsheet, both of which are used interchangeably. When you open Excel, you’ll be prompted to open or create a workbook.
- To start from scratch, click Blank workbook. Otherwise, you can open an existing workbook or create a new one from one of Excel’s helpful templates, such as those designed for budgeting.
-
2
Explore the worksheet. When you create a new blank workbook, you’ll have a single worksheet called Sheet1 (you’ll see that on the tab at the bottom) that contains a grid for your data. Worksheets are made of individual cells that are organized into columns and rows.
- Columns are vertical and labeled with letters, which appear above each column.
- Rows are horizontal and are labeled by numbers, which you’ll see running along the left side of the worksheet.
- Every cell has an address which contains its column letter and row number. For example, the top-left cell in your worksheet’s address is A1 because it’s in column A, row 1.
- A workbook can have multiple worksheets, all containing different sets of data. Each worksheet in your workbook has a name—you can rename a worksheet by right-clicking its tab and selecting Rename.
- To add another worksheet, just click the + next to the worksheet tab(s).
Advertisement
-
3
Save your workbook. Once you save your workbook once, Excel will automatically save any changes you make by default.[1]
This prevents you from accidentally losing data.- Click the File menu and select Save As.
- Choose a location to save the file, such as on your computer or in OneDrive.
- Type a name for your workbook. All workbooks will automatically inherit the the .XLSX file extension.
- Click Save.
Advertisement
-
1
Click a cell to select it. When you click a cell, it will highlight to indicate that it’s selected.
- When you type something into a cell, the input text is called a value. Entering data into Excel is as simple as typing values into each cell.
- When entering data, the first row of your worksheet (e.g., A1, B1, C1) is typically used as headers for each column. This is helpful when creating graphs or tables which require labels.
- For example, if you’re adding a list of dates in column A, you might click cell A1 and type Date into the cell as the column header.
-
2
Type a word or number into the cell. As you’re typing, you’ll see the letters and/or numbers appear in the cell, as well as in the formula bar at the top of the worksheet.
- When you start practicing more advanced Excel features like creating formulas, this bar will come in handy.
- You can also copy and paste text from other applications into your worksheet, tables from PDFs and the web.
-
3
Press ↵ Enter or ⏎ Return. This enters the data into the cell and moves to the next cell in the column.
-
4
Automatically fill columns based on existing data. Let’s say you want to make a list of consecutive dates or numbers. Or what if you want to fill a column with many of the same values that follow a pattern? As long as Excel can recognize some sort of pattern in your data, such as a particular order, you can use Autofill to automatically populate data into the rest of your column. Here’s a trick to see it in action.
- In a blank column, type 1 into the first cell, 2 into the second cell, and then 3 into the third cell.
- Hover your mouse cursor over the bottom-right corner of the last cell in your series—it will turn to a crosshair.
- Click and drag the crosshair down the column, then release the mouse button once you’ve gone down as far as you like. By default, this will fill the remaining cells with the value of the selected cell—at this point, you’ll probably have something like 1, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3.
- Click the small icon at the bottom-right corner of the filled data to open AutoFill options, and select Fill Series to automatically detect the series or pattern. Now you’ll have a list of consecutive numbers. Try this cool feature out with different patterns!
- Once you get the hang of AutoFill, you’ll have to try flash fill, which you can use to join two columns of data into a single merged column.
-
5
Adjust the column sizes so you can see all of the values. Sometimes typing long values into a cell hides the value and displays hash symbols ### instead of what you’ve typed. If you want to be able to see everything, you can snap the cell contents to the width of the widest cell. For example, let’s say we have some long values in column B:
- To expand the contents of column B, hover the cursor over the dividing line between the B and C at the top of the worksheet—once your cursor is right on the line, it will turn to two arrows pointing in either direction.[2]
- Click and drag the separator until the column is wide enough to accommodate your data, or just double-click the separator to instantly snap the column to the size of the widest value.
- To expand the contents of column B, hover the cursor over the dividing line between the B and C at the top of the worksheet—once your cursor is right on the line, it will turn to two arrows pointing in either direction.[2]
-
6
Wrap text in a cell. If your longer values are now awkwardly long, you can enable text wrapping in one or more cells. Just click a cell (or drag the mouse to select multiple cells), click the Home tab, and then click Wrap Text on the toolbar.
-
7
Edit a cell value. If you need to make a change to a cell, you can double-click the cell to activate the cursor, and then make any changes you need. When you’re finished, just press Enter or Return again.
- To delete the contents of a cell, click the cell once and press delete on your keyboard.
-
8
Apply styles to your data. Whether you want to highlight certain values with color so they stand out or just want to make your data look pretty, changing the colors of cells and their containing values is easy—especially if you’re used to Microsoft Word:
- Select a cell, column, row, or multiple cells at once.
- On the Home tab, click Cell Styles if you’d like to quickly apply quick color styles.
- If you’d rather use more custom options, right-click the selected cell(s) and select Format Cells. Then, use the colors on the Fill tab to customize the cell’s background, or the colors on the Font tab for value colors.
-
9
Apply number formatting to cells containing numbers. If you have data that contains numbers such as prices, measurements, dates, or times, you can apply number formatting to the data so it will display consistently.[3]
By default, the number format is General, which means numbers display exactly as you type them.- Select the cell you want to format. If you’re working with an entire column or row, you can just click the column letter or row number to select the whole thing.
- On the Home tab, click the drop-down menu at the top-center—it’ll say General by default, unless you selected cells that Excel recognizes as a different type of number like Currency or Time.
- Choose one of the formatting options in the list, such as Short Date or Percentage, or click More Number Formats at the bottom to expand all options (we recommend this!).
- If you selected More Number Formats, the Format Cells dialog will expand to the Number tab, where you’ll see several categories for number types.
- Select a category, such as Currency if working with money, or Date if working with dates. Then, choose your preferences, such as a currency symbol and/or decimal places.
- Click OK to apply your formatting.
Advertisement
-
1
Select all of the data you’ve entered so far. Adding your data to a table is the easiest way to work with and analyze data.[4]
Start by highlighting the values you’ve entered so far, including your column headers. Tables also make it easy to sort and filter your data based on values.- Tables traditionally apply different or alternating colors to every other row for easy viewing. Many table options also add borders between cells and/or columns and rows.
-
2
Click Format as Table. You’ll see this at the top-center part of the Home tab.[5]
-
3
Select a table style. Choose any of Excel’s default table styles to get started. You’ll see a small window titled «Create Table» once selected.
- Once you get the hang of tables, you can return here to customize your table further by selecting New Table Style.
-
4
Make sure «My table has headers» is selected and click OK. This tells Excel to turn your column headers into drop-down menus that you can easily sort and filter. Once you click OK, you’ll see that your data now has a color scheme and drop-down menus.
-
5
Click the drop-down menu at the top of a column. Now you’ll see options for sorting that column, as well as several options for filtering all of your data based on its values.
-
6
Choose which data to display based on values in this column. The simplest way to do this is to uncheck the values you don’t want to display—if you uncheck a particular date, for example, you’ll prevent rows that contain the selected date in from appearing in your data. You can also use Text Filters or Number Filters, depending on the type of data in the column:
- If you chose a numerical column, select Number Filters, then choose an option like Greater Than… or Does Not Equal to be extra specific about which values to hide.
- For text columns, you can choose Text Filters, where you can specify things like Begins with or Contains.
- You can also filter by cell color.
-
7
Click OK. Your data is now filtered based on your selections. You’ll also see a small funnel icon in the drop-down menu, which indicates that the data is filtering out certain values.
- To unfilter your data, click the funnel icon, click Clear filter from (column name), and then click OK.
- You can also filter columns that aren’t in tables. Just select a column and click Filter on the Data tab to add a drop-down to that column.
-
8
Sort your data in ascending or descending order. Click the drop-down arrow at the top of a column to view sorting options—these allow you to sort all of your data in order based on the current column.
- If you’re working with numbers, click Smallest to Largest to sort in ascending order, or Largest to Smallest for descending order.[6]
- If you’re working with text values, Sort A to Z will sort in ascending order, while Sort Z to A will sort in reverse.
- When it comes to sorting dates and times, Sort Oldest to Newest will sort with the earliest date at the top and the oldest date at the bottom, and Newest to Oldest displays the dates in descending order.
- When you sort a column, all other columns in the table adjust based on the sort.
- If you’re working with numbers, click Smallest to Largest to sort in ascending order, or Largest to Smallest for descending order.[6]
Advertisement
-
1
Select the data in your worksheet. Excel’s Quick Analysis feature is the easiest way to perform basic calculations (including totals, averages, and counts) and create meaningful tables or graphs without the need for advanced Excel knowledge.[7]
Use your mouse to select your data (including your column headers) to get started. -
2
Click the Quick Analysis icon. This is the small icon that pops up at the bottom-right corner of your selection. It looks like a window with some colored lines.
-
3
Select an analysis type. You’ll see several tabs running along the top of the window, each of which gives you different option for visualizing your data:
- For math calculations, click the Totals tab, where you can select Sum, Average, Count, %Total, or Running Total. You’ll be able to choose whether to display the results at the bottom of each column or to the right.
- To create a chart, click the Charts tab, then select a chart to visualize your data. Before you settle on a chart, just hover the cursor over each option to see a preview.
- To add quick chart data to individual cells, click the Sparklines tab and choose a format. Again, you can hover the cursor over each option to see a preview.
- To instantly apply conditional formatting (which is usually a little more complex in Excel) based on your data, use the Formatting tab. Here you can choose an option like Color or Data Bars, which apply colors to your data based on trends.
Advertisement
-
1
Quickly add data with AutoSum. AutoSum is a built-in Excel function that makes it easy to find the total of one or more columns in a few clicks. Functions or formulas that perform calculations and other tasks based on the values of cells. When you use a function to get something done, you’re creating a formula, which is like a math equation. If you have a column or row of numbers you want to add:
- Click the cell below the numbers you want to add (if a column) or to the right (if a row).[8]
- On the Home tab, click AutoSum toward the upper-right corner of the app. A formula beginning with =SUM(cell+cell) will appear in the field, and a dotted line will surround the numbers you’re adding.
- Press Enter or Return. You should now see the total of the numbers in the selected field. This is here because you created your first formula—which you didn’t have to write by hand!
- If you change any numbers in your data after using AutoSum, the AutoSum value will update automatically.
- Click the cell below the numbers you want to add (if a column) or to the right (if a row).[8]
-
2
Write a simple math formula. AutoSum is just the beginning—Excel is famous for its ability to do all sorts of simple and complex math calculations on data. Fortunately, you don’t have to be a math whiz to create simple formulas to create everyday math formulas, like adding, subtracting, and multiplying. Here’s some basic formulas to get you started:
-
Add: — Type =SUM(cell+cell) (e.g.,
=SUM(A3+B3)) to add two cells’ values together, or type =SUM(cell,cell,cell) (e.g.,=SUM(A2,B2,C2)) to add a series of cell values together.- If you want to add all of the numbers in a whole column (or in a section of a column), type =SUM(cell:cell) (e.g.,
=SUM(A1:A12)) into the cell you want to use to display the result.
- If you want to add all of the numbers in a whole column (or in a section of a column), type =SUM(cell:cell) (e.g.,
-
Subtract: Type =SUM(cell-cell) (e.g.,
=SUM(A3-B3)) to subtract one cell value from another cell’s value. -
Divide: Type =SUM(cell/cell) (e.g.,
=SUM(A6/C5)) to divide one cell’s value by another cell’s value. -
Multiply: Type =SUM(cell*cell) (e.g.,
=SUM(A2*A7)) to multiply two cell values together.
-
Add: — Type =SUM(cell+cell) (e.g.,
Advertisement
-
1
Select a cell for an advanced formula. What if you need to do something more complicated than just adding numbers? Even if you don’t know how to write formulas by hand, you can still create useful formulas that work with your data in various ways. Start by clicking the cell in which you want to display your formula.
-
2
Click the Formulas tab. It’s a tab at the top of the Excel window.
-
3
Explore the Function Library. Several function categories appear in the toolbar, such as Financial, Text, and Math & Trig. Click the options to check out the types of functions available, though they might not make a whole lot of sense just yet.
-
4
Click Insert Function. This option is in the far-left side of the Formulas toolbar. This opens the Insert Function window, which gives you a more detailed breakdown of each function.
-
5
Click a function to learn about it. You can type what you want to do (such as round), or choose a category to filter the list of functions. Then, click any function to read a description of how it works and view its syntax.
- For example, to select the formula for finding the tangent of an angle, you would scroll down and click the TAN option.
-
6
Select a function and click OK. This creates a formula based on the selected function.
-
7
Fill out the function’s formula. When prompted, type in the number or select a cell for which you want to use the formula.
- For example, if you select the TAN function, you’ll type in the number for which you want to find the tangent, or select the cell that contains that number.
- Depending on your selected function, you may need to click through a couple of on-screen prompts.
-
8
Press ↵ Enter or ⏎ Return to run the formula. Doing so applies your function and displays it in your selected cell.
Advertisement
-
1
Set up the chart’s data. If you’re creating a line graph or a bar graph, for example, you’ll want to use one column of cells for the horizontal axis and one column of cells for the vertical axis. The best way to do this is to place your data in a table.
- Typically speaking, the left column is used for the horizontal axis and the column immediately to the right of it represents the vertical axis.
-
2
Select the data in your table. Click and drag your mouse from the top-left cell of the data down to the bottom-right cell of the data.
-
3
Click the Insert tab. It’s a tab at the top of the Excel window.
-
4
Click Recommended Charts. You’ll find this option in the «Charts» section of the Insert toolbar. A window with different chart templates will appear.
-
5
Select a chart template. Click the chart template you want to use based on the type of data you’re working with. If you don’t see a chart type you like, click the All Charts tab to explore by category, such as Pie, Bar, and X Y Scatter.
-
6
Click OK. It’s at the bottom of the window. This creates your chart.
-
7
Use the Chart Design tab to customize your chart. Any time you click your chart, the Chart Design tab will appear at the top of Excel. You can adjust the chart style here, change colors, and add additional elements.
-
8
Double-click a chart element to manage it in the Format panel. When you double-click something on your chart, such as a value, line, or bar, you’ll see options you can edit in the panel on the right side of excel. Here you can change the axis labels, alignment, and legend data.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
How do you add a check mark or an X mark to a cell?
You can go into Insert, then Symbol, and choose the symbol you want. After that, you can just copy and paste the symbol from one cell to another.
-
Question
Can I add work sheets on Excel?
Yes. At the bottom left of the Excel you will see the list of sheets. To the left of those sheets you will find a «+» sign. Click on it.
-
Question
How do I move cell contents to another cell?
Highlight the cell, right-click, and click Copy. Click destination cell, right-click and Paste.
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Video
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
References
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Purchase and install Microsoft Office.
2. Enter data into individual cells.
3. Format cells based on certain criteria.
4. Organize data into rows and columns.
5. Perform math operations using formulas.
6. Use the Formulas tab to find additional formulas.
7. Use data to create charts.
8. Import data from other sources.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 646,684 times.
Reader Success Stories
-
«I am applying for a job that requires comprehensive knowledge of Excel. Well, I don’t have it, but this article…» more
Is this article up to date?
Developing Excel skills is a powerful way to start analyzing data like the professionals do. There are so many compelling reasons to learn how to use Excel!
Whether you’re navigating toward a future career as a data analyst, you want a new skill to leverage at work, or you want to turn your household budget into an impressive well-oiled machine, learning how to analyze data in Excel with Excel formulas and tools will definitely ramp up the efficiency of your life.
Here to let us in on his favorite Microsoft Excel skills is Excel professional Adam Lacey, managing director of Excel with Business. In this special guest post, he shares 19 basic, intermediate, and advanced Excel functions and formulas in Excel that you should know—with videos so you can follow along!
If you’re wondering how to become proficient in Excel, these top Excel functions to know will put you on the right path.
Take it away, Adam!
Disclosure: I’m a proud affiliate for some of the resources mentioned in this article. If you buy a product through my links on this page, I may get a small commission for referring you. Thanks!
Why Excel Skills Are Important in the Job Market
Over 30 years after its creation, Microsoft Excel remains the go-to software for the majority of people looking to do some quick data analysis.
Sure, there is bigger, better, more complex software available for data analysis these days, not to mention the free, web-based Google Sheets, but nothing has the broad appeal and powerful simplicity of analyzing data in Excel.
Start coding now
Stop waiting and start learning! Get my 10 tips on teaching yourself how to code.
Numbers rarely lie, which is why making data-driven decisions is so important. Companies need skilled professionals who are able to turn those raw numbers into actionable insights.
Of course, it would take thousands of hours to sift through it all manually and make connections with no tools to help. That’s why learning how to become proficient in Excel and other data programs is the first step for those looking to enter this highly sought-after tech career. The right data analysis skills—including advanced Excel functions—can turn raw information into sound business strategy.
Excel skills can come in handy for a variety of different jobs — not just for data analysts. Like marketing, sales, HR, accounting, admin assistants, the list goes on!
Regardless of your technical experience, understanding data is crucial. So what’s one of the simplest and most accessible ways to start? By mastering basic Excel skills, then leveling up to intermediate Excel skills and advanced Excel formulas.
What Can You Do With Excel Skills?
There are tons of different things you can do with Excel. It’s a super powerful tool that has a range of applications. Examples include:
- Balance sheets
- Budgets
- Editorial calendars
- Data calculators
- Inventory tracking
- Creating forms
- Project management
- Data visualization
- Simple games
- Forecasting
- Expense tracking
- And much more!
The best Excel functions for your needs depend on what you’re using them for. The best Excel skills for business use might be different from the most useful Excel functions for your personal tracking needs. You don’t necessarily need to know how to become an Excel expert just to make a grocery expense tracker. (Although once you start learning Excel skills, you might get addicted!)
Different Types of Excel Skills
So what exactly do we mean by Excel skills? The two most common types of Excel skills are referred to as functions and formulas.
A formula in Excel is an expression that returns a specific result, such as adding, taking the average, etc. Formulas in Excel must begin with an equal sign (=).
A function is a formula with a name and purpose; for example, one of the most useful Excel functions is “SUM,” which adds numbers together.
3 Basic Excel Skills to Start With
Over the last decade, we’ve taught over a million students valuable spreadsheet skills, and we’ve learned a thing or two ourselves. The biggest lesson is that you only need a little Excel training and a handful of Excel basic skills and formulas to start getting brilliant returns from it.
So we got all the Excel experts we know, together, looked at the data we had, and came up with The Definitive 100 Most Useful Excel Tips.
Here are some very basic Excel skills that will get you doing more with Excel than just listing things.
Excel Skill #1: SUM
The SUM function helps you add individual values, cell references or ranges or a mix of all three. If you need to add a column or row of numbers, Excel can do the math for you. All you have to do is select a cell next to the numbers you want to sum, click AutoSum on the Home tab, press Enter, and you’re done.
Excel Skill #2: COUNT
You can use the COUNT function in Excel to get the number of entries in a number field that is in a range of numbers. For example, if you want to count how many numbers are in a column, you can use a formula like A1:A20: =COUNT(A1:A20). If there are 10 numbers in that range, the result is 10.
Excel Skill #3: AVERAGE
Similar to the SUM function, AVERAGE in Excel gives you the average of a range of numbers. You can do this by clicking a cell below the numbers for which you want to find the average. On the Home tab, in the Editing group, click the arrow next to AutoSum, click Average, and then press Enter.
We’ve picked out the top 11 intermediate Excel skills that will help you supercharge your data analysis abilities and spreadsheet skills, preparing you for a fantastic career in tech. We’ve even included a difficulty rating and how long each Excel skill takes to master, so you can pick the best Excel functions and formulas for you.
Excel Skill #4: PivotTables
📈 Difficulty: 3 / 5
⏰ Mastery: 4 hours
At 4 hours to proficiency, PivotTables is one of the more time-intensive and most useful Excel functions to master, but it’s worth it. You can use them to sort, count, total, or average data stored in one large spreadsheet and display them in a new table, cut however you want.
🔎 Where to find it: Launch a PivotTable from the “Tables” section of the Insert tab once you have a table of data.
The versatility of PivotTables is what makes this Excel knowledge so powerful. You simply drag and drop the relevant column data to create the table format you want.
A PivotTable will automatically group matching data, giving you quick summaries from a giant table. For example, if you had a table full of sales data and each line was a product and an amount, in a couple of clicks you could display all the data summed and group by product (something that would take much longer just using formulas or functions). (As a warning, make sure your data is clean first!)
If you are analyzing data with Excel, then PivotTables are THE most valuable Excel skill you can learn.
The LinkedIn Learning course featured in the video is Excel 2016 Essential Training. I’d recommend taking the updated version, Excel 2021 Essential Training.
☝️ Back to top
Excel Skill #5: Flash Fill
📈 Difficulty: 2 / 5
⏰ Mastery: 30 minutes
Excel developed a mind of its own in 2013, which is perfectly illustrated by this Excel professional feature.
Say you have two columns of names and you need to construct email addresses from them all. With Flash Fill, you can just do it for the first row, and Excel will work out what you mean and do it for the rest (see image and video below). Pre-2013, this was possible but relied on a combination of functions (FIND, LEFT, &, etc). This way is much faster. If you learn how to use Excel tools like this, you WILL impress people even though it’s so easy!
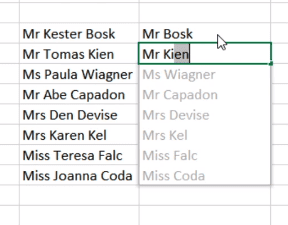
🔎 Where to find it: If Flash Fill is turned on (File Options Advanced) it should just start working as you type. Or, get it going manually by clicking Data > Flash Fill, or Ctrl-E.
👩💻 Where to learn more about Flash Fill: Complete Guide – Flash Fill in MS Excel on Udemy
☝️ Back to top
Excel Skill #6: Filters
📈 Difficulty: 2 / 5
⏰ Mastery: 1 hour
As you become proficient in Excel, you’ll probably want the ability to explore data in a table quickly. Filtering effectively hides data that is not of interest to you.
Usually there’s a value, e.g. ‘Blue cars,’ that you’re looking for, and Filters will bring up those and hide the rest. But in more modern versions of Excel, you can now also filter on number values (e.g. is greater than, top 10%, etc), and cell color.
Filtering becomes an even more useful Excel function when you need to filter more than one column in combination, e.g. both colors and vehicles, to find your blue car. Alt D F F is the shortcut (easier than it sounds—give it a go, pressing the keys in order rather than all together).
Conditional Formatting and Sorting serve related purposes. Sorting involves re-arranging your spreadsheet, which is intrusive and may not be desirable. Conditional formatting brings visualization. Filtering is fast and effective. Choose well. Knowing when to use each is a key part of Excel proficiency.
🔎 Where to find it: Apply filters by going to “Sort & Filter” in the Data tab.
The LinkedIn Learning course featured in the video is Excel: Filtering Data for Beginners.
☝️ Back to top
Excel Skill #7: Conditional Formatting
📈 Difficulty: 3 / 5
⏰ Mastery: 3 hours
Conditional Formatting is a useful Excel skill that can highlight or change the color/appearance of cells given a certain condition. For example, you might want to highlight any negative numbers in red, or cells that contain a certain word. Conditional formatting makes this a breeze and makes colorful sense of data in a noisy world.
Conditional Formatting can be sophisticated. But even the simplest color changes can be hugely beneficial. Suppose you have volumes sold by sales staff each month. Just three clicks can reveal the top 10% of salespeople by performance and tee up an important business conversation.
🔎 Where to find it: On the Home tab in the “Styles” section.
👩💻 Want to learn more about conditional formatting in Excel? Check out this conditional formatting tutorial on Skillshare. (You can even try it for free!)
☝️ Back to top
Excel Skill #8: COUNTIF
📈 Difficulty: 2 / 5
⏰ Mastery: 15 minutes
Next on the list of Excel functions to know, COUNTIF counts cells with certain properties. For example, you want to find out how often a certain entry appears in a list. COUNTIF will look at the list and count it if it matches your chosen criteria. It’s one of the top Excel functions, very simple to learn, and one you’ll use over and over again when analyzing data.
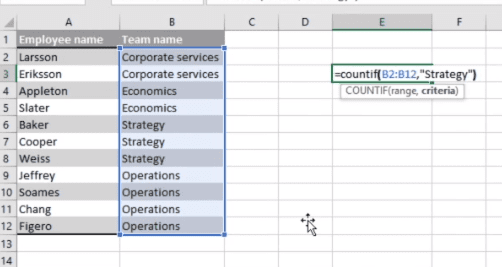
How it works: The syntax for COUNTIF is =COUNTIF(range [range of numbers you are looking at], criteria [criteria you are searching against]
👩💻 Want to learn to use COUNTIF? Check out Excel For Beginners: VLOOKUP, INDEX, MATCH, SUMIFS, COUNTIFS on Udemy.
☝️ Back to top
Excel Skill #9: Charts
📈 Difficulty: 3 / 5
⏰ Mastery: 3 hours
What Excel skills are employers looking for? If your role will involve any sort of data visualization, Charts will probably be one. There are more than 20 chart types in Excel. Most people get by with Bar, Column, Pie, Line, and Scatter charts.
With Bar, Column, Pie, and Line charts, you just need a single series of numbers to generate a chart. With a Scatter, you need two sets of corresponding data to compare (e.g. height vs. weight).
Charts are one of the most effective ways to display the data analysis you’ve conducted. Words and tables tell a story, but an image tells a thousand words; that’s why charts are one of the most useful Excel functions for data analysis.
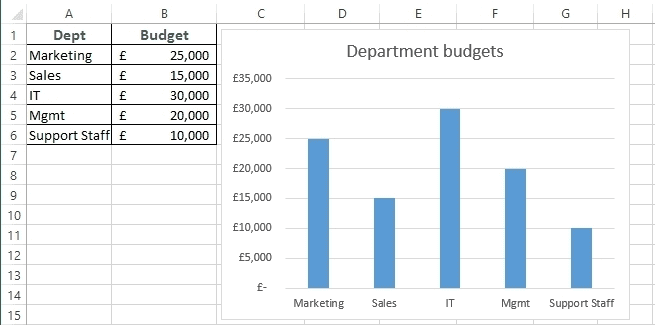
🔎 Where to find it: Start exploring charts from the “Charts” section of the Insert tab.
👩💻 Want to learn more about Excel charts? Check out this Excel Charts and Visualization course on Mammoth Interactive.
☝️ Back to top
Excel Skill #10: SUMIF
📈 Difficulty: 3 / 5
⏰ Mastery: 15 minutes
SUMIF adds cells with certain properties. Like COUNTIF, these properties include: being a certain number or word (most useful), being above/below certain values, not equaling a value (<>), etc.
Just like COUNTIF, SUMIF is incredibly useful when you want to pull out summary information from large datasets. In the example image below, we are adding together the sales that match the category Cola.
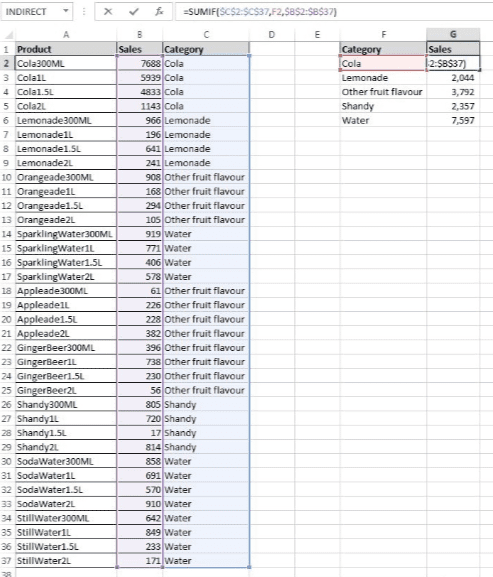
How it works: The syntax for SUMIF is: =SUMIF(range, [the range of cells to look at], criteria [the criteria determining which cells to add], sum range [the cells to add together]
👩💻 Want to learn to use SUMIF? Check out Excel ForBeginners: VLOOKUP, INDEX, MATCH, SUMIFS, COUNTIFS on Udemy.
☝️ Back to top
Excel Skill #11: IFERROR
📈 Difficulty: 2 / 5
⏰ Mastery: 30 minutes
Errors (#VALUE!, #####, #DIV/0!, #REF!, etc) look ugly and can stop calculations from working (e.g. summing over a range of values with a single #DIV/0!). You can avoid it by using =IFERROR().
You can wrap any formula in IFERROR to remove those ugly error codes. For example:
=IFERROR(VLOOKUP(B14,C6:D15,2,FALSE),””)
If this above VLOOKUP was returning an error, it would now return a blank cell. In Excel functions, quotation marks will return the information inside them, so if you put nothing between them (“”) then it returns an empty cell—genius.
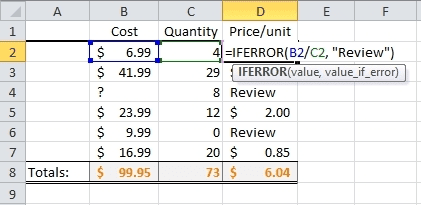
👩💻 Learn about IFERROR in this Microsoft tutorial
☝️ Back to top
Excel Skill #12: Slicers
📈 Difficulty: 2 / 5
⏰ Mastery: 45 minutes
PivotTable slicers do the same thing as Filters—they enable you to show certain data and hide other data as required. But rather than dull drop-down menus, slicers offer nice big friendly buttons to make the whole user experience nicer and easier.
As well as fast filtering, slicers also tell you what the current filtering state is so you know what’s currently in and out of the PivotTable report.
🔎 Where to find it: Add a slicer to your PivotTable from the “Filters” section of the Insert tab.
The LinkedIn Learning course featured in the video is Excel 2013 Essential Training. I’d recommend taking the updated version, Excel 2021 Essential Training.
☝️ Back to top
Excel Skill #13: Power Pivots
📈 Difficulty: 4 / 5
⏰ Mastery: 3 hours
This is a powerful Excel function to know: it brings a lot more firepower to PivotTables (e.g. COUNTROWS) and more processing power to deal with much larger data sets. Power Pivot connects your PivotTables with external databases and can be refreshed on cue.
For example, say you had millions of rows of data—too much for Excel to handle—you could have these saved in an Access or SQL database. Using Power Pivot, you can pull this data into Excel and then run PivotTables and Charts straight off that data.
You can also create relationships between multiple tables, so if you have some data in one database and other data in another, no problem. Bring them together in Power Pivot and display your analysis using PivotTables and Charts.
This is one of those Excel skills for business that is mostly for Excel experts and BI professionals. If you want to get serious about data analysis, then you need to spend some time learning Excel skills like Power Pivot.
🔎 Where to find it: Access it from the Data tab under “Data Tools”.
👩💻 Where to learn more about Power Pivot: Complete Introduction to Excel Power Pivot on Udemy
☝️ Back to top
Excel Skill #14: Sparkline
📈 Difficulty: 2 / 5
⏰ Mastery: 15 minutes
A Sparkline is a tiny chart in a worksheet cell that provides a visual representation of the data selected.
Sparklines are useful for showing useful Excel functions in a series of values, such as seasonal increases or decreases, economic cycles, or to highlight maximum and minimum values. Sparklines can be displayed as lines or columns and can also represent any negative values. Position a Sparkline near its data for greatest impact.
🔎 Where to find it: Add your first Sparkline to your table from the “Sparklines” section of the Insert tab.
👩💻 Where to learn more about Sparkline: Sparklines tutorial video on Coursera.
☝️ Back to top
5 Advanced Excel Skills to Consider Learning
The 14 Excel basic skills above are extremely useful, but they’re only scratching the surface of what this powerful program can do.
Looking to progress to more advanced Excel functions? Start with these 5 advanced Excel formulas and skills.
Start coding now
Stop waiting and start learning! Get my 10 tips on teaching yourself how to code.
Excel Skill #15: INDEX MATCH
This advanced Excel formula is essentially the combination of two functions in Excel. You can use it to look up a value in a big table of data and return a corresponding value in that table.
This is an advanced alternative to the VLOOKUP or HLOOKUP formulas (which have several drawbacks and limitations). It’s more flexible and therefore more powerful than VLOOKUPs.
👩💻 Where to learn it: Index Match video on Coursera
Excel Skill #16: Goal Seek
Goal Seek answers “what if” scenarios. It involves changing values in cells to see how those changes will affect the outcome of formulas on the worksheet.
If you know the result that you want from a formula, but are not sure what input value the formula needs to get that result, that’s where the Goal Seek advanced Excel feature comes in.
Get the course mentioned in the video below here: Learning Excel What-If Analysis via LinkedIn Learning
Excel Skill #17: Macros in Excel VBA
If you have tasks in Excel that you need to do repeatedly, you can use your Excel proficiency to record a macro to automate those tasks. This helps you cut down on annoying or time-consuming busywork so you can focus on more important things!
A macro is an action or a set of actions that you can run as many times as you want. When you create a macro, you are recording your mouse clicks and keystrokes. The macro can then be saved and run whenever it is needed.
Course mentioned in the video: Recording and Managing Excel Macros via Pluralsight
Excel Skill #18: INDIRECT
INDIRECT is an advanced Excel function used to convert a text string into a valid reference.
For instance, you can use it to convert a reference assembled as text (e.g. ‘Sheet1!A1’) into a value reference. So Excel knows to find the value from the cell in A1 rather than treat it as text.
👩💻 Where to learn it: Basic to Advance Excel Series3 on Udemy
Excel Skill #19: Get External Data (from Web)
Data that you want to use in Excel might not always be stored in another Excel workbook. Sometimes that data may exist externally, e.g. in an access file, in a database, or maybe on the web.
This data can be imported into Excel easily using the ‘Get External Data’ utility. The main benefit of connecting to external data is that you can periodically analyze it in Excel without having to repeatedly copy it, which can be time-consuming and error-prone.
Learn more about the course featured in this video.
☝️ Back to top
So, we’ve covered 19 of the best Excel functions—but there are still so many more to learn for proficiency in Excel. If you’re interested in seeing the Microsoft Excel skills that didn’t make this list, see the full 100 here!
Where to Learn More About Excel
To really learn how to get good at Excel and become an Excel expert, you need to turn to books and courses!
🖥️ Online Excel Courses
These ten courses will teach you the best Excel functions for your needs, whether you’re just after basic Excel knowledge or you want to know how to become proficient in Excel.
- Excel Skills for Business Specialization on Coursera: A 4-course specialization that teaches advanced Excel features and techniques.
- Excel/VBA for Creative Problem Solving Specialization on Coursera: Teaches you how to automate Excel spreadsheets with Visual Basic for Applications.
- Excel Tips Weekly on LinkedIn Learning: Tune in every Tuesday for a new Excel tip (e.g., productivity-boosting tricks, cool hidden features, need-to-know functions).
- Excel: Advanced Formulas and Functions on LinkedIn Learning: In this course, Excel expert Dennis Taylor demystifies hundreds of formulas and functions available in Excel.
- Microsoft Excel – Excel from Beginner to Advanced on Udemy: Taught by a Microsoft Certified Trainer (MCT) and certified Microsoft Office Master Instructor, this course is great for newcomers to Excel.
- The Ultimate Excel Programmer Course on Udemy: Learn Excel VBA from scratch through 12.5 hours of on-demand video.
- Excel Essentials for the Real World (Complete Excel Course) on Udemy: By the end of the course, you’ll be able to do things like organize, clean, and manage large data, turn messy data into helpful charts, and more.
- Microsoft Excel Programming on Pluralsight: In this learning path, you’ll learn Visual Basic for Applications, built-in Excel functions, Excel macros, and troubleshooting formulas.
- Excel for the Real World: Gain the Basic Skills of Microsoft Excel on Skillshare: A 3-part series that teaches you all the basics of Excel and its practical applications. Taught by a former financial analyst at Google.
- Complete Excel, Python and Machine Learning eDegree on Mammoth Interactive: Start as a beginner and progress throughout 6 courses, gaining skills in Python machine learning with Excel files, building internal apps with Amazon Honeycode and spreadsheets, and much more.
📚 Excel Books on Amazon
Note: All the books listed below are available on Amazon. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
- 101 Most Popular Excel Formulas by John Michaloudis: Nearly 500 pages with step-by-step instructions to take your Excel skills to the next level. Best for intermediate or advanced Excel users.
- Excel 2021: The Most Updated Guide to Master Microsoft Excel from Scratch in 7-Days or Less by Stan Webber: Over the course of 256 pages, learn the ins and outs of of Excel. A great guide for beginners and even seasoned users.
- Excel 2019 All-in-One For Dummies by Greg Harvey: Covers basic Excel functions all the way to editing macros with Visual Basic and everything in between. Great for beginners and intermediate Excel users.
- Excel 2019 Bible by Michael Alexander: Over 1,000 pages of Excel tips, tricks, and techniques. Great for all levels, from beginner to intermediate to power user.
- Excel 2019 Basics: A Quick and Easy Guide to Boosting Your Productivity with Excel by Nathan George: Offers a step-by-step process to becoming skilled with Excel, starting with introductory topics and ending with advanced ones like analyzing your data with charts.
- Excel Basics In 30 Minutes by Ian Lamont: Written in plain English, with lots of step-by-step instructions/screenshots to help you learn the fundamentals of Excel.
Frequently Asked Questions About Excel Skills
If you’re ready to learn how to get better at Excel, that’s excellent (pun intended)! Let’s finish up by covering a few final questions about being an Excel professional.
🧠 Is Excel hard to learn?
It depends on which skills you’re learning! Obviously, basic Excel skills will be faster and easier to learn than Excel advanced functions. But in general, it’s not too difficult to learn Excel functions, especially with plenty of practice.
❗ Which Excel skills are most important?
Understanding the basics as well as the most common and useful Excel functions is generally the most important, such as the 19 skills mentioned in this post. The advanced Excel skills you’ll need to know will differ from employer to employer as well as the type of project you’re working on.
📄 How to list Excel skills on a resume?
Are you learning Excel skills for business reasons? There are a few different ways to display your Excel experience on your resume. First, you can simply list “Excel” in your skill section. You can also say “Advanced Excel” or “Intermediate Excel” depending on your skill level.
Another great way to list Excel experience on your resume is to include it in your work history section. Explain how you specifically used Excel in a previous role or project and what impact it had (e.g. did you save the company time or money?). It can be helpful for employers to see how you used Excel in context to show, rather than just tell them that you know Excel.
👩💼 What Excel skills are employers looking for?
It depends on the employer and role. Skills like PivotTables, VLOOKUP, basic macros, data validation, and graphs/charts are common across a lot of roles. If you’re unsure, try looking up a job you’re interested in and see if the job description lists out any specific Excel skills you’ll need to know.
🎓 How to improve/practice your Excel skills?
There are lots of ways to practice and improve your Excel skills. Try taking a course or tutorial to learn how to use Excel. Then, start working on a project you’re interested in to see if you can apply the skill to your specific use case. You’ll learn a lot by simply doing.
Once you start mastering the power of spreadsheets skills, you’ll wonder how you ever got through life without them. If you want to work in a data-related career, getting proficient in Excel is the perfect first step!
And if you’re still keen to learn more data analysis skills after Excel? There are plenty of courses that teach the ins and outs of data, like the courses from DataCamp.

About the Author
Adam Lacey is Managing Director of Excel with Business, an online training company that has helped improve Excel and Microsoft Office skills for over 1 million people.
Who said Excel takes lot of time / steps do something? Here is a list of 15 incredibly fun things you can do to your spreadsheets and each takes no more than 5 seconds to do.
Happy Friday 🙂
1. Change the shape / color of cell comments
Just select the cell comment, go to draw menu in bottom left corner of the screen, and choose change auto shape option, select a 32 pointed star or heart symbol or a smiley face, just wow everyone 🙂
2. Filter unique items from a list
Select the data, go to data > filter > advanced filter and check the “unique items” option.
3. Sort from Left to Right
What if your data flows from left to right instead of top to bottom. Just change the sort orientation from “sort options” in the data > sort menu.
4. Hide the grid lines from your sheets
Go to Options dialog in tools menu, uncheck the “grid lines” option to remove gridlines from your worksheets. You can also change the color of grid line from here (not recommended)
5. Add rounded border to your charts, make them look smooth
Just right click on the chart, select format chart option, in the dialog, check the “rounded borders”. You can even add a shadow effect from here.
6. Fetch live stock quotes / company research with one click
Just enter the stock symbol (MSFT, GOOG, AAPL etc.) in a cell, alt+click on the cell to launch “research pane”, select stock quotes to see MSN Money quotes for the selected symbol. You can fetch company profiles in the same way. Learn more.
7. Repeat rows on top when printing, show table headers on every page
When you are on the sheet view, just hit menu > file > page setup, go to the last tab, specify “rows to repeat”. You can “repeat columns while printing” as well from the same menu.
8. Remove conditional formatting / all formatting with one click
Just go to Menu > Edit > Clear > All to remove all the formatting from selected cell / range.
9. Auto sum cells with one click
Select a bunch of cells and click on the Sigma symbol on the standard tool bar. Alternatively you can use Alt+= keyboard shortcut.
10. Find width of a column with formula, really!
Just use =cell("width") to find the width of the column to which that formula cell belongs. Width is returned as the nearest integer.
11. Find total working days between any two dates, including holidays
If you work on project plans, gantt charts alot, this can be totally handy. Just type =networkdays(start date, end date, list of holidays) to fetch the number of working days. In the above sample you can see the number of working days between New years day and September first of this year (labor day).
12. Freeze Rows / Columns in your sheet, Show important info even when scrolling
Select the cell diagonally beneath the row / columns you want to freeze (for eg. if you wan to freeze row 1&2 and columns A&B, click in C3), go to menu > window and click on freeze panes.
13. Split sheets in to two, compare side by side to be more productive
Just click on this little vertical bar on the bottom right corner of the sheet (see below) and drag it to create a vertical split. You can do the same way for a horizontal split as well 🙂
14. Change the color of various sheet name tabs
Right click on sheet and select “Tab color” option to change the worksheet tab colors. Group them with similar colors if you have lot of sheets, it looks nice.
15. Insert a quick organization chart
Click on menu > insert > diagram to open the above dialog, just select the organization chart option, enter node values and you have a pretty organization chart. Alternatively learn how to create org charts in excel.
So what do you say now? Isn’t Excel Exciting? 😀
Share this tip with your colleagues

Get FREE Excel + Power BI Tips
Simple, fun and useful emails, once per week.
Learn & be awesome.
-
121 Comments -
Ask a question or say something… -
Tagged under
cool, formatting, freeze panes, fun, how to, ideas, Learn Excel, microsoft, Microsoft Excel Formulas, spreadsheet, technology, tips, tricks
-
Category:
All Time Hits, Featured, hacks, ideas, Learn Excel

Welcome to Chandoo.org
Thank you so much for visiting. My aim is to make you awesome in Excel & Power BI. I do this by sharing videos, tips, examples and downloads on this website. There are more than 1,000 pages with all things Excel, Power BI, Dashboards & VBA here. Go ahead and spend few minutes to be AWESOME.
Read my story • FREE Excel tips book



Excel School made me great at work.
5/5

From simple to complex, there is a formula for every occasion. Check out the list now.

Calendars, invoices, trackers and much more. All free, fun and fantastic.

Power Query, Data model, DAX, Filters, Slicers, Conditional formats and beautiful charts. It’s all here.

Still on fence about Power BI? In this getting started guide, learn what is Power BI, how to get it and how to create your first report from scratch.
Related Tips
121 Responses to “Excel can be Exciting – 15 fun things you can do with your spreadsheet in less than 5 seconds”
-
Great tips! Another good one is highlighting a bunch of cells and changing the autosum visual at the bottom right to be Average or Count instead of auto sum.
-
[…] from a list, sorting data from left to right, freezing panes, and coloring your worksheet tabs. Excel can be Exciting : 15 Fun things to do with Microsoft Excel [Pointy Haired Dilbert — […]
-
[…] from a list, sorting data from left to right, freezing panes, and coloring your worksheet tabs. Excel can be Exciting : 15 Fun things to do with Microsoft Excel [Pointy Haired Dilbert — […]
-
Adam says:
one note on the «unique items» tip — this only works with numerical data — if you’re looking to weed out unique text entries, no dice — I work in Excel a lot with names and proprietary tags and would love a way to select a unique text entry — any suggestions?
-
badOedipus says:
You can filter duplicate text entries as described above if you use the advanced filter option, however it will not allow you to do an additional filter on an adjacent column afterwards without duplicating the data first.
The method detailed below will allow you to filter our duplicate entries based on a conditional format.Select the range from which you wish to filter out duplicate text entries
Click on Conditional Formatting > New Rule… > Use a formula to determine which cells to format
type the following formula in the text box: =AND(COUNTIF(«RangeAddress«, «FirstCellAddress«)>1, MATCH(«FirstCellAddress«,»RangeAddress«, 0)<> ROW()) making sure to substitute accordingly. Note: RangeAddress should be absolute(«$A$1:$A$20»), and FirstCellAddress should be relative («A1»).
Set the format to fill the cells with a color, depending on the application I use either a faint off-white to down play the color or a bright yellow to really make it pop — the choice is yours.
Ta-da your duplicates are now colored. You can now filter by color if you use 2010 to see only duplicates or only unique records (unique being only one record per value). Pre-2010 you can sort by color to get them at the top/bottom of your list. -
Adrian says:
Maybe if you use Access.
-
Vincent says:
First post on chandoo.org, wahoooo!
Anyways, after reading the above comments I just realized there’s a similar way to flag duplicate values with a formula, and one that works for strings as well as numbers. If you’re working in column A with a header row then your IDs will be in cells A2:A___. The following formula can be entered in B2 and filled downward to return FALSE when the ID is a repeated value, i.e. it is not the first instance of that value:
«=MATCH(A2,$A$2:$A$__,0)=(ROW(A2)-ROW($A$1))».-
Martin says:
Re: =MATCH(A2,$A$2:$A$__,0)=(ROW(A2)-ROW($A$1))
That’s a brilliant formula — I shall use that.
Many thanks for sharing!
-
-
-
Jason C says:
Just highlight duplicates and then filter out the highlighted cells.
-
-
Mazy says:
OK, my hint, I think this excel function have never been documented or referred even in manuals:)
If you want to insert a part of a worksheet as picture (e.g. you want to include a small chart to a preformatted excel document), do the following:
DRAW anything, a square, circle, etc.
SELECT the cells you want to insert as a picture
SELECT the object you made (square,etc.)
PASTEVoila:)
-
PK says:
I can’t get the comment to change. It just wants to draw a new autoshape.
-
Tom says:
To change the shape of the comment In Excel 2010 — I had to Customize the Ribbon [FILE, OPTIONS] and add a «Format» tab to the Main Tabs to allow the Format tab to be available all the time. Now I can Edit the shape.
-
-
@Adam.. It works for text data for me, which version of excel you are using, all these tips are tested in Excel 2003.
@PK … when you select comment to edit (shift+f2) click on the border of the comment, then go to bottom left corner in the screen and select draw > change auto shape. Should work in excel 2003 and above. Let me know if you see some problems 🙂
-
Renate Callahan says:
nope, it still doesn’t work. There is no draw -> change auto shape available for me. The left bottom corner of the screen just shows ‘Ready’ and if I right click on it it shows a lot of other things to activate, none of it is Draw or Auto options. I use Excel 2007
-
-
MM says:
You’ve missed an important step in your first tip. The Drawing toolbar must be active for this to work. Mine is not on by default, so I have to take the extra set to turn it on.
-
Jason says:
Very nice, thanks!
Could you clarify «You can also change the color of grid line from here (not recommended)» What is the recommended method.
-
The graphic designer-side of my job hates Excel, but the business owner side of me finds it to be essential. These tips help bring both sides (designer / business owner) closer together. Thanks!
-
@MM.. you are right, I have assumed the draw toolbar is on… thanks for pointing it out.
@Jason… “You can also change the color of grid line from here (not recommended)”, I said that to convey changing grid line colors is not recommended, as it can scare people or otherwise make your sheet look extremely busy… but you can change the color if you wish.. 😀
-
I use the NETWORKDAYS function all the time and it just blows people away.
-
Dude,
networkdays is my fav.🙂
Nice post.-Nikhil
-
My favorite excel command Ctrl and ~
displays all formulas -
Thanks you pointy haired Dilbert, this is definitely a great list, like always bookmarked for future uses 😀
-
greats tips
i like command for displaying all formulas
thanks -
Wade says:
Great tips!
However, #14 You need to right-click on the tab not the sheet.
#10 You can just left click and hold on the right most line of the column letter. Also, another tip a lot of users don’t know is that you can change a section of columns you want to one width by highlighting a column with the width you prefer and left-click-hold on the bottom right corner of that column letter and drag it through as many columns as you need. -
Excel can be Exciting : 15 Fun things to do with Microsoft Excel | Pointy Haired Dilbert — Chandoo.o…
Who said Excel takes lot of time steps do something Here is a list of 15 incredibly fun things you can do to your spreadsheets and each takes no more than 5…
-
hey says:
Great history class. Should have gone for Excel 97 while you were at it 😉
-
0751firewire says:
Hey, HEY
Don’t be rude. It’s a waste of everyone’s time — including yours. Totally unnecessary.
******
Thanks for this post! I really enjoyed reading these tips. I will bookmark this post and will also subscribe to your weekly newsletter!Thanks so much.
-
@Wade: you are right, you have to click on sheet name and not on sheet
and #10 was meant to show another way to find column width, but yeah, I always use the left click hold technique to see if the width is enough for me. Thanks for sharing it with everyone 🙂
@0751firewire: thanks 🙂
@everyone… I am happy so many of you liked this post and enjoyed these small but very useful stuff hidden away in the Excel.
-
LEO DA VINCI says:
Dear Chandoo,
I have discovered you only 3 days back . I want a help from you . I am using a software which makes a grid file of lat,long and elevn. data (x,y,z) on 25m into 25m mesh size . I feel that this grid file which is made from a xcel csv sheet containing random x,y,z points can be made on xcel sheet itself. Can i do that ? example of a source data shown belowx y z
100 50 12.5
200 40 14.0
220 75 12.0
202 60 15.0-
@Leo Da Vinci
You can either import and existing CSV file or setup the file directly in Excel as a workbook -
whatever says:
You can not make a grid gragh on xeel because it has boxes you would have too get speacial advanced software like the sciencestes do:
i know more that somebody from the GEEK squad!!
-
@Whatever
Can you post a sample of a Grid Graph or a link where we can see what your referring to?
-
-
-
-
[…] Excel can be Exciting : 15 Fun things to do with Microsoft Excel | Pointy Haired Dilbert — Chandoo.o… […]
-
Tip #13: In case anyone is an excel newbie like me, to remove the new vertical bar, just double click on the bar.
-
Rufus says:
Thanks fir the tip re vertical bar.
I am a baby Excel beginner at 86!!!!!
-
-
Roger says:
Unique text entries can be found easily — use COUNTIF function for each row. You can use autofilter to delete anything with result > 1.
-
LD says:
To the person joking about Excel 97 — that version of Office is still the standard at my workplace. No joke.
-
[…] Excel can be Exciting : 15 Fun things to do with Microsoft Excel | Pointy Haired Dilbert — Chandoo.o… […]
-
shivshankar says:
Adv
-
[…] Find total working days between any two dates, including holidays […]
-
Arti says:
I tried second tip to remove the duplicate entries from the row by copying it in another location but its not working if I use data in A’ th column as
A1 aa
A2 aa
A3 bband I am trying to copy the unique records to column B.
The above scenario is not working if duplicate entries are present in A1 and A2.
It will work if duplicate entries are present below first record. -
Robert says:
@Arti
Autofilter as well as advanced filter needs titles of the columns in the first row. If you have only the three items in your list, Excel assumes, the first «aa» is the title (field name) of your list, not an entry in the list itself. As a result, Excel writes into column B again the first aa as the title and the second aa and bb as the 2 entires.
Simply insert a row above your list and give your list a name in cell A1. Then it should work.
-
[…] more than 5 seconds to do. Happy Friday 1. Change the shape / color of cell comments Just select thhttp://chandoo.org/wp/2008/08/01/15-fun-things-with-excel/MI-INFO Tutorials — Excel BasicsFor large worksheets that span more than one screen of […]
-
[…] Excel can be Exciting : 15 Fun things to do with Microsoft Excel […]
-
[…] on September 13, 2008 Few weeks back, I came across a post about some useful tips in MS Excel — Excel can be exciting . So, I thought I’ll collate some of the helpful tips and tricks that I’ve come across while […]
-
[…] 15 Fun things you can do with Excel […]
-
Melli says:
Nr. 5
-> does not work. And I have Excel 2003! -
@Melli .. Welcome to PHD…
Are you sure rounded borders are not working. I have made this example in Excel 2003 and they are working alright for me. You have to select the entire chart to change borders to rounded, not the plot area alone.
-
[…] Excel can be Exciting : 15 Fun things to do with Microsoft Excel | Pointy Haired Dilbert — Chandoo.o… (tags: work windows useful tutorials tutorial tricks toread tools) […]
-
[…] But often we leave the last steps for manual processing. The article addresses one such problem (extracting unique cells from a range) and tells us how we can automate the whole […]
-
homepage templates…
I just wanted to share this nice address, where you can get wordpress themes for free. I use one of the designs for my own blog and it was really easy to install. Just activating it in admin and the job was done. :-)…
-
I did not know excel is this much fun.
-
Ketan says:
@ Adam & Chandoo…
For removing / filtering the duplicate entry / unique data…one can use the readymade menu from JMT utilities….very useful… -
[…] Using Advanced Data Filter […]
-
[…] Excel can be Exciting — 15 fun things you can do with excel […]
-
rayna says:
Thx so much PHD…tusi gr8 ho ji…:)
-
[…] > and un-check grid lines option. (Excel 2007: office button > excel option > advanced)… Get Full Tip 50. To hide a worksheet, go to menu > format > sheet > hide… Get Full Tip 51. To align […]
-
[…] Beautiful City Photography» and «10 Companies Hiring for Work from Home». (They’ve also included «15 fun things to do with Microsoft Excel», which may be the most terrifying title in blogging […]
-
[…] Learn Excel Formulas in Plain English | Executive Dashboards in Excel — 4 Part Tutorial | 15 Excel Fun Tips […]
-
[…] Related: How to change the shape of cell comments from rectangle to any other shape […]
-
[…] Learn how to color excel worksheet tabs. […]
-
[…] on excel comments: change the shape of excel comment box | pimp your comment boxes | extract comments using […]
-
Francis says:
i cannot find CHANGE AUTO SHAPE option in Excel 2007 to design my comment box. Please help?
-
@Francis… Excel 2007 has made it little difficult to change comment shapes, but it is still possible. First add a regular shape (like rectangle) to the worksheet. Now select it. This will show a new ribbon called «format». From here, you can find the change shape tool. Add this tool to Quick Access Bar.
Now Select the comment cell and edit comment. At this point, use the change shape tool from QAT to change the shape of comment.
-
Renate Callahan says:
all right!! Thanks, this answers my question posted above. Yes, now it does work and it looks great! 🙂
-
-
-
Ken Buffong says:
Its really made easy.
-
Paul says:
Its a bit of a faff in 2007, not sure if its just my work computer than won’t let me change the default shape for comment boxes… But for this one workbook i’ve added a simple:
ActiveCell.Comment.Shape.Select
Selection.ShapeRange.AutoShapeType = msoShapeVerticalScrollOr you can change msoShapeVeriticalScroll to any shape you like…
-
VENKATRAMAN V S says:
Dear All
Thank you all very much. You guys have taught me a lot of new things in Excel. Keep continuing the good work.
-
nazia says:
thanx so much…it really is of gr8 gr8 help to me…… :))
-
The color sheet tab option has disappeared. Was there and working fine but now when I right click there isn’t an option to change the color of my sheets. How can I get this option back?
-
@Deanna.. you can reach this from Format button on home ribbon. Key board short code — ALT + HOT (just press h,o and t one after another).
-
-
Sanjay says:
Hello,
Can I know the name of the last person who saved the file last.
In a team of 10 members working on a shared excel file, this information will help me to know the name of the person who modified the file.
-
Shouvik says:
@Sanjay: Open the workbook — Click on File -> Properties -> Click on the Statistics Tab for the information you are looking for.
-
mer says:
Wish I could see those images, because they’re now blocked by photobucket. Next time use imgur, or host it on your own server.
-
mimi says:
Brilliant!
Helped me teach my pupils loads in I.C.T today!
LOL -
irha says:
you don’t have references 🙁
-
Hussein says:
I liked a lot this web site
thanks
-
Rahul aggarwal says:
@chandoo ji
can we change default comment cell box shape in excel 2007or 2010? -
saravanan says:
Hi Friends
Can we Increase the Column width >500 in excel 2003.
Pls help…
-
losraiders says:
I really like tip #1 but I’m how can you do it if you’re using Excel 2007. I don’t see the drawing toolbar…I believe it’s gone in 2007 but not certain. I did see the autoshape when I select the commnent and right click but nothing happens when I select it.
-
This is possible in Excel 2007 (and 2010) too. Follow below steps:
- Add any drawing shape.
- Select it and go to format ribbon
- Right click on Edit shape and add it to «Quick Access toolbar»
- Now, remove the shape
- Select comment cell.
- Edit comment.
- Use quick access toolbar to change the shape to anything you want.
-
Sudhir says:
This is awesome Chandoo ! Tip#1 I was most impressed. #6 I was not able to replicate — if you meant Alt + (Mouse left) click, it did not work. But manually triggered the reference — but was unable again to make it available as embedded «auto look up» in the sheet itself.
-
-
steve says:
wow! this site is awesome
-
Some tricks are not working with Excel 2003
But others are too cool thanx
-
[…] and un-check grid lines option. (Excel 2007: office button > excel option > advanced)… Get Full Tip 50. To hide a worksheet, go to menu > format > sheet > hide… Get Full Tip 51. To […]
-
[…] Using too many tab colors on your excel workbooks [how to do this] […]
-
Can anyone help. I want to be able to hide a row for exampe row A if the Cell A1 is empty after i have sorted the rows.
I can write the macro to sort the list then I am stuck.Any HELP OUT THERE.
Regards ken
-
why isnt my thing working
=NETWORKDAYS(«11/11/2011″,»12/12/2012»,[holidays])-
D Gamlath says:
It’s not going to work that way. At least not with the parentheses. Try entering the two dates in two cells and referring those cells within your formula 🙂
-
Sudhir says:
It will work — a date in formula is entered as follows:
=NETWORKDAYS(DATE(2011,11,11),DATE(2012,12,12),0)
-
-
Marcia Fay Cobb says:
I’m doing an address directory. All I want to do is find out how to delete a blank line or move the second line up to the first line in the cell? Appreciate any help you can give. Thanks.
-
Shivani says:
How to make comments of different shapes in Excel 2010?
-
Jignesh says:
we have shared the workbook, so other user can access and feed data at their respective fields, all user can view list of users accessing the shared file,but unfortunately if a user removed from list of user name then that user will be disconnected and whatever changes made will be proved to be useless as file become exclusive.
Could you please anybody help me out how to protect the username list so nobody could removed from the list.
-
Abdul Azeez says:
how to change font color in cell by using formula
-
Sudhir says:
This can be done using conditional formatting. Is there a specific thing that you are looking at ?
-
-
Nadalvski says:
Hi Chandoo,
I bumped into your site two days ago and am hooked to it.
Very helpful and elaborate articles.
Thanks. -
[…] Check out why here. […]
-
Prakash says:
Can anyone help me to do the following:
Is there any option to copy all the procedures done for a set of values to other set of value which we will input in later stages.
In other words: Imagine I have a list of values(first set) for which I need to do some mathematical and logical operations and I will get the final required output.Also if I have one more set of values(second set) for which I need to do the same procedure to get required output.
So my question is : Is there any way to get the final output directly for set-2 values based on the steps(procedures) done for set-1 so that it will reduce lot of work.Please help me.
Thank you all.-
@Prakash
Can you ask the question in the forums
http://chandoo.org/forum/
Please also attach a sample file with an example of what results you want
-
-
nmsdfmn says:
whey it is appearing
-
Kris says:
I think you should mention that this feature available from WHAT Version otherwise users go crazy!
-
extreme x says:
Oh very cool stuff! Thanks
-
Rushabh Gala says:
This is really a good article even I read some comments which were really useful.
-
Chirag Parmar says:
That was cool Sir. Thanks for sharing these tricks with us.
-
Dustin says:
Help!! I just pulled data out of a different software and pasted values only in excel. Anything with a character other than a number is shifted to the left of the cell. Anything with only numbers is shifted to the right of the cell.
The VLOOKUP is only working on the ones shifted to the right. The formatting on the home tab is all the same. Why is it working on some but not the others? Is there underlying format that can be erased??
-
Dustin says:
The VLOOKUP is only working on the ones shifted to the left.********
(Only works for cells that have characters other than numbers, in addition to numbers)
-
-
thanks for your tips and tutorials excel for children… i like
-
sandeep kothari says:
Hat tip to you, OSUM Chandoo!
-
Sandy says:
I’m adding birthdates to a column. I need to know how to differentiate a birthdate in the 19 hundreds (19XX) from a birthdate in the 2 thousands (20XX).
I appreciate any help!!! Thank you
-
Chad Estes says:
Assuming your birth date column is G and is a date datatype:
=if(YEAR(G1) < 2000, «Born in 20th Century», «Born in 21st Century»)
-
Sagar says:
Is there any way that, I can overlap and compare between two worksheets. This is required in case to auto highlight edited data between the copies. Please help….
-
Nice post . Step -> 7. Repeat rows on top when printing, show table headers on every page — will be useful . Thank you.
-
Bhanu Prasad K S says:
Hi Chandoo,
Firstly, I wanted to say a big thank you for whatever you are doing for people like me who need knowledge of excel and power BI.
I wanted to know how we can highlight cells which have dates between the given range.
for example, i want to highlight cell which have dates between Jan 1, 2022 and June 30, 2022.

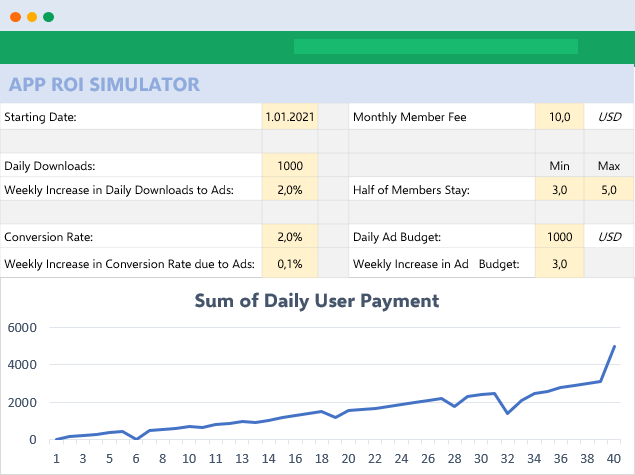
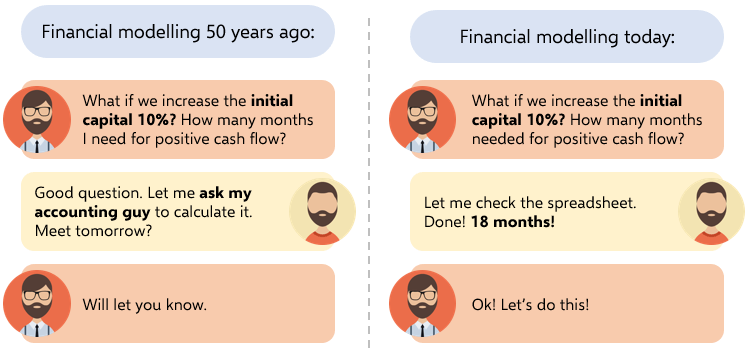
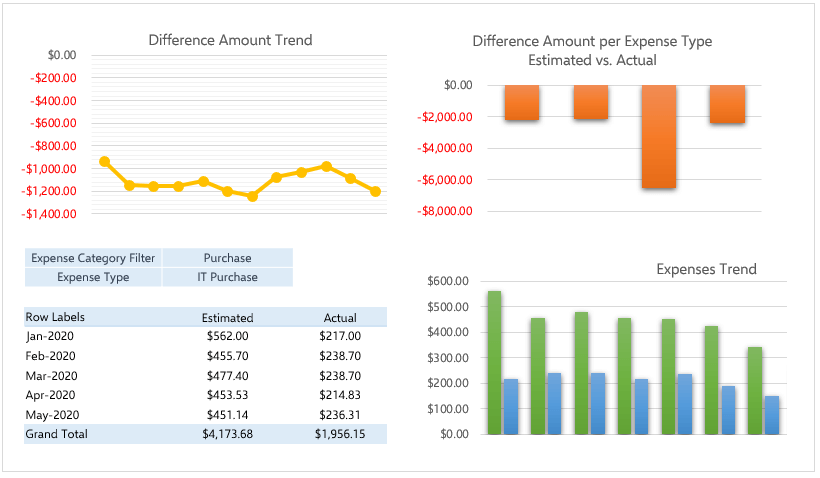
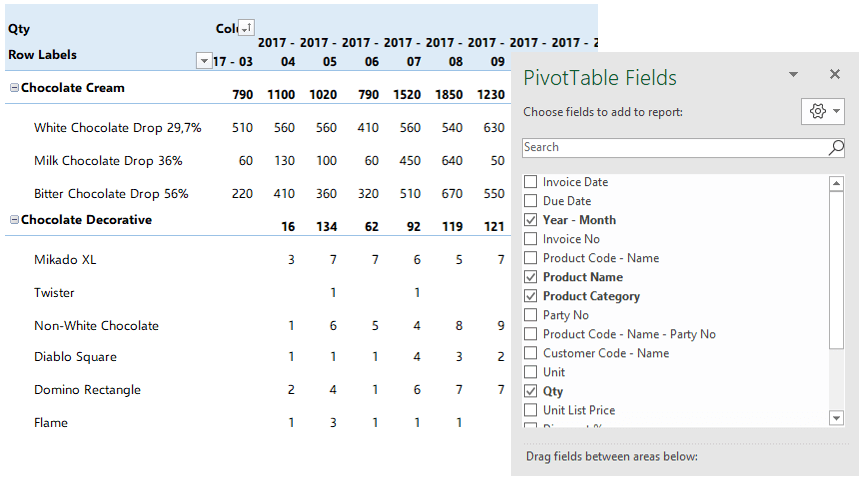
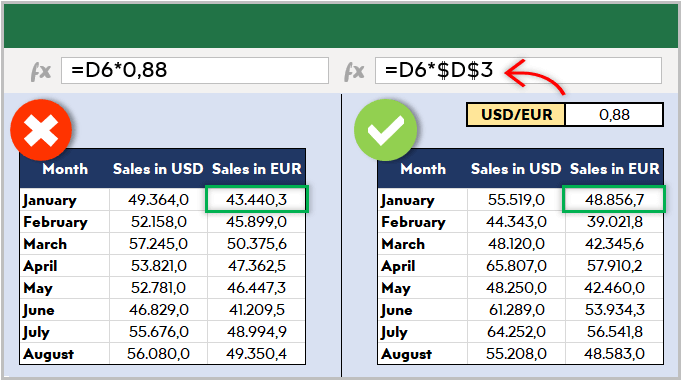
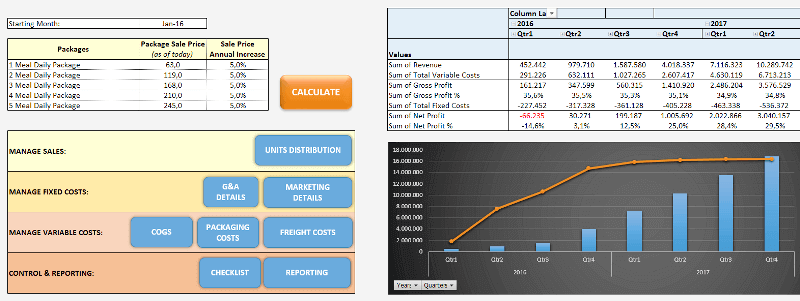
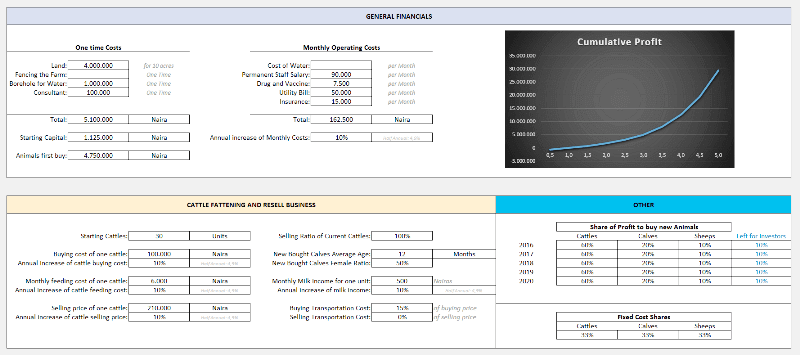
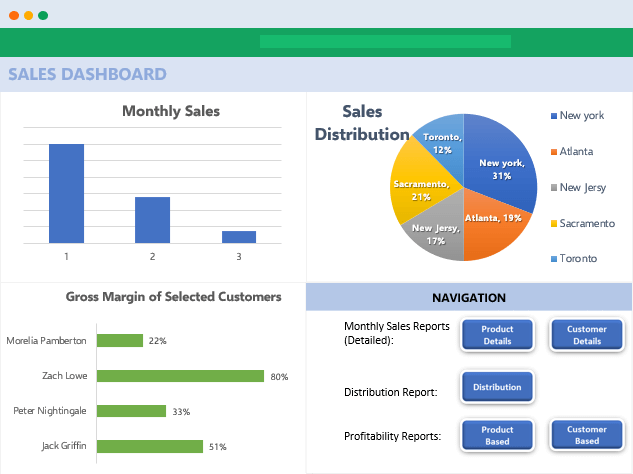
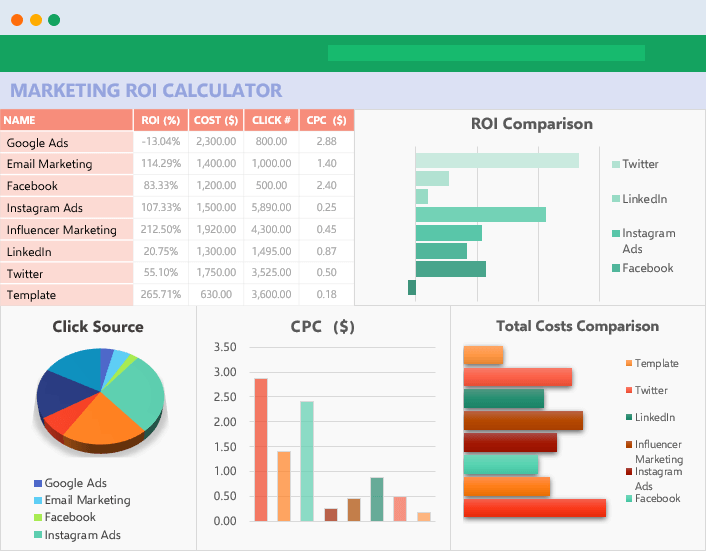
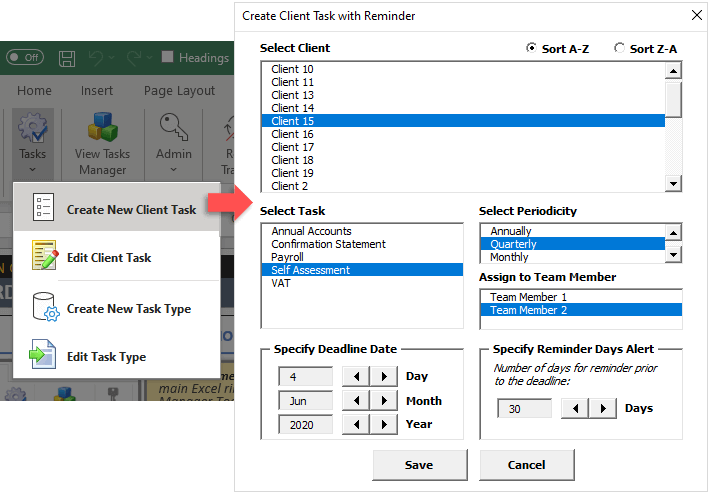
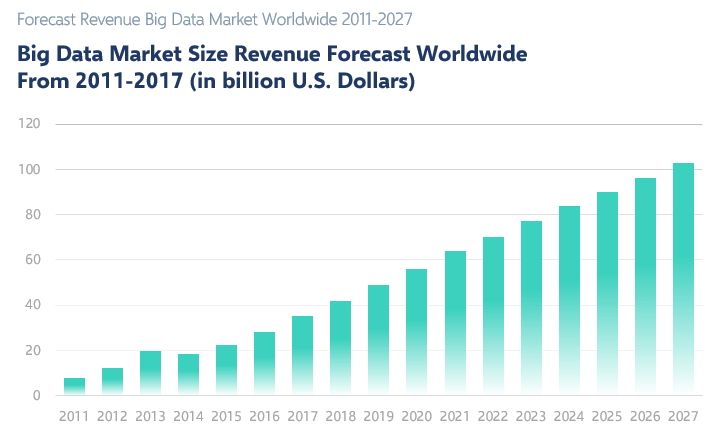
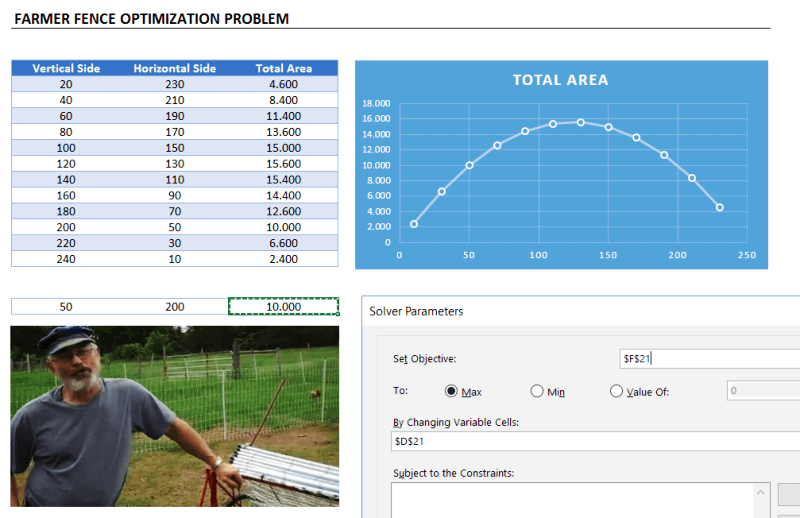
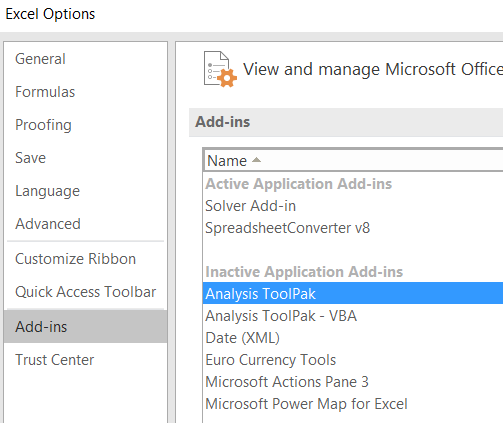
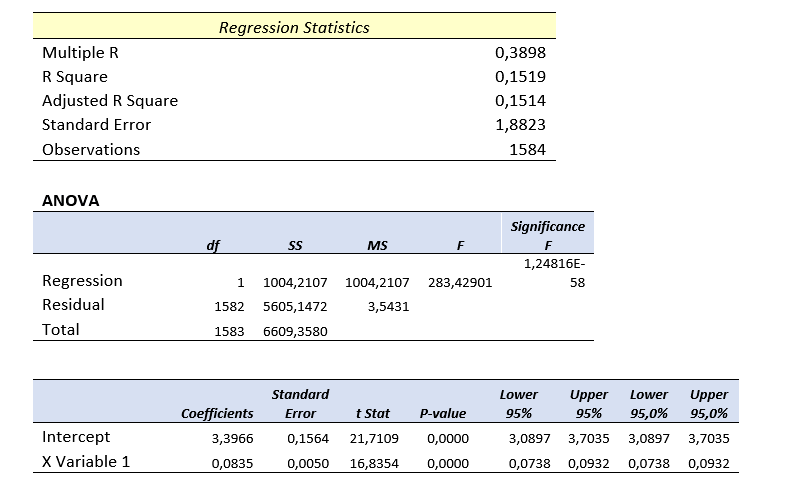
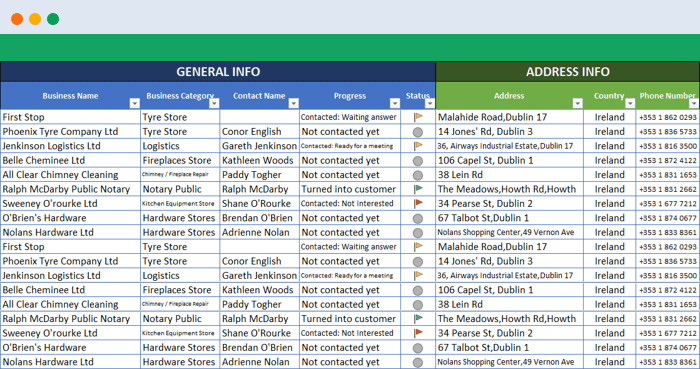
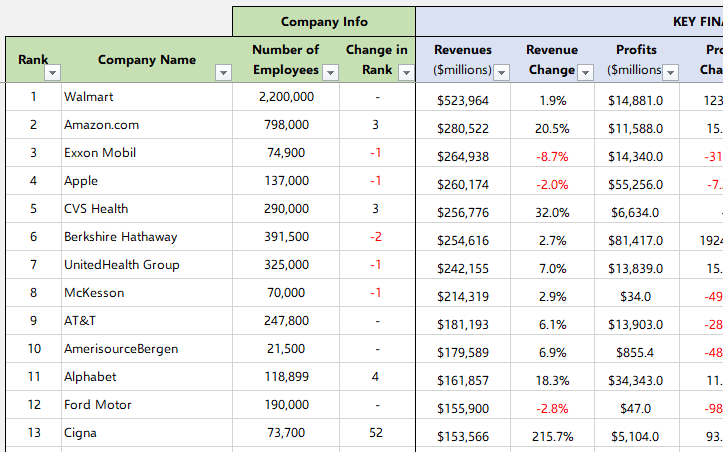
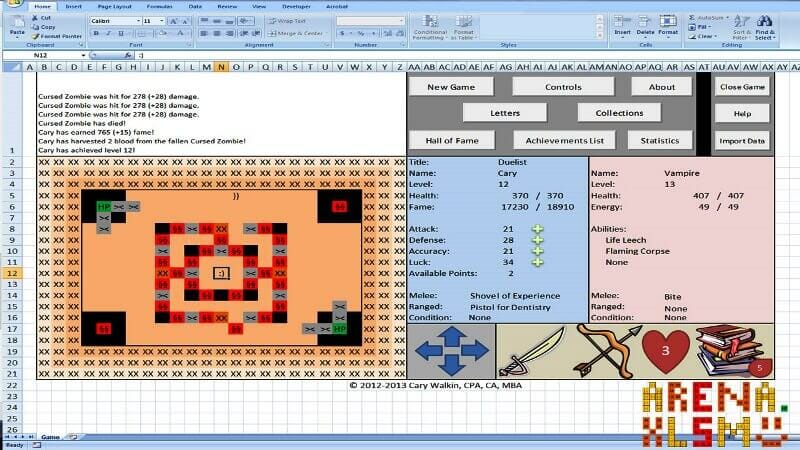
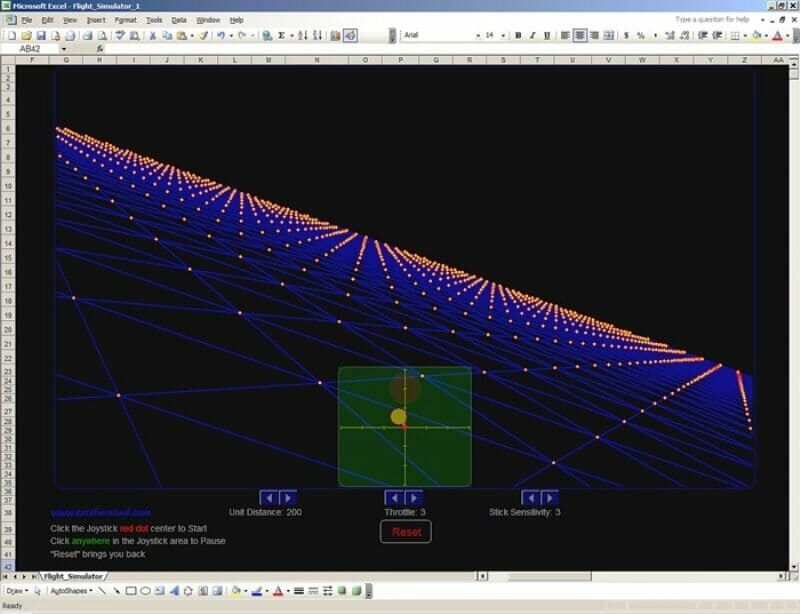
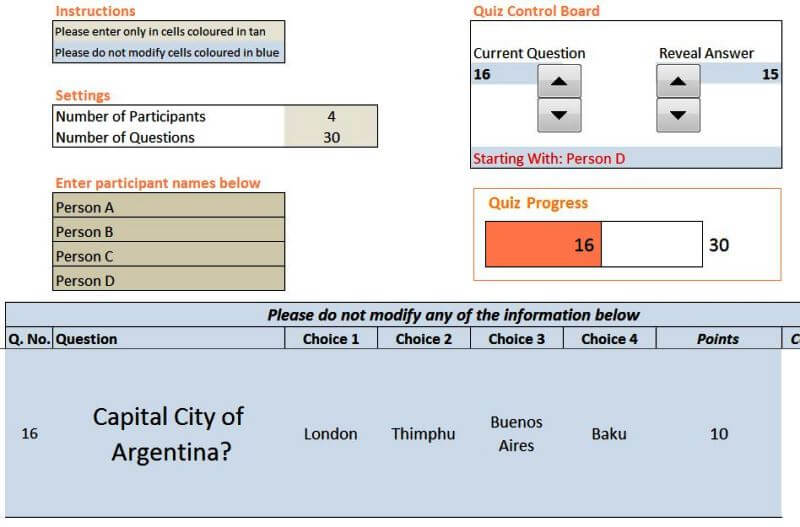
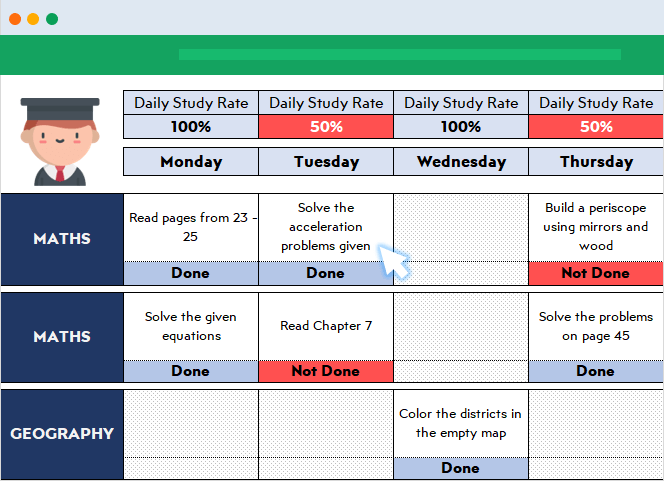
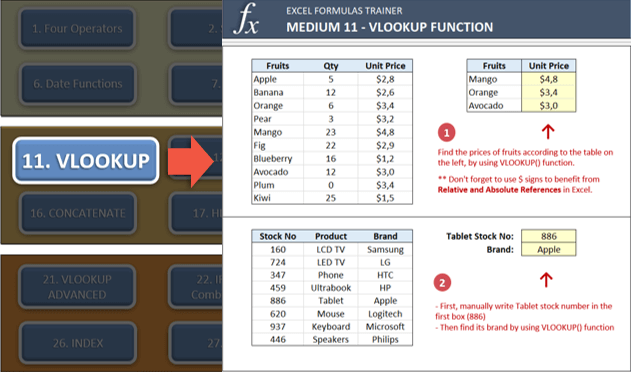
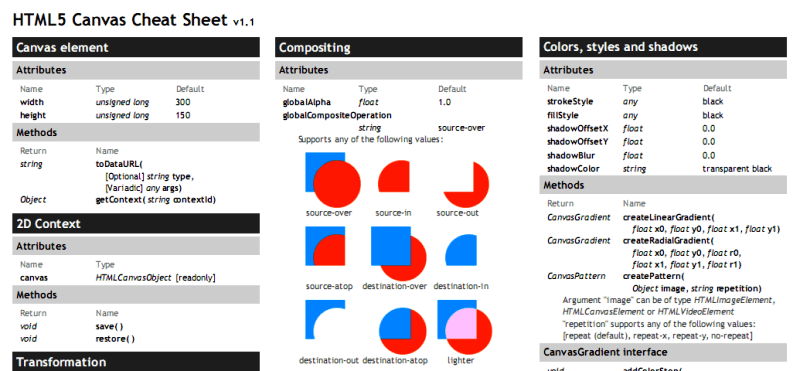
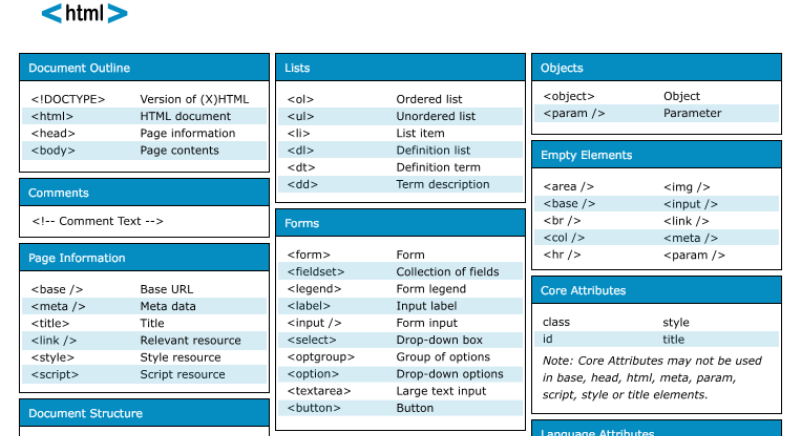
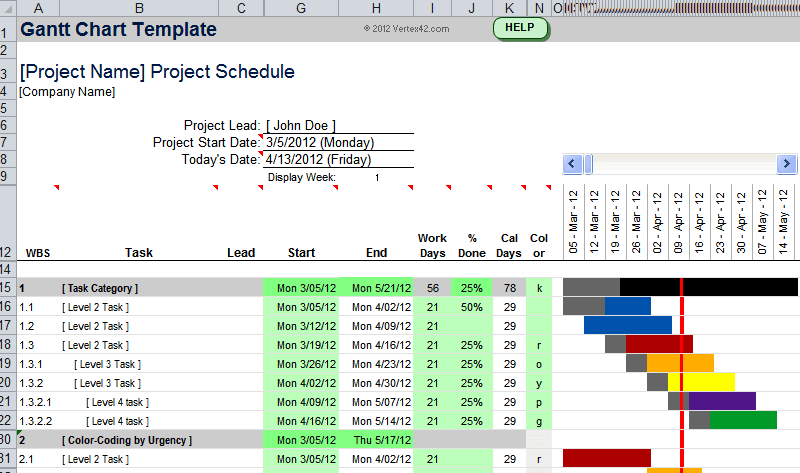
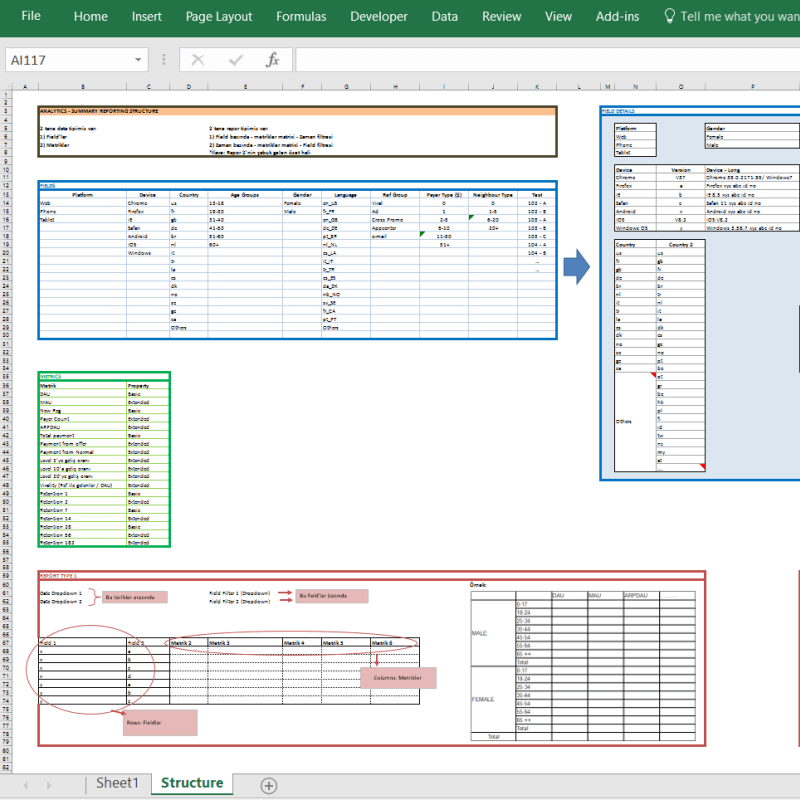


![Download 10 Excel Templates for Marketers [Free Kit]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/9ff7a4fe-5293-496c-acca-566bc6e73f42.png)
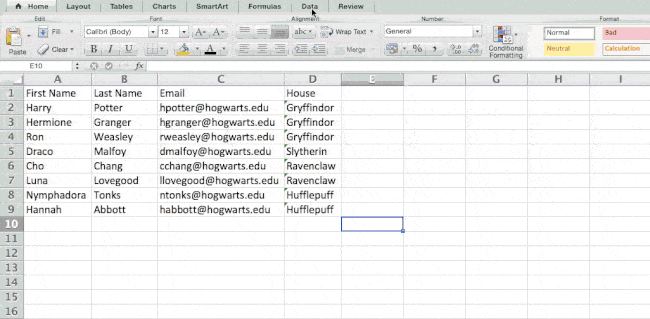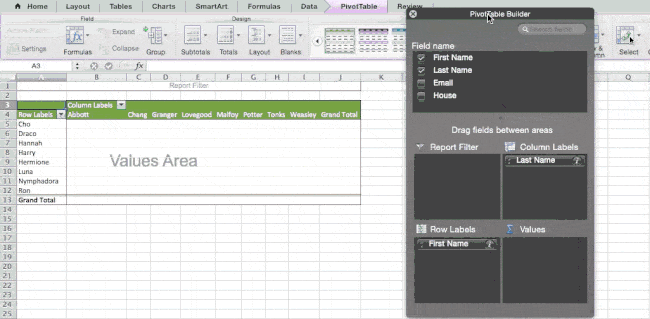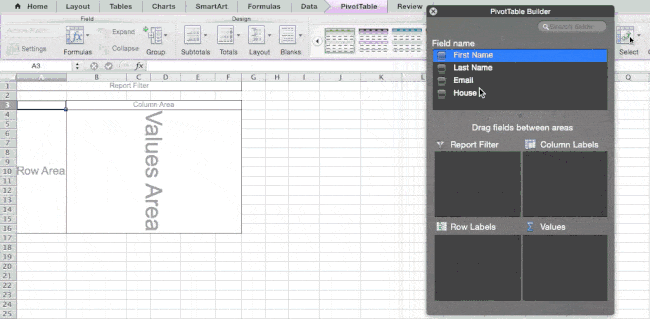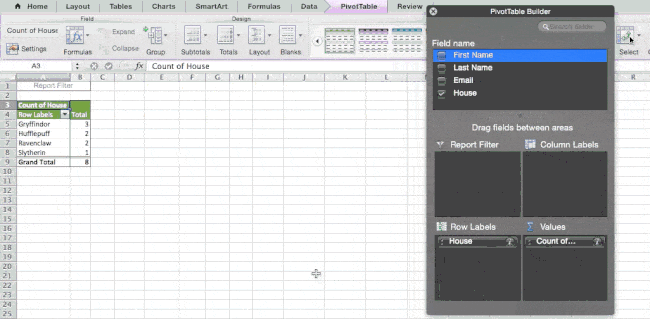
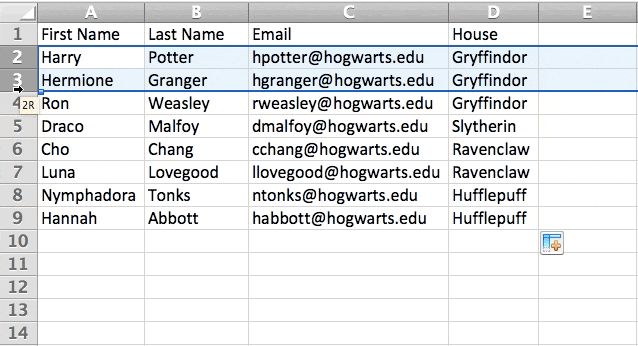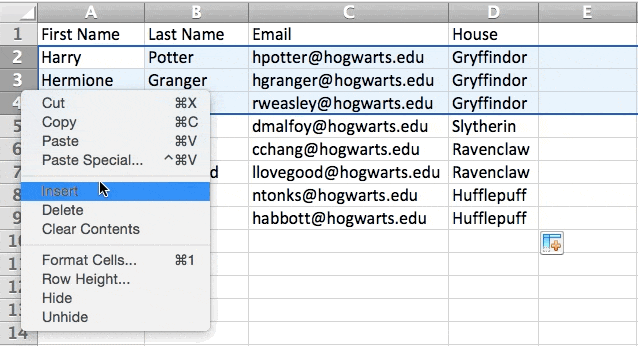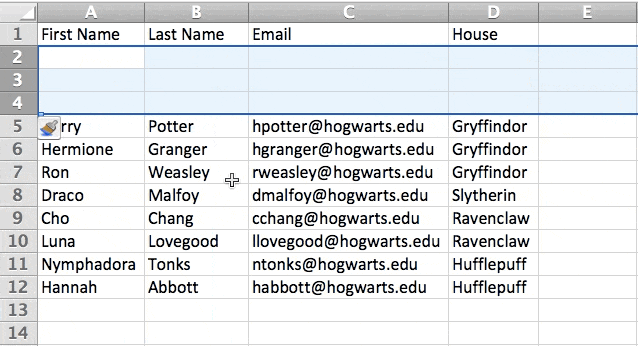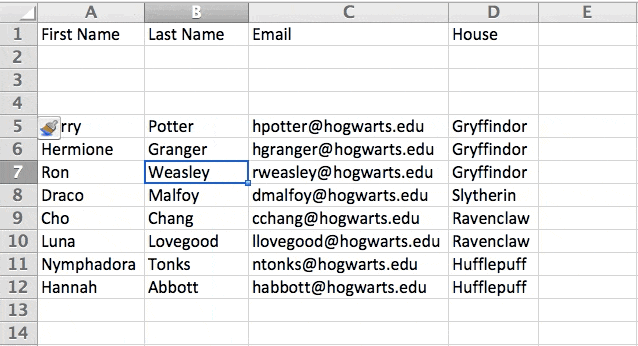
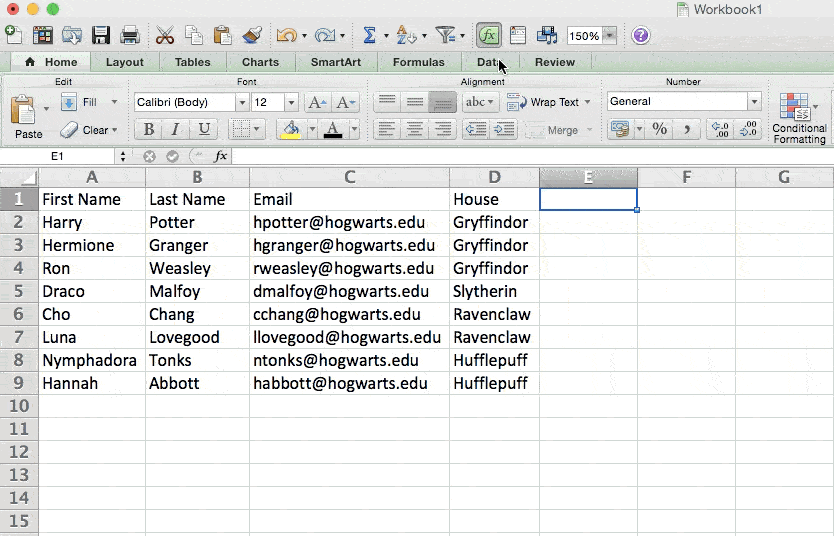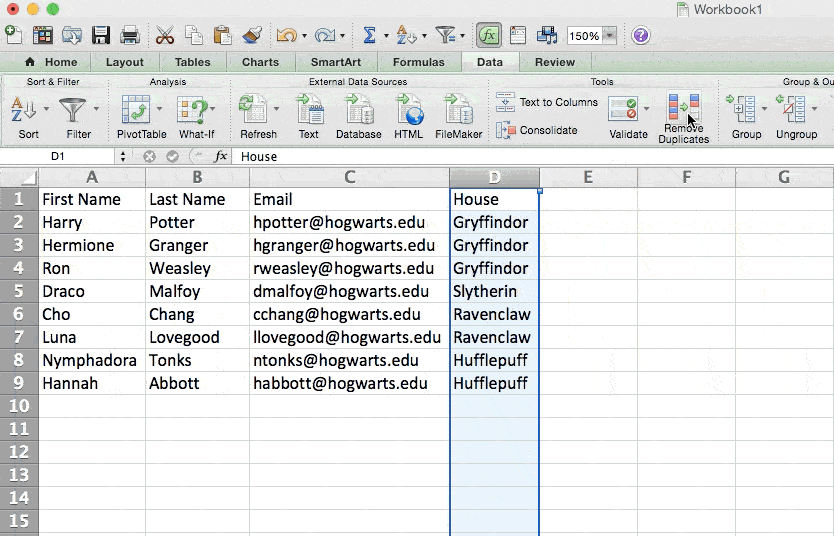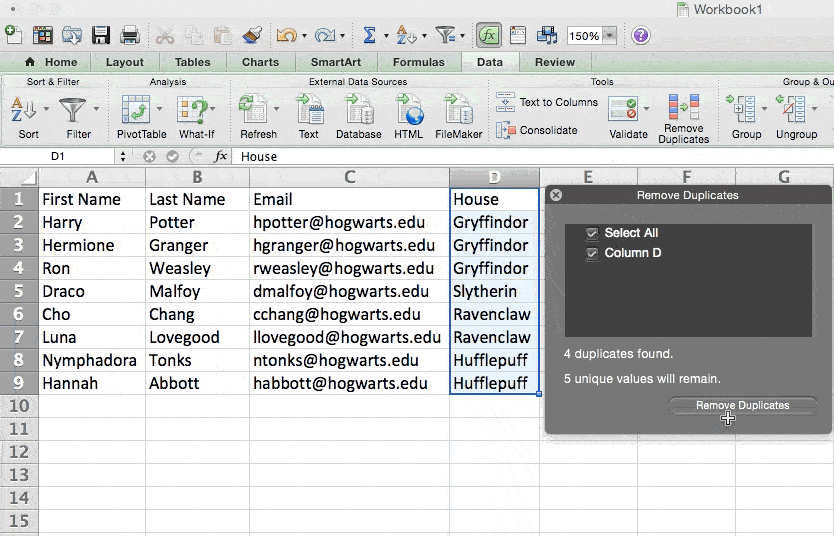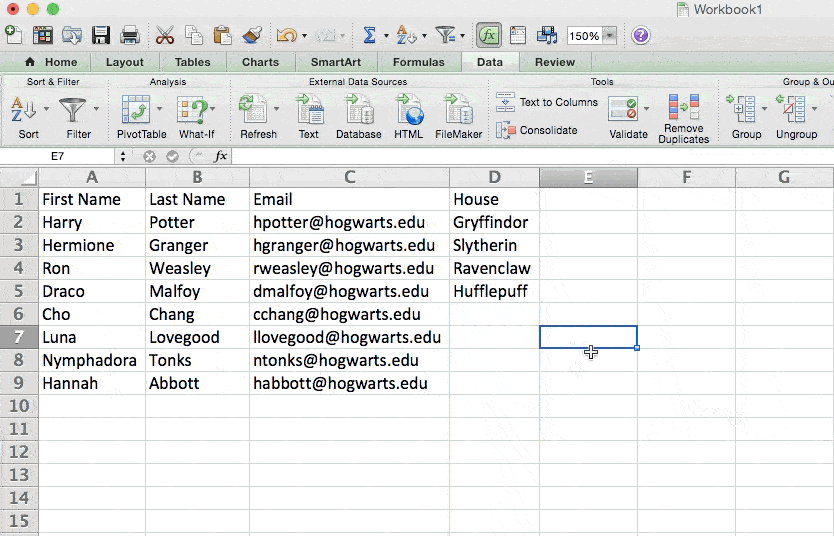
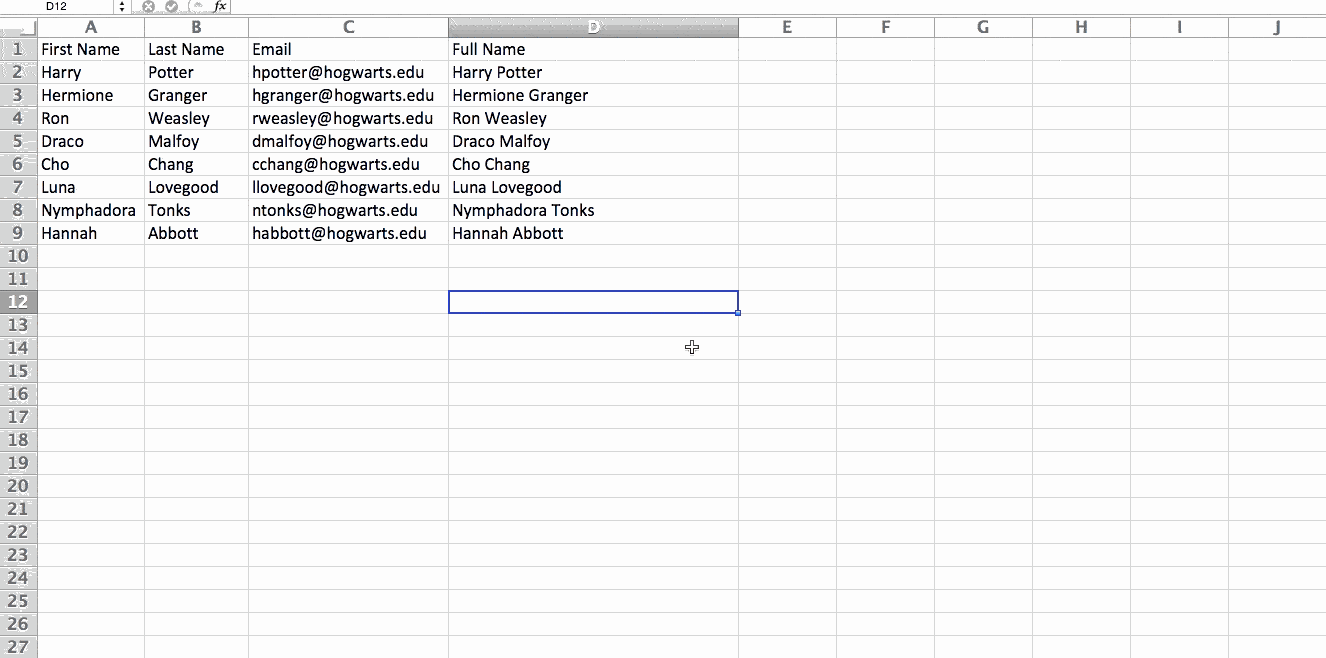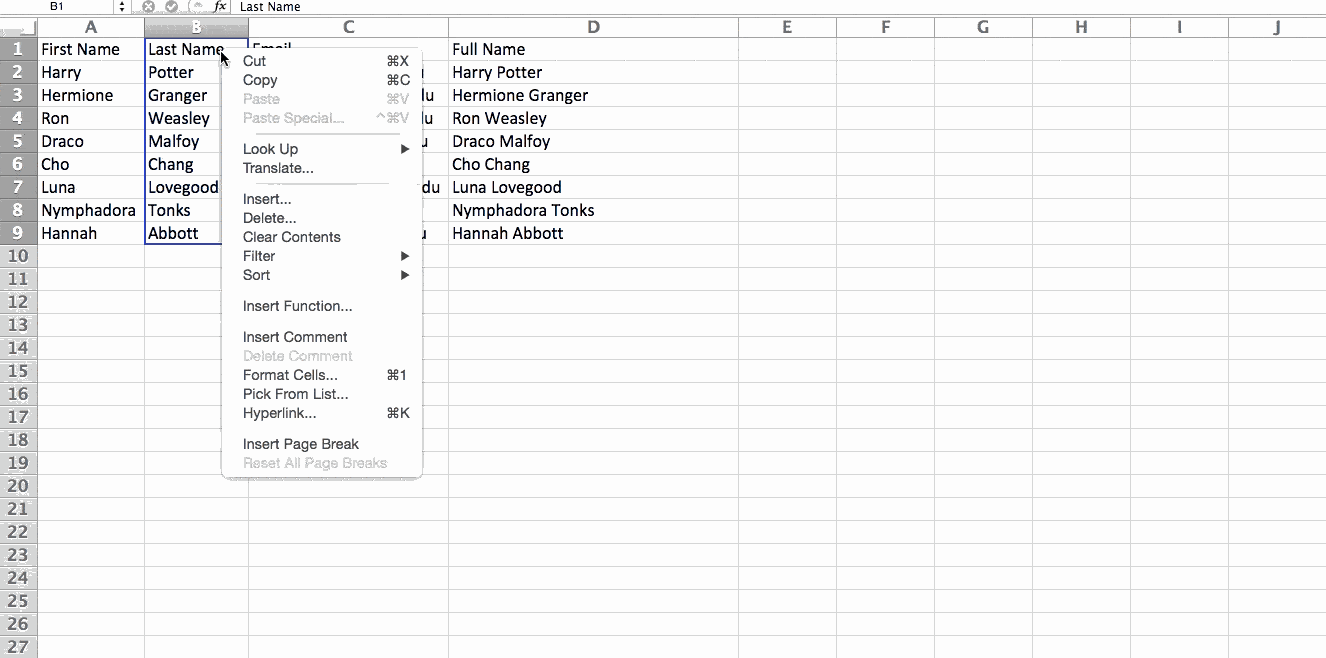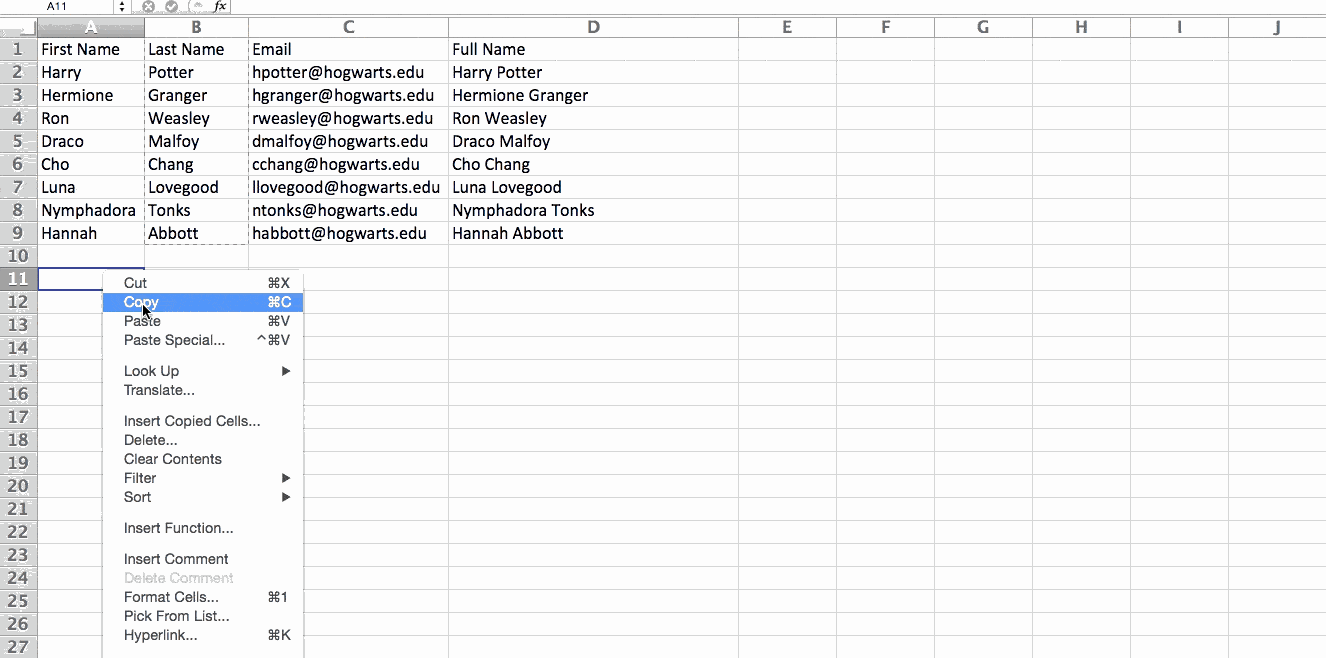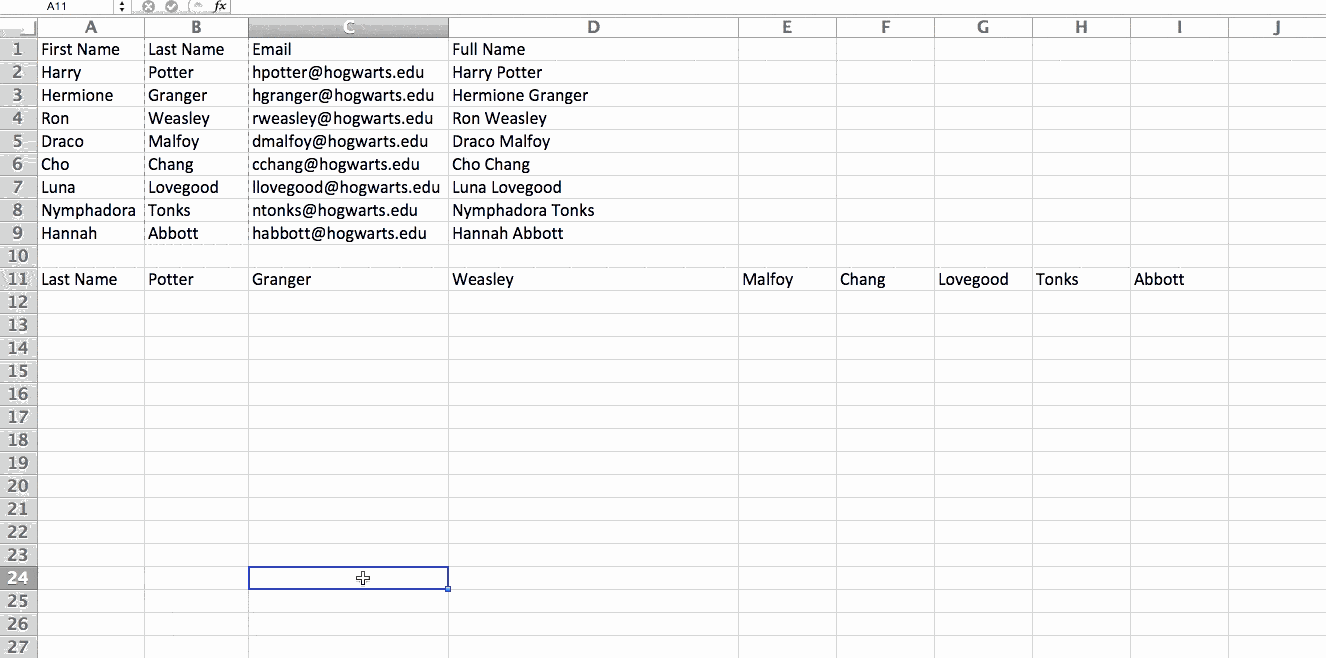
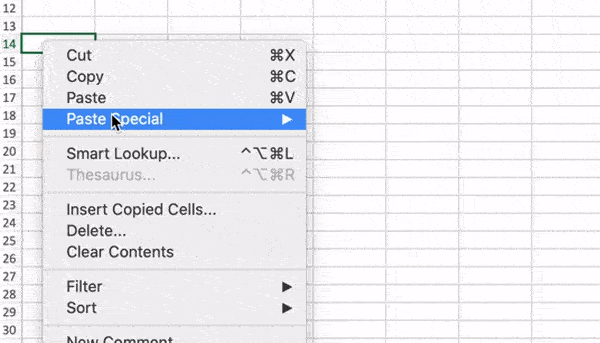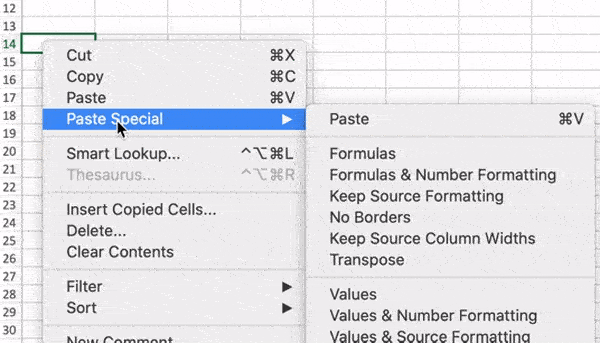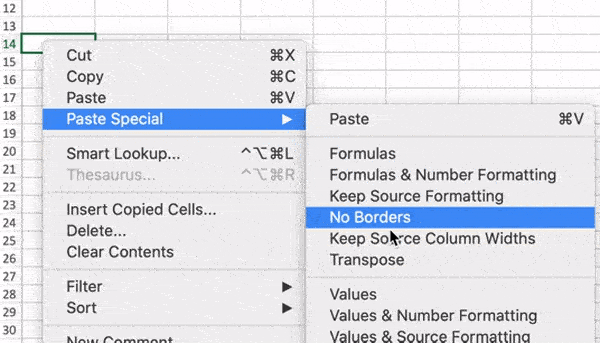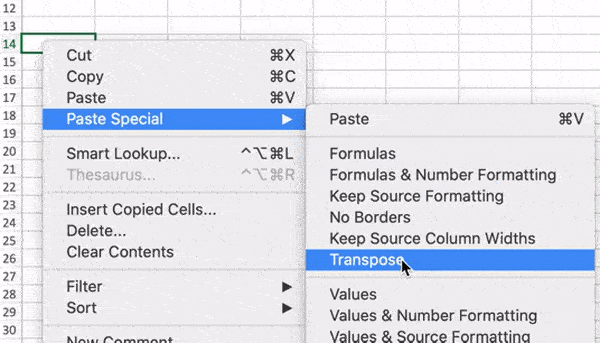
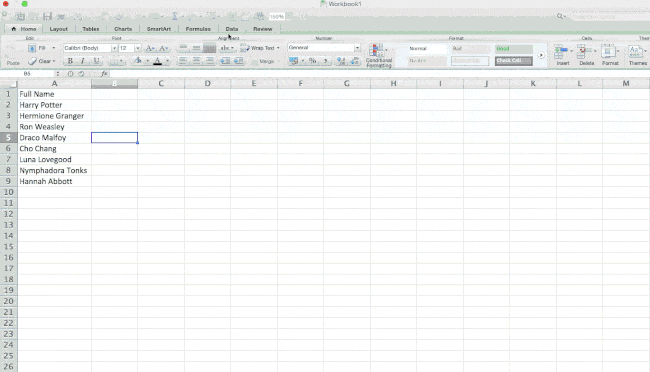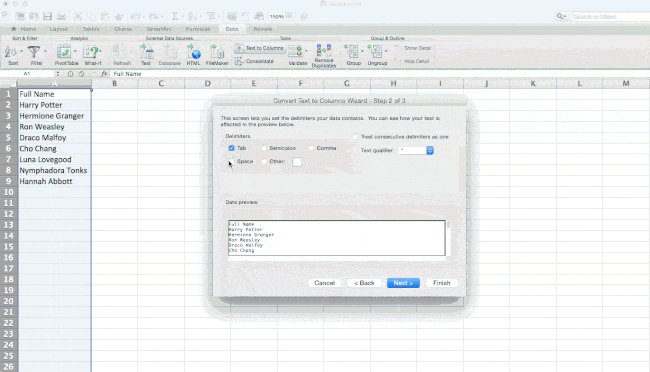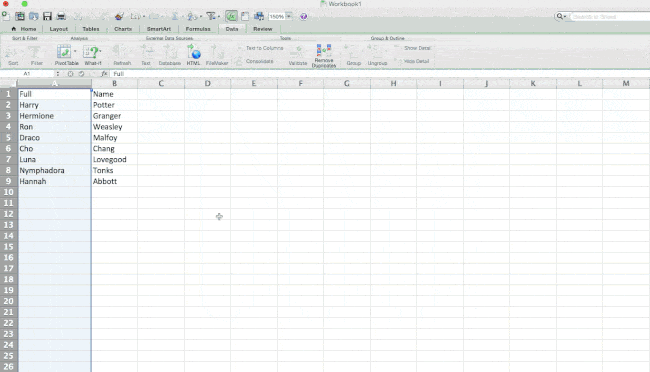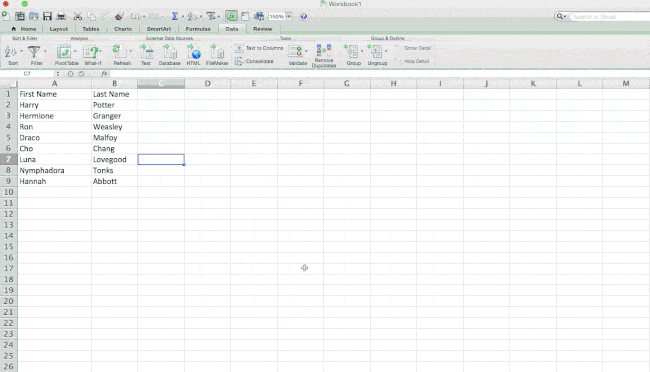
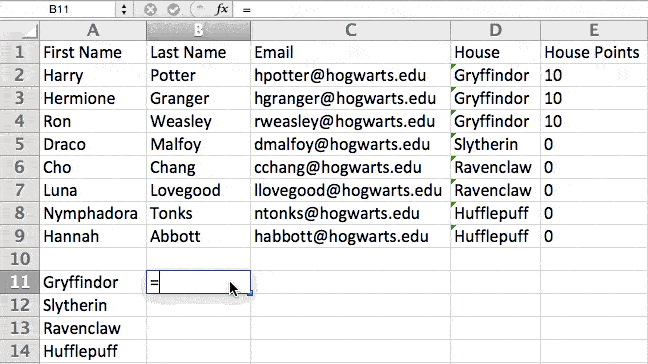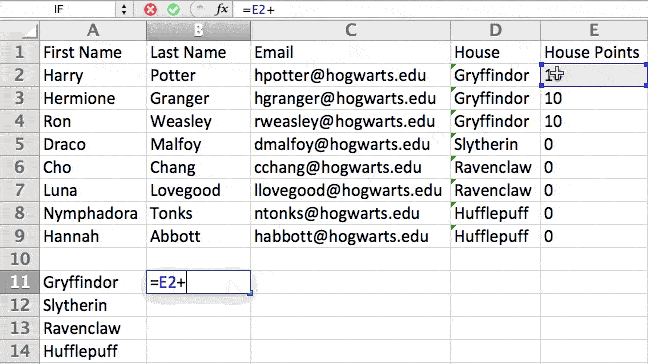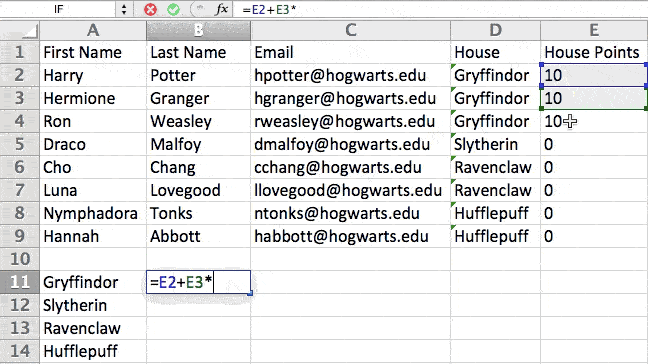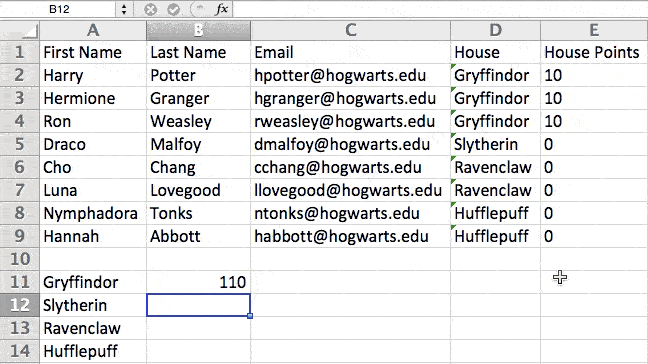
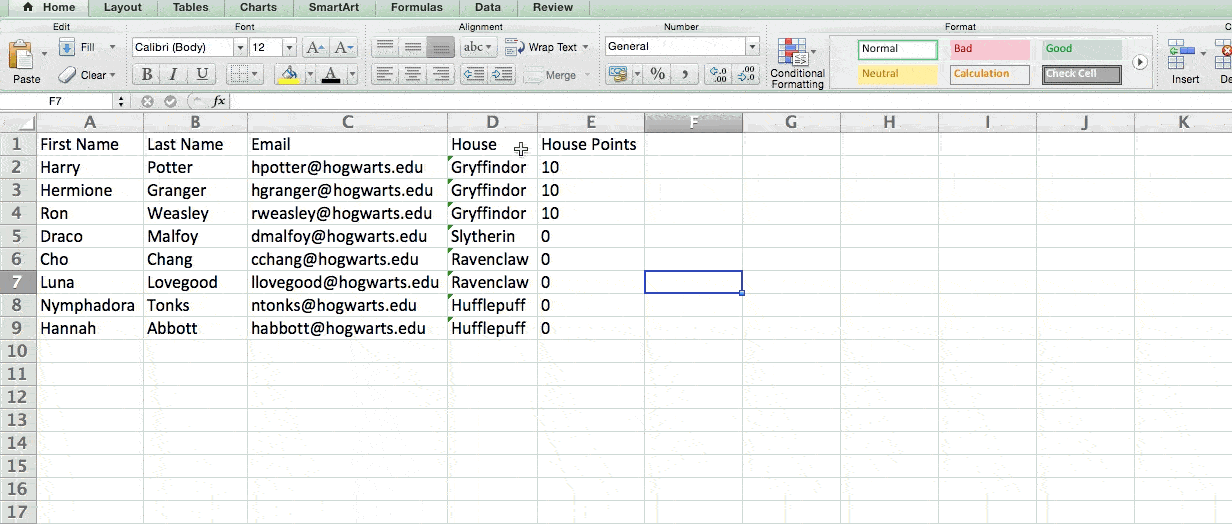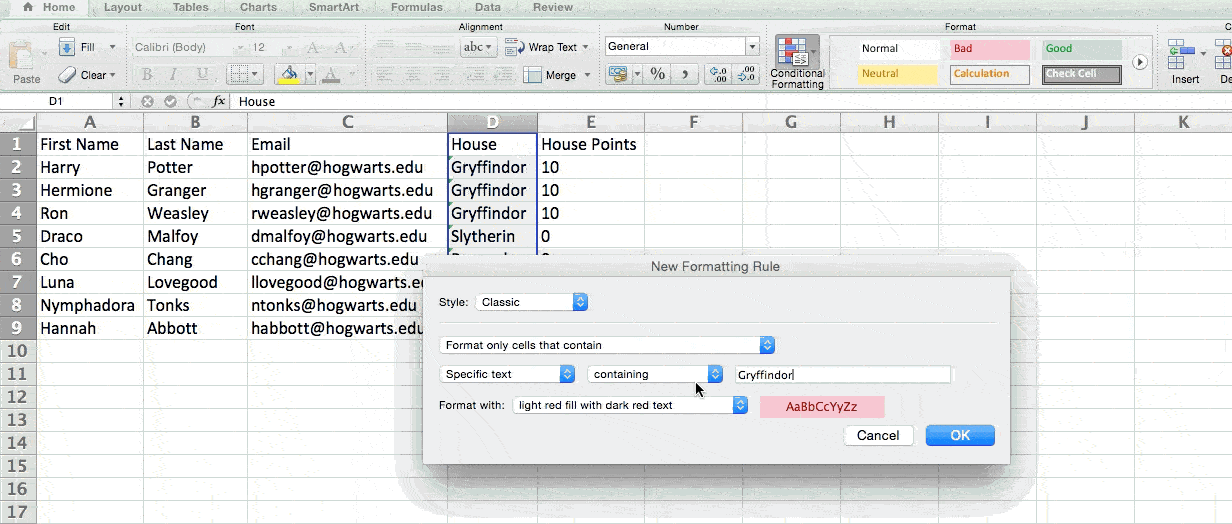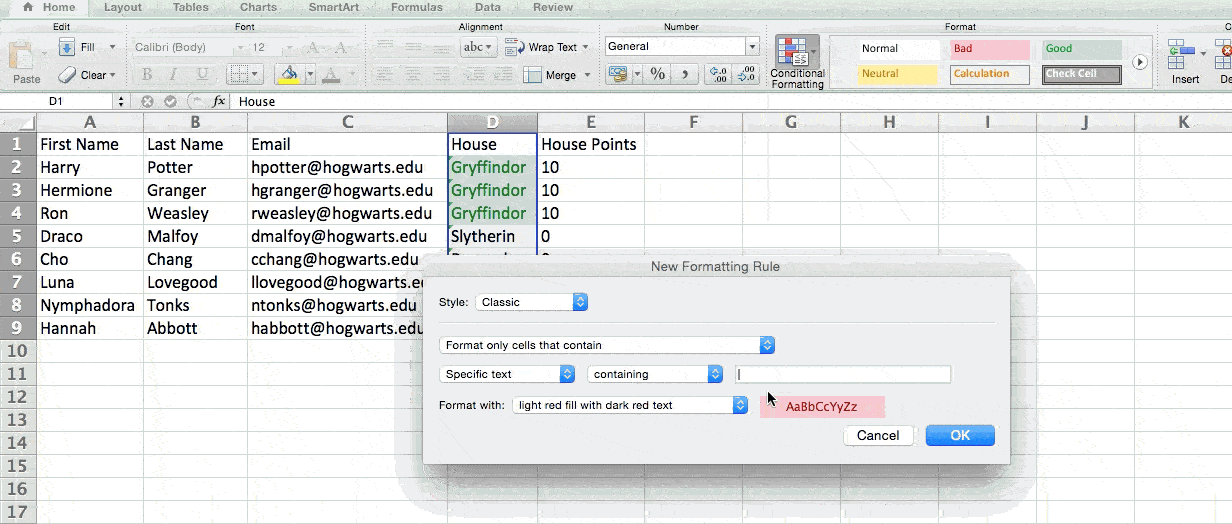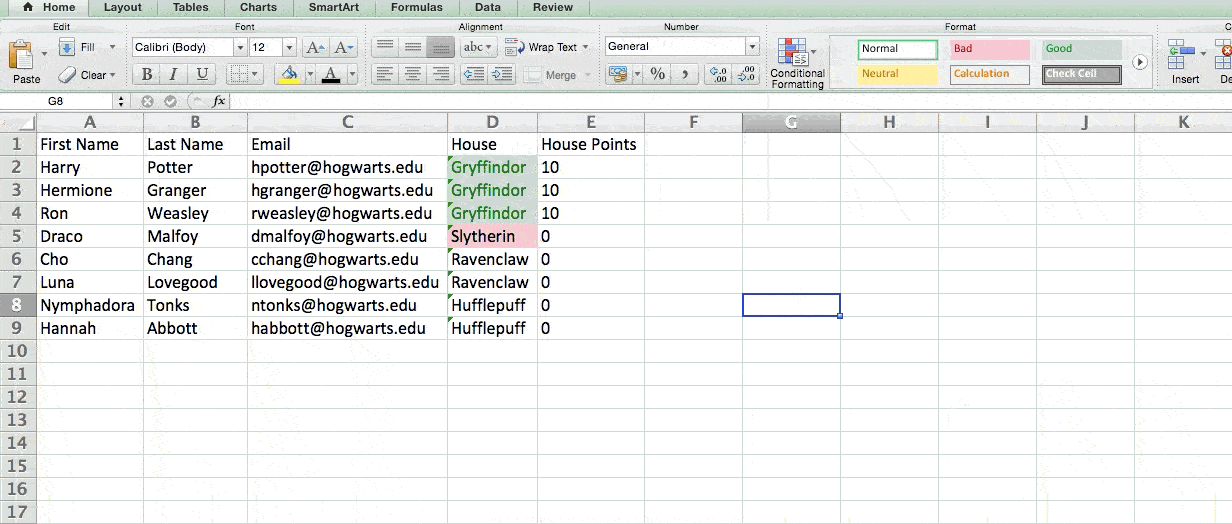
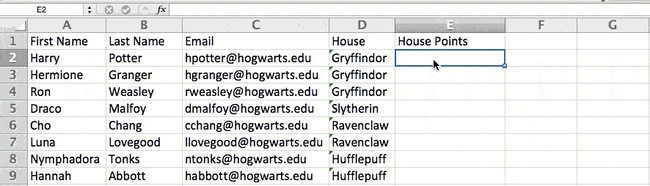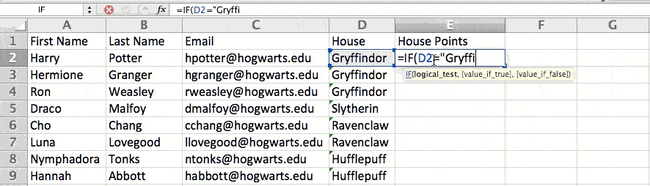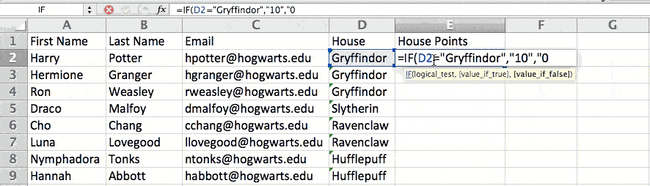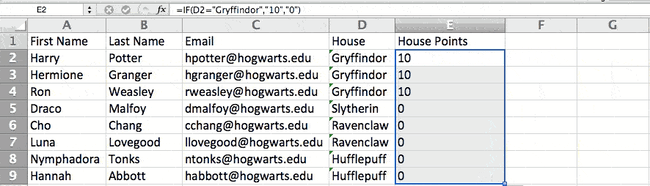
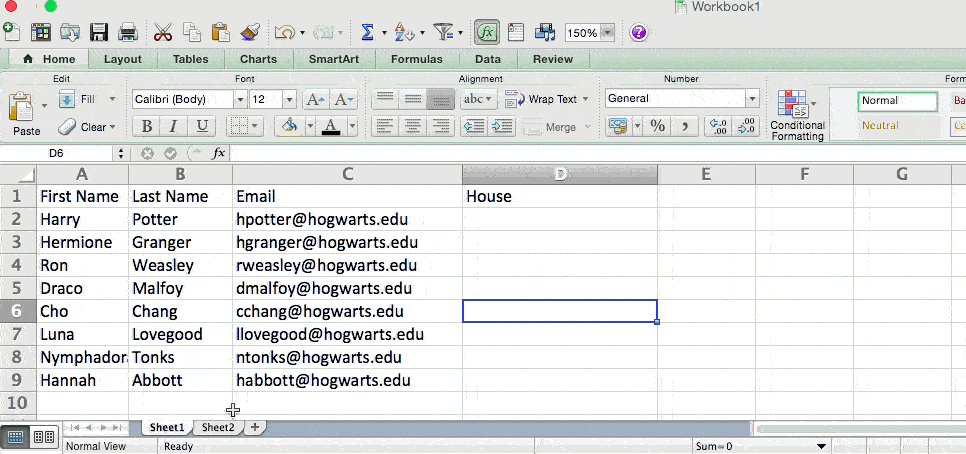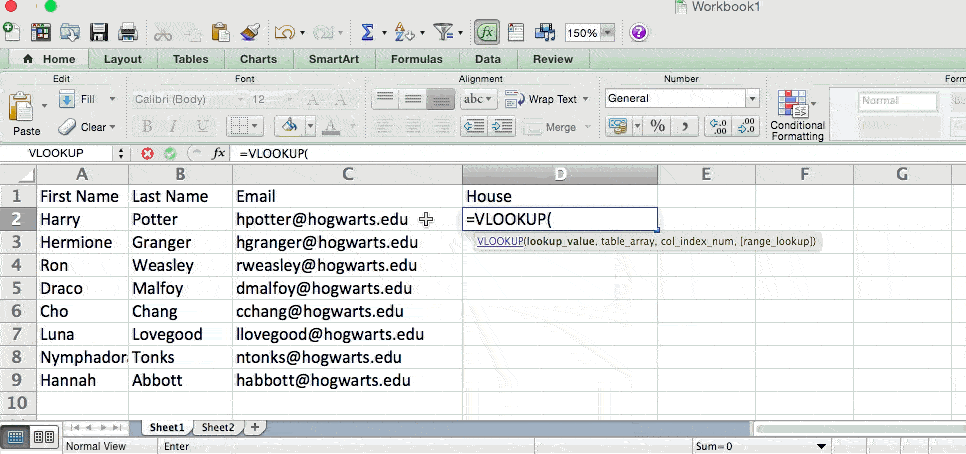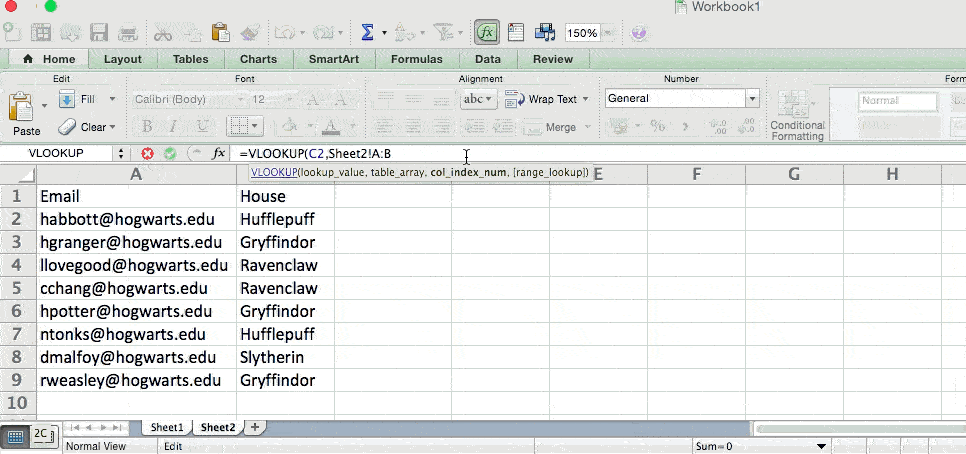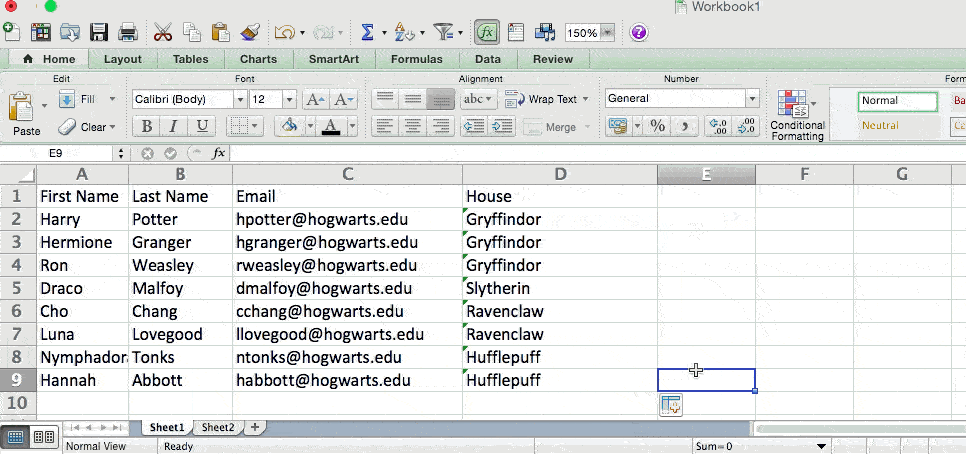
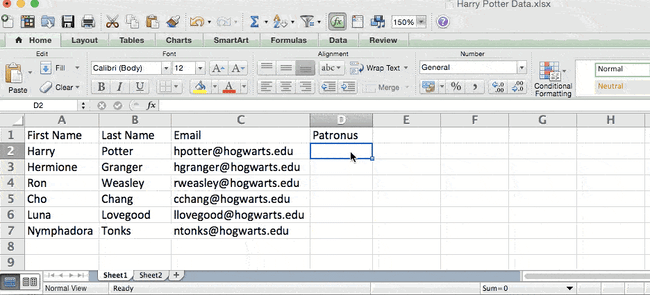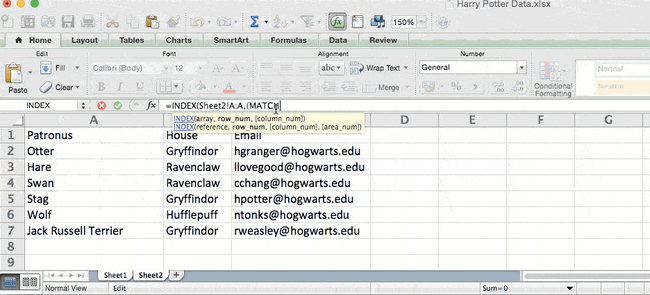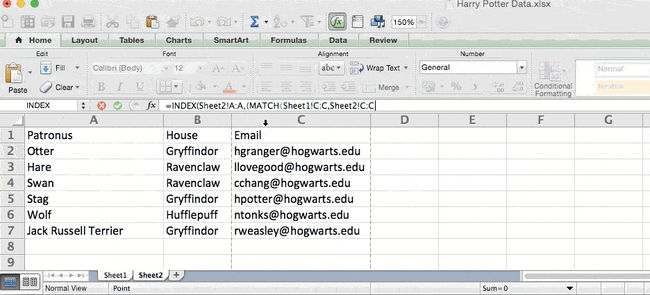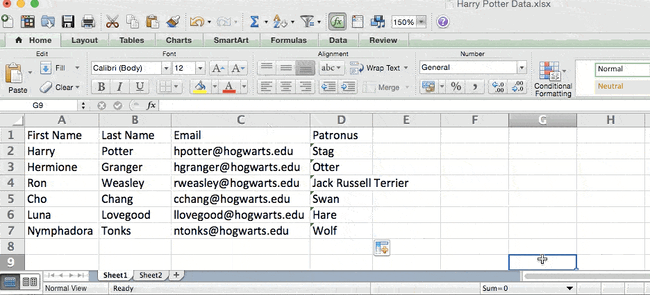
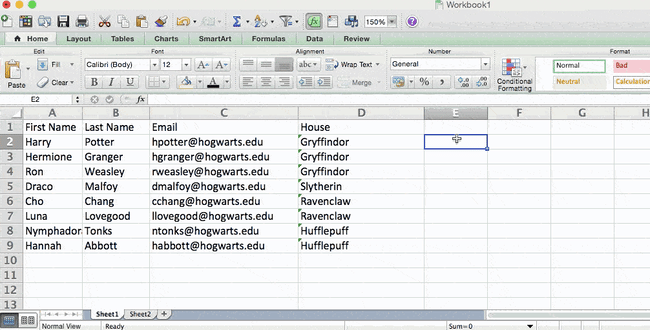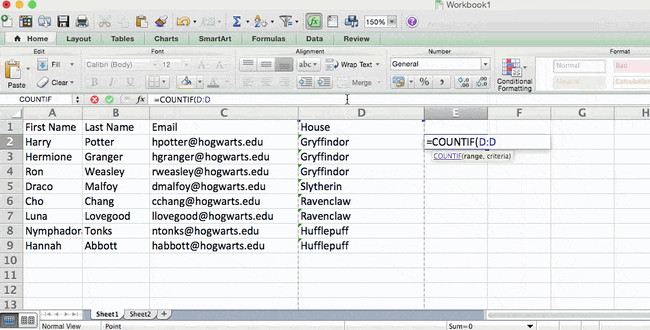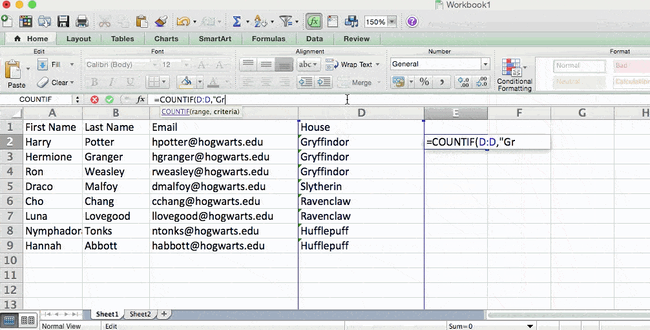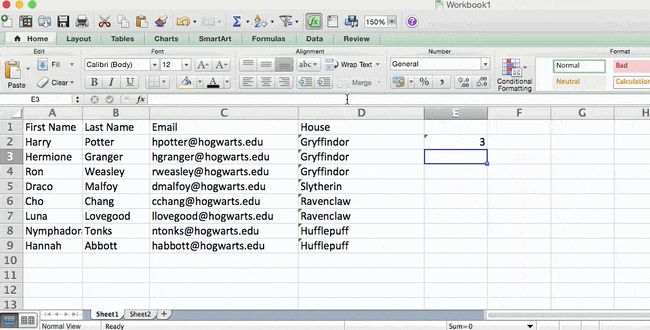
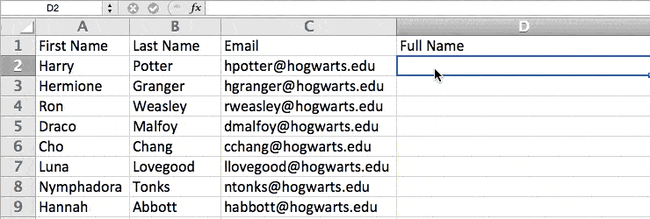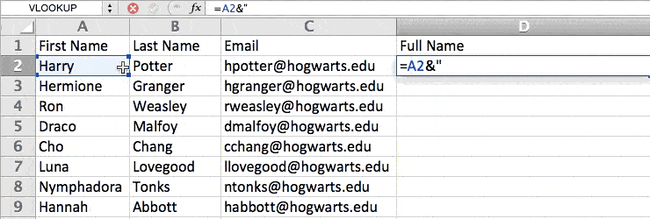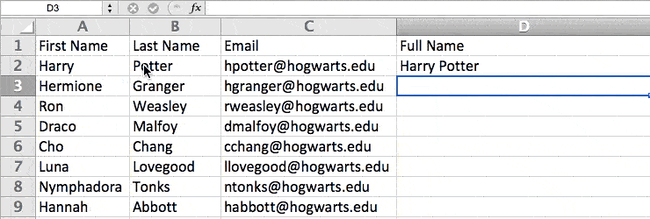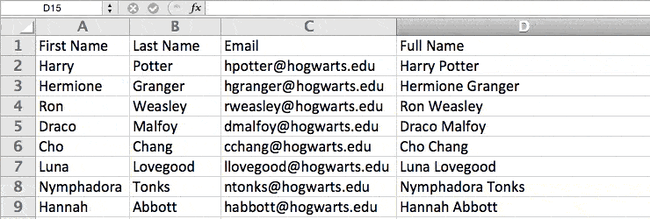

 , and then under Theme Colors or Standard Colors, select the color that you want.
, and then under Theme Colors or Standard Colors, select the color that you want.

 in the bottom-right corner of the selection.
in the bottom-right corner of the selection.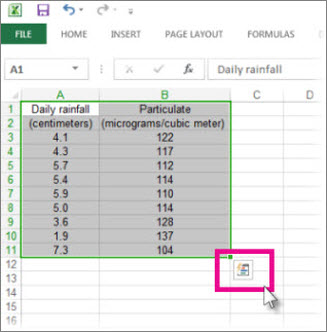

 in the table header of a column.
in the table header of a column.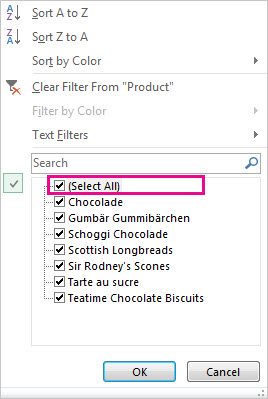
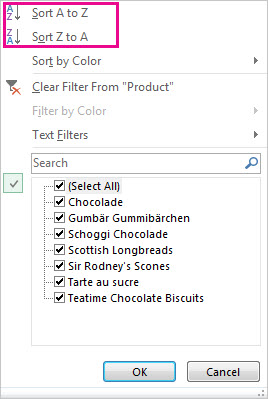
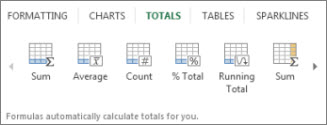
 in the bottom-right corner of the selection.
in the bottom-right corner of the selection.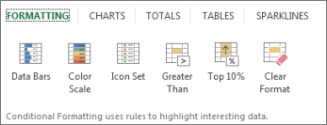
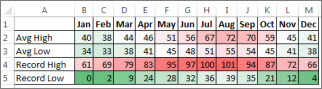

 to perform an ascending sort (A to Z or smallest number to largest).
to perform an ascending sort (A to Z or smallest number to largest). to perform a descending sort (Z to A or largest number to smallest).
to perform a descending sort (Z to A or largest number to smallest).